An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Springer Nature - PMC COVID-19 Collection


Lead Essay—Institutional Racism, Whiteness, and the Role of Critical Bioethics
Christopher mayes.
Alfred Deakin Institute, Faculty of Arts and Education, Deakin University, Geelong, VIC Australia
Yin Paradies
Amanuel elias.
Institutional racism can be defined as differential access to power, resources, and opportunities by race that further entrenches privilege and oppression (Paradies 2016 ). Along with similar concepts such as systemic, structural, cultural, and societal racism, this form of racism profoundly shapes almost all aspects of our lives, including health and healthcare (Williams, Lawrence, and Davis 2019 ). Yet, racism more broadly and institutional racism in particular has been a neglected subject in bioethical discourse and scholarship (Danis, Wilson, and White 2016 ).
Bioethics has the potential to make important contributions to anti-racist programmes and strategies addressing institutional racism, yet as scholars have argued, the “whiteness” of bioethics undermines its capacity to attend to institutionalized forms of racism (Mayes 2020 ; Russell 2016 ; Danis, Wilson, and White 2016 ). Catherine Myser argues that bioethics depends on social and ethical theories that normalize whiteness and that “we risk repeatedly re-inscribing white privilege—white supremacy even—into the very theoretical structures and methods we create as tools to identify and manage ethical issues in biomedicine” (Myser 2003 , 2). As such, whiteness not only contributes to bioethical problems such as discriminatory patient care, but it shapes the reality of what is considered an ethical problem and the way bioethicists think ethically about such problems.
To address institutional racism, and the compounding problem of whiteness, we need a bioethics that is reflexive and critical of whiteness and its relationship with institutional racism. This symposium brings together scholars and researchers from a variety of disciplines to examine how racism has been institutionalized in healthcare, how whiteness manifests in healthcare, and what bioethics can contribute towards anti-racism.
In October 2019, we invited researchers to consider the following questions:
- What are the historical and material processes that contributed to the institutionalization of racism in medicine and healthcare settings?
- What role can Indigenous knowledges play in de-centering whiteness and addressing racism?
- Does bioethics have a role in addressing racism or is it too entangled with histories of racism and whiteness?
The articles in this issue respond to these questions and articulate the affective dimension of race in clinical spaces, the economic and social costs of racialized health inequalities, the continuing effects of colonialism and complicity of bioethics in institutional racism.
The context in which this issue came together should also be noted. By early 2020, COVID-19 was quickly emerging as a global pandemic. In May 2020, the killing of George Floyd by Minneapolis police officers re-ignited Black Lives Matter protests globally. Racism associated with the COVID-19 pandemic has impacted minority groups worldwide, exacerbating pre-existing social, economic, and health vulnerabilities within an environment of populism, rampant neo-liberal capitalism, resurgent exclusionary ethno-nationalism, and retreating internationalism (Elias et al. 2020 ). These events prompted medical journals to publish editorials addressing the medical consequences of racism and highlighted the entanglement of medical institutions with racism (Hardeman, Medina, and Boyd 2020 ; Bond et al. 2020 ). Bioethicists also began to reflect on whether bioethics was complicit with institutional racism and racialized health disparities, in addition to questioning the silence of bioethics on issues of racial justice and re-thinking the role of bioethics in society (Mithani, Cooper, and Boyd 2020 ).
Many of the authors in this symposium were actively involved in organizing and responding to the racialized impacts of COVID-19. Some were also actively engaged in Black Lives Matter protests and events. We commend the authors for researching and writing under these conditions and extend our gratitude to the anonymous peer reviewers and editorial team at the Journal of Bioethical Inquiry who worked under these conditions.
Overview of the Issue
This symposium opens with an article from Yolonda Wilson arguing for the need to broaden the role and scope of bioethics to address contemptuous racism, which she defines as “disdain for the contemned patient that cannot be overcome” (Wilson 2021 , ¶6). Part of this broadening involves taking the social determinants of health seriously and recognizing the role racism plays in determining health outcomes. Wilson also argues that bioethics needs to be based on a commitment to justice that centres anti-racism.
Like Wilson’s attention to contempt, Belinda Borell critically examines the role of emotion in hospital spaces and the value placed on stoic ideals of individualism and controlled emotion. Borell argues the stoic ideal can make “hospitals emotionally unsafe spaces for Māori and other groups who place high importance in the collective sharing of emotion” (Borell 2021 , “Abstract”). Borell contends that bioethicists need to contribute to anti-racist interventions that “reclaim emotion as a measure of health” (Borell 2021 , “Conclusion”).
Bryan Mukandi’s paper draws on literature, art, and philosophy to reveal the function and effects of the racialized gaze in the clinical context. Mukandi outlines “a Canaanite reading” “to draw some of the lines that mark the Black person’s experience of the medical system” (Mukandi 2021 , ¶5). The lines that Mukandi tangles and disentangles serve to challenge bioethical thinking and writing, as well as critically analyses medical power and the way it denotes who is seen and who can speak in clinical spaces.
A series of articles expand the focus from the clinical to the institutional, constitutional, and legislative contexts. Amanuel Elias and Yin Paradies ( 2021 ) use a multidisciplinary approach to highlight the variety of costs associated with racism at the institutional level. They demonstrate that institutional racism imposes both social and economic costs that have significant ethical implications, such as avoidable disparities in healthcare, which to-date have beeng neglected by bioethicists.
Heather Came, Maria Baker, and Tim McCreanor ( 2021 ) provide a conceptual article that explores the Matike Mai Aotearoa report on constitutional transformation in New Zealand as a novel means to address structural racism within the health system. They argue that “constitutional transformation and decolonization are potentially powerful ethical sources of disruption to whiteness and structural racism,” which can help “to eliminate entrenched health disparities” (Came, Baker, and McCreanor 2021 , “Abstract”).
Thailia Anthony and Harry Blagg draw on Giorgio Agamben’s biopolitical theory to argue that settler-colonial legal and medical institutions rendered First Nations peoples as “bare life”; that is, lives “unworthy of the standard of care we owe to human beings” (Anthony and Blagg 2021 , “Aboriginal Deaths in Custody: Settler Colonial Thanatopower”). These institutions operate with and produce a “regime of truth” that denigrate Indigenous peoples, knowledges, and their bodies. Anthony and Blagg argue for a decolonizing bioethics that rethinks the colonial truths about Indigenous people, which results in the health system’s discriminatory disregard for their lives.
Chelsea Bond, David Singh, and Claudette Tyson offer a powerful article that centre stories as told by Black people that “bring Black bodies into full focus and serve as testaments to the racial violence that is meted out in the absence of care” (Bond, Singh, and Tyson 2021 , “Introduction” ¶5). They highlight the failure of bioethics and the assumed beneficence of Indigenous health research agendas to take Indigenous sovereignty and the experiences of black bodies more seriously. They argue that “the extent to which a radical bioethics can be put to service in the name of more just outcomes is dependent upon bringing Black bodies and lives into full view” (Bond, Singh, and Tyson 2021 , “Background” ¶5).
Warwick Anderson offers an insightful set of reflections on his career as a medical anthropologist and historian. Anderson notes the way ethical regimes that govern research have shifted over time and have been shaped by a (white) bioethical judgement that has an imperative for “white universal” or global application of ethical protocols. Anderson contends that we need a more flexible understanding of ethics and argues “we should recognize others as ethical agents and authorities, not just as moral subjects. We need wide-ranging bioethical reasoning, but must it be a white mythology?” (Anderson 2021 , ¶10).
In his review essay of Catherine Mills’s Biopolitics ( 2016 ) and Camisha Russell’s Assisted Reproduction of Race ( 2016 ) Christopher Mayes shows how biopolitical theory and critical philosophy of race can be useful in looking at bioethical problems from a new perspective that opens up different kinds of analyses, particularly around historically embedded problems like institutional racism and the legacies of colonialism in healthcare (Mayes 2021 ).
The symposium concludes with a provocation by Camisha Russell ( 2021 ) that bioethicists need to help scientists think about race. We sought responses from Mandy Truong and Mienah Sharif ( 2021 ) who argued that bioethics and public health can collectively advance scientific efforts towards addressing racism; and from Tessa Moll ( 2021 ) who recounted issues of medical mistrust and enduring racism in South Africa.
In 2016, John Hoberman argued that “[b]ioethicists have not embraced the opportunity to create a sociologically and historically informed bioethics that might be applied to the lives of [racial minorities] and their unending health crisis” (Hoberman 2016 , 13). Indeed, the issue of institutional racism represents a long overdue topic of interest that requires attention within the discipline. We hope that this symposium may provide some impetus to explore the possibilities for bioethics to address institutional racism more broadly and to be more aware of, and attenuate, its influence within bioethical thinking and research. More profoundly, there is a need to engage with decolonial ways of thinking, doing, and being that de-centre and rupture the largely unexamined foundations of whiteness within bioethics.
Chris Mayes receives funding from the Australian Research Council (DE170100550).
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Christopher Mayes, Email: [email protected] .
Yin Paradies, Email: [email protected] .
Amanuel Elias, Email: [email protected] .
- Anderson, W. 2021. The whiteness of bioethics. Journal of Bioethical Inquiry 18(1). 10.1007/s11673-020-10075-y. [ PubMed ]
- Antony, T., and H. Blagg. 2021. Biopower of colonialism in carceral contexts: Implications for Aboriginal deaths in custody. Journal of Bioethical Inquiry 18(1). 10.1007/s11673-020-10076-x. [ PubMed ]
- Bond, C.J., D. Singh, and C. Tyson. 2021. Black bodies and bioethics: Debunking mythologies of benevolence and beneficence in contemporary Indigenous health research in colonial Australia. Journal of Bioethical Inquiry 18(1). 10.1007/s11673-020-10079-8. [ PubMed ]
- Bond CJ, Whop LJ, Singh D, Kajlich H. Now we say Black Lives Matter but … the fact of the matter is, we just Black matter to them. The Medical Journal of Australia. 2020; 213 (6):248–250. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50727. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Borell, B. 2021. The role of emotion in understanding whiteness. Journal of Bioethical Inquiry 18(1). 10.1007/s11673-020-10074-z. [ PubMed ]
- Came, H., M. Baker, and T. McCreanor. 2021. Addressing structural racism through constitutional transformation and decolonization: Insights for the New Zealand health sector. Journal of Bioethical Inquiry 18(1). 10.1007/s11673-020-10077-w. [ PubMed ]
- Danis M, Wilson Y, White A. Bioethicists can and should contribute to addressing racism. The American Journal of Bioethics. 2016; 16 (4):3–12. doi: 10.1080/15265161.2016.1145283. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Elias, A., J. Ben, F. Mansouri, and Y. Paradies. 2020. Racism and nationalism during and beyond the COVID-19 pandemic. Ethnic and Racial Studies 44(5): 783–793.
- Elias, A., and Y. Paradies. 2021. The costs of institutional racisim and its ethical implications for healthcare. Journal of Bioethical Inquiry 18(1). 10.1007/s11673-020-10073-0. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Hardeman, R.R., E.M. Medina, and R.W. Boyd. 2020. Stolen breaths. New England Journal of Medicine . 10.1056/NEJMp2021072. [ PubMed ]
- Hoberman J. Why bioethics has a race problem. Hastings Center Report. 2016; 46 (2):12–18. doi: 10.1002/hast.542. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mayes C. White medicine, white ethics: On the historical formation of racism in Australian healthcare. Journal of Australian Studies. 2020; 44 (3):287–302. doi: 10.1080/14443058.2020.1796754. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mayes, C. 2021. Race, reproduction, and biopolitics: A review essay. Journal of Bioethical Inquiry 18(1). 10.1007/s11673-020-10071-2. [ PubMed ]
- Mithani, Z., J. Cooper, and J. W. Boyd. 2020. Bioethics and black lives: A call for bioethics to speak against racial injustice. Hastings Bioethics Forum , 3 June. https://www.thehastingscenter.org/bioethics-and-black-lives-a-call-for-bioethics-to-speak-against-racial-injustice/ . Accessed 30 Dec 2020.
- Moll, T. 2021. Medical mistrust and enduring racism in South Africa. Journal of Bioethical Inquiry 18(1). 10.1007/s11673-020-10072-1. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Mukandi, B. 2021. Being Seen by the Doctor: A Meditation on Power, Institutional Racism, and Medical Ethics. Journal of Bioethical Inquiry 18(1). 10.1007/s11673-021-10087-2. [ PubMed ]
- Myser C. Differences from somewhere: The normativity of whiteness in bioethics in the United States. The American Journal of Bioethics. 2003; 3 (2):1–11. doi: 10.1162/152651603766436072. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Paradies Y. Racism and health. In: Quah SR, Cockerham WC, editors. The International Encyclopedia of Public Health . Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2016. pp. 249–259. [ Google Scholar ]
- Russell C. Questions of race in bioethics: Deceit, disregard, disparity, and the work of decentering. Philosophy Compass. 2016; 11 (1):43–55. doi: 10.1111/phc3.12302. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- ______. 2021. Bioethicists should be helping scientists think about race. Journal of Bioethical Inquiry 18(1). 10.1007/s11673-020-10068-x. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Truong, M., and M.Z. Sharif. 2021. We’re in this together: A reflection on how bioethics and public health can collectively advance scientific efforts towards addressing racism. Journal of Bioethical Inquiry 18(1). 10.1007/s11673-020-10069-w. [ PubMed ]
- Williams DR, Lawrence JA, Davis BA. Racism and health: Evidence and needed research. Annual Review of Public Health. 2019; 40 (14):1–21. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wilson, Y.Y. 2021. Bioethics, race, and contempt. Journal of Bioethical Inquiry 18(1). 10.1007/s11673-020-10070-3. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
Lead Essay—Institutional Racism, Whiteness, and the Role of Critical Bioethics
- Symposium: Institutional Racism, Whiteness, and Bioethics
- Published: 06 April 2021
- Volume 18 , pages 9–12, ( 2021 )
Cite this article
- Christopher Mayes ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2674-6225 1 ,
- Yin Paradies 1 &
- Amanuel Elias 1
7118 Accesses
4 Citations
1 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Institutional racism can be defined as differential access to power, resources, and opportunities by race that further entrenches privilege and oppression (Paradies 2016 ). Along with similar concepts such as systemic, structural, cultural, and societal racism, this form of racism profoundly shapes almost all aspects of our lives, including health and healthcare (Williams, Lawrence, and Davis 2019 ). Yet, racism more broadly and institutional racism in particular has been a neglected subject in bioethical discourse and scholarship (Danis, Wilson, and White 2016 ).
Bioethics has the potential to make important contributions to anti-racist programmes and strategies addressing institutional racism, yet as scholars have argued, the “whiteness” of bioethics undermines its capacity to attend to institutionalized forms of racism (Mayes 2020 ; Russell 2016 ; Danis, Wilson, and White 2016 ). Catherine Myser argues that bioethics depends on social and ethical theories that normalize whiteness and that “we risk repeatedly re-inscribing white privilege—white supremacy even—into the very theoretical structures and methods we create as tools to identify and manage ethical issues in biomedicine” (Myser 2003 , 2). As such, whiteness not only contributes to bioethical problems such as discriminatory patient care, but it shapes the reality of what is considered an ethical problem and the way bioethicists think ethically about such problems.
To address institutional racism, and the compounding problem of whiteness, we need a bioethics that is reflexive and critical of whiteness and its relationship with institutional racism. This symposium brings together scholars and researchers from a variety of disciplines to examine how racism has been institutionalized in healthcare, how whiteness manifests in healthcare, and what bioethics can contribute towards anti-racism.
In October 2019, we invited researchers to consider the following questions:
What are the historical and material processes that contributed to the institutionalization of racism in medicine and healthcare settings?
What role can Indigenous knowledges play in de-centering whiteness and addressing racism?
Does bioethics have a role in addressing racism or is it too entangled with histories of racism and whiteness?
The articles in this issue respond to these questions and articulate the affective dimension of race in clinical spaces, the economic and social costs of racialized health inequalities, the continuing effects of colonialism and complicity of bioethics in institutional racism.
The context in which this issue came together should also be noted. By early 2020, COVID-19 was quickly emerging as a global pandemic. In May 2020, the killing of George Floyd by Minneapolis police officers re-ignited Black Lives Matter protests globally. Racism associated with the COVID-19 pandemic has impacted minority groups worldwide, exacerbating pre-existing social, economic, and health vulnerabilities within an environment of populism, rampant neo-liberal capitalism, resurgent exclusionary ethno-nationalism, and retreating internationalism (Elias et al. 2020 ). These events prompted medical journals to publish editorials addressing the medical consequences of racism and highlighted the entanglement of medical institutions with racism (Hardeman, Medina, and Boyd 2020 ; Bond et al. 2020 ). Bioethicists also began to reflect on whether bioethics was complicit with institutional racism and racialized health disparities, in addition to questioning the silence of bioethics on issues of racial justice and re-thinking the role of bioethics in society (Mithani, Cooper, and Boyd 2020 ).
Many of the authors in this symposium were actively involved in organizing and responding to the racialized impacts of COVID-19. Some were also actively engaged in Black Lives Matter protests and events. We commend the authors for researching and writing under these conditions and extend our gratitude to the anonymous peer reviewers and editorial team at the Journal of Bioethical Inquiry who worked under these conditions.
Overview of the Issue
This symposium opens with an article from Yolonda Wilson arguing for the need to broaden the role and scope of bioethics to address contemptuous racism, which she defines as “disdain for the contemned patient that cannot be overcome” (Wilson 2021 , ¶6). Part of this broadening involves taking the social determinants of health seriously and recognizing the role racism plays in determining health outcomes. Wilson also argues that bioethics needs to be based on a commitment to justice that centres anti-racism.
Like Wilson’s attention to contempt, Belinda Borell critically examines the role of emotion in hospital spaces and the value placed on stoic ideals of individualism and controlled emotion. Borell argues the stoic ideal can make “hospitals emotionally unsafe spaces for Māori and other groups who place high importance in the collective sharing of emotion” (Borell 2021 , “Abstract”). Borell contends that bioethicists need to contribute to anti-racist interventions that “reclaim emotion as a measure of health” (Borell 2021 , “Conclusion”).
Bryan Mukandi’s paper draws on literature, art, and philosophy to reveal the function and effects of the racialized gaze in the clinical context. Mukandi outlines “a Canaanite reading” “to draw some of the lines that mark the Black person’s experience of the medical system” (Mukandi 2021 , ¶5). The lines that Mukandi tangles and disentangles serve to challenge bioethical thinking and writing, as well as critically analyses medical power and the way it denotes who is seen and who can speak in clinical spaces.
A series of articles expand the focus from the clinical to the institutional, constitutional, and legislative contexts. Amanuel Elias and Yin Paradies ( 2021 ) use a multidisciplinary approach to highlight the variety of costs associated with racism at the institutional level. They demonstrate that institutional racism imposes both social and economic costs that have significant ethical implications, such as avoidable disparities in healthcare, which to-date have beeng neglected by bioethicists.
Heather Came, Maria Baker, and Tim McCreanor ( 2021 ) provide a conceptual article that explores the Matike Mai Aotearoa report on constitutional transformation in New Zealand as a novel means to address structural racism within the health system. They argue that “constitutional transformation and decolonization are potentially powerful ethical sources of disruption to whiteness and structural racism,” which can help “to eliminate entrenched health disparities” (Came, Baker, and McCreanor 2021 , “Abstract”).
Thailia Anthony and Harry Blagg draw on Giorgio Agamben’s biopolitical theory to argue that settler-colonial legal and medical institutions rendered First Nations peoples as “bare life”; that is, lives “unworthy of the standard of care we owe to human beings” (Anthony and Blagg 2021 , “Aboriginal Deaths in Custody: Settler Colonial Thanatopower”). These institutions operate with and produce a “regime of truth” that denigrate Indigenous peoples, knowledges, and their bodies. Anthony and Blagg argue for a decolonizing bioethics that rethinks the colonial truths about Indigenous people, which results in the health system’s discriminatory disregard for their lives.
Chelsea Bond, David Singh, and Claudette Tyson offer a powerful article that centre stories as told by Black people that “bring Black bodies into full focus and serve as testaments to the racial violence that is meted out in the absence of care” (Bond, Singh, and Tyson 2021 , “Introduction” ¶5). They highlight the failure of bioethics and the assumed beneficence of Indigenous health research agendas to take Indigenous sovereignty and the experiences of black bodies more seriously. They argue that “the extent to which a radical bioethics can be put to service in the name of more just outcomes is dependent upon bringing Black bodies and lives into full view” (Bond, Singh, and Tyson 2021 , “Background” ¶5).
Warwick Anderson offers an insightful set of reflections on his career as a medical anthropologist and historian. Anderson notes the way ethical regimes that govern research have shifted over time and have been shaped by a (white) bioethical judgement that has an imperative for “white universal” or global application of ethical protocols. Anderson contends that we need a more flexible understanding of ethics and argues “we should recognize others as ethical agents and authorities, not just as moral subjects. We need wide-ranging bioethical reasoning, but must it be a white mythology?” (Anderson 2021 , ¶10).
In his review essay of Catherine Mills’s Biopolitics ( 2016 ) and Camisha Russell’s Assisted Reproduction of Race ( 2016 ) Christopher Mayes shows how biopolitical theory and critical philosophy of race can be useful in looking at bioethical problems from a new perspective that opens up different kinds of analyses, particularly around historically embedded problems like institutional racism and the legacies of colonialism in healthcare (Mayes 2021 ).
The symposium concludes with a provocation by Camisha Russell ( 2021 ) that bioethicists need to help scientists think about race. We sought responses from Mandy Truong and Mienah Sharif ( 2021 ) who argued that bioethics and public health can collectively advance scientific efforts towards addressing racism; and from Tessa Moll ( 2021 ) who recounted issues of medical mistrust and enduring racism in South Africa.
In 2016, John Hoberman argued that “[b]ioethicists have not embraced the opportunity to create a sociologically and historically informed bioethics that might be applied to the lives of [racial minorities] and their unending health crisis” (Hoberman 2016 , 13). Indeed, the issue of institutional racism represents a long overdue topic of interest that requires attention within the discipline. We hope that this symposium may provide some impetus to explore the possibilities for bioethics to address institutional racism more broadly and to be more aware of, and attenuate, its influence within bioethical thinking and research. More profoundly, there is a need to engage with decolonial ways of thinking, doing, and being that de-centre and rupture the largely unexamined foundations of whiteness within bioethics.
Anderson, W. 2021. The whiteness of bioethics. Journal of Bioethical Inquiry 18(1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11673-020-10075-y .
Antony, T., and H. Blagg. 2021. Biopower of colonialism in carceral contexts: Implications for Aboriginal deaths in custody. Journal of Bioethical Inquiry 18(1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11673-020-10076-x .
Bond, C.J., D. Singh, and C. Tyson. 2021. Black bodies and bioethics: Debunking mythologies of benevolence and beneficence in contemporary Indigenous health research in colonial Australia. Journal of Bioethical Inquiry 18(1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11673-020-10079-8 .
Bond, C.J., L.J. Whop, D. Singh, and H. Kajlich. 2020. Now we say Black Lives Matter but … the fact of the matter is, we just Black matter to them. The Medical Journal of Australia 213(6): 248–250.
Article Google Scholar
Borell, B. 2021. The role of emotion in understanding whiteness. Journal of Bioethical Inquiry 18(1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11673-020-10074-z .
Came, H., M. Baker, and T. McCreanor. 2021. Addressing structural racism through constitutional transformation and decolonization: Insights for the New Zealand health sector. Journal of Bioethical Inquiry 18(1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11673-020-10077-w .
Danis, M., Y. Wilson, and A. White. 2016. Bioethicists can and should contribute to addressing racism. The American Journal of Bioethics 16(4): 3–12.
Elias, A., J. Ben, F. Mansouri, and Y. Paradies. 2020. Racism and nationalism during and beyond the COVID-19 pandemic. Ethnic and Racial Studies 44(5): 783–793.
Elias, A., and Y. Paradies. 2021. The costs of institutional racisim and its ethical implications for healthcare. Journal of Bioethical Inquiry 18(1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11673-020-10073-0 .
Hardeman, R.R., E.M. Medina, and R.W. Boyd. 2020. Stolen breaths. New England Journal of Medicine . https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMp2021072 .
Hoberman, J. 2016. Why bioethics has a race problem. Hastings Center Report 46(2): 12–18.
Mayes, C. 2020. White medicine, white ethics: On the historical formation of racism in Australian healthcare. Journal of Australian Studies 44(3): 287–302.
Mayes, C. 2021. Race, reproduction, and biopolitics: A review essay. Journal of Bioethical Inquiry 18(1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11673-020-10071-2 .
Mithani, Z., J. Cooper, and J. W. Boyd. 2020. Bioethics and black lives: A call for bioethics to speak against racial injustice. Hastings Bioethics Forum , 3 June. https://www.thehastingscenter.org/bioethics-and-black-lives-a-call-for-bioethics-to-speak-against-racial-injustice/ . Accessed 30 Dec 2020.
Moll, T. 2021. Medical mistrust and enduring racism in South Africa. Journal of Bioethical Inquiry 18(1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11673-020-10072-1 .
Mukandi, B. 2021. Being Seen by the Doctor: A Meditation on Power, Institutional Racism, and Medical Ethics. Journal of Bioethical Inquiry 18(1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11673-021-10087-2 .
Myser, C. 2003. Differences from somewhere: The normativity of whiteness in bioethics in the United States. The American Journal of Bioethics 3(2): 1–11.
Paradies, Y. 2016. Racism and health. In The International Encyclopedia of Public Health , edited by S.R. Quah and W.C. Cockerham, 249–259. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Google Scholar
Russell, C. 2016. Questions of race in bioethics: Deceit, disregard, disparity, and the work of decentering. Philosophy Compass 11(1): 43–55.
______. 2021. Bioethicists should be helping scientists think about race. Journal of Bioethical Inquiry 18(1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11673-020-10068-x .
Truong, M., and M.Z. Sharif. 2021. We’re in this together: A reflection on how bioethics and public health can collectively advance scientific efforts towards addressing racism. Journal of Bioethical Inquiry 18(1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11673-020-10069-w .
Williams, D.R., J.A. Lawrence, and B.A. Davis. 2019. Racism and health: Evidence and needed research. Annual Review of Public Health 40(14): 1–21.
Wilson, Y.Y. 2021. Bioethics, race, and contempt. Journal of Bioethical Inquiry 18(1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11673-020-10070-3 .
Download references
Chris Mayes receives funding from the Australian Research Council (DE170100550).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Alfred Deakin Institute, Faculty of Arts and Education, Deakin University, Geelong, VIC, Australia
Christopher Mayes, Yin Paradies & Amanuel Elias
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Christopher Mayes .
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Mayes, C., Paradies, Y. & Elias, A. Lead Essay—Institutional Racism, Whiteness, and the Role of Critical Bioethics . Bioethical Inquiry 18 , 9–12 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11673-021-10103-5
Download citation
Accepted : 17 March 2021
Published : 06 April 2021
Issue Date : March 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11673-021-10103-5
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Indigenous studies
- Biopolitics
- Critical bioethics
- Health policy
- Human rights
- Indigenous populations
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

