- Survey Software The world’s leading omnichannel survey software
- Online Survey Tools Create sophisticated surveys with ease.
- Mobile Offline Conduct efficient field surveys.
- Text Analysis
- Close The Loop
- Automated Translations
- NPS Dashboard
- CATI Manage high volume phone surveys efficiently
- Cloud/On-premise Dialer TCPA compliant Cloud on-premise dialer
- IVR Survey Software Boost productivity with automated call workflows.
- Analytics Analyze survey data with visual dashboards
- Panel Manager Nurture a loyal community of respondents.
- Survey Portal Best-in-class user friendly survey portal.
- Voxco Audience Conduct targeted sample research in hours.
- Predictive Analytics
- Customer 360
- Customer Loyalty
- Fraud & Risk Management
- AI/ML Enablement Services
- Credit Underwriting

Find the best survey software for you! (Along with a checklist to compare platforms)
Get Buyer’s Guide
- 100+ question types
- Drag-and-drop interface
- Skip logic and branching
- Multi-lingual survey
- Text piping
- Question library
- CSS customization
- White-label surveys
- Customizable ‘Thank You’ page
- Customizable survey theme
- Reminder send-outs
- Survey rewards
- Social media
- SMS surveys
- Website surveys
- Correlation analysis
- Cross-tabulation analysis
- Trend analysis
- Real-time dashboard
- Customizable report
- Email address validation
- Recaptcha validation
- SSL security
Take a peek at our powerful survey features to design surveys that scale discoveries.
Download feature sheet.
- Hospitality
- Financial Services
- Academic Research
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Product Experience
- Market Research
- Social Research
- Data Analysis
- Banking & Financial Services
- Retail Solution
- Risk Management
- Customer Lifecycle Solutions
- Net Promoter Score
- Customer Behaviour Analytics
- Customer Segmentation
- Data Unification
Explore Voxco
Need to map Voxco’s features & offerings? We can help!
Watch a Demo
Download Brochures
Get a Quote
- NPS Calculator
- CES Calculator
- A/B Testing Calculator
- Margin of Error Calculator
- Sample Size Calculator
- CX Strategy & Management Hub
- Market Research Hub
- Patient Experience Hub
- Employee Experience Hub
- Market Research Guide
- Customer Experience Guide
- The Voxco Guide to Customer Experience
- NPS Knowledge Hub
- Survey Research Guides
- Survey Template Library
- Webinars and Events
- Feature Sheets
- Try a sample survey
- Professional services
- Blogs & White papers
- Case Studies
Find the best customer experience platform
Uncover customer pain points, analyze feedback and run successful CX programs with the best CX platform for your team.
Get the Guide Now

We’ve been avid users of the Voxco platform now for over 20 years. It gives us the flexibility to routinely enhance our survey toolkit and provides our clients with a more robust dataset and story to tell their clients.
VP Innovation & Strategic Partnerships, The Logit Group
- Client Stories
- Voxco Reviews
- Why Voxco Research?
- Why Voxco Intelligence?
- Careers at Voxco
- Vulnerabilities and Ethical Hacking
Explore Regional Offices
- Cloud/On-premise Dialer TCPA compliant Cloud & on-premise dialer
- Fraud & Risk Management
Get Buyer’s Guide
- Banking & Financial Services
Explore Voxco
Watch a Demo
Download Brochures
- CX Strategy & Management Hub
- Blogs & White papers
VP Innovation & Strategic Partnerships, The Logit Group
- Our clients
- Client stories
- Featuresheets

Descriptive research questions: Definition, examples and designing methodology
- October 4, 2021
SHARE THE ARTICLE ON
Conducting thorough market research is all about framing the right questions that provide accurate answers to research questions. The two main categories of questions namely: Quantitative and Qualitative questions focus on differential aspects.
While quantitative research questions are based on numerical data that provides a substantial backing to the decision making process, qualitative research questions aim to derive insights based on textual responses. Both these questions are used based on their relevance and suitability to meet end objectives of the user.
One such useful quantitative question type are the descriptive research questions.
What is descriptive research?
Descriptive research questions aim to provide a description of the variable under consideration. It is one of the easiest and commonly used ways to quantify research variables.
Questions that begin with:
- How much: How much time does an average teenager spend on watching documentaries on OTT platforms?
Variable: time spent on watching documentaries
Group: Teenagers
- How often: How often do you take an international family trip in a year?
Variable: International trips
Group: Families
- How likely: How likely is it for a person to purchase life insurance within the age group of 20-26?
Variable: Likelihood of purchasing a life insurance
Group: People within the age group of 20-26
- What percentage: What percentage of high school students exercise on a daily basis?
Variable: Daily Exercise
Group: High School Students
- How many: How many smartphone users make use of curated apps to manage daily tasks?
Variable: Usage of curated apps
Group: Smartphone users
- What proportion: What proportion of students prefer online education to offline education?
Variable: Educational format
Group: Students
- How regularly: How regularly does a woman engage or purchase from a cosmetic brand outlet as against e-commerce websites?
Variable: Purchasing Behaviour of cosmetics
Group: Women

- What is: What is the ratio of passengers indulging in train travel to travelling by flight?
Variable: Travelling medium
Group: Passengers
- What are: What are the influencing factors that impact the choice of purchasing a house in the UK?
Variable: Influencing factors
Group: UK property investors/ New buyers
Among other such phrases are all classified as descriptive questions. By gathering sufficient responses to such questions, end users are able to make intelligent decisions based on hard figures that help in gathering stakeholder confidence.
For example: What percentage of college students make use of e-libraries for their academic needs. In this example the variable under observation is usage of e-libraries and the group that is evaluated are the college going students.
By providing percentages, averages, sum, proportions and other such figures, descriptive research questions provide a complete view of the target groups responses with respect to that variable. The above example has restricted the usage of variables to one, but many researchers alternatively choose to incorporate multiple variables under a single head.
Why are descriptive research questions important?
Descriptive research questions are a systematic methodology that helps in understanding the what, where, when and how. Important variables can be rigidly defined using descriptive research, unlike qualitative research where the subjectivity in responses makes it relatively difficult to get a grasp on the overall picture. The multiple methods available allow for in-person as well as online research to be carried out based on whatever the need of the end user is.
The data provided by descriptive research assists comprehensive understanding by providing an in-depth view of the variable that is being studied.
Steps to conduct Cluster Sampling
These are the following steps used to perform single-stage cluster sampling:
- Decide on a target population and desired sample size.
- Divide the target population into clusters based on a specific criteria.
- Select clusters using methods of random selection while keeping in mind the desired sample size.
- Collect data from the final sample group.
Further steps may be taken using two-stage or multistage sampling to achieve desired sample size if it cannot be achieved through one-stage sampling.
Types of descriptive research questions?
Descriptive research questions has divisions based on multiple business applications:
Market performance:
Descriptive research questions can be centred around organizational market performance in terms of sales figures, competitive appeal, updated practices, market share analytics, concept studies and other data collection processes that intend to gather market know-how. Target market analysis can also be done using descriptive question types wherein organizations can precisely define their niche audience.
Consumer behaviour:
Consumer perceptions and ideas about what suits them best can be understood using descriptive question types. These studies are used to design curated products that meet target market requirements. Anything from products, services, offers, incentives, promotions and marketing, pricing, packaging, feedback mechanism can be put into perspective and gauged to extract material results.

Internal trends:
While market performance looks at external variables, internal trends focus on departmental contributions, revenue generation, product specific demands, sales figures etc. This internal summary helps appraise performance within the organization and contrast it with external performance for benchmarking purposes.

How to frame descriptive research questions?
There is no rocket science behind framing the right question for your variable. It’s just a matter of figuring out what you want to assess and the numerical measure you’re looking for. The usage of descriptive questions in your study also comes with the condition of keeping the entire process concise and to the point.
To start off, figure out the variable that you wish to gauge and the target group that needs to be evaluated. This will determine the centre point of your research questions. Avoid providing vague descriptions and instead, try narrowing the details. Such a practice will direct the questioning to the exact audience you wish to examine without adding in unnecessary responses.
Choose the starting phrase that encompasses what you’re looking to measure. For example: If you’re looking to examine or separate a certain type of person from the entire target audience, phrases such as “what proportion” or “what percentage” can prove highly useful.
Questioning tips:
- Proceed from general to specific questions while making sure that you don’t lose focus of your target variable and audience.
- Avoid using ambiguous terminologies that are likely to confuse your respondents into misunderstanding questions as this can adversely affect the quality of your responses.
- Keep the questions simple and easy to understand in such a way that all targeted respondents are able to grasp the overall meaning equally.
- Avoid leading questions that skew the respondent into answering a certain way. Research is all about getting the information that you want in an authentic manner and such questions can sway the respondent into giving artificial responses.
Make sure that your answer choices are balanced. This is another bias that forces the respondent into altering their actual responses. Try to provide equal representation to all possible answers such that the probability of receiving each response is equally likely.
Lastly, look for variables of questions that you can club together without affecting the overall questioning process. However, it is often useful to bifurcate combined questions wherever you can, combining relevant questions together can provide useful information about existing relationships. This goes without saying that such clubbing must not act as a hindrance to the understanding of these variables as separate characteristics.
Explore Voxco Survey Software
+ Omnichannel Survey Software
+ Online Survey Software
+ CATI Survey Software
+ IVR Survey Software
+ Market Research Tool
+ Customer Experience Tool
+ Product Experience Software
+ Enterprise Survey Software

How Face-to-Face (CAPI) Surveys Can Push Your Research Forward
The Comprehensive Guide to Computer-Assisted Personal Interview (CAPI) Surveys SHARE THE ARTICLE ON Table of Contents In the world of data collection and research, technology

Psychographic segmentation
Psychographic segmentation See what question types are possible with a sample survey! Try a Sample Survey 01 What is psychographic segmentation? Psychographic segmentation is the

Top 12 Pulse Survey Tools: Boost Employee Engagement
Top 12 Pulse Survey Tools: Boost Employee Engagement SHARE THE ARTICLE ON Table of Contents Understanding your employee experience and satisfaction has become more harder,
Bar graphs/charts: a guide towards making bar graphs using Excel
Bar graphs/charts: a guide towards making bar graphs using Excel SHARE THE ARTICLE ON Share on facebook Share on twitter Share on linkedin Table of

7 reasons why every company should conduct concept tests
7 reasons why every company should conduct concept tests SHARE THE ARTICLE ON Share on facebook Share on twitter Share on linkedin Table of Contents
Mosaic Plot
Mosaic Plot SHARE THE ARTICLE ON Share on facebook Share on twitter Share on linkedin Table of Contents A mosaic plot is a sort of
We use cookies in our website to give you the best browsing experience and to tailor advertising. By continuing to use our website, you give us consent to the use of cookies. Read More
Looking for the best research tools?
Voxco offers the best online & offline survey research tools!
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Korean Med Sci
- v.37(16); 2022 Apr 25

A Practical Guide to Writing Quantitative and Qualitative Research Questions and Hypotheses in Scholarly Articles
Edward barroga.
1 Department of General Education, Graduate School of Nursing Science, St. Luke’s International University, Tokyo, Japan.
Glafera Janet Matanguihan
2 Department of Biological Sciences, Messiah University, Mechanicsburg, PA, USA.
The development of research questions and the subsequent hypotheses are prerequisites to defining the main research purpose and specific objectives of a study. Consequently, these objectives determine the study design and research outcome. The development of research questions is a process based on knowledge of current trends, cutting-edge studies, and technological advances in the research field. Excellent research questions are focused and require a comprehensive literature search and in-depth understanding of the problem being investigated. Initially, research questions may be written as descriptive questions which could be developed into inferential questions. These questions must be specific and concise to provide a clear foundation for developing hypotheses. Hypotheses are more formal predictions about the research outcomes. These specify the possible results that may or may not be expected regarding the relationship between groups. Thus, research questions and hypotheses clarify the main purpose and specific objectives of the study, which in turn dictate the design of the study, its direction, and outcome. Studies developed from good research questions and hypotheses will have trustworthy outcomes with wide-ranging social and health implications.
INTRODUCTION
Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses. 1 , 2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results. 3 , 4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the inception of novel studies and the ethical testing of ideas. 5 , 6
It is crucial to have knowledge of both quantitative and qualitative research 2 as both types of research involve writing research questions and hypotheses. 7 However, these crucial elements of research are sometimes overlooked; if not overlooked, then framed without the forethought and meticulous attention it needs. Planning and careful consideration are needed when developing quantitative or qualitative research, particularly when conceptualizing research questions and hypotheses. 4
There is a continuing need to support researchers in the creation of innovative research questions and hypotheses, as well as for journal articles that carefully review these elements. 1 When research questions and hypotheses are not carefully thought of, unethical studies and poor outcomes usually ensue. Carefully formulated research questions and hypotheses define well-founded objectives, which in turn determine the appropriate design, course, and outcome of the study. This article then aims to discuss in detail the various aspects of crafting research questions and hypotheses, with the goal of guiding researchers as they develop their own. Examples from the authors and peer-reviewed scientific articles in the healthcare field are provided to illustrate key points.
DEFINITIONS AND RELATIONSHIP OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
A research question is what a study aims to answer after data analysis and interpretation. The answer is written in length in the discussion section of the paper. Thus, the research question gives a preview of the different parts and variables of the study meant to address the problem posed in the research question. 1 An excellent research question clarifies the research writing while facilitating understanding of the research topic, objective, scope, and limitations of the study. 5
On the other hand, a research hypothesis is an educated statement of an expected outcome. This statement is based on background research and current knowledge. 8 , 9 The research hypothesis makes a specific prediction about a new phenomenon 10 or a formal statement on the expected relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable. 3 , 11 It provides a tentative answer to the research question to be tested or explored. 4
Hypotheses employ reasoning to predict a theory-based outcome. 10 These can also be developed from theories by focusing on components of theories that have not yet been observed. 10 The validity of hypotheses is often based on the testability of the prediction made in a reproducible experiment. 8
Conversely, hypotheses can also be rephrased as research questions. Several hypotheses based on existing theories and knowledge may be needed to answer a research question. Developing ethical research questions and hypotheses creates a research design that has logical relationships among variables. These relationships serve as a solid foundation for the conduct of the study. 4 , 11 Haphazardly constructed research questions can result in poorly formulated hypotheses and improper study designs, leading to unreliable results. Thus, the formulations of relevant research questions and verifiable hypotheses are crucial when beginning research. 12
CHARACTERISTICS OF GOOD RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Excellent research questions are specific and focused. These integrate collective data and observations to confirm or refute the subsequent hypotheses. Well-constructed hypotheses are based on previous reports and verify the research context. These are realistic, in-depth, sufficiently complex, and reproducible. More importantly, these hypotheses can be addressed and tested. 13
There are several characteristics of well-developed hypotheses. Good hypotheses are 1) empirically testable 7 , 10 , 11 , 13 ; 2) backed by preliminary evidence 9 ; 3) testable by ethical research 7 , 9 ; 4) based on original ideas 9 ; 5) have evidenced-based logical reasoning 10 ; and 6) can be predicted. 11 Good hypotheses can infer ethical and positive implications, indicating the presence of a relationship or effect relevant to the research theme. 7 , 11 These are initially developed from a general theory and branch into specific hypotheses by deductive reasoning. In the absence of a theory to base the hypotheses, inductive reasoning based on specific observations or findings form more general hypotheses. 10
TYPES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions and hypotheses are developed according to the type of research, which can be broadly classified into quantitative and qualitative research. We provide a summary of the types of research questions and hypotheses under quantitative and qualitative research categories in Table 1 .
Research questions in quantitative research
In quantitative research, research questions inquire about the relationships among variables being investigated and are usually framed at the start of the study. These are precise and typically linked to the subject population, dependent and independent variables, and research design. 1 Research questions may also attempt to describe the behavior of a population in relation to one or more variables, or describe the characteristics of variables to be measured ( descriptive research questions ). 1 , 5 , 14 These questions may also aim to discover differences between groups within the context of an outcome variable ( comparative research questions ), 1 , 5 , 14 or elucidate trends and interactions among variables ( relationship research questions ). 1 , 5 We provide examples of descriptive, comparative, and relationship research questions in quantitative research in Table 2 .
Hypotheses in quantitative research
In quantitative research, hypotheses predict the expected relationships among variables. 15 Relationships among variables that can be predicted include 1) between a single dependent variable and a single independent variable ( simple hypothesis ) or 2) between two or more independent and dependent variables ( complex hypothesis ). 4 , 11 Hypotheses may also specify the expected direction to be followed and imply an intellectual commitment to a particular outcome ( directional hypothesis ) 4 . On the other hand, hypotheses may not predict the exact direction and are used in the absence of a theory, or when findings contradict previous studies ( non-directional hypothesis ). 4 In addition, hypotheses can 1) define interdependency between variables ( associative hypothesis ), 4 2) propose an effect on the dependent variable from manipulation of the independent variable ( causal hypothesis ), 4 3) state a negative relationship between two variables ( null hypothesis ), 4 , 11 , 15 4) replace the working hypothesis if rejected ( alternative hypothesis ), 15 explain the relationship of phenomena to possibly generate a theory ( working hypothesis ), 11 5) involve quantifiable variables that can be tested statistically ( statistical hypothesis ), 11 6) or express a relationship whose interlinks can be verified logically ( logical hypothesis ). 11 We provide examples of simple, complex, directional, non-directional, associative, causal, null, alternative, working, statistical, and logical hypotheses in quantitative research, as well as the definition of quantitative hypothesis-testing research in Table 3 .
Research questions in qualitative research
Unlike research questions in quantitative research, research questions in qualitative research are usually continuously reviewed and reformulated. The central question and associated subquestions are stated more than the hypotheses. 15 The central question broadly explores a complex set of factors surrounding the central phenomenon, aiming to present the varied perspectives of participants. 15
There are varied goals for which qualitative research questions are developed. These questions can function in several ways, such as to 1) identify and describe existing conditions ( contextual research question s); 2) describe a phenomenon ( descriptive research questions ); 3) assess the effectiveness of existing methods, protocols, theories, or procedures ( evaluation research questions ); 4) examine a phenomenon or analyze the reasons or relationships between subjects or phenomena ( explanatory research questions ); or 5) focus on unknown aspects of a particular topic ( exploratory research questions ). 5 In addition, some qualitative research questions provide new ideas for the development of theories and actions ( generative research questions ) or advance specific ideologies of a position ( ideological research questions ). 1 Other qualitative research questions may build on a body of existing literature and become working guidelines ( ethnographic research questions ). Research questions may also be broadly stated without specific reference to the existing literature or a typology of questions ( phenomenological research questions ), may be directed towards generating a theory of some process ( grounded theory questions ), or may address a description of the case and the emerging themes ( qualitative case study questions ). 15 We provide examples of contextual, descriptive, evaluation, explanatory, exploratory, generative, ideological, ethnographic, phenomenological, grounded theory, and qualitative case study research questions in qualitative research in Table 4 , and the definition of qualitative hypothesis-generating research in Table 5 .
Qualitative studies usually pose at least one central research question and several subquestions starting with How or What . These research questions use exploratory verbs such as explore or describe . These also focus on one central phenomenon of interest, and may mention the participants and research site. 15
Hypotheses in qualitative research
Hypotheses in qualitative research are stated in the form of a clear statement concerning the problem to be investigated. Unlike in quantitative research where hypotheses are usually developed to be tested, qualitative research can lead to both hypothesis-testing and hypothesis-generating outcomes. 2 When studies require both quantitative and qualitative research questions, this suggests an integrative process between both research methods wherein a single mixed-methods research question can be developed. 1
FRAMEWORKS FOR DEVELOPING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions followed by hypotheses should be developed before the start of the study. 1 , 12 , 14 It is crucial to develop feasible research questions on a topic that is interesting to both the researcher and the scientific community. This can be achieved by a meticulous review of previous and current studies to establish a novel topic. Specific areas are subsequently focused on to generate ethical research questions. The relevance of the research questions is evaluated in terms of clarity of the resulting data, specificity of the methodology, objectivity of the outcome, depth of the research, and impact of the study. 1 , 5 These aspects constitute the FINER criteria (i.e., Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, and Relevant). 1 Clarity and effectiveness are achieved if research questions meet the FINER criteria. In addition to the FINER criteria, Ratan et al. described focus, complexity, novelty, feasibility, and measurability for evaluating the effectiveness of research questions. 14
The PICOT and PEO frameworks are also used when developing research questions. 1 The following elements are addressed in these frameworks, PICOT: P-population/patients/problem, I-intervention or indicator being studied, C-comparison group, O-outcome of interest, and T-timeframe of the study; PEO: P-population being studied, E-exposure to preexisting conditions, and O-outcome of interest. 1 Research questions are also considered good if these meet the “FINERMAPS” framework: Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, Relevant, Manageable, Appropriate, Potential value/publishable, and Systematic. 14
As we indicated earlier, research questions and hypotheses that are not carefully formulated result in unethical studies or poor outcomes. To illustrate this, we provide some examples of ambiguous research question and hypotheses that result in unclear and weak research objectives in quantitative research ( Table 6 ) 16 and qualitative research ( Table 7 ) 17 , and how to transform these ambiguous research question(s) and hypothesis(es) into clear and good statements.
a These statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
b These statements are direct quotes from Higashihara and Horiuchi. 16
a This statement is a direct quote from Shimoda et al. 17
The other statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
CONSTRUCTING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
To construct effective research questions and hypotheses, it is very important to 1) clarify the background and 2) identify the research problem at the outset of the research, within a specific timeframe. 9 Then, 3) review or conduct preliminary research to collect all available knowledge about the possible research questions by studying theories and previous studies. 18 Afterwards, 4) construct research questions to investigate the research problem. Identify variables to be accessed from the research questions 4 and make operational definitions of constructs from the research problem and questions. Thereafter, 5) construct specific deductive or inductive predictions in the form of hypotheses. 4 Finally, 6) state the study aims . This general flow for constructing effective research questions and hypotheses prior to conducting research is shown in Fig. 1 .

