What is The Null Hypothesis & When Do You Reject The Null Hypothesis
Julia Simkus
Editor at Simply Psychology
BA (Hons) Psychology, Princeton University
Julia Simkus is a graduate of Princeton University with a Bachelor of Arts in Psychology. She is currently studying for a Master's Degree in Counseling for Mental Health and Wellness in September 2023. Julia's research has been published in peer reviewed journals.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
A null hypothesis is a statistical concept suggesting no significant difference or relationship between measured variables. It’s the default assumption unless empirical evidence proves otherwise.
The null hypothesis states no relationship exists between the two variables being studied (i.e., one variable does not affect the other).
The null hypothesis is the statement that a researcher or an investigator wants to disprove.
Testing the null hypothesis can tell you whether your results are due to the effects of manipulating the dependent variable or due to random chance.

How to Write a Null Hypothesis
Null hypotheses (H0) start as research questions that the investigator rephrases as statements indicating no effect or relationship between the independent and dependent variables.
It is a default position that your research aims to challenge or confirm.
For example, if studying the impact of exercise on weight loss, your null hypothesis might be:
There is no significant difference in weight loss between individuals who exercise daily and those who do not.
Examples of Null Hypotheses
When do we reject the null hypothesis .
We reject the null hypothesis when the data provide strong enough evidence to conclude that it is likely incorrect. This often occurs when the p-value (probability of observing the data given the null hypothesis is true) is below a predetermined significance level.
If the collected data does not meet the expectation of the null hypothesis, a researcher can conclude that the data lacks sufficient evidence to back up the null hypothesis, and thus the null hypothesis is rejected.
Rejecting the null hypothesis means that a relationship does exist between a set of variables and the effect is statistically significant ( p > 0.05).
If the data collected from the random sample is not statistically significance , then the null hypothesis will be accepted, and the researchers can conclude that there is no relationship between the variables.
You need to perform a statistical test on your data in order to evaluate how consistent it is with the null hypothesis. A p-value is one statistical measurement used to validate a hypothesis against observed data.
Calculating the p-value is a critical part of null-hypothesis significance testing because it quantifies how strongly the sample data contradicts the null hypothesis.
The level of statistical significance is often expressed as a p -value between 0 and 1. The smaller the p-value, the stronger the evidence that you should reject the null hypothesis.
Usually, a researcher uses a confidence level of 95% or 99% (p-value of 0.05 or 0.01) as general guidelines to decide if you should reject or keep the null.
When your p-value is less than or equal to your significance level, you reject the null hypothesis.
In other words, smaller p-values are taken as stronger evidence against the null hypothesis. Conversely, when the p-value is greater than your significance level, you fail to reject the null hypothesis.
In this case, the sample data provides insufficient data to conclude that the effect exists in the population.
Because you can never know with complete certainty whether there is an effect in the population, your inferences about a population will sometimes be incorrect.
When you incorrectly reject the null hypothesis, it’s called a type I error. When you incorrectly fail to reject it, it’s called a type II error.
Why Do We Never Accept The Null Hypothesis?
The reason we do not say “accept the null” is because we are always assuming the null hypothesis is true and then conducting a study to see if there is evidence against it. And, even if we don’t find evidence against it, a null hypothesis is not accepted.
A lack of evidence only means that you haven’t proven that something exists. It does not prove that something doesn’t exist.
It is risky to conclude that the null hypothesis is true merely because we did not find evidence to reject it. It is always possible that researchers elsewhere have disproved the null hypothesis, so we cannot accept it as true, but instead, we state that we failed to reject the null.
One can either reject the null hypothesis, or fail to reject it, but can never accept it.
Why Do We Use The Null Hypothesis?
We can never prove with 100% certainty that a hypothesis is true; We can only collect evidence that supports a theory. However, testing a hypothesis can set the stage for rejecting or accepting this hypothesis within a certain confidence level.
The null hypothesis is useful because it can tell us whether the results of our study are due to random chance or the manipulation of a variable (with a certain level of confidence).
A null hypothesis is rejected if the measured data is significantly unlikely to have occurred and a null hypothesis is accepted if the observed outcome is consistent with the position held by the null hypothesis.
Rejecting the null hypothesis sets the stage for further experimentation to see if a relationship between two variables exists.
Hypothesis testing is a critical part of the scientific method as it helps decide whether the results of a research study support a particular theory about a given population. Hypothesis testing is a systematic way of backing up researchers’ predictions with statistical analysis.
It helps provide sufficient statistical evidence that either favors or rejects a certain hypothesis about the population parameter.
Purpose of a Null Hypothesis
- The primary purpose of the null hypothesis is to disprove an assumption.
- Whether rejected or accepted, the null hypothesis can help further progress a theory in many scientific cases.
- A null hypothesis can be used to ascertain how consistent the outcomes of multiple studies are.
Do you always need both a Null Hypothesis and an Alternative Hypothesis?
The null (H0) and alternative (Ha or H1) hypotheses are two competing claims that describe the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable. They are mutually exclusive, which means that only one of the two hypotheses can be true.
While the null hypothesis states that there is no effect in the population, an alternative hypothesis states that there is statistical significance between two variables.
The goal of hypothesis testing is to make inferences about a population based on a sample. In order to undertake hypothesis testing, you must express your research hypothesis as a null and alternative hypothesis. Both hypotheses are required to cover every possible outcome of the study.
What is the difference between a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis?
The alternative hypothesis is the complement to the null hypothesis. The null hypothesis states that there is no effect or no relationship between variables, while the alternative hypothesis claims that there is an effect or relationship in the population.
It is the claim that you expect or hope will be true. The null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis are always mutually exclusive, meaning that only one can be true at a time.
What are some problems with the null hypothesis?
One major problem with the null hypothesis is that researchers typically will assume that accepting the null is a failure of the experiment. However, accepting or rejecting any hypothesis is a positive result. Even if the null is not refuted, the researchers will still learn something new.
Why can a null hypothesis not be accepted?
We can either reject or fail to reject a null hypothesis, but never accept it. If your test fails to detect an effect, this is not proof that the effect doesn’t exist. It just means that your sample did not have enough evidence to conclude that it exists.
We can’t accept a null hypothesis because a lack of evidence does not prove something that does not exist. Instead, we fail to reject it.
Failing to reject the null indicates that the sample did not provide sufficient enough evidence to conclude that an effect exists.
If the p-value is greater than the significance level, then you fail to reject the null hypothesis.
Is a null hypothesis directional or non-directional?
A hypothesis test can either contain an alternative directional hypothesis or a non-directional alternative hypothesis. A directional hypothesis is one that contains the less than (“<“) or greater than (“>”) sign.
A nondirectional hypothesis contains the not equal sign (“≠”). However, a null hypothesis is neither directional nor non-directional.
A null hypothesis is a prediction that there will be no change, relationship, or difference between two variables.
The directional hypothesis or nondirectional hypothesis would then be considered alternative hypotheses to the null hypothesis.
Gill, J. (1999). The insignificance of null hypothesis significance testing. Political research quarterly , 52 (3), 647-674.
Krueger, J. (2001). Null hypothesis significance testing: On the survival of a flawed method. American Psychologist , 56 (1), 16.
Masson, M. E. (2011). A tutorial on a practical Bayesian alternative to null-hypothesis significance testing. Behavior research methods , 43 , 679-690.
Nickerson, R. S. (2000). Null hypothesis significance testing: a review of an old and continuing controversy. Psychological methods , 5 (2), 241.
Rozeboom, W. W. (1960). The fallacy of the null-hypothesis significance test. Psychological bulletin , 57 (5), 416.

Statistics Made Easy
When Do You Reject the Null Hypothesis? (3 Examples)
A hypothesis test is a formal statistical test we use to reject or fail to reject a statistical hypothesis.
We always use the following steps to perform a hypothesis test:
Step 1: State the null and alternative hypotheses.
The null hypothesis , denoted as H 0 , is the hypothesis that the sample data occurs purely from chance.
The alternative hypothesis , denoted as H A , is the hypothesis that the sample data is influenced by some non-random cause.
2. Determine a significance level to use.
Decide on a significance level. Common choices are .01, .05, and .1.
3. Calculate the test statistic and p-value.
Use the sample data to calculate a test statistic and a corresponding p-value .
4. Reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis.
If the p-value is less than the significance level, then you reject the null hypothesis.
If the p-value is not less than the significance level, then you fail to reject the null hypothesis.
You can use the following clever line to remember this rule:
“If the p is low, the null must go.”
In other words, if the p-value is low enough then we must reject the null hypothesis.
The following examples show when to reject (or fail to reject) the null hypothesis for the most common types of hypothesis tests.
Example 1: One Sample t-test
A one sample t-test is used to test whether or not the mean of a population is equal to some value.
For example, suppose we want to know whether or not the mean weight of a certain species of turtle is equal to 310 pounds.
We go out and collect a simple random sample of 40 turtles with the following information:
- Sample size n = 40
- Sample mean weight x = 300
- Sample standard deviation s = 18.5
We can use the following steps to perform a one sample t-test:
Step 1: State the Null and Alternative Hypotheses
We will perform the one sample t-test with the following hypotheses:
- H 0 : μ = 310 (population mean is equal to 310 pounds)
- H A : μ ≠ 310 (population mean is not equal to 310 pounds)
We will choose to use a significance level of 0.05 .
We can plug in the numbers for the sample size, sample mean, and sample standard deviation into this One Sample t-test Calculator to calculate the test statistic and p-value:
- t test statistic: -3.4187
- two-tailed p-value: 0.0015
Since the p-value (0.0015) is less than the significance level (0.05) we reject the null hypothesis .
We conclude that there is sufficient evidence to say that the mean weight of turtles in this population is not equal to 310 pounds.
Example 2: Two Sample t-test
A two sample t-test is used to test whether or not two population means are equal.
For example, suppose we want to know whether or not the mean weight between two different species of turtles is equal.
We go out and collect a simple random sample from each population with the following information:
- Sample size n 1 = 40
- Sample mean weight x 1 = 300
- Sample standard deviation s 1 = 18.5
- Sample size n 2 = 38
- Sample mean weight x 2 = 305
- Sample standard deviation s 2 = 16.7
We can use the following steps to perform a two sample t-test:
We will perform the two sample t-test with the following hypotheses:
- H 0 : μ 1 = μ 2 (the two population means are equal)
- H 1 : μ 1 ≠ μ 2 (the two population means are not equal)
We will choose to use a significance level of 0.10 .
We can plug in the numbers for the sample sizes, sample means, and sample standard deviations into this Two Sample t-test Calculator to calculate the test statistic and p-value:
- t test statistic: -1.2508
- two-tailed p-value: 0.2149
Since the p-value (0.2149) is not less than the significance level (0.10) we fail to reject the null hypothesis .
We do not have sufficient evidence to say that the mean weight of turtles between these two populations is different.
Example 3: Paired Samples t-test
A paired samples t-test is used to compare the means of two samples when each observation in one sample can be paired with an observation in the other sample.
For example, suppose we want to know whether or not a certain training program is able to increase the max vertical jump of college basketball players.
To test this, we may recruit a simple random sample of 20 college basketball players and measure each of their max vertical jumps. Then, we may have each player use the training program for one month and then measure their max vertical jump again at the end of the month:

We can use the following steps to perform a paired samples t-test:
We will perform the paired samples t-test with the following hypotheses:
- H 0 : μ before = μ after (the two population means are equal)
- H 1 : μ before ≠ μ after (the two population means are not equal)
We will choose to use a significance level of 0.01 .
We can plug in the raw data for each sample into this Paired Samples t-test Calculator to calculate the test statistic and p-value:
- t test statistic: -3.226
- two-tailed p-value: 0.0045
Since the p-value (0.0045) is less than the significance level (0.01) we reject the null hypothesis .
We have sufficient evidence to say that the mean vertical jump before and after participating in the training program is not equal.
Bonus: Decision Rule Calculator
You can use this decision rule calculator to automatically determine whether you should reject or fail to reject a null hypothesis for a hypothesis test based on the value of the test statistic.
Published by Zach
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
What 'Fail to Reject' Means in a Hypothesis Test
Casarsa Guru/Getty Images
- Inferential Statistics
- Statistics Tutorials
- Probability & Games
- Descriptive Statistics
- Applications Of Statistics
- Math Tutorials
- Pre Algebra & Algebra
- Exponential Decay
- Worksheets By Grade
- Ph.D., Mathematics, Purdue University
- M.S., Mathematics, Purdue University
- B.A., Mathematics, Physics, and Chemistry, Anderson University
In statistics , scientists can perform a number of different significance tests to determine if there is a relationship between two phenomena. One of the first they usually perform is a null hypothesis test. In short, the null hypothesis states that there is no meaningful relationship between two measured phenomena. After a performing a test, scientists can:
- Reject the null hypothesis (meaning there is a definite, consequential relationship between the two phenomena), or
- Fail to reject the null hypothesis (meaning the test has not identified a consequential relationship between the two phenomena)
Key Takeaways: The Null Hypothesis
• In a test of significance, the null hypothesis states that there is no meaningful relationship between two measured phenomena.
• By comparing the null hypothesis to an alternative hypothesis, scientists can either reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis.
• The null hypothesis cannot be positively proven. Rather, all that scientists can determine from a test of significance is that the evidence collected does or does not disprove the null hypothesis.
It is important to note that a failure to reject does not mean that the null hypothesis is true—only that the test did not prove it to be false. In some cases, depending on the experiment, a relationship may exist between two phenomena that is not identified by the experiment. In such cases, new experiments must be designed to rule out alternative hypotheses.
Null vs. Alternative Hypothesis
The null hypothesis is considered the default in a scientific experiment . In contrast, an alternative hypothesis is one that claims that there is a meaningful relationship between two phenomena. These two competing hypotheses can be compared by performing a statistical hypothesis test, which determines whether there is a statistically significant relationship between the data.
For example, scientists studying the water quality of a stream may wish to determine whether a certain chemical affects the acidity of the water. The null hypothesis—that the chemical has no effect on the water quality—can be tested by measuring the pH level of two water samples, one of which contains some of the chemical and one of which has been left untouched. If the sample with the added chemical is measurably more or less acidic—as determined through statistical analysis—it is a reason to reject the null hypothesis. If the sample's acidity is unchanged, it is a reason to not reject the null hypothesis.
When scientists design experiments, they attempt to find evidence for the alternative hypothesis. They do not try to prove that the null hypothesis is true. The null hypothesis is assumed to be an accurate statement until contrary evidence proves otherwise. As a result, a test of significance does not produce any evidence pertaining to the truth of the null hypothesis.
Failing to Reject vs. Accept
In an experiment, the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis should be carefully formulated such that one and only one of these statements is true. If the collected data supports the alternative hypothesis, then the null hypothesis can be rejected as false. However, if the data does not support the alternative hypothesis, this does not mean that the null hypothesis is true. All it means is that the null hypothesis has not been disproven—hence the term "failure to reject." A "failure to reject" a hypothesis should not be confused with acceptance.
In mathematics, negations are typically formed by simply placing the word “not” in the correct place. Using this convention, tests of significance allow scientists to either reject or not reject the null hypothesis. It sometimes takes a moment to realize that “not rejecting” is not the same as "accepting."
Null Hypothesis Example
In many ways, the philosophy behind a test of significance is similar to that of a trial. At the beginning of the proceedings, when the defendant enters a plea of “not guilty,” it is analogous to the statement of the null hypothesis. While the defendant may indeed be innocent, there is no plea of “innocent” to be formally made in court. The alternative hypothesis of “guilty” is what the prosecutor attempts to demonstrate.
The presumption at the outset of the trial is that the defendant is innocent. In theory, there is no need for the defendant to prove that he or she is innocent. The burden of proof is on the prosecuting attorney, who must marshal enough evidence to convince the jury that the defendant is guilty beyond a reasonable doubt. Likewise, in a test of significance, a scientist can only reject the null hypothesis by providing evidence for the alternative hypothesis.
If there is not enough evidence in a trial to demonstrate guilt, then the defendant is declared “not guilty.” This claim has nothing to do with innocence; it merely reflects the fact that the prosecution failed to provide enough evidence of guilt. In a similar way, a failure to reject the null hypothesis in a significance test does not mean that the null hypothesis is true. It only means that the scientist was unable to provide enough evidence for the alternative hypothesis.
For example, scientists testing the effects of a certain pesticide on crop yields might design an experiment in which some crops are left untreated and others are treated with varying amounts of pesticide. Any result in which the crop yields varied based on pesticide exposure—assuming all other variables are equal—would provide strong evidence for the alternative hypothesis (that the pesticide does affect crop yields). As a result, the scientists would have reason to reject the null hypothesis.
- Hypothesis Test for the Difference of Two Population Proportions
- Type I and Type II Errors in Statistics
- Null Hypothesis and Alternative Hypothesis
- Null Hypothesis Examples
- How to Conduct a Hypothesis Test
- An Example of a Hypothesis Test
- What Is a P-Value?
- The Difference Between Type I and Type II Errors in Hypothesis Testing
- What Is a Hypothesis? (Science)
- Null Hypothesis Definition and Examples
- Hypothesis Test Example
- The Runs Test for Random Sequences
- How to Do Hypothesis Tests With the Z.TEST Function in Excel
- Scientific Method Vocabulary Terms
- What Is the Difference Between Alpha and P-Values?
- Chi-Square Goodness of Fit Test
Hypothesis Testing (cont...)
Hypothesis testing, the null and alternative hypothesis.
In order to undertake hypothesis testing you need to express your research hypothesis as a null and alternative hypothesis. The null hypothesis and alternative hypothesis are statements regarding the differences or effects that occur in the population. You will use your sample to test which statement (i.e., the null hypothesis or alternative hypothesis) is most likely (although technically, you test the evidence against the null hypothesis). So, with respect to our teaching example, the null and alternative hypothesis will reflect statements about all statistics students on graduate management courses.
The null hypothesis is essentially the "devil's advocate" position. That is, it assumes that whatever you are trying to prove did not happen ( hint: it usually states that something equals zero). For example, the two different teaching methods did not result in different exam performances (i.e., zero difference). Another example might be that there is no relationship between anxiety and athletic performance (i.e., the slope is zero). The alternative hypothesis states the opposite and is usually the hypothesis you are trying to prove (e.g., the two different teaching methods did result in different exam performances). Initially, you can state these hypotheses in more general terms (e.g., using terms like "effect", "relationship", etc.), as shown below for the teaching methods example:
Depending on how you want to "summarize" the exam performances will determine how you might want to write a more specific null and alternative hypothesis. For example, you could compare the mean exam performance of each group (i.e., the "seminar" group and the "lectures-only" group). This is what we will demonstrate here, but other options include comparing the distributions , medians , amongst other things. As such, we can state:
Now that you have identified the null and alternative hypotheses, you need to find evidence and develop a strategy for declaring your "support" for either the null or alternative hypothesis. We can do this using some statistical theory and some arbitrary cut-off points. Both these issues are dealt with next.
Significance levels
The level of statistical significance is often expressed as the so-called p -value . Depending on the statistical test you have chosen, you will calculate a probability (i.e., the p -value) of observing your sample results (or more extreme) given that the null hypothesis is true . Another way of phrasing this is to consider the probability that a difference in a mean score (or other statistic) could have arisen based on the assumption that there really is no difference. Let us consider this statement with respect to our example where we are interested in the difference in mean exam performance between two different teaching methods. If there really is no difference between the two teaching methods in the population (i.e., given that the null hypothesis is true), how likely would it be to see a difference in the mean exam performance between the two teaching methods as large as (or larger than) that which has been observed in your sample?
So, you might get a p -value such as 0.03 (i.e., p = .03). This means that there is a 3% chance of finding a difference as large as (or larger than) the one in your study given that the null hypothesis is true. However, you want to know whether this is "statistically significant". Typically, if there was a 5% or less chance (5 times in 100 or less) that the difference in the mean exam performance between the two teaching methods (or whatever statistic you are using) is as different as observed given the null hypothesis is true, you would reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative hypothesis. Alternately, if the chance was greater than 5% (5 times in 100 or more), you would fail to reject the null hypothesis and would not accept the alternative hypothesis. As such, in this example where p = .03, we would reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative hypothesis. We reject it because at a significance level of 0.03 (i.e., less than a 5% chance), the result we obtained could happen too frequently for us to be confident that it was the two teaching methods that had an effect on exam performance.
Whilst there is relatively little justification why a significance level of 0.05 is used rather than 0.01 or 0.10, for example, it is widely used in academic research. However, if you want to be particularly confident in your results, you can set a more stringent level of 0.01 (a 1% chance or less; 1 in 100 chance or less).

