- More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
autobiography

Definition of autobiography
Examples of autobiography in a sentence.
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'autobiography.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
auto- + biography , perhaps after German Autobiographie
1797, in the meaning defined above
Phrases Containing autobiography
- semi - autobiography
Dictionary Entries Near autobiography
autobiographist
Cite this Entry
“Autobiography.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/autobiography. Accessed 9 Apr. 2024.
Kids Definition
Kids definition of autobiography, more from merriam-webster on autobiography.
Thesaurus: All synonyms and antonyms for autobiography
Nglish: Translation of autobiography for Spanish Speakers
Britannica English: Translation of autobiography for Arabic Speakers
Britannica.com: Encyclopedia article about autobiography
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
The tangled history of 'it's' and 'its', more commonly misspelled words, why does english have so many silent letters, your vs. you're: how to use them correctly, every letter is silent, sometimes: a-z list of examples, popular in wordplay, the words of the week - apr. 5, 12 bird names that sound like compliments, 10 scrabble words without any vowels, 12 more bird names that sound like insults (and sometimes are), 8 uncommon words related to love, games & quizzes.

- Literary Terms
- Autobiography
- Definition & Examples
- When & How to Write Autobiography
I. What is Autobiography?
An autobiography is a self-written life story.
It is different from a biography , which is the life story of a person written by someone else. Some people may have their life story written by another person because they don’t believe they can write well, but they are still considered an author because they are providing the information. Reading autobiographies may be more interesting than biographies because you are reading the thoughts of the person instead of someone else’s interpretation.
II. Examples of Autobiography
One of the United States’ forefathers wrote prolifically (that means a lot!) about news, life, and common sense. His readings, quotes, and advice are still used today, and his face is on the $100 bill. Benjamin Franklin’s good advice is still used through his sayings, such as “We are all born ignorant, but one must work hard to remain stupid.” He’s also the one who penned the saying that’s seen all over many schools: “Tell me and I forget. Teach me and I remember. Involve me and I learn.” His autobiography is full of his adventures , philosophy about life, and his wisdom. His autobiography shows us how much he valued education through his anecdotes (stories) of his constant attempts to learn and improve himself. He also covers his many ideas on his inventions and his thoughts as he worked with others in helping the United States become free from England.
III. Types of Autobiography
There are many types of autobiographies. Authors must decide what purpose they have for writing about their lives, and then they can choose the format that would best tell their story. Most of these types all share common goals: helping themselves face an issue by writing it down, helping others overcome similar events, or simply telling their story.
a. Full autobiography (traditional):
This would be the complete life story, starting from birth through childhood, young adulthood, and up to the present time at which the book is being written. Authors might choose this if their whole lives were very different from others and could be considered interesting.
There are many types of memoirs – place, time, philosophic (their theory on life), occupational, etc. A memoir is a snapshot of a person’s life. It focuses on one specific part that stands out as a learning experience or worth sharing.
c. Psychological illness
People who have suffered mental illness of any kind find it therapeutic to write down their thoughts. Therapists are specialists who listen to people’s problems and help them feel better, but many people find writing down their story is also helpful.
d. Confession
Just as people share a psychological illness, people who have done something very wrong may find it helps to write down and share their story. Sharing the story may make one feel he or she is making amends (making things right), or perhaps hopes that others will learn and avoid the same mistake.
e. Spiritual
Spiritual and religious experiences are very personal . However, many people feel that it’s their duty and honor to share these stories. They may hope to pull others into their beliefs or simply improve others’ lives.
f. Overcoming adversity
Unfortunately, many people do not have happy, shining lives. Terrible events such as robberies, assaults, kidnappings, murders, horrific accidents, and life-threatening illnesses are common in some lives. Sharing the story can inspire others while also helping the person express deep emotions to heal.
IV. The Importance of Autobiography
Autobiographies are an important part of history. Being able to read the person’s own ideas and life stories is getting the first-person story versus the third-person (he-said/she-said) version. In journalism, reporters go to the source to get an accurate account of an event. The same is true when it comes to life stories. Reading the story from a second or third source will not be as reliable. The writer may be incorrectly explaining and describing the person’s life events.
Autobiographies are also important because they allow other people in similar circumstances realize that they are not alone. They can be inspiring for those who are facing problems in their lives. For the author, writing the autobiography allows them to heal as they express their feelings and opinions. Autobiographies are also an important part of history.
V. Examples of Autobiography in Literature
A popular autobiography that has lasted almost 100 years is that of Helen Keller. Her life story has been made into numerous movies and plays. Her teacher, Anne Sullivan, has also had her life story written and televised multiple times. Students today still read and learn about this young girl who went blind and deaf at 19 months of age, causing her to also lose her ability to learn to speak. Sullivan’s entrance into Helen’s life when the girl was seven was the turning point. She learned braille and soon became an activist for helping blind and deaf people across the nation. She died in 1968, but her autobiography is still helping others.
Even in the days before my teacher came, I used to feel along the square stiff boxwood hedges, and, guided by the sense of smell, would find the first violets and lilies. There, too, after a fit of temper, I went to find comfort and to hide my hot face in the cool leaves and grass. What joy it was to lose myself in that garden of flowers, to wander happily from spot to spot, until, coming suddenly upon a beautiful vine, I recognized it by its leaves and blossoms, and knew it was the vine which covered the tumble-down summer-house at the farther end of the garden! (Keller).
An autobiography that many middle and high school students read every year is “Night” by Elie Wiesel. His story is also a memoir, covering his teen years as he and his family went from the comfort of their own home to being forced into a Jewish ghetto with other families, before ending up in a Nazi prison camp. His book is not that long, but the details and description he uses brings to life the horrors of Hitler’s reign of terror in Germany during World War II. Students also read “The Diary of Anne Frank,” another type of autobiography that shows a young Jewish girl’s daily life while hiding from the Nazis to her eventual capture and death in a German camp. Both books are meant to remind us to not be indifferent to the world’s suffering and to not allow hate to take over.
“The people were saying, “The Red Army is advancing with giant strides…Hitler will not be able to harm us, even if he wants to…” Yes, we even doubted his resolve to exterminate us. Annihilate an entire people? Wipe out a population dispersed throughout so many nations? So many millions of people! By what means? In the middle of the twentieth century! And thus my elders concerned themselves with all manner of things—strategy, diplomacy, politics, and Zionism—but not with their own fate. Even Moishe the Beadle had fallen silent. He was weary of talking. He would drift through synagogue or through the streets, hunched over, eyes cast down, avoiding people’s gaze. In those days it was still possible to buy emigration certificates to Palestine. I had asked my father to sell everything, to liquidate everything, and to leave” (Wiesel 8).
VI. Examples of Autobiography in Pop Culture
One example of an autobiography that was a hit in the movie theaters is “American Sniper,” the story of Navy SEAL Chris Kyle. According to an article in the Dallas, Texas, magazine D, Kyle donated all the proceeds from the film to veterans and their families. He had a story to tell, and he used it to help others. His story is a memoir, focusing on a specific time period of his life when he was overseas in the military.
An autobiography by a young Olympian is “Grace, Gold and Glory: My Leap of Faith” by Gabrielle (Gabby) Douglas. She had a writer, Michelle Burford, help her in writing her autobiography. This is common for those who have a story to tell but may not have the words to express it well. Gabby was the darling of the 2012 Olympics, winning gold medals for the U.S. in gymnastics along with being the All-Around Gold Medal winner, the first African-American to do so. Many young athletes see her as an inspiration. Her story also became a television movie, “The Gabby Douglas Story.”
VII. Related Terms
The life story of one person written by another. The purpose may to be highlight an event or person in a way to help the public learn a lesson, feel inspired, or to realize that they are not alone in their circumstance. Biographies are also a way to share history. Historic and famous people may have their biographies written by many authors who research their lives years after they have died.
VIII. Conclusion
Autobiographies are a way for people to share stories that may educate, inform, persuade, or inspire others. Many people find writing their stories to be therapeutic, healing them beyond what any counseling might do or as a part of the counseling. Autobiographies are also a way to keep history alive by allowing people in the present learn about those who lived in the past. In the future, people can learn a lot about our present culture by reading autobiographies by people of today.
List of Terms
- Alliteration
- Amplification
- Anachronism
- Anthropomorphism
- Antonomasia
- APA Citation
- Aposiopesis
- Bildungsroman
- Characterization
- Circumlocution
- Cliffhanger
- Comic Relief
- Connotation
- Deus ex machina
- Deuteragonist
- Doppelganger
- Double Entendre
- Dramatic irony
- Equivocation
- Extended Metaphor
- Figures of Speech
- Flash-forward
- Foreshadowing
- Intertextuality
- Juxtaposition
- Literary Device
- Malapropism
- Onomatopoeia
- Parallelism
- Pathetic Fallacy
- Personification
- Point of View
- Polysyndeton
- Protagonist
- Red Herring
- Rhetorical Device
- Rhetorical Question
- Science Fiction
- Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
- Synesthesia
- Turning Point
- Understatement
- Urban Legend
- Verisimilitude
- Essay Guide
- Cite This Website
autobiography
What is autobiography definition, usage, and literary examples, autobiography definition.
An autobiography (awe-tow-bye-AWE-gruh-fee) is a self-written biography . The author writes about all or a portion of their own life to share their experience, frame it in a larger cultural or historical context, and/or inform and entertain the reader.
Autobiographies have been a popular literary genre for centuries. The first Western autobiography is attributed to Saint Augustine of Hippo for his 13-book work titled Confessions , written between 397 and 400 CE. Some autobiographies are a straightforward narrative that recollects a linear chain of events as they unfolded. The genre has expanded and evolved to include different approaches to the form.
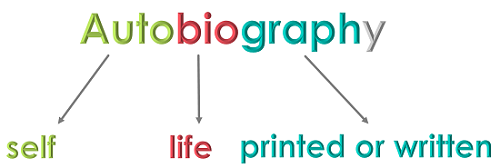
The word autobiography comes from the Ancient Greek auto (“self”) + bios (“life”) + graphein (“to write”) = “a self-written life.” It is also known as autography .
The History of Autobiography
Scholars regard Augustine’s Confessions as the first Western autobiography. Other autobiographical works from antiquity include Jewish historian Flavius Josephus’s Vita (circa 99 CE) and Greek scholar Libanius’s Oration I (374 CE). Works of this kind were called apologias, which essentially means “in my defense.” Writers approached these works not as acts of self-documentation but as self-defense. They represented a way to explain and provide rationale for their life, work, and escapades. There was also less focus on their emotional lives.
The Book of Margery Kempe , written in 1438 by an English Christian mystic, is the earliest known autobiography in English. (Though it didn’t see full publication until the 20th century.) Other early English-language biographies of note include:
- Lord Herbert of Cherbury’s 1764 memoirs
- John Bunyan’s Grace Abounding to the Chief of Sinners in 1666
- Jarena Lee’s The Life and Religious Experience of Jarena Lee (the first autobiography of an African American woman)
Philosopher Jean-Jacques Rousseau’s Confessions was published in 1782. It paved the way for the more thoughtful, emotionally centered autobiographies seen today. Autobiography as a literary genre emerged a few years later, when British scholar William Taylor first used the term to describe a self-written biography. He did so disparagingly, suggesting the form was pedantic . In 1809, English Romantic poet Robert Southey used the term more seriously to describe self-written biographies.
Starting in the 20th century, more young people started writing autobiographies. Perhaps the most famous example is Anne Frank’s The Diary of a Young Girl , about her time hiding from the Nazis in an Amsterdam attic. The 21st century saw an increase in autobiographical essay collections and memoirs by younger celebrities, including:
- Anna Kendrick
- Mindy Kaling
- Gabourey Sidibe
- Mike Birbiglia
- Lena Dunham
- Chelsea Handler
Autobiographies are not immune to controversy. One notable scandal involved author James Frey’s A Million Little Pieces . Originally billed as a memoir, evidence later emerged that Frey invented key parts of the story. This example underscores how easily authors can cross over into autofiction—fictional autobiography—and how seriously readers take authors’ responsibility to accurately and honestly market their books.
Types of Autobiographies
There are a few different types of self-written works that qualify as autobiography.
Standard Autobiographies
In the most traditional form, authors recount their life or specific formative events from their life. This approach often utilizes a chronological format of events, but it doesn’t necessarily have to. An author’s approach might include a framing device such as flashbacks, in which they move from the present to the past as they remember their lives. For example, Broadway star Patti LuPone’s self-titled autobiography begins on the opening night of Gypsy in 2004 before moving back in time to LuPone’s childhood. An author could take a more stream-of-consciousness style, in which one memory links to another by a common theme. Irish writer Seán O’Casey narrates his six-volume Autobiographies in this manner
This is a type of autobiography that is narrower in scope and focus. It places greater emphasis on particular memories, thoughts, and feelings. A standard autobiography can certainly cover some of this same ground—most do—but the memoir is more interested in individual events or defined portions of the author’s life and the emotions and lessons behind them.
Henry David Thoreau is a notable memoirist. In Walden , he reflects on his time spent living in solitude in the woods of Massachusetts and what he learned about life and nature throughout this experience. Another example is The Year of Magical Thinking by Joan Didion, which relates the death of her husband and its impact on her life and work. Another is Wild by Cheryl Strayed, wherein Strayed remembers her time hiking the Pacific Crest Trail during a period of great change in her life.
Autofiction