Research questions are used more frequently in qualitative research than objectives or hypotheses. 3 These questions seek to discover, understand, explore or describe experiences by asking “What” or “How.” The questions are open-ended to elicit a description rather than to relate variables or compare groups. The questions are continually reviewed, reformulated, and changed during the qualitative study. 3 Research questions are also used more frequently in survey projects than hypotheses in experiments in quantitative research to compare variables and their relationships.
Hypotheses are constructed based on the variables identified and as an if-then statement, following the template, ‘If a specific action is taken, then a certain outcome is expected.’ At this stage, some ideas regarding expectations from the research to be conducted must be drawn. 18 Then, the variables to be manipulated (independent) and influenced (dependent) are defined. 4 Thereafter, the hypothesis is stated and refined, and reproducible data tailored to the hypothesis are identified, collected, and analyzed. 4 The hypotheses must be testable and specific, 18 and should describe the variables and their relationships, the specific group being studied, and the predicted research outcome. 18 Hypotheses construction involves a testable proposition to be deduced from theory, and independent and dependent variables to be separated and measured separately. 3 Therefore, good hypotheses must be based on good research questions constructed at the start of a study or trial. 12
In summary, research questions are constructed after establishing the background of the study. Hypotheses are then developed based on the research questions. Thus, it is crucial to have excellent research questions to generate superior hypotheses. In turn, these would determine the research objectives and the design of the study, and ultimately, the outcome of the research. 12 Algorithms for building research questions and hypotheses are shown in Fig. 2 for quantitative research and in Fig. 3 for qualitative research.

EXAMPLES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS FROM PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Descriptive research question (quantitative research)
- - Presents research variables to be assessed (distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes)
- “BACKGROUND: Since COVID-19 was identified, its clinical and biological heterogeneity has been recognized. Identifying COVID-19 phenotypes might help guide basic, clinical, and translational research efforts.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Does the clinical spectrum of patients with COVID-19 contain distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes? ” 19
- EXAMPLE 2. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Shows interactions between dependent variable (static postural control) and independent variable (peripheral visual field loss)
- “Background: Integration of visual, vestibular, and proprioceptive sensations contributes to postural control. People with peripheral visual field loss have serious postural instability. However, the directional specificity of postural stability and sensory reweighting caused by gradual peripheral visual field loss remain unclear.
- Research question: What are the effects of peripheral visual field loss on static postural control ?” 20
- EXAMPLE 3. Comparative research question (quantitative research)
- - Clarifies the difference among groups with an outcome variable (patients enrolled in COMPERA with moderate PH or severe PH in COPD) and another group without the outcome variable (patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH))
- “BACKGROUND: Pulmonary hypertension (PH) in COPD is a poorly investigated clinical condition.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Which factors determine the outcome of PH in COPD?
- STUDY DESIGN AND METHODS: We analyzed the characteristics and outcome of patients enrolled in the Comparative, Prospective Registry of Newly Initiated Therapies for Pulmonary Hypertension (COMPERA) with moderate or severe PH in COPD as defined during the 6th PH World Symposium who received medical therapy for PH and compared them with patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH) .” 21
- EXAMPLE 4. Exploratory research question (qualitative research)
- - Explores areas that have not been fully investigated (perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment) to have a deeper understanding of the research problem
- “Problem: Interventions for children with obesity lead to only modest improvements in BMI and long-term outcomes, and data are limited on the perspectives of families of children with obesity in clinic-based treatment. This scoping review seeks to answer the question: What is known about the perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment? This review aims to explore the scope of perspectives reported by families of children with obesity who have received individualized outpatient clinic-based obesity treatment.” 22
- EXAMPLE 5. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Defines interactions between dependent variable (use of ankle strategies) and independent variable (changes in muscle tone)
- “Background: To maintain an upright standing posture against external disturbances, the human body mainly employs two types of postural control strategies: “ankle strategy” and “hip strategy.” While it has been reported that the magnitude of the disturbance alters the use of postural control strategies, it has not been elucidated how the level of muscle tone, one of the crucial parameters of bodily function, determines the use of each strategy. We have previously confirmed using forward dynamics simulations of human musculoskeletal models that an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. The objective of the present study was to experimentally evaluate a hypothesis: an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. Research question: Do changes in the muscle tone affect the use of ankle strategies ?” 23
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESES IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Working hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - A hypothesis that is initially accepted for further research to produce a feasible theory
- “As fever may have benefit in shortening the duration of viral illness, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response when taken during the early stages of COVID-19 illness .” 24
- “In conclusion, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response . The difference in perceived safety of these agents in COVID-19 illness could be related to the more potent efficacy to reduce fever with ibuprofen compared to acetaminophen. Compelling data on the benefit of fever warrant further research and review to determine when to treat or withhold ibuprofen for early stage fever for COVID-19 and other related viral illnesses .” 24
- EXAMPLE 2. Exploratory hypothesis (qualitative research)
- - Explores particular areas deeper to clarify subjective experience and develop a formal hypothesis potentially testable in a future quantitative approach
- “We hypothesized that when thinking about a past experience of help-seeking, a self distancing prompt would cause increased help-seeking intentions and more favorable help-seeking outcome expectations .” 25
- “Conclusion
- Although a priori hypotheses were not supported, further research is warranted as results indicate the potential for using self-distancing approaches to increasing help-seeking among some people with depressive symptomatology.” 25
- EXAMPLE 3. Hypothesis-generating research to establish a framework for hypothesis testing (qualitative research)
- “We hypothesize that compassionate care is beneficial for patients (better outcomes), healthcare systems and payers (lower costs), and healthcare providers (lower burnout). ” 26
- Compassionomics is the branch of knowledge and scientific study of the effects of compassionate healthcare. Our main hypotheses are that compassionate healthcare is beneficial for (1) patients, by improving clinical outcomes, (2) healthcare systems and payers, by supporting financial sustainability, and (3) HCPs, by lowering burnout and promoting resilience and well-being. The purpose of this paper is to establish a scientific framework for testing the hypotheses above . If these hypotheses are confirmed through rigorous research, compassionomics will belong in the science of evidence-based medicine, with major implications for all healthcare domains.” 26
- EXAMPLE 4. Statistical hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - An assumption is made about the relationship among several population characteristics ( gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD ). Validity is tested by statistical experiment or analysis ( chi-square test, Students t-test, and logistic regression analysis)
- “Our research investigated gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD in a Japanese clinical sample. Due to unique Japanese cultural ideals and expectations of women's behavior that are in opposition to ADHD symptoms, we hypothesized that women with ADHD experience more difficulties and present more dysfunctions than men . We tested the following hypotheses: first, women with ADHD have more comorbidities than men with ADHD; second, women with ADHD experience more social hardships than men, such as having less full-time employment and being more likely to be divorced.” 27
- “Statistical Analysis
- ( text omitted ) Between-gender comparisons were made using the chi-squared test for categorical variables and Students t-test for continuous variables…( text omitted ). A logistic regression analysis was performed for employment status, marital status, and comorbidity to evaluate the independent effects of gender on these dependent variables.” 27
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESIS AS WRITTEN IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES IN RELATION TO OTHER PARTS
- EXAMPLE 1. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “Pregnant women need skilled care during pregnancy and childbirth, but that skilled care is often delayed in some countries …( text omitted ). The focused antenatal care (FANC) model of WHO recommends that nurses provide information or counseling to all pregnant women …( text omitted ). Job aids are visual support materials that provide the right kind of information using graphics and words in a simple and yet effective manner. When nurses are not highly trained or have many work details to attend to, these job aids can serve as a content reminder for the nurses and can be used for educating their patients (Jennings, Yebadokpo, Affo, & Agbogbe, 2010) ( text omitted ). Importantly, additional evidence is needed to confirm how job aids can further improve the quality of ANC counseling by health workers in maternal care …( text omitted )” 28
- “ This has led us to hypothesize that the quality of ANC counseling would be better if supported by job aids. Consequently, a better quality of ANC counseling is expected to produce higher levels of awareness concerning the danger signs of pregnancy and a more favorable impression of the caring behavior of nurses .” 28
- “This study aimed to examine the differences in the responses of pregnant women to a job aid-supported intervention during ANC visit in terms of 1) their understanding of the danger signs of pregnancy and 2) their impression of the caring behaviors of nurses to pregnant women in rural Tanzania.” 28
- EXAMPLE 2. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “We conducted a two-arm randomized controlled trial (RCT) to evaluate and compare changes in salivary cortisol and oxytocin levels of first-time pregnant women between experimental and control groups. The women in the experimental group touched and held an infant for 30 min (experimental intervention protocol), whereas those in the control group watched a DVD movie of an infant (control intervention protocol). The primary outcome was salivary cortisol level and the secondary outcome was salivary oxytocin level.” 29
- “ We hypothesize that at 30 min after touching and holding an infant, the salivary cortisol level will significantly decrease and the salivary oxytocin level will increase in the experimental group compared with the control group .” 29
- EXAMPLE 3. Background, aim, and hypothesis are provided
- “In countries where the maternal mortality ratio remains high, antenatal education to increase Birth Preparedness and Complication Readiness (BPCR) is considered one of the top priorities [1]. BPCR includes birth plans during the antenatal period, such as the birthplace, birth attendant, transportation, health facility for complications, expenses, and birth materials, as well as family coordination to achieve such birth plans. In Tanzania, although increasing, only about half of all pregnant women attend an antenatal clinic more than four times [4]. Moreover, the information provided during antenatal care (ANC) is insufficient. In the resource-poor settings, antenatal group education is a potential approach because of the limited time for individual counseling at antenatal clinics.” 30
- “This study aimed to evaluate an antenatal group education program among pregnant women and their families with respect to birth-preparedness and maternal and infant outcomes in rural villages of Tanzania.” 30
- “ The study hypothesis was if Tanzanian pregnant women and their families received a family-oriented antenatal group education, they would (1) have a higher level of BPCR, (2) attend antenatal clinic four or more times, (3) give birth in a health facility, (4) have less complications of women at birth, and (5) have less complications and deaths of infants than those who did not receive the education .” 30
Research questions and hypotheses are crucial components to any type of research, whether quantitative or qualitative. These questions should be developed at the very beginning of the study. Excellent research questions lead to superior hypotheses, which, like a compass, set the direction of research, and can often determine the successful conduct of the study. Many research studies have floundered because the development of research questions and subsequent hypotheses was not given the thought and meticulous attention needed. The development of research questions and hypotheses is an iterative process based on extensive knowledge of the literature and insightful grasp of the knowledge gap. Focused, concise, and specific research questions provide a strong foundation for constructing hypotheses which serve as formal predictions about the research outcomes. Research questions and hypotheses are crucial elements of research that should not be overlooked. They should be carefully thought of and constructed when planning research. This avoids unethical studies and poor outcomes by defining well-founded objectives that determine the design, course, and outcome of the study.
Disclosure: The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author Contributions:
- Conceptualization: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Methodology: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - original draft: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - review & editing: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
Descriptive Research: Definition, Characteristics, Methods + Examples

Suppose an apparel brand wants to understand the fashion purchasing trends among New York’s buyers, then it must conduct a demographic survey of the specific region, gather population data, and then conduct descriptive research on this demographic segment.
The study will then uncover details on “what is the purchasing pattern of New York buyers,” but will not cover any investigative information about “ why ” the patterns exist. Because for the apparel brand trying to break into this market, understanding the nature of their market is the study’s main goal. Let’s talk about it.
What is descriptive research?
Descriptive research is a research method describing the characteristics of the population or phenomenon studied. This descriptive methodology focuses more on the “what” of the research subject than the “why” of the research subject.
The method primarily focuses on describing the nature of a demographic segment without focusing on “why” a particular phenomenon occurs. In other words, it “describes” the research subject without covering “why” it happens.
Characteristics of descriptive research
The term descriptive research then refers to research questions, the design of the study, and data analysis conducted on that topic. We call it an observational research method because none of the research study variables are influenced in any capacity.
Some distinctive characteristics of descriptive research are:
- Quantitative research: It is a quantitative research method that attempts to collect quantifiable information for statistical analysis of the population sample. It is a popular market research tool that allows us to collect and describe the demographic segment’s nature.
- Uncontrolled variables: In it, none of the variables are influenced in any way. This uses observational methods to conduct the research. Hence, the nature of the variables or their behavior is not in the hands of the researcher.
- Cross-sectional studies: It is generally a cross-sectional study where different sections belonging to the same group are studied.
- The basis for further research: Researchers further research the data collected and analyzed from descriptive research using different research techniques. The data can also help point towards the types of research methods used for the subsequent research.
Applications of descriptive research with examples
A descriptive research method can be used in multiple ways and for various reasons. Before getting into any survey , though, the survey goals and survey design are crucial. Despite following these steps, there is no way to know if one will meet the research outcome. How to use descriptive research? To understand the end objective of research goals, below are some ways organizations currently use descriptive research today:
- Define respondent characteristics: The aim of using close-ended questions is to draw concrete conclusions about the respondents. This could be the need to derive patterns, traits, and behaviors of the respondents. It could also be to understand from a respondent their attitude, or opinion about the phenomenon. For example, understand millennials and the hours per week they spend browsing the internet. All this information helps the organization researching to make informed business decisions.
- Measure data trends: Researchers measure data trends over time with a descriptive research design’s statistical capabilities. Consider if an apparel company researches different demographics like age groups from 24-35 and 36-45 on a new range launch of autumn wear. If one of those groups doesn’t take too well to the new launch, it provides insight into what clothes are like and what is not. The brand drops the clothes and apparel that customers don’t like.
- Conduct comparisons: Organizations also use a descriptive research design to understand how different groups respond to a specific product or service. For example, an apparel brand creates a survey asking general questions that measure the brand’s image. The same study also asks demographic questions like age, income, gender, geographical location, geographic segmentation , etc. This consumer research helps the organization understand what aspects of the brand appeal to the population and what aspects do not. It also helps make product or marketing fixes or even create a new product line to cater to high-growth potential groups.
- Validate existing conditions: Researchers widely use descriptive research to help ascertain the research object’s prevailing conditions and underlying patterns. Due to the non-invasive research method and the use of quantitative observation and some aspects of qualitative observation , researchers observe each variable and conduct an in-depth analysis . Researchers also use it to validate any existing conditions that may be prevalent in a population.
- Conduct research at different times: The analysis can be conducted at different periods to ascertain any similarities or differences. This also allows any number of variables to be evaluated. For verification, studies on prevailing conditions can also be repeated to draw trends.
Advantages of descriptive research
Some of the significant advantages of descriptive research are:

- Data collection: A researcher can conduct descriptive research using specific methods like observational method, case study method, and survey method. Between these three, all primary data collection methods are covered, which provides a lot of information. This can be used for future research or even for developing a hypothesis for your research object.
- Varied: Since the data collected is qualitative and quantitative, it gives a holistic understanding of a research topic. The information is varied, diverse, and thorough.
- Natural environment: Descriptive research allows for the research to be conducted in the respondent’s natural environment, which ensures that high-quality and honest data is collected.
- Quick to perform and cheap: As the sample size is generally large in descriptive research, the data collection is quick to conduct and is inexpensive.
Descriptive research methods
There are three distinctive methods to conduct descriptive research. They are:
Observational method
The observational method is the most effective method to conduct this research, and researchers make use of both quantitative and qualitative observations.
A quantitative observation is the objective collection of data primarily focused on numbers and values. It suggests “associated with, of or depicted in terms of a quantity.” Results of quantitative observation are derived using statistical and numerical analysis methods. It implies observation of any entity associated with a numeric value such as age, shape, weight, volume, scale, etc. For example, the researcher can track if current customers will refer the brand using a simple Net Promoter Score question .
Qualitative observation doesn’t involve measurements or numbers but instead just monitoring characteristics. In this case, the researcher observes the respondents from a distance. Since the respondents are in a comfortable environment, the characteristics observed are natural and effective. In a descriptive research design, the researcher can choose to be either a complete observer, an observer as a participant, a participant as an observer, or a full participant. For example, in a supermarket, a researcher can from afar monitor and track the customers’ selection and purchasing trends. This offers a more in-depth insight into the purchasing experience of the customer.
Case study method
Case studies involve in-depth research and study of individuals or groups. Case studies lead to a hypothesis and widen a further scope of studying a phenomenon. However, case studies should not be used to determine cause and effect as they can’t make accurate predictions because there could be a bias on the researcher’s part. The other reason why case studies are not a reliable way of conducting descriptive research is that there could be an atypical respondent in the survey. Describing them leads to weak generalizations and moving away from external validity.
Survey research
In survey research, respondents answer through surveys or questionnaires or polls . They are a popular market research tool to collect feedback from respondents. A study to gather useful data should have the right survey questions. It should be a balanced mix of open-ended questions and close ended-questions . The survey method can be conducted online or offline, making it the go-to option for descriptive research where the sample size is enormous.
Examples of descriptive research
Some examples of descriptive research are:
- A specialty food group launching a new range of barbecue rubs would like to understand what flavors of rubs are favored by different people. To understand the preferred flavor palette, they conduct this type of research study using various methods like observational methods in supermarkets. By also surveying while collecting in-depth demographic information, offers insights about the preference of different markets. This can also help tailor make the rubs and spreads to various preferred meats in that demographic. Conducting this type of research helps the organization tweak their business model and amplify marketing in core markets.
- Another example of where this research can be used is if a school district wishes to evaluate teachers’ attitudes about using technology in the classroom. By conducting surveys and observing their comfortableness using technology through observational methods, the researcher can gauge what they can help understand if a full-fledged implementation can face an issue. This also helps in understanding if the students are impacted in any way with this change.
Some other research problems and research questions that can lead to descriptive research are:
- Market researchers want to observe the habits of consumers.
- A company wants to evaluate the morale of its staff.
- A school district wants to understand if students will access online lessons rather than textbooks.
- To understand if its wellness questionnaire programs enhance the overall health of the employees.
FREE TRIAL LEARN MORE
MORE LIKE THIS

The Power of AI in Customer Experience — Tuesday CX Thoughts
Apr 16, 2024

Employee Lifecycle Management Software: Top of 2024
Apr 15, 2024
Top 15 Sentiment Analysis Software That Should Be on Your List

