
Top PhD in Nursing Programs
What is a ph.d. in nursing.
- Ph.D. in Nursing vs DNP
- Types of Programs
- Top Programs
- Program Overview
- Is a Nursing Ph.D. For Me?
The Ph.D. in Nursing degree opens career opportunities for nurses as researchers, forging new and cutting-edge nursing practices for future generations. This article explores this terminal nursing degree, how to get it, and the top Ph.D. in Nursing programs.

A Ph.D. in Nursing is the highest degree awarded to nurses and one of two terminal nursing degrees. Ph.D. stands for Doctor of Philosophy, and Ph.D. in Nursing programs focus on evidence-based research.
Throughout their 4-6 year study, nursing Ph.D. students learn how to conduct, analyze, and publish nursing research. The degree culminates in students conducting an independent research project and writing a dissertation on it.
Ph.D. in Nursing and DNP Differences
A Ph.D. in Nursing and a Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP) are both terminal nursing degrees. However, comparing a DNP vs. a Ph.D. in Nursing reveals distinct differences. Notably, the Ph.D. in Nursing prepares you for a science, academic, or research-focused career as opposed to a clinical one.
Key Ph.D. in Nursing vs. DNP Differences
>> Related: Top Online DNP Programs
Types of Ph.D. in Nursing Programs
The United States is home to over 135 Ph.D. in Nursing programs, which you can attend in multiple formats at nearly every educational level. The types of Ph.D. in nursing programs include the following:
- BSN to Ph.D. in Nursing: These Ph.D. in nursing programs allow nurses with a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) degree to pursue a career in nursing research without first attending an MSN program.
- MSN to Ph.D. in Nursing: Designed for Master of Science in Nursing (MSN) trained nurses, these programs typically include core courses for the doctoral program, electives, and dissertation study.
- DNP/Ph.D. Dual Degree: These rigorous programs allow students to concurrently attain expertise in scientific inquiry and faculty practice and hone the practical skills of expert nurse clinicians.
>> Show Me DNP Programs
Online Ph.D. in Nursing Programs
Are Ph.D. in Nursing programs available online? The answer is yes; you can find several online options to pursue this degree. Since a Ph.D. in Nursing focuses on scientific inquiry, it doesn't have the same onsite practical hours as other nursing degrees.
Program dependant, you may still need to show up on campus a few times each year. However, for the most part, all you need to earn a Ph.D. in nursing is Wi-Fi, good study habits, and determination.
Top Ph.D. in Nursing Programs
Each Ph.D. in Nursing program is unique, offering its own benefits and features. We assembled the top five Ph.D. in Nursing programs nationwide following Nurse.org's proprietary ranking algorithm , which considers and ranks schools based on factors like:
- Tuition costs
- Program length
- Nursing school accreditation
- Admission requirements
- The variety of available programs
- Additional program accolades
1. University of Pennsylvania
- Program Cost: $46,934 per academic year
- Program Length: 4-6 years
- Application Due Date: Dec. 1st
The University of Pennsylvania boasts one of the top Ph.D. in nursing programs nationwide. To offset the expensive tuition, the university offers full-time students stipends during their first four years. In exchange, students may work as Teaching Assistants within UPenn's School of Nursing for up to 16 hours a week.
Contact UPenn about this program:
- Phone: (215) 898-4271
- Email: [email protected]
Source: University of Pennsylvania
2. Duke University
- Program Cost: Fully funded (up to 5 years)
- Application Due Date: November 30th
In 2023, U.S. News & World Report named Duke University the second-best graduate school for nursing. Duke's Ph.D. in Nursing program prepares nurses to become stalwart scholars. Graduates will build nursing science by leading multidisciplinary research that determines the relationship between chronic illness and care systems.
Contact Duke University about this program:
- Phone: (919) 684-3786
- Email: Contact Request Form
Source: Duke University
3. Duquesne University
- Program Cost: $1,765 per credit
- Program Length: 3-4 years
- Application Due Date: February 1st
As the first fully online Ph.D. in Nursing program, Duquesne offers a highly flexible education option to many students nationwide. Additionally, students attending the program may get to study abroad at the Duquesne campus in Dublin, Ireland. The 56-credit program culminates in a dissertation proposal and final defense in which students orally defend their research thesis to the dissertation committee.
Contact Duquesne University about this program:
- Phone: (412) 396-6219
- Email: [email protected]
Source: Duquesne University
4. Columbia University
- Program Cost: Fully funded (up to 3 years)
- Application Due Date: November 15th
Ph.D. in Nursing student at Columbia choose one of three major areas to study, which include Theoretical Foundations of Nursing Science, Analytical Foundations of Nursing Science, and Electives and Applications. The programming heavily focuses on publication, grantsmanship, presentation, and networking. In addition to their coursework, students participate in research experience and training.
Contact Columbia University about this program:
- Phone: (212) 305-5756
- Email: [email protected]
Source: Columbia University
5. Rush University
- Program Cost: $1,344 per credit hour
- Program Length: 3-5 years
- Application Due Date: March 4th
Rush University's Ph.D. in Nursing is fully online except for an on-campus orientation and summer intensive learning sessions. The program focuses on preparing nurses and non-nurses with graduate degrees to become leaders in clinical research and educators who influence healthcare policy. While many students keep working throughout the program, they often must take fewer hours while completing their dissertation.
Contact Rush University about this program:
- Phone : (312) 942-7100
- Email: [email protected]
Source: Rush University
What to Expect in a Ph.D. in Nursing Program
Nursing Ph.D. degrees focus on scholarship and nursing research. By the end of the course, you'll be able to conduct and publish evidence-based research that can alter the face of nursing practice and healthcare policy for future generations.
Generally, these educational pathways combine graduate study and research activities and do not include clinical rotations. Instead, you will be required to complete a long-form research paper called a dissertation. To write your dissertation, you'll complete independent research based on a significant and relevant scientific inquiry in the nursing field.
>> Related: The Best Nursing Research Topics
What Can You Do With a Ph.D. in Nursing?
Ph.D. in Nursing programs prepare graduates to pursue careers in research and teaching, advanced clinical practice, health care administration, and policy. Following graduation, your future may hold a career as a nurse scientist, as an administrator, as a nurse educator, or in establishing health policy.
Ph.D. in Nursing Salary
Healthcare workers who hold a Ph.D. in nursing earn an average annual salary of $100,00 or $60.45 per hour , according to Payscale . However, your nursing salary will vary depending on your career, employer, location, experience, and other relevant factors.
How Much Does a Ph.D. in Nursing Degree Cost?
Ph.D. in nursing programs range from $400 to over $2,300 per credit hour at more distinguished institutions. However, several universities will fund your Ph.D. tuition itself or through a federal research grant. Most often, these funding opportunities are only available to full-time students, while part-timers must pay the full tuition costs.
How Long Do PhD in Nursing Programs Take?
Most Ph.D. in nursing programs take between 4-6 years to complete. Your educational timeline will vary based on your previous education and whether you attend full or part-time.
What Will You Learn in a PhD in Nursing Program?
Since all Ph.D. degrees in nursing emphasize healthcare research, their curriculums will all share certain core elements, which include:
- The philosophical and historical foundations of nursing knowledge
- Review of existing and evolving nursing theory
- Methods and process of developing theory
- Research methodology and data management
- Academic, research, practice, and policy development
Your graduate nursing program will consist of several key milestones to reinforce your education. These include:
- Leadership strategies related to nursing, healthcare, and research
- Mentorship and working alongside faculty on their individual research programs
- Immersion experiences are designed to encourage leadership and scholarship.
- Each student will be required to complete a dissertation.
Ph.D. in Nursing Program Requirements
Each university sets its own entry standards, which vary based on the type of program . However, general Ph.D. in nursing admission requirements include the following:
- BSN, MSN, or non-nursing graduate degree
- Personal research statement
- A minimum GPA of 3.0
- Admissions interview
- Writing sample
- Resume or curriculum vitae
- Letters of recommendation
- Unencumbered RN license
- Official post-secondary school transcripts
- TOEFL or IELTS scores
Is a Ph.D. in Nursing Degree Right for Me?
Your professional goals play a massive role in deciding whether to pursue a Ph.D. in nursing. If you're interested in scientific and academic nursing research, healthcare policy, or becoming a nurse educator, a Ph.D. in nursing is an excellent option. Remember, it will not qualify you for APRN positions, so if you have clinical aspirations, a DNP is the right doctoral nursing option.
Next Steps to Enroll in a PhD in Nursing Degree Program
Ready to start your educational journey toward earning a Ph.D. in Nursing? You can start working toward those goals today with these simple steps:
- Research Universities: Find a program that suits you based on your budget, attendance needs (e.g., part vs. full-time and in-person vs. online), and interests.
- Plan Applications: Understand the program requirements and application deadlines for each school you're applying to. Then, make a plan to collect and submit all the necessary materials and documentation on time.
- Prepare Properly: If a university considers you for Ph.D. candidacy, you'll attend an admissions interview. Planning and practicing this interview and paying close attention to why you chose the program and your research interests will optimize your chances of admission.

Plus, get exclusive access to discounts for nurses, stay informed on the latest nurse news, and learn how to take the next steps in your career.
By clicking “Join Now”, you agree to receive email newsletters and special offers from Nurse.org. We will not sell or distribute your email address to any third party, and you may unsubscribe at any time by using the unsubscribe link, found at the bottom of every email.
PhD Program in Nursing
Phd program in nursing goals.
The PhD Program in Nursing prepares nurse scholars who will advance nursing science and promote equitable health outcomes and care systems, with a focus on social determinants of health (SDOH). Students will acquire the knowledge and skills necessary to design, implement, and evaluate innovative models of care that improve health outcomes across diverse populations. Graduates of the program will be prepared to lead and transform nursing practice, policy, and research to promote health equity and social justice. PhD student tuition and 12-month stipends are fully funded for up to five years.
At Duke University School of Nursing we admit a small number of highly qualified, diverse applicants that work closely with one or more faculty members in a series of mentored experiences supported by formal coursework.

PhD Academic Calendar

PhD Admissions

PhD Financial Support

Current Research Grants

What Makes Duke Great?

Reasons to Choose Durham
Your work with our faculty will:
Socialize you to the role of nurse scientist;
Ensure you gain significant knowledge and acquire the skills for launching a successful independent program of research post-doctorate; and
Prepare yourself for an entry-level role as a nurse scientist in a research setting (e.g., academic, clinical, or industry).
To help our students succeed, the Duke School of Nursing PhD Program provides:
A broad perspective on the philosophy of science and its application to solving challenging health problems facing our nation, particularly those related to health equity, social determinants of health, and justice;
Experience with standard and emerging research designs and methods;
Rigorous training in statistics; and
Mentored research and teaching experiences to reinforce knowledge acquisition and skill development.
In addition to addressing the standards of Duke University and ensuring the highest-quality PhD education, the Duke PhD Program in Nursing is designed to meet the indicators of quality in research-focused doctoral programs set forth by the American Association of Colleges of Nursing.
Study with Duke expert faculty focused on:
Acute & Long-Term Care Systems
Adaptive Leadership
Data Science
Digital Health
Decision Making
Disease Prevention
Family Caregiving
Health Equity
Informatics
Mental Health
Multi-level Interventions
Nurse-led Models of Care
Palliative and End-of-Life Care
Perioperative Care
Social Determinants of Health
Symptom Management
Specialty Populations
Premature and High-Risk Infants
Children with Acute and Chronic Illnesses
Adults with HIV, Hepatitis C, Diabetes, Sickle Cell Disease, Cancer, or Cardiovascular Disease
Older Adults
PhD Program in Nursing Description
The program requires a minimum of 52 credit hours of graduate coursework. Students will work on research projects; it is expected most will graduate with several publications. Coursework is structured with a substantive core of nursing science and research methods to be taken in the School of Nursing. This core is expanded with elective courses that typically support the student’s dissertation and future research career. These can be taken in other Duke University departments or other Universities that have arrangement with Duke (i.e., University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, North Carolina State University, North Carolina Central University). Additional requirements include research practicums and elective credits that may count towards specialty certificates (i.e., teaching, global health, data science, entrepreneurship, etc.).
In addition to course work, the PhD Program in Nursing will require each student to develop a scholarly portfolio, successful completion of a preliminary examination, and a dissertation. Students are expected to disseminate their work through scholarly venues such as publications and conference presentations.
Terminal Objectives
After the PhD Program in Nursing, students will be able to:
- Demonstrate advanced knowledge and understanding of health equity, social determinants of health (SDOH), and nurse-led models of care to improve health outcomes for a population and/or system of care.
- Apply conceptual models and theories from nursing and other relevant disciplines to design and conduct research.
- Use a health equity, SDOH, and/or nurse-led models of care lens to critically evaluate and synthesize research conducted in nursing and other disciplines.
- Demonstrate scientific integrity and ethics in research across phases of the research process.
- Apply appropriate methods and analytic strategies to design, conduct, and evaluate research across phases of the research process, from discovery to translation.
- Collaborate effectively with interdisciplinary teams to perform research using socioculturally aligned approaches.
- Disseminate research findings through publications, presentations, and other scholarly venues to advance the evidence base for nursing and healthcare, with a focus on promoting health equity and social justice.
- Member Benefits
- Communities
- Grants and Scholarships
- Student Nurse Resources
- Member Directory
- Course Login
- Professional Development
- Institutions Hub
- ONS Course Catalog
- ONS Book Catalog
- ONS Oncology Nurse Orientation Program™
- Account Settings
- Help Center
- Print Membership Card
- Print NCPD Certificate
- Verify Cardholder or Certificate Status

- Trouble finding what you need?
- Check our search tips.

