What are supporting details in a body paragraph?

This is the first of three chapters about Supporting Details . To complete this reader, read each chapter carefully and then unlock and complete our materials to check your understanding.
– Review the various body-paragraph elements which are useful in academic essays
– Explore the importance of supporting details
– Introduce the various types of supporting details, such as evidence, examples and explanations
Chapter 1: What are supporting details in a body paragraph?
Chapter 2: How can I add evidence, examples and explanation?
Chapter 3: Why are implications important in body support?

Before you begin reading...
- video and audio texts
- knowledge checks and quizzes
- skills practices, tasks and assignments

The body of an essay is its most important section, and the trickiest part to get right. While the introduction and the conclusion can follow a fairly straightforward pattern, for the body section there is more variation in a how a student can structure their writing to create an effective essay. Thankfully, whether you’re writing a compare and contrast , evaluative or problem-solution essay, there are still a number of key body-paragraph elements you should try to include to help guarantee high grades – and the most important of these are called supporting details .
In this short three-chapter reader, we explore the concept of supporting details (Chapter 1), the different types of supporting detail on offer (Chapter 2) and why providing implications in your support is so important (Chapter 3). For a more general introduction to body sections, students may wish to first visit our short reader about body paragraphs .
Body-Section Elements
There are three key essay elements within a body paragraph that students should make sure they’ve included before submitting their assignment . These are topic sentences , supporting details and summary-transition sentences . An example of each element is provided for you below, taken from our example problem-solution essay about air pollution. Read these excerpts carefully and see if you can guess the purpose of each element:

Were you able to determine the following purpose for each element?
Topic Sentence = inform the reader of the main idea of the paragraph (which should connect with the introductory thesis, i.e., the focus of the whole essay)
Supporting detail = provide support for the main idea(s) stated in the topic sentence, usually by using evidence (facts and statistics), examples and explanations
Summary-transition sentence = remind the reader of the main idea being explored in the paragraph, summarise the key arguments or findings, or transition (move smoothly) from the main idea of this paragraph to the main idea of the next
The Importance of Supporting Details
Where topic and summary sentences take up only about 20% of a body paragraph, the remaining 80% of that paragraph should be dedicated to an exploration of the topic-sentence’s main idea(s). This is done through the inclusion of a variety of convincing and related supporting details. Because the key aim of an academic essay is to be persuasive, logical and concise , persuading your reader of your opinion or stance will require the inclusion and explanation of a number of sources and source-based experiments and examples in the form of supporting details.

Whenever you include statistics or facts, or case studies or historical events, or when you explain or contextualise such evidence, each of these sentences forms part of a supporting detail, and without such details your essay would have very little substance. That essay would not convince your reader of your viewpoint, and it would not receive a high grade.
Supporting-Detail Elements
Supporting details have a few dif ferent elements that students are encouraged to include, namely evidence, examples, explanation and implications. However, depending on the essay type being written, sentences which are dedicated to providing solutions to problems or to describing the effects caused by a particular situation may also be required.
To see examples of these elements, let’s look at the first body paragraph of an example evaluative essay which answers the question “Global warming is a relatively new phenomenon that may be providing more advantages than disadvantages for the future of healthy ecosystems on this planet. Discuss.”
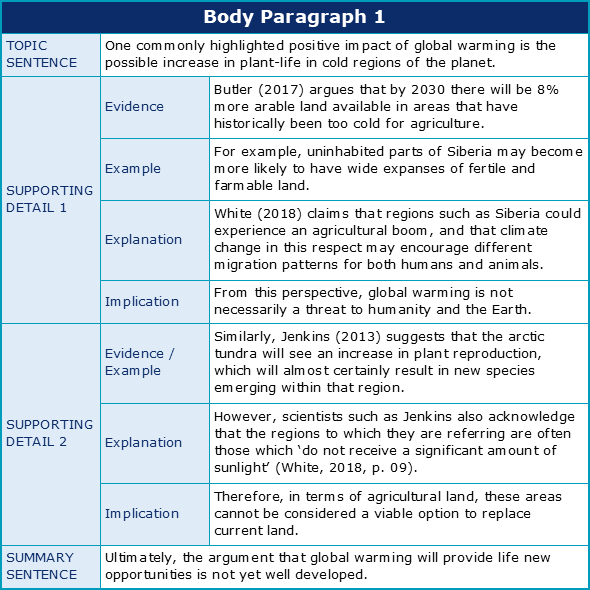
By studying this table carefully, you should be able to see how a body paragraph may have multiple supporting details (this paragraph has two) and how each supporting detail may be comprised of a number of elements, such as evidence, examples and explanation. For a closer look at how these supporting-detail elements function, and for guidance on how to include them in your own academic essay, continue reading on to Chapter 2 of this short reader.
To reference this reader:
Academic Marker (2022) Supporting Details . Available at: https://academicmarker.com/essay-writing/body-paragraphs/supporting-details/ (Accessed: Date Month Year).
- Massachusetts Libraries
- Open Oregon
- University of Waterloo Writing and Communication Center
Downloadables
Once you’ve completed all three chapters in this short reader about Supporting Details , you might then wish to download our Chapter Worksheets to check your progress or print for your students. These professional PDF worksheets can be easily accessed for only a few Academic Marks .
Chapter 1 explores the topic: What are supporting details in a body paragraph? Our Chapter 1 Worksheet (containing guidance, activities and answer keys) can be accessed here at the click of a button.
Chapter 2 explores the topic: How can I add evidence, examples and explanation? Our Chapter 2 Worksheet (containing guidance, activities and answer keys) can be accessed here at the click of a button.
Chapter 3 explores the topic: Why are implications important in body support? Our Chapter 3 Worksheet (containing guidance, activities and answer keys) can be accessed here at the click of a button.
To save yourself 2 Marks , click on the button below to gain unlimited access to all of our Supporting Details Chapter Worksheets. This All-in-1 Pack includes every chapter, activity and answer key related this topic in one handy and professional PDF.
Collect Academic Marks
- 15 Marks for joining
- 3 Marks for daily e-learning
- 10-20 for feedback and testimonials
- 10-50 for referring others

