Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates

How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
Published on January 2, 2023 by Shona McCombes . Revised on September 11, 2023.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research that you can later apply to your paper, thesis, or dissertation topic .
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates, and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarize sources—it analyzes, synthesizes , and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is the purpose of a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1 – search for relevant literature, step 2 – evaluate and select sources, step 3 – identify themes, debates, and gaps, step 4 – outline your literature review’s structure, step 5 – write your literature review, free lecture slides, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a thesis , dissertation , or research paper , you will likely have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and its scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position your work in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your research addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
- Evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic.
Writing literature reviews is a particularly important skill if you want to apply for graduate school or pursue a career in research. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research problem and questions .
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research question. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list as you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some useful databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can also use boolean operators to help narrow down your search.
Make sure to read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
You likely won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on your topic, so it will be necessary to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your research question.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models, and methods?
- Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible , and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can use our template to summarize and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using. Click on either button below to download.
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It is important to keep track of your sources with citations to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography , where you compile full citation information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
To begin organizing your literature review’s argument and structure, be sure you understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat—this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organizing the body of a literature review. Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order.
Try to analyze patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text , your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, you can follow these tips:
- Summarize and synthesize: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers — add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transition words and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts
In the conclusion, you should summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance.
When you’ve finished writing and revising your literature review, don’t forget to proofread thoroughly before submitting. Not a language expert? Check out Scribbr’s professional proofreading services !
This article has been adapted into lecture slides that you can use to teach your students about writing a literature review.
Scribbr slides are free to use, customize, and distribute for educational purposes.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarize yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your thesis or dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
A literature review is a survey of credible sources on a topic, often used in dissertations , theses, and research papers . Literature reviews give an overview of knowledge on a subject, helping you identify relevant theories and methods, as well as gaps in existing research. Literature reviews are set up similarly to other academic texts , with an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion .
An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that has a short description (called an annotation ) for each of the sources. It is often assigned as part of the research process for a paper .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, September 11). How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved April 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
How To Write An A-Grade Literature Review
3 straightforward steps (with examples) + free template.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewed By: Dr. Eunice Rautenbach | October 2019
Quality research is about building onto the existing work of others , “standing on the shoulders of giants”, as Newton put it. The literature review chapter of your dissertation, thesis or research project is where you synthesise this prior work and lay the theoretical foundation for your own research.
Long story short, this chapter is a pretty big deal, which is why you want to make sure you get it right . In this post, I’ll show you exactly how to write a literature review in three straightforward steps, so you can conquer this vital chapter (the smart way).
Overview: The Literature Review Process
- Understanding the “ why “
- Finding the relevant literature
- Cataloguing and synthesising the information
- Outlining & writing up your literature review
- Example of a literature review
But first, the “why”…
Before we unpack how to write the literature review chapter, we’ve got to look at the why . To put it bluntly, if you don’t understand the function and purpose of the literature review process, there’s no way you can pull it off well. So, what exactly is the purpose of the literature review?
Well, there are (at least) four core functions:
- For you to gain an understanding (and demonstrate this understanding) of where the research is at currently, what the key arguments and disagreements are.
- For you to identify the gap(s) in the literature and then use this as justification for your own research topic.
- To help you build a conceptual framework for empirical testing (if applicable to your research topic).
- To inform your methodological choices and help you source tried and tested questionnaires (for interviews ) and measurement instruments (for surveys ).
Most students understand the first point but don’t give any thought to the rest. To get the most from the literature review process, you must keep all four points front of mind as you review the literature (more on this shortly), or you’ll land up with a wonky foundation.
Okay – with the why out the way, let’s move on to the how . As mentioned above, writing your literature review is a process, which I’ll break down into three steps:
- Finding the most suitable literature
- Understanding , distilling and organising the literature
- Planning and writing up your literature review chapter
Importantly, you must complete steps one and two before you start writing up your chapter. I know it’s very tempting, but don’t try to kill two birds with one stone and write as you read. You’ll invariably end up wasting huge amounts of time re-writing and re-shaping, or you’ll just land up with a disjointed, hard-to-digest mess . Instead, you need to read first and distil the information, then plan and execute the writing.

Step 1: Find the relevant literature
Naturally, the first step in the literature review journey is to hunt down the existing research that’s relevant to your topic. While you probably already have a decent base of this from your research proposal , you need to expand on this substantially in the dissertation or thesis itself.
Essentially, you need to be looking for any existing literature that potentially helps you answer your research question (or develop it, if that’s not yet pinned down). There are numerous ways to find relevant literature, but I’ll cover my top four tactics here. I’d suggest combining all four methods to ensure that nothing slips past you:
Method 1 – Google Scholar Scrubbing
Google’s academic search engine, Google Scholar , is a great starting point as it provides a good high-level view of the relevant journal articles for whatever keyword you throw at it. Most valuably, it tells you how many times each article has been cited, which gives you an idea of how credible (or at least, popular) it is. Some articles will be free to access, while others will require an account, which brings us to the next method.
Method 2 – University Database Scrounging
Generally, universities provide students with access to an online library, which provides access to many (but not all) of the major journals.
So, if you find an article using Google Scholar that requires paid access (which is quite likely), search for that article in your university’s database – if it’s listed there, you’ll have access. Note that, generally, the search engine capabilities of these databases are poor, so make sure you search for the exact article name, or you might not find it.
Method 3 – Journal Article Snowballing
At the end of every academic journal article, you’ll find a list of references. As with any academic writing, these references are the building blocks of the article, so if the article is relevant to your topic, there’s a good chance a portion of the referenced works will be too. Do a quick scan of the titles and see what seems relevant, then search for the relevant ones in your university’s database.
Method 4 – Dissertation Scavenging
Similar to Method 3 above, you can leverage other students’ dissertations. All you have to do is skim through literature review chapters of existing dissertations related to your topic and you’ll find a gold mine of potential literature. Usually, your university will provide you with access to previous students’ dissertations, but you can also find a much larger selection in the following databases:
- Open Access Theses & Dissertations
- Stanford SearchWorks
Keep in mind that dissertations and theses are not as academically sound as published, peer-reviewed journal articles (because they’re written by students, not professionals), so be sure to check the credibility of any sources you find using this method. You can do this by assessing the citation count of any given article in Google Scholar. If you need help with assessing the credibility of any article, or with finding relevant research in general, you can chat with one of our Research Specialists .
Alright – with a good base of literature firmly under your belt, it’s time to move onto the next step.
Need a helping hand?
Step 2: Log, catalogue and synthesise
Once you’ve built a little treasure trove of articles, it’s time to get reading and start digesting the information – what does it all mean?
While I present steps one and two (hunting and digesting) as sequential, in reality, it’s more of a back-and-forth tango – you’ll read a little , then have an idea, spot a new citation, or a new potential variable, and then go back to searching for articles. This is perfectly natural – through the reading process, your thoughts will develop , new avenues might crop up, and directional adjustments might arise. This is, after all, one of the main purposes of the literature review process (i.e. to familiarise yourself with the current state of research in your field).
As you’re working through your treasure chest, it’s essential that you simultaneously start organising the information. There are three aspects to this:
- Logging reference information
- Building an organised catalogue
- Distilling and synthesising the information
I’ll discuss each of these below:
2.1 – Log the reference information
As you read each article, you should add it to your reference management software. I usually recommend Mendeley for this purpose (see the Mendeley 101 video below), but you can use whichever software you’re comfortable with. Most importantly, make sure you load EVERY article you read into your reference manager, even if it doesn’t seem very relevant at the time.
2.2 – Build an organised catalogue
In the beginning, you might feel confident that you can remember who said what, where, and what their main arguments were. Trust me, you won’t. If you do a thorough review of the relevant literature (as you must!), you’re going to read many, many articles, and it’s simply impossible to remember who said what, when, and in what context . Also, without the bird’s eye view that a catalogue provides, you’ll miss connections between various articles, and have no view of how the research developed over time. Simply put, it’s essential to build your own catalogue of the literature.
I would suggest using Excel to build your catalogue, as it allows you to run filters, colour code and sort – all very useful when your list grows large (which it will). How you lay your spreadsheet out is up to you, but I’d suggest you have the following columns (at minimum):
- Author, date, title – Start with three columns containing this core information. This will make it easy for you to search for titles with certain words, order research by date, or group by author.
- Categories or keywords – You can either create multiple columns, one for each category/theme and then tick the relevant categories, or you can have one column with keywords.
- Key arguments/points – Use this column to succinctly convey the essence of the article, the key arguments and implications thereof for your research.
- Context – Note the socioeconomic context in which the research was undertaken. For example, US-based, respondents aged 25-35, lower- income, etc. This will be useful for making an argument about gaps in the research.
- Methodology – Note which methodology was used and why. Also, note any issues you feel arise due to the methodology. Again, you can use this to make an argument about gaps in the research.
- Quotations – Note down any quoteworthy lines you feel might be useful later.
- Notes – Make notes about anything not already covered. For example, linkages to or disagreements with other theories, questions raised but unanswered, shortcomings or limitations, and so forth.
If you’d like, you can try out our free catalog template here (see screenshot below).

2.3 – Digest and synthesise
Most importantly, as you work through the literature and build your catalogue, you need to synthesise all the information in your own mind – how does it all fit together? Look for links between the various articles and try to develop a bigger picture view of the state of the research. Some important questions to ask yourself are:
- What answers does the existing research provide to my own research questions ?
- Which points do the researchers agree (and disagree) on?
- How has the research developed over time?
- Where do the gaps in the current research lie?
To help you develop a big-picture view and synthesise all the information, you might find mind mapping software such as Freemind useful. Alternatively, if you’re a fan of physical note-taking, investing in a large whiteboard might work for you.

Step 3: Outline and write it up!
Once you’re satisfied that you have digested and distilled all the relevant literature in your mind, it’s time to put pen to paper (or rather, fingers to keyboard). There are two steps here – outlining and writing:
3.1 – Draw up your outline
Having spent so much time reading, it might be tempting to just start writing up without a clear structure in mind. However, it’s critically important to decide on your structure and develop a detailed outline before you write anything. Your literature review chapter needs to present a clear, logical and an easy to follow narrative – and that requires some planning. Don’t try to wing it!
Naturally, you won’t always follow the plan to the letter, but without a detailed outline, you’re more than likely going to end up with a disjointed pile of waffle , and then you’re going to spend a far greater amount of time re-writing, hacking and patching. The adage, “measure twice, cut once” is very suitable here.
In terms of structure, the first decision you’ll have to make is whether you’ll lay out your review thematically (into themes) or chronologically (by date/period). The right choice depends on your topic, research objectives and research questions, which we discuss in this article .
Once that’s decided, you need to draw up an outline of your entire chapter in bullet point format. Try to get as detailed as possible, so that you know exactly what you’ll cover where, how each section will connect to the next, and how your entire argument will develop throughout the chapter. Also, at this stage, it’s a good idea to allocate rough word count limits for each section, so that you can identify word count problems before you’ve spent weeks or months writing!
PS – check out our free literature review chapter template…
3.2 – Get writing
With a detailed outline at your side, it’s time to start writing up (finally!). At this stage, it’s common to feel a bit of writer’s block and find yourself procrastinating under the pressure of finally having to put something on paper. To help with this, remember that the objective of the first draft is not perfection – it’s simply to get your thoughts out of your head and onto paper, after which you can refine them. The structure might change a little, the word count allocations might shift and shuffle, and you might add or remove a section – that’s all okay. Don’t worry about all this on your first draft – just get your thoughts down on paper.

Once you’ve got a full first draft (however rough it may be), step away from it for a day or two (longer if you can) and then come back at it with fresh eyes. Pay particular attention to the flow and narrative – does it fall fit together and flow from one section to another smoothly? Now’s the time to try to improve the linkage from each section to the next, tighten up the writing to be more concise, trim down word count and sand it down into a more digestible read.
Once you’ve done that, give your writing to a friend or colleague who is not a subject matter expert and ask them if they understand the overall discussion. The best way to assess this is to ask them to explain the chapter back to you. This technique will give you a strong indication of which points were clearly communicated and which weren’t. If you’re working with Grad Coach, this is a good time to have your Research Specialist review your chapter.
Finally, tighten it up and send it off to your supervisor for comment. Some might argue that you should be sending your work to your supervisor sooner than this (indeed your university might formally require this), but in my experience, supervisors are extremely short on time (and often patience), so, the more refined your chapter is, the less time they’ll waste on addressing basic issues (which you know about already) and the more time they’ll spend on valuable feedback that will increase your mark-earning potential.
Literature Review Example
In the video below, we unpack an actual literature review so that you can see how all the core components come together in reality.
Let’s Recap
In this post, we’ve covered how to research and write up a high-quality literature review chapter. Let’s do a quick recap of the key takeaways:
- It is essential to understand the WHY of the literature review before you read or write anything. Make sure you understand the 4 core functions of the process.
- The first step is to hunt down the relevant literature . You can do this using Google Scholar, your university database, the snowballing technique and by reviewing other dissertations and theses.
- Next, you need to log all the articles in your reference manager , build your own catalogue of literature and synthesise all the research.
- Following that, you need to develop a detailed outline of your entire chapter – the more detail the better. Don’t start writing without a clear outline (on paper, not in your head!)
- Write up your first draft in rough form – don’t aim for perfection. Remember, done beats perfect.
- Refine your second draft and get a layman’s perspective on it . Then tighten it up and submit it to your supervisor.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling Udemy Course, Literature Review Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

38 Comments
Thank you very much. This page is an eye opener and easy to comprehend.
This is awesome!
I wish I come across GradCoach earlier enough.
But all the same I’ll make use of this opportunity to the fullest.
Thank you for this good job.
Keep it up!
You’re welcome, Yinka. Thank you for the kind words. All the best writing your literature review.
Thank you for a very useful literature review session. Although I am doing most of the steps…it being my first masters an Mphil is a self study and one not sure you are on the right track. I have an amazing supervisor but one also knows they are super busy. So not wanting to bother on the minutae. Thank you.
You’re most welcome, Renee. Good luck with your literature review 🙂
This has been really helpful. Will make full use of it. 🙂
Thank you Gradcoach.
Really agreed. Admirable effort
thank you for this beautiful well explained recap.
Thank you so much for your guide of video and other instructions for the dissertation writing.
It is instrumental. It encouraged me to write a dissertation now.
Thank you the video was great – from someone that knows nothing thankyou
an amazing and very constructive way of presetting a topic, very useful, thanks for the effort,
It is timely
It is very good video of guidance for writing a research proposal and a dissertation. Since I have been watching and reading instructions, I have started my research proposal to write. I appreciate to Mr Jansen hugely.
I learn a lot from your videos. Very comprehensive and detailed.
Thank you for sharing your knowledge. As a research student, you learn better with your learning tips in research
I was really stuck in reading and gathering information but after watching these things are cleared thanks, it is so helpful.
Really helpful, Thank you for the effort in showing such information
This is super helpful thank you very much.
Thank you for this whole literature writing review.You have simplified the process.
I’m so glad I found GradCoach. Excellent information, Clear explanation, and Easy to follow, Many thanks Derek!
You’re welcome, Maithe. Good luck writing your literature review 🙂
Thank you Coach, you have greatly enriched and improved my knowledge
Great piece, so enriching and it is going to help me a great lot in my project and thesis, thanks so much
This is THE BEST site for ANYONE doing a masters or doctorate! Thank you for the sound advice and templates. You rock!
Thanks, Stephanie 🙂
This is mind blowing, the detailed explanation and simplicity is perfect.
I am doing two papers on my final year thesis, and I must stay I feel very confident to face both headlong after reading this article.
thank you so much.
if anyone is to get a paper done on time and in the best way possible, GRADCOACH is certainly the go to area!
This is very good video which is well explained with detailed explanation
Thank you excellent piece of work and great mentoring
Thanks, it was useful
Thank you very much. the video and the information were very helpful.
Good morning scholar. I’m delighted coming to know you even before the commencement of my dissertation which hopefully is expected in not more than six months from now. I would love to engage my study under your guidance from the beginning to the end. I love to know how to do good job
Thank you so much Derek for such useful information on writing up a good literature review. I am at a stage where I need to start writing my one. My proposal was accepted late last year but I honestly did not know where to start
Like the name of your YouTube implies you are GRAD (great,resource person, about dissertation). In short you are smart enough in coaching research work.
This is a very well thought out webpage. Very informative and a great read.
Very timely.
I appreciate.
Very comprehensive and eye opener for me as beginner in postgraduate study. Well explained and easy to understand. Appreciate and good reference in guiding me in my research journey. Thank you
Thank you. I requested to download the free literature review template, however, your website wouldn’t allow me to complete the request or complete a download. May I request that you email me the free template? Thank you.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Libraries | Research Guides
Literature reviews, what is a literature review, learning more about how to do a literature review.
- Planning the Review
- The Research Question
- Choosing Where to Search
- Organizing the Review
- Writing the Review
A literature review is a review and synthesis of existing research on a topic or research question. A literature review is meant to analyze the scholarly literature, make connections across writings and identify strengths, weaknesses, trends, and missing conversations. A literature review should address different aspects of a topic as it relates to your research question. A literature review goes beyond a description or summary of the literature you have read.
- Sage Research Methods Core Collection This link opens in a new window SAGE Research Methods supports research at all levels by providing material to guide users through every step of the research process. SAGE Research Methods is the ultimate methods library with more than 1000 books, reference works, journal articles, and instructional videos by world-leading academics from across the social sciences, including the largest collection of qualitative methods books available online from any scholarly publisher. – Publisher
- Next: Planning the Review >>
- Last Updated: Jan 17, 2024 10:05 AM
- URL: https://libguides.northwestern.edu/literaturereviews
Research Methods
- Getting Started
- Literature Review Research
- Research Design
- Research Design By Discipline
- SAGE Research Methods
- Teaching with SAGE Research Methods
Literature Review
- What is a Literature Review?
- What is NOT a Literature Review?
- Purposes of a Literature Review
- Types of Literature Reviews
- Literature Reviews vs. Systematic Reviews
- Systematic vs. Meta-Analysis
Literature Review is a comprehensive survey of the works published in a particular field of study or line of research, usually over a specific period of time, in the form of an in-depth, critical bibliographic essay or annotated list in which attention is drawn to the most significant works.
Also, we can define a literature review as the collected body of scholarly works related to a topic:
- Summarizes and analyzes previous research relevant to a topic
- Includes scholarly books and articles published in academic journals
- Can be an specific scholarly paper or a section in a research paper
The objective of a Literature Review is to find previous published scholarly works relevant to an specific topic
- Help gather ideas or information
- Keep up to date in current trends and findings
- Help develop new questions
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Helps focus your own research questions or problems
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Suggests unexplored ideas or populations
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Tests assumptions; may help counter preconceived ideas and remove unconscious bias.
- Identifies critical gaps, points of disagreement, or potentially flawed methodology or theoretical approaches.
- Indicates potential directions for future research.
All content in this section is from Literature Review Research from Old Dominion University
Keep in mind the following, a literature review is NOT:
Not an essay
Not an annotated bibliography in which you summarize each article that you have reviewed. A literature review goes beyond basic summarizing to focus on the critical analysis of the reviewed works and their relationship to your research question.
Not a research paper where you select resources to support one side of an issue versus another. A lit review should explain and consider all sides of an argument in order to avoid bias, and areas of agreement and disagreement should be highlighted.
A literature review serves several purposes. For example, it
- provides thorough knowledge of previous studies; introduces seminal works.
- helps focus one’s own research topic.
- identifies a conceptual framework for one’s own research questions or problems; indicates potential directions for future research.
- suggests previously unused or underused methodologies, designs, quantitative and qualitative strategies.
- identifies gaps in previous studies; identifies flawed methodologies and/or theoretical approaches; avoids replication of mistakes.
- helps the researcher avoid repetition of earlier research.
- suggests unexplored populations.
- determines whether past studies agree or disagree; identifies controversy in the literature.
- tests assumptions; may help counter preconceived ideas and remove unconscious bias.
As Kennedy (2007) notes*, it is important to think of knowledge in a given field as consisting of three layers. First, there are the primary studies that researchers conduct and publish. Second are the reviews of those studies that summarize and offer new interpretations built from and often extending beyond the original studies. Third, there are the perceptions, conclusions, opinion, and interpretations that are shared informally that become part of the lore of field. In composing a literature review, it is important to note that it is often this third layer of knowledge that is cited as "true" even though it often has only a loose relationship to the primary studies and secondary literature reviews.
Given this, while literature reviews are designed to provide an overview and synthesis of pertinent sources you have explored, there are several approaches to how they can be done, depending upon the type of analysis underpinning your study. Listed below are definitions of types of literature reviews:
Argumentative Review This form examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply imbedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. The purpose is to develop a body of literature that establishes a contrarian viewpoint. Given the value-laden nature of some social science research [e.g., educational reform; immigration control], argumentative approaches to analyzing the literature can be a legitimate and important form of discourse. However, note that they can also introduce problems of bias when they are used to to make summary claims of the sort found in systematic reviews.
Integrative Review Considered a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. The body of literature includes all studies that address related or identical hypotheses. A well-done integrative review meets the same standards as primary research in regard to clarity, rigor, and replication.
Historical Review Few things rest in isolation from historical precedent. Historical reviews are focused on examining research throughout a period of time, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, phenomena emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and to identify the likely directions for future research.
Methodological Review A review does not always focus on what someone said [content], but how they said it [method of analysis]. This approach provides a framework of understanding at different levels (i.e. those of theory, substantive fields, research approaches and data collection and analysis techniques), enables researchers to draw on a wide variety of knowledge ranging from the conceptual level to practical documents for use in fieldwork in the areas of ontological and epistemological consideration, quantitative and qualitative integration, sampling, interviewing, data collection and data analysis, and helps highlight many ethical issues which we should be aware of and consider as we go through our study.
Systematic Review This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect, report, and analyse data from the studies that are included in the review. Typically it focuses on a very specific empirical question, often posed in a cause-and-effect form, such as "To what extent does A contribute to B?"
Theoretical Review The purpose of this form is to concretely examine the corpus of theory that has accumulated in regard to an issue, concept, theory, phenomena. The theoretical literature review help establish what theories already exist, the relationships between them, to what degree the existing theories have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested. Often this form is used to help establish a lack of appropriate theories or reveal that current theories are inadequate for explaining new or emerging research problems. The unit of analysis can focus on a theoretical concept or a whole theory or framework.
* Kennedy, Mary M. "Defining a Literature." Educational Researcher 36 (April 2007): 139-147.
All content in this section is from The Literature Review created by Dr. Robert Larabee USC
Robinson, P. and Lowe, J. (2015), Literature reviews vs systematic reviews. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Public Health, 39: 103-103. doi: 10.1111/1753-6405.12393