Top 13 A/B Testing Software for Optimizing Your Website
Apr 12, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
- What is descriptive research?
Last updated
5 February 2023
Reviewed by
Cathy Heath
Descriptive research is a common investigatory model used by researchers in various fields, including social sciences, linguistics, and academia.
Read on to understand the characteristics of descriptive research and explore its underlying techniques, processes, and procedures.
Analyze your descriptive research
Dovetail streamlines analysis to help you uncover and share actionable insights
Descriptive research is an exploratory research method. It enables researchers to precisely and methodically describe a population, circumstance, or phenomenon.
As the name suggests, descriptive research describes the characteristics of the group, situation, or phenomenon being studied without manipulating variables or testing hypotheses . This can be reported using surveys , observational studies, and case studies. You can use both quantitative and qualitative methods to compile the data.
Besides making observations and then comparing and analyzing them, descriptive studies often develop knowledge concepts and provide solutions to critical issues. It always aims to answer how the event occurred, when it occurred, where it occurred, and what the problem or phenomenon is.
- Characteristics of descriptive research
The following are some of the characteristics of descriptive research:
Quantitativeness
Descriptive research can be quantitative as it gathers quantifiable data to statistically analyze a population sample. These numbers can show patterns, connections, and trends over time and can be discovered using surveys, polls, and experiments.
Qualitativeness
Descriptive research can also be qualitative. It gives meaning and context to the numbers supplied by quantitative descriptive research .
Researchers can use tools like interviews, focus groups, and ethnographic studies to illustrate why things are what they are and help characterize the research problem. This is because it’s more explanatory than exploratory or experimental research.
Uncontrolled variables
Descriptive research differs from experimental research in that researchers cannot manipulate the variables. They are recognized, scrutinized, and quantified instead. This is one of its most prominent features.
Cross-sectional studies
Descriptive research is a cross-sectional study because it examines several areas of the same group. It involves obtaining data on multiple variables at the personal level during a certain period. It’s helpful when trying to understand a larger community’s habits or preferences.
Carried out in a natural environment
Descriptive studies are usually carried out in the participants’ everyday environment, which allows researchers to avoid influencing responders by collecting data in a natural setting. You can use online surveys or survey questions to collect data or observe.
Basis for further research
You can further dissect descriptive research’s outcomes and use them for different types of investigation. The outcomes also serve as a foundation for subsequent investigations and can guide future studies. For example, you can use the data obtained in descriptive research to help determine future research designs.
- Descriptive research methods
There are three basic approaches for gathering data in descriptive research: observational, case study, and survey.
You can use surveys to gather data in descriptive research. This involves gathering information from many people using a questionnaire and interview .
Surveys remain the dominant research tool for descriptive research design. Researchers can conduct various investigations and collect multiple types of data (quantitative and qualitative) using surveys with diverse designs.
You can conduct surveys over the phone, online, or in person. Your survey might be a brief interview or conversation with a set of prepared questions intended to obtain quick information from the primary source.
Observation
This descriptive research method involves observing and gathering data on a population or phenomena without manipulating variables. It is employed in psychology, market research , and other social science studies to track and understand human behavior.
Observation is an essential component of descriptive research. It entails gathering data and analyzing it to see whether there is a relationship between the two variables in the study. This strategy usually allows for both qualitative and quantitative data analysis.
Case studies
A case study can outline a specific topic’s traits. The topic might be a person, group, event, or organization.
It involves using a subset of a larger group as a sample to characterize the features of that larger group.
You can generalize knowledge gained from studying a case study to benefit a broader audience.
This approach entails carefully examining a particular group, person, or event over time. You can learn something new about the study topic by using a small group to better understand the dynamics of the entire group.
- Types of descriptive research
There are several types of descriptive study. The most well-known include cross-sectional studies, census surveys, sample surveys, case reports, and comparison studies.
Case reports and case series
In the healthcare and medical fields, a case report is used to explain a patient’s circumstances when suffering from an uncommon illness or displaying certain symptoms. Case reports and case series are both collections of related cases. They have aided the advancement of medical knowledge on countless occasions.
The normative component is an addition to the descriptive survey. In the descriptive–normative survey, you compare the study’s results to the norm.
Descriptive survey
This descriptive type of research employs surveys to collect information on various topics. This data aims to determine the degree to which certain conditions may be attained.
You can extrapolate or generalize the information you obtain from sample surveys to the larger group being researched.
Correlative survey
Correlative surveys help establish if there is a positive, negative, or neutral connection between two variables.
Performing census surveys involves gathering relevant data on several aspects of a given population. These units include individuals, families, organizations, objects, characteristics, and properties.
During descriptive research, you gather different degrees of interest over time from a specific population. Cross-sectional studies provide a glimpse of a phenomenon’s prevalence and features in a population. There are no ethical challenges with them and they are quite simple and inexpensive to carry out.
Comparative studies
These surveys compare the two subjects’ conditions or characteristics. The subjects may include research variables, organizations, plans, and people.
Comparison points, assumption of similarities, and criteria of comparison are three important variables that affect how well and accurately comparative studies are conducted.
For instance, descriptive research can help determine how many CEOs hold a bachelor’s degree and what proportion of low-income households receive government help.
- Pros and cons
The primary advantage of descriptive research designs is that researchers can create a reliable and beneficial database for additional study. To conduct any inquiry, you need access to reliable information sources that can give you a firm understanding of a situation.
Quantitative studies are time- and resource-intensive, so knowing the hypotheses viable for testing is crucial. The basic overview of descriptive research provides helpful hints as to which variables are worth quantitatively examining. This is why it’s employed as a precursor to quantitative research designs.
Some experts view this research as untrustworthy and unscientific. However, there is no way to assess the findings because you don’t manipulate any variables statistically.
Cause-and-effect correlations also can’t be established through descriptive investigations. Additionally, observational study findings cannot be replicated, which prevents a review of the findings and their replication.
The absence of statistical and in-depth analysis and the rather superficial character of the investigative procedure are drawbacks of this research approach.
- Descriptive research examples and applications
Several descriptive research examples are emphasized based on their types, purposes, and applications. Research questions often begin with “What is …” These studies help find solutions to practical issues in social science, physical science, and education.
Here are some examples and applications of descriptive research:
Determining consumer perception and behavior
Organizations use descriptive research designs to determine how various demographic groups react to a certain product or service.
For example, a business looking to sell to its target market should research the market’s behavior first. When researching human behavior in response to a cause or event, the researcher pays attention to the traits, actions, and responses before drawing a conclusion.
Scientific classification
Scientific descriptive research enables the classification of organisms and their traits and constituents.
Measuring data trends
A descriptive study design’s statistical capabilities allow researchers to track data trends over time. It’s frequently used to determine the study target’s current circumstances and underlying patterns.
Conduct comparison
Organizations can use a descriptive research approach to learn how various demographics react to a certain product or service. For example, you can study how the target market responds to a competitor’s product and use that information to infer their behavior.
- Bottom line
A descriptive research design is suitable for exploring certain topics and serving as a prelude to larger quantitative investigations. It provides a comprehensive understanding of the “what” of the group or thing you’re investigating.
This research type acts as the cornerstone of other research methodologies . It is distinctive because it can use quantitative and qualitative research approaches at the same time.
What is descriptive research design?
Descriptive research design aims to systematically obtain information to describe a phenomenon, situation, or population. More specifically, it helps answer the what, when, where, and how questions regarding the research problem rather than the why.
How does descriptive research compare to qualitative research?
Despite certain parallels, descriptive research concentrates on describing phenomena, while qualitative research aims to understand people better.
How do you analyze descriptive research data?
Data analysis involves using various methodologies, enabling the researcher to evaluate and provide results regarding validity and reliability.
Get started today
Go from raw data to valuable insights with a flexible research platform
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 21 December 2023
Last updated: 16 December 2023
Last updated: 6 October 2023
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 25 November 2023
Last updated: 15 February 2024
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 10 April 2023
Last updated: 20 December 2023
Latest articles
Related topics, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples
Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples
Published on October 26, 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on November 21, 2023.
A research question pinpoints exactly what you want to find out in your work. A good research question is essential to guide your research paper , dissertation , or thesis .
All research questions should be:
- Focused on a single problem or issue
- Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources
- Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints
- Specific enough to answer thoroughly
- Complex enough to develop the answer over the space of a paper or thesis
- Relevant to your field of study and/or society more broadly
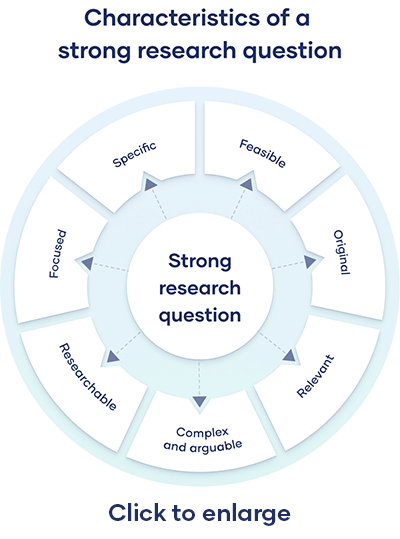
Table of contents
How to write a research question, what makes a strong research question, using sub-questions to strengthen your main research question, research questions quiz, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about research questions.
You can follow these steps to develop a strong research question:
- Choose your topic
- Do some preliminary reading about the current state of the field
- Narrow your focus to a specific niche
- Identify the research problem that you will address
The way you frame your question depends on what your research aims to achieve. The table below shows some examples of how you might formulate questions for different purposes.
Using your research problem to develop your research question
Note that while most research questions can be answered with various types of research , the way you frame your question should help determine your choices.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Research questions anchor your whole project, so it’s important to spend some time refining them. The criteria below can help you evaluate the strength of your research question.
Focused and researchable
Feasible and specific, complex and arguable, relevant and original.
Chances are that your main research question likely can’t be answered all at once. That’s why sub-questions are important: they allow you to answer your main question in a step-by-step manner.
Good sub-questions should be:
- Less complex than the main question
- Focused only on 1 type of research
- Presented in a logical order
Here are a few examples of descriptive and framing questions:
- Descriptive: According to current government arguments, how should a European bank tax be implemented?
- Descriptive: Which countries have a bank tax/levy on financial transactions?
- Framing: How should a bank tax/levy on financial transactions look at a European level?
Keep in mind that sub-questions are by no means mandatory. They should only be asked if you need the findings to answer your main question. If your main question is simple enough to stand on its own, it’s okay to skip the sub-question part. As a rule of thumb, the more complex your subject, the more sub-questions you’ll need.
Try to limit yourself to 4 or 5 sub-questions, maximum. If you feel you need more than this, it may be indication that your main research question is not sufficiently specific. In this case, it’s is better to revisit your problem statement and try to tighten your main question up.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
The way you present your research problem in your introduction varies depending on the nature of your research paper . A research paper that presents a sustained argument will usually encapsulate this argument in a thesis statement .
A research paper designed to present the results of empirical research tends to present a research question that it seeks to answer. It may also include a hypothesis —a prediction that will be confirmed or disproved by your research.
As you cannot possibly read every source related to your topic, it’s important to evaluate sources to assess their relevance. Use preliminary evaluation to determine whether a source is worth examining in more depth.
This involves:
- Reading abstracts , prefaces, introductions , and conclusions
- Looking at the table of contents to determine the scope of the work
- Consulting the index for key terms or the names of important scholars
A research hypothesis is your proposed answer to your research question. The research hypothesis usually includes an explanation (“ x affects y because …”).
A statistical hypothesis, on the other hand, is a mathematical statement about a population parameter. Statistical hypotheses always come in pairs: the null and alternative hypotheses . In a well-designed study , the statistical hypotheses correspond logically to the research hypothesis.

Formulating a main research question can be a difficult task. Overall, your question should contribute to solving the problem that you have defined in your problem statement .
However, it should also fulfill criteria in three main areas:
- Researchability
- Feasibility and specificity
- Relevance and originality
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, November 21). Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 15, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/research-questions/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to define a research problem | ideas & examples, how to write a problem statement | guide & examples, 10 research question examples to guide your research project, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

Education Scholarship in Healthcare pp 41–50 Cite as
Designing a Research Question
- Ahmed Ibrahim 3 &
- Camille L. Bryant 3
- First Online: 29 November 2023
380 Accesses
This chapter discusses (1) the important role of research questions for descriptive, predictive, and causal studies across the three research paradigms (i.e., quantitative, qualitative, and mixed methods); (2) characteristics of quality research questions, and (3) three frameworks to support the development of research questions and their dissemination within scholarly work. For the latter, a description of the P opulation/ P articipants, I ntervention/ I ndependent variable, C omparison, and O utcomes (PICO) framework for quantitative research as well as variations depending on the type of research is provided. Second, we discuss the P articipants, central Ph enomenon, T ime, and S pace (PPhTS) framework for qualitative research. The combination of these frameworks is discussed for mixed-methods research. Further, templates and examples are provided to support the novice health scholar in developing research questions for applied and theoretical studies. Finally, we discuss the Create a Research Space (CARS) model for introducing research questions as part of a research study, to demonstrate how scholars can apply their knowledge when disseminating research.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Buying options
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Onwuegbuzie A, Leech N. Linking research questions to mixed methods data analysis procedures 1. Qual Rep. 2006;11(3):474–98. https://doi.org/10.46743/2160-3715/2006.1663 .
Article Google Scholar
Creswell JW, Poth CN. Qualitative inquiry and research design: choosing among five approaches. 4th ed. Thousand Oaks: Sage; 2018.
Google Scholar
Johnson B, Christensen LB. Educational research: quantitative, qualitative, and mixed approaches. Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications, Inc.; 2020.
White P. Who’s afraid of research questions? The neglect of research questions in the methods literature and a call for question-led methods teaching. Int J Res Method Educ. 2013;36(3):213–27. https://doi.org/10.1080/1743727x.2013.809413 .
Lingard L. Joining a conversation: the problem/gap/hook heuristic. Perspect Med Educ. 2015;4(5):252–3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40037-015-0211-y .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Dillon JT. The classification of research questions. Rev Educ Res. 1984;54(3):327–61. https://doi.org/10.3102/00346543054003327 .
Dillon JT. Finding the question for evaluation research. Stud Educ Eval. 1987;13(2):139–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0191-491X(87)80027-5 .
Smith NL. Toward the justification of claims in evaluation research. Eval Program Plann. 1987;10(4):309–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/0149-7189(87)90002-4 .
Smith NL, Mukherjee P. Classifying research questions addressed in published evaluation studies. Educ Eval Policy Anal. 1994;16(2):223–30. https://doi.org/10.3102/01623737016002223 .
Shaughnessy JJ, Zechmeister EB, Zechmeister JS. Research methods in psychology. 9th ed. New York: McGraw Hill; 2011.
DeCuir-Gunby JT, Schutz PA. Developing a mixed methods proposal a practical guide for beginning researchers. Thousand Oaks: Sage; 2017.
Book Google Scholar
Creswell JW, Guetterman TC. Educational research: planning, conducting, and evaluating quantitative and qualitative research. 6th ed. New York: Pearson; 2019.
Ely M, Anzul M, Friedman T, Ganer D, Steinmetz AM. Doing qualitative research: circles within circles. London: Falmer Press; 1991.
Agee J. Developing qualitative research questions: a reflective process. Int J Qual Stud Educ. 2009;22(4):431–47. https://doi.org/10.1080/09518390902736512 .
Johnson RB, Onwuegbuzie AJ. Mixed methods research: a research paradigm whose time has come. Educ Res. 2004;33(7):14–26. https://doi.org/10.3102/0013189x033007014 .
Creamer EG. An introduction to fully integrated mixed methods research. Thousand Oaks: Sage; 2018.
Swales J. Genre analysis: English in academic and research settings. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 1990.
Swales J. Research genres: explorations and applications. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2004.
Kendall PC, Norris LA, Rifkin LS, Silk JS. Introducing your research report: writing the introduction. In: Sternberg RJ, editor. Guide to publishing in psychology journals. 2nd ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2018. p. 37–53. https://doi.org/10.1017/9781108304443.005 .
Thomson P, Kamler B. Writing for peer reviewed journals: strategies of getting published. Abingdon: Routledge; 2013.
Lingard L. Writing an effective literature review: Part I: Mapping the gap. Perspectives on Medical Education. 2018;7:47–49.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Johns Hopkins University School of Education, Baltimore, MD, USA
Ahmed Ibrahim & Camille L. Bryant
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Ahmed Ibrahim .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD, USA
April S. Fitzgerald
Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, MD, USA
Gundula Bosch
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter.
Ibrahim, A., Bryant, C.L. (2023). Designing a Research Question. In: Fitzgerald, A.S., Bosch, G. (eds) Education Scholarship in Healthcare. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-38534-6_4
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-38534-6_4
Published : 29 November 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-38533-9
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-38534-6
eBook Packages : Medicine Medicine (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Research Question 101 📖
Everything you need to know to write a high-quality research question
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By: Dr. Eunice Rautenbach | October 2023
If you’ve landed on this page, you’re probably asking yourself, “ What is a research question? ”. Well, you’ve come to the right place. In this post, we’ll explain what a research question is , how it’s differen t from a research aim, and how to craft a high-quality research question that sets you up for success.
Research Question 101
What is a research question.
- Research questions vs research aims
- The 4 types of research questions
- How to write a research question
- Frequently asked questions
- Examples of research questions
As the name suggests, the research question is the core question (or set of questions) that your study will (attempt to) answer .
In many ways, a research question is akin to a target in archery . Without a clear target, you won’t know where to concentrate your efforts and focus. Essentially, your research question acts as the guiding light throughout your project and informs every choice you make along the way.
Let’s look at some examples:
What impact does social media usage have on the mental health of teenagers in New York?
How does the introduction of a minimum wage affect employment levels in small businesses in outer London?
How does the portrayal of women in 19th-century American literature reflect the societal attitudes of the time?
What are the long-term effects of intermittent fasting on heart health in adults?
As you can see in these examples, research questions are clear, specific questions that can be feasibly answered within a study. These are important attributes and we’ll discuss each of them in more detail a little later . If you’d like to see more examples of research questions, you can find our RQ mega-list here .

Research Questions vs Research Aims
At this point, you might be asking yourself, “ How is a research question different from a research aim? ”. Within any given study, the research aim and research question (or questions) are tightly intertwined , but they are separate things . Let’s unpack that a little.
A research aim is typically broader in nature and outlines what you hope to achieve with your research. It doesn’t ask a specific question but rather gives a summary of what you intend to explore.
The research question, on the other hand, is much more focused . It’s the specific query you’re setting out to answer. It narrows down the research aim into a detailed, researchable question that will guide your study’s methods and analysis.
Let’s look at an example:
Research Aim: To explore the effects of climate change on marine life in Southern Africa.
Research Question: How does ocean acidification caused by climate change affect the reproduction rates of coral reefs?
As you can see, the research aim gives you a general focus , while the research question details exactly what you want to find out.
Need a helping hand?
Types of research questions
Now that we’ve defined what a research question is, let’s look at the different types of research questions that you might come across. Broadly speaking, there are (at least) four different types of research questions – descriptive , comparative , relational , and explanatory .
Descriptive questions ask what is happening. In other words, they seek to describe a phenomena or situation . An example of a descriptive research question could be something like “What types of exercise do high-performing UK executives engage in?”. This would likely be a bit too basic to form an interesting study, but as you can see, the research question is just focused on the what – in other words, it just describes the situation.
Comparative research questions , on the other hand, look to understand the way in which two or more things differ , or how they’re similar. An example of a comparative research question might be something like “How do exercise preferences vary between middle-aged men across three American cities?”. As you can see, this question seeks to compare the differences (or similarities) in behaviour between different groups.
Next up, we’ve got exploratory research questions , which ask why or how is something happening. While the other types of questions we looked at focused on the what, exploratory research questions are interested in the why and how . As an example, an exploratory research question might ask something like “Why have bee populations declined in Germany over the last 5 years?”. As you can, this question is aimed squarely at the why, rather than the what.
Last but not least, we have relational research questions . As the name suggests, these types of research questions seek to explore the relationships between variables . Here, an example could be something like “What is the relationship between X and Y” or “Does A have an impact on B”. As you can see, these types of research questions are interested in understanding how constructs or variables are connected , and perhaps, whether one thing causes another.
Of course, depending on how fine-grained you want to get, you can argue that there are many more types of research questions , but these four categories give you a broad idea of the different flavours that exist out there. It’s also worth pointing out that a research question doesn’t need to fit perfectly into one category – in many cases, a research question might overlap into more than just one category and that’s okay.
The key takeaway here is that research questions can take many different forms , and it’s useful to understand the nature of your research question so that you can align your research methodology accordingly.