The fictionalized autobiography, or autofiction, is another type of autobiography. The author presents their story not as fact but as fiction. This method gives them considerable space to take creative license with events and characters, thereby blurring the lines between reality and fiction. The overall goal is less about the author wanting to obscure facts and make things up and more a matter of taking another tactic to delve into their experiences in service of self-discovery. Taipei by Tao Lin is a work of autofiction. The central character, Paul, mirrors Lin’s own life and experiences, from the literary world of New York City to his ancestral roots in Taiwan.
Spiritual Autobiographies
These autobiographies center on the author’s religious or spiritual awakening and the subsequent journey their faith has taken them on. Common elements include struggles and doubt, a life-altering conversion, periods of regression, and sharing the “message.” These all act as endorsements of the author’s faith. Augustine’s Confessions , Paramahansa Yogananda’s Autobiography of a Yogi , and Augusten Burroughs’s Toil & Trouble: A Memoir are all spiritual autobiographies.
Autobiography vs. Biography
Both autobiographies and biographies are records of real lives, but there is one major distinction. A person other than the book’s subject writes a biography, while the subject themselves writes an autobiography. In this way, an autobiography is essentially a biography of the self. The biographer’s job is typically more involved, entailing detailed research into the life of the subject. The autobiographer, however, is usually not burdened by this because they lived through the events they write about. They may need only to confirm dates and stories to accurately relate the pertinent details.
The Function of Autobiography
An autobiography allows the author to tell the true story of their own life. This is the reason why autobiographies have always been written by famous people. History tends to remember notable individuals for just one significant contribution or event and, even then, the public’s perception of it may be inaccurate. Writing an autobiography allows the author to share the real story and put it into the larger context of their life and times.
Most readers pick up an autobiography expecting some degree of subjectivity from the author. After all, the events chronicled happened to the author, so the writing will of course have a biased perspective . There are advantages to this subjectivity, though. The reader gets the real story directly from the person who lived it, unvarnished by others’ opinions or erroneous historical data.
One way this subjectivity is problematic is that the author may not possess the ability to see the story they’re telling from other perspectives. For example, they may not acknowledge any hurt they caused others, dangerous behaviors they engaged in, or the “other side” of a controversial event in which there are equally valid opposing viewpoints and experiences. Any of these deficiencies can result in a somewhat skewed narrative.
Writers Known for Autobiography & Autobiography Books
- Maya Angelou, I Know Why the Caged Bird Sings , Gather Together in My Name
- Jung Chang, Wild Swans: Three Daughters of China
- Isak Dinesen, Out of Africa , Shadows on the Grass
- Carrie Fisher, Wishful Drinking , Shockaholic
- Anne Frank, The Diary of a Young Girl
- Ernest Hemingway, A Moveable Feast
- Karl Ove Knausgård, My Struggle
- Frank McCourt, Angela’s Ashes
- Anaïs Nin, The Diaries of Anaïs Nin
- Marcel Proust, Remembrance of Things Past
- Patti Smith, Just Kids , M Train
- Mark Twain, The Autobiography of Mark Twain
- Benjamin Franklin, The Autobiography of Benjamin Franklin
- Malcolm X, The Autobiography of Malcolm X
- Agatha Christie, Agatha Christie: An Autobiography
- Nelson Mandela, Long Walk to Freedom
- Mahatma Gandhi, Gandhi: An Autobiography
Examples of Autobiographies
1. Maya Angelou, I Know Why the Caged Bird Sings
Angelou’s autobiography is the first installment in a seven-volume series chronicling the life of the legendary poet, teacher, actress, director, dancer, and civil rights activist. Given all those roles, it’s easy to see why Angelou’s life story makes for interesting reading.
This volume centers primarily on her early life in Stamps, Arkansas, and the devastating effects of a childhood rape. It also explores racism in the American South. It discuses the important role reading plays in helping young Maya deal with the sexual assault and pervasive prejudice in her environment.
2. Helen Keller, The Story of My Life
Keller’s autobiography details her first 20 years, starting with the childhood illness that caused her blindness and deafness. She discusses the obstacles she had to overcome and the life-changing relationship she shared with her teacher, Anne Sullivan, who helped her learn to read and write. Keller also documents her friendships with several famous figures of her day, including Alexander Graham Bell, John Greenleaf Whittier, Oliver Wendell Holmes, and First Lady Frances Cleveland.
3. Vinh Chung, Where the Wind Leads
Chung’s autobiography recalls the harrowing story of a Vietnamese refugee and his journey to make the American Dream his own. Born in South Vietnam, Chung comes of age in a changing political climate that eventually compels his family to flee the country. Their voyage takes them through the South China Sea, run-ins with pirates, resettlement in Arkansas, and Chung’s graduation from Harvard Medical School.
How to Write an Autobiography
Autobiography is a truly universal art form and is accessible to anyone, whether you're in high school or 100 years old. Exploring the process of writing an autobiography deserves an article in itself, but the process should include these steps:
- Determine your "why." What lessons do you want to impart via your story, and why are they worth sharing with a broader audience?
- Draft an autobiographical outline. It should include information about your upbringing, impactful moments throughout your life, stories of failure and success, and meaningful mentors.
- Begin with the easiest sections. Getting started is often the greatest hurdle, so begin by writing the chapters that feel most accessible or enjoyable.
- Write your first draft. Once you write the first chapters, it will feel easier to write the rest. Capitalize on your momentum and write a full draft.
- Step away. As with anything, stepping away from your work will help foster fresh perspectives when you return.
- Edit and re-write your draft. Your first draft will probably benefit from thorough revisions, as will your second draft, and maybe your third. Continue to edit and revise until it feels right.
- Ask for help. Bring in a trusted family member or friend or professional editor to help with final edits.
Further Resources on Autobiography
ThoughtCo. shares some important points to consider before writing an autobiography .
The Living Handbook of Narratology delves into the history of the autobiography .
MasterClass breaks autobiography writing down into eight basic steps .
Pen & the Pad looks at the advantages and disadvantages of the autobiography .
Lifehack has a list of 15 autobiographies everyone should read at least once .
Related Terms
- Frame Story
- Point of View
What Is an Autobiography?
What to Consider Before You Start to Write
- Writing Research Papers
- Writing Essays
- English Grammar
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
Your life story, or autobiography , should contain the basic framework that any essay should have, with four basic elements. Begin with an introduction that includes a thesis statement , followed by a body containing at least several paragraphs , if not several chapters. To complete the autobiography, you'll need a strong conclusion , all the while crafting an interesting narrative with a theme.
Did You Know?
The word autobiography literally means SELF (auto), LIFE (bio), WRITING (graph). Or, in other words, an autobiography is the story of someone's life written or otherwise told by that person.
When writing your autobiography, find out what makes your family or your experience unique and build a narrative around that. Doing some research and taking detailed notes can help you discover the essence of what your narrative should be and craft a story that others will want to read.
Research Your Background
Just like the biography of a famous person, your autobiography should include things like the time and place of your birth, an overview of your personality, your likes and dislikes, and the special events that shaped your life. Your first step is to gather background detail. Some things to consider:
- What is interesting about the region where you were born?
- How does your family history relate to the history of that region?
- Did your family come to that region for a reason?
It might be tempting to start your story with "I was born in Dayton, Ohio...," but that is not really where your story begins. It's better to start with an experience. You may wish to start with something like why you were born where you were and how your family's experience led to your birth. If your narrative centers more around a pivotal moment in your life, give the reader a glimpse into that moment. Think about how your favorite movie or novel begins, and look for inspiration from other stories when thinking about how to start your own.
Think About Your Childhood
You may not have had the most interesting childhood in the world, but everyone has had a few memorable experiences. Highlight the best parts when you can. If you live in a big city, for instance, you should realize that many people who grew up in the country have never ridden a subway, walked to school, ridden in a taxi, or walked to a store a few blocks away.
On the other hand, if you grew up in the country you should consider that many people who grew up in the suburbs or inner city have never eaten food straight from a garden, camped in their backyards, fed chickens on a working farm, watched their parents canning food, or been to a county fair or a small-town festival.
Something about your childhood will always seem unique to others. You just have to step outside your life for a moment and address the readers as if they knew nothing about your region and culture. Pick moments that will best illustrate the goal of your narrative, and symbolism within your life.
Consider Your Culture
Your culture is your overall way of life , including the customs that come from your family's values and beliefs. Culture includes the holidays you observe, the customs you practice, the foods you eat, the clothes you wear, the games you play, the special phrases you use, the language you speak, and the rituals you practice.
As you write your autobiography, think about the ways that your family celebrated or observed certain days, events, and months, and tell your audience about special moments. Consider these questions:
- What was the most special gift you ever received? What was the event or occasion surrounding that gift?
- Is there a certain food that you identify with a certain day of the year?
- Is there an outfit that you wear only during a special event?
Think honestly about your experiences, too. Don't just focus on the best parts of your memories; think about the details within those times. While Christmas morning may be a magical memory, you might also consider the scene around you. Include details like your mother making breakfast, your father spilling his coffee, someone upset over relatives coming into town, and other small details like that. Understanding the full experience of positives and negatives helps you paint a better picture for the reader and lead to a stronger and more interesting narrative. Learn to tie together all the interesting elements of your life story and craft them into an engaging essay.
Establish the Theme
Once you have taken a look at your own life from an outsider’s point of view, you will be able to select the most interesting elements from your notes to establish a theme. What was the most interesting thing you came up with in your research? Was it the history of your family and your region? Here is an example of how you can turn that into a theme:
"Today, the plains and low hills of southeastern Ohio make the perfect setting for large cracker box-shaped farmhouses surrounded by miles of corn rows. Many of the farming families in this region descended from the Irish settlers who came rolling in on covered wagons in the 1830s to find work building canals and railways. My ancestors were among those settlers."
A little bit of research can make your own personal story come to life as a part of history, and historical details can help a reader better understand your unique situation. In the body of your narrative, you can explain how your family’s favorite meals, holiday celebrations, and work habits relate to Ohio history.
One Day as a Theme
You also can take an ordinary day in your life and turn it into a theme. Think about the routines you followed as a child and as an adult. Even a mundane activity like household chores can be a source of inspiration.
For example, if you grew up on a farm, you know the difference between the smell of hay and wheat, and certainly that of pig manure and cow manure—because you had to shovel one or all of these at some point. City people probably don’t even know there is a difference. Describing the subtle differences of each and comparing the scents to other scents can help the reader imagine the situation more clearly.
If you grew up in the city, you how the personality of the city changes from day to night because you probably had to walk to most places. You know the electricity-charged atmosphere of the daylight hours when the streets bustle with people and the mystery of the night when the shops are closed and the streets are quiet.
Think about the smells and sounds you experienced as you went through an ordinary day and explain how that day relates to your life experience in your county or your city:
"Most people don’t think of spiders when they bite into a tomato, but I do. Growing up in southern Ohio, I spent many summer afternoons picking baskets of tomatoes that would be canned or frozen and preserved for cold winter’s dinners. I loved the results of my labors, but I’ll never forget the sight of the enormous, black and white, scary-looking spiders that lived in the plants and created zigzag designs on their webs. In fact, those spiders, with their artistic web creations, inspired my interest in bugs and shaped my career in science."
One Event as a Theme
Perhaps one event or one day of your life made such a big impact that it could be used as a theme. The end or beginning of the life of another can affect our thoughts and actions for a long time:
"I was 12 years old when my mother passed away. By the time I was 15, I had become an expert in dodging bill collectors, recycling hand-me-down jeans, and stretching a single meal’s worth of ground beef into two family dinners. Although I was a child when I lost my mother, I was never able to mourn or to let myself become too absorbed in thoughts of personal loss. The fortitude I developed at a young age was the driving force that would see me through many other challenges."
Writing the Essay
Whether you determine that your life story is best summed up by a single event, a single characteristic, or a single day, you can use that one element as a theme . You will define this theme in your introductory paragraph .
Create an outline with several events or activities that relate back to your central theme and turn those into subtopics (body paragraphs) of your story. Finally, tie up all your experiences in a summary that restates and explains the overriding theme of your life.
- How to Write a Personal Narrative
- How to Write a Narrative Essay or Speech
- Compose a Narrative Essay or Personal Statement
- 7 Tips for Writing Personality Profiles That People Will Want to Read
- Common Application Essay, Option 1: Share Your Story
- FAQs About Writing Your Graduate Admissions Essay
- Memorable Graduation Speech Themes
- How to Write Your Family History
- How to Give an Impromptu Speech
- How to Create Your Own Curriculum
- How to Write Your Graduate School Admissions Essay
- What Is a Synopsis and How Do You Write One?
- How to Write a Graduation Speech as Valedictorian
- Write an Attention-Grabbing Opening Sentence for an Essay
- How to Conjugate Italian Verbs Like a Native
- How to Write the Graduate Admissions Essay
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Meaning of autobiography in English
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
- exercise book
- multi-volume
You can also find related words, phrases, and synonyms in the topics:
Related words
Autobiography | american dictionary, examples of autobiography, translations of autobiography.
Get a quick, free translation!