- Oncology Nursing Forum
- Number 2 / March 2016
The Research Doctorate in Nursing: The PhD
When nurses are considering an advanced degree beyond the master’s level of educational preparation, a number of considerations may direct the decision-making process. The doctorate of philosophy (PhD) in nursing is a research degree that will well serve nurses who have the desire to apply theory and develop formal programs of research, become faculty of nursing, combine clinical practice with formal research, and advance through professional leadership in the ranks of hospitals and health systems organizations.
Jump to a section
The research-focused doctorate in nursing prepares nurse scientists to lead the field and to advance the science of nursing. In addition to conducting independent research and developing their own programs of research, nurse scientists will also likely work in multidisciplinary and interprofessional teams to achieve broad research outcomes. They design and conduct studies to answer certain aims. These aims can be in response to theoretical questions, as well as to questions that derive from clinical practice or focus on individual, group, or population characteristics and behaviors—to name only a few prompts for inquiry. The findings of the inquiry are disseminated through scholarly publication and presentation, are likely to prompt additional research, and will ultimately inform an evidence base for practice, policy, and advocacy.
Historically, before doctoral degrees in nursing were available, nurses who pursued doctoral degrees did so in fields related to nursing (e.g., health education, public health, psychology, economics). However, the first doctorate that was available to nurses was established in 1924. This was the doctor of education (EdD) degree, awarded by the Teachers College of Columbia University in New York, New York. The EdD degree continues to this day, and it is a research-focused doctorate with an emphasis on education.
PhD programs in nursing began toward the end of the 20th century. However, in the 1970s, Boston University began the doctor of nursing science (DNS) degree. Further complicating the matter, Margaret Newman of New York University later promoted a purely practice-focused nursing doctorate (ND) (Schneckel, 2009). The first of these ND programs was offered in 1979 by Case Western Reserve University in Cleveland, Ohio (Reid Ponte & Nicholas, 2015).
The intent of the DNS or DNSc degree was to combine research with clinical practice rather than research with theory development and application (Loomis, Willard, & Cohen, 2006). Ultimately, the DNSc degree was considered to be equivalent to the PhD degree. The curricula, program design and expectations, and dissertation and research requirements were nearly the same across programs. For that reason, many colleges and universities have changed their DNSc programs to PhD programs, and many have allowed recipients of the DNSc degree to convert those degrees into PhDs. At the close of the 20th century, the vast majority of research-focused doctoral programs were PhD programs (79%), with the remaining shared among DNSc, DNS, or DSN programs (17%) and ND programs (5%) (American Association of Colleges of Nursing [AACN], 2001). As of 2013, the most recent year for which data are available, 132 research-focused doctoral programs, with 5,145 enrolled students, existed in the United States (AACN, 2014).
As of fall 2014, 81 U.S. colleges and universities also offer baccalaureate to research-focused doctoral programs (AACN Research and Data Services, 2015). These programs, designed for those who hold a bachelor’s degree in nursing, do not confer a master’s degree. Instead, they combine master’s and doctoral level course content, culminating in a PhD degree in nursing. Completion of these programs typically requires 85–90 hours of course and dissertation work.
Program Considerations
Nurses should commence the decision-making process by considering their professional goals, among other issues (see Figure 1). They should also search online for PhD programs in nursing, pull up the program web pages for several schools, and take a careful look. Many pages will include the program’s curriculum or a sample course of study. For programs that have specific foci of research, the program home page likely will offer details about research topics of interest and current work. In addition, faculty profiles will often provide details about each professor’s particular research interests, current work, grant funding, and publications. Programs will typically have coordinators and faculty contacts with whom potential students can talk. Many programs will have similar curricula (see Figure 2). Interested nurses should also seek out PhD-prepared nurses in their organizations and professional circles for their advice, guidance, and mentorship. Like most aspects of a nursing career, the opportunities for education are many, and the research-focused doctorate in nursing may lead nurses in directions they cannot begin to imagine.
[[{"type":"media","view_mode":"media_original","fid":"21871","attributes":{"alt":"","class":"media-image","height":"524","typeof":"foaf:Image","width":"504"}}]]
Educational Technology
All research-focused doctoral programs will use some elements of technology (e.g., message boards, interactive whiteboards, chat rooms, email, computers). However, some programs are delivered entirely online. Much or all of this content may be asynchronous and computer-based learning. This approach and type of learning requires that students be disciplined, focused individuals who can commit to computer-based learning without significant human interaction.
[[{"type":"media","view_mode":"media_original","fid":"21876","attributes":{"alt":"","class":"media-image","height":"399","typeof":"foaf:Image","width":"247"}}]]
Some schools have leveraged advanced technologies to deliver real-time classroom experiences via live teleconferencing and the use of program sharing via web-based systems. These programs are synchronous and bring together a cohort of students with like interests. This style of presentation and learning, in which learning involves live engagement with faculty and other students either in person or via videoconferencing technology, is many times more engaging than that which is asynchronous and the student is alone with only non-live, computer-based interaction. The College of Nursing at the University of Utah offers one example of a research-focused doctoral degree program that has delivered its content successfully via these methods. Several of the cohorts have been oncology focused.
The pursuit of a research-focused doctoral degree is intensive, rewarding, sometimes challenging, and always self-revelatory. Imagine the changes that can occur during the span of four to six years. Now, imagine those changes with the added context of experience and growth in a particular field of inquiry; exposure to the minds, works, and support of faculty, advisers, and dissertation chairs and members; and the shared learning with peer students. Picture the networks that will be built, the collaborations that will be fostered, and the body of work that will be produced and contribute to the science of nursing. Earning a research-focused doctorate in nursing is an amazing experience that will consistently inform the personal lives, interpersonal relationships, and the professional journeys and achievements of those who pursue it.
American Association of Colleges of Nursing. (2001). Indicators of quality in research-focused doctoral programs in nursing. Retrieved from http://bit.ly/20tdKF7
American Association of Colleges of Nursing. (2014). Annual report 2014: Building a framework for the future. Retrieved from http://bit.ly/1VQKilS
American Association of Colleges of Nursing Research and Data Services. (2015). Schools offering baccalaureate to research-focused doctoral programs, fall 2014 (N = 81). Retrieved from http://bit.ly/1nPAaiL
Loomis, J.A., Willard, B., & Cohen, J. (2006). Difficult professional choices: Deciding between the PhD and the DNP in nursing. Online Journal of Issues in Nursing, 12, 6.
Reid Ponte, P., & Nicholas, P.K. (2015). Addressing the confusion related to DNS, DNSc, and DSN degrees, with lessons for the nursing profession. Journal of Nursing Scholarship, 47, 347–353. doi:10.1111/jnu.12148
Schneckel, M. (2009). Nursing education: Past, present, future. In G. Roux & J.A. Halstead (Eds.), Issues and trends in nursing: Essential knowledge for today and tomorrow (pp. 27–62). Sudbury, MA: Jones and Bartlett.
About the Author(s)
Rice is the director of Professional Practice and Education at City of Hope National Medical Center in Duarte, CA. No financial relationships to disclose. Rice can be reached at [email protected] , with copy to editor at [email protected] .
Related Articles
Empowering oncology nurses to lead change through a shared governance project, a clinical librarian–nursing partnership to bridge clinical practice and research in an oncology setting, the value of mentoring in nursing: an honor and a gift.

Home / Getting Your Ph.D. in Nursing
Getting Your Ph.D. in Nursing
Becoming a ph.d. nurse, what does a ph.d. nurse do, ph.d. nurse salary & employment, ph.d. vs. dnp in nursing, helpful organizations, societies, and agencies, what is a ph.d. nurse.
A Ph.D. nurse is one who has completed a Doctor of Philosophy in Nursing degree. A Ph.D., or doctoral degree, is the highest level of education a nurse can achieve. Different from a Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP) degree, which focuses on advanced clinical practice, a Ph.D. in Nursing program is a research and science-focused degree that prepares nurses for careers conducting important medical research that will advance the entire nursing profession and for teaching nursing at the college level.

In order to become a Ph.D. nurse, of course, nurses must complete a Ph.D. in nursing program, which generally takes 4 to 6 years to finish. An aspiring Ph.D. nurse must have a strong interest in conducting medical research and/or teaching future nurses. Strong leadership skills are also important, as many Ph.D. nurses go on to supervise and mentor other nurses, whether they work in scientific research, management, or teaching capacity.
What Are the Educational Requirements For a Ph.D. Nurse Program?
A Ph.D. in Nursing program is known as a terminal degree, meaning it is the highest level of education for the nursing profession (in addition to the DNP degree, another separate nursing doctorate program track). Prior to entering a Ph.D. program, nurses must complete a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) degree and pass the NCLEX-RN exam. In some cases, applicants to a Ph.D. in Nursing program must also complete a Master of Science in Nursing (MSN) degree, which provides advanced education in nursing practice with courses in pharmacology, pathophysiology, and clinical practice.
Educational Prerequisites
Specific requirements to complete a Ph.D. in Nursing program will vary slightly from school to school. Schools offer Ph.D. in Nursing programs in traditional classroom formats, as well as online and hybrid styles that combine in-person study with online coursework. In addition to a variety of formats for Ph.D. in Nursing programs, students can also sometimes opt to take these programs on a full-time or part-time basis to suit their personal schedules.
The curriculum for a Ph.D. in Nursing program is research-focused, with coursework in advanced scientific research principles, data analysis, and statistical measurement. Ph.D. programs generally culminate in a dissertation and original research project. As an example of Ph.D. curriculum, below is a selection of courses offered by the Medical University of South Carolina as part of their online Ph.D. in Nursing Science program:
- Advanced Quantitative Research Methods
- Qualitative Research Methods
- Advanced Statistical Methods for Nursing Research
- Advanced Study Design and Methods
- Advanced Health Policy & Advocacy
- Research Team Leadership
A Ph.D. nurse conducts scientific research that advances the nursing profession. The knowledge that Ph.D. nurses gather and present as a part of their scientific research powers positive change in the quality of patient care and outcomes in the entire nursing field. In addition to their role as nurse scientists, Ph.D. nurses also teach and mentor nurses at the college/university level, working to shape the next generation of nurses.
What Are the Roles and Duties of a Ph.D. Nurse?
The majority of Ph.D. nurses pursue careers in either the research or teaching fields, so their day-to-day duties will vary depending on which career track they have chosen.
For a nurse researcher , typical duties may include:
- Identify research questions, and design and conduct scientific research in partnership with other scientists from various fields
- Collect and analyze scientific data and publish reports detailing findings
- Write proposals and apply for grants to help fund their research
- Establish and maintain quality assurance programs to ensure the validity of their data findings
- Train and supervise laboratory staff and other nurses or scientists
For a Ph.D. nurse educator who has chosen to pursue a faculty position, typical duties may include:
- Plan, prepare, and revise curriculum and study materials for nursing courses
- Deliver lectures to undergraduate and graduate level nursing students
- Supervise students' laboratory and clinical work
- Grade students' classwork, laboratory, and clinical performance
- Mentor and advise students regarding their future work in the nursing industry
For faculty members who pursue department chair or administration roles, additional duties may include:
- Hire, supervise and conduct performance reviews of faculty members
- Assist with the scheduling of classes and professors
- Oversee department curriculum and provide quality control as to the content and materials of given nursing courses
Workplace Settings
A Ph.D. nurse can work in a variety of settings, depending on the career path he or she has chosen. A Ph.D. nurse may find employment at a hospital, medical laboratory, research facility, or university as a research scientist, or may work at a nursing school, college, or university as a faculty member or department chair. In some cases, a Ph.D. nurse may also work as a public health nurse in a government setting, helping to develop research-based solutions to public health issues.
Salaries for Ph.D. nurses vary based on the type of employment a nurse seeks after graduation. Nurse researchers, a primary career path for Ph.D. nurses, can expect a median salary of $90,000 according to Payscale.com. For Ph.D. nurses who pursue a teaching position, the median annual wage for post-secondary nursing instructors is $77,440 according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics as of May 2021. Geographical location, career length, and experience level are all factors that can influence a Ph.D. nurse's annual salary.
The nursing profession as a whole has a particularly bright employment outlook, with the employment of registered nurses projected to grow 9 percent from 2020 to 2030 according to the BLS. In addition, a large number of healthcare facilities are looking for nursing professionals with higher degrees, which means the demand for Ph.D. and DNP level nurses will continue to grow. In fact, the Institute of Medicine 's 2015 "The Future of Nursing Report" emphasized the need for more Ph.D. level nurses.
As there are two doctorate-level nursing program types to choose from, there may be some confusion as to the differences between a Ph.D. nursing program and a Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP) degree. The primary difference between the two programs relates to nurses' career aspirations. A DNP program trains nurses to perform the highest level of nursing practice and to translate research into high-quality patient care, while a Ph.D. program prepares nurses to conduct cutting-edge research that will advance the science of nursing and patient care. In addition to research positions, a Ph.D. program prepares nurses for leadership and teaching positions at hospitals and colleges/universities. To simplify, a DNP is a nursing practice doctorate degree, while a Ph.D. is a research and teaching doctorate.
Other key differences between DNP and Ph.D. programs are curriculum and program length. A typical DNP program includes courses on advanced nursing practice, leadership, and management topics and requires patient care clinical hours as well as a final capstone project. A Ph.D. program includes coursework on research methodologies, data analysis, and healthcare leadership and policy, and requires students to complete original research and a dissertation. In general, a Ph.D. program takes longer to complete than a DNP program, with Ph.D. programs taking an average of 4 to 6 years to complete and a DNP program taking 3 to 4 years, but can be completed in as little as 2 years depending on the school and program chosen.
- American Association of Colleges of Nursing
- American Nurses Association
- International Association of Clinical Research Nurses
- National Institute of Nursing Research
- Connect with us:
- X (Twitter)
Is earning a Ph.D. in nursing worth it? MCN faculty say yes.
- Author By Bryanna Tidmarsh
- March 26, 2021

