- Graduate School
- Prospective Students
- Graduate Degree Programs

Doctor of Philosophy in Linguistics (PhD)
Canadian immigration updates.
Applicants to Master’s and Doctoral degrees are not affected by the recently announced cap on study permits. Review more details
Go to programs search
Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. Linguists are interested in questions such as the following:
- What are the structural properties of languages, at the level of sounds, words, sentences, and meaning?
- To what extent are the languages of the world similar or different?
- How is language acquired, by children and in adulthood?
- How is it processed in the mind/brain?
- How do people produce and perceive speech?
- How do languages change over time?
Linguistics is a highly interdisciplinary field which combines research methods from the humanities and the social, natural, and mathematical sciences.
Research in the Department covers a broad range of topics, with substantial coverage of syntax, semantics, morphology, phonetics, phonology, and pragmatics. We approach these topics from several different research traditions and backgrounds, with particular strengths in formal-theoretical linguistics, experimental and field linguistics, acquisition, and computational approaches to the study of communicative behaviour. These research areas intersect and overlap considerably, and faculty and students are often simultaneously involved in more than one area. This is part of the attention paid to interfaces between traditional subfields of linguistics and methodological traditions (e.g., laboratory phonology, gesture and speech and learning), one of the great strengths of the Department.
The Department also has a strong commitment to the study of Languages of the Americas, with particular focus on First Nations Languages of Canada, in the areas of documentation and theoretical research, something for which it is well known. Research is not restricted to Languages of the Americas, however; the department also has a long history of work on African languages and there is ongoing research on languages within the Indo-European, Japonic, Sino-Tibetan, and Uralic families as well as Korean.
For specific program requirements, please refer to the departmental program website
What makes the program unique?
Our linguists focus on data in all its forms – not just fieldwork, but also high-quality research in labs with cutting-edge resources and tools, such as those found and developed in the Communication Dynamics Lab, the Interdisciplinary Speech Research Lab , the Language and Learning Lab , the Speech In Context Lab , and the Phonological CorpusTools working group.
Students in the Department of Linguistics are given the opportunity to head out into the field and get their hands dirty. Many of the members of our department, from undergrads and grad students to post-docs and faculty members, work directly with language consultants to describe, analyze and revitalize the languages of the world.
Linguists in the department have active working relationships with scholars from many different disciplines and from across the UBC campus, across the country, and across the world.
Our students are actively engaged in research from the moment they enter the department, and they have an excellent track record of publishing and presenting their work at national and international conferences.
UBC Linguistics has an intellectually nourishing, well-respected, and diverse curriculum and research program.

Starr Sandoval
Quick Facts
Program enquiries, admission information & requirements, 1) check eligibility, minimum academic requirements.
The Faculty of Graduate and Postdoctoral Studies establishes the minimum admission requirements common to all applicants, usually a minimum overall average in the B+ range (76% at UBC). The graduate program that you are applying to may have additional requirements. Please review the specific requirements for applicants with credentials from institutions in:
- Canada or the United States
- International countries other than the United States
Each program may set higher academic minimum requirements. Please review the program website carefully to understand the program requirements. Meeting the minimum requirements does not guarantee admission as it is a competitive process.
English Language Test
Applicants from a university outside Canada in which English is not the primary language of instruction must provide results of an English language proficiency examination as part of their application. Tests must have been taken within the last 24 months at the time of submission of your application.
Minimum requirements for the two most common English language proficiency tests to apply to this program are listed below:
TOEFL: Test of English as a Foreign Language - internet-based
Overall score requirement : 90
IELTS: International English Language Testing System
Overall score requirement : 6.5
Other Test Scores
Some programs require additional test scores such as the Graduate Record Examination (GRE) or the Graduate Management Test (GMAT). The requirements for this program are:
The GRE is optional.
2) Meet Deadlines
3) prepare application, transcripts.
All applicants have to submit transcripts from all past post-secondary study. Document submission requirements depend on whether your institution of study is within Canada or outside of Canada.
Letters of Reference
A minimum of three references are required for application to graduate programs at UBC. References should be requested from individuals who are prepared to provide a report on your academic ability and qualifications.
Statement of Interest
Many programs require a statement of interest , sometimes called a "statement of intent", "description of research interests" or something similar.
Supervision
Students in research-based programs usually require a faculty member to function as their thesis supervisor. Please follow the instructions provided by each program whether applicants should contact faculty members.
Instructions regarding thesis supervisor contact for Doctor of Philosophy in Linguistics (PhD)
Citizenship verification.
Permanent Residents of Canada must provide a clear photocopy of both sides of the Permanent Resident card.
4) Apply Online
All applicants must complete an online application form and pay the application fee to be considered for admission to UBC.
Tuition & Financial Support
Financial support.
Applicants to UBC have access to a variety of funding options, including merit-based (i.e. based on your academic performance) and need-based (i.e. based on your financial situation) opportunities.
Program Funding Packages
The Department of Linguistics guarantees funding of $25,500 plus the cost of tuition per annum for the first two years of the MA program and the first five years of the Ph.D. program to all students accepted to our graduate programs.
Please note that as a condition for receiving this funding you will be expected to apply for any scholarships you are eligible for, either UBC-internally or from your home country.
Funding packages are made up of scholarships, research assistantships, and teaching assistantships depending on individual students, year of study, and the financial resources of the department.
Average Funding
- 15 students received Teaching Assistantships. Average TA funding based on 15 students was $11,724.
- 10 students received Research Assistantships. Average RA funding based on 10 students was $14,683.
- 4 students received Academic Assistantships. Average AA funding based on 4 students was $6,612.
- 18 students received internal awards. Average internal award funding based on 18 students was $14,833.
- 3 students received external awards. Average external award funding based on 3 students was $20,333.
Scholarships & awards (merit-based funding)
All applicants are encouraged to review the awards listing to identify potential opportunities to fund their graduate education. The database lists merit-based scholarships and awards and allows for filtering by various criteria, such as domestic vs. international or degree level.
Graduate Research Assistantships (GRA)
Many professors are able to provide Research Assistantships (GRA) from their research grants to support full-time graduate students studying under their supervision. The duties constitute part of the student's graduate degree requirements. A Graduate Research Assistantship is considered a form of fellowship for a period of graduate study and is therefore not covered by a collective agreement. Stipends vary widely, and are dependent on the field of study and the type of research grant from which the assistantship is being funded.
Graduate Teaching Assistantships (GTA)
Graduate programs may have Teaching Assistantships available for registered full-time graduate students. Full teaching assistantships involve 12 hours work per week in preparation, lecturing, or laboratory instruction although many graduate programs offer partial TA appointments at less than 12 hours per week. Teaching assistantship rates are set by collective bargaining between the University and the Teaching Assistants' Union .
Graduate Academic Assistantships (GAA)
Academic Assistantships are employment opportunities to perform work that is relevant to the university or to an individual faculty member, but not to support the student’s graduate research and thesis. Wages are considered regular earnings and when paid monthly, include vacation pay.
Financial aid (need-based funding)
Canadian and US applicants may qualify for governmental loans to finance their studies. Please review eligibility and types of loans .
All students may be able to access private sector or bank loans.
Foreign government scholarships
Many foreign governments provide support to their citizens in pursuing education abroad. International applicants should check the various governmental resources in their home country, such as the Department of Education, for available scholarships.
Working while studying
The possibility to pursue work to supplement income may depend on the demands the program has on students. It should be carefully weighed if work leads to prolonged program durations or whether work placements can be meaningfully embedded into a program.
International students enrolled as full-time students with a valid study permit can work on campus for unlimited hours and work off-campus for no more than 20 hours a week.
A good starting point to explore student jobs is the UBC Work Learn program or a Co-Op placement .
Tax credits and RRSP withdrawals
Students with taxable income in Canada may be able to claim federal or provincial tax credits.
Canadian residents with RRSP accounts may be able to use the Lifelong Learning Plan (LLP) which allows students to withdraw amounts from their registered retirement savings plan (RRSPs) to finance full-time training or education for themselves or their partner.
Please review Filing taxes in Canada on the student services website for more information.
Cost Estimator
Applicants have access to the cost estimator to develop a financial plan that takes into account various income sources and expenses.
Career Outcomes
31 students graduated between 2005 and 2013: 3 graduates are seeking employment; for 1 we have no data (based on research conducted between Feb-May 2016). For the remaining 27 graduates:
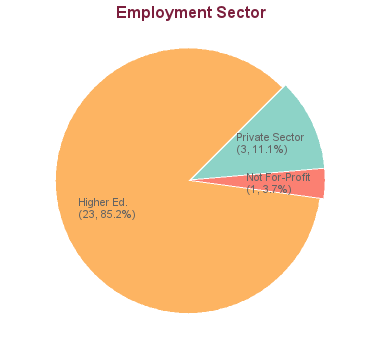
Sample Employers in Higher Education
Sample employers outside higher education, sample job titles outside higher education, phd career outcome survey, career options.
UBC’s Department of Linguistics alumni have a longstanding history of individual achievements and collective success. Since the first Department of Linguistics courses were offered at the University in 1967, our alumni have made a mark for themselves internationally and in a vast diversity of careers.
Enrolment, Duration & Other Stats
These statistics show data for the Doctor of Philosophy in Linguistics (PhD). Data are separated for each degree program combination. You may view data for other degree options in the respective program profile.
ENROLMENT DATA
Completion rates & times.
- Research Supervisors
Advice and insights from UBC Faculty on reaching out to supervisors
These videos contain some general advice from faculty across UBC on finding and reaching out to a supervisor. They are not program specific.