Search form
- Find Stories
- For Journalists
Stanford scholars examine racism, social change and how to build a more just future
The recent acts of violence perpetrated against Black communities has led many to question racism and racial injustice embedded in American society. Stanford scholars have been looking for ways to reduce racial disparities and how to create meaningful change.
The tragic deaths of George Floyd in Minneapolis, Ahmaud Arbery in Georgia and Breonna Taylor in Kentucky have shown the world how deeply embedded racial injustice and racism are in the social fabric of the United States.
These recent acts of violence have raised a set of complex and challenging questions about inequality in our society: Why are Black Americans repeatedly targeted by the police? What can be done to stop further atrocities against minority communities from occurring? As some protests against these deaths turn violent, are political protests and demonstrations an effective way to instigate change? How can we build a more just society?
These important questions are among the subjects of Stanford scholars’ work. Some researchers have worked with police agencies to develop recommendations for how officers can build safer and stronger relationships with the communities they serve. Others have examined what makes some political protests effective and why others turn violent. Researchers have also looked at how racial injustice cuts across other parts of society – such as schools and workplaces – and what can be done to reduce disparities. Here is some of that research and more.
Identifying bias in the police
Stanford social psychologist Jennifer Eberhardt has worked with police departments across the country to help them recognize implicit bias and understand racial disparities in policing. Her work with the Oakland Police Department, for example, resulted in 50 recommendations about how police agencies can build better relationships with the communities they serve.
Eberhardt’s work with the Oakland Police Department underscores how important data and transparency is for police agencies to identify specific problem areas and create evidence-based solutions.
“Our recommendations are broad but are anchored in our primary mission of pushing agencies to collect more data and to do more with the data they collect,” wrote Eberhardt in the report. “For many agencies, this will require a change in mindset: it requires seeing themselves not only as crime-fighting institutions but also as institutions of learning.”
Helping communities leverage better data between the police and the public are Sharad Goel, a professor of management science and engineering, and Cheryl Phillips, a computational journalist and lecturer at Stanford. Together, they founded the Stanford Open Policing Project , to help researchers, journalists, and policymakers investigate and improve interactions between police and the public.

Cops speak less respectfully to black community members
Professors Jennifer Eberhardt and Dan Jurafsky, along with other Stanford researchers, detected racial disparities in police officers’ speech after analyzing more than 100 hours of body camera footage from Oakland Police.

Stanford big data study finds racial disparities in Oakland, Calif., police behavior, offers solutions
Analyzing thousands of data points, the researchers found racial disparities in how Oakland officers treated African Americans on routine traffic and pedestrian stops. They suggest 50 measures to improve police-community relations.

Numbers about inequality don’t speak for themselves
In a new research paper, Stanford scholars Rebecca Hetey and Jennifer Eberhardt propose new ways to talk about racial disparities that exist across society, from education to health care and criminal justice systems.

Helping journalists use data for investigative reporting
Stanford University scholars are launching a data-driven initiative to help journalists find stories at a lower cost, to support local newsrooms explore public interest issues and fight against misinformation.

A ‘veil of darkness’ reduces racial bias in traffic stops
After analyzing 95 million traffic stop records, filed by officers with 21 state patrol agencies and 35 municipal police forces from 2011 to 2018, researchers concluded that “police stops and search decisions suffer from persistent racial bias.”

Race and mass criminalization in the U.S.
Stanford sociologist discusses how race and class inequalities are embedded in the American criminal legal system.
Raising awareness and creating change
As protest erupts across the country, what makes some demonstrations more effective than others? Stanford sociologist Robb Willer is studying what causes certain social protests to be successful and others to backfire. For example, he studied violent confrontations between white nationalist protesters and anti-racist counter-protesters in both Charlottesville, Virginia, and Berkeley, California, and found that violence by anti-racist protesters can lead people to view them as unreasonable, which may, in turn, lead to people identifying less with the group.
Willer, a professor in the School of Humanities and Sciences and the Graduate School of Business (GSB), also found that when anti-racists turn their protest into violence it can backfire even further: In some cases, it can even result in support for the other side.
Some of Willer’s colleagues in GSB have also studied what makes social movements successful. For example, Sarah A. Soule , the Morgridge Professor of Organizational Behavior, has studied how social movements are more effective when they are part of coordinated efforts with legislators.
“With the rise of the internet,” Soule said, “modern movements can mobilize constituents through their websites and social media. If your end goal is to get 500,000 people to turn up on the Mall in Washington, D.C., Twitter is great at that. Facebook is great at that. But if your goal is to actually make lasting change in the system, you have to work within the system – to essentially get a seat at the table.”

How violent protest can backfire
When a protest group with strong public support turns violent, people may perceive them as less reasonable. In turn, this leads people to identify with them less, and ultimately become less supportive, according to a new study by Stanford sociologist Robb Willer.

It takes more than mass protests to drive change
Those large-scale protests on everything from climate change to wealth inequality make for engaging news segments. But do they result in real change? It turns out social advocacy organizations have greater impact on federal legislation when their experts get to testify.

Robb Willer: The powerlessness paradox
Researchers find that feeling powerless can lead people to support systems that disadvantage them.

Seven factors contributing to American racism
Of the seven factors the researchers identified, perhaps the most insidious is passivism or passive racism, which includes an apathy toward systems of racial advantage or denial that those systems even exist.

Where do advocates come from?
A strong sense of conviction can both encourage and discourage people from speaking out.

How protests can swing elections
A new study shows that both liberal and conservative protests have had a real impact on U.S. House elections.

A better way to diffuse racial discrimination
Research shows why understanding the source of discrimination matters.
Building a more just future
Overcoming racial injustice requires a critical examination of how it cuts across different sectors of society, such as in the workplace and in schools.
Sean Reardon , a professor in the Graduate School of Education, has looked closely at how poverty intersects with the educational achievement gap. While racial segregation is a major indicator of educational inequality, Reardon’s research has also shown the impact of attending impoverished schools on Black and Hispanic students.
“It’s not the racial composition of the schools that matters. What matters is when Black or Hispanic students are concentrated in high-poverty schools in a district,” said Reardon, who has set up the Educational Opportunity Project to help other researchers identify solutions in their areas to reduce educational disparities throughout the U.S.
Meanwhile, other researchers have shown how academic achievement can be hindered in other ways. For example, Claude Steele , a professor of psychology in the School of Humanities and Sciences, found that even if students are well-prepared, negative stereotypes can affect how they perform.
School is not the only setting where stereotyping results in devastating consequences. Stanford research has also shown how it leads to hiring discrimination and underfunded companies, among other problems.

New evidence shows that school poverty shapes racial achievement gaps
Racial segregation leads to growing achievement gaps – but it does so entirely through differences in school poverty, according to new research from education Professor Sean Reardon, who is launching a new tool to help educators, parents and policymakers examine education trends by race and poverty level nationwide.

Access to program for black male students lowered dropout rates
New research led by Stanford education professor Thomas S. Dee provides the first evidence of effectiveness for a district-wide initiative targeted at black male high school students.

Science lessons through a different lens
In his new book, Science in the City, Stanford education professor Bryan A. Brown helps bridge the gap between students’ culture and the science classroom.

Toolkits help tackle real-world problems
A lab in the Psychology Department at Stanford has created a set of free toolkits to help people resolve complicated issues, including resources to help people deal with disagreements.

Stereotyping makes people more likely to act badly
Even slight cues, like reading a negative stereotype about your race or gender, can have an impact.

Race influences professional investors’ judgments
In their evaluations of high-performing venture capital funds, professional investors rate white-led teams more favorably than they do black-led teams with identical credentials, a new Stanford study led by Jennifer L. Eberhardt finds.

How emotions may result in hiring, workplace bias
Stanford study suggests that the emotions American employers are looking for in job candidates may not match up with emotions valued by jobseekers from some cultural backgrounds – potentially leading to hiring bias.

Racial disparities in school discipline are linked to the achievement gap between black and white students nationwide
Research using a Stanford database of test scores from all U.S. public schools is the first to document the relationship at a national level.

Teaching difficult histories
Michael Hines talks about why students need to hear their own stories reflected in history books and classes.

Reducing racial disparities in school discipline
Stanford psychologists find that brief exercises early in middle school can improve students’ relationships with their teachers, increase their sense of belonging and reduce teachers’ reports of discipline issues among black and Latino boys.
- - Google Chrome
Intended for healthcare professionals
- Access provided by Google Indexer
- My email alerts
- BMA member login
- Username * Password * Forgot your log in details? Need to activate BMA Member Log In Log in via OpenAthens Log in via your institution