It’s a story every nurse knows: the need for nurses is growing. Worldwide, health care faces growing nursing provider and educator shortages. One of the most important ways nurses can address this dire need is by earning a Ph.D. in nursing.
Only 13% of nurses in the United States currently hold a graduate degree. Fewer than 1 percent hold a doctorate. That means that just 13 percent of the nursing workforce is eligible to become nursing faculty at all, and less than 1 percent is eligible to teach at the highest level.
A Ph.D. prepares nurses to be experts in their field and to pursue a research-focused career. We need more PhD-prepared nurses now more than ever: to educate future nurses, to lead nursing teams, and to develop research that improves best practices. MCN’s Ph.D. in nursing aims to uplift nurses in their profession, preparing them to take on leadership roles and perform cutting edge research that shapes the health care landscape.
Who should consider a Ph.D. in nursing?
In short: everyone. Nursing is one of many fields in health care that are moving towards requiring masters and doctorate-level education.
Designed for those who want to focus on education and research, the doctorate of philosophy degree prepares nurse researchers with expertise in vulnerable populations. Many graduates of MCN’s Ph.D. program return to teach and conduct research, such as Dr. John Blakeman ‘20.
Take it from Blakeman: “With a PhD, we are expected to affect the whole nursing profession: how we shape practice and policy and education.”
Is research not for you? Consider earning a doctorate in nursing practice via MCN’s DNP program .
What can I do with a Ph.D. in nursing?
The PhD-prepared nurse serves the public by designing and conducting research on relevant clinical, educational, health systems, and/or health policy topics. Following graduation, a nurse with a PhD may pursue a research career in the academic, business, government, or industrial setting. Nurses with a PhD may also serve as educators and/or administrators and develop or consult on health care policy in a variety of settings.
Become a nurse educator —in a university or on the hospital floor.
As the field works to usher in more nurses, it lacks sufficient nurses who are trained to teach them. With a Ph.D. in nursing, you will be prepared to educate nursing students or take on an education role within a health care setting, helping to train current nurses in new research and best practices. with the latest research in best practices.
With a Ph.D. in nursing, you will be prepared to review health care policy, test it, and make recommendations for federal or state regulations. An example would be to study the need for annual flu vaccinations for health care staff and whether or not requirements are evidence-based. With a Ph.D. in nursing, you will be prepared to evaluate symptoms of health issues, such as: fatigue prior to heart attacks, exercise needs of rural post-menopausal women, or pain assessment of older adults. A PhD-prepared nurse could also work with a coroner to analyze older adult falls and community recommendations to prevent future falls.
Become a nurse researcher —a critical role to keeping health care facilities up-to-date with the latest research in best practices.
Advance your career. The Ph.D. opens up career opportunities such as serving as a nurse researcher, administrator, policymaker, leader, or educator.
“With a PhD in nursing, you are better positioned to be a leader in the area of nursing education or be hired as a full-time faculty member,” says Dr. Seon Yoon Chung, Associate Dean for Academics. “The Ph.D. allows one to be part of advancing the science of nursing education by generating and applying evidence and promoting evidence-based teaching.”
In what settings will a Ph.D. in nursing be applicable?
No matter what nursing role you’re in, the knowledge and skills you gain in the Ph.D. program is applicable, including in practice, in teaching, in your research, and in administrative roles. Nurses often encounter tough questions, whether from patients, our community members, our families, or even our own interests in learning how to improve nursing practice. A Ph.D. program gives you the space to pursue topics that interest you, and it provides you with the knowledge and skills necessary to answer these questions in ways that are systematic, valid, and reliable.
One growing need for Ph.D.-prepared nurses is the rising impact big data has in health care practice. “We are now living in the era of artificial intelligence and big data. Soon, it will be necessary to know how to deal with data—that is, generate and/or use existing data to inform your practice, teaching, research, administration,” says Chung.
She emphasizes the ways in which core competencies gained from MCN’s Ph.D. program are transferable to the real world. “The Ph.D. prepares you to be friends with data and information and understand how data-driven decisions are made. To be a leader who transforms health care and improves individual and population health, knowledge and skills acquired in a rigorous PhD program will be critical.”
How can I balance a Ph.D. program while working full-time and/or honoring my commitments to my family?
MCN’s Ph.D. program can be completed part-time, making it conducive for those balancing work, family, research, and education.
“The faculty all understood that we had full-time jobs. Most of us were either teaching, working as a nurse on the floor, or working as a clinical nurse. The faculty were able to maintain the appropriate amount of rigor and expectations while also granting students grace,” says Blakeman.
“The decision to complete a Ph.D. program is a commitment to yourself and your discipline,” affirms Melissa Moody, MCN’s academic advisor for post-licensure programs. “You may be balancing this new and exciting endeavor among many other obligations. The key to your success will be early planning, staying organized, managing your time well, maintaining open communication with faculty and staff, and staying the course—one day at a time.”
She adds, “MCN faculty and staff are here to guide and support you on the path. We share a common goal: we want to see you succeed.”
MCN’s PhD program offers a professional, efficient, supportive environment. With both online and in-person requirements, the coursework is designed to work around nurses’ busy schedules with work and family. In MCN’s program, the coursework and research projects are customized around the needs and interests of our Ph.D. students.
Students also benefit from the expertise of MCN’s faculty. From advisement to knowledge of current research in the field, our faculty provides individualized attention for each student in the program.
Dr. Kim Astroth notes how important it is to MCN faculty that they give their students the time and attention. “It’s what sets MCN apart,” says Astroth. “Our faculty are attentive, flexible, and giving, working to empower our students. And our students are prepared to create high quality work as a result.”
Blakeman agrees. “I wasn’t just one number in a large group of people,” he says. “The faculty really knew us and cared about our personal lives—and so did our classmates. There was a close sense of community.”
So, is the Ph.D. in nursing worth it?
A Ph.D. program gives nurses the opportunity to pursue their research and make a difference in the health care landscape. MCN’s Ph.D. program is flexible in order to serve the needs of working nurses with busy lives while still providing the rigorous training necessary to becoming an expert. Nurses with Ph.D.s are prepared to make a huge difference in their communities, in their workplaces, and in the larger landscape of health care.
“A Ph.D. opens doors to a wide variety of practice areas,” says Associate Dean of Research Mary Dyck. “I’ve had the opportunity to chair a board of directors at a retirement community where I impacted the care for all of the residents. I’ve testified as a legal expert on quality of care. And I’ve worked with students as they’ve implemented major projects in health care institutions in the area. The Ph.D. allows nurses to have a much broader impact on the quality of care.”
Ph.D.-prepared nurses help shape health care policy and practice, and they are crucial to addressing the nursing shortage. We need nurse leaders to rise to the challenge and meet this call.
At MCN, we ask: why not you?
MCN is providing leadership in nursing. Learn more.
Our undergraduate programs
- Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN)
- Accelerated BSN
- Online RN-to-BSN
Our graduate programs
- BSN to DNP: Family Nurse Practitioner
- BSN to DNP: Leadership & Management
- Ph.D. in nursing
- Online Doctor of Nursing Practice
Related Articles
- Privacy Statement
- Appropriate Use Policy
- Accessibility Resources
Michigan State University
College of Nursing
Get Connected:
Faculty/Staff Login:
Why join the PhD program
How has the phd program prepared you for advanced roles, and how will you apply the knowledge and skills gained from the program in your future work.
Embarking on a journey to pursue a PhD in nursing has been a transformative experience for me. This program has significantly enriched my skills and knowledge, empowering me to become a more proficient researcher, educator, and leader in the nursing field. My motivation for enrolling in a PhD program in nursing was driven by my aspiration to make a substantial impact on patient care and contribute to the advancement of nursing science. - Mohammed Alanazi
The PhD program has been instrumental in enhancing my skills and knowledge as a nurse and a research scientist. Since enrolling in the program, my critical thinking and academic writing capabilities have grown significantly. I've also honed leadership and service skills, along with gaining expertise in an area of research that resonates deeply with me. - Callie Harris
Embarking on a PhD program has significantly enhanced my skills and knowledge as a nurse and research scientist. This program has equipped me with a comprehensive understanding of diverse research methodologies, encompassing both qualitative and quantitative approaches, along with adeptness in data analysis techniques. In addition, I have cultivated critical thinking skills that empower me to identify and analyze intricate issues within the realm of nursing and healthcare. The program has also expanded my knowledge of nursing theories, patient care, and healthcare systems, which has proven instrumental in crafting effective interventions for enhanced patient outcomes. - Hesam Varpaei
What motivated you to pursue a PhD in nursing, and how has the program met or exceeded your expectations?
The program has not only fulfilled but surpassed my expectations by providing rigorous training in research methodologies, critical analysis, and theory development. It has continuously challenged me to think critically, explore innovative ideas, and engage in intellectual discourse with my peers and mentors. The PhD program has meticulously prepared me to be a nurse scientist through comprehensive coursework and immersive research experiences. I have acquired expertise in advanced statistical methods, grant proposal composition, and scholarly communication. - Mohammed Alanazi
After years of being an undergraduate clinical instructor, a desire for scholarly engagement and leadership roles prompted my pursuit of a PhD. The program has exceeded my expectations by not only equipping me with advanced skills but also by providing insights into the role of a nurse researcher within academia. - Callie Harris
My motivation to pursue a PhD in nursing emanated from a deep-seated desire to contribute to the advancement of nursing research and healthcare practices. The PhD program has exceeded my expectations by offering an academically challenging yet nurturing environment. It has provided avenues for rigorous scholarship, critical inquiry, and collaborative research. Exposure to diverse perspectives has fostered a comprehensive understanding of nursing and healthcare complexities. The faculty's guidance and mentorship have been invaluable in identifying avenues for personal and professional growth. - Hesam Varpaei
How has the PhD program improved your skills and knowledge as a nurse and/or research scientist?
Furthermore, the program has broadened my perspective, allowing me to think more expansively and creatively about the intricate social and cultural factors influencing health outcomes and healthcare provision. Looking ahead, I intend to employ the knowledge and skills gained from this PhD program to further my career. I plan to conduct research that addresses pivotal issues in nursing and healthcare, as well as share my expertise through teaching and mentoring the forthcoming generation of nursing scholars and practitioners. Additionally, I aim to leverage my insights to shape health policies and elevate the quality of care for diverse populations. All in all, this PhD program has been a transformative journey that has deepened my comprehension of nursing science and readied me for a gratifying career in the field. I express gratitude for the unwavering support and guidance of my mentors, colleagues, and the esteemed program faculty. I eagerly anticipate continuing my contributions to the nursing profession through research, education, and advocacy. - Mohammed Alanazi
The PhD program has readied me for more advanced roles in nursing research, academia, and healthcare leadership. It has endowed me with research, critical thinking, and leadership skills essential for securing a tenure-track position at a research-intensive university. - Callie Harris
The PhD program has primed me for advanced roles in nursing research, academia, and healthcare leadership. It has endowed me with the competence to design, execute, and disseminate research findings, contribute to healthcare policy formulation, and propel nursing science forward. The comprehensive coursework, research projects, and teaching experiences have equipped me to be an adept communicator, educator, and leader. I intend to apply the acquired knowledge and skills by engaging in interdisciplinary research collaborations, mentoring emerging researchers, and sharing research insights with a broader audience. - Hesam Varpaei
10 Pros and Cons Of Ph.D. In Nursing

A Ph.D. in Nursing is considered a prestigious accomplishment, but is having one all that they say it is cracked up to be? Are you not sure if this is the path you want to go down regarding your nursing career? I think the first thing that you need to look at is, is what are the pros and cons of a Ph.D. in nursing? It is a lot to think about, so don’t worry, I took the work out of it for you. Below you will find the top 10 pros and cons of a Ph.D. in nursing. This article will definitely help you decide whether this is the right career path for you.
TOP CONS OF Ph.D. In NURSING
1. the cost of tuition, 3. you will not be able to practice in the hospital setting as a provider, 4. length of the program, 5. you will have to write a dissertation, 6. you must successfully defend your dissertation, 7. you may not be able to work full-time, 8. tenure is not guaranteed, 9. no more free time, 10. it is not a necessary degree, top pros of ph.d. in nursing, 1. increased salary, 2. no more 12-hour shifts, 3. no more weekends or holidays to be worked, 4. you have earned a prestigious title, 5. you can juggle anything, 6. you have earned the highest degree, 7. you can influence policy and practice change, 8. can you see yourself as chief nursing officer, 9. you can earn a prestigious job, 10. you will be regarded as an expert in your field, the bottomline.

Doctoral Degrees in Nursing
Table of contents.