Word of the Day
a group of four people who play musical instruments or sing as a group

Shoots, blooms and blossom: talking about plants

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
- English Noun
- American Noun
- Translations
- All translations
Add autobiography to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.
Become a Bestseller
Follow our 5-step publishing path.
Fundantals of Fiction & Story
Bring your story to life with a proven plan.
Market Your Book
Learn how to sell more copies.
Edit Your Book
Get professional editing support.
Author Advantage Accelerator Nonfiction
Grow your business, authority, and income.
Author Advantage Accelerator Fiction
Become a full-time fiction author.
Author Accelerator Elite
Take the fast-track to publishing success.
Take the Quiz
Let us pair you with the right fit.
Free Copy of Published.
Book title generator, nonfiction outline template, writing software quiz, book royalties calculator.
Learn how to write your book
Learn how to edit your book
Learn how to self-publish your book
Learn how to sell more books
Learn how to grow your business
Learn about self-help books
Learn about nonfiction writing
Learn about fiction writing
How to Get An ISBN Number
A Beginner’s Guide to Self-Publishing
How Much Do Self-Published Authors Make on Amazon?
Book Template: 9 Free Layouts
How to Write a Book in 12 Steps
The 15 Best Book Writing Software Tools
What is an Autobiography? Definition, Elements, and Writing Tips
POSTED ON Oct 1, 2023
Written by Audrey Hirschberger
What is an autobiography, and how do you define autobiography, exactly? If you’re hoping to write an autobiography, it’s an important thing to know. After all, you wouldn’t want to mislabel your book.
What sets an autobiography apart from a memoir or a biography? And what type of writing is most similar to an autobiography? Should you even write one? How? Today we will be discussing all things autobiographical, so you can learn what an autobiography is, what sets it apart, and how to write one of your own – should you so choose.
But before we get into writing tips, we must first define autobiography. So what is an autobiography, precisely?
Need A Nonfiction Book Outline?
This Guide to Autobiographies Contains Information On:
What is an autobiography: autobiography meaning defined.
What is an autobiography? It’s a firsthand recounting of an author’s own life. So, if you were to write an autobiography, you would be writing a true retelling of your own life events.
Autobiography cannot be bound to only one type of work. What an autobiography is has more to do with the contents than the format. For example, autobiographical works can include letters, diaries, journals, or books – and may not have even been meant for publication.
An autobiography is what many celebrities, government officials, and important social figures sit down to write at the end of their lives or distinguished careers.
Of course, the work doesn’t have to cover your whole life. You can absolutely write an autobiography in your 20s or 30s if you’ve lived through events worth sharing!
If an autobiography doesn’t cover the entire lifespan of the author, it can start to get confused with another genre of writing. So what’s an autobiography most similar to? And how can you tell it apart from other genres of writing? Let’s dive into the details.
What type of writing is most similar to an autobiography?
A memoir is undoubtedly what type of writing is most similar to an autobiography. So what is the difference between an autobiography vs memoir ?
Simply put, a memoir is a book that an author writes about their own life with the intention of communicating a lesson or message to the reader. It doesn’t need to be written in chronological order, and only contains pieces of the author’s life story.
An autobiography, on the other hand, is the author’s life story from birth to present, and it’s much less concerned with theme than it is with communicating a “highlight reel” of the author’s biggest life events.
In addition to memoirs, there is also some confusion between autobiography vs biography . A biography is a true story about someone’s life, but it is not about the author’s life.
Is an autobiography always nonfiction?
When many people define autobiography, they say it is a true or “nonfiction” telling of an author’s life – but that’s not always the case.
There is actually such a thing as autobiographical fiction .
Autobiographical fiction refers to a story that is based on fact and inspired by the author’s actual experiences…but has made-up characters or events. Any element in the story can be embellished upon or fabricated.
Even the information in a standard “nonfiction” autobiography should be taken with a grain of salt. After all, anything written from the author’s perspective may contain certain biases, distortions, or unconscious omissions within the text.
So if being nonfiction isn’t a defining characteristic of an autobiography, what is an autobiography defined by?
The key elements of an autobiography
What’s an autobiography like from cover to cover? It should contain these key elements:
- A personal narrative : It is a firsthand account of the author's life experiences.
- A chronological structure : An autobiography typically follows a chronological order, tracing the author's life from birth to present.
- Reflection and insight : The book should contain the author's reflections, insights, and emotions about key life events.
- Key life events : The book should highlight significant events, milestones, and challenges in the author's life.
- Setting and context : There should be descriptions of the time period, cultural background, and environment to help the reader understand the author’s life.
- Authenticity : The author should be honest and sincere in presenting their life story.
- A personal perspective : An autobiography is written from the author's unique point of view.
- A strong conclusion : The ending of the book should reflect on the author's current state or outlook.
Famous Autobiography Examples
Now that you know what an autobiography is, let’s look at some famous autobiography examples .
The Diary of a Young Girl by Anne Frank (1947)

Perhaps no autobiography is more famous than The Diary of a Young Girl by Anne Frank. Her diary chronicles her profound thoughts, dreams, and fears as she hides with her family in the walls during the Holocaust.
Anne's words resonate with the enduring spirit of hope amid unimaginable darkness.
The Autobiography of Ben Franklin by Benjamin Franklin (1909)

Benjamin Franklin's autobiography follows Franklin’s life from humble origins to one of America's greatest forefathers. While originally intended as a collection of anecdotes for his son, this autobiography has become one of the most famous works of American literature.
Long Walk to Freedom by Nelson Mandela (1994)

Long Walk to Freedom narrates Nelson Mandela's epic odyssey from South African prisoner to revered statesman. This masterpiece of an autobiography is a portrait of resilience against the backdrop of apartheid – and his words are a bastion for courage and human rights.
Now you know what an autobiography is, and some examples of successful autobiographies, so it’s time to discuss what goes into actually writing one.
Who Should Write an Autobiography?
Celebrity autobiographies are popular for a reason – the people who wrote them were already popular.
The main purpose of an autobiography is to portray the life experiences and achievements of the author. If you haven’t made any massive achievements that people are already aware of, an autobiography might not be for you. Instead, you should learn how to write a memoir .
After all, what’s an autobiography worth if no one reads it?
If you have made an important contribution to society, or have amassed a massive following of fans, then writing an autobiography could be a fabulous idea.
An autobiography is what allows you to claim your rightful place in history. It provides a legacy for your life, helps you to better understand your life’s journey, and can even be deeply therapeutic to write.
But then comes the next problem: how to write an autobiography.
Tips on Writing Your Own Autobiography
While memoirs are the books that teach life lessons, that doesn’t mean you shouldn’t give your autobiography meaning. The best autobiographies paint a vivid tapestry of personal growth and introspection.
You don’t just want to tell the reader about your life – you want them to feel like they are living it with you.
And it’s not just about painting a picture with your prose. A lot of thought should go into everything from autobiography titles to page count. To get started, here are five tips for writing an autobiography:
- Know your audience : Understand who will read your autobiography and speak to them while writing.
- Be candid and authentic : A life seen through rose-colored glasses isn’t relatable. You should include your failures as well as your triumphs, and humanize yourself so your story resonates with your reader.
- Do your research : Of course you know what happened in your life, but how many details do you actually remember? You may need to sift through photos, archives, and diaries – and interview people close to you. Consider adding the photos to your book.
- Identify key themes : Identify key events and life lessons that have shaped you. Reflect on how these themes have evolved over time.
- Edit and edit again : Write freely first, then edit rigorously. Seek feedback from trusted individuals and consider professional editing to ensure clarity and coherence in your narrative. NO ONE writes perfectly the first time.
So there you have it, you are well on your way to understanding (and writing) an autobiography.
If you'd still like more guidance for writing your autobiography, you can check out our free autobiography template . We can’t wait for you to share your life story with the world.
FREE BOOK OUTLINE TEMPLATE
100% Customizable For Your Manuscript.
Related posts
Non-Fiction
Need Some Memorable Memoir Titles? Use These Tips
Business, Non-Fiction
How to Get More Patients With a Book & Brand
The only (free) autobiography template you need – 4 simple steps.
- Search Menu
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Anglo-Saxon and Medieval Archaeology
- Archaeological Methodology and Techniques
- Archaeology by Region
- Archaeology of Religion
- Archaeology of Trade and Exchange
- Biblical Archaeology
- Contemporary and Public Archaeology
- Environmental Archaeology
- Historical Archaeology
- History and Theory of Archaeology
- Industrial Archaeology
- Landscape Archaeology
- Mortuary Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Underwater Archaeology
- Urban Archaeology
- Zooarchaeology
- Browse content in Architecture
- Architectural Structure and Design
- History of Architecture
- Residential and Domestic Buildings
- Theory of Architecture
- Browse content in Art
- Art Subjects and Themes
- History of Art
- Industrial and Commercial Art
- Theory of Art
- Biographical Studies
- Byzantine Studies
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical History
- Classical Philosophy
- Classical Mythology
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Classical Art and Architecture
- Classical Oratory and Rhetoric
- Greek and Roman Epigraphy
- Greek and Roman Law
- Greek and Roman Papyrology
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Late Antiquity
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genealogy, Heraldry, Names, and Honours
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- Historical Geography
- History by Period
- History of Emotions
- History of Agriculture
- History of Education
- History of Gender and Sexuality
- Industrial History
- Intellectual History
- International History
- Labour History
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Local and Family History
- Maritime History
- Military History
- National Liberation and Post-Colonialism
- Oral History
- Political History
- Public History
- Regional and National History
- Revolutions and Rebellions
- Slavery and Abolition of Slavery
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Urban History
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Learning (Specific Skills)
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Computational Linguistics
- Forensic Linguistics
- Grammar, Syntax and Morphology
- Historical and Diachronic Linguistics
- History of English
- Language Acquisition
- Language Evolution
- Language Reference
- Language Variation
- Language Families
- Lexicography
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Linguistic Theories
- Linguistic Typology
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Psycholinguistics
- Sociolinguistics
- Translation and Interpretation
- Writing Systems
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Children's Literature Studies
- Literary Studies (Asian)
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Eco-criticism)
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies (Modernism)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (1500 to 1800)
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Fiction, Novelists, and Prose Writers)
- Literary Studies (Gender Studies)
- Literary Studies (Graphic Novels)
- Literary Studies (History of the Book)
- Literary Studies (Plays and Playwrights)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Postcolonial Literature)
- Literary Studies (Queer Studies)
- Literary Studies (Science Fiction)
- Literary Studies (Travel Literature)
- Literary Studies (War Literature)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Mythology and Folklore
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Dance and Music
- Ethics in Music
- Ethnomusicology
- Gender and Sexuality in Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Cultures
- Music and Religion
- Music and Media
- Music and Culture
- Music Education and Pedagogy
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Scores, Lyrics, and Libretti
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Performance Practice and Studies
- Race and Ethnicity in Music
- Sound Studies
- Browse content in Performing Arts
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- Feminist Philosophy
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Non-Western Philosophy
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Perception
- Philosophy of Action
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Biblical Studies
- Christianity
- East Asian Religions
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Qumran Studies
- Religion and Education
- Religion and Health
- Religion and Politics
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Cookery, Food, and Drink
- Cultural Studies
- Customs and Traditions
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Hobbies, Games, Arts and Crafts
- Lifestyle, Home, and Garden
- Natural world, Country Life, and Pets
- Popular Beliefs and Controversial Knowledge
- Sports and Outdoor Recreation
- Technology and Society
- Travel and Holiday
- Visual Culture
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Browse content in Company and Commercial Law
- Commercial Law
- Company Law
- Browse content in Comparative Law
- Systems of Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Government Powers
- Judicial Review
- Local Government Law
- Military and Defence Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Construction Law
- Contract Law
- Browse content in Criminal Law
- Criminal Procedure
- Criminal Evidence Law
- Sentencing and Punishment
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Browse content in Financial Law
- Banking Law
- Insolvency Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Politics
- Law and Society
- Browse content in Legal System and Practice
- Courts and Procedure
- Legal Skills and Practice
- Primary Sources of Law
- Regulation of Legal Profession
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Policing
- Criminal Investigation and Detection
- Police and Security Services
- Police Procedure and Law
- Police Regional Planning
- Browse content in Property Law
- Personal Property Law
- Study and Revision
- Terrorism and National Security Law
- Browse content in Trusts Law
- Wills and Probate or Succession
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Arts Therapies
- Clinical Science
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Occupational Therapy
- Operating Department Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Speech and Language Therapy
- Browse content in Anaesthetics
- General Anaesthesia
- Neuroanaesthesia
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Genetics
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Genito-urinary Medicine
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Toxicology
- Medical Oncology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Medicine
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine and Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports and Exercise Medicine
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Emergency Medicine
- Forensic Medicine
- Haematology
- History of Medicine
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Paediatric Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Surgical Dentistry
- Browse content in Medical Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Communication Skills
- Nursing Skills
- Surgical Skills
- Medical Ethics
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Clinical Neurophysiology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Browse content in Paediatrics
- Neonatology
- Browse content in Pathology
- Chemical Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Histopathology
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Popular Health
- Caring for Others
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Self-help and Personal Development
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Cell Biology
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Addiction Medicine
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Learning Disabilities
- Old Age Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- General Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Peri-operative Care
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Surgical Oncology
- Transplant Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Vascular Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Natural History
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Computational Chemistry
- Crystallography
- Environmental Chemistry
- Industrial Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Materials Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Polymer Chemistry
- Study and Communication Skills in Chemistry
- Theoretical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Game Studies
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Programming Languages
- Software Engineering
- Systems Analysis and Design
- Virtual Reality
- Browse content in Computing
- Business Applications
- Computer Security
- Computer Games
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Digital Lifestyle
- Graphical and Digital Media Applications
- Operating Systems
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Maps and Map-making
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Oceanography and Hydrology
- Palaeontology
- Physical Geography and Topography
- Regional Geography
- Soil Science
- Urban Geography
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- History of Engineering and Technology
- Mechanical Engineering and Materials
- Technology of Industrial Chemistry
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Applied Ecology (Environmental Science)
- Conservation of the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Environmental Sustainability
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Environmental Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environmental Science)
- Nuclear Issues (Environmental Science)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Environmental Science)
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Metals, Alloying, and Corrosion
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- History of Mathematics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Finance
- Mathematical Analysis
- Numerical and Computational Mathematics
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Development of the Nervous System
- Disorders of the Nervous System
- History of Neuroscience
- Invertebrate Neurobiology
- Molecular and Cellular Systems
- Neuroendocrinology and Autonomic Nervous System
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Sensory and Motor Systems
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Biological and Medical Physics
- Classical Mechanics
- Computational Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Electromagnetism, Optics, and Acoustics
- History of Physics
- Mathematical and Statistical Physics
- Measurement Science
- Nuclear Physics
- Particles and Fields
- Plasma Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Semiconductor and Mesoscopic Physics
- Browse content in Psychology
- Affective Sciences
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Criminal and Forensic Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems in Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Psychological Assessment and Testing
- Psychology of Human-Technology Interaction
- Psychology Professional Development and Training
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Anthropology of Religion
- Human Evolution
- Medical Anthropology
- Physical Anthropology
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Theory and Practice of Anthropology
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Business Strategy
- Business Ethics
- Business History
- Business and Government
- Business and Technology
- Business and the Environment
- Comparative Management
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Entrepreneurship
- Health Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- International Business
- Knowledge Management
- Management and Management Techniques
- Operations Management
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Pensions and Pension Management
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Strategic Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Forms of Crime
- International and Comparative Criminology
- Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice
- Development Studies
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Asian Economics
- Behavioural Finance
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic Systems
- Economic History
- Economic Methodology
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- General Economics and Teaching
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- History of Economic Thought
- International Economics
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Microeconomics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Welfare Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Adult Education and Continuous Learning
- Care and Counselling of Students
- Early Childhood and Elementary Education
- Educational Equipment and Technology
- Educational Strategies and Policy
- Higher and Further Education
- Organization and Management of Education
- Philosophy and Theory of Education
- Schools Studies
- Secondary Education
- Teaching of a Specific Subject
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Teaching Skills and Techniques
- Browse content in Environment
- Applied Ecology (Social Science)
- Climate Change
- Conservation of the Environment (Social Science)
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Social Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environment)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Social Science)
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Cultural Geography
- Economic Geography
- Political Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- African Politics
- Asian Politics
- Chinese Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- Elections and Electoral Studies
- Environmental Politics
- European Union
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- Human Rights and Politics
- Indian Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- International Political Economy
- Irish Politics
- Latin American Politics
- Middle Eastern Politics
- Political Methodology
- Political Communication
- Political Philosophy
- Political Sociology
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Political Theory
- Politics and Law
- Public Administration
- Public Policy
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Russian Politics
- Security Studies
- State and Local Government
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Asian Studies
- East Asian Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Native American Studies
- Scottish Studies
- Browse content in Research and Information
- Research Methods
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Adoption and Fostering
- Care of the Elderly
- Child and Adolescent Social Work
- Couple and Family Social Work
- Developmental and Physical Disabilities Social Work
- Direct Practice and Clinical Social Work
- Emergency Services
- Human Behaviour and the Social Environment
- International and Global Issues in Social Work
- Mental and Behavioural Health
- Social Justice and Human Rights
- Social Policy and Advocacy
- Social Work and Crime and Justice
- Social Work Macro Practice
- Social Work Practice Settings
- Social Work Research and Evidence-based Practice
- Welfare and Benefit Systems
- Browse content in Sociology
- Childhood Studies
- Community Development
- Comparative and Historical Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Marriage and the Family
- Migration Studies
- Occupations, Professions, and Work
- Organizations
- Population and Demography
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Theory
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Education
- Sport and Leisure
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Browse content in Warfare and Defence
- Defence Strategy, Planning, and Research
- Land Forces and Warfare
- Military Administration
- Military Life and Institutions
- Naval Forces and Warfare
- Other Warfare and Defence Issues
- Peace Studies and Conflict Resolution
- Weapons and Equipment