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
9.2 Writing Body Paragraphs
Learning objectives.
- Select primary support related to your thesis.
- Support your topic sentences.
If your thesis gives the reader a roadmap to your essay, then body paragraphs should closely follow that map. The reader should be able to predict what follows your introductory paragraph by simply reading the thesis statement.
The body paragraphs present the evidence you have gathered to confirm your thesis. Before you begin to support your thesis in the body, you must find information from a variety of sources that support and give credit to what you are trying to prove.
Select Primary Support for Your Thesis
Without primary support, your argument is not likely to be convincing. Primary support can be described as the major points you choose to expand on your thesis. It is the most important information you select to argue for your point of view. Each point you choose will be incorporated into the topic sentence for each body paragraph you write. Your primary supporting points are further supported by supporting details within the paragraphs.
Remember that a worthy argument is backed by examples. In order to construct a valid argument, good writers conduct lots of background research and take careful notes. They also talk to people knowledgeable about a topic in order to understand its implications before writing about it.
Identify the Characteristics of Good Primary Support
In order to fulfill the requirements of good primary support, the information you choose must meet the following standards:
- Be specific. The main points you make about your thesis and the examples you use to expand on those points need to be specific. Use specific examples to provide the evidence and to build upon your general ideas. These types of examples give your reader something narrow to focus on, and if used properly, they leave little doubt about your claim. General examples, while they convey the necessary information, are not nearly as compelling or useful in writing because they are too obvious and typical.
- Be relevant to the thesis. Primary support is considered strong when it relates directly to the thesis. Primary support should show, explain, or prove your main argument without delving into irrelevant details. When faced with lots of information that could be used to prove your thesis, you may think you need to include it all in your body paragraphs. But effective writers resist the temptation to lose focus. Choose your examples wisely by making sure they directly connect to your thesis.
- Be detailed. Remember that your thesis, while specific, should not be very detailed. The body paragraphs are where you develop the discussion that a thorough essay requires. Using detailed support shows readers that you have considered all the facts and chosen only the most precise details to enhance your point of view.
Prewrite to Identify Primary Supporting Points for a Thesis Statement
Recall that when you prewrite you essentially make a list of examples or reasons why you support your stance. Stemming from each point, you further provide details to support those reasons. After prewriting, you are then able to look back at the information and choose the most compelling pieces you will use in your body paragraphs.
Choose one of the following working thesis statements. On a separate sheet of paper, write for at least five minutes using one of the prewriting techniques you learned in Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” .
- Unleashed dogs on city streets are a dangerous nuisance.
- Students cheat for many different reasons.
- Drug use among teens and young adults is a problem.
- The most important change that should occur at my college or university is ____________________________________________.
Select the Most Effective Primary Supporting Points for a Thesis Statement
After you have prewritten about your working thesis statement, you may have generated a lot of information, which may be edited out later. Remember that your primary support must be relevant to your thesis. Remind yourself of your main argument, and delete any ideas that do not directly relate to it. Omitting unrelated ideas ensures that you will use only the most convincing information in your body paragraphs. Choose at least three of only the most compelling points. These will serve as the topic sentences for your body paragraphs.
Refer to the previous exercise and select three of your most compelling reasons to support the thesis statement. Remember that the points you choose must be specific and relevant to the thesis. The statements you choose will be your primary support points, and you will later incorporate them into the topic sentences for the body paragraphs.
Collaboration
Please share with a classmate and compare your answers.
When you support your thesis, you are revealing evidence. Evidence includes anything that can help support your stance. The following are the kinds of evidence you will encounter as you conduct your research:
- Facts. Facts are the best kind of evidence to use because they often cannot be disputed. They can support your stance by providing background information on or a solid foundation for your point of view. However, some facts may still need explanation. For example, the sentence “The most populated state in the United States is California” is a pure fact, but it may require some explanation to make it relevant to your specific argument.
- Judgments. Judgments are conclusions drawn from the given facts. Judgments are more credible than opinions because they are founded upon careful reasoning and examination of a topic.
- Testimony. Testimony consists of direct quotations from either an eyewitness or an expert witness. An eyewitness is someone who has direct experience with a subject; he adds authenticity to an argument based on facts. An expert witness is a person who has extensive experience with a topic. This person studies the facts and provides commentary based on either facts or judgments, or both. An expert witness adds authority and credibility to an argument.
- Personal observation. Personal observation is similar to testimony, but personal observation consists of your testimony. It reflects what you know to be true because you have experiences and have formed either opinions or judgments about them. For instance, if you are one of five children and your thesis states that being part of a large family is beneficial to a child’s social development, you could use your own experience to support your thesis.
Writing at Work
In any job where you devise a plan, you will need to support the steps that you lay out. This is an area in which you would incorporate primary support into your writing. Choosing only the most specific and relevant information to expand upon the steps will ensure that your plan appears well-thought-out and precise.
You can consult a vast pool of resources to gather support for your stance. Citing relevant information from reliable sources ensures that your reader will take you seriously and consider your assertions. Use any of the following sources for your essay: newspapers or news organization websites, magazines, encyclopedias, and scholarly journals, which are periodicals that address topics in a specialized field.
Choose Supporting Topic Sentences
Each body paragraph contains a topic sentence that states one aspect of your thesis and then expands upon it. Like the thesis statement, each topic sentence should be specific and supported by concrete details, facts, or explanations.
Each body paragraph should comprise the following elements.
topic sentence + supporting details (examples, reasons, or arguments)
As you read in Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” , topic sentences indicate the location and main points of the basic arguments of your essay. These sentences are vital to writing your body paragraphs because they always refer back to and support your thesis statement. Topic sentences are linked to the ideas you have introduced in your thesis, thus reminding readers what your essay is about. A paragraph without a clearly identified topic sentence may be unclear and scattered, just like an essay without a thesis statement.
Unless your teacher instructs otherwise, you should include at least three body paragraphs in your essay. A five-paragraph essay, including the introduction and conclusion, is commonly the standard for exams and essay assignments.
Consider the following the thesis statement:
Author J.D. Salinger relied primarily on his personal life and belief system as the foundation for the themes in the majority of his works.
The following topic sentence is a primary support point for the thesis. The topic sentence states exactly what the controlling idea of the paragraph is. Later, you will see the writer immediately provide support for the sentence.
Salinger, a World War II veteran, suffered from posttraumatic stress disorder, a disorder that influenced themes in many of his works.
In Note 9.19 “Exercise 2” , you chose three of your most convincing points to support the thesis statement you selected from the list. Take each point and incorporate it into a topic sentence for each body paragraph.
Supporting point 1: ____________________________________________
Topic sentence: ____________________________________________
Supporting point 2: ____________________________________________
Supporting point 3: ____________________________________________
Draft Supporting Detail Sentences for Each Primary Support Sentence
After deciding which primary support points you will use as your topic sentences, you must add details to clarify and demonstrate each of those points. These supporting details provide examples, facts, or evidence that support the topic sentence.
The writer drafts possible supporting detail sentences for each primary support sentence based on the thesis statement:
Thesis statement: Unleashed dogs on city streets are a dangerous nuisance.
Supporting point 1: Dogs can scare cyclists and pedestrians.
Supporting details:
- Cyclists are forced to zigzag on the road.
- School children panic and turn wildly on their bikes.
- People who are walking at night freeze in fear.
Supporting point 2:
Loose dogs are traffic hazards.
- Dogs in the street make people swerve their cars.
- To avoid dogs, drivers run into other cars or pedestrians.
- Children coaxing dogs across busy streets create danger.
Supporting point 3: Unleashed dogs damage gardens.
- They step on flowers and vegetables.
- They destroy hedges by urinating on them.
- They mess up lawns by digging holes.
The following paragraph contains supporting detail sentences for the primary support sentence (the topic sentence), which is underlined.
Salinger, a World War II veteran, suffered from posttraumatic stress disorder, a disorder that influenced the themes in many of his works. He did not hide his mental anguish over the horrors of war and once told his daughter, “You never really get the smell of burning flesh out of your nose, no matter how long you live.” His short story “A Perfect Day for a Bananafish” details a day in the life of a WWII veteran who was recently released from an army hospital for psychiatric problems. The man acts questionably with a little girl he meets on the beach before he returns to his hotel room and commits suicide. Another short story, “For Esmé – with Love and Squalor,” is narrated by a traumatized soldier who sparks an unusual relationship with a young girl he meets before he departs to partake in D-Day. Finally, in Salinger’s only novel, The Catcher in the Rye , he continues with the theme of posttraumatic stress, though not directly related to war. From a rest home for the mentally ill, sixteen-year-old Holden Caulfield narrates the story of his nervous breakdown following the death of his younger brother.
Using the three topic sentences you composed for the thesis statement in Note 9.18 “Exercise 1” , draft at least three supporting details for each point.
Thesis statement: ____________________________________________
Primary supporting point 1: ____________________________________________
Supporting details: ____________________________________________
Primary supporting point 2: ____________________________________________
Primary supporting point 3: ____________________________________________
You have the option of writing your topic sentences in one of three ways. You can state it at the beginning of the body paragraph, or at the end of the paragraph, or you do not have to write it at all. This is called an implied topic sentence. An implied topic sentence lets readers form the main idea for themselves. For beginning writers, it is best to not use implied topic sentences because it makes it harder to focus your writing. Your instructor may also want to clearly identify the sentences that support your thesis. For more information on the placement of thesis statements and implied topic statements, see Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” .
Print out the first draft of your essay and use a highlighter to mark your topic sentences in the body paragraphs. Make sure they are clearly stated and accurately present your paragraphs, as well as accurately reflect your thesis. If your topic sentence contains information that does not exist in the rest of the paragraph, rewrite it to more accurately match the rest of the paragraph.
Key Takeaways
- Your body paragraphs should closely follow the path set forth by your thesis statement.
- Strong body paragraphs contain evidence that supports your thesis.
- Primary support comprises the most important points you use to support your thesis.
- Strong primary support is specific, detailed, and relevant to the thesis.
- Prewriting helps you determine your most compelling primary support.
- Evidence includes facts, judgments, testimony, and personal observation.
- Reliable sources may include newspapers, magazines, academic journals, books, encyclopedias, and firsthand testimony.
- A topic sentence presents one point of your thesis statement while the information in the rest of the paragraph supports that point.
- A body paragraph comprises a topic sentence plus supporting details.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Supporting Detail in Composition and Speech
Glossary of Grammatical and Rhetorical Terms
Cultura RM/Gu/Getty Images
- An Introduction to Punctuation
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
In a composition or speech , a supporting detail is a fact, description , example , quotation , anecdote , or other item of information used to back up a claim , illustrate a point, explain an idea, or otherwise support a thesis or topic sentence .
Depending on a number of factors (including topic , purpose , and audience ), supporting details may be drawn from research or the personal experience of the writer or speaker. Even "the smallest detail," says Barry Lane, "can open up a new way of seeing the subject" ( Writing as a Road to Self-Discovery ).
Examples of Supporting Details in Paragraphs
- Descriptive Details in Stegner's "Town Dump"
- Hot Hands, by Stephen Jay Gould
- Poe's New York in the 1840s
- Status Details in Tom Wolfe's Descriptions
Examples and Observations
- "Good writers provide sufficient details such as examples, facts, quotations , and definitions to support their ideas. Writers use this information, known as supporting detail , to explain, clarify, or illustrate their main points. Without such specific material, a writer's ideas remain abstract and unconvincing. Experienced writers try, whenever possible, to show rather than simply tell their readers what their ideas mean." (Peter S. Gardner, New Directions: Reading, Writing, and Critical Thinking , 2nd ed. Cambridge University Press, 2005)
Supporting Details in a Paragraph on Solitary Prison Cells
- "Supermax prisons are exactingly designed to kill souls. A solitary cell (referred to as the 'hole' or the 'box') is typically between seventy and eighty square feet, and prisoners are kept alone in them for twenty-three hours a day, with one hour alone in a 'yard' barely twice the size of the cell and a shower perhaps three times a week. Practically all human contact is mediated by bars, mesh or manacles, and many cells are windowless, with an inmate’s exposure to the world outside the cell limited to the door slots through which food is passed by the gloved hands of jailers, often in the form of 'the loaf,' a disgusting pressed amalgam of pulverized food. Cells are, in most cases, deliberately colorless (any 'aesthetic' ingredient is considered an inappropriate privilege in an environment that seeks to level all distinctions to the basest level) and are built--bunks and all--from bare concrete; the only furnishing is a stainless steel toilet-and-sink combo positioned to deny privacy. The lighting is never turned off." (Michael Sorkin, "Drawing the Line." The Nation , September 16, 2013)
Supporting Details in a Paragraph on Baby Boomers
- "The truth is our generation was spoiled rotten from the start. We spent the entire 1950s on our butts in front of the television while Mom fed us Twinkies and Ring Dings through strawberry Flavor Straws and Dad ransacked the toy stores looking for hundred-mile-an-hour streamlined Schwinns, Daisy air howitzers, Lionel train sets larger than the New York Central system, and other novelties to keep us amused during the few hours when Pinky Lee and My Friend Flicka weren't on the air." (P.J. O'Rourke, "The 1987 Stock Market Crash." Age and Guile, Beat Youth, Innocence, and a Bad Haircut . Atlantic Monthly Press, 1995)
Supporting Details in a Paragraph on Segregation
- "In practice, of course, the 'separate but equal' doctrine perpetuated an oppressive and humiliating reality. To express the judgment that African Americans were inferior and that white people needed to be protected from their contaminating presence, black people were consigned to the back of the bus, directed to use distinct drinking fountains and telephone booths, excluded altogether from white schools and hospitals, permitted to visit zoos and museums only on certain days, confined to designated areas in courtrooms, and sworn in as witnesses using racially differentiated Bibles. Under segregation, white people routinely declined to bestow courtesy titles such as 'Mr.' or 'Mrs.' on black people, referring to them simply as 'boy' or 'girl,' regardless of age. Stores prohibited African Americans from trying on clothes before purchase. Telephone directories marked black residents by placing 'col' (for colored) in parentheses next to their names. Newspapers refused to carry notices for black weddings." (Randall Kennedy, "The Civil Rights Act's Unsung Victory." Harper's , June 2014)
Rachel Carson's Use of Supporting Details
- "For the first time in the history of the world, every human being is now subjected to contact with dangerous chemicals, from the moment of conception until death. In the less than two decades of their use, the synthetic pesticides have been so thoroughly distributed throughout the animate and inanimate world that they occur virtually everywhere. They have been recovered from most of the major river systems and even from streams of groundwater flowing unseen through the earth. Residues of these chemicals linger in soil to which they may have been applied a dozen years before. They have entered and lodged in the bodies of fish, birds, reptiles, and domestic and wild animals so universally that scientists carrying on animal experiments find it almost impossible to locate subjects free from such contamination. They have been found in fish in remote mountain lakes, in earthworms burrowing in soil, in the eggs of birds--and in man himself. For these chemicals are now stored in the bodies of the vast majority of human beings, regardless. of age. They occur in the mother's milk, and probably in the tissues of the unborn child." (Rachel Carson, Silent Spring . Houghton Mifflin, 1962)
The Purpose of Supporting Details
- "Once you have constructed a topic sentence made up of the topic and its controlling idea, you are ready to support your statement with details. The quality and number of these details will largely determine the effectiveness of the writing. . . . "As you choose your supporting details , keep in mind that the readers do not necessarily have to agree with your point of view. However, your supporting details must be good enough to make your readers at least respect your attitude. Your goal should be to educate your readers. Try to give them some understanding of your subject. Don't assume they know about your topic or are interested in it. If you provide enough specific details your readers will feel they have learned something new about the subject, and this alone is a satisfying experience for most people. Effective supporting details will encourage readers to keep on reading." (Sandra Scarry and John Scarry, The Writer's Workplace With Readings: Building College Writing Skills , 7th ed. Wadsworth, 2011)
Organizing Supporting Details in a Paragraph
- "Each body paragraph should contain only one main idea, and no detail or example should be in a paragraph if it doesn't support the topic sentence or help to transition from one paragraph to another. . . .
- "[H]ere's the way to organize a paragraph: Topic sentence First supporting detail or example Second supporting detail or example Third supporting detail or example Concluding or transitional sentence You should have several details to support each topic sentence. If you find that you have little to say after writing the topic sentence, ask yourself what details or examples will make your reader believe that the topic sentence is true for you." (Paige L. Wilson and Teresa Ferster Glazier, The Least You Should Know about English, Form B , 10th ed. Wadsworth, 2009)
Selective Supporting Details
- " Select details carefully . Good storytelling requires the purposeful selection of details. Some beginning writers include either the wrong details or more details than the effective relating of the event requires. In your narrative writing , you should select details that help you to convey to your readers the point of your essay. This is what [George] Orwell did in the passage from "A Hanging" [paragraphs 9 and 10]. The detail of the condemned man avoiding the puddle of water related to Orwell's purpose in telling the story and to the meaning he saw in it." (Morton A. Miller, Reading and Writing Short Essays . Random House, 1980)
- Unity in Composition
- Definition and Examples of Body Paragraphs in Composition
- Understanding Organization in Composition and Speech
- Topic In Composition and Speech
- How to Structure an Essay
- What Is Expository Writing?
- Outlines for Every Type of Writing Composition
- Development in Composition: Building an Essay
- An Essay Revision Checklist
- Understanding General-to-Specific Order in Composition
- The Ultimate Guide to the 5-Paragraph Essay
- Definition and Examples of Analysis in Composition
- How to Teach Topic Sentences Using Models
- Paragraph Length in Compositions and Reports
- detail (composition)
- Paragraph Writing
Supporting Details: Understanding Their Importance in Learning
When writing a piece of text, it is important to have a clear and concise main idea or topic sentence. However, in order to fully support and develop this idea, it is necessary to include supporting details. Supporting details are specific pieces of information that provide evidence and credibility to the main idea or topic sentence. They can be found in various forms, such as facts, examples, statistics, and explanations.

Understanding Supporting Details
When writing, supporting details are crucial to effectively convey your message. Supporting details are pieces of factual information that back up the main idea or topic sentence you are trying to convey. They provide clarification to the reader by explaining, describing, and illustrating the main idea within the text.
There are many different types of supporting details, and the type used will depend on the purpose and audience of your writing. Some examples of supporting details include:
- Facts and statistics
- Examples and anecdotes
- Quotations and expert opinions
- Definitions and explanations
- Descriptions and sensory details
When using supporting details, it is important to ensure that they are relevant and accurate. They should also be organized in a logical and coherent manner to help the reader understand the main idea or argument being presented.
To effectively use supporting details, it is helpful to start by identifying the main idea or topic sentence of your writing. Once you have identified the main idea, you can then brainstorm relevant supporting details that will help to clarify and expand upon it.
When incorporating supporting details into your writing, it is also important to consider the tone and style of your writing. For example, if you are writing an academic paper, you may need to use more formal language and include more research-based supporting details.
Types of Supporting Details
When writing an essay or a speech, supporting details are essential for providing credibility and depth to your arguments. There are several types of supporting details that you can use to reinforce your main points.
Factual Details
Factual details are pieces of information that are verifiable and true. These details can include historical events, scientific data, or other evidence that supports your argument. Factual details can be presented in tables, charts, or bullet points to help readers understand complex information. Using factual details can lend credibility to your argument and make it more convincing.
Anecdotal Details
Anecdotal details are personal stories or experiences that illustrate your point. These details can help readers relate to your argument on a more emotional level. Anecdotal details can be presented in a narrative format or as a quote from someone who has experienced the situation you are describing. Using anecdotal details can make your argument more relatable and engaging.
Statistical Details
Statistical details are numerical data that support your argument. These details can include percentages, averages, or other statistical measures. Statistical details can be presented in tables, graphs, or charts to help readers visualize the data. Using statistical details can make your argument more persuasive and provide evidence to support your claims.
Expert Testimony
Expert testimony is the opinion or analysis of an authority in a particular field. This can include quotes from experts, interviews with professionals, or research conducted by reputable sources. Expert testimony can lend credibility to your argument and provide readers with a deeper understanding of the topic. Using expert testimony can make your argument more authoritative and convincing.
Role of Supporting Details in Writing
Enhancing credibility.
Supporting details help to enhance the credibility of your writing. By providing evidence and examples, you can convince your readers that your ideas are valid and reliable. For example, if you are writing an essay about climate change, you can use scientific data and research to support your arguments. This will make your writing more credible and persuasive.
Creating Interest
Supporting details can also help to create interest in your writing. By providing vivid descriptions and engaging examples, you can capture the attention of your readers and keep them interested. For example, if you are writing a travel blog, you can use descriptive language and personal anecdotes to make your writing more engaging and entertaining.
Clarifying Points
Finally, supporting details can help to clarify points in your writing. By providing additional information and explanations, you can make your writing more clear and understandable. For example, if you are writing a technical manual, you can use diagrams and step-by-step instructions to clarify complex processes.
Identifying Supporting Details
Context clues.
Context clues are hints or clues that can help you understand the meaning of a word or phrase. When reading a text, pay attention to the context in which supporting details are presented. Look for words or phrases that provide clues about the purpose of the supporting details. For example, if a text is discussing the benefits of exercise, supporting details might include statistics about the health benefits of physical activity.
Signal Words
Signal words are words or phrases that indicate the relationship between ideas. When reading a text, look for signal words that indicate the presence of supporting details. Signal words that indicate the presence of supporting details include “for example,” “in addition,” “furthermore,” and “moreover.” These words signal that the author is providing additional information to support their main idea.
Logical Connections
Logical connections are the relationships between ideas presented in a text. When reading a text, look for logical connections between the main idea and supporting details. Supporting details should logically connect to the main idea and provide evidence to support it. For example, if a text is arguing that climate change is a serious threat, supporting details might include evidence of rising global temperatures and melting ice caps.
Effective Use of Supporting Details
One of the most important aspects of using supporting details effectively is ensuring that they are relevant to your main argument. This means that you should carefully consider each supporting detail and how it relates to the overall point you are trying to make. If a detail does not directly support your argument, it may be best to leave it out.
To help ensure relevance, consider creating an outline or a list of key points that you want to make in your writing. This can help you stay focused and on track, and can also make it easier to identify which supporting details are most relevant to each point.
Sufficiency
Another important factor to consider when using supporting details is sufficiency. You want to make sure that you provide enough evidence to support your argument, without overwhelming your readers with too much information. This can be a delicate balance, but one that is crucial for effective writing.
To ensure sufficiency, it can be helpful to think about the different types of supporting details you can use, such as examples, statistics , or expert opinions. By using a variety of types of evidence, you can provide a more well-rounded and convincing argument.
Finally, it is important to consider variety when using supporting details. This means that you should try to avoid using the same type of evidence over and over again, as this can become repetitive and dull for your readers. Instead, try to mix things up by using different types of evidence, or by presenting your evidence in different ways (such as through tables, graphs, or bullet points).
Challenges in Using Supporting Details
Avoiding redundancy.
One of the biggest challenges in using supporting details is avoiding redundancy. It can be easy to repeat information or provide details that are not necessary, which can make your writing feel repetitive and boring. To avoid this, make sure that each supporting detail you provide adds something new to your writing. Consider using examples, anecdotes, or statistics to provide unique and interesting details that support your main idea.
Maintaining Objectivity
Another challenge when using supporting details is maintaining objectivity. It is important to provide accurate and unbiased information to support your main idea, but it can be difficult to do so without injecting your own opinions or biases into your writing. To maintain objectivity, make sure that your supporting details are based on facts and evidence rather than personal opinions or beliefs. Use reputable sources and avoid using emotionally charged language that may sway your reader’s opinion.
Ensuring Accuracy
Finally, ensuring accuracy is another challenge when using supporting details. It is important to provide accurate and reliable information to support your main idea, but it can be difficult to verify the accuracy of the information you are using. To ensure accuracy, make sure that you are using reputable sources and double-check any statistics or data that you include in your writing. If you are unsure about the accuracy of a particular detail, consider leaving it out or finding additional sources to confirm its validity.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some examples of supporting details?
Supporting details are pieces of information that help to clarify the main idea of a paragraph or essay. Some examples of supporting details include descriptions, examples, reasons, explanations, and comparisons.
What are the two types of supporting details?
There are two types of supporting details: major and minor. Major supporting details are more important and provide a stronger support for the main idea, while minor supporting details are less important and provide a weaker support.
What is the purpose of supporting details in writing?
The purpose of supporting details in writing is to provide evidence to support the main idea of a paragraph or essay. Supporting details help to clarify and explain the main idea, making it easier for the reader to understand and follow the writer’s point of view.
How do supporting details contribute to the main idea of a paragraph?
Supporting details contribute to the main idea of a paragraph by providing evidence and examples that support and clarify the main idea. They help to make the main idea more convincing and persuasive, and they also help to make the paragraph more interesting and engaging for the reader.
What are some common types of supporting details used in writing?
Some common types of supporting details used in writing include descriptions, examples, reasons, explanations, and comparisons. These types of supporting details help to clarify and explain the main idea of a paragraph or essay, making it easier for the reader to understand and follow the writer’s point of view.
How can one effectively write supporting details in a paragraph?
To effectively write supporting details in a paragraph, one should start by identifying the main idea of the paragraph. Then, one should choose supporting details that are relevant and provide evidence to support the main idea. It is important to use a variety of supporting details, such as descriptions, examples, reasons, explanations, and comparisons, to make the paragraph more interesting and engaging for the reader. Finally, one should organize the supporting details in a logical and coherent manner that makes it easy for the reader to follow the writer’s point of view.
Last Updated on August 29, 2023