What's in the name? The difference between a Systematic Review and a Literature Review, and why it matters . By Lynn Kysh from University of Southern California

Systematic review or meta-analysis?
A systematic review answers a defined research question by collecting and summarizing all empirical evidence that fits pre-specified eligibility criteria.
A meta-analysis is the use of statistical methods to summarize the results of these studies.
Systematic reviews, just like other research articles, can be of varying quality. They are a significant piece of work (the Centre for Reviews and Dissemination at York estimates that a team will take 9-24 months), and to be useful to other researchers and practitioners they should have:
- clearly stated objectives with pre-defined eligibility criteria for studies
- explicit, reproducible methodology
- a systematic search that attempts to identify all studies
- assessment of the validity of the findings of the included studies (e.g. risk of bias)
- systematic presentation, and synthesis, of the characteristics and findings of the included studies
Not all systematic reviews contain meta-analysis.
Meta-analysis is the use of statistical methods to summarize the results of independent studies. By combining information from all relevant studies, meta-analysis can provide more precise estimates of the effects of health care than those derived from the individual studies included within a review. More information on meta-analyses can be found in Cochrane Handbook, Chapter 9 .
A meta-analysis goes beyond critique and integration and conducts secondary statistical analysis on the outcomes of similar studies. It is a systematic review that uses quantitative methods to synthesize and summarize the results.
An advantage of a meta-analysis is the ability to be completely objective in evaluating research findings. Not all topics, however, have sufficient research evidence to allow a meta-analysis to be conducted. In that case, an integrative review is an appropriate strategy.
Some of the content in this section is from Systematic reviews and meta-analyses: step by step guide created by Kate McAllister.
- << Previous: Getting Started
- Next: Research Design >>
- Last Updated: Aug 21, 2023 4:07 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.udel.edu/researchmethods
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER FEATURE
- 04 December 2020
- Correction 09 December 2020
How to write a superb literature review
Andy Tay is a freelance writer based in Singapore.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Literature reviews are important resources for scientists. They provide historical context for a field while offering opinions on its future trajectory. Creating them can provide inspiration for one’s own research, as well as some practice in writing. But few scientists are trained in how to write a review — or in what constitutes an excellent one. Even picking the appropriate software to use can be an involved decision (see ‘Tools and techniques’). So Nature asked editors and working scientists with well-cited reviews for their tips.
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
185,98 € per year
only 3,65 € per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-020-03422-x
Interviews have been edited for length and clarity.
Updates & Corrections
Correction 09 December 2020 : An earlier version of the tables in this article included some incorrect details about the programs Zotero, Endnote and Manubot. These have now been corrected.
Hsing, I.-M., Xu, Y. & Zhao, W. Electroanalysis 19 , 755–768 (2007).
Article Google Scholar
Ledesma, H. A. et al. Nature Nanotechnol. 14 , 645–657 (2019).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Brahlek, M., Koirala, N., Bansal, N. & Oh, S. Solid State Commun. 215–216 , 54–62 (2015).
Choi, Y. & Lee, S. Y. Nature Rev. Chem . https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-020-00221-w (2020).
Download references
Related Articles

- Research management

How I harnessed media engagement to supercharge my research career
Career Column 09 APR 24

How we landed job interviews for professorships straight out of our PhD programmes
Career Column 08 APR 24

Three ways ChatGPT helps me in my academic writing

How two PhD students overcame the odds to snag tenure-track jobs
Adopt universal standards for study adaptation to boost health, education and social-science research
Correspondence 02 APR 24

Is ChatGPT corrupting peer review? Telltale words hint at AI use
News 10 APR 24

Rwanda 30 years on: understanding the horror of genocide
Editorial 09 APR 24
Clinical Fellow
Memphis, Tennessee
St. Jude Children's Research Hospital (St. Jude)
Tenure-Track Assistant Professor, Associate Professor, and Professor
Founded at Hangzhou, China in 2018, Westlake University is a new type of non-profit research-oriented university, creating a stimulating, world-cla...
Westlake Center for Genome Editing, Westlake University
Postdoctoral Associate
Houston, Texas (US)
Baylor College of Medicine (BCM)
Associate or Senior Editor (clinical microbiology and infectious diseases)
Do you love science but feel that a career at the bench isn’t enough to sate your desire to learn more about the natural world?
London, New York, Pune – Hybrid working model.
Springer Nature Ltd
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
- UConn Library
- Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide
- Introduction
Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide — Introduction
- Getting Started
- How to Pick a Topic
- Strategies to Find Sources
- Evaluating Sources & Lit. Reviews
- Tips for Writing Literature Reviews
- Writing Literature Review: Useful Sites
- Citation Resources
- Other Academic Writings
What are Literature Reviews?
So, what is a literature review? "A literature review is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your argumentative thesis). It is not just a descriptive list of the material available, or a set of summaries." Taylor, D. The literature review: A few tips on conducting it . University of Toronto Health Sciences Writing Centre.
Goals of Literature Reviews
What are the goals of creating a Literature Review? A literature could be written to accomplish different aims:
- To develop a theory or evaluate an existing theory
- To summarize the historical or existing state of a research topic
- Identify a problem in a field of research
Baumeister, R. F., & Leary, M. R. (1997). Writing narrative literature reviews . Review of General Psychology , 1 (3), 311-320.
What kinds of sources require a Literature Review?
- A research paper assigned in a course
- A thesis or dissertation
- A grant proposal
- An article intended for publication in a journal
All these instances require you to collect what has been written about your research topic so that you can demonstrate how your own research sheds new light on the topic.
Types of Literature Reviews
What kinds of literature reviews are written?
Narrative review: The purpose of this type of review is to describe the current state of the research on a specific topic/research and to offer a critical analysis of the literature reviewed. Studies are grouped by research/theoretical categories, and themes and trends, strengths and weakness, and gaps are identified. The review ends with a conclusion section which summarizes the findings regarding the state of the research of the specific study, the gaps identify and if applicable, explains how the author's research will address gaps identify in the review and expand the knowledge on the topic reviewed.
- Example : Predictors and Outcomes of U.S. Quality Maternity Leave: A Review and Conceptual Framework: 10.1177/08948453211037398
Systematic review : "The authors of a systematic review use a specific procedure to search the research literature, select the studies to include in their review, and critically evaluate the studies they find." (p. 139). Nelson, L. K. (2013). Research in Communication Sciences and Disorders . Plural Publishing.
- Example : The effect of leave policies on increasing fertility: a systematic review: 10.1057/s41599-022-01270-w
Meta-analysis : "Meta-analysis is a method of reviewing research findings in a quantitative fashion by transforming the data from individual studies into what is called an effect size and then pooling and analyzing this information. The basic goal in meta-analysis is to explain why different outcomes have occurred in different studies." (p. 197). Roberts, M. C., & Ilardi, S. S. (2003). Handbook of Research Methods in Clinical Psychology . Blackwell Publishing.
- Example : Employment Instability and Fertility in Europe: A Meta-Analysis: 10.1215/00703370-9164737
Meta-synthesis : "Qualitative meta-synthesis is a type of qualitative study that uses as data the findings from other qualitative studies linked by the same or related topic." (p.312). Zimmer, L. (2006). Qualitative meta-synthesis: A question of dialoguing with texts . Journal of Advanced Nursing , 53 (3), 311-318.
- Example : Women’s perspectives on career successes and barriers: A qualitative meta-synthesis: 10.1177/05390184221113735
Literature Reviews in the Health Sciences
- UConn Health subject guide on systematic reviews Explanation of the different review types used in health sciences literature as well as tools to help you find the right review type
- << Previous: Getting Started
- Next: How to Pick a Topic >>
- Last Updated: Sep 21, 2022 2:16 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uconn.edu/literaturereview
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 5. The Literature Review
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
A literature review surveys prior research published in books, scholarly articles, and any other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, provides a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works in relation to the research problem being investigated. Literature reviews are designed to provide an overview of sources you have used in researching a particular topic and to demonstrate to your readers how your research fits within existing scholarship about the topic.
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . Fourth edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2014.
Importance of a Good Literature Review
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories . A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that informs how you are planning to investigate a research problem. The analytical features of a literature review might:
- Give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations,
- Trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates,
- Depending on the situation, evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant research, or
- Usually in the conclusion of a literature review, identify where gaps exist in how a problem has been researched to date.
Given this, the purpose of a literature review is to:
- Place each work in the context of its contribution to understanding the research problem being studied.
- Describe the relationship of each work to the others under consideration.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research.
- Reveal any gaps that exist in the literature.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies.
- Identify areas of prior scholarship to prevent duplication of effort.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important].
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper. 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2011; Knopf, Jeffrey W. "Doing a Literature Review." PS: Political Science and Politics 39 (January 2006): 127-132; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012.
Types of Literature Reviews
It is important to think of knowledge in a given field as consisting of three layers. First, there are the primary studies that researchers conduct and publish. Second are the reviews of those studies that summarize and offer new interpretations built from and often extending beyond the primary studies. Third, there are the perceptions, conclusions, opinion, and interpretations that are shared informally among scholars that become part of the body of epistemological traditions within the field.
In composing a literature review, it is important to note that it is often this third layer of knowledge that is cited as "true" even though it often has only a loose relationship to the primary studies and secondary literature reviews. Given this, while literature reviews are designed to provide an overview and synthesis of pertinent sources you have explored, there are a number of approaches you could adopt depending upon the type of analysis underpinning your study.
Argumentative Review This form examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply embedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. The purpose is to develop a body of literature that establishes a contrarian viewpoint. Given the value-laden nature of some social science research [e.g., educational reform; immigration control], argumentative approaches to analyzing the literature can be a legitimate and important form of discourse. However, note that they can also introduce problems of bias when they are used to make summary claims of the sort found in systematic reviews [see below].
Integrative Review Considered a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. The body of literature includes all studies that address related or identical hypotheses or research problems. A well-done integrative review meets the same standards as primary research in regard to clarity, rigor, and replication. This is the most common form of review in the social sciences.
Historical Review Few things rest in isolation from historical precedent. Historical literature reviews focus on examining research throughout a period of time, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, phenomena emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and to identify the likely directions for future research.
Methodological Review A review does not always focus on what someone said [findings], but how they came about saying what they say [method of analysis]. Reviewing methods of analysis provides a framework of understanding at different levels [i.e. those of theory, substantive fields, research approaches, and data collection and analysis techniques], how researchers draw upon a wide variety of knowledge ranging from the conceptual level to practical documents for use in fieldwork in the areas of ontological and epistemological consideration, quantitative and qualitative integration, sampling, interviewing, data collection, and data analysis. This approach helps highlight ethical issues which you should be aware of and consider as you go through your own study.
Systematic Review This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect, report, and analyze data from the studies that are included in the review. The goal is to deliberately document, critically evaluate, and summarize scientifically all of the research about a clearly defined research problem . Typically it focuses on a very specific empirical question, often posed in a cause-and-effect form, such as "To what extent does A contribute to B?" This type of literature review is primarily applied to examining prior research studies in clinical medicine and allied health fields, but it is increasingly being used in the social sciences.
Theoretical Review The purpose of this form is to examine the corpus of theory that has accumulated in regard to an issue, concept, theory, phenomena. The theoretical literature review helps to establish what theories already exist, the relationships between them, to what degree the existing theories have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested. Often this form is used to help establish a lack of appropriate theories or reveal that current theories are inadequate for explaining new or emerging research problems. The unit of analysis can focus on a theoretical concept or a whole theory or framework.
NOTE : Most often the literature review will incorporate some combination of types. For example, a review that examines literature supporting or refuting an argument, assumption, or philosophical problem related to the research problem will also need to include writing supported by sources that establish the history of these arguments in the literature.
Baumeister, Roy F. and Mark R. Leary. "Writing Narrative Literature Reviews." Review of General Psychology 1 (September 1997): 311-320; Mark R. Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Kennedy, Mary M. "Defining a Literature." Educational Researcher 36 (April 2007): 139-147; Petticrew, Mark and Helen Roberts. Systematic Reviews in the Social Sciences: A Practical Guide . Malden, MA: Blackwell Publishers, 2006; Torracro, Richard. "Writing Integrative Literature Reviews: Guidelines and Examples." Human Resource Development Review 4 (September 2005): 356-367; Rocco, Tonette S. and Maria S. Plakhotnik. "Literature Reviews, Conceptual Frameworks, and Theoretical Frameworks: Terms, Functions, and Distinctions." Human Ressource Development Review 8 (March 2008): 120-130; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Thinking About Your Literature Review
The structure of a literature review should include the following in support of understanding the research problem :
- An overview of the subject, issue, or theory under consideration, along with the objectives of the literature review,
- Division of works under review into themes or categories [e.g. works that support a particular position, those against, and those offering alternative approaches entirely],
- An explanation of how each work is similar to and how it varies from the others,
- Conclusions as to which pieces are best considered in their argument, are most convincing of their opinions, and make the greatest contribution to the understanding and development of their area of research.
The critical evaluation of each work should consider :
- Provenance -- what are the author's credentials? Are the author's arguments supported by evidence [e.g. primary historical material, case studies, narratives, statistics, recent scientific findings]?
- Methodology -- were the techniques used to identify, gather, and analyze the data appropriate to addressing the research problem? Was the sample size appropriate? Were the results effectively interpreted and reported?
- Objectivity -- is the author's perspective even-handed or prejudicial? Is contrary data considered or is certain pertinent information ignored to prove the author's point?
- Persuasiveness -- which of the author's theses are most convincing or least convincing?
- Validity -- are the author's arguments and conclusions convincing? Does the work ultimately contribute in any significant way to an understanding of the subject?
II. Development of the Literature Review
Four Basic Stages of Writing 1. Problem formulation -- which topic or field is being examined and what are its component issues? 2. Literature search -- finding materials relevant to the subject being explored. 3. Data evaluation -- determining which literature makes a significant contribution to the understanding of the topic. 4. Analysis and interpretation -- discussing the findings and conclusions of pertinent literature.
Consider the following issues before writing the literature review: Clarify If your assignment is not specific about what form your literature review should take, seek clarification from your professor by asking these questions: 1. Roughly how many sources would be appropriate to include? 2. What types of sources should I review (books, journal articles, websites; scholarly versus popular sources)? 3. Should I summarize, synthesize, or critique sources by discussing a common theme or issue? 4. Should I evaluate the sources in any way beyond evaluating how they relate to understanding the research problem? 5. Should I provide subheadings and other background information, such as definitions and/or a history? Find Models Use the exercise of reviewing the literature to examine how authors in your discipline or area of interest have composed their literature review sections. Read them to get a sense of the types of themes you might want to look for in your own research or to identify ways to organize your final review. The bibliography or reference section of sources you've already read, such as required readings in the course syllabus, are also excellent entry points into your own research. Narrow the Topic The narrower your topic, the easier it will be to limit the number of sources you need to read in order to obtain a good survey of relevant resources. Your professor will probably not expect you to read everything that's available about the topic, but you'll make the act of reviewing easier if you first limit scope of the research problem. A good strategy is to begin by searching the USC Libraries Catalog for recent books about the topic and review the table of contents for chapters that focuses on specific issues. You can also review the indexes of books to find references to specific issues that can serve as the focus of your research. For example, a book surveying the history of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict may include a chapter on the role Egypt has played in mediating the conflict, or look in the index for the pages where Egypt is mentioned in the text. Consider Whether Your Sources are Current Some disciplines require that you use information that is as current as possible. This is particularly true in disciplines in medicine and the sciences where research conducted becomes obsolete very quickly as new discoveries are made. However, when writing a review in the social sciences, a survey of the history of the literature may be required. In other words, a complete understanding the research problem requires you to deliberately examine how knowledge and perspectives have changed over time. Sort through other current bibliographies or literature reviews in the field to get a sense of what your discipline expects. You can also use this method to explore what is considered by scholars to be a "hot topic" and what is not.
III. Ways to Organize Your Literature Review
Chronology of Events If your review follows the chronological method, you could write about the materials according to when they were published. This approach should only be followed if a clear path of research building on previous research can be identified and that these trends follow a clear chronological order of development. For example, a literature review that focuses on continuing research about the emergence of German economic power after the fall of the Soviet Union. By Publication Order your sources by publication chronology, then, only if the order demonstrates a more important trend. For instance, you could order a review of literature on environmental studies of brown fields if the progression revealed, for example, a change in the soil collection practices of the researchers who wrote and/or conducted the studies. Thematic [“conceptual categories”] A thematic literature review is the most common approach to summarizing prior research in the social and behavioral sciences. Thematic reviews are organized around a topic or issue, rather than the progression of time, although the progression of time may still be incorporated into a thematic review. For example, a review of the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics could focus on the development of online political satire. While the study focuses on one topic, the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics, it would still be organized chronologically reflecting technological developments in media. The difference in this example between a "chronological" and a "thematic" approach is what is emphasized the most: themes related to the role of the Internet in presidential politics. Note that more authentic thematic reviews tend to break away from chronological order. A review organized in this manner would shift between time periods within each section according to the point being made. Methodological A methodological approach focuses on the methods utilized by the researcher. For the Internet in American presidential politics project, one methodological approach would be to look at cultural differences between the portrayal of American presidents on American, British, and French websites. Or the review might focus on the fundraising impact of the Internet on a particular political party. A methodological scope will influence either the types of documents in the review or the way in which these documents are discussed.
Other Sections of Your Literature Review Once you've decided on the organizational method for your literature review, the sections you need to include in the paper should be easy to figure out because they arise from your organizational strategy. In other words, a chronological review would have subsections for each vital time period; a thematic review would have subtopics based upon factors that relate to the theme or issue. However, sometimes you may need to add additional sections that are necessary for your study, but do not fit in the organizational strategy of the body. What other sections you include in the body is up to you. However, only include what is necessary for the reader to locate your study within the larger scholarship about the research problem.
Here are examples of other sections, usually in the form of a single paragraph, you may need to include depending on the type of review you write:
- Current Situation : Information necessary to understand the current topic or focus of the literature review.
- Sources Used : Describes the methods and resources [e.g., databases] you used to identify the literature you reviewed.
- History : The chronological progression of the field, the research literature, or an idea that is necessary to understand the literature review, if the body of the literature review is not already a chronology.
- Selection Methods : Criteria you used to select (and perhaps exclude) sources in your literature review. For instance, you might explain that your review includes only peer-reviewed [i.e., scholarly] sources.
- Standards : Description of the way in which you present your information.
- Questions for Further Research : What questions about the field has the review sparked? How will you further your research as a result of the review?
IV. Writing Your Literature Review
Once you've settled on how to organize your literature review, you're ready to write each section. When writing your review, keep in mind these issues.
Use Evidence A literature review section is, in this sense, just like any other academic research paper. Your interpretation of the available sources must be backed up with evidence [citations] that demonstrates that what you are saying is valid. Be Selective Select only the most important points in each source to highlight in the review. The type of information you choose to mention should relate directly to the research problem, whether it is thematic, methodological, or chronological. Related items that provide additional information, but that are not key to understanding the research problem, can be included in a list of further readings . Use Quotes Sparingly Some short quotes are appropriate if you want to emphasize a point, or if what an author stated cannot be easily paraphrased. Sometimes you may need to quote certain terminology that was coined by the author, is not common knowledge, or taken directly from the study. Do not use extensive quotes as a substitute for using your own words in reviewing the literature. Summarize and Synthesize Remember to summarize and synthesize your sources within each thematic paragraph as well as throughout the review. Recapitulate important features of a research study, but then synthesize it by rephrasing the study's significance and relating it to your own work and the work of others. Keep Your Own Voice While the literature review presents others' ideas, your voice [the writer's] should remain front and center. For example, weave references to other sources into what you are writing but maintain your own voice by starting and ending the paragraph with your own ideas and wording. Use Caution When Paraphrasing When paraphrasing a source that is not your own, be sure to represent the author's information or opinions accurately and in your own words. Even when paraphrasing an author’s work, you still must provide a citation to that work.
V. Common Mistakes to Avoid
These are the most common mistakes made in reviewing social science research literature.
- Sources in your literature review do not clearly relate to the research problem;
- You do not take sufficient time to define and identify the most relevant sources to use in the literature review related to the research problem;
- Relies exclusively on secondary analytical sources rather than including relevant primary research studies or data;
- Uncritically accepts another researcher's findings and interpretations as valid, rather than examining critically all aspects of the research design and analysis;
- Does not describe the search procedures that were used in identifying the literature to review;
- Reports isolated statistical results rather than synthesizing them in chi-squared or meta-analytic methods; and,
- Only includes research that validates assumptions and does not consider contrary findings and alternative interpretations found in the literature.
Cook, Kathleen E. and Elise Murowchick. “Do Literature Review Skills Transfer from One Course to Another?” Psychology Learning and Teaching 13 (March 2014): 3-11; Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . London: SAGE, 2011; Literature Review Handout. Online Writing Center. Liberty University; Literature Reviews. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2016; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012; Randolph, Justus J. “A Guide to Writing the Dissertation Literature Review." Practical Assessment, Research, and Evaluation. vol. 14, June 2009; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016; Taylor, Dena. The Literature Review: A Few Tips On Conducting It. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Writing a Literature Review. Academic Skills Centre. University of Canberra.
Writing Tip
Break Out of Your Disciplinary Box!
Thinking interdisciplinarily about a research problem can be a rewarding exercise in applying new ideas, theories, or concepts to an old problem. For example, what might cultural anthropologists say about the continuing conflict in the Middle East? In what ways might geographers view the need for better distribution of social service agencies in large cities than how social workers might study the issue? You don’t want to substitute a thorough review of core research literature in your discipline for studies conducted in other fields of study. However, particularly in the social sciences, thinking about research problems from multiple vectors is a key strategy for finding new solutions to a problem or gaining a new perspective. Consult with a librarian about identifying research databases in other disciplines; almost every field of study has at least one comprehensive database devoted to indexing its research literature.
Frodeman, Robert. The Oxford Handbook of Interdisciplinarity . New York: Oxford University Press, 2010.
Another Writing Tip
Don't Just Review for Content!
While conducting a review of the literature, maximize the time you devote to writing this part of your paper by thinking broadly about what you should be looking for and evaluating. Review not just what scholars are saying, but how are they saying it. Some questions to ask:
- How are they organizing their ideas?
- What methods have they used to study the problem?
- What theories have been used to explain, predict, or understand their research problem?
- What sources have they cited to support their conclusions?
- How have they used non-textual elements [e.g., charts, graphs, figures, etc.] to illustrate key points?
When you begin to write your literature review section, you'll be glad you dug deeper into how the research was designed and constructed because it establishes a means for developing more substantial analysis and interpretation of the research problem.
Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1 998.
Yet Another Writing Tip
When Do I Know I Can Stop Looking and Move On?
Here are several strategies you can utilize to assess whether you've thoroughly reviewed the literature:
- Look for repeating patterns in the research findings . If the same thing is being said, just by different people, then this likely demonstrates that the research problem has hit a conceptual dead end. At this point consider: Does your study extend current research? Does it forge a new path? Or, does is merely add more of the same thing being said?
- Look at sources the authors cite to in their work . If you begin to see the same researchers cited again and again, then this is often an indication that no new ideas have been generated to address the research problem.
- Search Google Scholar to identify who has subsequently cited leading scholars already identified in your literature review [see next sub-tab]. This is called citation tracking and there are a number of sources that can help you identify who has cited whom, particularly scholars from outside of your discipline. Here again, if the same authors are being cited again and again, this may indicate no new literature has been written on the topic.
Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: Sage, 2016; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
- << Previous: Theoretical Framework
- Next: Citation Tracking >>
- Last Updated: Apr 9, 2024 1:19 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)