What is a Doctoral Degree in Nursing?
A doctoral degree in any field is what we consider to be the terminal or final degree for that field. A doctorate is the highest degree you can possibly earn. When it comes to nursing, there are a couple of options to consider if you’re thinking about getting your Doctorate. Each has a different focus and specialization that uniquely supports the profession of nursing.
Doctor of Philosophy, PhD
The PhD is probably most likely what people think of when it comes to Doctoral degrees that are outside what a physician would have. There are numerous PhD focuses out there across many disciplines and professions, and they all focus on research within their field or specialty.
The PhD in nursing is a research-focused degree with an emphasis on creating new knowledge as it relates to things like nursing practices, healthcare, patient outcomes, and education. These nurse scientists identify a problem, create a hypothesis, develop a way to evaluate that hypothesis through statistical analysis, and synthesize new evidence and knowledge based on their findings.
The PhD project has some great resources you can check out for more insight into what the Doctor of Philosophy is all about.
Doctor of Nursing Practice, DNP
The DNP degree could be the doctoral degree most directly relatable to the practice of nursing at the bedside. Throughout the DNP academic program, the focus is on evidence-based practice and how to bring that practice to the patients. As a DNP, you are prepared to view potential problems in practice, identify the solution to that problem by investigating and reinforcing best practices, and assist in putting those best practices into action.
Another way to think of this is that the DNP can pick up where the PhD left off, because one complements the other.
A PhD-prepared nurse scientist conducts research and produces evidence from that research. The DNP-prepared nurse focuses on translating that evidence into practice to support optimal patient outcomes.
To learn more about the possibilities in achieving your Doctor of Nursing Practice Degree, check out Doctors of Nursing Practice .
Doctorate in Education, EdD
The EdD is, as you may have guessed, all about education. This is another degree that touches many different disciplines of education outside of nursing, such as those professionals directing school systems who seek to advance scholarly practices.
The EdD is available with a focus on nursing education through some universities and colleges. Those pursuing their EdD with a focus on nursing will be prepared to be leaders and innovators in the academic preparation of future nurses.
If you’re interested, a great resource to check out the EdD options out there is EdD Programs .
What Can You Do With a Doctoral Degree in Nursing?
Any of the Doctoral degrees mentioned here likely have some elements to set you up for success as a leader in your field. Depending on what you want to do with your professional life, or what your current professional role includes, one of the Doctoral pathways could be better suited than the others.
Nurses with Doctoral degrees have knowledge and skills that support roles outside of what many might consider traditional and can include roles like
- Academic faculty
- Advanced Practice Nurse (APRN)
- Nursing science and research
- Clinical leadership
- Health executive
- Health policy analyst
- Healthcare lobbyist
- Healthcare data analyst
- Health Writer
- Nurse consultant
- Health Program Director

Which Doctoral Degree is Right for Me?
Which Doctoral degree is right for you depends on you as a person, and the reasons you are considering it in the first place. The decision to pursue a Doctoral degree and the pathway to getting there should be guided by what you want to do with your degree when you’re done.
You don’t want to decide you’re going to get your PhD and then try and figure out what you’re going to do with it. You should be thinking in the reverse. Think about what roles you could see yourself in and make your decisions about which Doctoral pathway to pursue based on that. The last thing you want to do is labor through a PhD program geared toward research and academia when your true heart’s desire is to be a clinical leader.
If you think you want to be a member of the nursing faculty, then any of the three mentioned Doctoral programs will likely serve you well. If you want to be a nurse scientist focused on research, you would want to stick with a PhD. The end goal needs to justify the means.
Is a Doctoral Degree The Right Choice For Me?
If you’re thinking about someday pursuing a Doctoral degree you really need to make sure you want it badly enough to put in the work. Sometimes nurses like the sound of completing their Doctoral degree, but when it comes down to the work they run out of steam or they find it’s just too much with everything else in life they need to manage.
Completing a terminal degree is a tremendous amount of work. You will eat, breathe, and sleep school for a period of time, and it does get tiresome. By the time I finished my own DNP degree program I didn’t want to think about or speak about my chosen area of research at all. I was just plain sick of it for a while.
Trust me, there were many times throughout the program that I wanted to throw in the towel, but I’m very happy I didn’t. This is not meant to scare people, it is meant to make sure you have a realistic idea of what the expectations are. Ask around, and talk to some people you know who have been through it. See what their opinion on the workload is.
How Do I Get Started and When?
When and where you get started depends mostly on where you are now. Most Doctoral programs will require at least a Bachelor’s degree and Master’s level coursework to be completed as a component of their admission requirements.
There are some exceptions to this, especially with many of the APRN programs that have transitioned to DNP programs. For these programs, you can be accepted into the program with a Bachelor’s degree and work through the Master’s level coursework as a matriculated DNP student.
The timing of when to start depends a lot on what your life is like and what responsibilities you may be managing while also in school. Some people prefer to delay until their kids are in school or until some other major life event has passed. That is totally okay, and nobody is going to be able to make that decision better than you.
I will also say it’s never too soon or too late to start at least thinking about Doctoral programs if you’re interested, but you need to do your research.
You do not want to apply to and enroll in the first Doctoral program that shows up in your Google search. You need to research the program and think about its unique requirements and how they fit your needs.
Here are some things to consider when looking at programs:
- Does this program fit my future career goals?
- Does the enrollment timing of this program match the needs of me and my family?
- Do I need a program that is online, in-person, or a combination of both?
- Does the program have on-site residency requirements I might need to satisfy?
- How long is the program?
- How much is the program?
- What is the program’s reputation?
- Check out the faculty; are there any faculty members that have research interests that align with yours?
- What are the clinical or research requirements?
- Are you allowed to take any semesters off if needed?

Matt is a registered nurse currently working in nursing professional development specializing in supporting the development of current and future nurses. He obtained his Bachelors in Nursing from Utica College and both his Doctor of Nursing Practice degree and Master’s degree in Nursing Education from Sacred Heart University. Matt maintains two national board certifications as a Certified Emergency Nurse and a Trauma Certified Registered Nurse. Matt’s free time is mainly spent with his three children as they are always reliable in keeping him active.
Further Reading

What Type of Nurse Should I Be? How to Choose Your Specialty

Do Nurses Need Malpractice Insurance? Lawsuit Statistics and Advice

What Is a BSN, and What Can I Do With One?
Study with Lecturio for
Medical School
Nursing School
- Data Privacy
- Terms and Conditions
- Legal Information
USMLE™ is a joint program of the Federation of State Medical Boards (FSMB®) and National Board of Medical Examiners (NBME®). MCAT is a registered trademark of the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC). NCLEX®, NCLEX-RN®, and NCLEX-PN® are registered trademarks of the National Council of State Boards of Nursing, Inc (NCSBN®). None of the trademark holders are endorsed by nor affiliated with Lecturio.
User Reviews
Get premium to test your knowledge.
Lecturio Premium gives you full access to all content & features
Get Premium to watch all videos
Verify your email now to get a free trial.
Create a free account to test your knowledge
Lecturio Premium gives you full access to all contents and features—including Lecturio’s Qbank with up-to-date board-style questions.
- Visit Nurse.com on Facebook
- Visit Nurse.com on YouTube
- Visit Nurse.com on Instagram
- Visit Nurse.com on LinkedIn
Nurse.com by Relias . © Relias LLC 2024. All Rights Reserved.

The PhD Program in Nursing prepares scholars to be nursing scientists, educators and leaders who seek to improve health across the lifespan with a concentration on urban, vulnerable and underserved populations.
- Post-Baccalaureate and Master’s entry are available
- Opportunities for interdisciplinary study and research
- Assume leadership in the promotion of health and well-being of urban populations nationally and internationally.
- Design a program of research that builds upon the historical and philosophical foundations of nursing science.
- Implement research studies that advance health science outcomes.
- Participate as a member of an interdisciplinary research team.
- Conduct research that demonstrates the theoretical, methodological, and analytical knowledge, skills, and strategies to address population health.
- Assume faculty, leader, and/or nurse scientist roles.
- Apply principles of professional research ethics and judgment in the conduct of research.
“My experience at Northeastern is preparing me for leadership in the health care system in my country. I am learning how to approach both clinical and public health problems from a leadership perspective.” — Maram Alghabbashi, Alumna
All students are expected to participate in a Mentored Research Practicum with a seasoned researcher and his/her research team. In addition, you will have the opportunity to study with nursing faculty and faculty from other Northeastern departments. Collectively, the nursing faculty has expertise in a variety of research interests, such as health issues of women, children and families, HIV, cancer, mental health, depression, substance abuse, and perinatal injury. Our close ties with the University’s Institute on Urban Health Research and School of Social Science, Urban Affairs and Public Policy , as well as with the Center for Community Health Education, Research and Service and other organizations provide opportunities to work across disciplines and access populations and sites for your dissertation.
Our graduates pursue careers within academia and beyond.
- Institute for Aging Research, Hebrew Senior Life
- Mount Auburn Hospital
- Massachusetts General Hospital Institute of Health Professions
- University of New Hampshire School of Nursing
- University of Pennsylvania
- Boston Children’s Hospital
- Laboure College
- University of New Hampshire
- Ben Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, Isreal
- University of Massachusetts, Dartmouth
Application Materials
Application.
- Application fee – US $80
- Minimum GPA of 3.5
- Transcripts from all institutions attended
- Minimum GRE of 300 or equivalent for the verbal and quantitative combined, within the last 5 years
- Three letters of recommendation that address your potential for a career in nursing research, with at least 2 recommendations from persons who have a PhD and can speak to the applicant’s ability to be successful in a PhD program.
- Satisfactory completion of a basic statistic course
- Satisfactory completion of an epidemiology course (not required for post-baccalaureate entry)
- Personal Statement describing your goals and reason for pursuing a PhD in nursing and your research area of interest
- TOEFL or IELTS for applicants who do not hold a degree from a U.S. institution and whose native language is not English
- Current Nursing licensure
Deadline: December 15
- Program Website
Request Information for PhD in Nursing
- Login / Register