Search form
- Advanced search
- Search responses
- Search blogs
- News & Views
- Tackling racism in UK...
Tackling racism in UK health research
- Related content
- Peer review
This article has a correction. Please see:
- Errata - January 24, 2022
- Richard Antony Powell , project evaluation manager 1 2 ,
- Chidi Njoku , researcher 1 2 ,
- Ramyia Elangovan , junior doctor 3 ,
- Ganesh Sathyamoorthy , assistant director of business and partnerships 1 2 ,
- Josephine Ocloo , senior researcher 3 4 ,
- Sudhin Thayil , professor 5 ,
- Mala Rao , director 1 2
- 1 Ethnicity and Health Unit, NIHR Applied Research Collaboration Northwest London, London, UK
- 2 Department of Primary Care and Public Health, School of Public Health, Imperial College London, London, UK
- 3 Centre for Implementation Science, Health Service and Population Research Department, King’s College London, London, UK
- 4 NIHR Applied Research Collaboration South London at King’s College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, London, UK
- 5 Centre for Perinatal Neuroscience, Department of Brain Sciences, Faculty of Medicine, Imperial College London, London, UK
- Correspondence to: M Rao mala.rao{at}imperial.ac.uk
Richard A Powell and colleagues set out the barriers and solutions to eliminating inequalities embedded in the UK health research system
Seismic forces are challenging the UK’s ethno-racial status quo. 1 2 As a result, many organisations have made public commitments to listen to, learn from, and act on factors sustaining historical and current ethno-racial injustices and inequalities.
The UK health research landscape, with its vast influence on national and global strategy for health and wellbeing, has an opportunity and responsibility to advance a transformative, equity based agenda for change. 3 Racism is currently present throughout UK health research, including commissioning and implementation (both ostensibly underpinned by patient and public involvement), assessment, and dissemination, and we propose actions to produce systemic change. We use an equity approach that moves beyond creating an “equal, level playing field” and instead treats the unequal unequally. 4
Our analysis is based on an understanding of racism as “the normalisation and legitimisation of an array of dynamics—historical, cultural, institutional, and interpersonal—that routinely advantage white people while producing cumulative and chronic adverse outcomes for people of colour,” 5 based on their physiological appearance or cultural identity (ethnicity). The intersection between ethnicity, race, and health is a product of this systemic discrimination, in which racism—a social construct—not ethnicity causes health disparities. 6 7 However, reducing racism in health research infrastructure will not in itself solve population health problems. We use the descriptors “racialised minorities,” 8 recognising that disadvantage is not uniform among different minority groups, and “ethno-racial” to refer to the phenotype, ancestry, and self-identification of ethnic and racial groups. 9
Racism in research commissioning
The setting of research agendas may seem a racially neutral, objective process, but in reality these agendas are influenced by multiple potential biases. 10 The leadership of research commissioning bodies drives the research agenda, determining how questions are framed, what data informs them, and how patients and the public are involved. For example, questions can be framed to imply a “black deficit” (eg, what causes black people to have so many disadvantages compared with white people?), which places the culpability of individuals over structural failures and histories of exclusion. 11
Although inclusion of minority groups in leadership roles does not guarantee positive change, 12 evidence from other sectors suggests ethno-racial diversity has substantial benefits, 13 including a richer pool of critical ideas, innovation, and entrepreneurship. 14 15 Diversity also ensures that the workforce and cultural competence of an organisation better reflect changing population mix, and are able to meet the needs of all stakeholder communities. 16 Yet, data on the ethno-racial diversity of commissioning leadership teams is scant at best: the Wellcome Trust is one of very few research organisations to have provided information, acknowledging publicly that all members of its executive team are white. 17
Similarly exclusionary is the historical under-representation of racialised minority populations as participants in UK research despite comparatively worse rates of ill health. 18 For example, the underdetection of hypoxaemia by pulse oximetry 19 and the underdiagnosis of melanomas by cancer software 20 in black patients result from white patients being used as the default group in the algorithms used to develop and test these medical devices. Another example is the poorly evidenced, racially tailored care that can perpetuate harmful and unscientific ideas about biological differences between people of different ethnicities. These ideas persist in the medical guidelines that inform treatment decisions, 21 driving medical errors and increasing health inequities. 22 The current UK guidance on treating high blood pressure, for example, recommends angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors for everyone except people of “Black African or Black Caribbean heritage,” who are recommended calcium channel blockers initially. 23
Despite growing acknowledgement of the harmful implications of these anomalies in medical decision making and technology, research commissioners are failing to invest the resources required to ensure that devices work accurately across ethno-racial groups, and that treatment and care are not based on poor evidence, historical assumptions, and stereotypes. The interests and concerns of minorities must be represented in research planning and prioritisation.
The paucity of data on racialised minorities is itself a barrier to a diverse academic workforce and, by extension, to inclusive health research. In the Medical Research Council’s survey of research fellowships, data on the ethnicity and nationality of fellows were “very limited.” 24 The recent release of data showing the diversity of applicants for and recipients of funding from the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) showed that racialised minority applicants were less successful than white applicants (16.5% success rate v 21.2% for white applicants). This helps to fill the data gap, but NIHR recognises that more work is needed to track, report, and evaluate diversity throughout research organisations. 25
The absence of routinely collected and reported information undermines our understanding of the extent of biases in the research workforce. When data are reported, racialised minorities are often aggregated into one group, obscuring differences among distinct ethnicities. 26
Two decades ago, the seminal Stephen Lawrence inquiry in the UK triggered reflection on the need for better health related data, recommending that ethnic group rather than country of birth should be recorded on death certificates. 27 Problems associated with unreliable proxy measures of ethno-racial affiliation were highlighted again early in the covid-19 pandemic, preventing timely understanding of the virus’s differential effect on mortality, and delaying equity based remedial measures.
Patient and public involvement
Patient and public involvement in research is important because it can influence the research questions asked and the outcomes measured. Patients and the public can ensure that researchers measure outcomes that matter to them and their communities, improving the validity of data and the value of research findings. 28
Racialised minority groups are also under-represented in patient communities recruited to research. Consequently, their participation in research studies is inadequate, 29 30 31 including in covid-19 vaccine trials. 32 As others have said, “omission has consequences: people could miss out on important benefits or not be spared harms … there is no guarantee that the results will apply to populations not included in the research.” 32 Omission could also reinforce existing social injustices and health inequalities. Box 1 lists some measures to help eradicate racism in research commissioning
Potential solutions to racism in research
Include ethno-racial equity in all policies and decisions influencing the research commissioning agenda
Monitor and improve racialised minority representation in research commissioning leadership roles, on key committees and panels, and in patient and public communities involved in research
Quantify, report, and resolve variations in research funding, starting with reliable data on funding awards, stratified by ethno-racial group, as the NIHR has started to do 25
Prioritise research questions and outcomes of greatest importance to specific ethno-racial groups
Establish financial incentives to improve diversity in research institutions by developing criteria modelled on the Athena SWAN Charter 33 (linked to improving gender equality in academia), as a condition of NIHR funding
Racism in academia
Academics are responsible for implementing the research agenda and training the next generation of researchers, yet negative experiences are becoming normalised in a culture of silent acceptance. 34 In 2019, 24% of racialised minority university students reported experiencing racial harassment, 35 but, for example, only half of medical schools collected data on their complaints. 36 Racialised minority applicants are less likely than white applicants to be awarded funding grants by the UK’s Wellcome Trust 17 and are under-represented among UK Research and Innovation (UKRI) fellows and principal investigators, 26 echoing US funding differentials among African-American or black principal investigators. 37
The mechanisms by which the academic environment and structures reinforce existing inequities are complex, but core challenges include lack of diversity in executive leadership, ethno-racial discordance between students and teachers, unsupportive “soft learning” environments, and poorer research funding for racialised minority academics.
The executive leadership of all major UK medical schools is overwhelmingly white, 38 while 41% of medical students are from racialised minorities. 39 Such snowy white peaks at university potentially foster a networked club culture in which access to senior leadership positions can exclude racialised minority academics. Moreover, evidence suggests ethno-racial concordance between students and teachers benefits learning and achievement in medical and other disciplines. 40 41
Despite being selected for academic achievement, medical students from minority backgrounds perform worse educationally on average than white peers in the UK. 42 One explanation lies in the learning experience. Learning is an interactive social process between students, teachers, and peers, but these processes are patterned by ethnicity. 43 Learning environments must also be supportive and celebrate difference, a process aided by greater ethno-racial diversity among academics. In 2019, racialised minorities accounted for 22% of lecturers, readers, and senior lecturers in medical schools, but only 14% of medical professors. 44
Those charged with tackling these inequities could learn from the NHS, where the Workforce Race Equality Standard (WRES) 45 and, more recently, the Medical Workforce Race Equality Standard (MWRES) 46 have been collecting data on race inequality since 2015, holding up a mirror to the service and revealing disparities in career progression, experience, and opportunities that exist for people from racialised minorities compared with white staff. Although change may be slow, data collection has increased awareness and action to tackle many dimensions of structural racism in medicine, ranging from recruitment to bullying, education, and training. Importantly, it has resulted in modest but demonstrable improvements, including a small increase in the diversity of NHS “very senior managers” and trust board membership across England since 2017. 45
Indicators should be developed to monitor the recruitment, career progression, experience, and achievements (including funding awards) of academics and researchers from racialised minority groups. Strategies must also be developed to address any disparities exposed by these indicators, drawing on lessons from the response to WRES and MWRES in the NHS.
Racism in assessment of research excellence
A UK university’s research performance is appraised and ranked every six years using a system called the research excellence framework. The 2021 round of assessments—delayed by the pandemic—includes a measure of diversity and equality as part of the evaluation of “the vitality and sustainability of a university’s research environment.” However, it remains unclear what proportion of the overall environment score—which accounts for only 15% of a university’s overall assessment—will be determined by equality and diversity. 47 Furthermore, equality and diversity are assessed from written submissions. There is no requirement for data on how minorities experience a university environment, despite evidence that equality and diversity strategies correlate poorly with actual working conditions and progression for women and minorities. 48
The UK’s research excellence framework should be reformed to improve assessment of ethno-racial equity within universities, for both workforce and students. Importantly, academics and students from racialised minorities should be full partners in the design and implementation of these reforms. Related frameworks from other countries, including the US—where the National Institutes of Health seek to tackle structural racism and promote racial equity and inclusion internally and within the larger biomedical research enterprise 49 —could inform this process.
The ultimate goal is a more effective multidimensional assessment of research performance that does full justice to the importance of diversity, inclusion, and ethno-racial equity based on a dataset agreed by all stakeholders.
Racism in research dissemination
Substantial evidence exists of widespread ethno-racial bias in academic publishing. 50 51 52 53 In the US, journals have been criticised for denying ethno-racial bias, refusing to publish research identifying racism, 54 and recruiting and tolerating overwhelmingly white editorial boards. 55 In the UK, Nature has acknowledged that it is “one of the white institutions … responsible for bias in research and scholarship,” declaring that science “has been—and remains—complicit in systemic racism.” 56 Similarly, the Lancet described itself as having “a deep colonial history.” 57
It is important for journals to show a commitment to equity. Journal editors are powerful gatekeepers, determining what gets reviewed (by whom) and published, and publications matter. Publications and other academic outputs account for 60% of the overall score of institutions in the latest research excellence framework. 47 For academics, journal publications, membership of editorial boards, and invitations to review papers are key measures of success and requirements for career progression. Publications are also important for securing research funding; developing the analytical, reviewing, and writing skills of trainees; and disseminating knowledge and research.
The potential power of journals to effect change in key societal issues was shown by The BMJ’s 2020 themed issue on racism in medicine, 58 which substantially contributed to the subsequent decision to launch an NHS Race and Health Observatory. 59 In recognition of the role of journals in embedding justice and equity in research and scholarly communication, The BMJ has pledged a commitment to equality, diversity, and inclusion, 60 as have others. 56 57 Stated commitments of high impact journals to address inherent biases in the publication process, improve the publication chances of racialised minorities, and increase the publication of ethno-racial research are welcome. But journals could and should be more ambitious, committing to measurable targets and timetables to achieve justice and equity for under-represented groups. Journals could start by publishing regular data on the diversity of their authors, reviewers, and editorial boards. They could also audit and publish the proportion of content dedicated to ethno-racial research.
Commitment to change
For too long health research architecture in the UK has been guilty of reinforcing instead of reducing systemic ethno-racial inequities, fortifying “persistent, pervasive racism that exists across societies.” 61 Stakeholders in the UK must change their structures, systems, and processes to reflect the diversity of the population, optimise innovation, and inform inclusive decision making. 62 They must implement a transformative, anti-racist, equity based research agenda. By committing to this agenda, we can make substantive and permanent change tackling the structural determinants of health inequalities.
Key messages
Racism is evident across the UK health research landscape, from funding bodies through to peer reviewed journals
UK organisations are beginning to listen to, learn from, and act on factors maintaining historical ethno-racial injustice and social inequity
Stakeholders must collectively commit to improving equity, diversity, and inclusion in health research, by changing structures, systems, and processes
Ethno-racial equity requires a research community determined to ensure that health research does not reinforce and exacerbate existing health and social inequities
Contributors and sources: The authors have experience advocating for change in the UK NHS and research funding agencies. MR, GS, CN, ST, and JO have experienced ethno-racial discrimination within and outside academia, and JO is also a patient and public involvement representative and lived experience researcher. RAP has researched and commented on services received by, and provided to, people from racialised minority communities in the UK and diverse ethnic populations internationally. The article is based on peer reviewed publications, grey literature, and primary data collection by the authors. MR conceived this article. RAP initially drafted the paper, with all co-authors reviewing and contributing to its revision and finalisation. MR is the guarantor.
Competing interests: We have read and understood BMJ policy on declaration of interests and have no relevant interests to declare. The views expressed are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the NHS, the NIHR, or the Department of Health and Social Care.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
This is an Open Access article distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution Non Commercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial. See: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ .
- ↵ Gottbrath L-W. The Black Lives Matter movement shook the world. Al Jazeera 2020 Dec 31. https://www.aljazeera.com/features/2020/12/31/2020-the-year-black-lives-matter-shook-the-world
- ↵ Lawrence K, Keleher T. Structural racism. Race and Public Policy Conference, 2004. https://www.intergroupresources.com/rc/Definitions%20of%20Racism.pdf .
- ↵ Wallis C. Why racism, not race, is a risk factor for dying of covid-19. Scientific American 2020 Jun 12. https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/why-racism-not-race-is-a-risk-factor-for-dying-of-covid-191/
- ↵ Gabriel D. Racial categorisation and terminology. Black British Academics. https://blackbritishacademics.co.uk/about/racial-categorisation-and-terminology/
- Aeschbach M
- Hardeman RR ,
- ↵ Razai MS, Majeed A, Esmail A. Structural racism is a fundamental cause and driver of ethnic disparities in health. BMJ Opinion, 31 Mar 2021. https://blogs.bmj.com/bmj/2021/03/31/structural-racism-is-a-fundamental-cause-and-driver-of-ethnic-disparities-in-health/
- ↵ Hunt V, Prince S, Dixon-Fyle S, Dolan K. Diversity wins: how inclusion matters. 2020. https://www.mckinsey.com/~/media/McKinsey/Featured%20Insights/Diversity%20and%20Inclusion/Diversity%20wins%20How%20inclusion%20matters/Diversity-wins-How-inclusion-matters-vF.pdf
- ↵ Rock D, Grant H. Why diverse teams are smarter. Harvard Business Review 2016 Nov 4. https://hbr.org/2016/11/why-diverse-teams-are-smarter
- Breitenstine L ,
- Shreber L ,
- Moffitt T ,
- ↵ Wellcome Trust. Our commitment to tackling racism at Wellcome. Press release, 17 Jun 2020. https://wellcome.org/press-release/our-commitment-tackling-racism-wellcome
- Sjoding MW ,
- Dickson RP ,
- Iwashyna TJ ,
- Liverpool L ,
- Cerdeña JP ,
- Plaisime MV ,
- Medical Research Council
- ↵ National Institute of Health Research. Diversity data report 2020-21 . 2021. https://www.nihr.ac.uk/documents/diversity-data-report-202021/29410
- ↵ UK Research and Innovation. Diversity results for UKRI funding data: 2014-15 to 2018-19 . 2020. https://www.ukri.org/publications/diversity-results-analysis-for-ukri-funding-data-financial-years-2014-15-to-2018-19/
- Palmer-Cooper E
- ↵ Ocloo J. Being heard, not, “seldom heard”: democratising research with diverse communities during the covid-19 pandemic. BMJ Opinion, 2 Jun 2020. https://blogs.bmj.com/bmj/2020/06/02/being-heard-not-seldom-heard-democratising-research-with-diverse-communities-during-the-covid-19-pandemic/
- Treweek S ,
- Forouhi NG ,
- Narayan KMV ,
- ↵ Advance HE. Athena Swan Charter. https://www.advance-he.ac.uk/equality-charters/athena-swan-charter
- Elmorally R ,
- Copsey-Blake M ,
- Highwood E ,
- Singarayer J
- ↵ Equality and Human Rights Commission. Racial harassment inquiry: survey of university students. Research report No. 129. Equality and Human Rights Commission, 2019.
- Kmietowicz Z
- ↵ Park G. The colour of power. Green Park, 2020. https://www.green-park.co.uk/insights/the-colour-of-power/s191468/
- ↵ General Medical Council. Number of medical students per medical school by ethnicity in UK for 2016/2017. https://www.gmc-uk.org/-/media/documents/201617_Medical_School_Annual_Return_overall_student_numbers_and_demographics.xlsx_71843956.xlsx
- Potts HWW ,
- ↵ Medical Schools Council. Clinical academic survey, 2019. https://www.medschools.ac.uk/clinical-academic-survey
- ↵ NHS. Workforce race equality standard. 2020 data analysis report for NHS Trusts and clinical commissioning groups. NHS, 2021. https://www.england.nhs.uk/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/Workforce-Race-Equality-Standard-2020-report.pdf
- ↵ NHS. Medical workforce race equality standard. WRES indicators for the medical workforce 2020. 2021. https://www.england.nhs.uk/publication/medical-workforce-race-equality-standard-2020-data-report/
- ↵ National Institutes of Health. Ending structural racism. https://www.nih.gov/ending-structural-racism .
- Fortunato S
- Macinko J ,
- Jimenez G ,
- Mullachery P
- ↵ Krieger N, Boyd RW, De Maio F, Maybank A. Medicine’s privileged gatekeepers: producing harmful ignorance about racism and health. Health Affairs blog, 20 Apr 2021. https://www.healthaffairs.org/do/10.1377/hblog20210415.305480/full/ .
- ↵ McFarling UL. When a cardiologist flagged the lack of diversity at premier medical journals, the silence was telling. STAT 2021 Apr 12. https://www.statnews.com/2021/04/12/lack-of-diversity-at-premier-medical-journals-jama-nejm/
- ↵ Systemic racism: science must listen, learn and change . Nature 2020 ; 582 : 147 . doi: 10.1038/d41586-020-01678-x pmid: 32518347 OpenUrl CrossRef PubMed
- Editors of The Lancet Group
- ↵ Racism in medicine (special edition). BMJ 2020;368 (13 Feb). https://www.bmj.com/racism-in-medicine .
- ↵ Richards M, Franco J, Bloom T. A commitment to equality, diversity and inclusion for BMJ and our journals. BMJ Opinion, 23 Jul 2021. https://blogs.bmj.com/bmj/2021/07/23/a-commitment-to-equality-diversity-and-inclusion-for-bmj-and-our-journals/ .
- Adebowale V ,
- Tutorial Review
- Open access
- Published: 20 December 2021
Systemic racism: individuals and interactions, institutions and society
- Mahzarin R. Banaji 1 ,
- Susan T. Fiske ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1693-3425 2 &
- Douglas S. Massey 2
Cognitive Research: Principles and Implications volume 6 , Article number: 82 ( 2021 ) Cite this article
143k Accesses
45 Citations
253 Altmetric
Metrics details
Systemic racism is a scientifically tractable phenomenon, urgent for cognitive scientists to address. This tutorial reviews the built-in systems that undermine life opportunities and outcomes by racial category, with a focus on challenges to Black Americans. From American colonial history, explicit practices and policies reinforced disadvantage across all domains of life, beginning with slavery, and continuing with vastly subordinated status. Racially segregated housing creates racial isolation, with disproportionate costs to Black Americans’ opportunities, networks, education, wealth, health, and legal treatment. These institutional and societal systems build-in individual bias and racialized interactions, resulting in systemic racism. Unconscious inferences, empirically established from perceptions onward, demonstrate non-Black Americans’ inbuilt associations: pairing Black Americans with negative valences, criminal stereotypes, and low status, including animal rather than human . Implicit racial biases (improving only slightly over time) imbed within non-Black individuals’ systems of racialized beliefs, judgments, and affect that predict racialized behavior. Interracial interactions likewise convey disrespect and distrust. These systematic individual and interpersonal patterns continue partly due to non-Black people’s inexperience with Black Americans and reliance on societal caricatures. Despite systemic challenges, Black Americans are more diverse now than ever, due to resilience (many succeeding against the odds), immigration (producing varied backgrounds), and intermarriage (increasing the multiracial proportion of the population). Intergroup contact can foreground Black diversity, resisting systemic racism, but White advantages persist in all economic, political, and social domains. Cognitive science has an opportunity: to include in its study of the mind the distortions of reality about individual humans and their social groups.
Introduction
Significance.
American racial biases persist over time and permeate (a) institutional structures, (b) societal structures, (c) individual mental structures, (d) everyday interaction patterns. Systemic racism operates with or without intention and with or without awareness. But because these responses are based on socially defined racial categories, they are racialized, and because they are negative, they reveal the roots of racism. At the level of most behavior, they are also controllable, even if many non-Black people rarely notice these relentless patterns. Systemic racism is a unified arrangement of racial differentiation and discrimination across generations. Understanding these formidable challenges is necessary to understand and then dismantle them. Cognitive science can illuminate the fine-grained levels of inbuilt racial bias because it has the methods and the theories to do so. Moreover, studying racial bias is interesting; it will improve the science; and it is the obvious path to ensuring a mutually respectful, peaceful society that flourishes economically, politically, and socially.
At the Editor’s invitation, this article presents the social and behavioral science of systemic racism to a cognitive science audience. The tutorial defines systemic racism, describes its origins in US history, shows how the resulting racialized societal structures have become built-in cognitive structures that propagate in social interactions, resisting change. But these very societal-cognitive-social features can also be agents for change.
Systemic racism is said to occur when racially unequal opportunities and outcomes are inbuilt or intrinsic to the operation of a society’s structures. Simply put, systemic racism refers to the processes and outcomes of racial inequality and inequity in life opportunities and treatment. Systemic racism permeates a society’s (a) institutional structures (practices, policies, climate), (b) social structures (state/federal programs, laws, culture), (c) individual mental structures (e.g., learning, memory, attitudes, beliefs, values), and (d) everyday interaction patterns (norms, scripts, habits). Systemic racism not only operates at multiple levels, it can emerge with or without animus or intention to harm and with or without awareness of its existence. Its power derives from its being integrated into a unified system of racial differentiation and discrimination that creates, governs, and adjudicates opportunities and outcomes across generations. Racism represents the biases of the powerful (Jones, 1971 ), as the biases of the powerless have little consequence (Fiske, 1993 ). Footnote 1
We highlight the “inbuilt” aspect of systemic racism to be its signature feature and the touchstone necessary to understand the nature of systemic racism and its resistance to awareness and change. We begin with the concept’s more traditional domains: institutional and societal systems. Then, given the current venue, we expand the levels of analysis to include individual mental systems that have built in those systems of inequalities. We close with the interaction of those minds in social behavior, which can either maintain or change racial systems.
Institutions and Society . As the first section explains, the term systemic racism has traditionally referred to systems that uphold racism via institutional power (Feagin, 2006 ), with stark examples of what is also called institutional racism (Jones, 1972 ) visible in inequities in housing and lending, as well as more broadly in access to finance, education, healthcare, and justice. This section focuses on the institutional level in depth, as it provides the strongest evidence of systemic racism. At an even more macro s ocietal level, however, the inbuilt aspect of systemic racism is evident in race-based demarcations created by large-scale state and federal programs, which offer levers either to increase or decrease systemic racism. To remain within the scope of the paper, we consider the structures of institutional and societal racism in a single section.
Individuals and Interactions . In tandem with the previous section, this section focuses on individual bias and interactional racism, together bringing into view the inbuilt nature of systemic racism. To expand on this inclusive view of systemic racism, we end by reviewing what we know about the individual human being, alone and interacting with others. Individuals are agentic entities, the primary actors within all systems of life and living. Their attitudes (preferences, prejudices), beliefs (stereotypes), and behaviors (discrimination) are inbuilt or intrinsically enmeshed into the foundation of the mental systems that feed systemic racism. At the individual level, “inbuilt” refers to the common psychological processes that represent race in the minds of individuals. This evidence reveals systemic race bias.
Note that, here, we use slightly different terms: Systemic Racism refers to much of the sociological, demographic, and historic material as well as anything in the psychological section that is explicit and conscious racism. Systemic Race Bias is about implicit cognition—people who may not be aware of the harm they may cause. Implicit race bias does not mean a person is a racist. In this view, keeping racism and bias separate as terms seems advisable. Others view even unexamined racism as systemic racism in its individual manifestation. Each section elaborates on the meaning of racism in that context.
Individual racial bias propagates through both face-to-face and virtual interactions within families, classrooms, playfields, and workplaces, both verbally and non-verbally. Individual minds create and consume racial representations in books, social media, and entertainment. Footnote 2 We focus here on everyday interactions that convey disrespect and distrust of Black Americans.
Why? Role for psychological science in studying systemic racism
Individual humans are the creators and consumers of thoughts, feelings, and behaviors, but also the policies and practices that lie at the heart of systemic racism. Psychology as a field has historically remained silent on the topic of systemic racism, per se (e.g., Guthrie, 2004 , “Even the rat was white”; for exceptions, see: Jones, 1971 ; DuBois, 1925 ). Perhaps psychologists have regarded systemic racism to be a form of institutional racism and hence in the bailiwick of social scientists who study institutions and society, not individuals. Nonetheless, we attempt here to include individual minds and face-to-face interaction as playing a role. This goal has precedents: Early scholars who straddled disciplines, such as George Herbert Mead ( 1934 , p. 174), would likely find our attempt to be quite compatible with his stance that mind and society must be considered in intertwined fashion.
Today, psychologists are increasingly attempting to bridge the divide between the individual mind and society. Cultural psychology, for example, has attempted to analyze racism as the “budding product of psychological subjectivity and the structural foundation for dynamic reproduction of racist action” (Salter, Adams & Perez, 2018 , p. 151). This dynamic can emerge in individual racist actions (with or without awareness) that are fitted into the structure of everyday life and perpetuate systemic racism. Interpersonal interactions bridge individual and collective representations of race. Individual minds, sharing some notions about each other’s salient identities (e.g., probable race, gender, age) treat each other according to social norms, cultural habits, and cultural scripts. In the case of race, these individual mental representations and social interaction patterns rarely benefit Black participants facing Whites.
“Inbuilt”: A useful metaphor guiding the essay
There are these two fish swimming along and they happen to meet an older fish swimming the other way, who nods at them and says ’Morning, boys. How’s the water?’ And the two young fish swim on for a bit, and then eventually one of them looks over at the other and goes ‘What the hell is water?’ Wallace, 2009
The fable highlights a simple idea—that the most fundamental feature of any system may be so completely pervasive that it ceases to be perceptible or when perceptible, fails to be recognized in its true form. This paradox creates a challenge for social and behavioral scientists, who must not only generate evidence about the complexities of systemic racism, but we must also confront unthinking rejection of that evidence. Other scientists face similar challenges in documenting their own complex phenomena, such as the resistance faced by the theory of evolution or the denial of evidence about climate change.
In most cases, evidence eventually reaches a tipping point, after which it ceases to be denied and even becomes sufficiently commonplace that its previous denial itself is puzzling. An easy example is the denial of scientific evidence about the position of the earth in the solar system and its shape, with few arguments today (but not zero!) about a flat earth. However, we are far from that tipping point of knowledge and acceptance when it comes to the idea of systemic racism. This paper, then, is yet another attempt, by connecting across the individual, interactional, and institutional/societal levels, to shed light on its existence.
The obvious allegorical lesson from the fable about the fish is of course the ease of being ignorant of that which is pervasive. However, the fable also points out that not all the fish are ignorant of their surroundings. The older fish, swimming the same ocean as the young fish, seems to have figured out the truth about the substance that suffuses its environment so fully that it is imperceptible to its peers. Ignorance then, need not be the only guaranteed outcome, even when perception and awareness are hard. Hence, one section uses the term “unexamined” to describe controllable attention to or willful neglect of one’s own biases (see also Fiske, 1998 ). Social scientists commenting on resistance to socioeconomic inequality have used the term “clueless” (Williams, 2019 ), which is admittedly harsh but suggests that learning some facts would permit more evidence-based understanding. Regardless, the evidence for systemic racism, at the level of institutions and society or at the level of individuals and interactions, requires re-examining the taken-for-granted, whether the water we swim or the air we breathe.
Systemic racism: the role of institutional and societal structures
Contemporary societal racism rests on Black–White segregation, historical and current. This first substantive section presents evidence that systemic racism has long pervaded US institutional and societal systems—creating a context for the minds of individuals within these systems, enabling an omnipresent neglect. First, this section shows that continued housing segregation by race obstructs Black opportunity and mobility, perpetuating racial disparities, challenging many Black Americans in ways White Americans never experience (Massey, 2020 ). At a societal level, Black disadvantage and White advantage come in part from residential hypersegregation (Massey & Tannen, 2015 ). More than any other racial group, Whites live in racially isolated neighborhoods (Rugh & Massey, 2014 ); and in the US neighborhood segregation translates directly into school segregation (Massey & Tannen, 2016 ; Owens, 2020 ). Both segregation and local funding undermine the quality of predominantly Black schools.
To elaborate these points, this section describes the historical context for US racism, territory likely to be less familiar to cognitive scientists. Our takeaway: Systemic racism pervades US social institutions, policies, and practices; later sections show how the societal structures make into the minds of the humans within these systems.
History: segregation and systemic racism
To explain systemic racism, we start with the historical origins of race in the US—that is, the social/political/economic mechanisms that have maintained it over time. Race is baked into the history of the US going back to colonial times (Higginbotham, 1998 ; Jones, 1972 , 1997 ) and continuing through early independence when slavery was quietly written into the nation’s Constitution (Waldstreicher, 2009 ). Although the 13th, 14th, and 15th Amendments to the Constitution ended slavery and granted due process, equal protection, and voting rights to the formerly enslaved, efforts to combat systemic racism in the US faltered when Reconstruction collapsed in the disputed election of 1876, which triggered the withdrawal of federal troops from the South (Foner, 1990 ).
The absence of federal troops to enforce Black civil rights enabled states in the former Confederacy to construct a new system of racial subordination known as Jim Crow (Packard, 2003 ). It rested on a simple principle: in any social encounter, the lowest status White person was superior to the highest status Black person. By law and custom, Black voting rights were suppressed, and Black Americans were socially segregated from Whites, relegated to menial occupations, inferior schools, dilapidated housing, and deficient facilities throughout Southern society. Any challenges to the Jim Crow system, perceived or real, were met with violence, often lethal, both within and outside the legal system (Tolnay & Beck, 1995 ).
From 1876 to 1900, 90% of all African Americans lived in the South and were subject to the dictates of the repressive Jim Crow system; 83% lived in poor rural areas, occupying ramshackle dwellings clustered in small settlements in or near the plantations where they worked. Although conditions were somewhat better for the 10% of African Americans who lived outside the South (68% in cities), anti-Black prejudice was widespread, racial discrimination was common and, as in the South, the prospect of racial violence was never far away (Sugrue, 2008 ).
Before, 1900, few African Americans lived in cities, and levels of urban racial residential segregation were modest. Black workers and servants generally lived within walking distance of their workplaces, and social contact between the races was common (Massey & Denton, 1993 ). At that time, the share of Blacks among city residents was small, and they were not perceived to be a threat to White hegemony, obviating the need for spatial segregation. The Great Black Migration of the twentieth century changed this status quo and transformed race relations in the US, making race truly a national rather than regional issue (Lemann, 1991 ). This transformation also created a new system of racial subordination based on Black residential segregation.
Between 1900 and 1970, millions of African Americans left the rural South in search of better lives in industrializing cities throughout the nation. As a result of this migration, by 1970 nearly half of all African Americans had come to live outside the South, 90% in urban areas (Farley & Allen, 1987 ). It was during this period of Black urbanization that the ghetto emerged as a structural feature of American urbanism, making Black residential segregation into the linchpin of a new system of racial stratification that prevailed throughout the US irrespective of region (Pettigrew, 1979 ).
Black out-migration from the South began slowly at first, but accelerated after 1914, when the onset of the First World War curtailed the arrival of workers from Europe. It accelerated again after 1917, when the US entered the war, boosting labor demand as conscription drew workers out of the labor force. The imposition of strict immigration restrictions in 1921 and 1924 guaranteed that Black workers and their families would continue to pour into cities during the economic boom of the 1920s (Wilkerson, 2010 ). The entry of ever-larger cohorts of impoverished Black laborers and sharecroppers into the nation’s cities unnerved White urbanites, prompting them to organize collectively by creating “neighborhood improvement associations.” These organizations pressured landlords not to rent to Black tenants and tried to convince Black home seekers that it was in their best interest to locate elsewhere, using persuasion and payoffs when possible but resorting to violence when these blandishments failed (Massey & Denton, 1993 ).
As the number of incoming Black migrants continued to rise despite these efforts, White city residents demanded that politicians act to “do something” about the perceived “Black invasion.” Officials in smaller towns and cities responded by enacting “sundown laws” that required all Blacks to leave town by sunset (Loewen, 2018 ). In large cities, legislators passed municipal ordinances that confined Black residents to a specific set of already disadvantaged neighborhoods and excluded them from all others. These ordinances were the functional equivalent of South Africa’s Group Areas Act, which underlay the establishment of that country’s apartheid system in, 1948. These ordinances were widely copied and were spreading rapidly from city to city when, in 1917, the Supreme Court declared them to be unconstitutional (Massey & Denton, 1993 ). Sundown laws, however, were never challenged in court and remained in force well into the Civil Rights Era.
The end of legally mandated neighborhood segregation in cities occurred just as Black migration surged in the aftermath of America’s entry into the First World War. The sudden influx of workers caused existing areas of Black settlement to fill up rapidly and eventually overflow into adjacent White areas, where the arrivals met with increasingly violent resistance. The violence peaked in the late teens as anti-Black race riots swept through the nation’s cities, culminating in the Great Chicago Race Riot of 1919 (Tuttle, 1970 ). Even established Black neighborhoods were not safe, as evidenced by the Tulsa Massacre of 1921, in which the prosperous Black neighborhood of Greenwood was systematically attacked and razed by mobs of White vigilantes, leaving thousands homeless and dozens, perhaps hundreds, killed (Madigan, 2001 ).
Shocked by the wanton destruction of property, the real estate industry moved to institutionalize racial discrimination in housing markets and assert control over the process of racial change in cities (Massey & Denton, 1993 ). In 1924, the National Association of Real Estate Brokers adopted a code of ethics stating that “a Realtor should never be instrumental in introducing into a neighborhood a character of property or occupancy, members of any race or nationality, or any individuals whose presence will clearly be detrimental to property values in that neighborhood” (Helper, 1969 , p. 201). In 1927, the Chicago Real Estate Board devised a model racial covenant to block the entry of Blacks into White neighborhoods and offered it to other cities for adoption throughout the country (Massey & Denton, 1993 ). A racial covenant is a private contract in which property owners within a defined geographic area collectively agree not to rent or sell to African Americans. Once approved by a majority of property owners, the contract became enforceable, and violators could be sued in civil court.
As the real estate industry gradually assumed control of racial change in urban areas, racial violence abated and neighborhood transitions from White to Black came to be managed professionally by realtors who sought to minimize confrontation and maximize profits. As Black migration continued throughout the 1920s, recognized Black neighborhoods steadily increased in density as housing units were divided and subdivided. Basements, garages, attics, and even closets were converted into rental units. Eventually, however, no more living space could be squeezed into the confines of the existing ghetto. Realtors then conspired to move the residential color line, selecting an adjacent neighborhood for racial transition and initiating an institutionalized process known as “block busting” (Philpott, 1978 ).
Realtors began the process by choosing a few poor Black families just arrived from the rural South and obviously unused to city ways to be placed strategically into selected units within the targeted neighborhood. Agents then moved through the neighborhood block by block warning residents of a pending Black “invasion.” Panic selling ensued, enabling realtors to purchase homes cheaply for subdivision into smaller apartments, which were then leased at inflated rents to African Americans desperate for living space. Owing to these institutionalized practices, Black segregation levels steadily climbed through the 1920s and ghetto areas gradually expanded their boundaries through the profitable management of neighborhood racial turnover by realtors (Massey & Denton, 1993 ).
The exclusively private auspices of Black residential segregation ended with the onset of the Great Depression in 1929. When Franklin Roosevelt came to power with his New Deal in 1933, the nation was in the midst of a catastrophic banking crisis. Millions of middle-class homeowners had lost jobs and were in danger of defaulting on their mortgages, putting both their homes and their bankers at financial risk. In response, the Roosevelt Administration created the Home Owners Loan Corporation (HOLC) to help middle class homeowners refinance their mortgages using long-term, federally insured, low-interest loans (Jackson, 1985 ). Together the federal guarantees and extended amortization periods reduced monthly mortgage payments to affordable levels, saving both the banks and the homeowners from financial losses through foreclosure.
To qualify for the federal guarantees, however, HOLC loans had to meet certain government-mandated criteria. In addition to low interest rates, minimal down payments, and long amortization periods, lenders were obliged to consider the riskiness of the neighborhoods in which properties were located. To this end, HOLC officials worked with local realtors and bankers to create a series of Residential Security Maps for use in cities throughout the nation. These maps color-coded neighborhoods according to their creditworthiness. Green indicated a safe investment, yellow indicated caution, and red indicated excessive risk and hence ineligibility for HOLC lending. Black neighborhoods were invariably coded red, along with adjacent neighborhoods perceived to be at risk of Black settlement (Rothstein, 2017 ).
The HOLC lending program only helped the minority of families that already owned homes, however, and in order to spread housing wealth to a wider population and create jobs in the real estate and construction industries, in 1934 the Roosevelt Administration created a much larger loan program under the Federal Housing Authority. The FHA offered long-term loans to prospective home buyers , not just owners. As before, federally guaranteed loans had to meet federally mandated criteria, which evinced a strong anti-urban bias. Specifically, they excluded from eligibility all multiunit buildings, attached dwellings, row houses, and structures containing a business. These provisions effectively restricted FHA loans to single family houses on large lots, thus channeling housing investment away from central cities toward vacant land on the urban fringes (Jackson, 1985 ).
Reflecting the prejudices of the realtors, bankers, and builders who helped to design the program, FHA underwriters were also required to make use of the HOLC’s Residential Security Maps, formally institutionalizing the practice of redlining in real estate and banking and systematically cutting off investment in Black neighborhoods for decades to come. The FHA Underwriter’s Manual explicitly stated that “if a neighborhood is to retain stability, it is necessary that properties shall continue to be occupied by the same social and racial classes.” In addition to requiring the use of Residential Security Maps, the manual went on to advocate the use of racial covenants to protect FHA-insured properties. When a parallel loan program was created in the Veterans Administration by the 1944 Servicemen’s Readjustment Act, it adopted the FHA’s racialized practices and procedures (Katznelson, 2006 ).
The anti-urban biases and discriminatory practices built into federal loan programs had little effect on housing patterns during the 1930s and 1940s owing to the tiny amount of new residential construction that occurred during the Great Depression and Second World War. In the postwar period, however, FHA and VA lending drove forward a massive wave of suburban home construction that made new homes widely accessible to White but not Black households. Given high rents and home prices in central cities owing to the influx of workers during the war years, in the late 1940s and early 1950s it was cheaper to buy a brand-new house in the suburbs than to rent an apartment in the city (Massey & Denton, 1993 ).
The end result was a government-subsidized mass exodus of middle and working class White families from central cities to suburbs, creating a distinctly American urban configuration of Black cities surrounded by White suburbs. The homes left behind by the departing Whites seeking their piece of the American Dream in the suburbs were quickly occupied by Black in-movers coming to the city to take jobs in the still-vibrant urban manufacturing sector. Neighborhood turnover accelerated, and the nation’s urban Black ghettos rapidly expanded, both demographically and geographically (Massey & Denton, 1993 ).
Although neighborhood transitions in the 1950s and 1960s improved Black access to housing in the short term, in the long term the neighborhoods turned into poverty traps. Because of redlining and racial discrimination built into housing and credit markets by federal policies and private practices, once a neighborhood became Black, it was cut off from investment, ensuring that its housing stock and business infrastructure would progressively deteriorate. It also left the Black middle class without a means to finance the purchase of homes, and predatory lenders stepped into the resulting void.
Drawing on their own capital, these lenders purchased homes and then offered to “sell” them to middle class Black families by means of Loan Installment Contracts (Satter, 2009 ). LICs were essentially rent-to-own schemes with high interest rates, bloated monthly payments, and no property rights or transfer of title until the final contract payment was made. Any missed payment could bring about immediate eviction by the property owner, no matter how long the aspiring family had been making payments under the contract.
Other predatory investors also purchased ghetto properties to become landlords, subdividing them into ever-smaller units and leasing them to poor and working class Black tenants at inflated rents (Massey & Denton, 1993 ). Whether city housing was being sold under an installment contract or rented on usurious terms, however, the absentee owners could not themselves get loans to offset depreciation or purchase insurance policies to protect their properties, creating a strong financial incentive for landlords to defer maintenance, minimize capital investment, and extract high rents as long as possible until the properties deteriorated to the point of becoming uninhabitable.
As Black ghettos expanded geographically during the 1950s and 1960s in cities such as New York, Chicago, Philadelphia, Detroit, Cleveland, and St. Louis, they ultimately came to encroach on zones in which White elites had place-bound investments in universities, hospitals, museums, and business districts. In desperation, local politicians and civic leaders turned to state and federal agencies for help. Drawing on funding from the National Housing Act, they created locally controlled Urban Renewal Authorities with the power of eminent domain, thereby enabling White interests to gain control of the Black neighborhoods threatening their place-bound investments (Bauman, 1987 ; Hirsch, 1983 ). Once in control of the land, they evicted the residents, razed their homes, and demolished neighborhood businesses, replacing them either with large-scale middle-class housing projects or institutional developments that strategically blocked the expansion of the ghetto toward the threatened White properties, prompting James Baldwin to quip that “urban renewal means Negro removal” (Dickinson, 1963 ).
Because of a “one-for-one rule” embedded within the National Housing Act, for every unit of housing torn down in the name of renewal, planners had to identify another unit into which the displaced tenants could theoretically move. To satisfy this rule, local elites once again turned to the federal government, garnering additional funds authorized by the National Housing Act to construct large public housing projects for families displaced by renewal. Given that the displaced families were Black, it was politically impossible to build the housing project in a White district, so another Black neighborhood was targeted for renewal and torn down to build dense collections of high-rise projects that now had to house two neighborhood’s worth of displaced families (Massey & Denton, 1993 ).
This pairing of urban renewal and public housing did not itself increase the level of Black residential segregation (Bickford & Massey, 1991 ). Segregation levels were already high in the cities where this pairing occurred; but it did dramatically increase the spatial concentration of poverty within the ghetto by replacing relatively class-diverse Black neighborhoods and business districts with tightly packed blocks of high-rise projects in which being poor was a criterion for entry, yielding neighborhood poverty rates of 90% or more (Massey & Kanaiaupuni, 1993 ).
By 1970, high levels of Black residential segregation were universal throughout metropolitan America (Massey & Denton, 1993 ). Footnote 3 As of 1970, 61% of Black Americans living in US metropolitan areas lived under a regime of hypersegregation (Massey & Tannen, 2015 ), a circumstance unique to Americans. Although in theory, segregation should have withered away after the Civil Rights Era, it has not. In 2010, the average index of Black–White segregation remained high and a third of all Black metropolitan residents continued to live in hypersegregated areas (Massey & Tannen, 2015 ). This reality prevails despite the outlawing of racial discrimination in housing (the 1968 Fair Housing Act) and lending (the 1974 Equal Credit Opportunity Act and the 1977 Community Reinvestment Act).