One- and two-tailed predictions
When considering whether we reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative hypothesis, we need to consider the direction of the alternative hypothesis statement. For example, the alternative hypothesis that was stated earlier is:
The alternative hypothesis tells us two things. First, what predictions did we make about the effect of the independent variable(s) on the dependent variable(s)? Second, what was the predicted direction of this effect? Let's use our example to highlight these two points.
Sarah predicted that her teaching method (independent variable: teaching method), whereby she not only required her students to attend lectures, but also seminars, would have a positive effect (that is, increased) students' performance (dependent variable: exam marks). If an alternative hypothesis has a direction (and this is how you want to test it), the hypothesis is one-tailed. That is, it predicts direction of the effect. If the alternative hypothesis has stated that the effect was expected to be negative, this is also a one-tailed hypothesis.
Alternatively, a two-tailed prediction means that we do not make a choice over the direction that the effect of the experiment takes. Rather, it simply implies that the effect could be negative or positive. If Sarah had made a two-tailed prediction, the alternative hypothesis might have been:
In other words, we simply take out the word "positive", which implies the direction of our effect. In our example, making a two-tailed prediction may seem strange. After all, it would be logical to expect that "extra" tuition (going to seminar classes as well as lectures) would either have a positive effect on students' performance or no effect at all, but certainly not a negative effect. However, this is just our opinion (and hope) and certainly does not mean that we will get the effect we expect. Generally speaking, making a one-tail prediction (i.e., and testing for it this way) is frowned upon as it usually reflects the hope of a researcher rather than any certainty that it will happen. Notable exceptions to this rule are when there is only one possible way in which a change could occur. This can happen, for example, when biological activity/presence in measured. That is, a protein might be "dormant" and the stimulus you are using can only possibly "wake it up" (i.e., it cannot possibly reduce the activity of a "dormant" protein). In addition, for some statistical tests, one-tailed tests are not possible.
Rejecting or failing to reject the null hypothesis
Let's return finally to the question of whether we reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis.
If our statistical analysis shows that the significance level is below the cut-off value we have set (e.g., either 0.05 or 0.01), we reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative hypothesis. Alternatively, if the significance level is above the cut-off value, we fail to reject the null hypothesis and cannot accept the alternative hypothesis. You should note that you cannot accept the null hypothesis, but only find evidence against it.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 13: Inferential Statistics
Understanding Null Hypothesis Testing
Learning Objectives
- Explain the purpose of null hypothesis testing, including the role of sampling error.
- Describe the basic logic of null hypothesis testing.
- Describe the role of relationship strength and sample size in determining statistical significance and make reasonable judgments about statistical significance based on these two factors.
The Purpose of Null Hypothesis Testing
As we have seen, psychological research typically involves measuring one or more variables for a sample and computing descriptive statistics for that sample. In general, however, the researcher’s goal is not to draw conclusions about that sample but to draw conclusions about the population that the sample was selected from. Thus researchers must use sample statistics to draw conclusions about the corresponding values in the population. These corresponding values in the population are called parameters . Imagine, for example, that a researcher measures the number of depressive symptoms exhibited by each of 50 clinically depressed adults and computes the mean number of symptoms. The researcher probably wants to use this sample statistic (the mean number of symptoms for the sample) to draw conclusions about the corresponding population parameter (the mean number of symptoms for clinically depressed adults).
Unfortunately, sample statistics are not perfect estimates of their corresponding population parameters. This is because there is a certain amount of random variability in any statistic from sample to sample. The mean number of depressive symptoms might be 8.73 in one sample of clinically depressed adults, 6.45 in a second sample, and 9.44 in a third—even though these samples are selected randomly from the same population. Similarly, the correlation (Pearson’s r ) between two variables might be +.24 in one sample, −.04 in a second sample, and +.15 in a third—again, even though these samples are selected randomly from the same population. This random variability in a statistic from sample to sample is called sampling error . (Note that the term error here refers to random variability and does not imply that anyone has made a mistake. No one “commits a sampling error.”)
One implication of this is that when there is a statistical relationship in a sample, it is not always clear that there is a statistical relationship in the population. A small difference between two group means in a sample might indicate that there is a small difference between the two group means in the population. But it could also be that there is no difference between the means in the population and that the difference in the sample is just a matter of sampling error. Similarly, a Pearson’s r value of −.29 in a sample might mean that there is a negative relationship in the population. But it could also be that there is no relationship in the population and that the relationship in the sample is just a matter of sampling error.
In fact, any statistical relationship in a sample can be interpreted in two ways:
- There is a relationship in the population, and the relationship in the sample reflects this.
- There is no relationship in the population, and the relationship in the sample reflects only sampling error.
The purpose of null hypothesis testing is simply to help researchers decide between these two interpretations.
The Logic of Null Hypothesis Testing
Null hypothesis testing is a formal approach to deciding between two interpretations of a statistical relationship in a sample. One interpretation is called the null hypothesis (often symbolized H 0 and read as “H-naught”). This is the idea that there is no relationship in the population and that the relationship in the sample reflects only sampling error. Informally, the null hypothesis is that the sample relationship “occurred by chance.” The other interpretation is called the alternative hypothesis (often symbolized as H 1 ). This is the idea that there is a relationship in the population and that the relationship in the sample reflects this relationship in the population.
Again, every statistical relationship in a sample can be interpreted in either of these two ways: It might have occurred by chance, or it might reflect a relationship in the population. So researchers need a way to decide between them. Although there are many specific null hypothesis testing techniques, they are all based on the same general logic. The steps are as follows:
- Assume for the moment that the null hypothesis is true. There is no relationship between the variables in the population.
- Determine how likely the sample relationship would be if the null hypothesis were true.
- If the sample relationship would be extremely unlikely, then reject the null hypothesis in favour of the alternative hypothesis. If it would not be extremely unlikely, then retain the null hypothesis .
Following this logic, we can begin to understand why Mehl and his colleagues concluded that there is no difference in talkativeness between women and men in the population. In essence, they asked the following question: “If there were no difference in the population, how likely is it that we would find a small difference of d = 0.06 in our sample?” Their answer to this question was that this sample relationship would be fairly likely if the null hypothesis were true. Therefore, they retained the null hypothesis—concluding that there is no evidence of a sex difference in the population. We can also see why Kanner and his colleagues concluded that there is a correlation between hassles and symptoms in the population. They asked, “If the null hypothesis were true, how likely is it that we would find a strong correlation of +.60 in our sample?” Their answer to this question was that this sample relationship would be fairly unlikely if the null hypothesis were true. Therefore, they rejected the null hypothesis in favour of the alternative hypothesis—concluding that there is a positive correlation between these variables in the population.
A crucial step in null hypothesis testing is finding the likelihood of the sample result if the null hypothesis were true. This probability is called the p value . A low p value means that the sample result would be unlikely if the null hypothesis were true and leads to the rejection of the null hypothesis. A high p value means that the sample result would be likely if the null hypothesis were true and leads to the retention of the null hypothesis. But how low must the p value be before the sample result is considered unlikely enough to reject the null hypothesis? In null hypothesis testing, this criterion is called α (alpha) and is almost always set to .05. If there is less than a 5% chance of a result as extreme as the sample result if the null hypothesis were true, then the null hypothesis is rejected. When this happens, the result is said to be statistically significant . If there is greater than a 5% chance of a result as extreme as the sample result when the null hypothesis is true, then the null hypothesis is retained. This does not necessarily mean that the researcher accepts the null hypothesis as true—only that there is not currently enough evidence to conclude that it is true. Researchers often use the expression “fail to reject the null hypothesis” rather than “retain the null hypothesis,” but they never use the expression “accept the null hypothesis.”
The Misunderstood p Value
The p value is one of the most misunderstood quantities in psychological research (Cohen, 1994) [1] . Even professional researchers misinterpret it, and it is not unusual for such misinterpretations to appear in statistics textbooks!
The most common misinterpretation is that the p value is the probability that the null hypothesis is true—that the sample result occurred by chance. For example, a misguided researcher might say that because the p value is .02, there is only a 2% chance that the result is due to chance and a 98% chance that it reflects a real relationship in the population. But this is incorrect . The p value is really the probability of a result at least as extreme as the sample result if the null hypothesis were true. So a p value of .02 means that if the null hypothesis were true, a sample result this extreme would occur only 2% of the time.
You can avoid this misunderstanding by remembering that the p value is not the probability that any particular hypothesis is true or false. Instead, it is the probability of obtaining the sample result if the null hypothesis were true.
Role of Sample Size and Relationship Strength
Recall that null hypothesis testing involves answering the question, “If the null hypothesis were true, what is the probability of a sample result as extreme as this one?” In other words, “What is the p value?” It can be helpful to see that the answer to this question depends on just two considerations: the strength of the relationship and the size of the sample. Specifically, the stronger the sample relationship and the larger the sample, the less likely the result would be if the null hypothesis were true. That is, the lower the p value. This should make sense. Imagine a study in which a sample of 500 women is compared with a sample of 500 men in terms of some psychological characteristic, and Cohen’s d is a strong 0.50. If there were really no sex difference in the population, then a result this strong based on such a large sample should seem highly unlikely. Now imagine a similar study in which a sample of three women is compared with a sample of three men, and Cohen’s d is a weak 0.10. If there were no sex difference in the population, then a relationship this weak based on such a small sample should seem likely. And this is precisely why the null hypothesis would be rejected in the first example and retained in the second.
Of course, sometimes the result can be weak and the sample large, or the result can be strong and the sample small. In these cases, the two considerations trade off against each other so that a weak result can be statistically significant if the sample is large enough and a strong relationship can be statistically significant even if the sample is small. Table 13.1 shows roughly how relationship strength and sample size combine to determine whether a sample result is statistically significant. The columns of the table represent the three levels of relationship strength: weak, medium, and strong. The rows represent four sample sizes that can be considered small, medium, large, and extra large in the context of psychological research. Thus each cell in the table represents a combination of relationship strength and sample size. If a cell contains the word Yes , then this combination would be statistically significant for both Cohen’s d and Pearson’s r . If it contains the word No , then it would not be statistically significant for either. There is one cell where the decision for d and r would be different and another where it might be different depending on some additional considerations, which are discussed in Section 13.2 “Some Basic Null Hypothesis Tests”
Although Table 13.1 provides only a rough guideline, it shows very clearly that weak relationships based on medium or small samples are never statistically significant and that strong relationships based on medium or larger samples are always statistically significant. If you keep this lesson in mind, you will often know whether a result is statistically significant based on the descriptive statistics alone. It is extremely useful to be able to develop this kind of intuitive judgment. One reason is that it allows you to develop expectations about how your formal null hypothesis tests are going to come out, which in turn allows you to detect problems in your analyses. For example, if your sample relationship is strong and your sample is medium, then you would expect to reject the null hypothesis. If for some reason your formal null hypothesis test indicates otherwise, then you need to double-check your computations and interpretations. A second reason is that the ability to make this kind of intuitive judgment is an indication that you understand the basic logic of this approach in addition to being able to do the computations.
Statistical Significance Versus Practical Significance
Table 13.1 illustrates another extremely important point. A statistically significant result is not necessarily a strong one. Even a very weak result can be statistically significant if it is based on a large enough sample. This is closely related to Janet Shibley Hyde’s argument about sex differences (Hyde, 2007) [2] . The differences between women and men in mathematical problem solving and leadership ability are statistically significant. But the word significant can cause people to interpret these differences as strong and important—perhaps even important enough to influence the college courses they take or even who they vote for. As we have seen, however, these statistically significant differences are actually quite weak—perhaps even “trivial.”
This is why it is important to distinguish between the statistical significance of a result and the practical significance of that result. Practical significance refers to the importance or usefulness of the result in some real-world context. Many sex differences are statistically significant—and may even be interesting for purely scientific reasons—but they are not practically significant. In clinical practice, this same concept is often referred to as “clinical significance.” For example, a study on a new treatment for social phobia might show that it produces a statistically significant positive effect. Yet this effect still might not be strong enough to justify the time, effort, and other costs of putting it into practice—especially if easier and cheaper treatments that work almost as well already exist. Although statistically significant, this result would be said to lack practical or clinical significance.
Key Takeaways
- Null hypothesis testing is a formal approach to deciding whether a statistical relationship in a sample reflects a real relationship in the population or is just due to chance.
- The logic of null hypothesis testing involves assuming that the null hypothesis is true, finding how likely the sample result would be if this assumption were correct, and then making a decision. If the sample result would be unlikely if the null hypothesis were true, then it is rejected in favour of the alternative hypothesis. If it would not be unlikely, then the null hypothesis is retained.
- The probability of obtaining the sample result if the null hypothesis were true (the p value) is based on two considerations: relationship strength and sample size. Reasonable judgments about whether a sample relationship is statistically significant can often be made by quickly considering these two factors.
- Statistical significance is not the same as relationship strength or importance. Even weak relationships can be statistically significant if the sample size is large enough. It is important to consider relationship strength and the practical significance of a result in addition to its statistical significance.
- Discussion: Imagine a study showing that people who eat more broccoli tend to be happier. Explain for someone who knows nothing about statistics why the researchers would conduct a null hypothesis test.
- The correlation between two variables is r = −.78 based on a sample size of 137.
- The mean score on a psychological characteristic for women is 25 ( SD = 5) and the mean score for men is 24 ( SD = 5). There were 12 women and 10 men in this study.
- In a memory experiment, the mean number of items recalled by the 40 participants in Condition A was 0.50 standard deviations greater than the mean number recalled by the 40 participants in Condition B.
- In another memory experiment, the mean scores for participants in Condition A and Condition B came out exactly the same!
- A student finds a correlation of r = .04 between the number of units the students in his research methods class are taking and the students’ level of stress.
Long Descriptions
“Null Hypothesis” long description: A comic depicting a man and a woman talking in the foreground. In the background is a child working at a desk. The man says to the woman, “I can’t believe schools are still teaching kids about the null hypothesis. I remember reading a big study that conclusively disproved it years ago.” [Return to “Null Hypothesis”]
“Conditional Risk” long description: A comic depicting two hikers beside a tree during a thunderstorm. A bolt of lightning goes “crack” in the dark sky as thunder booms. One of the hikers says, “Whoa! We should get inside!” The other hiker says, “It’s okay! Lightning only kills about 45 Americans a year, so the chances of dying are only one in 7,000,000. Let’s go on!” The comic’s caption says, “The annual death rate among people who know that statistic is one in six.” [Return to “Conditional Risk”]
Media Attributions
- Null Hypothesis by XKCD CC BY-NC (Attribution NonCommercial)
- Conditional Risk by XKCD CC BY-NC (Attribution NonCommercial)
- Cohen, J. (1994). The world is round: p < .05. American Psychologist, 49 , 997–1003. ↵
- Hyde, J. S. (2007). New directions in the study of gender similarities and differences. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 16 , 259–263. ↵
Values in a population that correspond to variables measured in a study.
The random variability in a statistic from sample to sample.
A formal approach to deciding between two interpretations of a statistical relationship in a sample.
The idea that there is no relationship in the population and that the relationship in the sample reflects only sampling error.
The idea that there is a relationship in the population and that the relationship in the sample reflects this relationship in the population.
When the relationship found in the sample would be extremely unlikely, the idea that the relationship occurred “by chance” is rejected.
When the relationship found in the sample is likely to have occurred by chance, the null hypothesis is not rejected.
The probability that, if the null hypothesis were true, the result found in the sample would occur.
How low the p value must be before the sample result is considered unlikely in null hypothesis testing.
When there is less than a 5% chance of a result as extreme as the sample result occurring and the null hypothesis is rejected.
Research Methods in Psychology - 2nd Canadian Edition Copyright © 2015 by Paul C. Price, Rajiv Jhangiani, & I-Chant A. Chiang is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Hypothesis Testing | A Step-by-Step Guide with Easy Examples
Published on November 8, 2019 by Rebecca Bevans . Revised on June 22, 2023.
Hypothesis testing is a formal procedure for investigating our ideas about the world using statistics . It is most often used by scientists to test specific predictions, called hypotheses, that arise from theories.
There are 5 main steps in hypothesis testing:
- State your research hypothesis as a null hypothesis and alternate hypothesis (H o ) and (H a or H 1 ).
- Collect data in a way designed to test the hypothesis.
- Perform an appropriate statistical test .
- Decide whether to reject or fail to reject your null hypothesis.
- Present the findings in your results and discussion section.
Though the specific details might vary, the procedure you will use when testing a hypothesis will always follow some version of these steps.
Table of contents
Step 1: state your null and alternate hypothesis, step 2: collect data, step 3: perform a statistical test, step 4: decide whether to reject or fail to reject your null hypothesis, step 5: present your findings, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about hypothesis testing.
After developing your initial research hypothesis (the prediction that you want to investigate), it is important to restate it as a null (H o ) and alternate (H a ) hypothesis so that you can test it mathematically.
The alternate hypothesis is usually your initial hypothesis that predicts a relationship between variables. The null hypothesis is a prediction of no relationship between the variables you are interested in.
- H 0 : Men are, on average, not taller than women. H a : Men are, on average, taller than women.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