Leave a Comment Cancel reply

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
36 Writing the Essay Body: Supporting Your Ideas
Whether the drafting of a paragraph begins with a main idea or whether that idea surfaces in the revision process, once you have that main idea, you’ll want to make sure that the idea has enough support. The job of the paragraph body is to develop and support the topic. Here’s one way that you might think about it:
- Topic sentence : what is the main claim of your paragraph; what is the most important idea that you want your readers to take away from this paragraph?
- Support in the form of evidence : how can you prove that your claim or idea is true (or important, or noteworthy, or relevant)?
- Support in the form of analysis or evaluation : what discussion can you provide that helps your readers see the connection between the evidence and your claim?
- Transition : how can you help your readers move from the idea you’re currently discussing to the next idea presented? For more specific discussion about transitions, see the following section on “ Transitions .”
For more on methods of development that can help you to develop and organize your ideas within paragraphs, see “ Patterns of Organization and Methods of Development ” later in this text.
Types of support might include
Now that we have a good idea what it means to develop support for the main ideas of your paragraphs, let’s talk about how to make sure that those supporting details are solid and convincing.
Strong vs. Weak Support
What questions will your readers have? What will they need to know? What makes for good supporting details? Why might readers consider some evidence to be weak?
If you’re already developing paragraphs, it’s likely that you already have a plan for your essay, at least at the most basic level. You know what your topic is, you might have a working thesis, and you probably have at least a couple of supporting ideas in mind that will further develop and support your thesis.
So imagine you’re developing a paragraph on one of these supporting ideas and you need to make sure that the support that you develop for this idea is solid. Considering some of the points about understanding and appealing to your audience (from the Audience and Purpose and the Prewriting sections of this text) can also be helpful in determining what your readers will consider good support and what they’ll consider to be weak. Here are some tips on what to strive for and what to avoid when it comes to supporting details.
Breaking, Combining, or Beginning New Paragraphs
Like sentence length, paragraph length varies. There is no single ideal length for “the perfect paragraph.” There are some general guidelines, however.
Some writing handbooks or resources suggest that a paragraph should be at least three or four sentences; others suggest that 100 to 200 words is a good target to shoot for.
In academic writing, paragraphs tend to be longer, while in less formal or less complex writing, such as in a newspaper, paragraphs tend to be much shorter. Two-thirds to three-fourths of a page—or seven to twelve sentences—is usually a good target length for paragraphs at your current level of academic writing.
The amount of space needed to develop one idea will likely be different than the amount of space needed to develop another. So when is a paragraph complete? The answer is: when it’s fully developed. The guidelines above for providing good support should help.
Signs to end a paragraph and start a new one:
- You’re ready to begin developing a new idea.
- You want to emphasize a point by setting it apart.
- You’re getting ready to continue discussing the same idea but in a different way (e.g., shifting from comparison to contrast).
- You notice that your current paragraph is getting too long (more than three-fourths of a page or so), and you think your writers will need a visual break.
Signs to combine paragraphs include:
- You notice that some of your paragraphs appear to be short and choppy.
- You have multiple paragraphs on the same topic.
- You have undeveloped material that needs to be united under a clear topic.
Finally, paragraph number is a lot like paragraph length. You may have been asked in the past to write a five-paragraph essay. There’s nothing inherently wrong with a five-paragraph essay, but just like sentence length and paragraph length, the number of paragraphs in an essay depends upon what’s needed to get the job done. There’s really no way to know that until you start writing. So try not to worry too much about the proper length and number of things unless those are specified in your assignment. Just start writing and see where the essay and the paragraphs take you. There will be plenty of time to sort out the organization in the revision process. You’re not trying to fit pegs into holes here. You’re letting your ideas unfold. Give yourself—and them—the space to let that happen.
Text Attributions
- This chapter was adapted from “ The Paragraph Body: Supporting Your Ideas ” in The Word on College Reading and Writing by Carol Burnell, Jaime Wood, Monique Babin, Susan Pesznecker, and Nicole Rosevear, which is licensed under a CC BY-NC 4.0 Licence . Adapted by Allison Kilgannon.
Advanced English Copyright © 2021 by Allison Kilgannon is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Forgot your Password?
First, please create an account
Topic sentences and supporting details, topic sentence in a nutshell (indiana university), from indiana university writing tutorial services, topic sentences.
A well-organized paragraph supports or develops a single controlling idea, which is expressed in a sentence called the topic sentence. A topic sentence has several important functions: it substantiates or supports an essay’s thesis statement; it unifies the content of a paragraph and directs the order of the sentences; and it advises the reader of the subject to be discussed and how the paragraph will discuss it. Readers generally look to the first few sentences in a paragraph to determine the subject and perspective of the paragraph. That’s why it’s often best to put the topic sentence at the very beginning of the paragraph. In some cases, however, it’s more effective to place another sentence before the topic sentence—for example, a sentence linking the current paragraph to the previous one, or one providing background information.
Source: http://www.indiana.edu/~wts/pamphlets/paragraphs.shtml
The Topic Sentence and Its Supporting Details (The Oxford English Grammar, and The Elements of Style)
The Oxford English Grammar defines a topic sentence as "[C]ommonly, though not invariably, the first sentence of a paragraph. It . . . conveys a generalization followed by an example" (the supporting details). I should add here that a topic sentence is probably followed by "an example" which, itself, is explained in further detail. (italics added)
So, the topic sentence is general; the rest is detail.
Example: (topic sentence is italicized; remainder of paragraph is detail supporting the topic sentence)
At times, those who govern also regard particular circumstances as too uncomfortable, too painful, for most people to cope with rationally. [the generalization] They may believe, for instance, that their country must prepare for long-term challenges of great importance, such as a war, an epidemic, or a belt-tightening in the face of future shortages. [detail / examples] Yet they may fear that citizens will be able to respond only to short-range dangers. Deception at such times may seem to the government leaders as the only means of attaining the necessary results. [further detail] (from Lying: Moral Choice in Public and Private Life, by Sissela Bok, p. 168.)
Further explanation from The Elements of Style :
Ordinarily, . . .a subject requires division into topics, each of which would be dealt with within a paragraph, The object of treating each topic in a paragraph is, of course, to aid the reader. The beginning of each paragraph is a signal to [the reader] that a new step in the development of the subject has been reached. (italics added)
This is most true when there are several paragraphs regarding a theme. In those cases, the topic sentence is essential to "signal to the reader" that what follows is a different aspect of the theme.
Source: The Oxford English Grammar, by Sidney Greenbaum, 1st Ed.; Lying: Moral Choice In Public and Private Life, by Sissela Bok, p.168; The Elements of Style, by Strunk and White, p.16
How To Write A Topic Sentence (Video)
Monica Monk explains how to write topic sentences, using a paragraph which contains supporting detail, but is missing its topic sentence. She then writes an appropriate topic sentence for it.
Source: YouTube
Cohesion Between the Topic Sentence and the Details (the Rest of the Paragraph)
To reiterate: the topic sentence is the main idea, and the rest of the paragraph supports that main idea.
Creating the cohesion needed between the topic sentence and the details isn't easy. You have to try, try again. Write and rewrite. But all that work is the art of writing. And trust me, good writing is an art.
But I digress a bit. The point is the cohesion. To illustrate, let's work backwards, and see the details, the supporting information, first, as see if we can't come up with a decent topic sentence. Here we go:
For example, recently I began taking my two-year-old dog to obedience school. After four weeks of lessons and practice, she has learned to follow only three commands -- sit, stand and lie down -- and even those she often gets confused. Frustrating (and costly) as this is, I continue to work with her every day. After dog school, my grandmother and sometimes go grocery shopping. Inching along those aisles, elbowed by hundreds of fellow customers, backtracking to pick up forgotten items, and standing at the endless line at checkout, I could easily grow frustrated and cranky. But through years of trying times, I have learned to keep my temper in check. Finally, after putting away the groceries, I might go out to a movie with my fiance, to whom I have been engaged for three years. Layoffs, extra jobs, and problems at home have forced us to postpone our wedding date several times. Still, my patience has enabled me to cancel and reschedule our wedding plans again and again without fuss, fights, or tears.
( There are several parts I would rewrite, but let's just stick with the topic sentence for this lesson.)
Okay, there are three examples given of the main idea, about which the writer, let's assume a woman, gives us a hint in the final sentence. She mentions patience, and as we reread the paragraph, we see that the three examples are indeed about her patience. Her examples also mention that she keeps at it, "again and again," so this is also part of the topic.
Let's try this for a topic sentence: "My life is full of things that try my patience, but I have learned to keep at it, to try, try again."
Or this: "Nothing tests my patience more than just going through a normal day."
Maybe this: "I'm telling you, I may not have the patience of Job, but I'm getting there."
We could go on and write the main idea -- the topic sentence -- of patience any number of ways. That's the art of writing.
One more thing. That last sentence, the one that re-mentions patience (brought up originally in the topic sentence), is key to the cohesiveness of this paragraph, in that it brings the three examples back to the main idea. It's the old "tell 'em what you're going to say, say it, then tell 'em what you said."
Source: Practice in Composing Topic Sentences Paragraphs with Examples, by Richard Nordquist, About.com Guide ( http://grammar.about.com/od/developingparagraphs/a/practicetopic.htm )
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Terms of Use
© 2024 SOPHIA Learning, LLC. SOPHIA is a registered trademark of SOPHIA Learning, LLC.
Supporting Details

Let’s talk about supporting details and how they can help strengthen your writing. A paragraph usually starts with the main idea—also called the topic sentence—and the rest of the paragraph gives specific details to support and develop that point. Today, we’ll be talking about those details, called supporting details.
Supporting Details Definition
Think of it this way: If you’re building a table then you need a flat surface for the tabletop, this is like your main point or topic sentence. If that flat surface doesn’t have any legs to stand on, though, it’s no good as a table! The supporting details are like the legs of the table, propping up the topic sentence.
Types of Supporting Details
There are six main types of supporting details: descriptions, vocabulary, proof, voices, explanation, and importance.
Description
Description is fairly self-explanatory: the writer can use the five senses, comparison, and metaphors to help paint a vivid picture for the reader.
Vocabulary helps with clarification. For example, if you have a topic sentence that relies on the word pulchritudinous , it might help to include a definition of the word so the reader doesn’t get sidetracked. ( Pulchritudinous means “beautiful,” by the way.)
Proof is often made up of facts , statistics, and dates that are hard evidence for your main point
“Voices” are expert quotes, individual opinions, or different perspectives that can be considered “soft proof.”
Explanation
Explanation is restating the main point more simply, and “importance” is answering the question “so what?” after a fact or a quote.
Supporting Details Examples
Let’s take a look at a quick example.
Okay, so our main point is that first sentence: being a celebrity is difficult. The supporting details follow. You can see a voice is presented, that of Perez Hilton, a descriptive explanation, directing you to think about the paparazzi photos, and two simply descriptive phrases. This paragraph would be even stronger with a testimonial about a real-life story of a celebrity facing danger because of their place in the public image—that would be a proof-based supporting detail.
When you’re writing supporting details, it’s important not to stray too far from your original point. Remember, every paragraph in a written work is pointing back in some way to your overall thesis, and every sentence in the paragraph is pointing to the main point of that paragraph.
If you have a main point about, say, how dogs are man’s best friend, you wouldn’t want to use an example of how disloyal cats are in that paragraph. Save that point for another paragraph—stay focused on facts about dogs in the supporting paragraph about dogs. If you get off track from your main point, your reader might get confused and lose interest.
A common mistake in writing a paper is not providing enough specific details. The more specific, the better. A vague detail is like a thin table leg, it will make your entire point wobbly. Often vague details come when you’re pressed for time or don’t want to research a topic fully—take the time to make your paper worth reading. Let’s look at an example to further prove this point. You could write something like this:
Okay. You know in general what’s happening. But think how much more convincing the following sentence would be:
That’s a little more vivid, isn’t it? The details are strong and vibrant, not generic and vague. It makes the writer’s point much more clearly.
So let’s look back on what we’ve learned. Supporting details help hold up your main point. They should be specific, creative, and focused on the main point of the paragraph. Do this, and your writing will greatly improve.
I hope this video has been helpful and that you feel prepped and empowered. Thanks for watching!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are supporting details.
In a literary text, supporting details are general information that clarifies, supports, or explains the main idea or thesis in greater detail, proving the main idea’s credibility with supporting details and examples from the text in order to better understand the story and what the main idea is.
Where do supporting details usually appear in an essay?
Supporting details most often appear within the body of the essay.
How do I identify the main idea and supporting details?
The first sentence within the first paragraph generally contains the main idea. A thesis statement is often placed at the end of the introductory paragraph, followed by the essential supporting details, which are shared within the body paragraphs.
How do I write supporting details?
Supporting details are the well-researched facts and statements, detailed descriptions, examples, and specific details that lead the reader to comprehend the main idea of a paragraph. Supporting details provide clarification to the reader by explaining, describing, and illustrating the main idea within the text. Comparing and contrasting essays are good ways to write supporting details.
Return to Reading Comprehension Videos
by Mometrix Test Preparation | This Page Last Updated: September 29, 2023
Find Study Materials for
- Business Studies
- Combined Science
- Computer Science
- Engineering
- English Literature
- Environmental Science
- Human Geography
- Macroeconomics
- Microeconomics
- Social Studies
- Browse all subjects
- Read our Magazine
Create Study Materials
When writing a single-paragraph essay, it’s important to know what your point is and how you’re going to prove it, because unlike a traditional-length essay, you won’t have the space of several paragraphs to flesh it out. The main idea and support for the main idea should be carefully crafted in a single-paragraph essay so you can say what you need to say in the most direct and concise way.