- < Previous
- Next chapter >
(page 1) p. 1 Introduction
- Published: July 2018
- Cite Icon Cite
- Permissions Icon Permissions
Autobiography continues to be one of the most popular forms of writing, produced by authors from across the social and professional spectrum. It is also central to the work of literary critics, philosophers, historians, and psychologists, who have found in autobiographies not only an understanding of the ways in which lives have been lived, but the most fundamental accounts of what it means to be a self in the world. The Introduction describes what autobiography means and compares it to other forms of ‘life-writing’. Autobiographical writing is seen to act as a window on to concepts of self, identity, and subjectivity, and into the ways in which these are themselves determined by time and circumstance.
Signed in as
Institutional accounts.
- Google Scholar Indexing
- GoogleCrawler [DO NOT DELETE]
Personal account
- Sign in with email/username & password
- Get email alerts
- Save searches
- Purchase content
- Activate your purchase/trial code
Institutional access
- Sign in with a library card Sign in with username/password Recommend to your librarian
- Institutional account management
- Get help with access
Access to content on Oxford Academic is often provided through institutional subscriptions and purchases. If you are a member of an institution with an active account, you may be able to access content in one of the following ways:
IP based access
Typically, access is provided across an institutional network to a range of IP addresses. This authentication occurs automatically, and it is not possible to sign out of an IP authenticated account.
Sign in through your institution
Choose this option to get remote access when outside your institution. Shibboleth/Open Athens technology is used to provide single sign-on between your institution’s website and Oxford Academic.
- Click Sign in through your institution.
- Select your institution from the list provided, which will take you to your institution's website to sign in.
- When on the institution site, please use the credentials provided by your institution. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
- Following successful sign in, you will be returned to Oxford Academic.
If your institution is not listed or you cannot sign in to your institution’s website, please contact your librarian or administrator.
Sign in with a library card
Enter your library card number to sign in. If you cannot sign in, please contact your librarian.
Society Members
Society member access to a journal is achieved in one of the following ways:
Sign in through society site
Many societies offer single sign-on between the society website and Oxford Academic. If you see ‘Sign in through society site’ in the sign in pane within a journal:
- Click Sign in through society site.
- When on the society site, please use the credentials provided by that society. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
If you do not have a society account or have forgotten your username or password, please contact your society.
Sign in using a personal account
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members. See below.
A personal account can be used to get email alerts, save searches, purchase content, and activate subscriptions.
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members.
Viewing your signed in accounts
Click the account icon in the top right to:
- View your signed in personal account and access account management features.
- View the institutional accounts that are providing access.
Signed in but can't access content
Oxford Academic is home to a wide variety of products. The institutional subscription may not cover the content that you are trying to access. If you believe you should have access to that content, please contact your librarian.
For librarians and administrators, your personal account also provides access to institutional account management. Here you will find options to view and activate subscriptions, manage institutional settings and access options, access usage statistics, and more.
Our books are available by subscription or purchase to libraries and institutions.
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Rights and permissions
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
How to Write an Autobiography Fast

Writing your autobiography is like exploring a treasure trove of memories that make up your life. But starting can feel overwhelming. Where do you begin? How do you turn your experiences into a compelling story? Don't worry – this guide is here to help. Whether you're a seasoned writer or a total beginner, we'll break down the process of how to write your autobiography into easy-to-follow steps. Together, we'll uncover the magic of storytelling and turn your life into a captivating reflective essay that's uniquely yours. Get ready to start this adventure of self-discovery and creativity!
What Is an Autobiography
The autobiography definition explains it is a written account of a person's life penned by the individual who has lived those experiences. It is a personal narrative that chronicles significant events, reflections, and emotions throughout various stages of the author's life. Unlike a biography, which is typically written by someone else, an autobiography provides a firsthand perspective, allowing the author to share their thoughts, memories, and insights. It is a cogent medium for self-expression, enabling students to convey the essence of their unique journey, impart lessons learned, and leave a lasting record of their lives for themselves and others to explore.
Need Help With Writing an AUTOBIOGRAPHY?
All you have to do to get professional help is to us send your paper requirements and set the deadline.
Autobiography vs. Biography: What’s the Difference
The key distinction between an autobiography and a biography lies in the authorship and perspective. An autobiography is a personal account of one's own life written by the subject themselves. It offers an intimate insight into the author's experiences, emotions, and reflections. For instance, in "The Diary of a Young Girl," Anne Frank provides a poignant autobiographical account of her life hiding from the Nazis during World War II. On the other hand, a biography is a narrative of someone's life written by another person. It often involves extensive research and interviews to present a comprehensive and objective view. A notable example is "Steve Jobs" by Walter Isaacson, a biography offering an in-depth portrayal of the Apple co-founder, drawing on interviews with Jobs himself and those who knew him. While both genres illuminate lives, the crucial difference lies in the source of the narrative – whether it emanates directly from the subject or is crafted by an external observer.
A biography vs autobiography offers distinct perspectives on individuals' lives, shaping narratives through either personal reflections or external observations. Maya Angelou's "I Know Why the Caged Bird Sings" is a powerful autobiography chronicling her tumultuous childhood and journey toward self-discovery. In contrast, a notable biography like "Leonardo da Vinci" by Walter Isaacson delves into the life of the Renaissance polymath, painting a vivid picture through meticulous research and analysis. Autobiographies often provide a deeply personal lens, as seen in "The Glass Castle" by Jeannette Walls, where Walls recounts her unconventional upbringing. In contrast, biographies such as "Unbroken" by Laura Hillenbrand meticulously document the extraordinary life of Louis Zamperini, offering a comprehensive view shaped by the author's investigative work. These examples underscore the unique storytelling approaches each genre employs, either from the firsthand perspective of the subject or the external perspective of an author.
Autobiography Example
Ready to explore autobiography examples? We've got a cool section coming up where we'll check out two awesome examples. Autobiographies are like personal tours into someone's life, and we'll be looking at the stories of Alex Sterling and Trevor Noah. They've poured their experiences onto the pages, and we're going to see what we can learn from their journeys. Get ready to be inspired and maybe even think about telling your own story down the line. Let's dive in!
.webp)
Example 1: “Wanderer's Odyssey: The Uncharted Life of Alex Sterling”
This autobiography recounts the life of a character born in a bustling city who, driven by a thirst for adventure, leaves behind urban life to explore the open road. The narrative explores the protagonist's experiences of hitchhiking, forming connections, and finding self-discovery in the midst of the unpredictable journey. The story emphasizes the lessons learned from the road, the challenges faced, and the ultimate embrace of authenticity. The epilogue reflects on the character's life as a well-lived odyssey, highlighting themes of resilience, connection, and the pursuit of one's true identity.
Example 2: “Echoes of Eternity: The Memoirs of Amelia Reed”
This autobiography follows a character from a countryside village who harbors expansive dreams of adventure. The narrative unfolds as the protagonist sets out to pursue these dreams, facing trials and triumphs that shape their character and lead to self-discovery. The story emphasizes the transformative power of embracing the unknown, with the epilogue reflecting on a life well-lived, highlighting the legacy of fulfilled dreams and the enduring impact on future generations. In addition to examples, we have samples of narrative essay topics that might be useful for you as well.
Tell your story with EssayPro . Our skilled writers can help you craft an autobiography that truly reflects your journey. Share your unique experiences and life lessons in a way that resonates with readers.

Autobiography Elements Explained
Writing an autobiography provides a personal account of one's experiences, achievements, challenges, and personal growth. While each autobiography is unique, certain common elements are often found in this genre:
Introduction
- Autobiographies typically begin with an introduction where the author sets the stage for their life story.
- It may include background information such as birthplace, family, and early experiences.
Birth and Early Years
- Authors often include details about their birth, childhood, and family background.
- Early influences, relationships, and experiences that shaped the individual may be highlighted.
Significant Life Events
- Autobiographies focus on key events and milestones that have had a significant impact on the author's life.
- This could include achievements, failures, relationships, and other impactful experiences.
Challenges and Obstacles
- Autobiographies explore the challenges and obstacles the author faced throughout their life.
- This can include personal struggles, professional setbacks, or other difficulties.
Personal Growth and Development
- Authors reflect on their personal growth and development over the years.
- This may involve self-discovery, learning from experiences, and evolving perspectives.
Achievements and Milestones
- Autobiographies highlight the author's achievements, whether personal, professional, or both.
- Major milestones and successes are often detailed to showcase the individual's journey.
Influential Relationships
- Autobiographies frequently discuss relationships with family, friends, mentors, and significant others.
- The impact of these relationships on the author's life is explored.
Reflection and Insight
- Authors often reflect on their lives, offering insights into their beliefs, values, and lessons learned.
- This section may also include the author's perspective on the world and society.
Themes and Motifs
- Autobiographies may explore recurring themes or motifs that run throughout the individual's life.
- Common themes include resilience, determination, love, loss, and personal identity.
- Autobiographies typically conclude with a summary or reflection on the author's life.
- The author may share their current perspective and future aspirations.
Writing Style
- The writing style can vary, ranging from a formal tone to a more conversational and reflective approach.
- Authors may use literary devices and storytelling techniques to engage readers.
Remember that autobiographies are highly personal, and the structure and emphasis on different elements can vary widely depending on the author's preferences and purpose for writing.
Autobiographical Essay Structure
Autobiographies typically follow a chronological order, beginning with the author's early life and progressing towards the present or a significant moment. The introduction sets the stage, introducing the author and offering insight into the main themes. As you can see in an autobiography example, the narrative then unfolds, exploring the author's significant life events, challenges faced, and personal growth. Achievements and milestones are highlighted, and the impact of influential relationships is examined. Throughout, recurring themes and motifs add depth to the narrative. In the reflection and insight section, the author shares personal lessons learned and beliefs. The conclusion summarizes the autobiography, reflecting on the author's life and future aspirations.
.webp)
Learning how to start an autobiography involves captivating the reader's attention while providing context. Authors often employ engaging anecdotes, vivid descriptions, or thought-provoking statements related to the overarching theme of their lives. The goal is to draw readers in from the beginning and establish a connection between the author and the audience. In the introduction, authors can introduce themselves to the reader. This can be done by sharing a captivating snapshot of their life or posing a question that intrigues the audience. The autobiography introduction sets the tone for the entire narrative, providing a glimpse into the themes and events that will be explored in the autobiography.
The autobiography conclusion offers the culmination of the author's life story. Here, authors often summarize the key points and experiences shared throughout the narrative. It is a moment of reflection, where the author can offer insights into the significance of their journey and the lessons learned along the way. The conclusion may also touch on the author's current perspective, providing a sense of closure to the narrative while leaving room for future aspirations and growth.
Literary Forms of Autobiography
Autobiographies, while generally a non-fiction genre, can take on various literary forms and styles. Here are some literary forms commonly found in autobiographical works:
Traditional Autobiography
- The straightforward narrative of an individual's life, which is usually written by the person themselves. It follows a chronological order, covering significant events and experiences.
- Similar to an autobiography but often focusing on specific themes, periods, or aspects of the author's life rather than a comprehensive account. Memoirs often delve into personal reflections and emotions.
Diary or Journal Form
- Some autobiographies adopt the form of a diary or journal, presenting the author's life through dated entries. This format provides a more immediate and personal perspective.
Epistolary Autobiography
- Written in the form of letters, an epistolary autobiography may consist of the author addressing themselves or others. This style adds an intimate and conversational tone to the narrative.
Graphic Novel or Comic Memoir
- Autobiographical stories are presented in a graphic novel or comic format. Visual elements complement the written narrative, providing a unique and engaging way to convey personal experiences.
Experimental or Nonlinear Autobiography
- Some authors choose to play with the chronological order, presenting their life story non-linearly. This experimental approach can create a more artistic and challenging reading experience.
Biographical Fiction
- While not entirely autobiographical, some authors write fictionalized versions of their own lives. It allows for creative exploration and artistic liberties while drawing inspiration from real experiences.
Travelogue Autobiography
- Autobiographies that take on the form of a travelogue often focus on the author's journeys, both physical and metaphorical. The narrative is shaped by the places visited and the impact of these experiences on personal growth.
Essayistic Autobiography
- Autobiographies that incorporate elements of essays, exploring themes, ideas, and reflections on the author's life. This form allows for a more contemplative and philosophical approach.
Collaborative Autobiography
- Co-written autobiographies involve collaboration between the autobiographical subject and a professional writer. It is common when the subject may not be a writer but has a compelling story to share.
These literary forms highlight the versatility of autobiographical writing, showcasing how authors can creatively shape their life stories to engage readers in various ways. Are you working on other academic assignments? Use our term paper writing services to put your finger on any pending task at hand quickly and for a reasonable price.
How to Write an Autobiography in 5 Steps
Writing an autobiography can be a rewarding and reflective process. Here's a simplified guide in 5 steps to help you get started:
Step 1: Reflection and Brainstorming
Begin by reflecting on your life, considering important events, challenges, and moments of growth. Make a mental inventory of key experiences and people who have influenced you.
Step 2: Establish a Focus
Choose a central theme or focus for your autobiography. This could be a specific period of your life, a significant achievement, or a recurring theme that ties your experiences together. Having a clear focus will guide your writing.