‘There is no point in pouring staff into the funnel if they are not supported’
STEVE FORD, EDITOR
- You are here: Clinical research nurses
The challenges and benefits of undertaking a nursing PhD
17 February, 2020
Studying for a nursing PhD equips nurses as researchers to drive improvements in patient care. This article looks at what motivated two nurses to take the PhD route
Healthcare research is central to providing high-quality, evidence-based care and the role of nurses as researchers is being promoted and supported nationally. Despite this, nurses undertaking a PhD are under-represented compared with other professional groups, even though a nursing PhD can open up new career avenues. In this article, two general nurses describe their experiences of the PhD journey, including what motivated them, the routes they took and tips for getting started.
Citation: Lees-Deutsch L, Stafford-Umughele A (2020) The challenges and benefits of undertaking a nursing PhD. Nursing Times [online]; 116: 3, 24-26.
Authors: Liz Lees-Deutsch is consultant nurse in acute medicine, University Hospitals Birmingham, Heartlands Hospital and lecturer, University of Birmingham; Augusta Stafford-Umughele is return to practice student, Swansea University.
- This article has been double-blind peer reviewed
- Scroll down to read the article or download a print-friendly PDF here (if the PDF fails to fully download please try again using a different browser)
Introduction
The last 12 years has seen a drive by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) to develop the research skills of nurses and other health professionals to increase the body of healthcare knowledge and innovations that improve patient care. NIHR options for embarking on a clinical academic pathway include:
- Academic internships (including preclinical academic fellowships);
- Clinical doctoral research fellowships;
- Clinical lectureships;
- Senior clinical lectureships.
More recently, Health Education England laid out its vision for developing the NHS workforce that embraced five global drivers of change in delivering healthcare: demographics; technology; current and future service models; patient and staff expectations; and associated social, political and environmental factors (HEE, 2017). Specifically, in the area of research and practice, it highlighted the need to respond to “changing patterns of service and embrace research and innovation to enable it to adapt to the changing demands of public health, healthcare and care services”.
However, although research by nurses and other health professionals that supports innovative, high-quality and evidence-based patient care is being promoted and supported nationally, there are still fewer nurses taking NIHR-funded PhDs compared with other professionals (Council of Deans of Health, 2013). Nurses are by far the largest professional group in healthcare; the number of nurses on the Nursing and Midwifery Council register is greater than the combined registers of the General Medical Council and the Health and Care Professions Council, so it is clear that the profession is underrepresented.
This article describes the various routes to a PhD, what it involves and why nurses may choose to embark on this journey. It shares the experiences and insights of two general nurses who embarked on this journey.
Although we took different career routes and made different decisions at key points along the way, we both had similar motives for completing a PhD. By sharing our stories, we hope to encourage other nurses who are contemplating a research career to follow in our footsteps.
Funding routes
As well as the ongoing national drive by the NIHR, health and nursing charities advertise PhD studentships for themed research related to their cause. Universities also advertise PhD studentships for work on projects that already have funding. There may be ways to negotiate study leave and adjust your working hours to accommodate work and study. Another option is self-funding, which means you are not tied to research themes set by funders. Regardless of the route you take, your PhD will be closely governed by the university where you choose to study.
What does a PhD involve?
Nurses often consider a PhD if they want to challenge themselves and develop new skills; others may have a desire to ‘invent for the real world’ through a research career. Typically, a PhD requires you to:
- Produce a viable research proposal for the number of years you have allocated for your PhD;
- Conduct a literature review to identify the research gap;
- Work up your research proposal detailing your research methods;
- Conduct the research;
- Produce a thesis;
- Defend your thesis in an oral examination known as a viva.
Passing the viva by demonstrating your original contribution to knowledge is what distinguishes a PhD from any other degree, but each stage of a PhD brings its own challenges, because of the time required to complete the work.
Potential barriers
A PhD usually takes 3-5 years, depending on whether you choose full- or part-time study. Over this period, people’s life situations can change, it can require significant tenacity to balance PhD study with career, family and life events. It may take longer and changes are sometimes negotiated throughout the course of the PhD. Learning how to apportion your time is a crucial skill you will need to develop.
A PhD can also bring financial challenges, particularly if you are funding yourself, even if this is only a drop in salary during your period of study. Self-funding may also mean not having a base organisation where you can conduct your research. Securing the assistance of a gatekeeper, someone who is employed at the organisation where you wish to do the research is essential. Contact with researchers and clinical staff (as needed) at an early stage can save valuable time by helping with issues such as gaining access to the research site, and locating and introducing yourself in the area.
Although you will probably meet like-minded students on courses you choose to take, you will also need to be self-motivated to study alone for at least some of the time. Some people are put off taking a PhD because they fear it will be a long and lonely journey, but seeking support from supervisors, colleagues and former PhD students can help negate this.
Lack of a clear job plan/career prospects after completing a PhD can be an issue for some, but having a realistic idea of where you would like to be working or what you would like to do after your PhD can help with early preparation to steer you towards your goals. For example, training in additional skills, presenting at conferences and networking over the duration of the PhD will enhance your prospects of paid employment afterwards. Your PhD will also give you an in-depth understanding of your topic, and on-going research interests and methodological preferences, to take you forward.
The following case studies describe our experiences of embarking on a PhD, including our careers leading up to it and the different routes we took. They also describe the lessons we learned along the way, including our tips (Box 1 and Box 2) to ensure success.
Box 1. Tips from Liz Lees-Deutsch
- Be honest with yourself why you want to do a PhD
- Seek support early on from research and development, other academics and your local university
- Ask yourself whether you are self-motivated to study
- Choose a topic that holds your interest and that you would like to continue with in your career
- Think what you will do when you have finished the PhD
- Talk to others who have gained national funding
- Look up authors of key works in your chosen area of study to find a PhD supervisor
Box 2. Tips from Augusta Stafford-Umughele
- Apply for PhD funding if you can, as it can be hard covering fees and additional expenses as a self-funded student
- Select a topic that interests you and that you can build on in the future
- Choose your supervisor carefully – research the lecturers, their experience and special interests, their work with PhD students and their publications
- If you choose to study part time, allocate a couple of days a week to your PhD study
- Build a support network – studying for a PhD can be a lonely road at times
Case study 1: Liz Lees-Deutsch
I qualified as a general nurse in 1991. In the following eight years I gained a variety of nursing experience, including working in older persons’ care, acute surgery and medical admissions. I then moved to the US for a year on a Florence Nightingale Scholarship to study intermediate care delivery.
Following my return, I managed a community hospital in Birmingham. After a year, I moved to a community role as lead nurse in a rapid response nursing team before moving back into acute hospital care to take on the role of consultant nurse, where my main interest has been service improvement.
My journey into my current area of expertise, patient discharge, began when a former clinical director dared to suggest ‘nurses simply followed doctors’ discharge orders’.
Once I had managed to get work published, my mission was to share what I was doing through robust data collection and a systematic approach to writing, as I never saw the point of doing work unless it could be shared. At the back of my mind, I also had the idea of studying for a PhD to delve deeper into the theory and social science underpinning patient discharge.
As a consultant nurse, I took three secondments; in older persons care, at a faculty of education and my current secondment (one day a week) at the University of Birmingham. I also took a BSc degree in nursing, a master’s degree and a health service management diploma.
In 2013, while on secondment at the faculty of education, I was encouraged by the head of education to apply for a PhD fellowship. Although this seemed a natural next step for me, I was unsure what further study would add and was worried about leaving clinical practice behind. However, I felt a PhD could break the glass ceiling that I felt at times had held me back from academic career progression.
The research career pathways the NIHR provided were new to me, and the process of applying for a PhD felt like scaling a mountain without any equipment, putting me on a huge and rapid learning curve. When considering an application for national funding, the NIHR panels judge the merits of the applicant and the employing organisation, as well as the applicant’s research proposal and intended career pathway (Association of UK University Hospitals, 2016).
I wanted to create a risk assessment for discharge for patients admitted to hospital and my intended career pathway was to become a clinical academic nurse. My line manager provided guidance and a supporting statement. The proposal also required a full literature review to ensure the research gap I envisaged was real. I chose the University of Manchester as my place of study as I had studied there before, and was required to submit my research proposal and key milestones for three years of study.
Despite preparations over 12 months, my first application to the NIHR was unsuccessful. At interview, the panel felt I had the right attributes, but had insufficient support from my organisation. An onward career pathway is a critical aspect of gaining any research funding and they felt my organisation lacked the vision to find me suitable employment on completion. Undeterred, I reapplied a year later following a clear strategy (see tips in Box 1). In 2014 was offered full funding, along with three years’ salary and training costs.
The next stage was quite daunting, as I had to leave my full-time post, become a student and learn completely new skills. I met my supervisors every month; one supervisor gained a promotion and left soon after I started, but the other saw me through to the finish. I completed my PhD in 2018 and then had a post-doctoral fellowship funded by Health Education England and hosted through the University of Birmingham. This gave me time to complete further publications arising from my PhD, progress research work, consider funding streams and complete further research methods training. I got funding from the Burdett Trust for Nursing for evaluation work of an education programme in acute medicine (Lees-Deutsch et al, 2019).
I also got a place on the NIHR 70@70 national nurse and midwife leadership programme, giving me three years of part-time funding. As a result, my role is now much more collaborative with researchers, lecturers and clinicians, with the aim of securing further funding this year to continue my patient discharge research.
Case study 2: Augusta Stafford-Umughele
Having trained at the North Middlesex Hospital, I enjoyed working as part of a team helping patients move from an ill and helpless state to full recovery and discharge home.
I decided to study for a master’s degree in human resource management at Middlesex University Business School. Fundamental to this decision was my interest in staff behaviour across the team and my intention was to gain a management qualification I could combine with nursing. Throughout this time I worked as a staff nurse and then as a sister in a London nursing home.
As part of my master’s degree, I completed a placement in a personnel department at the hospital where I trained as a nurse and was asked by my mentor to evaluate the advanced nursing skills course for post-registration nurses. My findings showed nurses were not being given the opportunity to perform advanced skills and lacked confidence because they were not using the skills frequently enough. After completing my course, I worked in nurse recruitment, where I further developed my interest in advanced nursing roles.
In 2001, I decided to leave my job in nurse recruitment to look after my four young daughters. It was not until 2010 that I planned my return back to work. Having been out of work and education for nearly 10 years, and with a young family to support, the idea of resuming work or study was daunting, and I decided to search for courses that were more compatible with family life.
In January 2012, my New Year’s resolution was to take a PhD in nursing, which I had wanted to do for many years. I planned to explore advanced nursing roles, potentially building on elements from my master’s degree. My aim was to increase understanding of how advanced practice had developed and the benefits of having experienced highly skilled nurses in these roles. In particular, the shortage of doctors across the UK meant the topic and the timing felt right.
I looked into the distance learning PhD programme at the University of Manchester’s School of Nursing. Distance learning enabled me to be based at home in Wales and travel only occasionally to Manchester, access learning modules from home and attend courses as needed around the UK. I felt satisfied that advanced practice was worth exploring further and contacted two senior lecturers with an interest in nursing roles and patient care quality to see if they would be interested in supervising my research. I received a positive reply.
My PhD was self-funded. I chose this route as I was not employed so did not have an employing organisation to support my application. The online application process was straightforward; the only challenge was professional references, as I had been out of work and education for 10 years and had to establish my ability to study at PhD level. I was advised to do another master’s degree, which I was not keen to do. Then the university offered me the opportunity to take individual modules from its master of research programme as a route onto the PhD nursing programme. Having completed these, I was admitted onto the PhD nursing full-time programme in September 2013.
The programme involved me attending a couple of 3-4-day workshops in the first year and completing other elements via Blackboard, an online learning system provided by the university. I went to seminars and presentations and had supervision once a fortnight via Skype with my three supervisors, as well as arranging to see them whenever I was at the university.
Following my viva, my final submission was in March 2018 and, since then, I have provided qualitative analysis and a report for an educational research project, and I am gradually publishing aspects of my thesis. I am now taking a return to practice course to update and participate in clinical practice, with a view to working in nursing research, as opportunities arise.
Despite the inevitable hard work undertaking a PhD has been, we both thoroughly recommend PhD study to nurses. We have gained invaluable skills in research methods, ethics, theory and writing (to name a few) and these will help us to progress to the next stages of our career. Reflecting back, we are both approaching the last 10 years of our careers, ideally, the decision to undertake a PhD should be supported at a reasonably early career stage to build your research skills over your employment lifetime.
- There is a national drive to encourage more nurses into research
- Studying for a PhD equips nurses as researchers to increase knowledge and drive improvements in patient care
- As the largest professional group in healthcare, nurses taking PhDs are under-represented compared with other groups
- Nursing PhD programmes require commitment, but can offer flexibility, so you can pursue them at your own pace
- When applying to study for a PhD, it helps to learn from others who have already been down that route
Related files
200219 the challenges and benefits of undertaking a nursing phd.
- Add to Bookmarks
Related articles
Have your say.
Sign in or Register a new account to join the discussion.
Why Get a Doctorate in Nursing (DNP)?

NurseJournal.org is committed to delivering content that is objective and actionable. To that end, we have built a network of industry professionals across higher education to review our content and ensure we are providing the most helpful information to our readers.
Drawing on their firsthand industry expertise, our Integrity Network members serve as an additional step in our editing process, helping us confirm our content is accurate and up to date. These contributors:
- Suggest changes to inaccurate or misleading information.
- Provide specific, corrective feedback.
- Identify critical information that writers may have missed.
Integrity Network members typically work full time in their industry profession and review content for NurseJournal.org as a side project. All Integrity Network members are paid members of the Red Ventures Education Integrity Network.
Explore our full list of Integrity Network members.
Are you ready to earn your online nursing degree?

A doctor of nursing practice (DNP) degree can help nurses increase their salary potential, while also opening up career opportunities only available to those with advanced training.
In 2004, the American Association of Colleges of Nursing endorsed shifting the minimum education level for advanced nursing practice from a master of science in nursing (MSN) to a DNP. As more nurses pursue DNPs than ever before, the rise in the number of DNP-holders has made doctorate-level education necessary to compete in the job market.
The number of DNP programs has also grown. Nursing schools in all 50 states offer DNPs, and as of 2020, 13 states, including California, Illinois, Pennsylvania, and Texas, boast over 10 programs. Find out in this guide the advantages of earning a DNP, along with salary data and career path advice.
What Is a Doctor of Nursing Practice?
The doctor of nursing practice is a terminal nursing degree, the highest level of education available in the field. It is important to distinguish the DNP from other terminal degrees available to nursing professionals, including the doctor of philosophy (Ph.D.) in nursing, the doctor of nursing science (DNSc), and the nurse doctorate (ND). The DNP delivers practice-based training, while other terminal degrees focus on research skills, scholarly inquiry, or high-level specialty skills.
While some schools accept DNP students with a bachelor’s degree in nursing, most require applicants to hold a master’s degree, since doctoral programs build on MSN curricula. Most doctor of nursing practice programs emphasize areas that support nursing leadership , such as systems management, quality improvement, and data-driven decision-making.
Students already possessing a bachelor of science in nursing (BSN) typically complete a BSN-to-DNP program in 3-6 years, depending on the program and the student’s enrollment status. Students with MSNs can complete their DNPs in as little as 18 months to two years in an MSN-to-DNP program . Curriculum content is largely focused on statistics and data analysis, leadership skills, advanced clinical skills, and nursing philosophy.
Advantages to Getting a DNP
As the U.S. healthcare system evolves, DNPs in clinical practice are expected to take on larger roles in problem solving and advocacy, acting as liaisons with other healthcare professionals. This heightened responsibility comes with higher pay rates and opportunities for advancement, especially as current DNP-holders start to retire.
Nurse leaders must be familiar with a constantly growing base of medical knowledge, and they must stay current on evolving best practices. Patient care is complex, and industry-wide developments are shifting more responsibility to nurses. Anticipated shortages in physician staff and nursing faculty also place challenging intellectual demands on nurse leaders.
Expectations for nurse leaders are lofty, and a doctor of nursing practice program offers excellent preparation for advanced clinical practice.
What Is the Difference Between a DNP and a Nursing Ph.D.?
Both a DNP and a nursing Ph.D. are terminal degrees, but they require different academic focuses and lead to different career opportunities. To understand the difference between a DNP and a Ph.D. in nursing, consider the following:
How Much Can You Earn With a DNP?
DNP-holders enjoy higher salaries than nurses with BSNs and MSNs, making it well worth it for practitioners with nursing bachelor’s and master’s degrees to earn advanced education. According to Payscale in February 2023, MSN-holders earn an average of $100,000 annually , and DNP-holders earn an average of $110,000 annually .
Some DNP positions pay significantly more. Chief nursing officers earn an annual average of $138,130 and certified registered nurse anesthetists earn an average of $172,670 annually, as of February 2023 on Payscale.
Popular Careers for DNP Graduates
DNP graduates take on many different roles. Some become advanced clinicians, working with specific patient populations. Others work as high-level nursing administrators and focus on decision-making, policy, and education in areas like clinical training, executive leadership, and nursing informatics .
The career options listed below rank as a few of the most popular jobs among DNP graduates . In addition to a doctorate, the first three positions require nurse practitioner (NP) certification in the applicable specialization area, whether family nurse practice, adult care, or psychiatric nursing.
University nursing professors usually need a Ph.D.
Family Nurse Practitioner
Nearly 70% of NPs surveyed by the American Association of Nurse Practitioners (AANP) in 2020 held certification in family nurse practice. These professionals typically work alongside physicians as primary care providers, seeing patients of all ages for annual checkups and addressing illnesses or injuries. Family nurse practitioners also advise on wellness issues like diet and exercise.
Salary: $110,000 median annual base salary (Source: AANP report )
Adult Nurse Practitioner
The second most popular NP focus area accounted for about 11% of NPs surveyed by the AANP in 2020. Practitioners with adult nurse certification provide acute and chronic adult primary care in collaboration or consultation with physicians. They conduct exams and assessments, order tests, and formulate treatment and health maintenance plans.
Salary: $120,000 median annual base salary (Source: AANP report )
Psychiatric Nurse Practitioner
While just 4.7% of NPs surveyed by the AANP in 2020 were certified in psychiatric nurse practice, it remains one of the highest-paying clinical focus areas. Practitioners help patients suffering from such conditions as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, anxiety, behavioral and mood disorders, and substance misuse .
Salary: $129,000 median annual base salary (Source: AANP report )
University Nursing Professor
University nursing professors usually hold a Ph.D. They educate future nurses at the undergraduate and graduate levels, develop nursing science innovations, and publish their research. Nursing professors typically specialize in an area of clinical practice.
Salary: $77,440 median annual base salary (Source: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics )
Page last reviewed February 24, 2023
Whether you’re looking to get your pre-licensure degree or taking the next step in your career, the education you need could be more affordable than you think. Find the right nursing program for you.
You might be interested in

HESI vs. TEAS Exam: The Differences Explained
Nursing schools use entrance exams to make admissions decisions. Learn about the differences between the HESI vs. TEAS exams.

