- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research

Qualitative Market Research : The Complete Guide

Content Index
What is Qualitative Market Research?
Qualitative market research methods and techniques, 4 types of qualitative market research testing methods, examples of qualitative market research.
- Ethical Considerations for Qualitative Market Research?
What are the Applications of Qualitative Market Research?
Advantages of qualitative market research, disadvantages of qualitative market research, online qualitative market research software- questionpro communities.
Qualitative market research is an open ended questions (conversational) based research method that heavily relies on the following market research methods : focus groups, in-depth interviews, and other innovative research methods. It is based on a small but highly validated sample size, usually consisting of 6 to 10 respondents .
The small size enables cost saving, while the “importance” of the samples and the lack of a defined questionnaire allows free and in-depth discussion and analysis of topics. Usually, the discussion is directed by the discretion of the interviewer or market researcher. You can use single ease questions . A single-ease question is a straightforward query that elicits a concise and uncomplicated response.
It is always better to have more heads than one. By canvassing a group of respondents for ideas and competence the quality of the data that is obtained is far more superior. This concept is known as crowdsourcing, derived from the two words “crowd” and “outsourcing”.
LEARN ABOUT: Perceived Value
Qualitative market research is most frequently used in political campaigning to understand voter perception of political candidates and their policies, interviewing business leaders and diving deeper into topics of interest, psychological profile studies and so on.
Qualitative market research is a relatively less expensive method to understand 2 critical factors in details – “what” the respondents think and feel about a certain topic and “why” they think and feel that way.
LEARN ABOUT: Market research industry

Why do we ask for an opinion? Any opinion for that matter? We ask because the person’s opinion matters to our decision making. None of the successful organizational decisions are made through mere guesses or speculations, but through real information gathered from real and valuable people.
Market research , in general, has played a critical role in inducing a thought process in present day’s organizational leaders where information and data dictate policies and decisions.
However, in market research design , not all information is just numbers and quantitative research . Some are just – conversational and qualitative!
LEARN ABOUT: Research Process Steps
Remember the super hit series Desperate Housewives? And do you remember the lovely housewives calling their friends over for a cup of tea or a couple of drinks to discuss the flashy new products they have bought?
It is not just a vague practice to flaunt these products but a thoughtful one because it matters what the friends think. Whether, they agree or disagree with the quality, brand and other features of those products. It matters what people think. Voila! Welcome to the world of qualitative market research.
Qualitative market research is all about understanding people’s beliefs and point of views and what they feel about the situation and what are the deciding factors that influence their behavior.
LEARN ABOUT: Marketing Insight

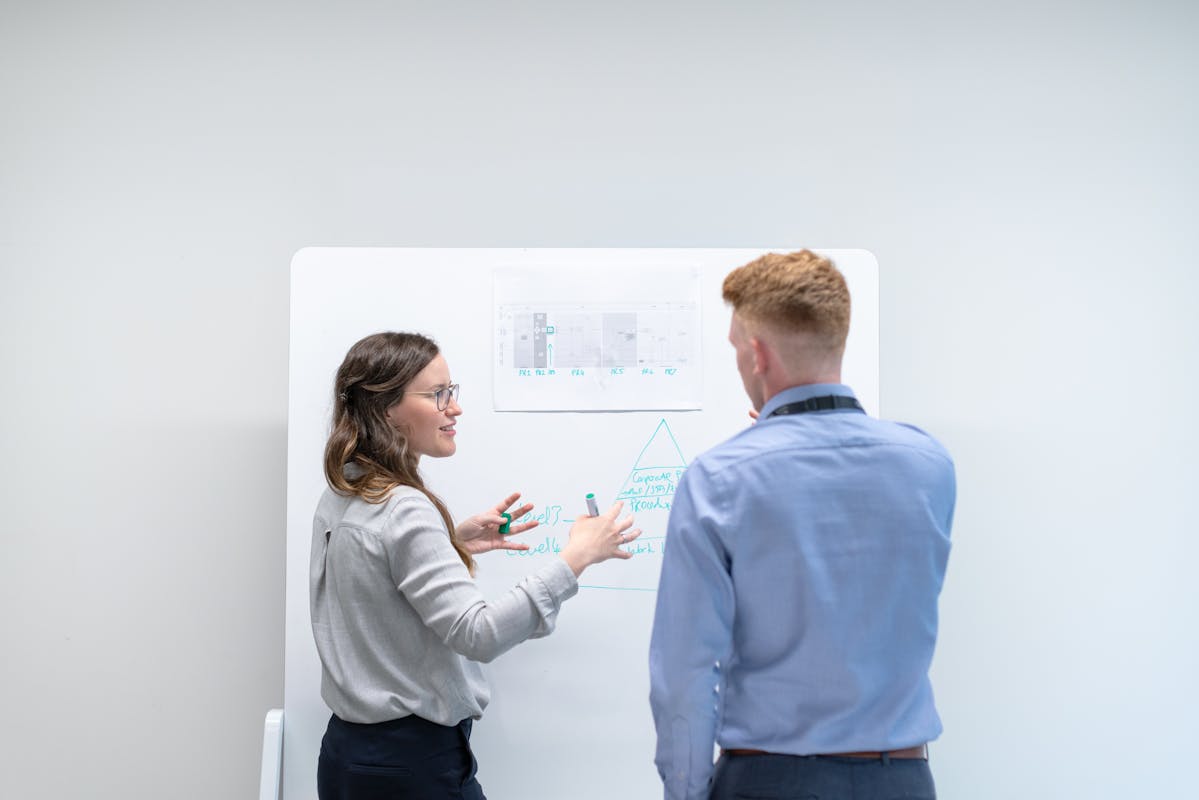
To conduct qualitative market research usually, one of these market research methods are used:
- Focus groups: As the name suggests, a group of people comprising usually of 6-10 members are brought together to discuss a particular product and its market strategies. Usually, experts in that particular field will comprise of the group. This group will have a moderator who will stimulate the discussion amongst the members to derive opinions. Since the focus groups are becoming a rare occurrence, platforms like Communities is on the rise.
- In-depth Interviews: It is usually a one-on-one interview method conducted with a group of people, either face to face or over the telephone. This method is more conversational and asking open-ended questions helps gather better data.
- Innovative research methods: In this method, the researcher can click photographs of the person who is answering the questions or can even record their videos. Observing these photographs or videos later would tell the researcher about their responses/reactions to various situations.
- Observations or “Shop-alongs”: Qualitative Observations or shop-alongs are now becoming an increasingly used research method in qualitative market research. This method allows the researcher to observe from afar and actually see how a consumer reacts to an actual product and purchase experience. This mitigates the scope to be dishonest with feedback or even forget about the shopping experience at a later stage.
LEARN ABOUT: Qualitative Interview
- Lifestyle Immersion: A newer method of conducting qualitative market research is attending a social or family event that user/s are at and collecting feedback. This helps with the getting feedback from users when they are in a comfortable environment. This is a great way to collect candid feedback in a comfortable environment.
- Online Focus Groups: With the ease of access to social media, online focus groups are becoming easier to manage. It is easy to recruit people to a focus group based study and even manage data collection and analytics.
- Ethnography: Ethnographic research is the process of being in an end user environment and seeing the user indulge with a product in a real-life example. This qualitative research method is best positioned to help create immediate and impactful product tweaks.
- Projective Techniques: Projective techniques are conducted by trained moderators who uncover hidden thoughts of the respondents. The questions or questioning methods are of an indirect nature and the moderator then deduces and uncovers underlying feelings that aren’t explicitly mentioned.
- Online Forums: Online forums is now becoming an increasingly preferred way of conducting qualitative market research. Members in a panel are brought onto a common platform to discuss a certain topic and the moderator ensures the discussion is driven in the direction of the outcome required. The moderator probes, asks the right questions and coerces to ensure a thorough discussion is conducted.
- Online Sentence Completion and Word Association: One of the easier but exhaustive nature of completing qualitative market research is to get respondents to match words that may be related to a product or even complete sentences online and this provides a deeper insight into the thoughts of the user.
Learn more about qualitative research methods
Here are the steps involved in conducting qualitative market research:
- Planning & Determining research objectives: Each research study needs to have a desired outcome at the outset so that the resources behind planning and executing are not wasted and it helps towards business agility.
- Deciding the method to conduct the research: Qualitative market research can be conducted in many ways. Depending on the nature of the study, target audience demographics , geographical location, a product that is being surveyed etc., would the survey method be utilized.
- Getting the right personnel for the job: Conducting a qualitative market research study requires moderators that know how to elicit and track responses from potential respondents.
- Purposive Sampling : In this method, the sample is created with a purpose in mind. The contours of the demographics are planned well in advance and users that fit this criterion are onboard for the market research survey.
- Quota Sampling: Quota sampling is the process of selecting samples from a given quota and the selected users are said to be a representative of the larger population. This can be a random sampling or put some qualifying criteria in.
- Snowball Sampling: Snowball sampling model is based on a reference model. Users that match criteria are asked to refer users that they are personally aware of that match the criteria.
- Survey design: The survey has to be designed in a way to elicit maximum value so that the responses received build towards robust and actionable feedback.
- Data collection: The data collection can be done via online or offline methods. It is imperative to collect the data in such a way that sense could be made of it and it could be used to analyze and report.
- Data Analysis: Data means nothing if it is not analyzed. Data that has been analyzed can give actionable insights for a product or brand to build on and this is imperative for a qualitative marketing research survey.
- Reporting: Once data has been collected and analyzed, it has to be reported in an easy to consume format to the relevant stakeholders as a milestone in the market research process.
LEARN ABOUT: Steps in Qualitative Research
There are 4 distinct types of qualitative market research testing methods that can be conducted. They are:
- Direct Exploration: This qualitative market research method is a no holds barred feedback method for a potential idea or product. This method is conducted where the users are told about the idea where no physical product is provided and all possible feedback is collected. This feedback is then collected and explored to form the basis of the new product.
- Monadic Testing: This method evaluates feedback by providing users with one single idea, concept, feature or product and asks for feedback. In this method, despite there being multiple concepts available, other designs are not shown. This method is important to elicit individual piece of feedback about a desired feature or concept.
- Sequential Monadic Testing: This testing method is similar to monadic testing because each concept, product or feature is shown one time. The only difference is that an alternate design to each concept is shown at the same time and feedback is collected on both from a user. This testing method is also called paired testing or paired nomadic testing.
- Discrete Choice Testing: Discrete choice testing is like paired nomadic testing but the only difference is that all choices are provided at once, not sequentially and the users are asked to pick one feature over another and then explain their choice.
LEARN ABOUT: User Experience Research
Successful businesses tend to use qualitative market research to keep pace with the ongoing market trend analysis , to make better-informed decisions and to achieve business excellence.
Whether your business is a start-up or a well-established entity, qualitative market research is a powerful method to identify your target audience and understand how they will respond to your product.
Before we dig deeper here are some of the real-time examples of qualitative market research case studies:
- AP, Norc and QuestionPro partner on geolocation exit polling app
- Washington State Ferry
Some examples of business expansion where qualitative market research plays a critical role by crowdsourcing concrete ideas for optimized decision-making :
- Branding : Many companies fail to understand how consumers perceive their brand or what is the brand positioning in comparison to their competitors. The research is typically done by conducting interviews with customers or organizing focus groups to collect feedback on marketing content and collaterals. In this way, the surveyor can explore different topics in-depth and get feedback from the respondents. Using this market research method, brands can gather information that can help them upscale and reposition their brand better in the market. LEARN ABOUT: Brand health
- Understanding the Consumer Behaviour: Sometimes, organizations/ companies/ entrepreneurs need more information about their consumer in order to place their product in a better manner. To do so they might need information about their gender, age, marital status etc. Qualitative market research helps them gather such information. For understanding the consumer behavior conducting in-depth interviews is the best option, as these interviews are conducted on one to one basis a decent amount of information can be collected.
- Measuring the reach of marketing activities: Many businesses go an extra mile to do a better job in promoting their brands. Here is where their marketing activities come into play. Market research can provide organizations with information about their marketing effectiveness by gathering first-hand information on how consumers look at their marketing message. This helps organizations maximize their marketing budget.
- Identifying new business opportunities: Market research helps organizations explore new opportunities leading to business expansion. By gathering data through market research through focus groups, organizations can pin a location, understand business dynamics, know their key competitors etc., to grow their business in the right direction.
- Getting insights on products: If a company comes up with a new product or looking to improve a current one, it is always better to take a market research in order to understand how acceptable is the product amongst the consumers. When a product comes to the market people have an opinion about its shape, size, utility, color, features etc. Qualitative market research through in-depth interviews will help gather systematic data that can be later used to modify or make the existing product better.
LEARN ABOUT: Market Evaluation
Employee Experience: Definition
Research ethics are as important as important as the ethics in any other research field. It is important to safeguard the participants’ interest. Like there is training and formal processes for researchers in other fields like in healthcare and medical research, market research is also governed by similar policies.
Due to the nature of qualitative market research, it is very important to have informed consent from a participant to be a part of the research study. This means that they are aware of basic information like:
- Nature of the research
- Expected time of completion
- If there are any sociological or physical risks or benefits
- Will a monetary or remuneration in other form be present
- Confidentiality protection
- How will the name and other personal details be used
- Any legal repercussions
Since this is a relatively less expensive and a more flexible method of market research there are a few applications of this market research methodology:
- It helps to understand the needs of the customers and their behavioral research pattern.
- What consumers think and perceive your product as.
- To understand the efficiency of your business planning and also to know if the strategies and planning that you put in place are working or not.
- What sort of marketing messages has a strong impact on the consumers and what just fall on deaf ears?
- Whether or not there is a demand for your product or services in the market?
LEARN ABOUT: Test Market Demand
Ultimately, qualitative market research is all about asking people to elaborate on their opinion to get a better insight into their behavioral pattern. It’s about understanding “Why” even before “What”.
LEARN ABOUT: Behavioral Targeting
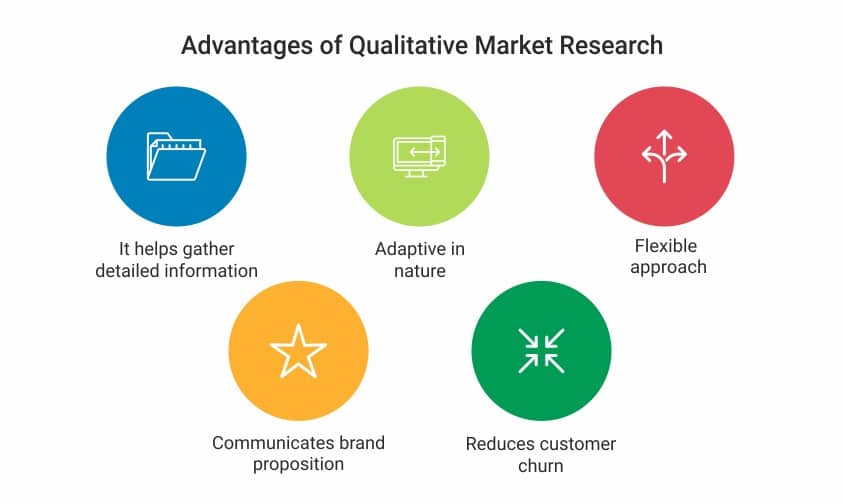
- It helps you gather detailed information: One of the major advantages of this market research method is that it helps you collect details information instead of just focusing on the metrics of data. It helps you understand the subtleties of the information obtained thus enabling in-depth analysis .
- It’s adaptive in nature: This market research can adapt to the quality of information that is collected. If the available data seems not to be providing any results, the researcher can immediately seek to collect data in a new direction. This offers more flexibility to collect data.
- It operates within structures that are fluid: The data collected through this research method is based on observation and experiences, therefore, an experienced researcher can follow up with additional open ended questions if needed to extract more information from the respondents.
- Helps communicate brand proposition accurately: Through this market research method, the consumers can communicate with the brand effectively and vice versa. Any product terminology, product jargons etc are effectively communicated as this research method gives a chance to the brand and the consumer to express their needs and values freely, thus minimizing any miscommunication.
- It helps reduce customer churn : Consumer behaviors can change overnight, leaving a brand to wonder what went wrong. By conducting qualitative market research, brands have a chance to understand what consumers want and if they are fulfilling their needs or not, thereby reducing customer churn . Thus the brand-consumer relationship is maintained.
LEARN ABOUT: Market research vs marketing research
- It is time-consuming: Qualitative market research can take days, weeks, months and in some cases even years to complete. This isn’t good to get quick actionable insights. In some cases, the premise with which the survey began may be non-existent due to market evolution.
- It is expensive: Due to the time taken to complete, qualitative market research is extremely expensive. They are also expensive to conduct and create actionable insights because the data is humungous and people with certain research skill sets are required to manage the research process.
- It is subjective: What one user may think could be very different from another. Due to this, there is no standardization of responses. This also means that the lines between true and false blur out to the point that each response is to be considered at face value.
- No result verification: Data collected cannot be verified because in most cases in a qualitative market research, the data is based on personal perceptions. Hence for analysis, each opinion is considered as it is valid.
- Halo effect: Due to the highly subjective nature of the research, the preconceived notion of the moderator or the person conducting the analysis skews the reporting of the research. It is human tendency to gravitate towards what’s known and it is very tough to get rid of this research bias .
LEARN ABOUT: Self-Selection Bias
With the increasing competition in the business world, the extensive need for business research has also increased. QuestionPro Communities is a qualitative research platform that is interactive, where existing customers can submit their feedback and also stay well informed about the market research activities, helps researchers undertake studies to maximize sales and profits. Through the communities platform, researchers can carry out research to effectively target and understand their customers, understand what is the market trend, prevent future research problems and thereby reduce customer churn .
This qualitative research platform helps in developing businesses to know their competitors and help identify the latest trends in the market. To carry out a well-directed research, businesses need a software platform that can help researchers understand the mindset of the consumers, interpret their thoughts and collect meaningful qualitative data .
QuestionPro Communities is the World’s leading platform for conducting analytics powered qualitative method . This online qualitative market research software helps researchers save their time, using niche technology like text analysis , where computers are used to extract worthwhile information from human language in an efficient manner, increase flexibility and improve the validity of qualitative research questions . This online platform help researchers reduce manual and clerical work.
QuestionPro Communities Qualitative Market Research Tools Includes:
Discussions
The online qualitative research software and tool, Discussions, allows a researcher to invite respondents to a community discussion session and moderate the focus group online. This can also be done live at a specific time that is convenient to the researcher and offer the users the flexibility to post responses when they login to their community. Invitations can be sent out well in advance to a specific target group the researcher would like to gather feedback from.
In case you are looking for respondents to share their ideas and allow others to analyze and offer a feedback and vote on the existing submissions, then this is a great tool to manage and present your results to the key stakeholders.
In this online community, you can submit topics, cast your vote in the existing posts and add comments or feedback instantly.

QuestionPro Communities is the only panel management and discussion platform that offers a seamless mobile communities experience. When it comes to engagement, how you reach respondents matter! Go mobile and take Discussions, Topics, and Idea Board anywhere your respondents go.
Feel free to explore our latest blog discussing practical examples of qualitative data in education – a valuable resource to deepen your insights into student experiences and learning dynamics. Why not give it a read and discover fresh perspectives for enhancing educational practices?
Learn about the other market research method: Quantitative Market Research
MORE LIKE THIS

Customer Communication Tool: Types, Methods, Uses, & Tools
Apr 23, 2024

Top 12 Sentiment Analysis Tools for Understanding Emotions

QuestionPro BI: From research data to actionable dashboards within minutes
Apr 22, 2024

21 Best Customer Experience Management Software in 2024
Other categories.
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
A comprehensive guide to qualitative market research
Last updated
3 April 2024
Reviewed by
Grow your business
Understand the needs of your customers
Launch a new product
Expand into new markets
Meet any lofty goals you set for your business
The two research methods you can use to glean these insights are quantitative and qualitative.
Quantitative research provides you with hard data you can use to find the size and scale of customer sentiment, discover causal relationships between variables, and support generalizations about macro-level populations.
Qualitative market research is an open-ended research method that looks at the reasons and motivations behind customer behavior, at the micro level. Qualitative market research gives you actionable insights you can use to improve everything from your customer service strategies to your products and services.
Market analysis template
Save time, highlight crucial insights, and drive strategic decision-making
- What is qualitative market research?
Qualitative market research is an open-ended research method that studies people's behavior and motivations within a specific market. While quantitative research is about hard numbers and analytics, qualitative market research takes a more generalized approach. It focuses on small sample sizes to encourage in-depth analysis of individual customers’ experiences.
The conversational nature of qualitative research is designed to encourage in-depth discussion. For businesses, qualitative market research is a powerful way to understand customers' points of view, as well as their pain points and desires.
- Why is it important to do qualitative market research?
Whether you are a CEO or a project manager, the thoughts and feelings of your customers should matter deeply to you. Through qualitative market research, you can identify the needs of your customers in a more nuanced, in-depth way than is possible with quantitative research.
Depending on the questions you pose, you can also get a feel for how customers perceive your marketing messages and communications, as well as more broad perceptions of your company as a whole.
If you're planning on launching a new product or service, qualitative market research can help you refine the launch and even make improvements. By using the feedback and insights from your research to make changes leading up to the launch, you are more likely to increase your revenue and receive glowing reviews.
- Advantages of qualitative market research
There are many advantages to qualitative market research. It's flexible, so you can adapt to the quality of information you receive. For example, if the available information isn't providing what you hoped, it's easy to change direction and collect more data using new questions.
Qualitative market research also helps you gather more detailed information than most quantitative data. While quantitative market research gives you metrics, qualitative market research allows you to better understand the subtleties within the data.
Long-term, qualitative market research can reduce customer churn. By conducting regular qualitative market research, businesses can better understand what consumers want (and what they don’t) and learn whether they are fulfilling their needs. This reduces customer churn and helps build a stronger relationship between a business and the people it serves.
- Disadvantages of qualitative market research
The most notable disadvantage of market research is that it’s time-consuming. Depending on the scope of the research and the amount of people dedicated to the project, it can take weeks or even months to complete. If you're working on a tight timeline, or if you have limited resources to dedicate to research, it might not be feasible.
Qualitative market research can also be expensive. While much of the cost will depend on the size and scope of the project, you might also need to hire additional people to help you complete the research.
If you compensate participants for their time (and experts advise some sort of compensation), that's another expense to consider.
Finally, qualitative market research is highly subjective, as the conclusions are drawn by individual researchers and their interpretation and analysis.
- Eight qualitative market research methods
The most common methods for qualitative market research include focus groups, individual interviews, and observations. However, many other methods should be considered as viable options for your market research.
Social media analysis
Social media has become an important part of many people's lives, with millions of people around the world interacting with their favorite platforms on a daily, even hourly, basis. Social media analysis can, therefore, be a powerful way to gather and analyze information.
If your brand is active on social media, take the opportunity to solicit responses from customers who follow you. This can be via a survey feedback form or some sort of direct response from customers.
You can also perform content analysis on social media, scanning comments left by consumers on your posts and checking for frequently used words.
For the most in-depth responses, consider gathering insights directly from the people who follow your pages and regularly interact with you.
Lifestyle immersion
If customer comfort is one of your top priorities as you conduct market research, lifestyle immersion might be the best option.
Lifestyle immersion is a research method that allows the researcher to observe the customer in their natural environment. By observing the participant in a natural setting, you can see their unguarded behavior and learn more about their needs and motives.
Focus groups
Focus groups are a popular method for conducting qualitative market research. Focus groups are typically comprised of 6–10 people, along with a market researcher who functions as a moderator.
During the focus group, participants are encouraged to share their unguarded thoughts and opinions on a product, service, or marketing campaign.
Traditionally, focus groups were held in person, since verbal and non-verbal reactions are an important part of measuring responses. However, web-based focus groups have been gaining popularity in recent years, especially in light of the COVID-19 pandemic. Online focus groups tend to be more cost-effective and convenient for most participants.
Observations
Observations, also known as shop-alongs, involve researchers following participants as they walk through a store. The goal of observations in qualitative market research is to gauge customers’ interactions and reactions to things they encounter, including products, displays, and advertising.
Observations don't require the market researcher to physically accompany participants. Typically, the researcher will observe from a distance or watch a camera feed.
Individual interviews
Individual interviews are a highly personalized method of conducting market research. These interviews are in person, over the phone, or through video-conferencing software.
They tend to be most successful when held as part of a free-flowing conversation that puts the participant at ease and makes them feel comfortable sharing their unfiltered thoughts and opinions. The interviews can be structured or unstructured, depending on the nature of the questions and your overall goals for the project.
Include plenty of open-ended questions in your interview outline to keep the conversation moving. Pay attention throughout the interview to see how the participant responds to the questions and if they seem uncomfortable or ill at ease. If they do, switch gears to make the conversation more relaxed again.
Diary or journal-logging
A diary study, also known as journal-logging, is a research method that aims to collect data about user behaviors, activities, and experiences over a set period.
During the designated reporting period, participants are asked to keep a diary and record specific information about the activities you want to analyze. The data is self-reported by participants when the reporting period is up.
Diary studies can be useful for gathering information about users’ habits and thought patterns. They can also effectively capture attitudes and motivations. However, it can be challenging to recruit dedicated users, since diary studies require greater involvement over a longer period than more traditional market research methods.
Surveys are a popular method of conducting market research. A powerful form of primary research, surveys are endlessly customizable. They can be done:
Over the phone
Via email or other online delivery method
If you opt for an online survey, test the software ahead of time, so you can be sure everything works properly and displays well on mobile devices.
It's also a good idea to run a test survey with a smaller group. This allows you to refine your questions and eliminate any confusing wording.
Ethnographic research
Ethnographic research involves observing participants in their natural environment, primarily how they go about mundane tasks such as cleaning their house or preparing a meal. Unlike observations, ethnography can involve a variety of approaches, including diary studies and video recordings.
The goal of ethnographic research is to understand the social dynamics, beliefs, and behaviors of participants through direct observation and participation in their daily activities. Ethnographic research can take place over an extended period, from a few weeks to a year or more. It's versatile and is best done with the assistance of an experienced ethnographic researcher.
- An example of qualitative market research
One of the main benefits of qualitative market research is its flexibility. No matter what your goal is or what outcome you're hoping for, you can design an effective study.
One example of qualitative market research using a focus group is a cereal company wishing to update the packaging of one of its most popular products. After producing several design concepts, the company opts to commission a series of focus groups to gauge responses to each concept.
During the focus groups, with the help of a moderator, participants discuss each design, evaluating the pros and cons. Based on the feedback received in the focus groups, the cereal company can move forward with the design most appealing to their customers.
- Best practices for qualitative market research
While qualitative research is flexible, there are still best practices to follow. Regardless of which research method you choose, consider these tips when crafting your approach and designing the questions.
Accurately identify research goals
Before embarking on any market research, you should know your end goal. Think about the specific questions you want answered, including the nature of the product or service you wish to refine or develop. Outline your goals and share them with every project stakeholder, including managers and the CEO, if necessary.
Understand your customers
Knowing your customers is vital for accurately targeting survey participants. Your business should have a customer profile that includes basic demographics such as:
Shopping habits
Use this profile to create questions that are useful for your study. When crafted thoughtfully, your questions will identify needs that aren't being met and meet study participants where they are.
Choose the most appropriate research method
There are many ways to conduct qualitative market research, but not all of them might be right for your unique needs. Think about what method will give you the optimal results and work best for the study participants you wish to recruit.
Focus groups are an ever-popular research method, but it isn't always possible to dedicate time and energy to moderating one. A survey or series of observations might be more effective, depending on your available resources and goals.
Use open-ended questions
The goal of qualitative market research is to gain thoughtful responses from participants. Use open-ended questions that require more than a simple yes or no response. The idea is to maintain an open dialogue, even through vehicles such as surveys or focus groups.
Test out questions on yourself and your team members before launching them to participants, so you can be sure they make sense and give people the chance to truly share their thoughts.
- Tips for qualitative data analysis
Qualitative data analysis is rarely a linear process. Since qualitative market research often doesn't result in hard numbers, be flexible in your approach to analysis.
After you finish your research, organize and collate your responses into one location for further analysis. If you have audio or video files, allocate time to transcribe the data, whether that means bringing in a transcriptionist or guiding your team members through the process.
As you go through the responses, become familiar with the data. This will help you better understand your customers and identify any potential gaps in the research. Always involve other stakeholders in the process, not only along the way but also once the final results have been collated. This promotes transparency in the project and improves communication across the board.
Are customer surveys qualitative?
Customer surveys are one method of market research. They can be made qualitative or quantitative, depending on the nature of the questions. They are one of the most popular forms of qualitative market research because they are versatile and highly customizable. Surveys can be done in person or through web software, such as email.
What are qualitative marketing objectives examples?
While quantitative objectives are usually specific and measurable, qualitative marketing objectives are more subjective. They tend to be conceptually broad, such as "we want to learn more about how our customers rank our service compared to our competitors,” "we want to increase brand awareness," and "we want to improve customer satisfaction." It can be helpful to have qualitative and quantitative objectives for your market research, depending on the nature of the project and whether it's related to a specific product or service.
Get started today
Go from raw data to valuable insights with a flexible research platform
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 3 April 2024
Last updated: 26 May 2023
Last updated: 11 April 2023
Last updated: 22 July 2023
Last updated: 1 June 2023
Latest articles
Related topics, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
Qualitative research in marketing: definition, methods and examples
Apr 7th, 2022

What is qualitative research?
Qualitative research methods, how to design qualitative research , qualitative research examples.
- Share this article
Qualitative research allows businesses to determine customers’ needs, generate ideas on improving the product or expanding the product line, clarify the marketing mix and understand how the product would fit into customers’ lifestyles. The research will be useful for businesses of any size and type. For example, entrepreneurs can use qualitative research to gain insight into customers’ feelings, values, and impressions of the product or service. With qualitative research, you can understand the reasons and motives of customers’ reactions and use this information to create marketing and sales strategies .
The research can also help you design products and services that meet the requirements of your target audience. For instance, imagine you are a restaurant owner and want to introduce a new menu; you can conduct qualitative research and invite local residents to give you feedback on the food, service, and pricing. This approach will increase your chances of success.
Qualitative research studies the motives that determine consumer behavior by employing observation methods and unstructured questioning techniques, such as individual in-depth interviews and group discussions. The approach involves the collection and analysis of primary and secondary non-numerical data. The goal of qualitative research is to understand the underlying reasons for making purchasing decisions and learn about customers’ values and beliefs.
Qualitative research asks open-ended questions beginning with the words “what”, “how”, and “why” to get feedback concerning a new product or service before the launch or development phase. This method reveals customers’ perceptions of the brand, buyers’ needs, advantages, and drawbacks of the product or service. Furthermore, it helps evaluate promotional materials and predict how the product or service can influence the lives of your customers.
This research method emerged in the early 1940s when American sociologist Paul Lazarsfeld introduced focus group interviews to study the impact of propaganda during World War II. In the late 1940s, American psychologist and marketing expert Ernest Dichter developed a new type of consumer research called motivational research. Dichter used Freudian psychoanalytic concepts to understand the motives of consumer behavior. He conducted in-depth interviews to learn more about customers’ needs and attitudes towards certain products.
In the 1960s, marketing academic John Howard began studying consumer behavior from the perspective of social sciences, including psychology, anthropology, and economics. At the same time, market researchers focused on the emotions, feelings, and attitudinal elements of consumption. As a result, in-depth interviews, video-recorded focus groups, and computer-assisted telephone interviews became prevalent qualitative research techniques.
With the advent of the Internet and mobile devices, qualitative research has undergone numerous changes. Today the Internet allows researchers to conduct surveys on a much larger scale. The marketers can use hyper-segmentation and hyper-personalization to launch targeted advertising campaigns, utilize market research analysis software and gather customer opinions using social media analysis. Let us take a detailed look at the basic methods of qualitative research.
The most common qualitative research methods include focus groups, individual interviews, observations, in-home videos, lifestyle immersion, ethnographic research, online sentence completion, and word association. We will consider each of them in more detail below.
Focus groups
Focus groups are discussions dedicated to a specific product and its marketing strategies . The groups typically consist of 6-10 people and a moderator who encourages them to express their opinions and feelings about the product. Usually, focus groups are held in-person to study consumers’ verbal and non-verbal reactions to the product or advertising campaign.

This method has several applications, including testing marketing programs, evaluating the overall concept for a product, examining the copy and images of the advertisements, and analyzing the new types of product packaging. Nowadays, in-person focus groups are losing popularity, while online discussions via video conferencing tools are attracting a lot of attention from researchers.
Social media analysis
Social media and mobile devices give brands more opportunities to gather and analyze information. Customers now interact directly with brands on social media platforms where they spend their free time. Content analysis of Facebook posts, comments, tweets, YouTube videos , and Instagram photos allows brands to track consumers’ activities, locations, and commonly used words.
You can ask for users’ feedback , encourage them to fill out a brief survey, or engage with customers to inform them of your marketing plans and the development of new products. Furthermore, the qualitative research participants can provide additional contextual information like photos and videos, which gives a better understanding of their thoughts and attitudes.
Individual interviews
An individual interview is usually conducted in person, over the phone, or via video conferencing platforms. The interviewer asks the existing customer a number of questions to determine his motivation to buy a particular product. One-to-one interviews are held as a free-flowing conversation and include open-ended questions. The interviews can be flexible, semi-structured, and unstructured. You can ask about the customer’s frustrations concerning the product, motivations and reasons for purchase, and the sources of information from which they learned about the product.
Observations
Observations allow researchers to see how the customers react to the products in the store and analyze their shopping behavior and purchase experience. This method is more effective than written surveys as it provides better insight into consumer reactions. For example, the researchers can observe how customers stop outside the store, what attracts them to the shop window and which way they walk once they enter the store. In addition, observations help determine problems related to product placement on store shelves, clutter, or products that are out of stock. You can also collect customer feedback to improve some aspects of the shopping process, like packaging design.
In-home videos
In-home videos allow researchers to watch how customers engage with the product in the comfort of their own homes. Using this method, you can monitor user behavior in a natural and relaxed environment. Thus, you can have a better picture of the ways people use your product. The customers can keep video diaries or film the videos with detailed comments concerning your product. You can store the qualitative content in one place and create an insight hub to analyze and reuse the collected information in the future.
Lifestyle immersion
Lifestyle immersion is another method that allows obtaining customer feedback in a comfortable environment. Immersion refers to the researcher’s profound personal involvement in a customer’s life. For instance, the researcher visits an event, such as a party or family gathering, and observes the user’s reactions and behaviors in a familiar setting. Watching how users speak to their family and friends is an increasingly effective technique that allows learning more about their needs, challenges, and motives.
Ethnographic research
Ethnography is a type of research that originates from 20th-century anthropology and involves observing people in a natural environment rather than a lab. Namely, the researchers watch how respondents cope with their daily tasks, such as grocery shopping or preparing dinner. This helps see what people actually do instead of what they claim to do.
Ethnography applies a variety of approaches, including direct observation, video recordings, diary studies, and photography. Researchers can observe the user’s behavior at home, at the workplace, or with their family or friends. Passive observation as a method of ethnographic research implies following and watching users without interacting with them or interfering with their actions. Active observation, in contrast, entails working or cooperating with consumers, asking them questions about a product or service, and joining their team or group.
Online sentence completion and word association
Sentence completion is a projective technique used in qualitative research to allow customers to express their opinions and feelings. According to this method, the respondents receive the survey with unfinished sentences. They should complete sentences that describe the product or find the words that would be appropriate in the context of the sentence. With this method, the researcher can put qualitative data in a structured form.

Word association is a similar technique that helps researchers gather information about brand awareness , images, and associations related to a specific product or brand. The respondents are given the trigger words and instructed to write the first word, association, or image that comes to mind. In contrast to the interviews and focus groups, sentence completion and word association techniques can reach more people when conducted online. Moreover, it takes less time to analyze the results and understand users’ perceptions.
Once you have learned about the most widely used qualitative research methods, it is time to plan the research process step by step.
The success of your research outcomes greatly depends on adequate planning and appropriate strategy. Here we will list some general guidelines on how to conduct qualitative research.
Determine research objectives
The first step to designing or running qualitative market research is understanding the goals you want to achieve with your study. In particular, the research objectives might include discovering the existing or potential product or brand positioning , understanding perceptions about the company or product, investigating how people react to advertising campaigns, packaging or design, evaluating website usability, and identifying strengths and weaknesses in the product. The absence of clear objectives would create challenges for the researcher as qualitative research involves open-ended questions and in-depth replies that are difficult to interpret and analyze directly.
Choose the methodology to conduct the research
Determine the most suitable method to perform market research taking into account demographics, geographical location of your target audience, lifestyle behaviors, and the product that is being examined. Market researchers usually collaborate with professional recruiters who find and screen the participants. A significant part of the researcher’s work is to develop a list of topics for discussion in small groups. You need to involve moderators who would spend from 90 to 120 minutes with the group asking questions, observing their reactions, and analyzing behavior.
Investigate various data collection methods
Once you have chosen the observation method, you need to involve a moderator to examine the participants’ behavior and take notes. This approach usually requires a video camera or a one-way mirror. You can also combine qualitative and quantitative research to collect numerical data and analyze metrics together with customers’ replies and observation results.
When running focus groups, you can either organize one discussion with eight to ten participants or a series of online meetings which will last three-four days. Respondents will answer the questions from the moderator or react to prerecorded videos.
When you conduct one-on-one interviews, you need to speak with the respondents on the phone or organize a personal meeting. This method will be suitable if you want customers to try the product and share their impressions.
Analyze the collected data
Researchers will typically need a few days to a few weeks to collect the information. Then researchers will examine the data to provide responses to your questions. The next step is qualitative coding or the technique of categorizing the findings to identify themes and patterns. The specialists might also include the statistics to explain what the data is indicating. Besides, the report might contain a narrative analysis of underlying messages and phrasings.
Study the report and recommendations
The final step is to review the report provided by the researchers. It can be a written document or video recording. The paper, based on MECE principles , will help you group the patterns and similarities and sort them according to demographics and other customer characteristics. The document will contain specific recommendations, so you can draw conclusions and start making improvements to your product marketing strategy .
In the next section of this article, we will review how famous brands have put qualitative research methods into practice.
Qualitative market research helps brands strengthen their reputation and credibility, segment customers , identify market trends, increase awareness, rebrand products , and get feedback from the consumers on their preferences. Let us discover how McDonald’s, Starbucks, and LEGO use data to confront tough competition.
When conducting market research, McDonald’s asks the customers several critical questions regarding best-performing products, the most appropriate pricing , the effective advertisements, and the most attended restaurants. Finding answers to these questions allows for analyzing whether the company managed to expand its customer base.
Furthermore, McDonald’s collects customer feedback to improve the products. In particular, many customers were disappointed with the lack of healthy and organic options on the menu. As a result, the company added apple slices and other healthy items to the menu and launched an advertising campaign to show that chicken nuggets and burgers were made of real meat.

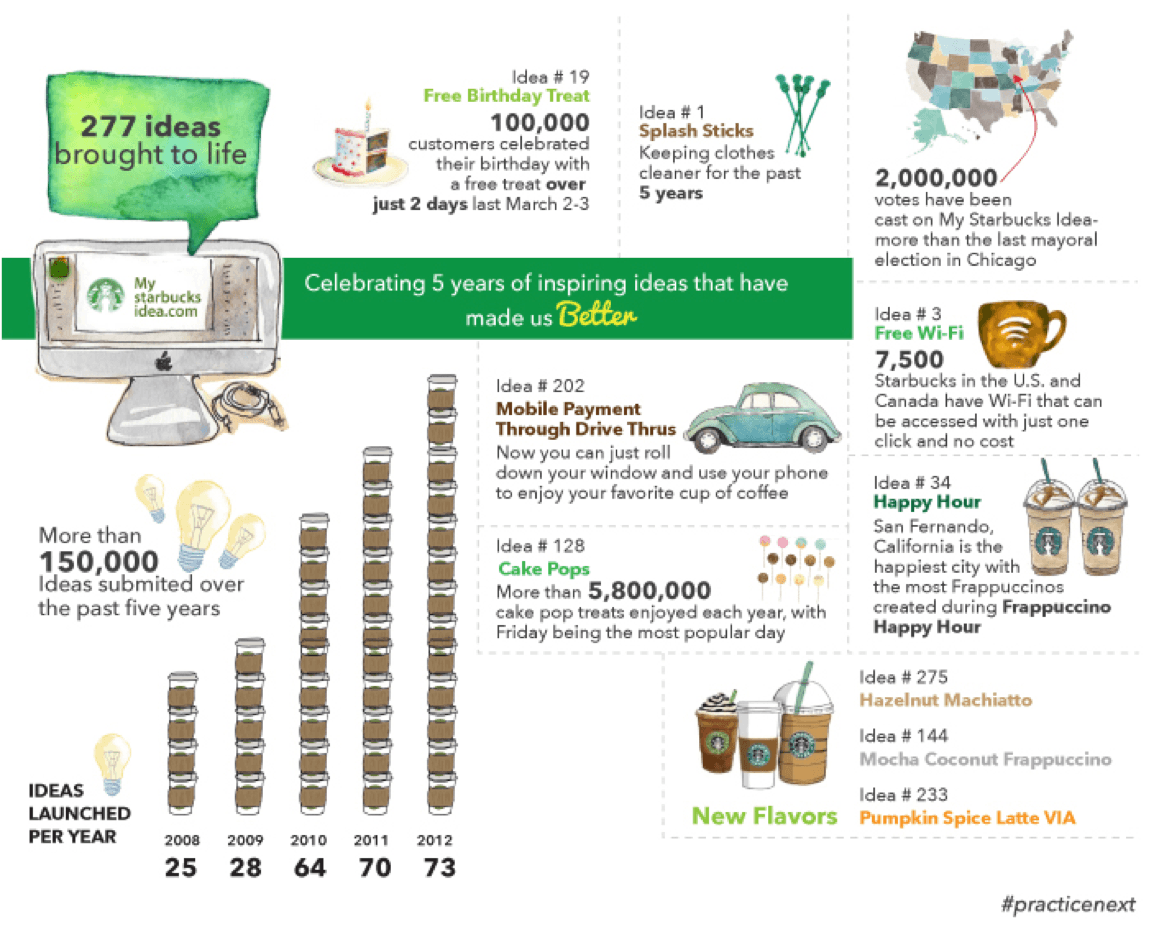
Starbucks encourages customers to share feedback on the official site and contribute ideas via Twitter . The company monitors social media, tracks cultural trends, and offers customers to test the products in the stores. From 2008 to 2018, Starbucks used the My Starbucks Idea platform to collect ideas and continuously improve its products. The company implemented over 275 consumer ideas, including recommendations about new products and methods to improve corporate responsibility.
Some years before, LEGO was considered to be primarily a boy-oriented company. Then LEGO decided to promote inclusivity and create toys targeted at all genders. The company conducted research involving 3,500 girls and their parents to examine children’s behavior while playing with toys. Later LEGO used the collected data to determine the size of the figures and create bright packaging for the new toy line called “Friends” which was designed specifically for girls.
Companies would not create new offers, improve their existing products, satisfy the needs of their customers, or solve the most difficult challenges without market research. Qualitative research will help you obtain a clear understanding of your target customers, recognize the emotional connections to your brand, identify potential obstacles to purchase and features that are missing in your offer, and as a result, develop an outstanding product.

- Marketing Strategy & Branding
- Content Marketing & SEO
- Product Focused Marketing
- Digital Experience Design
- Marketing Automation
- Video Production
© 2023 Awware
The qualitative market research guide: actionable methods for best results
What is qualitative market research, the ethics of qualitative market research, how to conduct qualitative market research, what are the applications of qualitative market research, overcoming the challenges of qualitative market research.
If you’re thinking about skipping qualitative market research and just going with your gut, this article is a must-read.
While some brands and products in the past have won big based on someone’s intuition, it certainly isn’t a reliable recipe for success — because many more who’ve invested based on an instinct, have failed. Hard.
That’s why we want to highlight the importance and value of qualitative market research. It’s what explains why people pick one product over another that seems just as good.
Qualitative research digs into the nuances, offering insights that can significantly impact your marketing approach and product development. Here we’ll show you exactly how you can turn it into your secret weapon.
Qualitative market research goes straight to the core of your customer’s thoughts and feelings. It’s not just about how many people clicked or bought, but why they did it, or even why they didn’t.
This kind of research lets you in on the stories behind the statistics, giving you a more in-depth understanding of your target audience’s behaviors, perceptions and motivations. And with this rich insights and data, you can tailor your products and marketing strategies to truly resonate with your audience.
Here’s a quick rundown of the types of market research out there:
- Quantitative research: Deals with numbers and measurable forms.
- Qualitative research: Focuses on understanding the quality of consumer interactions and thoughts.
- Mixed methods: Combines both quantitative and qualitative research.
It’s good to know qualitative and quantitative research make a great pair – it helps you give context to numbers, and vice versa. And it’s good to know when you could run qualitative research:
- Before your quantitative research ? If you’re grasping for ideas and inspiration, qualitative market research can be a great source. Your respondents will often flag issues or make suggestions that you and your team might never have thought of. And for extra peace of mind, you can follow-up your qualitative research with quantitative studies to make sure that inspo is truly representative.
- After your quantitative research ? Often teams will have run quantitative studies and spotted threads they’d like to pull at and see whether there’s more to learn. This is where qualitative market research comes in – it can add flavor and context to your quant data. And it can be a great way to personalize your data for internal or client signoff.
Of course, there are different ways of gathering qualitative data. So when we talk qualitative research, these are the main methods you’ll come across:
- Ethnographic research: observing your customers in their natural environment, seeing how they live, work, and play.
- Narrative research: collecting stories from individuals to better understand their experiences.
- Phenomenological research: used to understand common experiences among a group of people, researching shared perceptions.
- Grounded theory: developing a theory based on the data you collect, starting with the data and working towards a theory.
- Action research: a collaborative approach, working with groups to identify solutions to problems and implement changes.
Each of these approaches gives you unique insights into the minds and lives of your customers, helping you make more informed decisions that can drive your brand forward.
If you want to know more about the ins and outs of different research types, check out our blog about the difference between quantitative vs qualitative research , and here’s a quick video summary to get you started…
While it’s not exactly mind reading, qualitative market research does touch more on personal thoughts and opinions than, for instance, quantitative research does. That means it requires trust – and that’s where ethics come into play. Here’s what keeping it ethical looks like:
- Participant confidentiality : Keeping the identities of your participants under wraps is a non-negotiable.
- Informed consent : Participants need to know what they’re getting into, how their insights will be used, and how they can change their involvement.
- Sensitive information : Any data that could be considered sensitive deserves extra protection and consideration.
Data isn’t high quality when it isn’t ethical, and vice versa. If your respondents don’t feel that their answers will be handled with care, they might not answer honestly – if at all.
At Attest, we’re all about making sure your insights are built on a solid foundation of excellent data quality, trust and transparency – for both you and your respondents.
Because what’s the point of qualitative research if you can’t trust the results? Check out how we assure data quality that you can rely on.
The research you do should be the foundation of the actions that follow — don’t just conduct research for the sake of it. Choosing the right qualitative research methods and tools is crucial, but there’s more to it.
By following the steps below, you’ll not only gather rich, qualitative data but also pave the way for meaningful changes in your product development, marketing strategy, and overall brand experience.
1. Create a research plan
When you conduct qualitative research, or any kind really, the steps you take should be based on your research objectives, and related to the actual changes you might be making. This is what makes market research crucial for marketing experts : it shows you which actions to take, instead of just doing creative guesswork.
First, decide on your qualitative research methods—will you go for surveys, focus groups, or a mix? Define clear objectives. What do you want to learn? Keep in mind how to balance your research approach: you can opt for direct exploration for fresh insights, monadic testing for focused feedback, sequential monadic testing for comparative insights, or discrete choice testing to understand preferences. Each method has its place, and combining them strategically can offer a fuller picture of your market.
Next up, consider your sampling methods. Who are your ideal participants? Where can you find them? (Hint: we help you with this!)
Once you know what to ask and who you’ll be speaking to, it’s time to start crafting your survey — and using our templates makes that even easier. Take your pick and start tweaking.
The final step of your research plan, is choosing which qualitative market research tool to choose for. The steps below give you some guidance on what to look for.
2. Recruit the right participants
The power of qualitative research lies not in the most fancy tools, but in the quality of your participants.
You’re looking for individuals who reflect your target audience or represent a new market you’re exploring. The key is to ensure diversity and relevance to get a comprehensive understanding of consumer behavior and opinions. Read more about how we help you get in touch with the right people — picking from an audience of 125 million people in 59 markets spread across the globe.
3. Conduct interviews, surveys or focus group research
Jumping into your audience’s world, interviews, surveys, and focus groups are essential tools in your research kit. But how do these qualitative market research methods add value?
- One-on-one interviews offer a closer look into what your consumers are thinking and feeling, providing valuable insights into their personal experiences and expectations. This intimate format fosters detailed conversations that can uncover deep-seated motivations and stories.
- Surveys allow for a broad reach, enabling you to connect with a wide audience very quickly to collect various data points. This method is great for identifying trends, preferences and behaviors on a larger scale.
- Focus groups, on the other hand, bring a unique dynamic. In these sessions, participants’ interactions can generate new insights and perspectives, offering a diverse view of your product or service. This collaborative environment encourages research participants to build on each other’s ideas, revealing insights that might not emerge in individual settings.
Remember: you don’t have to limit yourself to only one option – but pick a mix that works best for your research goals, and your audience. Their participation is key here.
4. Conduct observational research (optional)
Now this is optional, but if you want an extra layer to your research process, observational research is a great supplement to your qualitative study.
Instead of just hearing what your target audience is thinking, you are going to see how it affects their actions, by tracking how they interact with your products, navigate your stores or use your website.
Watching from a distance, you might discover that consumers use your product in ways you hadn’t imagined. It might also clarify some statements you heard or uncovered during the survey or interview phase – observational research can unearth gems of insights that are invisible in one-on-one conversations or online focus groups.
Of course, this approach requires patience and a non-intrusive stance. You don’t want to influence people, and it’s not easy to do it at a large scale – but in some scenarios adding an extra research method like this certainly gives extra depth to your findings.
5. Analyze your research data
With data in hand, it’s time to sift through the stories and sentiments to find patterns and themes. Qualitative data analysis can be complex, but it’s where you begin to understand the ‘why’ behind the behaviors that drive your customers’ choices.
Don’t just use qualitative insights to confirm your hopes and beliefs. Actively look for commonalities, differences, and surprising insights that can guide your strategy.
6. Report and communicate findings to key stakeholders
This is the springboard to action. If you can package your findings in a way that resonates with your team, management, or clients, you’re one step closer to meaningful and impactful changes.
Clear, compelling reporting translates your research into actionable insights – and our tool helps you get them.
Share stories, highlight key themes, and suggest next steps. Make your qualitative research findings a cornerstone for your decision-making and strategy development.

Get the full picture with qualitative research from Attest
Whether you’re looking for inspo, or backing up your quant research with qual context, you can run your research studies side-by-side with Attest
You can use qualitative market research for practically every aspect of your business. But let’s highlight some of the most popular applications first:
- Product development: Before your product hits the shelves or the digital marketplace, qualitative research helps you tune into what your customers really need and want. Insights gained can directly inform product features, design and enhancements to meet consumer needs effectively.
- Creating data-driven marketing strategies: Armed with qualitative insights, you can craft marketing campaigns that resonate deeply with your audience. Tailored messaging and campaigns can address specific consumer pain points, preferences and values, increasing engagement and conversion rates.
- Understanding customer perceptions: Ever wonder how your brand is viewed through the eyes of your consumers? If you haven’t, you should. It’s not something to be scared of, it’s something to learn from – through, you guessed it, qualitative research. It will uncover the perceptions, misconceptions, and the emotional ties customers have with your brand, and be a trusted guide on how to position yourself in the market.
- Consumer segmentation: Two customers might seem alike, but not shop alike. That’s because there are underlying differences. By identifying distinct consumer segments within your broader audience, qualitative research allows for more targeted and personalized marketing efforts. Understanding the varied needs and motivations of each segment leads to more effective and efficient marketing strategies.
Beyond the usual suspects, qualitative market research has some lesser-known yet incredibly valuable applications.
- Examining the impact of customer service language tweaks on overall customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Exploring consumer reactions to different packaging materials to align brand perception with sustainability goals.
- Refining the user experience on your website based on nuanced user feedback about navigation and content.
The possible applications of qualitative market research are limitless – and brands who experiment with really specific, seemingly small applications, often find suggestions for meaningful changes that drive big results. Just check out our customers’ stories for some inspiration.
We won’t tell you that qualitative market research is something you can do on autopilot or with your eyes closed – doing it right is challenging in some ways. But not in ways you can overcome.
Let’s walk through some common obstacles and how to vault over them, and how using Attest can turn these challenges into opportunities for richer insights.
- What to do : Use targeted recruitment to ensure your sample closely mirrors your target market. Attest helps you find and engage with the right participants, making even small sample sizes filled with insights.
- What to do : Streamline the process with efficient planning and execution. Attest offers streamlined survey design and distribution tools that cut down on both time and cost, making in-depth qualitative research more accessible. And with your designated research manager to guide you , you know your studies will be well designed and give you reliable results.
- What to do 2 : Bear in mind that good qualitative market research, with a clear purpose and action plan, will lead to better business results. It could affect your bottom line, increase sales or impact your ROI in other ways. It’s not investing in qualitative research that could cost you way more money.
- What to do : It starts with awareness, and implementing protocols that avoid bias. Attest’s platform is designed to ensure unbiased data collection, with features that support anonymity and objectivity in responses. And this is also where you Customer Research Manager can steer you towards honest, unbiased research.
- What to do : Make the most of technology to conduct efficient and effective research within your means. Better yet, choose Attest. You’ll get access to your very own dedicated research expert that will help you get the most value out of your research.
Get the best of quantitative and qualitative research with Attest
To ensure your market research truly hits the mark, blending the depth of qualitative insights with the breadth of quantitative data is key. For the clearest picture of your market landscape and the most informed decisions, a platform that offers both qualitative and quantitative insights is your best bet. Attest provides this comprehensive approach, equipping you with the tools to not just navigate but thrive in your market. Ready to see the full picture?
Discover how Attest can elevate your research game and support your brand’s growth with expert-backed insights.

Customer Research Manager
Related articles
Attest’s enhanced parental leave policy, attest’s fertility treatment and family support policy, quantitative market research questions to ask for actionable insights, subscribe to our newsletter.
Fill in your email and we’ll drop fresh insights and events info into your inbox each week.
* I agree to receive communications from Attest. Privacy Policy .
You're now subscribed to our mailing list to receive exciting news, reports, and other updates!

- Pollfish School
- Market Research
- Survey Guides
- Get started
The Complete Guide to Qualitative Market Research

So what exactly is qualitative research? At a glance, this type of research method seeks to gather in-depth data about a phenomenon without focusing on numerical data or on quantities.
But there is much more to this kind of study method. Learn holistically about qualitative market research with this complete guide.
What Defines & Makes Up Qualitative Research?
Qualitative research is centered around experiences, ideas and opinions. As such, it does not focus on statistical or quantitative outcomes. Instead, it seeks out an in-depth understanding of an issue, occurrence or phenomenon.
Thus, this research method zeroes in on the “what” and more importantly, the “why” of a research subject. (Unlike quantitative research, which focuses on the “how much”).
Here are some of the applications of qualitative research:
Understanding an issue in greater depth
Finding the reason behind an occurrence (whether it’s desirable or undesirable)
Uncovering trends in target market opinions
Forming educated solutions to address customer/studied subject concerns
Discovering the causes of certain actions
Qualitative research generally relies on a smaller sample size in order to get a deep read of happenings, causes and motivations. This kind of research method functions through the usage of open-ended and exploratory questions.
Understanding the “why” behind an issue is then used to make decisions on how to resolve the issue or how to improve on an existing productive situation.
Qualitative data must occur in natural environments. This denotes a kind of environment in which participants discuss their opinions at length and at ease, which researchers use to gain deeper knowledge and form inferences around a topic.
Prior to the internet, this kind of research was conducted in-person, but with the advent of the internet and innovations in market research, qualitative data has been collected online. The digital space can also serve as a natural environment.
The Five Main Types of Qualitative Research
Just as with quantitative research, there is not a single approach to conducting qualitative research. On the contrary, there are five main varieties of performing qualitative research. Aside from their methodology, these sub-categories also seek different types of answers and conclusions.

1. Narrative Research
This research is used to form a cohesive story, or narrative, by way of consolidating several events from a small group of people. It involves running in-depth interviews and reading up on documents featuring similar actions as a means of theme-searching.
The point of this is to discover how one narrative is shaped by larger contextual influences. Interviews should be conducted for weeks to months and sometimes even for years. The narrative that the researcher uncovers does not have to be presented in sequential order.
Instead, it should be projected as one with defined themes that attempt to reconcile inconsistent stories. This method can highlight the research study’s ongoing challenges and hardships, which can be used to make any improvements.
2. Ethnographic Research
The most common qualitative research method, ethnography relies on entrenching oneself in various participant environments to extract challenges, goals, themes and cultures.
As the name suggests, it involves taking an ethnographic approach to research, meaning that researchers would experience an environment themselves to draw research. Using this firsthand observation, the researcher would not need to then rely on interviews or surveys.
This approach may seem to be far-fetched where market research is concerned, but it is doable. For example, you’d like to see the effectiveness or frustration that customers face when using your product. Since you can’t follow them home, you can request videos that show them using it. Many big brands have call-outs on their websites (ex: on product pages) for their customers to send in videos of their interactions with the products.
3. Phenomenological Research
This qualitative method entails researchers having to probe a phenomenon or event by bringing lived experiences to light and then interpreting them. In order to achieve this, researchers use several methods in combination.
These include conducting surveys, interviews and utilizing secondary research such as available documents and videos on the studied phenomenon. Additionally, as in ethnographic research, phenomenological research involves visiting places to collect research.
These will help you understand how your participants view your subject of examination. In turn, you will gain insight into the participants’ motivations.
In this research type, you would conduct between 5 and 25 surveys or interviews, then peruse them for themes. Once again, you would scrutinize experiences and sentiment over numerical data.
4. Grounded Theory Research
In contrast to phenomenological research, which seeks to fully form the core of an issue, grounded theory attempts to find explanations (the why) behind an issue. To achieve this, researchers use interviews, surveys and secondary research to form a theory around the issue/occurrence.
The sample of this study tends to be on the larger side, at 20-60 participants. Data extracted from this type of research is interpreted to determine the reasoning behind, for example, heavy usage of or frustration with a product. These types of studies help a business innovate an existing product by getting into the weeds of how it’s used.
5. Action Research

This type of research involves researchers and participants working collaboratively to bring theory to practice. Also called participatory research, collaborative inquiry, emancipatory research and action learning, this method entails the act of “learning by doing.”
This means a group of researchers come together to find and address a problem, resolve it and then study the success of their endeavors. If they underperformed or their outcomes don’t satisfy their expectations, they would then reattempt the process.
In action research , a researcher spends a considerable amount of time on collecting, analyzing, and presenting data in an ongoing, periodic process. This involves researchers coming up with their own surveys and interviews around a subject matter, then presenting their findings to one another to draw conclusions and solutions.
They would put into practice the means to improve a situation and continue measuring their success throughout the process.
Examples of Questions for Qualitative Research
When working within the capacity of any of the above research types, it’s crucial to ask the right questions. Here you’ll find the questions you can use when conducting each of the five types of qualitative research.
Bear in mind that some of these questions will appear to be similar in nature; some are even interchangeable. That is normal, as researchers may search for the same answers, but apply a different approach in their research method.
In any case, all of the below features questions that fit within the larger qualitative research framework.
Learn more about asking insightful market research questions . Here are a few examples of the questions within the five categories:
1. How do people who witnessed domestic violence understand its effects in their own relationships?
Variable: Views of domestic violence on one’s own relationships
Demographic: People in relationships, who’ve witnessed domestic violence
Qualitative Research Type : Narrative
2. What are the lived experiences of working-class Americans between the ages of 20 and 40?
Variable: Experiences and views of a working-class background
Demographic: Working-class Americans ages 20-40
3. How do Asian Americans experience reaching out to address mental health concerns?
Variable: The experiences in seeking out care for mental health
Demographic: Asian Americans seeking help for mental health
Qualitative Research Type: Ethnographic
4. What do you enjoy about this product or service?
Variable: The positive experiences of using a particular product/service
Demographic: The target market of a product or service
5. How have people who have experienced poverty changed their shopping habits when they entered the middle (or higher) class?
Variable: The changes or stagnation in shopping habits
Demographic: those who experienced poverty, but climbed the social ladder
Qualitative Research Type : Phenomenological
6. What was it like when you had a negative online shopping experience?
Variable: unpleasant shopping experiences
Demographic: a group that is most likely to shop at a particular online store
7. What influences managers in private sectors to seek further professional advancement?
Variable: Motivation for seniority
Demographic: Managers in the private sector
Qualitative Research Type: Grounded Theory
8. How do women in third world countries set up financial independence?
Variable: Efforts at reaching financial independence
Demographic: Women in third-world countries
9. What impact does collaborative working have on the UX optimization efforts of a telecommunications company?
Variable: effects of collaboration on the UX of a telecommunications company
Demographic: workers in the telecommunications space
Qualitative Research Type: Action Research
10. What strategies can marketing managers use to improve the reach of millennial customers?
Variable: Strategies to improve millennial reach and their outcomes
Demographic: Marketing managers
When to Use the Research and How to Analyze It
The qualitative research method has specific use cases. You ought to consider which is best for your particular business, which includes your strategy, your marketing and other facets.
The core of qualitative research is to understand a phenomenon (a problem, an inadequacy, and a slew of other occurrences) including its causes, its motivations, its goals and its solutions. Researchers do this by observing smaller portions of a population.
Researchers should use this form of research whenever you need to get the gist of a particular occurrence or event. It is particularly useful for studying how your target market experiences certain situations and how it feels about them.
There are several more specific ways that elucidate why this research style is valuable if not completely necessary. Here are some of the most crucial ways this method of research is vital:
Helps brands see the emotional connections customers have with them
Allows brands to find gaps in customer experience (CX) and user experience (UX)
Enables brands to create experiences that are more tailored to their target market
Helps businesses understand how they can improve on their product, service or CX
Finds experiences that customers had that highlight sensitive topics/language for them
Shows businesses how customers compare them to their competitors
Identifies possible solutions and innovations based on customer attitudes and experiences
To analyze qualitative research, you should first identify your subject of study and decide on the type of research you need to conduct based on the five types of research that fall under the qualitative category.
Then, brainstorm several questions that you can use to form the base of your studies. During the process make sure to jot down (either digitally or otherwise) your observations. For example, record interviews and store surveys in an organized database.
Make sure you ask open-ended questions in surveys, interviews, focus groups, et al. Aggregate secondary research such as government database documents, articles in your niche, images, videos and more.
Search for patterns or similarities within your findings. When you group them together and organize them by demographics, you can start drawing conclusions and proposing solutions.
The Benefits and Drawbacks of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research can be extraordinarily beneficial. But as with other aspects of research and beyond, it too comes with a set of drawbacks. As a business owner, marketer or market researcher, you should know both the pros and cons. Here are some notable ones:
More intimate understanding of context and causation: besides understanding “what” in a granular way, you also learn the “why” and “how” of a particular situation.
Understanding key experiences: Open-ended questions lead to unique answers, exposing things numerical-based surveys can’t answer.
A foundation of deep insights: The design of the study is made to understand how customers relate to particular occurrences, events, ideas and products.
Context-driven: Finding insights on motivation and past behaviors allows researchers to understand what their target market needs and what it tries to avoid.
No need to find and create the correct measuring units: Open-ended questions don’t require a scale, a number range or any other measuring tools — one less thing to worry about.
Smaller sample size: Smaller sample sizes allow researchers to study responses more thoroughly to form more accurate hypotheses and conclusions.
Inspirational : The responses received can also help researchers form new studies.
Flexible and detail-oriented : Since questions aren’t based on scales and other units, you can ask more creative and in-depth questions. Questions focus on details and subtleties for robust insights.
Relies on researcher experience: It relies on the researchers’ experience; not all are familiar with industry topics.
Not statistically representative: Only collects perspective-based research; does not provide statistical representation. Only comparisons, not measurements can be executed.
Difficult to make copies of data. Individual perspectives make it hard to replicate findings, making it it more difficult to form conclusions.
More likely to have researcher bias: Both conscious or subconscious of the researcher can affect the data. The conclusions they draw can thus be influenced by their bias. (This can be avoided by using controls in data collection.
The Final Word
Market research is a wide-spanning undertaking. It has a wide swath of aspects, practices and applications. As such, researchers should know its main categories and qualitative research is one such category of significance.
As opposed to quantitative research, which has four methods, qualitative research has five — not all of which will be of use to your particular market research needs. In any case, this type of research involves imbuing as much context and particularities around a phenomenon as possible.
As such, researchers should create questions more specific to the aforementioned examples of this article. That is because those are more encompassing, generalized questions that researchers can attempt to answer after conducting all of their research and parsing of the findings.
But prior to that, researchers should ask several related questions around a particular topic and tailor those questions as best as possible to the target audience.
Frequently asked questions
What is qualitative research.
Qualitative research is a type of research that is conducted to gain deep or unexpected insights rather than focusing on numeral or quantitative data.
Why is qualitative research conducted?
Qualitative research is conducted to find the “why” of the research subject, rather than the “what’ of that subject. For example, qualitative research might be conducted to understand an issue more deeply, to understand why something is happening, or to learn how to address a target market’s concerns.
What is narrative research?
Narrative research is a type of research that is used to create an in-depth story about a phenomenon or event. It is conducted by interviewing a small group of people who were directly involved in the event.
How is ethnographic research conducted?
When conducting ethnographic research, the researchers use firsthand observations of an environment to more deeply understand the goals, challenges, or opinions of the target audience.
What is action research?
Action research is a type of qualitative research in which researchers and participants collaborate to better understand a phenomenon. Together the group works to find and solve the problem by gathering information on an ongoing and evolving basis.
Do you want to distribute your survey? Pollfish offers you access to millions of targeted consumers to get survey responses from $0.95 per complete. Launch your survey today.
Privacy Preference Center
Privacy preferences.

83 Qualitative Research Questions & Examples

Qualitative research questions help you understand consumer sentiment. They’re strategically designed to show organizations how and why people feel the way they do about a brand, product, or service. It looks beyond the numbers and is one of the most telling types of market research a company can do.
The UK Data Service describes this perfectly, saying, “The value of qualitative research is that it gives a voice to the lived experience .”
Read on to see seven use cases and 83 qualitative research questions, with the added bonus of examples that show how to get similar insights faster with Similarweb Research Intelligence.

What is a qualitative research question?
A qualitative research question explores a topic in-depth, aiming to better understand the subject through interviews, observations, and other non-numerical data. Qualitative research questions are open-ended, helping to uncover a target audience’s opinions, beliefs, and motivations.
How to choose qualitative research questions?
Choosing the right qualitative research questions can be incremental to the success of your research and the findings you uncover. Here’s my six-step process for choosing the best qualitative research questions.
- Start by understanding the purpose of your research. What do you want to learn? What outcome are you hoping to achieve?
- Consider who you are researching. What are their experiences, attitudes, and beliefs? How can you best capture these in your research questions ?
- Keep your questions open-ended . Qualitative research questions should not be too narrow or too broad. Aim to ask specific questions to provide meaningful answers but broad enough to allow for exploration.
- Balance your research questions. You don’t want all of your questions to be the same type. Aim to mix up your questions to get a variety of answers.
- Ensure your research questions are ethical and free from bias. Always have a second (and third) person check for unconscious bias.
- Consider the language you use. Your questions should be written in a way that is clear and easy to understand. Avoid using jargon , acronyms, or overly technical language.

Types of qualitative research questions
For a question to be considered qualitative, it usually needs to be open-ended. However, as I’ll explain, there can sometimes be a slight cross-over between quantitative and qualitative research questions.
Open-ended questions
These allow for a wide range of responses and can be formatted with multiple-choice answers or a free-text box to collect additional details. The next two types of qualitative questions are considered open questions, but each has its own style and purpose.
- Probing questions are used to delve deeper into a respondent’s thoughts, such as “Can you tell me more about why you feel that way?”
- Comparative questions ask people to compare two or more items, such as “Which product do you prefer and why?” These qualitative questions are highly useful for understanding brand awareness , competitive analysis , and more.
Closed-ended questions
These ask respondents to choose from a predetermined set of responses, such as “On a scale of 1-5, how satisfied are you with the new product?” While they’re traditionally quantitative, adding a free text box that asks for extra comments into why a specific rating was chosen will provide qualitative insights alongside their respective quantitative research question responses.
- Ranking questions get people to rank items in order of preference, such as “Please rank these products in terms of quality.” They’re advantageous in many scenarios, like product development, competitive analysis, and brand awareness.
- Likert scale questions ask people to rate items on a scale, such as “On a scale of 1-5, how satisfied are you with the new product?” Ideal for placement on websites and emails to gather quick, snappy feedback.
Qualitative research question examples
There are many applications of qualitative research and lots of ways you can put your findings to work for the success of your business. Here’s a summary of the most common use cases for qualitative questions and examples to ask.
Qualitative questions for identifying customer needs and motivations
These types of questions help you find out why customers choose products or services and what they are looking for when making a purchase.
- What factors do you consider when deciding to buy a product?
- What would make you choose one product or service over another?
- What are the most important elements of a product that you would buy?
- What features do you look for when purchasing a product?
- What qualities do you look for in a company’s products?
- Do you prefer localized or global brands when making a purchase?
- How do you determine the value of a product?
- What do you think is the most important factor when choosing a product?
- How do you decide if a product or service is worth the money?
- Do you have any specific expectations when purchasing a product?
- Do you prefer to purchase products or services online or in person?
- What kind of customer service do you expect when buying a product?
- How do you decide when it is time to switch to a different product?
- Where do you research products before you decide to buy?
- What do you think is the most important customer value when making a purchase?
Qualitative research questions to enhance customer experience
Use these questions to reveal insights into how customers interact with a company’s products or services and how those experiences can be improved.
- What aspects of our product or service do customers find most valuable?
- How do customers perceive our customer service?
- What factors are most important to customers when purchasing?
- What do customers think of our brand?
- What do customers think of our current marketing efforts?
- How do customers feel about the features and benefits of our product?
- How do customers feel about the price of our product or service?
- How could we improve the customer experience?
- What do customers think of our website or app?
- What do customers think of our customer support?
- What could we do to make our product or service easier to use?
- What do customers think of our competitors?
- What is your preferred way to access our site?
- How do customers feel about our delivery/shipping times?
- What do customers think of our loyalty programs?
Qualitative research question example for customer experience
- ♀️ Question: What is your preferred way to access our site?
- Insight sought: How mobile-dominant are consumers? Should you invest more in mobile optimization or mobile marketing?
- Challenges with traditional qualitative research methods: While using this type of question is ideal if you have a large database to survey when placed on a site or sent to a limited customer list, it only gives you a point-in-time perspective from a limited group of people.
- A new approach: You can get better, broader insights quicker with Similarweb Digital Research Intelligence. To fully inform your research, you need to know preferences at the industry or market level.
- ⏰ Time to insight: 30 seconds
- ✅ How it’s done: Similarweb offers multiple ways to answer this question without going through a lengthy qualitative research process.
First, I’m going to do a website market analysis of the banking credit and lending market in the finance sector to get a clearer picture of industry benchmarks.
Here, I can view device preferences across any industry or market instantly. It shows me the device distribution for any country across any period. This clearly answers the question of how mobile dominate my target audience is , with 59.79% opting to access site via a desktop vs. 40.21% via mobile
I then use the trends section to show me the exact split between mobile and web traffic for each key player in my space. Let’s say I’m about to embark on a competitive campaign that targets customers of Chase and Bank of America ; I can see both their audiences are highly desktop dominant compared with others in their space .
Qualitative question examples for developing new products or services
Research questions like this can help you understand customer pain points and give you insights to develop products that meet those needs.
- What is the primary reason you would choose to purchase a product from our company?
- How do you currently use products or services that are similar to ours?
- Is there anything that could be improved with products currently on the market?
- What features would you like to see added to our products?
- How do you prefer to contact a customer service team?
- What do you think sets our company apart from our competitors?
- What other product or service offerings would like to see us offer?
- What type of information would help you make decisions about buying a product?
- What type of advertising methods are most effective in getting your attention?
- What is the biggest deterrent to purchasing products from us?
Qualitative research question example for service development
- ♀️ Question: What type of advertising methods are most effective in getting your attention?
- Insight sought: The marketing channels and/or content that performs best with a target audience .
- Challenges with traditional qualitative research methods: When using qualitative research surveys to answer questions like this, the sample size is limited, and bias could be at play.
- A better approach: The most authentic insights come from viewing real actions and results that take place in the digital world. No questions or answers are needed to uncover this intel, and the information you seek is readily available in less than a minute.
- ⏰ Time to insight: 5 minutes
- ✅ How it’s done: There are a few ways to approach this. You can either take an industry-wide perspective or hone in on specific competitors to unpack their individual successes. Here, I’ll quickly show a snapshot with a whole market perspective.

Using the market analysis element of Similarweb Digital Intelligence, I select my industry or market, which I’ve kept as banking and credit. A quick click into marketing channels shows me which channels drive the highest traffic in my market. Taking direct traffic out of the equation, for now, I can see that referrals and organic traffic are the two highest-performing channels in this market.
Similarweb allows me to view the specific referral partners and pages across these channels.

Looking closely at referrals in this market, I’ve chosen chase.com and its five closest rivals . I select referrals in the channel traffic element of marketing channels. I see that Capital One is a clear winner, gaining almost 25 million visits due to referral partnerships.

Next, I get to see exactly who is referring traffic to Capital One and the total traffic share for each referrer. I can see the growth as a percentage and how that has changed, along with an engagement score that rates the average engagement level of that audience segment. This is particularly useful when deciding on which new referral partnerships to pursue.
Once I’ve identified the channels and campaigns that yield the best results, I can then use Similarweb to dive into the various ad creatives and content that have the greatest impact.

These ads are just a few of those listed in the creatives section from my competitive website analysis of Capital One. You can filter this list by the specific campaign, publishers, and ad networks to view those that matter to you most. You can also discover video ad creatives in the same place too.
In just five minutes ⏰
- I’ve captured audience loyalty statistics across my market
- Spotted the most competitive players
- Identified the marketing channels my audience is most responsive to
- I know which content and campaigns are driving the highest traffic volume
- I’ve created a target list for new referral partners and have been able to prioritize this based on results and engagement figures from my rivals
- I can see the types of creatives that my target audience is responding to, giving me ideas for ways to generate effective copy for future campaigns
Qualitative questions to determine pricing strategies
Companies need to make sure pricing stays relevant and competitive. Use these questions to determine customer perceptions on pricing and develop pricing strategies to maximize profits and reduce churn.
- How do you feel about our pricing structure?
- How does our pricing compare to other similar products?
- What value do you feel you get from our pricing?
- How could we make our pricing more attractive?
- What would be an ideal price for our product?
- Which features of our product that you would like to see priced differently?
- What discounts or deals would you like to see us offer?
- How do you feel about the amount you have to pay for our product?
Get Faster Answers to Qualitative Research Questions with Similarweb Today
Qualitative research question example for determining pricing strategies.
- ♀️ Question: What discounts or deals would you like to see us offer?
- Insight sought: The promotions or campaigns that resonate with your target audience.
- Challenges with traditional qualitative research methods: Consumers don’t always recall the types of ads or campaigns they respond to. Over time, their needs and habits change. Your sample size is limited to those you ask, leaving a huge pool of unknowns at play.
- A better approach: While qualitative insights are good to know, you get the most accurate picture of the highest-performing promotion and campaigns by looking at data collected directly from the web. These analytics are real-world, real-time, and based on the collective actions of many, instead of the limited survey group you approach. By getting a complete picture across an entire market, your decisions are better informed and more aligned with current market trends and behaviors.
- ✅ How it’s done: Similarweb’s Popular Pages feature shows the content, products, campaigns, and pages with the highest growth for any website. So, if you’re trying to unpack the successes of others in your space and find out what content resonates with a target audience, there’s a far quicker way to get answers to these questions with Similarweb.

Here, I’m using Capital One as an example site. I can see trending pages on their site showing the largest increase in page views. Other filters include campaign, best-performing, and new–each of which shows you page URLs, share of traffic, and growth as a percentage. This page is particularly useful for staying on top of trending topics , campaigns, and new content being pushed out in a market by key competitors.
Qualitative research questions for product development teams
It’s vital to stay in touch with changing consumer needs. These questions can also be used for new product or service development, but this time, it’s from the perspective of a product manager or development team.
- What are customers’ primary needs and wants for this product?
- What do customers think of our current product offerings?
- What is the most important feature or benefit of our product?
- How can we improve our product to meet customers’ needs better?
- What do customers like or dislike about our competitors’ products?
- What do customers look for when deciding between our product and a competitor’s?
- How have customer needs and wants for this product changed over time?
- What motivates customers to purchase this product?
- What is the most important thing customers want from this product?
- What features or benefits are most important when selecting a product?
- What do customers perceive to be our product’s pros and cons?
- What would make customers switch from a competitor’s product to ours?
- How do customers perceive our product in comparison to similar products?
- What do customers think of our pricing and value proposition?
- What do customers think of our product’s design, usability, and aesthetics?
Qualitative questions examples to understand customer segments
Market segmentation seeks to create groups of consumers with shared characteristics. Use these questions to learn more about different customer segments and how to target them with tailored messaging.
- What motivates customers to make a purchase?
- How do customers perceive our brand in comparison to our competitors?
- How do customers feel about our product quality?
- How do customers define quality in our products?
- What factors influence customers’ purchasing decisions ?
- What are the most important aspects of customer service?
- What do customers think of our customer service?
- What do customers think of our pricing?
- How do customers rate our product offerings?
- How do customers prefer to make purchases (online, in-store, etc.)?
Qualitative research question example for understanding customer segments
- ♀️ Question: Which social media channels are you most active on?
- Insight sought: Formulate a social media strategy . Specifically, the social media channels most likely to succeed with a target audience.
- Challenges with traditional qualitative research methods: Qualitative research question responses are limited to those you ask, giving you a limited sample size. Questions like this are usually at risk of some bias, and this may not be reflective of real-world actions.
- A better approach: Get a complete picture of social media preferences for an entire market or specific audience belonging to rival firms. Insights are available in real-time, and are based on the actions of many, not a select group of participants. Data is readily available, easy to understand, and expandable at a moment’s notice.
- ✅ How it’s done: Using Similarweb’s website analysis feature, you can get a clear breakdown of social media stats for your audience using the marketing channels element. It shows the percentage of visits from each channel to your site, respective growth, and specific referral pages by each platform. All data is expandable, meaning you can select any platform, period, and region to drill down and get more accurate intel, instantly.

This example shows me Bank of America’s social media distribution, with YouTube , Linkedin , and Facebook taking the top three spots, and accounting for almost 80% of traffic being driven from social media.
When doing any type of market research, it’s important to benchmark performance against industry averages and perform a social media competitive analysis to verify rival performance across the same channels.
Qualitative questions to inform competitive analysis
Organizations must assess market sentiment toward other players to compete and beat rival firms. Whether you want to increase market share , challenge industry leaders , or reduce churn, understanding how people view you vs. the competition is key.
- What is the overall perception of our competitors’ product offerings in the market?
- What attributes do our competitors prioritize in their customer experience?
- What strategies do our competitors use to differentiate their products from ours?
- How do our competitors position their products in relation to ours?
- How do our competitors’ pricing models compare to ours?
- What do consumers think of our competitors’ product quality?
- What do consumers think of our competitors’ customer service?
- What are the key drivers of purchase decisions in our market?
- What is the impact of our competitors’ marketing campaigns on our market share ? 10. How do our competitors leverage social media to promote their products?
Qualitative research question example for competitive analysis
- ♀️ Question: What other companies do you shop with for x?
- Insight sought: W ho are your competitors? Which of your rival’s sites do your customers visit? How loyal are consumers in your market?
- Challenges with traditional qualitative research methods: Sample size is limited, and customers could be unwilling to reveal which competitors they shop with, or how often they around. Where finances are involved, people can act with reluctance or bias, and be unwilling to reveal other suppliers they do business with.
- A better approach: Get a complete picture of your audience’s loyalty, see who else they shop with, and how many other sites they visit in your competitive group. Find out the size of the untapped opportunity and which players are doing a better job at attracting unique visitors – without having to ask people to reveal their preferences.
- ✅ How it’s done: Similarweb website analysis shows you the competitive sites your audience visits, giving you access to data that shows cross-visitation habits, audience loyalty, and untapped potential in a matter of minutes.

Using the audience interests element of Similarweb website analysis, you can view the cross-browsing behaviors of a website’s audience instantly. You can see a matrix that shows the percentage of visitors on a target site and any rival site they may have visited.

With the Similarweb audience overlap feature, view the cross-visitation habits of an audience across specific websites. In this example, I chose chase.com and its four closest competitors to review. For each intersection, you see the number of unique visitors and the overall proportion of each site’s audience it represents. It also shows the volume of unreached potential visitors.

Here, you can see a direct comparison of the audience loyalty represented in a bar graph. It shows a breakdown of each site’s audience based on how many other sites they have visited. Those sites with the highest loyalty show fewer additional sites visited.
From the perspective of chase.com, I can see 47% of their visitors do not visit rival sites. 33% of their audience visited 1 or more sites in this group, 14% visited 2 or more sites, 4% visited 3 or more sites, and just 0.8% viewed all sites in this comparison.
How to answer qualitative research questions with Similarweb
Similarweb Research Intelligence drastically improves market research efficiency and time to insight. Both of these can impact the bottom line and the pace at which organizations can adapt and flex when markets shift, and rivals change tactics.
Outdated practices, while still useful, take time . And with a quicker, more efficient way to garner similar insights, opting for the fast lane puts you at a competitive advantage.
With a birds-eye view of the actions and behaviors of companies and consumers across a market , you can answer certain research questions without the need to plan, do, and review extensive qualitative market research .
Wrapping up
Qualitative research methods have been around for centuries. From designing the questions to finding the best distribution channels, collecting and analyzing findings takes time to get the insights you need. Similarweb Digital Research Intelligence drastically improves efficiency and time to insight. Both of which impact the bottom line and the pace at which organizations can adapt and flex when markets shift.
Similarweb’s suite of digital intelligence solutions offers unbiased, accurate, honest insights you can trust for analyzing any industry, market, or audience.
- Methodologies used for data collection are robust, transparent, and trustworthy.
- Clear presentation of data via an easy-to-use, intuitive platform.
- It updates dynamically–giving you the freshest data about an industry or market.
- Data is available via an API – so you can plug into platforms like Tableau or PowerBI to streamline your analyses.
- Filter and refine results according to your needs.
Are quantitative or qualitative research questions best?
Both have their place and purpose in market research. Qualitative research questions seek to provide details, whereas quantitative market research gives you numerical statistics that are easier and quicker to analyze. You get more flexibility with qualitative questions, and they’re non-directional.
What are the advantages of qualitative research?
Qualitative research is advantageous because it allows researchers to better understand their subject matter by exploring people’s attitudes, behaviors, and motivations in a particular context. It also allows researchers to uncover new insights that may not have been discovered with quantitative research methods.
What are some of the challenges of qualitative research?
Qualitative research can be time-consuming and costly, typically involving in-depth interviews and focus groups. Additionally, there are challenges associated with the reliability and validity of the collected data, as there is no universal standard for interpreting the results.
Related Posts

What is a Niche Market? And How to Find the Right One

The Future of UK Finance: Top Trends to Watch in 2024

From AI to Buy: The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Retail
How to Conduct a Social Media Competitor Analysis: 5 Quick Steps

Industry Research: The Data-Backed Approach
How to Do a Competitive Analysis: A Complete Guide
Wondering what similarweb can do for you.
Here are two ways you can get started with Similarweb today!

Introduction to Qualitative Consumer and Marketing Research
- First Online: 14 February 2019
Cite this chapter

- Krittinee Nuttavuthisit 2
2217 Accesses
1 Citations
Consumer and marketing research has long been a central focus in academic development and market practices due to the need to understand changing consumption behavior and marketing strategies.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Arnold SJ, Fischer E (1994) Hermeneutics and consumer research. J Consum Res 21:55–70
Article Google Scholar
Arnould EJ, Thompson CJ (2005) Consumer Culture Theory (CCT): twenty years of research. J Consum Res 31(4):868–882
Baudrillard J (1981) Simulacra and simulations. Semiotext(e), New York
Google Scholar
Baudrillard J (1983) Simulations. Semiotext(e), New York
Belk RW (2009) The modeling—empiricism gap: lessons from the qualitative—qualitative gap in consumer research. J Supply Chain Manage 45:35–37. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-493X.2009.03153
Belk RW, Bahn KD, Mayer RN (1982) Developmental recognition of consumption symbolism. J Consum Res 9(1):4–17
Belk RW, Ostergaard P, Groves R (1998) Sexual consumption in the time of AIDS: a study of prostitute patronage in Thailand. J Pub Policy Mark 17(2):197–214
Belk RW, Fischer E, Kozinets R (2013) Qualitative consumer & marketing research. Sage Publications, London
Berger P, Luckman T (1967) The social construction of reality a treatise in the sociology of knowledge. Random House, New York
Bernstein R (1983) Beyond Objectivism and relativism: science, hermeneutics, and praxis. University of Pennsylvania Press, Pennsylvania
Bleicher J (1980) Contemporary hermeneutics: hermeneutics as method, philosophy, and critique. Routledge and Kegan Paul, London
Bourdieu P (1984) Distinction: a social critique of the judgement of taste (trans: Nice R). Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA
Catterall M (1998) Academics, practitioners and qualitative market research. Qual Mark Res Int J 1(2):69–76
Comstock DE (1982) Power in organizations: toward a critical theory. Pac Sociol Rev 25(2):139–162
Eckhardt GM, Dholakia N (2013) Addressing the mega imbalance: interpretive exploration of Asia. Qual Mark Res Int J 16(1):4–11. https://doi.org/10.1108/13522751311289785
Featherstone M (1991) Consumer culture and postmodernism. Sage Publications, London
Fuhrman E (1979) The normative structure of critical theory. Hum Stud 2(3):209–227
Gadamer HG (1989) Truth and method. Sheed and Ward, London
Gardner B, Levy S (1955) The product and the brand. Editorial Harvard Bus Rev 33:33–39
Geertz C (1973a) The interpretation of cultures: selected essays. Basic Books, New York
Geertz C (1973b) Thick description. The interpretation of cultures. Basic Books, New York, pp 3–30
Habermas J (1971) Toward a rational society (trans: Jeremy J). Shapiro. Heinemann, London
Habermas J (1980a) The hermeneutic claim to universality. In: Bleicher Josef (ed) Contemporary hermeneutics: method, philosophy, and critique. Routledge and Kegan Paul, London
Habermas J (1980b) The hermeneutic claim to universality. In: Bleicher Josef (ed) Contemporary hermeneutics. Routledge, Boston, MA, pp 181–211
Heidegger M (1962) Being and time. Blackwell Publishing, Oxford
Henry WE (1956) The analysis of fantasy: the thematic apperception technique in the study of personality. John Wiley and Sons, Oxford, England
Hirschman EC (1986) Humanistic inquiry in marketing research: philosophy, method, and criteria. J Mark Res 23:237–249
Holbrook MB (1978) Beyond Attitude structure: toward the informational determinants of attitude. J Mark Res 15:545–556
Holbrook MB, Hirschman EC (1982) The experiential aspects of consumption: consumer fantasies, feelings, and fun. J Consum Res 9(2):132–140
Hsiung P-C (2012). The globalization of qualitative research: challenging Anglo-American domination and local hegemonic discourse. Qual Soc Res 13(1), Art 21
Hudson LA, Ozanne JL (1988) Alternative ways of seeking knowledge in consumer research. J Consum Res 14(4):508–521
Jameson F (1984) Postmodernism or the cultural logic of late capitalism. New Left Rev 146:53–92
Jay M (1973) The dialectical imagination. Little, Brown and Company, Boston
Kassarjian HH (1995) In: Kardes FR, Sujan M (eds) Some recollections from a quarter century ago, vol 22. Advances in Consumer Research, pp 550–552
Kvale S (1983) The qualitative research interview: a phenomenological and a hermeneutical mode of understanding. J Phenomenological Psychol 14:171–196
Lafley, Charan (2008) The consumer is boss. In: Fortune 10 Mar 2008. http://archive.fortune.com/2008/03/07/news/companies/lafley_charan.fortune/index.htm?postversion=2008031012
Levy SJ (1959) Symbols for sale. Harvard Bus Rev 37:117–124
Levy SJ (1963) Symbolism and Life style. In: Proceedings of American marketing association annual conference, Chicago
Levy SJ (1981) Intepreting consumer mythology: a structural approach to consumer behavior. J Mark 45(3):49–61
Levy SJ (1985) Dreams, fairy tales, animals, and cars. Psychology & Marketing 2(2):67–81
Levy SJ (2006) In: Belk RW (ed) History of qualitative research methods in marketing. Edward Elgar Publishing, pp 3–18
Lincoln YS, Guba EG (1985) Naturalistic inquiry. Sage Publications, Beverly Hills
Book Google Scholar
Liu JH (2011) Asian epistemologies and contemporary social psychological Research. In: Denzin NK, Lincoln YS (eds) Sage handbook of qualitative research. Sage Thousand Oaks, CA, pp 213–226
Marcuse H (1964) One-dimensional man: studies in the ideology of advanced industrial society. Beacon, Boston, MA
Mick DG (1986) Consumer research and semiotics: exploring the morphology of signs, symbols, and significance. J Consum Res 13(2):196–213
Morgan DL, Krueger RA (1993) When to use focus groups and why. In: Morgan DL (Ed) Sage focus editions, vol. 156, Successful focus groups: advancing the state of the art. Sage Publications, Thousand Oaks, CA, pp 3–19
Murray JB (2002) The politics of consumption: a re-inquiry on Thompson and Haytko's (1997) Speaking of Fashion, J Consum Res (29)3:427–440
Murray JB, Ozanne JL (1991) The critical imagination: emancipatory interests in consumer research. J Consum Res 18(2):129–144
Nguyen TDT (2015a) Conducting semi-structured interviews with the Vietnamese. Qual Res J 15(1):35–46
Nguyen TDT (2015b) Gender discrimination in the way the Vietnamese talk about face the dien: results from interviews with Vietnamese teachers. Qual Res J 15(2):147–154
Oswald L (2012) Marketing semiotics: signs, strategies, and brand value. Oxford University Press, New York
Oswald L (2015) Creating value: the theory and practice of marketing semiotics research. Oxford University Press, New York
Park S, Lunt N (2015) Confucianism and qualitative interviewing: working seoul to soul. Qual Soc Res 16(2), Art 7
Polsa P (2013) Crystallization and research in Asia. Qual Mark Res 16(1):76–93. https://doi.org/10.1108/13522751311289776
Rogers CR (1956) Client-centered therapy: a current view. In: Fromm-Reichmann F, Moreno JL (eds). Grune and Stratton, New York, pp 199–209
Rorty R (1985) Philosophy without principles. Crit Inq 11(3):459–465
Ross A (ed) (1988) Universal abandon?. University of Minnesota Press, Minneapolis, MN
Rubinstein D (1981) Marx and Wittgenstein. Routledge & Kegan Paul, London
Sartre JP (1956) Being and nothingness. Philosophical Library, Oxford
Seo Y, Fam K-S (2015) Researching Asian consumer culture in the global marketplace. Qual Mark Res Int J 18(4):386–390. https://doi.org/10.1108/qmr-05-2015-0048
Sidney J, Levy (2017) Sidney J. Levy: an autobiography. J Hist Res Mark 9(2):127–143
Solomon MR (1983) The role of products as social stimuli: a symbolic interactionism perspective. J Consum Res 10(3):319–329
Thompson C, Locander W, Pollio H (1989) Putting consumer experience back into consumer research: the philosophy and method of existential-phenomenology. J Consum Res 16(2):133–146
Times 100 (2014) “Kit, Kat: Revitalizing a brand leader,” The Times 100 Case Studies (2014). www.thetimes100.co.uk
Tischler (2004) Every move you make. In: Fast Company 4 Jan 2004. https://www.fastcompany.com/48949/every-move-you-make
Vattimo G (1992) The transparent society. English Edition (trans: Webb D). Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore
Venkatesh A (1995) Ethnoconsumerism: A new paradigm to study cultural and cross-cultural consumer behavior. In: Costa JA. and Bamossy GJ (eds) Marketing in a multicultural world: Ethnicity, nationalism, and cultural Identity. Sage Publications, Thousand Oaks, CA, pp. 26–67
Zhou L, Nunes M (2013) Doing qualitative research in Chinese contexts: lessons learned from conducting interviews in a Chinese healthcare environment. Library Hi Tech 3:419–434
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Sasin Graduate Institute of Business Administration, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand
Krittinee Nuttavuthisit
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Krittinee Nuttavuthisit .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Nuttavuthisit, K. (2019). Introduction to Qualitative Consumer and Marketing Research. In: Qualitative Consumer and Marketing Research. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-6142-5_1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-6142-5_1
Published : 14 February 2019
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-13-6141-8
Online ISBN : 978-981-13-6142-5
eBook Packages : Business and Management Business and Management (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Employee Exit Interviews
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
Market Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
- Qualitative Research
Try Qualtrics for free
Your ultimate guide to qualitative research (with methods and examples).
16 min read You may be already using qualitative research and want to check your understanding, or you may be starting from the beginning. Learn about qualitative research methods and how you can best use them for maximum effect.
What is qualitative research?
Qualitative research is a research method that collects non-numerical data. Typically, it goes beyond the information that quantitative research provides (which we will cover below) because it is used to gain an understanding of underlying reasons, opinions, and motivations.
Qualitative research methods focus on the thoughts, feelings, reasons, motivations, and values of a participant, to understand why people act in the way they do .
In this way, qualitative research can be described as naturalistic research, looking at naturally-occurring social events within natural settings. So, qualitative researchers would describe their part in social research as the ‘vehicle’ for collecting the qualitative research data.
Qualitative researchers discovered this by looking at primary and secondary sources where data is represented in non-numerical form. This can include collecting qualitative research data types like quotes, symbols, images, and written testimonials.
These data types tell qualitative researchers subjective information. While these aren’t facts in themselves, conclusions can be interpreted out of qualitative that can help to provide valuable context.
Because of this, qualitative research is typically viewed as explanatory in nature and is often used in social research, as this gives a window into the behavior and actions of people.
It can be a good research approach for health services research or clinical research projects.
Free eBook: The qualitative research design handbook
Quantitative vs qualitative research
In order to compare qualitative and quantitative research methods, let’s explore what quantitative research is first, before exploring how it differs from qualitative research.
Quantitative research
Quantitative research is the research method of collecting quantitative research data – data that can be converted into numbers or numerical data, which can be easily quantified, compared, and analyzed .
Quantitative research methods deal with primary and secondary sources where data is represented in numerical form. This can include closed-question poll results, statistics, and census information or demographic data.
Quantitative research data tends to be used when researchers are interested in understanding a particular moment in time and examining data sets over time to find trends and patterns.
The difference between quantitative and qualitative research methodology
While qualitative research is defined as data that supplies non-numerical information, quantitative research focuses on numerical data.
In general, if you’re interested in measuring something or testing a hypothesis, use quantitative research methods. If you want to explore ideas, thoughts, and meanings, use qualitative research methods.
While qualitative research helps you to properly define, promote and sell your products, don’t rely on qualitative research methods alone because qualitative findings can’t always be reliably repeated. Qualitative research is directional, not empirical.
The best statistical analysis research uses a combination of empirical data and human experience ( quantitative research and qualitative research ) to tell the story and gain better and deeper insights, quickly.
Where both qualitative and quantitative methods are not used, qualitative researchers will find that using one without the other leaves you with missing answers.
For example, if a retail company wants to understand whether a new product line of shoes will perform well in the target market:
- Qualitative research methods could be used with a sample of target customers, which would provide subjective reasons why they’d be likely to purchase or not purchase the shoes, while
- Quantitative research methods into the historical customer sales information on shoe-related products would provide insights into the sales performance, and likely future performance of the new product range.
Approaches to qualitative research
There are five approaches to qualitative research methods:
- Grounded theory: Grounded theory relates to where qualitative researchers come to a stronger hypothesis through induction, all throughout the process of collecting qualitative research data and forming connections. After an initial question to get started, qualitative researchers delve into information that is grouped into ideas or codes, which grow and develop into larger categories, as the qualitative research goes on. At the end of the qualitative research, the researcher may have a completely different hypothesis, based on evidence and inquiry, as well as the initial question.
- Ethnographic research : Ethnographic research is where researchers embed themselves into the environment of the participant or group in order to understand the culture and context of activities and behavior. This is dependent on the involvement of the researcher, and can be subject to researcher interpretation bias and participant observer bias . However, it remains a great way to allow researchers to experience a different ‘world’.
- Action research: With the action research process, both researchers and participants work together to make a change. This can be through taking action, researching and reflecting on the outcomes. Through collaboration, the collective comes to a result, though the way both groups interact and how they affect each other gives insights into their critical thinking skills.
- Phenomenological research: Researchers seek to understand the meaning of an event or behavior phenomenon by describing and interpreting participant’s life experiences. This qualitative research process understands that people create their own structured reality (‘the social construction of reality’), based on their past experiences. So, by viewing the way people intentionally live their lives, we’re able to see the experiential meaning behind why they live as they do.
- Narrative research: Narrative research, or narrative inquiry, is where researchers examine the way stories are told by participants, and how they explain their experiences, as a way of explaining the meaning behind their life choices and events. This qualitative research can arise from using journals, conversational stories, autobiographies or letters, as a few narrative research examples. The narrative is subjective to the participant, so we’re able to understand their views from what they’ve documented/spoken.
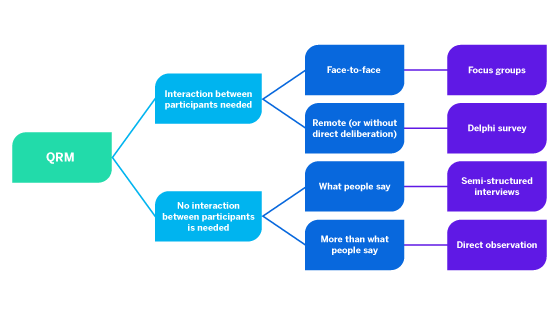
Qualitative research methods can use structured research instruments for data collection, like:
Surveys for individual views
A survey is a simple-to-create and easy-to-distribute qualitative research method, which helps gather information from large groups of participants quickly. Traditionally, paper-based surveys can now be made online, so costs can stay quite low.
Qualitative research questions tend to be open questions that ask for more information and provide a text box to allow for unconstrained comments.
Examples include:
- Asking participants to keep a written or a video diary for a period of time to document their feelings and thoughts
- In-Home-Usage tests: Buyers use your product for a period of time and report their experience
Surveys for group consensus (Delphi survey)
A Delphi survey may be used as a way to bring together participants and gain a consensus view over several rounds of questions. It differs from traditional surveys where results go to the researcher only. Instead, results go to participants as well, so they can reflect and consider all responses before another round of questions are submitted.
This can be useful to do as it can help researchers see what variance is among the group of participants and see the process of how consensus was reached.
- Asking participants to act as a fake jury for a trial and revealing parts of the case over several rounds to see how opinions change. At the end, the fake jury must make a unanimous decision about the defendant on trial.
- Asking participants to comment on the versions of a product being developed , as the changes are made and their feedback is taken onboard. At the end, participants must decide whether the product is ready to launch .
Semi-structured interviews
Interviews are a great way to connect with participants, though they require time from the research team to set up and conduct, especially if they’re done face-to-face.
Researchers may also have issues connecting with participants in different geographical regions. The researcher uses a set of predefined open-ended questions, though more ad-hoc questions can be asked depending on participant answers.
- Conducting a phone interview with participants to run through their feedback on a product . During the conversation, researchers can go ‘off-script’ and ask more probing questions for clarification or build on the insights.
Focus groups
Participants are brought together into a group, where a particular topic is discussed. It is researcher-led and usually occurs in-person in a mutually accessible location, to allow for easy communication between participants in focus groups.
In focus groups , the researcher uses a set of predefined open-ended questions, though more ad-hoc questions can be asked depending on participant answers.
- Asking participants to do UX tests, which are interface usability tests to show how easily users can complete certain tasks
Direct observation
This is a form of ethnographic research where researchers will observe participants’ behavior in a naturalistic environment. This can be great for understanding the actions in the culture and context of a participant’s setting.
This qualitative research method is prone to researcher bias as it is the researcher that must interpret the actions and reactions of participants. Their findings can be impacted by their own beliefs, values, and inferences.
- Embedding yourself in the location of your buyers to understand how a product would perform against the values and norms of that society
Qualitative data types and category types
Qualitative research methods often deliver information in the following qualitative research data types:
- Written testimonials
Through contextual analysis of the information, researchers can assign participants to category types:
- Social class
- Political alignment
- Most likely to purchase a product
- Their preferred training learning style
Advantages of qualitative research
- Useful for complex situations: Qualitative research on its own is great when dealing with complex issues, however, providing background context using quantitative facts can give a richer and wider understanding of a topic. In these cases, quantitative research may not be enough.
- A window into the ‘why’: Qualitative research can give you a window into the deeper meaning behind a participant’s answer. It can help you uncover the larger ‘why’ that can’t always be seen by analyzing numerical data.
- Can help improve customer experiences: In service industries where customers are crucial, like in private health services, gaining information about a customer’s experience through health research studies can indicate areas where services can be improved.
Disadvantages of qualitative research
- You need to ask the right question: Doing qualitative research may require you to consider what the right question is to uncover the underlying thinking behind a behavior. This may need probing questions to go further, which may suit a focus group or face-to-face interview setting better.
- Results are interpreted: As qualitative research data is written, spoken, and often nuanced, interpreting the data results can be difficult as they come in non-numerical formats. This might make it harder to know if you can accept or reject your hypothesis.
- More bias: There are lower levels of control to qualitative research methods, as they can be subject to biases like confirmation bias, researcher bias, and observation bias. This can have a knock-on effect on the validity and truthfulness of the qualitative research data results.
How to use qualitative research to your business’s advantage?
Qualitative methods help improve your products and marketing in many different ways:
- Understand the emotional connections to your brand
- Identify obstacles to purchase
- Uncover doubts and confusion about your messaging
- Find missing product features
- Improve the usability of your website, app, or chatbot experience
- Learn about how consumers talk about your product
- See how buyers compare your brand to others in the competitive set
- Learn how an organization’s employees evaluate and select vendors
6 steps to conducting good qualitative research
Businesses can benefit from qualitative research by using it to understand the meaning behind data types. There are several steps to this:
- Define your problem or interest area: What do you observe is happening and is it frequent? Identify the data type/s you’re observing.
- Create a hypothesis: Ask yourself what could be the causes for the situation with those qualitative research data types.
- Plan your qualitative research: Use structured qualitative research instruments like surveys, focus groups, or interviews to ask questions that test your hypothesis.
- Data Collection: Collect qualitative research data and understand what your data types are telling you. Once data is collected on different types over long time periods, you can analyze it and give insights into changing attitudes and language patterns.
- Data analysis: Does your information support your hypothesis? (You may need to redo the qualitative research with other variables to see if the results improve)
- Effectively present the qualitative research data: Communicate the results in a clear and concise way to help other people understand the findings.
Qualitative data analysis
Evaluating qualitative research can be tough when there are several analytics platforms to manage and lots of subjective data sources to compare.
Qualtrics provides a number of qualitative research analysis tools, like Text iQ , powered by Qualtrics iQ, provides powerful machine learning and native language processing to help you discover patterns and trends in text.
This also provides you with:
- Sentiment analysis — a technique to help identify the underlying sentiment (say positive, neutral, and/or negative) in qualitative research text responses
- Topic detection/categorisation — this technique is the grouping or bucketing of similar themes that can are relevant for the business & the industry (eg. ‘Food quality’, ‘Staff efficiency’ or ‘Product availability’)
How Qualtrics products can enhance & simplify the qualitative research process
Even in today’s data-obsessed marketplace, qualitative data is valuable – maybe even more so because it helps you establish an authentic human connection to your customers. If qualitative research doesn’t play a role to inform your product and marketing strategy, your decisions aren’t as effective as they could be.
The Qualtrics XM system gives you an all-in-one, integrated solution to help you all the way through conducting qualitative research. From survey creation and data collection to textual analysis and data reporting, it can help all your internal teams gain insights from your subjective and categorical data.
Qualitative methods are catered through templates or advanced survey designs. While you can manually collect data and conduct data analysis in a spreadsheet program, this solution helps you automate the process of qualitative research, saving you time and administration work.
Using computational techniques helps you to avoid human errors, and participant results come in are already incorporated into the analysis in real-time.
Our key tools, Text IQ™ and Driver IQ™ make analyzing subjective and categorical data easy and simple. Choose to highlight key findings based on topic, sentiment, or frequency. The choice is yours.
Some examples of your workspace in action, using drag and drop to create fast data visualizations quickly:
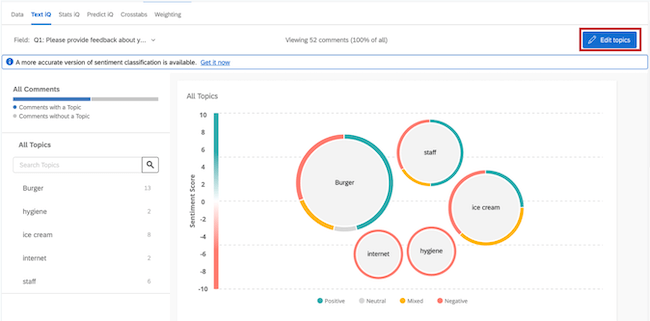
Related resources
Market intelligence 10 min read, marketing insights 11 min read, ethnographic research 11 min read, qualitative vs quantitative research 13 min read, qualitative research questions 11 min read, qualitative research design 12 min read, primary vs secondary research 14 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
- Survey Software The world’s leading omnichannel survey software
- Online Survey Tools Create sophisticated surveys with ease.
- Mobile Offline Conduct efficient field surveys.
- Text Analysis
- Close The Loop
- Automated Translations
- NPS Dashboard
- CATI Manage high volume phone surveys efficiently
- Cloud/On-premise Dialer TCPA compliant Cloud on-premise dialer
- IVR Survey Software Boost productivity with automated call workflows.
- Analytics Analyze survey data with visual dashboards
- Panel Manager Nurture a loyal community of respondents.
- Survey Portal Best-in-class user friendly survey portal.
- Voxco Audience Conduct targeted sample research in hours.
- Predictive Analytics
- Customer 360
- Customer Loyalty
- Fraud & Risk Management
- AI/ML Enablement Services
- Credit Underwriting

Find the best survey software for you! (Along with a checklist to compare platforms)
Get Buyer’s Guide
- 100+ question types
- Drag-and-drop interface
- Skip logic and branching
- Multi-lingual survey
- Text piping
- Question library
- CSS customization
- White-label surveys
- Customizable ‘Thank You’ page
- Customizable survey theme
- Reminder send-outs
- Survey rewards
- Social media
- SMS surveys
- Website surveys
- Correlation analysis
- Cross-tabulation analysis
- Trend analysis
- Real-time dashboard
- Customizable report
- Email address validation
- Recaptcha validation
- SSL security
Take a peek at our powerful survey features to design surveys that scale discoveries.
Download feature sheet.
- Hospitality
- Financial Services
- Academic Research
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Product Experience
- Market Research
- Social Research
- Data Analysis
- Banking & Financial Services
- Retail Solution
- Risk Management
- Customer Lifecycle Solutions
- Net Promoter Score
- Customer Behaviour Analytics
- Customer Segmentation
- Data Unification
Explore Voxco
Need to map Voxco’s features & offerings? We can help!
Watch a Demo
Download Brochures
Get a Quote
- NPS Calculator
- CES Calculator
- A/B Testing Calculator
- Margin of Error Calculator
- Sample Size Calculator
- CX Strategy & Management Hub
- Market Research Hub
- Patient Experience Hub
- Employee Experience Hub
- Market Research Guide
- Customer Experience Guide
- The Voxco Guide to Customer Experience
- NPS Knowledge Hub
- Survey Research Guides
- Survey Template Library
- Webinars and Events
- Feature Sheets
- Try a sample survey
- Professional services
- Blogs & White papers
- Case Studies
Find the best customer experience platform
Uncover customer pain points, analyze feedback and run successful CX programs with the best CX platform for your team.
Get the Guide Now

We’ve been avid users of the Voxco platform now for over 20 years. It gives us the flexibility to routinely enhance our survey toolkit and provides our clients with a more robust dataset and story to tell their clients.
VP Innovation & Strategic Partnerships, The Logit Group
- Client Stories
- Voxco Reviews
- Why Voxco Research?
- Why Voxco Intelligence?
- Careers at Voxco
- Vulnerabilities and Ethical Hacking
Explore Regional Offices
- Cloud/On-premise Dialer TCPA compliant Cloud & on-premise dialer
- Fraud & Risk Management
Get Buyer’s Guide
- Banking & Financial Services
Explore Voxco
Watch a Demo
Download Brochures
- CX Strategy & Management Hub
- Blogs & White papers
VP Innovation & Strategic Partnerships, The Logit Group
- Our clients
- Client stories
- Featuresheets
Qualitative Research


SURVEY METHODOLOGIES
Qualitative market research: the ultimate guide.
Try a free Voxco Online sample survey!
SHARE THE ARTICLE ON
Qualitative market research help businesses understand customers’ needs, identify market potential, uncover ideas for product launch/improvement, or understand how the product fits the target customer’s lifestyle.
Any business of any type or size can benefit from qualitative research as it helps you find out how the target market feels about your product and uncover how you can improve it to increase sales.
In this article, we’ll dive into qualitative research methods, how to conduct them, how to use them for market research, and more.
What is qualitative market research?
In simple terms, qualitative research can be defined as a method used for market research that aims at obtaining data with open-ended questions and conversations with the target consumers.
This method helps establish not only “what” consumers think but also “how” they come to that opinion and “why” they think so.
For instance, if you find out that more men are visiting your online garment shop than women, it is just a systematic observation. Qualitative market research will help you understand why women do not visit the store.
You can gain this information by conducting an in-depth interview of potential women who could become customers, i.e., women who shop online regularly. In this way, qualitative research focuses on understanding a query or problem statement in a humanistic or idealistic approach.
- Qualitative research methods are used to understand the beliefs, experiences, attitudes, and behaviors of people.
- It also helps in understanding the interactions people have with others who are similar to them.
- Qualitative research is increasingly becoming popular because it gives a voice to the participants.
- It gives us valuable insights into each individual and their feedback can prove to be valuable and enriching.
What is the difference between qualitative and quantitative market research?
We have described what qualitative market research is, but let’s also see how it differs from quantitative.
Quantitative Vs Qualitative market research:
Quantitative research gathers numerical data that helps you test and draw conclusions regarding your research. The data helps you generate conclusive results.
- It helps answer the “what” people think.
- You can use it to confirm a hypothesis.
- You can collect quantitative data via surveys , experiments, and observations.
Qualitative research helps you gather non-numerical data that digs deeper to understand customer behavior.
- It helps answer “why,” people think the way they do & “how” they make decisions.
- You can use it to understand concepts.
- You can gather qualitative data via interviews, ethnography, focus groups, case studies, and observation.
You can leverage a market research tool to conduct research of your choice using multiple channels and gather integrated data.
Additional read: Qualitative Vs quantitative research – Know the difference!
Create interactive and personalized surveys with Voxco.
100+ question types, white-labeling, skip-logic, branching, 100+ language capabilities, and more.
5 qualitative market research methods
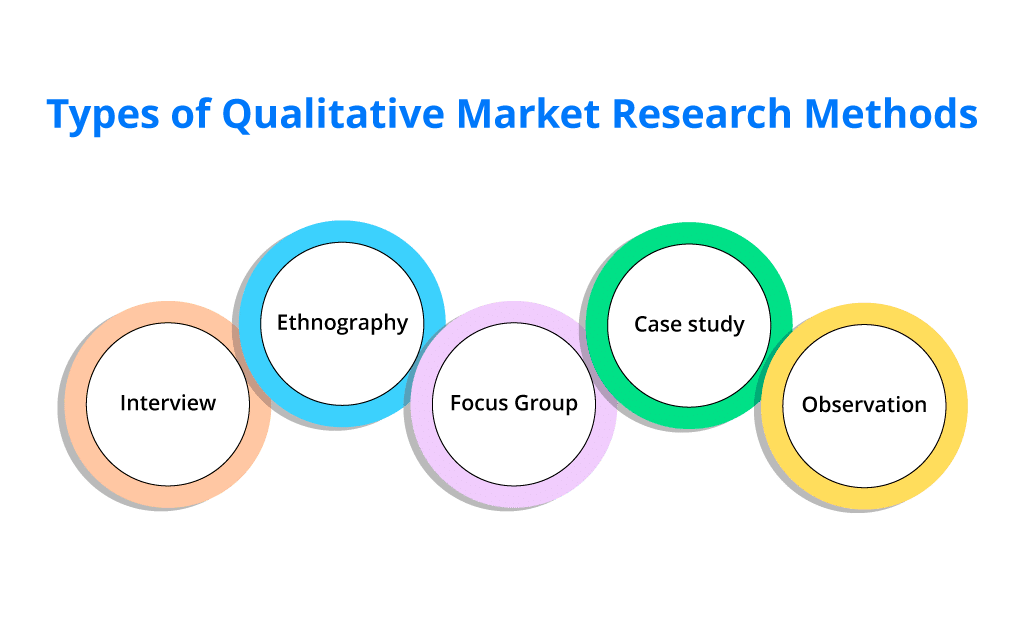
Qualitative research methods have originated from social and behavioral sciences. There are five common methods that researchers and marketers use to collect qualitative research data.
These five methods are based on how you can collect data from the target audience. So, let’s discuss these five data collection methods.
1. Interview
Interviewing the target audience is one of the most common practices in qualitative market research. You can carry out an interview either face-to-face, on phone , or online with one respondent at a time. This is a conversational method of gathering information and allows the researcher to get a detailed response from the respondent.
The advantage of the interview method is that it gives one an opportunity to gather detailed and precise information about people’s beliefs, motivations, and experiences.
If the researcher has experience in asking relevant and correct questions, it can help them collect meaningful data. These interviews usually last up to an hour or two, depending on how detailed and specific the researcher wants the data to be.
Interviews can be structured, semi-structured, or unstructured. Semi-structured interviews are most commonly used because they give researchers an outline of what topics and areas to cover. Also permitting them to tap into any area relevant to the participant’s experiences.
Additional read: Research Interviews – Uncovering their types and methods.
2. Ethnography
Ethnographic research includes direct observation of the concerned group you want to study. This qualitative market research involves studying video recordings of the interactions between customers and products as they indulge in the purchased product in real life.
Ethnographic researchers can observe their clients or participants of the research from anywhere, including the individual’s workplace, their familial environment, or when the individual is spending time with their peers.
Researchers fully immerse themselves into the lives of the customers. They observe and listen to the customers in their natural settings in a nondirected way. The goal, here, is to see people’s behaviors as they occur and on their terms, not our interpretation of those terms.
This observational method enlightens researchers about the context in which consumers are using the products they are analyzing and the meaningful contribution of the product in their lives.
3. Focus Groups
Another most commonly used method in qualitative market research is the focus group. In this method, the researcher gathers a limited number of consumers from the target market to create a focus group.
The main aim of this focus group is to answer questions relating to the “why” “what” and “how” of behaviors.
In a focus group, a trained moderator usually leads a discussion lasting about 30-90 minutes that is designed to gather useful information. The moderator’s main task is to hear the responses and probe respondents for any other specifications required while answering the questions.
Focus groups can now be sent an online survey on their preferred devices and their feedback can be collected through that. However, a disadvantage of focus groups is that they are time-consuming and costly.
This method is usually recommended when the market is launching a new product and needs in-depth insight from the target audience’s perspective.
4. Case Studies
Case studies have evolved to become a valuable method for qualitative market research . It is used for explaining a case of an organization or an entity. This is one of the simplest ways of conducting research because it involves an exhaustive understanding of the data collected and the interpretation of the same.
5. Observation
Observation can be systematic or naturalistic. Qualitative observation of respondents’ answers or their behaviors in particular settings can yield enriching insights.
The research observes the customer/consumer from a distance to see how they interact with an actual product. Often also called “shop-alongs”, this method reduces the possibility of a customer forgetting their shopping experience and providing false feedback at a later stage.
[Free Webinar Recording]
Want to know how to increase your survey response rates.
Learn how to meet respondents where they are, drive survey completion while offering a seamless experience, Every Time!
Methods to analyze qualitative market research data
There are different methods that are used to analyze qualitative market research data. The most commonly used method is the thematic analysis and text analysis.
Text analysis:
In text analysis , researchers analyze the qualitative data collected directly from the audience and decode the sentiment and meaning behind the feedback. The analysis method helps identify a pattern/trend and make sense of the sentiment associated with the words used by the audience.
Thematic analysis:
In thematic analysis , researchers find out the major themes or patterns in the respondents’ answers that are repeated several times.
This kind of analysis helps researchers understand the themes that are important in the respondents’ life and the experiences that matter the most to them. They can then understand how the product they are aiming to improve or launch can affect these major themes in the lives of the respondents.
Other qualitative analysis methods include content analysis, discourse analysis, and grounded theory. These methods differ in difficulty levels of conducting the analysis, and the steps to be followed while analyzing data.
Get started with Voxco's Market Research Tool kit.
- 5 Market Research Templates
- B2B Market Research Trends
- Guide to Agile Market Research
- Guide to using Online surveys to conduct Market Research
What are the uses of qualitative market research?
Qualitative data helps you uncover hidden data and make meaning of customers’ purchase behavior. You can use qualitative research in business to make important decisions.
Qualitative market research helps you gather contextual and unbiased feedback. You can gather deeper insights from the target market to understand consumers’ feelings about your brand and evaluate the brand-customer relationship.
It provides you with hard facts on where you stand and helps you benchmark your performance.
2. Consumer behavior insights:
You can use qualitative data to create an in-depth buyer/consumer persona. The customer behavior survey helps brands understand the needs, demands, and wants of the customers which helps them better market the product.
3. Market/business opportunities:
Explore new markets for business expansion by gathering qualitative insights. Leverage market research surveys to understand business trends, key competition, potential, or an ideal location for new opportunities.
4. Product research:
Be it a product upgrade or a new product concept , market research will help you understand if the target consumers will accept the product. Gather opinions and suggestions from consumers on various aspects of the product to create
How to conduct qualitative market research?
We have discussed the methods of data collection and uses of qualitative research so now let’s look at the steps to conduct qualitative market research.
1. Determine the objective for conducting research:
The research you want to conduct must have the desired outcome which explains what you want to achieve with this research. Determining the objective helps you map the research process and keep it aligned with the ultimate goal.
2. Decide what methodology to use:
You can conduct qualitative research in many ways. We have explained five common methods – interview, ethnography, focus group, case study, and observation – above.
3. Sample respondents:
It’s not practical to gather responses from the entire target audience . Creating a sample audience enables you to gather relevant data that represents the target audience.
It’s important to note a large sample size, gives you more accurate responses. There are three sampling methods – purpose, quota, and snowball sampling.
You can also leverage a market research panel, like Voxco Audience , to create an ideal respondent panel for your research. A research panel gives you access to verified respondents willing to participate in research.
Additional reads : What are sample surveys?
4. Design your survey:
The questions you ask play an important role in the type of responses you gather. Personalize the survey, and write relevant and meaningful questions to engage the audience.
5. Determine the data collection channels:
You can gather customer data online, offline, or by phone. For example, you can conduct a phone interview, a face-to-face interview, or a mobile-offline interview. Depending on the nature of the research, location, and the research topic, you can use a channel that will bring the most responses.
6. Analyze the gathered data:
Data analysis helps you make sense of your customer’s feedback. It helps you convert the data into actionable insights so you can make strategic business decisions. We have explained the analysis methods used for qualitative market research data above.
7. Report the findings:
Share the findings with stakeholders, colleagues, executives, and everyone else in a way that is easy to understand. Use charts and graphs to give context to the findings instead of handing over long paragraphs.
This sums up the seven steps to conducting qualitative research. Let’s look at some of its benefits.
Create surveys. Uncover insights. Scale growth.
See how Voxco can help you enhance your research requirements.
Benefits of qualitative market research
Qualitative research is often used because it preserves the voice and perspectives of the respondents which are usually converted into numerics in quantitative research. The advantages of qualitative research are listed below:
- The process of data collection and analysis is flexible and conversational in qualitative research; they are not rigidly defined and do not have to be systematically planned or decided beforehand.
- Qualitative research takes place in a naturalistic environment and provides insight into how individuals behave in natural settings.
- Since qualitative market research uses open-ended questions when collecting data, they offer a huge deal of new information that can be uncovered and studied by the researcher.
- Qualitative research is recommended when studying the launch of a new product in the market, developing a new product in the market, understanding the strength and weaknesses of the product in the market, and exploring the marke t in terms of consumer behavior, demographics, perception of the brand and product under study.
Be it a start-up or an established company, qualitative market research helps you understand customers’ motivation, feelings, and perceptions of your products and services. This research method enables you to learn why consumers make certain decisions and use the feedback to build your marketing and sales strategies.
FAQs on qualitative market research
Qualitative market research helps you gather data that explains why customers make certain purchase decision. It enables you to understand customers’ feelings, values, and thoughts about your products or services.
The four types of qualitative research are:
- Focus group
- Ethnography
Quantitative market research gathers numerical data that you can quantify and convert into statistical insights. It helps you find out “what” customers think of your brand.
Qualitative research gathers textual or verbal data that you can use to understand “why” customers buy your products and “how” they make that decision.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
We use cookies in our website to give you the best browsing experience and to tailor advertising. By continuing to use our website, you give us consent to the use of cookies. Read More
- Privacy Policy

Home » Qualitative Research – Methods, Analysis Types and Guide
Qualitative Research – Methods, Analysis Types and Guide
Table of Contents

Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is a type of research methodology that focuses on exploring and understanding people’s beliefs, attitudes, behaviors, and experiences through the collection and analysis of non-numerical data. It seeks to answer research questions through the examination of subjective data, such as interviews, focus groups, observations, and textual analysis.
Qualitative research aims to uncover the meaning and significance of social phenomena, and it typically involves a more flexible and iterative approach to data collection and analysis compared to quantitative research. Qualitative research is often used in fields such as sociology, anthropology, psychology, and education.
Qualitative Research Methods

Qualitative Research Methods are as follows:
One-to-One Interview
This method involves conducting an interview with a single participant to gain a detailed understanding of their experiences, attitudes, and beliefs. One-to-one interviews can be conducted in-person, over the phone, or through video conferencing. The interviewer typically uses open-ended questions to encourage the participant to share their thoughts and feelings. One-to-one interviews are useful for gaining detailed insights into individual experiences.
Focus Groups
This method involves bringing together a group of people to discuss a specific topic in a structured setting. The focus group is led by a moderator who guides the discussion and encourages participants to share their thoughts and opinions. Focus groups are useful for generating ideas and insights, exploring social norms and attitudes, and understanding group dynamics.
Ethnographic Studies
This method involves immersing oneself in a culture or community to gain a deep understanding of its norms, beliefs, and practices. Ethnographic studies typically involve long-term fieldwork and observation, as well as interviews and document analysis. Ethnographic studies are useful for understanding the cultural context of social phenomena and for gaining a holistic understanding of complex social processes.
Text Analysis
This method involves analyzing written or spoken language to identify patterns and themes. Text analysis can be quantitative or qualitative. Qualitative text analysis involves close reading and interpretation of texts to identify recurring themes, concepts, and patterns. Text analysis is useful for understanding media messages, public discourse, and cultural trends.
This method involves an in-depth examination of a single person, group, or event to gain an understanding of complex phenomena. Case studies typically involve a combination of data collection methods, such as interviews, observations, and document analysis, to provide a comprehensive understanding of the case. Case studies are useful for exploring unique or rare cases, and for generating hypotheses for further research.
Process of Observation
This method involves systematically observing and recording behaviors and interactions in natural settings. The observer may take notes, use audio or video recordings, or use other methods to document what they see. Process of observation is useful for understanding social interactions, cultural practices, and the context in which behaviors occur.
Record Keeping
This method involves keeping detailed records of observations, interviews, and other data collected during the research process. Record keeping is essential for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the data, and for providing a basis for analysis and interpretation.
This method involves collecting data from a large sample of participants through a structured questionnaire. Surveys can be conducted in person, over the phone, through mail, or online. Surveys are useful for collecting data on attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors, and for identifying patterns and trends in a population.
Qualitative data analysis is a process of turning unstructured data into meaningful insights. It involves extracting and organizing information from sources like interviews, focus groups, and surveys. The goal is to understand people’s attitudes, behaviors, and motivations
Qualitative Research Analysis Methods
Qualitative Research analysis methods involve a systematic approach to interpreting and making sense of the data collected in qualitative research. Here are some common qualitative data analysis methods:
Thematic Analysis
This method involves identifying patterns or themes in the data that are relevant to the research question. The researcher reviews the data, identifies keywords or phrases, and groups them into categories or themes. Thematic analysis is useful for identifying patterns across multiple data sources and for generating new insights into the research topic.
Content Analysis
This method involves analyzing the content of written or spoken language to identify key themes or concepts. Content analysis can be quantitative or qualitative. Qualitative content analysis involves close reading and interpretation of texts to identify recurring themes, concepts, and patterns. Content analysis is useful for identifying patterns in media messages, public discourse, and cultural trends.
Discourse Analysis
This method involves analyzing language to understand how it constructs meaning and shapes social interactions. Discourse analysis can involve a variety of methods, such as conversation analysis, critical discourse analysis, and narrative analysis. Discourse analysis is useful for understanding how language shapes social interactions, cultural norms, and power relationships.
Grounded Theory Analysis
This method involves developing a theory or explanation based on the data collected. Grounded theory analysis starts with the data and uses an iterative process of coding and analysis to identify patterns and themes in the data. The theory or explanation that emerges is grounded in the data, rather than preconceived hypotheses. Grounded theory analysis is useful for understanding complex social phenomena and for generating new theoretical insights.
Narrative Analysis
This method involves analyzing the stories or narratives that participants share to gain insights into their experiences, attitudes, and beliefs. Narrative analysis can involve a variety of methods, such as structural analysis, thematic analysis, and discourse analysis. Narrative analysis is useful for understanding how individuals construct their identities, make sense of their experiences, and communicate their values and beliefs.
Phenomenological Analysis
This method involves analyzing how individuals make sense of their experiences and the meanings they attach to them. Phenomenological analysis typically involves in-depth interviews with participants to explore their experiences in detail. Phenomenological analysis is useful for understanding subjective experiences and for developing a rich understanding of human consciousness.
Comparative Analysis
This method involves comparing and contrasting data across different cases or groups to identify similarities and differences. Comparative analysis can be used to identify patterns or themes that are common across multiple cases, as well as to identify unique or distinctive features of individual cases. Comparative analysis is useful for understanding how social phenomena vary across different contexts and groups.
Applications of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research has many applications across different fields and industries. Here are some examples of how qualitative research is used:
- Market Research: Qualitative research is often used in market research to understand consumer attitudes, behaviors, and preferences. Researchers conduct focus groups and one-on-one interviews with consumers to gather insights into their experiences and perceptions of products and services.
- Health Care: Qualitative research is used in health care to explore patient experiences and perspectives on health and illness. Researchers conduct in-depth interviews with patients and their families to gather information on their experiences with different health care providers and treatments.
- Education: Qualitative research is used in education to understand student experiences and to develop effective teaching strategies. Researchers conduct classroom observations and interviews with students and teachers to gather insights into classroom dynamics and instructional practices.
- Social Work : Qualitative research is used in social work to explore social problems and to develop interventions to address them. Researchers conduct in-depth interviews with individuals and families to understand their experiences with poverty, discrimination, and other social problems.
- Anthropology : Qualitative research is used in anthropology to understand different cultures and societies. Researchers conduct ethnographic studies and observe and interview members of different cultural groups to gain insights into their beliefs, practices, and social structures.
- Psychology : Qualitative research is used in psychology to understand human behavior and mental processes. Researchers conduct in-depth interviews with individuals to explore their thoughts, feelings, and experiences.
- Public Policy : Qualitative research is used in public policy to explore public attitudes and to inform policy decisions. Researchers conduct focus groups and one-on-one interviews with members of the public to gather insights into their perspectives on different policy issues.
How to Conduct Qualitative Research
Here are some general steps for conducting qualitative research:
- Identify your research question: Qualitative research starts with a research question or set of questions that you want to explore. This question should be focused and specific, but also broad enough to allow for exploration and discovery.
- Select your research design: There are different types of qualitative research designs, including ethnography, case study, grounded theory, and phenomenology. You should select a design that aligns with your research question and that will allow you to gather the data you need to answer your research question.
- Recruit participants: Once you have your research question and design, you need to recruit participants. The number of participants you need will depend on your research design and the scope of your research. You can recruit participants through advertisements, social media, or through personal networks.
- Collect data: There are different methods for collecting qualitative data, including interviews, focus groups, observation, and document analysis. You should select the method or methods that align with your research design and that will allow you to gather the data you need to answer your research question.
- Analyze data: Once you have collected your data, you need to analyze it. This involves reviewing your data, identifying patterns and themes, and developing codes to organize your data. You can use different software programs to help you analyze your data, or you can do it manually.
- Interpret data: Once you have analyzed your data, you need to interpret it. This involves making sense of the patterns and themes you have identified, and developing insights and conclusions that answer your research question. You should be guided by your research question and use your data to support your conclusions.
- Communicate results: Once you have interpreted your data, you need to communicate your results. This can be done through academic papers, presentations, or reports. You should be clear and concise in your communication, and use examples and quotes from your data to support your findings.
Examples of Qualitative Research
Here are some real-time examples of qualitative research:
- Customer Feedback: A company may conduct qualitative research to understand the feedback and experiences of its customers. This may involve conducting focus groups or one-on-one interviews with customers to gather insights into their attitudes, behaviors, and preferences.
- Healthcare : A healthcare provider may conduct qualitative research to explore patient experiences and perspectives on health and illness. This may involve conducting in-depth interviews with patients and their families to gather information on their experiences with different health care providers and treatments.
- Education : An educational institution may conduct qualitative research to understand student experiences and to develop effective teaching strategies. This may involve conducting classroom observations and interviews with students and teachers to gather insights into classroom dynamics and instructional practices.
- Social Work: A social worker may conduct qualitative research to explore social problems and to develop interventions to address them. This may involve conducting in-depth interviews with individuals and families to understand their experiences with poverty, discrimination, and other social problems.
- Anthropology : An anthropologist may conduct qualitative research to understand different cultures and societies. This may involve conducting ethnographic studies and observing and interviewing members of different cultural groups to gain insights into their beliefs, practices, and social structures.
- Psychology : A psychologist may conduct qualitative research to understand human behavior and mental processes. This may involve conducting in-depth interviews with individuals to explore their thoughts, feelings, and experiences.
- Public Policy: A government agency or non-profit organization may conduct qualitative research to explore public attitudes and to inform policy decisions. This may involve conducting focus groups and one-on-one interviews with members of the public to gather insights into their perspectives on different policy issues.
Purpose of Qualitative Research
The purpose of qualitative research is to explore and understand the subjective experiences, behaviors, and perspectives of individuals or groups in a particular context. Unlike quantitative research, which focuses on numerical data and statistical analysis, qualitative research aims to provide in-depth, descriptive information that can help researchers develop insights and theories about complex social phenomena.
Qualitative research can serve multiple purposes, including:
- Exploring new or emerging phenomena : Qualitative research can be useful for exploring new or emerging phenomena, such as new technologies or social trends. This type of research can help researchers develop a deeper understanding of these phenomena and identify potential areas for further study.
- Understanding complex social phenomena : Qualitative research can be useful for exploring complex social phenomena, such as cultural beliefs, social norms, or political processes. This type of research can help researchers develop a more nuanced understanding of these phenomena and identify factors that may influence them.
- Generating new theories or hypotheses: Qualitative research can be useful for generating new theories or hypotheses about social phenomena. By gathering rich, detailed data about individuals’ experiences and perspectives, researchers can develop insights that may challenge existing theories or lead to new lines of inquiry.
- Providing context for quantitative data: Qualitative research can be useful for providing context for quantitative data. By gathering qualitative data alongside quantitative data, researchers can develop a more complete understanding of complex social phenomena and identify potential explanations for quantitative findings.
When to use Qualitative Research
Here are some situations where qualitative research may be appropriate:
- Exploring a new area: If little is known about a particular topic, qualitative research can help to identify key issues, generate hypotheses, and develop new theories.
- Understanding complex phenomena: Qualitative research can be used to investigate complex social, cultural, or organizational phenomena that are difficult to measure quantitatively.
- Investigating subjective experiences: Qualitative research is particularly useful for investigating the subjective experiences of individuals or groups, such as their attitudes, beliefs, values, or emotions.
- Conducting formative research: Qualitative research can be used in the early stages of a research project to develop research questions, identify potential research participants, and refine research methods.
- Evaluating interventions or programs: Qualitative research can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of interventions or programs by collecting data on participants’ experiences, attitudes, and behaviors.
Characteristics of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is characterized by several key features, including:
- Focus on subjective experience: Qualitative research is concerned with understanding the subjective experiences, beliefs, and perspectives of individuals or groups in a particular context. Researchers aim to explore the meanings that people attach to their experiences and to understand the social and cultural factors that shape these meanings.
- Use of open-ended questions: Qualitative research relies on open-ended questions that allow participants to provide detailed, in-depth responses. Researchers seek to elicit rich, descriptive data that can provide insights into participants’ experiences and perspectives.
- Sampling-based on purpose and diversity: Qualitative research often involves purposive sampling, in which participants are selected based on specific criteria related to the research question. Researchers may also seek to include participants with diverse experiences and perspectives to capture a range of viewpoints.
- Data collection through multiple methods: Qualitative research typically involves the use of multiple data collection methods, such as in-depth interviews, focus groups, and observation. This allows researchers to gather rich, detailed data from multiple sources, which can provide a more complete picture of participants’ experiences and perspectives.
- Inductive data analysis: Qualitative research relies on inductive data analysis, in which researchers develop theories and insights based on the data rather than testing pre-existing hypotheses. Researchers use coding and thematic analysis to identify patterns and themes in the data and to develop theories and explanations based on these patterns.
- Emphasis on researcher reflexivity: Qualitative research recognizes the importance of the researcher’s role in shaping the research process and outcomes. Researchers are encouraged to reflect on their own biases and assumptions and to be transparent about their role in the research process.
Advantages of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research offers several advantages over other research methods, including:
- Depth and detail: Qualitative research allows researchers to gather rich, detailed data that provides a deeper understanding of complex social phenomena. Through in-depth interviews, focus groups, and observation, researchers can gather detailed information about participants’ experiences and perspectives that may be missed by other research methods.
- Flexibility : Qualitative research is a flexible approach that allows researchers to adapt their methods to the research question and context. Researchers can adjust their research methods in real-time to gather more information or explore unexpected findings.
- Contextual understanding: Qualitative research is well-suited to exploring the social and cultural context in which individuals or groups are situated. Researchers can gather information about cultural norms, social structures, and historical events that may influence participants’ experiences and perspectives.
- Participant perspective : Qualitative research prioritizes the perspective of participants, allowing researchers to explore subjective experiences and understand the meanings that participants attach to their experiences.
- Theory development: Qualitative research can contribute to the development of new theories and insights about complex social phenomena. By gathering rich, detailed data and using inductive data analysis, researchers can develop new theories and explanations that may challenge existing understandings.
- Validity : Qualitative research can offer high validity by using multiple data collection methods, purposive and diverse sampling, and researcher reflexivity. This can help ensure that findings are credible and trustworthy.
Limitations of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research also has some limitations, including:
- Subjectivity : Qualitative research relies on the subjective interpretation of researchers, which can introduce bias into the research process. The researcher’s perspective, beliefs, and experiences can influence the way data is collected, analyzed, and interpreted.
- Limited generalizability: Qualitative research typically involves small, purposive samples that may not be representative of larger populations. This limits the generalizability of findings to other contexts or populations.
- Time-consuming: Qualitative research can be a time-consuming process, requiring significant resources for data collection, analysis, and interpretation.
- Resource-intensive: Qualitative research may require more resources than other research methods, including specialized training for researchers, specialized software for data analysis, and transcription services.
- Limited reliability: Qualitative research may be less reliable than quantitative research, as it relies on the subjective interpretation of researchers. This can make it difficult to replicate findings or compare results across different studies.
- Ethics and confidentiality: Qualitative research involves collecting sensitive information from participants, which raises ethical concerns about confidentiality and informed consent. Researchers must take care to protect the privacy and confidentiality of participants and obtain informed consent.
Also see Research Methods
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples

Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide

Observational Research – Methods and Guide

Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and...

Qualitative Research Methods

Explanatory Research – Types, Methods, Guide
Conversion Rate Optimization Blog

7 Types of Qualitative Research + 6 Types of Qualitative Methods of Research

Do you want to learn about the types of qualitative research and some examples of methodologies?
Qualitative studies are vital to the market research process. They provide an understanding of the reasons and motivations behind consumer decisions. You can use this information to improve your marketing and increase sales.
What does that mean for your business?
If you have a product that isn’t selling as well as you expected, qualitative research can help you understand why. Or, if you’re launching a new marketing campaign, qualitative studies can help you create ads that will entice your target audience.
If you’re new to this kind of market research, you’re in the right place.
In this guide, you’ll learn the basics of qualitative market research. We’ll also share how your business can use qualitative data to better appeal to your customers.
What is Qualitative Research?
Why use qualitative research, 7 types of qualitative research, 6 types of qualitative methods of research.
- Ideas for Analyzing Qualitative Data
Qualitative research is any research that provides subjective, non-numerical information. It focuses on people: their experiences, beliefs, and behaviors. It’s generally conducted using observation or unstructured questioning.

Qualitative research is used across many fields and industries, including sales, marketing, health care, education, and social sciences.
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research
You likely hear the term “qualitative” used in contrast with “quantitative.”
Quantitative research generates specific numerical data. Its goal is to quantify and generalize the results of a study through numbers, percentages, and statistics. Quantitative research seeks to answer the what , where , when, and who of decision-making.
Qualitative market research, on the other hand, provides insights into the deeper motives behind consumer purchases. Qualitative research answers the why and how .
Why should your business use qualitative research as opposed to quantitative research?
Well, first of all, you should not use qualitative market research instead of quantitative. The 2 are complementary to each other.
Qualitative research on its own is not conclusive. However, you can use it to:
- Explain quantitative research results.
- Conduct market research when traditional surveys are unavailable. For instance, when your topic involves sensitive or complex questions.
- Conduct market research when more structured research is not possible.
Let’s look at an example of combining quantitative and qualitative research.
For instance, we’ll say that your business wants to conduct research to improve your website.
Quantitative research would give you information such as:
- The number of website visitors
- The length of time users stay on each page
- The number of leads generated from each email signup form
- More quantitative data, such as online shopping statistics and conversion rates
This information is all important data about user behavior. But it doesn’t give you the why behind this behavior.
Qualitative research fills in the rest of the picture with information such as:
- Which parts of your website users find difficult to use
- Whether users find your lightbox popups to be intrusive
- Which special offers and coupon codes shoppers find exciting
- More subjective information about how users view the style, relevance, and usability of your site
A complete website study should include both quantitative and qualitative research. Then, you can improve your website based both on hard numbers and users’ experiences and opinions.
Qualitative market research collects subjective feedback and observations from consumers and users. However, as with most data collection, it’s much more complicated in practice.
Experts divide qualitative research into 7 main types. These are also sometimes called types of qualitative research designs.
Below, we’ll quickly explain the basics of each qualitative research approach before diving into qualitative research methods you can use for your market research.
Don’t feel like you have to memorize and fully understand all of these approaches. However, reviewing them will give you a good introduction to the field of qualitative research.
1. Phenomenology
Phenomenological research is based on the root word “phenomena.” It seeks to discover how individual people view specific experiences. Phenomenology focuses on lived experiences and individuality instead of generalizations about larger groups.
2. Ethnography
In the ethnography approach, researchers immerse themselves in a specific culture to gain qualitative data through observation and interaction. Ethnographic research provides more in-depth and nuanced information than, say, questionnaires or interviews. This approach also provides data about specific demographics.
3. Grounded Theory
The term “grounded theory” essentially describes the order in which researchers develop a theory.
In most other types of qualitative research, researchers start with a hypothesis and then conduct a study to test that hypothesis. However, researchers using grounded theory begin with qualitative data, such as interviews and observations, and then analyze it to develop a theory. This approach is helpful when you have no working theory for why consumers behave in a certain way.
4. Case Study
Case studies are in-depth examinations of a business, process, product, person, or group of people. They also often include quantitative research, but they become qualitative when they focus on the reasons behind that data and the participants’ individual experiences.
For instance, in our case study of AdamEnfroy.com , we present subjective feedback in addition to quantitative data:

See more examples of OptinMonster’s case study research.
5. Historical Research
The historical approach to research is reasonably self-explanatory. Researchers analyze data from the past to form expectations about the present and future. In qualitative market research, this might mean analyzing consumer feedback from throughout the history of your company or industry.
6. Narrative Research
The narrative approach seeks to tell a story about people’s experiences. Researchers conduct interviews and collect observations over a period of time. Then, they use this information to develop a narrative about the experiences of an individual or small group of people.
7. Action Research
Action research aims to investigate and solve a specific, immediate problem. This type of research is cyclical. Researchers apply an action, analyze the data, draw conclusions, and start again.
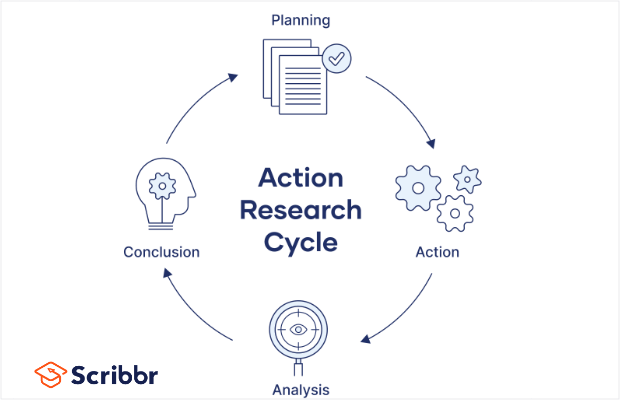
Now that you have an overview of the different types of qualitative research, we’ll explore types of qualitative methods of research along with some practical examples.
The approaches above are fairly abstract. Now, we’ll share some concrete qualitative methods to collect data for your business. Even beginners and small businesses can use these methodologies.
Here are some of the most common types of qualitative research methods to give you greater insight into your customers. Next time that you are ready to launch a new product or start a new marketing campaign, try out one or more of these methods. You’ll get valuable feedback that will help you succeed.
1. In-Depth Interviews Let You Dig Deep
In-depth interviews (IDIs) are a great way to get detailed consumer feedback. An IDI can be conducted over the phone, in person, or via webcam, using services like Skype or Zoom.
Webcam interviews have become the most common qualitative research method. 34% of researchers report regularly conducting webcam IDIs as 1 of their top 3 data collection methods.
Regardless of your interview method, your IDIs should focus on your ideal user or an existing customer. You ask each person a series of research questions and follow-ups to learn what motivates them to buy a product like yours.
For qualitative research, you should always ask open-ended questions. Avoid simple yes/no questions that provide only quantitative data.
You should go into the interview with some questions prepared, but you shouldn’t stick to a script. If the participant says something interesting, ask follow-up questions that dig deeper.
Here are a few initial questions you could ask:
- What frustrates you about [your topic]?
- If I had a magic wand and could give you the perfect product, what would it look like?
- Have you bought [your type of product] before? If so, what motivated you to buy it?
IDIs provide detailed information about individuals. Therefore, they are especially common in the phenomenology and narrative types of qualitative research.
2. Focus Groups Allow for the Exchange of Ideas
Like IDIs, focus groups can be face-to-face or online. These groups usually involve sample sizes of 6-10 people. They provide a safe and comfortable environment for your users to talk about their thoughts and feelings surrounding your product.
The advantage of in-person focus groups is that you observe the consumer’s verbal and non-verbal reaction to your product or advertising. Group members can also bounce off each other’s thoughts and ideas, which means you’ll get even greater insights.
You can use focus groups to:
- Test a new product or website
- Explore the general concept for your product
- Evaluate your advertising copy and imagery
- Explore new packaging ideas
Online focus groups are similar to in-person ones. They’re more cost-efficient, allow you to include more people, and are less time-consuming to organize. Now that more people are comfortable with Zoom and Skype, online focus groups are more accessible than ever before.

You can also use social media to your advantage. Create a community of people interested in your topic and use it to foster a conversation. Then, observe the dialogue. You’ll gain a lot of interesting insights!
3. Shopping Observations, or “Shop-Alongs,” Give Real-Time Insight
An in-person observation of shopping behavior lets you watch the consumer react to your products in-store. With a shop-along, you get to see consumers’ real-life shopping behavior. Because you see immediate reactions, this method provides different insight than a written survey.
These qualitative studies highlight problems with shelf displays, clutter, or out-of-stock products. You may also interact with consumers to get deeper insights during the shopping process. You can get real-time feedback on package design, for example.
4. In-Home Videos Show Realistic Product Use
In-home videos allow you to observe how users interact with your product in real life, in their own homes.
This research method’s advantage is the setting of the participant observation. You can see your user’s behavior in a natural, comfortable environment. You’ll get a more realistic view of how people use your product.
5. Lifestyle Immersion Lets You Hear Real-World Dialogue
Lifestyle immersion is when you attend an event, such as a party or a family gathering. This research method gives you an uninterrupted view of users’ attitudes and behaviors. Immersion is another excellent way to get candid insight in a comfortable, familiar setting.
During these activities, observe your users having a dialogue with their friends. Listen to these real-world conversations to learn about consumers’ desires, frustrations, and motivations.
6. Journal or Diary Studies for Honest Feedback
Have your user or potential customer keep a journal or a diary to document their experience with your topic or product. Users may be more likely to be completely honest when they’re not face-to-face with an interviewer or moderator.
Journals can be handwritten or digital. Either way, it will capture your user’s voice, which is extremely valuable for optimizing your marketing copy.
3 Tips for Qualitative Data Analysis (to Help You Understand Your Customers)
Using the methods and types of qualitative research discussed above, you can gather excellent information about consumers’ opinions, experiences, and behaviors. The next step is to analyze your data.
Since qualitative data is unstructured, it can be tricky to draw conclusions, let alone present your findings. While qualitative data is not conclusive in and of itself, here are a few tips for analyzing qualitative research data.
1. Summarize the Key Points
For interviews and focus groups, have the moderator write up some key points from the discussion. For example: “Common concerns among participants about our pizza were cheese overuse, greasiness, and bland sauce.”
Here is an example of a qualitative summary from a market research project for Pizza Hut Pakistan

2. Code Responses
Coding is the process of organizing and labeling your qualitative data into categories. You can “code” your unstructured data into labels you can summarize with tables or charts.
For example, a researcher might have asked the open-ended question, “How often do you wear a watch?”
Every respondent’s answer would likely be a little different. But you could code them in categories such as:
- Once in a while
This process gives you coded data sets to analyze and report.
3. Create a Word Cloud
Create a “word cloud” out of the keywords used by consumers. Put your field notes into a word cloud generator like WordClouds.com . In your cloud, the words that research participants used most often will be the largest. You’ll be able to spot the most prominent words easily.

Use Qualitative Research to Improve Marketing and Sales
You can use these qualitative research types, methods, and analysis strategies to understand your users and customers. Qualitative data collection will help you improve your product development and marketing strategy, leading to more sales and revenue.
If online surveys are part of your research process, check out our survey best practices .
Once you clearly understand your customers, apply what you’ve learned to your email marketing strategy . Using in-depth qualitative data, you’ll generate more leads and sales than ever before.
Disclosure: Our content is reader-supported. This means if you click on some of our links, then we may earn a commission. We only recommend products that we believe will add value to our readers.
Add a Comment Cancel reply
We're glad you have chosen to leave a comment. Please keep in mind that all comments are moderated according to our privacy policy , and all links are nofollow. Do NOT use keywords in the name field. Let's have a personal and meaningful conversation.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Get More Subscribers & Customers NOW
Unleash the power of OptinMonster on your website today!
What is Marketing Research? Examples and Best Practices
12 min read

Marketing research is essentially a method utilized by companies to collect valuable information regarding their target market. Through the common practice of conducting market research, companies gather essential information that enables them to make informed decisions and develop products that resonate with consumers. It encompasses the gathering, analysis, and interpretation of data, which aids in identifying consumer demands, anticipating market trends, and staying ahead of the competition.
Exploratory research is one of the initial steps in the marketing research process. It helps businesses gain broad insights when specific information is unknown. If you are seeking insight into how marketing research can influence the trajectory of your SaaS, then you have come to the right place!
- Market research is a systematic and objective process crucial for understanding target markets, refining business strategies, and informing decisions, which includes collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data on customers, competitors, and the industry.
- Primary market research gathers specific data directly from the target audience using tools like surveys and focus groups, while secondary market research utilizes existing data from various sources to provide broader market insights.
- Effective market research combines both qualitative methods, which explore consumer motivations, and quantitative methods, which provide measurable statistics, to create comprehensive insights that guide business strategy and decision-making.
Try Userpilot and Take Your Product Marketing to the Next Level
- 14 Day Trial
- No Credit Card Required

Defining marketing research

Launching a product without knowing what your target audience wants is like walking in the dark. Market research lights the way, helping you collect, analyze, and understand information about your target market. This allows you to refine your business strategies and make decisions based on solid evidence.
Gone are the days when just intuition or subjective judgment was enough. Objective insights from market research help avoid costly mistakes and meet consumer needs by identifying trends and changes in the market. This is crucial for assessing a product’s potential success, optimizing marketing strategies, and preparing for market shifts.
Market research is a systematic approach that provides essential information, helping businesses navigate the complexities of the commercial world. Partnering with market research companies can offer additional benefits, leveraging their expertise in understanding market demands, trends, market size, economic indicators, location, market saturation, and pricing. Whether starting a new business, developing products, or updating marketing plans, understanding how to conduct effective market research is key to success.
To conduct market research effectively, businesses must determine study goals, identify target consumers, collect and analyze data, and use the findings to make informed decisions. This process is vital for evaluating past performance, measuring changes over time, and addressing specific business needs. It guides businesses in product development, marketing strategies, and overall decision-making, ensuring a better ROI and providing an eye-opening view of the market through various research methods, whether conducted in-house or outsourced.
The purpose of marketing research
Conducting marketing research is more than just gathering data; it’s about turning that data into actionable insights to refine your business strategies. This process helps you understand what motivates your customers, enabling you to tailor your products and services to minimize risks from the start. Importantly, market research plays a pivotal role in measuring and enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty, which are critical for understanding key demographics, improving user experience, designing better products, and driving customer retention. Customer satisfaction is measured as a key outcome, directly linked to the success of marketing strategies and business activities.
For SaaS product managers, market research, including competitive analysis, is crucial. It evaluates past strategies and gauges the potential success of new offerings. This research provides essential insights into brand strength, consumer behavior, and market position, which are vital for teams focused on sales, marketing, and product development.
A key aspect of market research is analyzing customer attitudes and usage. This analysis offers detailed insights into what customers want, the choices they make, and the challenges they face. It helps identify opportunities in the market and aids in formulating effective strategies for market entry.
Overall, market research equips SaaS entrepreneurs with the knowledge to meet their target audience’s needs effectively, guiding product adjustments and innovations based on informed decisions.
Key components of market research
Conducting market research is analogous to preparing a cake, requiring precise ingredients in specific quantities to achieve the intended outcome. Within this realm, necessary components consist of primary and secondary data gathering, thorough analysis, and insightful interpretation.
Primary research techniques such as exploratory studies, product evolution inquiries, estimations of market dimensions and shares, and consumer behavior examinations play a crucial role in collecting targeted information that can be directly applied. These methods afford a deeper understanding of your target demographic, allowing for customized strategy development.
In contrast, secondary research enriches the specificity of primary findings by adding wider context. It taps into external resources encompassing works from other investigators, sector-specific reports, and demographics data, which provide an expansive yet less particularized landscape view of the marketplace.
The subsequent phase involves meticulous analysis of collated data offering unbiased perspectives critical for identifying deficiencies while recognizing emerging patterns. Technological progress now facilitates examination efforts on both structured and unstructured datasets effectively addressing large-scale analytical complexities.
Ultimately, it’s through expert-led interpretation that value transcends raw figures, yielding strategies grounded in deep comprehension. Akin to decoding recipes using selected ingredients—this interpretative step enables crafting optimal business maneuvers just as one would bake their ideal confectionery creation utilizing proper culinary guidance.
Types of market research: primary and secondary
Now that you know the importance of clear research objectives, let’s explore the different types of market research and the techniques available to achieve these goals. Market research methods can be divided into two main categories: primary research and secondary research . The choice between these depends on factors like your budget, time constraints, and whether you need exploratory data or definitive answers.
Primary research involves collecting new data directly from sources. This process is like mining for precious metals, as it requires using various methods to gather fresh insights.
- Surveys (here – in-app survey templates from Userpilot ).
- Interviews.
- Focus groups.
- Product trials.
This approach gives you first-hand insight into your target audience.
Conversely, secondary research uses already established datasets of primary data – which can add depth and reinforcement to your firsthand findings.
Conducting your own market research using primary research tools can be a cost-effective strategy, allowing businesses to gather valuable insights directly and tailor their research to specific needs.
Let’s look a bit deeper into them now.
What is primary market research?
Market research uses primary market research as an essential tool. This involves collecting new data directly from your target audience using various methods, such as surveys , focus groups, and interviews.
Each method has its benefits. For example, observational studies allow you to see how consumers interact with your product.
There are many ways to conduct primary research.
Focus Groups : Hold discussions with small groups of 5 to 10 people from your target audience. These discussions can provide valuable feedback on products, perceptions of your company’s brand name, or opinions on competitors. Additionally, these discussions can help understand the characteristics, challenges, and buying habits of target customers, optimizing brand strategy.
Interviews : Have one-on-one conversations to gather detailed information from individuals in your target audience.
Surveys : These are a common tool in primary market research and can be used instead of focus groups to understand consumer attitudes. Surveys use structured questions and can reach a broad audience efficiently.
Navigating secondary market research
While marketing research using primary methods is like discovering precious metals, secondary market research technique is like using a treasure map. This approach uses data collected by others from various sources, providing a broad industry view. These sources include market analyses from agencies like Statista, historical data such as census records, and academic studies.
Secondary research provides the basic knowledge necessary for conducting primary market research goals but may lack detail on specific business questions and could also be accessible to competitors.
To make the most of secondary market research, it’s important to analyze summarized data to identify trends, rely on reputable sources for accurate data, and remain unbiased in data collection methods.
The effectiveness of secondary research depends significantly on how well the data is interpreted, ensuring that this information complements the insights from primary research.
Qualitative vs quantitative research
Market research employs both qualitative and quantitative methods, offering distinct insights that complement each other. Qualitative research aims to understand consumer behaviors and motivations through detailed analysis, while quantitative research collects measurable data for statistical analysis.
The selection of qualitative or quantitative methods should align with your research goals. If you need to uncover initial insights or explore deep consumer motivations, qualitative techniques like surveys or interviews are ideal.
On the other hand, if you need data that can be measured and analyzed for reliability, quantitative methods are more suitable.
However, these approaches don’t have to be used separately. Combining qualitative and quantitative methods in mixed-method studies allows you to capture both detailed exploratory responses and concrete numerical data. This integration offers a comprehensive view of the market, leveraging the strengths of both approaches to provide a fuller understanding of market conditions.
Implementing market research tools: Userpilot’s role
Similar to how a compass is essential for navigation at sea, businesses need appropriate instruments to carry out effective market research. Userpilot’s suite of product analytics and in-app engagement tools are critical components for this purpose.
Acting as a Buyer Persona Research instrument, Userpilot’s product analytics provide key quantitative research capabilities. This helps clearly define and comprehend the attributes and behaviors of potential customers, providing you with insights into your ICP (Ideal Customer Persona), user preferences, and product-market fit.
Beyond product analytics, Userpilot offers robust in-app engagement features such as modals and surveys that support real time collection of market research information. These interactive features work synergistically with the analytical tools to enable companies to gather detailed data and feedback crucial for informed business decision-making.
Marketing research process: Step-by-step guide
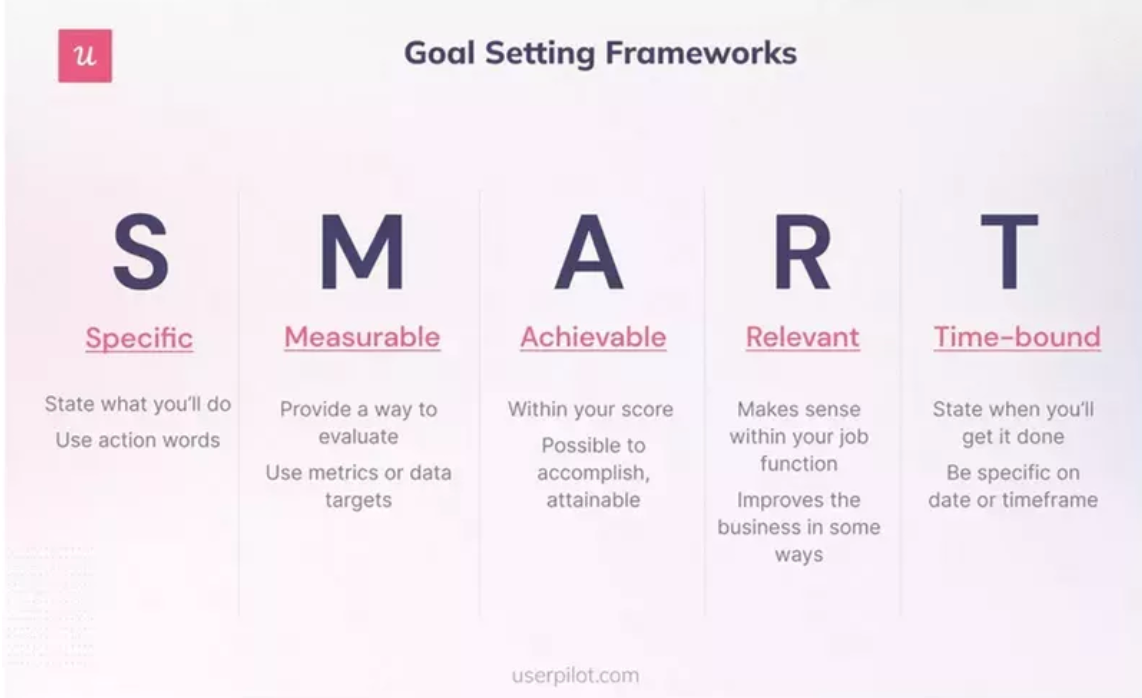
Marketing research conists of several critical stages:
- Defining precise goals.
- Delving into the knowledge of your target demographic.
- Collecting and scrutinizing data.
- Revealing insights that can be translated into tangible actions.
Following these steps allows you to gather critical information that guides business decisions.
An effective research strategy is crucial and involves:
- Properly allocating funds.
- Formulating testable hypotheses.
- Choosing appropriate methods for the study.
- Determining the number of study participants.
- Considering external variables.
A well-planned strategy ensures that your market research is focused, efficient, and produces useful outcomes.
After collecting data, the next step is to analyze it. This involves comparing the data to your initial questions to draw conclusions relevant to your business strategies.
Userpilot makes your data analysis easier by providing handy analytics dashboards for key user metrics such as activation, engagement, core feature adoption, and retention out of the box:
Finally, you report the findings and the process, providing recommendations based on the evidence. This is like solving a puzzle: each piece helps to complete the overall picture.
Challenges and best practices in market research
Delving into market research comes with its own set of hurdles. Those conducting the research must deliver more profound insights within increasingly shorter timespans, and they need to cultivate strategic, continuous research methods to stay abreast of an ever-changing business landscape.
Ensuring high-quality data can be demanding due to issues such as disjointed tools or insufficient analytical expertise. New solutions like Userpilot are surfacing that make these obstacles less daunting by offering accessible and user-friendly options. Maintaining clear lines of communication with your market research team is crucial for achieving both punctuality and quality in outcomes.
The advantages of engaging in marketing research cannot be overstated.
Real-life examples of successful market research
Real-life examples of market research in the SaaS industry often showcase innovative approaches to understanding customer needs and product-market fit.
For instance, Slack, the communication platform, utilized extensive market research to identify gaps in communication tools and understand the workflows of teams. This led to the development of features that seamlessly integrated with other tools and catered to the needs of various team sizes and structures.
Another example is HubSpot, which conducted market research to understand the pain points of small to medium-sized businesses in managing customer relationships. The insights gained helped shape their all-in-one inbound marketing, sales, and service platform, which has become integral to their users’ daily operations. These examples demonstrate how SaaS companies can employ market research to inform product development, improve user experience, and strategically position themselves in a competitive market.
Choosing the right market research tools
For B2B SaaS product managers aiming to do market research, having the right set of tools can make a significant difference. Here’s a list of valuable SaaS tools that can be leveraged for effective market research:
- Userpilot : A comprehensive Product Growth Platform offering in-depth product analytics, a code-free in-app experience builder, bespoke in-app survey capabilities, and robust integration options with platforms like Salesforce and Hubspot. This tool is particularly useful for understanding user behavior, enhancing user engagement, and gathering targeted feedback.
- Qualtrics : Known for its powerful survey tools, Qualtrics helps businesses gather and analyze customer feedback effectively. Its advanced analytics features are ideal for testing market hypotheses and understanding customer sentiments.
- SurveyMonkey : A versatile tool that enables product managers to create, send, and analyze surveys quickly and easily. SurveyMonkey is suitable for gauging customer satisfaction and collecting feedback on potential new features.
- Mixpanel : Specializes in user behavior analytics, offering detailed insights into how users interact with your product. This is essential for identifying patterns and optimizing product features.
- Hotjar : Combines analytics and feedback tools to give teams insights into user behavior and preferences. Hotjar’s heatmaps and session recordings are invaluable for understanding the user experience on a deeper level.
- Tableau : A leading platform for business intelligence and data visualization, Tableau allows product managers to create comprehensive visual reports that can inform strategic decisions based on user data analysis.
Each of these tools provides unique functionalities that can assist SaaS product managers in conducting thorough market research, thereby ensuring that their products are perfectly aligned with user needs and market demands.
Measuring the impact of market research
The pivotal challenge for market research lies in demonstrating its return on investment (ROI) and overall influence on corporate success sufficiently enough to justify regular financial commitment from company leaders. The worth attributed to a market research firm hinges not only on their ability to deliver relevant and high-caliber information, but also on their pricing structures and their contribution towards propelling organizational growth.
To gauge how effectively business choices made based on market research findings succeed, various metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) are utilized. These numerical tools act as navigational aids directing enterprises toward achieving objectives while simultaneously verifying that efforts invested in conducting market analysis are yielding fruitful guidance.
Throughout our look at market research, we’ve seen its importance and impact. Our discussion covered the basics of market research, its key components, and different types, including both qualitative and quantitative methods, and the role of Userpilot’s tools. We’ve examined the details of the market research process, tackled challenges, identified best practices, and shared success stories. We also provided advice on choosing the right market research partner and how to measure the effectiveness of your market research.
In today’s data-driven world, comprehensive market research is crucial for companies that want to succeed. It acts like a guide, helping businesses navigate the complex market landscape. Start your own detailed research today, supported by insightful analytics to help you succeed.
Frequently asked questions
What is market research and why is it important.
Understanding your target market, honing business strategies, and making informed decisions are all essential components that depend heavily on effective market research. It offers objective insights to help avoid expensive errors and foresees the needs of customers .
What is the difference between primary and secondary market research?
Primary market research is characterized by the direct gathering of data, in contrast to secondary market research which leverages existing information from alternative sources for addressing research inquiries.
Such a distinction can guide you in selecting an approach that aligns with your precise needs for conducting specific research.
What are some examples of successful market research?
Examples of successful market research are evident in the operations of well-known companies such as Starbucks, Apple, and McDonald’s. They have harnessed this tool to fine-tune their business strategies and make decisions based on solid information.
By employing market research, these businesses have managed to gain insight into their customers’ desires and needs, which has contributed significantly to their success.
How can I choose the right market research partner?
Selecting an ideal market research ally involves identifying a firm that resonates with your project requirements, financial plan, and corporate goals while also verifying their track record of dependability and consistency via reviews from previous clients.
Best wishes on your endeavor!
How is the impact of market research measured?
The effectiveness of market research hinges on the precision, representativeness, and pertinence of its data, along with how successful business decisions are when they’re based on the findings from this research. These elements define the impact of the research conducted.
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Get The Insights!
The fastest way to learn about Product Growth,Management & Trends.
The coolest way to learn about Product Growth, Management & Trends. Delivered fresh to your inbox, weekly.
The fastest way to learn about Product Growth, Management & Trends.
You might also be interested in ...
Funnel marketing: definition and strategies that work for saas, how to do market research: a step-by-step guide.
- Faculty & Staff
- Graduate Programs
- Parents & Families
- Prospective Students
- Undergraduate Students
- Disabled Students
- International
- Transfer Students
- Architecture, Construction & Operations
- Arts, Entertainment, Fashion, & Multi-Media Production
- Business Management & Administration
- Criminal Justice & Sociology
- Entrepreneurship
- Finance & Accounting
- Health Professions
- Hospitality & Tourism
- Human Services, Education & Nonprofits
- Information Technology & Cybersecurity
- Journalism, Public Relations, Marketing & Communications
- Life Sciences & Engineering
- Create a Resume / Cover Letter
- Expand Your Network / Mentor
- Explore Your Interests / Self Assessment
- Find Funding Opportunities
- Negotiate an Offer
- Prepare for an Interview
- Prepare for Graduate School
- Professional Photo Booth
- Start Your Job/Internship Search
- Explore Career Paths & Current Job Market Data
- Search for Jobs in Our Database
- Meet the Team
- Overview of Services
- Student Outcomes
What is Qualitative Research? Methods and Examples
- Share This: Share What is Qualitative Research? Methods and Examples on Facebook Share What is Qualitative Research? Methods and Examples on LinkedIn Share What is Qualitative Research? Methods and Examples on X
What is Qualitative Research? Methods and Examples was originally published on Forage .

Qualitative research seeks to gain insights and understand people’s experiences and perspectives by studying social organizations and human behavior. Data in qualitative studies focuses on people’s beliefs and emotional responses. Qualitative data is especially helpful when a company wants to know how customers feel about a product or service, such as in user experience (UX) design or marketing .
In this guide, we’ll go over:
Qualitative Research Definition
Qualitative research methods and examples, advantages and disadvantages of qualitative approaches, qualitative vs. quantitative research, showing qualitative research skills on resumes.
Researchers use qualitative approaches to “determine answers to research questions on human behavior and the cultural values that drive our thinking and behavior,” says Margaret J. King, director at The Center for Cultural Studies & Analysis in Philadelphia.
Data in qualitative research typically can’t be assessed mathematically — the data is not sets of numbers or quantifiable information. Rather, it’s collections of images, words, notes on behaviors, descriptions of emotions, and historical context. Data is collected through observations, interviews, surveys, focus groups, and secondary research.
However, a qualitative study needs a “clear research question at its base,” notes King, and the research needs to be “observed, categorized, compared, and evaluated (along a scale or by a typology chart) by reference to a baseline in order to determine an outcome with value as new and reliable information.”
Who Uses Qualitative Research?
Researchers in social sciences and humanities often use qualitative research methods, especially in specific areas of study like anthropology, history, education, and sociology.
Qualitative methods are also applicable in business, technology , and marketing spaces. For example, product managers use qualitative research to understand how target audiences respond to their products. They may use focus groups to gain insights from potential customers on product prototypes and improvements or surveys from existing customers to understand what changes users want to see.

Accenture and New York Jobs CEO Council Product Design
Learn how qualitative methods inform product development with Accenture’s free job simulation.
Avg. Time: 4 hours
Skills you’ll build: Research, user research, user design, product design, critical thinking, product design
Grounded Theory
Grounded theory is an inductive approach to theory development. In many forms of research, you begin with a hypothesis and then test it to see if you’re correct. In grounded theory, though, you go in without any assumptions and rely on the data you collect to form theories. You start with an open question about a phenomenon you are studying and collect and analyze data until you can form a fully-fledged theory from the information.
Example: A company wants to improve its brand and marketing strategies. The company performs a grounded theory approach to solving this problem by conducting interviews and surveys with past, current, and prospective customers. The information gathered from these methods helps the company understand what type of branding and marketing their customer-base likes and dislikes, allowing the team to inductively craft a new brand and marketing strategy from the data.
Action Research
Action research is one part study and one part problem-solving. Through action research, analysts investigate a problem or weakness and develop practical solutions. The process of action research is cyclical —- researchers assess solutions for efficiency and effectiveness and create further solutions to correct any issues found.
Example: A manager notices her employees struggle to cooperate on group projects. She carefully reviews how team members interact with each other and asks them all to respond to a survey about communication. Through the survey and study, she finds that guidelines for group projects are unclear. After changing the guidelines, she reviews her team again to see if there are any changes to their behavior.
>>MORE: Explore how action research helps consultants serve clients with Accenture’s Client Research and Problem Identification job simulation .
Phenomenological Research
Phenomenological research investigates a phenomenon in depth, looking at people’s experiences and understanding of the situation. This sort of study is primarily descriptive and seeks to broaden understanding around a specific incident and the people involved. Researchers in phenomenological studies must be careful to set aside any biases or assumptions because the information used should be entirely from the subjects themselves.
Example : A researcher wants to better understand the lived experience of college students with jobs. The purpose of this research is to gain insights into the pressures of college students who balance studying and working at the same time. The researcher conducts a series of interviews with several college students, learning about their past and current situations. Through the first few interviews, the researcher builds a relationship with the students. Later discussions are more targeted, with questions prompting the students to discuss their emotions surrounding both work and school and the difficulties and benefits arising from their situation. The researcher then analyzes these interviews, and identifies shared themes to contextualize the experiences of the students.
Ethnography
Ethnography is an immersive study of a particular culture or community. Through ethnographic research, analysts aim to learn about a group’s conventions, social dynamics, and cultural norms. Some researchers use active observation methods, finding ways to integrate themselves into the culture as much as possible. Others use passive observation, watching closely from the outside but not fully immersing themselves.
Example: A company hires an external researcher to learn what their company’s culture is actually like. The researcher studies the social dynamics of the employees and may even look at how these employees interact with clients and with each other outside of the office. The goal is to deliver a comprehensive report of the company’s culture and the social dynamics of its employees.
Case Studies
A case study is a type of in-depth analysis of a situation. Case studies can focus on an organization, belief system, event, person, or action. The goal of a case study is to understand the phenomenon and put it in a real-world context. Case studies are also commonly used in marketing and sales to highlight the benefits of a company’s products or services.
Example: A business performs a case study of its competitors’ strategies. This case study aims to show why the company should adopt a specific business strategy. The study looks at each competitor’s business structure, marketing campaigns, product offerings, and historical growth trends. Then, using this data on other businesses, the researcher can theorize how that strategy would benefit their company.
>>MORE: Learn how companies use case study interviews to assess candidates’ research and problem-solving skills.
Qualitative research methods are great for generating new ideas. The exploratory nature of qualitative research means uncovering unexpected information, which often leads to new theories and further research topics. Additionally, qualitative findings feel meaningful. These studies focus on people, emotions, and societies and may feel closer to their communities than quantitative research that relies on more mathematical and logical data.
However, qualitative research can be unreliable at times. It’s difficult to replicate qualitative studies since people’s opinions and emotions can change quickly. For example, a focus group has a lot of variables that can affect the outcome, and that same group, asked the same questions a year later, may have entirely different responses. The data collection can also be difficult and time-consuming with qualitative research. Ultimately, interviewing people, reviewing surveys, and understanding and explaining human emotions can be incredibly complex.
Showcase new skills
Build the confidence and practical skills that employers are looking for with Forage virtual work experiences.
Sign up for free
While qualitative research deals with data that isn’t easily manipulated by mathematics, quantitative research almost exclusively involves numbers and numerical data. Quantitative studies aim to find concrete details, like units of time, percentages, or statistics.
Besides the types of data used, a core difference between quantitative and qualitative research is the idea of control and replication.
“Qualitative is less subject to control (as in lab studies) and, therefore, less statistically measurable than quantitative approaches,” says King.
One person’s interview about a specific topic can have completely different responses than every other person’s interview since there are so many variables in qualitative research. On the other hand, quantitative studies can often be replicated. For instance, when testing the effects of a new medication, quantifiable data, like blood test results, can be repeated. Qualitative data, though, like how people feel about the medication, may differ from person to person and from moment to moment.

JPMorgan Commercial Banking
Discover how bankers use qualitative and quantitative methods to analyze businesses and industry trends with this free job simulation.
Avg. Time: 5 hours
Skills you’ll build: Qualitative research, quantitative research, spreadsheets, accounting, credit analysis, industry analysis
You can show your experience with qualitative research on your resume in your skills or work experience sections and your cover letter .
In your skills section, you can list types of qualitative research you are skilled at, like conducting interviews, performing grounded theory research, or crafting case studies.
You can highlight specific examples in the description of your past work or internship experiences. For example, you can talk about a time you used action research to solve a complex issue at your last job.
Your cover letter is an excellent place to discuss in-depth qualitative research projects you’ve completed. For instance, say you spent a summer conducting ethnographic research or a whole semester running focus groups to get feedback on a product. You can talk about these experiences in your cover letter and note how these skills make you a great fit for the job.
Grow your skills and explore your career options with Forage’s free job simulations .
Image credit: Canva
The post What is Qualitative Research? Methods and Examples appeared first on Forage .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Qualitative market research is an open ended questions (conversational) based research method that heavily relies on the following market research methods: focus groups, in-depth interviews, and other innovative research methods. It is based on a small but highly validated sample size, usually consisting of 6 to 10 respondents.
Example 1: This Voice of Customer questionnaire is an example of qualitative research we use here at Similarweb. Example 2: A market research survey used in retail. It's sent out with a digital copy of a store receipt and aims to explore how people feel about their in-store experience.
Qualitative market research is defined as a systematic and open-ended market research method used to gain understanding of consumer behaviour, perceptions, preferences, and motivations. Learn more about qualitative market research methods, examples, types and best practices.
One example of qualitative market research using a focus group is a cereal company wishing to update the packaging of one of its most popular products. After producing several design concepts, the company opts to commission a series of focus groups to gauge responses to each concept.
Qualitative research allows businesses to determine customers' needs, generate ideas on improving the product or expanding the product line, clarify the marketing mix and understand how the product would fit into customers' lifestyles. The research will be useful for businesses of any size and type. For example, entrepreneurs can use ...
Examples of qualitative market research You can study these examples to gain a deeper understanding of the kinds of insight that qualitative market research can provide: Example one A cosmetics retailer wishes to evaluate the in-store marketing strategies of its principal competitor relative to its own. It hires market researchers to enter the ...
Here's a quick rundown of the types of market research out there: Quantitative research: Deals with numbers and measurable forms. Qualitative research: Focuses on understanding the quality of consumer interactions and thoughts. Mixed methods: Combines both quantitative and qualitative research. It's good to know qualitative and quantitative ...
The Complete Guide to Qualitative Market Research. Qualitative research is one of the most prominent research methods in the ever-increasing research sphere. Running counter to quantitative research, qualitative research encompasses a distinct set of differentiating qualities (no pun intended). These attributes prove that these two methods ...
Qualitative consumer and marketing research involves a range of methods and approaches to explore and provide richly detailed data such as meanings, experiences, characteristics,metaphors,symbols,descriptions,feelings,interactions,impressions, motivations, and perspectives of consumer behaviors and marketing phenomena (Belk et al. 2013).
Qualitative marketing research involves a natural or observational examination of the philosophies that govern consumer behavior. The direction and framework of the research is often revised as new information is gained, allowing the researcher to evaluate issues and subjects in an in-depth manner. ... Customer behaviour is a good example for ...
Qualitative research involves collecting and analyzing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio) to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. It can be used to gather in-depth insights into a problem or generate new ideas for research. Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research, which involves collecting and ...
Qualitative research is designed to generate in-depth and subjective findings to build theory. Combined with the quantitative bias of top-tier journals, many qualitative researchers do not utilise the full-benefits of their adopted methodologies. This makes it challenging for qualitative researchers to publish their work at this level.
Qualitative research questions help you understand consumer sentiment. They're strategically designed to show organizations how and why people feel the way they do about a brand, product, or service.It looks beyond the numbers and is one of the most telling types of market research a company can do.. The UK Data Service describes this perfectly, saying, "The value of qualitative research ...
The major difference between qualitative and quantitative consumer and marketing research lies in their essential data characteristics. While qualitative research provides detailed observation and interpretation of phenomena with illustrations of words and/or images, quantitative research gathers and measures data from variables, scales, or dimensions to derive quantified numbers that can be ...
Quantitative research is the research method of collecting quantitative research data - data that can be converted into numbers or numerical data, which can be easily quantified, compared, and analyzed. Quantitative research methods deal with primary and secondary sources where data is represented in numerical form.
6. AI and qualitative market research. In the continually evolving realm of qualitative market research, innovation is the name of the game. One of the most exciting, forward-thinking developments in the field of market research is the application of AI. AI is revolutionizing the way researchers process and analyze qualitative data.
Qualitative market research help businesses understand customers' needs, identify market potential, uncover ideas for product launch/improvement, or understand how the product fits the target customer's lifestyle. ... For example, you can conduct a phone interview, a face-to-face interview, or a mobile-offline interview. Depending on the ...
Here are some examples of how qualitative research is used: Market Research: Qualitative research is often used in market research to understand consumer attitudes, behaviors, and preferences. Researchers conduct focus groups and one-on-one interviews with consumers to gather insights into their experiences and perceptions of products and services.
The historical approach to research is reasonably self-explanatory. Researchers analyze data from the past to form expectations about the present and future. In qualitative market research, this might mean analyzing consumer feedback from throughout the history of your company or industry. 6. Narrative Research.
It is here that qualitative research finds its greatest role, in its potential to understand and explain complex phenomena and situation, in acquiring everyday knowledge and in building theories (Cooper, 2008; Gummesson, 2005; Hirschman, 1986). While the role of qualitative research in the marketing discipline has evolved in both
Qualitative research is a behavioral research method that seeks to understand the undertones, motivations, and subjective interpretations inherent in human behavior. It involves gathering nonnumerical data, such as text, audio, and video, allowing you to explore nuances and patterns that quantitative data can't capture.
Effective market research combines both qualitative methods, which explore consumer motivations, and quantitative methods, which provide measurable statistics, to create comprehensive insights that guide business strategy and decision-making. ... Examples of successful market research are evident in the operations of well-known companies such ...
Qualitative methods are also applicable in business, technology, and marketing spaces. For example, product managers use qualitative research to understand how target audiences respond to their products. They may use focus groups to gain insights from potential customers on product prototypes and improvements or surveys from existing customers ...
Examples include: Launching a new business. Introducing a new product or service. Building a positioning strategy as part of a marketing plan. Determining a roadmap for future enhancements to an ...
provides a literature review and analysis on the role and relation of qualitative. methods with quantitative methods in marketing research. The paper analyzes. research articles that include ...