Step 3: Create a Chronological Outline
Develop a rough chronological outline of your life story, starting from your early years and progressing through significant events to the present or another crucial point. Identify key moments and experiences to include in each section.
Step 4: Write with Detail and Emotion
An important aspect of how to write an autobiography for college is appealing to emotion. As you delve into each body paragraph, share your story with vivid details. Use descriptive language to bring your experiences to life for the reader. Infuse your writing with emotion, allowing readers to connect with the depth of your personal journey.
Step 5: Conclude Reflectively
In the concluding section, summarize the key aspects of your life story. Reflect on the significance of your journey, the lessons you've learned, and how you've grown. Provide insights into your current perspective and aspirations for the future, bringing your autobiography to a thoughtful conclusion.
Writing Techniques to Use in an Autobiography
When you write an autobiography, the process involves employing various techniques to make the narrative engaging, evocative, and compelling. Here are some tips for writing autobiography commonly used in autobiographies:
Descriptive Language
- Use vivid and descriptive language to paint a detailed picture of events, people, and settings. Engage the reader's senses to create a more immersive experience.
- Incorporate dialogue to bring conversations to life. Direct quotes can provide authenticity and convey the personalities of the people involved.
Show, Don't Tell
- Instead of merely stating facts, show the emotions and experiences through actions, reactions, and sensory details.
Flashbacks and Foreshadowing
- Employ flashbacks to delve into past events and foreshadowing to create anticipation about future developments.
Metaphors and Similes
- Use metaphors and similes to enhance descriptions and convey complex emotions. Comparisons can make abstract concepts more relatable.
- Integrate symbols and motifs that hold personal significance. This adds depth to the narrative and can be a thematic thread throughout the autobiography.
Humor and Wit
- Infuse your writing with humor and wit when appropriate.
- Introduce suspense by strategically withholding information or revealing key details at crucial moments.
First-Person Perspective
- Utilize the first-person point of view to offer a direct and personal connection between the author and the reader.
Dramatic Irony
- Introduce dramatic irony by revealing information to the reader that the author may not have known at the time.
Parallelism
- Create parallel structures within the narrative, drawing connections between different periods, events, or themes in your life.
Experimenting with different styles can make your story more engaging and memorable for readers. If you haven’t used these techniques in your paper, simply say, ‘ edit my essay ,’ and our experts will imbue stylistic and creative devices in your document to increase its scholarly value.
Benefits of Writing an Autobiography
Working on an autobiography can be incredibly beneficial on a personal level. When you take the time to reflect on your life and put it into words, you gain a deeper understanding of yourself. It's like a journey of self-discovery where you uncover patterns, values, and beliefs that have shaped who you are. This process not only promotes self-awareness but can also help you grow and bounce back from tough times. Writing about challenging moments can be a therapeutic release, allowing you to confront and make sense of your experiences, leading to emotional healing.
On a broader scale, sharing your life story through an autobiography has its impact. It becomes a piece of history, offering insights into the times you've lived through, the culture around you, and societal changes. Your personal narrative connects you with others, creating empathy and understanding. Autobiographies often inspire people by showing that it's possible to overcome challenges, find purpose, and navigate the ups and downs of life. By sharing your story, you become a part of the larger human experience, contributing to a rich tapestry of diverse stories that help us better understand the shared journey of being human. Order an essay or any other type of task to streamline your educational progress is only a few clicks.
Best Piece of Advice for Making Your Autobiography Spot-on
The most valuable advice on how to write an autobiography is to infuse authenticity into every word. Be genuine, raw, and honest about your experiences, emotions, and growth. Readers connect deeply with authenticity, and it's what makes your story uniquely yours. Don't shy away from expressing vulnerability, as it adds a human touch and makes your narrative relatable. Share the highs and lows, the triumphs and struggles, with sincerity, and let your true self shine through. This honesty not only enhances the impact of your autobiography but also contributes to a more profound connection between you and your readers, creating an authentic and memorable narrative. Here are additional tips for bringing your autobiography assignment up to par:
- Essential Details. Focus on key moments that significantly contribute to your story, avoiding unnecessary details.
- Thematic Cohesion. Introduce and explore recurring themes to add depth and coherence to your narrative.
- Authentic Expression. Embrace your unique voice, personality, and storytelling style to create an authentic connection with readers.
- Dialogue and Monologue. Use genuine dialogue and inner monologue to provide insights into your thoughts and emotions during pivotal moments.
- Symbolic Elements. Incorporate symbolic imagery or metaphors to convey deeper meanings and emotions.
- Strategic Foreshadowing. Use foreshadowing purposefully, providing subtle hints that contribute meaningfully to the overall narrative.
- Reflective Closure. Conclude your autobiography with a reflective summary that offers insights into the broader significance of your journey.
Our essay writers know many more tips regarding all possible types of academic tasks. If you ever find yourself in writer’s block, not knowing how to tackle any particular assignment, let us know!
Final Words
If you want to understand how to write a good autobiography, think of it as painting a vivid picture of your life for others to see. It's about being real, digging deep into your memories, and choosing the moments that really matter. Let your personality shine through in your writing – be yourself because that's what makes your story unique. Weave in themes that tie everything together, and use storytelling techniques like dialogue and symbolism to make your narrative come alive. And as you reach the end, leave your readers with some food for thought – a reflection on the bigger lessons learned from your journey. If you ever need assistance with this or any other college assignment, use our research paper services without hesitation.
Do You Need Some Help With Your AUTOBIOGRAPHY?
Address to out professional writers to get your paper done asap
How to Write an Autobiography?
How to start an autobiography essay, what is the difference between autobiography and biography, related articles.
.webp)
Definition of Biography
A biography is the non- fiction , written history or account of a person’s life. Biographies are intended to give an objective portrayal of a person, written in the third person. Biographers collect information from the subject (if he/she is available), acquaintances of the subject, or in researching other sources such as reference material, experts, records, diaries, interviews, etc. Most biographers intend to present the life story of a person and establish the context of their story for the reader, whether in terms of history and/or the present day. In turn, the reader can be reasonably assured that the information presented about the biographical subject is as true and authentic as possible.
Biographies can be written about a person at any time, no matter if they are living or dead. However, there are limitations to biography as a literary device. Even if the subject is involved in the biographical process, the biographer is restricted in terms of access to the subject’s thoughts or feelings.
Biographical works typically include details of significant events that shape the life of the subject as well as information about their childhood, education, career, and relationships. Occasionally, a biography is made into another form of art such as a film or dramatic production. The musical production of “Hamilton” is an excellent example of a biographical work that has been turned into one of the most popular musical productions in Broadway history.
Common Examples of Biographical Subjects
Most people assume that the subject of a biography must be a person who is famous in some way. However, that’s not always the case. In general, biographical subjects tend to be interesting people who have pioneered something in their field of expertise or done something extraordinary for humanity. In addition, biographical subjects can be people who have experienced something unusual or heartbreaking, committed terrible acts, or who are especially gifted and/or talented.
As a literary device, biography is important because it allows readers to learn about someone’s story and history. This can be enlightening, inspiring, and meaningful in creating connections. Here are some common examples of biographical subjects:
- political leaders
- entrepreneurs
- historical figures
- serial killers
- notorious people
- political activists
- adventurers/explorers
- religious leaders
- military leaders
- cultural figures
Famous Examples of Biographical Works
The readership for biography tends to be those who enjoy learning about a certain person’s life or overall field related to the person. In addition, some readers enjoy the literary form of biography independent of the subject. Some biographical works become well-known due to either the person’s story or the way the work is written, gaining a readership of people who may not otherwise choose to read biography or are unfamiliar with its form.
Here are some famous examples of biographical works that are familiar to many readers outside of biography fans:
- Alexander Hamilton (Ron Chernow)
- Prairie Fires: The American Dreams of Laura Ingalls Wilder (Caroline Fraser)
- Steve Jobs (Walter Isaacson)
- Churchill: A Life (Martin Gilbert)
- The Professor and the Madman: A Tale of Murder, Insanity, and the Making of the Oxford English Dictionary (Simon Winchester)
- A Beautiful Mind (Sylvia Nasar)
- The Black Rose (Tananarive Due)
- John Adams (David McCullough)
- Into the Wild ( Jon Krakauer )
- John Brown (W.E.B. Du Bois)
- Frida: A Biography of Frida Kahlo (Hayden Herrera)
- The Immortal Life of Henrietta Lacks (Rebecca Skloot)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham Lincoln (Doris Kearns Goodwin)
- Shirley Jackson : A Rather Haunted Life ( Ruth Franklin)
- the stranger in the Woods: The Extraordinary Story of the Last True Hermit (Michael Finkel)
Difference Between Biography, Autobiography, and Memoir
Biography, autobiography , and memoir are the three main forms used to tell the story of a person’s life. Though there are similarities between these forms, they have distinct differences in terms of the writing, style , and purpose.
A biography is an informational narrative and account of the life history of an individual person, written by someone who is not the subject of the biography. An autobiography is the story of an individual’s life, written by that individual. In general, an autobiography is presented chronologically with a focus on key events in the person’s life. Since the writer is the subject of an autobiography, it’s written in the first person and considered more subjective than objective, like a biography. In addition, autobiographies are often written late in the person’s life to present their life experiences, challenges, achievements, viewpoints, etc., across time.
Memoir refers to a written collection of a person’s significant memories, written by that person. Memoir doesn’t generally include biographical information or chronological events unless it’s relevant to the story being presented. The purpose of memoir is reflection and an intention to share a meaningful story as a means of creating an emotional connection with the reader. Memoirs are often presented in a narrative style that is both entertaining and thought-provoking.
Examples of Biography in Literature
An important subset of biography is literary biography. A literary biography applies biographical study and form to the lives of artists and writers. This poses some complications for writers of literary biographies in that they must balance the representation of the biographical subject, the artist or writer, as well as aspects of the subject’s literary works. This balance can be difficult to achieve in terms of judicious interpretation of biographical elements within an author’s literary work and consideration of the separate spheres of the artist and their art.
Literary biographies of artists and writers are among some of the most interesting biographical works. These biographies can also be very influential for readers, not only in terms of understanding the artist or writer’s personal story but the context of their work or literature as well. Here are some examples of well-known literary biographies:
Example 1: Savage Beauty: The Life of Edna St. Vincent Millay (Nancy Milford)
One of the first things Vincent explained to Norma was that there was a certain freedom of language in the Village that mustn’t shock her. It wasn’t vulgar. ‘So we sat darning socks on Waverly Place and practiced the use of profanity as we stitched. Needle in, . Needle out, piss. Needle in, . Needle out, c. Until we were easy with the words.’
This passage reflects the way in which Milford is able to characterize St. Vincent Millay as a person interacting with her sister. Even avid readers of a writer’s work are often unaware of the artist’s private and personal natures, separate from their literature and art. Milford reflects the balance required on the part of a literary biographer of telling the writer’s life story without undermining or interfering with the meaning and understanding of the literature produced by the writer. Though biographical information can provide some influence and context for a writer’s literary subjects, style, and choices , there is a distinction between the fictional world created by a writer and the writer’s “real” world. However, a literary biographer can illuminate the writer’s story so that the reader of both the biography and the biographical subject’s literature finds greater meaning and significance.
Example 2: The Invisible Woman: The Story of Nelly Ternan and Charles Dickens (Claire Tomalin)
The season of domestic goodwill and festivity must have posed a problem to all good Victorian family men with more than one family to take care of, particularly when there were two lots of children to receive the demonstrations of paternal love.
Tomalin’s literary biography of Charles Dickens reveals the writer’s extramarital relationship with a woman named Nelly Ternan. Tomalin presents the complications that resulted for Dickens from this relationship in terms of his personal and family life as well as his professional writing and literary work. Revealing information such as an extramarital relationship can influence the way a reader may feel about the subject as a person, and in the case of literary biography it can influence the way readers feel about the subject’s literature as well. Artists and writers who are beloved , such as Charles Dickens, are often idealized by their devoted readers and society itself. However, as Tomalin’s biography of Dickens indicates, artists and writers are complicated and as subject to human failings as anyone else.
Example 3: Virginia Woolf (Hermione Lee)
‘A self that goes on changing is a self that goes on living’: so too with the biography of that self. And just as lives don’t stay still, so life-writing can’t be fixed and finalised. Our ideas are shifting about what can be said, our knowledge of human character is changing. The biographer has to pioneer, going ‘ahead of the rest of us, like the miner’s canary, testing the atmosphere , detecting falsity, unreality, and the presence of obsolete conventions’. So, ‘There are some stories which have to be retold by each generation’. She is talking about the story of Shelley, but she could be talking about her own life-story.
In this passage, Lee is able to demonstrate what her biographical subject, Virginia Woolf, felt about biography and a person telling their own or another person’s story. Literary biographies of well-known writers can be especially difficult to navigate in that both the author and biographical subject are writers, but completely separate and different people. As referenced in this passage by Lee, Woolf was aware of the subtleties and fluidity present in a person’s life which can be difficult to judiciously and effectively relay to a reader on the part of a biographer. In addition, Woolf offers insight into the fact that biographers must make choices in terms of what information is presented to the reader and the context in which it is offered, making them a “miner’s canary” as to how history will view and remember the biographical subject.
Post navigation

We have sent you an email with a 6 digit code to:
Didn't receive an email? Check your spam folder and mark the email as not spam!. If you Skip this step, you won't be able to receive order-related updates via email.
Biography Vs Autobiography: Similarities and Differences with Examples