10 Nursing Schools That Don’t Require TEAS or HESI Exam

For Chiefs’ RB Clyde Edwards-Helaire, Nursing Runs in the Family

Data Spotlight: A Closer Look at PhD in Nursing Program Enrollment and Graduations
In May 2023, AACN announced that enrollments in research-focused doctoral level nursing programs declined , with an average decline in research-focused doctoral enrollments of 4.1% from the 2021 to 2022 school year. The greatest regional decline in enrollment was seen in the schools in the North Atlantic region, with a 7.8% decline.
Graduation rates also declined between the 2021 and 2022 academic school years, with an average decrease in research-focused doctoral graduations of 4.8%. Graduation rates rose in some regions, increasing the most in the North Atlantic region, with an average increase in research-focused doctoral graduations of 23.8% or 37 additional graduates. The Midwest, however, experienced the largest decline in research-focused doctoral graduations, with an average decrease of 15% or 28 fewer graduates.
Figure 1: Enrollment Changes in Research-Focused Doctoral Nursing Programs 2021-2022 Datasource: AACN Annual Surveys, n = 146 schools
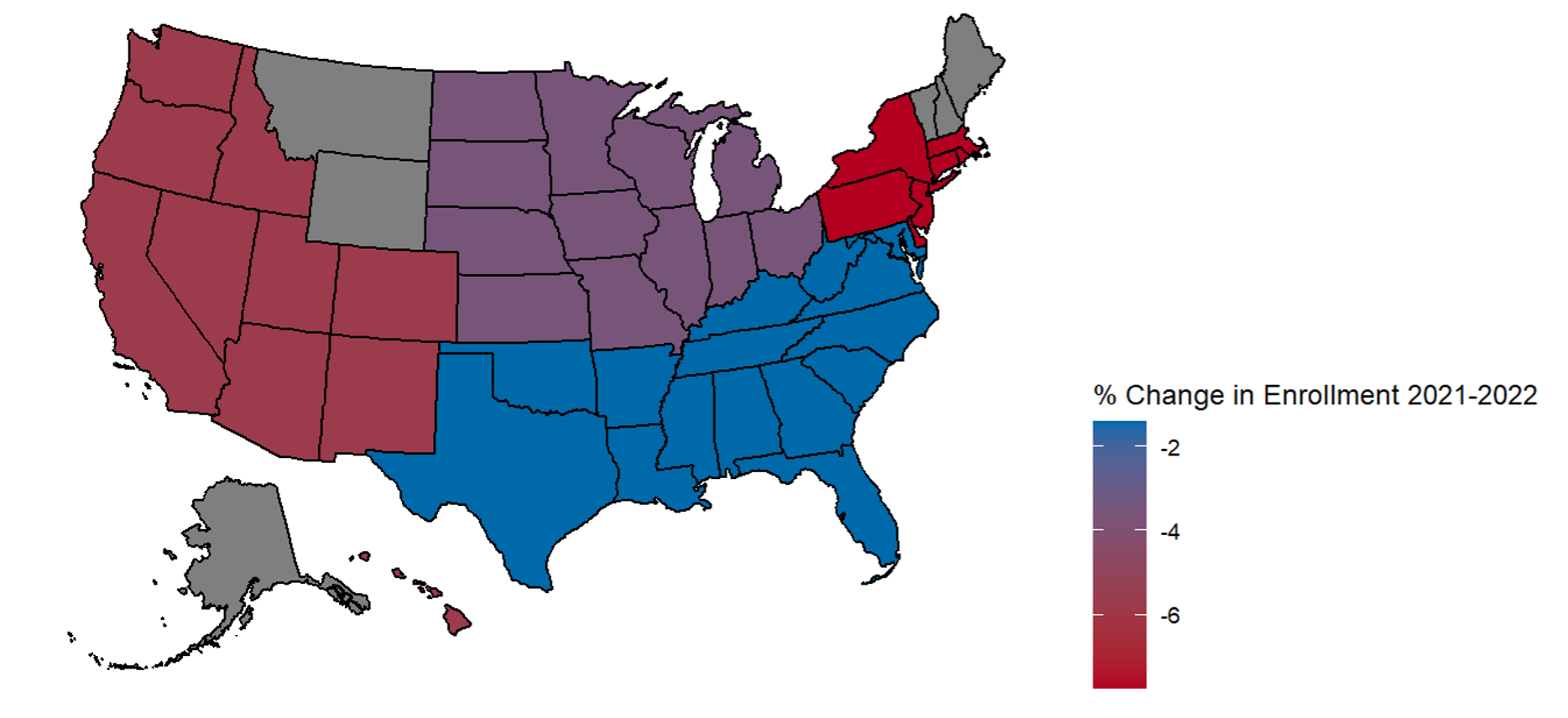
Figure 2: Graduation Changes in Research-Focused Doctoral Nursing Programs 2021-2022 Datasource: AACN Annual Surveys, n = 146 schools
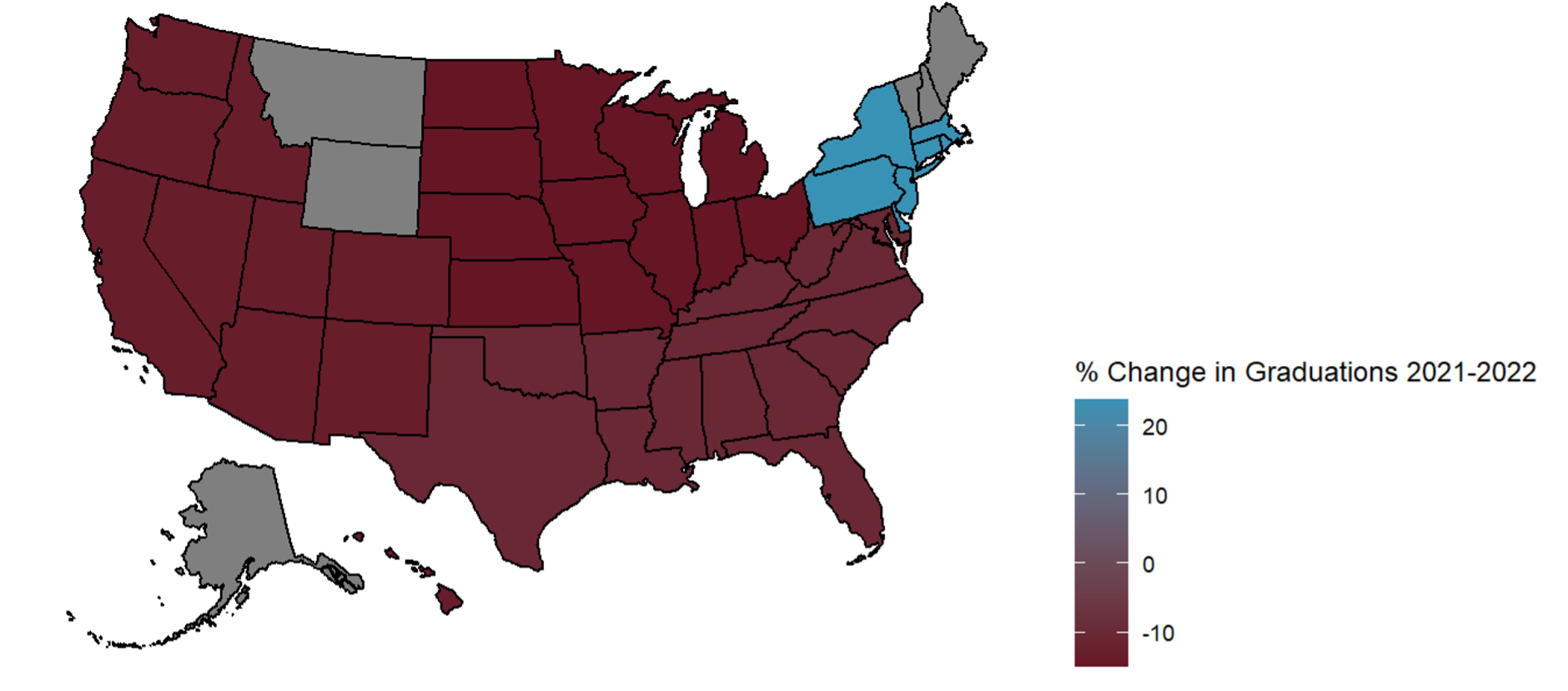
From 2021 to 2022, private religious schools reported an 8.4% decline in enrollment in research-focused doctoral programs. Similarly, public schools reported a 3.8% decrease in enrollment. Private secular schools reported the smallest decline, at 1.3%. In contrast, private religious schools increased graduations within their research-focused doctoral programs from 2021 to 2022, with an average increase of 4.5%. In contrast, from 2021 to 2022, private secular schools saw a decrease in graduations of 1.2% and public schools a decrease of 8.5%. Figures 3 and 4 describe these changes.
Figure 3: Research-Focused Doctoral Enrollment Percentage Change 2021 to 2022, Public and Private Schools
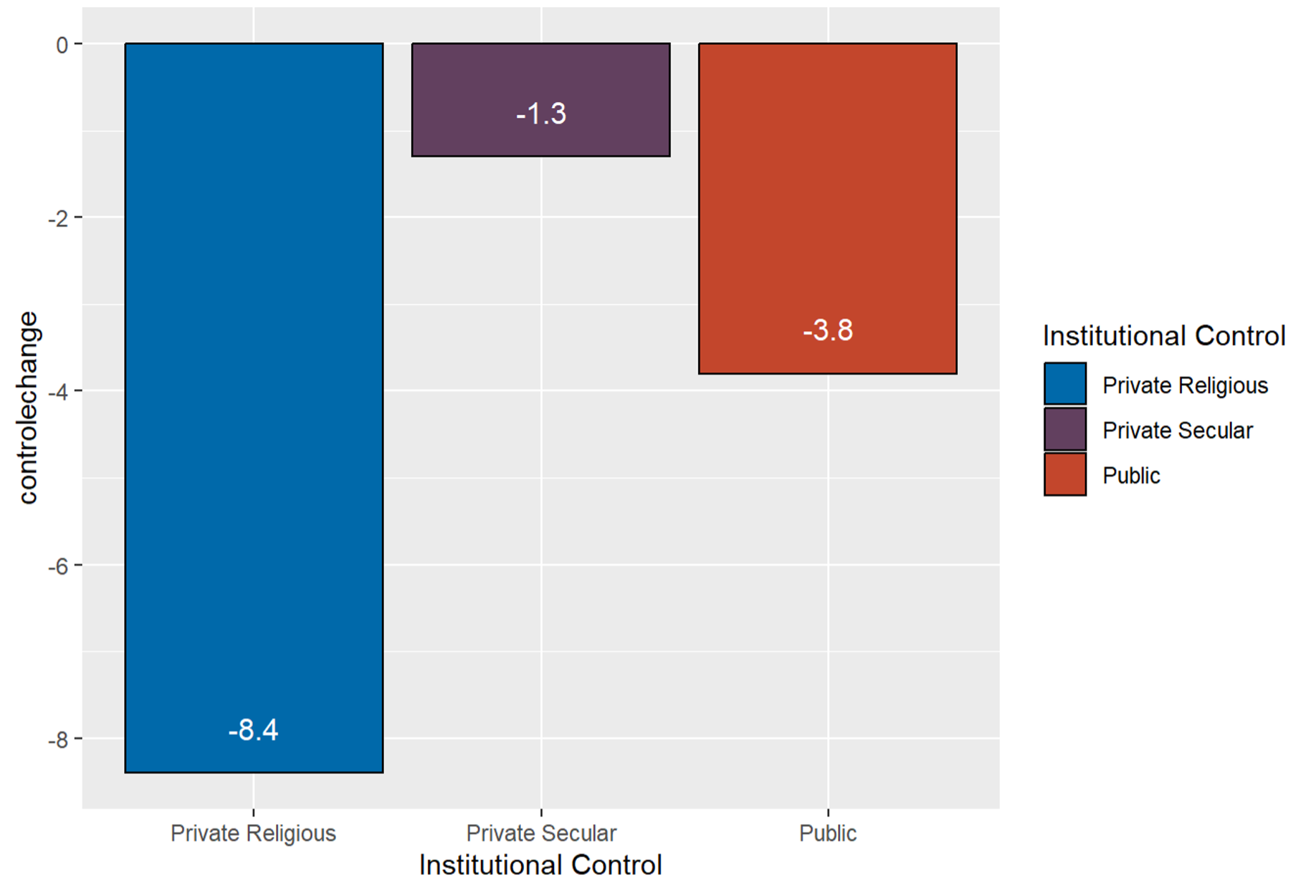
Figure 4: Research-Focused Doctoral Graduation Percentage Change 2021 to 2022, Public and Private Schools
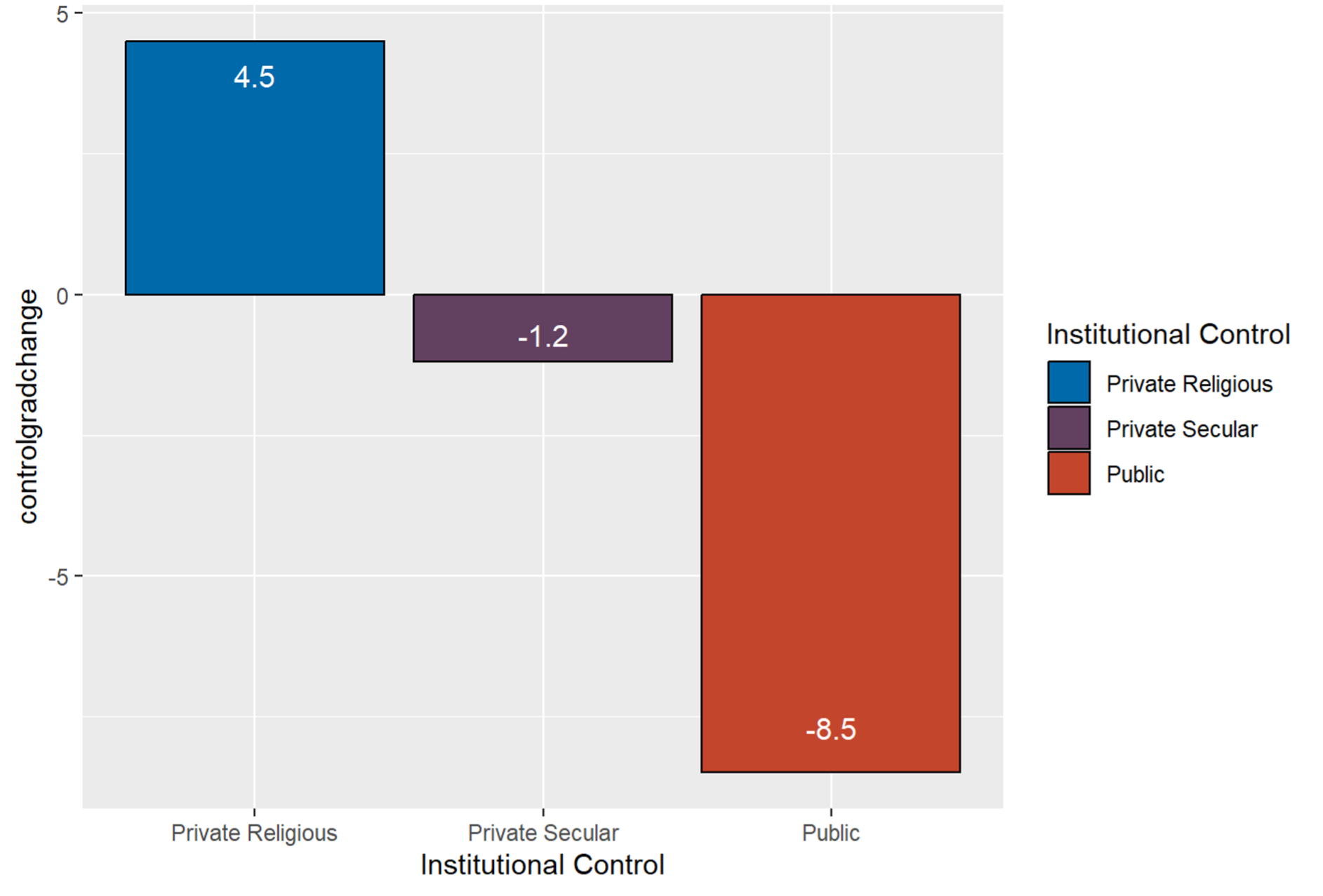
News Categories
- Accreditation Expand/Collapse
- Certification Expand/Collapse
- Diversity, Equity, & Inclusion Expand/Collapse
- Education Expand/Collapse
- Enrollment Expand/Collapse
- Essentials Expand/Collapse
- Grant Initiatives Expand/Collapse
- Foundation Expand/Collapse
- Funding Opportunities Expand/Collapse
- Membership Announcements Expand/Collapse
- Member Resolutions Expand/Collapse
- Syllabus Expand/Collapse
- Faculty Link Expand/Collapse
- GNSA Bulletin Expand/Collapse
- Diversity Digest Expand/Collapse
- ELNEC Connections Expand/Collapse
- Policy & Advocacy Expand/Collapse
- Population Health Expand/Collapse
- Press Release Expand/Collapse
- Professional Development Expand/Collapse
- Research & Data Expand/Collapse
- Rounds with Leadership Expand/Collapse
- Scholarships Expand/Collapse
- Student News Expand/Collapse
- Well-being Expand/Collapse
- Crimson Careers
- For Employers
- Harvard College
- Harvard Kenneth C. Griffin Graduate School of Arts & Sciences
- Harvard Extension School
- Premed / Pre-Health
- Families & Supporters
- Faculty & Staff
- Prospective Students
- First Generation / Low Income
- International Students
- Students of Color
- Students with Disabilities
- Undocumented Students
- Explore Interests & Make Career Decisions
- Create a Resume/CV or Cover Letter
- Expand Your Network
- Engage with Employers
- Search for a Job
- Find an Internship
- January Experiences (College)
- Find & Apply for Summer Opportunities Funding
- Prepare for an Interview
- Negotiate an Offer
- Apply to Graduate or Professional School
- Access Resources
- AI for Professional Development and Exploration
- Arts & Entertainment
- Business & Entrepreneurship
- Climate, Sustainability, Environment, Energy
- Government, Int’l Relations, Education, Law, Nonprofits
- Life Sciences & Health
- Technology & Engineering
- Still Exploring
- Talk to an Advisor
Leveraging Your PhD: Why Employers Value Your Skills
- Share This: Share Leveraging Your PhD: Why Employers Value Your Skills on Facebook Share Leveraging Your PhD: Why Employers Value Your Skills on LinkedIn Share Leveraging Your PhD: Why Employers Value Your Skills on X
Guest post by Heer Joisher (Griffin GSAS Candidate in Developmental Biology) for MCS.
Harvard’s Mignone Center for Career Success recently hosted an insightful discussion spotlighting the remarkable journeys of a select group of GSAS alumni who have masterfully leveraged their Ph.D. degrees to forge unique and gratifying career paths. Their experiences not only illuminate the expansive landscape of career possibilities for graduate students but also stand as beacons of inspiration for Ph.D. students and recent graduates navigating their own professional journeys. Here are some reflections I’ve summarized from the panel discussion on exploring non-academic career paths: the motivations, the timing, and the process.
Why? – A Multitude of Motivations
Dean Emma Dench’s opening remarks for the panel, noting that approximately 50% of Harvard PhDs become intellectual leaders outside academia, set the stage for a discussion on the motivations driving individuals to explore non-academic career paths. These motivations are as diverse as the individuals themselves, ranging from financial considerations to differing interpretations of job satisfaction and expectations. Moreover, panelists emphasized the presence of abundant opportunities available beyond academia and the importance of gaining a comprehensive understanding of the broader professional landscape. Embracing this perspective involves stepping outside the traditional academic paradigms, challenging preconceptions about career paths dictated by one’s degree or department. Instead, it involves introspectively questioning what truly fosters personal fulfillment and utilizing one’s unique background and expertise to craft a career trajectory that aligns with individual aspirations.