Explore our app and discover over 50 million learning materials for free.
- Main Idea and Supporting Detail
- Explanations
- StudySmarter AI
- Textbook Solutions
- 5 Paragraph Essay
- Argumentative Essay
- Cues and Conventions
- English Grammar
- English Language Study
- Essay Prompts
- Essay Writing Skills
- Global English
- History of English Language
- International English
- Key Concepts in Language and Linguistics
- Language Acquisition
- Language Analysis
- Language and Social Groups
- Lexis and Semantics
- Linguistic Terms
- Listening and Speaking
- Multiple Choice Questions
- Research and Composition
- Rhetorical Analysis Essay
Statistical Evidence
- Sociolinguistics
- Summary Text
- Synthesis Essay
- Textual Analysis
Lerne mit deinen Freunden und bleibe auf dem richtigen Kurs mit deinen persönlichen Lernstatistiken
Nie wieder prokastinieren mit unseren Lernerinnerungen.
When writing a single-paragraph essay, it’s important to know what your point is and how you’re going to prove it, because unlike a traditional-length essay, you won’t have the space of several paragraphs to flesh it out. The main idea and support for the main idea should be carefully crafted in a single-paragraph essay so you can say what you need to say in the most direct and concise way.
Main Idea And Supporting Detail: Meaning
In a single-paragraph essay, the main idea is the writer’s position or principal concept, and the supporting details are the means by which they develop and prove that idea. This might sound similar to a thesis statement . That’s because a thesis statement should include the main idea and supporting details for an essay.
Remember, a thesis statement is a single declarative sentence that includes the main idea, or position on a topic, and mentions the way(s) you intend to prove or support that idea. A thesis acts as a blueprint for the body of your essay. It lays out the expectation for the audience of what your point is and how you intend to prove it.
If you’re writing a single-paragraph essay, you might be wondering whether you need to include a thesis statement. The short answer is, yes you do! In this case, because your essay will only be the length of a paragraph, the thesis statement will function the exact same way as a topic sentence for a regular paragraph.
A topic sentence functions much the same as a thesis statement. It is a single sentence, usually the first sentence of a paragraph, that introduces the main argument or idea for that paragraph. It’s a helpful technique so your audience knows the principal point of each paragraph because it is expressly stated.
It’s also useful as a way to organize your argument . Each piece of support for your main idea can serve as the topic sentence for an entire paragraph that develops that supporting detail in relation to the main idea. Or, in the case of a single-paragraph essay, the topic sentence is the thesis for the entire essay.
A single-paragraph essay should be concise and to the point. There is no room for filler language or information that is not absolutely necessary. Because of the length of a single-paragraph essay, it is important to state your main point at the very beginning.
In a single-paragraph essay you don’t need to spend much time providing background information on the topic. Your main objective is to express your main idea and support it with concrete details. You can assume your audience already has a working knowledge of the subject.
How To Organize The Main Idea And Supporting Details
There is a basic structure for a single-paragraph essay that is similar to that of the basic multi-paragraph essay. It includes the topic sentence (or thesis statement), at least two pieces of supporting information, concrete evidence for and commentary on the supporting information, and a conclusion. See the layout below.

Fig. 1 - How to organize support for main idea.
Topic sentence (thesis statement)
Body support 1
Concrete details
Body support 2
Closing statement
In a single-paragraph essay, the thesis statement will come first and usher in the main idea. It isn’t always possible to fit the main idea and a reference to the supporting details into a single sentence, but it is a good goal.
In Around the World in Eighty Days (1873) Jules Verne explores the themes of calmness and persistence with his character Phileas Fogg; Mr. Fogg remains calm in the face of extreme circumstances as he travels the world, and remains persistent to his goal despite many setbacks.
This example demonstrates how to include support for the main idea within a single sentence (i.e. thesis statement). In a single-paragraph essay, the segment following the thesis statement is considered the body of the essay. This is where you provide support for the main idea.
What Can Be The Support For The Main Idea?
For a single-paragraph essay, support for the main idea must be specific and brief; you won’t have the space of several paragraphs to expound on the details. Because of this, it’s especially important for your support to be effective.
Below are some of the most constructive pieces of information to include to support your main idea.
Facts and Data
Sometimes the best support of the main idea is simply stating relevant facts. If, for example, you’re discussing why bats are a positive addition to your outdoor living space, you might include that they like to eat mosquitoes. Remember, you’ll need to choose only the most relevant information to make your point in the fewest possible sentences.
Quotes are an effective way to prove a point in a very concise way. This is true whether you’re quoting a text you’re discussing, or quoting an expert or authoritative source on the subject.
An authoritative source is one that can be trusted because it is widely recognized in the field as authentic and/or expert.
Quotes taken from the text under discussion are effective because this is the primary source . Quoting the source directly is the best way to prove your point about a text.
Statistical evidence is numerical data organized to show a trend or some information about a particular subject. This is great evidence because it usually represents large numbers of participants or objects; the larger the group, the more reliable the information. Some statistics you could use in a one paragraph essay are percentages or statistics.
The best places to get statistical data are from government organizations and other trusted sources in the field.
Examples of Relevant Details
Examples are the best way to support your main idea. You can use examples from the text you’re referencing, real life experiences, or anything else that will expand the main idea.
How To Identify The Main Idea And Supporting Details
Identifying the main idea and its supporting details improves your reading and understanding of a text and its topic. Once you’ve identified these elements, you can follow the author’s logic through their use of examples or other support.

Fig. 2 - Neoclassical pillars represent support for main idea.
One way to quickly recognize the main idea is to use these tips:
Scan the title of the text
Look for significance in the pictures included
Note words and phrases that are repeated often
Summarize the text in your own words (in a sentence, if possible)
Ask yourself - what is this text mostly about?
Relationship Between The Main Idea And Supporting Details
The supporting details are not the main idea, but are the pillars that hold up the main idea. These details are kind of like an extension of the main idea, and so can be confused with it sometimes.
Supporting details are meant to offer evidence of the accuracy or truth of the main idea. They offer more specific information about the topic.
The main idea in an article about global warming is, “Global warming is the long-term warming of Earth’s overall temperature and is the most pressing issue facing humanity today.” That is the concept that will be discussed in the body of the article. The following sentence is an example of a supporting detail for that main idea, “Fossil fuels are burned, which produce gasses that trap heat on the earth’s surface.”
The sentence about fossil fuels should not be confused with the main idea of the article. It is a single point that the author is using to explain the concept of global warming and its danger to humanity. It supports the idea that global warming is a danger to the planet, and humanity.
More Examples Of The Main Idea And Supporting Details
Below are a few examples of a main idea and its supporting details. Think about how these interact with one another as you read them.
Main idea: People suffering from neuroticism experience anger, anxiety, self-consciousness, irritability and depression, but their complaints of further physical ailments have largely been discounted by physicians until recently.
Supporting detail a: Research now shows that neuroticism is linked to five physical ailments: arthritis, ulcers, asthma, heart disease, and headaches.
Supporting detail b: Similarly, there is evidence that people who display pessimistic behavior in their teens or twenties or more likely to become seriously ill or die in their forties.
Main idea: Mental illness has been explained in many different ways over the course of the last several hundred years.
Supporting detail a: In ancient times, irrational behavior was thought to be the result of demons or evil spirits.
Supporting detail b: The Greeks believed irrational behavior was an imbalance of body fluids, called “humors,” or some organs being misplaced in the body.
Supporting detail c: After a resurgence in the belief of demons thanks to the highly superstitious Middle Ages, the last one hundred years have finally seen a true medical acceptance and explanation of mental illness.
Can you think of any more supporting details for the two examples above? Use these, or come up with some ideas of your own for more practice.
Support for Main Idea - Key Takeaways
- In a single-paragraph essay, the main idea is the writer’s position or principal concept they would like to express, and the supporting details are the means by which they develop and prove that idea.
- Single-paragraph essays demand a concise and to-the-point main idea and supporting details.
- The thesis statement contains the main idea, and should also refer to the support for the main idea.
- Support for the main idea are like pillars that hold up the main idea when it is scrutinized.
- Support for the main idea can be statistical data, quotes, facts and data, and examples of relevant information.
Frequently Asked Questions about Main Idea and Supporting Detail
--> what is the difference between main idea and supporting details.
The difference between the main idea and supporting details is that supporting details are an extension of the main idea; they are meant to offer evidence of the accuracy or truth of the main idea.
--> How to find main ideas and supporting details in a text?
You can find the main idea and supporting details in a text using the following tips:
--> What is a supporting detail?
A supporting detail is the means by which a writer develops and/or proves their main idea.

--> What is main idea and example?
A main idea is the principal concept an author wishes to express. An example would be, "The advancement of technology has removed us entirely from the use of physical money, and so has made it obsolete."
--> What is an example of supporting details?
An example of supporting details would be any facts, quotes, statistical evidence, or examples of details relevant to the main idea.
Test your knowledge with multiple choice flashcards
True or false: a single-paragraph essay doesn't need a thesis statement?
Because of the length of a single-paragraph essay, it is important to state your main point _____________
Which of the following is not something recommended to support the main idea?
Your score:

Join the StudySmarter App and learn efficiently with millions of flashcards and more!
Learn with 162 main idea and supporting detail flashcards in the free studysmarter app.
Already have an account? Log in
Why is it important to carefully craft the main idea and supporting details of a single-paragraph essay?
Because you must be concise; unlike a traditional-length essay, you won’t have the space of several paragraphs to flesh these things out.
What is the main idea of a text?
The main idea is the writer’s position or principal concept they would like to express
What does "support for the main idea" mean?
Supporting details are the means by which the author develops and proves the main idea.
True or false: a single-paragraph essay doesn't need a thesis statement?
The thesis statement of a single-paragraph essay will function the exact same way as a ____________ for a regular paragraph.
Topic sentence
At the beginning of the paragraph

- Text Comparison
of the users don't pass the Main Idea and Supporting Detail quiz! Will you pass the quiz?
How would you like to learn this content?
Free english cheat sheet!
Everything you need to know on . A perfect summary so you can easily remember everything.
Join over 22 million students in learning with our StudySmarter App
The first learning app that truly has everything you need to ace your exams in one place
- Flashcards & Quizzes
- AI Study Assistant
- Study Planner
- Smart Note-Taking

Sign up to highlight and take notes. It’s 100% free.
This is still free to read, it's not a paywall.
You need to register to keep reading, create a free account to save this explanation..
Save explanations to your personalised space and access them anytime, anywhere!
By signing up, you agree to the Terms and Conditions and the Privacy Policy of StudySmarter.
Entdecke Lernmaterial in der StudySmarter-App