How To Write A Research Question
As we alluded earlier, a well-crafted research question needs to possess very specific attributes, including focus , clarity and feasibility . But that’s not all – a rock-solid research question also needs to be rooted and aligned . Let’s look at each of these.
A strong research question typically has a single focus. So, don’t try to cram multiple questions into one research question; rather split them up into separate questions (or even subquestions), each with their own specific focus. As a rule of thumb, narrow beats broad when it comes to research questions.
Clear and specific
A good research question is clear and specific, not vague and broad. State clearly exactly what you want to find out so that any reader can quickly understand what you’re looking to achieve with your study. Along the same vein, try to avoid using bulky language and jargon – aim for clarity.
Unfortunately, even a super tantalising and thought-provoking research question has little value if you cannot feasibly answer it. So, think about the methodological implications of your research question while you’re crafting it. Most importantly, make sure that you know exactly what data you’ll need (primary or secondary) and how you’ll analyse that data.
A good research question (and a research topic, more broadly) should be rooted in a clear research gap and research problem . Without a well-defined research gap, you risk wasting your effort pursuing a question that’s already been adequately answered (and agreed upon) by the research community. A well-argued research gap lays at the heart of a valuable study, so make sure you have your gap clearly articulated and that your research question directly links to it.
As we mentioned earlier, your research aim and research question are (or at least, should be) tightly linked. So, make sure that your research question (or set of questions) aligns with your research aim . If not, you’ll need to revise one of the two to achieve this.
FAQ: Research Questions
Research question faqs, how many research questions should i have, what should i avoid when writing a research question, can a research question be a statement.
Typically, a research question is phrased as a question, not a statement. A question clearly indicates what you’re setting out to discover.
Can a research question be too broad or too narrow?
Yes. A question that’s too broad makes your research unfocused, while a question that’s too narrow limits the scope of your study.
Here’s an example of a research question that’s too broad:
“Why is mental health important?”
Conversely, here’s an example of a research question that’s likely too narrow:
“What is the impact of sleep deprivation on the exam scores of 19-year-old males in London studying maths at The Open University?”
Can I change my research question during the research process?
How do i know if my research question is good.
A good research question is focused, specific, practical, rooted in a research gap, and aligned with the research aim. If your question meets these criteria, it’s likely a strong question.
Is a research question similar to a hypothesis?
Not quite. A hypothesis is a testable statement that predicts an outcome, while a research question is a query that you’re trying to answer through your study. Naturally, there can be linkages between a study’s research questions and hypothesis, but they serve different functions.
How are research questions and research objectives related?
The research question is a focused and specific query that your study aims to answer. It’s the central issue you’re investigating. The research objective, on the other hand, outlines the steps you’ll take to answer your research question. Research objectives are often more action-oriented and can be broken down into smaller tasks that guide your research process. In a sense, they’re something of a roadmap that helps you answer your research question.
Need some inspiration?
If you’d like to see more examples of research questions, check out our research question mega list here . Alternatively, if you’d like 1-on-1 help developing a high-quality research question, consider our private coaching service .

Psst… there’s more (for free)
This post is part of our dissertation mini-course, which covers everything you need to get started with your dissertation, thesis or research project.
You Might Also Like:

Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Literature Searching

Types of Research Questions
Research questions can be categorized into different types, depending on the type of research to be undertaken.
Qualitative questions concern broad areas or more specific areas of research and focus on discovering, explaining and exploring. Types of qualitative questions include:
- Exploratory Questions, which seeks to understand without influencing the results. The objective is to learn more about a topic without bias or preconceived notions.
- Predictive Questions, which seek to understand the intent or future outcome around a topic.
- Interpretive Questions, which tries to understand people’s behavior in a natural setting. The objective is to understand how a group makes sense of shared experiences with regards to various phenomena.
Quantitative questions prove or disprove a researcher’s hypothesis and are constructed to express the relationship between variables and whether this relationship is significant. Types of quantitative questions include:
- Descriptive questions , which are the most basic type of quantitative research question and seeks to explain the when, where, why or how something occurred.
- Comparative questions are helpful when studying groups with dependent variables where one variable is compared with another.
- Relationship-based questions try to answer whether or not one variable has an influence on another. These types of question are generally used in experimental research questions.
References/Additional Resources
Lipowski, E. E. (2008). Developing great research questions . American Journal of Health-System Pharmacy, 65(17), 1667–1670.
Ratan, S. K., Anand, T., & Ratan, J. (2019). Formulation of Research Question - Stepwise Approach . Journal of Indian Association of Pediatric Surgeons , 24 (1), 15–20.
Fandino W.(2019). Formulating a good research question: Pearls and pitfalls . I ndian J Anaesth. 63(8) :611-616.
Beck, L. L. (2023). The question: types of research questions and how to develop them . In Translational Surgery: Handbook for Designing and Conducting Clinical and Translational Research (pp. 111-120). Academic Press.
Doody, O., & Bailey, M. E. (2016). Setting a research question, aim and objective. Nurse Researcher, 23(4), 19–23.
Plano Clark, V., & Badiee, M. (2010). Research questions in mixed methods research . In: SAGE Handbook of Mixed Methods in Social & Behavioral Research . SAGE Publications, Inc.,
Agee, J. (2009). Developing qualitative research questions: A reflective process . International journal of qualitative studies in education , 22 (4), 431-447.
Flemming, K., & Noyes, J. (2021). Qualitative Evidence Synthesis: Where Are We at? I nternational Journal of Qualitative Methods, 20.
Research Question Frameworks
Research question frameworks have been designed to help structure research questions and clarify the main concepts. Not every question can fit perfectly into a framework, but using even just parts of a framework can help develop a well-defined research question. The framework to use depends on the type of question to be researched. There are over 25 research question frameworks available. The University of Maryland has a nice table listing out several of these research question frameworks, along with what the acronyms mean and what types of questions/disciplines that may be used for.
The process of developing a good research question involves taking your topic and breaking each aspect of it down into its component parts.
Booth, A., Noyes, J., Flemming, K., Moore, G., Tunçalp, Ö., & Shakibazadeh, E. (2019). Formulating questions to explore complex interventions within qualitative evidence synthesis. BMJ global health , 4 (Suppl 1), e001107. (See supplementary data#1)
The "Well-Built Clinical Question“: PICO(T)
One well-established framework that can be used both for refining questions and developing strategies is known as PICO(T). The PICO framework was designed primarily for questions that include interventions and comparisons, however other types of questions may also be able to follow its principles. If the PICO(T) framework does not precisely fit your question, using its principles (see alternative component suggestions) can help you to think about what you want to explore even if you do not end up with a true PICO question.
A PICO(T) question has the following components:
- P : The patient’s disorder or disease or problem of interest / research object
- I: The intervention, exposure or finding under review / Application of a theory or method
- C: A comparison intervention or control (if applicable- not always present)/ Alternative theories or methods (or, in their absence, the null hypothesis)
- O : The outcome(s) (desired or of interest) / Knowledge generation
- T : (The time factor or period)
Keep in mind that solely using a tool will not enable you to design a good question. What is required is for you to think, carefully, about exactly what you want to study and precisely what you mean by each of the things that you think you want to study.
Rzany, & Bigby, M. (n.d.). Formulating Well-Built Clinical Questions. In Evidence-based dermatology / (pp. 27–30). Blackwell Pub/BMJ Books.
Nishikawa-Pacher, A. (2022). Research questions with PICO: a universal mnemonic. Publications , 10 (3), 21.
- << Previous: Characteristics of a good research question
- Next: Choosing the Search Terms >>
- Research Questions: Definitions, Types + [Examples]

Research questions lie at the core of systematic investigation and this is because recording accurate research outcomes is tied to asking the right questions. Asking the right questions when conducting research can help you collect relevant and insightful information that ultimately influences your work, positively.
The right research questions are typically easy to understand, straight to the point, and engaging. In this article, we will share tips on how to create the right research questions and also show you how to create and administer an online questionnaire with Formplus .
What is a Research Question?
A research question is a specific inquiry which the research seeks to provide a response to. It resides at the core of systematic investigation and it helps you to clearly define a path for the research process.
A research question is usually the first step in any research project. Basically, it is the primary interrogation point of your research and it sets the pace for your work.
Typically, a research question focuses on the research, determines the methodology and hypothesis, and guides all stages of inquiry, analysis, and reporting. With the right research questions, you will be able to gather useful information for your investigation.
Types of Research Questions
Research questions are broadly categorized into 2; that is, qualitative research questions and quantitative research questions. Qualitative and quantitative research questions can be used independently and co-dependently in line with the overall focus and objectives of your research.
If your research aims at collecting quantifiable data , you will need to make use of quantitative research questions. On the other hand, qualitative questions help you to gather qualitative data bothering on the perceptions and observations of your research subjects.
Qualitative Research Questions
A qualitative research question is a type of systematic inquiry that aims at collecting qualitative data from research subjects. The aim of qualitative research questions is to gather non-statistical information pertaining to the experiences, observations, and perceptions of the research subjects in line with the objectives of the investigation.
Types of Qualitative Research Questions
- Ethnographic Research Questions
As the name clearly suggests, ethnographic research questions are inquiries presented in ethnographic research. Ethnographic research is a qualitative research approach that involves observing variables in their natural environments or habitats in order to arrive at objective research outcomes.
These research questions help the researcher to gather insights into the habits, dispositions, perceptions, and behaviors of research subjects as they interact in specific environments.
Ethnographic research questions can be used in education, business, medicine, and other fields of study, and they are very useful in contexts aimed at collecting in-depth and specific information that are peculiar to research variables. For instance, asking educational ethnographic research questions can help you understand how pedagogy affects classroom relations and behaviors.
This type of research question can be administered physically through one-on-one interviews, naturalism (live and work), and participant observation methods. Alternatively, the researcher can ask ethnographic research questions via online surveys and questionnaires created with Formplus.
Examples of Ethnographic Research Questions
- Why do you use this product?
- Have you noticed any side effects since you started using this drug?
- Does this product meet your needs?
- Case Studies
A case study is a qualitative research approach that involves carrying out a detailed investigation into a research subject(s) or variable(s). In the course of a case study, the researcher gathers a range of data from multiple sources of information via different data collection methods, and over a period of time.
The aim of a case study is to analyze specific issues within definite contexts and arrive at detailed research subject analyses by asking the right questions. This research method can be explanatory, descriptive , or exploratory depending on the focus of your systematic investigation or research.
An explanatory case study is one that seeks to gather information on the causes of real-life occurrences. This type of case study uses “how” and “why” questions in order to gather valid information about the causative factors of an event.
Descriptive case studies are typically used in business researches, and they aim at analyzing the impact of changing market dynamics on businesses. On the other hand, exploratory case studies aim at providing answers to “who” and “what” questions using data collection tools like interviews and questionnaires.
Some questions you can include in your case studies are:
- Why did you choose our services?
- How has this policy affected your business output?
- What benefits have you recorded since you started using our product?
An interview is a qualitative research method that involves asking respondents a series of questions in order to gather information about a research subject. Interview questions can be close-ended or open-ended , and they prompt participants to provide valid information that is useful to the research.
An interview may also be structured, semi-structured , or unstructured , and this further influences the types of questions they include. Structured interviews are made up of more close-ended questions because they aim at gathering quantitative data while unstructured interviews consist, primarily, of open-ended questions that allow the researcher to collect qualitative information from respondents.
You can conduct interview research by scheduling a physical meeting with respondents, through a telephone conversation, and via digital media and video conferencing platforms like Skype and Zoom. Alternatively, you can use Formplus surveys and questionnaires for your interview.
Examples of interview questions include:
- What challenges did you face while using our product?
- What specific needs did our product meet?
- What would you like us to improve our service delivery?
Quantitative Research Questions
Quantitative research questions are questions that are used to gather quantifiable data from research subjects. These types of research questions are usually more specific and direct because they aim at collecting information that can be measured; that is, statistical information.
Types of Quantitative Research Questions
- Descriptive Research Questions
Descriptive research questions are inquiries that researchers use to gather quantifiable data about the attributes and characteristics of research subjects. These types of questions primarily seek responses that reveal existing patterns in the nature of the research subjects.
It is important to note that descriptive research questions are not concerned with the causative factors of the discovered attributes and characteristics. Rather, they focus on the “what”; that is, describing the subject of the research without paying attention to the reasons for its occurrence.
Descriptive research questions are typically closed-ended because they aim at gathering definite and specific responses from research participants. Also, they can be used in customer experience surveys and market research to collect information about target markets and consumer behaviors.
Descriptive Research Question Examples
- How often do you make use of our fitness application?
- How much would you be willing to pay for this product?
- Comparative Research Questions
A comparative research question is a type of quantitative research question that is used to gather information about the differences between two or more research subjects across different variables. These types of questions help the researcher to identify distinct features that mark one research subject from the other while highlighting existing similarities.
Asking comparative research questions in market research surveys can provide insights on how your product or service matches its competitors. In addition, it can help you to identify the strengths and weaknesses of your product for a better competitive advantage.
The 5 steps involved in the framing of comparative research questions are:
- Choose your starting phrase
- Identify and name the dependent variable
- Identify the groups you are interested in
- Identify the appropriate adjoining text
- Write out the comparative research question
Comparative Research Question Samples
- What are the differences between a landline telephone and a smartphone?
- What are the differences between work-from-home and on-site operations?
- Relationship-based Research Questions
Just like the name suggests, a relationship-based research question is one that inquires into the nature of the association between two research subjects within the same demographic. These types of research questions help you to gather information pertaining to the nature of the association between two research variables.
Relationship-based research questions are also known as correlational research questions because they seek to clearly identify the link between 2 variables.
Read: Correlational Research Designs: Types, Examples & Methods
Examples of relationship-based research questions include:
- What is the relationship between purchasing power and the business site?
- What is the relationship between the work environment and workforce turnover?
Examples of a Good Research Question
Since research questions lie at the core of any systematic investigations, it is important to know how to frame a good research question. The right research questions will help you to gather the most objective responses that are useful to your systematic investigation.
A good research question is one that requires impartial responses and can be answered via existing sources of information. Also, a good research question seeks answers that actively contribute to a body of knowledge; hence, it is a question that is yet to be answered in your specific research context.
- Open-Ended Questions
An open-ended question is a type of research question that does not restrict respondents to a set of premeditated answer options. In other words, it is a question that allows the respondent to freely express his or her perceptions and feelings towards the research subject.
Examples of Open-ended Questions
- How do you deal with stress in the workplace?
- What is a typical day at work like for you?
- Close-ended Questions
A close-ended question is a type of survey question that restricts respondents to a set of predetermined answers such as multiple-choice questions . Close-ended questions typically require yes or no answers and are commonly used in quantitative research to gather numerical data from research participants.
Examples of Close-ended Questions
- Did you enjoy this event?
- How likely are you to recommend our services?
- Very Likely
- Somewhat Likely
- Likert Scale Questions
A Likert scale question is a type of close-ended question that is structured as a 3-point, 5-point, or 7-point psychometric scale . This type of question is used to measure the survey respondent’s disposition towards multiple variables and it can be unipolar or bipolar in nature.
Example of Likert Scale Questions
- How satisfied are you with our service delivery?
- Very dissatisfied
- Not satisfied
- Very satisfied
- Rating Scale Questions
A rating scale question is a type of close-ended question that seeks to associate a specific qualitative measure (rating) with the different variables in research. It is commonly used in customer experience surveys, market research surveys, employee reviews, and product evaluations.
Example of Rating Questions
- How would you rate our service delivery?
Examples of a Bad Research Question
Knowing what bad research questions are would help you avoid them in the course of your systematic investigation. These types of questions are usually unfocused and often result in research biases that can negatively impact the outcomes of your systematic investigation.
- Loaded Questions
A loaded question is a question that subtly presupposes one or more unverified assumptions about the research subject or participant. This type of question typically boxes the respondent in a corner because it suggests implicit and explicit biases that prevent objective responses.
Example of Loaded Questions
- Have you stopped smoking?
- Where did you hide the money?
- Negative Questions
A negative question is a type of question that is structured with an implicit or explicit negator. Negative questions can be misleading because they upturn the typical yes/no response order by requiring a negative answer for affirmation and an affirmative answer for negation.
Examples of Negative Questions
- Would you mind dropping by my office later today?
- Didn’t you visit last week?
- Leading Questions
A l eading question is a type of survey question that nudges the respondent towards an already-determined answer. It is highly suggestive in nature and typically consists of biases and unverified assumptions that point toward its premeditated responses.
Examples of Leading Questions
- If you enjoyed this service, would you be willing to try out our other packages?
- Our product met your needs, didn’t it?
Read More: Leading Questions: Definition, Types, and Examples
How to Use Formplus as Online Research Questionnaire Tool
With Formplus, you can create and administer your online research questionnaire easily. In the form builder, you can add different form fields to your questionnaire and edit these fields to reflect specific research questions for your systematic investigation.
Here is a step-by-step guide on how to create an online research questionnaire with Formplus:
- Sign in to your Formplus accoun t, then click on the “create new form” button in your dashboard to access the Form builder.
- In the form builder, add preferred form fields to your online research questionnaire by dragging and dropping them into the form. Add a title to your form in the title block. You can edit form fields by clicking on the “pencil” icon on the right corner of each form field.
- Save the form to access the customization section of the builder. Here, you can tweak the appearance of your online research questionnaire by adding background images, changing the form font, and adding your organization’s logo.
- Finally, copy your form link and share it with respondents. You can also use any of the multiple sharing options available.
Conclusion
The success of your research starts with framing the right questions to help you collect the most valid and objective responses. Be sure to avoid bad research questions like loaded and negative questions that can be misleading and adversely affect your research data and outcomes.
Your research questions should clearly reflect the aims and objectives of your systematic investigation while laying emphasis on specific contexts. To help you seamlessly gather responses for your research questions, you can create an online research questionnaire on Formplus.

Connect to Formplus, Get Started Now - It's Free!
- abstract in research papers
- bad research questions
- examples of research questions
- types of research questions
- busayo.longe

You may also like:

How to do a Meta Analysis: Methodology, Pros & Cons
In this article, we’ll go through the concept of meta-analysis, what it can be used for, and how you can use it to improve how you...

How to Write An Abstract For Research Papers: Tips & Examples
In this article, we will share some tips for writing an effective abstract, plus samples you can learn from.
How to Write a Problem Statement for your Research
Learn how to write problem statements before commencing any research effort. Learn about its structure and explore examples
Research Summary: What Is It & How To Write One
Introduction A research summary is a requirement during academic research and sometimes you might need to prepare a research summary...
Formplus - For Seamless Data Collection
Collect data the right way with a versatile data collection tool. try formplus and transform your work productivity today..
Ohio State nav bar
The Ohio State University
- BuckeyeLink
- Find People
- Search Ohio State
Research Questions & Hypotheses
Generally, in quantitative studies, reviewers expect hypotheses rather than research questions. However, both research questions and hypotheses serve different purposes and can be beneficial when used together.
Research Questions
Clarify the research’s aim (farrugia et al., 2010).
- Research often begins with an interest in a topic, but a deep understanding of the subject is crucial to formulate an appropriate research question.
- Descriptive: “What factors most influence the academic achievement of senior high school students?”
- Comparative: “What is the performance difference between teaching methods A and B?”
- Relationship-based: “What is the relationship between self-efficacy and academic achievement?”
- Increasing knowledge about a subject can be achieved through systematic literature reviews, in-depth interviews with patients (and proxies), focus groups, and consultations with field experts.
- Some funding bodies, like the Canadian Institute for Health Research, recommend conducting a systematic review or a pilot study before seeking grants for full trials.
- The presence of multiple research questions in a study can complicate the design, statistical analysis, and feasibility.
- It’s advisable to focus on a single primary research question for the study.
- The primary question, clearly stated at the end of a grant proposal’s introduction, usually specifies the study population, intervention, and other relevant factors.
- The FINER criteria underscore aspects that can enhance the chances of a successful research project, including specifying the population of interest, aligning with scientific and public interest, clinical relevance, and contribution to the field, while complying with ethical and national research standards.
- The P ICOT approach is crucial in developing the study’s framework and protocol, influencing inclusion and exclusion criteria and identifying patient groups for inclusion.
- Defining the specific population, intervention, comparator, and outcome helps in selecting the right outcome measurement tool.
- The more precise the population definition and stricter the inclusion and exclusion criteria, the more significant the impact on the interpretation, applicability, and generalizability of the research findings.
- A restricted study population enhances internal validity but may limit the study’s external validity and generalizability to clinical practice.
- A broadly defined study population may better reflect clinical practice but could increase bias and reduce internal validity.
- An inadequately formulated research question can negatively impact study design, potentially leading to ineffective outcomes and affecting publication prospects.
Checklist: Good research questions for social science projects (Panke, 2018)
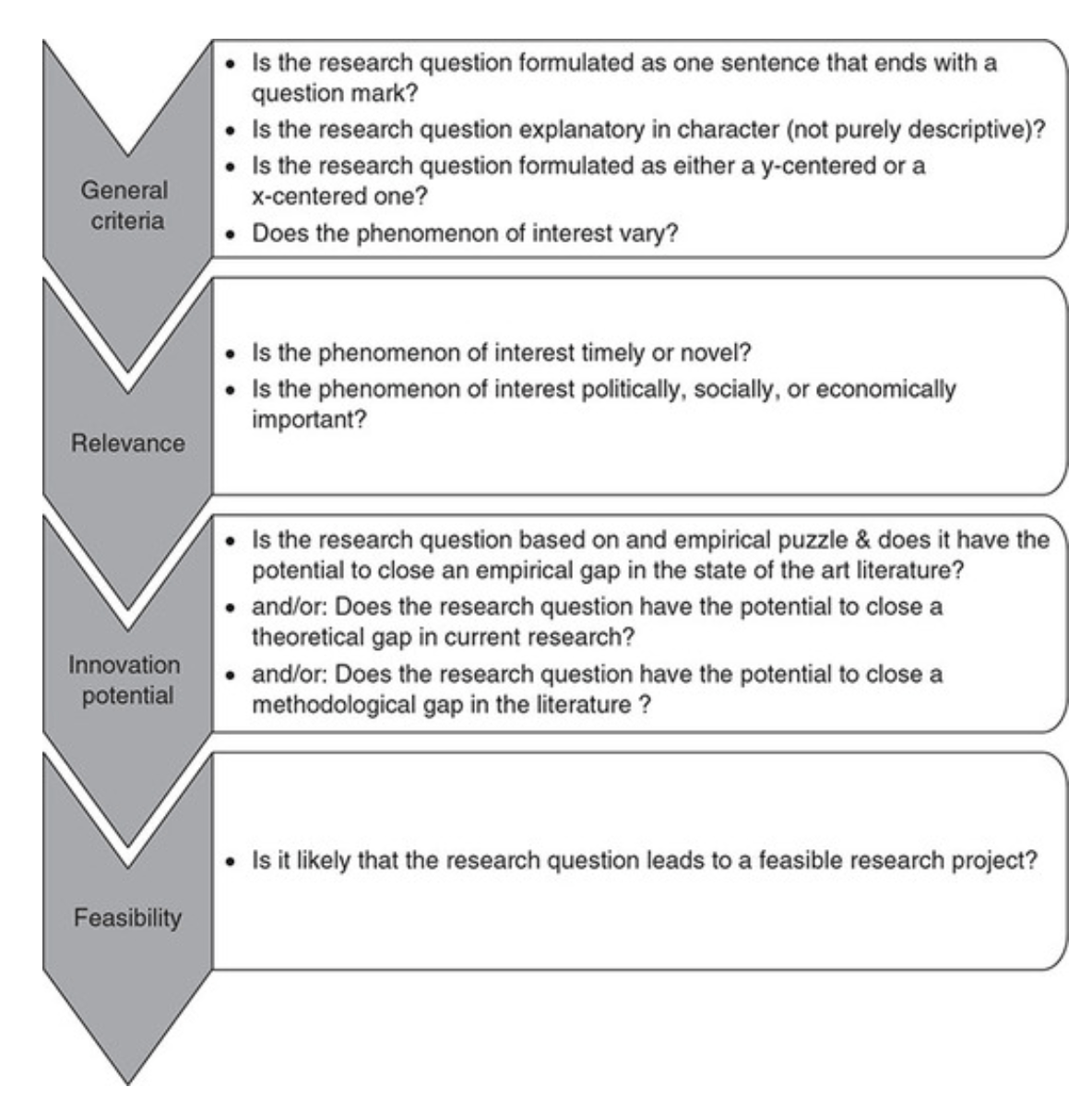
Research Hypotheses
Present the researcher’s predictions based on specific statements.
- These statements define the research problem or issue and indicate the direction of the researcher’s predictions.
- Formulating the research question and hypothesis from existing data (e.g., a database) can lead to multiple statistical comparisons and potentially spurious findings due to chance.
- The research or clinical hypothesis, derived from the research question, shapes the study’s key elements: sampling strategy, intervention, comparison, and outcome variables.
- Hypotheses can express a single outcome or multiple outcomes.
- After statistical testing, the null hypothesis is either rejected or not rejected based on whether the study’s findings are statistically significant.
- Hypothesis testing helps determine if observed findings are due to true differences and not chance.
- Hypotheses can be 1-sided (specific direction of difference) or 2-sided (presence of a difference without specifying direction).
- 2-sided hypotheses are generally preferred unless there’s a strong justification for a 1-sided hypothesis.
- A solid research hypothesis, informed by a good research question, influences the research design and paves the way for defining clear research objectives.
Types of Research Hypothesis
- In a Y-centered research design, the focus is on the dependent variable (DV) which is specified in the research question. Theories are then used to identify independent variables (IV) and explain their causal relationship with the DV.
- Example: “An increase in teacher-led instructional time (IV) is likely to improve student reading comprehension scores (DV), because extensive guided practice under expert supervision enhances learning retention and skill mastery.”
- Hypothesis Explanation: The dependent variable (student reading comprehension scores) is the focus, and the hypothesis explores how changes in the independent variable (teacher-led instructional time) affect it.
- In X-centered research designs, the independent variable is specified in the research question. Theories are used to determine potential dependent variables and the causal mechanisms at play.
- Example: “Implementing technology-based learning tools (IV) is likely to enhance student engagement in the classroom (DV), because interactive and multimedia content increases student interest and participation.”
- Hypothesis Explanation: The independent variable (technology-based learning tools) is the focus, with the hypothesis exploring its impact on a potential dependent variable (student engagement).
- Probabilistic hypotheses suggest that changes in the independent variable are likely to lead to changes in the dependent variable in a predictable manner, but not with absolute certainty.
- Example: “The more teachers engage in professional development programs (IV), the more their teaching effectiveness (DV) is likely to improve, because continuous training updates pedagogical skills and knowledge.”
- Hypothesis Explanation: This hypothesis implies a probable relationship between the extent of professional development (IV) and teaching effectiveness (DV).
- Deterministic hypotheses state that a specific change in the independent variable will lead to a specific change in the dependent variable, implying a more direct and certain relationship.
- Example: “If the school curriculum changes from traditional lecture-based methods to project-based learning (IV), then student collaboration skills (DV) are expected to improve because project-based learning inherently requires teamwork and peer interaction.”
- Hypothesis Explanation: This hypothesis presumes a direct and definite outcome (improvement in collaboration skills) resulting from a specific change in the teaching method.
- Example : “Students who identify as visual learners will score higher on tests that are presented in a visually rich format compared to tests presented in a text-only format.”
- Explanation : This hypothesis aims to describe the potential difference in test scores between visual learners taking visually rich tests and text-only tests, without implying a direct cause-and-effect relationship.
- Example : “Teaching method A will improve student performance more than method B.”
- Explanation : This hypothesis compares the effectiveness of two different teaching methods, suggesting that one will lead to better student performance than the other. It implies a direct comparison but does not necessarily establish a causal mechanism.
- Example : “Students with higher self-efficacy will show higher levels of academic achievement.”
- Explanation : This hypothesis predicts a relationship between the variable of self-efficacy and academic achievement. Unlike a causal hypothesis, it does not necessarily suggest that one variable causes changes in the other, but rather that they are related in some way.
Tips for developing research questions and hypotheses for research studies
- Perform a systematic literature review (if one has not been done) to increase knowledge and familiarity with the topic and to assist with research development.
- Learn about current trends and technological advances on the topic.
- Seek careful input from experts, mentors, colleagues, and collaborators to refine your research question as this will aid in developing the research question and guide the research study.
- Use the FINER criteria in the development of the research question.
- Ensure that the research question follows PICOT format.
- Develop a research hypothesis from the research question.
- Ensure that the research question and objectives are answerable, feasible, and clinically relevant.
If your research hypotheses are derived from your research questions, particularly when multiple hypotheses address a single question, it’s recommended to use both research questions and hypotheses. However, if this isn’t the case, using hypotheses over research questions is advised. It’s important to note these are general guidelines, not strict rules. If you opt not to use hypotheses, consult with your supervisor for the best approach.
Farrugia, P., Petrisor, B. A., Farrokhyar, F., & Bhandari, M. (2010). Practical tips for surgical research: Research questions, hypotheses and objectives. Canadian journal of surgery. Journal canadien de chirurgie , 53 (4), 278–281.
Hulley, S. B., Cummings, S. R., Browner, W. S., Grady, D., & Newman, T. B. (2007). Designing clinical research. Philadelphia.
Panke, D. (2018). Research design & method selection: Making good choices in the social sciences. Research Design & Method Selection , 1-368.
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Descriptive Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
Descriptive Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
Table of Contents

Descriptive Research Design
Definition:
Descriptive research design is a type of research methodology that aims to describe or document the characteristics, behaviors, attitudes, opinions, or perceptions of a group or population being studied.
Descriptive research design does not attempt to establish cause-and-effect relationships between variables or make predictions about future outcomes. Instead, it focuses on providing a detailed and accurate representation of the data collected, which can be useful for generating hypotheses, exploring trends, and identifying patterns in the data.
Types of Descriptive Research Design
Types of Descriptive Research Design are as follows:
Cross-sectional Study
This involves collecting data at a single point in time from a sample or population to describe their characteristics or behaviors. For example, a researcher may conduct a cross-sectional study to investigate the prevalence of certain health conditions among a population, or to describe the attitudes and beliefs of a particular group.
Longitudinal Study
This involves collecting data over an extended period of time, often through repeated observations or surveys of the same group or population. Longitudinal studies can be used to track changes in attitudes, behaviors, or outcomes over time, or to investigate the effects of interventions or treatments.
This involves an in-depth examination of a single individual, group, or situation to gain a detailed understanding of its characteristics or dynamics. Case studies are often used in psychology, sociology, and business to explore complex phenomena or to generate hypotheses for further research.
Survey Research
This involves collecting data from a sample or population through standardized questionnaires or interviews. Surveys can be used to describe attitudes, opinions, behaviors, or demographic characteristics of a group, and can be conducted in person, by phone, or online.
Observational Research
This involves observing and documenting the behavior or interactions of individuals or groups in a natural or controlled setting. Observational studies can be used to describe social, cultural, or environmental phenomena, or to investigate the effects of interventions or treatments.
Correlational Research
This involves examining the relationships between two or more variables to describe their patterns or associations. Correlational studies can be used to identify potential causal relationships or to explore the strength and direction of relationships between variables.
Data Analysis Methods
Descriptive research design data analysis methods depend on the type of data collected and the research question being addressed. Here are some common methods of data analysis for descriptive research:
Descriptive Statistics
This method involves analyzing data to summarize and describe the key features of a sample or population. Descriptive statistics can include measures of central tendency (e.g., mean, median, mode) and measures of variability (e.g., range, standard deviation).
Cross-tabulation
This method involves analyzing data by creating a table that shows the frequency of two or more variables together. Cross-tabulation can help identify patterns or relationships between variables.
Content Analysis
This method involves analyzing qualitative data (e.g., text, images, audio) to identify themes, patterns, or trends. Content analysis can be used to describe the characteristics of a sample or population, or to identify factors that influence attitudes or behaviors.
Qualitative Coding
This method involves analyzing qualitative data by assigning codes to segments of data based on their meaning or content. Qualitative coding can be used to identify common themes, patterns, or categories within the data.
Visualization
This method involves creating graphs or charts to represent data visually. Visualization can help identify patterns or relationships between variables and make it easier to communicate findings to others.
Comparative Analysis
This method involves comparing data across different groups or time periods to identify similarities and differences. Comparative analysis can help describe changes in attitudes or behaviors over time or differences between subgroups within a population.
Applications of Descriptive Research Design
Descriptive research design has numerous applications in various fields. Some of the common applications of descriptive research design are:
- Market research: Descriptive research design is widely used in market research to understand consumer preferences, behavior, and attitudes. This helps companies to develop new products and services, improve marketing strategies, and increase customer satisfaction.
- Health research: Descriptive research design is used in health research to describe the prevalence and distribution of a disease or health condition in a population. This helps healthcare providers to develop prevention and treatment strategies.
- Educational research: Descriptive research design is used in educational research to describe the performance of students, schools, or educational programs. This helps educators to improve teaching methods and develop effective educational programs.
- Social science research: Descriptive research design is used in social science research to describe social phenomena such as cultural norms, values, and beliefs. This helps researchers to understand social behavior and develop effective policies.
- Public opinion research: Descriptive research design is used in public opinion research to understand the opinions and attitudes of the general public on various issues. This helps policymakers to develop effective policies that are aligned with public opinion.
- Environmental research: Descriptive research design is used in environmental research to describe the environmental conditions of a particular region or ecosystem. This helps policymakers and environmentalists to develop effective conservation and preservation strategies.
Descriptive Research Design Examples
Here are some real-time examples of descriptive research designs:
- A restaurant chain wants to understand the demographics and attitudes of its customers. They conduct a survey asking customers about their age, gender, income, frequency of visits, favorite menu items, and overall satisfaction. The survey data is analyzed using descriptive statistics and cross-tabulation to describe the characteristics of their customer base.
- A medical researcher wants to describe the prevalence and risk factors of a particular disease in a population. They conduct a cross-sectional study in which they collect data from a sample of individuals using a standardized questionnaire. The data is analyzed using descriptive statistics and cross-tabulation to identify patterns in the prevalence and risk factors of the disease.
- An education researcher wants to describe the learning outcomes of students in a particular school district. They collect test scores from a representative sample of students in the district and use descriptive statistics to calculate the mean, median, and standard deviation of the scores. They also create visualizations such as histograms and box plots to show the distribution of scores.
- A marketing team wants to understand the attitudes and behaviors of consumers towards a new product. They conduct a series of focus groups and use qualitative coding to identify common themes and patterns in the data. They also create visualizations such as word clouds to show the most frequently mentioned topics.
- An environmental scientist wants to describe the biodiversity of a particular ecosystem. They conduct an observational study in which they collect data on the species and abundance of plants and animals in the ecosystem. The data is analyzed using descriptive statistics to describe the diversity and richness of the ecosystem.
How to Conduct Descriptive Research Design
To conduct a descriptive research design, you can follow these general steps:
- Define your research question: Clearly define the research question or problem that you want to address. Your research question should be specific and focused to guide your data collection and analysis.
- Choose your research method: Select the most appropriate research method for your research question. As discussed earlier, common research methods for descriptive research include surveys, case studies, observational studies, cross-sectional studies, and longitudinal studies.
- Design your study: Plan the details of your study, including the sampling strategy, data collection methods, and data analysis plan. Determine the sample size and sampling method, decide on the data collection tools (such as questionnaires, interviews, or observations), and outline your data analysis plan.
- Collect data: Collect data from your sample or population using the data collection tools you have chosen. Ensure that you follow ethical guidelines for research and obtain informed consent from participants.
- Analyze data: Use appropriate statistical or qualitative analysis methods to analyze your data. As discussed earlier, common data analysis methods for descriptive research include descriptive statistics, cross-tabulation, content analysis, qualitative coding, visualization, and comparative analysis.
- I nterpret results: Interpret your findings in light of your research question and objectives. Identify patterns, trends, and relationships in the data, and describe the characteristics of your sample or population.
- Draw conclusions and report results: Draw conclusions based on your analysis and interpretation of the data. Report your results in a clear and concise manner, using appropriate tables, graphs, or figures to present your findings. Ensure that your report follows accepted research standards and guidelines.
When to Use Descriptive Research Design
Descriptive research design is used in situations where the researcher wants to describe a population or phenomenon in detail. It is used to gather information about the current status or condition of a group or phenomenon without making any causal inferences. Descriptive research design is useful in the following situations:
- Exploratory research: Descriptive research design is often used in exploratory research to gain an initial understanding of a phenomenon or population.
- Identifying trends: Descriptive research design can be used to identify trends or patterns in a population, such as changes in consumer behavior or attitudes over time.
- Market research: Descriptive research design is commonly used in market research to understand consumer preferences, behavior, and attitudes.
- Health research: Descriptive research design is useful in health research to describe the prevalence and distribution of a disease or health condition in a population.
- Social science research: Descriptive research design is used in social science research to describe social phenomena such as cultural norms, values, and beliefs.
- Educational research: Descriptive research design is used in educational research to describe the performance of students, schools, or educational programs.
Purpose of Descriptive Research Design
The main purpose of descriptive research design is to describe and measure the characteristics of a population or phenomenon in a systematic and objective manner. It involves collecting data that describe the current status or condition of the population or phenomenon of interest, without manipulating or altering any variables.
The purpose of descriptive research design can be summarized as follows:
- To provide an accurate description of a population or phenomenon: Descriptive research design aims to provide a comprehensive and accurate description of a population or phenomenon of interest. This can help researchers to develop a better understanding of the characteristics of the population or phenomenon.
- To identify trends and patterns: Descriptive research design can help researchers to identify trends and patterns in the data, such as changes in behavior or attitudes over time. This can be useful for making predictions and developing strategies.
- To generate hypotheses: Descriptive research design can be used to generate hypotheses or research questions that can be tested in future studies. For example, if a descriptive study finds a correlation between two variables, this could lead to the development of a hypothesis about the causal relationship between the variables.
- To establish a baseline: Descriptive research design can establish a baseline or starting point for future research. This can be useful for comparing data from different time periods or populations.
Characteristics of Descriptive Research Design
Descriptive research design has several key characteristics that distinguish it from other research designs. Some of the main characteristics of descriptive research design are:
- Objective : Descriptive research design is objective in nature, which means that it focuses on collecting factual and accurate data without any personal bias. The researcher aims to report the data objectively without any personal interpretation.
- Non-experimental: Descriptive research design is non-experimental, which means that the researcher does not manipulate any variables. The researcher simply observes and records the behavior or characteristics of the population or phenomenon of interest.
- Quantitative : Descriptive research design is quantitative in nature, which means that it involves collecting numerical data that can be analyzed using statistical techniques. This helps to provide a more precise and accurate description of the population or phenomenon.
- Cross-sectional: Descriptive research design is often cross-sectional, which means that the data is collected at a single point in time. This can be useful for understanding the current state of the population or phenomenon, but it may not provide information about changes over time.
- Large sample size: Descriptive research design typically involves a large sample size, which helps to ensure that the data is representative of the population of interest. A large sample size also helps to increase the reliability and validity of the data.
- Systematic and structured: Descriptive research design involves a systematic and structured approach to data collection, which helps to ensure that the data is accurate and reliable. This involves using standardized procedures for data collection, such as surveys, questionnaires, or observation checklists.
Advantages of Descriptive Research Design
Descriptive research design has several advantages that make it a popular choice for researchers. Some of the main advantages of descriptive research design are:
- Provides an accurate description: Descriptive research design is focused on accurately describing the characteristics of a population or phenomenon. This can help researchers to develop a better understanding of the subject of interest.
- Easy to conduct: Descriptive research design is relatively easy to conduct and requires minimal resources compared to other research designs. It can be conducted quickly and efficiently, and data can be collected through surveys, questionnaires, or observations.
- Useful for generating hypotheses: Descriptive research design can be used to generate hypotheses or research questions that can be tested in future studies. For example, if a descriptive study finds a correlation between two variables, this could lead to the development of a hypothesis about the causal relationship between the variables.
- Large sample size : Descriptive research design typically involves a large sample size, which helps to ensure that the data is representative of the population of interest. A large sample size also helps to increase the reliability and validity of the data.
- Can be used to monitor changes : Descriptive research design can be used to monitor changes over time in a population or phenomenon. This can be useful for identifying trends and patterns, and for making predictions about future behavior or attitudes.
- Can be used in a variety of fields : Descriptive research design can be used in a variety of fields, including social sciences, healthcare, business, and education.
Limitation of Descriptive Research Design
Descriptive research design also has some limitations that researchers should consider before using this design. Some of the main limitations of descriptive research design are:
- Cannot establish cause and effect: Descriptive research design cannot establish cause and effect relationships between variables. It only provides a description of the characteristics of the population or phenomenon of interest.
- Limited generalizability: The results of a descriptive study may not be generalizable to other populations or situations. This is because descriptive research design often involves a specific sample or situation, which may not be representative of the broader population.
- Potential for bias: Descriptive research design can be subject to bias, particularly if the researcher is not objective in their data collection or interpretation. This can lead to inaccurate or incomplete descriptions of the population or phenomenon of interest.
- Limited depth: Descriptive research design may provide a superficial description of the population or phenomenon of interest. It does not delve into the underlying causes or mechanisms behind the observed behavior or characteristics.
- Limited utility for theory development: Descriptive research design may not be useful for developing theories about the relationship between variables. It only provides a description of the variables themselves.
- Relies on self-report data: Descriptive research design often relies on self-report data, such as surveys or questionnaires. This type of data may be subject to biases, such as social desirability bias or recall bias.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples

Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide

Observational Research – Methods and Guide

Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and...

Qualitative Research Methods

Explanatory Research – Types, Methods, Guide
- Cookies & Privacy
- GETTING STARTED
- Introduction
- FUNDAMENTALS
- Acknowledgements
- Research questions & hypotheses
- Concepts, constructs & variables
- Research limitations
- Getting started
- Sampling Strategy
- Research Quality
- Research Ethics
- Data Analysis
Types of quantitative research question
Dissertations that are based on a quantitative research design attempt to answer at least one quantitative research question . In some cases, these quantitative research questions will be followed by either research hypotheses or null hypotheses . However, this article focuses solely on quantitative research questions. Furthermore, since there is more than one type of quantitative research question that you can attempt to answer in a dissertation (i.e., descriptive research questions, comparative research questions and relationship-based research questions), we discuss each of these in this article. If you do not know much about quantitative research and quantitative research questions at this stage, we would recommend that you first read the article, Quantitative research questions: What do I have to think about , as well as an overview article on types of variables , which will help to familiarise you with terms such as dependent and independent variable , as well as categorical and continuous variables [see the article: Types of variables ]. The purpose of this article is to introduce you to the three different types of quantitative research question (i.e., descriptive, comparative and relationship-based research questions) so that you can understand what type(s) of quantitative research question you want to create in your dissertation. Each of these types of quantitative research question is discussed in turn:
Descriptive research questions
Comparative research questions.
- Relationship-based research questions
Descriptive research questions simply aim to describe the variables you are measuring. When we use the word describe , we mean that these research questions aim to quantify the variables you are interested in. Think of research questions that start with words such as "How much?" , "How often?" , "What percentage?" , and "What proportion?" , but also sometimes questions starting "What is?" and "What are?" . Often, descriptive research questions focus on only one variable and one group, but they can include multiple variables and groups. We provide some examples below:
In each of these example descriptive research questions, we are quantifying the variables we are interested in. However, the units that we used to quantify these variables will differ depending on what is being measured. For example, in the questions above, we are interested in frequencies (also known as counts ), such as the number of calories, photos uploaded, or comments on other users? photos. In the case of the final question, What are the most important factors that influence the career choices of Australian university students? , we are interested in the number of times each factor (e.g., salary and benefits, career prospects, physical working conditions, etc.) was ranked on a scale of 1 to 10 (with 1 = least important and 10 = most important). We may then choose to examine this data by presenting the frequencies , as well as using a measure of central tendency and a measure of spread [see the section on Data Analysis to learn more about these and other statistical tests].
However, it is also common when using descriptive research questions to measure percentages and proportions , so we have included some example descriptive research questions below that illustrate this.
In terms of the first descriptive research question about daily calorific intake , we are not necessarily interested in frequencies , or using a measure of central tendency or measure of spread , but instead want understand what percentage of American men and women exceed their daily calorific allowance . In this respect, this descriptive research question differs from the earlier question that asked: How many calories do American men and women consume per day? Whilst this question simply wants to measure the total number of calories (i.e., the How many calories part that starts the question); in this case, the question aims to measure excess ; that is, what percentage of these two groups (i.e., American men and American women) exceed their daily calorific allowance, which is different for males (around 2500 calories per day) and females (around 2000 calories per day).
If you are performing a piece of descriptive , quantitative research for your dissertation, you are likely to need to set quite a number of descriptive research questions . However, if you are using an experimental or quasi-experimental research design , or a more involved relationship-based research design , you are more likely to use just one or two descriptive research questions as a means to providing background to the topic you are studying, helping to give additional context for comparative research questions and/or relationship-based research questions that follow.
Comparative research questions aim to examine the differences between two or more groups on one or more dependent variables (although often just a single dependent variable). Such questions typically start by asking "What is the difference in?" a particular dependent variable (e.g., daily calorific intake) between two or more groups (e.g., American men and American women). Examples of comparative research questions include:
Groups reflect different categories of the independent variable you are measuring (e.g., American men and women = "gender"; Australian undergraduate and graduate students = "educational level"; pirated music that is freely distributed and pirated music that is purchased = "method of illegal music acquisition").
Comparative research questions also differ in terms of their relative complexity , by which we are referring to how many items/measures make up the dependent variable or how many dependent variables are investigated. Indeed, the examples highlight the difference between very simple comparative research questions where the dependent variable involves just a single measure/item (e.g., daily calorific intake) and potentially more complex questions where the dependent variable is made up of multiple items (e.g., Facebook usage behaviour including a wide range of items, such as logins, weekly photo uploads, status changes, etc.); or where each of these items should be written out as dependent variables.
Overall, whilst the dependent variable(s) highlight what you are interested in studying (e.g., attitudes towards music piracy, perceptions towards Internet banking security), comparative research questions are particularly appropriate if your dissertation aims to examine the differences between two or more groups (e.g., men and women, adolescents and pensioners, managers and non-managers, etc.).
Relationship research questions
Whilst we refer to this type of quantitative research question as a relationship-based research question, the word relationship should be treated simply as a useful way of describing the fact that these types of quantitative research question are interested in the causal relationships , associations , trends and/or interactions amongst two or more variables on one or more groups. We have to be careful when using the word relationship because in statistics, it refers to a particular type of research design, namely experimental research designs where it is possible to measure the cause and effect between two or more variables; that is, it is possible to say that variable A (e.g., study time) was responsible for an increase in variable B (e.g., exam scores). However, at the undergraduate and even master's level, dissertations rarely involve experimental research designs , but rather quasi-experimental and relationship-based research designs [see the section on Quantitative research designs ]. This means that you cannot often find causal relationships between variables, but only associations or trends .
However, when we write a relationship-based research question , we do not have to make this distinction between causal relationships, associations, trends and interactions (i.e., it is just something that you should keep in the back of your mind). Instead, we typically start a relationship-based quantitative research question, "What is the relationship?" , usually followed by the words, "between or amongst" , then list the independent variables (e.g., gender) and dependent variables (e.g., attitudes towards music piracy), "amongst or between" the group(s) you are focusing on. Examples of relationship-based research questions are:
As the examples above highlight, relationship-based research questions are appropriate to set when we are interested in the relationship, association, trend, or interaction between one or more dependent (e.g., exam scores) and independent (e.g., study time) variables, whether on one or more groups (e.g., university students).
The quantitative research design that we select subsequently determines whether we look for relationships , associations , trends or interactions . To learn how to structure (i.e., write out) each of these three types of quantitative research question (i.e., descriptive, comparative, relationship-based research questions), see the article: How to structure quantitative research questions .
Child Care and Early Education Research Connections
Descriptive research studies.
Descriptive research is a type of research that is used to describe the characteristics of a population. It collects data that are used to answer a wide range of what, when, and how questions pertaining to a particular population or group. For example, descriptive studies might be used to answer questions such as: What percentage of Head Start teachers have a bachelor's degree or higher? What is the average reading ability of 5-year-olds when they first enter kindergarten? What kinds of math activities are used in early childhood programs? When do children first receive regular child care from someone other than their parents? When are children with developmental disabilities first diagnosed and when do they first receive services? What factors do programs consider when making decisions about the type of assessments that will be used to assess the skills of the children in their programs? How do the types of services children receive from their early childhood program change as children age?
Descriptive research does not answer questions about why a certain phenomenon occurs or what the causes are. Answers to such questions are best obtained from randomized and quasi-experimental studies . However, data from descriptive studies can be used to examine the relationships (correlations) among variables. While the findings from correlational analyses are not evidence of causality, they can help to distinguish variables that may be important in explaining a phenomenon from those that are not. Thus, descriptive research is often used to generate hypotheses that should be tested using more rigorous designs.
A variety of data collection methods may be used alone or in combination to answer the types of questions guiding descriptive research. Some of the more common methods include surveys, interviews, observations, case studies, and portfolios. The data collected through these methods can be either quantitative or qualitative. Quantitative data are typically analyzed and presenting using descriptive statistics . Using quantitative data, researchers may describe the characteristics of a sample or population in terms of percentages (e.g., percentage of population that belong to different racial/ethnic groups, percentage of low-income families that receive different government services) or averages (e.g., average household income, average scores of reading, mathematics and language assessments). Quantitative data, such as narrative data collected as part of a case study, may be used to organize, classify, and used to identify patterns of behaviors, attitudes, and other characteristics of groups.
Descriptive studies have an important role in early care and education research. Studies such as the National Survey of Early Care and Education and the National Household Education Surveys Program have greatly increased our knowledge of the supply of and demand for child care in the U.S. The Head Start Family and Child Experiences Survey and the Early Childhood Longitudinal Study Program have provided researchers, policy makers and practitioners with rich information about school readiness skills of children in the U.S.
Each of the methods used to collect descriptive data have their own strengths and limitations. The following are some of the strengths and limitations of descriptive research studies in general.
Study participants are questioned or observed in a natural setting (e.g., their homes, child care or educational settings).
Study data can be used to identify the prevalence of particular problems and the need for new or additional services to address these problems.
Descriptive research may identify areas in need of additional research and relationships between variables that require future study. Descriptive research is often referred to as "hypothesis generating research."
Depending on the data collection method used, descriptive studies can generate rich datasets on large and diverse samples.
Limitations:
Descriptive studies cannot be used to establish cause and effect relationships.
Respondents may not be truthful when answering survey questions or may give socially desirable responses.
The choice and wording of questions on a questionnaire may influence the descriptive findings.
Depending on the type and size of sample, the findings may not be generalizable or produce an accurate description of the population of interest.
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
How to Write a Research Question: Types and Examples

The first step in any research project is framing the research question. It can be considered the core of any systematic investigation as the research outcomes are tied to asking the right questions. Thus, this primary interrogation point sets the pace for your research as it helps collect relevant and insightful information that ultimately influences your work.
Typically, the research question guides the stages of inquiry, analysis, and reporting. Depending on the use of quantifiable or quantitative data, research questions are broadly categorized into quantitative or qualitative research questions. Both types of research questions can be used independently or together, considering the overall focus and objectives of your research.
What is a research question?
A research question is a clear, focused, concise, and arguable question on which your research and writing are centered. 1 It states various aspects of the study, including the population and variables to be studied and the problem the study addresses. These questions also set the boundaries of the study, ensuring cohesion.
Designing the research question is a dynamic process where the researcher can change or refine the research question as they review related literature and develop a framework for the study. Depending on the scale of your research, the study can include single or multiple research questions.
A good research question has the following features:
- It is relevant to the chosen field of study.
- The question posed is arguable and open for debate, requiring synthesizing and analysis of ideas.
- It is focused and concisely framed.
- A feasible solution is possible within the given practical constraint and timeframe.
A poorly formulated research question poses several risks. 1
- Researchers can adopt an erroneous design.
- It can create confusion and hinder the thought process, including developing a clear protocol.
- It can jeopardize publication efforts.
- It causes difficulty in determining the relevance of the study findings.
- It causes difficulty in whether the study fulfils the inclusion criteria for systematic review and meta-analysis. This creates challenges in determining whether additional studies or data collection is needed to answer the question.
- Readers may fail to understand the objective of the study. This reduces the likelihood of the study being cited by others.
Now that you know “What is a research question?”, let’s look at the different types of research questions.
Types of research questions
Depending on the type of research to be done, research questions can be classified broadly into quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-methods studies. Knowing the type of research helps determine the best type of research question that reflects the direction and epistemological underpinnings of your research.
The structure and wording of quantitative 2 and qualitative research 3 questions differ significantly. The quantitative study looks at causal relationships, whereas the qualitative study aims at exploring a phenomenon.
- Quantitative research questions:
- Seeks to investigate social, familial, or educational experiences or processes in a particular context and/or location.
- Answers ‘how,’ ‘what,’ or ‘why’ questions.
- Investigates connections, relations, or comparisons between independent and dependent variables.
Quantitative research questions can be further categorized into descriptive, comparative, and relationship, as explained in the Table below.
- Qualitative research questions
Qualitative research questions are adaptable, non-directional, and more flexible. It concerns broad areas of research or more specific areas of study to discover, explain, or explore a phenomenon. These are further classified as follows:
- Mixed-methods studies
Mixed-methods studies use both quantitative and qualitative research questions to answer your research question. Mixed methods provide a complete picture than standalone quantitative or qualitative research, as it integrates the benefits of both methods. Mixed methods research is often used in multidisciplinary settings and complex situational or societal research, especially in the behavioral, health, and social science fields.
What makes a good research question
A good research question should be clear and focused to guide your research. It should synthesize multiple sources to present your unique argument, and should ideally be something that you are interested in. But avoid questions that can be answered in a few factual statements. The following are the main attributes of a good research question.
- Specific: The research question should not be a fishing expedition performed in the hopes that some new information will be found that will benefit the researcher. The central research question should work with your research problem to keep your work focused. If using multiple questions, they should all tie back to the central aim.
- Measurable: The research question must be answerable using quantitative and/or qualitative data or from scholarly sources to develop your research question. If such data is impossible to access, it is better to rethink your question.
- Attainable: Ensure you have enough time and resources to do all research required to answer your question. If it seems you will not be able to gain access to the data you need, consider narrowing down your question to be more specific.
- You have the expertise
- You have the equipment and resources
- Realistic: Developing your research question should be based on initial reading about your topic. It should focus on addressing a problem or gap in the existing knowledge in your field or discipline.
- Based on some sort of rational physics
- Can be done in a reasonable time frame
- Timely: The research question should contribute to an existing and current debate in your field or in society at large. It should produce knowledge that future researchers or practitioners can later build on.
- Novel
- Based on current technologies.
- Important to answer current problems or concerns.
- Lead to new directions.
- Important: Your question should have some aspect of originality. Incremental research is as important as exploring disruptive technologies. For example, you can focus on a specific location or explore a new angle.
- Meaningful whether the answer is “Yes” or “No.” Closed-ended, yes/no questions are too simple to work as good research questions. Such questions do not provide enough scope for robust investigation and discussion. A good research question requires original data, synthesis of multiple sources, and original interpretation and argumentation before providing an answer.
Steps for developing a good research question
The importance of research questions cannot be understated. When drafting a research question, use the following frameworks to guide the components of your question to ease the process. 4
- Determine the requirements: Before constructing a good research question, set your research requirements. What is the purpose? Is it descriptive, comparative, or explorative research? Determining the research aim will help you choose the most appropriate topic and word your question appropriately.
- Select a broad research topic: Identify a broader subject area of interest that requires investigation. Techniques such as brainstorming or concept mapping can help identify relevant connections and themes within a broad research topic. For example, how to learn and help students learn.
- Perform preliminary investigation: Preliminary research is needed to obtain up-to-date and relevant knowledge on your topic. It also helps identify issues currently being discussed from which information gaps can be identified.
- Narrow your focus: Narrow the scope and focus of your research to a specific niche. This involves focusing on gaps in existing knowledge or recent literature or extending or complementing the findings of existing literature. Another approach involves constructing strong research questions that challenge your views or knowledge of the area of study (Example: Is learning consistent with the existing learning theory and research).
- Identify the research problem: Once the research question has been framed, one should evaluate it. This is to realize the importance of the research questions and if there is a need for more revising (Example: How do your beliefs on learning theory and research impact your instructional practices).
How to write a research question
Those struggling to understand how to write a research question, these simple steps can help you simplify the process of writing a research question.
Sample Research Questions
The following are some bad and good research question examples
- Example 1
- Example 2
References:
- Thabane, L., Thomas, T., Ye, C., & Paul, J. (2009). Posing the research question: not so simple. Canadian Journal of Anesthesia/Journal canadien d’anesthésie , 56 (1), 71-79.
- Rutberg, S., & Bouikidis, C. D. (2018). Focusing on the fundamentals: A simplistic differentiation between qualitative and quantitative research. Nephrology Nursing Journal , 45 (2), 209-213.
- Kyngäs, H. (2020). Qualitative research and content analysis. The application of content analysis in nursing science research , 3-11.
- Mattick, K., Johnston, J., & de la Croix, A. (2018). How to… write a good research question. The clinical teacher , 15 (2), 104-108.
- Fandino, W. (2019). Formulating a good research question: Pearls and pitfalls. Indian Journal of Anaesthesia , 63 (8), 611.
- Richardson, W. S., Wilson, M. C., Nishikawa, J., & Hayward, R. S. (1995). The well-built clinical question: a key to evidence-based decisions. ACP journal club , 123 (3), A12-A13
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Scientific Writing Style Guides Explained
- Ethical Research Practices For Research with Human Subjects
- 8 Most Effective Ways to Increase Motivation for Thesis Writing
- 6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Transitive and Intransitive Verbs in the World of Research
Language and grammar rules for academic writing, you may also like, phd qualifying exam: tips for success , quillbot review: features, pricing, and free alternatives, what is an academic paper types and elements , publish research papers: 9 steps for successful publications , what are the different types of research papers, how to make translating academic papers less challenging, 6 tips for post-doc researchers to take their..., presenting research data effectively through tables and figures, ethics in science: importance, principles & guidelines , jenni ai review: top features, pricing, and alternatives.
- Translators
- Graphic Designers
Please enter the email address you used for your account. Your sign in information will be sent to your email address after it has been verified.
415 Research Question Examples Across 15 Disciplines

A research question is a clearly formulated query that delineates the scope and direction of an investigation. It serves as the guiding light for scholars, helping them to dissect, analyze, and comprehend complex phenomena. Beyond merely seeking answers, a well-crafted research question ensures that the exploration remains focused and goal-oriented.
The significance of framing a clear, concise, and researchable question cannot be overstated. A well-defined question not only clarifies the objective of the research but also determines the methodologies and tools a researcher will employ. A concise question ensures precision, eliminating the potential for ambiguity or misinterpretation. Furthermore, the question must be researchable—posing a question that is too broad, too subjective, or unanswerable can lead to inconclusive results or an endless loop of investigation. In essence, the foundation of any meaningful academic endeavor rests on the articulation of a compelling and achievable research question.
Research questions can be categorized based on their intent and the nature of the information they seek. Recognizing the different types is essential for crafting an effective inquiry and guiding the research process. Let's delve into the various categories:
- Descriptive Research Questions: These types of questions aim to outline and characterize specific phenomena or attributes. They seek to provide a clear picture of a situation or context without necessarily diving into causal relationships. For instance, a question like "What are the main symptoms of the flu?" is descriptive as it seeks to list the symptoms.
- Explanatory (or Causal) Research Questions: Explanatory questions delve deeper, trying to uncover the reasons or causes behind certain phenomena. They are particularly common in experimental research where researchers are attempting to establish cause-and-effect relationships. An example might be, "Does smoking increase the risk of lung cancer?"
- Exploratory Research Questions: As the name suggests, these questions are used when researchers are entering uncharted territories. They are designed to gather preliminary information on topics that haven't been studied extensively. A question like "How do emerging technologies impact remote tribal communities?" can be seen as exploratory if there's limited existing research on the topic.
- Comparative Research Questions: These questions are formulated when the objective is to compare two or more groups, conditions, or variables. Comparative questions might look like "How do test scores differ between students who study regularly and those who cram?"
- Predictive Research Questions: The goal here is to forecast or predict potential outcomes based on certain variables or conditions. Predictive research might pose questions such as "Based on current climate trends, how will average global temperatures change by 2050?"
Here are examples of research questions across various disciplines, shedding light on queries that stimulate intellectual curiosity and advancement. In this post, we will delve into disciplines ranging from the Natural Sciences, such as Physics and Biology, to the Social Sciences, including Sociology and Anthropology, as well as the Humanities, like Literature and Philosophy. We'll also explore questions from fields as varied as Health Sciences, Engineering, Business, Environmental Sciences, Mathematics, Education, Law, Agriculture, Arts, Computer Science, Architecture, and Languages. This comprehensive overview aims to illustrate the breadth and depth of inquiries that shape our world of knowledge.
Agriculture and forestry examples
Architecture and planning examples, arts and design examples, business and finance examples, computer science and informatics examples, education examples, engineering and technology examples, environmental sciences examples, health sciences examples, humanities examples, languages and linguistics examples, law examples, mathematics and statistics examples, natural sciences examples, social sciences examples.
- Descriptive: What are the primary factors that influence crop yield in temperate climates?
- Explanatory: Why do certain soil types yield higher grain production than others?
- Exploratory: How might new organic farming techniques influence soil health over a decade?
- Comparative: How do the growth rates differ between genetically modified and traditional corn crops?
- Predictive: Based on current climate models, how will changing rain patterns impact wheat production in the next 20 years?
Animal science
- Descriptive: What are the common behavioral traits of domesticated cattle in grass-fed conditions?
- Explanatory: Why do certain breeds of chickens have a higher egg production rate?
- Exploratory: What potential benefits could arise from integrating tech wearables in livestock management?
- Comparative: How does the milk yield differ between Holstein and Jersey cows when given the same diet?
- Predictive: How might increasing global temperatures influence the reproductive cycles of swine?
Aquaculture
- Descriptive: What are the most commonly farmed fish species in Southeast Asia?
- Explanatory: Why do shrimp farms have a higher disease outbreak rate compared to fish farms?
- Exploratory: How might innovative recirculating aquaculture systems revolutionize the industry's environmental impact?
- Comparative: How do growth rates of salmon differ between open-net pens and land-based tanks?
- Predictive: What will be the impact of ocean acidification on mollusk farming over the next three decades?
- Descriptive: What tree species dominate the temperate rainforests of North America?
- Explanatory: Why are certain tree species more resistant to pest infestations?
- Exploratory: What are the potential benefits of integrating drone technology in forest health monitoring?
- Comparative: How do deforestation rates compare between legally protected and unprotected areas in the Amazon?
- Predictive: Given increasing global demand for timber, how might tree populations in Siberia change in the next half-century?
Horticulture
- Descriptive: What are the common characteristics of plants suitable for urban vertical farming?
- Explanatory: Why do roses require specific pH levels in the soil for optimal growth?
- Exploratory: What potential methods might promote year-round vegetable farming in colder regions?
- Comparative: How does fruit yield differ between traditionally planted orchards and high-density planting systems?
- Predictive: How might changing global temperatures affect wine grape production in traditional regions?
Soil science
- Descriptive: What are the main components of loamy soil?
- Explanatory: Why does clay-rich soil retain more water compared to sandy soil?
- Exploratory: How might biochar applications transform nutrient availability in degraded soils?
- Comparative: How do nutrient levels vary between soils managed with organic versus inorganic fertilizers?
- Predictive: Based on current farming practices, how will soil quality in the Midwest U.S. evolve over the next 30 years?
Architectural design
- Descriptive: What are the dominant architectural styles of public buildings constructed in the 21st century?
- Explanatory: Why do certain architectural elements from classical periods continue to influence modern designs?
- Exploratory: How might sustainable materials revolutionize the future of architectural design?
- Comparative: How do energy consumption levels differ between buildings with passive design elements and those without?
- Predictive: Based on urbanization trends, how will the design of residential buildings evolve in the next two decades?
Landscape architecture
- Descriptive: What are the primary components of a successful urban park design?
- Explanatory: Why do certain types of vegetation promote greater biodiversity in urban settings?
- Exploratory: What innovative techniques can be employed to restore and integrate wetlands into urban landscapes?
- Comparative: How does visitor satisfaction vary between nature-inspired landscapes and more structured, geometric designs?
- Predictive: With the effects of climate change, how might coastal landscape architecture adapt to rising sea levels over the coming century?
Urban planning
- Descriptive: What are the main components of a pedestrian-friendly city center?
- Explanatory: Why do certain urban layouts promote more efficient traffic flow than others?
- Exploratory: How might the integration of vertical farming impact urban food security and cityscape aesthetics?
- Comparative: How do the air quality levels differ between cities with green belts and those without?
- Predictive: Based on increasing telecommuting trends, how will urban planning strategies adjust to potentially reduced daily commutes in the future?
Graphic design
- Descriptive: What are the prevailing typography trends in modern branding?
- Explanatory: Why do certain color schemes evoke specific emotions or perceptions in consumers?
- Exploratory: How is augmented reality reshaping the landscape of interactive graphic design?
- Comparative: How do print and digital designs differ in terms of elements and principles when targeting a young adult audience?
- Predictive: Based on evolving digital platforms, what are potential future trends in web design aesthetics?
Industrial design
- Descriptive: What characterizes the ergonomic features of leading office chairs in the market?
- Explanatory: Why have minimalist designs become more prevalent in consumer electronics over the past decade?
- Exploratory: How might bio-inspired design influence the future of transportation vehicles?
- Comparative: How does user satisfaction differ between traditional versus modular product designs?
- Predictive: Given the push towards sustainability, how will material selection evolve in the next decade of product design?
Multimedia arts
- Descriptive: What techniques define the most popular virtual reality (VR) experiences currently available?
- Explanatory: Why do certain sound designs enhance immersion in video games more effectively than others?
- Exploratory: How might holographic technologies revolutionize stage performances or public installations in the future?
- Comparative: How do user engagement levels differ between 2D animations and 3D animations in educational platforms?
- Predictive: With the rise of augmented reality (AR) wearables, what might be the next frontier in multimedia art installations?
Performing arts
- Descriptive: What styles of dance are currently predominant in global theater productions?
- Explanatory: Why do certain rhythms or beats universally resonate with audiences across cultures?
- Exploratory: How might digital avatars or AI entities play roles in future theatrical performances?
- Comparative: How does audience reception differ between traditional plays and experimental, interactive performances?
- Predictive: Considering global digitalization, how might virtual theaters redefine the experience of live performances in the future?
Visual arts
- Descriptive: What themes are prevalent in contemporary art exhibitions worldwide?
- Explanatory: Why have mixed media installations gained prominence in the 21st-century art scene?
- Exploratory: How is the intersection of technology and art opening new mediums or platforms for artists?
- Comparative: How do traditional painting techniques, such as oil and watercolor, contrast in terms of texture and luminosity?
- Predictive: With the evolution of digital art platforms, how might the definition and appreciation of "original" artworks change in the coming years?
Entrepreneurship
- Descriptive: What are the main challenges faced by startups in the tech industry?
- Explanatory: Why do some entrepreneurial ventures succeed while others fail within their first five years?
- Exploratory: How are emerging digital platforms reshaping the entrepreneurial landscape?
- Comparative: How do funding opportunities for entrepreneurs differ between North America and Europe?
- Predictive: What sectors are predicted to see the most startup growth in the next decade?
- Descriptive: What are the primary sources of external funding for large corporations?
- Explanatory: Why did the stock market experience a significant drop in Q4 2022?
- Exploratory: How might blockchain technology revolutionize the future of banking?
- Comparative: How do the financial markets in developing countries compare to those in developed countries?
- Predictive: Based on current economic indicators, what is the forecasted health of the global economy for the next five years?
Human resources
- Descriptive: What are the most sought-after employee benefits in the tech industry?
- Explanatory: Why is there a high turnover rate in the retail sector?
- Exploratory: How might the rise of remote work affect HR practices in the next decade?
- Comparative: How do HR practices in multinational corporations differ from those in local companies?
- Predictive: What skills will be in highest demand in the workforce by 2030?
- Descriptive: What are the core responsibilities of middle management in large manufacturing firms?
- Explanatory: Why do some management strategies fail in diverse cultural environments?
- Exploratory: How are companies adapting their management structures in response to the gig economy?
- Comparative: How does management style in Eastern companies compare with Western businesses?
- Predictive: How might artificial intelligence reshape management practices in the next decade?
- Descriptive: What are the most effective digital marketing channels for e-commerce businesses?
- Explanatory: Why did a particular viral marketing campaign succeed in reaching a global audience?
- Exploratory: How might virtual reality change the landscape of product advertising?
- Comparative: How do marketing strategies differ between B2B and B2C sectors?
- Predictive: What consumer behaviors are forecasted to dominate online shopping trends in the next five years?
Operations research
- Descriptive: What are the primary optimization techniques used in supply chain management?
- Explanatory: Why do certain optimization algorithms perform better in specific industries?
- Exploratory: How can quantum computing impact the future of operations research?
- Comparative: How does operations strategy differ between service and manufacturing industries?
- Predictive: Based on current technological advancements, how might automation reshape supply chain strategies by 2035?
Artificial intelligence
- Descriptive: What are the primary algorithms used in deep learning?
- Explanatory: Why do certain neural network architectures outperform others in image recognition tasks?
- Exploratory: How might quantum computing influence the development of AI models?
- Comparative: How do reinforcement learning methods compare to supervised learning in game playing scenarios?
- Predictive: Based on current trends, how will AI impact the job market over the next decade?
Cybersecurity
- Descriptive: What are the most common types of cyberattacks reported in 2022?
- Explanatory: Why are certain industries more vulnerable to ransomware attacks?
- Exploratory: How might advances in quantum computing challenge existing encryption methods?
- Comparative: How do open-source software vulnerabilities compare to those in proprietary systems?
- Predictive: Given emerging technologies, what types of cyber threats will likely dominate in the next five years?
Data science
- Descriptive: What are the main tools used by data scientists in large-scale data analysis?
- Explanatory: Why does algorithm X yield more accurate predictions than algorithm Y for certain datasets?
- Exploratory: How can machine learning models improve real-time data processing in IoT devices?
- Comparative: How does the performance of traditional statistical models compare to machine learning models in predicting stock prices?
- Predictive: Based on current data trends, what industries will likely benefit the most from data analytics advancements in the coming decade?
Information systems
- Descriptive: What are the core components of a modern enterprise resource planning (ERP) system?
- Explanatory: Why have cloud-based information systems seen a rapid adoption rate in recent years?
- Exploratory: How might the integration of blockchain technology revolutionize supply chain information systems?
- Comparative: How do information system strategies differ between e-commerce and brick-and-mortar retailers?
- Predictive: Given the rise of remote work, how will information systems evolve to support decentralized teams in the future?
Software engineering
- Descriptive: What are the standard practices in agile software development?
- Explanatory: Why do some software projects face significant delays despite rigorous planning?
- Exploratory: How are emerging programming languages shaping the future of software development?
- Comparative: How does the software development lifecycle in startup environments compare to that in large corporations?
- Predictive: Based on current development trends, which software platforms are forecasted to dominate market share by 2030?
Adult education
- Descriptive: What are the primary motivations behind adults seeking further education later in life?
- Explanatory: Why do some adult education programs have a higher success rate compared to others?
- Exploratory: How might online learning platforms revolutionize adult education in the next decade?
- Comparative: How do adult education methodologies differ from traditional collegiate teaching techniques?
- Predictive: Given current trends, how will the demand for adult education courses change in the upcoming years?
Curriculum studies
- Descriptive: What are the core components of a modern high school curriculum in the United States?
- Explanatory: Why have certain subjects, like financial literacy, become more emphasized in recent curriculum updates?
- Exploratory: How can interdisciplinary studies be better incorporated into traditional curricula?
- Comparative: How does the math curriculum in the US compare to that in other developed countries?
- Predictive: Based on pedagogical research, what subjects are forecasted to gain prominence in curricula over the next decade?
Educational administration
- Descriptive: What are the main responsibilities of a school principal in large urban schools?
- Explanatory: Why do some schools consistently perform better in standardized testing than others, despite similar resources?
- Exploratory: How might emerging technologies shape the administrative tasks of educational institutions in the future?
- Comparative: How does school administration differ between private and public educational institutions?
- Predictive: Given the rise of online education, how will the role of educational administrators evolve in the coming years?
Educational psychology
- Descriptive: What cognitive strategies are commonly used by students to enhance memory retention during studies?
- Explanatory: Why do certain teaching methodologies resonate better with students having specific learning styles?
- Exploratory: How can insights from behavioral psychology improve student engagement in virtual classrooms?
- Comparative: How does the motivation level of students differ between self-paced versus instructor-led courses?
- Predictive: With the increasing integration of technology in education, how will student learning behaviors change in the next decade?
Special education
- Descriptive: What interventions are commonly used to support students with autism spectrum disorders in inclusive classrooms?
- Explanatory: Why do some special education programs yield better academic outcomes for students with specific learning disabilities?
- Exploratory: How can augmented reality technologies be utilized to enhance learning for students with visual impairments?
- Comparative: How does special education support differ between urban and rural school districts?
- Predictive: Based on advancements in assistive technologies, how will the landscape of special education transform in the near future?
Aerospace engineering
- Descriptive: What are the key materials and technologies utilized in modern spacecraft design?
- Explanatory: Why are certain alloys preferred in high-temperature aerospace applications?
- Exploratory: How might advances in propulsion technologies revolutionize space travel in the next decade?
- Comparative: How do commercial aircraft designs differ from military aircraft designs in terms of aerodynamics?
- Predictive: Given current research trends, how will the efficiency of jet engines change in the upcoming years?
Biomedical engineering
- Descriptive: What are the foundational principles behind the design of modern prosthetic limbs?
- Explanatory: Why have bio-compatible materials like titanium become crucial in implantable medical devices?
- Exploratory: How can nanotechnology be leveraged to improve drug delivery systems in the future?
- Comparative: How do MRI machines differ from CT scanners in terms of their underlying technology and application?
- Predictive: Based on emerging trends, how will wearable health monitors evolve in the next decade?
Chemical engineering
- Descriptive: What processes are involved in the large-scale production of ethylene?
- Explanatory: Why is distillation the most common separation method in the petroleum industry?
- Exploratory: How might green chemistry principles transform traditional chemical manufacturing processes?
- Comparative: How does the production of biofuels compare to traditional fossil fuels in terms of yield and environmental impact?
- Predictive: Given global sustainability goals, how will the chemical industry's reliance on fossil resources shift in the future?
Civil engineering
- Descriptive: What are the primary considerations in the structural design of skyscrapers in earthquake-prone regions?
- Explanatory: Why are steel-reinforced concrete beams commonly used in bridge construction?
- Exploratory: How can smart city concepts influence the infrastructure planning of urban centers in the future?
- Comparative: How do tunneling methods differ between soft soil and hard rock terrains?
- Predictive: With the increasing threat of climate change, how will coastal infrastructure design criteria change to account for rising sea levels?
Computer engineering
- Descriptive: What are the main components of a modern central processing unit (CPU) and their functions?
- Explanatory: Why is silicon predominantly used in semiconductor manufacturing?
- Exploratory: How might quantum computing redefine the landscape of traditional computing architectures?
- Comparative: How do solid-state drives (SSDs) compare to traditional hard disk drives (HDDs) in terms of performance and longevity?
- Predictive: Given advancements in chip miniaturization, how will the form factor of consumer electronics evolve in the coming years?
Electrical engineering
- Descriptive: What are the standard stages involved in the transmission and distribution of electrical power?
- Explanatory: Why are transformers essential in the power distribution network?
- Exploratory: How can emerging smart grid technologies improve the efficiency and reliability of electrical distribution systems?
- Comparative: How do AC and DC transmission methods differ in terms of efficiency and infrastructure requirements?
- Predictive: With the rise of renewable energy sources, how will power grid management complexities change in the next decade?
Mechanical engineering
- Descriptive: What are the fundamental principles behind the operation of a four-stroke internal combustion engine?
- Explanatory: Why are certain polymers used as vibration dampeners in machinery?
- Exploratory: How might advancements in materials science impact the design of future automotive systems?
- Comparative: How do hydraulic systems compare to pneumatic systems in terms of energy efficiency and application?
- Predictive: With the push towards sustainability, how will traditional manufacturing methods evolve to reduce their carbon footprint?
Climatology
- Descriptive: What are the primary factors that influence the El Niño and La Niña phenomena?
- Explanatory: Why have certain regions experienced more intense and frequent heatwaves in the past decade?
- Exploratory: How might changing atmospheric CO2 concentrations impact global wind patterns in the future?
- Comparative: How do urban areas differ from rural areas in terms of microclimate conditions?
- Predictive: Given current greenhouse gas emission trends, what will be the average global temperature increase by the end of the century?
Conservation science
- Descriptive: What are the primary threats faced by tropical rainforests around the world?
- Explanatory: Why are certain species more vulnerable to habitat fragmentation than others?
- Exploratory: How can community involvement enhance conservation efforts in protected areas?
- Comparative: How does the effectiveness of in-situ conservation compare to ex-situ conservation for endangered species?
- Predictive: If current deforestation rates continue, how many species are predicted to go extinct in the next 50 years?
- Descriptive: What are the dominant flora and fauna in a temperate deciduous forest biome?
- Explanatory: Why do certain ecosystems, like wetlands, have higher biodiversity than others?
- Exploratory: How might the spread of invasive species alter nutrient cycling in freshwater lakes?
- Comparative: How do the trophic dynamics of grassland ecosystems differ from those of desert ecosystems?
- Predictive: How will global ecosystems change if bee populations continue to decline at current rates?
Environmental health
- Descriptive: What are the major pollutants found in urban air?
- Explanatory: Why do certain pollutants cause respiratory diseases in humans?
- Exploratory: How might green building designs reduce the health risks associated with indoor air pollutants?
- Comparative: How do the health impacts of living near coal-fired power plants compare to living near nuclear power plants?
- Predictive: Given increasing urbanization trends, how will air quality in major cities change over the next two decades?
Marine biology
- Descriptive: What are the primary species that comprise a coral reef ecosystem?
- Explanatory: Why are coral reefs particularly sensitive to changes in sea temperature?
- Exploratory: How might deep-sea exploration reveal unknown marine species and their adaptations?
- Comparative: How do the feeding strategies of pelagic fish differ from benthic fish in oceanic ecosystems?
- Predictive: If ocean acidification trends continue, what will be the impact on shell-forming marine organisms in the next 30 years?
- Descriptive: What are the most common oral health issues faced by elderly individuals?
- Explanatory: Why do sugary foods lead to a higher prevalence of cavities?
- Exploratory: How might emerging technologies revolutionize dental procedures in the coming decade?
- Comparative: How do the effects of electric toothbrushes compare to manual ones in reducing plaque?
- Predictive: Given current trends, how might the prevalence of gum diseases change in populations with increased sugar consumption over the next decade?
Kinesiology
- Descriptive: What are the primary physiological changes that occur during aerobic exercise?
- Explanatory: Why do some athletes experience muscle cramps during extensive physical activity?
- Exploratory: How might different stretching routines impact athletic performance?
- Comparative: How do the biomechanics of running on a treadmill differ from running outdoors?
- Predictive: If sedentary lifestyles continue to rise, what could be the potential impact on musculoskeletal health in the next 20 years?
- Descriptive: What are the main symptoms associated with the early stages of Parkinson's disease?
- Explanatory: Why are some viruses, like the flu, more prevalent in colder months?
- Exploratory: How might genetic editing technologies, like CRISPR, be utilized to treat hereditary diseases in the future?
- Comparative: How does the efficacy of traditional chemotherapy compare to targeted therapy in treating certain cancers?
- Predictive: Given advances in telemedicine, how might patient-doctor interactions evolve over the next decade?
- Descriptive: What are the primary responsibilities of nurses in intensive care units?
- Explanatory: Why is there a higher burnout rate among nurses compared to other healthcare professionals?
- Exploratory: How can training programs be improved to better equip nurses for challenges in emergency situations?
- Comparative: How does the patient recovery rate differ when cared for by specialized nurses versus general ward nurses?
- Predictive: How will the role of nurses change with the integration of more AI-based diagnostic tools in hospitals?
- Descriptive: What are the main nutritional components of a Mediterranean diet?
- Explanatory: Why does a diet high in processed sugars lead to increased risks of type 2 diabetes?
- Exploratory: How might gut microbiota be influenced by various diets and what are the potential health implications?
- Comparative: How does the nutritional profile of plant-based proteins compare to animal-based proteins?
- Predictive: If global meat consumption trends continue, what could be the implications for population-wide nutritional health in 30 years?
- Descriptive: What are the primary active ingredients in over-the-counter pain relievers?
- Explanatory: Why do certain medications cause drowsiness as a side effect?
- Exploratory: How might nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems enhance the efficacy of certain treatments?
- Comparative: How do the effects of generic drugs compare to their brand-name counterparts?
- Predictive: Given the rise of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, how might pharmaceutical approaches to bacterial infections change in the future?
Public health
- Descriptive: What are the main factors contributing to public health disparities in urban vs rural areas?
- Explanatory: Why did certain regions have higher transmission rates during the COVID-19 pandemic?
- Exploratory: How can community engagement strategies be optimized for more effective health campaigns?
- Comparative: How do vaccination rates and outcomes differ between countries with public vs private healthcare systems?
- Predictive: Based on current trends, how will global public health challenges evolve over the next 50 years?
Art history
- Descriptive: What are the primary artistic styles observed in the Renaissance era?
- Explanatory: Why did the Baroque art movement emerge after the Renaissance?
- Exploratory: How might newly discovered ancient art pieces reshape our understanding of prehistoric artistic practices?
- Comparative: How does European Romantic art differ from Asian Romantic art of the same period?
- Predictive: Given current trends, how might digital art impact traditional art gallery setups in the next decade?
- Descriptive: What are the primary themes in Homer's "Odyssey"?
- Explanatory: Why did Greek tragedies place a strong emphasis on the concept of fate?
- Exploratory: Are there undiscovered works that might provide more insight into daily life in ancient Rome?
- Comparative: How do Roman epics compare to their Greek counterparts in terms of character development?
- Predictive: How will emerging technologies like virtual reality affect the study of ancient ruins?
Cultural studies
- Descriptive: How is the concept of family portrayed in contemporary American media?
- Explanatory: Why has the influence of Western culture grown in certain Eastern countries over the last century?
- Exploratory: What are the emerging subcultures in the digital age and how do they communicate?
- Comparative: How does the representation of masculinity vary between Eastern and Western films?
- Predictive: In what ways might globalization affect cultural identities in the next two decades?
- Descriptive: What events led to the fall of the Berlin Wall?
- Explanatory: Why did the Industrial Revolution begin in Britain?
- Exploratory: Are there undocumented civilizational interactions in ancient times that new archaeological findings might reveal?
- Comparative: How did the responses to the Black Plague differ between European and Asian nations?
- Predictive: Given historical patterns, how might major global powers react to dwindling natural resources in the future?
- Descriptive: What are the main narrative techniques used in James Joyce's "Ulysses"?
- Explanatory: Why did the Gothic novel become popular in 19th-century England?
- Exploratory: How might translations of ancient texts reveal different interpretations based on the translator's cultural background?
- Comparative: How does the portrayal of war differ between post-WWII American and French literature?
- Predictive: How might the rise of AI-authored literature change the publishing industry?
- Descriptive: What are the core principles of existentialism as described by Jean-Paul Sartre?
- Explanatory: Why did the philosophy of existentialism gain prominence post-WWII?
- Exploratory: How might ancient Eastern philosophies provide insights into modern ethical dilemmas surrounding technology?
- Comparative: How does Nietzsche's concept of the "Ubermensch" compare to Aristotle's "virtuous person"?
- Predictive: As AI becomes more prevalent, how might philosophical discussions around consciousness evolve?
Religious studies
- Descriptive: What are the Five Pillars of Islam?
- Explanatory: Why did Protestantism emerge within Christianity during the 16th century?
- Exploratory: Are there common motifs in creation myths across various religions?
- Comparative: How do concepts of the afterlife compare between Christianity, Buddhism, and Ancient Egyptian beliefs?
- Predictive: How might interfaith dialogue shape religious practices in multi-faith societies over the next decade?
Classic languages
- Descriptive: What are the primary grammatical structures in Ancient Greek?
- Explanatory: Why did Latin play a foundational role in the development of many modern European languages?
- Exploratory: Are there yet-to-be-deciphered scripts from ancient civilizations that might provide insight into lost languages?
- Comparative: How do the verb conjugation patterns in Latin compare to those in Sanskrit?
- Predictive: Given the ongoing research in classical studies, how might our understanding of certain ancient texts change in the next decade?
Comparative literature
- Descriptive: What are the main themes in Japanese Haiku and English Sonnets?
- Explanatory: Why do certain folklore tales appear with variations across different cultures?
- Exploratory: How might newly translated works from lesser-known languages reshape the world literature canon?
- Comparative: How does the role of the tragic hero in French literature differ from its portrayal in Russian literature?
- Predictive: As global communication becomes more interconnected, how might the study of world literature evolve in universities?
Modern languages
- Descriptive: What are the primary tonal patterns observed in Mandarin Chinese?
- Explanatory: Why has English become a dominant lingua franca in international business and diplomacy?
- Exploratory: Which lesser-studied languages might become more prominent due to socio-political changes in their regions?
- Comparative: How do the grammatical complexities of Russian compare to those of German?
- Predictive: Given current global trends, which languages are predicted to become more widely spoken in the next two decades?
- Descriptive: What are the primary articulatory features of plosive sounds?
- Explanatory: Why do certain accents develop specific pitch fluctuations and intonations?
- Exploratory: How do various environmental factors affect vocal cord vibrations and sound production?
- Comparative: How does the pronunciation of fricatives differ between Spanish and Portuguese speakers?
- Predictive: How might advancements in voice recognition technology influence phonetics research in the next decade?
- Descriptive: What are the primary signs and symbols used in American road signage?
- Explanatory: Why do red roses universally symbolize love or passion in many cultures?
- Exploratory: Are there emerging symbols in digital communication that could become universally recognized signs in the future?
- Comparative: How do the semiotic structures in print advertisements differ between Western and Eastern cultures?
- Predictive: As emoji usage becomes more widespread, how might they impact written language semantics in the coming years?
- Descriptive: What are the key statutes governing tenant rights in residential leases?
- Explanatory: Why do personal injury claims vary significantly in settlement amounts even under similar circumstances?
- Exploratory: How might alternative dispute resolution mechanisms evolve in civil law contexts over the next decade?
- Comparative: How do defamation laws differ between jurisdictions that adopt the British common law system versus the Napoleonic code?
- Predictive: How might the rise of online transactions affect the volume and nature of civil law cases related to contract disputes?
Constitutional law
- Descriptive: What are the main principles enshrined in the First Amendment of the U.S. Constitution?
- Explanatory: Why have some constitutional rights been subject to varying interpretations over time?
- Exploratory: Are there emerging debates around digital rights and freedoms that might reshape constitutional interpretations in the future?
- Comparative: How does the protection of freedom of speech differ between the U.S. Constitution and the German Basic Law?
- Predictive: Given global socio-political trends, how might constitutional democracies adjust their foundational texts in the next two decades?
Corporate law
- Descriptive: What are the primary duties and liabilities of a board of directors in a publicly traded company?
- Explanatory: Why do mergers and acquisitions often involve extensive due diligence processes?
- Exploratory: How might the rise of digital currencies impact the regulatory landscape for corporations in the finance sector?
- Comparative: How does the legal framework for shareholder rights in the U.S. compare to that of Japan?
- Predictive: How might changing global trade dynamics influence corporate structuring and international partnerships?
Criminal law
- Descriptive: What constitutes first-degree murder in the majority of jurisdictions?
- Explanatory: Why are certain offenses classified as misdemeanors while others are felonies?
- Exploratory: Are there emerging patterns in cybercrime that suggest new areas of legal vulnerability?
- Comparative: How does the treatment of juvenile offenders differ between Scandinavian countries and the U.S.?
- Predictive: Given advancements in technology, how might criminal law evolve to address potential misuses of artificial intelligence?
International law
- Descriptive: What are the foundational principles of the Geneva Conventions?
- Explanatory: Why have some nations refused to recognize or be bound by certain international treaties?
- Exploratory: How might global climate change reshape international agreements and treaties in the coming years?
- Comparative: How do regional trade agreements in Africa compare to those in Southeast Asia in terms of provisions and enforcement mechanisms?
- Predictive: How might geopolitical shifts influence the role and effectiveness of international courts in resolving state disputes?
Applied mathematics
- Descriptive: What are the primary mathematical models used to predict the spread of infectious diseases?
- Explanatory: Why does the Navier–Stokes equation play a pivotal role in fluid dynamics?
- Exploratory: How might new computational methods enhance the efficiency of existing algorithms in applied mathematics?
- Comparative: How do optimization techniques in operations research differ from those in machine learning applications?
- Predictive: Given the rapid growth of quantum computing, how might it reshape the landscape of applied mathematical problems in the next decade?
Applied statistics
- Descriptive: What are the standard procedures for handling missing data in a large-scale survey?
- Explanatory: Why do statisticians use bootstrapping techniques in hypothesis testing?
- Exploratory: How might emerging data sources, like wearables and IoT devices, introduce new challenges and opportunities in applied statistics?
- Comparative: How does the performance of Bayesian methods compare to frequentist methods in complex hierarchical models?
- Predictive: With the increasing availability of big data, how might the role of applied statisticians evolve in the next five years?
Pure mathematics
- Descriptive: What are the axioms underpinning Euclidean geometry?
- Explanatory: Why is Gödel's incompleteness theorem considered a foundational result in the philosophy of mathematics?
- Exploratory: Are there newly emerging areas of study within number theory due to advancements in computational mathematics?
- Comparative: How do algebraic structures differ between rings and fields?
- Predictive: Considering current research trends, what areas of pure mathematics are poised for significant breakthroughs in the next decade?
Theoretical statistics
- Descriptive: What foundational principles underlie the Central Limit Theorem?
- Explanatory: Why is the concept of sufficiency crucial in the design of statistical tests?
- Exploratory: How might advances in artificial intelligence influence theoretical developments in statistical inference?
- Comparative: How do likelihood-based inference methods compare to Bayesian methods in terms of theoretical underpinnings?
- Predictive: As data generation mechanisms evolve, how might the theoretical foundations of statistics need to adapt in the future?
- Descriptive: What are the key features and behaviors of black holes?
- Explanatory: Why does the expansion of the universe appear to be accelerating?
- Exploratory: What potential insights might the study of exoplanets provide about the conditions necessary for life?
- Comparative: How do the properties of spiral galaxies differ from those of elliptical galaxies?
- Predictive: Based on current data, what are the projected future behaviors of our sun as it ages?
- Descriptive: What are the primary functions and structures of ribosomes in a cell?
- Explanatory: Why does DNA replication occur semi-conservatively?
- Exploratory: How might emerging technologies like CRISPR redefine our understanding of genetic engineering?
- Comparative: How do the metabolic processes of prokaryotic cells differ from those of eukaryotic cells?
- Predictive: Given the current trajectory of climate change, how might the biodiversity in tropical rainforests be affected over the next century?
- Descriptive: What are the key properties and uses of the noble gases?
- Explanatory: Why do exothermic reactions release heat?
- Exploratory: How might advances in nanochemistry influence drug delivery systems?
- Comparative: How do ionic bonds differ in strength and characteristics from covalent bonds?
- Predictive: Considering the rise in antibiotic-resistant bacteria, how might the field of medicinal chemistry adapt to produce effective treatments in the future?
Earth science
- Descriptive: What are the primary layers of Earth's atmosphere and their respective characteristics?
- Explanatory: Why do certain regions experience more seismic activity than others?
- Exploratory: How might the study of ancient ice cores provide insights into past climate conditions?
- Comparative: How do the processes of weathering differ between arid and humid climates?
- Predictive: Given current data on deforestation, what could be its impact on global soil quality and erosion patterns over the next 50 years?
- Descriptive: What are the fundamental principles underlying quantum mechanics?
- Explanatory: Why does the speed of light in a vacuum remain constant regardless of the observer's frame of reference?
- Exploratory: How might studies in string theory reshape our understanding of the universe at the smallest scales?
- Comparative: How do the effects of general relativity contrast with predictions from Newtonian physics under extreme gravitational conditions?
- Predictive: With advancements in particle physics, what potential new particles or phenomena might be discovered in the next decade?
Anthropology
- Descriptive: What are the primary rituals and customs of the indigenous tribes of the Amazon?
- Explanatory: Why did the ancient Mayan civilization collapse?
- Exploratory: How might modern urbanization impact the preservation of ancient burial sites?
- Comparative: How do hunter-gatherer societies differ from agricultural societies in terms of social structures?
- Predictive: Given global trends, how might indigenous cultures evolve over the next century?
Communication
- Descriptive: What are the main modes of communication used by millennials compared to baby boomers?
- Explanatory: Why has the usage of social media platforms surged in the last two decades?
- Exploratory: How might advancements in virtual reality reshape interpersonal communication in the future?
- Comparative: How do written communication skills differ between those educated in traditional schools versus online schools?
- Predictive: How might the nature of journalism change with the rise of automated content generation?
- Descriptive: What are the primary components of a nation's gross domestic product (GDP)?
- Explanatory: Why did the economic recession of 2008 occur?
- Exploratory: How might the concept of universal basic income impact labor market dynamics?
- Comparative: How do free market economies differ from command economies in terms of resource allocation?
- Predictive: Based on current global economic trends, which industries are predicted to boom in the next decade?
- Descriptive: What are the geographical features of the Himalayan mountain range?
- Explanatory: Why do desert regions exist on the western coasts of continents, such as the Atacama in South America?
- Exploratory: How might rising sea levels reshape the world's coastlines over the next century?
- Comparative: How does urban planning in European cities differ from that in American cities?
- Predictive: Given current urbanization rates, which cities are poised to become megacities by 2050?
Political science
- Descriptive: What are the foundational principles of a parliamentary democracy?
- Explanatory: Why do certain nations adopt federal systems while others prefer unitary systems?
- Exploratory: How might the rise of populism influence global diplomatic relations in the 21st century?
- Comparative: How do the rights of citizens in liberal democracies differ from those in authoritarian regimes?
- Predictive: Based on current political trends, which nations might see significant shifts in governance models over the next two decades?
- Descriptive: What are the primary stages of cognitive development in children according to Piaget?
- Explanatory: Why do certain individuals develop phobias?
- Exploratory: How might emerging neuroscientific tools, like fMRI, alter our understanding of human emotions?
- Comparative: How do coping mechanisms differ between individuals with high resilience versus those with low resilience?
- Predictive: Given the rise in digital communication, how might human attention spans evolve in future generations?
Social work
- Descriptive: What are the core principles and practices in child protective services?
- Explanatory: Why do certain communities have higher rates of child neglect and abuse?
- Exploratory: How might the integration of artificial intelligence in social work affect decision-making in child welfare cases?
- Comparative: How do intervention strategies for substance abuse differ between urban and rural settings?
- Predictive: Based on current societal trends, what challenges might social workers face in the next decade?
- Descriptive: What are the defining characteristics of Generation Z as a social cohort?
- Explanatory: Why have nuclear families become less prevalent in Western societies?
- Exploratory: How might the widespread adoption of virtual realities impact social interactions and community structures in the future?
- Comparative: How do the roles and perceptions of elderly individuals differ between Eastern and Western societies?
- Predictive: Given the rise in remote work, how might urban and suburban living patterns change over the next three decades?
In synthesizing the vast range of research questions posed across diverse disciplines, it becomes clear that every academic field, from the humanities to the social sciences, offers unique perspectives and methodologies to uncover and understand various facets of our world. These questions, whether descriptive, explanatory, exploratory, comparative, or predictive, serve as guiding lights, driving scholarship and innovation. As academia continues to evolve and adapt, these inquiries not only define the boundaries of current knowledge but also pave the way for future discoveries and insights, emphasizing the invaluable role of continuous inquiry in the ever-evolving tapestry of human understanding.
Header image by Zetong Li .
Related Posts