When? – The Sooner, the Better

The panel collectively emphasized the importance of early exploration into non-academic career paths, highlighting the immense value in stepping beyond conventional trajectories and embracing diverse experiences. Their insight underscores that this journey isn’t solely about finding a different career path; it’s about broadening perspectives and building a vibrant professional community, irrespective of the ultimate career trajectory. While transitioning out of academia may be smoother for some fields or labs compared to others, actively delving into learning about alternative career paths enables individuals to challenge norms and foster connections with mentors who can offer invaluable support along the way. The environment at Harvard, with its diverse peers and alumni network, facilitates this exploration and openness to new opportunities, acting as a catalyst for personal and professional growth.
How? – Navigating the Process
Drawing from their diverse career paths, the panelists offered valuable strategies and frameworks to guide individuals through the transition process. Each insight struck a chord with attendees, offering relatable anecdotes and invaluable guidance. Below is a compilation of key takeaways distilled from the discussion:
- Embrace Career Exploration and Experimentation:
- Explore diverse opportunities and pathways even if they seem unconventional or outside your comfort zone
- Recognize that your first job doesn’t have to be perfect, and that career progression often involves trying different roles and industries
- Utilize resources like alumni and LinkedIn to learn about different careers, and experiences
- Identify the transferable skills gained during your academic journey and identify your strengths. Introspect on how your strengths align with roles outside academia, consider doubling down on skills you excel in and enjoy.

- Cultivate Meaningful Professional Relationships:
- Approach networking with a mindset of curiosity and growth, fostering genuine relationships that support your career development.
- Articulate your accomplishments and expertise with confidence to bolster your credibility and draw opportunities towards you.
- Engage in informational interviews to gain valuable insights into various job responsibilities, organizational cultures, and career paths, allowing you to assess your fit within different professional contexts.
- Take a proactive approach to relationship-building by categorizing connections based on shared interests and goals. Remember, networking is a two-way street; look for opportunities to offer support, share insights, and connect others within your network.

- Invest in Your Professional Growth:
- View informational interviews, hands-on learning opportunities and internships as pivotal investments in shaping your future career path.
- Proactively seek out opportunities that foster continuous learning, cultivate enduring professional relationships, and steer your career in desired direction.
- Hone the art of articulation and effective communication to confidently convey your skills, experiences, and achievements, aligning them with the needs of different roles and organizations.
- Conquer decision paralysis by taking action: apply for open positions and initiate conversations with new connections. Embrace the interview process as an opportunity for growth and learning, gaining valuable insights along the way.

In conclusion, the panel discussion offered profound insights into navigating non-academic career paths. These key takeaways underscore the significance of charting one’s unique path with confidence and purpose in the dynamic landscape of non-academic careers.
Meet the Panelists:
- Elias Bruegmann, PhD : Head of Product Data Science at Stripe
- Victoria Tillson Evans, PhD : Founder & President of Distinctive College Consulting
- Marinna Madrid, PhD : Co-Founder and Chief Product Officer at Cellino
- Jessica Paige, PhD : Social Scientist at RAND
- Paul Schwerda, PhD : Investment Manager at Baillie Gifford
- Roger Vargas, PhD : Computational Scientist at Moderna
Quotes from Attendees:
“As an upper-level PhD student, the seminar provided valuable information and insights on careers outside of academia. It was great to hear from a diversity of people with different perspectives and who followed various career paths.” – Stephan Foianini, G5, Department of Molecular and Cellular Biology, Harvard University
- What Can You Be with a PhD
- Beyond the Professoriate
Seven Things You Can Do With a Bachelor's in Nursing
- Health Sciences
- Careers for Veterans
- College Advice
- Completing Your Degree
- Dental Hygiene
- Marketing and Communications
- Medical Imaging
- Seven Things You Can Do With a Bachelor's in Nursing
- Timeline: How Long Is a DNP Program?
Why Magnet Status Is Important in Nursing and How Regis Can Prepare You
- How to Expedite Your Bachelor's Degree in Nursing
- A DNP Made Them “Part of the Change”
- How Much Does a DNP Program Cost?
- Nurse Educators: Roles and Responsibilities
- How To Become a Nurse Educator
- Five Reasons It's Worth Getting A DNP Degree
- What Can You Do With a DNP Degree? Three Nursing Careers
- From Procrastination to Acceleration
- What Is a DNP Degree and Why Do You Need It?
- From Patent to Practice
- A Mother’s Career, A Daughter’s Legacy
- 24-Month Transformation
- “This is What Nursing is All About”
- What Does a Clinical Nurse Leader Do?
- CNL vs. CNS: What’s the Difference?
- What Degree Do I Need to Become a Clinical Nurse Leader?
- Clinical Nurse Leader Career Path: Five Key Steps
- Clinical Nurse Leader vs. Registered Nurse: Key Differences
- How to Become a Clinical Nurse Leader
- How Long Does It Take To Become A Clinical Nurse Leader
- Clinical Nurse Leader Role and Responsibilities
- Nurse Practitioner Role and Responsibilities
- Clinical Nurse Leader Salary: How Much Does a CNL Make?
- CNL vs. NP: What’s the Difference?
- What’s the Difference Between a Nurse Practitioner and a Doctor?
- What’s the Difference Between a Nurse Practitioner and Physician Assistant?
- Five Nurse Practitioner Specialities to Consider
- What Does the Typical Nurse Practitioner Career Path Look Like?
- How to Become a Nurse Practitioner
- How Much Does a Nurse Practitioner Make?
- What Does a Nurse Practitioner Do?
- What is a Registered Nurse’s Responsibilities?
- Eight Registered Nurse Careers to Consider
- Nine Registered Nurse Specialties and Certifications to Explore
- What Degree Do I Need to Become a Nurse Practitioner?
- What Degree Do You Need to Become a Registered Nurse?
- Registered Nurse vs CNA: Choosing the Right Career Path
- Registered Nurse vs LPN: Understanding the Key Differences
- Registered Nurse vs. Nurse Practitioner: What’s the Difference?
- How to Become a Registered Nurse: Three Key Steps
- Registered Nurse Salary: How Much Does an RN Make?
- What Does a Registered Nurse (RN) Do?
- How to Become a Nurse: Five Key Steps
- How to Become a Nurse in Massachusetts
- How Long Does it Take to Become a Nurse Practitioner?
- How Long Does it Take to Become a Registered Nurse?
- Nursing as a Second Career: Three Tips to Make a Career Change to Nursing
- Accelerated Nursing Programs: Everything You Need to Know
- You Want to be a Nurse Now?
- Training The Trainers
- Nurse Angelina Damiano and How to Thrive on Uncertainty
- Program Director of Regis’ Accelerated BSN
- Colleen Fagan ABSN ’20 in Her Own Words
- Samikshya Dhital ABSN in her own words
- From Trainer to Nurse: Kathleen Geoghegan
- Clinical Nurse Leader in Her Own Words
- EMT to Nurse | Taylor Bronson
- PTSD in Nursing: Why We Stress Prevention
- Occupational Therapy
- Online Learning
- Public Health
- Speech-Language Pathology
The nursing field has no shortage of opportunities for professionals who want a flexible career with wide-ranging options for advancement. However, as a registered nurse with an associate degree, you may find it challenging to pursue leadership or specialty roles that require additional education
Not only that, more hospitals are requiring bachelor’s-level degree nurses in their facilities. According to the latest AACN survey on the Employment of New Nurse Graduates , 28 percent of employers require a bachelor's degree among new hires, while 72 percent strongly prefer it.
But what can you do with a bachelor's in nursing, and will the investment offer professional benefits? Here’s an overview of rewarding career paths you can pursue with a bachelor’s degree in nursing and the impact of this education.
Download our guide to discover which nursing degree is right for you.