Do you ever get confused between biography and autobiography? If so, you're not alone. These terms are used interchangeably, but each has its own unique approach. In this blog, we'll discuss biography vs autobiography. After reading this guide, you'll be able to make the difference between an autobiography and a biography.
What is biography?
Here is a simple definition of biography: 'A biography is a detailed account of an individual's life written by someone else. The author is not the subject of the story. It is also referred to as a bio.' A biography can be about someone who is alive or deceased. It highlights essential moments and happenings in the life of the person in question. This genre essentially incorporates a person's extensive data, including given name, origin, birth date,occupation, and connections. Creating an exceptional piece requires perusing diverse materials such as records, manuals, memoirs, pictures, and interviews. Effective biographies come in writing; however, they can also take other forms such as music, movies. If the targeted subject is dead, then the writer has to do an immense amount of research. You may need to interview the people who knew that person or read already written biographies about that person. But if the person is alive, the writer can interview the target person several times to know about their life experiences. Biography writing seems like a tiresome job. But you can ease this task by reading our latest guide on professional biography writing .
Purpose of Biography
The primary goal of biography writing is to tell the readers about the subject's life from childhood to adult life and the rest of the years. Additionally, the biography tells a story of how the person learned life lessons and navigated through the challenges. The person's biography should give a clear picture to the reader about the subject's personality, traits, and how they interact with the world. You must cover all the essential features of biography.
Definition of Autobiography
The story about a person's life written by that person himself or herself is called an autobiography. The literal meaning of the word auto is 'self.' It covers all the elements of the biography but is narrated by the writer himself. Anyone can write their life story as an autobiography. Moreover, the author is himself the subject of the biography.
Purpose of Autobiography
The basic purpose of an autobiography is to portray the author's accomplishments and experiences of life. The majority of autobiographies are written from the author's perspective later in the person's life. So, the first person account is used to tell the author's story. An autobiography usually starts with the early childhood years. Then, covers information about the person's brought up place, their education years, career, challenges they faced and how they tackled them. These are the key features of autobiography. It is created from the person's diaries. Moreover, the story may have flashbacks and flash forwards, but it must follow the chronological order. Describe the person's life occasions in a sequential manner from early life to their current years.
Important Aspects of a Strong Autobiography
The primary features of autobiography are as follows:
- The facts are always told in the first person.
- More in-depth and personal than a biography.
- Goes into great depth about the character's life.
- It also explains the motivation behind the main character's behavior.
Common Elements of Biography and Autobiography
Here are a few elements that are common in both types of written formats:
- The purpose of both is to portray a person's life.
- Both are nonfiction because they deal with real-life events that occur during the subject's life.
- Both follow the same chronological order, starting from their early life to the various life stages.
- They include personal insights about the subject's life.
- Both genres may use multiple sources like newspapers, interviews, diaries, photographs and other documents to provide context and in depth narrative.
- The key elements, such as growth, character development, and transformation, are discussed in both.
Recommended Reading : How to write a biography essay with tips, sample & outline
What is the difference between biography and autobiography?
Along with the similarities, there are also some notable differences between them. The basic difference between autobiography and biography is that autobiography tends to be more subjective in nature. That's why they are written by the subject themselves. Let’s explain the difference between autobiography and biography in detail.
Autobiography Vs Biography Examples
Biography example.
- Name: Alexander Hamilton Author name: Ron Chernow Alexander Hamilton is one of the most fascinating founding fathers of America, and Ron Chernow tells his story in great detail. Chernow traces Hamilton's transformation from an orphan into a political genius by fusing in-depth research with a narrative style. The book clarifies Hamilton's political beliefs and his pivotal role in the development of the US financial system (Chernow, 2004).
- Name: The Life of Samuel Jhonson Author name: Boswell Boswell delves deeply into the life of Dr. Samuel Johnson, his mentor and friend. The biography portrays Dr. Johnson's life, character, unique traits, and intellectual prowess in a fascinating way (Boswell, 1791). Boswell's vivid portrayal brings Johnson to life for the readers, making this one of the best biographies in English literature.
- Name: The Lives of the Most Eminent English Poets Author name: Dr. Samuel Jhonson Some of the 17th and 18th century's greatest poets, such as Alexander Pope and John Milton, are discussed in Dr. Johnson's work. In addition to critiquing the works, he delves into the authors' private lives and the geopolitical context of their eras (Johnson, 1781). Johnson's research is very significant because it takes a combined historical and biographical approach.
Autobiography Examples
- Name: The Diary of a Young Girl Author: Anne Frank It is a unique story of a little Jewish girl. Her name is Anne Frank. This book told the story of her and her family's escape from Nazis in Amsterdam during World War II. She spent two years in hiding, and her diary writings provide important insights into the dread, hope, and resiliency she faced (Frank, 1947). Frank's autobiography posthumously acts as both a symbol of perseverance in the face of adversity and a reminder of the injustices of the past.
- Name: I Know Why the Caged Bird Sings Author: Maya Angelou This moving autobiography traces the early years of Maya Angelou, from being the first black streetcar operator in San Francisco to facing racial discrimination in the South. With incredible grace and courage, Angelou depicts her path of self-discovery and overcoming catastrophic events, including personal pain and racial prejudice. Her narrative of tenacity conveys a powerful message about discovering one's voice (Angelou, 1969).
- Name: Night Author: Elie Wiesel The autobiographical story " Night " by Elie Wiesel describes his and his father's experiences in Nazi concentration camps during WWII. This devastating story explores the loss of innocence and the fight to hold onto faith in humanity in addition to detailing physical suffering and cruel acts. It is proof of the human spirit's ability to persevere in the face of unimaginable evil (Wiesel, 1960).
Bottom Line
It's often challenging to distinguish between an autobiography and a biography. Although there are some significant distinctions between the two genres, you should be aware of them if your aim is to write in any of them. While both biographies and autobiographies are valuable sources of information and amusement about historical personalities (or current figures! ), they serve different purposes. We can enhance our media knowledge and gain a better understanding of the author's aim and appropriate approach to the material by being aware of the distinct objectives of each. We really hope you find this information useful. You can get in touch with experienced writers who are highly qualified and have years of experience in providing biography writing services . Take your time and make sure you are creating an engaging narrative that makes the reader feel as though they are right there with you when writing your own life story.
Table of Contents
Persuasive essay topics – how to choose one for you, how to write a persuasive essay- expert tips.

Autobiography
Definition of autobiography.
Autobiography is one type of biography , which tells a life story of its author, meaning it is a written record of the author’s life. Rather than being written by somebody else, an autobiography comes through the person’s own pen, in his own words. Some autobiographies are written in the form of a fictional tale; as novels or stories that closely mirror events from the author’s real life. Such stories include Charles Dickens’ David Copperfield , and J.D Salinger’s The Catcher in the Rye . In writing about personal experience, one discovers himself. Therefore, it is not merely a collection of anecdotes – it is a revelation to the readers about author’s self-discovery.
Difference between Autobiography and Memoir
In an autobiography, the author attempts to capture important elements of his life. He not only deals with his career, and growth as a person, he also uses emotions and facts related to family life, relationships, education, travels, sexuality, and any types of inner struggles. A memoir is a record of memories, and particular events that have taken place in the author’s life. In fact, it is the telling of a story or an event from his life; an account that does not tell the full record of a life.
Examples of Autobiography in Literature
Example #1: the box: tales from the darkroom (by gunter grass).
A noble laureate and novelist, Gunter Grass, has shown a new perspective of self-examination by mixing up his quilt of fictionalized approach in his autobiographical book, “The Box: Tales from the Darkroom.” Adopting the individual point of view of each of his children, Grass narrates what his children think about him as their father and a writer. Though it is really an experimental approach, due to Grass’ linguistic creativity and dexterity, it gains an enthralling momentum.
Example #2: The Story of My Life (by Helen Keller)
In her autobiography, The Story of My Life , Helen Keller recounts her first twenty years, beginning with the events of the childhood illness that left her deaf and blind. In her childhood, a writer sent her a letter and prophesied, “Someday you will write a great story out of your own head that will be a comfort and help to many.”
In this book, Keller mentions prominent historical personalities, such as Alexander Graham Bell, whom she met at the age of six, and with whom she remained friends for several years. Keller paid a visit to John Greenleaf Whittier , a famous American poet, and shared correspondence with other eminent figures, including Oliver Wendell Holmes, and Mrs. Grover Cleveland. Generally, Keller’s autobiography is about overcoming great obstacles through hard work and pain.
Example #3: Self Portraits: Fictions (by Frederic Tuten)
In his autobiography, “Self Portraits: Fictions,” Frederic Tuten has combined fringes of romantic life with reality. Like postmodern writers, such as Jorge Luis Borges, and Italo Calvino, the stories of Tuten skip between truth and imagination, time and place, without warning. He has done the same with his autobiography, where readers are eager to move through fanciful stories about train rides, circus bears, and secrets to a happy marriage; all of which give readers glimpses of the real man.
Example #4: My Prizes (by Thomas Bernhard)
Reliving his success of his literary career through the lens of the many prizes he has received, Thomas Bernhard presents a sarcastic commentary in his autobiography, “My Prizes.” Bernhard, in fact, has taken few things too seriously. Rather, he has viewed his life as a farcical theatrical drama unfolding around him. Although Bernhard is happy with the lifestyle and prestige of being an author, his blasé attitude and scathing wit make this recollection more charmingly dissident and hilarious.
Example #5: The Autobiography of Benjamin Franklin (by Benjamin Franklin)
“The Autobiography of Benjamin Franklin” is written by one of the founding fathers of the United States. This book reveals Franklin’s youth, his ideas, and his days of adversity and prosperity. He is one of the best examples living the American dream – sharing the idea that one can gain financial independence, and reach a prosperous life through hard work.
Through autobiography, authors can speak directly to their readers, and to their descendants. The function of the autobiography is to leave a legacy for its readers. By writing an autobiography, the individual shares his triumphs and defeats, and lessons learned, allowing readers to relate and feel motivated by inspirational stories. Life stories bridge the gap between peoples of differing ages and backgrounds, forging connections between old and new generations.

25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

What is an Autobiography?
- Updated on
- Sep 6, 2021
Are you fond of writing? Then, you might have considered writing an autobiography at some point in your writing journey. An autobiography is a firsthand account of the author’s own life that provides readers with an unparalleled degree of intimacy. Read the full blog to know how to write an autobiography, the difference between an autobiography and a biography, and look at some outstanding examples of autobiographies that everyone must read at least once in their lives.
This Blog Includes:
Autobiography vs. biography vs. memoir, what to include in an autobiography, place your story order, speak in the first person, define your characters, getting the facts right, the little elements, famous autobiographies to read, important tips on writing an autobiography, what is the appropriate length for an autobiography, how to write a short autobiography.
An autobiography is a non-fiction account of a person’s life written from their own perspective by the subject. Autobiographies are a subgenre of biographies, however, unlike a standard biography, which is usually written by someone other than the subject, an autobiography is written by the subject himself/herself. Autobiographies are personal stories written by individuals about themselves. These can be true accounts of noteworthy, unique, or dramatic events. They might be tributes to famous , interesting or inspiring people in society.
Autobiographie, biographies and memoirs are frequently available in almost every library or bookshop we visit. As a result, the readers are always confused about the difference between each of them. However, we are here to inform you that they are not the same.
You are not alone in scratching your head, unsure of what to put in your autobiography. After all, knowing what to include and exclude from your life narrative is an important aspect of how to write an autobiography. Do you pay attention to every detail? Is it true that everyone just wants to read long stories? Isn’t it possible that your autobiography will be too long?
The Movie Trailer Method is an excellent approach to think about how to write an autobiography. Focus on what would make the cut for a movie trailer of your life when deciding what to include in your autobiography:
- People with the most influence (like family, friends, mentors, coaches, etc.)
- Important events (like your origin story, vacations, graduations, life turning points, life lessons)
- Moments of emotion (When you were homeless, when you battled a life-threatening condition, or when you fell in love)
- Suspense or drama? (Did you get accepted to Harvard ? Was your first operation a success?)
How to Start Writing Your Autobiography?
It is crucial to consider the critical aspects of an autobiography while writing one since you want a story that is not only representative of your life, but also simple to read and engaging enough that the reader will not want to put the book down. So, what should you include on your list? Here is how you may start your autobiography:
While it may be tempting to repeat a tale in the order in which you remember it, bouncing back and forth in time can be extremely confusing. It’s possible that your ideas may come out jumbled when you start pulling them out, but you must put them in the right chronological sequence. Try to keep it in order, whether you’re starting from childhood – which is the most common starting point – or having a more focused picture of a certain era of your adult life.
People expect an autobiography to be written in the first person since it is about you. When discussing events, you might use ‘I,’ ‘Me,’ or ‘Mine,’ rather than she or he. If you’re sharing a story about a key person in your life, you’ll naturally refer to them as he or she.
Even if this is a non-fiction work, it is still important for the viewer to grasp how you fit into your family and who the people around you are. You’ll need to remember the events as well as bring your characters to life. Make sure to include essential facts about a character’s personality and how they contributed to your tale.
It’s critical to build your location in order to help the audience understand who shared your trip and how they influenced what occurred to you. Where were you while all of this was going on? From major information such as where you were born or raised to minor ones such as the mouth-watering and nostalgic aroma of the Sunday roast cooking in the kitchen as you were playing with your siblings.
When discussing how to write an autobiography, it’s occasionally the tiny details that make work come alive. Telling spontaneous stories is very appropriate. Include them if they are part of your recollection and history. People aren’t simply interested in reading about important events, rather they want to learn about the individuals and what they did. Who they are, what makes them tick; and don’t be afraid to relate a tale about your background, even if you think it’s trivial. Include it if you believe it is relevant.
Here is an exciting list of some of the best-written autobiographies written by famous writers from around the world:
- The Autobiography of Benjamin Franklin by Benjamin Franklin
- Long Walk to Freedom by Nelson Mandela
- The Story of My Experiments with Truth by Mahatma Gandhi
- The Diary of a Young Girl by Anne Frank
- Chronicles, Vol 1 by Bob Dylan
- I Know Why the Caged Bird Sings by Maya Angelou
- Agatha Christie: An Autobiography by Agatha Christie
- Open: An Autobiography by Andre Agassi
- On Writing: A Memoir of the Craft by Stephen King
- A Moveable Feast by Ernest Hemingway
Keep the following pro tips in mind now that you’re set and ready to write your draft copy:
- Allow yourself to be vulnerable. The finest autobiographies are full of defects, weaknesses, quirks, and missteps. Allow your readers to see the genuine ‘you’.
- Skip the sections that are boring. There’s no need to go into great detail about every meal, vehicle ride, or a tense trip to the supermarket.
- Keep your autobiography focused on the characters.
- Remember that this is YOUR tale to tell!
- Be (or don’t be) nice to others. Keep in mind that there may be consequences or reactions if you write about people in your narrative.
- Consider a theme to follow ! Many autobiographies are divided into sections based on a common theme. Themes run throughout the autobiography, connecting and uplifting each section.
- Create snippets for your tale (or vignette). Each vignette is a standalone tale with a beginning, middle, and conclusion. Each story builds on the previous one. Instead of informing the reader about the experience, each vignette should be presented in rich sensory language that shows the reader the experience.
- Pick a tone! Your narrative (like most stories) will most likely contain a range of emotions, but pick one and stay with it.
- Engage the readers! Always consider how you might make each part, chapter, page, paragraph, and phrase more engaging. You want to speak the truth, but it’s up to you how you say it. Suspense, tension, and mystery should all be present. Allow drama to fester until it becomes unbearable. Don’t try to fix problems or relieve tension straight away.
There are no hard and fast rules about how long an autobiography should be, but a good starting point is between 200 and 400 pages. This can help you get your book officially published or promote your self-published book by keeping it in line with what most people expect from novels in general.
A short autobiography is written in the same way as a large autobiography. You just leave out more information from the narrative. You reduced everything down to the bare necessities. Alternatively, you might pick a segment of your life, like in a memoir. This usually entails minimizing the number of characters in your book, lowering the number of events and experiences, and compressing your tale to just a few key times in your life.
We hope you understood all about Autobiography! Connect with Leverage Edu today, our trained experts will help you in choosing the right university and will guide you through the application process.
Team Leverage Edu
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
September 2024
January 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- Health and social care
- National Health Service
- Health workforce
Working definition of trauma-informed practice
- Office for Health Improvement & Disparities
Published 2 November 2022