Privacy Overview

Writing Body Paragraphs
University of Minnesota
Learning Objectives
- Select Primary Support related to your thesis
- Support your topic sentence
If your thesis gives the reader a roadmap to your essay, then body paragraphs should closely follow that map. The reader should be able to predict what follows your introductory paragraph by simply reading the thesis statement.
The body paragraphs present the evidence you have gathered to confirm your thesis. Before you begin to support your thesis in the body, you must find information from a variety of sources that support and give credit to what you are trying to prove.
SELECT PRIMARY SUPPORT FOR YOUR THESIS
Without primary support, your argument is not likely to be convincing. Primary support can be described as the major points you choose to expand on your thesis. It is the most important information you select to argue for your point of view. Each point you choose will be incorporated into the topic sentence for each body paragraph you write. Your primary supporting points are further supported by supporting details within the paragraphs.
Remember that a worthy argument is backed by examples. In order to construct a valid argument, good writers conduct lots of background research and take careful notes. They also talk to people knowledgeable about a topic in order to understand its implications before writing about it.
IDENTIFY THE CHARACTERISTICS OF GOOD PRIMARY SUPPORT
In order to fulfill the requirements of good primary support, the information you choose must meet the following standards:
• Be specific. The main points you make about your thesis and the examples you use to expand on those points need to be specific. Use specific examples to provide the evidence and to build upon your general ideas. These types of examples give your reader something narrow to focus on, and if used properly, they leave little doubt about your claim. General examples, while they convey the necessary information, are not nearly as compelling or useful in writing because they are too obvious and typical.
• Be relevant to the thesis. Primary support is considered strong when it relates directly to the thesis. Primary support should show, explain, or prove your main argument without delving into irrelevant details. When faced with lots of information that could be used to prove your thesis, you may think you need to include it all in your body paragraphs. But effective writers resist the temptation to lose focus. Choose your examples wisely by making sure they directly connect to your thesis.
• Be detailed. Remember that your thesis, while specific, should not be very detailed. The body paragraphs are where you develop the discussion that a thorough essay requires. Using detailed support shows readers that you have considered all the facts and chosen only the most precise details to enhance your point of view.
PREWRITE TO IDENTIFY PRIMARY SUPPORTING POINTS FOR A THESIS STATEMENT
Recall that when you prewrite you essentially make a list of examples or reasons why you support your stance. Stemming from each point, you further provide details to support those reasons. After prewriting, you are then able to look back at the information and choose the most compelling pieces you will use in your body paragraphs.
Choose one of the following working thesis statements. On a separate sheet of paper, write for at least five minutes using one of the prewriting techniques you learned in Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?”.
- Unleashed dogs on city streets are a dangerous nuisance.
- Students cheat for many different reasons.
- Drug use among teens and young adults is a problem.
- The most important change that should occur at my college or university is ____________________________________________.
SELECT THE MOST EFFECTIVE PRIMARY SUPPORTING POINTS FOR A THESIS STATEMENT
After you have prewritten about your working thesis statement, you may have generated a lot of information, which may be edited out later. Remember that your primary support must be relevant to your thesis. Remind yourself of your main argument, and delete any ideas that do not directly relate to it. Omitting unrelated ideas ensures that you will use only the most convincing information in your body paragraphs. Choose at least three of only the most compelling points. These will serve as the topic sentences for your body paragraphs.
Refer to the previous exercise and select three of your most compelling reasons to support the thesis statement. Remember that the points you choose must be specific and relevant to the thesis. The statements you choose will be your primary support points, and you will later incorporate them into the topic sentences for the body paragraphs.
Collaboration
Please share with a classmate and compare your answers.
When you support your thesis, you are revealing evidence. Evidence includes anything that can help support your stance. The following are the kinds of evidence you will encounter as you conduct your research:
Facts . Facts are the best kind of evidence to use because they often cannot be disputed. They can support your stance by providing background information on or a solid foundation for your point of view. However, some facts may still need explanation. For example, the sentence “The most populated state in the United States is California” is a pure fact, but it may require some explanation to make it relevant to your specific argument.
Judgments . Judgments are conclusions drawn from the given facts. Judgments are more credible than opinions because they are founded upon careful reasoning and examination of a topic.
Testimony . Testimony consists of direct quotations from either an eyewitness or an expert witness. An eyewitness is someone who has direct experience with a subject; he adds authenticity to an argument based on facts. An expert witness is a person who has extensive experience with a topic. This person studies the facts and provides commentary based on either facts or judgments, or both. An expert witness adds authority and credibility to an argument.
Personal observation . Personal observation is similar to testimony, but personal observation consists of your testimony. It reflects what you know to be true because you have experiences and have formed either opinions or judgments about them. For instance, if you are one of five children and your thesis states that being part of a large family is beneficial to a child’s social development, you could use your own experience to support your thesis.
WRITING AT WORK
In any job where you devise a plan, you will need to support the steps that you lay out. This is an area in which you would incorporate primary support into your writing. Choosing only the most specific and relevant information to expand upon the steps will ensure that your plan appears well-thought-out and precise.
You can consult a vast pool of resources to gather support for your stance. Citing relevant information from reliable sources ensures that your reader will take you seriously and consider your assertions. Use any of the following sources for your essay: newspapers or news organization websites, magazines, encyclopedias, and scholarly journals, which are periodicals that address topics in a specialized field.
CHOOSE SUPPORTING TOPIC SENTENCES
Each body paragraph contains a topic sentence that states one aspect of your thesis and then expands upon it. Like the thesis statement, each topic sentence should be specific and supported by concrete details, facts, or explanations.
Each body paragraph should comprise the following elements.
topic sentence + supporting details (examples, reasons, or arguments)
Topic sentences indicate the location and main points of the basic arguments of your essay. These sentences are vital to writing your body paragraphs because they always refer back to and support your thesis statement. Topic sentences are linked to the ideas you have introduced in your thesis, thus reminding readers what your essay is about. A paragraph without a clearly identified topic sentence may be unclear and scattered, just like an essay without a thesis statement.
Unless your teacher instructs otherwise, you should include at least three body paragraphs in your essay. A five-paragraph essay, including the introduction and conclusion, is commonly the standard for exams and essay assignments.
Consider the following the thesis statement:
Author J.D. Salinger relied primarily on his personal life and belief system as the foundation for the themes in the majority of his works.
The following topic sentence is a primary support point for the thesis. The topic sentence states exactly what the controlling idea of the paragraph is. Later, you will see the writer immediately provide support for the sentence.
Salinger, a World War II veteran, suffered from post-traumatic stress disorder, a disorder that influenced themes in many of his works.
In “Exercise 2”, you chose three of your most convincing points to support the thesis statement you selected from the list. Take each point and incorporate it into a topic sentence for each body paragraph.
Supporting point 1: ____________________________________________
Topic sentence: ____________________________________________
Supporting point 2: ____________________________________________
Supporting point 3: ____________________________________________
DRAFT SUPPORTING DETAIL SENTENCES FOR EACH PRIMARY SUPPORT SENTENCE
After deciding which primary support points you will use as your topic sentences, you must add details to clarify and demonstrate each of those points. These supporting details provide examples, facts, or evidence that support the topic sentence.
The writer drafts possible supporting detail sentences for each primary support sentence based on the thesis statement:
The following paragraph contains supporting detail sentences for the primary support sentence (the topic sentence), which is underlined.
Using the three topic sentences you composed for the thesis statement in “Exercise 1”, draft at least three supporting details for each point.
Thesis statement: ____________________________________________
Primary supporting point 1: ____________________________________________
Supporting details: ____________________________________________
Primary supporting point 2: ____________________________________________
Primary supporting point 3: ____________________________________________
You have the option of writing your topic sentences in one of three ways. You can state it at the beginning of the body paragraph, or at the end of the paragraph, or you do not have to write it at all. This is called an implied topic sentence. An implied topic sentence lets readers form the main idea for themselves. For beginning writers, it is best to not use implied topic sentences because it makes it harder to focus your writing. Your instructor may also want to clearly identify the sentences that support your thesis.
Print out the first draft of your essay and use a highlighter to mark your topic sentences in the body paragraphs. Make sure they are clearly stated and accurately present your paragraphs, as well as accurately reflect your thesis. If your topic sentence contains information that does not exist in the rest of the paragraph, rewrite it to more accurately match the rest of the paragraph.
Key Takeaways
- Your body paragraphs should closely follow the path set forth by your thesis statement.
- Strong body paragraphs contain evidence that supports your thesis.
- Primary support comprises the most important points you use to support your thesis.
- Strong primary support is specific, detailed, and relevant to the thesis.
- Prewriting helps you determine your most compelling primary support.
- Evidence includes facts, judgments, testimony, and personal observation.
- Reliable sources may include newspapers, magazines, academic journals, books, encyclopedias, and firsthand testimony.
- A topic sentence presents one point of your thesis statement while the information in the rest of the paragraph supports that point.
- A body paragraph comprises a topic sentence plus supporting details.
Writing Body Paragraphs Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Feedback/errata.
Comments are closed.
Supporting Details
In a unified paragraph, all of the sentences directly support the main idea or topic sentence. Including details that are not relevant to the main idea makes your paragraph unclear and distracts your reader from the point you are making.
The Purpose of Supporting Details
- Keep the reader focused on the main idea of the paragraph
- Demonstrate that your topic sentence or main idea is accurate and believable
- Make your meaning clear and forceful with concrete, specific information
Questions to Consider
- Does this sentence directly explain the topic sentence or main idea? What new information does it add?
- Would any essential information be lost if this sentence were deleted? If not, delete it.
- Is this information distracting or unimportant? If so, delete it.
Types of Supporting Details
- Reasons — explanations that tell why an opinion is valid
- Facts — statements that can be proved
- Statistics — facts expressed in numbers
- Examples — specific instances that explain or demonstrate a point
- Sensory Details — appeals to one or more of the physical senses
- Anecdotes — brief stories about a character or event
NOTE: Using a quote or paraphrasing another author’s ideas is not, in and of itself, a good supporting detail! To use citation effectively, you need to explain the connection between the citation and your main point in your own words.
Sample Paragraph with Supporting Details
Reality TV shows that followed Survivor had none of the interesting elements that it had. Big Brother was the first spin-off reality TV show to try to repeat the success of Survivor , but it did not offer the drama that Survivor did. In Big Brother , contestants were locked in a house without any outside contact for weeks. As in Survivor , there was a cash prize on the line, but in Big Brother there were not any competitions or struggles. Contestants were expelled by a viewer phone poll, so the poll gave them no motive to scheme and plot allegiances the way Survivor contestants did. In fact, the contestants had little to do except bicker and fight. Viewers lost interest in players who were not up against any challenge except weeks of boredom. In the end, Big Brother was simply not interesting.
Guidelines for Supporting Details
Focus on who, what, when, where, why, and how questions.
Vague: Some animals hibernate for part of the year. (What animals? Where?)
Specific: Some bears hibernate for three to four months each winter.
Name names.
Vague: When my sixty-three-year-old aunt was refused a job, she became an angry victim of age discrimination.
Specific: When my sixty-three-year-old Aunt Angela was refused a job at Vicki’s Nail Salon, she became an angry victim of age discrimination.
Use action verbs.
Vague: When Silina came on stage, the audience became excited.
Specific: When Silina burst onto the stage, the audience screamed, cheered, and chanted “Silina, Silina!”
Use descriptive language that appeals to the senses (smell, touch, taste, sound, sight).
Vague: It’s relaxing to walk on the beach.
Specific: I walked in the sand next to the ocean, breathing in the smell of the salt water and listening to the rhythmic sound of the waves.
Use adjectives and adverbs.
Vague: As I weeded my garden, I let my eyes wander over the meadow sweets and hydrangeas, all the while listening to the chirping of a cardinal.
Specific: As I slowly weeded my perennial garden, I let my eyes wander over the pink meadow sweets and blue hydrangeas, all the while listening absent-mindedly to the chirping of a bright red cardinal.
NOTE: Use adjectives and adverbs carefully. A passage filled with too many modifiers will be tiring to your reader. Think about which modifiers help to make the idea feel concrete and real to your readers and choose wisely.
Kaylan | 2019
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/.
Chapter 6 Drafting
6.3 supporting a thesis, learning objectives.
- Understand the general goal of writing a paper.
- Be aware of how you can create supporting details.
- Recognize procedures for using supporting details.
Supporting your thesis is the overall goal of your whole paper. It means presenting information that will convince your readers that your thesis makes sense. You need to take care to choose the best supporting details for your thesis.
Creating Supporting Details

You can and should use a variety of kinds of support for your thesis. One of the easiest forms of support to use is personal observations and experiences. The strong point in favor of using personal anecdotes is that they add interest and emotion, both of which can pull audiences along. On the other hand, the anecdotal and subjective nature of personal observations and experiences makes them too weak to support a thesis on their own.
Since they can be verified, facts can help strengthen personal anecdotes by giving them substance and grounding. For example, if you tell a personal anecdote about having lost twenty pounds by using a Hula-Hoop for twenty minutes after every meal, the story seems interesting, but readers might not think it is a serious weight-loss technique. But if you follow up the story with some facts about the benefit of exercising for twenty minutes after every meal, the Hula-Hoop story takes on more credibility. Although facts are undeniably useful in writing projects, a paper full of nothing but fact upon fact would not be very interesting to read.
Like anecdotal information, your opinions can help make facts more interesting. On their own, opinions are weak support for a thesis. But coupled with specific relevant facts, opinions can add a great deal of interest to your work. In addition, opinions are excellent tools for convincing an audience that your thesis makes sense.
Similar to your opinions are details from expert testimony and personal interviews. Both of these kinds of sources provide no shortage of opinions. Expert opinions can carry a little more clout than your own, but you should be careful not to rely too much on them. However, it’s safe to say that finding quality opinions from others and presenting them in support of your ideas will make others more likely to agree with your ideas.
Statistics can provide excellent support for your thesis. Statistics are facts expressed in numbers. For example, say you relay the results of a study that showed that 90 percent of people who exercise for twenty minutes after every meal lose two pounds per week. Such statistics lend strong, credible support to a thesis.
Examples —real or made up—are powerful tools you can use to clarify and support your facts, opinions, and statistics. A detail that sounds insignificant or meaningless can become quite significant when clarified with an example. For example, you could cite your sister Lydia as an example of someone who lost thirty pounds in a month by exercising after every meal. Using a name and specifics makes it seem very personal and real. As long as you use examples ethically and logically, they can be tremendous assets. On the other hand, when using examples, take care not to intentionally mislead your readers or distort reality. For example, if your sister Lydia also gave birth to a baby during that month, leaving that key bit of information out of the example would be misleading.
Procedures for Using Supporting Details
You are likely to find or think of details that relate to your topic and are interesting, but that do not support your thesis. Including such details in your paper is unwise because they are distracting and irrelevant.
In today’s rich world of technology, you have many options when it comes to choosing sources of information. Make sure you choose only reliable sources. Even if some information sounds absolutely amazing, if it comes from an unreliable source, don’t use it. It might sound amazing for a reason—because it has been amazingly made up.