Why does modern segregation persist, despite Whites’ reported racial attitudes improving?
Accompanying these legislative changes was a pronounced shift in White racial attitudes. In the early 1960s, more than 60% of White Americans agreed that Whites have a right to keep Blacks out of their neighborhoods. By the 1980s, however, the percentage had dropped to 13% (Schuman et al., 1998 ). The fact that discrimination is illegal, and White support for segregation has plummeted, begs the question of why segregation persists. The reasons are multiple.
First, although the Fair Housing Act banned discrimination in the rental and sale of housing, enforcement mechanisms in the original legislation were eliminated as part of a compromise to secure the bill’s passage (Metcalf, 1988 ). Federal authorities were likewise granted only limited powers to enforce the Equal Credit Opportunity Act and the Community Reinvestment Act (Massey & Denton, 1993 ).
Although overt discrimination in housing and lending has clearly declined in response to legislation, covert discrimination continues. Rental and sales agents today are less likely to respond to emails from people with stereotypically Black names (Carpusor & Loges, 2006 ; Hanson & Hawley, 2011 ) or to reply to phone messages left by speakers who “sound Black” (Massey & Fischer, 2004 ; Massey & Lundy, 2001 ). A recent meta-analysis of 16 experimental housing audit studies and 19 lending analyses conducted since 1970 revealed that sharp racial differentials in the number of units recommended by realtors and inspected by clients have persisted and that racial gaps in loan denial rates and borrowing cost have barely changed in 40 years (Quillian, Lee, & Honoré, 2020 ).
Audit studies, conducted across the social and behavioral sciences, include a subset of resume studies in which researchers send the same resume out to apply for jobs, but change just one item: the candidate’s name is Lisa Smith or Lakisha Smith. Then, they wait to see who gets the callback. The bias is clear: employers avoid “Black-sounding” names (Bertrand & Mullainathan, 2004 ). In fact, in both Milwaukee’s and New York City’s low-wage job market, Black applicants with no criminal background were called back with the same frequency or less as White applicants just released from prison (Pager, 2003 ; Pager, Western & Bonikowski, 2009 ).
That is, in the minds of hiring managers whose mental make-up is expected to be no different than the readers of this article, a White felon is equivalent to a Black non-felon. The same housing application, the same bank loan application, the same health data, the same behavior, lead to different outcomes depending on the race of the applicant, even though the decision-makers believe they are paying attention to the merits of the case and explicitly not to race, which most decision makers in these studies regard to be irrelevant to the decision.
What makes the problem of systemic racism so perverse is that “good people” with no explicit expression of we would call “racism” are the contributors to such decisions that produce widespread and unnoticed bias, resulting in systemic racism (Banaji & Greenwald, 2013 ). Racial discrimination continues because, although White support for Black segregation may have declined in principle, Whites nonetheless continue to harbor negative racial stereotypes about Black people , which limit their tolerance for integration in practice. Indeed, the willingness of Whites to enter or remain in a neighborhood declines steadily as the percentage of Black neighbors rises (Charles, 2003 ; Emerson, Chai & Yancey, 2001 ). And negative racial stereotyping of Black Americans strongly predicts White opposition to government efforts to enforce Black civil rights (Bobo, Charles, Krysan & Simmons, 2012 ).
In White American social cognition, as later sections elaborate, racial biases remain entrenched both explicitly (Moberg, Krysan & Christianson, 2019 ) and implicitly (Eberhardt, 2019 ). This extends to preferred neighborhoods : Residential searches are inevitably embedded within racialized expectations about neighborhoods and homes that reflect the racially segregated world that most Americans inhabit (Krysan & Crowder, 2017 ). The “correlated characteristics heuristic” relies on a single salient neighborhood trait—in this case racial composition—to represent an area’s acceptability. In White social cognition, the mere presence of Blacks denotes lower property values, higher crime rates, and struggling schools, irrespective of what the objective neighborhood conditions are (Krysan, Couper, Farley & Forman, 2009 ; Quillian & Pager, 2001 , 2010 ). Although Whites in surveys and interviews say they welcome the presence of Black neighbors, in practice Whites avoid neighborhoods containing more than a few Blacks and confine their searches to overwhelmingly White residential areas exhibiting White percentages well above those they report in describing their “ideal” neighborhood on surveys (Krysan & Crowder, 2017 ).
Although rarely admitted, explicit prejudice against Black Americans has hardly disappeared. Google search frequencies on the epithet “nigger” for different metropolitan areas strongly predicted an area’s level of Black residential segregation (Rugh & Massey, 2014 ). This index of explicit racism also strongly predicts the degree to which a city’s suburbs are covered by restrictive density zoning regimes (Massey and Rugh ( 2018 ), a key proximate cause of both racial and class segregation (Rothwell & Massey, 2009 , 2010 ). Owing to the persistence of discrimination, Black Americans are far less able that other Americans to translate their income attainments into residential mobility, greatly compromising their ability to access more integrated and favored neighborhoods (Massey & Denton, 1985 ). As of 2010, the most affluent Black Americans were still more segregated from Whites than the poorest Hispanics (Intrator, Tannen & Massey, 2016 ).
No other group in the history of the US has ever experienced such intense residential segregation in so many areas and over such a long period of time (Massey & Denton, 1993 ; Rugh & Massey, 2014 ). Systemic racism in federal housing policies (Katznelson, 2006 ), real estate (Helper, 1969 ), banking (Ross & Yinger, 2002 ), and insurance (Orren, 1974 ) has ensured a vicious cycle of racial turnover and neighborhood deterioration for most of the past century. As a result, many Black Americans have been compelled to live in societally isolated, economically disadvantaged, physically deteriorated neighborhoods produced and sustained by powerful external forces beyond their ability to control, the precise embodiment of systemic racism.
Because of racial residential segregation and the blocked mobility and spatial concentration of poverty it produces, neighborhoods have become the key nexus for the transmission of Black socioeconomic disadvantage over the life course and across the generations (Sharkey, 2013 ). Half of all Black Americans have lived in the poorest quartile of urban neighborhoods for two consecutive generations, compared with just 7% of Whites, a gap that cannot be explained by individual or family characteristics.
Whereas in the 1960s Black poverty was transmitted across generations by the inheritance of race and the discrimination and exclusion that came with it (Duncan, 1969 ), in the twenty-first century Black poverty is transmitted by the inheritance of place and the concentrated poverty it entails (Massey, 2013 ; Massey & Brodmann, 2014 ; Peterson & Krivo, 2010 ; Sampson, 2012 ; Sharkey, 2013 ). Black disadvantage with respect to income and social mobility is explained almost entirely by the poor neighborhood circumstances they experience (Chetty, Hendren, Jones & Porter, 2020 ; Massey & Brodmann, 2014 ). Racial residential segregation has become linchpin for systemic racism in the US in the twenty-first century (Massey, 2016 , 2020 ).
Discussions of segregation typically highlight how it operates to increase the social isolation of Blacks, but in fact it does more to isolate Whites, who are by far the most spatially isolated group in the US. In 2010, the average Black metropolitan resident lived in a neighborhood that was 45% Black, but the average White metropolitan resident occupied a neighborhood that was 74% White (Massey, 2018 ), and in suburbs the figure rose to 80% (Massey & Tannen, 2017 ). As a result, the advantages of segregation to Whites and the disadvantages to Blacks are invisible to most White Americans.
Feagin ( 1999 , p. 79), put this paradox into perspective by relating the experience of a British immigrant’s confrontation with the realities of race in the US:
Some time after English writer Henry Fairlie emigrated to the USA in the mid-1960s, he visited Thomas Jefferson’s Monticello plantation and took the standard tour. When the White guide asked for questions, Fairlie inquired, “Where did he keep his slaves?” Fairlie reports that the other tourists looked at him in disturbed silence, while the guide “swallowed hard” and said firmly that “the slaves’ quarters are not included in the official tour.” (Fairlie, 1985 .) Housing segregation, and the systemic racism it reveals, are still not on the official tour.”
Two decades later, the question we must answer is whether we are willing, as scientists and citizens, to put housing segregation—and all the other institutions that do so much to dictate the vicissitudes of Black life—on the official tour of the USA.
Systemic racial bias: the role of mental structures and resulting social interactions
We began with institutions and society. Now, we move to individual minds surrounded and shaped by these societal structures. Next, we then move to interacting minds, which further perpetuate societal and individual racial distinctions. Racial bias at each level supports bias at the other levels, creating a racist system.
To understand individual mental structures, we start with unconscious inference, identified by Helmholtz, and its heir, implicit bias, most relevantly as expressed by Whites associating Black racial cues with negative concepts. Socially motivated (mis)perception goes one stage earlier to bias information seeking and interpretation. More specific links among racial bias in perceiving physiognomy, linked to dehumanizing associations, and aggressive behavior close this first section on the individual.
Unconscious inference
Among the intellectuals who contributed to the emergence of experimental psychology as an independent discipline in the nineteenth century was the German polymath, Herman von Helmholtz, whose numerous contributions to science include the concept of “ Unbewuste Schluss ” or “ unconscious inference .” Helmholtz’s concept was simple, but its implications are profound, even more so today with recent advances in the mind and brain sciences. Given the complexity of just the visual world, how are humans to represent it based on their individual-level, meager sensory and perceptual system, which entails the shunting of packets of data from the world outside, through the eyes and into the brain? Helmholtz offered two ideas. First, perception is not veridical, given the complexity of the world and the rudimentary nature of the minds attempting to make sense of it. Second, as implied by the word inference , what one deduces from the evidence provided by the senses is not a replica of what is out there. Rather, mental representations of the physical world are mere approximations.
Whittling the self-esteem of Homo sapiens down further, Helmholtz went on to say that perception is not controllable, but rather that it unfolds automatically. He used a commonplace example to make this point. We know that it is not the Sun that rises, but rather that the Earth revolves around it. But when we sit on our porch at sunrise, and look toward the horizon, we incontrovertibly experience ourselves as being fixed, and the Sun, however bulky, pushing itself up to meet us. To say about the Sun that “it rises” is completely inaccurate yet completely compelling. That incorrect perception is not something over which we have choice. To think otherwise is to delude ourselves.
Helmholtz’s two ideas contained in the phrase “unconscious inference,” with many additional levels of social complexity, summarizes the challenge when we confront systemic racism. On the one hand, we “know” the facts about an economy purportedly mounted on free labor for 250 years, the undelivered promise of 40 acres and a mule, the failure of Reconstruction, the resistance to desegregation, the history of redlining and gerrymandering, a history of unequal access to education, jobs, housing, finance, healthcare, and a lack of equal protection under the law. On the other hand, the limited sensory, perceptual, learning, and memory systems of humans set up a built-in blindness and automatic inferences that generate the illusions that, for instance, White people experience more discrimination than Black people (Norton & Sommers, 2011 ). Or, if Black Americans have any challenges, they have created their own situation in America today (Pettigrew, 1979 ) and therefore are responsible for getting themselves out of that situation. Not that minorities have no illusions, but the illusions of the higher-status group have more consequences because they usually also have more power.
The features of human minds that feed into the production of systemic racism come in two forms: ordinary errors of perception, attention, learning, memory, and reasoning that are the hallmarks of all thinking systems with human-like intelligence. In addition, we add another level of theorizing familiar to psychologists, that of motivated reasoning , the idea that our preferences, goals, and desires can bias our reasoning and lead to prejudicial decisions and outcomes (Fiske & Taylor, 2021 ; Kunda, 1990 ).
Another hallmark of human cognition is the phenomenon of loss aversion , the finding human beings much prefer avoiding losses to acquiring equivalent gains (Kahneman & Tversky, 1979 ). Even as White Americans resist and deny the reality of systemic racism, they nonetheless feel the loss of White privilege and social status quite keenly, creating powerful resentments that motivate them to reason away the potential existence of systemic racism (Craig & Richeson, 2014 ; Parker, 2021 ).
Implicit racial bias
Beginning in the 1980s, psychologists began to document a puzzling result. Individuals who claimed to have no racial animus showed evidence of negative attitudes and stereotypes toward Black Americans (Devine, 1989 ; Dovidio & Gaertner, 1986 ). Soon, the hunt for methods to better access “implicit bias” (as contrasted with standard, explicit bias measured in surveys) was underway, with specific calls for the invention of better technologies that could bypass conscious awareness or conscious control (Greenwald & Banaji, 1995 ).
One such measure, the Implicit Association Test (IAT), has demonstrated a wide array of group evaluative associations. Typically, people can pair own-group cues faster with positive concepts, and other-group cues faster with negative ones—compared with vice versa. For example, White and other non-Black Americans show robust race bias in their inability to associate “good” and “bad” equally rapidly with the social categories Black and White. The IAT has attracted considerable attention (see Greenwald et al., 2020 , for best practices, reliable effects, and ongoing investigations). A public online location, since 1998, has provided data from millions of tests taken by volunteer participants at http://www.implicit.harvard.edu . Several signature results have replicated multiple times with large samples over time:
Race bias is consistently visible in the data.
A small positive correlation between stated and implicit race attitudes exists, but the two are largely dissociated, i.e., many of those who report being neutral (no negative explicit attitudes toward Black or White Americans), do carry implicit associations of Black + bad and White + good to a larger extent than White + bad and Black + good. This result prompts us to yet again note that the term “racism” has been used by contemporary psychologists to refer to conscious forms of race prejudice and to emphasize its semi-independence from less conscious or implicit forms of race bias. To make this distinction clear, researchers who study implicit race bias have gone to great lengths to reserve the term racism to only refer to conscious expressions of racial animus. Our usage of the term systemic racism in this article is undertaken is in the interest of including all levels of analysis (individual, institutional, societal) and all forms, from the most explicit to the most implicit. The result of a low correlation between explicit racism and implicit race bias makes the point empirically that the two are not the same. Of course, implicit race bias feeds into what may become racism, and for this reason it is best to think about implicit race bias as the roots of racism, not the above ground, visible structure. Implicit race bias also results from systemic racism.
Asian Americans show the same pattern as White Americans, even though as a third-party group in response to a Black–White test, they might be assumed to have neutrality. From the point of view of systemic racism, this is an example of what it means to live in a system of inequity at all levels. Even third-party groups will acquire negative and positive attitudes toward groups that are not their own.
Black Americans express strong positive feelings toward their own group but on the measure of implicit cognition, they show no preference for their own group, with scores of almost any sample of Black Americans showing relative neutrality, i.e., equal association of good and bad for Black and White Americans. This absence of ingroup-favoring attitudes—juxtaposed with the ingroup-favoring lack of neutrality in all other groups in the same society—is open to various interpretations, from moral balance to internalized racism to astute pragmatism; all await other data.
Tests of anti-gay bias revealed it to be quite high in 2007 but steadily dropping off (by 64% since 2013) to be at an all-time low today. By comparison, anti-Black bias has dropped, but to a much lesser extent, by about 25% (Charlesworth & Banaji, in press). A 25% drop-off in race bias is not insignificant, and although the genders differ in magnitude of bias, both men and women are losing bias at equal speed. Although all demographic groups are changing, young Americans are changing faster than older Americans, suggesting that the world they inhabit is signaling a less biased set of attitudes.
Together, these data point to the individual manifestation of systemic racial bias, hidden from view but robustly present. However, psychologists have also gone beyond such demonstrations of basic cognitive associations as markers of implicit mental content to show that individual and institutional change is possible if the will to create change exists.
Socially motivated (mis)perception
The idea of motivated reasoning or motivated cognition gathers several useful ideas to understand how individual humans shape and even distort perception to deal with real or perceived threats to self. Kunda ( 1990 ), for example, posited that the individual need for accuracy is thwarted by the demand to reach a conclusion prior to the evidence being satisfactorily in place and that one’s goals and motives often drive decisions. These decisions reveal many identifiable biases that emerge to weaken the orientation toward accuracy (see Fiske & Taylor, 2021 ).
With more direct focus on motivated reasoning as it concerns social change, Kay et al., ( 2009 ) presented empirical evidence for a motivated tendency to view things as they are and conclude that such a state of affairs exists because it is reasonable and even representative of how things ought to be. The connection to systemic racism is quite clear, as the authors further demonstrate that motivated cognition exists in the interest of justifying sociopolitical systems that maintain inequality and resist change. People justify the status quo, preferring stability especially if they are privileged, but even if not (Jost & Banaji, 1994 ). Groups in a secure position show the cultural equivalent of inertia, seeking stability, but groups on the move express inertia as continuing to move (e.g., acquiring mainstream standing) (Zárate et al., 2019 ).
Two substantive theoretical accounts undergird these ideas as they concern complex interactions of within-person and across-person phenomena such as systemic racism. First, Sidanius and Pratto’s ( 1999 ) Theory of Social Dominance offers evolutionary and cultural evidence to support the idea that hierarchies are an almost obligatory feature of human social groups. A related but independent idea may be found in Jost’s System Justification Theory (Jost, 2020 ), which explicitly makes the case that individuals will sacrifice self and group interest in order to maintain larger “systems” of social arrangements and work to keep them in place. The reason, Jost argues, is that such a motivation serves to meet deep psychological needs for certainty, security, and acceptance by others. The overarching social structure is important to protect because if it is stable, then all within it will be safe, including those disadvantaged by established hierarchies.
Perception of phenotypes, deadly associations, and system-maintaining behavior
With regard to perceptions of race, the mere categorization of someone as Black shifts perceptions of their phenotype. For example, a series of experiments documented that people’s knowledge about race phenotypes drives perception of lightness of the skin tone (Levin & Banaji, 2006 ). In other words, experiments held skin-tone constant and varied only the features, from Afrocentric to Eurocentric; this variation in features shifts perception of skin tone, such that Afrocentric faces are viewed to be darker skinned than Eurocentric ones, despite the same gray-scale tone.
Skin tone and features are critical cues to make life and death decisions, especially in ambiguous situations that are often present in so many interactions between police and Black citizens. In simulations of police-citizen encounters, people are more likely to “shoot” unarmed Black men than otherwise equally unarmed White men (Correll, Wittenbrink, Park, Judd, & Goyle, 2010 ). Black men with more phenotypically Black features are more likely to receive the death penalty for murdering a White person, holding constant the features of the crime (Eberhardt, 2019 ). The phenotypicality effect extends even to Whites with Afrocentric features (Blair, Judd, & Chapleau, 2004 ). Judgments of criminality can be primed by a Black face (Eberhardt, 2019 ).
And there’s more: the race–crime association overlaps the dehumanizing association of Black faces with great ape faces, that Staples ( 2018 ) called the “racist trope that won’t die”; Goff, Eberhardt, Williams and Jackson ( 2008 ) provide evidence from policing that links apes and Black people, from the first moments of perception to the radio dispatch and other media, with systemic implications. In more recent work, Morehouse et al., ( 2021 ) have shown that White Americans associate White with human and Black, Asian, and Latinx with animal with greater ease than the opposite pairing (White with animal), regardless of the category of animal (generic or specific). Implicit racial biases (Whites favoring Whites) are consequential, correlating with judged trustworthiness and economic investment (Stanley, Sokol-Hessner, Banaji & Phelps, 2011 ).
More recently, Kurdi et al., ( 2021 ) measured attitudes toward a phenotypic feature that happens to be a dominant perceptual marker of race, Afrocentric and Eurocentric types of hair. First participants took an IAT measuring their implicit attitude toward Black women with natural or straightened hair. Then, subjects read a summary of a real legal case involving a corporation that fired a Black employee for refusing to change her natural hair ( Equal Employment Opportunity Commission v. Catastrophe Management Solutions , 2016). The more negative the implicit attitude toward Afrocentric hair, the greater the sympathy with the corporation’s position rather than the plaintiff’s position in the legal case.
A relatively new approach to racial associations comes with the promise of epitomizing the term “systemic” in systemic racism. These are studies of large language corpora that are now possible using machine learning approaches to natural language. With the increasing availability of trained datasets—including large samples of the language of the Internet (content archives continuously collected by the nonprofit Common Crawl) or specific trained datasets of media such as books, TV shows, etc.—allow measuring the extent to which language contains attitudes and beliefs about Black and White Americans across time. Charlesworth and Banaji (in preparation) analyzed data from Google Books from 1800 to 1990. Setting aside the data from older books to focus on whether bias is present in the language today, these are the traits most associated with Black Americans (and not with White Americans) in the late twentieth century: earthy, lonely, sensual, cruel, lifeless, deceitful, meek, rebellious, headstrong, lazy . By contrast, these are the traits associated with White Americans (and not with Black Americans): critical, decisive, hostile, friendly, polite, able, diplomatic, belligerent, understanding, confident . Other work in natural language processing (NLP) sorts adjectives into 13 stereotype-content dictionaries (Nicolas, Bai, & Fiske, 2021 ). The above adjectives convey ambivalent reactions to Black Americans on several dimensions, but notably neglect competence; Whites in contrast feature several competence adjectives. NLP allows efficient analysis of language in the culture or in spontaneous, open-ended descriptions (Nicolas, Bai, & Fiske, under review). Footnote 4
Words have an important role to play. People often express surprise about implicit biases in the minds of individuals who have no intent to harbor them. Considering how and why it occurs—plausible mechanisms—may prove convincing. One causal candidate is language , the predominant way humans communicate and express themselves. Words undertake much of the labor of creating racism in thoughts and feelings that are reflected in speech. Machine learning approaches to understanding racial bias in language will likely be a critical method to objectively uncover how words, spoken and written, create systemic racism. That is, linguistic patterns connect groups with valenced concepts, and the repeated pairings create associations. Without awareness, language produces the inbuilt in the architecture of social cognition (as an example, the NLP stereotype-dimensions dictionaries capture more than 80% of spontaneous stereotype content; Nicolas, Bai, & Fiske, under review).