How to Write a Definition Essay (Plus Topics You Can Use and a Sample Essay)

How to Write a Thematic Analysis
- Academic Writing Advice
- All Blog Posts
- Writing Advice
- Admissions Writing Advice
- Book Writing Advice
- Short Story Advice
- Employment Writing Advice
- Business Writing Advice
- Web Content Advice
- Article Writing Advice
- Magazine Writing Advice
- Grammar Advice
- Dialect Advice
- Editing Advice
- Freelance Advice
- Legal Writing Advice
- Poetry Advice
- Graphic Design Advice
- Logo Design Advice
- Translation Advice
- Blog Reviews
- Short Story Award Winners
- Scholarship Winners

Need an academic editor before submitting your work?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Descriptive research questions are a systematic methodology that helps in understanding the what, where, when and how. Important variables can be rigidly defined using descriptive research, unlike qualitative research where the subjectivity in responses makes it relatively difficult to get a grasp on the overall picture. The multiple methods ...
Descriptive research aims to accurately and systematically describe a population, situation or phenomenon. It can answer what, where, when and how questions, but not why questions. A descriptive research design can use a wide variety of research methods to investigate one or more variables. Unlike in experimental research, the researcher does ...
These questions can function in several ways, such as to 1) identify and describe existing conditions (contextual research questions); 2) describe a phenomenon (descriptive research questions); 3) assess the effectiveness of existing methods, protocols, theories, or procedures (evaluation research questions); 4) examine a phenomenon or analyze ...
A previous Evidence in Practice article explained why a specific and answerable research question is important for clinicians and researchers. Determining whether a study aims to answer a descriptive, predictive, or causal question should be one of the first things a reader does when reading an article. Any type of question can be relevant and useful to support evidence-based practice, but ...
Characteristics of descriptive research. The term descriptive research then refers to research questions, the design of the study, and data analysis conducted on that topic. We call it an observational research method because none of the research study variables are influenced in any capacity. Some distinctive characteristics of descriptive ...
Descriptive research is a common investigatory model used by researchers in various fields, including social sciences, linguistics, and academia. ... Research questions often begin with "What is …" These studies help find solutions to practical issues in social science, physical science, and education. Here are some examples and ...
The first question asks for a ready-made solution, and is not focused or researchable. The second question is a clearer comparative question, but note that it may not be practically feasible. For a smaller research project or thesis, it could be narrowed down further to focus on the effectiveness of drunk driving laws in just one or two countries.
A good research question is essential to guide your research paper, dissertation, or thesis. All research questions should be: Focused on a single problem or issue. Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources. Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints. Specific enough to answer thoroughly.
for the study methods. Good-quality, clinically useful research begins. question. Research questions fall into 1 of 3 mutu-ally exclusive types: descriptive, predic-tive, or causal. Imagine you are seeking information about whiplash injuries. You might find studies that address the fol-lowing questions. 1.
This chapter discusses (1) the important role of research questions for descriptive, predictive, and causal studies across the three research paradigms (i.e., quantitative, qualitative, and mixed methods); (2) characteristics of quality research questions, and (3) three frameworks to support the development of research questions and their dissemination within scholarly work.
Types of research questions. Now that we've defined what a research question is, let's look at the different types of research questions that you might come across. Broadly speaking, there are (at least) four different types of research questions - descriptive, comparative, relational, and explanatory. Descriptive questions ask what is happening. In other words, they seek to describe a ...
Descriptive questions, which are the most basic type of quantitative research question and seeks to explain the when, where, why or how something occurred. ... Research question frameworks have been designed to help structure research questions and clarify the main concepts. Not every question can fit perfectly into a framework, but using even ...
These questions help to define the scope of the research and provide a clear focus for the study. Research questions are usually developed at the beginning of a research project and are designed to address a particular research problem or objective. Types of Research Questions. Types of Research Questions are as follows: Descriptive Research ...
Research questions may also be characterized based on function—exploratory, explanatory, descriptive, and emancipatory as detailed by Marshall and Rossman. 8 Exploratory questions are usually answered in the beginning phases of a project, via a thorough literature review or preliminary pilot study. Investigators glean an outline of what has ...
Descriptive research questions are typically closed-ended because they aim at gathering definite and specific responses from research participants. Also, they can be used in customer experience surveys and market research to collect information about target markets and consumer behaviors. Descriptive Research Question Examples
Additionally, descriptive research can contribute to the development of hypotheses and guide the formulation of research questions for subsequent studies. Researcher.Life is a subscription-based platform that unifies top AI tools and services designed to speed up, simplify, and streamline a researcher's journey, from reading to writing ...
Research Questions Clarify the research's aim (Farrugia et al., 2010) Research often begins with an interest in a topic, but a deep understanding of the subject is crucial to formulate an appropriate research question. They identify the problem or issue the research seeks to address. The nature of the research question (descriptive ...
To generate hypotheses: Descriptive research design can be used to generate hypotheses or research questions that can be tested in future studies. For example, if a descriptive study finds a correlation between two variables, this could lead to the development of a hypothesis about the causal relationship between the variables.
Descriptive research questions attempt to describe a phenomenon. Emancipatory research questions aim to produce knowledge that allows for engagement in social action, especially for the benefit of disadvantaged people. Evaluative research questions assess the effectiveness of existing methods or paradigms.
The quantitative research design that we select subsequently determines whether we look for relationships, associations, trends or interactions. To learn how to structure (i.e., write out) each of these three types of quantitative research question (i.e., descriptive, comparative, relationship-based research questions), see the article: How to ...
Descriptive research is a type of research that is used to describe the characteristics of a population. It collects data that are used to answer a wide range of what, when, and how questions pertaining to a particular population or group. For example, descriptive studies might be used to answer questions such as: What percentage of Head Start ...
Choose a broad topic, such as "learner support" or "social media influence" for your study. Select topics of interest to make research more enjoyable and stay motivated. Preliminary research. The goal is to refine and focus your research question. The following strategies can help: Skim various scholarly articles.
A research question is a clearly formulated query that delineates the scope and direction of an investigation. It serves as the guiding light for scholars, helping them to dissect, analyze, and comprehend complex phenomena. Beyond merely seeking answers, a well-crafted research question ensures that the exploration remains focused and goal-oriented. The significance of framing a clear, concise ...