This list shows faculty members with full supervisory privileges who are affiliated with this program. It is not a comprehensive list of all potential supervisors as faculty from other programs or faculty members without full supervisory privileges can request approvals to supervise graduate students in this program.
- Abdul-Mageed, Muhammad (Artificial intelligence (AI); Deep Learning; Natural Language Processing; Machine Learning; Computational Linguistics; Social Media Mining; Arabic)
- Babel, Molly (Linguistics; Phonetics; Recognition of Speech; Perception and Representation; Acoustics; Dialects; acoustics of speech production; phonetic variation; speech perception; spoken word recognition)
- Bochnak, Ryan
- Davis, Henry Thomas (First Nations languages)
- Dechaine, Rose-Marie (Native American languages; Algonquian language family, Cree, Blackfoot, Ojibwe; French / English bilingualism policy; formal linguistics; generative grammar (Chomsky); West African languages (Niger-Congo, Yoruba, Igbo, Edo); Nigerian languages; literacy vs. oralcy; language planning re: French, Indigenous languages, Speech/gesture coordination, syntactic interface relations)
- Gick, Bryan (phonetics, speech science, speech motor control, speech perception, multimodal perception, tactile perception, ultrasound imaging of speech, sounds of the world’s languages, Physical mechanisms of speech production, speech research)
- Hall, Kathleen (Linguistics; Phonology; Phonetics; Laboratory Phonology)
- Hammerly, Christopher (Syntax & Morphology; Psycholinguistics; Anishinaabemowin (Ojibwe))
- Hansson, Gunnar (Linguistic structures (including grammar, phonology, lexicon and semantics); Cognitive sciences; theoretical phonology; morphology-phonology interface; phonological typology; historical linguistics (language change); locality relations; Icelandic)
- Hudson Kam, Carla (Language development, second language acquisition, critical periods for learning, input and language learning, language learning and language change, Psychology, First and second language acquisition, gesture and language learning, language contact and language change)
- Matthewson, Lisa (Linguistics; Semantics; Austronesian languages; Cross-linguistic variation and universals; Salish languages; Semantic fieldwork; Tsimshianic languages)
- Morzycki, Marcin (Linguistics; adverbial modification; degree modifiers; expressive meaning; grammar of modification; knowledge of meaning; measure phrases; modification of quantifiers; nonrestrictive modification; semantic restrictions on modifier order; Semantics, syntax, and their interface)
- Pulleyblank, Douglas (Linguistics; Phonology; Morphology; African languages; Yoruba)
- Rullmann, Hotze (Linguistics; Semantics)
- Silfverberg, Miikka Pietari (Natural Language Processing; NLP for morphologically complex languages; Morphological tagging; Parsing; Computational phonology and morphology; Deep Learning for NLP; Structured Prediction; Computational Semantics; Morphologically Complex Languages; Computational Linguistics)
- Soskuthy, Marton (language change; Computational modeling; Statistics; Phonetics; Cognitive systems)
- Tessier, Anne-Michelle (Linguistic structures (including grammar, phonology, lexicon and semantics); Constraint-based grammars; L2 production and perception in childhood; Language Acquisition; Lexical avoidance; Phonology; Prosodic processing with cochlear implants; Shitgibbons; U-shaped development)
- Zhu, Jian (Computational Linguistics, Natural Language Processing, Speech Sciences)
Doctoral Citations
Sample thesis submissions.
- Towards Afrocentric natural language processing
- Functional categorization parameters : argumenthood with functional heads other than D in Carioca Brazilian Portuguese and Pirahã
- Perception, recognition, and encoding of Cantonese sound change variants
- Aspects of the morphophonology of Dagaare
- Second-position clitics, from morphosyntax to semantics : the ʔayʔaǰuθəm (Comox-Sliammon) perspective
- Embodiment and emergent phonology in the visual-manual modality : factors enabling sublexical componentiality
- Post-stop fundamental frequency perturbation in production and perception of Mandarin stop voicing
Related Programs
Same specialization.
- Master of Arts in Linguistics (MA)
Same Academic Unit
- Master of Data Science in Computational Linguistics (MDSCL)
Further Information
Specialization.
Linguistics covers the core areas of phonetics, phonology, semantics, and syntax with the possibility of specializing in First Nations languages, African languages, first language acquisition, and experimental linguistics as well as specialized interaction with other disciplines such as art, computer science, music, philosophy, and psychology in the cognitive systems stream.
UBC Calendar
Program website, faculty overview, academic unit, program identifier, classification, social media channels, supervisor search.
Departments/Programs may update graduate degree program details through the Faculty & Staff portal. To update contact details for application inquiries, please use this form .

Michelle Kamigaki-Baron
I read a paper a few years prior that was co-authored by my current supervisor Dr. Molly Babel which helped me imagine the research question of my current PhD project. Upon doing more research on UBC, it became clear that UBC was an ideal choice for me. The graduate students were doing a broad...
Ife Adebara
UBC was the only school I found that readily provided the type of interdisciplinary support that I needed. Most computational linguistic programs usually focus on either computer science or linguistics and I wanted both. I have been able to develop both linguistic and computing skills on this...

Roger Yu-Hsiang Lo
The linguistics department at UBC is well respected and highly regarded, with faculty members working in various subfields. Also, the diverse programs hosted at UBC allow me to take courses from different departments and to easily do interdisciplinary research. Metro Vancouver also features a...

Considering Vancouver as your next home?
This city won’t disappoint. It has it all: sea, parks, mountains, beaches and all four seasons, including beautiful summers and mild, wet winters with snow.
- Why Grad School at UBC?
- Application & Admission
- Info Sessions
- Research Projects
- Indigenous Students
- International Students
- Tuition, Fees & Cost of Living
- Newly Admitted
- Student Status & Classification
- Student Responsibilities
- Supervision & Advising
- Managing your Program
- Health, Wellbeing and Safety
- Professional Development
- Dissertation & Thesis Preparation
- Final Doctoral Exam
- Final Dissertation & Thesis Submission
- Life in Vancouver
- Vancouver Campus
- Graduate Student Spaces
- Graduate Life Centre
- Life as a Grad Student
- Graduate Student Ambassadors
- Meet our Students
- Award Opportunities
- Award Guidelines
- Minimum Funding Policy for PhD Students
- Killam Awards & Fellowships
- Policies & Procedures
- Information for Supervisors
- Dean's Message
- Leadership Team
- Strategic Plan & Priorities
- Vision & Mission
- Equity, Diversity & Inclusion
- Initiatives, Plans & Reports
- Graduate Education Analysis & Research
- Media Enquiries
- Newsletters
- Giving to Graduate Studies
Strategic Priorities
- Strategic Plan 2019-2024
- Improving Student Funding
- Promoting Excellence in Graduate Programs
- Enhancing Graduate Supervision
- Advancing Indigenous Inclusion
- Supporting Student Development and Success
- Reimagining Graduate Education
- Enriching the Student Experience
Initiatives
- Public Scholars Initiative
- 3 Minute Thesis (3MT)
- PhD Career Outcomes
- Great Supervisor Week

Welcome to Calgary Linguistics!
Home of ‘A Higher Clause’, the Graduate Students’ Association of Linguistics at the University of Calgary

We are a passionate group of Master’s and PhD linguistics students at the University of Calgary dedicated to fostering growth, collaboration, and connection among students in the field. At Calgary Linguistics, you’ll find a diverse group of scholars sharing groundbreaking research, thought-provoking discussions, paper writing, and innovative ideas in linguistic exploration. Whether you’re diving into phonetics, phonology, morphology, syntax, semantics, pragmatics, first language acquisition, or historical linguistics, Calgary Linguistics is the place to be.
Explore our website to find information on our graduate students (A Higher Clause), undergraduate students (Verbatim), research groups led by our faculty, and information on events, including colloquium talks and seminars by professors and professionals across North America aimed at developing our understanding of current linguistic research, and interdisciplinary nature of linguistics. Follow our social media to keep up to date on all things #UCalgaryLING!

Upcoming Events
- Verbatim’s Student Colloquium April 6th, 2024 ~ 10am-4pm ~ PF 114 / ZOOM
- SLLLC Grad Forum April 10th, 2024 ~ 10am-3pm ~ CHE 212
Craigie Hall (University of Calgary) 2940 University Way NW Calgary, Alberta [email protected]


- Associate Dean, Teacher Education message
- Primary/Junior Program
- Junior/Intermediate Program
- Intermediate/Senior Program
- ASPIRE - Additional Qualifications
- How to Apply
- Current Teacher Ed Students
- Contact The Teacher Ed Office
- Master of Arts
- Master of Professional Education
- Doctor of Education
- Doctor of Philosophy
- Current Graduate Students
- Contact The Grad Office
- Teacher Education
- Graduate Education
- International Baccalaureate
- Field of Applied Linguistics
Western Education's PhD | Field of Applied Linguistics
The PhD program in the field of Applied Linguistics challenges you to engage with foundational theories and educational research focusing on language-related issues. As you develop expertise in a specific field of Applied Linguistics, you will contribute to existing bodies of knowledge and extend the reach of research to influence theory, policy, and educational practice.
Create your own research
Influence theory, policy and practice
Possibilities to go to conferences
Become a valued expert

What I like about my PhD program is the amazing support and guidance provided to me by experienced faculty and staff, coupled with knowledge I have learned.
My PhD program has helped me have a comprehensive understanding of the topics I am passionate about and helped me become a leader in higher education.
- Sarah Halabi, Current Student
Beyond the program details
- Research based Master's degree in Education or equivalent from an accredited university
- Normally an "A" standing (80%) or equivalent in previous graduate work
- Evidence of previous scholarly research, such as a Master's Thesis, Masters Research Project, or Qualifying Research Paper acceptable to the Doctoral Admissions Committee and the Associate Dean of Graduate Programs
- Clear statement of plans for future study and research
Recommended:
- Professional qualifications and work in an educational setting (teaching experience or other)
Notes & Exceptions:
- Students with Master's degrees and an excellent academic record in a related field, who have experience in education and teaching in universities, colleges, or organizations other than public schools, and who may not have professional teaching credentials or qualifications, will also be considered for admission.
- Students may be required to make up for any deficiencies in their specific backgrounds by taking appropriate additional course work.
Tuition amounts are set each year by Senate and then published on the Office of the Registrar's Fees Schedules web page. Fees are assessed once each term (Fall, Winter, Summer).
Current students can access fee information by logging into the Student Centre (use your Western email log in and password). Students are notified each term once fee amounts have been posted in the Student Centre; it is each student's responsibility to log into the Student Centre and pay fees by the due date indicated. Failure to do so may result in a late payment fee or deregistration.
For questions about fees, including how to pay fees and the methods of payment that are accepted, students should go to the Student Financial Services pages of the Office of the Registrar's web site or contact Student Financial Services (Office of the Registrar) at 519-661-2100.
PhD students receive a funding package that includes the cost of annual tuition plus an additional $17,000. A portion of the funding package involves an Assistantship Role requiring 10 hours of work per week for 28 weeks (September to April) in the Faculty of Education. Details of the assignments are determined in consultation with students after they have formally accepted the offer of admission from the School of Graduate and Postdoctoral Studies. Taking on an Assistantship Role provides students with crucial experience for their academic career after completion of the Ph.D.
The maximum time for funding is 4 (four) years or 12 (twelve) terms. Please note that those who win major financial awards (OGS, Tri-Council or other awards valued at $15,000 or more) will be responsible for their own tuition and ancillary fees.
Also, the following funding scholarships are available at the Faculty of Education (The process for each is described in the link below.):
- Students living with disabilities
- Indigenous students
- Ontario Graduate Scholarship (OGS)
- Canadian Graduate Scholarship – Doctoral (CGS-D)
See further details about funding opportunities available through the Faculty of Education.
Instructors of onsite courses use the Sakai OWL platform, although it is not required. Access to a course in Sakai OWL is typically opened the first business day of each term. Please note that although your own access may be granted prior to the first business day, course content may not be posted until closer to the scheduled term start. Your Western University login and password is required to access the course (your Western email without the @uwo.ca and its accompanying password). Access to Sakai OWL is found here: https://owl.uwo.ca/portal .
For online courses, students are required to have access to the following:
- High speed Internet access
- Access to a computer that enables connection to outside websites (flexible firewall restrictions)
- Multimedia playback capabilities (video/audio)
- Computer capable of running a recent version of Internet Explorer, Safari, or Firefox; and/or Cisco MOVI client for PC or Mac
- Audio headset and microphone for computer
Program information
Description.
The PhD program in the field of Applied Linguistics challenges you to engage with foundational theories and educational research focusing on language-related issues and offers you an opportunity to engage with top-tier researchers and academics. As you develop expertise in a specific field of Applied Linguistics, you will contribute to existing bodies of knowledge and extend the reach of research to influence theory, policy, and educational practice.
Prospective students are strongly encouraged to visit our Faculty Research page for more information on the exciting research being conducted at the Faculty of Education.
Important note: When submitting an application to the PhD in Education Studies program, applicants must indicate their preferred Thesis Supervisor in their Statement of Intent. Applicants are advised to review the Faculty Research page and contact faculty in their area of interest to confirm that this potential exists.
Comprehensive Examination
A comprehensive exam will be implemented in the PhD program to meet requirements for the depth and breadth outcomes from the Graduate Degree Level Expectations. The goal of the exam is for students to demonstrate a depth of information concerning their specific program of research and a breath of knowledge of their focus within the field (e.g., mathematics curriculum; ESL/EFL).
- Format: One written question that asks students to discuss their program of research and how it relates to their focus within the field.
- Length: 8,000-10,000 words.
- Draft question: While cognizant that Applied Linguistics is a highly interdisciplinary field, you will demonstrate knowledge of key aspects of the development of your area of specialization in Applied Linguistics, including its evolution, seminal works and contemporary knowledge and issues in the area (e.g., educational linguistics related to second/foreign language teaching; discourse or genre approaches to EAP, etc.), describe your proposed program of research and how it relates to said area. Students are encouraged to discuss their papers with anyone, including supervisors, but not show them drafts.
- Timeframe: As soon as you have completed your coursework, you will start your Comprehensive Exam process and must be completed in one term. Comprehensive Exams are a Milestone and will not show up as a course in your Student Centre. Once you have passed your Comprehensive Exam, it will appear at the end of your transcript under the Milestones area.
- Administration: Students must submit the following to the Graduate Programs Office at least four weeks prior to the end of the term of registration: 1 electronic copy of comprehensive examination and Request for Administration of Qualifying Examination form.
- Reviewers: The student’s supervisor and one committee member or alternative that has knowledge of the field shall be completed. Each reader will independently determine whether the paper is satisfactory or not and notify the Graduate Programs Office within two weeks after the submission date. The Graduate Programs Office will then notify the Supervisor who will share the results with the student.
- Grading: Grading will be satisfactory or unsatisfactory. The paper must be judged satisfactory by both reviewers in order to be marked “Pass”. If a student’s paper does not pass, the student will be permitted to resubmit a revised version of the paper within two weeks of its return. The revised paper will be re-read by the same reader(s) who had marked it unsatisfactory. If the revised paper is not assigned a “Pass”, the student will be asked to withdraw from the program. If the paper is assigned a “Pass”, the student may proceed in the program to complete degree requirements.
Thesis Proposal and Presentation
Within six months following successful completion of the comprehensive examinations, a student must make an oral presentation to their Thesis Advisory Committee, then submit a written research proposal in which the research problem, theoretical framework and methodology are explained and satisfactorily defended. The presentation will be open to all members of graduate faculty and to all graduate students. To schedule a Proposal Presentation a student should work with their Supervisor to set a date and time then please inform the Graduate Programs Office for public announcement.
Thesis Examination/Defence
When the thesis has been completed and approved by the Supervisor and the Thesis Advisory Committee, the candidate may submit the thesis for examination. The candidate submits the Application for Thesis Examination (PDF) and the Doctoral Thesis Supervisor Approval (PDF) forms to the Graduate Programs Office. The forms have to be submitted a minimum of seven weeks prior to the defence date. The thesis is uploaded to Scholarship@Western, Electronic Thesis and Dissertation Repository, a minimum of six weeks prior to the defence date.
The examination includes a Public Lecture which provides both a valuable means of disseminating research findings within the academic community, and an opportunity for all graduate students of education to participate in and contribute to the scholarly discourse of the university. In accordance with the appropriate regulations, the public lecture will be advertised in the University's Western News and on the University's web site, and be open to all members of the community. The examination normally follows within 24 hours of the lecture.
Details of the examination process are located in Section 8 of Graduate Regulations .
Timing/Delivery
Below is the typical program of study for a full-time PhD student:
Full-time - 12 terms (4 years)
Full-Time students can take a maximum of 3 course per term.
PhD students in the area of Applied Linguistics will be required to complete:
- 9715 - PhD Seminar
- 1 Additional Research Methodology course - as approved by supervisor
- 9711 - Qualitative Research in Education
- 9705 - Advanced Quantitative Research Methods
- 9302 - Teaching and Learning Vocabulary
- 9308 - Teaching and Learning Grammar
- 9309 - Second Language Assessment
- 9301 - Social approaches to language learning and teaching
- 9307 - Language Teacher Education
- 9305 - Discourse analysis and language teaching
- 9300 - Understanding second language learning and teaching
- 9303 - Computer-assisted language learning
- 9306 - Syllabus and materials design
- 9625 - Critical Issues in Language & Literacy Education
- 9580 - Introduction to Curriculum ( prerequisite for Advanced Topics )
- 9599 - Early Literacy Curriculum, Pedagogy, and Learning
- 9683 - Critical Pedagogy
- 9203 - Globalization and education
- 9425 - Language, Identity, Pedagogy
- 9730 - Advanced Topics in Curriculum ( must have completed 9580 )
- Comprehensive Exam
- Thesis Proposal (oral presentation and written submission)
- Thesis examination/defense
Note: In lieu of the recommended courses, up to two electives inside or outside the ARC can be taken with the approval of the student's supervisor. Students may also have the option to enroll in an Independent Reading and Research Course as an elective.
Potential Supervisor
Frank Boers
Julie Byrd Clark
Farahnaz Faez
Shelley Taylor
Stuart Webb
Ruslan Suvorov
Faculty of Education 1137 Western Road London, Ontario, Canada, N6G 1G7 Tel: 519-661-3182 [email protected] Privacy | Web Standards | Terms of Use | Accessibility
News and Events
Support Services
Social Media
Faculty Events
Education Support Portal
Current Students
Education Library
- BA Linguistics
- BA Speech Sciences
- Diploma in Linguistics
- Opportunities
- Beyond the BA
- Masters’ Programs
PhD Program
- Theses & Dissertations
- Continuing Education
- Graduate Students
- In Memoriam
- Labs & Groups
- First Nations Languages
- Research Interest Registration
- Field Methods Class
- Publications
- Recurring Events
- Equity, Diversity and Inclusion
- Job Opportunities
The PhD program is for those interested in advanced research training and developing expertise in an area of their choice.
Program Overview
Our department covers a broad range of research topics, with substantial coverage of phonetics, phonology, morphology, syntax, semantics, and pragmatics. We approach these topics from several different research traditions and backgrounds, with particular strengths in formal-theoretical linguistics, experimental and field linguistics, acquisition, and computational approaches to the study of communicative behaviour.

Program Requirements
Students in the PhD Linguistics program must complete coursework under the following requirements:
- LING 508: Phonetic Theory and Analysis (3 credits)
- LING 510: Phonological Theory and Analysis (3 credits)
- LING 520: Syntactic Theory and Analysis (3 credits)
- LING 525: Semantic Theory and Analysis (3 credits)
- First-year breadth courses may be waived if equivalent courses have been taken elsewhere.
- LING 505A: Issues in Morphological Theory and Analysis (3 credits)
- LING 511 : Topics in Phonology (3 credits)
- LING 513: Topics in Phonetics (3 credits)
- LING 521: Topics in Syntax (3 credits)
- LING 527: Topics in Semantics (3 credits)
- More than one section of LING 530 can be counted towards this requirement, with each three-credit section counting as one course.
- LING 531: Field Methods in Linguistics I (3 credits)
- The remaining six credits can be completed with either LING 532, LING 518, and/or an appropriate methods-related course within in Linguistics or in a different department
The first-year breadth courses and methods courses (except Field Methods) are waived if equivalent courses have been taken elsewhere, subject to an evaluation of the relevant syllabus.
First-year graduate students who do not have sufficient background for the first-year graduate courses (this is most typically an issue for LING 525 and LING 508) are expected to take the appropriate undergraduate courses (e.g., LING 325, LING 313) prior to registration in the graduate course.
Here are three sample course sequences that students usually take:
Sequence 1:
Term 1: Breadth: LING 510, LING 520; Depth: LING 503
Term 2: Breadth: LING 508, LING 525; Depth: LING 511
Term 3: Depth: LING 513; Methods: LING 518, LING 531
Term 4: Depth: LING 530; Depth/Methods: LING 532
Sequence 2:
Term 1: Breadth: LING 510, LING 520; Depth: LING 530
Term 2: Breadth: LING 525; Depth: LING 505A, LING 521
Term 3: Depth LING 527; Methods: LING 518, LING 531
Term 4: Depth/Methods LING 532
Sequence 3:
Term 1: Breadth: LING 510; Depth: LING 503; Methods: 3 credits in statistics
Term 3: Depth LING 513; Methods: LING 518, LING 531
Term 4: Depth LING 530; LING 530
Qualifying papers
The QP process is an opportunity to develop, strengthen, and broaden research skills. Whether a student chooses the one-QP or two-QP option and the specific topic(s) are decisions students discuss and make in discussion with their committee. Discussions of what constitutes appropriate scope should take place within the committee.
Two-QP option (default): Students who select to write two QPs are acknowledging that they would benefit from the experience of engaging in two separate research topics under the guidance of a committee. Each committee must have three members, but each QP will have two readers. (The third member may be the Graduate Advisor.) The length of these QPs is to be the scope of a discipline-specific conference proceedings paper.
One-QP option: Students who select to write one QP are eager to engage more deeply with a single topic and set of research methods. Under this option, QPs will have three readers. The scope of this QP is to be appropriate for a journal manuscript, which is discipline specific.
While QPs may feed into dissertation projects, there is no established expectation that they will or will not.
No defences, but QP presentations. Under neither of these options will students be required to defend their QPs. But, developing presentation skills is important to a scholar’s development. Students are required to present each QP. Such a presentation is a presentation and not a defence. The evaluation of a presentation is thus formative, and not summative. A QP does not need to be presented upon completion, but rather it is up to the committee to decide the presentation timing that is appropriate for a student. To facilitate this, there will be a Graduate Student Research Day at the end of every term, and all students will be invited to present.
As part of the Qualifying Paper process, and before beginning work on the paper, a student must have a short proposal for each paper approved by the supervisory committee. The proposal must establish the specific area and problem(s) to be addressed and cite a few key references from the literature which will be surveyed. The committee will normally respond to the proposal within 2 weeks of its submission. The Qualifying Paper proposal should follow the formatting guidelines of an abstract for the Annual Conference of the Canadian Linguistic Association, with the following addition: without exceeding the one-page length limit, the proposal should include a short budget (if there will be costs associated with completing the Qualifying Paper), budget justification and funding source (faculty member’s grant, outside grant, private funds, etc.). Also note that the content for a proposal will normally be more speculative than a conference abstract. Once approved, the Qualifying Paper proposal should be electronically filed with the Grad Admin and circulated electronically to the Department.
The final paper will be submitted to UBC Working Papers in Linguistics and must follow the UBCWPL style guidelines for length and formatting.
Dissertation
The dissertation marks the culmination of the PhD program. A dissertation should be an original and independent research project which makes some contribution to knowledge in the special area elected by the student.The dissertation marks the culmination of the PhD program. A dissertation should be an original and independent research project which makes some contribution to knowledge in the special area elected by the student.
By the end of a student’s third year, the student must submit to the Graduate Advisor a dissertation prospectus, along with the appropriate approval form signed by the members of the dissertation committee, and circulate the prospectus electronically to the Department. The content of a dissertation prospectus should be along the lines of an NSERC Discovery Grant or a SSHRC Insight Grant; it should have the following components:
- Summary (1 page maximum)
- Detailed description (6 pages maximum)
- Bibliography
- Budget (if there will be costs associated with completing the dissertation research)
- Budget justification (as appropriate)
Dissertations should be prepared in accordance with the thesis formatting regulations required by Graduate and Postdoctoral Studies. Dissertations which do not meet the standards specified may be rejected. Documentation should follow the style guide of the Canadian Journal of Linguistics, Language, or the American Psychological Association.
The completed dissertation will be read by a specialist from outside the University, arranged by the Dean of Graduate and Postdoctoral Studies at least three months before the candidate expects to take the final oral examination. The student’s research supervisor and the Graduate Advisor will forward a list of names of specialists who might serve as External Examiner using the Doctoral Dissertation Form. When the dissertation has been approved for submission to the External Examiner, the candidate will take the final oral defence. This is a formal, public examination, chaired by an appointee of the Dean of Graduate and Postdoctoral Studies, and attended by the members of the examining committee and other interested persons.
Students nearing the final stages of thesis writing should familiarize themselves with the timeline to the oral dissertation defense . During the weeks prior to the oral examination, students are strongly encouraged to give a practice oral presentation, ideally during a departmental research seminar slot. Practice orals should follow the Graduate and Postdoctoral Studies format, allowing 30 minutes for a presentation, and a longer period for questions. While examining committee members are not prohibited from attending, practice orals should not be viewed as an opportunity to prepare students for specific questions that students will be asked by committee members at the official defence.
The candidate submits an electronic copy of the final dissertation to the Faculty of Graduate and Postdoctoral Studies. The electronic copy will be deposited in the cIRcle on-line repository, and linked from the department website. The final oral exam may be held at any time of the year (except from mid-December to mid-January) provided that the examining committee can be assembled.
Language requirement
In order to graduate, students must have a sound knowledge of one language other than English. They must fulfill this language requirement by the time of their thesis prospectus submission.
The language to fulfill this requirement is expected to be chosen on the basis of its relevance for the student’s research program, in consultation and by approval of the student’s supervisory committee. Relevance can be determined by a variety of factors such as the following:
- The language is the object of the student’s research, or is closely related to the language of research; for example, where a student’s research focuses on Yoruba, knowledge of Yoruba could fulfill the requirement, or where the student’s research is on St’at’imcets, knowledge of Halkomelem could fulfill the requirement.
- There is a significant and relevant linguistic literature in the language; for example, Chinese, French, German, Japanese, and Russian could fulfill the requirement.
- The language serves as a medium for conducting linguistic research relevant to the student’s program of research; for example, Hausa could fulfill the language requirement for a student conducting research on a language of northern Nigeria.
Students may fulfill the language requirements in various ways:
- Certain departments at UBC periodically schedule reading knowledge examinations. This exam evaluates a student’s language competence based on the translation of a text (approximately 1000 words) relating to the student’s field of study. A minimum second class standing (B- or better) must be obtained on this exam in order to satisfy the Foreign Language Requirement. For further information on such examinations, contact the appropriate departments.
- If you speak a language natively, your native proficiency can be accepted by the supervisory committee.
- If you have completed a program of post-secondary language study (a minimum of 12 credits or equivalent). A minimum second class standing (B- or better) must be obtained for these credits in order to satisfy the Foreign Language Requirement.
- For other languages, it may be necessary to establish an ad hoc mechanism for conducting an evaluation of the student’s knowledge. In such cases, the student should make a written request to their supervisory committee, including a proposal for how such an examination can take place, and including a proposal for a qualified examiner. Students considering this option should be aware that the requirements (including the required level of competence in the language and how to demonstrate it) may vary extensively from case to case, depending on the norms of the language community involved.
Continuous enrolment
Until their MA thesis prospectus has been approved, all MA students are expected to maintain a regular, active, physical presence in the Department. This can include participation in lab/project/reading groups, attending colloquia, research seminars or other ad hoc departmental events, meetings with their supervisor, committee members or other researchers in relevant areas. Certain circumstances may necessitate a student’s absence during some of this period (e.g. for field work); such absences should be discussed with the supervisory committee.
At all stages of the program, a student and their supervisor should be in regular contact and communication. At the thesis/dissertation stage, such contact should happen at least once a month (again, barring extenuating circumstances), either through in-person meetings, videoconferencing, or communication/reporting over email.
Supervision
A Research Supervisor is appointed for a student before the beginning of their first year in the program. The Graduate Advisor and the Research Supervisor, in consultation with the incoming student, will establish a three-member Temporary Supervisory Committee no later than the end of the first week of the first term.
Prior to registration for the second year, the Temporary Supervisory Committee shall be dissolved and a new Supervisory Committee shall be established. A MA Supervisory Committee consists minimally of the Research Supervisor and two additional members. Normally the members of the supervisory committee are from the Department of Linguistics; if the students committee includes members from outside the Department of Linguistics, a majority must be departmental members. Establishing a Research Supervisor is the joint responsibility of the student and the Graduate Advisor.
Both new and continuing MA students will have a meeting with their Supervisory Committee during the last week of August or in early September. At this meeting students can discuss their course work and other aspects of their program. Incoming students are requested to bring with them copies of the calendars of course offerings from the institutions they previously attended (other than UBC). At the end of April or the beginning of May, all students will meet with their Supervisory Committee to discuss the year’s progress and to plan further work. Any changes in a graduate student’s program must be approved by the Supervisory Committee.
The Graduate Advisor, in advising students, makes every effort to ensure that they have satisfied all the requirements for the degree — language requirements, course work, etc. However, it is ultimately every student’s responsibility to ensure that at the time he/she applies for the degree he/she has met all the requirements. Separate records of a student’s program and progress are kept by the Faculty of Graduate Studies; these records are obtained from information provided by the Graduate Advisor and are used to determine a student’s ultimate eligibility for graduation.
Annual evaluation
The Faculty will meet in April or May each year to discuss the progress of each student in the PhD program. The student’s supervisor will inform them of the results of the evaluation. If a student is not making satisfactory progress, they will either be required to withdraw from the program immediately or will be placed on probation and told what conditions must be fulfilled to obtain a satisfactory standing. If a student on probation has not fulfilled these conditions by the end of the following semester, they will then normally be required to withdraw from the program.
Quick Links
FACULTY OF HUMANITIES
Linguistics & languages.

- Undergraduate Programs
- Graduate Programs
- Our Community
- Request Info
PhD Program in Cognitive Science of Language

Join our world-class Languages & Linguistics Department to continue your study of language structure, language processing and the neural basis of language in the Cognitive Science of Language PhD Program.

Our courses are so hands-on and application based that you end up developing a unique and valuable skillset, which ends up leading into a variety of career paths that would otherwise have been difficult to grow accustomed to.
Meliha Horzum '20
Honours Cognitive Science of Language
About the Program
Based in the Department of Linguistics and Languages, the PhD program in Cognitive Science of Language is interdisciplinary and includes faculty from Humanities, Science, and Health Sciences. The program has a strong research orientation with expertise in cognitive science, corpus linguistics, neurolinguistics, psycholinguistics, sociolinguistics and theoretical linguistics. The program introduces students to the issues in those fields that form the nexus of linguistics, cognitive science and cognitive neuroscience, and trains students in the research methods employed to study them.

Admission Requirements
A MSc in the Cognitive Science of Language or an equivalent Master’s degree is required for entrance into the PhD program. Some applicants may require additional courses in core areas (e.g. linguistics or cognitive science) in order to be eligible for admission. Each application will be evaluated on an individual basis.
Language Requirement
In order to ensure language diversity and breadth, the Department has a second-language requirement for the PhD degree, in addition to the general Graduate School requirement of English proficiency. Candidates should have, as a minimum, intermediate knowledge of a language other than English, defined as having passed the equivalent of two (2) full year courses. Candidates admitted without this requirement will be expected to pass the equivalent of two (2) full year courses or to pass a Qualifying Exam. The Department will evaluate each student’s language preparation at the Admission stage.
Application Process
The official electronic transcripts should be sent from the issuing institution directly to our department’s email: [email protected]
The online application portal for our graduate program in Cognitive Science of Language unlocks November 1st each year for September admission only.
THOSE WHO SUBMIT THEIR COMPLETED APPLICATIONS (BOTH DOMESTIC AND INTERNATIONAL) BY THE JANUARY 31ST DEADLINE WILL HAVE FIRST CONSIDERATION.
- Complete the online application -> McMaster University Application
- Statement of Interest (identify the faculty member you wish to work with)
- Writing Sample (any type of academic writing i.e. term paper, thesis chapter)
- Two academic references (McMaster University uses an Electronic Referencing System. By entering the email address of your referee through the online application, the system will automatically send an e-Reference request on your behalf)
- English Language Proficiency (if English is not your native language)
- Official transcripts of all post-secondary academic work completed to date (transcripts must be sent directly from the issuing institution to our Department, please include English translation if applicable)
- Official copy of your TOEFL or IELTS scores or any other evidence of English proficiency (TOEFL: minimum score of 92 (internet based), 237 (computer based) or 580 (paper based), minimum of 20 per band; for the Faculty of Engineering a minimum score of 88 (internet based) or 213 on the (computer based) or 550 (paper based) IELTS (Academic): minimum overall score of 6.5, with at least 5.5 in each section)
- **NOTE** Applicants from outside of Canada should begin the application process as early as possible to allow time to obtain all necessary documents.
Program Timelines
Students entering with a MSc in the Cognitive Science of Language are required to complete three half courses plus one pass/fail module. If the following courses were not completed in the MSc program, they must be included in the PhD program of study:
- COGSCIL 730 / Language Analysis Methods: Phonology and Morphology
- COGSCIL 731 / Language Analysis Methods: Syntax and Semantics
- COGSCIL 726 / The Cognitive Science of Language Ph.D. Lecture Series must be completed in Year 1 of the PhD program
- Plus additional courses approved by the student’s supervisory committee to total three half courses
Students entering with a Master’s degree but not an MSc in the Cognitive Science of Language are required to complete seven half courses plus one pass/fail lecture series module as listed below. The Lecture series must be completed in year one of the program.
Required courses:
- COGSCIL 721 / Fundamentals of the Cognitive Neuroscience of Language
- COGSCIL 722 / Contemporary Issues in the Cognitive Neuroscience of Language
- COGSCIL 726 / The Cognitive Science of Language Ph.D. Lecture Series
- Plus additional courses approved by the student’s supervisory committee to total seven half courses
The Comprehensive Examination is intended to ensure that the student develops competence in a subfield of Cognitive Science of Language beyond the focus of the thesis. In consultation with the supervisory committee, the student will identify a topic for the Comprehensive that is distinct from the thesis topic.
In most cases, the Director of the Comprehensive will not be the thesis supervisor. The student and the Comprehensive Director agree in writing on the nature of the deliverable for the Comprehensive and on interim and final deadlines. At a minimum, the Comprehensive consists of a written paper and oral examination of the topic of the paper. The paper may consist of a literature review, proposal for a research project, report of a research project or report of a teaching project. The scope of the project should be such that it can reasonably be completed within one semester. The paper will usually be 20-30 pages long.
The Comprehensive Director identifies at least one other faculty member; together, the Director and these other faculty members constitute the Comprehensive Exam Committee. (Comprehensive Directors are encouraged to recruit Comprehensive Examiners from beyond the Department of Linguistics & Languages.) The Comprehensive Director advises the student on the preparation of the paper. The Comprehensive Exam Committee determines whether the paper is ready for an oral defense, and conducts the oral examination. The oral examination consists of a brief presentation by the student regarding the content of the paper followed by questions from the Committee. The Comprehensive Exam must be successfully completed within 20 months of entering the PhD program.
All students are expected to attend the talks in the Cognitive Science of Language Lecture Series, where scholars from around the world in the fields of Linguistics, Psychology, and Cognitive Neuroscience discuss their research.
Tuition & Program Fees
Visit Graduate Studies to learn more about tuition, supplementary fees and everything you need to know about being paid as a Teaching or Research Assistant. Tuition fees are assessed on a term by term basis, depending on the number of courses a student takes or if they are paying by term.
Apply to an PhD Program in Linguistics & Languages

LEARN MORE ABOUT OUR GRADUATE SUPERVISORS
Research your passion in Linguistics & Languages with supervision from our world-class faculty.

SEE OUR CURRENT AND FORMER PhD STUDENTS
Supplemental information.
Graduate Courses in Linguistics and Languages
Course outlines 2023-2024
- Cogscil 6LB3 – Advanced Phonetics and Phonology
- Cogscil 6XX3 – Topics in Linguistic Theory
- Cogscil 712 – Reading Course (Linguistics)
- Cogscil 713 – Reading Course (Cognitive Science)
- Cogscil 722 – Contemporary Issues in the Cognitive Neuroscience of Language
- Cogscil 726A – The Cognitive Science of Language Ph.D. Lecture Series
Winter 2024
- Cogscil 6G03- Language, Sex and Gender
- Cogscil 6NN3 – Cognitive Neurolinguistics Lab
- Cogscil 713 – Reading Course (Cognitive Science)
- Cogscil 721 – Fundamentals of the Cognitive Neuroscience of Language
- Cogscil 726B– The Cognitive Science of Language Ph.D. Lecture Series
- Cogscil 731 – Language Analysis Methods: Syntax and Semantics
- Cogscil 734 – Issues in Syntax
Course outlines 2022-2023
- Cogscil 6D03 – Computers and Linguistic Analysis
- Cogscil 730 – Language Analysis Methods: Phonology and Morphology
Winter 2023
- Cogscil 6AS3 – Topics in Advanced Semantics
- Cogscil 6EL3 – Experimental Lab in Cognitive Science of Language
- Cogscil 6LC3 – Advanced Morphology and Syntax
- Cogscil 726B – The Cognitive Science of Language Ph.D. Lecture Series
- Cogscil 749 – Lab Visual Language
Domestic MSc students usually receive a funding package consisting of a teaching assistantship and scholarship. The total value of the funding package ranges from $16,000 to $19,000 per year.
Currently all domestic PhD students receive a funding package of $23,500 per year, usually including a teaching assistantship of 260 hours plus a scholarship.
McMaster Graduate Studies Scholarship Information
The School of Graduate Studies provides funding to our graduate students so they can devote their time and energy to the successful completion of their studies.
External Graduate Scholarships
All eligible students are also strongly encouraged to apply for external scholarships such as the Ontario Graduate Scholarship and Canada Graduate Scholarships.
Ontario Graduate Scholarship
Note that applications must be submitted directly to the institution(s) where you plan to pursue graduate studies. The deadline is normally in the fall, before the application deadline for graduate school.
Canada Graduate Scholarships-Master’s Program
Graduate Scholarship – As with OGS, applications for the Canada Graduate Scholarship must be submitted through an eligible institution. The deadline is usually December 1, before the application deadline for graduate school.
All applicants and current students will be considered for funding support from McMaster, including TAships.
- Thesis Defence
- Program Handbook
- Graduate Calendar
- School of Graduate Studies Graduate Resources
- Graduate Association
- Where to find jobs

PAST MAJOR RESEARCH PROJECTS
Department life.
The Department of Linguistics & Languages welcomes scholars from around the world to participate in the Cognitive Science of Language Lecture Series. The lecture series is a forum where all are welcome to attend talks by established researchers on recent innovations and current trends in Language and Cognition.
UPCOMING EVENTS
Find a Humanities Expert

Research-focused and student-centered. Humanities researchers promote interdisciplinary approaches to local and global leadership. Learn more about our researchers by searching by name or keyword.
- My UCalgary
- Class Schedule
- UCalgary Directory
- Continuing Education
- Active Living
- Academic Calendar
- UCalgary Maps
- Close Faculty Websites List Viewing: Faculty Websites
- Cumming School of Medicine
- Faculty of Arts
- Faculty of Graduate Studies
- Faculty of Kinesiology
- Faculty of Law
- Faculty of Nursing
- Faculty of Nursing (Qatar)
- Faculty of Science
- Faculty of Social Work
- Faculty of Veterinary Medicine
- Haskayne School of Business
- School of Architecture, Planning and Landscape
- School of Public Policy
- Schulich School of Engineering
Werklund School of Education
- Future Students
- Explore programs
- How to apply
- Understanding graduate studies
- Indigenous graduate students
- Financing grad school
- International students
- Graduate Student life
- Current Students
- Indigenous Graduate Students
- Newly Admitted
- Graduate Orientation
- Pre-arrival
- Registration
- Annual Registration
- Concurrent Registration
- Flexible Grading Option (CG Grade)
- Confirmation of registration
- Course registration
- Leave of absence
- Registration status
- Studying at another university
- Updating personal information (included preferred name)
- Thesis-based students
Fees and funding
- Understanding your fees
- Paying your fees
- Funding options
- Payment plan
- Supervision
- Best practices and guidelines
- Conflict of interest
- Changing supervision
- Academic integrity
- Annual progress report
- Intellectual property
- Building a thesis
- Submit your thesis
- Conducting oral exams remotely
- Thesis defence
- Course-based Students
- Academic Integrity
- Sources of funding
- Payment Plan
- NEW: Term-Based Registration
- Completing my degree
- Important dates and resources
- Forms and documents
- Graduate Calendar
- Service Requests and eForms
- News, updates and events
- Find your Graduate Program Administrator
- Calendar Archives
- Award Opportunities
- Graduate Awards Database
- Award opportunities
- Doctoral Recruitment Scholarships
- Award Guide
- Step 1: Applying
- Looking for awards
- Eligibility
- Preparing your application
- Step 2: Receiving
- Accept/Decline your award
- Getting paid
- Step 3: Managing your award
- Renewing your award
- Award interruption
- Award Termination
- Policies and Regulations
- Regulations
- Contact the Scholarship Office
- My GradSkills
- Academic Success
- My GradSkills Partners
- Communication Skills
- Research Communications Feedback Sessions
- Oral communication
- Visual communication
- Written communication
- Experiential Learning
- Internships
- For employers
- For graduate students
- Finding an internship
- Making your internship a TTI
- Applying for a TTI
- For graduate supervisors
- Images of Research
- Three Minute Thesis
- 2024 UCalgary 3MT Finalists
- 2024 3MT Finals' Hosts and Judges
- Past Three Minute Thesis Videos
- Workshops and Resources
- Career planning and professional development resources
- My GradSkills Calendar
- My GradSkills Workshop Matrix
- Online/Virtual Training
- UCalgary Alumni Mentorship Program
- Exceptional scholars
- Graduate Mental Health Survey
- Test metrics
- Demographics
- Circumstances
- Mental Health
- What I wish I knew
- FGS Services
- Supervisory Renewal
- Supports for graduate students
- Graduate Academic and International Specialists
- Graduate supervisors
- Thesis and candidacy exams
- Supervisor resources
- Maintaining your supervisor profile
- Supervisory privileges
- Leadership team
- FGS Council
- Committees of Council
- Minutes and meetings
- Website Feedback

Educational Research
Doctor of Philosophy (PhD)
Thesis-based program
Program overview.
The Doctor of Philosophy degree prepares scholars for leadership careers in research and teaching. Students engage with established and emerging ideas in the theory and practice of pedogogy, leading to comprehensive and specialized understanding of their area of study. Through original research, students help to open and extend the field of educational research. By critiquing and building upon scholarly and practical research and contemporary discourses in education, students will participate in creating the next generation of ethical and ecologically sustainable educational systems. A two-year, on-campus residency is required for this research-intensive and thesis-based program, which is delivered on-campus only.
Completing this program
- Adult Learning: Students take courses in research methods, advanced topics in adult learning and electives.
- Language and Literacy: Students take courses in research methods and on theory and research in language and literacy.
- Learning Sciences: Students take courses in research methods and electives in educational research from the learning sciences specialization.
- Curriculum and Learning: Students take courses in research methods, interpretive study of curriculum and additional seminars.
- Leadership: Students take courses in research methods, a seminar in educational leadership and electives in educational research.
- Candidacy and Thesis: Students complete a research proposal and oral and written candidacy exams, and submit and defend an original thesis.
Specializations
- Adult Learning
- Curriculum and Learning
- Language and Literacy
- Learning Sciences
Professor, Research and Not-for-profit organizations, Bilingual Education, Intercultural Communication, English Language Arts, Media Education, Culture Studies, Curricular Consultant, Public and Private Education, Community and Non-governmental agencies, School management, Policy and governance.
A PhD in educational research is usually considered a final degree.
Students are required to prepare a thesis and successfully defend in an open oral defense.
Five core courses, and up to three electives depending on specialization
Learn more about program requirements in the Academic Calendar
Classroom delivery
Time commitment.
Four years full-time; six years maximum; two year residency requirement
A supervisor is required, but is not required prior to the start of the program
See the Graduate Calendar for information on fees and fee regulations, and for information on awards and financial assistance .
Virtual Tour
Explore the University of Calgary (UCalgary) from anywhere. Experience all that UCalgary has to offer for your graduate student journey without physically being on campus. Discover the buildings, student services and available programs all from your preferred device.
Supervisors
Learn about faculty available to supervise this degree. Please note: additional supervisors may be available. Contact the program for more information.

Maren Aukerman

Subrata Bhowmik

Barbara Brown

Tonya Callaghan

Catherine Chua

Roswita Dressler

Sarah Elaine Eaton

Janet Groen

Michele Jacobsen
Admission Requirements
A minimum of 3.5 GPA on a 4.0 point system, over the past two years of full-time study (a minimum of 10 full-course equivalents or 60 units) of the undergraduate degree.
Minimum education
A thesis-based master's degree in an appropriate field from a recognized institution.
Work samples
- A statement outlining the applicant's interests and reasons for wishing to pursue graduate work in this department. Clearly identify your thesis research area
Reference letters
Test scores, admission portfolio.
Applicants to the Doctor of Philosophy program are encouraged to submit an Admission Portfolio containing examples of their work.The Doctoral Admission Portfolio may contain the following:
- Thesis (if applicable).
- Research grants or scholarships.
- Curriculum documents.
- Non-print materials, (e.g. multimedia).
- Evidence of relevant prior learning (see graduate calendar).
- Personal statement documenting research skills and interests.
English language proficiency
An applicant whose primary language is not English may fulfill the English language proficiency requirement in one of the following ways:
- Test of English as a Foreign Language (TOEFL ibt) score of 97.
- International English Language Testing System (IELTS) score of 7.0.
- Canadian Academic English Language test (CAEL) score of 70 (no less than 70 in each section).
- Academic Communication Certificate (ACC) score of A- in each course.
For admission on September 1:
- Canadians and permanent residents: Dec. 1 application deadline
- International students: Dec. 1 application deadline
If you're not a Canadian or permanent resident, or if you have international credentials, make sure to learn about international requirements
Are you ready to apply?
Learn more about this program, educational research graduate program.
Education Tower, Room 114 2500 University Drive NW Calgary, ABT2N 1N4 403.220.5675
Contact the Graduate Program Administrator
Visit the departmental website
University of Calgary 2500 University Drive NW Calgary, AB, T2N 1N4
Visit the Werklund School of Education's website
Learn more about UCalgary by taking a virtual tour
Related programs
If you're interested in this program, you might want to explore other UCalgary programs.
Thesis- based EdD
Thesis- based MA
Course-based MEd - Int
Course-based MEd - Spec
Thesis-based MSc
Curious about the University of Calgary?
Located in the nation's most enterprising city, we are a living, growing and youthful institution that embraces change and opportunity with a can-do attitude.
Dušan Nikolić
Hi, I am Dušan Nikolić, a phonetician who earned his PhD in Linguistics at the University of Calgary under the supervision of Dr. Stephen Winters. In my work, I want to understand what the processing mechanisms of prosodic categories are and how they relate to communication.
I am a recipient of the prestigious Izaak-Walton Killam Award, University of Calgary International Eyes High Award, University of Calgary Open Doctoral Award, and Dositeja Award by Serbian Ministry of Education. I was a proud member of the UofC’s Phonetics Lab , and the president of the UofC’s graduate student association, “ A Higher Clause ”,
As for my non-academic activities, I was the host of the spoken word program – Linguistically Aware – which was broadcast once monthly on a local radio station, CJSW 90.9 FM. I was an usher at Calgary Theatre , and I love(d) going to plays! I am an ardent sports enthusiast, a huge fan of Partizan and Arsenal.

Key Publications
Nikolic, D. & Winters, S. (2022). Are Serbian and English Listeners Insensitive to Lexical Pitch Accents in Serbian?. Phonetica , Karger. https://doi/10.1515/phon-2022-2023/html
Nikolic, D. (2021). Effects of F0 Acoustic Parameters on the Perception of Serbian Lexical Pitch Accents. Anali Filoloskog Fakulteta .Vol.33, n.1, 13–27. https://doi.org/10.18485/analiff.2021.33.1.1
Nikolic, D. (2016). Acoustic Analysis of English Vowels Produced by American Speakers and Highly Competent Serbian L2 Speakers. Facta Universitatis, Series: Linguistics and Literature . Vol. 14, n. 1, 85-101. http://casopisi.junis.ni.ac.rs/index.php/FULingLit/article/view/1683
Career in a Nutshell
2011 – 2015 BA in English Language and Literature – University of Niš
2015 – 2017 MA in English Language (with the focus on Linguistics) – University of Niš
2015 – 2016 MA in Language Teaching – University of Belgrade
2018 – 2023 PhD in Linguistics (Phonetics) – University of Calgary
University emails: [email protected] | [email protected]
Visit also: calgarylinguistics.ca
Main navigation
- Graduate programs
- How to apply
- Research & supervision
- Student experience
- Connect with us
The majority of graduate programs are NOT impacted by recent government announcements about tuition increases. PhD students from the rest of Canada will continue to pay Quebec fees. International PhD fees will see the same 3% increase as Quebec fees.
Linguistics (PhD)
Program description.
The Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) in Linguistics offered by the Department of Linguistics in the Faculty of Arts is a research-intensive program that emphasizes specialized and well-researched learning opportunities. The program's objective is to equip students with skills in self-direction, visionary thinking, and scientific communication to pursue professional opportunities in academia or industry.
The program may also be taken with a Language Acquisition option where students focus their thesis on the research area of language acquisition.
Keywords: Theoretical linguistics, experimental linguistics, computational linguistics, quantitative methods, linguistic field work, language acquisition, sociolinguistics, psycholinguistics, linguistics
Unique Program Features
- The program which provides training in the fundamentals of theoretical and experimental linguistics also offers a competitive funding package (covering living expenses, tuition and fees) for the length of the program (i.e., five years);
- Students benefit from access to a rich research landscape in cognitive science where many Faculty members are associated with leading research centers including the Centre for Research on Brain, Language and Music (CRBLM) and Mila - Quebec AI Institute;
- The Department has several labs for conducting research including rooms for elicitation, running experiments including in sound booths and with an eye-tracker, and access to high performance computing infrastructure.
University-Level Admission Requirements
- An eligible Bachelor's degree with a minimum 3.0 GPA out of a possible 4.0 GPA
- English-language proficiency
Each program has specific admission requirements including required application documents. Please visit the program website for more details.
Visit our Educational credentials and grade equivalencies and English language proficiency webpages for additional information.
Program Website
PhD in Linguistics website
Department Contact
Graduate Program gradprogram.linguistics [at] mcgill.ca (subject: PhD%20in%20Linguistics) (email)
Available Intakes
Application deadlines.
Note : Application deadlines are subject to change without notice. Please check the application portal for the most up-to-date information.
Application Resources
- Application Steps webpage
- Submit Your Application webpage
- Connecting with a supervisor webpage
- Graduate Funding webpage
Application Workshops
Consult our full list of our virtual application-focused workshops on the Events webpage.
Department and University Information
Graduate and postdoctoral studies.
- Post published: March 30, 2024
Interview with Danielle Goldberg, MSU Japanese and Linguistics Graduate
Mariko Kawaguchi, Senior Instructor of Japanese, caught up with Danielle Goldberg, who graduated from MSU in spring 2023 with a B.S. in Communicative Sciences and Disorders with an additional major in Linguistics. She also minored in Japanese and Cognitive Science.

Q1. What do you do in the JET program, and what is it like teaching English in Japan?
I am an Assistant Language Teacher through the JET Program at a rural junior high school in Gunma, Japan. In my placement, I assist three English teachers, one for each grade within my school. My responsibilities vary slightly in each class, but I typically assist in reading practice, accurate pronunciation, and improving English comprehension. I also participate in cultural exchange through presentations and communication boards about various holidays, religions, and special events within diverse American cultures.
Teaching English in Japan is nothing less than an absolute blast. With a linguistics and speech-language pathology background, I’m fascinated to see my students absorb language in real-time. I can use my limited Japanese skills with my students when English doesn’t suffice while also improving my language skills. Although I am an assistant to the head teachers, I’m grateful that my teachers seek input from me regarding native English phrasing and cultural differences that appear within the language.
Q2. Why did you choose to join the JET program?
I decided to join the JET program to better understand language teaching and comprehension and improve my teaching rapport before heading to graduate school. I want to empower my students to have a curiosity for language and other parts of different cultures other than their own. That curiosity within myself led me to study Japanese initially, and my passion for language learning continued my studies. I wanted to create a space for students to be comfortable with their mistakes and to encourage language learning, not for perfection, but for communication. I hope to incorporate the skills I learn in the JET program into my speech-language pathology master’s program.
Q3. What is it like living in a different country, especially where English isn’t an official language? What were some challenges you ran into (or still run into)? Was it hard to adjust at first?
Adjusting to life in Japan had a steep learning curve, but humility and curiosity led me to try my best and be comfortable asking for help. Initially, I ran into problems communicating with my supervisor about logistics, but we both work together whenever we communicate and use Google Translate when necessary. Also, I had to learn quickly that in small interactions where I used the wrong conjugated verb or pronounced a word strangely, I had to push past the embarrassment. Getting over this hill and focusing on trying my best in Japanese conversations has relieved much of the stress I held when first arriving in Japan.
I cannot emphasize enough how excellent my support teacher has been in my daily school life. My junior high school has one English support teacher, and she has been instrumental in helping me adjust to my personal and school lives. She makes sure I understand every announcement, know every meeting, and asks many questions on my behalf when my language skills don’t suffice.
Q4. How have your Linguistics and Japanese degrees from MSU prepared you for your current position at JET and the master’s program you will start in the fall?
My linguistics and Japanese language studies at MSU continue to have a direct benefit during my time on the JET Program. Although my Japanese language skills will continue to need improvement, my formal education at MSU allows me to communicate with my coworkers and students. In the classroom, I am able to help my students better understand grammar and vocabulary because of my Japanese education. I can assist my students in finding English vocabulary when needed, translate sentences into Japanese for better comprehension, and interact with my students in English and Japanese. In addition, after studying many aspects of language, I can better assist my students in understanding English phonetics and using accurate language to understand English syntax and its difference from Japanese syntax.
Heading into my master’s program in the fall, my linguistics and Japanese studies create an innate curiosity for language learning and acquisition. The LiLAC Department instilled a passion for other cultures and languages that will assist in cultural competency practices within graduate school learning.

Q5. Why was your MSU education special? What lessons did you learn here?
My MSU education prepared me not only to attend graduate school but also to move across the world. This speaks to the success of MSU’s incredible faculty and staff. In my time at Michigan State, my professors created an environment of curiosity within learning and compelled me to be curious about other cultures, languages, and ways of thinking. I always felt grateful to the College of Arts and Letters for making an overwhelmingly large university feel small and supportive. My professors created personal relationships with me even through the challenges of the pandemic.
My time at MSU gave me a phenomenal education that continues to aid me in my current position, and I’m confident in its lifelong impact on me.
Q6. I remember you studied in the UK while you were at MSU. Please tell me the program name, time, & location, and how your study abroad experience contributed to your overall education at MSU.
I studied in London, England, under the `Communication Disorders in the UK’ for about three weeks in July 2022. Within this study abroad experience, my cohort learned about and compared the UK treatment of communication disorders to the US system. Primarily, I compared a national healthcare system to a privatized healthcare system. This stark contrast between these two approaches of speech-language pathology solidified a passion for access to care in my future profession. Within my classes, I considered many perspectives providers have toward patients and continue to compare various ways of thinking within my time in Japan.
Q7. What was your senior thesis about? What went into this research, and what did you get out of that experience?
Because linguistics was my additional major, I did not need to do a senior thesis. However, I participated in a CSD research lab, the Developmental Speech Lab, under Dr. Bridget Walsh. My time in the lab taught me further empathy and understanding for those with speech differences, especially children. Studying the adverse effects stuttering has on children is crucial in understanding stuttering in general. The work Dr. Walsh and her team research will profoundly influence future speech-language pathology practices.
Q8. What’s next for you? Tell us about the graduate program you will start in the fall and your plans after that.
I will begin my Master of Science in Speech-Language Pathology at Boston University’s Sargent College beginning fall 2024. The MS-SLP program at BU provides a unique experience with world-renowned faculty, diverse clinical placements, and interdisciplinary studies with other programs within the Sargent College of Health and Rehabilitative Sciences. I look forward to learning more about working with various age groups, identities, and communication challenges. Although I am interested in working with the pediatric population, I look forward to various clinical placements and experiencing unique parts of speech-language pathology. After graduating, I hope to work with children in clinical or school settings. I am passionate about creating empowering spaces for young children with negative perceptions of their speech challenges. I also hope to work in advocacy for access to care for speech-language pathology within marginalized communities.
Q9. What advice would you give to students looking to live outside the United States or pursue a graduate degree?
For those looking to live outside the US, I encourage you to take the leap. I woke up on the day of my departure and thought, “I shouldn’t go. I need to stay home.” And that was clearly fear talking. I was incredibly nervous, but I knew I needed to take this step to better myself and have rich experiences beyond what I knew. I also encourage those who seek to live abroad to approach different cultures with humility, not superiority. While the culture I’m currently living in is entirely different than the one I grew up with, I’m learning new values and practices that challenge my preconceived way of life. And finally, if someone wishes to live in a different country that speaks a different language- you must learn the language. Showing effort to locals to communicate in their native language can go a long way and make life significantly easier. Language connects people, and you will have a richer experience.
For those seeking a graduate degree, don’t be afraid to take a gap year or gap years. Deferring from my graduate school of choice allowed me to experience the JET program, and this year is truly changing my life for the better. Do not rush into a graduate program simply because you think it is an obligation but because it is something you are passionate about. Additionally, this gap year would have sincerely strengthened my second round of applications if I had not been accepted into graduate schools. I am so grateful to my professors, both within ComArtSci and CAL, who encouraged me to embark on the JET program before my graduate schooling and I’m thankful every day that I listened to them.
Q10. What is your favorite part of your day-to-day?
My favorite part of my day-to-day life is my connections with coworkers and students. In particular, I can participate in daily cultural and language exchanges with two of my teachers- one English support teacher and one Japanese language teacher. Each day, I write a new word or phrase commonly used within English that likely is not formally taught. I find Japanese translations and write phrases or words within an example sentence. My teachers put the sticky notes in a notebook and collect all of them to refer back to. This part of my daily routine teaches me interesting Japanese phrases while sharing useful English with my coworkers!
You Might Also Like

Russian Program Initiates New Study Abroad Program in Latvia

Citizen Scholar Makes an Impact at MSU and Now Looks Toward Graduation

CREATE! Micro-Grant Virtual Exhibit Displays Winning Projects
The UCLA Linguistics Department’s normal business hours are M-F 8am-12pm, 1-4pm. Office schedule and availability may change based on UCLA protocol ( www.covid-19.ucla.edu). Masks are optional but strongly recommended indoors. All UCLA affiliates and visitors must self-screen for symptoms before coming to campus.

The Department of Linguistics
- Christine Prechtel accepts job at the Marcus Autism Center at Emory University
We are excited to announce that Christine Prechtel (PhD alumna) has accepted a job as a Research Administrative Coordinator in the Spoken Communication Lab at the Marcus Autism Center at Emory University. Congratulations Christine!
, Christine!
News Categories
- Celebrations
- Conferences
- Graduate Students
- Journal Publications
- Publications
- Undergraduate Students
Recent News
- Yang Wang accepts position at the University of Utah
- Congratulations to Daria Bahtina and Giusi Silvestri on getting a grant to organize a Spring workshop titled Rethinking Bilingualism: Applied Approaches
- Katya Khlystova makes it to the final round of Grad Slam
- Winning of New Trust Building Space
- Department Overview
- Job Opportunties
- Ph.D. Recipients
- Faculty Office Hours
- TA Office Hours
- In Memoriam
- What is Linguistics?
- Prospective Students
- Majors and Minor
- Opportunities
- American Sign Language
- Bruin Linguists Society
- Student Resources
- The Graduate Program
- For Prospective Students
- For Current Students
- Course Schedule
- Undergraduate Courses
- Current Proseminars
- Archive of past proseminars
- Summer Courses
- Course Technology Requirements
- Overview of Research
- UCLA Working Papers
- Psycholinguistics Laboratory
- Digital and other research resources
- Visiting Scholar Requirements
- Room Reservation Request
- Key Loan Request
- General Information for Students
- For Department Members

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A PhD in linguistics is usually considered a final degree. Thesis-based program. Students are required to prepare a thesis and successfully defend in an open oral defense. Courses. Three core courses and three electives. ... The University of Calgary, located in the heart of Southern Alberta, both acknowledges and pays tribute to the ...
English Language Test. Applicants from a university outside Canada in which English is not the primary language of instruction must provide results of an English language proficiency examination as part of their application. Tests must have been taken within the last 24 months at the time of submission of your application.. Minimum requirements for the two most common English language ...
PhD Program. The PhD program in our Department requires the completion of 18 credits (6 courses) of coursework, selected by students in conjunction with their Supervisor, plus two additional courses (Ling 693-Generals Papers I, and Ling 694-Generals Papers II). Coursework is followed by writing a dissertation prospectus, and an oral doctoral ...
The PhD in Educational Research is a full-time program that is normally delivered on campus for the first two years of the program for either a Summer term start or a Fall term start. Admission Requirements ... The University of Calgary, located in the heart of Southern Alberta, both acknowledges and pays tribute to the traditional territories ...
About. The School of Languages, Linguistics, Literatures and Cultures at the University of Calgary offers a rigorous doctoral program in theoretical linguistics, drawing on work in syntax, phonology, phonetics, morphology and more to train authoritative scholars with a comprehensive understanding of the discipline. University of Calgary.
Welcome to Calgary Linguistics! Home of 'A Higher Clause', the Graduate Students' Association of Linguistics at the University of Calgary. We are a passionate group of Master's and PhD linguistics students at the University of Calgary dedicated to fostering growth, collaboration, and connection among students in the field. At Calgary ...
The PhD program in the field of Applied Linguistics challenges you to engage with foundational theories and educational research focusing on language-related issues. ... exam will be implemented in the PhD program to meet requirements for the depth and breadth outcomes from the Graduate Degree Level ... Canada, N6G 1G7 Tel: 519-661-3182 ...
Students in the PhD Linguistics program must complete coursework under the following requirements: Breadth requirement (9 credits): A minimum of nine credits from the following courses or equivalents: LING 508: Phonetic Theory and Analysis (3 credits) LING 510: Phonological Theory and Analysis (3 credits) LING 520: Syntactic Theory and Analysis ...
The School of Languages, Linguistics, Literatures and Cultures at the University of Calgary offers a rigorous doctoral program in theoretical linguistics, drawing on work in syntax, phonology, phonetics, morphology and more to train authoritative scholars with a comprehensive understanding of the discipline.
The Associate Chair - Graduate Studies is: Professor Johanne Paradis. Office: Assiniboia Hall 4-57. Phone: 780-492-0805. E-mail: [email protected]. Office hours: by appointment. Specific information about being a graduate student in the Department of Linguistics can be found on this website.
University of Calgary. This page shows a selection of the available PhDs in Canada. If you're interested in studying a Linguistics degree in Canada you can view all 22 PhDs. You can also read more about Linguistics degrees in general, or about studying in Canada. Many universities and colleges in Canada offer English-taught PhD's degrees.
About. This Languages, Literatures and Cultures program at the University of Calgary has three streams - applied linguistics, literature and/or film studies, and transcultural studies. Students in each stream enjoy personal attention and interaction with professors with far-reaching subject-area expertise who embrace a range of theoretical ...
Based in the Department of Linguistics and Languages, the PhD program in Cognitive Science of Language is interdisciplinary and includes faculty from Humanities, Science, and Health Sciences. ... Graduate Scholarship - As with OGS, applications for the Canada Graduate Scholarship must be submitted through an eligible institution. The deadline ...
Our PhD program is housed in the School of Linguistics and Languages Studies (SLaLS). Emphasizing the central role that language plays in educational, workplace, community, and other social contexts the doctoral program focuses on the following four areas: second and foreign language teaching and learning, including Teaching English as a Second Language (TESL); the nature, learning, and ...
Educational Research graduate program. Education Tower, Room 114. 2500 University Drive NW. Calgary, ABT2N 1N4. 403.220.5675. Contact the Graduate Program Administrator.
Hi, I am Dušan Nikolić, a phonetician who earned his PhD in Linguistics at the University of Calgary under the supervision of Dr. Stephen Winters. In my work, I want to understand what the processing mechanisms of prosodic categories are and how they relate to communication. I am a recipient of the prestigious Izaak-Walton Killam Award ...
PhD students from the rest of Canada will continue to pay Quebec fees. International PhD fees will see the same 3% increase as Quebec fees. ... The Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) in Linguistics offered by the Department of Linguistics in the Faculty of Arts is a research-intensive program that emphasizes specialized and well-researched learning ...
Community and Public Health. South Dakota State University. Brookings, United States. More interesting programmes for you. Find the best PhD programmes in the field of Linguistics from top universities in Canada. Check all 0 programmes.
Mariko Kawaguchi, Senior Instructor of Japanese, caught up with Danielle Goldberg, who graduated from MSU in spring 2023 with a B.S. in Communicative Sciences and Disorders with an additional major in Linguistics. She also minored in Japanese and Cognitive Science.…
The UCLA Linguistics Department's normal business hours are M-F 8am-12pm, 1-4pm. Office schedule and availability may change based on UCLA protocol ... (PhD alumna) has accepted a job as a Research Administrative Coordinator in the Spoken Communication Lab at the Marcus Autism Center at Emory University.