From cognitive racial bias to aggregate racialized behavior
Individual implicit attitudes have been repeatedly shown to predict behavior; Kurdi et al. ( 2019 ) offer the largest number of studies included in a meta-analysis to date. However, as the authors note, the actual attitude–behavior relationship is marred by the poor quality of many studies, especially given the lack of psychometric control over the predicted behavior. Among the controversies that have marked this work is an intriguing idea put forth by Payne, Vuletich and Lundberg ( 2017 ), who proposed that the small correlations between individual attitude and behavior must be acknowledged as a function of what they call the “bias of crowds,” the idea that an individual’s behavior is determined by the larger social context in which that individual exists. A number of studies have appeared recently to challenge the idea that individual attitude–behavior correlations is the right place to be looking. That the actual correlation between implicit attitude and behavior is larger than it may have appeared has been revealed in a series of studies that predict behavior at the aggregate level by using aggregate IAT scores by region, such as metropolitan areas, counties, and states. Charlesworth and Banaji ( 2021 ) reviewed these studies to demonstrate more substantive relationships between IAT racial bias and consequential social outcomes.
For example, the studies reviewed reveal that the greater the implicit bias against Blacks in a region (using average IAT scores of a region) the greater is the lethal use of force by police, the greater the Black American deaths from circulatory diseases, the lower is spending on Medicaid disability programs (more likely to assist Black Americans), the greater the Black–White gap in infant low birth weight and preterm births, the greater the Black–White gap in school disciplining (suspension, law enforcement referrals, expulsions, in-school arrests), the Black–White gap in standardized testing scores (3rd–8th grade for math and English), and lower upward mobility.
To grasp the meaning of systemic racism as it exists at the individual level within larger society, not just in a single moment by across time, a study by Payne, Vuletich and Brown-Iannuzzi ( 2019 ) is illustrative. Their analysis of IAT data today yields strong correlations with the ratio of enslaved to free people in the southern US in 1860. States with a larger ratio in 1860 are the states with greater race bias today, 160 years later (r = 0.64). This correlation is much larger in magnitude than even the correlation between regional IAT race bias and Black American representation across the US (r = 0.32). As Charlesworth and Banaji ( 2021 ) note, “the result also suggests that today’s Americans who live in regions with greater historical legacies of slavery must be acquiring the particles of race bias embedded in the social atmosphere. Systemic discrimination is a useful term in this case as it helps capture the pervasiveness of race bias as it extends across both space and time.”
Summary. As explicit bias decreased, measured forms of implicit bias have persisted, potentially attributable to racial segregation. White Americans have limited direct experience with Black Americans, so cultural associations substitute for more individuated impressions. Implicit associations of “Black-bad” and “White-good” are weakening, but far from neutral. Meanwhile, socially motivated (mis)perception favors these system-justifying biases. Together, they support a syndrome linking racial phenotypes, deadly associations, and system-maintaining behavior. Further, cognitive racial biases underpin aggregate racialized behavior. These are some cognitive-motivational mechanisms of systemic racism. Other mechanisms involve everyday interactions that perpetuate bias. In particular, predictable patterns of disrespect and distrust maintain the interpersonal racial divide.
Racialized social interactions
Face-to-face behavior propagates bias. Individuals carry racial biases into their social settings largely by interacting with others. Repeated patterns of behavior that differ by race are, at a minimum, racialized (defined by race) and often experienced as racist. Individual racial biases, enacted in daily life, perpetuate bias, which then links the individual to the norms, scripts, and habits that constitute the social system. Interpersonal interaction conveys bias, intentionally or not. In scores of studies, White Americans distance themselves from Black interaction partners, express non-verbal discomfort, and avoid them (e.g., Dovidio, Kawakami & Gaertner, 2002 ; Richeson & Shelton, 2007 ; Word, Zanna & Cooper, 1974 ). In the aggregate, these patterns constitute the concrete manifestations of a racially biased social system.
We have already seen White people’s generically negative default associations with Black Americans, linking them to crime (untrustworthy) and to animals (incompetent). These reflect the two key stereotype dimensions in intergroup perception (Fiske, 2018 ): warmth and competence. These dimensions organize people’s perceptions of social systems: perceived competence reflects groups’ stereotypic status in society. The hierarchy supposedly reflects merit, so rank predicts their supposed competence and evokes respect—or supposed incompetence and disrespect. Besides groups’ status (competence), the other aspect of social structure is groups’ apparent cooperative or competitive goals, interdependencies that stereotypically predict warmth and trustworthiness. Cooperators on our side are nice; competitors are not. Stereotypes derive from social structural perceptions (status and interdependence), especially when people learn about others they might encounter (Fiske, Cuddy, Glick & Xu, 2002 ; Nicolas et al., 2021 ). Black Americans do not get a break on either dimension. And because these racialized perceptions derive from social structure, they pave the way for systemic racism. Consider the evidence for these two dimensions: competence and warmth in racialized perceptions and behavior.
Disrespect communicates Whites’ view of Blacks as low status and incompetent
The default representation of Black Americans is low status (Dupree, Torrez, Obioha & Fiske, 2021 ). Whites spontaneously associate Black faces with low-status jobs, compared to Whites. The structural belief that Blacks are low status appears in associating them with jobs such as janitor, dishwasher, garbage collector, taxi driver, cashier, maid, prostitute. This race–status association correlates with endorsing social dominance (believing that some groups inevitably dominate others, and it is better that way) and with meritocracy (group get what they deserve). All these judgments share a common element of disrespect and assumed incompetence.
Race–status associations emerge in behavior that maintains Black people at the bottom of the hierarchy. Respondents endorsed Black applicants for lower status jobs and withheld support for organizations and government policies aiding minorities. Thus, racialized associations, assumptions, and preferences all identify a view of Black people's structural position as low status, on average. Behavior communicates these attitudes, whether examined or not. Thus, race–status associations imply Black incompetence, covarying with feeling-thermometer (0–100) ratings of interracial bias, social dominance orientation, meritocracy beliefs, as well as hierarchy-maintaining hiring and policy preferences.
Disrespectful behavior that presumes incompetence of Blacks appears in another series of studies. Well-meaning liberals, expected to introduce themselves to a Black partner, dumbed-down their speech, as they did in vocabulary for a task assignment (Dupree & Fiske, 2019 ). Similarly, White Democratic presidential candidates also showed a competence downshift in speeches to minority audiences only (Dupree & Fiske, 2019 ).
This pattern reproduces itself when respondents imagine introducing themselves to a lower-status person (race unspecified) at work (Swencionis & Fiske, 2016 ). They claim their goal is to communicate their own warmth (as they downplay their competence), but this rests on the presumption of the other’s incompetence. Trying to be folksy does not communicate respect.
The presumption that structural status predicts competence is widespread (averaging r > 0.80 across US and international samples; Fiske & Durante, 2016 ). The implication is that for most White Americans, the association that pops into their minds will link a Black person with incompetence. People communicate such disrespect by failing to bet on or invest in the other’s performance (Walsh, Vaida, & Fiske, under review).
Structurally, this amounts to racism. Black people are widely perceived as inferior in these ways, which are baked into the social hierarchy, reflecting disrespectful patterns of interpersonal behavior. All of this perpetuates the social hierarchy and the image of Blacks as incompetent.
Worse yet, disrespect surfaces in police encountering Black drivers. From the first moment (“Hey” instead of “Sir” or “Ma’am”), police officer language shows computationally derived, measurably lower respect (Voigt et al., 2017 ). Given the already fraught relationships between police and Black community members, this worsens an already dangerous encounter and undermines the chances to create trust.
Distrust communicates Whites’ views of Blacks as uncooperative and not warm
Besides incompetence, the other major dimension of social cognition is warmth (trustworthy, friendly), as noted. The default stereotype of a Black person is probably also untrustworthy, but the data on this point are surprisingly indirect. Whites can be expected to distrust Blacks as part of the larger principle that, categorically, people mistrust outgroups. More specifically, as noted, Whites associate Blacks with crime, which certainly undermines trust. Footnote 5 This configuration fits survey data showing that ratings of poor (i.e., explicitly low-status) Black people allege incompetence (disrespecting them) but also lack of warmth (distrusting them).
Plotting these ratings in a warmth x competence space, poor Blacks are frequently judged as low on both. Because White Americans link race and status, the low-income Black person is the default Black person, allegedly incompetent, but also untrustworthy. Mistrust is indicated by excessive surveillance of Black Americans (driving while Black, shopping while Black, false accusations of theft or assault, police shootings…). Footnote 6
Distrust can be operationalized as behavior: In the economic Trust Game, a player must decide how much of their starting endowment to share, on the knowledge that it will be tripled, and on the hope that their partner will share back, generously. Incentivized trust-game behavior closely tracks warmth ratings; that is, societal groups rated as low warmth and untrustworthy receive less shared endowment, presumably because they are not trusted to share it back. In nationally representative samples, people of color do not fare well in the Trust Game (Walsh et al., under review). In more prosaic settings, non-verbal behavior reveals unmonitored dislike (if not specifically mistrust), as noted.
Black Americans experience repeated treatment as incompetent and untrustworthy. Because this stereotype and ensuing behavior is racially category-based and negative, as well as potentially controllable, it is racist. Because the behavior comes from societal stereotypes, which come from social structure, Footnote 7 it is systemic.
Whites’ potential control implies responsibility for reinforcing system racism
Racialized interactions could also be termed racist, in the sense that White people could potentially observe their own inequitable behavior if they chose (Fiske, 1989 ). People rarely examine these unwritten rules, typical behaviors, but conceivably they could, so “unexamined” bias captures the higher potential control for behavior than for implicit associations. Control implies responsibility in the minds of lay people and the law, so this interpretation of “racialized” as “racist” creates concern and is likely to be contested. But the science makes the empirical point here that racialized social behavior is demonstrably controllable, given sufficient incentive (Monteith, Lybarger & Woodcock, 2009 ; Sinclair, Lowery, Hardin & Colangelo, 2005 ). So systematically different behavior by race reflects a racist habit, script, or norm, the components of a system from the bottom up.
The challenge in controlling racist habits is that they are the cultural default. Much of this systematic behavior results from White Americans’ inexperience with Black Americans, thereby substituting societal representations for individuating information about the unique human (Fiske & Neuberg, 1990 ). People use especially those default representations that fit their natural human tendency to detect and prefer people they view as similar to themselves. To unpack this, consider some basic principles of affiliation that would predispose Whites to favor other Whites and exclude Black people. First is the basic tendency to categorize others and to favor those of the ingroup. For decades, principles of attraction have established its foundations in similarity (Byrne, 1971 ; Montoya & Horton, 2013 ) or homophily (McPherson, Smith-Lovin & Cook, 2001 ). And mere categorization suffices to produce ingroup favoritism (Tajfel & Turner, 1979 ). No animus is necessary, although it easily develops. As a basis for categorization, race is arbitrary (more so than gender and age; Kurzban, Tooby & Cosmides, 2001 ) but common (Sidanius & Pratto, 1999 ). Thus, race-based ingroup favoritism is a default, in the absence of other experience. Footnote 8 This makes it hard to over-ride.
Societal segregation by race makes difficulties for overcoming the racial default. Segregation limits White exposure to Blacks, undermining their direct experience, leaving Whites to rely on cognitive shortcuts to represent Blacks as a group. Indeed, the less exposure people have to outgroups, the more clearly they differentiate among them–stereotypically. That is, White Americans who know the least about other races have the clearest stereotypes about them; the less diversity, the more differentiated their cognitive representations (Bai, Ramos & Fiske, 2020 ).
What’s wrong with that?
As a scientific question, a skeptic might ask, what’s wrong with differentiating by stereotypes? One set of answers concerns the demeaning individual and face-to-face interaction, just addressed. The other answers pertain to sheer demographic diversity of Black Americans, covered next.
Given its racial history and ongoing systems, societal patterns and cultural stereotypes prevailing in the US tend to associate Blacks with low status and Whites with high status as noted. To the extent this race–status association has a kernel of statistical accuracy (Blacks are over-represented in low-status jobs), it fails several tests as an argument for using stereotypes as a constructive strategy of intergroup relations. First, it ignores variability, individuality, and (especially) Black diversity. Second, category-based thinking exaggerates perceived between-group variability and minimizes perceived within-group variability (Tajfel & Turner 1979 ; Taylor, Fiske, Etcoff & Ruderman, 1978 ). So “nouns that cut slices” (Allport’s, 1954 felicitous phrase for category labels) do violence to the human data. What’s more, society has civil rights laws protecting people from being judged by their group membership, so the consensus is that this is not only wrong, but illegal.
Race–status associations, in practice, ignore all the structural contributors to race–status associations, such as the neighborhood effects, already described. Whites assume meritocracy, believing that status accurately reflects individual competence (Fiske, Dupree, Nicolas & Swencionis, 2016 ); globally, the perceived status—perceived competence correlation hovers around 0.80. (The only countries where people are more cynical about the status-merit link are former Communist ones; Grigoryan et al., 2020 .) The point here is that status has many antecedents, and not all of them are merit (or other personal, stereotypical explanations, e.g., innately good/bad at math). Systemic factors such as neighborhood, school, family resources, connections, and especially race all receive no mention in the meritocracy account.
Whites do differentiate Black Americans by subcategories, e.g., by status, specifically social class, viewing low-income Black people as incompetent and untrustworthy, but Black professionals as competent and trustworthy (Fiske, Cuddy, Glick & Xu, 2002 ). Black Americans themselves differentiate several subtypes of Blacks likewise along a social-class dimension (Fiske, Bergsieker, Russell & Williams, 2009 ).
Status-keeping shortcuts are easier to maintain without information to the contrary, such as experiencing human variability. Whites with less exposure to Blacks are more overtly prejudiced as a function of structural features such as rural residence, where they encounter less diversity (Bai et al., 2020 ), and lack of education, where they experience less variability of ideas. As a structural matter, segregated White rural residence also predicts lower school quality partly because of the American policy of locally funding schools; this creates an association between a weaker tax base, rural location, ethnic homogeneity, and overt bias. These systemic factors interact to produce prejudice. As an earlier section shows, the social structure permeates American arrangements since the arrival of Whites on native lands.
Nevertheless, for most Whites, their isolated lives make them inexperienced about their Black fellow citizens. Housing segregation disfavors most Whites in experience with diversity, making them often inept and naïve when speaking about issues that are facts of Black lives. This means that Whites rely on cultural shortcuts to understand the Black people whose life experience they do not know. These cognitive representations derive from perceived structural patterns such as race–status associations and race-resource unfairness (Krysan & Crowder, 2017 ).
We have seen that Whites’ racial beliefs are relatively automatic (implicit bias) and ambivalent (warmth/competence). The resulting associations (stereotypes) are more subtle than most people believe. They are consequently hard for anyone to detect in themselves (unexamined) or in any one person (under the radar), but the patterns appear systemically as aggregate biases. Supposing the aggregate biases are problematic, at least because they ignore variability, examine that more closely.
Aggregate bias ignores diversity
So far, this review has described the relentless systems of racism that limit opportunity and outcomes by race. Many Black Americans nevertheless succeed despite the rigged system. Black diversity thus results from those who escape the system, but also from African and Caribbean immigration, and from intermarriage. For Black students enrolled at selective colleges, especially, the diversity of their backgrounds is the main fact that underscores their success (Charles, Kramer, Massey & Torres, 2021 ). Any given White student’s background is far more predictable than any given Black student’s, which potentially ranges from extreme disadvantage to extreme wealth. For that minority (a third) of Black students whose segregated neighborhoods entail underfunded schools, gang violence, and concentrated police violence, their presence in college testifies to extraordinary resilience (Charles, Fischer, Mooney & Massey, 2009 ).
Most non-Black people do not realize that Black Americans are more diverse than most American ethnic groups. Underestimating their variety allows an oversimplified image to dominate every level, from mind to society, making it a systemic racism. This section describes diversity based on place, intermarriage, immigrant experience, parent education, and sheer escape.
A century ago, most Black Americans lived in the rural South, but after the Great Migration, most lived in cities, often in the North, usually hyper-segregated, but with family roots in both the North and South. By the turn of the current century, Black American student bodies at selective colleges were the most diverse in history, more biracial, more immigrant, more middle or upper class, and equally identifying themselves as both American and as Black (Charles et al., 2021 ). Black students, even as elites, show “unprecedented variation in terms of racial origins, skin tone, nativity, generation, class, and segregation” (Charles et al., 2021 , Ch. 10).
Clusters of characteristics and attitudes illustrate the variety. Mixed-race students identify less with being Black, are comfortable with both Blacks and Whites, see Whites as less discriminatory, and report deep parental involvement in their schooling and cultural experiences. Mixed race students also have more White friends and fewer Black friends than their monoracial peers and are more likely to date outside the group, especially with Whites. In addition, mixed-race students are less likely to join majority-Black organizations on campus, and thus report less intense interaction with Blacks . Psychologically, the White view of biracial individuals continues to demonstrate hypodescent, i.e., the view that biracial individuals belong to the less advantaged group, or the cognitive expression of the “one drop rule.” Combining the sociological and psychological angle demonstrates the lack of consistency between how biracial Americans are viewed and the way they see themselves.
Black students with an immigrant background are most comfortable with other Black students, and report having strict parents who expect obedience, respect, hard work, and family loyalty without hands-on, hovering involvement. First-generation immigrants, especially African immigrants (versus Caribbean ones), believe in meritocracy and see Whites as not so discriminatory. After a generation, idealism gives way to pragmatism: Hard work pays off. African immigrant origins predict reliably higher grades.
As for segregation, Black students growing up with more exposure to Whites feel closer to them but also view Whites as more discriminatory, a psychologically complex mental state to manage. In contrast, living in segregated neighborhoods especially exposes Black students to higher (the top third) levels of disorder and violence, leading them to view Whites as more distant and discriminatory. But parents are more protective, relying on strict discipline but not trying to use shame or guilt as an influence strategy (more frequent in Asian families).
As with all students, high-school GPA predicts college GPA. Besides that, again as with all students, Black women do better than Black men, as do those with educated parents . Differences in academic preparation vary by segregation in two ways: the more White students in their schools, the worse Black students’ grades but the higher their SATs, suggesting more rigorous standards. Thus, the portraits of Black college students are diverse; generalizations are unreliable, except perhaps for one: resilience in the face of systemic bias and a diversity of adaptations to a variety of challenges.
We document Black diversity here for these reasons: First, to avoid making the litany of systemic Black disadvantages the sole image conveyed here. Second, because of segregation, many White people, including University faculty, see a Black person on campus and—assuming they realize this is a student—they presume the person comes from a low-income background, unprepared for college, with uneducated parents, native born, but with little experience outside the imagined ghetto, etc. This may be true for some small fraction of students, but not just the Black ones, and not true of most Black students on campus today. A third reason to remind the reader of Black diversity on campus is to highlight experiences of inter-racial contact as important one mechanism for overcoming racial bias, and—if scaled up to integrated neighborhoods, schools, and workplaces—for shifting systemic racism.
Contact: exposure to racial diversity
People with least exposure to diversity have the most differentiated images of the outgroups they have never met (Bai et al., 2020 ). And the prospect and first experience of diversity is not salutary; newly diverse contexts show lower well-being (Putnam, 2007 ; Ramos, Bennett, Massey & Hewstone, 2019 ). But over time, people get used to each other: well-being is higher and stereotypes melt into each, forming an undifferentiated cluster of people like us, mostly warm and competent.
Psychology has 70 years of research to explain how this works, following Allport’s ( 1954 ) contact hypothesis. In one meta-analytic perspective (Pettigrew & Tropp, 2006 ), intergroup contact reduces prejudice, the more it meets Allport’s conditions: shared goals, non-trivial interactions, authority sanctions, and rewarding results. Much of the process seems to be affect-driven. If the contact setting would afford the opportunity for friendship, the contact effect is stronger (Tropp & Pettigrew, 2005 ). This is a useful reminder that much prejudice is emotional, not cognitive. In fact, a meta-analysis of 50 years of research on racist attitudes found that they predict racist behavior the most when they are emotions (“hating them”) rather than stereotypes (“they are lazy”) or even simple evaluations (2 on a 5-point scale) (Talaska et al., 2008 ).
Nevertheless, the core element of successful contact, goal interdependence, does operate via information processing. In laboratory experiments, interdependence makes people attend specifically to unexpected, stereotype-inconsistent information, and they make dispositional inferences, generating an individualized coherent impression of the teammate (Ames & Fiske, 2013 ; Erber & Fiske, 1984 ). Neural signatures of mindreading prominently include the mPFC regions that reliably activate when people are inferring another’s predispositions. The mind-reading mPFC activates most for an interdependent partner’s stereotype-inconsistent attributes. Although supporting evidence includes these mechanisms, a subsequent meta-analysis (Paluck, Porat, Clark & Green, 2021 ) notes that few high-quality intergroup studies have focused on race per se, few look at adults, few are experiments. We have much to learn.
Conclusion: systemic racism is individual/interpersonal and institutional/societal but rarely recognized