For a statistical test to be valid , it is important to perform sampling and collect data in a way that is designed to test your hypothesis. If your data are not representative, then you cannot make statistical inferences about the population you are interested in.
There are a variety of statistical tests available, but they are all based on the comparison of within-group variance (how spread out the data is within a category) versus between-group variance (how different the categories are from one another).
If the between-group variance is large enough that there is little or no overlap between groups, then your statistical test will reflect that by showing a low p -value . This means it is unlikely that the differences between these groups came about by chance.
Alternatively, if there is high within-group variance and low between-group variance, then your statistical test will reflect that with a high p -value. This means it is likely that any difference you measure between groups is due to chance.
Your choice of statistical test will be based on the type of variables and the level of measurement of your collected data .
- an estimate of the difference in average height between the two groups.
- a p -value showing how likely you are to see this difference if the null hypothesis of no difference is true.
Based on the outcome of your statistical test, you will have to decide whether to reject or fail to reject your null hypothesis.
In most cases you will use the p -value generated by your statistical test to guide your decision. And in most cases, your predetermined level of significance for rejecting the null hypothesis will be 0.05 – that is, when there is a less than 5% chance that you would see these results if the null hypothesis were true.
In some cases, researchers choose a more conservative level of significance, such as 0.01 (1%). This minimizes the risk of incorrectly rejecting the null hypothesis ( Type I error ).
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
The results of hypothesis testing will be presented in the results and discussion sections of your research paper , dissertation or thesis .
In the results section you should give a brief summary of the data and a summary of the results of your statistical test (for example, the estimated difference between group means and associated p -value). In the discussion , you can discuss whether your initial hypothesis was supported by your results or not.
In the formal language of hypothesis testing, we talk about rejecting or failing to reject the null hypothesis. You will probably be asked to do this in your statistics assignments.
However, when presenting research results in academic papers we rarely talk this way. Instead, we go back to our alternate hypothesis (in this case, the hypothesis that men are on average taller than women) and state whether the result of our test did or did not support the alternate hypothesis.
If your null hypothesis was rejected, this result is interpreted as “supported the alternate hypothesis.”
These are superficial differences; you can see that they mean the same thing.
You might notice that we don’t say that we reject or fail to reject the alternate hypothesis . This is because hypothesis testing is not designed to prove or disprove anything. It is only designed to test whether a pattern we measure could have arisen spuriously, or by chance.
If we reject the null hypothesis based on our research (i.e., we find that it is unlikely that the pattern arose by chance), then we can say our test lends support to our hypothesis . But if the pattern does not pass our decision rule, meaning that it could have arisen by chance, then we say the test is inconsistent with our hypothesis .
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Descriptive statistics
- Measures of central tendency
- Correlation coefficient
Methodology
- Cluster sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Types of interviews
- Cohort study
- Thematic analysis
Research bias
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Survivorship bias
- Availability heuristic
- Nonresponse bias
- Regression to the mean
Hypothesis testing is a formal procedure for investigating our ideas about the world using statistics. It is used by scientists to test specific predictions, called hypotheses , by calculating how likely it is that a pattern or relationship between variables could have arisen by chance.
A hypothesis states your predictions about what your research will find. It is a tentative answer to your research question that has not yet been tested. For some research projects, you might have to write several hypotheses that address different aspects of your research question.
A hypothesis is not just a guess — it should be based on existing theories and knowledge. It also has to be testable, which means you can support or refute it through scientific research methods (such as experiments, observations and statistical analysis of data).
Null and alternative hypotheses are used in statistical hypothesis testing . The null hypothesis of a test always predicts no effect or no relationship between variables, while the alternative hypothesis states your research prediction of an effect or relationship.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Bevans, R. (2023, June 22). Hypothesis Testing | A Step-by-Step Guide with Easy Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 3, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/statistics/hypothesis-testing/
Is this article helpful?
Rebecca Bevans
Other students also liked, choosing the right statistical test | types & examples, understanding p values | definition and examples, what is your plagiarism score.
13.1 Understanding Null Hypothesis Testing
Learning objectives.
- Explain the purpose of null hypothesis testing, including the role of sampling error.
- Describe the basic logic of null hypothesis testing.
- Describe the role of relationship strength and sample size in determining statistical significance and make reasonable judgments about statistical significance based on these two factors.
The Purpose of Null Hypothesis Testing
As we have seen, psychological research typically involves measuring one or more variables in a sample and computing descriptive statistics for that sample. In general, however, the researcher’s goal is not to draw conclusions about that sample but to draw conclusions about the population that the sample was selected from. Thus researchers must use sample statistics to draw conclusions about the corresponding values in the population. These corresponding values in the population are called parameters . Imagine, for example, that a researcher measures the number of depressive symptoms exhibited by each of 50 adults with clinical depression and computes the mean number of symptoms. The researcher probably wants to use this sample statistic (the mean number of symptoms for the sample) to draw conclusions about the corresponding population parameter (the mean number of symptoms for adults with clinical depression).
Unfortunately, sample statistics are not perfect estimates of their corresponding population parameters. This is because there is a certain amount of random variability in any statistic from sample to sample. The mean number of depressive symptoms might be 8.73 in one sample of adults with clinical depression, 6.45 in a second sample, and 9.44 in a third—even though these samples are selected randomly from the same population. Similarly, the correlation (Pearson’s r ) between two variables might be +.24 in one sample, −.04 in a second sample, and +.15 in a third—again, even though these samples are selected randomly from the same population. This random variability in a statistic from sample to sample is called sampling error . (Note that the term error here refers to random variability and does not imply that anyone has made a mistake. No one “commits a sampling error.”)
One implication of this is that when there is a statistical relationship in a sample, it is not always clear that there is a statistical relationship in the population. A small difference between two group means in a sample might indicate that there is a small difference between the two group means in the population. But it could also be that there is no difference between the means in the population and that the difference in the sample is just a matter of sampling error. Similarly, a Pearson’s r value of −.29 in a sample might mean that there is a negative relationship in the population. But it could also be that there is no relationship in the population and that the relationship in the sample is just a matter of sampling error.
In fact, any statistical relationship in a sample can be interpreted in two ways:
- There is a relationship in the population, and the relationship in the sample reflects this.
- There is no relationship in the population, and the relationship in the sample reflects only sampling error.
The purpose of null hypothesis testing is simply to help researchers decide between these two interpretations.
The Logic of Null Hypothesis Testing
Null hypothesis testing is a formal approach to deciding between two interpretations of a statistical relationship in a sample. One interpretation is called the null hypothesis (often symbolized H 0 and read as “H-naught”). This is the idea that there is no relationship in the population and that the relationship in the sample reflects only sampling error. Informally, the null hypothesis is that the sample relationship “occurred by chance.” The other interpretation is called the alternative hypothesis (often symbolized as H 1 ). This is the idea that there is a relationship in the population and that the relationship in the sample reflects this relationship in the population.
Again, every statistical relationship in a sample can be interpreted in either of these two ways: It might have occurred by chance, or it might reflect a relationship in the population. So researchers need a way to decide between them. Although there are many specific null hypothesis testing techniques, they are all based on the same general logic. The steps are as follows:
- Assume for the moment that the null hypothesis is true. There is no relationship between the variables in the population.
- Determine how likely the sample relationship would be if the null hypothesis were true.
- If the sample relationship would be extremely unlikely, then reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative hypothesis. If it would not be extremely unlikely, then retain the null hypothesis .
Following this logic, we can begin to understand why Mehl and his colleagues concluded that there is no difference in talkativeness between women and men in the population. In essence, they asked the following question: “If there were no difference in the population, how likely is it that we would find a small difference of d = 0.06 in our sample?” Their answer to this question was that this sample relationship would be fairly likely if the null hypothesis were true. Therefore, they retained the null hypothesis—concluding that there is no evidence of a sex difference in the population. We can also see why Kanner and his colleagues concluded that there is a correlation between hassles and symptoms in the population. They asked, “If the null hypothesis were true, how likely is it that we would find a strong correlation of +.60 in our sample?” Their answer to this question was that this sample relationship would be fairly unlikely if the null hypothesis were true. Therefore, they rejected the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative hypothesis—concluding that there is a positive correlation between these variables in the population.
A crucial step in null hypothesis testing is finding the likelihood of the sample result if the null hypothesis were true. This probability is called the p value . A low p value means that the sample result would be unlikely if the null hypothesis were true and leads to the rejection of the null hypothesis. A p value that is not low means that the sample result would be likely if the null hypothesis were true and leads to the retention of the null hypothesis. But how low must the p value be before the sample result is considered unlikely enough to reject the null hypothesis? In null hypothesis testing, this criterion is called α (alpha) and is almost always set to .05. If there is a 5% chance or less of a result as extreme as the sample result if the null hypothesis were true, then the null hypothesis is rejected. When this happens, the result is said to be statistically significant . If there is greater than a 5% chance of a result as extreme as the sample result when the null hypothesis is true, then the null hypothesis is retained. This does not necessarily mean that the researcher accepts the null hypothesis as true—only that there is not currently enough evidence to reject it. Researchers often use the expression “fail to reject the null hypothesis” rather than “retain the null hypothesis,” but they never use the expression “accept the null hypothesis.”
The Misunderstood p Value
The p value is one of the most misunderstood quantities in psychological research (Cohen, 1994) [1] . Even professional researchers misinterpret it, and it is not unusual for such misinterpretations to appear in statistics textbooks!
The most common misinterpretation is that the p value is the probability that the null hypothesis is true—that the sample result occurred by chance. For example, a misguided researcher might say that because the p value is .02, there is only a 2% chance that the result is due to chance and a 98% chance that it reflects a real relationship in the population. But this is incorrect . The p value is really the probability of a result at least as extreme as the sample result if the null hypothesis were true. So a p value of .02 means that if the null hypothesis were true, a sample result this extreme would occur only 2% of the time.
You can avoid this misunderstanding by remembering that the p value is not the probability that any particular hypothesis is true or false. Instead, it is the probability of obtaining the sample result if the null hypothesis were true.

“Null Hypothesis” retrieved from http://imgs.xkcd.com/comics/null_hypothesis.png (CC-BY-NC 2.5)
Role of Sample Size and Relationship Strength
Recall that null hypothesis testing involves answering the question, “If the null hypothesis were true, what is the probability of a sample result as extreme as this one?” In other words, “What is the p value?” It can be helpful to see that the answer to this question depends on just two considerations: the strength of the relationship and the size of the sample. Specifically, the stronger the sample relationship and the larger the sample, the less likely the result would be if the null hypothesis were true. That is, the lower the p value. This should make sense. Imagine a study in which a sample of 500 women is compared with a sample of 500 men in terms of some psychological characteristic, and Cohen’s d is a strong 0.50. If there were really no sex difference in the population, then a result this strong based on such a large sample should seem highly unlikely. Now imagine a similar study in which a sample of three women is compared with a sample of three men, and Cohen’s d is a weak 0.10. If there were no sex difference in the population, then a relationship this weak based on such a small sample should seem likely. And this is precisely why the null hypothesis would be rejected in the first example and retained in the second.
Of course, sometimes the result can be weak and the sample large, or the result can be strong and the sample small. In these cases, the two considerations trade off against each other so that a weak result can be statistically significant if the sample is large enough and a strong relationship can be statistically significant even if the sample is small. Table 13.1 shows roughly how relationship strength and sample size combine to determine whether a sample result is statistically significant. The columns of the table represent the three levels of relationship strength: weak, medium, and strong. The rows represent four sample sizes that can be considered small, medium, large, and extra large in the context of psychological research. Thus each cell in the table represents a combination of relationship strength and sample size. If a cell contains the word Yes , then this combination would be statistically significant for both Cohen’s d and Pearson’s r . If it contains the word No , then it would not be statistically significant for either. There is one cell where the decision for d and r would be different and another where it might be different depending on some additional considerations, which are discussed in Section 13.2 “Some Basic Null Hypothesis Tests”
Although Table 13.1 provides only a rough guideline, it shows very clearly that weak relationships based on medium or small samples are never statistically significant and that strong relationships based on medium or larger samples are always statistically significant. If you keep this lesson in mind, you will often know whether a result is statistically significant based on the descriptive statistics alone. It is extremely useful to be able to develop this kind of intuitive judgment. One reason is that it allows you to develop expectations about how your formal null hypothesis tests are going to come out, which in turn allows you to detect problems in your analyses. For example, if your sample relationship is strong and your sample is medium, then you would expect to reject the null hypothesis. If for some reason your formal null hypothesis test indicates otherwise, then you need to double-check your computations and interpretations. A second reason is that the ability to make this kind of intuitive judgment is an indication that you understand the basic logic of this approach in addition to being able to do the computations.
Statistical Significance Versus Practical Significance
Table 13.1 illustrates another extremely important point. A statistically significant result is not necessarily a strong one. Even a very weak result can be statistically significant if it is based on a large enough sample. This is closely related to Janet Shibley Hyde’s argument about sex differences (Hyde, 2007) [2] . The differences between women and men in mathematical problem solving and leadership ability are statistically significant. But the word significant can cause people to interpret these differences as strong and important—perhaps even important enough to influence the college courses they take or even who they vote for. As we have seen, however, these statistically significant differences are actually quite weak—perhaps even “trivial.”
This is why it is important to distinguish between the statistical significance of a result and the practical significance of that result. Practical significance refers to the importance or usefulness of the result in some real-world context. Many sex differences are statistically significant—and may even be interesting for purely scientific reasons—but they are not practically significant. In clinical practice, this same concept is often referred to as “clinical significance.” For example, a study on a new treatment for social phobia might show that it produces a statistically significant positive effect. Yet this effect still might not be strong enough to justify the time, effort, and other costs of putting it into practice—especially if easier and cheaper treatments that work almost as well already exist. Although statistically significant, this result would be said to lack practical or clinical significance.

“Conditional Risk” retrieved from http://imgs.xkcd.com/comics/conditional_risk.png (CC-BY-NC 2.5)
Key Takeaways
- Null hypothesis testing is a formal approach to deciding whether a statistical relationship in a sample reflects a real relationship in the population or is just due to chance.
- The logic of null hypothesis testing involves assuming that the null hypothesis is true, finding how likely the sample result would be if this assumption were correct, and then making a decision. If the sample result would be unlikely if the null hypothesis were true, then it is rejected in favor of the alternative hypothesis. If it would not be unlikely, then the null hypothesis is retained.
- The probability of obtaining the sample result if the null hypothesis were true (the p value) is based on two considerations: relationship strength and sample size. Reasonable judgments about whether a sample relationship is statistically significant can often be made by quickly considering these two factors.
- Statistical significance is not the same as relationship strength or importance. Even weak relationships can be statistically significant if the sample size is large enough. It is important to consider relationship strength and the practical significance of a result in addition to its statistical significance.
- Discussion: Imagine a study showing that people who eat more broccoli tend to be happier. Explain for someone who knows nothing about statistics why the researchers would conduct a null hypothesis test.
- The correlation between two variables is r = −.78 based on a sample size of 137.
- The mean score on a psychological characteristic for women is 25 ( SD = 5) and the mean score for men is 24 ( SD = 5). There were 12 women and 10 men in this study.
- In a memory experiment, the mean number of items recalled by the 40 participants in Condition A was 0.50 standard deviations greater than the mean number recalled by the 40 participants in Condition B.
- In another memory experiment, the mean scores for participants in Condition A and Condition B came out exactly the same!
- A student finds a correlation of r = .04 between the number of units the students in his research methods class are taking and the students’ level of stress.
- Cohen, J. (1994). The world is round: p < .05. American Psychologist, 49 , 997–1003. ↵
- Hyde, J. S. (2007). New directions in the study of gender similarities and differences. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 16 , 259–263. ↵

Share This Book
- Increase Font Size
- Null hypothesis
by Marco Taboga , PhD
In a test of hypothesis , a sample of data is used to decide whether to reject or not to reject a hypothesis about the probability distribution from which the sample was extracted.
The hypothesis is called the null hypothesis, or simply "the null".
Table of contents
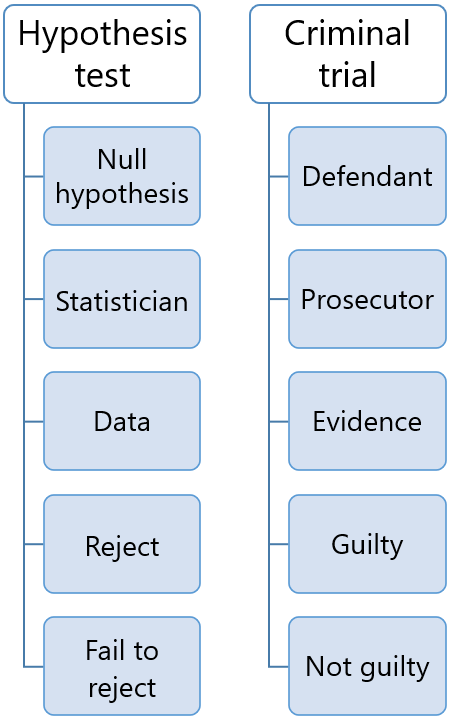
The null is like the defendant in a criminal trial
How is the null hypothesis tested, example 1 - proportion of defective items, measurement, test statistic, critical region, interpretation, example 2 - reliability of a production plant, rejection and failure to reject, not rejecting and accepting are not the same thing, failure to reject can be due to lack of power, rejections are easier to interpret, but be careful, takeaways - how to (and not to) formulate a null hypothesis, more examples, more details, best practices in science, keep reading the glossary.
Formulating null hypotheses and subjecting them to statistical testing is one of the workhorses of the scientific method.
Scientists in all fields make conjectures about the phenomena they study, translate them into null hypotheses and gather data to test them.
This process resembles a trial:
the defendant (the null hypothesis) is accused of being guilty (wrong);
evidence (data) is gathered in order to prove the defendant guilty (reject the null);
if there is evidence beyond any reasonable doubt, the defendant is found guilty (the null is rejected);
otherwise, the defendant is found not guilty (the null is not rejected).
Keep this analogy in mind because it helps to better understand statistical tests, their limitations, use and misuse, and frequent misinterpretation.
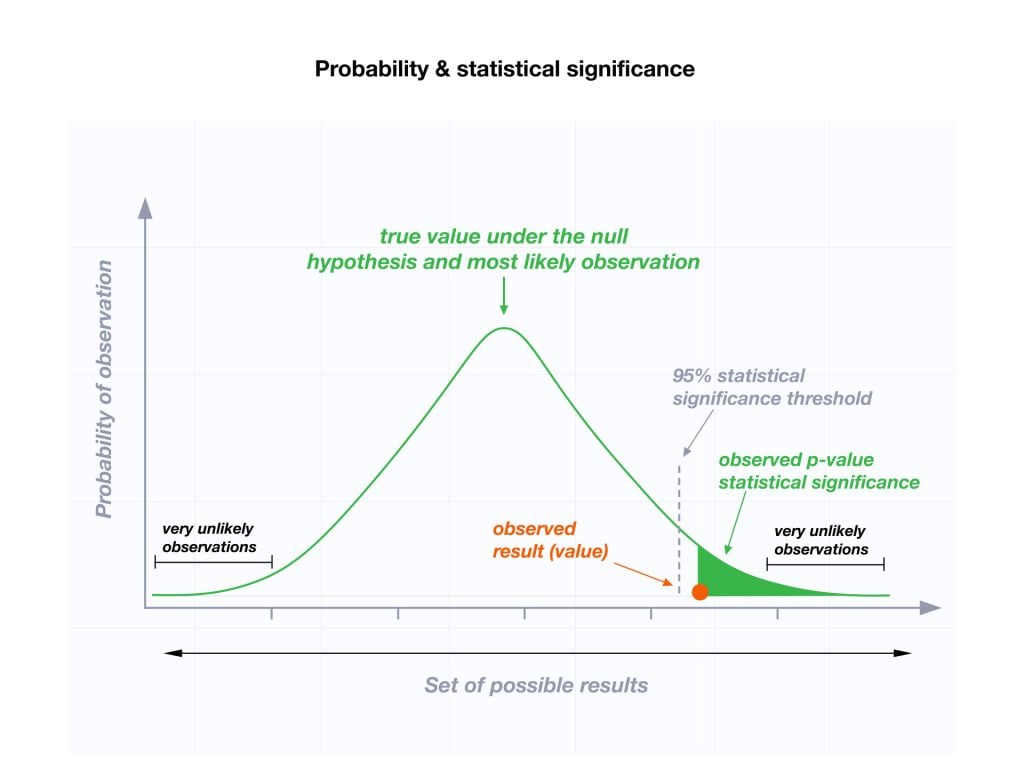
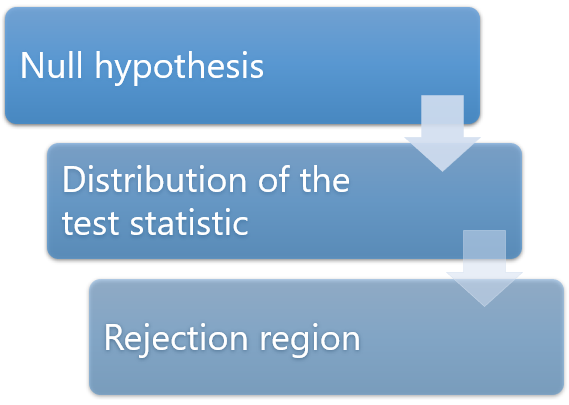
Before collecting the data:
we decide how to summarize the relevant characteristics of the sample data in a single number, the so-called test statistic ;
we derive the probability distribution of the test statistic under the hypothesis that the null is true (the data is regarded as random; therefore, the test statistic is a random variable);
we decide what probability of incorrectly rejecting the null we are willing to tolerate (the level of significance , or size of the test ); the level of significance is typically a small number, such as 5% or 1%.
we choose one or more intervals of values (collectively called rejection region) such that the probability that the test statistic falls within these intervals is equal to the desired level of significance; the rejection region is often a tail of the distribution of the test statistic (one-tailed test) or the union of the left and right tails (two-tailed test).