When you find a new detail, make sure you can find it in at least one more source so you can safely accept it as true. Take this step even when you think the source is reliable because even reliable sources can include errors. When you find new information, make sure to put it into your essay or file of notes right away. Never rely on your memory.
Take great care to organize your supporting details so that they can best support your thesis. One strategy is to list the most powerful information first. Another is to present information in a natural sequence, such as chronological order. A third option is to use a compare/contrast format. Choose whatever method you think will most clearly support your thesis.
Make sure to use at least two or three supporting details for each main idea. In a longer essay, you can easily include more than three supporting details per idea, but in a shorter essay, you might not have space for any more.
Key Takeaways
- A thesis gives an essay a purpose, which is to present details that support the thesis.
- To create supporting details, you can use personal observations and experiences, facts, opinions, statistics, and examples.
- When choosing details for your essay, exclude any that do not support your thesis, make sure you use only reliable sources, double-check your facts for accuracy, organize your details to best support your thesis, and include at least two or three details to support each main idea.
- Choose a topic of interest to you and write a possible thesis related to the topic. Write one sentence that is both related to the topic and relevant to the thesis. Write one sentence that is related to the topic but not relevant to the thesis.
- Writers Handbook. Authored by : Anonymous. Provided by : Anonymous. Located at : http://2012books.lardbucket.org/books/writers-handbook/ . License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike

Privacy Policy
Single Controlling Idea that Ties Back to the Thesis Statement
The first thing a solid body paragraph needs to do is focus on one controlling idea, one that directly ties back to the thesis statement of the paper. While the basic paragraph only requires a controlling idea specific to that paragraph’s content, any body paragraph in an essay must always take into account what the thesis statement (or controlling idea of the essay) is. It must also take into account what role the controlling idea of that specific paragraph will play within its context.
To illustrate, let’s look at an example prompt question:
Based on that prompt, a potential thesis statement could be the following:
This thesis statement only mentions one thing the writer can do to overcome a specific thinking error (that of giving up). The writer suggests paying more attention to the circumstances in which the thinking error tends to occur. This means that the writer will only need one body paragraph to explain this step he or she intends to take. In other words, since the thesis statement, or controlling idea of the whole essay, only has one idea in it, the essay only needs one body paragraph to discuss that one idea.
Not all essay prompts are that simple though. In the future, it is very likely that you will be asked a prompt question that will require you to share two or even three ideas instead of just the one. This would mean you would need more than one body paragraph to answer the prompt question. Look at the following example:
Ponder and Record
How might the controlling idea of this body paragraph (or even the number of body paragraphs) be different if the thesis statement were the following instead:
Three things I could do to overcome the thinking error of giving up would be to pay more attention to the conditions in which the thinking error tends to occur, act to immediately change my physical and mental state so I can stop the thinking error, and then consistently reflect and evaluate how successful I was in stopping the thinking error.
- How many controlling ideas are outlined in this thesis example?
- How many body paragraphs would this essay need since each body paragraph should contain no more than one controlling idea?
In the Ponder and Record exercise above, you probably deduced that the thesis statement outlines three controlling ideas. They are the following:
- Pay more attention to the conditions in which the thinking error occurs.
- Act immediately to change physical and mental state to stop the thinking error.
- Reflect and evaluate how successful efforts to stop the thinking error were.
This means that, according to this thesis, this particular essay would have three body paragraphs—one focused on each of the three controlling ideas.
Moving forward, as you examine your prompt questions and create thesis statements, allow the number of controlling ideas you outline to be your guide. This will help you determine how many body paragraphs you will have and what each of those body paragraphs will focus on.
Topic Sentence
The basic paragraph lessons teach that the purpose of the topic sentence is to indicate what controlling idea that paragraph is going to explore . With the body paragraph, the purpose of the topic sentence is no different.
As mentioned in the section above, the only thing that changes in the body paragraph is the fact that its controlling idea (the idea shared in the topic sentence of that paragraph) must tie back to the thesis statement of the paper. All while still serving its purpose of showing what the controlling idea of that particular paragraph will be.
Let’s return to our example thesis statement to illustrate this idea:
With this as the thesis statement of the introductory paragraph, the topic sentence of the body paragraph might be something like the following:
Notice how the topic sentence strengthens the thesis statement while also creating the controlling idea and supporting details for that body paragraph? It is clear that increased awareness of the conditions in which thinking errors occur will be the controlling idea of this paragraph (as illustrated by the thesis). But it is also clear that this controlling idea will be supported by details centered on the expert testimony (if the first topic sentence example is used) or with personal experience (if the second topic sentence example is used).
- How does the topic sentence above support the thesis while also clearly creating the controlling idea of that specific paragraph?
- How does the topic sentence effectively outline the type of supporting details that will be shared in that body paragraph?
Supporting Detail
You’ll remember from your lessons on the basic paragraph that there are four basic types of supporting details you could use to support the controlling idea of your paragraph:
- Expert testimony
- Personal experiences
The body paragraph is no different. The same types of supporting details will work. Much like with your basic paragraph assignment, your Basic Essay assignment also requires you to use supporting details in your body paragraph that directly support your controlling idea. The only difference is instead of integrating two supporting details, you only need to integrate one. If you are unsure of what that might look like, let’s return to our example topic sentences:
The first topic sentence example (Example 1) indicates that an expert testimony will serve as the supporting detail for the body paragraph. So what might this look like in practice?
- Many experts in the field of psychology have highlighted the importance of not only correctly identifying the thinking errors we suffer from, but also the conditions in which they tend to occur most frequently in our lives. As Dr. John M. Grohol explained in his article “10 Proven Methods for Fixing Cognitive Distortions,” “Much like a judge overseeing a trial, [you] must remove yourself from the emotionality of the episode of irrational thinking in order to examine the evidence more objectively. A thorough examination of an experience allows you to identify the basis for your distorted thoughts.” In other words, before a thinking error can be successfully overcome, it must first be analyzed as objectively as possible so the cause of the thinking error (and the conditions that tend to cause it) can be identified and modified.
The second topic sentence example (Example 2) indicates that a personal experience will serve as the supporting detail for the body paragraph. What might that look like in practice?
- Because one of my thinking errors is a tendency to want to give up and quit, I made the decision to actually keep a record of my thinking patterns over the course of a week. Anytime I had the thought to give up on a task, big or small, I would open up my notebook and write it down. I would describe what I was doing when the thought occurred and how it made me feel. By the end of the week, I realized that a lot of the time, my desire to give up happened during times of stress. In other words, I could handle a lot more (and avoid the thinking error of giving up) when I kept my stress level down. This discovery has helped me realize an important connection that I can now work toward resolving in order to lessen this thinking error’s impact on my life.
- How do the supporting detail examples above support the controlling idea established by the example topic sentence?
- What could your topic sentence and accompanying supporting details be for your own essay?
Don’t forget , if you choose to use a personal experience as a supporting detail, make sure it is based on a specific experience . It is not enough to reflect on a principle as it relates to your life in general.
The Concluding and the Transition Sentence
The final sentence of the body paragraph is the concluding and transition sentence. While similar to the simple concluding sentence of the basic paragraph, the concluding and transition sentence not only serves the purpose of providing closure for the controlling idea shared throughout the paragraph, but also the purpose of transitioning the reader to the next paragraph (whether it be another body paragraph or the concluding paragraph).
In the basic paragraph this sentence should not be a simple restatement of the topic sentence. Rather, it should be a brief summary of how the supporting details shared throughout the paragraph support the controlling idea of that paragraph. The same is true of the concluding and transition sentence in the body paragraph with this small addition—this sentence can also serve as a link back to the thesis statement (the controlling idea of the essay) as well.
Let’s return to our example to illustrate. Based on all of the example sentences shared in this lesson so far, the body paragraph for this particular essay prompt (with its topic sentence and supporting detail) might look like the following:
Based on the paragraph above, a possible concluding and transition sentence might be the following:
Notice how this sentence provides a sense of completion in terms of the controlling idea and supporting details shared throughout the paragraph? Do you also see how the sentence transitions the reader from the controlling idea of that paragraph back to the controlling idea—or thesis statement—of the entire essay?
- How could you avoid making your concluding and transition sentence a simple restatement of your topic sentence?
- What might your own concluding and transition sentence be based on the topic sentence and supporting details you plan to share?
Need More Help?
- Study other Writing Lessons in the Resource Center.
- Visit the Online Tutoring Resources in the Resource Center.
- Contact your Instructor.
- If you still need help, Schedule a Tutor .
Northern Illinois University Effective Writing Practices Tutorial
- Make a Gift
- MyScholarships
- Huskie Link
- Anywhere Apps
- Huskies Get Hired
- Student Email
- Password Self-Service
- Quick Links
- Effective Writing Practices Tutorial
- Organization
- Supporting Paragraphs
"A paragraph is a sentence or group of sentences that develops a main idea. Paragraphs serve as the primary building blocks of essays, reports, memos, and other forms of written composition" (Hult and Huckin, The New Century Handbook , 103).
In essence, paragraphs control the design and structure of the written composition. Paragraphs in the middle of your composition develop the thesis statement and provide transition ideas between supporting details.
Paragraphs should be " unified, coherent, and adequately developed , while flowing from one to the next as smoothly as possible" (Hult and Huckin, The New Century Handbook , 103).
Rule to Remember
Make sure all your paragraphs are unified, coherent, and adequately developed.
"A unified paragraph focuses on and develops a single main idea . This idea is typically captured in a single sentence, called a topic sentence . The other sentences in the paragraph, the supporting sentences , should elaborate on the topic sentence in a logical fashion (Hult and Huckin, The New Century Handbook , 104).
The supporting sentences, also called the body of the paragraph , are used to support, explain, illustrate, or provide evidence for the idea expressed in the topic sentence.
The main characteristics of a well-written paragraph
Introduce a topic sentence in your paragraph and then let the rest of the sentences build details to support it.
A paragraph should not introduce any other evidence or provide information that does not support the main idea; otherwise, the paragraph will lack unity and coherence.
Find logical subdivisions in your argument and organize them into unified paragraphs.
It is common to start a paragraph with a topic sentence and then let the rest of the sentences build details to support it. However, this is not by any means the only or the best pattern. The topic sentence can appear in any part of the paragraph or sometimes it can be implied.
Topic sentences at the beginning of a paragraph
In the following two paragraphs, the topic sentence appears at the beginning:
The environment the teacher creates in the classroom plays one of the most crucial roles in successful learning . This is true of any setting, whether the teaching occurs in a long academic program or in a tutoring situation. The teacher is a role model, a person students can trust, a guide, and a mentor. It is the responsibility of the teacher to create a low-anxiety environment in order to allow the students to enjoy the learning process. A good teacher tries to find out what works best with a particular learner or a group of learners and goes from there. What needs to come first in any learning situation is not a specific aspect or principle of methodology but the learners themselves.
From a Teaching Practicum Reflection Paper
Online education has become more popular than other forms of distance education because it offers learners a great deal of flexibility . Students have the freedom to work at their own pace, time, and chosen location. The flexibility of online learning makes it a very powerful tool that enhances learning, provides motivation for self-directed study, and, at the same time, increases convenience for learners with effective use of place and time. Online education is an excellent solution for those who consider learning to be a lifelong process. For adult learners, it provides the possibility to manage work, family, and other activities while still being able to take classes.
From a student research paper on Advantages and Limitations of Web-Based Instruction
"A topic sentence should, if possible, do four things: (1) provide a transition from a the preceding paragraph, (2) introduce the topic of the paragraph, (3) make a main point about this topic, and (4) suggest how the rest of the paragraph will develop this point" (Hult and Huckin, The New Century Handbook , 104).
Suggestions for writing paragraphs
- Avoid paragraphs that are either too long or too short
- Develop a single idea in a paragraph
- Use different patterns of paragraph development (narration, description, definition, example, comparison and contrast, analogy, cause and effect, or process)
- Provide transitions between paragraphs to make your writing flow smoothly (refer to the section on Transitions )
Audience also affects the choice of language, vocabulary, and sentence structures.
Reasons to start a new paragraph
- Introduce a new idea
- Emphasize an idea
- Introduce a logical pause
- Introduce a subtopic
- Conclude the composition
(Lunsford, The Everyday Writer , 48)
- Punctuation
- Reading the Assignment
- Addressing the Audience
- Introduction
- Thesis Statement
- Transitions
- Revision Process

Outlining an Essay
LESSON Using an outline A preliminary plan for a piece of a writing, often in the form of a list. It should include a topic, audience, purpose, thesis statement, and main and supporting points. is helpful when you are reading a textbook or an essay A short piece of writing that focuses on at least one main idea. Some essays are also focused on the author's unique point of view, making them personal or autobiographical, while others are focused on a particular literary, scientific, or political subject. or taking notes in class. It is also helpful when you are the writer. Outlining is an excellent tool for planning and organizing your content The text in a writing that includes facts, thoughts, and ideas. The information that forms the body of the work. . Different types of writing styles can use various outlining formats, but all outlines contain the same basic elements: main idea The most important or central thought of a reading selection. It also includes what the author wants the reader to understand about the topic he or she has chosen to write about. , major supporting details Statements within a reading that tie directly to the work's main idea. These can be provided in examples, statistics, anecdotes, definitions, descriptions, or comparisons within the work. , and minor supporting details Smaller statements within a reading that tie directly to major details. .
When writing an essay that uses examples from personal experience to support an opinion Point of view that shows a personal belief or bias and cannot be proven to be completely true. —sometimes called an exemplification A style of writing that uses personal experience to support an opinion. essay—the outline should list the opinion (main idea), followed by the supporting details. Remember that if you are outlining a paragraph, the main idea is the topic sentence; whereas, in a longer passage the main idea is the thesis statement A brief statement that identifies a writer's thoughts, opinions, or conclusions about a topic. Thesis statements bring unity to a piece of writing, giving it a focus and a purpose. You can use three questions to help form a thesis statement: What is my topic? What am I trying to say about that topic? Why is this important to me or my reader? .
- Minor Supporting Detail
For example, if a writer was describing how his father influenced his musical career, he would use examples showing how that was true. One example might be that his father taught him how to play the guitar when he was young. Another example might be that his father took him to his first performance in front of a crowd. These examples would be supporting details and depending on how in-depth the essay was to be, there might also be minor supporting details for each of the examples.
Writing is like building a house. It is ill-advised to just begin building one day without planning. In fact, most cities and towns require the home builder to submit blueprints before the foundation is poured. This ensures that the house will be constructed solidly without a chance of falling down. It also allows the builder to save both time and money.
Likewise, outlines help writers develop solid research papers An academic essay that usually includes research and citations. , business reports, and cover letters A letter that is sent along with a resume that provides context and more information for the reader. . It may seem unexpected, but taking the time to plan before you begin writing creates a foundation that will actually save you time overall because you will have a clear idea of what you will write. Planning allows you to spend less time in the revision The process of making changes to a work by editing and proofreading it to improve, correct, and increase clarity. process, which is a benefit whether you are writing for your college classes or your job.
Here is an example of how a writer can create a formal outline An outline that is traditional and structured, follows a set pattern, and uses a combination of Roman numerals, letters, and numbers to show a hierarchy of information based on the major and minor details or ideas. or informal outline A simplified outline that presents an overview of the placement of information in a reading. for the topic of an influential person. In the outlines below, the bolded items are the examples discussed earlier. These can be used as supporting details in one paragraph about the writer's father, or they can be separated into individual paragraphs as part of a longer essay. Also notice that the main idea will be either the topic sentence of a paragraph or the thesis of an essay.
Formal Outline:
Informal Outline:
Using the topic provided, create a sample formal and informal outline you could use to write an essay about that topic.
TOPIC: Best or Worst Job(s)
Use this template to create a formal outline.
Sample Answer
- One of the reasons I'm going to college is that I've had horrible jobs.
- I dug night crawlers.
- I smelled like fish all day.
- I served hungry and mean people.
- I smelled like hot dogs all day.
- I cleaned up messes.
- I smelled like play-dough all day.
Use this template to create an informal outline.
I. Main Idea - Supporting Idea - Supporting Idea - Supporting Idea
I. Worst Jobs - Bob's Bait and Tackle - Hot Dog Heaven - Happy Kids Play Land
Creating an outline will help me think through the assignment more at the beginning of the writing process. In the end, I will have a much better essay because I planned it.
I was always taught to use the formal outline structure, and I still think that is a good way of planning to write because it makes me include more detail than I might otherwise. However, I also like the informal outline because sometimes thinking about creating a formal outline seems like a big task. If I just think about creating an informal outline, I may be less hesitant to make one.
Copyright ©2022 The NROC Project
Table of Contents
Collaboration, information literacy, writing process, check relevance of supporting details, how are supporting details used.
When a writer makes a claim, the position should be backed with supporting details and examples. These details supply evidence that defends the validity of the claim, and they should be relevant, credible, and verifiable.
Why is it important to relate supporting details directly to the thesis or topic sentence?
In an academic paper, the claim and main ideas stated in the thesis and topic sentences require further explanation and support. The major components of a paper—the thesis, the topic sentences, and the supporting details—should work together to create a strong and stable essay. The thesis should be supported by each paragraph, and each paragraph’s topic sentence should be supported with relevant details and examples. If one of those components fails to do its job, the foundation of the paper is compromised and the argument is weakened.
Without relevant supporting details, the paper may lack cohesiveness and credibility. The reader may be unable to follow the progression of the argument and remain unconvinced that the claim or ideas have a credible foundation. To maintain the credibility of the author and the paper, include details and examples that clearly correspond to the claim and main ideas. It may be helpful to list some of these potential supporting details and select the most relevant before writing.
Let’s look at an example:
Claim: A stay-at-home parent performs a number of important tasks that others are paid to do.
Relevant supporting details: This list should include jobs that others are commonly paid to perform. These items on the following list could be considered relevant to the claim and could be verified by many stay-at-home parents and by reliable research:
- nanny : children are cared for
- chauffer: children may be transported to school and a variety of activities
- tutor : assistance with homework and projects may be provided
- manager: a wide variety of household tasks are organized and performed
- chef: meals are planned and prepared
- accountant: finances are managed
Irrelevant details : These ideas would not be appropriate to support the writer’s claim, because these activities are not usually performed by paid workers and would be considered irrelevant to the claim.
- coach : youth sports are often coached by the parent of one of the team members
- volunteer: parents may do volunteer work at their child’s school
- scout leader: boy scout and girl scout troops are usually led by a parent volunteer