A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing how your work contributes to the ongoing conversation in the field. Learning how to write a literature review is a critical tool for successful research. Your ability to summarize and synthesize prior research pertaining to a certain topic demonstrates your grasp on the topic of study, and assists in the learning process.
Table of Contents
- What is the purpose of literature review?
- a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
- b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
- c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
- d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
- How to write a good literature review
- Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Select Databases for Searches:
- Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Review the Literature:
- Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Frequently asked questions
What is a literature review?
A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the existing literature, establishes the context for their own research, and contributes to scholarly conversations on the topic. One of the purposes of a literature review is also to help researchers avoid duplicating previous work and ensure that their research is informed by and builds upon the existing body of knowledge.

What is the purpose of literature review?
A literature review serves several important purposes within academic and research contexts. Here are some key objectives and functions of a literature review: 2
- Contextualizing the Research Problem: The literature review provides a background and context for the research problem under investigation. It helps to situate the study within the existing body of knowledge.
- Identifying Gaps in Knowledge: By identifying gaps, contradictions, or areas requiring further research, the researcher can shape the research question and justify the significance of the study. This is crucial for ensuring that the new research contributes something novel to the field.
- Understanding Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks: Literature reviews help researchers gain an understanding of the theoretical and conceptual frameworks used in previous studies. This aids in the development of a theoretical framework for the current research.
- Providing Methodological Insights: Another purpose of literature reviews is that it allows researchers to learn about the methodologies employed in previous studies. This can help in choosing appropriate research methods for the current study and avoiding pitfalls that others may have encountered.
- Establishing Credibility: A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with existing scholarship, establishing their credibility and expertise in the field. It also helps in building a solid foundation for the new research.
- Informing Hypotheses or Research Questions: The literature review guides the formulation of hypotheses or research questions by highlighting relevant findings and areas of uncertainty in existing literature.
Literature review example
Let’s delve deeper with a literature review example: Let’s say your literature review is about the impact of climate change on biodiversity. You might format your literature review into sections such as the effects of climate change on habitat loss and species extinction, phenological changes, and marine biodiversity. Each section would then summarize and analyze relevant studies in those areas, highlighting key findings and identifying gaps in the research. The review would conclude by emphasizing the need for further research on specific aspects of the relationship between climate change and biodiversity. The following literature review template provides a glimpse into the recommended literature review structure and content, demonstrating how research findings are organized around specific themes within a broader topic.
Literature Review on Climate Change Impacts on Biodiversity:
Climate change is a global phenomenon with far-reaching consequences, including significant impacts on biodiversity. This literature review synthesizes key findings from various studies:
a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
Climate change-induced alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns contribute to habitat loss, affecting numerous species (Thomas et al., 2004). The review discusses how these changes increase the risk of extinction, particularly for species with specific habitat requirements.
b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
Observations of range shifts and changes in the timing of biological events (phenology) are documented in response to changing climatic conditions (Parmesan & Yohe, 2003). These shifts affect ecosystems and may lead to mismatches between species and their resources.
c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
The review explores the impact of climate change on marine biodiversity, emphasizing ocean acidification’s threat to coral reefs (Hoegh-Guldberg et al., 2007). Changes in pH levels negatively affect coral calcification, disrupting the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
Recognizing the urgency of the situation, the literature review discusses various adaptive strategies adopted by species and conservation efforts aimed at mitigating the impacts of climate change on biodiversity (Hannah et al., 2007). It emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary approaches for effective conservation planning.

How to write a good literature review
Writing a literature review involves summarizing and synthesizing existing research on a particular topic. A good literature review format should include the following elements.
Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your literature review, providing context and introducing the main focus of your review.
- Opening Statement: Begin with a general statement about the broader topic and its significance in the field.
- Scope and Purpose: Clearly define the scope of your literature review. Explain the specific research question or objective you aim to address.
- Organizational Framework: Briefly outline the structure of your literature review, indicating how you will categorize and discuss the existing research.
- Significance of the Study: Highlight why your literature review is important and how it contributes to the understanding of the chosen topic.
- Thesis Statement: Conclude the introduction with a concise thesis statement that outlines the main argument or perspective you will develop in the body of the literature review.
Body: The body of the literature review is where you provide a comprehensive analysis of existing literature, grouping studies based on themes, methodologies, or other relevant criteria.
- Organize by Theme or Concept: Group studies that share common themes, concepts, or methodologies. Discuss each theme or concept in detail, summarizing key findings and identifying gaps or areas of disagreement.
- Critical Analysis: Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each study. Discuss the methodologies used, the quality of evidence, and the overall contribution of each work to the understanding of the topic.
- Synthesis of Findings: Synthesize the information from different studies to highlight trends, patterns, or areas of consensus in the literature.
- Identification of Gaps: Discuss any gaps or limitations in the existing research and explain how your review contributes to filling these gaps.
- Transition between Sections: Provide smooth transitions between different themes or concepts to maintain the flow of your literature review.
Conclusion: The conclusion of your literature review should summarize the main findings, highlight the contributions of the review, and suggest avenues for future research.
- Summary of Key Findings: Recap the main findings from the literature and restate how they contribute to your research question or objective.
- Contributions to the Field: Discuss the overall contribution of your literature review to the existing knowledge in the field.
- Implications and Applications: Explore the practical implications of the findings and suggest how they might impact future research or practice.
- Recommendations for Future Research: Identify areas that require further investigation and propose potential directions for future research in the field.
- Final Thoughts: Conclude with a final reflection on the importance of your literature review and its relevance to the broader academic community.

Conducting a literature review
Conducting a literature review is an essential step in research that involves reviewing and analyzing existing literature on a specific topic. It’s important to know how to do a literature review effectively, so here are the steps to follow: 1
Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Select a topic that is relevant to your field of study.
- Clearly define your research question or objective. Determine what specific aspect of the topic do you want to explore?
Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Determine the timeframe for your literature review. Are you focusing on recent developments, or do you want a historical overview?
- Consider the geographical scope. Is your review global, or are you focusing on a specific region?
- Define the inclusion and exclusion criteria. What types of sources will you include? Are there specific types of studies or publications you will exclude?
Select Databases for Searches:
- Identify relevant databases for your field. Examples include PubMed, IEEE Xplore, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar.
- Consider searching in library catalogs, institutional repositories, and specialized databases related to your topic.
Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Develop a systematic search strategy using keywords, Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT), and other search techniques.
- Record and document your search strategy for transparency and replicability.
- Keep track of the articles, including publication details, abstracts, and links. Use citation management tools like EndNote, Zotero, or Mendeley to organize your references.
Review the Literature:
- Evaluate the relevance and quality of each source. Consider the methodology, sample size, and results of studies.
- Organize the literature by themes or key concepts. Identify patterns, trends, and gaps in the existing research.
- Summarize key findings and arguments from each source. Compare and contrast different perspectives.
- Identify areas where there is a consensus in the literature and where there are conflicting opinions.
- Provide critical analysis and synthesis of the literature. What are the strengths and weaknesses of existing research?
Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Literature review outline should be based on themes, chronological order, or methodological approaches.
- Write a clear and coherent narrative that synthesizes the information gathered.
- Use proper citations for each source and ensure consistency in your citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
- Conclude your literature review by summarizing key findings, identifying gaps, and suggesting areas for future research.
The literature review sample and detailed advice on writing and conducting a review will help you produce a well-structured report. But remember that a literature review is an ongoing process, and it may be necessary to revisit and update it as your research progresses.
Frequently asked questions
A literature review is a critical and comprehensive analysis of existing literature (published and unpublished works) on a specific topic or research question and provides a synthesis of the current state of knowledge in a particular field. A well-conducted literature review is crucial for researchers to build upon existing knowledge, avoid duplication of efforts, and contribute to the advancement of their field. It also helps researchers situate their work within a broader context and facilitates the development of a sound theoretical and conceptual framework for their studies.
Literature review is a crucial component of research writing, providing a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. The aim is to keep professionals up to date by providing an understanding of ongoing developments within a specific field, including research methods, and experimental techniques used in that field, and present that knowledge in the form of a written report. Also, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the scholar in his or her field.
Before writing a literature review, it’s essential to undertake several preparatory steps to ensure that your review is well-researched, organized, and focused. This includes choosing a topic of general interest to you and doing exploratory research on that topic, writing an annotated bibliography, and noting major points, especially those that relate to the position you have taken on the topic.
Literature reviews and academic research papers are essential components of scholarly work but serve different purposes within the academic realm. 3 A literature review aims to provide a foundation for understanding the current state of research on a particular topic, identify gaps or controversies, and lay the groundwork for future research. Therefore, it draws heavily from existing academic sources, including books, journal articles, and other scholarly publications. In contrast, an academic research paper aims to present new knowledge, contribute to the academic discourse, and advance the understanding of a specific research question. Therefore, it involves a mix of existing literature (in the introduction and literature review sections) and original data or findings obtained through research methods.
Literature reviews are essential components of academic and research papers, and various strategies can be employed to conduct them effectively. If you want to know how to write a literature review for a research paper, here are four common approaches that are often used by researchers. Chronological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the chronological order of publication. It helps to trace the development of a topic over time, showing how ideas, theories, and research have evolved. Thematic Review: Thematic reviews focus on identifying and analyzing themes or topics that cut across different studies. Instead of organizing the literature chronologically, it is grouped by key themes or concepts, allowing for a comprehensive exploration of various aspects of the topic. Methodological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the research methods employed in different studies. It helps to highlight the strengths and weaknesses of various methodologies and allows the reader to evaluate the reliability and validity of the research findings. Theoretical Review: A theoretical review examines the literature based on the theoretical frameworks used in different studies. This approach helps to identify the key theories that have been applied to the topic and assess their contributions to the understanding of the subject. It’s important to note that these strategies are not mutually exclusive, and a literature review may combine elements of more than one approach. The choice of strategy depends on the research question, the nature of the literature available, and the goals of the review. Additionally, other strategies, such as integrative reviews or systematic reviews, may be employed depending on the specific requirements of the research.
The literature review format can vary depending on the specific publication guidelines. However, there are some common elements and structures that are often followed. Here is a general guideline for the format of a literature review: Introduction: Provide an overview of the topic. Define the scope and purpose of the literature review. State the research question or objective. Body: Organize the literature by themes, concepts, or chronology. Critically analyze and evaluate each source. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the studies. Highlight any methodological limitations or biases. Identify patterns, connections, or contradictions in the existing research. Conclusion: Summarize the key points discussed in the literature review. Highlight the research gap. Address the research question or objective stated in the introduction. Highlight the contributions of the review and suggest directions for future research.
Both annotated bibliographies and literature reviews involve the examination of scholarly sources. While annotated bibliographies focus on individual sources with brief annotations, literature reviews provide a more in-depth, integrated, and comprehensive analysis of existing literature on a specific topic. The key differences are as follows:
References
- Denney, A. S., & Tewksbury, R. (2013). How to write a literature review. Journal of criminal justice education , 24 (2), 218-234.
- Pan, M. L. (2016). Preparing literature reviews: Qualitative and quantitative approaches . Taylor & Francis.
- Cantero, C. (2019). How to write a literature review. San José State University Writing Center .
Paperpal is an AI writing assistant that help academics write better, faster with real-time suggestions for in-depth language and grammar correction. Trained on millions of research manuscripts enhanced by professional academic editors, Paperpal delivers human precision at machine speed.
Try it for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime , which unlocks unlimited access to premium features like academic translation, paraphrasing, contextual synonyms, consistency checks and more. It’s like always having a professional academic editor by your side! Go beyond limitations and experience the future of academic writing. Get Paperpal Prime now at just US$19 a month!
Related Reads:
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
- How to Write a Scientific Paper in 10 Steps
- Life Sciences Papers: 9 Tips for Authors Writing in Biological Sciences
- What is an Argumentative Essay? How to Write It (With Examples)
6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how to avoid it, you may also like, ai + human expertise – a paradigm shift..., how to use paperpal to generate emails &..., ai in education: it’s time to change the..., is it ethical to use ai-generated abstracts without..., do plagiarism checkers detect ai content, word choice problems: how to use the right..., how to avoid plagiarism when using generative ai..., what are journal guidelines on using generative ai..., types of plagiarism and 6 tips to avoid..., how to write an essay introduction (with examples)....
- University of Oregon Libraries
- Research Guides
How to Write a Literature Review
Who is my subject librarian.
- Literature Reviews: A Recap
- Reading Journal Articles
- Does it Describe a Literature Review?
- 1. Identify the Question
- 2. Review Discipline Styles
- Searching Article Databases
- Finding Full-Text of an Article
- Citation Chaining
- When to Stop Searching
- 4. Manage Your References
- 5. Critically Analyze and Evaluate
- 6. Synthesize
- 7. Write a Literature Review
This guide has a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike (CC BY-NC-SA) License.

This license lets others remix, tweak, and build upon your work non-commercially, as long as they credit you and license their new creations under the identical terms.
- Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0) License Deed
This guide is organized around the 7 steps in the graphic to the left to help you understand the process of writing a literature review.
This guide will help you to
- Define a literature review
- Recognize that different fields of study have their own way to perform and write literature reviews
- Prepare to search the literature
- Read critically -- analyze and synthesize
- Prepare to write a literature review
At the end of the tutorial, you will find a quiz that you can submit through Canvas for course credit.
Graphic from Literature Review (2009) by Machi and McEvoy.
Text description of "Literature Review Process" for web accessibility
If you have questions related to a field or discipline, consider reaching out to a Subject Librarian by email, phone, or by scheduling an appointment for a free consultation:
- Subject Librarians
- Next: What's a Literature Review? >>
- Last Updated: Jan 10, 2024 4:46 PM
- URL: https://researchguides.uoregon.edu/litreview
Contact Us Library Accessibility UO Libraries Privacy Notices and Procedures

1501 Kincaid Street Eugene, OR 97403 P: 541-346-3053 F: 541-346-3485
- Visit us on Facebook
- Visit us on Twitter
- Visit us on Youtube
- Visit us on Instagram
- Report a Concern
- Nondiscrimination and Title IX
- Accessibility
- Privacy Policy
- Find People
News alert: UC Berkeley has announced its next university librarian
Secondary menu
- Log in to your Library account
- Hours and Maps
- Connect from Off Campus
- UC Berkeley Home
Search form
Conducting a literature review: how to find "the literature".
- Why Do A Literature Review?
- How To Find "The Literature"
- Found it -- Now What?
Finding The Literature
Research literature is vast. In the English language alone, over 2.5 million articles are published in peer reviewed journals each year . Sifting through the books and journals to find the most relevant research is challenging, but some of the resources on this page can help you.
To start, write down your research question and think about all the ways it could be described. (A thesaurus - online or in a database , can be helpful!) Think about the approach you are taking -- are you looking at it through the lens of Social Work? Is it also related to other fields, for example, Public Health, Education, Ethnic Studies? What research methods will you use -- how will you research the problem, or evaluate the intervention or policy to address it?
Subject Databases Can Help Find Articles
Powerful features vary by database, but many include the ability to:
- Combine search terms using AND and OR
- Search for exact phrases by using quotation marks " "
- Use controlled vocabulary (Thesaurus)
- Find material organized within a discipline -- law or policy, for example.
- Search by "fields" such as author, journal name, title
- Restrict by the age of the subject (infants vs. very old)
- Limit by research method (including literature reviews!)
Snowballing aka Citation Slogging
If an article is relevant to your topic, you want to look at the research it cited ( backward citation ). But it can also be very helpful to see who has cited it ( forward citation ). There are several different ways to do this, and the results will overlap -- no single method is comprehensive.
Google Scholar provides forward citations for some articles. It has a broader range of documents included (not just peer reviewed journals, but reports, pre-prints, etc.) and doesn't eliminate self citation or de-duplicate the results.
ISI Web of Science contains the Social Science Citation Index which allows you to do a "Cited Reference" search. This shows other articles (from a prestigious list of peer reviewed journals) which have cited the target article, and it also shows the references for the the original article... both forward and backward citation.
Screenshot below on how to get to the Cited Reference Search from the Social Science Citation Index .

Cited References From Within a Database

Using the Cited Reference Search

Oxford Bibliographies -- Great Starting Point for Social Welfare!
Oxford Bibliographies Online: Social Work -- leading social work scholars identify the most important and significant sources in their areas, and UC-elinks gets you to the cited articles and books.

Snowballing

http://hlwiki.slais.ubc.ca/index.php/Snowballing
- << Previous: Why Do A Literature Review?
- Next: Found it -- Now What? >>
- Last Updated: Dec 8, 2023 10:11 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.berkeley.edu/litreview

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
2.3 Reviewing the Research Literature
Learning objectives.
- Define the research literature in psychology and give examples of sources that are part of the research literature and sources that are not.
- Describe and use several methods for finding previous research on a particular research idea or question.
Reviewing the research literature means finding, reading, and summarizing the published research relevant to your question. An empirical research report written in American Psychological Association (APA) style always includes a written literature review, but it is important to review the literature early in the research process for several reasons.
- It can help you turn a research idea into an interesting research question.
- It can tell you if a research question has already been answered.
- It can help you evaluate the interestingness of a research question.
- It can give you ideas for how to conduct your own study.
- It can tell you how your study fits into the research literature.
What Is the Research Literature?
The research literature in any field is all the published research in that field. The research literature in psychology is enormous—including millions of scholarly articles and books dating to the beginning of the field—and it continues to grow. Although its boundaries are somewhat fuzzy, the research literature definitely does not include self-help and other pop psychology books, dictionary and encyclopedia entries, websites, and similar sources that are intended mainly for the general public. These are considered unreliable because they are not reviewed by other researchers and are often based on little more than common sense or personal experience. Wikipedia contains much valuable information, but the fact that its authors are anonymous and its content continually changes makes it unsuitable as a basis of sound scientific research. For our purposes, it helps to define the research literature as consisting almost entirely of two types of sources: articles in professional journals, and scholarly books in psychology and related fields.
Professional Journals
Professional journals are periodicals that publish original research articles. There are thousands of professional journals that publish research in psychology and related fields. They are usually published monthly or quarterly in individual issues, each of which contains several articles. The issues are organized into volumes, which usually consist of all the issues for a calendar year. Some journals are published in hard copy only, others in both hard copy and electronic form, and still others in electronic form only.
Most articles in professional journals are one of two basic types: empirical research reports and review articles. Empirical research reports describe one or more new empirical studies conducted by the authors. They introduce a research question, explain why it is interesting, review previous research, describe their method and results, and draw their conclusions. Review articles summarize previously published research on a topic and usually present new ways to organize or explain the results. When a review article is devoted primarily to presenting a new theory, it is often referred to as a theoretical article .
Figure 2.6 Small Sample of the Thousands of Professional Journals That Publish Research in Psychology and Related Fields

Most professional journals in psychology undergo a process of peer review . Researchers who want to publish their work in the journal submit a manuscript to the editor—who is generally an established researcher too—who in turn sends it to two or three experts on the topic. Each reviewer reads the manuscript, writes a critical review, and sends the review back to the editor along with his or her recommendations. The editor then decides whether to accept the article for publication, ask the authors to make changes and resubmit it for further consideration, or reject it outright. In any case, the editor forwards the reviewers’ written comments to the researchers so that they can revise their manuscript accordingly. Peer review is important because it ensures that the work meets basic standards of the field before it can enter the research literature.
Scholarly Books
Scholarly books are books written by researchers and practitioners mainly for use by other researchers and practitioners. A monograph is written by a single author or a small group of authors and usually gives a coherent presentation of a topic much like an extended review article. Edited volumes have an editor or a small group of editors who recruit many authors to write separate chapters on different aspects of the same topic. Although edited volumes can also give a coherent presentation of the topic, it is not unusual for each chapter to take a different perspective or even for the authors of different chapters to openly disagree with each other. In general, scholarly books undergo a peer review process similar to that used by professional journals.
Literature Search Strategies
Using psycinfo and other databases.
The primary method used to search the research literature involves using one or more electronic databases. These include Academic Search Premier, JSTOR, and ProQuest for all academic disciplines, ERIC for education, and PubMed for medicine and related fields. The most important for our purposes, however, is PsycINFO , which is produced by the APA. PsycINFO is so comprehensive—covering thousands of professional journals and scholarly books going back more than 100 years—that for most purposes its content is synonymous with the research literature in psychology. Like most such databases, PsycINFO is usually available through your college or university library.
PsycINFO consists of individual records for each article, book chapter, or book in the database. Each record includes basic publication information, an abstract or summary of the work, and a list of other works cited by that work. A computer interface allows entering one or more search terms and returns any records that contain those search terms. (These interfaces are provided by different vendors and therefore can look somewhat different depending on the library you use.) Each record also contains lists of keywords that describe the content of the work and also a list of index terms. The index terms are especially helpful because they are standardized. Research on differences between women and men, for example, is always indexed under “Human Sex Differences.” Research on touching is always indexed under the term “Physical Contact.” If you do not know the appropriate index terms, PsycINFO includes a thesaurus that can help you find them.
Given that there are nearly three million records in PsycINFO, you may have to try a variety of search terms in different combinations and at different levels of specificity before you find what you are looking for. Imagine, for example, that you are interested in the question of whether women and men differ in terms of their ability to recall experiences from when they were very young. If you were to enter “memory for early experiences” as your search term, PsycINFO would return only six records, most of which are not particularly relevant to your question. However, if you were to enter the search term “memory,” it would return 149,777 records—far too many to look through individually. This is where the thesaurus helps. Entering “memory” into the thesaurus provides several more specific index terms—one of which is “early memories.” While searching for “early memories” among the index terms returns 1,446 records—still too many too look through individually—combining it with “human sex differences” as a second search term returns 37 articles, many of which are highly relevant to the topic.
Depending on the vendor that provides the interface to PsycINFO, you may be able to save, print, or e-mail the relevant PsycINFO records. The records might even contain links to full-text copies of the works themselves. (PsycARTICLES is a database that provides full-text access to articles in all journals published by the APA.) If not, and you want a copy of the work, you will have to find out if your library carries the journal or has the book and the hard copy on the library shelves. Be sure to ask a librarian if you need help.
Using Other Search Techniques
In addition to entering search terms into PsycINFO and other databases, there are several other techniques you can use to search the research literature. First, if you have one good article or book chapter on your topic—a recent review article is best—you can look through the reference list of that article for other relevant articles, books, and book chapters. In fact, you should do this with any relevant article or book chapter you find. You can also start with a classic article or book chapter on your topic, find its record in PsycINFO (by entering the author’s name or article’s title as a search term), and link from there to a list of other works in PsycINFO that cite that classic article. This works because other researchers working on your topic are likely to be aware of the classic article and cite it in their own work. You can also do a general Internet search using search terms related to your topic or the name of a researcher who conducts research on your topic. This might lead you directly to works that are part of the research literature (e.g., articles in open-access journals or posted on researchers’ own websites). The search engine Google Scholar is especially useful for this purpose. A general Internet search might also lead you to websites that are not part of the research literature but might provide references to works that are. Finally, you can talk to people (e.g., your instructor or other faculty members in psychology) who know something about your topic and can suggest relevant articles and book chapters.
What to Search For
When you do a literature review, you need to be selective. Not every article, book chapter, and book that relates to your research idea or question will be worth obtaining, reading, and integrating into your review. Instead, you want to focus on sources that help you do four basic things: (a) refine your research question, (b) identify appropriate research methods, (c) place your research in the context of previous research, and (d) write an effective research report. Several basic principles can help you find the most useful sources.
First, it is best to focus on recent research, keeping in mind that what counts as recent depends on the topic. For newer topics that are actively being studied, “recent” might mean published in the past year or two. For older topics that are receiving less attention right now, “recent” might mean within the past 10 years. You will get a feel for what counts as recent for your topic when you start your literature search. A good general rule, however, is to start with sources published in the past five years. The main exception to this rule would be classic articles that turn up in the reference list of nearly every other source. If other researchers think that this work is important, even though it is old, then by all means you should include it in your review.
Second, you should look for review articles on your topic because they will provide a useful overview of it—often discussing important definitions, results, theories, trends, and controversies—giving you a good sense of where your own research fits into the literature. You should also look for empirical research reports addressing your question or similar questions, which can give you ideas about how to operationally define your variables and collect your data. As a general rule, it is good to use methods that others have already used successfully unless you have good reasons not to. Finally, you should look for sources that provide information that can help you argue for the interestingness of your research question. For a study on the effects of cell phone use on driving ability, for example, you might look for information about how widespread cell phone use is, how frequent and costly motor vehicle crashes are, and so on.
How many sources are enough for your literature review? This is a difficult question because it depends on how extensively your topic has been studied and also on your own goals. One study found that across a variety of professional journals in psychology, the average number of sources cited per article was about 50 (Adair & Vohra, 2003). This gives a rough idea of what professional researchers consider to be adequate. As a student, you might be assigned a much lower minimum number of references to use, but the principles for selecting the most useful ones remain the same.
Key Takeaways
- The research literature in psychology is all the published research in psychology, consisting primarily of articles in professional journals and scholarly books.
- Early in the research process, it is important to conduct a review of the research literature on your topic to refine your research question, identify appropriate research methods, place your question in the context of other research, and prepare to write an effective research report.
- There are several strategies for finding previous research on your topic. Among the best is using PsycINFO, a computer database that catalogs millions of articles, books, and book chapters in psychology and related fields.
- Practice: Use the techniques discussed in this section to find 10 journal articles and book chapters on one of the following research ideas: memory for smells, aggressive driving, the causes of narcissistic personality disorder, the functions of the intraparietal sulcus, or prejudice against the physically handicapped.
Adair, J. G., & Vohra, N. (2003). The explosion of knowledge, references, and citations: Psychology’s unique response to a crisis. American Psychologist, 58 , 15–23.
Research Methods in Psychology Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Log in using your username and password
- Search More Search for this keyword Advanced search
- Latest content
- Current issue
- Write for Us
- BMJ Journals More You are viewing from: Google Indexer
You are here
- Volume 24, Issue 2
- Five tips for developing useful literature summary tables for writing review articles
- Article Text
- Article info
- Citation Tools
- Rapid Responses
- Article metrics
- http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0157-5319 Ahtisham Younas 1 , 2 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7839-8130 Parveen Ali 3 , 4
- 1 Memorial University of Newfoundland , St John's , Newfoundland , Canada
- 2 Swat College of Nursing , Pakistan
- 3 School of Nursing and Midwifery , University of Sheffield , Sheffield , South Yorkshire , UK
- 4 Sheffield University Interpersonal Violence Research Group , Sheffield University , Sheffield , UK
- Correspondence to Ahtisham Younas, Memorial University of Newfoundland, St John's, NL A1C 5C4, Canada; ay6133{at}mun.ca
https://doi.org/10.1136/ebnurs-2021-103417
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Request permissions.
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the link below which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center’s RightsLink service. You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways.
Introduction
Literature reviews offer a critical synthesis of empirical and theoretical literature to assess the strength of evidence, develop guidelines for practice and policymaking, and identify areas for future research. 1 It is often essential and usually the first task in any research endeavour, particularly in masters or doctoral level education. For effective data extraction and rigorous synthesis in reviews, the use of literature summary tables is of utmost importance. A literature summary table provides a synopsis of an included article. It succinctly presents its purpose, methods, findings and other relevant information pertinent to the review. The aim of developing these literature summary tables is to provide the reader with the information at one glance. Since there are multiple types of reviews (eg, systematic, integrative, scoping, critical and mixed methods) with distinct purposes and techniques, 2 there could be various approaches for developing literature summary tables making it a complex task specialty for the novice researchers or reviewers. Here, we offer five tips for authors of the review articles, relevant to all types of reviews, for creating useful and relevant literature summary tables. We also provide examples from our published reviews to illustrate how useful literature summary tables can be developed and what sort of information should be provided.
Tip 1: provide detailed information about frameworks and methods
- Download figure
- Open in new tab
- Download powerpoint
Tabular literature summaries from a scoping review. Source: Rasheed et al . 3
The provision of information about conceptual and theoretical frameworks and methods is useful for several reasons. First, in quantitative (reviews synthesising the results of quantitative studies) and mixed reviews (reviews synthesising the results of both qualitative and quantitative studies to address a mixed review question), it allows the readers to assess the congruence of the core findings and methods with the adapted framework and tested assumptions. In qualitative reviews (reviews synthesising results of qualitative studies), this information is beneficial for readers to recognise the underlying philosophical and paradigmatic stance of the authors of the included articles. For example, imagine the authors of an article, included in a review, used phenomenological inquiry for their research. In that case, the review authors and the readers of the review need to know what kind of (transcendental or hermeneutic) philosophical stance guided the inquiry. Review authors should, therefore, include the philosophical stance in their literature summary for the particular article. Second, information about frameworks and methods enables review authors and readers to judge the quality of the research, which allows for discerning the strengths and limitations of the article. For example, if authors of an included article intended to develop a new scale and test its psychometric properties. To achieve this aim, they used a convenience sample of 150 participants and performed exploratory (EFA) and confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) on the same sample. Such an approach would indicate a flawed methodology because EFA and CFA should not be conducted on the same sample. The review authors must include this information in their summary table. Omitting this information from a summary could lead to the inclusion of a flawed article in the review, thereby jeopardising the review’s rigour.
Tip 2: include strengths and limitations for each article
Critical appraisal of individual articles included in a review is crucial for increasing the rigour of the review. Despite using various templates for critical appraisal, authors often do not provide detailed information about each reviewed article’s strengths and limitations. Merely noting the quality score based on standardised critical appraisal templates is not adequate because the readers should be able to identify the reasons for assigning a weak or moderate rating. Many recent critical appraisal checklists (eg, Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool) discourage review authors from assigning a quality score and recommend noting the main strengths and limitations of included studies. It is also vital that methodological and conceptual limitations and strengths of the articles included in the review are provided because not all review articles include empirical research papers. Rather some review synthesises the theoretical aspects of articles. Providing information about conceptual limitations is also important for readers to judge the quality of foundations of the research. For example, if you included a mixed-methods study in the review, reporting the methodological and conceptual limitations about ‘integration’ is critical for evaluating the study’s strength. Suppose the authors only collected qualitative and quantitative data and did not state the intent and timing of integration. In that case, the strength of the study is weak. Integration only occurred at the levels of data collection. However, integration may not have occurred at the analysis, interpretation and reporting levels.
Tip 3: write conceptual contribution of each reviewed article
While reading and evaluating review papers, we have observed that many review authors only provide core results of the article included in a review and do not explain the conceptual contribution offered by the included article. We refer to conceptual contribution as a description of how the article’s key results contribute towards the development of potential codes, themes or subthemes, or emerging patterns that are reported as the review findings. For example, the authors of a review article noted that one of the research articles included in their review demonstrated the usefulness of case studies and reflective logs as strategies for fostering compassion in nursing students. The conceptual contribution of this research article could be that experiential learning is one way to teach compassion to nursing students, as supported by case studies and reflective logs. This conceptual contribution of the article should be mentioned in the literature summary table. Delineating each reviewed article’s conceptual contribution is particularly beneficial in qualitative reviews, mixed-methods reviews, and critical reviews that often focus on developing models and describing or explaining various phenomena. Figure 2 offers an example of a literature summary table. 4
Tabular literature summaries from a critical review. Source: Younas and Maddigan. 4
Tip 4: compose potential themes from each article during summary writing
While developing literature summary tables, many authors use themes or subthemes reported in the given articles as the key results of their own review. Such an approach prevents the review authors from understanding the article’s conceptual contribution, developing rigorous synthesis and drawing reasonable interpretations of results from an individual article. Ultimately, it affects the generation of novel review findings. For example, one of the articles about women’s healthcare-seeking behaviours in developing countries reported a theme ‘social-cultural determinants of health as precursors of delays’. Instead of using this theme as one of the review findings, the reviewers should read and interpret beyond the given description in an article, compare and contrast themes, findings from one article with findings and themes from another article to find similarities and differences and to understand and explain bigger picture for their readers. Therefore, while developing literature summary tables, think twice before using the predeveloped themes. Including your themes in the summary tables (see figure 1 ) demonstrates to the readers that a robust method of data extraction and synthesis has been followed.
Tip 5: create your personalised template for literature summaries
Often templates are available for data extraction and development of literature summary tables. The available templates may be in the form of a table, chart or a structured framework that extracts some essential information about every article. The commonly used information may include authors, purpose, methods, key results and quality scores. While extracting all relevant information is important, such templates should be tailored to meet the needs of the individuals’ review. For example, for a review about the effectiveness of healthcare interventions, a literature summary table must include information about the intervention, its type, content timing, duration, setting, effectiveness, negative consequences, and receivers and implementers’ experiences of its usage. Similarly, literature summary tables for articles included in a meta-synthesis must include information about the participants’ characteristics, research context and conceptual contribution of each reviewed article so as to help the reader make an informed decision about the usefulness or lack of usefulness of the individual article in the review and the whole review.
In conclusion, narrative or systematic reviews are almost always conducted as a part of any educational project (thesis or dissertation) or academic or clinical research. Literature reviews are the foundation of research on a given topic. Robust and high-quality reviews play an instrumental role in guiding research, practice and policymaking. However, the quality of reviews is also contingent on rigorous data extraction and synthesis, which require developing literature summaries. We have outlined five tips that could enhance the quality of the data extraction and synthesis process by developing useful literature summaries.
- Aromataris E ,
- Rasheed SP ,
Twitter @Ahtisham04, @parveenazamali
Funding The authors have not declared a specific grant for this research from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Competing interests None declared.
Patient consent for publication Not required.
Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Read the full text or download the PDF:
CPS Online Library Research Guide (UNH Manchester Library): Create a Literature Review
- Home & Table of Contents
- Different Types of Information
- The Savvy Information Consumer
- Primary & Secondary Sources
- Periodical Literature
- Peer Review
- Research Glossary
- Business Research Databases
- Understanding the Assignment
- Preliminary Considerations
- 7 Steps to Completing a Research Assignment
- Define the Topic
- Find & Evaluate Your Sources
- Research Integrity & Citing Your Sources
- Searching for Information
- Evaluating Information
- How to Read an Academic Journal Article This link opens in a new window
- Evaluating Social Media Sources
- Writing Your Research Paper
- Create a Literature Review
- Summarize an Article
- How to Write an Abstract
- How to Write a Book Review
- How to Do an Annotated Bibliography
- Finding Professional Organizations
- Find Key Journals in Your Field of Study
- Find Peer-Reviewed Articles
- Write a Research Paper Proposal
- Research a Company This link opens in a new window
- Citing Your Sources
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- NHCUC Libraries
- Other Types of Research
- Academic Libraries in NH
- Government Documents
- Using Google for Academic Research
- Information Literacy
- Developing Effective Library Research Assignments
- Using Permalinks
- Primary Source Websites
What is a literature review?
A literature review discusses published information in a particular subject area, and sometimes information in a particular subject area within a certain time period.
A literature review can be just a simple summary of the sources, but it usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis. A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information. It might give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations. Or it might trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates. And depending on the situation, the literature review may evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant.
But how is a literature review different from an academic research paper?
The main focus of an academic research paper is to develop a new argument, and a research paper is likely to contain a literature review as one of its parts. In a research paper, you use the literature as a foundation and as support for a new insight that you contribute. The focus of a literature review, however, is to summarize and synthesize the arguments and ideas of others without adding new contributions.
Why do we write literature reviews?
Literature reviews provide you with a handy guide to a particular topic. If you have limited time to conduct research, literature reviews can give you an overview or act as a stepping stone. For professionals, they are useful reports that keep them up to date with what is current in the field. For scholars, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the writer in his or her field. Literature reviews also provide a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. Comprehensive knowledge of the literature of the field is essential to most research papers.
Strategies for writing the literature review
Find a focus.
A literature review, like a term paper, is usually organized around ideas, not the sources themselves as an annotated bibliography would be organized. This means that you will not just simply list your sources and go into detail about each one of them, one at a time. No. As you read widely but selectively in your topic area, consider instead what themes or issues connect your sources together. Do they present one or different solutions? Is there an aspect of the field that is missing? How well do they present the material and do they portray it according to an appropriate theory? Do they reveal a trend in the field? A raging debate? Pick one of these themes to focus the organization of your review.
Convey it to your reader
A literature review may not have a traditional thesis statement (one that makes an argument), but you do need to tell readers what to expect. Try writing a simple statement that lets the reader know what is your main organizing principle. Here are a couple of examples:
The current trend in treatment for congestive heart failure combines surgery and medicine.
More and more cultural studies scholars are accepting popular media as a subject worthy of academic consideration.
Consider organization
You’ve got a focus, and you’ve stated it clearly and directly. Now what is the most effective way of presenting the information? What are the most important topics, subtopics, etc ., that your review needs to include? And in what order should you present them? Develop an organization for your review at both a global and local level:
First, cover the basic categories
Just like most academic papers, literature reviews are likely to contain at least three basic elements: an introduction or background information section; the body of the review containing the discussion of sources; and, finally, a conclusion and/or recommendations section to end the paper. The following provides a brief description of the content of each:
- Introduction: Gives a quick idea of the topic of the literature review, such as the central theme or organizational pattern.
- Body: Contains your discussion of sources and is organized either chronologically, thematically, or methodologically (see below for more information on each).
- Conclusions/Recommendations: Discuss what you have drawn from reviewing literature so far. Where might the discussion proceed?
Organizing the body
Once you have the basic categories in place, then you must consider how you will present the sources themselves within the body of your paper. Create an organizational method to focus this section even further.
To help you come up with an overall organizational framework for your review, consider the following scenario:
You’ve decided to focus your literature review on materials dealing with sperm whales. This is because you’ve just finished reading Moby Dick, and you wonder if that whale’s portrayal is really real. You start with some articles about the physiology of sperm whales in biology journals written in the 1980’s. But these articles refer to some British biological studies performed on whales in the early 18th century. So you check those out. Then you look up a book written in 1968 with information on how sperm whales have been portrayed in other forms of art, such as in Alaskan poetry, in French painting, or on whale bone, as the whale hunters in the late 19th century used to do. This makes you wonder about American whaling methods during the time portrayed in Moby Dick, so you find some academic articles published in the last five years on how accurately Herman Melville portrayed the whaling scene in his novel.
Now consider some typical ways of organizing the sources into a review:
- Chronological: If your review follows the chronological method, you could write about the materials above according to when they were published. For instance, first you would talk about the British biological studies of the 18th century, then about Moby Dick, published in 1851, then the book on sperm whales in other art (1968), and finally the biology articles (1980s) and the recent articles on American whaling of the 19th century. But there is relatively no continuity among subjects here. And notice that even though the sources on sperm whales in other art and on American whaling are written recently, they are about other subjects/objects that were created much earlier. Thus, the review loses its chronological focus.
- By publication: Order your sources by publication chronology, then, only if the order demonstrates a more important trend. For instance, you could order a review of literature on biological studies of sperm whales if the progression revealed a change in dissection practices of the researchers who wrote and/or conducted the studies.
- By trend: A better way to organize the above sources chronologically is to examine the sources under another trend, such as the history of whaling. Then your review would have subsections according to eras within this period. For instance, the review might examine whaling from pre-1600-1699, 1700-1799, and 1800-1899. Under this method, you would combine the recent studies on American whaling in the 19th century with Moby Dick itself in the 1800-1899 category, even though the authors wrote a century apart.
- Thematic: Thematic reviews of literature are organized around a topic or issue, rather than the progression of time. However, progression of time may still be an important factor in a thematic review. For instance, the sperm whale review could focus on the development of the harpoon for whale hunting. While the study focuses on one topic, harpoon technology, it will still be organized chronologically. The only difference here between a “chronological” and a “thematic” approach is what is emphasized the most: the development of the harpoon or the harpoon technology.But more authentic thematic reviews tend to break away from chronological order. For instance, a thematic review of material on sperm whales might examine how they are portrayed as “evil” in cultural documents. The subsections might include how they are personified, how their proportions are exaggerated, and their behaviors misunderstood. A review organized in this manner would shift between time periods within each section according to the point made.
- Methodological: A methodological approach differs from the two above in that the focusing factor usually does not have to do with the content of the material. Instead, it focuses on the “methods” of the researcher or writer. For the sperm whale project, one methodological approach would be to look at cultural differences between the portrayal of whales in American, British, and French art work. Or the review might focus on the economic impact of whaling on a community. A methodological scope will influence either the types of documents in the review or the way in which these documents are discussed. Once you’ve decided on the organizational method for the body of the review, the sections you need to include in the paper should be easy to figure out. They should arise out of your organizational strategy. In other words, a chronological review would have subsections for each vital time period. A thematic review would have subtopics based upon factors that relate to the theme or issue.
Sometimes, though, you might need to add additional sections that are necessary for your study, but do not fit in the organizational strategy of the body. What other sections you include in the body is up to you. Put in only what is necessary. Here are a few other sections you might want to consider:
- Current Situation: Information necessary to understand the topic or focus of the literature review.
- History: The chronological progression of the field, the literature, or an idea that is necessary to understand the literature review, if the body of the literature review is not already a chronology.
- Methods and/or Standards: The criteria you used to select the sources in your literature review or the way in which you present your information. For instance, you might explain that your review includes only peer-reviewed articles and journals.
Questions for Further Research: What questions about the field has the review sparked? How will you further your research as a result of the review?
Attribution
"Create a Literature Review" is derivative of Literature Reviews by The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill licensed Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 4.0 License .
- << Previous: Other Types of Research Assignments
- Next: Summarize an Article >>
- Last Updated: Apr 9, 2024 2:30 PM
- URL: https://libraryguides.unh.edu/CPSonlineLibraryResearch
How to undertake a literature search: a step-by-step guide
Affiliation.
- 1 Literature Search Specialist, Library and Archive Service, Royal College of Nursing, London.
- PMID: 32279549
- DOI: 10.12968/bjon.2020.29.7.431
Undertaking a literature search can be a daunting prospect. Breaking the exercise down into smaller steps will make the process more manageable. This article suggests 10 steps that will help readers complete this task, from identifying key concepts to choosing databases for the search and saving the results and search strategy. It discusses each of the steps in a little more detail, with examples and suggestions on where to get help. This structured approach will help readers obtain a more focused set of results and, ultimately, save time and effort.
Keywords: Databases; Literature review; Literature search; Reference management software; Research questions; Search strategy.
- Databases, Bibliographic*
- Information Storage and Retrieval / methods*
- Nursing Research
- Review Literature as Topic*
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Med Libr Assoc
- v.106(4); 2018 Oct
A systematic approach to searching: an efficient and complete method to develop literature searches
Associated data.
Creating search strategies for systematic reviews, finding the best balance between sensitivity and specificity, and translating search strategies between databases is challenging. Several methods describe standards for systematic search strategies, but a consistent approach for creating an exhaustive search strategy has not yet been fully described in enough detail to be fully replicable. The authors have established a method that describes step by step the process of developing a systematic search strategy as needed in the systematic review. This method describes how single-line search strategies can be prepared in a text document by typing search syntax (such as field codes, parentheses, and Boolean operators) before copying and pasting search terms (keywords and free-text synonyms) that are found in the thesaurus. To help ensure term completeness, we developed a novel optimization technique that is mainly based on comparing the results retrieved by thesaurus terms with those retrieved by the free-text search words to identify potentially relevant candidate search terms. Macros in Microsoft Word have been developed to convert syntaxes between databases and interfaces almost automatically. This method helps information specialists in developing librarian-mediated searches for systematic reviews as well as medical and health care practitioners who are searching for evidence to answer clinical questions. The described method can be used to create complex and comprehensive search strategies for different databases and interfaces, such as those that are needed when searching for relevant references for systematic reviews, and will assist both information specialists and practitioners when they are searching the biomedical literature.
INTRODUCTION
Librarians and information specialists are often involved in the process of preparing and completing systematic reviews (SRs), where one of their main tasks is to identify relevant references to include in the review [ 1 ]. Although several recommendations for the process of searching have been published [ 2 – 6 ], none describe the development of a systematic search strategy from start to finish.
Traditional methods of SR search strategy development and execution are highly time consuming, reportedly requiring up to 100 hours or more [ 7 , 8 ]. The authors wanted to develop systematic and exhaustive search strategies more efficiently, while preserving the high sensitivity that SR search strategies necessitate. In this article, we describe the method developed at Erasmus University Medical Center (MC) and demonstrate its use through an example search. The efficiency of the search method and outcome of 73 searches that have resulted in published reviews are described in a separate article [ 9 ].
As we aimed to describe the creation of systematic searches in full detail, the method starts at a basic level with the analysis of the research question and the creation of search terms. Readers who are new to SR searching are advised to follow all steps described. More experienced searchers can consider the basic steps to be existing knowledge that will already be part of their normal workflow, although step 4 probably differs from general practice. Experienced searchers will gain the most from reading about the novelties in the method as described in steps 10–13 and comparing the examples given in the supplementary appendix to their own practice.
CREATING A SYSTEMATIC SEARCH STRATEGY
Our methodology for planning and creating a multi-database search strategy consists of the following steps:
- Determine a clear and focused question
- Describe the articles that can answer the question
- Decide which key concepts address the different elements of the question
- Decide which elements should be used for the best results
- Choose an appropriate database and interface to start with
- Document the search process in a text document
- Identify appropriate index terms in the thesaurus of the first database
- Identify synonyms in the thesaurus
- Add variations in search terms
- Use database-appropriate syntax, with parentheses, Boolean operators, and field codes
- Optimize the search
- Evaluate the initial results
- Check for errors
- Translate to other databases
- Test and reiterate
Each step in the process is reflected by an example search described in the supplementary appendix .
1. Determine a clear and focused question
A systematic search can best be applied to a well-defined and precise research or clinical question. Questions that are too broad or too vague cannot be answered easily in a systematic way and will generally result in an overwhelming number of search results. On the other hand, a question that is too specific will result into too few or even zero search results. Various papers describe this process in more detail [ 10 – 12 ].
2. Describe the articles that can answer the question
Although not all clinical or research questions can be answered in the literature, the next step is to presume that the answer can indeed be found in published studies. A good starting point for a search is hypothesizing what the research that can answer the question would look like. These hypothetical (when possible, combined with known) articles can be used as guidance for constructing the search strategy.
3. Decide which key concepts address the different elements of the question
Key concepts are the topics or components that the desired articles should address, such as diseases or conditions, actions, substances, settings, domains (e.g., therapy, diagnosis, etiology), or study types. Key concepts from the research question can be grouped to create elements in the search strategy.
Elements in a search strategy do not necessarily follow the patient, intervention, comparison, outcome (PICO) structure or any other related structure. Using the PICO or another similar framework as guidance can be helpful to consider, especially in the inclusion and exclusion review stage of the SR, but this is not necessary for good search strategy development [ 13 – 15 ]. Sometimes concepts from different parts of the PICO structure can be grouped together into one search element, such as when the desired outcome is frequently described in a certain study type.
4. Decide which elements should be used for the best results
Not all elements of a research question should necessarily be used in the search strategy. Some elements are less important than others or may unnecessarily complicate or restrict a search strategy. Adding an element to a search strategy increases the chance of missing relevant references. Therefore, the number of elements in a search strategy should remain as low as possible to optimize recall.
Using the schema in Figure 1 , elements can be ordered by their specificity and importance to determine the best search approach. Whether an element is more specific or more general can be measured objectively by the number of hits retrieved in a database when searching for a key term representing that element. Depending on the research question, certain elements are more important than others. If articles (hypothetically or known) exist that can answer the question but lack a certain element in their titles, abstracts, or keywords, that element is unimportant to the question. An element can also be unimportant because of expected bias or an overlap with another element.

Schema for determining the optimal order of elements
Bias in elements
The choice of elements in a search strategy can introduce bias through use of overly specific terminology or terms often associated with positive outcomes. For the question “does prolonged breastfeeding improve intelligence outcomes in children?,” searching specifically for the element of duration will introduce bias, as articles that find a positive effect of prolonged breastfeeding will be much more likely to mention time factors in their titles or abstracts.
Overlapping elements
Elements in a question sometimes overlap in their meaning. Sometimes certain therapies are interventions for one specific disease. The Lichtenstein technique, for example, is a repair method for inguinal hernias. There is no need to include an element of “inguinal hernias” to a search for the effectiveness of the Lichtenstein therapy. Likewise, sometimes certain diseases are only found in certain populations. Adding such an overlapping element could lead to missing relevant references.
The elements to use in a search strategy can be found in the plot of elements in Figure 1 , by following the top row from left to right. For this method, we recommend starting with the most important and specific elements. Then, continue with more general and important elements until the number of results is acceptable for screening. Determining how many results are acceptable for screening is often a matter of negotiation with the SR team.
5. Choose an appropriate database and interface to start with
Important factors for choosing databases to use are the coverage and the presence of a thesaurus. For medically oriented searches, the coverage and recall of Embase, which includes the MEDLINE database, are superior to those of MEDLINE [ 16 ]. Each of these two databases has its own thesaurus with its own unique definitions and structure. Because of the complexity of the Embase thesaurus, Emtree, which contains much more specific thesaurus terms than the MEDLINE Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) thesaurus, translation from Emtree to MeSH is easier than the other way around. Therefore, we recommend starting in Embase.
MEDLINE and Embase are available through many different vendors and interfaces. The choice of an interface and primary database is often determined by the searcher’s accessibility. For our method, an interface that allows searching with proximity operators is desirable, and full functionality of the thesaurus, including explosion of narrower terms, is crucial. We recommend developing a personal workflow that always starts with one specific database and interface.
6. Document the search process in a text document
We advise designing and creating the complete search strategies in a log document, instead of directly in the database itself, to register the steps taken and to make searches accountable and reproducible. The developed search strategies can be copied and pasted into the desired databases from the log document. This way, the searcher is in control of the whole process. Any change to the search strategy should be done in the log document, assuring that the search strategy in the log is always the most recent.
7. Identify appropriate index terms in the thesaurus of the first database
Searches should start by identifying appropriate thesaurus terms for the desired elements. The thesaurus of the database is searched for matching index terms for each key concept. We advise restricting the initial terms to the most important and most relevant terms. Later in the process, more general terms can be added in the optimization process, in which the effect on the number of hits, and thus the desirability of adding these terms, can be evaluated more easily.
Several factors can complicate the identification of thesaurus terms. Sometimes, one thesaurus term is found that exactly describes a specific element. In contrast, especially in more general elements, multiple thesaurus terms can be found to describe one element. If no relevant thesaurus terms have been found for an element, free-text terms can be used, and possible thesaurus terms found in the resulting references can be added later (step 11).
Sometimes, no distinct thesaurus term is available for a specific key concept that describes the concept in enough detail. In Emtree, one thesaurus term often combines two or more elements. The easiest solution for combining these terms for a sensitive search is to use such a thesaurus term in all elements where it is relevant. Examples are given in the supplementary appendix .
8. Identify synonyms in the thesaurus
Most thesauri offer a list of synonyms on their term details page (named Synonyms in Emtree and Entry Terms in MeSH). To create a sensitive search strategy for SRs, these terms need to be searched as free-text keywords in the title and abstract fields, in addition to searching their associated thesaurus terms.
The Emtree thesaurus contains more synonyms (300,000) than MeSH does (220,000) [ 17 ]. The difference in number of terms is even higher considering that many synonyms in MeSH are permuted terms (i.e., inversions of phrases using commas).
Thesaurus terms are ordered in a tree structure. When searching for a more general thesaurus term, the more specific (narrower) terms in the branches below that term will also be searched (this is frequently referred to as “exploding” a thesaurus term). However, to perform a sensitive search, all relevant variations of the narrower terms must be searched as free-text keywords in the title or abstract, in addition to relying on the exploded thesaurus term. Thus, all articles that describe a certain narrower topic in their titles and abstracts will already be retrieved before MeSH terms are added.
9. Add variations in search terms (e.g., truncation, spelling differences, abbreviations, opposites)
Truncation allows a searcher to search for words beginning with the same word stem. A search for therap* will, thus, retrieve therapy, therapies, therapeutic, and all other words starting with “therap.” Do not truncate a word stem that is too short. Also, limitations of interfaces should be taken into account, especially in PubMed, where the number of search term variations that can be found by truncation is limited to 600.
Databases contain references to articles using both standard British and American English spellings. Both need to be searched as free-text terms in the title and abstract. Alternatively, many interfaces offer a certain code to replace zero or one characters, allowing a search for “pediatric” or “paediatric” as “p?ediatric.” Table 1 provides a detailed description of the syntax for different interfaces.
Field codes in five most used interfaces for biomedical literature searching
Searching for abbreviations can identify extra, relevant references and retrieve more irrelevant ones. The search can be more focused by combining the abbreviation with an important word that is relevant to its meaning or by using the Boolean “NOT” to exclude frequently observed, clearly irrelevant results. We advise that searchers do not exclude all possible irrelevant meanings, as it is very time consuming to identify all the variations, it will result in unnecessarily complicated search strategies, and it may lead to erroneously narrowing the search and, thereby, reduce recall.
Searching partial abbreviations can be useful for retrieving relevant references. For example, it is very likely that an article would mention osteoarthritis (OA) early in the abstract, replacing all further occurrences of osteoarthritis with OA . Therefore, it may not contain the phrase “hip osteoarthritis” but only “hip oa.”
It is also important to search for the opposites of search terms to avoid bias. When searching for “disease recurrence,” articles about “disease free” may be relevant as well. When the desired outcome is survival , articles about mortality may be relevant.
10. Use database-appropriate syntax, with parentheses, Boolean operators, and field codes
Different interfaces require different syntaxes, the special set of rules and symbols unique to each database that define how a correctly constructed search operates. Common syntax components include the use of parentheses and Boolean operators such as “AND,” “OR,” and “NOT,” which are available in all major interfaces. An overview of different syntaxes for four major interfaces for bibliographic medical databases (PubMed, Ovid, EBSCOhost, Embase.com, and ProQuest) is shown in Table 1 .
Creating the appropriate syntax for each database, in combination with the selected terms as described in steps 7–9, can be challenging. Following the method outlined below simplifies the process:
- Create single-line queries in a text document (not combining multiple record sets), which allows immediate checking of the relevance of retrieved references and efficient optimization.
- Type the syntax (Boolean operators, parentheses, and field codes) before adding terms, which reduces the chance that errors are made in the syntax, especially in the number of parentheses.
- Use predefined proximity structures including parentheses, such as (() ADJ3 ()) in Ovid, that can be reused in the query when necessary.
- Use thesaurus terms separately from free-text terms of each element. Start an element with all thesaurus terms (using “OR”) and follow with the free-text terms. This allows the unique optimization methods as described in step 11.
- When adding terms to an existing search strategy, pay close attention to the position of the cursor. Make sure to place it appropriately either in the thesaurus terms section, in the title/abstract section, or as an addition (broadening) to an existing proximity search.
The supplementary appendix explains the method of building a query in more detail, step by step for different interfaces: PubMed, Ovid, EBSCOhost, Embase.com, and ProQuest. This method results in a basic search strategy designed to retrieve some relevant references upon which a more thorough search strategy can be built with optimization such as described in step 11.
11. Optimize the search
The most important question when performing a systematic search is whether all (or most) potentially relevant articles have been retrieved by the search strategy. This is also the most difficult question to answer, since it is unknown which and how many articles are relevant. It is, therefore, wise first to broaden the initial search strategy, making the search more sensitive, and then check if new relevant articles are found by comparing the set results (i.e., search for Strategy #2 NOT Strategy #1 to see the unique results).
A search strategy should be tested for completeness. Therefore, it is necessary to identify extra, possibly relevant search terms and add them to the test search in an OR relationship with the already used search terms. A good place to start, and a well-known strategy, is scanning the top retrieved articles when sorted by relevance, looking for additional relevant synonyms that could be added to the search strategy.
We have developed a unique optimization method that has not been described before in the literature. This method often adds valuable extra terms to our search strategy and, therefore, extra, relevant references to our search results. Extra synonyms can be found in articles that have been assigned a certain set of thesaurus terms but that lack synonyms in the title and/or abstract that are already present in the current search strategy. Searching for thesaurus terms NOT free-text terms will help identify missed free-text terms in the title or abstract. Searching for free-text terms NOT thesaurus terms will help identify missed thesaurus terms. If this is done repeatedly for each element, leaving the rest of the query unchanged, this method will help add numerous relevant terms to the query. These steps are explained in detail for five different search platforms in the supplementary appendix .
12. Evaluate the initial results
The results should now contain relevant references. If the interface allows relevance ranking, use that in the evaluation. If you know some relevant references that should be included in the research, search for those references specifically; for example, combine a specific (first) author name with a page number and the publication year. Check whether those references are retrieved by the search. If the known relevant references are not retrieved by the search, adapt the search so that they are. If it is unclear which element should be adapted to retrieve a certain article, combine that article with each element separately.
Different outcomes are desired for different types of research questions. For instance, in the case of clinical question answering, the researcher will not be satisfied with many references that contain a lot of irrelevant references. A clinical search should be rather specific and is allowed to miss a relevant reference. In the case of an SR, the researchers do not want to miss any relevant reference and are willing to handle many irrelevant references to do so. The search for references to include in an SR should be very sensitive: no included reference should be missed. A search that is too specific or too sensitive for the intended goal can be adapted to become more sensitive or specific. Steps to increase sensitivity or specificity of a search strategy can be found in the supplementary appendix .
13. Check for errors
Errors might not be easily detected. Sometimes clues can be found in the number of results, either when the number of results is much higher or lower than expected or when many retrieved references are not relevant. However, the number expected is often unknown, and very sensitive search strategies will always retrieve many irrelevant articles. Each query should, therefore, be checked for errors.
One of the most frequently occurring errors is missing the Boolean operator “OR.” When no “OR” is added between two search terms, many interfaces automatically add an “AND,” which unintentionally reduces the number of results and likely misses relevant references. One good strategy to identify missing “OR”s is to go to the web page containing the full search strategy, as translated by the database, and using Ctrl-F search for “AND.” Check whether the occurrences of the “AND” operator are deliberate.
Ideally, search strategies should be checked by other information specialists [ 18 ]. The Peer Review of Electronic Search Strategies (PRESS) checklist offers good guidance for this process [ 4 ]. Apart from the syntax (especially Boolean operators and field codes) of the search strategy, it is wise to have the search terms checked by the clinician or researcher familiar with the topic. At Erasmus MC, researchers and clinicians are involved during the complete process of structuring and optimizing the search strategy. Each word is added after the combined decision of the searcher and the researcher, with the possibility of directly comparing results with and without the new term.
14. Translate to other databases
To retrieve as many relevant references as possible, one has to search multiple databases. Translation of complex and exhaustive queries between different databases can be very time consuming and cumbersome. The single-line search strategy approach detailed above allows quick translations using the find and replace method in Microsoft Word (<Ctrl-H>).
At Erasmus MC, macros based on the find-and-replace method in Microsoft Word have been developed for easy and fast translation between the most used databases for biomedical and health sciences questions. The schema that is followed for the translation between databases is shown in Figure 2 . Most databases simply follow the structure set by the Embase.com search strategy. The translation from Emtree terms to MeSH terms for MEDLINE in Ovid often identifies new terms that need to be added to the Embase.com search strategy before the translation to other databases.

Schematic representation of translation between databases used at Erasmus University Medical Center
Dotted lines represent databases that are used in less than 80% of the searches.
Using five different macros, a thoroughly optimized query in Embase.com can be relatively quickly translated into eight major databases. Basic search strategies will be created to use in many, mostly smaller, databases, because such niche databases often do not have extensive thesauri or advanced syntax options. Also, there is not much need to use extensive syntax because the number of hits and, therefore, the amount of noise in these databases is generally low. In MEDLINE (Ovid), PsycINFO (Ovid), and CINAHL (EBSCOhost), the thesaurus terms must be adapted manually, as each database has its own custom thesaurus. These macros and instructions for their installation, use, and adaptation are available at bit.ly/databasemacros.
15. Test and reiterate
Ideally, exhaustive search strategies should retrieve all references that are covered in a specific database. For SR search strategies, checking searches for their recall is advised. This can be done after included references have been determined by the authors of the systematic review. If additional papers have been identified through other non-database methods (i.e., checking references in included studies), results that were not identified by the database searches should be examined. If these results were available in the databases but not located by the search strategy, the search strategy should be adapted to try to retrieve these results, as they may contain terms that were omitted in the original search strategies. This may enable the identification of additional relevant results.
A methodology for creating exhaustive search strategies has been created that describes all steps of the search process, starting with a question and resulting in thorough search strategies in multiple databases. Many of the steps described are not new, but together, they form a strong method creating high-quality, robust searches in a relatively short time frame.
Our methodology is intended to create thoroughness for literature searches. The optimization method, as described in step 11, will identify missed synonyms or thesaurus terms, unlike any other method that largely depends on predetermined keywords and synonyms. Using this method results in a much quicker search process, compared to traditional methods, especially because of the easier translation between databases and interfaces (step 13). The method is not a guarantee for speed, since speed depends on many factors, including experience. However, by following the steps and using the tools as described above, searchers can gain confidence first and increase speed through practice.
What is new?
This method encourages searchers to start their search development process using empty syntax first and later adding the thesaurus terms and free-text synonyms. We feel this helps the searcher to focus on the search terms, instead of on the structure of the search query. The optimization method in which new terms are found in the already retrieved articles is used in some other institutes as well but has to our knowledge not been described in the literature. The macros to translate search strategies between interfaces are unique in this method.
What is different compared to common practice?
Traditionally, librarians and information specialists have focused on creating complex, multi-line (also called line-by-line) search strategies, consisting of multiple record sets, and this method is frequently advised in the literature and handbooks [ 2 , 19 – 21 ]. Our method, instead, uses single-line searches, which is critical to its success. Single-line search strategies can be easily adapted by adding or dropping a term without having to recode numbers of record sets, which would be necessary in multi-line searches. They can easily be saved in a text document and repeated by copying and pasting for search updates. Single-line search strategies also allow easy translation to other syntaxes using find-and-replace technology to update field codes and other syntax elements or using macros (step 13).
When constructing a search strategy, the searcher might experience that certain parentheses in the syntax are unnecessary, such as parentheses around all search terms in the title/abstract portion, if there is only one such term, there are double parentheses in the proximity statement, or one of the word groups exists for only one word. One might be tempted to omit those parentheses for ease of reading and management. However, during the optimization process, the searcher is likely to find extra synonyms that might consist of one word. To add those terms to the first query (with reduced parentheses) requires adding extra parentheses (meticulously placing and counting them), whereas, in the latter search, it only requires proper placement of those terms.
Many search methods highly depend on the PICO framework. Research states that often PICO or PICOS is not suitable for every question [ 22 , 23 ]. There are other acronyms than PICO—such as sample, phenomenon of interest, design, evaluation, research type (SPIDER) [ 24 ]—but each is just a variant. In our method, the most important and specific elements of a question are being analyzed for building the best search strategy.
Though it is generally recommended that searchers search both MEDLINE and Embase, most use MEDLINE as the starting point. It is considered the gold standard for biomedical searching, partially due to historical reasons, since it was the first of its kind, and more so now that it is freely available via the PubMed interface. Our method can be used with any database as a starting point, but we use Embase instead of MEDLINE or another database for a number of reasons. First, Embase provides both unique content and the complete content of MEDLINE. Therefore, searching Embase will be, by definition, more complete than searching MEDLINE only. Second, the number of terms in Emtree (the Embase thesaurus) is three times as high as that of MeSH (the MEDLINE thesaurus). It is easier to find MeSH terms after all relevant Emtree terms have been identified than to start with MeSH and translate to Emtree.
At Erasmus MC, the researchers sit next to the information specialist during most of the search strategy design process. This way, the researchers can deliver immediate feedback on the relevance of proposed search terms and retrieved references. The search team then combines knowledge about databases with knowledge about the research topic, which is an important condition to create the highest quality searches.
Limitations of the method
One disadvantage of single-line searches compared to multi-line search strategies is that errors are harder to recognize. However, with the methods for optimization as described (step 11), errors are recognized easily because missed synonyms and spelling errors will be identified during the process. Also problematic is that more parentheses are needed, making it more difficult for the searcher and others to assess the logic of the search strategy. However, as parentheses and field codes are typed before the search terms are added (step 10), errors in parentheses can be prevented.
Our methodology works best if used in an interface that allows proximity searching. It is recommended that searchers with access to an interface with proximity searching capabilities select one of those as the initial database to develop and optimize the search strategy. Because the PubMed interface does not allow proximity searches, phrases or Boolean “AND” combinations are required. Phrase searching complicates the process and is more specific, with the higher risk of missing relevant articles, and using Boolean “AND” combinations increases sensitivity but at an often high loss of specificity. Due to some searchers’ lack of access to expensive databases or interfaces, the freely available PubMed interface may be necessary to use, though it should never be the sole database used for an SR [ 2 , 16 , 25 ]. A limitation of our method is that it works best with subscription-based and licensed resources.
Another limitation is the customization of the macros to a specific institution’s resources. The macros for the translation between different database interfaces only work between the interfaces as described. To mitigate this, we recommend using the find-and-replace functionality of text editors like Microsoft Word to ease the translation of syntaxes between other databases. Depending on one’s institutional resources, custom macros can be developed using similar methods.
Results of the method
Whether this method results in exhaustive searches where no important article is missed is difficult to determine, because the number of relevant articles is unknown for any topic. A comparison of several parameters of 73 published reviews that were based on a search developed with this method to 258 reviews that acknowledged information specialists from other Dutch academic hospitals shows that the performance of the searches following our method is comparable to those performed in other institutes but that the time needed to develop the search strategies was much shorter than the time reported for the other reviews [ 9 ].
CONCLUSIONS
With the described method, searchers can gain confidence in their search strategies by finding many relevant words and creating exhaustive search strategies quickly. The approach can be used when performing SR searches or for other purposes such as answering clinical questions, with different expectations of the search’s precision and recall. This method, with practice, provides a stepwise approach that facilitates the search strategy development process from question clarification to final iteration and beyond.
SUPPLEMENTAL FILE
Acknowledgments.
We highly appreciate the work that was done by our former colleague Louis Volkers, who in his twenty years as an information specialist in Erasmus MC laid the basis for our method. We thank Professor Oscar Franco for reviewing earlier drafts of this article.
Retirement planning – a systematic review of literature and future research directions
- Published: 28 October 2023
Cite this article
- Kavita Karan Ingale ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3570-4211 1 &
- Ratna Achuta Paluri 2
508 Accesses
Explore all metrics
Rising life expectancy and an aging population across nations are leading to an increased need for long-term financial savings and a focus on the financial well-being of retired individuals amidst changing policy framework. This study is a systematic review based on a scientific way of producing high-quality evidence based on 191 articles from the Scopus and Web of Science databases. It adopts the Theory, Context, Characteristics, and Method (TCCM) framework to analyze literature. This study provides collective insights into financial decision-making for retirement savings and identifies constructs for operationalizing and measuring financial behavior for retirement planning. Further, it indicates the need for an interdisciplinary approach. Though cognitive areas were studied extensively, the non-cognitive areas received little attention. Qualitative research design is gaining prominence in research over other methods, with the sparse application of mixed methods design. The study’s TCCM framework explicates several areas for further research. Furthermore, it guides the practice and policy by integrating empirical evidence and concomitant findings. Coherent synthesis of the extant literature reconciles the highly fragmented field of retirement planning. No research reports prospective areas for further analysis based on the TCCM framework on retirement planning, which highlights the uniqueness of the study.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

A Research Proposal to Examine Psychological Factors Influence on Financial Planning for Retirement in China
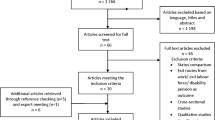
Domains and determinants of retirement timing: A systematic review of longitudinal studies
Micky Scharn, Ranu Sewdas, … Allard J. van der Beek

Reinventing Retirement
Deanna L. Sharpe
Data Availability
The research data will be made available on request.
Acknowledgment.
Elderly population is defined as a population aged 65 years and over.
Defined benefit plan guarantees benefits to the employee, while defined contribution plan requires employees to decide on their own investment and bear the financial risks identified with it.
“The old-age dependency ratio is defined as the number of individuals aged 65 and over per 100 people of working age defined as those at ages 20 to 64”(OECD 2023 ).
Adams GA, Rau BL (2011) Putting off tomorrow to do what you want today: planning for Retirement. Am Psychol 66(3):180–192. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0022131
Article Google Scholar
Aegon Cfor, Longevity, Retirement ICR (2016) The Aegon Retirement Readiness Survey 2016. In The Aegon Retirement Readiness Survey 2016 . https://www.aegon.com/contentassets/c6a4b1cdded34f1b85a4f21d4c66e5d3/2016-aegon-retirement-readiness-report-india.pdf
Agarwalla SK, Barua SK, Jacob J, Varma JR (2015) Financial Literacy among Working Young in Urban India. World Development , 67 (2013), 101–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.worlddev.2014.10.004
Ajzen I (1991) The theory of Planned Behavior. Organ Behav Hum Decis Process 50:179–211. https://doi.org/10.47985/dcidj.475
Anderson A, Baker F, Robinson DT (2017) Precautionary savings, retirement planning, and misperceptions of financial literacy. J Financ Econ 126(2):383–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfineco.2017.07.008
Atkinson A, Messy FA (2011) Assessing financial literacy in 12 countries: an OECD/INFE international pilot exercise. J Pension Econ Finance 10(4):657–665. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1474747211000539`
Aydin AE, Akben Selcuk E (2019) An investigation of financial literacy, money ethics, and time preferences among college students: a structural equation model. Int J Bank Mark 37(3):880–900. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJBM-05-2018-0120
Bapat D (2020) Antecedents to responsible financial management behavior among young adults: the moderating role of financial risk tolerance. Int J Bank Mark 38(5):1177–1194. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJBM-10-2019-0356
Beckett A, Hewer P, Howcroft B (2000) An exposition of consumer behaviour in the financial services industry. Int J Bank Mark 18(1):15–26. https://doi.org/10.1108/02652320010315325
Białowolski P (2019) Economic sentiment as a driver for household financial behavior. J Behav Experimental Econ 80(August 2017):59–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socec.2019.03.006
Binswanger J, Carman KG (2012) How real people make long-term decisions: the case of retirement preparation. J Economic Behav Organ 81(1):39–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jebo.2011.08.010
Brounen D, Koedijk KG, Pownall RAJ (2016) Household financial planning and savings behavior. J Int Money Finance 69:95–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jimonfin.2016.06.011
Brown R, Jones M (2015) Mapping and exploring the topography of contemporary financial accounting research. Br Acc Rev 47(3):237–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bar.2014.08.006
Brown S, Gray D (2016) Household finances and well-being in Australia: an empirical analysis of comparison effects. J Econ Psychol 53:17–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joep.2015.12.006
Brown S, Taylor K (2014) Household finances and the big five personality traits. J Econ Psychol 45:197–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joep.2014.10.006
Brown S, Taylor K (2016) Early influences on saving behaviour: analysis of British panel data. J Bank Finance 62:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbankfin.2015.09.011
Brüggen EC, Post T, Schmitz K (2019) Interactivity in online pension planners enhances engagement with retirement planning – but not for everyone. J Serv Mark 33(4):488–501. https://doi.org/10.1108/JSM-02-2018-0082
Bruggen E, Post T, Katharina S (2019) Interactivity in online pension planners enhances engagement with retirement planning but not for everyone. J Serv Mark 33(4):488–501
Calcagno R, Monticone C (2015) Financial literacy and the demand for financial advice. J Bank Finance 50:363–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbankfin.2014.03.013
Campbell JY (2006) Household finance. J Finance 61(4):1553–1604. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-6261.2006.00883.x
Choudhury K (2015) Service quality and customers’ behavioural intentions: class and mass banking and implications for the consumer and society. Asia Pac J Mark Logistics 27(5):735–757
Chowdhry N, Jung J, Dholakia U (2018) Association for consumer research. Adv Consum Res 42:42–46
Google Scholar
Clark GL, Knox-Hayes J, Strauss K (2009) Financial sophistication, salience, and the scale of deliberation in UK retirement planning. Environ Plann A 41(10):2496–2515. https://doi.org/10.1068/a41265
Clark R, Lusardi A, Mitchell OS (2017) Employee Financial Literacy and Retirement Plan Behavior: a case study. Econ Inq 55(1):248–259. https://doi.org/10.1111/ecin.12389
Collins JM, Urban C (2016) The role of information on Retirement Planning: evidence from a field study. Econ Inq 54(4):1860–1872. https://doi.org/10.1111/ecin.12349
Creswell J (2009) Research Design Qualitative Quantitative and Mixed Methods Approaches. In Sage Publishing: Vol. Third edit . https://doi.org/10.1002/tl.20234
Csorba L (2020) The determining factors of financial culture, financial literacy, and financial behavior. Public Finance Q 65:67–83. https://doi.org/10.35551/PFQ_2020_1_6
Davidoff T, Gerhard P, Post T (2017) Reverse mortgages: what homeowners (don’t) know and how it matters. J Economic Behav Organ 133:151–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jebo.2016.11.007
Davis FD (1989) Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology. MIS Quarterly: Management Information Systems 13(3):319–339. https://doi.org/10.2307/249008
Devlin J (2001) Consumer evaluation and competitive advantage in retail financial services - a research agenda. Eur J Mark 35(5/6):639–660
Dholakia U, Tam L, Yoon S, Wong N (2016) The ant and the grasshopper: understanding personal saving orientation of consumers. J Consum Res 43(1):134–155. https://doi.org/10.1093/jcr/ucw004
Dolls M, Doerrenberg P, Peichl A, Stichnoth H (2018) Do retirement savings increase in response to information about retirement and expected pensions? J Public Econ 158(July 2017):168–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpubeco.2017.12.014
Dragos SL, Dragos CM, Muresan GM (2020) From intention to the decision in purchasing life insurance and private pensions: different effects of knowledge and behavioural factors. J Behav Experimental Econ 87(March):101555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socec.2020.101555
Drever AI, Odders-white E, Kalish CW, Hoagland EM, Nelms EN, Drever AI, Odders-white E, Charles W, Else-quest NM, Hoagland EM, Nelms EN (2015) Foundations of Financial Weil-Being: Insights into the Role of Executive Function, Financial Socialization, and Experience-Based Learning in Childhood and Youth Source : The Journal of Consumer Affairs, Vol. 49, No. 1, Special Issue on Starting Ea. The Journal of Consumer Affairs , 49 (1)
Duflo E, Saez E (2002) Participation and investment decisions in a retirement plan: the influence of colleagues’ choices. J Public Econ 85(1):121–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0047-2727(01)00098-6
Duxbury D, Summers B, Hudson R, Keasey K (2013) How people evaluate defined contribution, annuity-based pension arrangements: a behavioral exploration. J Econ Psychol 34:256–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joep.2012.10.008
Earl J, Bednall T, Muratore A (2015) A matter of time: why some people plan for retirement and others do not. Work Aging and Retirement 1(2):181–189. https://doi.org/10.1093/workar/wau005
Employees Benefits Research Institute (2020) EBRI Retirement Confidence Survey Report (Issue 202)
Engel JF, Kollat DT, Blackwell RD (1968) A model of consumer motivation and behavior. In: Research in consumer behavior. Holt, Rinehart and Winston, Inc., New York, pp 3–20
Erasmus A, Boshoff E, Rousseau G (2001) Consumer decision-making models within the discipline of consumer science: a critical approach. J Family Ecol Consumer Sci /Tydskrif Vir Gesinsekologie En Verbruikerswetenskappe 29(1):82–90. https://doi.org/10.4314/jfecs.v29i1.52799
Farrell L, Fry TRL, Risse L (2016) The significance of financial self-efficacy in explaining women’s personal finance behaviour. J Econ Psychol 54:85–99
Fernandes D, Lynch JG, Netemeyer RG (2014) Financial literacy, financial education, and downstream financial behaviors. Manage Sci 60(8):1861–1883. https://doi.org/10.1287/mnsc.2013.1849
Filbec G, Ricciardi V, Evensky H, Fan S, Holzhauer H, Spieler A (2017) Behavioral finance: a panel discussion. J Behav Experimental Finance 15:52–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbef.2015.07.003
Fishbein M (1979) A theory of reasoned action: some applications and implications. Nebraska Symposium on Motivation 27:65–116
Fisher PJ, Montalto CP (2010) Effect of saving motives and horizon on saving behaviors. J Econ Psychol 31(1):92–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joep.2009.11.002
Flores SAM, Vieira KM (2014) Propensity toward indebtedness: an analysis using behavioral factors. J Behav Exp Finance 3:1–10
Foxall GR, Pallister JG (1998) Measuring purchase decision involvement for financial services: comparison of the Zaichkowsky and Mittal scales. Int J Bank Mark 16(5):180–194. https://doi.org/10.1108/02652329810228181
Friedman M (1957) Introduction to “A theory of the consumption function”. In: A theory of the consumption function. Princeton University Press, pp 1–6
Frydman C, Camerer CF (2016) The psychology and neuroscience of financial decision making. Trends Cogn Sci 20(9):661–675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2016.07.003
Gardarsdóttir RB, Dittmar H (2012) The relationship of materialism to debt and financial well-being: the case of Iceland’s perceived prosperity. J Econ Psychol 33(3):471–481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joep.2011.12.008
Gathergood J (2012) Self-control, financial literacy and consumer over-indebtedness. J Econ Psychol 33(3):590–602
Gerhard P, Gladstone JJ, Hoffmann AOI (2018) Psychological characteristics and household savings behavior: the importance of accounting for latent heterogeneity. J Economic Behav Organ 148:66–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jebo.2018.02.013
Gibbs PT (2009) Time, temporality, and
Goedde-Menke M, Lehmensiek-Starke M, Nolte S (2014) An empirical test of competing hypotheses for the annuity puzzle. J Econ Psychol 43:75–91
Gough O, Nurullah M (2009) Understanding what drives the purchase decision in pension and investment products. J Financial Serv Mark 14(2):152–172. https://doi.org/10.1057/fsm.2009.14
Griffin B, Loe D, Hesketh B (2012) Using Proactivity, Time Discounting, and the theory of Planned Behavior to identify predictors of Retirement Planning. Educ Gerontol 38(12):877–889. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601277.2012.660857
Gritten A (2011) New insights into consumer confidence in financial services. Int J Bank Mark 29(2):90–106. https://doi.org/10.1108/02652321111107602
Grohmann A (2018) Financial literacy and financial behavior: Evidence from the emerging Asian middle class. Pacific Basin Finance Journal , 48 (November 2017), 129–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pacfin.2018.01.007
Grohmann A, Kouwenberg R, Menkhoff L (2015) Childhood roots of financial literacy. J Econ Psychol 51:114–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joep.2015.09.002
Hair JF, Sarstedt M, Ringle CM, Mena JA (2012) An assessment of the use of partial least squares structural equation modeling in marketing research . 414–433. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11747-011-0261-6
Hanna SD, Kim KT, Chen SCC (2016) Retirement savings. In: Handbook of consumer finance research, pp 33–43
Harrison T, Waite K, White P (2006) Analysis by paralysis: the pension purchase decision process. Int J Bank Mark 24(1):5–23. https://doi.org/10.1108/02652320610642317
Hastings J, Mitchell O (2011) How financial literact and impatience shape retirement wealth and investment behaviors. Pengaruh Harga Diskon Dan Persepsi Produk Terhadap Nilai Belanja Serta Perilaku Pembelian Konsumen, NBER Working paper, 1–28
Hauff J, Carlander A, Amelie G, Tommy G, Holmen M (2016) Breaking the ice of low financial involvement: does narrative information format from a trusted sender increase savings in mutual funds? Int J Bank Mark 34(2):151–170
Hentzen JK, Hoffmann A, Dolan R, Pala E (2021) Artificial intelligence in customer-facing financial services: a systematic literature review and agenda for future research. Int J Bank Mark. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJBM-09-2021-0417
Hershey DA, Mowen JC (2000) Psychological determinants of financial preparedness for retirement. Gerontologist 40(6):687–697. https://doi.org/10.1093/geront/40.6.687
Hershey DA, Henkens K, Van Dalen HP (2007) Mapping the minds of retirement planners: a cross-cultural perspective. J Cross-Cult Psychol 38(3):361–382. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022022107300280
Hershey DA, Jacobs-Lawson JM, McArdle JJ, Hamagami F (2007b) Psychological foundations of financial planning for retirement. J Adult Dev 14(1–2):26–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10804-007-9028-1
Hershey DA, Jacobs-Lawson JM, McArdle JJ, Hamagami F (2008) Psychological foundations of financial planning for retirement. J Adult Dev 14(1–2):26–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10804-007-9028-1
Hershfield H, Goldstein D, Sharpe W, Fox J, Yeykelis L, Carstensen L, Bailenson J (2011) Increasing saving behavior through age-progressed renderings of the future self. J Mark Res 48:23–37
Hoffmann AOI, Broekhuizen TLJ (2009) Susceptibility to and impact of interpersonal influence in an investment context. J Acad Mark Sci 37:488–503
Hoffmann AOI, Broekhuizen TLJ (2010) Understanding investors’ decisions to purchase innovative products: drivers of adoption timing and range. Int J Res Mark 27(4):342–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijresmar.2010.08.002
Hoffmann AOI, Plotkina D (2020a) Positive framing when assessing the personal resources to manage one’s finances increases consumers’ retirement self-efficacy and improves retirement goal clarity. Psychol Mark 38(12):2286–2304. https://doi.org/10.1002/mar.21563
Hoffmann AOI, Plotkina D (2020b) Why and when does financial information affect retirement planning intentions and which consumers are more likely to act on them? Journal of Business Research , 117 (September 2019), 411–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2020.06.023
Hoffmann AOI, Plotkina D (2021) Let your past define your future. How recalling successful financial experiences can increase beliefs of self-efficacy in financial planning. J Consum Aff 55(3):847–871. https://doi.org/10.1111/joca.12378
Hoffmann AOI, Risse L (2020) Do good things come in pairs? How personality traits help explain individuals’ simultaneous pursuit of a healthy lifestyle and financially responsible behavior. J Consum Aff 54(3):1082–1120. https://doi.org/10.1111/joca.12317
Hsiao YJ, Tsai WC (2018) Financial literacy and participation in the derivatives markets. J Bank Finance 88:15–29
Huhmann BA, McQuitty S (2009) A model of consumer financial numeracy. Int J Bank Mark 27(4):270–293. https://doi.org/10.1108/02652320910968359
Huston SJ (2010) Measuring financial literacy. J Consum Aff 44(2):296–316. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6606.2010.01170.x
Ijevleva K, Arefjevs I (2014) Analysis of the Aggregate Financial Behaviour of customers using the Transtheoretical Model of Change. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 156(April):435–438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.11.217
Ingale KK, Paluri RA (2020) Financial literacy and financial behavior: a bibliometric analysis. Rev Behav Finance. https://doi.org/10.1108/RBF-06-2020-0141
Jacobs-Lawson J, Hershey D (2005) Influence of future time perspective, financial knowledge, and financial risk tolerance on retirement savings behavior. Financial Serv Rev 14:331–344. https://doi.org/10.1088/1751-8113/44/8/085201
Jappelli T, Padula M (2013) Investment in financial literacy and saving decisions. J Bank Finance 37(8):2779–2792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbankfin.2013.03.019
Kadoya Y, Rahim Khan MS (2020) Financial literacy in Japan: new evidence using financial knowledge, behavior, and attitude. Sustain (Switzerland) 12(9). https://doi.org/10.3390/su12093683
Kamil NSSN, Musa R, Sahak SZ (2014) Examining the Role of Financial Intelligence Quotient (FiQ) in explaining credit card usage behavior: a conceptual Framework. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 130:568–576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.04.066
Kerry MJ (2018) Psychological antecedents of retirement planning: a systematic review. Front Psychol 9(OCT). https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2018.01870
Kerry MJ, Embretson SE (2018) An experimental evaluation of competing age predictions of future time perspective between workplace and retirement domains. Front Psychol 8(JAN):1–9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2017.02316
Kiliyanni AL, Sivaraman S (2016) The perception-reality gap in financial literacy: evidence from the most literate state in India. Int Rev Econ Educ 23:47–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iree.2016.07.001
Kimiyaghalam F, Mansori S, Safari M, Yap S (2017) Parents’ influence on retirement planning in Malaysia. Family Consumer Sci Res J 45(3):315–325
Klapper L, Lusardi A, Panos GA (2013) Financial literacy and its consequences: evidence from Russia during the financial crisis. J Bank Finance 37(10):3904–3923
Koehler DJ, Langstaff J, Liu WQ (2015) A simulated financial savings task for studying consumption and retirement decision-making. J Econ Psychol 46:89–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joep.2014.12.004
Kramer MM (2016) Financial literacy, confidence, and financial advice seeking. Journal of Economic Behavior and Organization , 131 (June 2015), 198–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jebo.2016.08.016
Kumar S, Tomar S, Verma D (2019) Women’s financial planning for retirement: systematic literature review and future research agenda. Int J Bank Mark 37(1):120–141. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJBM-08-2017-0165
Kwon KN, Lee J (2009) The effects of reference point, knowledge, and risk propensity on the evaluation of financial products. J Bus Res 62(7):719–725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2008.07.002
Landerretche OM, Martínez C (2013) Voluntary savings, financial behavior, and pension finance literacy: evidence from Chile. J Pension Econ Finance 12(3):251–297. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1474747212000340
Lee T (2017) (David). Clear, conspicuous, and improving: US corporate websites for critical financial literacy in retirement. International Journal of Bank Marketing , 35 (5), 761–780. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJBM-01-2016-0010
Liang C-J, Wang Wen‐Hung, Farquhar JD (2009) (2009). The influence of customer perceptions on financial performance in financial services. International Journal of Bank Marketing , 27 (2), 129–149
Liberman N, Trope Y (2003) Construal level theory of intertemporal judgment and decision. In: Loewenstein G, Read D, Baumeister R (eds) Time and decision: economic and psychological perspectives on intertemporal choice, pp 245–276
Lim KL, Soutar GN, Lee JA (2013) Factors affecting investment intentions: a consumer behaviour perspective. J Financ Serv Mark 18:301–315
Lin C, Hsiao YJ, Yeh CY (2017) Financial literacy, financial advisors, and information sources on demand for life insurance. Pac Basin Finance J 43(March):218–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pacfin.2017.04.002
Lown JM (2011) Development and validation of a Financial Self-Efficacy Scale. J Financial Couns Plann 22(2):54–63
Lusardi A, Mitchell OS (2007) Baby Boomer retirement security: the roles of planning, financial literacy, and housing wealth. J Monet Econ 54(1):205–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmoneco.2006.12.001
Maloney M, McCarthy A (2017) Understanding pension communications at the organizational level: insights from bounded rationality theory & implications for HRM. Hum Resource Manage Rev 27(2):338–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrmr.2016.08.001
Marjanovic Z, Fiksenbaum L, Greenglass E (2018) Financial threat correlates with acute economic hardship and behavioral intentions that can improve one’s personal finances and health. J Behav Experimental Econ 77(April):151–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socec.2018.09.012
Marques S, Mariano J, Lima ML, Abrams D (2018) Are you talking to the future me? The moderator role of future self-relevance on the effects of aging salience in retirement savings. J Appl Soc Psychol 48(7):360–368. https://doi.org/10.1111/jasp.12516
McKechnie S (1992) Consumer buying behaviour in financial services: an overview. Int J Bank Mark 10(5):5–39. https://doi.org/10.1108/02652329210016803
Milner T, Rosenstreich D (2013a) A review of consumer decision-making models and development of a new model for financial services. J Financial Serv Mark 18(2):106–120. https://doi.org/10.1057/fsm.2013.7
Milner T, Rosenstreich D (2013b) Insights into mature consumers of financial services. J Consumer Mark 30(3):248–257. https://doi.org/10.1108/07363761311328919
Mitchell OS, Mukherjee A (2017) Assessing the demand for micro pensions among India’s poor. J Econ Ageing 9:30–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeoa.2016.05.004
Mitchell O, Utkus S (2003) Lessons from Behavioral Finance for Retirement Plan Design (PRC WP 2003-6). http://prc.wharton.upenn.edu/prc/prc.html
Modigliani F, Brumberg RH (1954) Utility analysis and the consumption function: an interpretation of cross-section data. In: Kurihara KK (ed) Post-Keynesian economics. Rutgers University Press, New Brunswick, pp 388–436
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Altman D, Antes G, Atkins D, Barbour V, Barrowman N, Berlin JA, Clark J, Clarke M, Cook D, D’Amico R, Deeks JJ, Devereaux PJ, Dickersin K, Egger M, Ernst E, …, Tugwell P (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med 6(7). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097
Monti M, Pelligra V, Martignon L, Berg N (2014) Retail investors and financial advisors: new evidence on trust and advice taking heuristics. J Bus Res 67(8):1749–1757. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2014.02.022
Mouna A, Anis J (2017) Financial literacy in Tunisia: its determinants and its implications on investment behavior. Res Int Bus Finance 39:568–577
Mullainathan S, Thaler R (2000) Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Economics Working Paper Series . September
Nga KH, Yeoh KK (2018) An exploratory model on retirement savings behaviour: a Malaysian study. Int J Bus Soc 19(3):637–659
OECD (2023) Old-age dependency ratio (indicator). https://doi.org/10.1787/e0255c98-en . Accessed 13 Oct 2023
Onwuegbuzie AJ, Collins KM (2007) A typology of mixed methods sampling designs in social science research. Qualitative Rep 12(2):474–498
Pallister JG, Wang HC, Foxall GR (2007) An application of the style/involvement model to financial services. Technovation 27(1–2):78–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.technovation.2005.10.001
Pan L, Pezzuti T, Lu W, Pechmann C (2019) Hyperopia and frugality: different motivational drivers and yet similar effects on consumer spending. J Bus Res 95(August 2018):347–356
Parise G, Peijnenburg K (2017) Understanding the Determinants of Financial Outcomes and Choices: The Role of Noncognitive Abilities. BIS Working Papers
Paul J, Rosado-Serrano A (2019) Gradual internationalization vs Born-Global/International new venture models: a review and research agenda. Int Mark Rev 36(6):830–858. https://doi.org/10.1108/IMR-10-2018-0280
Paul J, Criado AR (2020) The art of writing literature review: what do we know and what do we need to know? Int Bus Rev 29(4):101717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibusrev.2020.101717
Paul J, Khatri P, Kaur Duggal H (2023) Frameworks for developing impactful systematic literature reviews and theory building: what, why and how? J Decis Syst 00(00):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1080/12460125.2023.2197700
Petkoska J, Earl JK (2009) Understanding the influence of demographic and psychological variables on Retirement Planning. Psychol Aging 24(1):245–251. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0014096
Piotrowska M (2019) The importance of personality characteristics and behavioral constraints for retirement saving. Econ Anal Policy 64:194–220
Plath DA, Stevenson TH (2005) Financial services consumption behavior across Hispanic American consumers. J Bus Res 58(8):1089–1099. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2004.03.003
Poterba JM (2015) Saver heterogeneity and the challenge of assessing retirement saving adequacy. Natl Tax J 68(2):377–388. https://doi.org/10.17310/ntj.2015.2.06
Potrich ACG, Vieira KM, Kirch G (2018) How well do women do when it comes to financial literacy? Proposition of an indicator and analysis of gender differences. J Behav Experimental Finance 17:28–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbef.2017.12.005
Rai D, Lin CW (2019) (Wilson). The influence of implicit self-theories on consumer financial decision making. Journal of Business Research , 95 (August 2018), 316–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2018.08.016
Ramalho TB, Forte D (2019) Financial literacy in Brazil – do knowledge and self-confidence relate with behavior? RAUSP Manage J 54(1):77–95. https://doi.org/10.1108/RAUSP-04-2018-0008
Rana J, Paul J (2017) Consumer behavior and purchase intention for organic food: a review and research agenda. J Retailing Consumer Serv 38(June):157–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretconser.2017.06.004
Ranyard R, McNair S, Nicolini G, Duxbury D (2020) An item response theory approach to constructing and evaluating brief and in-depth financial literacy scales. J Consum Aff 54(3):1121–1156. https://doi.org/10.1111/joca.12322
RBI Household Finance Committee (2017) Indian household finance. Reserve Bank of India, Mumbai
Ruefenacht M, Schlager T, Maas P, Puustinen P (2015) Drivers of long-term savings behavior from consumer’s perspective. Electron Libr 34(1):1–5
Scholz JK, Seshadri A, Khitatrakun S (2006) Are Americans saving “optimally” for retirement? J Polit Econ 114(4):607–643
Schuabb T, França LH, Amorim SM (2019) Retirement savings model tested with Brazilian private health care workers. Front Psychol 10(JULY):1–11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01701
Schuhen M, Schurkmann S (2014) International Review of Economics Education. Int Rev Econ Educ 16:1–11
Segel-Karpas D, Werner P (2014) Perceived financial retirement preparedness and its correlates: a national study in Israel. Int J Aging Hum Dev 79(4):279–301. https://doi.org/10.1177/0091415015574177
Seth H, Talwar S, Bhatia A, Saxena A, Dhir A (2020) Consumer resistance and inertia of retail investors: Development of the resistance adoption inertia continuance (RAIC) framework. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services , 55 (August 2019), 102071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretconser.2020.102071
Sewell M (2008) Behavioural finance. Economist 389(8604):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1057/9780230280786_5
Shefrin HM, Thaler RH (1988) The behavioral life‐cycle hypothesis. Econ Inq 26(4):609–643
Shim S, Serido J, Tang C (2012) The ant and the grasshopper revisited: the present psychological benefits of saving and future oriented financial behavior. J Econ Psychol 33(1):155–165
Simon HA (1978) Information-processing theory of human problem solving. In: Handbook of learning and cognitive processes, vol 5, pp 271–295
Sivaramakrishnan S, Srivastava M, Rastogi A (2017) Attitudinal factors, financial literacy, and stock market participation. Int J Bank Mark 34(1):1–5
Snyder H (2019) Literature review as a research methodology: an overview and guidelines. J Bus Res 104(August):333–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2019.07.039
Stawski RS, Hershey DA, Jacobs-Lawson JM (2007) Goal clarity and financial planning activities as determinants of retirement savings contributions. Int J Aging Hum Dev 64(1):13–32. https://doi.org/10.2190/13GK-5H72-H324-16P2
Steinert JI, Zenker J, Filipiak U, Movsisyan A, Cluver LD, Shenderovich Y (2018) Do saving promotion interventions increase household savings, consumption, and investments in Sub-saharan Africa? A systematic review and meta-analysis. World Dev 104:238–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.worlddev.2017.11.018
Steinhart Y, Mazursky D (2010) Purchase availability and involvement antecedents among financial products. Int J Bank Mark 28(2):113–135. https://doi.org/10.1108/02652321011018314
Strömbäck C, Lind T, Skagerlund K, Västfjäll D, Tinghög G (2017) Does self-control predict financial behavior and financial well-being? J Behav Experimental Finance 14:30–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbef.2017.04.002
Strömbäck C, Skagerlund K, Västfjäll D, Tinghög G (2020) Subjective self-control but not objective measures of executive functions predict financial behavior and well-being. Journal of Behavioral and Experimental Finance , 27 . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbef.2020.100339
Tam L, Dholakia U (2014) Saving in cycles: how to get people to save more money. Psychol Sci 25(2):531–537. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797613512129
Tang N, Baker A (2016) Self-esteem, financial knowledge and financial behavior. J Econ Psychol 54:164–176
Tate M, Evermann J, Gable G (2015) An integrated framework for theories of individual attitudes toward technology. Inform Manage 52(6):710–727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.im.2015.06.005
Taylor MP, Jenkins SP, Sacker A (2011) Financial capability and psychological health. J Econ Psychol 32(5):710–723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joep.2011.05.006
Tennyson S, Yang HK (2014) The role of life experience in long-term care insurance decisions. Journal of Economic Psychology , 42 (2014), 175–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joep.2014.04.002
Thaler BRH (1994) Psychology and savings policies. Am Econ Rev 84(2):175–179. http://www.jstor.org/stable/3132220
Thaler R (1980) Toward a positive theory of consumer choice. J Econ Behav Organ 1:39–60
Thaler RH (2005) Advances in behavioral finance. Adv Behav Finance 2:1–694. https://doi.org/10.2307/2329257
Thaler R, Shefrin H (1981) An economic theory of self-control. J Polit Econ 89(2):392–406
Tomar S, Kent Baker H, Kumar S, Hoffmann AOI (2021) Psychological determinants of retirement financial planning behavior. Journal of Business Research , 133 (November 2020), 432–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.05.007
Topa G, Moriano JA, Depolo M, Alcover CM, Morales JF (2009) Antecedents and consequences of retirement planning and decision-making: a meta-analysis and model. J Vocat Behav 75(1):38–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvb.2009.03.002
Topa G, Moriano JA, Depolo M, Alcover CM, Moreno A (2011) Retirement and wealth relationships: Meta-analysis and SEM. Res Aging 33(5):501–528. https://doi.org/10.1177/0164027511410549
Tranfield D, Denyer D, Smart P (2003) Towards a methodology for developing evidence-informed management knowledge by means of systematic review. Br J Manag 14(3):207–222. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8551.00375
Ülkümen G, Cheema A (2011) Framing goals to influence personal savings: the role of specificity and construal level. J Mark Res 48(6):958–969. https://doi.org/10.1509/jmr.09.0516
United Nations, Department of Economic and Social, Affairs PD (2020) (2019). World Population Ageing 2019. In United Nations . http://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/ 978-94-007-5204-7_6
Utkarsh, Pandey A, Ashta A, Spiegelman E, Sutan A (2020) Catch them young: impact of financial Socialization, financial literacy and attitude towards money on the financial well-being of young adults. Int J Consumer Stud 44(6):531–541. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijcs.12583
Valente TW, Paredes P, Poppe P (1998) Matching the message to the process: the relative ordering of knowledge, attitudes, and practices in behavior change research. Hum Commun Res 24(3):366–385
Van Rooij M, Teppa F (2014) Personal traits and individual choices: taking action in economic and non-economic decisions. J Econ Behav Organ 100:33–43
van Rooij M, Lusardi A, Alessie R (2011) Financial literacy and stock market participation. J Financ Econ 101(2):449–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfineco.2011.03.006
Van Rooij MCJ, Lusardi A, Alessie RJM (2011a) Financial literacy and retirement planning in the Netherlands. J Econ Psychol 32(4):593–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joep.2011.02.004
van Schie RJG, Dellaert BGC, Donkers B (2015) Promoting later planned retirement: construal level intervention impact reverses with age. J Econ Psychol 50:124–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joep.2015.06.010
Venkatesh V, Morris M, Davis G, Davis F (2003) Factors influencing the Use of M-Banking by academics: Case Study sms-based M-Banking. MIS Q 27(3):425–478
Vitt LA (2004) Consumers’ financial decisions and the psychology of values. J Financial Service Professionals 58(November):68–77. http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true &db=bth&AN=14888952&site=ehost-live
Wang L, Lu W, Malhotra NK (2011) Demographics, attitude, personality, and credit card features correlate with credit card debt: a view from China. J Econ Psychol 32(1):179–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joep.2010.11.006
World Economic Forum (2019) Investing in (and for) our future. Issue June. www.weforum.org
Xia T, Wang Z, Li K (2014) Financial literacy overconfidence and stock market participation. Soc Indic Res 119(3):1233–1245. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-013-0555-9
Xiao JJ, Chen C, Chen F (2014) Consumer financial capability and financial satisfaction. Soc Indic Res 118(1):415–432. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-013-0414-8
Yeung DY, Zhou X (2017) Planning for retirement: longitudinal effect on retirement resources and post-retirement well-being. Front Psychol 8:1300
Zhou R, Pham MT (2004) Promotion and prevention across mental accounts: when financial products dictate consumers’ investment goals. J Consum Res 31(1):125–135. https://doi.org/10.1086/383429
Download references
Acknowledgements
Authors would like to acknowledge the academicians and researchers who guided the search of the article and would like to thank the experts for the valuable inputs to refine the work.
There is no funding received for this research.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Symbiosis International (Deemed University), Pune, India
Kavita Karan Ingale
Symbiosis Institute of Operations Management, Symbiosis International (Deemed) University, Pune, India
Ratna Achuta Paluri
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Both authors contributed to the conceptualization, research design, methodology, analysis of the data,writing of the manuscript and its revision.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Kavita Karan Ingale .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Ingale, K.K., Paluri, R.A. Retirement planning – a systematic review of literature and future research directions. Manag Rev Q (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11301-023-00377-x
Download citation
Received : 14 December 2022
Accepted : 04 October 2023
Published : 28 October 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11301-023-00377-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Retirement planning
- Systematic literature review
- Financial behavior
- Household finance
- Long-term savings
- Pension plan
- Financial literacy
- TCCM framework
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Harvard Library
- Research Guides
- Faculty of Arts & Sciences Libraries
Expos 20 | Problems of Meaning: Language, Literature, and Life
- Subject Databases: Tools for Deep-Searching and Close-Looking
- Problems of Meaning in Language, Literature, and Life
- HOLLIS: Searching Panoramically Across Harvard's Discovery Space
Databases: Why Use Them?
Top picks for essay 3.
- Generating Research Leads From What You Have in Hand
- Getting around Paywalls on the Web
- Citing Your Sources

Research projects often require you to look close up at a body of research produced by scholars in a particular field. This research is typically collected, codified, and made findable in a tool called a subject database .
Every academic discipline has at least one subject database that's considered the disciplinary gold standard -- a reliable, (relatively) comprehensive, and accurate record of the books that scholars are publishing, and the ideas they're debating and discussing in important and influential journals.
Databases are like lenses: they change what you see and how you see it -- and they offer you easy and efficient ways to bring your questions into sharper focus.
Philosophy
Stanford encyclopedia of philosophy .
- Excellent for overview essays written by recognized subject experts and prominent academics, and accompanied by bibliography leads.
Oxford Bibliographies Online: Philosophy Harvard Key
- Annotated reading lists curated by experts, regularly checked for their currency and updated when necessary, OBOs aim to be representative, not comprehensive -- of the most impactful scholarship that's been produced to date.
- An online databas of scholarship maintained by philosophers themselves that collects, categorizes, and makes philosophy research findable. Specially curated pages perhaps pertinent to course themes include Philosophy of Language (which identifies key works and key introductory texts); Philosophy of Literature ; and Literary Values .
LINGUISTICS
Oxford bibliographies online: linguistics harvard key , linguistics and language behavior abstracts harvard key .
- A database that identifies articles, books, and other scholarly materials on linguistics and its related fields.
Psychology
Oxford bibliographies online: language (psychology) , apa psycinfo harvard key .
- The most important database access to research on all aspects of psychology,
LITERATURE
Johns hopkins guide to literary theory and criticism harvard key .
- A comprehensive survey of the the most important figures, schools, and movements in literary theory.
Oxford Bibliographies Online: Literary and Cultural Theory Harvard Key
Mla international bibliography harvard key .
- The gold standard database for topics related to literature in all languages, folklore, cultural studies, theory, and more.
Multidisciplinary
Google scholar.
Although it's not a Harvard Library "database," Google Scholar is perfectly acceptable for most general forays into scholarship; its algorithms are excellent and do return relevant results.
One of the best ways to generate research leads with Scholar is to use it to follow citation trails when you have a known source -- a class reading, a book you've found on HOLLIS that looks promising, an article that's so "perfect" for a research project that you want to see if there's "more like it" out there, waiting to be discovered.
For example:
- You can click on cited by to see which scholars picked up and used a research article/book in research. Just enter the title.
- Big "cited by" lists can be whittled down by adding keywords and clicking on the search within cited reference option.
- Related articles helps you identify r esearch that's close ----algorithmically, at least -- to the item you started with.
- Authors whose names are hotlinked reveal publications pages -- where you migth find additional/related publications (and see their times cited, too!)
- << Previous: HOLLIS: Searching Panoramically Across Harvard's Discovery Space
- Next: Generating Research Leads From What You Have in Hand >>
Except where otherwise noted, this work is subject to a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which allows anyone to share and adapt our material as long as proper attribution is given. For details and exceptions, see the Harvard Library Copyright Policy ©2021 Presidents and Fellows of Harvard College.

AI-Based Research Tools
Your librarian.

Introduction: Conducting AI Powered Research
AI tools for research can help you to discover new sources for your research assignment or literature review! These tools will synthesize information from large databases of scholarly output with the aim of finding the most relevant articles, thereby saving researchers' time. As with our research databases or any other search tool, however, it's important to:
1) always evaluate results/output;
2) not rely on any one tool for all of your research,
as you will risk missing important information on your topic of interest.
As always, if you have questions about using these tools for your research, please contact your friendly Rider librarian!
Disclaimer: Rider University Libraries do not have subscription access to the AI-powered tools listed below. The guide serves solely as an informational resource. It is recommended that you assess these tools and their usage methodologies independently.

- ELICIT IS AN "AI-POWERED RESEARCH ASSISTANT" - useful for finding papers, filtering study types, automating research flow, brainstorming, summarizing and more.
- Elicit is a research assistant using language models like GPT-3 to automate parts of researchers' workflows.
- Currently, the main workflow in Elicit is Literature Review--if you ask a question, Elicit will show relevant papers and summaries of key information about those papers in an easy-to-use table.
- Access the Elicit FAQ here.
Research Rabbit

- RESEARCH RABBIT IS A CITATION-BASED MAPPING TOOL that focuses on the relationships between research works.
- Bills itself as the "Spotify for Papers" !
- It uses visualizations to help researchers find similar papers and locate other researchers in their field.
- Research Rabbit uses multiple databases, but does not name them (more information can be found on the FAQ page).
- Keep up with the latest research related to your collections using the "Personalized Digests" feature.

- PERPLEXITY IS A SEARCH ENGINE THAT SEARCHES Large Language Models (LLMs) to provide AI-generated answers (much like ChatGPT)
- Billed as "an alternative to traditional search engines, where you can directly pose your questions and receive concise, accurate answers backed up by a curated set of sources."
- It has a conversational interface, "contextual awareness" and "personalization" to learn your interests and preferences over time.
- Using an "advanced search engine, it processes your questions and tasks it then uses predictive text capabilities to generate useful responses, choosing the best one from multiple sources, and summarizes the results in a concise way."
- Access the Perplexity FAQ here.

- CONSENSUS USES LARGE LANGUAGE MODELS (like Elicit) to help researchers find and synthesize answers to research questions, focusing on scholarly authors' findings and claims in each paper.
- Bills itself as the "ChatGPT of research!"--simply type in your research questions and off you go!
- Consensus provides helpful guidance on question prompts for different question types.
- Example topics are provided in browseable format
- Access the Consensus FAQ here.
Semantic Scholar

- SEMANTIC SCHOLAR PROVIDES BRIEF SUMMARIES of the main objectives and results of papers. (It supplies underlying data for several of the other tools above).
- "We index over 200 million academic papers from publisher partnerships, data providers, and web crawls."
- "Accelerating Scientific Breakthroughs Using AI"
- Developed by the Allen Institute for AI
- Access Semantic Scholar's FAQ here.
More AI Research Tools!
To learn about additional AI research tools, check out these research guides!
- AI Research Tools (Rutgers University Library)
- AI Research Tools (Georgetown University Library)
- Selected AI Based Literature Review Tools (Texas A&M University)
- Last Updated: Apr 9, 2024 8:34 PM
- URL: https://guides.rider.edu/aitools
- Collection edited by Yogita Goyal broadens research on African American literature

Marta Wallien | April 10, 2024
Although contemporary African American writing has evolved in remarkable fashion within the last five decades, scholarship on the subject remains sparse. A new essay collection edited by UCLA professor Yogita Goyal, “ The Cambridge Companion to Contemporary African American Literature , ” aims to widen its discourse.
“I’ve always been struck by how difficult it is — both for the classroom and for our own research — to find extensive scholarship on the subject. We tend to favor research on historically more distant eras,” said Goyal, a professor of English and African American studies. “I wanted to put together a resource for those of us who work in contemporary African American literature, which I define as post-1975 for this volume, as the Black Arts Movement was waning, and new forms of writing were coming into view.”
Goyal’s previous essay collection for Cambridge University Press, “ The Cambridge Companion to Transnational American Literature ,” centered on the global shift American literary studies took within the last century. Goyal explained that the 17 essays in this new book highlight the shift taking place within Black studies and the need for further research.
“My hope is that readers appreciate the enormous vitality of the field. There has been another cultural renaissance of sorts in the last few decades in Black studies and all the essays in the volume are alive to the vibrancy of the debates about racial justice, the afterlife of slavery, literary experimentation and play, and attention to new audiences and critical methods.”
Recent News
- ‘Art of the Benshi’ debut draws rave reviews; D.C., Chicago, L.A. dates are next
- Poetry in motion: A forthcoming anthology showcases the genius of UCLA’s Harryette Mullen
Sign up for our newsletter
Enter your email address to receive our monthly update on the latest UCLA Humanities news and upcoming events.
- Dean’s Office Staff
- Dean’s Discretionary Fund
- Division of Humanities Communication Request
- Departments & Programs
- Research Centers
- Holistic Graduate Admissions
- Partnerships
- Commencement
- Editor in Residence
- Humanities Dialogues
- Humanities Undergraduate Career Panel Series
- Possible Worlds
- World Languages Day
- Forum on Diversity, Race, & Immigration
- Diversity Courses
- Campus Resources
- Undergraduate
- Divisional Fellowships
- Dean’s Circle
- UCLA Division of Humanities Dean’s Advisory Board

COMMENTS
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
Writing a literature review requires a range of skills to gather, sort, evaluate and summarise peer-reviewed published data into a relevant and informative unbiased narrative. Digital access to research papers, academic texts, review articles, reference databases and public data sets are all sources of information that are available to enrich ...
As mentioned previously, there are a number of existing guidelines for literature reviews. Depending on the methodology needed to achieve the purpose of the review, all types can be helpful and appropriate to reach a specific goal (for examples, please see Table 1).These approaches can be qualitative, quantitative, or have a mixed design depending on the phase of the review.
Quality research is about building onto the existing work of others, "standing on the shoulders of giants", as Newton put it.The literature review chapter of your dissertation, thesis or research project is where you synthesise this prior work and lay the theoretical foundation for your own research.. Long story short, this chapter is a pretty big deal, which is why you want to make sure ...
A literature review is meant to analyze the scholarly literature, make connections across writings and identify strengths, weaknesses, trends, and missing conversations. A literature review should address different aspects of a topic as it relates to your research question. A literature review goes beyond a description or summary of the ...
Literature Review is a comprehensive survey of the works published in a particular field of study or line of research, usually over a specific period of time, in the form of an in-depth, critical bibliographic essay or annotated list in which attention is drawn to the most significant works.. Also, we can define a literature review as the collected body of scholarly works related to a topic:
Mapping the gap. The purpose of the literature review section of a manuscript is not to report what is known about your topic. The purpose is to identify what remains unknown—what academic writing scholar Janet Giltrow has called the 'knowledge deficit'—thus establishing the need for your research study [].In an earlier Writer's Craft instalment, the Problem-Gap-Hook heuristic was ...
Literature Reviews that are organized methodologically consist of paragraphs/sections that are based on the methods used in the literature found.This approach is most appropriate when you are using new methods on a research question that has already been explored.Since literature review structures are not mutually exclusive, you can organize the use of these methods in chronological order.
The best proposals are timely and clearly explain why readers should pay attention to the proposed topic. It is not enough for a review to be a summary of the latest growth in the literature: the ...
What's a Literature Review? A literature review (or "lit review," for short) is an in-depth critical analysis of published scholarly research related to a specific topic. Published scholarly research (aka, "the literature") may include journal articles, books, book chapters, dissertations and thesis, or conference proceedings. A solid lit ...
Systematic review: "The authors of a systematic review use a specific procedure to search the research literature, select the studies to include in their review, and critically evaluate the studies they find." (p. 139). ... Nelson, L. K. (2013). Research in Communication Sciences and Disorders. Plural Publishing. Example: The effect of leave ...
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories.A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that ...
A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing ...
This guide will help you to. Define a literature review. Recognize that different fields of study have their own way to perform and write literature reviews. Prepare to search the literature. Read critically -- analyze and synthesize. Prepare to write a literature review. Graphic from Literature Review (2009) by Machi and McEvoy.
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications .For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively .Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every ...
A Literature Review surveys scholarly source materials that are relevant to a person's research thesis/problem and/or a particular issue or theory. It provides a critical analysis that summarizes and synthesizes previous work while also demonstrating how a person's research pertains to or fits within the larger discipline of study. Purpose:
Finding The Literature. Research literature is vast. In the English language alone, over 2.5 million articles are published in peer reviewed journals each year. Sifting through the books and journals to find the most relevant research is challenging, but some of the resources on this page can help you. To start, write down your research ...
Describe and use several methods for finding previous research on a particular research idea or question. Reviewing the research literature means finding, reading, and summarizing the published research relevant to your question. An empirical research report written in American Psychological Association (APA) style always includes a written ...
Literature reviews offer a critical synthesis of empirical and theoretical literature to assess the strength of evidence, develop guidelines for practice and policymaking, and identify areas for future research.1 It is often essential and usually the first task in any research endeavour, particularly in masters or doctoral level education. For effective data extraction and rigorous synthesis ...
Google Scholar provides a simple way to broadly search for scholarly literature. Search across a wide variety of disciplines and sources: articles, theses, books, abstracts and court opinions.
But how is a literature review different from an academic research paper? The main focus of an academic research paper is to develop a new argument, and a research paper is likely to contain a literature review as one of its parts. In a research paper, you use the literature as a foundation and as support for a new insight that you contribute.
Abstract. Undertaking a literature search can be a daunting prospect. Breaking the exercise down into smaller steps will make the process more manageable. This article suggests 10 steps that will help readers complete this task, from identifying key concepts to choosing databases for the search and saving the results and search strategy.
1. Determine a clear and focused question. A systematic search can best be applied to a well-defined and precise research or clinical question. Questions that are too broad or too vague cannot be answered easily in a systematic way and will generally result in an overwhelming number of search results.
To investigate current practices and main research themes in fiction-based research, I conducted a critical review to classify and integrate existing studies, closely following best-practice recommendations for (methodological) literature reviews in the process (Aguinis et al., 2023; Celik et al., 2023; Hiebl, 2021; Koseoglu et al., 2022; Kunisch et al., 2023).
Rising life expectancy and an aging population across nations are leading to an increased need for long-term financial savings and a focus on the financial well-being of retired individuals amidst changing policy framework. This study is a systematic review based on a scientific way of producing high-quality evidence based on 191 articles from the Scopus and Web of Science databases. It adopts ...
Access 160+ million publications and connect with 25+ million researchers. Join for free and gain visibility by uploading your research.
4.2.2.1. Research front #1: psychological contracts and psychological capital. Research front #1 covers 28 percent of the organizational socialization and onboarding articles published in the last 5 years. A central theme in this cluster is the concept of psychological contracts in the organizational socialization domain.
Research projects often require you to look close up at a body of research produced by scholars in a particular field. This research is typically collected, codified, and made findable in a tool called a subject database.. Every academic discipline has at least one subject database that's considered the disciplinary gold standard -- a reliable, (relatively) comprehensive, and accurate record ...
ELICIT IS AN "AI-POWERED RESEARCH ASSISTANT" - useful for finding papers, filtering study types, automating research flow, brainstorming, summarizing and more.; Elicit is a research assistant using language models like GPT-3 to automate parts of researchers' workflows. Currently, the main workflow in Elicit is Literature Review--if you ask a question, Elicit will show relevant papers and ...
We tend to favor research on historically more distant eras," said Goyal, a professor of English and African American studies. "I wanted to put together a resource for those of us who work in contemporary African American literature, which I define as post-1975 for this volume, as the Black Arts Movement was waning, and new forms of writing ...