Then, the data is collected and used to compute the value of the test statistic.
A decision is taken as follows:
if the test statistic falls within the rejection region, then the null hypothesis is rejected;
otherwise, it is not rejected.
We now make two examples of practical problems that lead to formulate and test a null hypothesis.
A new method is proposed to produce light bulbs.
The proponents claim that it produces less defective bulbs than the method currently in use.
To check the claim, we can set up a statistical test as follows.
We keep the light bulbs on for 10 consecutive days, and then we record whether they are still working at the end of the test period.
The probability that a light bulb produced with the new method is still working at the end of the test period is the same as that of a light bulb produced with the old method.
100 light bulbs are tested:
50 of them are produced with the new method (group A)
the remaining 50 are produced with the old method (group B).
The final data comprises 100 observations of:
an indicator variable which is equal to 1 if the light bulb is still working at the end of the test period and 0 otherwise;
a categorical variable that records the group (A or B) to which each light bulb belongs.
We use the data to compute the proportions of working light bulbs in groups A and B.
The proportions are estimates of the probabilities of not being defective, which are equal for the two groups under the null hypothesis.
We then compute a z-statistic (see here for details) by:
taking the difference between the proportion in group A and the proportion in group B;
standardizing the difference:
we subtract the expected value (which is zero under the null hypothesis);
we divide by the standard deviation (it can be derived analytically).
The distribution of the z-statistic can be approximated by a standard normal distribution .
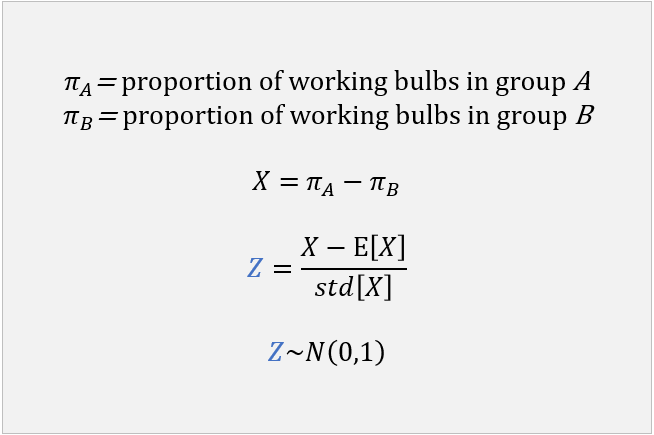
We decide that the level of confidence must be 5%. In other words, we are going to tolerate a 5% probability of incorrectly rejecting the null hypothesis.
The critical region is the right 5%-tail of the normal distribution, that is, the set of all values greater than 1.645 (see the glossary entry on critical values if you are wondering how this value was obtained).
If the test statistic is greater than 1.645, then the null hypothesis is rejected; otherwise, it is not rejected.
A rejection is interpreted as significant evidence that the new production method produces less defective items; failure to reject is interpreted as insufficient evidence that the new method is better.
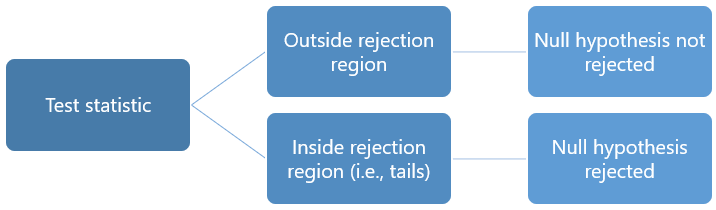
A production plant incurs high costs when production needs to be halted because some machinery fails.
The plant manager has decided that he is not willing to tolerate more than one halt per year on average.
If the expected number of halts per year is greater than 1, he will make new investments in order to improve the reliability of the plant.
A statistical test is set up as follows.
The reliability of the plant is measured by the number of halts.
The number of halts in a year is assumed to have a Poisson distribution with expected value equal to 1 (using the Poisson distribution is common in reliability testing).
The manager cannot wait more than one year before taking a decision.
There will be a single datum at his disposal: the number of halts observed during one year.
The number of halts is used as a test statistic. By assumption, it has a Poisson distribution under the null hypothesis.
The manager decides that the probability of incorrectly rejecting the null can be at most 10%.
A Poisson random variable with expected value equal to 1 takes values:
larger than 1 with probability 26.42%;
larger than 2 with probability 8.03%.
Therefore, it is decided that the critical region will be the set of all values greater than or equal to 3.
If the test statistic is strictly greater than or equal to 3, then the null is rejected; otherwise, it is not rejected.
A rejection is interpreted as significant evidence that the production plant is not reliable enough (the average number of halts per year is significantly larger than tolerated).
Failure to reject is interpreted as insufficient evidence that the plant is unreliable.
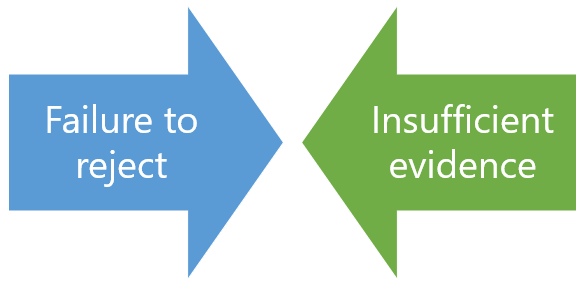
This section discusses the main problems that arise in the interpretation of the outcome of a statistical test (reject / not reject).
When the test statistic does not fall within the critical region, then we do not reject the null hypothesis.
Does this mean that we accept the null? Not really.
In general, failure to reject does not constitute, per se, strong evidence that the null hypothesis is true .
Remember the analogy between hypothesis testing and a criminal trial. In a trial, when the defendant is declared not guilty, this does not mean that the defendant is innocent. It only means that there was not enough evidence (not beyond any reasonable doubt) against the defendant.
In turn, lack of evidence can be due:
either to the fact that the defendant is innocent ;
or to the fact that the prosecution has not been able to provide enough evidence against the defendant, even if the latter is guilty .
This is the very reason why courts do not declare defendants innocent, but they use the locution "not guilty".
In a similar fashion, statisticians do not say that the null hypothesis has been accepted, but they say that it has not been rejected.

To better understand why failure to reject does not in general constitute strong evidence that the null hypothesis is true, we need to use the concept of statistical power .
The power of a test is the probability (calculated ex-ante, i.e., before observing the data) that the null will be rejected when another hypothesis (called the alternative hypothesis ) is true.
Let's consider the first of the two examples above (the production of light bulbs).
In that example, the null hypothesis is: the probability that a light bulb is defective does not decrease after introducing a new production method.
Let's make the alternative hypothesis that the probability of being defective is 1% smaller after changing the production process (assume that a 1% decrease is considered a meaningful improvement by engineers).
How much is the ex-ante probability of rejecting the null if the alternative hypothesis is true?
If this probability (the power of the test) is small, then it is very likely that we will not reject the null even if it is wrong.
If we use the analogy with criminal trials, low power means that most likely the prosecution will not be able to provide sufficient evidence, even if the defendant is guilty.
Thus, in the case of lack of power, failure to reject is almost meaningless (it was anyway highly likely).
This is why, before performing a test, it is good statistical practice to compute its power against a relevant alternative .
If the power is found to be too small, there are usually remedies. In particular, statistical power can usually be increased by increasing the sample size (see, e.g., the lecture on hypothesis tests about the mean ).
As we have explained above, interpreting a failure to reject the null hypothesis is not always straightforward. Instead, interpreting a rejection is somewhat easier.
When we reject the null, we know that the data has provided a lot of evidence against the null. In other words, it is unlikely (how unlikely depends on the size of the test) that the null is true given the data we have observed.
There is an important caveat though. The null hypothesis is often made up of several assumptions, including:
the main assumption (the one we are testing);
other assumptions (e.g., technical assumptions) that we need to make in order to set up the hypothesis test.
For instance, in Example 2 above (reliability of a production plant), the main assumption is that the expected number of production halts per year is equal to 1. But there is also a technical assumption: the number of production halts has a Poisson distribution.
It must be kept in mind that a rejection is always a joint rejection of the main assumption and all the other assumptions .
Therefore, we should always ask ourselves whether the null has been rejected because the main assumption is wrong or because the other assumptions are violated.
In the case of Example 2 above, is a rejection of the null due to the fact that the expected number of halts is greater than 1 or is it due to the fact that the distribution of the number of halts is very different from a Poisson distribution?
When we suspect that a rejection is due to the inappropriateness of some technical assumption (e.g., assuming a Poisson distribution in the example), we say that the rejection could be due to misspecification of the model .
The right thing to do when these kind of suspicions arise is to conduct so-called robustness checks , that is, to change the technical assumptions and carry out the test again.
In our example, we could re-run the test by assuming a different probability distribution for the number of halts (e.g., a negative binomial or a compound Poisson - do not worry if you have never heard about these distributions).
If we keep obtaining a rejection of the null even after changing the technical assumptions several times, the we say that our rejection is robust to several different specifications of the model .

What are the main practical implications of everything we have said thus far? How does the theory above help us to set up and test a null hypothesis?
What we said can be summarized in the following guiding principles:
A test of hypothesis is like a criminal trial and you are the prosecutor . You want to find evidence that the defendant (the null hypothesis) is guilty. Your job is not to prove that the defendant is innocent. If you find yourself hoping that the defendant is found not guilty (i.e., the null is not rejected) then something is wrong with the way you set up the test. Remember: you are the prosecutor.
Compute the power of your test against one or more relevant alternative hypotheses. Do not run a test if you know ex-ante that it is unlikely to reject the null when the alternative hypothesis is true.
Beware of technical assumptions that you add to the main assumption you want to test. Make robustness checks in order to verify that the outcome of the test is not biased by model misspecification.
More examples of null hypotheses and how to test them can be found in the following lectures.
The lecture on Hypothesis testing provides a more detailed mathematical treatment of null hypotheses and how they are tested.
This lecture on the null hypothesis was featured in Stanford University's Best practices in science .

Previous entry: Normal equations
Next entry: Parameter
How to cite
Please cite as:
Taboga, Marco (2021). "Null hypothesis", Lectures on probability theory and mathematical statistics. Kindle Direct Publishing. Online appendix. https://www.statlect.com/glossary/null-hypothesis.
Most of the learning materials found on this website are now available in a traditional textbook format.
- Permutations
- Characteristic function
- Almost sure convergence
- Likelihood ratio test
- Uniform distribution
- Bernoulli distribution
- Multivariate normal distribution
- Chi-square distribution
- Maximum likelihood
- Mathematical tools
- Fundamentals of probability
- Probability distributions
- Asymptotic theory
- Fundamentals of statistics
- About Statlect
- Cookies, privacy and terms of use
- Precision matrix
- Distribution function
- Mean squared error
- IID sequence
- To enhance your privacy,
- we removed the social buttons,
- but don't forget to share .
9.1 Null and Alternative Hypotheses
The actual test begins by considering two hypotheses . They are called the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis . These hypotheses contain opposing viewpoints.
H 0 , the — null hypothesis: a statement of no difference between sample means or proportions or no difference between a sample mean or proportion and a population mean or proportion. In other words, the difference equals 0.
H a —, the alternative hypothesis: a claim about the population that is contradictory to H 0 and what we conclude when we reject H 0 .
Since the null and alternative hypotheses are contradictory, you must examine evidence to decide if you have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis or not. The evidence is in the form of sample data.
After you have determined which hypothesis the sample supports, you make a decision. There are two options for a decision. They are reject H 0 if the sample information favors the alternative hypothesis or do not reject H 0 or decline to reject H 0 if the sample information is insufficient to reject the null hypothesis.
Mathematical Symbols Used in H 0 and H a :
H 0 always has a symbol with an equal in it. H a never has a symbol with an equal in it. The choice of symbol depends on the wording of the hypothesis test. However, be aware that many researchers use = in the null hypothesis, even with > or < as the symbol in the alternative hypothesis. This practice is acceptable because we only make the decision to reject or not reject the null hypothesis.
Example 9.1
H 0 : No more than 30 percent of the registered voters in Santa Clara County voted in the primary election. p ≤ 30 H a : More than 30 percent of the registered voters in Santa Clara County voted in the primary election. p > 30
A medical trial is conducted to test whether or not a new medicine reduces cholesterol by 25 percent. State the null and alternative hypotheses.
Example 9.2
We want to test whether the mean GPA of students in American colleges is different from 2.0 (out of 4.0). The null and alternative hypotheses are the following: H 0 : μ = 2.0 H a : μ ≠ 2.0
We want to test whether the mean height of eighth graders is 66 inches. State the null and alternative hypotheses. Fill in the correct symbol (=, ≠, ≥, <, ≤, >) for the null and alternative hypotheses.
- H 0 : μ __ 66
- H a : μ __ 66
Example 9.3
We want to test if college students take fewer than five years to graduate from college, on the average. The null and alternative hypotheses are the following: H 0 : μ ≥ 5 H a : μ < 5
We want to test if it takes fewer than 45 minutes to teach a lesson plan. State the null and alternative hypotheses. Fill in the correct symbol ( =, ≠, ≥, <, ≤, >) for the null and alternative hypotheses.
- H 0 : μ __ 45
- H a : μ __ 45

Example 9.4
An article on school standards stated that about half of all students in France, Germany, and Israel take advanced placement exams and a third of the students pass. The same article stated that 6.6 percent of U.S. students take advanced placement exams and 4.4 percent pass. Test if the percentage of U.S. students who take advanced placement exams is more than 6.6 percent. State the null and alternative hypotheses. H 0 : p ≤ 0.066 H a : p > 0.066
On a state driver’s test, about 40 percent pass the test on the first try. We want to test if more than 40 percent pass on the first try. Fill in the correct symbol (=, ≠, ≥, <, ≤, >) for the null and alternative hypotheses.
- H 0 : p __ 0.40
- H a : p __ 0.40
Collaborative Exercise
Bring to class a newspaper, some news magazines, and some internet articles. In groups, find articles from which your group can write null and alternative hypotheses. Discuss your hypotheses with the rest of the class.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute Texas Education Agency (TEA). The original material is available at: https://www.texasgateway.org/book/tea-statistics . Changes were made to the original material, including updates to art, structure, and other content updates.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/statistics/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Barbara Illowsky, Susan Dean
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Statistics
- Publication date: Mar 27, 2020
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/statistics/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/statistics/pages/9-1-null-and-alternative-hypotheses
© Jan 23, 2024 Texas Education Agency (TEA). The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
Chapter 2: Summarizing and Visualizing Data
Chapter 3: measure of central tendency, chapter 4: measures of variation, chapter 5: measures of relative standing, chapter 6: probability distributions, chapter 7: estimates, chapter 8: distributions, chapter 9: hypothesis testing, chapter 10: analysis of variance, chapter 11: correlation and regression, chapter 12: statistics in practice.
The JoVE video player is compatible with HTML5 and Adobe Flash. Older browsers that do not support HTML5 and the H.264 video codec will still use a Flash-based video player. We recommend downloading the newest version of Flash here, but we support all versions 10 and above.
In an experiment, a farm with infected plants is subjected to a widely applicable insecticide.
This insecticide is expected to increase the number of healthy plants after its application. However, at the end of the experiment, the proportion of healthy and infected plants remained the same.
Here, the null hypothesis that the insecticide has no effect seems to hold, but should one accept the hypothesis or fail to reject it?
Accepting this hypothesis would mean that the insecticide is ineffective and cannot improve the plants' health.
This decision actually overlooks the other plausible explanations for the observed results.
In this case, using an unprescribed amount or concentration of insecticide might have resulted in no effect.
There is a possibility of plants being infected by something that the insecticide cannot target.
Failing to reject a null hypothesis means there is no sufficient evidence for the expected or the observed effect.
Today, if scientists had accepted null hypotheses, the discovery of plant viruses or the rediscovery of many extinct species would not have been possible.
9.8: Hypothesis: Accept or Fail to Reject?
The outcome of any hypothesis testing leads to rejecting or not rejecting the null hypothesis. This decision is taken based on the analysis of the data, an appropriate test statistic, an appropriate confidence level, the critical values, and P -values. However, when the evidence suggests that the null hypothesis cannot be rejected, is it right to say, 'Accept' the null hypothesis?
There are two ways to indicate that the null hypothesis is not rejected. 'Accept' the null hypothesis and 'fail to reject' the null hypothesis. Superficially, both these phrases mean the same, but in statistics, the meanings are somewhat different. The phrase 'accept the null hypothesis' implies that the null hypothesis is by nature true, and it is proved. But a hypothesis test simply provides information that there is no sufficient evidence in support of the alternative hypothesis, and therefore the null hypothesis cannot be rejected. The null hypothesis cannot be proven, although the hypothesis test begins with an assumption that the hypothesis is true, and the final result indicates the failure of the rejection of the null hypothesis. Thus, it is always advisable to state 'fail to reject the null hypothesis' instead of 'accept the null hypothesis.'
'Accepting' a hypothesis may also imply that the given hypothesis is now proven, so there is no need to study it further. Nevertheless, that is never the case, as newer scientific evidence often challenges the existing studies. Discovery of viruses and fossils, rediscovery of presumed extinct species, criminal trials, and novel drug tests follow the same principles of testing hypotheses. In those cases, 'accepting' a hypothesis may lead to severe consequences.
Get cutting-edge science videos from J o VE sent straight to your inbox every month.
mktb-description
We use cookies to enhance your experience on our website.
By continuing to use our website or clicking “Continue”, you are agreeing to accept our cookies.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

8.1.1: Null and Alternative Hypotheses
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 10971

The actual test begins by considering two hypotheses . They are called the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis . These hypotheses contain opposing viewpoints.
\(H_0\): The null hypothesis: It is a statement of no difference between the variables—they are not related. This can often be considered the status quo and as a result if you cannot accept the null it requires some action.
\(H_a\): The alternative hypothesis: It is a claim about the population that is contradictory to \(H_0\) and what we conclude when we reject \(H_0\). This is usually what the researcher is trying to prove.
Since the null and alternative hypotheses are contradictory, you must examine evidence to decide if you have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis or not. The evidence is in the form of sample data.
After you have determined which hypothesis the sample supports, you make a decision. There are two options for a decision. They are "reject \(H_0\)" if the sample information favors the alternative hypothesis or "do not reject \(H_0\)" or "decline to reject \(H_0\)" if the sample information is insufficient to reject the null hypothesis.
\(H_{0}\) always has a symbol with an equal in it. \(H_{a}\) never has a symbol with an equal in it. The choice of symbol depends on the wording of the hypothesis test. However, be aware that many researchers (including one of the co-authors in research work) use = in the null hypothesis, even with > or < as the symbol in the alternative hypothesis. This practice is acceptable because we only make the decision to reject or not reject the null hypothesis.
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\)
- \(H_{0}\): No more than 30% of the registered voters in Santa Clara County voted in the primary election. \(p \leq 30\)
- \(H_{a}\): More than 30% of the registered voters in Santa Clara County voted in the primary election. \(p > 30\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{1}\)
A medical trial is conducted to test whether or not a new medicine reduces cholesterol by 25%. State the null and alternative hypotheses.
- \(H_{0}\): The drug reduces cholesterol by 25%. \(p = 0.25\)
- \(H_{a}\): The drug does not reduce cholesterol by 25%. \(p \neq 0.25\)
Example \(\PageIndex{2}\)
We want to test whether the mean GPA of students in American colleges is different from 2.0 (out of 4.0). The null and alternative hypotheses are:
- \(H_{0}: \mu = 2.0\)
- \(H_{a}: \mu \neq 2.0\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{2}\)
We want to test whether the mean height of eighth graders is 66 inches. State the null and alternative hypotheses. Fill in the correct symbol \((=, \neq, \geq, <, \leq, >)\) for the null and alternative hypotheses.
- \(H_{0}: \mu \_ 66\)
- \(H_{a}: \mu \_ 66\)
- \(H_{0}: \mu = 66\)
- \(H_{a}: \mu \neq 66\)
Example \(\PageIndex{3}\)
We want to test if college students take less than five years to graduate from college, on the average. The null and alternative hypotheses are:
- \(H_{0}: \mu \geq 5\)
- \(H_{a}: \mu < 5\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{3}\)
We want to test if it takes fewer than 45 minutes to teach a lesson plan. State the null and alternative hypotheses. Fill in the correct symbol ( =, ≠, ≥, <, ≤, >) for the null and alternative hypotheses.
- \(H_{0}: \mu \_ 45\)
- \(H_{a}: \mu \_ 45\)
- \(H_{0}: \mu \geq 45\)
- \(H_{a}: \mu < 45\)
Example \(\PageIndex{4}\)
In an issue of U. S. News and World Report , an article on school standards stated that about half of all students in France, Germany, and Israel take advanced placement exams and a third pass. The same article stated that 6.6% of U.S. students take advanced placement exams and 4.4% pass. Test if the percentage of U.S. students who take advanced placement exams is more than 6.6%. State the null and alternative hypotheses.
- \(H_{0}: p \leq 0.066\)
- \(H_{a}: p > 0.066\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{4}\)
On a state driver’s test, about 40% pass the test on the first try. We want to test if more than 40% pass on the first try. Fill in the correct symbol (\(=, \neq, \geq, <, \leq, >\)) for the null and alternative hypotheses.
- \(H_{0}: p \_ 0.40\)
- \(H_{a}: p \_ 0.40\)
- \(H_{0}: p = 0.40\)
- \(H_{a}: p > 0.40\)
COLLABORATIVE EXERCISE
Bring to class a newspaper, some news magazines, and some Internet articles . In groups, find articles from which your group can write null and alternative hypotheses. Discuss your hypotheses with the rest of the class.
In a hypothesis test , sample data is evaluated in order to arrive at a decision about some type of claim. If certain conditions about the sample are satisfied, then the claim can be evaluated for a population. In a hypothesis test, we:
- Evaluate the null hypothesis , typically denoted with \(H_{0}\). The null is not rejected unless the hypothesis test shows otherwise. The null statement must always contain some form of equality \((=, \leq \text{or} \geq)\)
- Always write the alternative hypothesis , typically denoted with \(H_{a}\) or \(H_{1}\), using less than, greater than, or not equals symbols, i.e., \((\neq, >, \text{or} <)\).
- If we reject the null hypothesis, then we can assume there is enough evidence to support the alternative hypothesis.
- Never state that a claim is proven true or false. Keep in mind the underlying fact that hypothesis testing is based on probability laws; therefore, we can talk only in terms of non-absolute certainties.
Formula Review
\(H_{0}\) and \(H_{a}\) are contradictory.
- If \(\alpha \leq p\)-value, then do not reject \(H_{0}\).
- If\(\alpha > p\)-value, then reject \(H_{0}\).
\(\alpha\) is preconceived. Its value is set before the hypothesis test starts. The \(p\)-value is calculated from the data.References
Data from the National Institute of Mental Health. Available online at http://www.nimh.nih.gov/publicat/depression.cfm .

User Preferences
Content preview.
Arcu felis bibendum ut tristique et egestas quis:
- Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris
- Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate
- Excepteur sint occaecat cupidatat non proident
Keyboard Shortcuts
S.3.1 hypothesis testing (critical value approach).
The critical value approach involves determining "likely" or "unlikely" by determining whether or not the observed test statistic is more extreme than would be expected if the null hypothesis were true. That is, it entails comparing the observed test statistic to some cutoff value, called the " critical value ." If the test statistic is more extreme than the critical value, then the null hypothesis is rejected in favor of the alternative hypothesis. If the test statistic is not as extreme as the critical value, then the null hypothesis is not rejected.
Specifically, the four steps involved in using the critical value approach to conducting any hypothesis test are:
- Specify the null and alternative hypotheses.
- Using the sample data and assuming the null hypothesis is true, calculate the value of the test statistic. To conduct the hypothesis test for the population mean μ , we use the t -statistic \(t^*=\frac{\bar{x}-\mu}{s/\sqrt{n}}\) which follows a t -distribution with n - 1 degrees of freedom.
- Determine the critical value by finding the value of the known distribution of the test statistic such that the probability of making a Type I error — which is denoted \(\alpha\) (greek letter "alpha") and is called the " significance level of the test " — is small (typically 0.01, 0.05, or 0.10).
- Compare the test statistic to the critical value. If the test statistic is more extreme in the direction of the alternative than the critical value, reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative hypothesis. If the test statistic is less extreme than the critical value, do not reject the null hypothesis.
Example S.3.1.1
Mean gpa section .
In our example concerning the mean grade point average, suppose we take a random sample of n = 15 students majoring in mathematics. Since n = 15, our test statistic t * has n - 1 = 14 degrees of freedom. Also, suppose we set our significance level α at 0.05 so that we have only a 5% chance of making a Type I error.
Right-Tailed
The critical value for conducting the right-tailed test H 0 : μ = 3 versus H A : μ > 3 is the t -value, denoted t \(\alpha\) , n - 1 , such that the probability to the right of it is \(\alpha\). It can be shown using either statistical software or a t -table that the critical value t 0.05,14 is 1.7613. That is, we would reject the null hypothesis H 0 : μ = 3 in favor of the alternative hypothesis H A : μ > 3 if the test statistic t * is greater than 1.7613. Visually, the rejection region is shaded red in the graph.
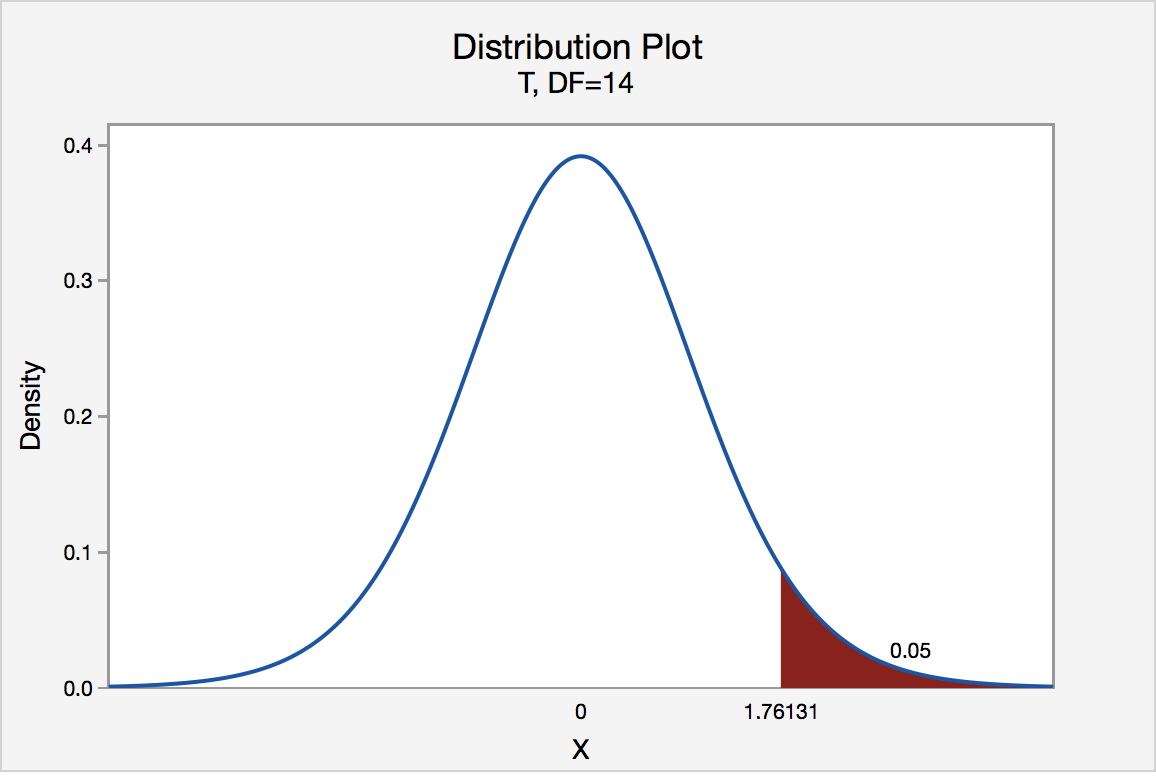
Left-Tailed
The critical value for conducting the left-tailed test H 0 : μ = 3 versus H A : μ < 3 is the t -value, denoted -t ( \(\alpha\) , n - 1) , such that the probability to the left of it is \(\alpha\). It can be shown using either statistical software or a t -table that the critical value -t 0.05,14 is -1.7613. That is, we would reject the null hypothesis H 0 : μ = 3 in favor of the alternative hypothesis H A : μ < 3 if the test statistic t * is less than -1.7613. Visually, the rejection region is shaded red in the graph.
There are two critical values for the two-tailed test H 0 : μ = 3 versus H A : μ ≠ 3 — one for the left-tail denoted -t ( \(\alpha\) / 2, n - 1) and one for the right-tail denoted t ( \(\alpha\) / 2, n - 1) . The value - t ( \(\alpha\) /2, n - 1) is the t -value such that the probability to the left of it is \(\alpha\)/2, and the value t ( \(\alpha\) /2, n - 1) is the t -value such that the probability to the right of it is \(\alpha\)/2. It can be shown using either statistical software or a t -table that the critical value -t 0.025,14 is -2.1448 and the critical value t 0.025,14 is 2.1448. That is, we would reject the null hypothesis H 0 : μ = 3 in favor of the alternative hypothesis H A : μ ≠ 3 if the test statistic t * is less than -2.1448 or greater than 2.1448. Visually, the rejection region is shaded red in the graph.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List

- PMC5635437.1 ; 2015 Aug 25
- PMC5635437.2 ; 2016 Jul 13
- ➤ PMC5635437.3; 2016 Oct 10
Null hypothesis significance testing: a short tutorial
Cyril pernet.
1 Centre for Clinical Brain Sciences (CCBS), Neuroimaging Sciences, The University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UK
Version Changes
Revised. amendments from version 2.
This v3 includes minor changes that reflect the 3rd reviewers' comments - in particular the theoretical vs. practical difference between Fisher and Neyman-Pearson. Additional information and reference is also included regarding the interpretation of p-value for low powered studies.
Peer Review Summary
Although thoroughly criticized, null hypothesis significance testing (NHST) remains the statistical method of choice used to provide evidence for an effect, in biological, biomedical and social sciences. In this short tutorial, I first summarize the concepts behind the method, distinguishing test of significance (Fisher) and test of acceptance (Newman-Pearson) and point to common interpretation errors regarding the p-value. I then present the related concepts of confidence intervals and again point to common interpretation errors. Finally, I discuss what should be reported in which context. The goal is to clarify concepts to avoid interpretation errors and propose reporting practices.
The Null Hypothesis Significance Testing framework
NHST is a method of statistical inference by which an experimental factor is tested against a hypothesis of no effect or no relationship based on a given observation. The method is a combination of the concepts of significance testing developed by Fisher in 1925 and of acceptance based on critical rejection regions developed by Neyman & Pearson in 1928 . In the following I am first presenting each approach, highlighting the key differences and common misconceptions that result from their combination into the NHST framework (for a more mathematical comparison, along with the Bayesian method, see Christensen, 2005 ). I next present the related concept of confidence intervals. I finish by discussing practical aspects in using NHST and reporting practice.
Fisher, significance testing, and the p-value
The method developed by ( Fisher, 1934 ; Fisher, 1955 ; Fisher, 1959 ) allows to compute the probability of observing a result at least as extreme as a test statistic (e.g. t value), assuming the null hypothesis of no effect is true. This probability or p-value reflects (1) the conditional probability of achieving the observed outcome or larger: p(Obs≥t|H0), and (2) is therefore a cumulative probability rather than a point estimate. It is equal to the area under the null probability distribution curve from the observed test statistic to the tail of the null distribution ( Turkheimer et al. , 2004 ). The approach proposed is of ‘proof by contradiction’ ( Christensen, 2005 ), we pose the null model and test if data conform to it.
In practice, it is recommended to set a level of significance (a theoretical p-value) that acts as a reference point to identify significant results, that is to identify results that differ from the null-hypothesis of no effect. Fisher recommended using p=0.05 to judge whether an effect is significant or not as it is roughly two standard deviations away from the mean for the normal distribution ( Fisher, 1934 page 45: ‘The value for which p=.05, or 1 in 20, is 1.96 or nearly 2; it is convenient to take this point as a limit in judging whether a deviation is to be considered significant or not’). A key aspect of Fishers’ theory is that only the null-hypothesis is tested, and therefore p-values are meant to be used in a graded manner to decide whether the evidence is worth additional investigation and/or replication ( Fisher, 1971 page 13: ‘it is open to the experimenter to be more or less exacting in respect of the smallness of the probability he would require […]’ and ‘no isolated experiment, however significant in itself, can suffice for the experimental demonstration of any natural phenomenon’). How small the level of significance is, is thus left to researchers.
What is not a p-value? Common mistakes
The p-value is not an indication of the strength or magnitude of an effect . Any interpretation of the p-value in relation to the effect under study (strength, reliability, probability) is wrong, since p-values are conditioned on H0. In addition, while p-values are randomly distributed (if all the assumptions of the test are met) when there is no effect, their distribution depends of both the population effect size and the number of participants, making impossible to infer strength of effect from them.
Similarly, 1-p is not the probability to replicate an effect . Often, a small value of p is considered to mean a strong likelihood of getting the same results on another try, but again this cannot be obtained because the p-value is not informative on the effect itself ( Miller, 2009 ). Because the p-value depends on the number of subjects, it can only be used in high powered studies to interpret results. In low powered studies (typically small number of subjects), the p-value has a large variance across repeated samples, making it unreliable to estimate replication ( Halsey et al. , 2015 ).
A (small) p-value is not an indication favouring a given hypothesis . Because a low p-value only indicates a misfit of the null hypothesis to the data, it cannot be taken as evidence in favour of a specific alternative hypothesis more than any other possible alternatives such as measurement error and selection bias ( Gelman, 2013 ). Some authors have even argued that the more (a priori) implausible the alternative hypothesis, the greater the chance that a finding is a false alarm ( Krzywinski & Altman, 2013 ; Nuzzo, 2014 ).
The p-value is not the probability of the null hypothesis p(H0), of being true, ( Krzywinski & Altman, 2013 ). This common misconception arises from a confusion between the probability of an observation given the null p(Obs≥t|H0) and the probability of the null given an observation p(H0|Obs≥t) that is then taken as an indication for p(H0) (see Nickerson, 2000 ).
Neyman-Pearson, hypothesis testing, and the α-value
Neyman & Pearson (1933) proposed a framework of statistical inference for applied decision making and quality control. In such framework, two hypotheses are proposed: the null hypothesis of no effect and the alternative hypothesis of an effect, along with a control of the long run probabilities of making errors. The first key concept in this approach, is the establishment of an alternative hypothesis along with an a priori effect size. This differs markedly from Fisher who proposed a general approach for scientific inference conditioned on the null hypothesis only. The second key concept is the control of error rates . Neyman & Pearson (1928) introduced the notion of critical intervals, therefore dichotomizing the space of possible observations into correct vs. incorrect zones. This dichotomization allows distinguishing correct results (rejecting H0 when there is an effect and not rejecting H0 when there is no effect) from errors (rejecting H0 when there is no effect, the type I error, and not rejecting H0 when there is an effect, the type II error). In this context, alpha is the probability of committing a Type I error in the long run. Alternatively, Beta is the probability of committing a Type II error in the long run.
The (theoretical) difference in terms of hypothesis testing between Fisher and Neyman-Pearson is illustrated on Figure 1 . In the 1 st case, we choose a level of significance for observed data of 5%, and compute the p-value. If the p-value is below the level of significance, it is used to reject H0. In the 2 nd case, we set a critical interval based on the a priori effect size and error rates. If an observed statistic value is below and above the critical values (the bounds of the confidence region), it is deemed significantly different from H0. In the NHST framework, the level of significance is (in practice) assimilated to the alpha level, which appears as a simple decision rule: if the p-value is less or equal to alpha, the null is rejected. It is however a common mistake to assimilate these two concepts. The level of significance set for a given sample is not the same as the frequency of acceptance alpha found on repeated sampling because alpha (a point estimate) is meant to reflect the long run probability whilst the p-value (a cumulative estimate) reflects the current probability ( Fisher, 1955 ; Hubbard & Bayarri, 2003 ).

The figure was prepared with G-power for a one-sided one-sample t-test, with a sample size of 32 subjects, an effect size of 0.45, and error rates alpha=0.049 and beta=0.80. In Fisher’s procedure, only the nil-hypothesis is posed, and the observed p-value is compared to an a priori level of significance. If the observed p-value is below this level (here p=0.05), one rejects H0. In Neyman-Pearson’s procedure, the null and alternative hypotheses are specified along with an a priori level of acceptance. If the observed statistical value is outside the critical region (here [-∞ +1.69]), one rejects H0.
Acceptance or rejection of H0?
The acceptance level α can also be viewed as the maximum probability that a test statistic falls into the rejection region when the null hypothesis is true ( Johnson, 2013 ). Therefore, one can only reject the null hypothesis if the test statistics falls into the critical region(s), or fail to reject this hypothesis. In the latter case, all we can say is that no significant effect was observed, but one cannot conclude that the null hypothesis is true. This is another common mistake in using NHST: there is a profound difference between accepting the null hypothesis and simply failing to reject it ( Killeen, 2005 ). By failing to reject, we simply continue to assume that H0 is true, which implies that one cannot argue against a theory from a non-significant result (absence of evidence is not evidence of absence). To accept the null hypothesis, tests of equivalence ( Walker & Nowacki, 2011 ) or Bayesian approaches ( Dienes, 2014 ; Kruschke, 2011 ) must be used.
Confidence intervals
Confidence intervals (CI) are builds that fail to cover the true value at a rate of alpha, the Type I error rate ( Morey & Rouder, 2011 ) and therefore indicate if observed values can be rejected by a (two tailed) test with a given alpha. CI have been advocated as alternatives to p-values because (i) they allow judging the statistical significance and (ii) provide estimates of effect size. Assuming the CI (a)symmetry and width are correct (but see Wilcox, 2012 ), they also give some indication about the likelihood that a similar value can be observed in future studies. For future studies of the same sample size, 95% CI give about 83% chance of replication success ( Cumming & Maillardet, 2006 ). If sample sizes however differ between studies, CI do not however warranty any a priori coverage.
Although CI provide more information, they are not less subject to interpretation errors (see Savalei & Dunn, 2015 for a review). The most common mistake is to interpret CI as the probability that a parameter (e.g. the population mean) will fall in that interval X% of the time. The correct interpretation is that, for repeated measurements with the same sample sizes, taken from the same population, X% of times the CI obtained will contain the true parameter value ( Tan & Tan, 2010 ). The alpha value has the same interpretation as testing against H0, i.e. we accept that 1-alpha CI are wrong in alpha percent of the times in the long run. This implies that CI do not allow to make strong statements about the parameter of interest (e.g. the mean difference) or about H1 ( Hoekstra et al. , 2014 ). To make a statement about the probability of a parameter of interest (e.g. the probability of the mean), Bayesian intervals must be used.
The (correct) use of NHST
NHST has always been criticized, and yet is still used every day in scientific reports ( Nickerson, 2000 ). One question to ask oneself is what is the goal of a scientific experiment at hand? If the goal is to establish a discrepancy with the null hypothesis and/or establish a pattern of order, because both requires ruling out equivalence, then NHST is a good tool ( Frick, 1996 ; Walker & Nowacki, 2011 ). If the goal is to test the presence of an effect and/or establish some quantitative values related to an effect, then NHST is not the method of choice since testing is conditioned on H0.
While a Bayesian analysis is suited to estimate that the probability that a hypothesis is correct, like NHST, it does not prove a theory on itself, but adds its plausibility ( Lindley, 2000 ). No matter what testing procedure is used and how strong results are, ( Fisher, 1959 p13) reminds us that ‘ […] no isolated experiment, however significant in itself, can suffice for the experimental demonstration of any natural phenomenon'. Similarly, the recent statement of the American Statistical Association ( Wasserstein & Lazar, 2016 ) makes it clear that conclusions should be based on the researchers understanding of the problem in context, along with all summary data and tests, and that no single value (being p-values, Bayesian factor or else) can be used support or invalidate a theory.
What to report and how?
Considering that quantitative reports will always have more information content than binary (significant or not) reports, we can always argue that raw and/or normalized effect size, confidence intervals, or Bayes factor must be reported. Reporting everything can however hinder the communication of the main result(s), and we should aim at giving only the information needed, at least in the core of a manuscript. Here I propose to adopt optimal reporting in the result section to keep the message clear, but have detailed supplementary material. When the hypothesis is about the presence/absence or order of an effect, and providing that a study has sufficient power, NHST is appropriate and it is sufficient to report in the text the actual p-value since it conveys the information needed to rule out equivalence. When the hypothesis and/or the discussion involve some quantitative value, and because p-values do not inform on the effect, it is essential to report on effect sizes ( Lakens, 2013 ), preferably accompanied with confidence or credible intervals. The reasoning is simply that one cannot predict and/or discuss quantities without accounting for variability. For the reader to understand and fully appreciate the results, nothing else is needed.
Because science progress is obtained by cumulating evidence ( Rosenthal, 1991 ), scientists should also consider the secondary use of the data. With today’s electronic articles, there are no reasons for not including all of derived data: mean, standard deviations, effect size, CI, Bayes factor should always be included as supplementary tables (or even better also share raw data). It is also essential to report the context in which tests were performed – that is to report all of the tests performed (all t, F, p values) because of the increase type one error rate due to selective reporting (multiple comparisons and p-hacking problems - Ioannidis, 2005 ). Providing all of this information allows (i) other researchers to directly and effectively compare their results in quantitative terms (replication of effects beyond significance, Open Science Collaboration, 2015 ), (ii) to compute power to future studies ( Lakens & Evers, 2014 ), and (iii) to aggregate results for meta-analyses whilst minimizing publication bias ( van Assen et al. , 2014 ).
[version 3; referees: 1 approved
Funding Statement
The author(s) declared that no grants were involved in supporting this work.
- Christensen R: Testing Fisher, Neyman, Pearson, and Bayes. The American Statistician. 2005; 59 ( 2 ):121–126. 10.1198/000313005X20871 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cumming G, Maillardet R: Confidence intervals and replication: Where will the next mean fall? Psychological Methods. 2006; 11 ( 3 ):217–227. 10.1037/1082-989X.11.3.217 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dienes Z: Using Bayes to get the most out of non-significant results. Front Psychol. 2014; 5 :781. 10.3389/fpsyg.2014.00781 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fisher RA: Statistical Methods for Research Workers . (Vol. 5th Edition). Edinburgh, UK: Oliver and Boyd.1934. Reference Source [ Google Scholar ]
- Fisher RA: Statistical Methods and Scientific Induction. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B. 1955; 17 ( 1 ):69–78. Reference Source [ Google Scholar ]
- Fisher RA: Statistical methods and scientific inference . (2nd ed.). NewYork: Hafner Publishing,1959. Reference Source [ Google Scholar ]
- Fisher RA: The Design of Experiments . Hafner Publishing Company, New-York.1971. Reference Source [ Google Scholar ]
- Frick RW: The appropriate use of null hypothesis testing. Psychol Methods. 1996; 1 ( 4 ):379–390. 10.1037/1082-989X.1.4.379 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gelman A: P values and statistical practice. Epidemiology. 2013; 24 ( 1 ):69–72. 10.1097/EDE.0b013e31827886f7 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Halsey LG, Curran-Everett D, Vowler SL, et al.: The fickle P value generates irreproducible results. Nat Methods. 2015; 12 ( 3 ):179–85. 10.1038/nmeth.3288 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hoekstra R, Morey RD, Rouder JN, et al.: Robust misinterpretation of confidence intervals. Psychon Bull Rev. 2014; 21 ( 5 ):1157–1164. 10.3758/s13423-013-0572-3 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hubbard R, Bayarri MJ: Confusion over measures of evidence (p’s) versus errors ([alpha]’s) in classical statistical testing. The American Statistician. 2003; 57 ( 3 ):171–182. 10.1198/0003130031856 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ioannidis JP: Why most published research findings are false. PLoS Med. 2005; 2 ( 8 ):e124. 10.1371/journal.pmed.0020124 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Johnson VE: Revised standards for statistical evidence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013; 110 ( 48 ):19313–19317. 10.1073/pnas.1313476110 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Killeen PR: An alternative to null-hypothesis significance tests. Psychol Sci. 2005; 16 ( 5 ):345–353. 10.1111/j.0956-7976.2005.01538.x [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kruschke JK: Bayesian Assessment of Null Values Via Parameter Estimation and Model Comparison. Perspect Psychol Sci. 2011; 6 ( 3 ):299–312. 10.1177/1745691611406925 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Krzywinski M, Altman N: Points of significance: Significance, P values and t -tests. Nat Methods. 2013; 10 ( 11 ):1041–1042. 10.1038/nmeth.2698 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lakens D: Calculating and reporting effect sizes to facilitate cumulative science: a practical primer for t -tests and ANOVAs. Front Psychol. 2013; 4 :863. 10.3389/fpsyg.2013.00863 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lakens D, Evers ER: Sailing From the Seas of Chaos Into the Corridor of Stability: Practical Recommendations to Increase the Informational Value of Studies. Perspect Psychol Sci. 2014; 9 ( 3 ):278–292. 10.1177/1745691614528520 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lindley D: The philosophy of statistics. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. 2000; 49 ( 3 ):293–337. 10.1111/1467-9884.00238 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Miller J: What is the probability of replicating a statistically significant effect? Psychon Bull Rev. 2009; 16 ( 4 ):617–640. 10.3758/PBR.16.4.617 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Morey RD, Rouder JN: Bayes factor approaches for testing interval null hypotheses. Psychol Methods. 2011; 16 ( 4 ):406–419. 10.1037/a0024377 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Neyman J, Pearson ES: On the Use and Interpretation of Certain Test Criteria for Purposes of Statistical Inference: Part I. Biometrika. 1928; 20A ( 1/2 ):175–240. 10.3389/fpsyg.2015.00245 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Neyman J, Pearson ES: On the problem of the most efficient tests of statistical hypotheses. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser A. 1933; 231 ( 694–706 ):289–337. 10.1098/rsta.1933.0009 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Nickerson RS: Null hypothesis significance testing: a review of an old and continuing controversy. Psychol Methods. 2000; 5 ( 2 ):241–301. 10.1037/1082-989X.5.2.241 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Nuzzo R: Scientific method: statistical errors. Nature. 2014; 506 ( 7487 ):150–152. 10.1038/506150a [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Open Science Collaboration. PSYCHOLOGY. Estimating the reproducibility of psychological science. Science. 2015; 349 ( 6251 ):aac4716. 10.1126/science.aac4716 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosenthal R: Cumulating psychology: an appreciation of Donald T. Campbell. Psychol Sci. 1991; 2 ( 4 ):213–221. 10.1111/j.1467-9280.1991.tb00138.x [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Savalei V, Dunn E: Is the call to abandon p -values the red herring of the replicability crisis? Front Psychol. 2015; 6 :245. 10.3389/fpsyg.2015.00245 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tan SH, Tan SB: The Correct Interpretation of Confidence Intervals. Proceedings of Singapore Healthcare. 2010; 19 ( 3 ):276–278. 10.1177/201010581001900316 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Turkheimer FE, Aston JA, Cunningham VJ: On the logic of hypothesis testing in functional imaging. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2004; 31 ( 5 ):725–732. 10.1007/s00259-003-1387-7 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- van Assen MA, van Aert RC, Nuijten MB, et al.: Why Publishing Everything Is More Effective than Selective Publishing of Statistically Significant Results. PLoS One. 2014; 9 ( 1 ):e84896. 10.1371/journal.pone.0084896 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Walker E, Nowacki AS: Understanding equivalence and noninferiority testing. J Gen Intern Med. 2011; 26 ( 2 ):192–196. 10.1007/s11606-010-1513-8 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wasserstein RL, Lazar NA: The ASA’s Statement on p -Values: Context, Process, and Purpose. The American Statistician. 2016; 70 ( 2 ):129–133. 10.1080/00031305.2016.1154108 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wilcox R: Introduction to Robust Estimation and Hypothesis Testing . Edition 3, Academic Press, Elsevier: Oxford, UK, ISBN: 978-0-12-386983-8.2012. Reference Source [ Google Scholar ]
Referee response for version 3
Dorothy vera margaret bishop.
1 Department of Experimental Psychology, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK
I can see from the history of this paper that the author has already been very responsive to reviewer comments, and that the process of revising has now been quite protracted.
That makes me reluctant to suggest much more, but I do see potential here for making the paper more impactful. So my overall view is that, once a few typos are fixed (see below), this could be published as is, but I think there is an issue with the potential readership and that further revision could overcome this.
I suspect my take on this is rather different from other reviewers, as I do not regard myself as a statistics expert, though I am on the more quantitative end of the continuum of psychologists and I try to keep up to date. I think I am quite close to the target readership , insofar as I am someone who was taught about statistics ages ago and uses stats a lot, but never got adequate training in the kinds of topic covered by this paper. The fact that I am aware of controversies around the interpretation of confidence intervals etc is simply because I follow some discussions of this on social media. I am therefore very interested to have a clear account of these issues.
This paper contains helpful information for someone in this position, but it is not always clear, and I felt the relevance of some of the content was uncertain. So here are some recommendations:
- As one previous reviewer noted, it’s questionable that there is a need for a tutorial introduction, and the limited length of this article does not lend itself to a full explanation. So it might be better to just focus on explaining as clearly as possible the problems people have had in interpreting key concepts. I think a title that made it clear this was the content would be more appealing than the current one.
- P 3, col 1, para 3, last sentence. Although statisticians always emphasise the arbitrary nature of p < .05, we all know that in practice authors who use other values are likely to have their analyses queried. I wondered whether it would be useful here to note that in some disciplines different cutoffs are traditional, e.g. particle physics. Or you could cite David Colquhoun’s paper in which he recommends using p < .001 ( http://rsos.royalsocietypublishing.org/content/1/3/140216) - just to be clear that the traditional p < .05 has been challenged.
What I can’t work out is how you would explain the alpha from Neyman-Pearson in the same way (though I can see from Figure 1 that with N-P you could test an alternative hypothesis, such as the idea that the coin would be heads 75% of the time).
‘By failing to reject, we simply continue to assume that H0 is true, which implies that one cannot….’ have ‘In failing to reject, we do not assume that H0 is true; one cannot argue against a theory from a non-significant result.’
I felt most readers would be interested to read about tests of equivalence and Bayesian approaches, but many would be unfamiliar with these and might like to see an example of how they work in practice – if space permitted.
- Confidence intervals: I simply could not understand the first sentence – I wondered what was meant by ‘builds’ here. I understand about difficulties in comparing CI across studies when sample sizes differ, but I did not find the last sentence on p 4 easy to understand.
- P 5: The sentence starting: ‘The alpha value has the same interpretation’ was also hard to understand, especially the term ‘1-alpha CI’. Here too I felt some concrete illustration might be helpful to the reader. And again, I also found the reference to Bayesian intervals tantalising – I think many readers won’t know how to compute these and something like a figure comparing a traditional CI with a Bayesian interval and giving a source for those who want to read on would be very helpful. The reference to ‘credible intervals’ in the penultimate paragraph is very unclear and needs a supporting reference – most readers will not be familiar with this concept.
P 3, col 1, para 2, line 2; “allows us to compute”
P 3, col 2, para 2, ‘probability of replicating’
P 3, col 2, para 2, line 4 ‘informative about’
P 3, col 2, para 4, line 2 delete ‘of’
P 3, col 2, para 5, line 9 – ‘conditioned’ is either wrong or too technical here: would ‘based’ be acceptable as alternative wording
P 3, col 2, para 5, line 13 ‘This dichotomisation allows one to distinguish’
P 3, col 2, para 5, last sentence, delete ‘Alternatively’.
P 3, col 2, last para line 2 ‘first’
P 4, col 2, para 2, last sentence is hard to understand; not sure if this is better: ‘If sample sizes differ between studies, the distribution of CIs cannot be specified a priori’
P 5, col 1, para 2, ‘a pattern of order’ – I did not understand what was meant by this
P 5, col 1, para 2, last sentence unclear: possible rewording: “If the goal is to test the size of an effect then NHST is not the method of choice, since testing can only reject the null hypothesis.’ (??)
P 5, col 1, para 3, line 1 delete ‘that’
P 5, col 1, para 3, line 3 ‘on’ -> ‘by’
P 5, col 2, para 1, line 4 , rather than ‘Here I propose to adopt’ I suggest ‘I recommend adopting’
P 5, col 2, para 1, line 13 ‘with’ -> ‘by’
P 5, col 2, para 1 – recommend deleting last sentence
P 5, col 2, para 2, line 2 ‘consider’ -> ‘anticipate’
P 5, col 2, para 2, delete ‘should always be included’
P 5, col 2, para 2, ‘type one’ -> ‘Type I’
I have read this submission. I believe that I have an appropriate level of expertise to confirm that it is of an acceptable scientific standard, however I have significant reservations, as outlined above.
The University of Edinburgh, UK
I wondered about changing the focus slightly and modifying the title to reflect this to say something like: Null hypothesis significance testing: a guide to commonly misunderstood concepts and recommendations for good practice
Thank you for the suggestion – you indeed saw the intention behind the ‘tutorial’ style of the paper.
- P 3, col 1, para 3, last sentence. Although statisticians always emphasise the arbitrary nature of p < .05, we all know that in practice authors who use other values are likely to have their analyses queried. I wondered whether it would be useful here to note that in some disciplines different cutoffs are traditional, e.g. particle physics. Or you could cite David Colquhoun’s paper in which he recommends using p < .001 ( http://rsos.royalsocietypublishing.org/content/1/3/140216) - just to be clear that the traditional p < .05 has been challenged.
I have added a sentence on this citing Colquhoun 2014 and the new Benjamin 2017 on using .005.
I agree that this point is always hard to appreciate, especially because it seems like in practice it makes little difference. I added a paragraph but using reaction times rather than a coin toss – thanks for the suggestion.
Added an example based on new table 1, following figure 1 – giving CI, equivalence tests and Bayes Factor (with refs to easy to use tools)
Changed builds to constructs (this simply means they are something we build) and added that the implication that probability coverage is not warranty when sample size change, is that we cannot compare CI.
I changed ‘ i.e. we accept that 1-alpha CI are wrong in alpha percent of the times in the long run’ to ‘, ‘e.g. a 95% CI is wrong in 5% of the times in the long run (i.e. if we repeat the experiment many times).’ – for Bayesian intervals I simply re-cited Morey & Rouder, 2011.
It is not the CI cannot be specified, it’s that the interval is not predictive of anything anymore! I changed it to ‘If sample sizes, however, differ between studies, there is no warranty that a CI from one study will be true at the rate alpha in a different study, which implies that CI cannot be compared across studies at this is rarely the same sample sizes’
I added (i.e. establish that A > B) – we test that conditions are ordered, but without further specification of the probability of that effect nor its size
Yes it works – thx
P 5, col 2, para 2, ‘type one’ -> ‘Type I’
Typos fixed, and suggestions accepted – thanks for that.
Stephen J. Senn
1 Luxembourg Institute of Health, Strassen, L-1445, Luxembourg
The revisions are OK for me, and I have changed my status to Approved.
I have read this submission. I believe that I have an appropriate level of expertise to confirm that it is of an acceptable scientific standard.
Referee response for version 2
On the whole I think that this article is reasonable, my main reservation being that I have my doubts on whether the literature needs yet another tutorial on this subject.
A further reservation I have is that the author, following others, stresses what in my mind is a relatively unimportant distinction between the Fisherian and Neyman-Pearson (NP) approaches. The distinction stressed by many is that the NP approach leads to a dichotomy accept/reject based on probabilities established in advance, whereas the Fisherian approach uses tail area probabilities calculated from the observed statistic. I see this as being unimportant and not even true. Unless one considers that the person carrying out a hypothesis test (original tester) is mandated to come to a conclusion on behalf of all scientific posterity, then one must accept that any remote scientist can come to his or her conclusion depending on the personal type I error favoured. To operate the results of an NP test carried out by the original tester, the remote scientist then needs to know the p-value. The type I error rate is then compared to this to come to a personal accept or reject decision (1). In fact Lehmann (2), who was an important developer of and proponent of the NP system, describes exactly this approach as being good practice. (See Testing Statistical Hypotheses, 2nd edition P70). Thus using tail-area probabilities calculated from the observed statistics does not constitute an operational difference between the two systems.
A more important distinction between the Fisherian and NP systems is that the former does not use alternative hypotheses(3). Fisher's opinion was that the null hypothesis was more primitive than the test statistic but that the test statistic was more primitive than the alternative hypothesis. Thus, alternative hypotheses could not be used to justify choice of test statistic. Only experience could do that.
Further distinctions between the NP and Fisherian approach are to do with conditioning and whether a null hypothesis can ever be accepted.
I have one minor quibble about terminology. As far as I can see, the author uses the usual term 'null hypothesis' and the eccentric term 'nil hypothesis' interchangeably. It would be simpler if the latter were abandoned.
Referee response for version 1
Marcel alm van assen.
1 Department of Methodology and Statistics, Tilburgh University, Tilburg, Netherlands
Null hypothesis significance testing (NHST) is a difficult topic, with misunderstandings arising easily. Many texts, including basic statistics books, deal with the topic, and attempt to explain it to students and anyone else interested. I would refer to a good basic text book, for a detailed explanation of NHST, or to a specialized article when wishing an explaining the background of NHST. So, what is the added value of a new text on NHST? In any case, the added value should be described at the start of this text. Moreover, the topic is so delicate and difficult that errors, misinterpretations, and disagreements are easy. I attempted to show this by giving comments to many sentences in the text.
Abstract: “null hypothesis significance testing is the statistical method of choice in biological, biomedical and social sciences to investigate if an effect is likely”. No, NHST is the method to test the hypothesis of no effect.
Intro: “Null hypothesis significance testing (NHST) is a method of statistical inference by which an observation is tested against a hypothesis of no effect or no relationship.” What is an ‘observation’? NHST is difficult to describe in one sentence, particularly here. I would skip this sentence entirely, here.
Section on Fisher; also explain the one-tailed test.
Section on Fisher; p(Obs|H0) does not reflect the verbal definition (the ‘or more extreme’ part).
Section on Fisher; use a reference and citation to Fisher’s interpretation of the p-value
Section on Fisher; “This was however only intended to be used as an indication that there is something in the data that deserves further investigation. The reason for this is that only H0 is tested whilst the effect under study is not itself being investigated.” First sentence, can you give a reference? Many people say a lot about Fisher’s intentions, but the good man is dead and cannot reply… Second sentence is a bit awkward, because the effect is investigated in a way, by testing the H0.
Section on p-value; Layout and structure can be improved greatly, by first again stating what the p-value is, and then statement by statement, what it is not, using separate lines for each statement. Consider adding that the p-value is randomly distributed under H0 (if all the assumptions of the test are met), and that under H1 the p-value is a function of population effect size and N; the larger each is, the smaller the p-value generally is.
Skip the sentence “If there is no effect, we should replicate the absence of effect with a probability equal to 1-p”. Not insightful, and you did not discuss the concept ‘replicate’ (and do not need to).
Skip the sentence “The total probability of false positives can also be obtained by aggregating results ( Ioannidis, 2005 ).” Not strongly related to p-values, and introduces unnecessary concepts ‘false positives’ (perhaps later useful) and ‘aggregation’.
Consider deleting; “If there is an effect however, the probability to replicate is a function of the (unknown) population effect size with no good way to know this from a single experiment ( Killeen, 2005 ).”
The following sentence; “ Finally, a (small) p-value is not an indication favouring a hypothesis . A low p-value indicates a misfit of the null hypothesis to the data and cannot be taken as evidence in favour of a specific alternative hypothesis more than any other possible alternatives such as measurement error and selection bias ( Gelman, 2013 ).” is surely not mainstream thinking about NHST; I would surely delete that sentence. In NHST, a p-value is used for testing the H0. Why did you not yet discuss significance level? Yes, before discussing what is not a p-value, I would explain NHST (i.e., what it is and how it is used).
Also the next sentence “The more (a priori) implausible the alternative hypothesis, the greater the chance that a finding is a false alarm ( Krzywinski & Altman, 2013 ; Nuzzo, 2014 ).“ is not fully clear to me. This is a Bayesian statement. In NHST, no likelihoods are attributed to hypotheses; the reasoning is “IF H0 is true, then…”.
Last sentence: “As Nickerson (2000) puts it ‘theory corroboration requires the testing of multiple predictions because the chance of getting statistically significant results for the wrong reasons in any given case is high’.” What is relation of this sentence to the contents of this section, precisely?
Next section: “For instance, we can estimate that the probability of a given F value to be in the critical interval [+2 +∞] is less than 5%” This depends on the degrees of freedom.
“When there is no effect (H0 is true), the erroneous rejection of H0 is known as type I error and is equal to the p-value.” Strange sentence. The Type I error is the probability of erroneously rejecting the H0 (so, when it is true). The p-value is … well, you explained it before; it surely does not equal the Type I error.
Consider adding a figure explaining the distinction between Fisher’s logic and that of Neyman and Pearson.
“When the test statistics falls outside the critical region(s)” What is outside?
“There is a profound difference between accepting the null hypothesis and simply failing to reject it ( Killeen, 2005 )” I agree with you, but perhaps you may add that some statisticians simply define “accept H0’” as obtaining a p-value larger than the significance level. Did you already discuss the significance level, and it’s mostly used values?
“To accept or reject equally the null hypothesis, Bayesian approaches ( Dienes, 2014 ; Kruschke, 2011 ) or confidence intervals must be used.” Is ‘reject equally’ appropriate English? Also using Cis, one cannot accept the H0.
Do you start discussing alpha only in the context of Cis?
“CI also indicates the precision of the estimate of effect size, but unless using a percentile bootstrap approach, they require assumptions about distributions which can lead to serious biases in particular regarding the symmetry and width of the intervals ( Wilcox, 2012 ).” Too difficult, using new concepts. Consider deleting.
“Assuming the CI (a)symmetry and width are correct, this gives some indication about the likelihood that a similar value can be observed in future studies, with 95% CI giving about 83% chance of replication success ( Lakens & Evers, 2014 ).” This statement is, in general, completely false. It very much depends on the sample sizes of both studies. If the replication study has a much, much, much larger N, then the probability that the original CI will contain the effect size of the replication approaches (1-alpha)*100%. If the original study has a much, much, much larger N, then the probability that the original Ci will contain the effect size of the replication study approaches 0%.
“Finally, contrary to p-values, CI can be used to accept H0. Typically, if a CI includes 0, we cannot reject H0. If a critical null region is specified rather than a single point estimate, for instance [-2 +2] and the CI is included within the critical null region, then H0 can be accepted. Importantly, the critical region must be specified a priori and cannot be determined from the data themselves.” No. H0 cannot be accepted with Cis.
“The (posterior) probability of an effect can however not be obtained using a frequentist framework.” Frequentist framework? You did not discuss that, yet.
“X% of times the CI obtained will contain the same parameter value”. The same? True, you mean?
“e.g. X% of the times the CI contains the same mean” I do not understand; which mean?
“The alpha value has the same interpretation as when using H0, i.e. we accept that 1-alpha CI are wrong in alpha percent of the times. “ What do you mean, CI are wrong? Consider rephrasing.
“To make a statement about the probability of a parameter of interest, likelihood intervals (maximum likelihood) and credibility intervals (Bayes) are better suited.” ML gives the likelihood of the data given the parameter, not the other way around.
“Many of the disagreements are not on the method itself but on its use.” Bayesians may disagree.
“If the goal is to establish the likelihood of an effect and/or establish a pattern of order, because both requires ruling out equivalence, then NHST is a good tool ( Frick, 1996 )” NHST does not provide evidence on the likelihood of an effect.
“If the goal is to establish some quantitative values, then NHST is not the method of choice.” P-values are also quantitative… this is not a precise sentence. And NHST may be used in combination with effect size estimation (this is even recommended by, e.g., the American Psychological Association (APA)).
“Because results are conditioned on H0, NHST cannot be used to establish beliefs.” It can reinforce some beliefs, e.g., if H0 or any other hypothesis, is true.
“To estimate the probability of a hypothesis, a Bayesian analysis is a better alternative.” It is the only alternative?
“Note however that even when a specific quantitative prediction from a hypothesis is shown to be true (typically testing H1 using Bayes), it does not prove the hypothesis itself, it only adds to its plausibility.” How can we show something is true?
I do not agree on the contents of the last section on ‘minimal reporting’. I prefer ‘optimal reporting’ instead, i.e., the reporting the information that is essential to the interpretation of the result, to any ready, which may have other goals than the writer of the article. This reporting includes, for sure, an estimate of effect size, and preferably a confidence interval, which is in line with recommendations of the APA.
I have read this submission. I believe that I have an appropriate level of expertise to state that I do not consider it to be of an acceptable scientific standard, for reasons outlined above.
The idea of this short review was to point to common interpretation errors (stressing again and again that we are under H0) being in using p-values or CI, and also proposing reporting practices to avoid bias. This is now stated at the end of abstract.
Regarding text books, it is clear that many fail to clearly distinguish Fisher/Pearson/NHST, see Glinet et al (2012) J. Exp Education 71, 83-92. If you have 1 or 2 in mind that you know to be good, I’m happy to include them.
I agree – yet people use it to investigate (not test) if an effect is likely. The issue here is wording. What about adding this distinction at the end of the sentence?: ‘null hypothesis significance testing is the statistical method of choice in biological, biomedical and social sciences used to investigate if an effect is likely, even though it actually tests for the hypothesis of no effect’.
I think a definition is needed, as it offers a starting point. What about the following: ‘NHST is a method of statistical inference by which an experimental factor is tested against a hypothesis of no effect or no relationship based on a given observation’
The section on Fisher has been modified (more or less) as suggested: (1) avoiding talking about one or two tailed tests (2) updating for p(Obs≥t|H0) and (3) referring to Fisher more explicitly (ie pages from articles and book) ; I cannot tell his intentions but these quotes leave little space to alternative interpretations.
The reasoning here is as you state yourself, part 1: ‘a p-value is used for testing the H0; and part 2: ‘no likelihoods are attributed to hypotheses’ it follows we cannot favour a hypothesis. It might seems contentious but this is the case that all we can is to reject the null – how could we favour a specific alternative hypothesis from there? This is explored further down the manuscript (and I now point to that) – note that we do not need to be Bayesian to favour a specific H1, all I’m saying is this cannot be attained with a p-value.
The point was to emphasise that a p value is not there to tell us a given H1 is true and can only be achieved through multiple predictions and experiments. I deleted it for clarity.
This sentence has been removed
Indeed, you are right and I have modified the text accordingly. When there is no effect (H0 is true), the erroneous rejection of H0 is known as type 1 error. Importantly, the type 1 error rate, or alpha value is determined a priori. It is a common mistake but the level of significance (for a given sample) is not the same as the frequency of acceptance alpha found on repeated sampling (Fisher, 1955).
A figure is now presented – with levels of acceptance, critical region, level of significance and p-value.
I should have clarified further here – as I was having in mind tests of equivalence. To clarify, I simply states now: ‘To accept the null hypothesis, tests of equivalence or Bayesian approaches must be used.’
It is now presented in the paragraph before.
Yes, you are right, I completely overlooked this problem. The corrected sentence (with more accurate ref) is now “Assuming the CI (a)symmetry and width are correct, this gives some indication about the likelihood that a similar value can be observed in future studies. For future studies of the same sample size, 95% CI giving about 83% chance of replication success (Cumming and Mallardet, 2006). If sample sizes differ between studies, CI do not however warranty any a priori coverage”.
Again, I had in mind equivalence testing, but in both cases you are right we can only reject and I therefore removed that sentence.
Yes, p-values must be interpreted in context with effect size, but this is not what people do. The point here is to be pragmatic, does and don’t. The sentence was changed.
Not for testing, but for probability, I am not aware of anything else.
Cumulative evidence is, in my opinion, the only way to show it. Even in hard science like physics multiple experiments. In the recent CERN study on finding Higgs bosons, 2 different and complementary experiments ran in parallel – and the cumulative evidence was taken as a proof of the true existence of Higgs bosons.
Daniel Lakens
1 School of Innovation Sciences, Eindhoven University of Technology, Eindhoven, Netherlands
I appreciate the author's attempt to write a short tutorial on NHST. Many people don't know how to use it, so attempts to educate people are always worthwhile. However, I don't think the current article reaches it's aim. For one, I think it might be practically impossible to explain a lot in such an ultra short paper - every section would require more than 2 pages to explain, and there are many sections. Furthermore, there are some excellent overviews, which, although more extensive, are also much clearer (e.g., Nickerson, 2000 ). Finally, I found many statements to be unclear, and perhaps even incorrect (noted below). Because there is nothing worse than creating more confusion on such a topic, I have extremely high standards before I think such a short primer should be indexed. I note some examples of unclear or incorrect statements below. I'm sorry I can't make a more positive recommendation.
“investigate if an effect is likely” – ambiguous statement. I think you mean, whether the observed DATA is probable, assuming there is no effect?
The Fisher (1959) reference is not correct – Fischer developed his method much earlier.
“This p-value thus reflects the conditional probability of achieving the observed outcome or larger, p(Obs|H0)” – please add 'assuming the null-hypothesis is true'.
“p(Obs|H0)” – explain this notation for novices.
“Following Fisher, the smaller the p-value, the greater the likelihood that the null hypothesis is false.” This is wrong, and any statement about this needs to be much more precise. I would suggest direct quotes.
“there is something in the data that deserves further investigation” –unclear sentence.
“The reason for this” – unclear what ‘this’ refers to.
“ not the probability of the null hypothesis of being true, p(H0)” – second of can be removed?
“Any interpretation of the p-value in relation to the effect under study (strength, reliability, probability) is indeed
wrong, since the p-value is conditioned on H0” - incorrect. A big problem is that it depends on the sample size, and that the probability of a theory depends on the prior.
“If there is no effect, we should replicate the absence of effect with a probability equal to 1-p.” I don’t understand this, but I think it is incorrect.
“The total probability of false positives can also be obtained by aggregating results (Ioannidis, 2005).” Unclear, and probably incorrect.
“By failing to reject, we simply continue to assume that H0 is true, which implies that one cannot, from a nonsignificant result, argue against a theory” – according to which theory? From a NP perspective, you can ACT as if the theory is false.
“(Lakens & Evers, 2014”) – we are not the original source, which should be cited instead.
“ Typically, if a CI includes 0, we cannot reject H0.” - when would this not be the case? This assumes a CI of 1-alpha.
“If a critical null region is specified rather than a single point estimate, for instance [-2 +2] and the CI is included within the critical null region, then H0 can be accepted.” – you mean practically, or formally? I’m pretty sure only the former.
The section on ‘The (correct) use of NHST’ seems to conclude only Bayesian statistics should be used. I don’t really agree.
“ we can always argue that effect size, power, etc. must be reported.” – which power? Post-hoc power? Surely not? Other types are unknown. So what do you mean?
The recommendation on what to report remains vague, and it is unclear why what should be reported.
This sentence was changed, following as well the other reviewer, to ‘null hypothesis significance testing is the statistical method of choice in biological, biomedical and social sciences to investigate if an effect is likely, even though it actually tests whether the observed data are probable, assuming there is no effect’
Changed, refers to Fisher 1925
I changed a little the sentence structure, which should make explicit that this is the condition probability.
This has been changed to ‘[…] to decide whether the evidence is worth additional investigation and/or replication (Fisher, 1971 p13)’
my mistake – the sentence structure is now ‘ not the probability of the null hypothesis p(H0), of being true,’ ; hope this makes more sense (and this way refers back to p(Obs>t|H0)
Fair enough – my point was to stress the fact that p value and effect size or H1 have very little in common, but yes that the part in common has to do with sample size. I left the conditioning on H0 but also point out the dependency on sample size.
The whole paragraph was changed to reflect a more philosophical take on scientific induction/reasoning. I hope this is clearer.
Changed to refer to equivalence testing
I rewrote this, as to show frequentist analysis can be used - I’m trying to sell Bayes more than any other approach.
I’m arguing we should report it all, that’s why there is no exhausting list – I can if needed.
Rejecting the Null Hypothesis Using Confidence Intervals

After a discussion on the two primary methods of statistical inference, viz. hypothesis tests and confidence intervals, it is shown that these two methods are actually equivalent.
In an introductory statistics class, there are three main topics that are taught: descriptive statistics and data visualizations, probability and sampling distributions, and statistical inference. Within statistical inference, there are two key methods of statistical inference that are taught, viz. confidence intervals and hypothesis testing . While these two methods are always taught when learning data science and related fields, it is rare that the relationship between these two methods is properly elucidated.
In this article, we’ll begin by defining and describing each method of statistical inference in turn and along the way, state what statistical inference is, and perhaps more importantly, what it isn’t. Then we’ll describe the relationship between the two. While it is typically the case that confidence intervals are taught before hypothesis testing when learning statistics, we’ll begin with the latter since it will allow us to define statistical significance.
Hypothesis Tests
The purpose of a hypothesis test is to answer whether random chance might be responsible for an observed effect. Hypothesis tests use sample statistics to test a hypothesis about population parameters. The null hypothesis, H 0 , is a statement that represents the assumed status quo regarding a variable or variables and it is always about a population characteristic. Some of the ways the null hypothesis is typically glossed are: the population variable is equal to a particular value or there is no difference between the population variables . For example:
- H 0 : μ = 61 in (The mean height of the population of American men is 69 inches)
- H 0 : p 1 -p 2 = 0 (The difference in the population proportions of women who prefer football over baseball and the population proportion of men who prefer football over baseball is 0.)
Note that the null hypothesis always has the equal sign.
The alternative hypothesis, denoted either H 1 or H a , is the statement that is opposed to the null hypothesis (e.g., the population variable is not equal to a particular value or there is a difference between the population variables ):
- H 1 : μ > 61 im (The mean height of the population of American men is greater than 69 inches.)
- H 1 : p 1 -p 2 ≠ 0 (The difference in the population proportions of women who prefer football over baseball and the population proportion of men who prefer football over baseball is not 0.)
The alternative hypothesis is typically the claim that the researcher hopes to show and it always contains the strict inequality symbols (‘<’ left-sided or left-tailed, ‘≠’ two-sided or two-tailed, and ‘>’ right-sided or right-tailed).
When carrying out a test of H 0 vs. H 1 , the null hypothesis H 0 will be rejected in favor of the alternative hypothesis only if the sample provides convincing evidence that H 0 is false. As such, a statistical hypothesis test is only capable of demonstrating strong support for the alternative hypothesis by rejecting the null hypothesis.
When the null hypothesis is not rejected, it does not mean that there is strong support for the null hypothesis (since it was assumed to be true); rather, only that there is not convincing evidence against the null hypothesis. As such, we never use the phrase “accept the null hypothesis.”
In the classical method of performing hypothesis testing, one would have to find what is called the test statistic and use a table to find the corresponding probability. Happily, due to the advancement of technology, one can use Python (as is done in the Flatiron’s Data Science Bootcamp ) and get the required value directly using a Python library like stats models . This is the p-value , which is short for the probability value.
The p-value is a measure of inconsistency between the hypothesized value for a population characteristic and the observed sample. The p -value is the probability, under the assumption the null hypothesis is true, of obtaining a test statistic value that is a measure of inconsistency between the null hypothesis and the data. If the p -value is less than or equal to the probability of the Type I error, then we can reject the null hypothesis and we have sufficient evidence to support the alternative hypothesis.
Typically the probability of a Type I error ɑ, more commonly known as the level of significance , is set to be 0.05, but it is often prudent to have it set to values less than that such as 0.01 or 0.001. Thus, if p -value ≤ ɑ, then we reject the null hypothesis and we interpret this as saying there is a statistically significant difference between the sample and the population. So if the p -value=0.03 ≤ 0.05 = ɑ, then we would reject the null hypothesis and so have statistical significance, whereas if p -value=0.08 ≥ 0.05 = ɑ, then we would fail to reject the null hypothesis and there would not be statistical significance.
Confidence Intervals
The other primary form of statistical inference are confidence intervals. While hypothesis tests are concerned with testing a claim, the purpose of a confidence interval is to estimate an unknown population characteristic. A confidence interval is an interval of plausible values for a population characteristic. They are constructed so that we have a chosen level of confidence that the actual value of the population characteristic will be between the upper and lower endpoints of the open interval.
The structure of an individual confidence interval is the sample estimate of the variable of interest margin of error. The margin of error is the product of a multiplier value and the standard error, s.e., which is based on the standard deviation and the sample size. The multiplier is where the probability, of level of confidence, is introduced into the formula.
The confidence level is the success rate of the method used to construct a confidence interval. A confidence interval estimating the proportion of American men who state they are an avid fan of the NFL could be (0.40, 0.60) with a 95% level of confidence. The level of confidence is not the probability that that population characteristic is in the confidence interval, but rather refers to the method that is used to construct the confidence interval.
For example, a 95% confidence interval would be interpreted as if one constructed 100 confidence intervals, then 95 of them would contain the true population characteristic.
Errors and Power
A Type I error, or a false positive, is the error of finding a difference that is not there, so it is the probability of incorrectly rejecting a true null hypothesis is ɑ, where ɑ is the level of significance. It follows that the probability of correctly failing to reject a true null hypothesis is the complement of it, viz. 1 – ɑ. For a particular hypothesis test, if ɑ = 0.05, then its complement would be 0.95 or 95%.
While we are not going to expand on these ideas, we note the following two related probabilities. A Type II error, or false negative, is the probability of failing to reject a false null hypothesis where the probability of a type II error is β and the power is the probability of correctly rejecting a false null hypothesis where power = 1 – β. In common statistical practice, one typically only speaks of the level of significance and the power.
The following table summarizes these ideas , where the column headers refer to what is actually the case, but is unknown. (If the truth or falsity of the null value was truly known, we wouldn’t have to do statistics.)

Hypothesis Tests and Confidence Intervals
Since hypothesis tests and confidence intervals are both methods of statistical inference, then it is reasonable to wonder if they are equivalent in some way. The answer is yes, which means that we can perform hypothesis testing using confidence intervals.
Returning to the example where we have an estimate of the proportion of American men that are avid fans of the NFL, we had (0.40, 0.60) at a 95% confidence level. As a hypothesis test, we could have the alternative hypothesis as H 1 ≠ 0.51. Since the null value of 0.51 lies within the confidence interval, then we would fail to reject the null hypothesis at ɑ = 0.05.
On the other hand, if H 1 ≠ 0.61, then since 0.61 is not in the confidence interval we can reject the null hypothesis at ɑ = 0.05. Note that the confidence level of 95% and the level of significance at ɑ = 0.05 = 5% are complements, which is the “H o is True” column in the above table.
In general, one can reject the null hypothesis given a null value and a confidence interval for a two-sided test if the null value is not in the confidence interval where the confidence level and level of significance are complements. For one-sided tests, one can still perform a hypothesis test with the confidence level and null value. Not only is there an added layer of complexity for this equivalence, it is the best practice to perform two-sided hypothesis tests since one is not prejudicing the direction of the alternative.
In this discussion of hypothesis testing and confidence intervals, we not only understand when these two methods of statistical inference can be equivalent, but now have a deeper understanding of statistical significance itself and therefore, statistical inference.
Learn More About Data Science at Flatiron
The curriculum in our Data Science Bootcamp incorporates the latest technologies, including artificial intelligence (AI) tools. Download the syllabus to see what you can learn, or book a 10-minute call with Admissions to learn about full-time and part-time attendance opportunities.
Disclaimer: The information in this blog is current as of February 28, 2024. Current policies, offerings, procedures, and programs may differ.

About Brendan Patrick Purdy
Brendan is the senior curriculum developer for data science at the Flatiron School. He holds degrees in mathematics, data science, and philosophy, and enjoys modeling neural networks with the Python library TensorFlow.
Related Posts

Learn to Code Python: Free Lesson for Beginners

The Case for Accessible Design

From Script to Screen: Introduction to Web Development Basics
Related resources.

Behind JavaScript, HTML/CSS, and SQL, Python is the fourth most popular language with 44.1% of developers. Check out this article on how you can learn this popular programming language for free.

Accessible design, defined as design that specifically considers the needs of users with disabilities, seems like an obvious win for designers. Yet many organizations are reluctant to invest in the process of planning, designing, and testing with accessibility in mind. What arguments can designers use to convince companies to prioritize accessibility?

Web development basics include HTML, Cascading Style Sheets (CSS), and JavaScript. Learn how all three are employed to bring websites to life.
Privacy Overview

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
13.1 Understanding Null Hypothesis Testing
Learning objectives.
- Explain the purpose of null hypothesis testing, including the role of sampling error.
- Describe the basic logic of null hypothesis testing.
- Describe the role of relationship strength and sample size in determining statistical significance and make reasonable judgments about statistical significance based on these two factors.
The Purpose of Null Hypothesis Testing
As we have seen, psychological research typically involves measuring one or more variables for a sample and computing descriptive statistics for that sample. In general, however, the researcher’s goal is not to draw conclusions about that sample but to draw conclusions about the population that the sample was selected from. Thus researchers must use sample statistics to draw conclusions about the corresponding values in the population. These corresponding values in the population are called parameters . Imagine, for example, that a researcher measures the number of depressive symptoms exhibited by each of 50 clinically depressed adults and computes the mean number of symptoms. The researcher probably wants to use this sample statistic (the mean number of symptoms for the sample) to draw conclusions about the corresponding population parameter (the mean number of symptoms for clinically depressed adults).
Unfortunately, sample statistics are not perfect estimates of their corresponding population parameters. This is because there is a certain amount of random variability in any statistic from sample to sample. The mean number of depressive symptoms might be 8.73 in one sample of clinically depressed adults, 6.45 in a second sample, and 9.44 in a third—even though these samples are selected randomly from the same population. Similarly, the correlation (Pearson’s r ) between two variables might be +.24 in one sample, −.04 in a second sample, and +.15 in a third—again, even though these samples are selected randomly from the same population. This random variability in a statistic from sample to sample is called sampling error . (Note that the term error here refers to random variability and does not imply that anyone has made a mistake. No one “commits a sampling error.”)
One implication of this is that when there is a statistical relationship in a sample, it is not always clear that there is a statistical relationship in the population. A small difference between two group means in a sample might indicate that there is a small difference between the two group means in the population. But it could also be that there is no difference between the means in the population and that the difference in the sample is just a matter of sampling error. Similarly, a Pearson’s r value of −.29 in a sample might mean that there is a negative relationship in the population. But it could also be that there is no relationship in the population and that the relationship in the sample is just a matter of sampling error.
In fact, any statistical relationship in a sample can be interpreted in two ways:
- There is a relationship in the population, and the relationship in the sample reflects this.
- There is no relationship in the population, and the relationship in the sample reflects only sampling error.
The purpose of null hypothesis testing is simply to help researchers decide between these two interpretations.
The Logic of Null Hypothesis Testing
Null hypothesis testing is a formal approach to deciding between two interpretations of a statistical relationship in a sample. One interpretation is called the null hypothesis (often symbolized H 0 and read as “H-naught”). This is the idea that there is no relationship in the population and that the relationship in the sample reflects only sampling error. Informally, the null hypothesis is that the sample relationship “occurred by chance.” The other interpretation is called the alternative hypothesis (often symbolized as H 1 ). This is the idea that there is a relationship in the population and that the relationship in the sample reflects this relationship in the population.
Again, every statistical relationship in a sample can be interpreted in either of these two ways: It might have occurred by chance, or it might reflect a relationship in the population. So researchers need a way to decide between them. Although there are many specific null hypothesis testing techniques, they are all based on the same general logic. The steps are as follows:
- Assume for the moment that the null hypothesis is true. There is no relationship between the variables in the population.
- Determine how likely the sample relationship would be if the null hypothesis were true.
- If the sample relationship would be extremely unlikely, then reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative hypothesis. If it would not be extremely unlikely, then retain the null hypothesis .
Following this logic, we can begin to understand why Mehl and his colleagues concluded that there is no difference in talkativeness between women and men in the population. In essence, they asked the following question: “If there were no difference in the population, how likely is it that we would find a small difference of d = 0.06 in our sample?” Their answer to this question was that this sample relationship would be fairly likely if the null hypothesis were true. Therefore, they retained the null hypothesis—concluding that there is no evidence of a sex difference in the population. We can also see why Kanner and his colleagues concluded that there is a correlation between hassles and symptoms in the population. They asked, “If the null hypothesis were true, how likely is it that we would find a strong correlation of +.60 in our sample?” Their answer to this question was that this sample relationship would be fairly unlikely if the null hypothesis were true. Therefore, they rejected the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative hypothesis—concluding that there is a positive correlation between these variables in the population.
A crucial step in null hypothesis testing is finding the likelihood of the sample result if the null hypothesis were true. This probability is called the p value . A low p value means that the sample result would be unlikely if the null hypothesis were true and leads to the rejection of the null hypothesis. A high p value means that the sample result would be likely if the null hypothesis were true and leads to the retention of the null hypothesis. But how low must the p value be before the sample result is considered unlikely enough to reject the null hypothesis? In null hypothesis testing, this criterion is called α (alpha) and is almost always set to .05. If there is less than a 5% chance of a result as extreme as the sample result if the null hypothesis were true, then the null hypothesis is rejected. When this happens, the result is said to be statistically significant . If there is greater than a 5% chance of a result as extreme as the sample result when the null hypothesis is true, then the null hypothesis is retained. This does not necessarily mean that the researcher accepts the null hypothesis as true—only that there is not currently enough evidence to conclude that it is true. Researchers often use the expression “fail to reject the null hypothesis” rather than “retain the null hypothesis,” but they never use the expression “accept the null hypothesis.”
The Misunderstood p Value
The p value is one of the most misunderstood quantities in psychological research (Cohen, 1994). Even professional researchers misinterpret it, and it is not unusual for such misinterpretations to appear in statistics textbooks!
The most common misinterpretation is that the p value is the probability that the null hypothesis is true—that the sample result occurred by chance. For example, a misguided researcher might say that because the p value is .02, there is only a 2% chance that the result is due to chance and a 98% chance that it reflects a real relationship in the population. But this is incorrect . The p value is really the probability of a result at least as extreme as the sample result if the null hypothesis were true. So a p value of .02 means that if the null hypothesis were true, a sample result this extreme would occur only 2% of the time.
You can avoid this misunderstanding by remembering that the p value is not the probability that any particular hypothesis is true or false. Instead, it is the probability of obtaining the sample result if the null hypothesis were true.
Role of Sample Size and Relationship Strength
Recall that null hypothesis testing involves answering the question, “If the null hypothesis were true, what is the probability of a sample result as extreme as this one?” In other words, “What is the p value?” It can be helpful to see that the answer to this question depends on just two considerations: the strength of the relationship and the size of the sample. Specifically, the stronger the sample relationship and the larger the sample, the less likely the result would be if the null hypothesis were true. That is, the lower the p value. This should make sense. Imagine a study in which a sample of 500 women is compared with a sample of 500 men in terms of some psychological characteristic, and Cohen’s d is a strong 0.50. If there were really no sex difference in the population, then a result this strong based on such a large sample should seem highly unlikely. Now imagine a similar study in which a sample of three women is compared with a sample of three men, and Cohen’s d is a weak 0.10. If there were no sex difference in the population, then a relationship this weak based on such a small sample should seem likely. And this is precisely why the null hypothesis would be rejected in the first example and retained in the second.
Of course, sometimes the result can be weak and the sample large, or the result can be strong and the sample small. In these cases, the two considerations trade off against each other so that a weak result can be statistically significant if the sample is large enough and a strong relationship can be statistically significant even if the sample is small. Table 13.1 “How Relationship Strength and Sample Size Combine to Determine Whether a Result Is Statistically Significant” shows roughly how relationship strength and sample size combine to determine whether a sample result is statistically significant. The columns of the table represent the three levels of relationship strength: weak, medium, and strong. The rows represent four sample sizes that can be considered small, medium, large, and extra large in the context of psychological research. Thus each cell in the table represents a combination of relationship strength and sample size. If a cell contains the word Yes , then this combination would be statistically significant for both Cohen’s d and Pearson’s r . If it contains the word No , then it would not be statistically significant for either. There is one cell where the decision for d and r would be different and another where it might be different depending on some additional considerations, which are discussed in Section 13.2 “Some Basic Null Hypothesis Tests”
Table 13.1 How Relationship Strength and Sample Size Combine to Determine Whether a Result Is Statistically Significant
Although Table 13.1 “How Relationship Strength and Sample Size Combine to Determine Whether a Result Is Statistically Significant” provides only a rough guideline, it shows very clearly that weak relationships based on medium or small samples are never statistically significant and that strong relationships based on medium or larger samples are always statistically significant. If you keep this in mind, you will often know whether a result is statistically significant based on the descriptive statistics alone. It is extremely useful to be able to develop this kind of intuitive judgment. One reason is that it allows you to develop expectations about how your formal null hypothesis tests are going to come out, which in turn allows you to detect problems in your analyses. For example, if your sample relationship is strong and your sample is medium, then you would expect to reject the null hypothesis. If for some reason your formal null hypothesis test indicates otherwise, then you need to double-check your computations and interpretations. A second reason is that the ability to make this kind of intuitive judgment is an indication that you understand the basic logic of this approach in addition to being able to do the computations.
Statistical Significance Versus Practical Significance
Table 13.1 “How Relationship Strength and Sample Size Combine to Determine Whether a Result Is Statistically Significant” illustrates another extremely important point. A statistically significant result is not necessarily a strong one. Even a very weak result can be statistically significant if it is based on a large enough sample. This is closely related to Janet Shibley Hyde’s argument about sex differences (Hyde, 2007). The differences between women and men in mathematical problem solving and leadership ability are statistically significant. But the word significant can cause people to interpret these differences as strong and important—perhaps even important enough to influence the college courses they take or even who they vote for. As we have seen, however, these statistically significant differences are actually quite weak—perhaps even “trivial.”
This is why it is important to distinguish between the statistical significance of a result and the practical significance of that result. Practical significance refers to the importance or usefulness of the result in some real-world context. Many sex differences are statistically significant—and may even be interesting for purely scientific reasons—but they are not practically significant. In clinical practice, this same concept is often referred to as “clinical significance.” For example, a study on a new treatment for social phobia might show that it produces a statistically significant positive effect. Yet this effect still might not be strong enough to justify the time, effort, and other costs of putting it into practice—especially if easier and cheaper treatments that work almost as well already exist. Although statistically significant, this result would be said to lack practical or clinical significance.
Key Takeaways
- Null hypothesis testing is a formal approach to deciding whether a statistical relationship in a sample reflects a real relationship in the population or is just due to chance.
- The logic of null hypothesis testing involves assuming that the null hypothesis is true, finding how likely the sample result would be if this assumption were correct, and then making a decision. If the sample result would be unlikely if the null hypothesis were true, then it is rejected in favor of the alternative hypothesis. If it would not be unlikely, then the null hypothesis is retained.
- The probability of obtaining the sample result if the null hypothesis were true (the p value) is based on two considerations: relationship strength and sample size. Reasonable judgments about whether a sample relationship is statistically significant can often be made by quickly considering these two factors.
- Statistical significance is not the same as relationship strength or importance. Even weak relationships can be statistically significant if the sample size is large enough. It is important to consider relationship strength and the practical significance of a result in addition to its statistical significance.
- Discussion: Imagine a study showing that people who eat more broccoli tend to be happier. Explain for someone who knows nothing about statistics why the researchers would conduct a null hypothesis test.
Practice: Use Table 13.1 “How Relationship Strength and Sample Size Combine to Determine Whether a Result Is Statistically Significant” to decide whether each of the following results is statistically significant.
- The correlation between two variables is r = −.78 based on a sample size of 137.
- The mean score on a psychological characteristic for women is 25 ( SD = 5) and the mean score for men is 24 ( SD = 5). There were 12 women and 10 men in this study.
- In a memory experiment, the mean number of items recalled by the 40 participants in Condition A was 0.50 standard deviations greater than the mean number recalled by the 40 participants in Condition B.
- In another memory experiment, the mean scores for participants in Condition A and Condition B came out exactly the same!
- A student finds a correlation of r = .04 between the number of units the students in his research methods class are taking and the students’ level of stress.
Cohen, J. (1994). The world is round: p < .05. American Psychologist, 49 , 997–1003.
Hyde, J. S. (2007). New directions in the study of gender similarities and differences. Current Directions in Psychological Science , 16 , 259–263.
Research Methods in Psychology Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
If the collected data does not meet the expectation of the null hypothesis, a researcher can conclude that the data lacks sufficient evidence to back up the null hypothesis, and thus the null hypothesis is rejected. Rejecting the null hypothesis means that a relationship does exist between a set of variables and the effect is statistically ...
The null hypothesis in statistics states that there is no difference between groups or no relationship between variables. It is one of two mutually exclusive hypotheses about a population in a hypothesis test. When your sample contains sufficient evidence, you can reject the null and conclude that the effect is statistically significant.
A hypothesis test is a formal statistical test we use to reject or fail to reject a statistical hypothesis. We always use the following steps to perform a hypothesis test: Step 1: State the null and alternative hypotheses. The null hypothesis, denoted as H0, is the hypothesis that the sample data occurs purely from chance.
Use the P-Value method to support or reject null hypothesis. Step 1: State the null hypothesis and the alternate hypothesis ("the claim"). H o :p ≤ 0.23; H 1 :p > 0.23 (claim) Step 2: Compute by dividing the number of positive respondents from the number in the random sample: 63 / 210 = 0.3.
Consequently, we fail to reject it. Failing to reject the null indicates that our sample did not provide sufficient evidence to conclude that the effect exists. However, at the same time, that lack of evidence doesn't prove that the effect does not exist. Capturing all that information leads to the convoluted wording!
Key Takeaways: The Null Hypothesis. • In a test of significance, the null hypothesis states that there is no meaningful relationship between two measured phenomena. • By comparing the null hypothesis to an alternative hypothesis, scientists can either reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis. • The null hypothesis cannot be positively ...
Let's return finally to the question of whether we reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis. If our statistical analysis shows that the significance level is below the cut-off value we have set (e.g., either 0.05 or 0.01), we reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative hypothesis. Alternatively, if the significance level is above ...
The null hypothesis is the claim that there's no effect in the population. If the sample provides enough evidence against the claim that there's no effect in the population (p ≤ α), then we can reject the null hypothesis. Otherwise, we fail to reject the null hypothesis. Although "fail to reject" may sound awkward, it's the only ...
A crucial step in null hypothesis testing is finding the likelihood of the sample result if the null hypothesis were true. This probability is called the p value. A low p value means that the sample result would be unlikely if the null hypothesis were true and leads to the rejection of the null hypothesis. A high p value means that the sample ...
There are 5 main steps in hypothesis testing: State your research hypothesis as a null hypothesis and alternate hypothesis (H o) and (H a or H 1 ). Collect data in a way designed to test the hypothesis. Perform an appropriate statistical test. Decide whether to reject or fail to reject your null hypothesis. Present the findings in your results ...
Review. In a hypothesis test, sample data is evaluated in order to arrive at a decision about some type of claim.If certain conditions about the sample are satisfied, then the claim can be evaluated for a population. In a hypothesis test, we: Evaluate the null hypothesis, typically denoted with \(H_{0}\).The null is not rejected unless the hypothesis test shows otherwise.
The first step in hypothesis testing is to set up two competing hypotheses. The hypotheses are the most important aspect. If the hypotheses are incorrect, your conclusion will also be incorrect. The two hypotheses are named the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis. The null hypothesis is typically denoted as H 0.
Null hypothesis. In scientific research, the null hypothesis (often denoted H0) [1] is the claim that the effect being studied does not exist. Note that the term "effect" here is not meant to imply a causative relationship. The null hypothesis can also be described as the hypothesis in which no relationship exists between two sets of data or ...
A crucial step in null hypothesis testing is finding the likelihood of the sample result if the null hypothesis were true. This probability is called the p value. A low p value means that the sample result would be unlikely if the null hypothesis were true and leads to the rejection of the null hypothesis. A p value that is not low means that ...
Does this mean that we accept the null? Not really. In general, failure to reject does not constitute, per se, strong evidence that the null hypothesis is true. Remember the analogy between hypothesis testing and a criminal trial. In a trial, when the defendant is declared not guilty, this does not mean that the defendant is innocent.
The actual test begins by considering two hypotheses.They are called the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis.These hypotheses contain opposing viewpoints. H 0, the —null hypothesis: a statement of no difference between sample means or proportions or no difference between a sample mean or proportion and a population mean or proportion. In other words, the difference equals 0.
There are two ways to indicate that the null hypothesis is not rejected. 'Accept' the null hypothesis and 'fail to reject' the null hypothesis. Superficially, both these phrases mean the same, but in statistics, the meanings are somewhat different. The phrase 'accept the null hypothesis' implies that the null hypothesis is by nature true, and ...
Review. In a hypothesis test, sample data is evaluated in order to arrive at a decision about some type of claim.If certain conditions about the sample are satisfied, then the claim can be evaluated for a population. In a hypothesis test, we: Evaluate the null hypothesis, typically denoted with \(H_{0}\).The null is not rejected unless the hypothesis test shows otherwise.
The critical value for conducting the right-tailed test H0 : μ = 3 versus HA : μ > 3 is the t -value, denoted t\ (\alpha\), n - 1, such that the probability to the right of it is \ (\alpha\). It can be shown using either statistical software or a t -table that the critical value t 0.05,14 is 1.7613. That is, we would reject the null ...
Abstract: "null hypothesis significance testing is the statistical method of choice in biological, biomedical and social sciences to investigate if an effect is likely". No, NHST is the method to test the hypothesis of no effect. I agree - yet people use it to investigate (not test) if an effect is likely.
As such, a statistical hypothesis test is only capable of demonstrating strong support for the alternative hypothesis by rejecting the null hypothesis. When the null hypothesis is not rejected, it does not mean that there is strong support for the null hypothesis (since it was assumed to be true); rather, only that there is not convincing ...
A crucial step in null hypothesis testing is finding the likelihood of the sample result if the null hypothesis were true. This probability is called the p value. A low p value means that the sample result would be unlikely if the null hypothesis were true and leads to the rejection of the null hypothesis. A high p value means that the sample ...
Question: Suppose the null hypothesis is rejected. State the conclusion based on the results of the test.Three years ago, the mean price of a single-family home was $243 comma 705. A real estate broker believes that the mean price has decreased since then. Suppose the null hypothesis is rejected. State the conclusion based on the ...