Segregated housing disadvantages many Black Americans, and its effects are far-reaching, not only in life opportunities and outcomes (education, employment, health, well-being) but also in the psychology of systemic racism. We have argued that case here. Most Whites fail to recognize and appreciate the growing diversity of America’s Black population, which has arisen from a mixture of Black resilience, a growing middle class, rising intermarriage, and global-South immigration. Generally, White Americans—because of the segregation perpetuated to sustain their advantage—have limited exposure to Black Americans, so their knowledge is indirect, and based on cultural caricatures. Segregation allows White people to be clueless about race, and because racial bias is more automatic, ambiguous, and ambivalent than people think, they fail to detect it in themselves and others. As a result, White people have many unexamined biases, undergirded by earlier stages of information processing (e.g., attention, perception, learning, memory, reasoning) that sustain such a lack of awareness. These cognitive errors and biases stem from lack of exposure, lack of the accurate evidence, and a lack of necessary knowledge.
The assumption here is that if people were simply made aware of the facts that have been described in the earlier sections, they would slap their palm to their head and immediately vote for reparations. But as readers may no doubt deduce on their own, confronting accurate data and internalizing it is not a smooth or pretty process. That our minds resist information that challenges certain types of prior beliefs is a fundamental discovery from the mind sciences. Basic cognitive processes such as motivated cognition help to maintain a lack of awareness of racial experiences as they exist on the ground. But no lack of awareness need exist.
The human ability for conscious awareness, deliberate thought, and the motivation to link values to behavior cannot be underestimated as vehicles of change. We have accomplished this regarding how we understand the relationship of Earth to our Sun, so we know it is not as it seems. If we choose, we can similarly put our minds to derive the best evidence to learn about the presence or absence of systemic racism. If we can acquire the appropriate knowledge (often hidden from our conscious perception), we will be more likely to remain open to evidence that shows its presence.
If we do not undertake this effort, it is at our own peril. If, in the twenty-first century, we cannot mount a new struggle to see the social world for what it is, we are by choice dooming ourselves to extended ignorance that will be costly to us, our society, and the world we inevitably leave to our descendants. Earlier we provided evidence about unexpected (by scientists) decreases in implicit sexuality bias (massive drop) and race bias (more modest change) since 2007. These data provide optimism that mental content that we cannot change at will is nonetheless capable of movement toward racial neutrality across the US.
In other words, who-we-have-been need not be the future-selves-we-are-becoming. Here, we demonstrated that grappling with the correct data is a necessary step on the path to understanding our role in the creation of systemic racism. Among the blind spots that we will need to shake off, once and for all, is the belief that racism is the product of a few bad people in our society, and that removing them from power will suffice to deal with the issue.
Space and time preclude our covering the targets’ perspective, identity, resilience. Nor do we cover racial socialization in children.
Through the sensory and perceptual systems granted to our species by evolution, these dyadic and small-group social interactions evolve into larger and larger social units, such as the hundreds of so-called friends or millions of so-called followers on more recent forms of social media. Today we transcend ancestral, small-group interactions to generate larger-scale groups whose interactions occur on an exponential scale. The internet provides avenues for the high-speed transmission of individual attitudes, beliefs, values, as well as for propelling action across communities and nations. These communications have the potential to spread both social good and social harm, with explicit racial animus and implicit prejudicial bias being examples of the latter.
Using the most common measure of segregation (the dissimilarity index), in that year 94% Black metropolitan residents lived under conditions of “high” segregation (an index of 60 or greater on a 0–100 scale), meaning that at least 60% of Blacks would have to exchange neighborhoods with Whites to achieve an even distribution of the races across neighborhoods (Rugh & Massey, 2014 ). Moreover, in a subset of metropolitan areas, not only were Black residents unevenly distributed across neighborhoods, they were also isolated within overwhelmingly Black districts that were themselves densely clustered near the central business district, a geographic pattern that Massey and Denton ( 1989 ) labeled "hypersegregation.”
The NLP fits more traditional findings, a form of cross-validation. Based on content analysis of an 84-adjective checklist, the language describing Black Americans did not change much, across samples from 1933 to 2007 (Bergsieker, Leslie, Constantine, & Fiske, 2012 , Study 4): The most recent data describe ambivalent view of sociality (aggressive, gregarious, passionate), and some specific stereotypes (loud, talkative, religious, loyal to family, sportsmanlike, musical, materialistic), but saying nothing about competence. Neglecting to mention an obvious dimension can reveal taboo topics, stereotyping by omission (Bergsieker et al., 2012 ).
Black people may distrust Whites, too, but they have less standing (status and power) to do damage.
An odd anomaly: Abundant research describes Black people’s generalized trust as lower then Whites’ generalized trust. Also, social science has studied Black Americans’ mistrust of government, business, healthcare, and education systems that have historically abused them (see next section). This would hardly seem puzzling enough to be the lion’s share of the trust literature and to eclipse White Americans’ pockets of mistrust. Specifically, no one seems to study Whites’ mistrust of Black people. Overlooking the obvious is one symptom of a systemic bias.
The combination of status-competence and warmth-trustworthiness creates remarkably stable perceptions of social structure (Durante et al., 2015). In social systems across the globe, middle classes are stereotypically competent and warm (trustworthy) whereas homeless people are neither. And in the mixed quadrants, rich people seem competent but cold, whereas old people seem well-intentioned but incompetent. These class and age patterns are nearly universal. In contrast, ethnic, racial, religious, and other cultural stereotypes are accidents of history, reflecting what subset of a group arrived under what circumstances. Compare stereotypes of Chinese railroad workers in the nineteenth century to stereotypes of Chinese entrepreneurs in the twenty-first century.
Implicit bias is difficult to monitor, as noted. Yet another way that prejudice goes undetected, is in its modern form, of being exhibited less as outgroup harm and instead as ingroup help (Greenwald & Pettigrew, 2014 ). Despite this ambiguity, the net effect is the same—just harder to detect, and even lauded, because helping is a prosocial act that garners praise.
Allport, G. (1954). The nature of prejudice . Addison-Wesley.
Google Scholar
Ames, D. L., & Fiske, S. T. (2013). Outcome dependency alters the neural substrates of impression formation. NeuroImage, 83 , 599–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.07.001
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Bai, X., Ramos, M. R., & Fiske, S. T. (2020). As diversity increases, people paradoxically perceive social groups as more similar. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 117 (23), 12741–12749.
Article Google Scholar
Banaji, M. R., & Greenwald, A. G. (2013). Blindspot: Hidden biases of good people . Random House.
Bauman, J. F. (1987). Public housing, race, and renewal: Urban planning in Philadelphia, 1920–1974 . Temple University Press.
Bergsieker, H. B., Leslie, L. M., Constantine, V. S., & Fiske, S. T. (2012). Stereotyping by omission: Eliminate the negative, accentuate the positive. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 102 (6), 1214–1238. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0027717
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Bertrand, M., & Mullainathan, S. (2004). Are Emily and Greg more employable than Lakisha and Jamal? A field experiment on labor market discrimination. American Economic Review, 94 (4), 991–1013.
Bickford, A., & Massey, D. S. (1991). Segregation in the second ghetto: Racial and ethnic segregation in American public housing, 1977. Social Forces, 69 , 1011–1038.
Blair, I. V., Judd, C. M., & Chapleau, K. M. (2004). The influence of Afrocentric facial features in criminal sentencing. Psychological Science, 15 , 674–679.
Bobo, L. D., Charles, C. Z., Krysan, M., & Simmons, A. D. (2012). The real record on racial attitudes. In P. V. Marsden (Ed.), Social trends in the United States: Evidence from the General Social Survey since, 1972 (pp. 38–93). Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Byrne, D. (1971). The attraction paradigm . Academic Press.
Carpusor, A. G., & Loges, W. E. (2006). Rental discrimination and ethnicity in names. Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 36 (4), 934–952. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0021-9029.2006.00050.x
Charles, C. Z. (2003). “The dynamics of racial residential segregation. Annual Review of Sociology, 29 , 167–207.
Charles, C. Z., Fischer, M. J., Mooney, M. A., & Massey, D. S. (2009). Taming the river: Negotiating the academic, financial, and social currents in America’s Selective Colleges and Universities . Princeton University Press.
Charles, C. Z., Kramer, R. A., Massey, D. S., & Torres, K. C. (2021). Divergent currents: The diverse origins of the new black elite . Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Charlesworth, T. E. S., & Banaji, M. R. (2021). Patterns of implicit and explicit stereotypes III: Long-term change in gender stereotypes. Social Psychological and Personality Science . https://doi.org/10.1177/1948550620988425
Charlesworth, T.E.S., & Banaji, M. R. (in press). The relationship of implicit social cognition and discriminatory behavior. In A. Deshpande (Ed.) Handbook on the Economics of Discrimination and Affirmative Action . Edward Elgar.
Chetty, R., Hendren, N., Jones, M. R., & Porter, S. R. (2020). Race and economic opportunity in the United States: An intergenerational perspective. The Quarterly Journal of Economics, 135 (2), 711–783. https://doi.org/10.1093/qje/qjz042
Correll, J., Wittenbrink, B., Park, B., Judd, C. M., & Goyle, A. (2010). Dangerous enough: Moderating racial bias with contextual threat cues. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 47 , 184–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jesp.2010.08.017
Craig, M. A., & Richeson, J. A. (2014). More diverse yet less tolerant? How the increasingly diverse racial landscape affects Americans’ racial attitudes. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 40 (6), 750–761. https://doi.org/10.1177/0146167214524993
Devine, P. G. (1989). Stereotypes and prejudice: Their automatic and controlled components. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 56 (1), 5–18. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.56.1.5
Dickinson Jr., W. B. (1963). Urban renewal under fire. Editorial Research Reports , 1963 (Vol. II). Available at http://library.cqpress.com/cqresearcher/cqresrre1963082100
Dovidio, J. F., & Gaertner, S. L. (Eds.). (1986). Prejudice, discrimination, and racism . Academic Press.
Dovidio, J. F., Kawakami, K., & Gaertner, S. L. (2002). Implicit and explicit prejudice and interracial interaction. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 82 (1), 62–68. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.82.1.62
DuBois, W. E. B. (1925). Worlds of color. Foreign Affairs, 3 (3), 423–444.
Duncan, O. D. (1969). Inheritance of poverty or inheritance of race? In D. P. Moynihan (Ed.), On understanding poverty: Perspectives from the social sciences (pp. 85–110). Basic Books.
Dupree, C. H., & Fiske, S. T. (2019). Self-presentation in interracial settings: The competence downshift by white liberals. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 117 (3), 579–604. https://doi.org/10.1037/pspi0000166
Dupree, C. H., Torrez, B., Obioha, O. A., & Fiske, S. T. (2021). Race-status associations: Distinct effects of three novel measures among white and black perceivers. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 120 (3), 601–625. https://doi.org/10.1037/pspa0000257
Eberhardt, J. L. (2019). Biased: Uncovering the hidden prejudice that shapes what we see, think, and do . New York: Viking.
Emerson, M. O., Chai, K. J., & Yancey, G. (2001). Does race matter in residential segregation? Exploring the preferences of white Americans. American Sociological Review, 66 (6), 922–935. https://doi.org/10.2307/3088879
Erber, R., & Fiske, S. T. (1984). Outcome dependency and attention to inconsistent information. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 47 , 709–726.
Fairlie, H. 1985. The art of revival: Washington diarist-ex-presidents. The New Republic , May 6.
Farley, R., & Allen, W. R. (1987). The color line and the quality of life in America . Russell Sage Foundation.
Feagin, J. R. (1999). Excluding blacks and others from housing: The foundation of white racism. Cityscape, 4 (3), 79–91.
Feagin, J. R. (2006). Systemic racism: A theory of oppression . Routledge.
Fiske, S. T. (1989). Examining the role of intent: Toward understanding its role in stereotyping and prejudice. In J. Uleman & J. Bargh (Eds.), Unintended thought: The limits of awareness, intention, and control (pp. 253–283). Guilford.
Fiske, S. T. (1993). Controlling other people: The impact of power on stereotyping. American Psychologist , 48 , 621–628.
Fiske, S. T. (1998). Stereotyping, prejudice, and discrimination. In The handbook of social psychology, Vols. 1–2, 4th ed (pp. 357–411). McGraw-Hill.
Fiske, S. T. (2018). Stereotype content: Warmth and competence endure. Current Directions in Psychological Science , 27 (2), 67–73.
Fiske, S. T., Bergsieker, H., Russell, A. M., & Williams, L. (2009). Images of Black Americans: Then, “them” and now, “Obama!” DuBois Review: Social Science Research on Race, 6 , 83–101. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1742058X0909002X
Fiske, S. T., Cuddy, A. J., Glick, P., & Xu, J. (2002). A model of (often mixed) stereotype content: Competence and warmth respectively follow from perceived status and competition. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 82 , 878–902. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.82.6.878
Fiske, S. T., Dupree, C. H., Nicolas, G., & Swencionis, J. K. (2016). Status, power, and intergroup relations: The personal is the societal. Current Opinion in Psychology, 11 , 44–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copsyc.2016.05.012
Fiske, S. T., & Durante, F. (2016). Stereotype content across cultures: Variations on a few themes. In M. J. Gelfand, C.-Y. Chiu, & Y.-Y. Hong (Eds.), Handbook of advances in culture and psychology (Vol. 6, pp. 209–258). Oxford University Press.
Fiske, S. T., & Neuberg, S. L. (1990). A continuum model of impression formation, from category-based to individuating processes: Influence of information and motivation on attention and interpretation. In M. P. Zanna (Ed.), Advances in experimental social psychology (Vol. 23, pp. 1–74). Academic Press.
Fiske, S. T., & Taylor, S. E. (2021). Social cognition: From brains to culture (4/e) . London: Sage.
Foner, E. (1990). A short history of reconstruction, 1863–1877 . Harper & Row.
Goff, P. A., Eberhardt, J. L., Williams, M. J., & Jackson, M. C. (2008). Not yet human: Implicit knowledge, historical dehumanization, and contemporary consequences. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 94 (2), 292–306. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.94.2.292
Greenwald, A. G., & Banaji, M. R. (1995). Implicit social cognition: attitudes, self-esteem, and stereotypes. Psychological Review , 102 (1), 4–27.
Greenwald, A. G., & Pettigrew, T. F. (2014). With malice toward none and charity for some: Ingroup favoritism enables discrimination. American Psychologist, 69 (7), 669–684. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0036056
Greenwald, A. G., Brendl, M., Cai, H., Cvencek, D., Dovidio, J., Friese, M., Hahn, A., Hehman, E., Hofmann, W., Hughes, S., Hussey, I., Jordan, C. H., Jost, J., Kirby, T. A., Lai, C. K., Lang, J. W. B., Lindgren, K. P., Maison, D., Ostafin, B., Rae, J. R., ... Wiers, R. (2020). The implicit association test at age 20: What is known and what is not known about implicit bias. https://psyarxiv.com/bf97c .
Grigoryan, L., Bai, X., Durante, F., Fiske, S. T., Berdyna, E. M., Fabrykant, M., Hakobjanyan, K. A., Kotova, M., Makashvili, A., Morozova-Larina, O., Mullabaeva, N., Samekin, A., Verbilovich, V., & Yahiiaiev, I. (2020). Stereotypes as Historical Accidents: Images of Social Class Stereotypes in Postcommunist Versus Capitalist Societies. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 46 (6), 927–943. https://doi.org/10.1177/0146167219881434
Guthrie, R. V. (2004). Even the rat was white: A historical view of psychology (Classic ed., 2nd ed). Allyn and Bacon.
Hanson, A., & Hawley, Z. (2011). Do landlords discriminate in the rental housing market? Evidence from an internet field experiment in US Cities. Journal of Urban Economics, 70 (2), 99–114.
Helper, R. (1969). Racial policies and practices of real estate brokers . University of Minnesota Press.
Higginbotham, A. L. (1998). Shades of freedom: Racial politics and presumptions of the American legal process . Oxford University Press.
Hirsch, A. R. (1983). Making the second ghetto: Race and housing in Chicago, 1940–1960 . Cambridge University Press.
Intrator, J., Tannen, J., & Massey, D. S. (2016). Segregation by Race and Income in the United States, 1970–2010. Social Science Research, 60 (1), 45–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssresearch.2016.08.003
Jackson, K. T. (1985). Crabgrass frontier: The suburbanization of the United States . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Jones, J. M. (1971). The political dimensions of black liberation. The Black Scholar, 3 (1), 67–75.
Jones, J. M. (1972). Prejudice and racism . Addison-Wesley.
Jones, J. M. (1997). Prejudice and racism (2nd ed). McGraw-Hill Companies.
Jost, J. T. (2020). A theory of system justification . Harvard University Press.
Book Google Scholar
Jost, J. T., & Banaji, M. R. (1994). The role of stereotyping in system-justification and the production of false consciousness. British Journal of Social Psychology, 33 (1), 1–27. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2044-8309.1994.tb01008.x
Kahneman, D., & Tversky, A. (1979). Prospect theory: An analysis of decision under risk. Econometrica, 47 (4), 263–291. https://doi.org/10.2307/1914185
Katznelson, I. (2006). When affirmative action was white: An untold history of racial inequality in twentieth-century America . W. W. Norton.
Kay, A. C., Gaucher, D., Peach, J. M., Laurin, K., Friesen, J., Zanna, M. P., & Spencer, S. J. (2009). Inequality, discrimination, and the power of the status quo: Direct evidence for a motivation to see the way things are as the way they should be. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 97 (3), 421–434. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0015997
Krysan, M., Couper, M. P., Farley, R., & Forman, T. (2009). Does race matter in neighborhood preferences? Results from a video experiment. AJS; American Journal of Sociology, 115 (2), 527–559.
Krysan, M., & Crowder, K. (2017). Cycle of segregation: Social processes and residential stratification . Russell Sage Foundation.
Kunda, Z. (1990). The case for motivated reasoning. Psychological Bulletin, 108 (3), 480–498. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.108.3.480
Kurdi, B., Carroll, T. J., & Banaji, M. R. (2021). Specificity and incremental predictive validity of implicit attitudes: Studies of a race-based phenotype. Cognitive Research: Principles and Implications, 6 , 61. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41235-021-00324-y
Kurdi, B., Seitchik, A. E., Axt, J. R., Carroll, T. J., Karapetyan, A., Kaushik, N., Tomezsko, D., Greenwald, A. G., & Banaji, M. R. (2019). Relationship between the implicit association test and intergroup behavior: A meta-analysis. American Psychologist, 74 (5), 569–586. https://doi.org/10.1037/amp0000364
Kurzban, R., Tooby, J., & Cosmides, L. (2001). Can race be erased? Coalitional computation and social categorization. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 98 (26), 15387–15392. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.251541498
Lemann, N. (1991). The promised land: The great black migration and how it changed America . Knopf.
Levin, D. T., & Banaji, M. R. (2006). Distortions in the perceived lightness of faces: The role of race categories. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General , 135 (4), 501–512.
Loewen, J. W. (2018). Sundown towns: A hidden dimension of American racism . New Press.
Madigan, T. (2001). The burning: Massacre, destruction, and the Tulsa race riot of, 1921 . Martin’s Press.
Massey, D. S. (2013). Inheritance of poverty or inheritance of place? The emerging consensus on neighborhoods and stratification. Contemporary Sociology, 42 , 690–697.
Massey, D. S. (2016). Residential segregation is the linchpin of racial stratification. City and Community, 15 (1), 4–7. https://doi.org/10.1111/cico.12145
Massey, D. S. (2018). Segregation in 21st century America. Journal of Catholic Social Thought, 15 (2), 235–260.
Massey, D. S. (2020). Still the linchpin: Segregation and stratification in the USA. Race and Social Problems, 12 (1), 1–12.
Massey, D. S., & Brodmann, S. (2014). Spheres of influence: The social ecology of racial and class inequality . Russell Sage Foundation.
Massey, D. S., & Denton, N. A. (1985). Spatial assimilation as a socioeconomic outcome. American Sociological Review, 50 (1), 94–105.
Massey, D. S., & Denton, N. A. (1989). Hypersegregation in US metropolitan areas: Black and Hispanic segregation along five dimensions. Demography, 26 (3), 373–393.
Massey, D. S., & Denton, N. A. (1993). American apartheid: Segregation and the making of the underclass . Harvard University Press.
Massey, D. S., & Fischer, M. J. (2004). The ecology of racial discrimination. City and Community, 3 (3), 221–243.
Massey, D. S., & Kanaiaupuni, S. M. (1993). Public housing and the concentration of poverty. Social Science Quarterly, 74 (1), 109–123.
Massey, D. S., & Lundy, G. (2001). Use of black English and racial discrimination in urban housing markets: New methods and findings. Urban Affairs Review, 36 (4), 470–96.
Massey, D. S., & Tannen, J. (2015). A research note on trends in black hypersegregation. Demography, 52 (3), 1025–1034. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13524-015-0381-6
Massey, D. S., & Tannen, J. (2017). Suburbanization and segregation in the United States: 1970–2010. Ethnic and Racial Studies, 41 (9), 1594–1611.
Massey, D. S., & Tannen, J. (2016). Segregation, race, and the social worlds of rich and poor. In H. Braun & I. Kirsch (Eds.), The dynamics of opportunity in America: Evidence and perspectives (pp. 13–33). Springer.
Chapter Google Scholar
Massey, D. S., & Rugh, J. S. (2018). The intersection of race and class: Zoning, affordable housing, and segregation in U.S. Metropolitan Areas. In: Gregory Squires (Ed.), The fight for fair housing: Causes, consequences and future implications of the 1968 federal fair housing act (pp. 245–265). Taylor and Francis.
McPherson, M., Smith-Lovin, L., & Cook, J. M. (2001). Birds of a feather: Homophily in social networks. Annual Review of Sociology, 27 (1), 415–444. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.soc.27.1.415
Mead, G. H. (1934). Mind, self, and society: from the standpoint of a social behaviorist . University of Chicago Press.
Metcalf, G. R. (1988). Fair housing comes of age . Greenwood Press.
Moberg, S. P., Krysan, M., & Christianson, D. (2019). Racial attitudes in America. Public Opinion Quarterly, 83 (2), 450–471. https://doi.org/10.1093/poq/nfz014
Monteith, M. J., Lybarger, J. E., & Woodcock, A. (2009). Schooling the cognitive monster: the role of motivation in the regulation and control of prejudice. Social and Personality Psychology Compass, 3 (3), 211–226. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-9004.2009.00177.x
Montoya, R. M., & Horton, R. S. (2013). A meta-analytic investigation of the processes underlying the similarity-attraction effect. Journal of Social and Personal Relationships, 30 (1), 64–94. https://doi.org/10.1177/0265407512452989
Morehouse, K., Maddox, K., & Banaji, M. (2021). All human groups are human, but some groups are more human than others. In: Poster presentation at the APS annual convention conference .
Nicolas, G., Fiske, S. T., Koch, A., Imhoff, R., Unkelbach, C., Terache, J., Carrier, A., & Yzerbyt, V. (2021). Relational versus structural goals prioritize different social information. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology . https://doi.org/10.1037/pspi0000366
Norton, M. I., & Sommers, S. R. (2011). Whites see racism as a zero-sum game that they are now losing. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 6 (3), 215–218. https://doi.org/10.1177/1745691611406922
Orren, K. (1974). Corporate power and social change: The politics of the life insurance industry . The Johns Hopkins University Press.
Owens, A. (2020). Unequal opportunity: School and neighborhood segregation in the USA. Race and Social Problems, 12 (1), 29–41.
Packard, J. M. (2003). American nightmare: The history of Jim Crow . Martin’s Press.
Pager, D. (2003). The mark of a criminal record. American Journal of Sociology, 108 (5), 937–975.
Pager, D., Western, B., & Bonikowski, B. (2009). Discrimination in a low-wage labor market: A field experiment. American Sociological Review, 74 (5), 777–799. https://doi.org/10.1177/000312240907400505
Paluck, E. L., Porat, R., Clark, C. S., & Green, D. P. (2021). Prejudice reduction: Progress and challenges. Annual Review of Psychology, 72 (1), 533–560. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-psych-071620-030619
Parker, C. S. (2021). Status threat: Moving the right further to the right? Daedalus, 150 (2), 56–75.
Payne, B. K., Vuletich, H. A., & Brown-Iannuzzi, J. L. (2019). Historical roots of implicit bias in slavery. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 116 , 11693–11698. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1818816116
Payne, B. K., Vuletich, H. A., & Lundberg, K. B. (2017). The bias of crowds: How implicit bias bridges personal and systemic prejudice. Psychological Inquiry, 28 , 233–248. https://doi.org/10.1080/1047840X.2017.1335568
Peterson, R. D., & Krivo, L. J. (2010). Divergent Social Worlds: Neighborhood Crime and the Racial-Spatial Divide . Russell Sage Foundation.
Pettigrew, T. (1979). Racial change and social policy. Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Science, 441 , 114–131.
Pettigrew, T. F., & Tropp, L. R. (2006). A meta-analytic test of intergroup contact theory. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 90 (5), 751–783. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.90.5.751
Philpott, T. (1978). The slum and the ghetto: Neighborhood deterioration and middle class reform, Chicago 1880–1930 . Oxford University Press.
Putnam, R. (2007). E Pluribus Unum: Diversity and community in the twenty-first century: The 2006 Johan Skytte prize lecture. Scandinavian Political Studies, 30 (2), 137–174. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9477.2007.00176.x
Quillian, L., Lee, J. J., & Honoré, B. (2020). Racial discrimination in the U.S. housing and mortgage lending markets: a quantitative review of trends, 1976–2016. Race and Social Problems, 12 (1), 13–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12552-019-09276-x
Quillian, L., & Pager, D. (2001). Black neighbors, higher crime? The role of racial stereotypes in evaluations of neighborhood crime. American Journal of Sociology, 107 (3), 717–767. https://doi.org/10.1086/338938
Quillian, L., & Pager, D. (2010). Estimating risk: Stereotype Amplification and the perceived risk of criminal victimization. Social Psychology Quarterly, 73 (1), 79–104. https://doi.org/10.1177/0190272509360763
Ramos, M. R., Bennett, M. R., Massey, D. S., & Hewstone, M. (2019). Humans adapt to social diversity over time. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 116 (25), 12244–12249. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1818884116
Richeson, J. A., & Shelton, J. N. (2007). Negotiating interracial interactions: Costs, consequences, and possibilities. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 16 (6), 316–320. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8721.2007.00528.x
Ross, S. L., & Yinger, J. (2002). The color of credit: Mortgage discrimination, research methodology, and fair-lending enforcement . MIT Press.
Rothstein, R. (2017). The color of law: A forgotten history of how our government segregated America . Liveright.
Rothwell, J., & Massey, D. S. (2009). The effect of density zoning on racial segregation in U.S. Urban areas. Urban Affairs Review, 44 (6), 779–806. https://doi.org/10.1177/1078087409334163
Rothwell, J. T., & Massey, D. S. (2010). Density zoning and class segregation in U.S. metropolitan areas. Social Science Quarterly, 91 (5), 1123–1143.
Rugh, J. S., & Massey, D. S. (2014). Segregation in post-civil rights America: Stalled integration or end of the segregated century? The DuBois Review , 11 (2), 202–232.
Salter, P. S., Adams, G., & Perez, M. J. (2018). Racism in the structure of everyday worlds: A cultural-psychological perspective. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 27 (3), 150–155. https://doi.org/10.1177/0963721417724239
Sampson, R. J. (2012). Great American City: Chicago and the enduring neighborhood effect . University of Chicago Press.
Satter, B. (2009). Family properties: How the struggle over race and real estate transformed Chicago and Urban America . Picador.
Sharkey, P. (2013). Stuck in Place: Urban neighborhoods and the end of progress toward racial equality . University of Chicago Press.
Schuman, H., Steeh, C., Bobo, L. D., & Krysan, M. (1998). Racial attitudes in America: Trends and interpretations (Revised ed.). Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Sidanius, J., & Pratto, F. (1999). Social dominance: An intergroup theory of social hierarchy and Oppression . Cambridge University Press.
Sinclair, S., Lowery, B. S., Hardin, C. D., & Colangelo, A. (2005). Social tuning of automatic racial attitudes: The role of affiliative motivation. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 89 (4), 583–592. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.89.4.583
Stanley, D. A., Sokol-Hessner, P., Banaji, M. R., & Phelps, E. A. (2011). Implicit race attitudes predict trustworthiness judgments and economic trust decisions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 108 (19), 7710–7715. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1014345108
Staples, B. (2018, June 17). Opinion | The racist trope that won’t die. The New York Times . https://www.nytimes.com/2018/06/17/opinion/roseanne-racism-blacks-apes.html .
Sugrue, T. (2008). Sweet land of liberty: The forgotten struggle for civil rights in the north . Random House.
Swencionis, J. K., & Fiske, S. T. (2016). Promote up, ingratiate down: Status comparisons drive warmth-competence tradeoffs in impression management. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 64 , 27–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jesp.2016.01.004
Tajfel, H., & Turner, J. C. (1979). An integrative theory of intergroup conflict. In W. G. Austin & S. Worchel (Eds.), The social psychology of inter-group relations (pp. 33–47). Brooks/Cole.
Talaska, C. A., Fiske, S. T., & Chaiken, S. (2008). Legitimating racial discrimination: A meta-analysis of the racial attitude-behavior literature shows that emotions, not beliefs, best predict discrimination. Social Justice Research: Social Power in Action , 21 , 263–296.
Taylor, S. E., Fiske, S. T., Etcoff, N. L., & Ruderman, A. J. (1978). Categorical and contextual bases of person memory and stereotyping. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 36 , 778–793. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.36.7.778
Tolnay, S. E., & Beck, E. M. (1995). A festival of violence: An analysis of southern lynchings, 1882–1930 . University of Illinois Press.
Tropp, L. R., & Pettigrew, T. F. (2005). Differential relationships between intergroup contact and affective and cognitive indicators of prejudice. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 31 , 1145–1158.
Tuttle, W. M. (1970). Race riot: Chicago in the red summer of 1919 . Atheneum.
Voigt, R., Camp, N. P., Prabhakaran, V., Hamilton, W. L., Hetey, R. C., Griffiths, C. M., et al. (2017). Language from police body camera footage shows racial disparities in officer respect. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences , 114 (25), 6521–6526.
Waldstreicher, D. (2009). Slavery’s Constitution: From Revolution to Ratification . Hill and Wang.
Wallace DF (2009) This is water: Some thoughts, delivered on a significant occasion, about living a compassionate life . Little, Brown and Company. (2005 Kenyon College Commencement address). https://fs.blog/david-foster-wallace-this-is-water/ .
Wilkerson, I. (2010). The warmth of other suns: The epic story of America’s great migration . Random House.
Williams, J. C. (2019). White working class: Overcoming class cluelessness in America . Harvard Business Press.
Word, C. O., Zanna, M. P., & Cooper, J. (1974). The nonverbal mediation of self-fulfilling prophecies in interracial interaction. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 10 (2), 109–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1031(74)90059-6
Zárate, M. A., Reyna, C., & Alvarez, M. J. (2019). Cultural inertia, identity, and intergroup dynamics in a changing context. In Advances in Experimental Social Psychology (Vol. 59, pp. 175–233). Academic Press.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the constructive comments of James Jones, Jeremey Wolfe, and Reviewer 1.
No funding and no major differences in the active participation in all phases of planning and producing this paper.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Harvard University, Cambridge, MA, USA
Mahzarin R. Banaji
Princeton University, Princeton, NJ, USA
Susan T. Fiske & Douglas S. Massey
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors planned, wrote, read, and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Susan T. Fiske .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Because this is a review of published work, this paper is not itself new human subjects research, so it required no new ethics approval, no consent to participate, and no new data to share.
Consent for publication
The authors do consent to publish this paper in this journal.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Banaji, M.R., Fiske, S.T. & Massey, D.S. Systemic racism: individuals and interactions, institutions and society. Cogn. Research 6 , 82 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41235-021-00349-3
Download citation
Received : 09 September 2021
Accepted : 03 December 2021
Published : 20 December 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s41235-021-00349-3
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Study protocol
- Open access
- Published: 28 March 2019
The impact of racism on the future health of adults: protocol for a prospective cohort study
- James Stanley ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8572-1047 1 ,
- Ricci Harris 2 ,
- Donna Cormack 2 ,
- Andrew Waa 2 &
- Richard Edwards 1
BMC Public Health volume 19 , Article number: 346 ( 2019 ) Cite this article
232k Accesses
21 Citations
238 Altmetric
Metrics details
Racial discrimination is recognised as a key social determinant of health and driver of racial/ethnic health inequities. Studies have shown that people exposed to racism have poorer health outcomes (particularly for mental health), alongside both reduced access to health care and poorer patient experiences. Most of these studies have used cross-sectional designs: this prospective cohort study (drawing on critical approaches to health research) should provide substantially stronger causal evidence regarding the impact of racism on subsequent health and health care outcomes.
Participants are adults aged 15+ sampled from 2016/17 New Zealand Health Survey (NZHS) participants, sampled based on exposure to racism (ever exposed or never exposed, using five NZHS questions) and stratified by ethnic group (Māori, Pacific, Asian, European and Other). Target sample size is 1680 participants (half exposed, half unexposed) with follow-up survey timed for 12–24 months after baseline NZHS interview. All exposed participants are invited to participate, with unexposed participants selected using propensity score matching (propensity scores for exposure to racism, based on several major confounders). Respondents receive an initial invitation letter with choice of paper or web-based questionnaire. Those invitees not responding following reminders are contacted for computer-assisted telephone interview (CATI).
A brief questionnaire was developed covering current health status (mental and physical health measures) and recent health-service utilisation (unmet need and experiences with healthcare measures). Analysis will compare outcomes between those exposed and unexposed to racism, using regression models and inverse probability of treatment weights (IPTW) to account for the propensity score sampling process.
This study will add robust evidence on the causal links between experience of racism and subsequent health. The use of the NZHS as a baseline for a prospective study allows for the use of propensity score methods during the sampling phase as a novel approach to recruiting participants from the NZHS. This method allows for management of confounding at the sampling stage, while also reducing the need and cost of following up with all NZHS participants.
Peer Review reports
Differential access to the social determinants of health both creates and maintains unjust and avoidable health inequities [ 1 ]. In New Zealand, these inequities are largely patterned by ethnicity, particularly for Māori (the indigenous peoples) and Pacific peoples, and intertwined with ethnic distributions of socioeconomic status [ 2 , 3 ]. In models of health, racism is recognised as a key social determinant that underpins systemic ethnic health and social inequities, as is evident in New Zealand and elsewhere [ 4 , 5 ].
Racism can be understood as an organised system based on the categorisation and ranking of racial/ethnic groups into social hierarchies whereby ethnic groups are assigned differential value and have differential access to power, opportunities and resources, resulting in disadvantage for some groups and advantage for others [ 4 , 6 ]. Historical power relationships underpin systems of racism [ 7 ], which in New Zealand relates specifically to our colonial history and ongoing colonial processes [ 8 ].
Racism can be expressed at structural and individual levels, with several taxonomies describing different levels of racism. Institutionalised racism, for example, has been defined as, “the structures, policies, practices, and norms resulting in differential access to the goods, services, and opportunities of society by race[/ethnicity]” (p. 10) [ 6 ]. In contrast, personally-mediated racism has been defined as, “prejudice and discrimination, where prejudice is differential assumptions about the abilities, motives, and intents of others by ‘race[/ethnicity],’ and discrimination is differential actions towards others by ‘race[/ethnicity]’” (p. 10) [ 6 ].
The multifarious expressions of racism can affect health via several recognised direct and indirect pathways. Indirect pathways include differential access to societal resources and health determinants by race/ethnicity, as evidenced by long-standing ethnic inequities in income, education, employment and living standards in New Zealand, with subsequent impacts on living environments and exposure to risk and protective factors [ 4 , 6 , 9 , 10 ]. At the individual level, experience of racism can affect health directly through physical violence and stress pathways, with negative psychological and physiological impacts leading to subsequent mental and physical health consequences. In addition, racism influences healthcare via institutions and individual health providers, leading to ethnic inequities in access to and quality of care. For example, ethnic disparities in socioeconomic status can indirectly result in differential access to care, while health provider ethnic bias can influence the quality and outcomes of healthcare interactions [ 11 ].
There has been considerable recent growth in research supporting a direct link between experience of racism and health. A recent systematic review and meta-analysis summarised the evidence for direct links between self-reported personally-mediated racism and negative physical and mental health outcomes [ 12 ], with the strongest effect sizes demonstrated for mental health. Related work has also shown that experience of racial discrimination is associated with other adverse health outcomes and preclinical indicators of disease and health risk across various ethnic groups and countries, including in New Zealand [ 9 , 13 , 14 , 15 ]. Experience of racism has also been linked to a range of negative health care-related measures [ 16 ].
However, most studies have used cross-sectional designs: very few of the articles in a recent systematic review [ 12 ] used prospective or longitudinal designs ( n = 30, 9% of total, including multiple articles from some studies), limiting our ability to draw strong causal conclusions as the direction of causality cannot be determined when racism exposure and health outcomes are measured at the same time. Additionally, cross-sectional studies may give biased estimates of the magnitude of association between experience of racism and health: for example, bias may occur if experience of ill health (outcome) increases reporting or perception of racism (exposure) [ 12 ]. This is suggested by meta-analyses where effect sizes for the association between racism and mental health were larger for cross-sectional compared to longitudinal studies [ 12 ]. Longitudinal research on the effects of racism has been particularly limited with respect to physical health outcomes and measures of healthcare access and quality [ 12 , 16 ]. Finally, existing prospective studies have largely been restricted to quite specific groups (e.g. adolescents, females, particular ethnic groups), with a limited number of studies undertaken at a national population level and few with sufficient data to explore the impact of racism on the health of Indigenous populations [ 12 ].
In New Zealand, reported experience of racism is substantially higher among Māori, Asian and Pacific ethnic groupings compared to European [ 3 , 17 ]. In our own research, we have examined cross-sectional links between reported experience of racism and various measures of adult health in New Zealand using data from the New Zealand Health Survey (NZHS), an annual national survey by the Ministry of Health including ~ 13,000 adults per annum [ 2 , 18 , 19 ]. In these studies [ 17 , 20 , 21 , 22 ] we have shown that both individual experience of racism (e.g. personal attacks or unfair treatment) and markers of structural racism (deprivation, other socioeconomic indicators) are independently associated with poor health (mental health, physical health, cardiovascular disease), health risks (smoking, hazardous alcohol consumption) and healthcare experience and use (screening, unmet need and negative patient experiences). Other New Zealand researchers have reported similar findings including studies among older Māori [ 23 ], adolescents [ 24 ], and for maternal and child health outcomes [ 25 ]. However, evidence from New Zealand prospective studies is still limited. The NZ Attitudes and Values study showed that, among Māori, experience of racism was negatively linked to subsequent wellbeing [ 26 ], and the Growing Up in New Zealand study reported that maternal experience of racism (measured antenatally) was linked to a higher risk of postnatal depression among Māori, Pacific and Asian women [ 27 ].
While empirical evidence of the links between racism and health is growing in New Zealand, it remains limited in several areas. There is consistent evidence from cross-sectional studies for the hypothesis that racism is associated with poorer health and health care. This study seeks to build on existing research to provide more robust causal evidence using a prospective design that helps to rule out reverse causality, in order to inform policy and healthcare interventions.
Theoretical and conceptual approaches
Addressing racism as a health determinant is intrinsically linked to addressing ethnic health inequities. In New Zealand, Māori health is of special relevance given Māori rights under the Treaty of Waitangi [ 28 ] and the United Nations Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous People [ 29 ], and in recognition of the inequities for Māori across most major health indicators [ 28 ]. We recognise the direct significance of this project to Māori and understand racism in its broader sense as underpinning our colonial history with ongoing contemporary manifestations and effects [ 8 ]. As such, our work is informed by critical approaches to health research that are explicitly concerned with understanding inequity and transforming systems and structures to achieve the goal of health equity. This includes decolonising and transformative research principles [ 30 ] that influence our approach to the research question, data collection, analysis and interpretation of data, and translation of research findings. The team includes senior Māori researchers as well as advisors with experience in Māori health research and policy.
Aims and research questions
The overall aim is to examine the relationship between reported experience of racism and a range of subsequent health measures. The specific objectives are:
To determine whether experience of racism leads to poorer mental health and/or physical health.
To determine the impact of racism on subsequent use and experience of health services.
Study design
The proposed study uses a prospective cohort study design. Respondents from the 2016/17 New Zealand Health Survey [ 2 , 18 , 19 ] (NZHS) provide the source of the follow-up cohort sample and the NZHS provides baseline data. The follow-up survey will be conducted between one and two years after respondents completed the NZHS. Using the NZHS data as our sampling frame provides access to exposure status (experience of racism), along with data on a substantial number of covariates (including age, gender, and socioeconomic variables) allowing us to select an appropriate study cohort for answering our research questions. Participant follow-up will be conducted by a multi-modality survey (mail, web and telephone modalities).
This study explores the impact of racism on health in the general NZ adult population (which is the target population of the NZHS that forms the baseline of the study).
Participants
Participants were selected from adult NZHS 2016/17 interviewees ( n = 13,573, aged 15+ at NZHS interview) who consented to re-contact for future research within a 2 year re-contact window (92% of adult respondents). The NZHS is a complex-sample design survey with an 80% response rate for adults [ 18 ] and oversampling of Māori, Pacific, and Asian populations (who experience higher levels of racism), which facilitates studying the impact of racism on subsequent health status. Participants who had consented to re-contact ( n = 12,530) also needed to have contact details recorded and sufficient data on exposures/confounders to be included in the sampling frame ( n = 11,775, 93.9% of consenting adults). All invited participants will be aged at least 16 at the time of follow-up, as at least one year will have passed since participation in the NZHS (where all participants were aged at least 15).
Exposure to racism was determined from the five previously validated NZHS items [ 31 ] asked of all adult respondents (see Table 1 ) about personal experience of racism across five domains (verbal and physical attack; unfair treatment in health, housing, or work). Response options for each question cover recent exposure (within the past 12 months), more historical exposure (> 12 months ago), or no exposure to racism.
Identification of exposed and unexposed individuals
Individuals were classified as exposed to racism if they answered “yes” to any question in Table 1 , in either timeframe (recent or historical: referred to as “ever” exposure). This allows for analysis restricted to the nested subset of individuals reporting recent exposure to racism (past 12 months) and those only reporting more historical exposure (> 12 months ago). The unexposed group comprised all individuals answering “No” to all five domains of experience of racism. We selected all exposed individuals for follow-up, along with a matched sample of unexposed individuals. Individuals missing exposure data were explicitly excluded.
Matching of exposed and unexposed individuals
To address potential confounding, we used propensity score matching methods in our sampling stage to remove the impact of major confounders (as measured in the NZHS) of the causal association between experience of racism and health outcomes. Propensity score methods are increasingly used in observational epidemiology as a robust method for dealing with confounding in the analysis stage [ 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 ] and have more recently been considered as a useful approach for secondary sampling of participants from existing cohorts for subsequent follow up [ 37 ].
All exposed NZHS respondents will be invited into the follow-up survey. To find matched unexposed individuals, potential participants were stratified based on self-reported ethnicity (Māori, Pacific, Asian, European and Other; using prioritised ethnicity for individuals identifying with more than one grouping) [ 38 ] and then further matched for potential sociodemographic and socioeconomic confounders using propensity score methods [ 39 , 40 ]. Stratification by ethnicity reflects the differential prevalence of racism by ethnic group, and furthermore allows ethnically-stratified estimates of the impact of racism [ 22 ].
Propensity scores were modelled using logistic regression for “ever” exposure to racism based on major confounder variables of the association between racism and poor health (Table 2 ), with modelling stratified by ethnic group. Selection of appropriate confounders was based on past work using cross-sectional analysis of the 2011/12 NZHS (e.g. [ 21 , 22 ]) and the wider literature that informed the conceptual model for the project. Some additional variables were considered for inclusion in the matching process but were removed prior to finalisation (details in Table 2 ).
Within each ethnic group stratum, exposed individuals were matched with unexposed individuals (1:1 matching) based on propensity scores to make these two groups approximately exchangeable (confounders balanced between exposure groups). The matching process [ 41 ] used nearest neighbour matching as implemented in MatchIt [ 42 ] in R 3.4 (R Institute, Vienna, Austria). As the propensity score modelling is blind to participants’ future outcome status, the final propensity score models were refined using just the baseline NZHS data to achieve maximal balance of confounders between exposure groups, without risking bias to the subsequent primary causal analyses [ 39 ]. Balance between groups was then checked on all matching variables prior to finalisation of the sampling lists.
Questionnaire development
Development of the follow-up questionnaire was informed by a literature review and a conceptual model (Figs. 1 and 2 ) of the potential pathways from racism to health outcomes (Fig. 1 ) and health service utilisation (Fig. 2 ) [ 4 , 10 , 16 , 43 , 44 ]. The literature review focussed on longitudinal studies of racism and health among adolescents and adults that included health or health service outcomes. The literature review covered longitudinal studies post-dating the 2015 systematic review by Paradies et al. [ 12 ], using similar search terms for papers between 2013 and 2017 indexed in Medline and PubMed databases, alongside additional studies from systematic reviews [ 12 , 16 ].
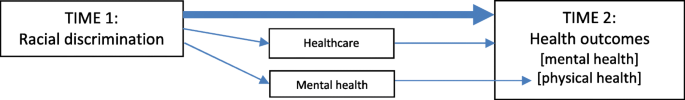
Potential pathways between racism and health outcomes. Direct pathway: Main arrow represents the direct biopsychosocial and trauma pathways between experience of racial discrimination (Time 1) and negative health outcomes (Time 2) Indirect pathways: Racial discrimination (Time 1) can impact negatively on health outcomes (Time 2) via healthcare pathways (e.g. less engagement, unmet need). Racial discrimination (Time 1) can impact negatively on physical health outcomes (Time 2) via mental health pathways