© Crown copyright 2022
This publication is licensed under the terms of the Open Government Licence v3.0 except where otherwise stated. To view this licence, visit nationalarchives.gov.uk/doc/open-government-licence/version/3 or write to the Information Policy Team, The National Archives, Kew, London TW9 4DU, or email: [email protected] .
Where we have identified any third party copyright information you will need to obtain permission from the copyright holders concerned.
This publication is available at https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/working-definition-of-trauma-informed-practice/working-definition-of-trauma-informed-practice
Trauma-informed approaches have become increasingly cited in policy and adopted in practice as a means for reducing the negative impact of trauma experiences and supporting mental and physical health outcomes. They build on evidence developed over several decades. However, there has been a lack of consensus within the health and social care sector on how trauma-informed practice is defined, what its key principles are and how it can be built into services and systems.
This document seeks to address this gap by providing a working definition of trauma-informed practice for practitioners working in the health and care sector. The working definition presented in this document reflects the original internationally recognised definition developed by the United States Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) . The evidence base exploring the use of trauma-informed practice in different settings and sectors is still being developed. This working definition will be kept under review and updated where appropriate to reflect new evidence.
Trauma results from an event, series of events, or set of circumstances that is experienced by an individual as harmful or life threatening. While unique to the individual, generally the experience of trauma can cause lasting adverse effects, limiting the ability to function and achieve mental, physical, social, emotional or spiritual well-being.
Realise that trauma can affect individuals, groups and communities
Trauma-informed practice is an approach to health and care interventions which is grounded in the understanding that trauma exposure can impact an individual’s neurological, biological, psychological and social development.
Recognise the signs, symptoms and widespread impact of trauma
Trauma-informed practice aims to increase practitioners’ awareness of how trauma can negatively impact on individuals and communities, and their ability to feel safe or develop trusting relationships with health and care services and their staff.
It aims to improve the accessibility and quality of services by creating culturally sensitive, safe services that people trust and want to use. It seeks to prepare practitioners to work in collaboration and partnership with people and empower them to make choices about their health and wellbeing.
Trauma-informed practice acknowledges the need to see beyond an individual’s presenting behaviours and to ask, ‘What does this person need?’ rather than ‘What is wrong with this person?’.
Prevent re-traumatisation
It seeks to avoid re-traumatisation which is the re-experiencing of thoughts, feelings or sensations experienced at the time of a traumatic event or circumstance in a person’s past. Re-traumatisation is generally triggered by reminders of previous trauma which may or may not be potentially traumatic in themselves.
The purpose of trauma-informed practice is not to treat trauma-related difficulties, which is the role of trauma-specialist services and practitioners. Instead, it seeks to address the barriers that people affected by trauma can experience when accessing health and care services.
Key principles of trauma-informed practice
There are 6 principles of trauma-informed practice: safety, trust, choice, collaboration, empowerment and cultural consideration.
The physical, psychological and emotional safety of service users and staff is prioritised, by:
- people knowing they are safe or asking what they need to feel safe
- there being reasonable freedom from threat or harm
- attempting to prevent re-traumatisation
- putting policies, practices and safeguarding arrangements in place
Trustworthiness
Transparency exists in an organisation’s policies and procedures, with the objective of building trust among staff, service users and the wider community, by:
- the organisation and staff explaining what they are doing and why
- the organisation and staff doing what they say they will do
- expectations being made clear and the organisation and staff not overpromising
Service users are supported in shared decision-making, choice and goal setting to determine the plan of action they need to heal and move forward, by:
- ensuring service users and staff have a voice in the decision-making process of the organisation and its services
- listening to the needs and wishes of service users and staff
- explaining choices clearly and transparently
- acknowledging that people who have experienced or are experiencing trauma may feel a lack of safety or control over the course of their life which can cause difficulties in developing trusting relationships
Collaboration
The value of staff and service user experience is recognised in overcoming challenges and improving the system as a whole, by:
- using formal and informal peer support and mutual self-help
- the organisation asking service users and staff what they need and collaboratively considering how these needs can be met
- focussing on working alongside and actively involving service users in the delivery of services
Empowerment
Efforts are made to share power and give service users and staff a strong voice in decision-making, at both individual and organisational level, by:
- validating feelings and concerns of staff and service users
- listening to what a person wants and needs
- supporting people to make decisions and take action
- acknowledging that people who have experienced or are experiencing trauma may feel powerless to control what happens to them, isolated by their experiences and have feelings of low self-worth
Cultural consideration
Move past cultural stereotypes and biases based on, for example, gender, sexual orientation, age, religion, disability, geography, race or ethnicity by:
- offering access to gender responsive services
- leveraging the healing value of traditional cultural connections
- incorporating policies, protocols and processes that are responsive to the needs of individuals served
Other professional resources and tools
- Office of Health Improvement and Disparities’ Vulnerabilities: applying All Our Health
- e-learning for healthcare: All Our Health: Vulnerabilities and trauma-informed practice
- Trauma-informed practice toolkit: Scottish Government
- Trauma-Informed Wales
Is this page useful?
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. We’ll send you a link to a feedback form. It will take only 2 minutes to fill in. Don’t worry we won’t send you spam or share your email address with anyone.
What is a Point Spread in Sports Betting?…
Share this:.
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Entertainment
- Immigration
- Sports Betting
What is a Point Spread in Sports Betting? Definition, Examples, and FAQs

Along with moneylines and totals, point spread betting is one of the most popular wagering markets. A point spread moves the favorite and underdog closer with a “handicap” and allows bettors to predict who will cover the spread.
Spread betting is relatively straightforward, and understanding how it works is vital to your sports betting journey.
In this page, we’ll discuss how point spread betting works, explain how to read point spreads, and provide you with real-world examples of spreads in action.
What Is a Point Spread?
A point spread is a handicap that provides a buffer between a favorite and an underdog in a matchup. For example, if a team is heavily favored in an NFL game, you might see them draw a -10.5 spread. Conversely, the underdog in the matchup would draw a +10.5 spread.
These point spreads provide a benchmark for how many points a team is expected to win or lose the game by. In the example above, the favorite would have to win by 11 or more points to “cover” the spread of 10.5 points. The underdog must win the game outright or lose by less than 11 points to cover the spread.
Unlike a moneyline bet, point spread bets don’t always require your team to win the game. If you pick the underdog, you can win your bet if they lose by less than the spread.