Brevity – Say More with Less

Clarity (in Speech and Writing)

Coherence – How to Achieve Coherence in Writing

Flow – How to Create Flow in Writing

Inclusivity – Inclusive Language

The Elements of Style – The DNA of Powerful Writing

Suggested Edits
- Please select the purpose of your message. * - Corrections, Typos, or Edits Technical Support/Problems using the site Advertising with Writing Commons Copyright Issues I am contacting you about something else
- Your full name
- Your email address *
- Page URL needing edits *
- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Featured Articles

Academic Writing – How to Write for the Academic Community

Professional Writing – How to Write for the Professional World

Authority – How to Establish Credibility in Speech & Writing
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
New York Takes Crucial Step Toward Making Congestion Pricing a Reality
The board of the Metropolitan Transportation Authority voted to approve a new $15 toll to drive into Manhattan. The plan still faces challenges from six lawsuits before it can begin in June.

By Winnie Hu and Ana Ley
New York City completed a crucial final step on Wednesday in a decades-long effort to become the first American city to roll out a comprehensive congestion pricing program, one that aims to push motorists out of their cars and onto mass transit by charging new tolls to drive into Midtown and Lower Manhattan.
The program could start as early as mid-June after the board of the Metropolitan Transportation Authority, the state agency that will install and manage the program, voted 11-to-1 to approve the final tolling rates, which will charge most passenger cars $15 a day to enter at 60th Street and below in Manhattan. The program is expected to reduce traffic and raise $1 billion annually for public transit improvements.
It was a historic moment for New York’s leaders and transportation advocates after decades of failed attempts to advance congestion pricing even as other gridlocked cities around the world, including London, Stockholm and Singapore, proved that similar programs could reduce traffic and pollution.
While other American cities have introduced related concepts by establishing toll roads or closing streets to traffic, the plan in New York is unmatched in ambition and scale.
Congestion pricing is expected to reduce the number of vehicles that enter Lower Manhattan by about 17 percent, according to a November study by an advisory committee reporting to the M.T.A. The report also said that the total number of miles driven in 28 counties across the region would be reduced.
“This was the right thing to do,” Janno Lieber, the authority’s chairman and chief executive, said after the vote. “New York has more traffic than any place in the United States, and now we’re doing something about it.”
Congestion pricing has long been a hard sell in New York, where many people commute by car from the boroughs outside of Manhattan and the suburbs, in part because some of them do not have access to public transit.
New York State legislators finally approved congestion pricing in 2019 after Gov. Andrew M. Cuomo helped push it through. A series of recent breakdowns in the city’s subway system had underscored the need for billions of dollars to update its aging infrastructure.
It has taken another five years to reach the starting line. Before the tolling program can begin, it must be reviewed by the Federal Highway Administration, which is expected to approve it.
Congestion pricing also faces legal challenges from six lawsuits that have been brought by elected officials and residents from across the New York region. Opponents have increasingly mobilized against the program in recent months, citing the cost of the tolls and the potential environmental effects from shifting traffic and pollution to other areas as drivers avoid the tolls.
A court hearing is scheduled for April 3 and 4 on a lawsuit brought by the State of New Jersey, which is seen as the most serious legal challenge. The mayor of Fort Lee, N.J., Mark J. Sokolich, has filed a related lawsuit.
Four more lawsuits have been brought in New York: by Ed Day, the Rockland County executive; by Vito Fossella, the Staten Island borough president, and the United Federation of Teachers; and by two separate groups of city residents.
Amid the litigation, M.T.A. officials have suspended some capital construction projects that were to be paid for by the program, and they said at a committee meeting on Monday that crucial work to modernize subway signals on the A and C lines had been delayed.
Nearly all the toll readers have been installed, and will automatically charge drivers for entering the designated congestion zone at 60th Street or below. There is no toll for leaving the zone or driving around in it. Through traffic on Franklin D. Roosevelt Drive and the West Side Highway will not be tolled.
Under the final tolling structure, which was based on recommendations by the advisory panel, most passenger vehicles will be charged $15 a day from 5 a.m. to 9 p.m. on weekdays, and from 9 a.m. to 9 p.m. on weekends. The toll will be $24 for small trucks and charter buses, and will rise to $36 for large trucks and tour buses. It will be $7.50 for motorcycles.
Those tolls will be discounted by 75 percent at night, dropping the cost for a passenger vehicle to $3.75.
Fares will go up by $1.25 for taxis and black car services, and by $2.50 for Uber and Lyft. Passengers will be responsible for paying the new fees, and they will be added to every ride that begins, ends or occurs within the congestion zone. There will be no nighttime discounts. (The new fees come on top of an existing congestion surcharge that was imposed on for-hire vehicles in 2019.)
The tolls will mostly be collected using the E-ZPass system. Electronic detection points have been placed at entrances and exits to the tolling zone. Drivers who do not use an E-ZPass will pay significantly higher fees — for instance, $22.50 instead of $15 during peak hours for passenger vehicles.
Emergency vehicles like fire trucks, ambulances and police cars, as well as vehicles carrying people with disabilities, were exempted from the new tolls under the state’s congestion pricing legislation .
As for discounts, low-income drivers who make less than $50,000 annually can apply to receive half off the daytime toll after their first 10 trips in a calendar month. In addition, low-income residents of the congestion zone who make less than $60,000 a year can apply for a state tax credit.
All drivers entering the zone directly from four tolled tunnels — the Lincoln, Holland, Hugh L. Carey and Queens-Midtown — will receive a “crossing credit” that will be applied against the daytime toll. The credit will be $5 round-trip for passenger vehicles, $12 for small trucks and intercity and charter buses, $20 for large trucks and tour buses, and $2.50 for motorcycles. No credits will be offered at night.
Grace Ashford contributed reporting.
Winnie Hu is a Times reporter covering the people and neighborhoods of New York City. More about Winnie Hu
Ana Ley is a Times reporter covering New York City’s mass transit system and the millions of passengers who use it. More about Ana Ley
Florida Supreme Court puts abortion on the ballot – and hands Trump a serious problem
You can parse these sunshine state developments any way you like, but there's no version that’s good for trump, the republican presidential nominee in waiting..
In the end, Ron “DeSanctimonious” DeSantis may get his revenge on Donald Trump – just not in the way he expected.
The Florida governor’s draconian six-week abortion ban – which he pushed as part of his presidential run, thinking he could out-extreme Trump and the other GOP candidates – got the green light from the Florida Supreme Court on Monday. It will go into effect in 30 days , with the state’s previous 15-week abortion ban kicking in until then.
That’s horrific, but the state’s high court also ruled that an amendment protecting abortion rights will be on the Florida ballot in November , giving voters a chance to strike down DeSantis’ ban and, if past elections are any evidence, driving voter turnout considerably.
DeSantis and Florida's Supreme Court lend Biden a hand
You can parse these Sunshine State developments any way you like, but there’s no version that’s good for Trump, the Republican presidential nominee in waiting.
He has previously described DeSantis’ six-week ban as “terrible,” knowing how unpopular it is with voters. So now, in his home state, Trump will face three not-good-for-him-but-great-for-Joe-Biden choices:
- Embrace the six-week ban he pilloried and tell his supporters to oppose the abortion-rights protection amendment.
- Maintain his opposition to the six-week ban and support the abortion-rights protection amendment, something he can’t do without alienating evangelical voters.
- Say that when he becomes president, he’ll override the six-week state ban with a federal abortion ban at 15 or 16 weeks, which would be a gift to President Biden’s reelection campaign.
Oh, Ron. If only you had planned this as a way of getting back at the guy who dubbed you “ Ron DeSanctimonious ,” people might think you’re crafty.
A six-week abortion ban in Florida is basically a complete abortion ban
In Monday’s rulings , Florida’s conservative Supreme Court decided that the state’s constitution doesn’t protect abortion rights. That put Florida’s existing 15-week abortion ban back in place.
The six-week ban that DeSantis signed into law last April was designed to start 30 days after a Supreme Court ruling upholding the 15-week ban. So the clock on that starts now.
For Floridians, a six-week ban is essentially a complete ban on abortion, as most people don’t even know they’re pregnant before six weeks. It will also further limit abortion access in the South.
Lauren Brenzel, the campaign director for Floridians Protecting Freedom, which fought to get the abortion amendment on the state’s 2024 ballot, told The Washington Post : “There is nowhere in the Southeast that can absorb Florida’s patient base. It’s simply not possible. That is simply an unmanageable volume of patients to try to offset to another state.”
Why doesn't Biden sell Bibles? Joe Biden hasn't targeted a judge's daughter or sold a single Bible. What a LOSER!
Trump is going to struggle to reckon with this Florida ballot issue
The real-world consequences of DeSantis’ ban will be felt long before the November election, and it will not be an issue Trump can sidestep.
Women in his state will have fully lost abortion rights, first thanks to Trump’s U.S. Supreme Court picks helping overturn Roe v. Wade and then thanks to DeSantis’ abortion ban, which was upheld by the conservatives he put on the state’s supreme court.
Trump has tried ineffectively to straddle this issue, taking credit for Roe getting overturned then criticizing DeSantis’ state ban, all while mumbling nonspecifically that “deals are going to be made” when it comes to a national abortion ban.
At a CNN town hall last May , Trump was asked whether he would sign a 15-week federal abortion ban and he wouldn’t answer, saying only: “What I'll do is negotiate, so that people are happy.”
Good luck with that, bubba.
Recent Fox News poll shows widespread support for abortion access
To summarize voters’ views on the issue, I’ll quote from this Fox News report published last week : “Nearly two years after the Supreme Court overturned Roe v. Wade, a record number of voters think abortion should be legal, with two-thirds favoring nationwide law guaranteeing access, according to a Fox News national survey.”
That Truth Social stock: Thinking about buying Truth Social stock? Trump's own filing offers these warnings.
That’s “guaranteeing” access, not banning it.
The poll found 59% of voters think abortion should be legal in all or most cases. And 54% oppose a 15-week federal abortion ban, with far more opposing more restrictive legislation.
Biden will still have an uphill fight in Florida, but this changes outlook
Since Roe was overturned, this has been a losing issue for Republicans. Trump knows that, but he can’t figure out how to dance around it the way he does most things.
Thanks to the actions of DeSantis, the GOP primary opponent Trump vanquished and humiliated, that dance just got orders of magnitude more complicated.
And Florida – the seemingly bright-red state that features Mar-a-Lago and Trump himself – just got a whole lot more interesting.
Follow USA TODAY columnist Rex Huppke on X, formerly Twitter, @RexHuppke and Facebook facebook.com/RexIsAJerk
We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.
- Commercial Insights
- Wealth Insights
- Online Banking Login
- Regions Total Wealth
- Investment Account Access
- Open an Account
- En Español
Regions Riding Forward® Scholarship Contest

Their Story. Your Voice.
Your voice is your own. But it's also been impacted by others. Who, we wonder, has inspired you? Let us know by entering the Regions Riding Forward Scholarship Contest.
You could win an $8,000 college scholarship
For the opportunity to win an $8,000 scholarship, submit a video or written essay about an individual you know personally (who lives in your community) who has inspired you and helped you build the confidence you need to achieve your goals.