What Is a Bachelor’s Degree in Nursing?
A bachelor’s (BS) degree in nursing is a four-year undergraduate degree that provides the skills and knowledge to work as a registered nurse (RN).
“A bachelor's degree in nursing gives nurses a more well-rounded education as they move forward in their career,” says Deborah Roy, Director of Regis College’s RN-to-BS in Nursing degree program.
Students can pursue this degree after earning a high school diploma or through a bridge program after obtaining a two-year Associate Degree in Nursing (ADN).
While an associate degree is the minimum requirement to become a licensed RN, a bachelor's degree program develops clinical skills with a focus on:
- Critical thinking
- Public health
“This allows them to address more complex issues within the healthcare arena,” Roy continues.
A BS in nursing also makes nurses eligible for more career advancement opportunities down the line. This is because healthcare facilities require staff to hold a four-year degree for nursing leadership positions and specialized fields.
If you’re committed to the nursing field and want to continue growing in your career, consider these seven advanced nursing roles that are available to professionals with a BS in nursing degree.
What Can You Do With a Bachelor's in Nursing?
1. nurse manager.
Nurse managers coordinate the nursing operations of a healthcare facility.
This can include:
- Staff management
- Resource allocation
- Regulatory compliance
Nurse managers are an integral part of the leadership team at a healthcare facility, responsible for implementing policies that improve patient care and create a safe environment. As a result, nurse managers earn an average annual salary of $104,830 .
Nurse managers need a BS in nursing to develop the leadership skills needed to effectively manage nursing teams. The curriculum covers critical areas of healthcare management that are essential for this role.
2. Nursing Research
Nurse research is an exciting field that offers many career opportunities. For example, a nurse researcher conducts studies, collects data, and investigates healthcare issues to continually improve and optimize best practices in nursing. These findings are published in scholarly journals and academic publications like the Journal of Advanced Nursing and the American Journal of Nursing .
This particular role requires extensive education though. Nurse researchers often hold a doctoral degree—either a PhD or DNP. However, if you’re interested in entering the research field, you will need to gain additional education with at least a bachelor’s degree.
Research topics can cover a variety of topics in nursing care, such as:
- Clinical interventions
- Patient outcomes
- Aging populations
- Nursing education
Nurse researchers can expect to earn a rewarding annual average salary of $97,088 , while assistant positions earn an average wage of $70,000 per year.
3. Telemedicine Nurse
With such a steep rise in telehealth visits , there’s a greater need for more effective coordinated virtual care. As a result, telemedicine nurses are becoming more in-demand over the years .
A telemedicine nurse collaborates with healthcare providers to deliver remote patient care. By communicating with patients online and by phone, nurses can assess symptoms, provide treatment recommendations, and offer assistance with tasks like managing medication and accessing medical services.
The average salary of a telemedicine nurse is $93,248 a year, but this often depends on your work experience.
Telemedicine nurses need a BS in nursing to navigate the complexities of delivering healthcare remotely. The curriculum ensures nurses are comfortable working with digital health tools and methods in providing high-quality, virtual care.
4. Quality Assurance Manager
Hospitals are increasingly adopting quality assurance methods focused on improving patient safety. This is why quality assurance managers are becoming a common role among nursing staff.
A quality assurance manager helps to maintain optimal patient care in a healthcare facility. They monitor the quality standards and adherence to safety protocols in the healthcare environment. The goal of quality assurance is to address care deficiencies, performance issues, and regulatory risks in a timely manner.
As a result, the role offers a competitive average annual salary of $88,469 .
Nurses aspiring to become quality assurance managers need a BS in nursing to understand the various healthcare policies, standards, and practices essential to the role. This is because BS in nursing coursework explores evidence-based practices and patient safety protocols, which are essential to effectively leading quality improvement initiatives.
5. Nurse Educator
Nurse educators provide training and mentorship for prospective nurses and continuing education for experienced professionals. After working in hands-on roles in clinical settings, nurse educators have the insight to develop curriculum, monitor student progress, and give lectures that encourage other nurses to think critically about best practices in patient care.
Professionals in nursing education careers typically earn an average salary of $84,180 a year.
Since many seasoned nurses transition into this role, it might be puzzling why a BS in nursing degree is needed. However, nurse educators need at least a BS in nursing to gain the academic knowledge and methodologies needed to effectively teach nursing. In addition, nurses need to earn a BS in nursing before enrolling in an MSN program—the educational requirement for most nurse educator positions.
6. Clinic Manager
A clinic manager is in charge of a healthcare facility’s daily operations, such as patient appointments, staff schedules, and budgeting. They also make sure the facility meets all required standards of cleanliness and safety and oversee administrative tasks, such as communicating with other healthcare providers.
A clinic manager’s average salary is $80,442 per year, depending on factors like the size, location, and specialization of the facility.
Clinic managers need a bachelor’s degree in nursing to acquire the comprehensive healthcare management skills and in-depth knowledge of nursing practice required to efficiently oversee clinic operations and ensure high-quality patient care.
7. Nurse Informaticist
Nurse informaticist roles combine health science with information technology and data analytics. Using a variety of software and databases, they design efficient systems for managing health records, create tools to support decision-making, and analyze data sets to identify trends or areas of improvement.
As gatekeepers of patient data, these skilled professionals are also responsible for protecting sensitive health data security, which earns them an average annual salary of $58,250 .
Since this role moves away from clinical work, it isn’t surprising that nurses need a BS in nursing to obtain this position. As a result, the BS in nursing curriculum aims to help students understand the integration of nursing science with information management and analytical sciences.
The Impact of a Bachelor’s Degree on Career Advancement
Working as an RN can be an incredibly satisfying career that never runs out of opportunities to make a difference in the lives of patients. However, associate-level nurses are often barred from exciting opportunities to take their careers to the next level.
Earning a bachelor's degree, on the other hand, can increase your earning potential and open up a world of new career pathways that allow you to combine nursing experience with other professional interests. Even if you’re unsure what specialization interests you, this degree program can help you discover subject areas you’re passionate about.
“In a bachelor's degree program, we go into more detail as to, what are we doing this for?” Roy continues. “How do we interpret this data? How do we apply that to how we're going to care for our patients? Nurses learn critical leadership behaviors on how to build teams, how to communicate, and how to deal with things like instability in the workplace.”
No matter what roles interest you, getting an advanced education makes it possible to compete for jobs in specialized departments and at top-tier, magnet-status healthcare facilities.
Choosing the Right Bachelor’s in Nursing Program
Choosing the right bachelor’s degree in nursing program ensures you develop the right skills for your professional goals. As you compare programs, consider factors like student services, job placement rates, and opportunities for internships or research experience since these directly impact your ability to succeed both in and outside the classroom.
The online RN-to-BS program at Regis College is designed for current RNs with an associate degree who want to develop their existing knowledge and skills. The curriculum emphasizes emerging trends in healthcare, leadership, and advanced health assessment methods to equip you for the next phase of your nursing career.
To learn more about what you can do with a bachelor's in nursing, consult an admissions counselor and find out how Regis faculty members work with students to create a personalized curriculum plan.

Related Blogs

Six Ways to Navigate the Cost of Advancing Your Nursing Career
Looking to advance your nursing career by earning a bachelor’s degree? Here are six ways to maximize your return on your investment.

How to Expedite Your Bachelor's Degree in Nursing
Discover effective strategies to fast-track your bachelor's degree in nursing.

Looking to earn your degree? Discover how Regis College can prepare you to succeed at a magnet hospital.
- 235 Wellesley Street, Weston MA 02493
- 781.768.7000
- © 2024
- Privacy Policy

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The PhD program prepares the nurse scholar to develop and conduct scientific research that advances the theoretical foundation of nursing practice and healthcare delivery. The program is designed to prepare nurses for careers as research scientists, often in academic or governmental positions.
Advantage #5: Career Flexibility. If you earn a PhD in nursing, you're most likely going to work in research or academia. That being said, there are plenty of PhD nursing programs with specializations in management and administration. Because of this, you also have the option to use your PhD degree to take a leadership role in your organization.
Each Ph.D. in Nursing program is unique, offering its own benefits and features. We assembled the top five Ph.D. in Nursing programs nationwide following Nurse.org's proprietary ranking algorithm, which considers and ranks schools based on factors like: 1. University of Pennsylvania.
DNP and Ph.D. in Nursing Key Similarities and Differences. A DNP and Ph.D. are both terminal degrees, meaning they are the highest degree a nurse can earn. Regardless of their choice of program, interested nurses need a bachelor of science (BSN) degree in nursing, an active and unencumbered registered nurse (RN) license, and clinical experience ...
1) Develop the science for the discipline. A PhD program in Nursing focuses on the skills needed to conduct research that extends the body of nursing knowledge, addresses complex health-related issues, improves outcomes, advances health equity and inclusion, and informs policy. PhD-prepared nurses conduct primary research investigations to ...
A practice-based Doctor of Nursing Practice degree program can provide you with the knowledge and leadership skills to lead nursing teams to provide optimum patient care. On the other hand, a PhD in Nursing program will enable you to conduct original research that could shape the future of healthcare, from the halls of hospitals to the halls of ...
The PhD is a research-focused degree that prepares individuals to create, translate, and communicate new knowledge as leaders within institutions of higher education and outside of academia. ... In the field of nursing, the PhD graduate is prepared to steward the profession, develop its science, define its uniqueness, maintain its professional ...
To achieve the prerequisites and earn a Ph.D. in nursing, you can follow these steps: 1. Complete a Bachelor of Science in nursing degree. Earn a bachelor's degree in nursing or a related field if you're interested in pursuing this career. During your education, you may take courses in nursing research, health care law and ethics, chemistry ...
Earn a GW Nursing Doctor of Philosophy in Nursing to advance the theoretical foundation of healthcare delivery and nursing practice. Our PhD program is designed to equip graduates with the knowledge and skills in theoretical, methodological, and analytical approaches needed to conduct research and apply knowledge in the fields of nursing science and healthcare.
PhD Program in Nursing Description. The program requires a minimum of 52 credit hours of graduate coursework. Students will work on research projects; it is expected most will graduate with several publications. Coursework is structured with a substantive core of nursing science and research methods to be taken in the School of Nursing.
When nurses are considering an advanced degree beyond the master's level of educational preparation, a number of considerations may direct the decision-making process. The doctorate of philosophy (PhD) in nursing is a research degree that will well serve nurses who have the desire to apply theory and develop formal programs of research, become faculty of nursing, combine clinical practice ...
Ph.D. Nurse Salary & Employment. Salaries for Ph.D. nurses vary based on the type of employment a nurse seeks after graduation. Nurse researchers, a primary career path for Ph.D. nurses, can expect a median salary of $90,000 according to Payscale.com. For Ph.D. nurses who pursue a teaching position, the median annual wage for post-secondary ...
Develop the interdisciplinary knowledge to lead and work with diverse healthcare teams. Earning a PhD degree in nursing can help you climb the career ladder, positioning you to take on leadership roles within a variety of healthcare settings. The ability to work effectively with diverse populations and teams is an integral aspect of PhD in ...
That means that just 13 percent of the nursing workforce is eligible to become nursing faculty at all, and less than 1 percent is eligible to teach at the highest level. A Ph.D. prepares nurses to be experts in their field and to pursue a research-focused career. We need more PhD-prepared nurses now more than ever: to educate future nurses, to ...
My motivation for enrolling in a PhD program in nursing was driven by my aspiration to make a substantial impact on patient care and contribute to the advancement of nursing science. - Mohammed Alanazi . The PhD program has been instrumental in enhancing my skills and knowledge as a nurse and a research scientist. Since enrolling in the program ...
In NURSING. (The following are the top 10 pros of Ph.D. in Nursing.) 1. Increased Salary. Those who earn their Ph.D. in nursing can expect to earn a higher salary. A pay increase is one of the top advantages of a Ph.D. in nursing. The average salary for those with their Ph.D. in nursing is around $98,619/year.
Generating strong interest in the PhD in nursing (and similar research-focused doctorates) is a priority for the profession. Although less than 1% of today's nursing workforce has earned a PhD (NCSBN, 2021), these individuals are in high demand with the need for nurse scientists, faculty, and leaders on the rise. Despite this great need, AACN has seen a steady decline in enrollment in PhD ...
The PhD in nursing is a research-focused degree with an emphasis on creating new knowledge as it relates to things like nursing practices, healthcare, patient outcomes, and education. These nurse scientists identify a problem, create a hypothesis, develop a way to evaluate that hypothesis through statistical analysis, and synthesize new ...
A richer more reflective understanding of the PhD in nursing is that it is heavily grounded in the science and philosophy of knowledge. DNP programs, on the other hand, prepare nurses at the highest level of nursing practice to improve patient outcomes and translate research into practice. A PhD-prepared nurse can contribute to the profession ...
The PhD Program in Nursing prepares scholars to be nursing scientists, educators and leaders who seek to improve health across the lifespan with a concentration on urban, vulnerable and underserved populations. As a nursing PhD student, you will be mentored by Northeastern University's distinguished faculty and scientists and expected to ...
Abstract Healthcare research is central to providing high-quality, evidence-based care and the role of nurses as researchers is being promoted and.
Sharrica Miller, PhD, Class of 2017, explains why nurses should get a PhD in Nursing. A PhD in Nursing is the pinnacle of nursing excellence. It is about bei...
The DNP emphasizes higher-level skills in nursing practice. DNPs strive to improve patient outcomes. The Ph.D. in nursing focuses on scholarly inquiry and research. A nurse with a Ph.D. seeks to enlarge and further the body of nursing knowledge. A DNP curriculum centers on leadership in healthcare, evidence-based practice, and advanced practice ...
In May 2023, AACN announced that enrollments in research-focused doctoral level nursing programs declined, with an average decline in research-focused doctoral enrollments of 4.1% from the 2021 to 2022 school year. The greatest regional decline in enrollment was seen in the schools in the North Atlantic region, with a 7.8% decline. Graduation rates also declined between the 2021 and 2022 ...
Guest post by Heer Joisher (Griffin GSAS Candidate in Developmental Biology) for MCS.. Harvard's Mignone Center for Career Success recently hosted an insightful discussion spotlighting the remarkable journeys of a select group of GSAS alumni who have masterfully leveraged their Ph.D. degrees to forge unique and gratifying career paths.
This particular role requires extensive education though. Nurse researchers often hold a doctoral degree—either a PhD or DNP. However, if you're interested in entering the research field, you will need to gain additional education with at least a bachelor's degree. Research topics can cover a variety of topics in nursing care, such as: