
- Project Management
Home » Free Resources » »

What Is Problem Solving in Project Management? Here’s Everything You Need to Know
- Written by Contributing Writer
- Updated on August 4, 2023

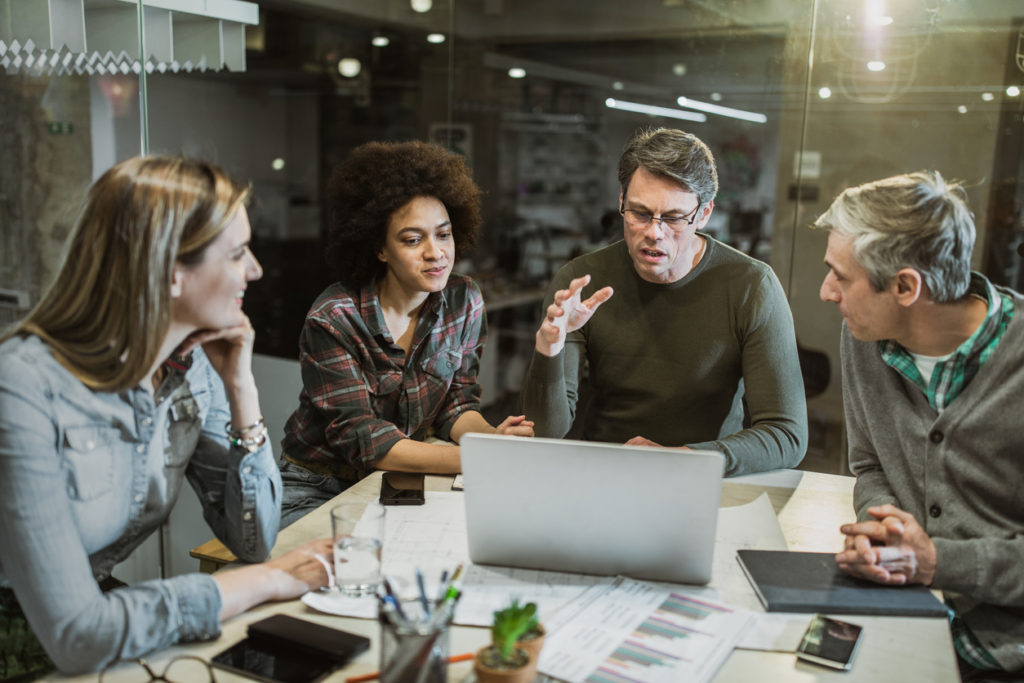
In project management , problem-solving is a crucial and necessary skill. Whether you have failed to consider every possible factor impacting a project, a problem arises through no fault of your own, or conditions change that create issues, problems must be addressed promptly to keep projects on track.
In this article, we will define problem-solving and how it impacts projects, provide real-world examples of problem-solving, and give you a structured, step-by-step process to solve problems. We’ll also show you how earning a project management certification can help you gain practical experience in problem-solving methods.
What Is Problem-Solving?
Problem-solving is a process to identify roadblocks or defects that arise during a project. A structured system to define problems, identify root causes, brainstorm and test solutions, and monitor results can affect change to improve performance and overcome challenges.
Effective problem-solving enables teams to deal with uncertainties or gaps in planning to minimize the impact on outcomes.
The Importance of Problem-Solving in Project Management
During a project and operation, problems can arise at any time. You may find that your planning before launching a product, for example, did not consider all the factors that impact results. You may find that you were too optimistic about project timelines, performance, or workforce. Or, as many of us discovered over the past few years, supply chain disruption may make even the best project plans obsolete.
Regardless, your job is identifying, solving, and overcoming these problems. Project managers must be skilled in leading team members through a structured approach to resolving problems.
Proactive problem-solving requires careful consideration of all the variables in a project, including preparation to:
- Achieve project objectives
- Address obstacles before they arise
- Manage project risks and contingency plans
- Manage communication and collaboration
- Provide a framework for time and cost management
- Provide a pathway for continuous improvement
Also Read: 10 Tips on How to Increase Productivity in the Workplace
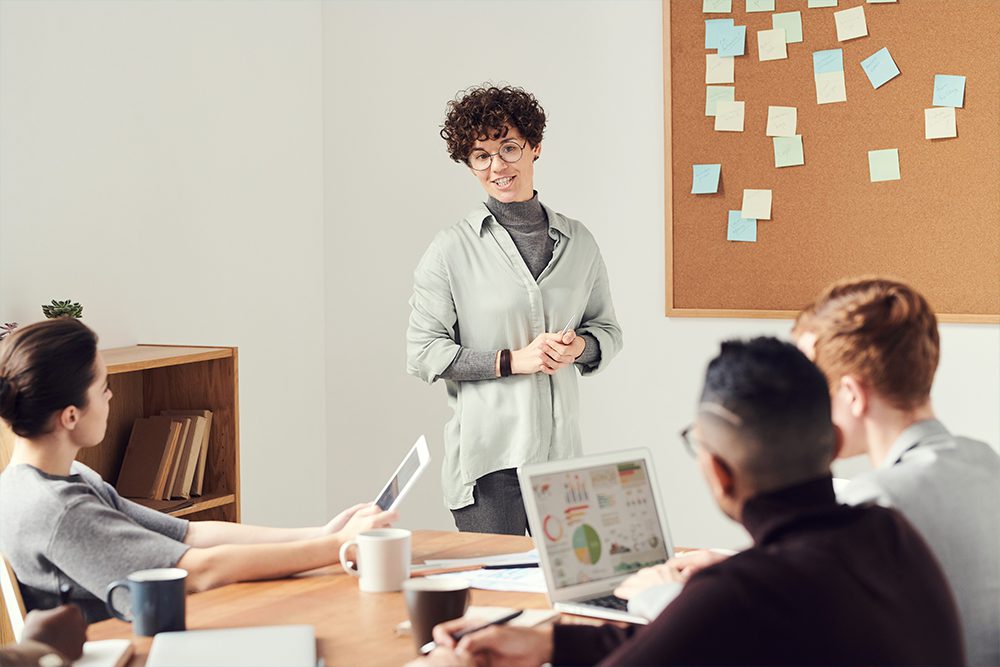
Problem-Solving Steps in Project Management
While the process you choose to solve problems may vary, here is a seven-step framework many project managers use. This problem-solving method combines primary and secondary problem-solving steps.
#1. Define the Problem
- Gather data and information from key stakeholders, team members, and project documentation. Include any relevant reporting or data analysis
- Itemized key details, such as a description of the problem, timelines, outcomes, and impact
- Frame the issue as a problem statement
A good example of a problem statement might be: An unexpected demand spike has exceeded our current production capacity. How can we still meet customer deadlines for delivery?
#2. Analyze Root Causes
- Break down issues into smaller components to diagnose bottlenecks or problems
- Identify the organizational, mechanical, environmental, or operational factors that contribute
- Distinguish between one-time issues vs. systematic, ongoing areas that need improvement
When analyzing root causes, it’s common to find multiple factors contributing to a problem. As such, it is essential to prioritize issues that have the most significant impact on outcomes.
#3. Brainstorm Potential Solutions
- Holding specific sessions focused on brainstorming ideas to resolve root causes
- Build on ideas or suggest combinations or iterations
- Categorize solutions by types, such as process or input changes, adding additional resources, outsourcing, etc.)
In brainstorming, you should refrain from immediately analyzing suggestions to keep ideas coming.
#4. Evaluate Potential Solutions
- Reframe the problem and concern for team members, providing a framework for evaluation such as cost, timing, and feasibility
- With ideas in hand, it is time to evaluate potential solutions. Project managers often employ strategies such as weighted scoring models to rank ideas.
- Consider the pros and cons in relation to project objectives
As you narrow the list, getting additional insight from subject matter experts to evaluate real-world viability is helpful. For example, if you are proposing a process change in operating a machine, get feedback from skilled operators before implementing changes.
#5. Decide on a Plan of Action
- Make a decision on which course of action you want to pursue and make sure the solution aligns with your organizational goals
- Create an action plan to implement the changes, including key milestones
- Assign project ownership, deadlines, resources, and budgets
Defining what outcomes you need to achieve to declare success is also essential. Are you looking for incremental change or significant improvements, and what timeline are you establishing for measurement?
#6. Implement the Action Plan
- Communicate the plan with key stakeholders
- Provide any training associated with the changes
- Allocate resources necessary for implementation
As part of the action plan, you will also want to detail the measures and monitoring you will put in place to assess process outcomes.
#7. Monitor and Track Results
- Track solution performance against the action plan and key milestones
- Solicit feedback from the project team on problem-solving effectiveness
- Ensure the solution resolves the root cause, creating the desired results without negatively impacting other areas of the operation
You should refine results or start the process over again to increase performance. For example, you may address the root cause but find a need for secondary problem-solving in project management, focusing on other factors.
These problem-solving steps are used repeatedly in lean management and Six Sigma strategies for continuous improvement.
Also Read: 5 Project Management Steps You Need to Know
How Project Management Tools Can Help You in Problem-Solving
Project management software can guide teams through problem-solving, acting as a central repository to provide visibility into the stages of a project.
The best project management software will include the following:
- Issue tracking to capture problems as they arise
- Chat and real-time collaboration for discussion and brainstorming
- Templates for analysis, such as fishbone diagrams
- Action plans, assigning tasks, ownership, and accountability
- Dashboards for updates to monitor solutions
- Reporting on open issues, mitigation, and resolution
Examples of Problem-Solving
Here are some examples of the problem-solving process demonstrating how team members can work through the process to achieve results.
Sign-ups for a New Software Solution Were Well Below First-Month Targets
After analyzing the data, a project team identifies the root cause as inefficient onboarding and account configurations. They then brainstorm solutions. Ideas include re-architecting the software, simplifying onboarding steps, improving the initial training and onboarding process, or applying additional resources to guide customers through the configuration process.
After weighing alternatives, the company invests in streamlining onboarding and developing software to automate configuration.
A Project Was at Risk of Missing a Hard Deadline Due to Supplier Delays
In this case, you already know the root cause: Your supplier cannot deliver the necessary components to complete the project on time. Brainstorming solutions include finding alternative sources for components, considering project redesigns to use different (available) components, negotiating price reductions with customers due to late delivery, or adjusting the scope to complete projects without this component.
After evaluating potential solutions, the project manager might negotiate rush delivery with the original vendor. While this might be more expensive, it enables the business to meet customer deadlines. At the same time, project schedules might be adjusted to account for later-than-expected part delivery.
A Construction Project Is Falling Behind Due to Inclement Weather
Despite months of planning, a major construction project has fallen behind schedule due to bad weather, preventing concrete and masonry work. The problem-solving team brainstorms the problem and evaluates solutions, such as constructing temporary protection from the elements, heating concrete to accelerate curing, and bringing on additional crews once the weather clears.
The project team might decide to focus on tasks not impacted by weather earlier in the process than expected to postpone exterior work until the weather clears.
Also Read: Understanding KPIs in Project Management
Improve Your Problem-Solving and Project Management Skills
This project management course delivered by Simpliearn, in collaboration wiht the University of Massachusetts, can boost your career journey as a project manager. This 24-week online bootcamp aligns with Project Management Institute (PMI) practices, the Project Management Professional (PMP®) certification, and IASSC-Lean Six Sigma.
This program teaches skills such as:
- Agile management
- Customer experience design
- Design thinking
- Digital transformation
- Lean Six Sigma Green Belt
You might also like to read:
5 Essential Project Management Steps You Need to Know
Project Management Frameworks and Methodologies Explained
13 Key Project Management Principles and How to Use Them
Project Management Phases: A Full Breakdown
How To Develop a Great Project Management Plan in 2023
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Recommended Articles

What is Project Resource Management? Everything You Need to Know
If you’re asking, “What is project resource management,” and want to learn the tools, techniques, and best practices involved, our comprehensive guide covers everything you need.

Best Apps for Project Management You Should Know in 2024
Every project needs a manager, especially in today’s fast-paced digital world. And every project manager needs tools to manage projects. Learn about some of the best project management apps you can choose from today in this blog.

20 Best Practices in Project Management [2024 Guide]
Explore our guide to the top best practices in project management. Strengthen your foundation and take your career to new heights.

How to Measure Project Success? A 2024 Guide
One person’s definition of success can vary wildly from another’s. That’s why project managers need definitive ways to measure project success. This article will share tips, best practices, and methods to determine whether you are hitting the mark.

Remote Project Management: How to Manage Remote Teams Effectively
Remote working became a harsh reality during the COVID-19 pandemic. Yet, many employers and their employees adapted to it quickly and still prefer it, making remote project management an essential skill for professionals.

What are Project Management Skills? Here are Top Skills You should Know in 2024
Here are the top project management skills you will need to master project management in 2024. This article will help you get started with both hard and soft skills.
Project Management Bootcamp
Learning Format
Online Bootcamp
Program benefits.
- 25 in-demand tools covered
- Aligned with PMI-PMP® and IASSC-Lean Six Sigma
- Masterclasses from top faculty of UMass Amherst
- UMass Amherst Alumni Association membership
- Become a Project Manager
- Certification
Problem Solving Techniques for Project Managers
Learn which problem solving techniques and strategies can help you effectively handle the challenges you face in your projects.
Problem Solving Techniques: A 5-Step Approach
Some problems are small and can be resolved quickly. Other problems are large and may require significant time and effort to solve. These larger problems are often tackled by turning them into formal projects.
"A project is a problem scheduled for solution."
- Joseph M. Juran

Problem Solving is one of the Tools & Techniques used for Managing Quality and Controlling Resources.
Modules 8 and 9 of the PM PrepCast cover Project Quality Management and Project Resource Management.
Consider this study program if you're preparing to take your CAPM or PMP Certification exam.
Disclosure: I may receive a commission if you purchase the PM PrepCast with this link.
Whether the problem you are focusing on is small or large, using a systematic approach for solving it will help you be a more effective project manager.
This approach defines five problem solving steps you can use for most problems...
Define the Problem
Determine the causes, generate ideas, select the best solution, take action.
The most important of the problem solving steps is to define the problem correctly. The way you define the problem will determine how you attempt to solve it.
For example, if you receive a complaint about one of your project team members from a client, the solutions you come up with will be different based on the way you define the problem.
If you define the problem as poor performance by the team member you will develop different solutions than if you define the problem as poor expectation setting with the client.
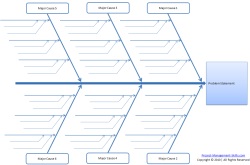
Once you have defined the problem, you are ready to dig deeper and start to determine what is causing it. You can use a fishbone diagram to help you perform a cause and effect analysis.
If you consider the problem as a gap between where you are now and where you want to be, the causes of the problem are the obstacles that are preventing you from closing that gap immediately.
This level of analysis is important to make sure your solutions address the actual causes of the problem instead of the symptoms of the problem. If your solution fixes a symptom instead of an actual cause, the problem is likely to reoccur since it was never truly solved.
Once the hard work of defining the problem and determining its causes has been completed, it's time to get creative and develop possible solutions to the problem.
Two great problem solving methods you can use for coming up with solutions are brainstorming and mind mapping .
After you come up with several ideas that can solve the problem, one problem solving technique you can use to decide which one is the best solution to your problem is a simple trade-off analysis .
To perform the trade-off analysis, define the critical criteria for the problem that you can use to evaluate how each solution compares to each other. The evaluation can be done using a simple matrix. The highest ranking solution will be your best solution for this problem.

Pass your PMP Exam!
The PM Exam Simulator is an online exam simulator.
Realistic exam sample questions so you can pass your CAPM or PMP Certification exam.
Disclosure: I may receive a commission if you purchase the PM Exam Simulator with this link.
Once you've determined which solution you will implement, it's time to take action. If the solution involves several actions or requires action from others, it is a good idea to create an action plan and treat it as a mini-project.
Using this simple five-step approach can increase the effectiveness of your problem solving skills .
For more problem solving strategies and techniques, subscribe to my newsletter below.
Related Articles About Problem Solving Techniques
Fishbone Diagram: Cause and Effect Analysis Using Ishikawa Diagrams
A fishbone diagram can help you perform a cause and effect analysis for a problem. Step-by-step instructions on how to create this type of diagram. Also known as Ishikara or Cause and Effect diagrams.
Do You Want More Project Management Tips?

Subscribe to Project Success Tips , my FREE Project Management Newsletter where I share tips and techniques that you can use to get your Project Management Career off to a great start .
As a BONUS for signing up, you'll receive access to my Subscribers Only Download Page ! This is where you can download my " Become A Project Manager Checklist " and other project management templates.
Don't wait...
- Become a PM
- Problem Solving Techniques
New! Comments
Home Privacy Policy About Contact
Copyright © 2010-2021 | ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
Project-Management-Skills.com
19 Sep 2020
A Project Manager's Short Guide to Effective Problem-Solving in 6 Steps
Role of the Project Manager | By Duncan Haughey | Read time minutes

For project managers and business analysts like you, effective problem-solving remains an ever-important soft skill that requires you to combine creative thinking and strong analytical skills. The simple six-step process outlined below will help you master effective problem-solving — a skill that will provide you with the ability to bring a new perspective to problems, helping you to design, and implement, effective solutions.
Step #1: Identify the Problem
First, make sure you're dealing with the real problem, not just its symptoms. In information technology, we use root cause analysis to trace back to the origin of a problem. Take the time needed to do this tracing and discover the real reason for a problem by looking at it from different angles. Here are a few tools that can help:
- Cause and effect diagrams: These diagrams help you gain a solid understanding of what's actually causing the problem.
- Drill-down technique: This technique helps you split problems into decreasingly smaller parts to gain an increasingly more in-depth understanding of the cause.
- 5 whys: This approach helps you drill down to a problem's root cause by asking why five times.
Ultimately, all problems fall into three basic cause types:
- Physical cause: Equipment has had a material failure and stopped working.
- Human cause: Someone made a mistake or forgot to do something.
- Organisational cause: A system or process was flawed and/or failed.
Step #2: List All Possible Solutions
Once you understand the problem, it's time to think about possible solutions. If your problem is simple, the solution will often be clear straightaway. But more complex problems may require a formal approach to finding solutions. Here are some potential techniques you could employ:
- Hold a brainstorming session with your team to identify and explore answers to the problem.
- Use mind mapping to focus your mind, gain clarity and quickly identify solutions.
- Ask a coach to employ the GROW model to help you identify the obstacles preventing you from achieving your goal.
Step #3: Evaluate the Solutions
Once you have your list of solutions, evaluate each one by asking a few questions:
- What are the pros and cons?
- Which measures will resolve the problem and prevent it from re-occurring?
Step #4: Pick the Best Solution
Weigh the solutions against a good outcome versus risk. Here are a few questions you should be asking to help guide this process:
- What options can you discard straightaway?
- Which option will have the best outcome at an acceptable risk level?
- What is your best option?
Step #5: Document the Selected Solution
Once you've identified the best solution, write it down. This action helps you think through the solution thoroughly and identify any implications of implementing the solution. This step is especially useful when solutions are complex, when they require organising, to ensure a specific process order is followed or when you don't want to rely solely on your memory.
Step #6: Create a Contingency Plan
Circumstances may (and often do!) change, so create a plan of what you will do for any foreseeable futures. Don't be caught unprepared when and if things change.
What Would You Do?
Here are three scenarios you may encounter as a project manager. Faced with these situations, what would you do? Click the down arrow to see answer.
Scenario 1: The Urgent Project You have been asked by your director to plan an urgent project. However, you cannot start the project because a colleague with vital information and expertise is away on an extended holiday, and both are essential for project success. How would you approach this situation?
Scenario 2: the unhappy customer your customer is unhappy with the service you're providing on their project. you have not done anything wrong. the customer has been the cause of several delays through last minute and unexpected changes. how would you approach this situation, scenario 3: the serious mistake halfway through a project, you realise you have made a serious mistake. the situation may require significant extra time to resolve and could cause you to miss an important go-live deadline. how would you deal with this situation to ensure you still met the deadline.
As is usually the case, there's no single right answer to each problem, and the answers provided in the example scenarios are just one possibility. Other solutions exist and may, in some cases, even provide a better outcome.
How would you tackle the problems outlined in these scenarios?
Recommended read: How to Perform a Project Handover by Duncan Haughey.
Advertisment
What's Next?
You may also be interested in, my story: working smarter; not harder.
- When you realise that you have the power to change your beliefs and remove a limiting factor that has been constraining you, you have an AHA! moment.
Project Planning in a Nutshell
- This article provides an overview of why it is important to prepare a project plan. It also shows what elements a good project plan will include.
Building Your Project Team
- How should you set about choosing people for your project and forming them into a well functioning project team?
How Agile Practices Reduce Requirements Risks
- Every software project carries some risk, but many of these risks can be mitigated. That's true of problems related to product requirements.

Twproject: project management software,resource management, time tracking, planning, Gantt, kanban
Twproject is a full featured web based project management software that gives you full visibility and control over your projects.Twproject is also a time tracking software, a bug tracking software, a project planning software.
Problem solving: a Project Manager skill
Problem solving is a project manager skill that facilitates effective problem solving by combining creative thinking and strong analytical skills.
Problem-solving techniques: a 5-step approach
Problem solving step 1: problem definition, problem solving step 2: cause determination, problem solving step 3: ideas generation, problem solving step 4: best solution selection, problem solving step 5: act, problem solving: creativity, problem solving: communication, problem solving: willpower.
This is a skill that provides the capability to bring a different perspective to problems, helping to design and implement effective solutions.
It’s easy to realize how in problem solving the identification of simple solutions to big problems can provide benefits to the project and the company, but there are not always successful Project Managers capable of finding them.
In this article we will try to give a hand to the less creative and more accustomed to patterns minds by suggesting some techniques that if properly implemented can be extremely beneficial.
Let’s start from the premise that some problems are small and can be solved quickly, while others may involve considerable time and effort.
Regardless of whether the problem you’re focusing on is small or large, using a systemic approach to solving it will certainly help you be a more effective project manager .
Here are what are the five problem solving step s that you can use for most problems.
The most important step in problem solving is to properly define the problem.
How you define the problem will determine how you will attempt to solve it.
For example, if you get a complaint regarding one of your project team members from a client, the solutions you will assess will be different based on how you define the problem.
If you choose a poor performance approach for the team member, different solutions will unfold as opposed to an approach where you give little consideration to what the client said.
After you have defined the issue, you can proceed to dig deeper and begin to determine what is causing it.
This level of analysis is important to ensure that solutions address the actual causes of the problem rather than the symptoms of the problem.
If the solution solves a symptom instead of an actual cause, in fact, the problem is likely to reoccur because it was never truly solved.
After the hard work of defining the problem and determining its causes is complete, then it is time to get creative and develop possible solutions to the problem.
Two great problem solving methods that you can use to come up with solutions are brainstorming and mind mapping.
After figuring up with several ideas that could solve the problem, one way to decide which is the best solution is a simple trade-off analysis .
We can find this analysis when performing a project feasibility study as well.
To carry out the trade-off analysis, you must first define the critical criteria for the problem that you can use to evaluate the comparison between each solution.

After having established the solution to be implemented, it’s time to take action.
If the solution requires several actions or necessitates an effort by others, it’s a good idea to make a plan and treat it as a mini-project.
Yet, problem solving as a project manager’s skill is not just limited to this tangible process for solving problems.
Let’s see what other skills are key to problem solving.
This is not just something related to artists.
Creativity is about being able to simply come up with a unique solution and thinking “outside of the box”.
This means not responding to problems with a knee-jerk reaction or a safe solution that might lead to poor results.
What creativity requires is being able to actually take a look at a problem from multiple perspectives, not just the typical one.
Stepping out of your comfort zone, thinking outside the box , going beyond. This is what creativity in problem solving is all about.
Solutions to serious problems may in fact not be found within standard processes.
Like with almost everything, nothing can be achieved without the communication skills to provide the solution to those who must solve it.
Even simple ideas are often muddied by poor rhetoric, let alone failed attempts to convey complex ones and solve problems.
And we’re not just referring to being able to clearly impart orders; it’s also important to know the right channel to deliver your message.
That message needs to reach the right people, in the right way, and get to them as quickly as possible.
Finding a solution to a problem is just one link in a larger chain.
If that solution isn’t delivered to the parties that need it to fix the problem in order for the project to move forward, then it’s all in vain.
Not all people are born great communicators, but there are ways to learn how to better communicate, especially with team members .
It takes empathy and active listening to develop trust and loyalty and without this connection, no matter how explicitly you communicate a message, it will be misinterpreted or even ignored.
All of the above may be quite fascinating, but if the project manager is not committed to their work and to improving themselves in problem solving, everything is pointless.
There are exercises you can do to master problem solving skills that help you respond better to problems and solve them quickly.
For example, there are logical reasoning tests that help you clearly organize your thoughts, analyze them, and quickly choose the best course of action.
However, all this takes willpower; the project manager must be aware of what they are doing and must want to do it.
Only in this way will it be possible to develop the best problem solving skills .
When presented with a problem, some project managers may be inclined to procrastinate or avoid the problem altogether.
However, avoiding problems is a short-term solution. It is problem solving that keeps things moving forward.
Therefore, the faster and more effectively you can solve a problem, the faster you can get the job done and successfully complete a project.
Keep up with the times.
Related posts.

.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:42px;color:#F5F4F3;}@media (max-width: 1120px){.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:12px;}} AI that works. Coming June 5, Asana redefines work management—again. .css-1ixh9fn{display:inline-block;}@media (max-width: 480px){.css-1ixh9fn{display:block;margin-top:12px;}} .css-1uaoevr-heading-6{font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-1uaoevr-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} .css-ora5nu-heading-6{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-box-pack:start;-ms-flex-pack:start;-webkit-justify-content:flex-start;justify-content:flex-start;color:#0D0E10;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s;transition:all 0.3s;position:relative;font-size:16px;line-height:28px;padding:0;font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{border-bottom:0;color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover path{fill:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div{border-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div:before{border-left-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active{border-bottom:0;background-color:#EBE8E8;color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active path{fill:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div{border-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div:before{border-left-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} Get early access .css-1k6cidy{width:11px;height:11px;margin-left:8px;}.css-1k6cidy path{fill:currentColor;}
- Product overview
- All features
- App integrations
CAPABILITIES
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- asana-intelligence icon Asana Intelligence
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Campaign management
- Creative production
- Marketing strategic planning
- Request tracking
- Resource planning
- Project intake
- View all uses arrow-right icon
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- What's new Learn about the latest and greatest from Asana
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Support Need help? Contact the Asana support team
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
Featured Reads

- Project management |
- The 25 project management skills you ne ...
The 25 project management skills you need to succeed

Anyone who oversees projects is a project manager, but to become a more thoughtful manager (with a higher impact), you need to develop the right project management skills. Learn what skills are necessary to become a successful project manager and how to build them.
If you’re interested in honing and developing your project management skills, you’re in the right place. In this guide, we’ll cover 25 key skills you need to succeed as a project manager or project administrator , and how you can develop those skills over time.
What are project management skills (and why do they matter?)
Project management skills are the attributes you develop to become a more experienced project manager. Building a project management skill set includes learning technical and hard skills, such as portfolio management and project scoping, and soft skills (for example, adaptability).In honing these skills, you’re preparing yourself to more effectively perform in your role.
Project management is the practice of organizing and executing work efficiently—and helping your team do the same. For a while, project managers had to be trained and certified in complicated project management technology. Traditional project management tools were hard to set up and required constant maintenance, which is where the position “project manager” comes from.
Modern project management tools
Modern project management evolved from traditional project management in two distinct ways. As companies and teams democratized their project management processes, they needed more team members and team leads who were able to manage a process from conception to completion. In order to support those team leads, project management software has also evolved, from complex mechanisms to flexible and easy-to-use tools.
![problem solving pm [Product UI] Work requests project example (Boards)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/4afbad21-f79b-4beb-86d1-6c12952d414f/inline-boards-work-requests-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Today, any team member may be called upon to run a project and become the de-facto project manager—which is why modern project management tools are built to be flexible enough for anyone to use on any project, so you’re able to jump in and hit the ground running.
These tools, like Asana , make it easy to track, manage, and organize work—without the learning curve associated with traditional tools. With today's project management tools , you can easily implement project management best practices and bring a new level of clarity and visibility to your project team.
How to use your project management skills
Project management tools do the heavy lifting when it comes to reducing silos, increasing visibility, and facilitating cross-functional collaboration. As the project manager, you can use these tools to give your team the insight they need to get their best work done. While you don’t need to learn complicated skills or tools in order to become a successful project manager , there are hard, soft, and technical skills you can develop in order to improve your management and collaboration skills.
Some of these skills might not apply to you—while others might be things you’re already seasoned in. Like everything in the five phases of project management , approach this list with flexibility and work on the skills that are most relevant to you.
10 soft skills for project managers
Soft skills are what we call “non-technical skills,” or skills that can help you improve your quality of work—without a specific tool or technical requirement. These are also called “people skills” or “interpersonal skills” because they often help you work with and relate to others in your workspace. These 10 skills are the most important soft skills for project management:
1. Collaboration
Collaboration is the cornerstone of all project management skills. In project management, collaboration helps you get work done quickly and more efficiently. When you can coordinate across teams, you gain valuable insights into your project that you might not find within your team. If more minds are involved in the work, projects are inherently more creative and well developed.
To improve your collaboration skills, practice having conversations. Use techniques like active listening , where you stay engaged and focused when others are speaking to you. It sounds simple, but learning how to have open communication, reduce boundaries, and co-create are critical for a collaborative team.
2. Teamwork
Everyone on your team has something to bring to the table, and your team is more effective working together than they would be alone. Teamwork ensures that everyone feels welcome, valued, and they are supported to contribute.
If you’re working to boost your teamwork skills, dig deeper into team brainstorms , 1:1 conversations, and ask for feedback from your team—how can you be a better team member? Notice if there’s someone who hasn’t spoken up in a while, and be supportive when another team member has a new idea.
3. Communication
Miscommunications are common when you’re working with a group of people. Learning how to communicate well and avoid these will make projects run more smoothly and be more enjoyable.
To develop your communication skills, practice being open and honest with your coworkers. This requires a lot of trust between you and your team members. To build this trust, encourage your team members to bring any thoughts into a discussion—even if you disagree with them.
4. Time management
Time management and organization skills go hand in hand. As you become better at organizing your tasks, you’ll also have a clearer sense of everything that’s on your plate and how long your upcoming tasks are going to take.
Still, it can be hard to buckle down and prioritize your work. To improve your time management skills and reduce procrastination, try prioritizing tasks. When you’re clear on which tasks are higher priority, you can tackle them first, to make sure nothing gets left behind or falls through the cracks.
5. Leadership
Even if you don’t think of yourself as a leader or have a role in team management, when you’re managing a project, your project team is looking to you for leadership, guidance, and support.
To develop your leadership skills, practice approaching situations with empathy and understanding. Good leaders bring everyone together and make them feel supported to foster teamwork and collaboration.
6. Organization
For a lot of project managers, organization is the most intimidating soft skill. You might think organization is either something you “have” or “don’t have.” But, like every other project management skill in this article, you can develop your organizational skills and become a Marie Kondo in your own right.
The best way to become a better organizer is to create (and maintain) a central source of truth for your work and your team’s work. We’re often disorganized because work is disconnected—in fact, the average employee switches between 10 tools per day . Instead of splitting your time between 10 tools, try using a digital organization tool to act as that one central source of truth for your team.
7. Problem solving
Problem solving skills are collaborative, iterative skills that help you approach a problem and, ultimately, solve it. Developing problem solving skills isn’t about always having the “right” answer to every problem—rather, people with great problem solving skills practice approaching problems from new perspectives and methodically working towards a solution.
To become a better problem solver, use data-driven decision-making frameworks or routine analyses. For example, if you need to solve for how to boost sales by 10% over your competition, you can run a competitive analysis to determine where you currently stand in the market. Then, use that information to solve the problem of lower sales. In this case, you could develop a new marketing strategy coordinated with the sales team.
8. Critical thinking
Critical thinking, like problem solving, doesn’t have a “solution.” You can’t “win” at critical thinking, but you can practice approaching problems logically instead of making decisions based on your emotions. Good critical thinkers practice analyzing information in front of them and forming their own conclusions based on the facts—the way Sherlock Holmes solves a mystery.
To practice critical thinking, always take a step back and ask yourself: how did I come to this conclusion? Could there be another answer? Am I being swayed by something other than factual information? Emotional decisions aren’t necessarily bad—in fact, some of the best decisions are those we’re passionate about. But critical thinking is a helpful way to make sure you’re approaching a situation from the right perspective.
9. Adaptability
At some point, whether it’s this project or the next one, aspects of your project plan will change. Maybe your deadline or priorities shifts, and you need to adapt your workflow accordingly. Great project managers are able to pivot and adapt to new situations to continue steering their project team in the right direction.
Becoming more adaptable is all about understanding when and how to shift gears. To do this, you need to understand yourself. Developing other soft skills, such as self-awareness and mindfulness, can help you be more in touch with and manage your emotions, which are often in flux during times of change.
10. Conflict resolution
Inevitably, conflict will arise during the projects you manage. It could be that a stakeholder wants to change the project scope. Or maybe you missed your budget or deadline. Conflict resolution is about addressing both sides of the conflict so everyone feels heard and supported. If there are harmed parties, take the time to listen to them and try to find a solution that works for everyone. Even when that can’t happen, approaching the conversation with patience and empathy can help defuse a potentially frustrating situation and lead to a better result.
7 hard skills for project managers
Unlike soft skills, hard skills are quantifiable abilities. While the soft skills mentioned above are applicable for many work skills, these seven hard skills are relevant specifically to project management. Developing these will help you become a more well rounded and efficient project manager.
1. Project planning
At its core, a project plan (sometimes called a project charter) is a blueprint of the key elements your project needs to succeed. Typically a project plan will include seven things:
Goals and project objectives
Success metrics
Stakeholders and roles
Scope and budget
Milestones , deliverables , and project dependencies
Timeline and schedule
Communication plan
Some of these things, like your goals or your milestones, might already be defined in your project roadmap or brief. But your project plan is where all of these project elements come together to create a cohesive picture of your upcoming work.
A lot of planning goes into the beginning of the year for what our vision is and where we will be by the end of that particular year. Once that is done, we summarize it in a project so it's visible to everyone... Having that visual representation in Asana makes it easier to move things around.”
2. Project scoping
![problem solving pm [Product ui] Scope management project in Asana, spreadsheet-style project view (List)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/728f6575-937e-44bc-98b2-cf8cbc464d41/TG23-web-hero-51-scope-management-static-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Project scope is the size, goals, and limitations (i.e., deadlines and resources) for your project. Your project scope will define what you can achieve within a certain timeframe and budget. Setting and defining your project scope is important in order to prevent scope creep , which is when your project deliverables outgrow your original project scope.
In order to improve your project scoping skills, practice setting project scope early and often. Once you’ve set your project scope, share it with stakeholders and surface it frequently, so everyone is on the same page about the project’s aims and limitations. Use it as a point of reference, so you know when to say no to new asks.
We have been able to reduce the number of products that we’ve oversold and the number of times we have to contact the customer to push a ship date out.”
3. Writing a project brief
![problem solving pm [Product UI] Example project brief in Asana (Project Brief)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/977bb6a3-07f4-498b-a9e7-c3fc9b82c9a1/inline-project-management-skills-2-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Your project brief outlines your general project objectives and how you plan to get there. This can serve as a helpful North Star to guide planning sessions.
The most important thing to remember about your project brief is that it’s a living document. As you develop your project plan and get input from stakeholders, you can adapt and update your project brief. In general, your project brief should contain a link to your project roadmap if you created one, a list of your project stakeholders and their responsibilities (sometimes called a RACI chart), other relevant documentation or files, and any other high-level information your team might need.
Having executive oversight and insight into projects is key so we can quickly get up to speed on what is happening at any point.”
4. Hosting a project kickoff meeting
![problem solving pm [Product ui] Kickoff meeting project in Asana, spreadsheet-style view (List)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/9170a22c-5222-47e9-bc10-44edbe56e10e/TG23-web-hero-026-kickoff-meeting-static-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
A kickoff meeting is an opportunity to align with your project stakeholders. This is your chance to clarify your project goals and scope, and share any documents you’ve already put together like your project roadmap, project brief, or supplemental documentation like a bill of materials for a marketing campaign or a creative brief for a design team.
To host a successful kickoff meeting, plan to share the documentation you have put together with project stakeholders. Then, host a brainstorming or Q&A session to align on any additional variables, like budget, resources , or final deliverables.
5. Project roadmapping
![problem solving pm [product ui] milestone chart template in Asana (timeline view)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/46f9b6dc-a110-4348-9670-7e49f79b897e/TG23-web-hero-003-milestone-chart-static-2x-en?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
A project roadmap is a high-level overview of your project’s key deliverables and timeline. Project roadmaps are helpful for complex initiatives with a lot of stakeholders because they help the entire project team get on the same page before the project even starts.
Traditionally, project roadmaps are created in Gantt chart-like software , in order to display a general schedule of your project as a horizontal bar chart. To create a project roadmap, use a tool like Timeline in Asana to create a rough timeline of your project, adding key milestones or important dependencies.
6. Mapping your project timeline
![problem solving pm [Product ui] Timeline in Asana, Gantt chart-style view (Timeline)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/79f35737-4e03-4527-91cf-fb88073e11e2/TG23-web-hero-017-timeline-static-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Your project timeline is the order and duration of events during your project lifecycle. Knowing your project timeline helps your team track project success and deliver the right assets on time.
In order to build a great project timeline, make sure you clarify the start and end dates of your project, as well as any key milestones. As you continue building out individual tasks and deliverables, set dependencies between tasks, and clarify the start and end date of each piece of work.
7. Task management
Once your project is officially underway, task management refers to how well you manage your and your team’s time. The best project managers have visibility into what their team is working on in real-time, so they can help their team effectively prioritize and execute work.
But you don’t have to magically know everything that’s happening in your project—instead, use task management software. Task management software is more than a to-do list—it’s a way to get a holistic view of all of the work happening in your project. With effective task management, you can empower your team to work more productively, efficiently, and effectively.
With Asana, we can see project progress and blockers, plus feedback and action items, all in one place. We're now able to complete work more efficiently and effectively, which has become even more critical while working from home. We’d be lost without it!”
8 technical skills all project managers need
Soft skills: check. Hard skills: got it. The only thing you have left to master are technical skills!
Technical skills refer to your knowledge of specific tools and softwares within project management. These tools aren’t hard to learn—as we mentioned before, modern project management is built to be flexible and easy to use. These eight skills are aspects of project management roles you should become familiar with, so you know when and how to leverage them.
1. Project management software skills
Project management software has come a long way from legacy tools that were difficult to use and required a project management professional to implement. But like any tool, even easy-to-use ones, the software you choose takes time to learn and truly master. Make sure the tool you select has a written guide and helpful videos to teach you the ins and outs of how to use it.
2. Gantt charts
![problem solving pm [Product ui] Product launch Gantt chart project in Asana (Timeline)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/d25dcaf2-e57e-4a6a-8528-0e429f95ff76/TG23-web-hero-025-gantt-chart-static-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Gantt charts are a way to visualize your project as a horizontal bar chart, where each bar represents a piece of work and the length of each bar represents the amount of time that work will take.
Project milestones
Dependencies
Real-time project progress
Start and end dates
Traditional Gantt chart technology can be tricky to use and limited in scope, which is why, at Asana, we took the best of Gantt chart technology and created Timeline , a Gantt-chart like tool that helps you see how all of the pieces fit together.
Launching an album has so many moving parts, and Asana helps us track every detail, who’s responsible for it, and when it needs to be completed.”
3. Kanban boards
![problem solving pm [Product UI] Sprint plans project in Asana (Boards)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/9d21e8c7-9627-42eb-bda4-ac321d42c821/engineering-kanban-view?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Another popular type of visual project management is the Kanban board . Each column in a Kanban board represents a stage of work, like New , In progress , or Done . Individual work is represented by cards, which move through the columns until they’re completed.
Kanban boards tools are a popular visual project management tool for lean project management teams, particularly product, engineering, and software development teams. They’re an Agile methodology , designed to be adaptable and flexible to adjust to development needs in real-time.
4. Agile management
Agile management is a lean project management methodology that’s particularly popular with product, engineering, and software development teams. Agile operates on a system of continuous improvement and incremental evolution, and it encompasses several lean methodologies, like lean portfolio management , Scrum , and Kanban .
In order to manage an Agile team, it's the project manager’s job to coordinate between team members and stay flexible. This can mean changing the project schedule, aligning with teams working on a different project, or just staying in touch with effective communication.
5. Workload management
![problem solving pm [Product UI] Workload management in Asana (Workload)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/04f7d02f-1ce7-48dc-91d4-d17f2d3b3f9e/inline-generic-workload-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
If you’ve managed projects before, you know how hard it is to gain clarity on who is working on what—but it doesn’t have to be. Workload management helps you measure your team’s bandwidth and make sure they aren’t over- or under-worked. It’s an interactive process that doesn’t have a beginning or end state—rather, an effective project manager will continuously monitor their team’s workload to ensure no one is burning out.
There are two steps to using workload management software . First, start by figuring out your team’s capacity, competencies, and current workload. From there, allocate resources based on individual workload, or rebalance workloads as needed.
6. Cost management
In project management, cost management is considering how each task impacts your budget at every stage of the project. Cost management is a key part of project leadership, and an important element of whether or not your project is a success. Staying within budget is as important as hitting your project due date, and cost management can help you get there.
To manage cost effectively, good project managers define their costs and budget at the beginning of a project. Make sure project stakeholders and team members all understand the budget. Then, during the project, keep cost and budget in mind. Check in on your spending several times during the project to make sure you aren’t overshooting your budget. Once the project is completed, tally predicted cost vs. actual cost to determine how effective your cost management strategies were. This can also help you benchmark for future projects.
7. Project portfolio management
![problem solving pm [Product UI] Project Management Skills - project portfolio management (Portfolios)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/403373e9-e601-48c3-9fcc-5aac7847ee2d/inline-generic-portfolios-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
With project portfolio management (PMM), you can get a bird’s-eye view of your team’s work across multiple projects. Unlike traditional project management, PMM involves working on multiple projects or large-scale initiatives simultaneously. Project portfolio management tools help you get a holistic view of all of your team’s work in real-time, so you can connect strategy to execution.
Portfolios are also a key Asana feature for our team. It is a great tool for our executive team so they can see our big pieces of work all in a single place with the status, progress and ownership. Our CEO visits our portfolio daily and adds comments. He loves to be able to see what's going on in a snapshot.”
8. Change management
If you’ve ever rolled out a big organizational change, you’ve likely practiced change management, even if you didn’t know it. Change management is the process of introducing organizational change—like new processes or tools—over a set period of time to make them easier to adapt to.
At Asana, we use the Asana Way of Change, a six step process developed by our Customer Success team that incorporates proven change management strategies. To learn more, read our guide to change management .
The standard of our creative team, for a while, was just to react to work. But we’ll never do the best work we possibly can without a clear process.”
How to build your project management skills
Twenty five skills might feel like a lot, but remember that you don’t need to master every skill in this list. Some, like Agile, are only relevant for specific teams. Others, like organization, become virtually effortless with a little focus and great tools .
Keep in mind that developing your project management skills takes practice. Challenge yourself to focus on one or two new skills for each project—whether that’s trying out a new visual form of project management like Kanban, drafting your first ever project plan, or leaning into time-management.
There are also classes you can take to develop hard and soft project management skills. Though you no longer need certifications in order to be considered a project manager, the Project Management Institute (PMI) offers courses, learning events, and their famous Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK® Guide) , which was the first project management guide ever published.
Finally, once you’ve selected a project management tool , you can also take their classes to learn technical project management skills. At Asana, we’ve developed the Asana Academy and How to Asana series to help new project managers learn new soft, hard, and technical skills.
Build your project management toolkit
If you manage a project, you’re a project manager—and you likely already have some key project management skills. The most important thing is to be intentional, listen to your team, and collaborate with your team members. The rest will follow.
Project management doesn’t need to be complex. Asana was designed specifically to keep project manager’s organized, with tools, automations, and customizations built for collaborating and coordinating everything from a simple brainstorming session to a full-fledged product launch.
Related resources
3 visual project management layouts (and how to use them)
Grant management: A nonprofit’s guide
Everything you need to know about waterfall project management
Smooth product launches are simpler than you think
- Integrations
- Learning Center
CIRCLES Method
What is the circles method.
The CIRCLES method is a problem-solving framework that helps product managers (PMs) make a thorough and thoughtful response to any design question.
The seven linear steps of the process form the CIRCLES acronym: C omprehend the situation; i dentify the customer; r eport the customer’s needs; c ut, through prioritization; l ist solutions; e valuate tradeoffs, and s ummarize your recommendation.

Key Concepts of the CIRCLES Method
The sequential structure of the CIRCLES method enables PMs to move through essential questions to understand what needs to design and why fully. Some consider the CIRCLES method to be a checklist for asking the right questions when forming an exhaustive and organized response to a design question.
According to Lewis C. Lin, author of Decode and Conquer and creator of the CIRCLES method, the first critical step — comprehending the situation — is a three-fold process that involves:
- Clarifying the goal (e.g., increase revenue, market share, or engagement).
- Understanding the constraints you have for the problem upfront (e.g., how much time do you have, how many engineer resources are available, etc.).
- Understanding the context of the situation that gives you foundational knowledge (i.e., don’t guess or make assumptions–instead ask questions that help you understand, like “What is it?” and “Who is it for?”).
Hear Lewis C. Lin walk through the CIRCLES method .
Here are the seven steps to the CIRCLES method:
Alicia Newman at Learn Worthy writes:
“The CIRCLES framework is put together so that you can use mental cues to structure your response to a product design question. Knowing the backbone of the framework ensures that once you get that product design question, you will know which elements to include in your answer no matter what the product is.”
Why Is the CIRCLES Method Important to Product Management?
The CIRCLES method is useful in product management because it:
- Keeps the focus on users by distilling who PMs are building the product or feature for. Communicates why they are building it.
- Helps PMs prioritize things like product features, execution, user feedback, and the product roadmap
- Enables PMs to ask the right questions during the critical first step (comprehend the situation) to gather ample information before rushing to a solution
- Encourages PMs to keep an open mind as they move through the sequential steps of the framework instead of jumping to conclusions or a solution
Related terms: Customer Empathy / User Experience / Product Design / Product Discovery / Design Thinking
Subscribe to our Newsletter
Share on mastodon.

Nishit’s Newsletter

Cracking PM Interview: Problem Solving Question
Problem-solving/product question is something that you'll come across in every pm interview. here's a way on how shall one approach it. (not my technique, an amalgamation of the best possible ways).

Among everything that you read on the internet about Product Managers, problem-solving is one of the key (most commonly) qualities attributed to a good PM.
Read the summary again- As I mentioned, the idea is to help on “how shall one approach the question”. We need to understand that every time the interviewers are not looking just at the solution. It’s how does one reach those solutions also matter. Having said that, I am not trying to undercut the importance of a good solution that moves the needle for the product in a significant manner. ( We will come to this)
Question Type: There are different versions of this but broadly these question looks like the one mentioned below:
What is your favorite app and what would you improve in it?
Design an alarm clock for the blind? or Design navigation for the blind?
Questions asked will be designed to unsettle you and will not something your mind is familiar with.
Skills being looked for: how do you think, strategize, prioritize and design the features
Don’ts: Again, before we jump into what to do, most important is what not to do
Please do not directly jump into solutioning and start throwing solutions features.
The features/solutions suggested should not on the lines of visual element changes or an incremental feature. The solution should fundamentally impact the product and its users. Additionally, the feature should have a significant desired impact. (moving the needle)
Solving framework:
Lay the Approach: To begin with, always layout your approach on how you’re going to solve the question.
First, I’ll discuss the problem in depth to make sure I understand it correctly. Then we can discuss the business situation and our objective in details. Subsequently, I will focus on defining the target user and brainstorming what problems we could solve for them. And lastly, I will try to generate solutions for these problems, prioritize them, and make a recommendation .
Focus on the problem: Sounds counterintuitive, huh? It’s not. The very first thing that you should do is clarify the problems and break them into smaller problems. Always start with the application of the first principle . The first principles will be one of the most important skillsets in your gamut.
Clarify assumptions: The problem given might seem very obvious but still do clarify every pointer which is not stated.
Define the business/product objective: This is a very important step to zero in on what exactly is expected to be solved or achieved. Sometimes we jump into solutions only to be made aware that we aren’t solving the right problems and end up embarrassing ourselves.

Define the target groups: Once we have the simplified problem statements and the business objective, clearly define the target groups for which you’re trying to solve. There can be possibly different segments. In order to keep the solution focussed, choose the target group with a maximum base or the group that can make the most impact.

Use cases definition : Explain why the users are/will use the product for. Also, this step really helps in setting up the base for your solutions. Explain in detail, how the current product is faring in addressing those use cases and are there any weak spots.
Narrowing down the weak spots/problems: Once we have identified the weak spots, narrow down the weak spot or challenge that you’ll address which shall circle back to the objective by making a significant impact.
Suggest features to address the weak spots: Suggest all the features that you can think of which can address the weak spots. Among all the features suggested, do pay heed to prioritization and explain the order in which these features can be implemented and how.
First and second-order impact analysis: Once features are suggested, please do highlight the metrics and impact on them. Also, be mindful of the second-order impact analysis of each feature.
Sometimes interviewers might give inputs about say which target user to solve for or what particular aspect needs to be addressed. Please do skip steps as per your recognizance.
Also, after each step or after a couple of steps, do keep checking with the interviewer if he/she thinks the approach is okay or if there is any feedback. It really helps to keep correcting the way rather than going off track.
I have not mentioned any examples here because learning from examples sometimes hinders the scope of absorbing the details and understanding their application across the horizon. If needed, I can pick a detailed case study implementing the framework in one of the subsequent news letter. Please let me know in the comments.
Ready for more?

Problem-Solving and Continuous Improvement
Problem Solving and Continuous Improvement - Two Sides of the Same Coin
Complex technical change projects are inherently risky; problems will arise that may not have been considered during risk planning. A design verification test may fail; a supplier may be late delivering a critical piece of process or test equipment; a competitor may announce a new product feature that will adversely affect your new product’s market acceptance.
Furthermore, any change project involves uncertainties in the planning stage that, during execution, may result in schedule slips, resource allocation conflicts, and/or unforeseen costs.
Lean Six Sigma (LSS) problem solving tools – 8D analysis, cause-effect analysis, root cause and corrective action, and others – provide a disciplined approach to solving complex technical problems. Following LSS practices helps teams move methodically from observed symptoms to drill down to the source of problems, in order to implement permanent solutions .
LSS continuous improvement methods – PDSA, kaizen, 5-Why, and others – can be proactively applied to manage project flow, minimize schedule disruptions, recover time lost in early project phases , and document decisions and actions taken.
Learning, applying, and mastering certain Lean Six Sigma PM techniques advances the team and business organization in several ways:
♦ From patching symptoms, to permanently solving problems ♦ From over-reliance on one expert, to building skills across the business ♦ From accepting project delays, to having confidence that early delays can be recovered
In short, from working hard to working smart.
When it's time to take Action --

Here’s some disconcerting news you probably already know. The number of possible problems that can occur during your project is infinite. And your ability to know and plan fully for all of them in advance is zero!
Chances are you have a PMP® certification, and access to the project manager’s most cited reference, the PMBOK®. Good – that’s an excellent source of information! Let’s see what it says about problem solving.
Uh-oh. A few sentences in 7 locations. Nothing that is actionable, I’m afraid.
What about continuous improvement ? Even less, it turns out.
How about available Project Manager training?
Uh-oh again. For example, one of the most widely available PM training courses offers this 6-step approach to problem solving in your project.
(a). Only focus on the important issues. (b). Understand and state the problem. (c). Prioritize, if there are multiple problems. (d). Don’t spend time on unimportant things. (e). Sometimes the best answer is to do nothing. (f). If you need help, ask for it.
Go for Extraordinary!
I don’t want to be there when your VP of Operations presses you about how you’re planning to resolve the 84% failure rate at final test on your new product pilot build, and you offer up answer (d) or (e)!
The book, Shuttle, Houston! My Life in the Center Seat of Mission Control , by Paul Dye , (Hachette Books, 2020) has a thought-provoking section about problem solving during manned space flight missions in the Space Shuttle program. Sub-titled “The First Answer is Always Wrong,” the section describes “the tendency of flight controllers to want to solve every problem within milliseconds of seeing something happening in their system.” Frequently, however, the first observed anomaly is not by itself indicative of the underlying cause; other observations have to be made that in most cases lead to a small number of possibilities from which to choose a course of action. For that reason, NASA emphasized “fast thinking but slow action,” recognizing the timetable available for deciding and acting on a solution. That timetable is inevitably short, but it’s not milliseconds short.
The rush to judgment is not confined to space flight programs. For a down-to-earth example, see the case study “ Product Upgrade Pre-launch Out of Box Failure (OOBF) ”. In that situation, the fastest thinking senior leaders focused first on ‘defective lithium batteries’ and second on ‘defective memory chips’ provided by their suppliers as the cause of the OOBF. Reading the case, you will see that taking action on either or both of those obvious – but wrong – causes would have meant weeks of fruitless activity, leaving the organization with the same problem in the end.
Consider, then, the problem solving tools and techniques developed by Lean Six Sigma practitioners. As a project manager, you could enroll in training for a green or black belt if you have math, statistics, and technical skills attained with an engineering degree or MBA. By all means, do it. That is a very useful skill enhancement for a PM, long term; unfortunately, it won’t happen in time to save your current project.
For today’s problems and challenges, focus on a couple of LSS methods, including our old friend PDSA and a few related useful tools.
Ping me, [email protected] , to discuss your immediate issues, and how to employ LSS problem solving and continuous improvement tools to get your project back on track.
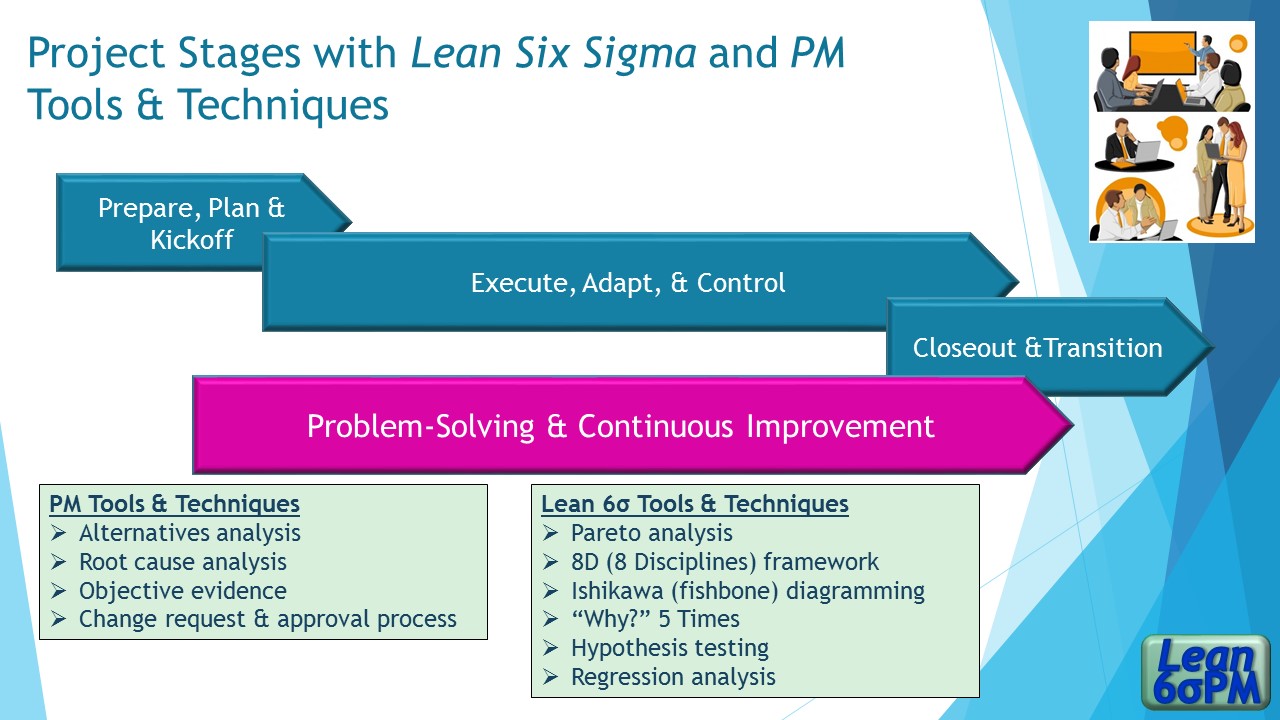
4 Project Stages
Go: prepare, plan, kickoff, go: execute, adapt, control, go: closeout and transition, go: problem solving, continuous improvement, putting ideas into practice, ⟫ faster problem-solving with a fishbone diagram, ⟫ from root cause to robust corrective action, ⟫ see the data: you can't manage a secret, ⟫ teams work better when using "lean a3", return to lean six sigma pm resources landing page.
35 problem-solving techniques and methods for solving complex problems

Design your next session with SessionLab
Join the 150,000+ facilitators using SessionLab.
Recommended Articles
A step-by-step guide to planning a workshop, how to create an unforgettable training session in 8 simple steps, 47 useful online tools for workshop planning and meeting facilitation.
All teams and organizations encounter challenges as they grow. There are problems that might occur for teams when it comes to miscommunication or resolving business-critical issues . You may face challenges around growth , design , user engagement, and even team culture and happiness. In short, problem-solving techniques should be part of every team’s skillset.
Problem-solving methods are primarily designed to help a group or team through a process of first identifying problems and challenges , ideating possible solutions , and then evaluating the most suitable .
Finding effective solutions to complex problems isn’t easy, but by using the right process and techniques, you can help your team be more efficient in the process.
So how do you develop strategies that are engaging, and empower your team to solve problems effectively?
In this blog post, we share a series of problem-solving tools you can use in your next workshop or team meeting. You’ll also find some tips for facilitating the process and how to enable others to solve complex problems.
Let’s get started!
How do you identify problems?
How do you identify the right solution.
- Tips for more effective problem-solving
Complete problem-solving methods
- Problem-solving techniques to identify and analyze problems
- Problem-solving techniques for developing solutions
Problem-solving warm-up activities
Closing activities for a problem-solving process.
Before you can move towards finding the right solution for a given problem, you first need to identify and define the problem you wish to solve.
Here, you want to clearly articulate what the problem is and allow your group to do the same. Remember that everyone in a group is likely to have differing perspectives and alignment is necessary in order to help the group move forward.
Identifying a problem accurately also requires that all members of a group are able to contribute their views in an open and safe manner. It can be scary for people to stand up and contribute, especially if the problems or challenges are emotive or personal in nature. Be sure to try and create a psychologically safe space for these kinds of discussions.
Remember that problem analysis and further discussion are also important. Not taking the time to fully analyze and discuss a challenge can result in the development of solutions that are not fit for purpose or do not address the underlying issue.
Successfully identifying and then analyzing a problem means facilitating a group through activities designed to help them clearly and honestly articulate their thoughts and produce usable insight.
With this data, you might then produce a problem statement that clearly describes the problem you wish to be addressed and also state the goal of any process you undertake to tackle this issue.
Finding solutions is the end goal of any process. Complex organizational challenges can only be solved with an appropriate solution but discovering them requires using the right problem-solving tool.
After you’ve explored a problem and discussed ideas, you need to help a team discuss and choose the right solution. Consensus tools and methods such as those below help a group explore possible solutions before then voting for the best. They’re a great way to tap into the collective intelligence of the group for great results!
Remember that the process is often iterative. Great problem solvers often roadtest a viable solution in a measured way to see what works too. While you might not get the right solution on your first try, the methods below help teams land on the most likely to succeed solution while also holding space for improvement.
Every effective problem solving process begins with an agenda . A well-structured workshop is one of the best methods for successfully guiding a group from exploring a problem to implementing a solution.
In SessionLab, it’s easy to go from an idea to a complete agenda . Start by dragging and dropping your core problem solving activities into place . Add timings, breaks and necessary materials before sharing your agenda with your colleagues.
The resulting agenda will be your guide to an effective and productive problem solving session that will also help you stay organized on the day!
Tips for more effective problem solving
Problem-solving activities are only one part of the puzzle. While a great method can help unlock your team’s ability to solve problems, without a thoughtful approach and strong facilitation the solutions may not be fit for purpose.
Let’s take a look at some problem-solving tips you can apply to any process to help it be a success!
Clearly define the problem
Jumping straight to solutions can be tempting, though without first clearly articulating a problem, the solution might not be the right one. Many of the problem-solving activities below include sections where the problem is explored and clearly defined before moving on.
This is a vital part of the problem-solving process and taking the time to fully define an issue can save time and effort later. A clear definition helps identify irrelevant information and it also ensures that your team sets off on the right track.
Don’t jump to conclusions
It’s easy for groups to exhibit cognitive bias or have preconceived ideas about both problems and potential solutions. Be sure to back up any problem statements or potential solutions with facts, research, and adequate forethought.
The best techniques ask participants to be methodical and challenge preconceived notions. Make sure you give the group enough time and space to collect relevant information and consider the problem in a new way. By approaching the process with a clear, rational mindset, you’ll often find that better solutions are more forthcoming.
Try different approaches
Problems come in all shapes and sizes and so too should the methods you use to solve them. If you find that one approach isn’t yielding results and your team isn’t finding different solutions, try mixing it up. You’ll be surprised at how using a new creative activity can unblock your team and generate great solutions.
Don’t take it personally
Depending on the nature of your team or organizational problems, it’s easy for conversations to get heated. While it’s good for participants to be engaged in the discussions, ensure that emotions don’t run too high and that blame isn’t thrown around while finding solutions.
You’re all in it together, and even if your team or area is seeing problems, that isn’t necessarily a disparagement of you personally. Using facilitation skills to manage group dynamics is one effective method of helping conversations be more constructive.
Get the right people in the room
Your problem-solving method is often only as effective as the group using it. Getting the right people on the job and managing the number of people present is important too!
If the group is too small, you may not get enough different perspectives to effectively solve a problem. If the group is too large, you can go round and round during the ideation stages.
Creating the right group makeup is also important in ensuring you have the necessary expertise and skillset to both identify and follow up on potential solutions. Carefully consider who to include at each stage to help ensure your problem-solving method is followed and positioned for success.
Document everything
The best solutions can take refinement, iteration, and reflection to come out. Get into a habit of documenting your process in order to keep all the learnings from the session and to allow ideas to mature and develop. Many of the methods below involve the creation of documents or shared resources. Be sure to keep and share these so everyone can benefit from the work done!
Bring a facilitator
Facilitation is all about making group processes easier. With a subject as potentially emotive and important as problem-solving, having an impartial third party in the form of a facilitator can make all the difference in finding great solutions and keeping the process moving. Consider bringing a facilitator to your problem-solving session to get better results and generate meaningful solutions!
Develop your problem-solving skills
It takes time and practice to be an effective problem solver. While some roles or participants might more naturally gravitate towards problem-solving, it can take development and planning to help everyone create better solutions.
You might develop a training program, run a problem-solving workshop or simply ask your team to practice using the techniques below. Check out our post on problem-solving skills to see how you and your group can develop the right mental process and be more resilient to issues too!
Design a great agenda
Workshops are a great format for solving problems. With the right approach, you can focus a group and help them find the solutions to their own problems. But designing a process can be time-consuming and finding the right activities can be difficult.
Check out our workshop planning guide to level-up your agenda design and start running more effective workshops. Need inspiration? Check out templates designed by expert facilitators to help you kickstart your process!
In this section, we’ll look at in-depth problem-solving methods that provide a complete end-to-end process for developing effective solutions. These will help guide your team from the discovery and definition of a problem through to delivering the right solution.
If you’re looking for an all-encompassing method or problem-solving model, these processes are a great place to start. They’ll ask your team to challenge preconceived ideas and adopt a mindset for solving problems more effectively.
- Six Thinking Hats
- Lightning Decision Jam
- Problem Definition Process
- Discovery & Action Dialogue
Design Sprint 2.0
- Open Space Technology
1. Six Thinking Hats
Individual approaches to solving a problem can be very different based on what team or role an individual holds. It can be easy for existing biases or perspectives to find their way into the mix, or for internal politics to direct a conversation.
Six Thinking Hats is a classic method for identifying the problems that need to be solved and enables your team to consider them from different angles, whether that is by focusing on facts and data, creative solutions, or by considering why a particular solution might not work.
Like all problem-solving frameworks, Six Thinking Hats is effective at helping teams remove roadblocks from a conversation or discussion and come to terms with all the aspects necessary to solve complex problems.
2. Lightning Decision Jam
Featured courtesy of Jonathan Courtney of AJ&Smart Berlin, Lightning Decision Jam is one of those strategies that should be in every facilitation toolbox. Exploring problems and finding solutions is often creative in nature, though as with any creative process, there is the potential to lose focus and get lost.
Unstructured discussions might get you there in the end, but it’s much more effective to use a method that creates a clear process and team focus.
In Lightning Decision Jam, participants are invited to begin by writing challenges, concerns, or mistakes on post-its without discussing them before then being invited by the moderator to present them to the group.
From there, the team vote on which problems to solve and are guided through steps that will allow them to reframe those problems, create solutions and then decide what to execute on.
By deciding the problems that need to be solved as a team before moving on, this group process is great for ensuring the whole team is aligned and can take ownership over the next stages.
Lightning Decision Jam (LDJ) #action #decision making #problem solving #issue analysis #innovation #design #remote-friendly The problem with anything that requires creative thinking is that it’s easy to get lost—lose focus and fall into the trap of having useless, open-ended, unstructured discussions. Here’s the most effective solution I’ve found: Replace all open, unstructured discussion with a clear process. What to use this exercise for: Anything which requires a group of people to make decisions, solve problems or discuss challenges. It’s always good to frame an LDJ session with a broad topic, here are some examples: The conversion flow of our checkout Our internal design process How we organise events Keeping up with our competition Improving sales flow
3. Problem Definition Process
While problems can be complex, the problem-solving methods you use to identify and solve those problems can often be simple in design.
By taking the time to truly identify and define a problem before asking the group to reframe the challenge as an opportunity, this method is a great way to enable change.
Begin by identifying a focus question and exploring the ways in which it manifests before splitting into five teams who will each consider the problem using a different method: escape, reversal, exaggeration, distortion or wishful. Teams develop a problem objective and create ideas in line with their method before then feeding them back to the group.
This method is great for enabling in-depth discussions while also creating space for finding creative solutions too!
Problem Definition #problem solving #idea generation #creativity #online #remote-friendly A problem solving technique to define a problem, challenge or opportunity and to generate ideas.
4. The 5 Whys
Sometimes, a group needs to go further with their strategies and analyze the root cause at the heart of organizational issues. An RCA or root cause analysis is the process of identifying what is at the heart of business problems or recurring challenges.
The 5 Whys is a simple and effective method of helping a group go find the root cause of any problem or challenge and conduct analysis that will deliver results.
By beginning with the creation of a problem statement and going through five stages to refine it, The 5 Whys provides everything you need to truly discover the cause of an issue.
The 5 Whys #hyperisland #innovation This simple and powerful method is useful for getting to the core of a problem or challenge. As the title suggests, the group defines a problems, then asks the question “why” five times, often using the resulting explanation as a starting point for creative problem solving.

5. World Cafe
World Cafe is a simple but powerful facilitation technique to help bigger groups to focus their energy and attention on solving complex problems.
World Cafe enables this approach by creating a relaxed atmosphere where participants are able to self-organize and explore topics relevant and important to them which are themed around a central problem-solving purpose. Create the right atmosphere by modeling your space after a cafe and after guiding the group through the method, let them take the lead!
Making problem-solving a part of your organization’s culture in the long term can be a difficult undertaking. More approachable formats like World Cafe can be especially effective in bringing people unfamiliar with workshops into the fold.
World Cafe #hyperisland #innovation #issue analysis World Café is a simple yet powerful method, originated by Juanita Brown, for enabling meaningful conversations driven completely by participants and the topics that are relevant and important to them. Facilitators create a cafe-style space and provide simple guidelines. Participants then self-organize and explore a set of relevant topics or questions for conversation.
6. Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD)
One of the best approaches is to create a safe space for a group to share and discover practices and behaviors that can help them find their own solutions.
With DAD, you can help a group choose which problems they wish to solve and which approaches they will take to do so. It’s great at helping remove resistance to change and can help get buy-in at every level too!
This process of enabling frontline ownership is great in ensuring follow-through and is one of the methods you will want in your toolbox as a facilitator.
Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD) #idea generation #liberating structures #action #issue analysis #remote-friendly DADs make it easy for a group or community to discover practices and behaviors that enable some individuals (without access to special resources and facing the same constraints) to find better solutions than their peers to common problems. These are called positive deviant (PD) behaviors and practices. DADs make it possible for people in the group, unit, or community to discover by themselves these PD practices. DADs also create favorable conditions for stimulating participants’ creativity in spaces where they can feel safe to invent new and more effective practices. Resistance to change evaporates as participants are unleashed to choose freely which practices they will adopt or try and which problems they will tackle. DADs make it possible to achieve frontline ownership of solutions.
7. Design Sprint 2.0
Want to see how a team can solve big problems and move forward with prototyping and testing solutions in a few days? The Design Sprint 2.0 template from Jake Knapp, author of Sprint, is a complete agenda for a with proven results.
Developing the right agenda can involve difficult but necessary planning. Ensuring all the correct steps are followed can also be stressful or time-consuming depending on your level of experience.
Use this complete 4-day workshop template if you are finding there is no obvious solution to your challenge and want to focus your team around a specific problem that might require a shortcut to launching a minimum viable product or waiting for the organization-wide implementation of a solution.
8. Open space technology
Open space technology- developed by Harrison Owen – creates a space where large groups are invited to take ownership of their problem solving and lead individual sessions. Open space technology is a great format when you have a great deal of expertise and insight in the room and want to allow for different takes and approaches on a particular theme or problem you need to be solved.
Start by bringing your participants together to align around a central theme and focus their efforts. Explain the ground rules to help guide the problem-solving process and then invite members to identify any issue connecting to the central theme that they are interested in and are prepared to take responsibility for.
Once participants have decided on their approach to the core theme, they write their issue on a piece of paper, announce it to the group, pick a session time and place, and post the paper on the wall. As the wall fills up with sessions, the group is then invited to join the sessions that interest them the most and which they can contribute to, then you’re ready to begin!
Everyone joins the problem-solving group they’ve signed up to, record the discussion and if appropriate, findings can then be shared with the rest of the group afterward.
Open Space Technology #action plan #idea generation #problem solving #issue analysis #large group #online #remote-friendly Open Space is a methodology for large groups to create their agenda discerning important topics for discussion, suitable for conferences, community gatherings and whole system facilitation
Techniques to identify and analyze problems
Using a problem-solving method to help a team identify and analyze a problem can be a quick and effective addition to any workshop or meeting.
While further actions are always necessary, you can generate momentum and alignment easily, and these activities are a great place to get started.
We’ve put together this list of techniques to help you and your team with problem identification, analysis, and discussion that sets the foundation for developing effective solutions.
Let’s take a look!
- The Creativity Dice
- Fishbone Analysis
- Problem Tree
- SWOT Analysis
- Agreement-Certainty Matrix
- The Journalistic Six
- LEGO Challenge
- What, So What, Now What?
- Journalists
Individual and group perspectives are incredibly important, but what happens if people are set in their minds and need a change of perspective in order to approach a problem more effectively?
Flip It is a method we love because it is both simple to understand and run, and allows groups to understand how their perspectives and biases are formed.
Participants in Flip It are first invited to consider concerns, issues, or problems from a perspective of fear and write them on a flip chart. Then, the group is asked to consider those same issues from a perspective of hope and flip their understanding.
No problem and solution is free from existing bias and by changing perspectives with Flip It, you can then develop a problem solving model quickly and effectively.
Flip It! #gamestorming #problem solving #action Often, a change in a problem or situation comes simply from a change in our perspectives. Flip It! is a quick game designed to show players that perspectives are made, not born.
10. The Creativity Dice
One of the most useful problem solving skills you can teach your team is of approaching challenges with creativity, flexibility, and openness. Games like The Creativity Dice allow teams to overcome the potential hurdle of too much linear thinking and approach the process with a sense of fun and speed.
In The Creativity Dice, participants are organized around a topic and roll a dice to determine what they will work on for a period of 3 minutes at a time. They might roll a 3 and work on investigating factual information on the chosen topic. They might roll a 1 and work on identifying the specific goals, standards, or criteria for the session.
Encouraging rapid work and iteration while asking participants to be flexible are great skills to cultivate. Having a stage for idea incubation in this game is also important. Moments of pause can help ensure the ideas that are put forward are the most suitable.
The Creativity Dice #creativity #problem solving #thiagi #issue analysis Too much linear thinking is hazardous to creative problem solving. To be creative, you should approach the problem (or the opportunity) from different points of view. You should leave a thought hanging in mid-air and move to another. This skipping around prevents premature closure and lets your brain incubate one line of thought while you consciously pursue another.
11. Fishbone Analysis
Organizational or team challenges are rarely simple, and it’s important to remember that one problem can be an indication of something that goes deeper and may require further consideration to be solved.
Fishbone Analysis helps groups to dig deeper and understand the origins of a problem. It’s a great example of a root cause analysis method that is simple for everyone on a team to get their head around.
Participants in this activity are asked to annotate a diagram of a fish, first adding the problem or issue to be worked on at the head of a fish before then brainstorming the root causes of the problem and adding them as bones on the fish.
Using abstractions such as a diagram of a fish can really help a team break out of their regular thinking and develop a creative approach.
Fishbone Analysis #problem solving ##root cause analysis #decision making #online facilitation A process to help identify and understand the origins of problems, issues or observations.
12. Problem Tree
Encouraging visual thinking can be an essential part of many strategies. By simply reframing and clarifying problems, a group can move towards developing a problem solving model that works for them.
In Problem Tree, groups are asked to first brainstorm a list of problems – these can be design problems, team problems or larger business problems – and then organize them into a hierarchy. The hierarchy could be from most important to least important or abstract to practical, though the key thing with problem solving games that involve this aspect is that your group has some way of managing and sorting all the issues that are raised.
Once you have a list of problems that need to be solved and have organized them accordingly, you’re then well-positioned for the next problem solving steps.
Problem tree #define intentions #create #design #issue analysis A problem tree is a tool to clarify the hierarchy of problems addressed by the team within a design project; it represents high level problems or related sublevel problems.
13. SWOT Analysis
Chances are you’ve heard of the SWOT Analysis before. This problem-solving method focuses on identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats is a tried and tested method for both individuals and teams.
Start by creating a desired end state or outcome and bare this in mind – any process solving model is made more effective by knowing what you are moving towards. Create a quadrant made up of the four categories of a SWOT analysis and ask participants to generate ideas based on each of those quadrants.
Once you have those ideas assembled in their quadrants, cluster them together based on their affinity with other ideas. These clusters are then used to facilitate group conversations and move things forward.
SWOT analysis #gamestorming #problem solving #action #meeting facilitation The SWOT Analysis is a long-standing technique of looking at what we have, with respect to the desired end state, as well as what we could improve on. It gives us an opportunity to gauge approaching opportunities and dangers, and assess the seriousness of the conditions that affect our future. When we understand those conditions, we can influence what comes next.
14. Agreement-Certainty Matrix
Not every problem-solving approach is right for every challenge, and deciding on the right method for the challenge at hand is a key part of being an effective team.
The Agreement Certainty matrix helps teams align on the nature of the challenges facing them. By sorting problems from simple to chaotic, your team can understand what methods are suitable for each problem and what they can do to ensure effective results.
If you are already using Liberating Structures techniques as part of your problem-solving strategy, the Agreement-Certainty Matrix can be an invaluable addition to your process. We’ve found it particularly if you are having issues with recurring problems in your organization and want to go deeper in understanding the root cause.
Agreement-Certainty Matrix #issue analysis #liberating structures #problem solving You can help individuals or groups avoid the frequent mistake of trying to solve a problem with methods that are not adapted to the nature of their challenge. The combination of two questions makes it possible to easily sort challenges into four categories: simple, complicated, complex , and chaotic . A problem is simple when it can be solved reliably with practices that are easy to duplicate. It is complicated when experts are required to devise a sophisticated solution that will yield the desired results predictably. A problem is complex when there are several valid ways to proceed but outcomes are not predictable in detail. Chaotic is when the context is too turbulent to identify a path forward. A loose analogy may be used to describe these differences: simple is like following a recipe, complicated like sending a rocket to the moon, complex like raising a child, and chaotic is like the game “Pin the Tail on the Donkey.” The Liberating Structures Matching Matrix in Chapter 5 can be used as the first step to clarify the nature of a challenge and avoid the mismatches between problems and solutions that are frequently at the root of chronic, recurring problems.
Organizing and charting a team’s progress can be important in ensuring its success. SQUID (Sequential Question and Insight Diagram) is a great model that allows a team to effectively switch between giving questions and answers and develop the skills they need to stay on track throughout the process.
Begin with two different colored sticky notes – one for questions and one for answers – and with your central topic (the head of the squid) on the board. Ask the group to first come up with a series of questions connected to their best guess of how to approach the topic. Ask the group to come up with answers to those questions, fix them to the board and connect them with a line. After some discussion, go back to question mode by responding to the generated answers or other points on the board.
It’s rewarding to see a diagram grow throughout the exercise, and a completed SQUID can provide a visual resource for future effort and as an example for other teams.
SQUID #gamestorming #project planning #issue analysis #problem solving When exploring an information space, it’s important for a group to know where they are at any given time. By using SQUID, a group charts out the territory as they go and can navigate accordingly. SQUID stands for Sequential Question and Insight Diagram.
16. Speed Boat
To continue with our nautical theme, Speed Boat is a short and sweet activity that can help a team quickly identify what employees, clients or service users might have a problem with and analyze what might be standing in the way of achieving a solution.
Methods that allow for a group to make observations, have insights and obtain those eureka moments quickly are invaluable when trying to solve complex problems.
In Speed Boat, the approach is to first consider what anchors and challenges might be holding an organization (or boat) back. Bonus points if you are able to identify any sharks in the water and develop ideas that can also deal with competitors!
Speed Boat #gamestorming #problem solving #action Speedboat is a short and sweet way to identify what your employees or clients don’t like about your product/service or what’s standing in the way of a desired goal.
17. The Journalistic Six
Some of the most effective ways of solving problems is by encouraging teams to be more inclusive and diverse in their thinking.
Based on the six key questions journalism students are taught to answer in articles and news stories, The Journalistic Six helps create teams to see the whole picture. By using who, what, when, where, why, and how to facilitate the conversation and encourage creative thinking, your team can make sure that the problem identification and problem analysis stages of the are covered exhaustively and thoughtfully. Reporter’s notebook and dictaphone optional.
The Journalistic Six – Who What When Where Why How #idea generation #issue analysis #problem solving #online #creative thinking #remote-friendly A questioning method for generating, explaining, investigating ideas.
18. LEGO Challenge
Now for an activity that is a little out of the (toy) box. LEGO Serious Play is a facilitation methodology that can be used to improve creative thinking and problem-solving skills.
The LEGO Challenge includes giving each member of the team an assignment that is hidden from the rest of the group while they create a structure without speaking.
What the LEGO challenge brings to the table is a fun working example of working with stakeholders who might not be on the same page to solve problems. Also, it’s LEGO! Who doesn’t love LEGO!
LEGO Challenge #hyperisland #team A team-building activity in which groups must work together to build a structure out of LEGO, but each individual has a secret “assignment” which makes the collaborative process more challenging. It emphasizes group communication, leadership dynamics, conflict, cooperation, patience and problem solving strategy.
19. What, So What, Now What?
If not carefully managed, the problem identification and problem analysis stages of the problem-solving process can actually create more problems and misunderstandings.
The What, So What, Now What? problem-solving activity is designed to help collect insights and move forward while also eliminating the possibility of disagreement when it comes to identifying, clarifying, and analyzing organizational or work problems.
Facilitation is all about bringing groups together so that might work on a shared goal and the best problem-solving strategies ensure that teams are aligned in purpose, if not initially in opinion or insight.
Throughout the three steps of this game, you give everyone on a team to reflect on a problem by asking what happened, why it is important, and what actions should then be taken.
This can be a great activity for bringing our individual perceptions about a problem or challenge and contextualizing it in a larger group setting. This is one of the most important problem-solving skills you can bring to your organization.
W³ – What, So What, Now What? #issue analysis #innovation #liberating structures You can help groups reflect on a shared experience in a way that builds understanding and spurs coordinated action while avoiding unproductive conflict. It is possible for every voice to be heard while simultaneously sifting for insights and shaping new direction. Progressing in stages makes this practical—from collecting facts about What Happened to making sense of these facts with So What and finally to what actions logically follow with Now What . The shared progression eliminates most of the misunderstandings that otherwise fuel disagreements about what to do. Voila!
20. Journalists
Problem analysis can be one of the most important and decisive stages of all problem-solving tools. Sometimes, a team can become bogged down in the details and are unable to move forward.
Journalists is an activity that can avoid a group from getting stuck in the problem identification or problem analysis stages of the process.
In Journalists, the group is invited to draft the front page of a fictional newspaper and figure out what stories deserve to be on the cover and what headlines those stories will have. By reframing how your problems and challenges are approached, you can help a team move productively through the process and be better prepared for the steps to follow.
Journalists #vision #big picture #issue analysis #remote-friendly This is an exercise to use when the group gets stuck in details and struggles to see the big picture. Also good for defining a vision.
Problem-solving techniques for developing solutions
The success of any problem-solving process can be measured by the solutions it produces. After you’ve defined the issue, explored existing ideas, and ideated, it’s time to narrow down to the correct solution.
Use these problem-solving techniques when you want to help your team find consensus, compare possible solutions, and move towards taking action on a particular problem.
- Improved Solutions
- Four-Step Sketch
- 15% Solutions
- How-Now-Wow matrix
- Impact Effort Matrix
21. Mindspin
Brainstorming is part of the bread and butter of the problem-solving process and all problem-solving strategies benefit from getting ideas out and challenging a team to generate solutions quickly.
With Mindspin, participants are encouraged not only to generate ideas but to do so under time constraints and by slamming down cards and passing them on. By doing multiple rounds, your team can begin with a free generation of possible solutions before moving on to developing those solutions and encouraging further ideation.
This is one of our favorite problem-solving activities and can be great for keeping the energy up throughout the workshop. Remember the importance of helping people become engaged in the process – energizing problem-solving techniques like Mindspin can help ensure your team stays engaged and happy, even when the problems they’re coming together to solve are complex.
MindSpin #teampedia #idea generation #problem solving #action A fast and loud method to enhance brainstorming within a team. Since this activity has more than round ideas that are repetitive can be ruled out leaving more creative and innovative answers to the challenge.
22. Improved Solutions
After a team has successfully identified a problem and come up with a few solutions, it can be tempting to call the work of the problem-solving process complete. That said, the first solution is not necessarily the best, and by including a further review and reflection activity into your problem-solving model, you can ensure your group reaches the best possible result.
One of a number of problem-solving games from Thiagi Group, Improved Solutions helps you go the extra mile and develop suggested solutions with close consideration and peer review. By supporting the discussion of several problems at once and by shifting team roles throughout, this problem-solving technique is a dynamic way of finding the best solution.
Improved Solutions #creativity #thiagi #problem solving #action #team You can improve any solution by objectively reviewing its strengths and weaknesses and making suitable adjustments. In this creativity framegame, you improve the solutions to several problems. To maintain objective detachment, you deal with a different problem during each of six rounds and assume different roles (problem owner, consultant, basher, booster, enhancer, and evaluator) during each round. At the conclusion of the activity, each player ends up with two solutions to her problem.
23. Four Step Sketch
Creative thinking and visual ideation does not need to be confined to the opening stages of your problem-solving strategies. Exercises that include sketching and prototyping on paper can be effective at the solution finding and development stage of the process, and can be great for keeping a team engaged.
By going from simple notes to a crazy 8s round that involves rapidly sketching 8 variations on their ideas before then producing a final solution sketch, the group is able to iterate quickly and visually. Problem-solving techniques like Four-Step Sketch are great if you have a group of different thinkers and want to change things up from a more textual or discussion-based approach.
Four-Step Sketch #design sprint #innovation #idea generation #remote-friendly The four-step sketch is an exercise that helps people to create well-formed concepts through a structured process that includes: Review key information Start design work on paper, Consider multiple variations , Create a detailed solution . This exercise is preceded by a set of other activities allowing the group to clarify the challenge they want to solve. See how the Four Step Sketch exercise fits into a Design Sprint
24. 15% Solutions
Some problems are simpler than others and with the right problem-solving activities, you can empower people to take immediate actions that can help create organizational change.
Part of the liberating structures toolkit, 15% solutions is a problem-solving technique that focuses on finding and implementing solutions quickly. A process of iterating and making small changes quickly can help generate momentum and an appetite for solving complex problems.
Problem-solving strategies can live and die on whether people are onboard. Getting some quick wins is a great way of getting people behind the process.
It can be extremely empowering for a team to realize that problem-solving techniques can be deployed quickly and easily and delineate between things they can positively impact and those things they cannot change.
15% Solutions #action #liberating structures #remote-friendly You can reveal the actions, however small, that everyone can do immediately. At a minimum, these will create momentum, and that may make a BIG difference. 15% Solutions show that there is no reason to wait around, feel powerless, or fearful. They help people pick it up a level. They get individuals and the group to focus on what is within their discretion instead of what they cannot change. With a very simple question, you can flip the conversation to what can be done and find solutions to big problems that are often distributed widely in places not known in advance. Shifting a few grains of sand may trigger a landslide and change the whole landscape.
25. How-Now-Wow Matrix
The problem-solving process is often creative, as complex problems usually require a change of thinking and creative response in order to find the best solutions. While it’s common for the first stages to encourage creative thinking, groups can often gravitate to familiar solutions when it comes to the end of the process.
When selecting solutions, you don’t want to lose your creative energy! The How-Now-Wow Matrix from Gamestorming is a great problem-solving activity that enables a group to stay creative and think out of the box when it comes to selecting the right solution for a given problem.
Problem-solving techniques that encourage creative thinking and the ideation and selection of new solutions can be the most effective in organisational change. Give the How-Now-Wow Matrix a go, and not just for how pleasant it is to say out loud.
How-Now-Wow Matrix #gamestorming #idea generation #remote-friendly When people want to develop new ideas, they most often think out of the box in the brainstorming or divergent phase. However, when it comes to convergence, people often end up picking ideas that are most familiar to them. This is called a ‘creative paradox’ or a ‘creadox’. The How-Now-Wow matrix is an idea selection tool that breaks the creadox by forcing people to weigh each idea on 2 parameters.
26. Impact and Effort Matrix
All problem-solving techniques hope to not only find solutions to a given problem or challenge but to find the best solution. When it comes to finding a solution, groups are invited to put on their decision-making hats and really think about how a proposed idea would work in practice.
The Impact and Effort Matrix is one of the problem-solving techniques that fall into this camp, empowering participants to first generate ideas and then categorize them into a 2×2 matrix based on impact and effort.
Activities that invite critical thinking while remaining simple are invaluable. Use the Impact and Effort Matrix to move from ideation and towards evaluating potential solutions before then committing to them.
Impact and Effort Matrix #gamestorming #decision making #action #remote-friendly In this decision-making exercise, possible actions are mapped based on two factors: effort required to implement and potential impact. Categorizing ideas along these lines is a useful technique in decision making, as it obliges contributors to balance and evaluate suggested actions before committing to them.
27. Dotmocracy
If you’ve followed each of the problem-solving steps with your group successfully, you should move towards the end of your process with heaps of possible solutions developed with a specific problem in mind. But how do you help a group go from ideation to putting a solution into action?
Dotmocracy – or Dot Voting -is a tried and tested method of helping a team in the problem-solving process make decisions and put actions in place with a degree of oversight and consensus.
One of the problem-solving techniques that should be in every facilitator’s toolbox, Dot Voting is fast and effective and can help identify the most popular and best solutions and help bring a group to a decision effectively.
Dotmocracy #action #decision making #group prioritization #hyperisland #remote-friendly Dotmocracy is a simple method for group prioritization or decision-making. It is not an activity on its own, but a method to use in processes where prioritization or decision-making is the aim. The method supports a group to quickly see which options are most popular or relevant. The options or ideas are written on post-its and stuck up on a wall for the whole group to see. Each person votes for the options they think are the strongest, and that information is used to inform a decision.
All facilitators know that warm-ups and icebreakers are useful for any workshop or group process. Problem-solving workshops are no different.
Use these problem-solving techniques to warm up a group and prepare them for the rest of the process. Activating your group by tapping into some of the top problem-solving skills can be one of the best ways to see great outcomes from your session.
- Check-in/Check-out
- Doodling Together
- Show and Tell
- Constellations
- Draw a Tree
28. Check-in / Check-out
Solid processes are planned from beginning to end, and the best facilitators know that setting the tone and establishing a safe, open environment can be integral to a successful problem-solving process.
Check-in / Check-out is a great way to begin and/or bookend a problem-solving workshop. Checking in to a session emphasizes that everyone will be seen, heard, and expected to contribute.
If you are running a series of meetings, setting a consistent pattern of checking in and checking out can really help your team get into a groove. We recommend this opening-closing activity for small to medium-sized groups though it can work with large groups if they’re disciplined!
Check-in / Check-out #team #opening #closing #hyperisland #remote-friendly Either checking-in or checking-out is a simple way for a team to open or close a process, symbolically and in a collaborative way. Checking-in/out invites each member in a group to be present, seen and heard, and to express a reflection or a feeling. Checking-in emphasizes presence, focus and group commitment; checking-out emphasizes reflection and symbolic closure.
29. Doodling Together
Thinking creatively and not being afraid to make suggestions are important problem-solving skills for any group or team, and warming up by encouraging these behaviors is a great way to start.
Doodling Together is one of our favorite creative ice breaker games – it’s quick, effective, and fun and can make all following problem-solving steps easier by encouraging a group to collaborate visually. By passing cards and adding additional items as they go, the workshop group gets into a groove of co-creation and idea development that is crucial to finding solutions to problems.
Doodling Together #collaboration #creativity #teamwork #fun #team #visual methods #energiser #icebreaker #remote-friendly Create wild, weird and often funny postcards together & establish a group’s creative confidence.
30. Show and Tell
You might remember some version of Show and Tell from being a kid in school and it’s a great problem-solving activity to kick off a session.
Asking participants to prepare a little something before a workshop by bringing an object for show and tell can help them warm up before the session has even begun! Games that include a physical object can also help encourage early engagement before moving onto more big-picture thinking.
By asking your participants to tell stories about why they chose to bring a particular item to the group, you can help teams see things from new perspectives and see both differences and similarities in the way they approach a topic. Great groundwork for approaching a problem-solving process as a team!
Show and Tell #gamestorming #action #opening #meeting facilitation Show and Tell taps into the power of metaphors to reveal players’ underlying assumptions and associations around a topic The aim of the game is to get a deeper understanding of stakeholders’ perspectives on anything—a new project, an organizational restructuring, a shift in the company’s vision or team dynamic.
31. Constellations
Who doesn’t love stars? Constellations is a great warm-up activity for any workshop as it gets people up off their feet, energized, and ready to engage in new ways with established topics. It’s also great for showing existing beliefs, biases, and patterns that can come into play as part of your session.
Using warm-up games that help build trust and connection while also allowing for non-verbal responses can be great for easing people into the problem-solving process and encouraging engagement from everyone in the group. Constellations is great in large spaces that allow for movement and is definitely a practical exercise to allow the group to see patterns that are otherwise invisible.
Constellations #trust #connection #opening #coaching #patterns #system Individuals express their response to a statement or idea by standing closer or further from a central object. Used with teams to reveal system, hidden patterns, perspectives.
32. Draw a Tree
Problem-solving games that help raise group awareness through a central, unifying metaphor can be effective ways to warm-up a group in any problem-solving model.
Draw a Tree is a simple warm-up activity you can use in any group and which can provide a quick jolt of energy. Start by asking your participants to draw a tree in just 45 seconds – they can choose whether it will be abstract or realistic.
Once the timer is up, ask the group how many people included the roots of the tree and use this as a means to discuss how we can ignore important parts of any system simply because they are not visible.
All problem-solving strategies are made more effective by thinking of problems critically and by exposing things that may not normally come to light. Warm-up games like Draw a Tree are great in that they quickly demonstrate some key problem-solving skills in an accessible and effective way.
Draw a Tree #thiagi #opening #perspectives #remote-friendly With this game you can raise awarness about being more mindful, and aware of the environment we live in.
Each step of the problem-solving workshop benefits from an intelligent deployment of activities, games, and techniques. Bringing your session to an effective close helps ensure that solutions are followed through on and that you also celebrate what has been achieved.
Here are some problem-solving activities you can use to effectively close a workshop or meeting and ensure the great work you’ve done can continue afterward.
- One Breath Feedback
- Who What When Matrix
- Response Cards
How do I conclude a problem-solving process?
All good things must come to an end. With the bulk of the work done, it can be tempting to conclude your workshop swiftly and without a moment to debrief and align. This can be problematic in that it doesn’t allow your team to fully process the results or reflect on the process.
At the end of an effective session, your team will have gone through a process that, while productive, can be exhausting. It’s important to give your group a moment to take a breath, ensure that they are clear on future actions, and provide short feedback before leaving the space.
The primary purpose of any problem-solving method is to generate solutions and then implement them. Be sure to take the opportunity to ensure everyone is aligned and ready to effectively implement the solutions you produced in the workshop.
Remember that every process can be improved and by giving a short moment to collect feedback in the session, you can further refine your problem-solving methods and see further success in the future too.
33. One Breath Feedback
Maintaining attention and focus during the closing stages of a problem-solving workshop can be tricky and so being concise when giving feedback can be important. It’s easy to incur “death by feedback” should some team members go on for too long sharing their perspectives in a quick feedback round.
One Breath Feedback is a great closing activity for workshops. You give everyone an opportunity to provide feedback on what they’ve done but only in the space of a single breath. This keeps feedback short and to the point and means that everyone is encouraged to provide the most important piece of feedback to them.
One breath feedback #closing #feedback #action This is a feedback round in just one breath that excels in maintaining attention: each participants is able to speak during just one breath … for most people that’s around 20 to 25 seconds … unless of course you’ve been a deep sea diver in which case you’ll be able to do it for longer.
34. Who What When Matrix
Matrices feature as part of many effective problem-solving strategies and with good reason. They are easily recognizable, simple to use, and generate results.
The Who What When Matrix is a great tool to use when closing your problem-solving session by attributing a who, what and when to the actions and solutions you have decided upon. The resulting matrix is a simple, easy-to-follow way of ensuring your team can move forward.
Great solutions can’t be enacted without action and ownership. Your problem-solving process should include a stage for allocating tasks to individuals or teams and creating a realistic timeframe for those solutions to be implemented or checked out. Use this method to keep the solution implementation process clear and simple for all involved.
Who/What/When Matrix #gamestorming #action #project planning With Who/What/When matrix, you can connect people with clear actions they have defined and have committed to.
35. Response cards
Group discussion can comprise the bulk of most problem-solving activities and by the end of the process, you might find that your team is talked out!
Providing a means for your team to give feedback with short written notes can ensure everyone is head and can contribute without the need to stand up and talk. Depending on the needs of the group, giving an alternative can help ensure everyone can contribute to your problem-solving model in the way that makes the most sense for them.
Response Cards is a great way to close a workshop if you are looking for a gentle warm-down and want to get some swift discussion around some of the feedback that is raised.
Response Cards #debriefing #closing #structured sharing #questions and answers #thiagi #action It can be hard to involve everyone during a closing of a session. Some might stay in the background or get unheard because of louder participants. However, with the use of Response Cards, everyone will be involved in providing feedback or clarify questions at the end of a session.
Save time and effort discovering the right solutions
A structured problem solving process is a surefire way of solving tough problems, discovering creative solutions and driving organizational change. But how can you design for successful outcomes?
With SessionLab, it’s easy to design engaging workshops that deliver results. Drag, drop and reorder blocks to build your agenda. When you make changes or update your agenda, your session timing adjusts automatically , saving you time on manual adjustments.
Collaborating with stakeholders or clients? Share your agenda with a single click and collaborate in real-time. No more sending documents back and forth over email.
Explore how to use SessionLab to design effective problem solving workshops or watch this five minute video to see the planner in action!

Over to you
The problem-solving process can often be as complicated and multifaceted as the problems they are set-up to solve. With the right problem-solving techniques and a mix of creative exercises designed to guide discussion and generate purposeful ideas, we hope we’ve given you the tools to find the best solutions as simply and easily as possible.
Is there a problem-solving technique that you are missing here? Do you have a favorite activity or method you use when facilitating? Let us know in the comments below, we’d love to hear from you!
thank you very much for these excellent techniques
Certainly wonderful article, very detailed. Shared!
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Going from a mere idea to a workshop that delivers results for your clients can feel like a daunting task. In this piece, we will shine a light on all the work behind the scenes and help you learn how to plan a workshop from start to finish. On a good day, facilitation can feel like effortless magic, but that is mostly the result of backstage work, foresight, and a lot of careful planning. Read on to learn a step-by-step approach to breaking the process of planning a workshop into small, manageable chunks. The flow starts with the first meeting with a client to define the purposes of a workshop.…

How does learning work? A clever 9-year-old once told me: “I know I am learning something new when I am surprised.” The science of adult learning tells us that, in order to learn new skills (which, unsurprisingly, is harder for adults to do than kids) grown-ups need to first get into a specific headspace. In a business, this approach is often employed in a training session where employees learn new skills or work on professional development. But how do you ensure your training is effective? In this guide, we'll explore how to create an effective training session plan and run engaging training sessions. As team leader, project manager, or consultant,…

Effective online tools are a necessity for smooth and engaging virtual workshops and meetings. But how do you choose the right ones? Do you sometimes feel that the good old pen and paper or MS Office toolkit and email leaves you struggling to stay on top of managing and delivering your workshop? Fortunately, there are plenty of online tools to make your life easier when you need to facilitate a meeting and lead workshops. In this post, we’ll share our favorite online tools you can use to make your job as a facilitator easier. In fact, there are plenty of free online workshop tools and meeting facilitation software you can…
Design your next workshop with SessionLab
Join the 150,000 facilitators using SessionLab
Sign up for free

5 Conflict Resolution Techniques in Project Management
Fahad Usmani, PMP
July 24, 2022

Today we will discuss the five conflict resolution techniques we use in project management to resolve conflict.
These techniques are universal to any type of workplace.
However, in project management, the work environment is dynamic and stressful, unlike the functional environment. Conflicts are common occurrences. If you are managing projects , you know how important it is to manage conflicts, and that is why you should understand conflict resolution techniques.
Conflict Resolution Techniques
Conflict can occur when two or more stakeholders have different opinions or interests.
Schedule priorities, scarce resources, technical reasons, and personal issues can all cause clashes. According to the American Management Association, managers manage conflicts 24% of their time.
Don’t panic; the situation is usually not as bad as you think. Resolving conflicts appropriately can build trust and sometimes bring new ideas and opportunities. This can make the difference between a positive and negative outcome.
If you don’t solve the conflict, your team members will lose trust. It will weaken your position as a project manager and the ability of your team to bond, which may affect your project’s success. You must deal with conflict before it is beyond resolution.
The following are a few consequences of improper conflict management:
- Low team morale
- Negative impact on the project manager’s authority
- Increased number of personal clashes
- Low productivity and efficiency
- Low-quality work
If required, project managers must monitor and resolve conflicts as quickly as possible to keep them from becoming bigger issues.
Now, we will talk about conflict resolution techniques.
This blog follows the PMI guidelines and PMBOK Guide. Here are the five techniques:
- Withdraw/Avoid
- Smooth/Accommodate
- Compromise/Reconcile
- Force/Direct
- Collaborate/Problem Solve
These conflict management strategies are also known as Thomas-Kilmann’s five approaches to resolving conflict.
Let’s discuss each technique in detail.
#1. Withdraw of Avoid

In this conflict resolution technique, you avoid the conflict or retreat and allow the conflict to resolve itself. This is for when stakes are low, and the conflict is likely to disappear on its own.
Use this technique in the following cases:
- Individuals involved in the conflict are not influential stakeholders.
- The issue does not require a time investment.
- An intense argument has already happened, and the individuals need time to cool off.
- You do not have enough information to pursue other techniques.
This technique saves time that you can invest elsewhere. It is a good conflict management strategy to apply to low-level disagreements and gives you enough time to prepare if the conflict re-emerges.
Disadvantages
Withdrawing or avoiding is not really a resolution, does not resolve a conflict, and may weaken your position because parties may assume you have an unfair bias. Team members may think you are lacking skills or are not authoritative.
Many experts don’t consider this technique as a conflict management strategy because avoiding and escaping is not a solution.
#2. Smooth or Accommodate

In this conflict resolution strategy, you find areas of agreement, try to smooth out the situation, and circumvent tough discussions.
The smoothing technique gives more consideration to one party than the other. You downplay the seriousness and behave as if the conflict never existed.
This technique is helpful in the following cases:
- You don’t have time to deal with it.
- You require a temporary solution to the problem.
- The conflict is minor and involves less influential stakeholders.
This conflict resolution strategy does not require much effort. You can focus on essential issues by ignoring unimportant arguments. Situations can be potentially handled simply while bringing harmony, creating goodwill, and providing enough time to find a permanent solution.
If you fail to bring a balanced approach, one party may take advantage since you are giving them more consideration. Other parties not being accommodated may question your authority or stop reporting conflicts.
This conflict resolution strategy is not recommended as it often weakens the project manager’s authority.
#3. Compromise or Reconcile

In this conflict management strategy, you take suggestions from both sides and partially satisfy them. This technique is useful when the stakeholders involved hold equal power.
You may use this technique in the following cases:
- All parties involved need to win
- When you have an equal relationship with both parties
- Collaborative and forcing techniques have failed
- When you need a temporary solution
This technique brings quick results, lowers stress, and keeps all parties placated until you can find a permanent solution. You can cool off and revisit the situation later.
This conflict management technique does not generate trust in the long run; all parties remain unsatisfied, and the conflict could resurface at any time. Morals are not being strengthened. You may have to ensure all parties abide by the agreement.
#4. Force or Direct

In this conflict management strategy, you agree with one party’s viewpoint and enforce their wishes. This is a win-lose situation and risks demoralizing the team.
You can use this conflict resolution technique in the following cases:
- When you need a quick solution
- When you know that one party is right
- You do not have time to investigate
- When the conflict is not very important
- When the relationship with stakeholders is not essential
This technique provides a quick solution. It requires almost no effort from the project manager and may help establish their authority.
Using this technique may cause a negative impression on you. You may lose opportunities gained from the opposing party’s viewpoint. You cannot apply this technique with powerful stakeholders. It may backfire and worsen the conflict.
#5. Collaborate or Problem Solve

In a collaborative conflict resolution strategy, you discuss the issue with all parties and agree on a solution while considering multiple viewpoints.
- When incorporating multiple views
- If influential stakeholders are involved
- When a consensus is required
- If you want to distribute responsibility
This is a real problem-solving technique that provides a solution to the conflict. It brings consensus, commitment, and shared responsibility for the outcome. This technique creates a win-win situation, builds your team’s confidence, earns respect, and establishes your authority.
You cannot use this technique when you need a quick solution because it takes time and effort. It is generally used for conflicts that may affect your project, not all issues.
Which Conflict Resolution Technique Should I Use?
The PMI does not recommend using any specific technique for all conflicts; it depends on the situation and the stakeholders involved.
For example, if two ground-level laborers have a conflict, what should you do?
You may ignore it.
However, if you see that some important stakeholders have a conflict, you will intervene, solve the conflict, and spare your project from harm.
Although no single technique can be used for all conflicts, it is thought that the “Collaborate or Problem Solve” method brings the most consensus and commitment.
How to Prevent Conflict
You cannot keep all conflict from happening, but following a few rules can minimize it. These guidelines are:
- Establish Strict Ground Rules: These help discipline team members, which results in less conflict.
- Have an Effective Communication Plan: This can help you avoid many conflicts. Define how much and how often you will communicate with your stakeholders.
- Have a Better Stakeholder Management Plan: Your project is successful if your stakeholders are happy. Project management is all about managing stakeholders’ requirements.
- Solve Conflict Early: This takes less time and effort. Make sure an unresolved conflict doesn’t resurface again later.
The Role of the Project Manager in Conflict Resolution
I have explained all strategies to resolve conflicts and how you can use them. As a project manager, you have to respond rationally and reach a solution that best serves your objective.
While resolving a conflict, keep the following points in mind:
- Each participant deserves respect
- Be calm and rational.
- People are separate from problems
- Each participant should be listened to patiently
- There are always areas of agreement and disagreement
- You should explore all possible solutions.
- Mind your biases and don’t pick sides
- Don’t force or pressure participants
- Postponed conflicts may fester.
- Focus on the conflict, don’t let escalate the issue or generalize it.
As a project manager, you are responsible for keeping conflicts under control. You cannot use any single technique for all types of conflict. However, you should use a conflict resolution strategy that inspires consensus and commitment from team members.
This is where this blog post on conflict resolution techniques ends.
Below is my old blog post on conflict resolution strategies based on the fourth edition of the PMBOK Guide. Since I have re-written it based on the sixth edition of the PMBOK Guide , the old blog post is no longer relevant, but I am keeping it archived.
“Conflict Resolution Techniques” was one of my favorite topics during my PMP certification exam preparation . Although, I observed a discrepancy between the PMP exam reference books and the PMBOK guide.
All the reference books suggest that confronting is the best conflict resolution technique and that a project manager should use this technique to resolve conflicts in all cases. However, the PMBOK Guide (fourth edition) favors the collaborative technique.
I have repeatedly reviewed this edition of the PMBOK Guide but could not find any support for this. To my surprise, nobody is discussing this discrepancy.
Therefore, I am launching my blog to address this issue, which is my first blog post.
Let’s get started.
Conflict happens while managing projects. The PMI recognizes this fact, and they have incorporated conflict resolution techniques into the PMBOK Guide.
Sources of conflict include scheduling priorities, technical problems, personal issues, scarcity of resources, etc.
According to the PMBOK Guide (fourth edition), you can use six conflict resolution techniques to resolve conflicts:
- Withdrawing or Avoiding
- Smoothing or Accommodating
- Compromising
- Collaborating
- Problem Solving or Confronting
Now I will discuss each technique and the best conflict resolution as per the PMBOK Guide.
- Withdrawing or Avoiding: The project manager chooses to avoid the conflict, and those involved find a solution.
- Smoothing or Accommodating: The project manager is involved in the conflict, tries to avoid areas of disagreement and tough discussions, and focuses on commonalities. Smoothing is a way to avoid tough discussions.
- Compromising: This is a mid-way approach. Here, everybody gains some, but no one gets exactly what they want. This is a lose-lose approach.
- Forcing: The project manager favors one party at the expense of the others. This technique risks demoralizing team members and may cause serious conflict in the future. This is a win-lose approach.
- Collaborating: The project manager works with all parties to find a resolution that involves multiple viewpoints to create the best solution. This technique reinforces mutual trust and commitment. This is an example of a win-win approach.
In the fourth edition of the PMBOK Guide, Collaborating and Problem Solving were different techniques. However, the fifth and sixth editions, both are the same technique. Also, problem-solving was known as confronting in the fourth edition, but it no longer appears in current PMBOK Guides.
A Note on Problem Solving or Confronting Technique
In confronting technique, the project manager must find a solution for a conflict. He will conduct a root cause analysis and provide a platform for all parties to express their disagreements and arrive at a solution.
So, Which is the Best Technique to Resolve a Conflict?
I have reviewed many books and internet resources to discover the best conflict resolution technique. Amazingly, I got the same answer: Confronting or Problem-Solving is the best technique for conflict resolution.
However, I do not agree with this.
A project manager’s job is not easy; they must constantly deal with multiple conflicts. No two conflicts are the same, so why would you always use one technique?
Project managers must use their judgment and experience to decide which conflict resolution technique is most suitable for each situation. The technique selected depends on the situation, timing, and the individuals involved.
The primary objective of the project manager is to complete the project successfully.
A project manager is not a detective. It’s not their job to look for the root cause, dig every available detail and scraps of evidence, and then reach a conclusion.
With problem-solving techniques, one person wins, and another loses; this is not a win-win situation and will leave one party unsatisfied even if they are in the wrong.
A prudent project manager will try to avoid this situation and look for a solution to satisfy all parties. The collaborating conflict resolution technique, which is a win-win situation for all.
Let us see what the PMBOK Guide says:
Page-239, second paragraph:
“If conflict escalates, the project manager should help facilitate a satisfactory resolution. Conflict should be addressed early and usually in private, using a direct, collaborative approach.”
Page-229, last paragraph:
“… managing conflicts in a constructive manner, and encouraging collaborative problem solving and decision-making.”
No statement in the PMBOK Guide suggests using the problem solving/confrontation technique for all conflicts; however, I noticed that the PMBOK Guide recommends the collaborative technique.
It seems that the PMI agrees with me too!
I do not recommend using the collaborative technique to solve all conflicts. However, it is the only technique that leads to consensus and commitment among all parties involved in the conflict.
The strategy of conflict management depends on the conflict. You can use the technique you think best suits the situation to resolve the conflict. However, I cannot agree that confronting is the best conflict resolution technique, and you should not use it blindly.
What conflict resolution techniques help you most to resolve conflicts? Please share your experience through the comments section.

I am Mohammad Fahad Usmani, B.E. PMP, PMI-RMP. I have been blogging on project management topics since 2011. To date, thousands of professionals have passed the PMP exam using my resources.
PMP Question Bank
This is the most popular Question Bank for the PMP Exam. To date, it has helped over 10,000 PMP aspirants prepare for the exam.
PMP Training Program
This is a PMI-approved 35 contact hours training program and it is based on the latest exam content outline applicable in 2024.
Similar Posts

7 Best Resource Management Software: Free & Paid
This article will discuss the 7 best resource management software, their features, ratings, pros and cons, and how much they cost. But before I delve into detail about these resource management tools, let’s have a brief overview of resource management and how this type of software can be useful. A resource can be man, machine,…

Verification Vs Validation
Validation and verification are two important terms in project management; they seem very similar, and it’s easy to get them confused.
These are important concepts and any PMP aspirants needs to understand them well. I will explain these terms fully, so you will have a better understanding of them when you finish this blog post.
This topic is not very important from the PMP exam point of view. However, as a project manager, you must know the difference between these terms.

Work Performance Information (WPI) vs Work Performance Measurements (WPM)
This blog post was based on the 4th edition of the PMBOK Guide, and from the 5th edition of the PMBOK Guide, the PMI has changed the definitions of terms used in this blog post; therefore, this post is now obsolete.
I have re-written this blog post based on the current version of the PMBOK Guide (6th edition). Please visit: Work Performance Data and Work Performance Information. I am leaving this post in case someone wants to review the old post under the PMBOK Guide (4th edition).
Management is always interested in the status and progress of the project. They want to know:

Leadership Styles: Definition, Meaning, & Types of Leadership Styles
Definition: A leadership style is a method of managing, directing, and motivating followers. Leadership styles define how leaders strategize their relationships with their followers. Therefore, knowing the leadership style is vital to gaining followers’ loyalty and increasing the leader’s effectiveness. This article overviews seven leadership styles, their pros and cons, factors affecting leadership styles, and…

S-Curve in Project Management: Examples with Definitions
Today we will discuss the s-curve in project management and provide you with its definitions and examples. S-curve is a graph that shows the relevant cumulative data for your project. The data can be costs, person-hours, etc. S-curve is a good communication tool and helps project managers communicate project progress to project stakeholders. Let’s dive…

What is the Best Power of the Project Manager?
A project’s environment is much like a startup company’s environment. There is continuous pressure to perform with a limited budget and a fixed schedule. More importantly, you will always have new team members.
In this situation, you will have to manage your team and motivate them to perform their best.
This is not an easy task, and you will have to use your soft and hard skills to push team members continuously.
As a project manager, you can have many powers. The sixth edition of the PMBOK Guide recognizes the following fourteen powers:
64 Comments
Sir, i realy appreaciat your idea and its very educative, please sir what technique should be use in resolving the conflict over land.
I am really impressed with the topics dealt with conflict resolutions
Thanks Elfatih.
what the role as the PM or team member if conflict start to effect core project or one constrains should i start interfere to solve it or ask them to solve it by them self.
or should i report it
If you are not PM, you should report to PM.
If you are a PM you should use your best judgement to handle the issue.
Thanks for your notes and questions bank. Your notes really inspired me how to study PMP exam and I got it passed yesterday.
Congratulations Albert on passing the PMP exam.
Very informative,thanks.
You are welcome Rondity.
Hi Fahad, I failed my first test and preparing for the second one.I prepared well with lot of material including PMBOK. But,i am unable to justify my weak areas.I purchased your 400 questions and scored 80% .Practiced well in all the areas.Can you advise me please?
Send me an email at [email protected] with all details, I will reply you.
Is I have to explain again the need of new requirements to members, which technique should I use? And when we are discussing alternative which one? I found the blog quite clear but to be honest I fail to differentiate when to use collaboration and compromise. Pls can you help me
Compromise is relatively quicker process where you take suggestion from both parties and reach on a conclusion.
In collaborative approach you have a detailed discussion with both parties to reach on a best solution.
may be you are right but in my opinion all strategy are for work and in my case the compromise is the best option for me. Thankyou for your material.
It depends on the situation and stakeholders involve with the conflicts.
Hello Fahad,
I successfully completed the exam and now Certified PM :) I want to thank you for these notes that really helped me understand the processes better in simpler terms. You are great teacher! I had purchased your formula guide and EVM guide as well which was immense help as well. Thank you and God bless you.
Congratulations Hazra on passing the PMP exam.
Your blog is great help. I am currently preparing for my PMP exam. Every time I am stuck or fail to understand a term/usage/formula, I come here and your explanation(s) helps me understand it. I want to thank you for that. And I also appreciate that you update your notes when there is a new edition of PMBOK. So this is a great reference site for people like me preparing to give their exams. Best
You are welcome Hazra. Now the six edition of the PMBOK is arriving next year, so I will have update them again.
Thanks for your comment.
Hey Fahad, Thanks for your awesome notes. I also purchased the question set on Kindle. Helped me clear the test on first attempt.
Regards, Amol
Congratulations Anmol on passing the PMP exam, and I am glad that I could be of help to you.
I like your post, Thank you for the efforts in updating to latest PMBOK and helping the community.
Thanks Qhayum
Thanks Qhayum.
Can I please ask this question?
Is problem solving the most effective, sustainable conflict resolution technique? Please provide reasons to substantiate your response. Discuss your opinion point by point. Thank you
Please read the blog post again till end. This topic has been explained in detail.
Okay Ram, in future update I will try to include some scenario based examples.
I do see 3 to 5 questions coming out in MOCK Exams from Conflict resolution techniques. They are very close in resemblance among each other. However I commit the mistake between Smooth/Accomodate, Compromise/Reconciliation and also between Force/Direct, Withdraw/Avoid.
Judgement becomes tough & above explanations are quite lengthy to recall/remember. In such case, is it possible to provide one scenario(Same people) with different situations that match the 5 conflict resolution techniques to understand?
Many Thanks.
Regards, Ram Narayan
No more conflicts. These techniques are great(Withdraw/Avoid,Smooth/Accommodate, Compromise/Reconcile,Force/Direct,Collaborate/Problem Solve) http://ku.ac.ke
Thanks James for visiting and leaving comment.
I checked the PMOBOK fifth ed. and as you mention, but I also noticed the word confront (in pencil) near the word collaborate. I remembered that our instructor told us they have same meaning.
“but I also noticed the word confront (in pencil) near the word collaborate” – I did not understand what do you mean?
Another nice post. In fact, conflict management technique is a fav topic of mine as well.
However, I am unable to get – how compromise is loose-loose. Wont it be loose-win, even if temporary?
In compromise both parties have to give up something to reach on a common consensus.
(Please note that this article is based on the fourth edition of the PMBOK Guide, in fifth edition, PMI has amalgamated collaborative and problem solving techniques.)
Hello All Which one is the worst conflict resolution method? I think its :forcing/directing, but ive seen places which advocate that withdrawing/avoiding is the worst one. Please share your thoughts.
It depends on situation.
In PMBook 5th edition, collaborating and problem solving are given as synonyms. As for confronting it disappeared, however I just did the exam and it is still the term they use for this. The way I see it, confronting is the same general ideology than collaborating and problem solving, all seeks win-win situation.
Here is an excerpt from 5th ed.: “There are five general techniques for resolving conflict. As each one has its place and use, these are not given in any particular order” […] “Collaborate/Problem Solve. Incorporating multiple viewpoints and insights from differing perspectives; requires a cooperative attitude and open dialogue that typically leads to consensus and commitment.”
I also think confronting/problem solving/collaborating leads to best solutions. As with many other things in life, we often have to select optimal result given the constrains rather than the very best one.
Confronting is not a win-lose, its aim at win-win. you confront ideas of both party and the aim (the very reason why it’s time consuming) is by sharing actively their point of view, a common agreement will emerge (which can be to agree about one or the other party position or on a new position). Since it must be common agreement, it can only be win-win (unless it is a disguised compromise because one of the party pretend to agree). It is really the equivalent of collaborating/problem solving.
In the fourth edition of the PMBOK Guide, confronting and collaborative approach were different, now they are synonyms….
I’m sorry. Read the PMBOK again, and your sources. The PMBOK and PMI reinforce that the book is a “best practices” book, every management book is; take great care to understand and internalize that because the real world is quite different. No credible source can provide us with the “one and only” way, or the best way for all management situations.
The PMBOK does not say (quoting you) “applying the same technique to all conflicts” would be justified.
It actually says the opposite, which ironically is the case your’re making. “…each one has its place and use,”. For example, avoiding a problem, can be VERY effective in certain situation; particularly on a “high functioning” team.
Now, you’re right about the industry consensus on confronting providing the best outcomes and usually as the favorable approach… It is! You just have to know when you have the OPPORTUNITY to use it, and how to employ it.
(I’m a PMP and a “seasoned” Construction PM) Good luck to you!
I should add; collaborating and confronting are cross from parallels. That might be confusing you. If you read the Thomas-Kilman Conflict Mode Instrument; that definition of collaboration is very close to confronting. That and correctly diagnosing the issue goes hand in hand.
However, collaboration is less optimal since it takes time. Every time a conflict comes up; there’s not always time to have a campfire and roast marshmallows. I think the PMBOK is trying to show that finding the root problem, is not always an outcome of collaboration.
You said that:
‘No credible source can provide us with the “one and only” way, or the best way for all management situations.’
I am agree with you on it.
Again you’ re saying:
The PMBOK does not say (quoting you) “applying the same technique to all conflicts” would be justified.
I’m totally agree with you here again, and in fact to prove this point I wrote this blog post. In this blog post I’m only trying to say that PMBOK does not say that you should apply one technique on all conflicts.
I would agree on collaborating is best solution and that also eventually goes to the root cause and as well buys in everybody OK which is a permanent solution than confronting/problem solving.
for the purpose of get few marks we have to choose confronting !
Thanks for agreeing with me.
I feel Fahad is right. Collaborating is the best technique to resolve the conflicts. In most of the real situations , we need all the team members to get along / participate without any grudges. This technique generally helps to take all the team members towards goals without hurting individual’s self esteem. Confronting can not be win – win always. I feel usage of techniques depends upon situation and project managers understanding.
thank you for this post. I really liked it. Although I am still not sure I fully understand the difference between confonting and collaborating. Are there any specific features of these techniquest that can help differentiate them clearly? Currently, I have a feeling that Confronting and Collaborating are almost the same thing
In collaborating, you incorporate multiple viewpoints and negotiate for the best solution. It is a win win approach, on the other hand confronting is problem solving technique. In confronting you will find the root cause of the problem and then reach to its solution. Confronting is a win lose situation.
I was going through the above comments where you mentioned that confronting is a win-lose situation. But if go by Rita Mulcahy , she mentioned confronting as Win-win situation. Even in some of the multiple choice questions is it considered as win-win situation. can you please help to understand this better. Thanks in advance.
Regards, Gagan
In problem solving one loses and other wins regardless of who is on right path.
Not exactly. 2 people may be, dont have any right path, they go to discussion/argument to figure out what is the best way to deal with the conflict.
Confronting/problem solving includes: – Find the root cause of problem, not what is presented to you or what appears to be the problem – Analyze the problem – Identify solution – Pick a solution – Implement a solution – Review the solution and confirm that the solution can deal with the problem.
Hence, Confronting is win-win situation. Win-lose situation refer to Forcing solution (1 win, 1 lose)
Two team members are having conflict, most of the time one is correct and other is wrong.
In this case, if you go for the confronting then obviously the person who is in right path will win and other loses.
Collaborating does not necessarily fix the problem and may show up again, only Confronting does this, it gets to the “root cause”
Yes, you are right but it does not mean that the project manager should always go for confronting.
A project manager has to decide that which technique suits best to the situation.
I see your point thank you.
You are welcome.
What technique is used when a PM suggests to the Team members to contribute their respective PROS and CONS about the issue at hand and then suggests they discuss it. Is this collaborative or confronting?
It depends on what resolution he takes at the end. If he combines multiple view point and find the best agreeable solution, then it will be collaborative. And if he takes resolution of conflicts based on only facts then it will be confronting.
I think confronting will work here because PM trying to go to the root cause of this problem
You may be right but only discussion does not mean that he will chose the confronting. He may also go with the collaborative technique or try to smooth the situation. All depends on the situation and problem at the hand.
Yes you are absolutely right ! good
Thanks for agreeing with me! :)
I like your post very much and am in a project management class right now. Although confronting has a negative connotation, it is not always such. Confronting a problem and dictating how it should be resolved is the PM's job and if the other techniques do not work this approach should be taken. PM'S will run into personalities that will have a conflict with everything or everyone. Taking a direct confrontational approach may be required and should not be seen as a negative componant. Your assessment is great and accurrate.
Thank you for liking my post.
My point is—there is no single universal technique which applies to all conflicts and the PMBOK Guide does not recommend using conflict resolution technique every time a conflict occurs.
good I appreciate yourwork I using as a projects references
Thanks Nasry.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Data Center
The 3 pillars of successful collaborative problem solving.

We already covered quite a lot of ground when it comes to assuming a leadership position and building a positive team environment . But there is still one topic missing: how can you bring the best out of the group efforts? How can you stimulate people to solve problems together and to join forces towards a common goal?
This article will cover the subject of collaborative problem solving, and we will explore its many dimensions and particularities. While there are certain situations where individual decision making is recommended, there is a wide body of research that shows group decisions as superior to individual ones. Groups usually bring more background information, different perspectives, and a broader range of solutions to the problem at hand.
While there are many components to analyze in collaborative problem solving, we will focus on three during this article:
Analyzing the Problem from the Perspective of the Group
- Managing Conflict within a Group
- Creating an Environment for Continuous Learning
People have different approaches to problem solving. Some prefer to go with their guts and solve the problems as they come without looking at the big picture or at possible consequences of a choice; others – like me – prefer to conduct a more detailed analysis of the different possible scenarios and to try to forecast the most likely implications of each decision.
Bringing together people with different attitudes definitely has its benefits, but you should keep an eye for the conflicts that might arise. People who rely on their guts might simply become annoyed by the level of details demanded by the more rational fellows. These, on the other hand, might not like the quick decisions made by intuitive people and decide to become less active in the project.
It is important to understand that there are both risks and benefits to group problem solving. However, if the situation is managed properly, the benefits usually outweigh the risks.
The 7-Steps Divergent-Convergent Method for Problem Analysis
We already discussed several brainstorming techniques for managing risks in a project . Brainstorming, however, is just one of the steps in solving problems collaboratively, so let’s discuss a more general framework to address the issue. But before, I would like to make a quick remark. As the leader of your team , it is your responsibility to provide an established method for solving the challenges your project faces. If you use a different method each time you get together to discuss an issue, it will take time for your team to adapt and the members might feel a bit lost. Therefore, a recommended practice is to develop a unified framework that is both broad enough to be useful in most future situations and practical enough to be easily implemented. This standardization also addresses the problem of different perspectives, since all the members are aware of the steps involved in the process.
While there are many variations and possibilities to create a framework for collaborative problem solving, I am particularly fond of a 7-steps divergent-convergent approach presented by this Project Management Book . The figure below details the steps, and the following discussion explains each one.
Step 01 – Identifying the Problem
Identifying the problem is the most critical part of problem solving because it directs all the following project efforts. If a rocket is not perfectly aligned at the launching time, there is almost nothing the crew can do to fix the situation. In competitions such as Bobsleigh, the beginning is the most crucial moment. The same is valid for our projects: if we don’t start right, we will not finish right.
Step 02 – Identifying the Real Cause of the Problem
What is actually causing your company to lose money? Is it low demand (i.e. the market’s “fault”) or a bad product (i.e. your fault)? How can you identify it?
Looking for the source of the problem is a process that might require some time and the analysis of several sources of data. Regarding our previous question, how can you identify if it’s the general demand that is low or if it’s a flaw in your product that is making people run away? Looking at the competitors’ situations is a good start. How are they doing in the market? Are they successful? If yes, then chances are high that the customers are leaving you because they don’t like your product or service. If you want to dig deeper into the cause of it, look at past data from your company. At which exact moment did you experience losses in the number of customers? After which update? What does your competition have that you don’t?
Looking for the real source of the problem is much more efficient if you have multiple perspectives, so group decision earns a plus point here. Different heads eliminate the confirmation bias of an individual decision maker.
Step 03 – Setting the Prerequisites for Your Solution
What does the final solution for the problem look like? When will you achieve it? The prerequisites of a solution define exactly that: the ideal conditions of solving the problem at hand. In our previous example, we can think of several intermediate and final requirements for the solution: broadly speaking, our problem will be solved when we implement a product that not only solves the previous flaws but also meets the demands of the market. The discussion about how to create a highly effective work breakdown structure might prove itself useful in identifying the different components of the problem and in establishing a precise end-point to the process.
Step 04 – Generating Alternatives
This is the time when brainstorming is most useful. Once you specify where you want to go, it is time to start thinking about how to get there. Naturally, creativity is something that requires time, and the creative process might even seem inefficient to some. This step, however, is extremely important in solving problems, since one among the alternatives generated will be the base for the future work. Therefore, you should really spend some time here to make sure that you have a very relevant (doesn’t need to be exhaustive though, that’s impossible) list of alternatives from which you can choose the best one for the moment.
Step 05 – Selecting an Alternative among the Options
If you don’t have good options, you will not have a good solution. Now it is time to scrutinize the alternatives created by using the prerequisites defined earlier. You might want to look at both qualitative and quantitative components of an alternative, and search for the one that offers the highest benefits at the lowest costs. Evidently, this is not an easy step: there is a lot of uncertainty going on, and it is simply not possible to know for sure which alternative is the absolute best to solve your problem.
Step 06 – Performing a Risk Analysis and a Cost-Benefit Evaluation of the Alternative
This is why the next step involves performing a risk analysis and a profit vs. cost evaluation of the selected alternative. It might be the case that, after looking at the risks involved and at the potential profits, the team decides to go back and choose another possible solution. This is totally fine and is part of the process, but you should also consider what made you choose the wrong alternative in the first place. Maybe you overlooked a critical component? Maybe you did not consider the consequences and the costs in details? If you want to improve your problem solving skills, it is not enough to correct wrong decisions. You have to look back and identify why the wrong decision was made, which data was missing, and how you can fix it to improve future decision making.
Step 07 – Create a Plan of Action
Once you have chosen which alternative to pursue, it is time to create an actionable plan to implement it. I explore in details the art of creating a work breakdown structure in a separate article, and the process can be used here as well.
How to Manage Conflict within Your Project Team
Any group working on the same project is destined to fight. Conflicts might happen early in the course of the project, or they might come in more advanced stages. It’s not an “if”, but a when” matter. So what should you do when they appear? Should you simply run away and try to avoid all types of conflict? Should you just assume a totalitarian approach and impose yourself as the boss and holder of the right opinion? Hopefully I don’t even need to answer these questions for you. But while many people see conflict as something negative to the health of the project, I would like to propose a way to look at conflict as a positive step in collaborative problem solving. What if you could use conflict to boost the performance of your team? Wouldn’t that be great?
The two main problems that conflicts cause are (1) making the wrong decision, and (2) damaging team relationships. While making the wrong decision is quite straightforward to solve – you just need to carry a rational analysis of the consequences of the action -, managing the relationships is a bit harder. This happens because, well, if there is conflict in the problem solving process, there will inevitably be a losing side. The key is to find a way to work together with your team in order to show to everyone why certain decisions are made, as well as to maintain a good relationship among all team members.
So before we move to the right way of dealing with conflict, let’s have a look at the wrong way of doing it.
4 Wrong Ways of Dealing with Conflict

Avoiding or Moving Away from the Conflict
This happens quite often. When people see they will not win the argument, they sometimes just walk away. It’s the “I prefer leaving rather than admitting I was wrong” mindset. From a leader perspective, the issue is a bit broader: you might not only want to avoid your personal conflicts, but you may also choose to withdraw from conflicts in your team. If two people disagree on something, walking away and not acknowledging that there is a conflict is one of the worst ways to deal with it. If the conflict is an actual problem – and not just a discussion about whether cats are better than dogs -, walking away will just postpone the matter until you can’t hide anymore. The problem is: if you can’t hide, it means the problem has become really big. So, instead of running away at the first sign of conflicts, acknowledge their presence and work together with your team to solve them.
Hide or Smooth Over the Conflict
While this might be a suitable short-term solution, prioritizing relationships over decisions will cause you to do suboptimal choices. Camouflaging conflicts is the practice of “ focusing on the positive side ” of the relationships instead of looking at the whole picture. Even though this hides the problem, it doesn’t solve it.
Forcing the Solutions of Disagreements
This is one of the main differences between leaders and bosses . The boss will normally approach the conflict as something negative and, if no agreement is reached, will impose his or her own opinion grounded on the fact that “he (or she) is the boss”. The boss might do it through raising his voice, laughing at your idea, or just the argument that he is the decision maker.
Hopefully, the destructive nature of such approach is as clear for you as it is for me. Forcing a decision impacts negatively both components of conflict: it does not ensure that the right decision will be made, and it for sure damages the relationships in the project team.
Accepting a Lose-Lose Solution
If not everyone can have it, then nobody will have it. This approach usually involves reducing the solution to give both parts of the conflict a “fair share”: both of them don’t get exactly what they want, but in the end they are somewhat satisfied because the other side didn’t get it either. Despite sounding “fair”, this approach is as bad as the previous one in a sense that it also impacts negatively both components of the conflict: there is no guarantee that relationships will be improved, and the results will certainly be suboptimal.
The Right Way of Dealing with Conflict – Confronting It
Now that we know what not to do, it is time to talk about what to do when there is a conflict to solve.
The first step is to try to prevent the conflict. And I’m not talking about a laissez-faire approach of letting your team move by itself in the hope that if no active actions are taken, no real conflicts will arise. I’m talking about actively setting up the environment in order to maximize the chances of “conflictless” collaborative problem solving. Have a look at the article on how to build a positive team environment in order to get great insights on how to manage your project environment.
If, despite your efforts, the conflict still happens, it is your job to acknowledge it. Make it clear to people why there is a conflict, what is the subject or decision related to it, and how people are dealing with the situation. Normally the disagreement will be about some aspect of the project, and not about the people working on the team. Therefore, acknowledging the problem will help you detach it from the personal level and avoid hurting people.
Once the conflict is acknowledged, it is time to position it in the context of the project. Which components of the project will be affected by the decision at hand? Do you have to solve the conflict now or can you wait for more information before issuing an ultimatum?
We already agreed that forcing a decision is not helpful at all. So on what should you focus if not on positions? My suggestion is to try to understand the interests of each part. What are they looking for? If people are asking for more memory on the computers you are about to buy, why do they need it? Is it a sensible argument? Interests, goals, and requirements will give you a better understanding of what each side is trying to achieve with the decision at hand. This, in turn, will help you manage the conflict more efficiently than before.
Once you have a good understanding of the problem, it is time to discuss the alternatives. We already discussed it earlier in this articles, so I will not go through everything again. The process is pretty similar to the steps 04 and 05 in the divergent-convergent framework for problem solving .
Ok, I know it all sounds wonderful in theory, but the problems start when we move to practice. Well, I’m sorry to disappoint you, but there is not much more I can do here apart from discussing the general guidelines for dealing with conflicts. I simply cannot provide a detailed guideline to each and every specific situation you might encounter. This is why conflict management relies a lot on experience and on observing how the team behaves while working together. You must deeply understand the members of your team before you are able to provide a solution that fits all sides.
Creating the Environment for Continuous Learning
Continuous learning makes the third pillar of our successful collaborative problem solving framework. This concept has two sides: it encourages people to take more risks, and it helps learning and improvement through mistakes.
Creating the Right Culture for Continuous Learning
The speed and the efficiency with which people learn depend not only on themselves as individuals but also on the organizational culture that permeates the project team. If you punish every failure of your team members, do you really expect them to try something new? If you shout every time they give a different idea, do you really expect them to actively contribute during team meetings?
Here are a few guidelines that project managers can follow to speed up the process of continuous learning:
- Be accessible to your team and welcome new ideas and opinions.
- Ask for the opinion of your team members when discussing topics related to the project.
- Serve as a model of curiosity and humility.
- Encourage everyone to participate, despite the mistakes they might do during the process.
- Eliminate people’s fear of being punished because of their mistakes.
- Praise the team members when they are successful in accomplishing a task or when they offer valuable input to a situation.
The idea of continuous learning is kind of a consequence of what we already discussed. Having a good set of ground rules , listening actively to your team members, and promoting honest discussions are just a few among the many key elements that define an effective culture for continuous learning. Here are a few other components that you want to keep in mind:
Notice and Question Assumptions
This is really a skill for life. Learning how to question assumptions and how to properly address them brings you a much more complete understanding of the reality around you. I’ve experienced that myself, and I would never choose to remain ignorant to this skill. In the context of project management, questioning assumptions is about questioning the basis of your information. What are the statements on which you are grounding your analysis? What is the evidence behind each statement? Are your assumptions in accordance to your data?
Make Learning a Conscious and Recurring Activity
Many people think that learning is restricted to school and university. There is a time in life when you “study”, and there is a time when you “work”. What they are missing is the fact that these can (and should) be integrated into a broader concept of “learning to improve yourself”. Whether at university or at work, learning for self-improvement is the most effective way of learning new things. My own example comes in handy again (no, I’m not a narcissistic person). In high school, I would learn just for sake of entering university. I’ve spent 11 years of my childhood and adolescence studying every single basic field of science to literally flush it away of my mind after the final exams. I don’t really regret that, specially because regretting too long over the past brings unnecessary pain, but I wish it had been different. In any case, I am lucky to have learned my lesson early in life, while still in my early 20s. Now everything that I study, every single article I read, every post I write, everything is for the sake of developing a better version of myself day after day. I am learning consciously, and this makes all the difference.
Stimulate Creativity and Provide a Structured Approach To It
A structured approach to creativity, really? Are you serious? Hell yeah. Creativity is not a single event in our days. We don’t wake up and *poof!* “Now I am creative!” You might wake up and have a great idea right after opening your eyes, but this is just the tangible manifestation of days and months of apparently uncreative effort. The creative *poof* (or eureka, if you prefer), is just the tip of the iceberg. It is, however, the part that gets the most attention. And if you know a bit of psychology, you know that this conditions create the perfect scenario for the very interesting availability heuristic . In one sentence: the availability heuristic says that we judge the likelihood of an event based on how easily we can retrieve instances of similar situations from our memory. So if we just receive information saying that creativity is a magical moment, we will hardly ever see it as a laborious process. The truth, however, is that we must be disciplined and consume a lot of information before we are capable of producing valuable insights on our own.
Question the Goals, Scope, and Plan of the Project
Last but not least, you should always go back and take another look at the goals, scope, and plan of your project. There is a well-known saying: “Every new information modifies a decision.” Continuous learning presupposes reviewing early decisions once you have gathered more data in the course of the project.
Final Words
And with this article we are done covering the three most important aspects of how to effectively manage a team. There is much more to discuss, I know, but these are the most fundamental skills you must incorporate before moving to other topics. Hopefully the article was helpful and see in the next post!
Start a Free Trial
Your 14-day trial comes with sample data for a quick evaluation
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Overview of the Problem-Solving Mental Process
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Rachel Goldman, PhD FTOS, is a licensed psychologist, clinical assistant professor, speaker, wellness expert specializing in eating behaviors, stress management, and health behavior change.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Rachel-Goldman-1000-a42451caacb6423abecbe6b74e628042.jpg)
- Identify the Problem
- Define the Problem
- Form a Strategy
- Organize Information
- Allocate Resources
- Monitor Progress
- Evaluate the Results
Frequently Asked Questions
Problem-solving is a mental process that involves discovering, analyzing, and solving problems. The ultimate goal of problem-solving is to overcome obstacles and find a solution that best resolves the issue.
The best strategy for solving a problem depends largely on the unique situation. In some cases, people are better off learning everything they can about the issue and then using factual knowledge to come up with a solution. In other instances, creativity and insight are the best options.
It is not necessary to follow problem-solving steps sequentially, It is common to skip steps or even go back through steps multiple times until the desired solution is reached.
In order to correctly solve a problem, it is often important to follow a series of steps. Researchers sometimes refer to this as the problem-solving cycle. While this cycle is portrayed sequentially, people rarely follow a rigid series of steps to find a solution.
The following steps include developing strategies and organizing knowledge.
1. Identifying the Problem
While it may seem like an obvious step, identifying the problem is not always as simple as it sounds. In some cases, people might mistakenly identify the wrong source of a problem, which will make attempts to solve it inefficient or even useless.
Some strategies that you might use to figure out the source of a problem include :
- Asking questions about the problem
- Breaking the problem down into smaller pieces
- Looking at the problem from different perspectives
- Conducting research to figure out what relationships exist between different variables
2. Defining the Problem
After the problem has been identified, it is important to fully define the problem so that it can be solved. You can define a problem by operationally defining each aspect of the problem and setting goals for what aspects of the problem you will address
At this point, you should focus on figuring out which aspects of the problems are facts and which are opinions. State the problem clearly and identify the scope of the solution.
3. Forming a Strategy
After the problem has been identified, it is time to start brainstorming potential solutions. This step usually involves generating as many ideas as possible without judging their quality. Once several possibilities have been generated, they can be evaluated and narrowed down.
The next step is to develop a strategy to solve the problem. The approach used will vary depending upon the situation and the individual's unique preferences. Common problem-solving strategies include heuristics and algorithms.
- Heuristics are mental shortcuts that are often based on solutions that have worked in the past. They can work well if the problem is similar to something you have encountered before and are often the best choice if you need a fast solution.
- Algorithms are step-by-step strategies that are guaranteed to produce a correct result. While this approach is great for accuracy, it can also consume time and resources.
Heuristics are often best used when time is of the essence, while algorithms are a better choice when a decision needs to be as accurate as possible.
4. Organizing Information
Before coming up with a solution, you need to first organize the available information. What do you know about the problem? What do you not know? The more information that is available the better prepared you will be to come up with an accurate solution.
When approaching a problem, it is important to make sure that you have all the data you need. Making a decision without adequate information can lead to biased or inaccurate results.
5. Allocating Resources
Of course, we don't always have unlimited money, time, and other resources to solve a problem. Before you begin to solve a problem, you need to determine how high priority it is.
If it is an important problem, it is probably worth allocating more resources to solving it. If, however, it is a fairly unimportant problem, then you do not want to spend too much of your available resources on coming up with a solution.
At this stage, it is important to consider all of the factors that might affect the problem at hand. This includes looking at the available resources, deadlines that need to be met, and any possible risks involved in each solution. After careful evaluation, a decision can be made about which solution to pursue.
6. Monitoring Progress
After selecting a problem-solving strategy, it is time to put the plan into action and see if it works. This step might involve trying out different solutions to see which one is the most effective.
It is also important to monitor the situation after implementing a solution to ensure that the problem has been solved and that no new problems have arisen as a result of the proposed solution.
Effective problem-solvers tend to monitor their progress as they work towards a solution. If they are not making good progress toward reaching their goal, they will reevaluate their approach or look for new strategies .
7. Evaluating the Results
After a solution has been reached, it is important to evaluate the results to determine if it is the best possible solution to the problem. This evaluation might be immediate, such as checking the results of a math problem to ensure the answer is correct, or it can be delayed, such as evaluating the success of a therapy program after several months of treatment.
Once a problem has been solved, it is important to take some time to reflect on the process that was used and evaluate the results. This will help you to improve your problem-solving skills and become more efficient at solving future problems.
A Word From Verywell
It is important to remember that there are many different problem-solving processes with different steps, and this is just one example. Problem-solving in real-world situations requires a great deal of resourcefulness, flexibility, resilience, and continuous interaction with the environment.
Get Advice From The Verywell Mind Podcast
Hosted by therapist Amy Morin, LCSW, this episode of The Verywell Mind Podcast shares how you can stop dwelling in a negative mindset.
Follow Now : Apple Podcasts / Spotify / Google Podcasts
You can become a better problem solving by:
- Practicing brainstorming and coming up with multiple potential solutions to problems
- Being open-minded and considering all possible options before making a decision
- Breaking down problems into smaller, more manageable pieces
- Asking for help when needed
- Researching different problem-solving techniques and trying out new ones
- Learning from mistakes and using them as opportunities to grow
It's important to communicate openly and honestly with your partner about what's going on. Try to see things from their perspective as well as your own. Work together to find a resolution that works for both of you. Be willing to compromise and accept that there may not be a perfect solution.
Take breaks if things are getting too heated, and come back to the problem when you feel calm and collected. Don't try to fix every problem on your own—consider asking a therapist or counselor for help and insight.
If you've tried everything and there doesn't seem to be a way to fix the problem, you may have to learn to accept it. This can be difficult, but try to focus on the positive aspects of your life and remember that every situation is temporary. Don't dwell on what's going wrong—instead, think about what's going right. Find support by talking to friends or family. Seek professional help if you're having trouble coping.
Davidson JE, Sternberg RJ, editors. The Psychology of Problem Solving . Cambridge University Press; 2003. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511615771
Sarathy V. Real world problem-solving . Front Hum Neurosci . 2018;12:261. Published 2018 Jun 26. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2018.00261
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
P-M Analysis Basics
P dash M Analysis is a systematic Problem-Solving Philosophy for Chronic Losses. The term P-M Analysis comes from the following origin: P – Phenomena(non), Physical; M – Mechanism, Relationship (Machine, Man/Woman, Material, Method)
When To Use P-M Analysis?
Root Cause Analysis
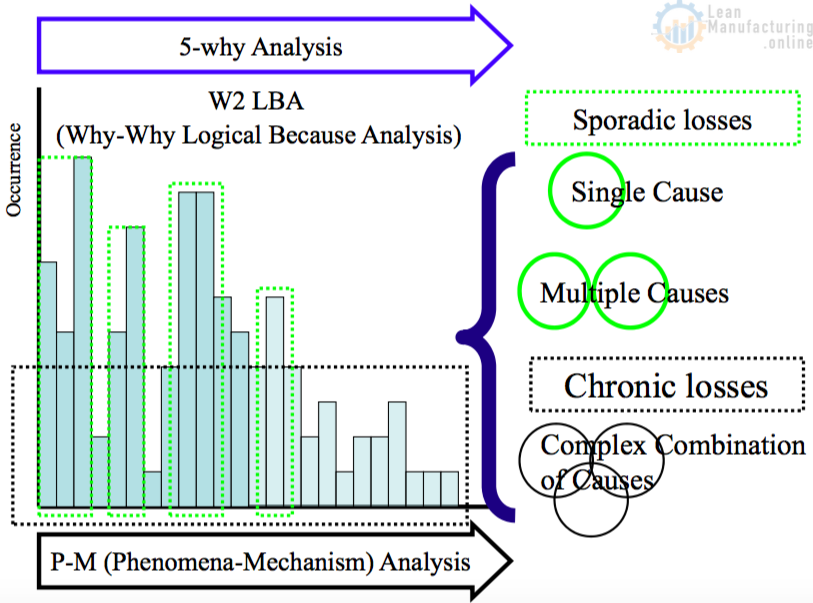
Two Types of Problem Solving Techniques
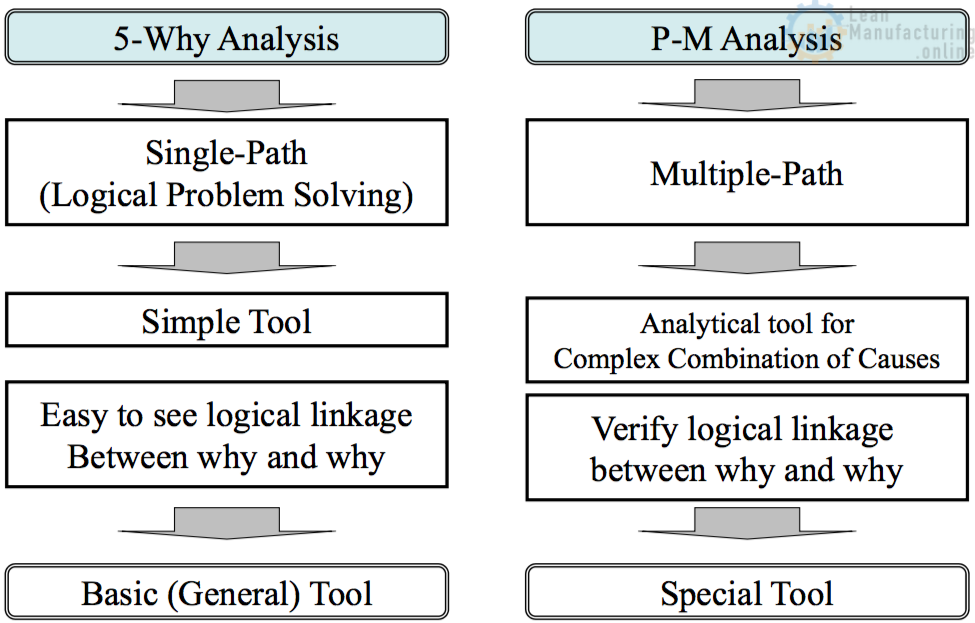
Why is the 5-why Analysis effective?
Problem: no.1 conveyor stopped..
What is Actually happening (Phenomenon):
Overload and the fuse blew.
Why-1 Why was there an overload? The bearing was not sufficiently lubricated.
Why-2 Why was it not lubricated sufficiently? The lubricating pump was not pumping.
Why-3 Why was it not pumping sufficiently? The shaft of the pump was worn and rattling.
Why-4 Why was the shaft of the pump was worn and rattling. There was no strainer attached and metal scrap got in.
Why-5 Why was no strainer attached?
There are no checking rules.
Action is taken for Root-Cause
How can we identify what is actually happening.
- Identify specific problems, which is the deviation between our expectations and actually happening.
- Before identifying specific problems, jump to action.
- Talking with just feeling.
The 5-why analysis must be used when to identify “ Phenomenon” What is “Phenomenon”.
Is (What is actually happening)
- The fact you observed with your eyes and numeric data.
- The fact without presumption
- Your own opinion, feeling.
5-Why Analysis vs. P-M Analysis

Features in P-M Analysis
P-m analysis.
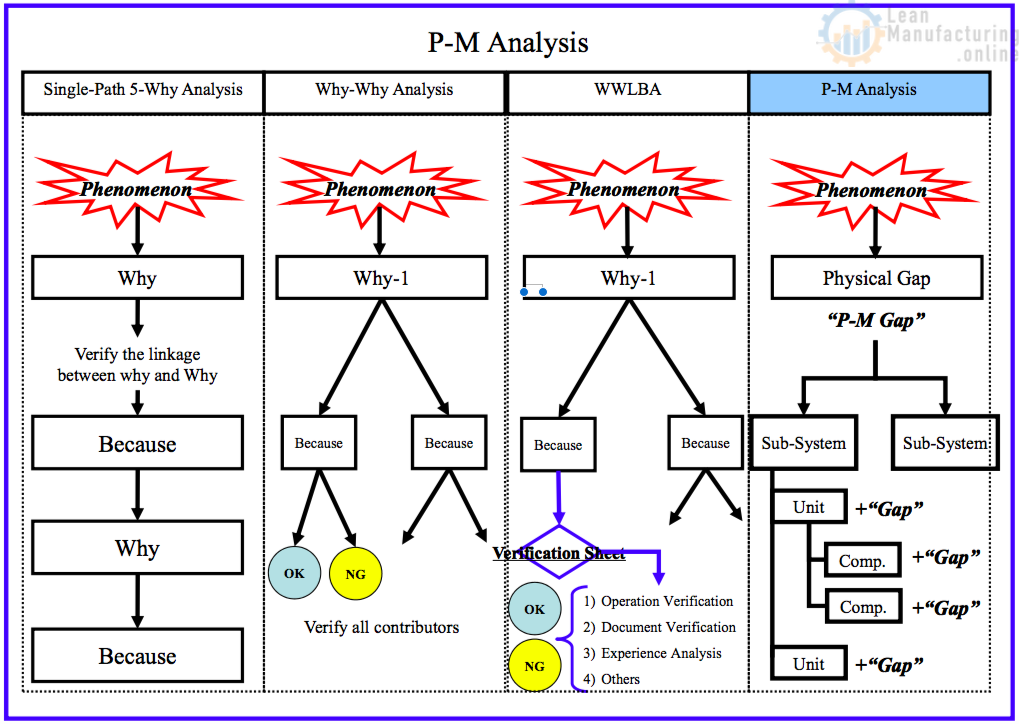
What % of Problems can be solved by P-M Analysis
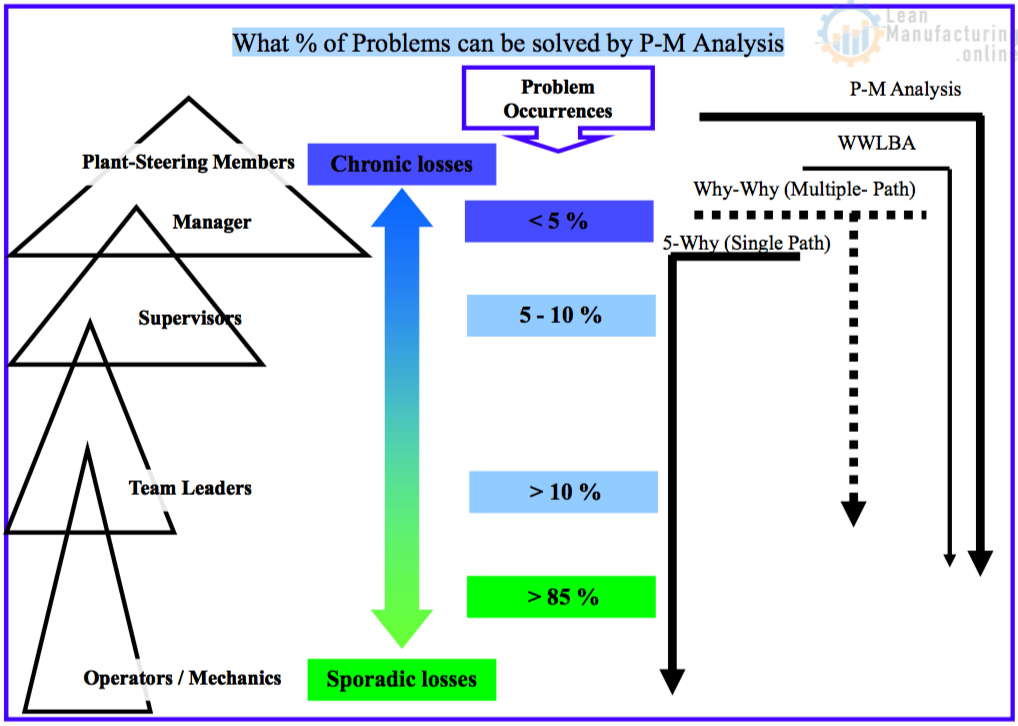
Steps of P-M Analysis
P-m analysis story board layout.
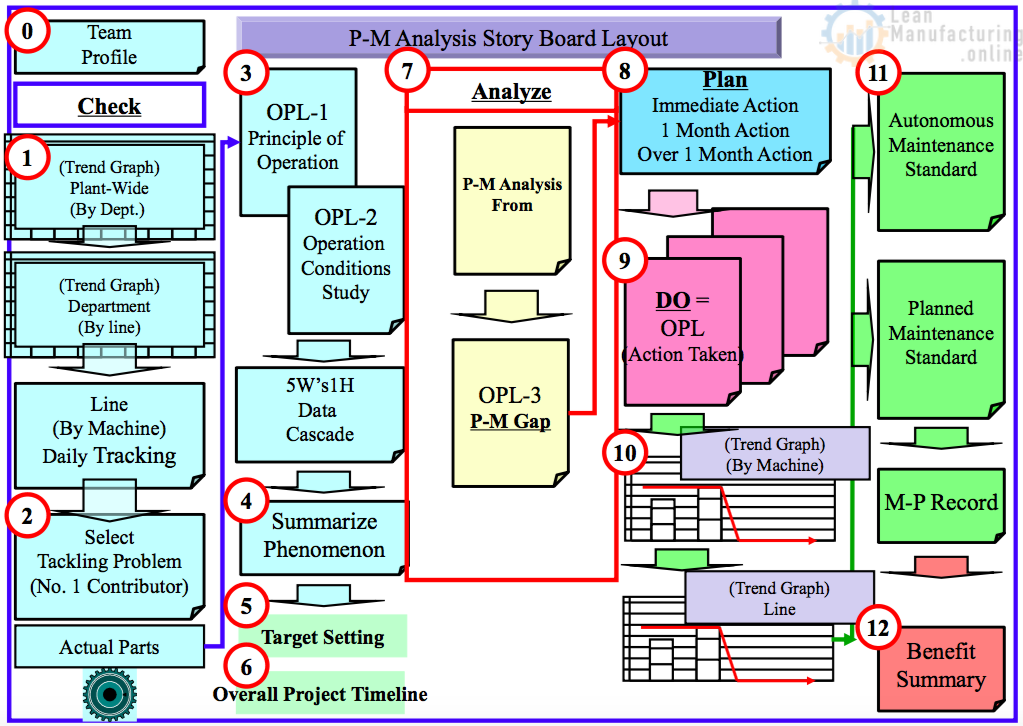
Problem-Solving Story by P-M Analysis
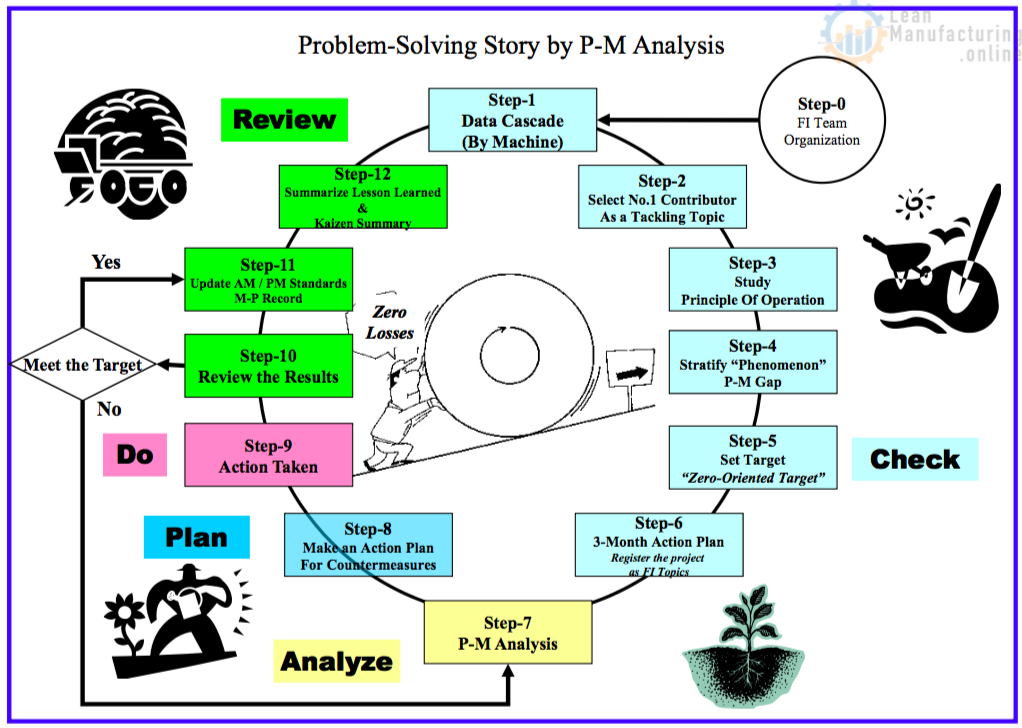
CAP-Do Cycle & P-M Analysis
- More By sensei
- More In Blog
Harnessing Business Excellence in Manufacturing Through the PDCA Approach
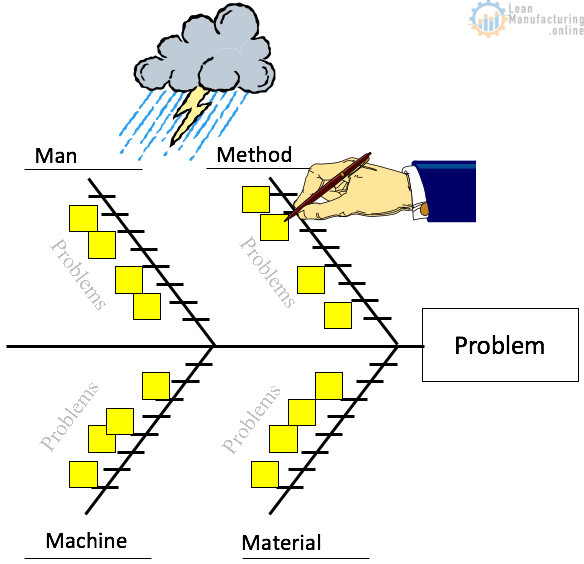
The Fishbone Diagram
Unlock the Power of Continuous Learning with Udemy’s Frequent Sales

How to Ace Your Next Job Interview: Expert Insights and Strategies

Mastering the Trio: Project, Program & Portfolio Management

The Evolution of Performance Reviews: From Annual Appraisals to Continuous Feedback

Behaviors that kill employee motivation

Common Interview Questions for Project Management Roles

The Pillars of Corporate Success: Key Responsibilities of Top Executives
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Most Popular

4M Analysis Process
The purpose of this procedure is to define the steps to do a 4M …

PDCA – A Process Approach

OPL – One Point Lesson Template – Free Download

5S Audit Checklist and Report

Why-Why Analysis
Blog Search

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- About Our Ads

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Problem-Solving Steps in Project Management. While the process you choose to solve problems may vary, here is a seven-step framework many project managers use. This problem-solving method combines primary and secondary problem-solving steps. #1. Define the Problem. Gather data and information from key stakeholders, team members, and project ...
Problem Solving is one of the Tools & Techniques used for Managing Quality and Controlling Resources. Modules 8 and 9 of the PM PrepCast cover Project Quality Management and Project Resource Management. Consider this study program if you're preparing to take your CAPM or PMP Certification exam. Disclosure: I may receive a commission if you ...
The simple six-step process outlined below will help you master effective problem-solving — a skill that will provide you with the ability to bring a new perspective to problems, helping you to design, and implement, effective solutions. Step #1: Identify the Problem. First, make sure you're dealing with the realproblem, not just its symptoms.
Problem Solving: Willpower. All of the above may be quite fascinating, but if the project manager is not committed to their work and to improving themselves in problem solving, everything is pointless. There are exercises you can do to master problem solving skills that help you respond better to problems and solve them quickly.
Product Manager Interview Problem Solving Questions. Over 2,500 product manager interview questions from the best tech companies in the world. Post Question.
Choose. Now that you've analyzed the problem and understand contributing factors, identify the areas to address first. Your team likely can't address all elements of a problem at once, so they need to prioritize solutions in ways that will give the project the best ROI of energy and time. 4. Implement.
How Wicked Problem Solving Works. This interactive course and toolkit will teach you how to bring yourself or your team, from irresolution to resolution, using a simple, powerful, scalable approach to tackle any problem and make solutions visible. Watch quick videos, then get hands-on experience working through your problems in your companion ...
7. Problem solving. Problem solving skills are collaborative, iterative skills that help you approach a problem and, ultimately, solve it. Developing problem solving skills isn't about always having the "right" answer to every problem—rather, people with great problem solving skills practice approaching problems from new perspectives ...
What is the CIRCLES Method? The CIRCLES method is a problem-solving framework that helps product managers (PMs) make a thorough and thoughtful response to any design question.. The seven linear steps of the process form the CIRCLES acronym: Comprehend the situation; identify the customer; report the customer's needs; cut, through prioritization; list solutions; evaluate tradeoffs, and ...
All the analytical techniques revolving around problem-solving center around having great teamwork. Techniques like Brainstorming, Root-cause analysis, and Fishbone (Ishikawa) diagram can only be ...
IntroductionTo solve seemingly impossible problems, you can't always make a "best guess" and hope for the best. The tendency to jump to conclusions results in costly mistakes. Hunches, instinct and pure intuition may be inspiring, but they can lead to unforeseen problems and erroneous decisions that can lead to the project's death. Problem solving today is a totally different animal.Problem ...
🚀 Take the 1st step in Product Management with our Live Program - https://pmschool.io/course/ 🔔 Subscribe to our channel - https://tinyurl.com/ne4jc2dcHey ...
Solving framework: Lay the Approach: To begin with, always layout your approach on how you're going to solve the question. First, I'll discuss the problem in depth to make sure I understand it correctly. Then we can discuss the business situation and our objective in details.
Lean Six Sigma (LSS) problem solving tools - 8D analysis, cause-effect analysis, root cause and corrective action, and others - provide a disciplined approach to solving complex technical problems. Following LSS practices helps teams move methodically from observed symptoms to drill down to the source of problems, in order to implement ...
6. Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD) One of the best approaches is to create a safe space for a group to share and discover practices and behaviors that can help them find their own solutions. With DAD, you can help a group choose which problems they wish to solve and which approaches they will take to do so.
Withdraw/Avoid. Smooth/Accommodate. Compromise/Reconcile. Force/Direct. Collaborate/Problem Solve. These conflict management strategies are also known as Thomas-Kilmann's five approaches to resolving conflict. Let's discuss each technique in detail. #1. Withdraw of Avoid.
1. Define the problem. Diagnose the situation so that your focus is on the problem, not just its symptoms. Helpful problem-solving techniques include using flowcharts to identify the expected steps of a process and cause-and-effect diagrams to define and analyze root causes.. The sections below help explain key problem-solving steps.
Every great answer in the PM interview will follow the same general format, regardless of the question. Use a simple framework to keep your ideas organized during PM interviews. Listen: Actively listen and take notes as your interviewer talks. Clarify: Ask questions to better understand the problem. Pause: Stop and think before blurting out an ...
Problem solving is an essential team skill in successful project teams. We explore how you can stimulate your team to work together and face the projects challenges in the most efficient way!. PM Course - The 3 Pillars of Successful Collaborative Problem Solving - Celoxis®
Adaptive reasoning and problem-solving skills have become increasingly important in project management, where decisions based on sometimes sparse, voluminous, or contradictory data must be dealt with, verified and conveyed to a diversity of team members - often under stressful, time-sensitive circumstances. In such situations, project ...
Problem-solving is a mental process that involves discovering, analyzing, and solving problems. The ultimate goal of problem-solving is to overcome obstacles and find a solution that best resolves the issue. The best strategy for solving a problem depends largely on the unique situation. In some cases, people are better off learning everything ...
In the beginning of my career as PM, I struggled in solving problems and asked my peers and leaders to know how they solve problems, and they recommended a book about problem solving: Problem ...
Problem-Solving Story by P-M Analysis. CAP-Do Cycle & P-M Analysis. CAP-Do Cycle Process. P-M Analysis Step. Check. 1-1 Analyze the "Gap" between Target and Actual situation. 1-2 Prioritize No.1 Contributor as FI Theme (Topics) 1-3 Stratify Problem into Phenomenon. Step-1.