The details
The 2024 Regions Riding Forward Scholarship Contest consists of four (4) separate Quarterly Contests - one for each calendar quarter of 2024. Regions is awarding four $8,000 scholarships through each Quarterly Contest.
Each Quarterly Contest has its own separate entry period, as provided in the chart below.
The entry deadline for each Quarterly Contest is 11:59:59 PM Central Time on the applicable Quarterly Contest period end date (set forth in the chart above).
No purchase or banking relationship required.
Regions believes in supporting the students whose passion and actions every day will continue to make stories worth sharing. That’s why we have awarded over $1 million in total scholarships to high school and college students.
How to enter, 1. complete an online quarterly contest application.
Enter the Regions Riding Forward Scholarship Contest by completing a Quarterly Contest application. The second Quarterly Contest runs from April 1, 2024 through June 30, 2024. Complete and save all requested information.
2. Prepare your Written Essay or Video Essay
For each Quarterly Contest, the topic of your Written Essay or Video Essay (your “Essay Topic”) must be an individual you know personally, who lives in your community. Your Written Essay or Video Essay must address how the individual you have selected as your Essay Topic has inspired you and helped you build the confidence you need to achieve your goals.
Written Essay and Video Essay submissions must meet all of the requirements described in the contest Official Rules. Your Written Essay or Video Essay must be (i) in English, (ii) your own original work, created solely by you (and without the use of any means of artificial intelligence (“AI”)), and (iii) the exclusive property of you alone.
Written Essays must be 500 words or less. You can write your Written Essay directly in the application, or you can copy and paste it into the appropriate area in the application form.
Video Essay submissions must be directly uploaded to the contest application site. Video Essays must be no more than 3 minutes in length and no larger than 1 GB. Only the following file formats are accepted: MP4, MPG, MOV, AVI, and WMV. Video Essays must not contain music of any kind nor display any illegal, explicit, or inappropriate material, and Video Essays must not be password protected or require a log-in/sign-in to view. You must upload your Video Essay to the application, and you may not submit your Video Essay in DVD or other physical form. (Video Essays submitted via mail will not be reviewed or returned.)
Tips to Record Quality Videos on a Smartphone:
- Don’t shoot vertical video. Computer monitors have landscape-oriented displays, so shoot your video horizontally.
- Use a tripod. Even small movements can make a big difference when editing.
- Don’t use zoom. If you need to get a close shot of the subject, move closer as zooming can cause pixilation.
- Use natural lighting. Smartphone lighting can wash out your video.
3. Review and submit your Quarterly Contest application
Review your information on your Quarterly Application (and check the spelling of a Written Essay) and submit your entry by 11:59:59 p.m. Central Time on the applicable Quarterly Contest period end date. The second Quarterly Contest period end date is June 30, 2024.
4. Await notification
Winning entries are selected by an independent panel of judges who are not affiliated with Regions. If your entry is selected as a Quarterly Contest winner, you will need to respond to ISTS with the required information.
Eligibility
For purposes of this contest:
- The “Eligible States” are defined as the following states: Alabama, Arkansas, Florida, Georgia, Iowa, Illinois, Indiana, Kentucky, Louisiana, Mississippi, Missouri, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee and Texas.
- An “accredited college” is defined as a nonprofit, two- or four-year college or university located within one of the fifty (50) United States or the District of Columbia.
To be eligible to enter this contest and to win an award in a Quarterly Contest, at the time of entry, you must:
- Be a legal U.S. resident of one of the Eligible States.
- Be age 16 or older.
- Have at least one (1) year (or at least 18 semester hours) remaining before college graduation.
- If you are not yet in college, begin your freshman year of college no later than the start of the 2025 – 2026 college academic school year.
- As of your most recent school enrollment period, have a cumulative grade point average of at least 2.0 in school (and if no GPA is provided at school, be in “good standing” or the equivalent thereof in school).
View Official Rules
NO PURCHASE OR BANKING RELATIONSHIP REQUIRED. PURCHASE OR BANKING RELATIONSHIP WILL NOT INCREASE YOUR CHANCES OF WINNING. VOID WHERE PROHIBITED. The 2024 Regions Riding Forward Scholarship Contest (the “Contest”) consists of four (4) separate quarterly contests (each a “Quarterly Contest”): (1) the “Q-1 Contest;” (2) the “Q-2 Contest;” (3) the “Q-3 Contest;” and (4) the “Q-4 Contest.” The Q-1 Contest begins on 02/01/24 and ends on 03/31/24; the Q-2 Contest begins on 04/01/24 and ends on 06/30/24; the Q-3 Contest begins on 07/01/24 and ends on 09/30/24; and the Q-4 Contest begins on 10/01/24 and ends on 12/31/24. (For each Quarterly Contest, entries must be submitted and received by 11:59:59 PM CT on the applicable Quarterly Contest period end date.) To enter and participate in a particular Quarterly Contest, at the time of entry, you must: (a) be a legal U.S. resident of one of the Eligible States; (b) be 16 years of age or older; (c) have at least one (1) year (or at least 18 semester hours) remaining before college graduation; (d) (if you are not yet in college) begin your freshman year of college no later than the start of the 2025 – 2026 college academic school year; and (e) as of your most recent school enrollment period, have a cumulative grade point average of at least 2.0 in school (and if no grade point average is provided at school, be in “good standing” or the equivalent thereof in school). (For purposes of Contest, the “Eligible States” are defined as the states of AL, AR, FL, GA, IA, IL, IN, KY, LA, MS, MO, NC, SC, TN and TX.) Visit regions.com/ridingforward for complete Contest details, including eligibility and Written Essay and Video Essay requirements and Official Rules. (Limit one (1) entry per person, per Quarterly Contest.) For each Quarterly Contest, eligible entries will be grouped according to form of entry (Written Essay or Video Essay) and judged by a panel of independent, qualified judges. A total of four (4) Quarterly Contest Prizes will be awarded in each Quarterly Contest, consisting of two (2) Quarterly Contest Prizes for the Written Essay Entry Group and two (2) Quarterly Contest Prizes for the Video Essay Entry Group. Each Quarterly Contest Prize consists of a check in the amount of $8,000 made out to winner’s designated accredited college. (Limit one (1) Quarterly Contest Prize per person; a contestant is permitted to win only one (1) Quarterly Contest Prize through the Contest.) Sponsor: Regions Bank, 1900 Fifth Ave. N., Birmingham, AL 35203.
© 2024 Regions Bank. All rights reserved. Member FDIC. Equal Housing Lender. Regions and the Regions logo are registered trademarks of Regions Bank. The LifeGreen color is a trademark of Regions Bank.
2023 Winners
High school:.
- Amyrrean Acoff
- Leon Aldridge
- Kharis Andrews
- Colton Collier
- Indya Griffin
- Christopher Hak
- Aquil Hayes
- Jayden Haynes
- McKenna Jodoin
- Paris Kelly
- Liza Latimer
- Dylan Lodle
- Anna Mammarelli
- Karrington Manley
- Marcellus Odum
- Gautami Palthepu
- Melody Small
- Lauryn Tanner
- Joshua Wilson
- Mohamed Ali
- Kayla Bellamy
- Lauren Boxx
- Alexandria Brown
- Samuel Brown
- Thurston Brown
- Conner Daehler
- Tsehai de Souza
- Anjel Echols
- Samarion Flowers
- Trinity Griffin
- Kristina Hilton
- Ryan Jensen
- Miracle Jones
- Shaniece McGhee
- Chelby Melvin
- Lamiya Ousley
- Kiera Phillips
- Gabrielle Pippins
- Ethan Snead
- Sydney Springs
- Kirsten Tilford
- Tamira Weeks
- Justin Williams
2022 Winners
- Paul Aucremann
- William Booker
- Robyn Cunningham
- Kani'ya Davis
- Oluwatomi Dugbo
- Lillian Goins
- Parker Hall
- Collin Hatfield
- Gabrielle Izu
- Kylie Lauderdale
- Jacob Milan
- Jackson Mitchell
- Carmen Moore
- Madison Morgan
- Kaden Oquelí-White
- Kaylin Parks
- Brian Perryman
- De'Marco Riggins
- Brianna Roundtree
- Sydney Russell
- Carlie Spore
- Morgan Standifer
- Ionia Thomas
- Ramaya Thomas
- Jaylen Toran
- Amani Veals
- Taylor Williams
- Alana Wilson
- Taryn Wilson
- Aryaunna Armstrong
- Hannah Blackwell
- T'Aneka Bowers
- Naomi Bradley
- Arianna Cannon
- Taylor Cline
- Catherine Cummings
- Margaret Fitzgerald
- Chloe Franklin
- Camryn Gaines
- Thomas Greer
- Kayla Helleson
- Veronica Holmes
- Logan Kurtz
- Samuel Lambert
- Jaylon Muchison
- Teresa Odom
- Andrew Payne
- Carey Price
- Emily SantiAnna
- Curtis Smith
- Jered Smith
- Mariah Standifer
- Maura Taylor
- Anna Wilkes

COMMENTS
Supporting details in fiction essays generally expand on the main idea and serve to paint a clearer picture of what the essay is about. Main ideas are like the bun of a hamburger, and the ...
Topic Sentence = inform the reader of the main idea of the paragraph (which should connect with the introductory thesis, i.e., the focus of the whole essay) Supporting detail = provide support for the main idea (s) stated in the topic sentence, usually by using evidence (facts and statistics), examples and explanations.
Supporting point 1: Dogs can scare cyclists and pedestrians. Supporting details: Cyclists are forced to zigzag on the road. School children panic and turn wildly on their bikes. People who are walking at night freeze in fear. Supporting point 2: Loose dogs are traffic hazards. Supporting details: Dogs in the street make people swerve their cars.
Exercise 3.8.1 3.8. 1. Read the following paragraph and then decide what the main idea is. One myth about exercise is that if a woman lifts weights, she will develop muscles as large as a man's. Without male hormones, however, a woman cannot increase her muscle bulk as much as a man's.
Updated on February 03, 2019. In a composition or speech, a supporting detail is a fact, description, example, quotation, anecdote, or other item of information used to back up a claim, illustrate a point, explain an idea, or otherwise support a thesis or topic sentence . Depending on a number of factors (including topic, purpose, and audience ...
Here are some tips on what to strive for and what to avoid when it comes to supporting details. Good support. Is relevant and focused (sticks to the point). Is well developed. Provides sufficient detail. Is vivid and descriptive. Is well organized. Is coherent and consistent. Highlights key terms and ideas.
The purpose of supporting details in writing is to provide evidence to support the main idea of a paragraph or essay. Supporting details help to clarify and explain the main idea, making it easier for the reader to understand and follow the writer's point of view. How do supporting details contribute to the main idea of a paragraph?
Writing the Essay Body: Supporting Your Ideas. Whether the drafting of a paragraph begins with a main idea or whether that idea surfaces in the revision process, once you have that main idea, you'll want to make sure that the idea has enough support. The job of the paragraph body is to develop and support the topic.
A topic sentence has several important functions: it substantiates or supports an essay's thesis statement; it unifies the content of a paragraph and directs the order of the sentences; and it advises the reader of the subject to be discussed and how the paragraph will discuss it. Readers generally look to the first few sentences in a ...
A. Supporting details are the well-researched facts and statements, detailed descriptions, examples, and specific details that lead the reader to comprehend the main idea of a paragraph. Supporting details provide clarification to the reader by explaining, describing, and illustrating the main idea within the text.
Supporting details are pieces of information that can bolster an idea through facts. Learn more about what they are and what they might look like here.
Support for Main Idea - Key Takeaways. In a single-paragraph essay, the main idea is the writer's position or principal concept they would like to express, and the supporting details are the means by which they develop and prove that idea. Single-paragraph essays demand a concise and to-the-point main idea and supporting details.
These supporting details provide examples, facts, or evidence that support the topic sentence. The writer drafts possible supporting detail sentences for each primary support sentence based on the thesis statement: The following paragraph contains supporting detail sentences for the primary support sentence (the topic sentence), which is ...
The Purpose of Supporting Details. Keep the reader focused on the main idea of the paragraph. Demonstrate that your topic sentence or main idea is accurate and believable. Make your meaning clear and forceful with concrete, specific information.
Creating Supporting Details. Figure 6.1. You can and should use a variety of kinds of support for your thesis. One of the easiest forms of support to use is personal observations and experiences. The strong point in favor of using personal anecdotes is that they add interest and emotion, both of which can pull audiences along.
The same types of supporting details will work. Much like with your basic paragraph assignment, your Basic Essay assignment also requires you to use supporting details in your body paragraph that directly support your controlling idea. The only difference is instead of integrating two supporting details, you only need to integrate one.
Supporting Paragraphs. "A paragraph is a sentence or group of sentences that develops a main idea. Paragraphs serve as the primary building blocks of essays, reports, memos, and other forms of written composition" (Hult and Huckin, The New Century Handbook, 103). In essence, paragraphs control the design and structure of the written composition.
Supporting reasons explain the main idea and present facts that help explain the main idea. Supporting details clarify the major reasons with examples. How to find the element in an academic essay: We can find the topic in the title and introduction. We can find the main idea or thesis of the entire essay at the end of the introduction.
In this lesson, you will learn how to identify both major and minor supporting details in a reading. When looking at a full reading such as an article or essay, the major and minor details relate to the thesis statement like this: Major supporting details: topic sentences. A sentence that contains the controlling idea for an entire paragraph ...
, and minor supporting details Smaller statements within a reading that tie directly to major details.. When writing an essay that uses examples from personal experience to support an opinion Point of view that shows a personal belief or bias and cannot be proven to be completely true. —sometimes called an exemplification A style of writing ...
The thesis should be supported by each paragraph, and each paragraph's topic sentence should be supported with relevant details and examples. If one of those components fails to do its job, the foundation of the paper is compromised and the argument is weakened. Without relevant supporting details, the paper may lack cohesiveness and credibility.
Travis Kelce reveals why the secret to his Taylor Swift relationship is mutual support. The media could not be loaded, either because the server or network failed or because the format is not ...
Fares will go up by $1.25 for taxis and black car services, and by $2.50 for Uber and Lyft. Passengers will be responsible for paying the new fees, and they will be added to every ride that begins ...
In Monday's rulings, Florida's conservative Supreme Court decided that the state's constitution doesn't protect abortion rights. That put Florida's existing 15-week abortion ban back in ...
Listen. 3:06. Google said it would delete millions of records of user's browsing activities as part of a settlement of a class-action lawsuit that alleged it tracked people without their ...
2:02. Walmart Inc. will withdraw and refile the paperwork associated with its deal to buy smart-TV maker Vizio Holding Corp. a routine step designed to give federal authorities more time to decide ...
The 2024 Regions Riding Forward Scholarship Contest consists of four (4) separate Quarterly Contests - one for each calendar quarter of 2024. Regions is awarding four $8,000 scholarships through each Quarterly Contest. Each Quarterly Contest has its own separate entry period, as provided in the chart below. The entry deadline for each Quarterly ...