How Do Point Spreads Work?
Point spread betting is relatively simple. There’s a favorite and an underdog, and the point spread evens the odds. Moneyline wagers don’t do this, so point spread betting has become attractive to sports bettors.
The institution of spread betting allows you to bet on teams you otherwise wouldn’t. Only some people are interested in taking a longshot moneyline, but you can get the team you’re interested in plus a certain number of points to even it out.
A spread has two sides. The favorite always draws the “-” spread, while the underdog draws the “+” spread. The spread usually contains a “.5” to ensure that there is an outcome and that the wager doesn’t result in a push.
For example, an NFL team is favored at -2.5 points against the spread. Their opponent is automatically an underdog at +2.5. For the favorite to cover the spread, they must win the game by three or more points. For the underdog to cover the spread, they must win the game outright or lose by two points or fewer.
A significant aspect of spread betting is that odds are typically within the -120 to +100 range. Moneyline odds are different and can fluctuate heavily since there’s no handicap in place to even things out.
How to Read Point Spreads
Point spreads come in many different formats and combinations. In this section, we’ll discuss how to read a point spread so you can start placing bets on it yourself.
The Meaning of -110
Most point spreads have -110 odds attached to both sides of the wager. This makes perfect sense, considering that the motivation for a point spread is to bring two opponents in a game as close to even as possible.
Sportsbook apps have to make money somehow, so they charge a roughly 9% commission on your wager at -110. Most bets will be at -110 odds, which means that for every $11 in bets you place, you will get $10 in winnings.
Spread odds can be -120 odds or +100 odds, too. In some sports, these odds can vary even further. MLB’s run line and NHL’s puck line markets can see “spreads” as heavy as -250 or +250 in either direction.
For example, let’s say that the Dallas Cowboys are favored with a -6.5 point spread against the Washington Commanders at +6.5. Both options are -110 odds. If you decide to place a $100 bet on either team, a winning wager would grant you $90.91 in profit.
This is what your options could look like at an online sportsbook:
- Cowboys: DAL -6.5 (-110)
- Commanders: WAS +6.5 (-110)
As alluded to, every game has a favorite. When it comes to betting on a point spread, you can easily tell which team is the favorite by observing whether they have a “-” before the number.
If a team is favored, it must win the game outright by a certain number of points. For example, if a team is favored by 3.5 points, denoted by “-3.5,” it must win the game by at least 3.5 points. Because scoring doesn’t incorporate a half-point, it must win by four or more. Say the Dallas Mavericks are -3.5 against the Chicago Bulls.
- Mavericks 115, Bulls 98: Mavericks cover the spread because they won by more than four points. Mavericks 115, Bulls 112: Mavericks don’t cover the spread because they didn’t win by more than four points.
For every favorite, there must be an underdog. The underdog is the team that is less likely to win a game. If you’re searching for a point spread wager to make on an underdog, look for the “+” sign before their number.
For example, the Kansas City Chiefs are +3.5 point underdogs against the Philadelphia Eagles. The Chiefs must win the game outright or lose by less than 3.5 points to cover the spread. Here’s a look at how the spread would work out based on the outcome.
- Chiefs 28, Eagles 21: Chiefs cover the spread.
- Eagles 27, Chiefs 24: Chiefs cover the spread.
- Eagles 33, Chiefs 27: Chiefs don’t cover the spread.
In the above example, the Chiefs can lose the game and still cover the spread. They are given free points against the spread to beat the Eagles.
Pick ‘Em
In rare cases, you might see that two teams’ spreads are listed as “PK.” The two sides are so evenly matched that there is no spread, leading to a wager known as a “pick ’em.” These bets are essentially moneyline wagers, considering you are backing a team +0 against the spread.
Your team must win outright to win a “pick ’em” spread bet. You can push a pick ’em bet in some sports that can tie, like soccer or regulation hockey. A pick ’em is usually listed as -110 odds for both sides.
Possible Outcomes of Point Spread Bets
Point spreads can have three possible outcomes (two if the spread contains “.5”). The favorite or underdog can cover the point spread, or the bet can result in a push. Let’s discuss what each outcome for your point spread bets entails.
Favorite Covers the Spread
One of the options for point spread betting is the favorite covering. The spread with the “-” in front of it wins, with the team that was most likely to win the game also winning against the spread.
When the favorite covers the point spread, your odds are usually -110. Suppose the Miami Dolphins were favored at -9.5 against the New England Patriots, with both sides of the point spread listed at -110 odds. For the Dolphins to win against the point spread, they must win the game by at least ten points.
- If we place a $10 bet on the Dolphins -9.5, we earn $9.09 in profit as long as Miami wins by ten or more points.
- If Miami wins by nine points or less or loses outright, we lose our $10 bet.
Underdog Covers the Spread
The underdog has a “+” attached to the point spread, like +2.5, +8.5, or +10.5. The underdog is the team that is less likely to win the game, so they get points to help them stay even with the favorite.
As with most bets on the point spread, standard odds are -110. Say the Chicago Bulls are underdogs against the Los Angeles Lakers, denoted by a +7.5 spread at -110 odds. For the Bulls to win against the point spread, they must win outright or lose by seven or fewer points.
- If we place a $10 bet on the Bulls +7.5, we earn $9.09 in profit if the Bulls win the game or lose by seven or fewer.
- We lose our bet on the point spread if Chicago loses by eight or more.
“Push” or Draw
Point spread bets can result in a push, meaning there doesn’t have to be a clear winner. Pushes can only occur when no half-point is added to a spread. For example, a +7.5 spread must have a decided winner. However, a +7 spread can “push” if the game ends with a victory by the favorite by precisely seven points.
Pushing spread bets is one of the most annoying events in sports betting. You’re extremely close to notching a win but can’t quite get there.
Suppose the Atlanta Falcons are -6 against the spread versus the New Orleans Saints. Say we place $10 on the Falcons at -110 odds.
- If the Falcons win by more than six points, the bet wins for $9.09 in profit.
- If the Falcons win by exactly six points, it’s a push and we get our $10 back.
- We lose the bet if the Falcons win by less than six points or lose outright.
What Is a Negative Spread?
As mentioned throughout this guide to point spreads in sports betting, you can have negative, positive, or pick’em point spread lines. A negative spread that carries a “-” in front is for the favorite in a matchup. Let’s examine samples of how a negative spread works with the final score.
A -7 spread means the favorite is expected to win by seven points. It’s one of the most common point spread lines, particularly when it comes to NFL and college football betting because of the combined value of a touchdown and an extra point.
Here’s an example. Suppose the San Francisco 49ers are -7 against the spread versus the Los Angeles Rams, listed at -110 odds. We decide to place a $20 bet on the Niners.
- If the 49ers win by more than seven points, we have a winning bet for a $18.18 profit.
- If the 49ers win by precisely seven points, we have a push and receive our $20 stake back.
- We have a losing bet if the 49ers win by fewer than seven points or lose outright.
A -3 spread means the favorite is expected to win by three points. For the favorite to “cover” the -3 spread, they must win by four more points or more.
Let’s look at an example. Suppose the Boston Celtics are -3 against the spread versus the Los Angeles Lakers, listed at -110 odds. We decide to place a $20 bet on the Celtics.
- If the Celtics win by more than three points, we win the bet for $18.18 in profit.
- If the Celtics win by precisely three points, we have a push and receive our $20 back.
- If the Celtics win by fewer than three points or lose outright, we lose the bet.
A -4 spread means the favorite is expected to win by four points. For the favorite to “cover” the -4 spread, they must by five more points or more.
Suppose the Minnesota Timberwolves are -4 against the spread versus the San Antonio Spurs, listed at -110 odds. We decide to place a $50 bet on the Timberwolves.
- T’Wolves 124, Spurs 108: T’Wolves cover the spread.
- T’Wolves 114, Spurs 110: The spread pushes.
- T’Wolves 112, Spurs 110: T’Wolves don’t cover the spread.
What Is a Positive Spread?
A positive spread, like +3.5, is the side of a spread attached to the underdog in a game. This buffer afforded to the underdog evens the odds between the two teams. In this section, we’ll explore some examples of different positive spreads. The typical betting odds for a positive spread are -110.
+3.5 Spread
A +3.5 spread indicates that an underdog is expected to lose a game by 3.5 points. A team can’t lose by half points, so it ensures a bet doesn’t push and that there is a clear winner against the spread.
Say that the Bulls are 3.5-point underdogs against the Knicks. Here is how the spread works based on prospective final scores.
- If the Bulls lose by three or fewer points or win, they cover the spread.
- If the Bulls lose by more than three points, they failed to cover the spread.
A +7 spread indicates that an underdog is expected to lose a game by seven points. Suppose that the Carolina Panthers are 7-point underdogs against the Buffalo Bills.
- The Panthers cover the spread if they lose by six or fewer points or win.
- The spread pushes if the Panthers lose the game by precisely seven points.
- The Panthers don’t cover the spread if they lose by more than seven points.
+1.5 Spread
While +1.5 spreads are reasonably uncommon in the NFL and NBA, they can be found for almost any NHL or MLB game as a puck line or run line, respectively. It indicates that the underdog is expected to lose by 1.5 points.
Suppose the San Diego Padres are +1.5 run line underdogs against the Los Angeles Dodgers.
- If the Padres win outright or lose by a run, they cover the run line.
- If the Padres lose by two or more runs, they don’t cover the run line.
+2.5 Spread
A +2.5 spread indicates that an underdog is expected to lose a game by 2.5 points. If the Patriots are 2.5-point underdogs against the Bears, here’s how it could look:
- Bears 24, Patriots 23: Patriots cover the +2.5 point spread.
- Bears 24, Patriots 21: Patriots don’t cover the +2.5 point spread.
A +5 spread indicates that an underdog is expected to lose a game by five points. Suppose that the Patriots are five-point underdogs against the Buffalo Bills.
- The Patriots cover the spread if they lose by four or fewer points or win.
- The spread pushes if the Patriots lose the game by precisely five points.
- The Patriots don’t cover the spread if they lose by more than five points.
Point Spread Betting FAQs
We have answered frequently asked questions about the point spread bet and how they work at your favorite online sportsbook .
Why do point spreads change?
Point spreads shift to react to the amount of money and action on each side of a sportsbook. An opening line changes according to various factors and settles at a closing line right before the event begins.
What do I do if one of my point spread bets is canceled?
In rare cases, you might have a point spread bet that gets canceled. You will receive your money back as if you never placed the bet. A spread bet can get canceled for various reasons, including a shortening of a game, weather impacts, etc.
What sport is the best for point spread betting?
The best betting market for point spread betting is the NFL. NFL sportsbooks draw the most handle on spreads.
Can I use a point spread bet in a parlay?
Yes, you can add point spread bets to a parlay. You can combine spreads from any betting market with moneylines, totals, and other wager types.
Can overtime affect the spread?
Overtime can affect the spread in some sports, particularly hockey. In most sports, overtime or extra innings has no effect because the game’s final score after regulation play is all that matters. However, an NHL game betting market allows you to wager on regulation time or the entire game, which includes overtime. This can ultimately affect the puck line or spread.
More in Betting
![For the second time in five days, the New York Knicks and Chicago Bulls are meeting at United Center. The Bulls knocked off the Knicks in the first game on Friday, 108-100, as 1.5-point underdogs. Javonte Green gave Chicago a huge boost off the bench with 25 points and 13 rebounds, while guard Ayo Dosunmu scored 24 points. What’s in store Tuesday night? Let’s take a closer look at the matchup and make a prediction. Knicks vs. Bulls odds Spread: Knicks -5 (-108), Bulls +5 (-112) Total: o212.5 (-114), u212.5 (-106) Moneyline: Knicks -200, Bulls +165 Odds via FanDuel Maximize […] For the second time in five days, the New York Knicks and Chicago Bulls are meeting at United Center. The Bulls knocked off the Knicks in the first game on Friday, 108-100, as 1.5-point underdogs. Javonte Green gave Chicago a huge boost off the bench with 25 points and 13 rebounds, while guard Ayo Dosunmu scored 24 points. What’s in store Tuesday night? Let’s take a closer look at the matchup and make a prediction. Knicks vs. Bulls odds Spread: Knicks -5 (-108), Bulls +5 (-112) Total: o212.5 (-114), u212.5 (-106) Moneyline: Knicks -200, Bulls +165 Odds via FanDuel Maximize […]](https://www.chicagotribune.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/CTC-L-BULLS-KNICKS-040524-09_187286930.jpg?w=506)
Betting | Knicks vs. Bulls odds, predictions: NBA picks, best bets for Tuesday, April 9

BetMGM bonus codes: $1.5K bet insurance or 20 percent deposit match in 18 states, $150 in NC

bet365 bonus code North Carolina CTNEWS: $1K bet insurance or $200, similar dual offers in nine other states
![The Chicago Cubs venture west for a nine-game road trip starting Monday night against the San Diego Padres. The Cubs captured two of three games at home this past weekend against the Los Angeles Dodgers, capped off by Sunday’s 8-1 blowout win. After dropping its first two contests of the season, Chicago has won six of its last seven games. Can they continue that success in the West? Let’s take a closer look at Monday night’s matchup at Petco Park. Cubs vs. Padres odds Moneyline: Cubs +116, Padres -134 Runs line: Cubs +1.5 (-188), Padres -1.5 (+155) Total: o7.5 (-108), […] The Chicago Cubs venture west for a nine-game road trip starting Monday night against the San Diego Padres. The Cubs captured two of three games at home this past weekend against the Los Angeles Dodgers, capped off by Sunday’s 8-1 blowout win. After dropping its first two contests of the season, Chicago has won six of its last seven games. Can they continue that success in the West? Let’s take a closer look at Monday night’s matchup at Petco Park. Cubs vs. Padres odds Moneyline: Cubs +116, Padres -134 Runs line: Cubs +1.5 (-188), Padres -1.5 (+155) Total: o7.5 (-108), […]](https://www.chicagotribune.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/CTC-L-cubs-rockies026_187189520.jpg?w=482)
Betting | Cubs vs. Padres odds, prediction: MLB picks, best bets for Monday, April 8
Trending nationally.
- 'Deeply disturbing': Harrowing video released of fatal Chicago police shooting of Dexter Reed
- Las Vegas law office shooting victims were gunman’s ex-daughter-in-law, new husband
- Infant’s death on LA Freeway potentially tied to killing and fatal crash 30 miles apart
- Eclipse traveler dies after falling out of moving trailer in upstate New York
- Disneyland threatens lifetime ban for disability cheats

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
autobiography, the biography of oneself narrated by oneself. Autobiographical works can take many forms, from the intimate writings made during life that were not necessarily intended for publication (including letters, diaries, journals, memoirs, and reminiscences) to a formal book-length autobiography. Formal autobiographies offer a special ...
Autobiography: A personal account that a person writes himself/herself. Memoir: An account of one's memory. Reflective Essay: One's thoughts about something. Confession: An account of one's wrong or right doings. Monologue: An address of one's thoughts to some audience or interlocuters. Biography: An account of the life of other persons ...
Examples and Observations of Autobiographical Compositions "An autobiography is an obituary in serial form with the last installment missing." (Quentin Crisp, The Naked Civil Servant, 1968) "Putting a life into words rescues it from confusion even when the words declare the omnipresence of confusion, since the art of declaring implies dominance."
A memoir is a type of autobiography that focuses on a particular period in the author's life rather than their whole life. The strict definition of autobiography is a first-person account of its author's entire life. A memoir does not document the memoirist's full life story but rather a selected era or a specific multi-era journey within ...
autobiography: [noun] the biography of a person narrated by himself or herself.
Definition & Examples. I. What is Autobiography? An autobiography is a self-written life story. It is different from a biography, which is the life story of a person written by someone else. Some people may have their life story written by another person because they don't believe they can write well, but they are still considered an author ...
An autobiography is a kind of literary nonfiction, which means it is a factual story that features real people and events. It also has features like plot, character, and setting that are common in ...
Autobiography Definition. An autobiography (awe-tow-bye-AWE-gruh-fee) is a self-written biography. The author writes about all or a portion of their own life to share their experience, frame it in a larger cultural or historical context, and/or inform and entertain the reader. Autobiographies have been a popular literary genre for centuries.
The word autobiography literally means SELF (auto), LIFE (bio), WRITING (graph). Or, in other words, an autobiography is the story of someone's life written or otherwise told by that person. When writing your autobiography, find out what makes your family or your experience unique and build a narrative around that.
AUTOBIOGRAPHY definition: 1. a book about a person's life, written by that person: 2. the area of literature relating to…. Learn more.
Autobiography cannot be bound to only one type of work. What an autobiography is has more to do with the contents than the format. For example, autobiographical works can include letters, diaries, journals, or books - and may not have even been meant for publication.
The term 'autobiography' (coined at the close of the 18th century) breaks down into its component parts—'auto' (self), 'bios' (life), 'graphein' (writing). The element of writing or text is inscribed in the term itself. Language, as well as the workings of memory, shapes the past. The neologism autobiography has been followed ...
Definition of Autobiography. An autobiography is a type of non-fiction writing that provides a firsthand account of a person's life. The author recounts their own experiences, thoughts, emotions, and insights, often focusing on how these events have shaped their life. Typically structured around a chronological narrative, an autobiography ...
The autobiography definition explains it is a written account of a person's life penned by the individual who has lived those experiences. It is a personal narrative that chronicles significant events, reflections, and emotions throughout various stages of the author's life.
Definition of Biography. A biography is the non- fiction, written history or account of a person's life. Biographies are intended to give an objective portrayal of a person, written in the third person. Biographers collect information from the subject (if he/she is available), acquaintances of the subject, or in researching other sources such ...
Additionally, the biography tells a story of how the person learned life lessons and navigated through the challenges. The person's biography should give a clear picture to the reader about the subject's personality, traits, and how they interact with the world. You must cover all the essential features of biography. Definition of Autobiography
An autobiography is an account of one's life written by the subject. E.g. In her compelling autobiography, the author delved into the intimate details of her life, recounting personal experiences, triumphs, and challenges in a candid narrative. Related terms: Narration, novel, coming-of-age novel, first person point of view.
Definition of Autobiography. Autobiography is one type of biography, which tells a life story of its author, meaning it is a written record of the author's life. Rather than being written by somebody else, an autobiography comes through the person's own pen, in his own words. Some autobiographies are written in the form of a fictional tale ...
An autobiography is an account of a person's life written by that person or subject itself. A biography is an account of someone's life written by someone else. A memoir is also an account of someone's life but of during a specific time in the journey of his/her life. This means it only covers a part of the author's life.
Defining Biography. A biography is a detailed account of a person's life, written by someone other than the subject. The term "biography" is derived from two Greek words: "bio," which means life, and "graphy," which signifies writing. Thus, a biography is the written history of someone's life, offering an in-depth look at their ...
Working definition of trauma-informed practice ... Move past cultural stereotypes and biases based on, for example, gender, sexual orientation, age, religion, disability, geography, race or ...
For example, if a team is favored by 3.5 points, denoted by "-3.5," it must win the game by at least 3.5 points. Because scoring doesn't incorporate a half-point, it must win by four or more.
SWOT Analysis is a strategic planning tool utilized to evaluate the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats involved in a project or in a business venture. Advertisements. It aids individuals and organizations in identifying both internal and external factors that could impact their objectives. By analyzing strengths and weaknesses ...
Examples. Microsoft Update Catalog. Microsoft Update Catalog is a centralized resource for managing software updates, drivers and hotfixes, i.e., quickly deployed bug fixes. It can be highly useful for IT administrators and system managers who need to deploy specific updates across their local and enterprise networks. Key features include the ...