Potential pathways between racism and healthcare utilisation outcomes. Main pathway: Main arrow represents the pathway between experience of racial discrimination (Time 1) and negative healthcare measures (Time 2), via negative perceptions and expectations of healthcare (providers, organisations, systems) and future engagement. Secondary pathway: Racial discrimination (T1) can impact negatively on healthcare (Time 2) via negative impacts on health increasing healthcare need
We used several criteria for considering and prioritising variables for the questionnaire. The conceptual model also informed prioritisation of variables for the questionnaire. For outcome measures, these included: alignment with study aims and objectives; existing evidence of a relationship between racism and outcome; New Zealand evidence of ethnic inequities in outcome; previous cross-sectional relationships between racism and outcome in New Zealand data; availability of baseline measures (for health outcomes); plausibility of health effects manifesting within a 1–2 year follow-up period; and data quality (e.g. validated measures, low missing data, questions suitable for multimodal administration). Mediators and confounders were considered for variables not available in the baseline NZHS survey, as was recent experience of racism (following the NZHS interview) to provide additional measurement of exposure to recent racism. A final consideration for prioritising items for inclusion was keeping the length of the questionnaire short in order to maximise response rates (while being able to fully address the study aims). The questionnaire was extensively discussed by the research team and reviewed by the study advisors prior to finalisation.
Table 3 summarises the outcome measures by topic domain and original source (with references). The final questionnaire content can be found in the Additional file 1 , and includes: health outcome measures of mental and physical health (using SF12-v2 and K10 scales); health service measures (unmet need, satisfaction with usual medical centre, experiences with general practitioners); experience of racism in the last 12 months (adapted from items in the NZHS); and variables required to restrict data (e.g. having a usual medical centre, type of centre, having a General Practitioner [GP] visit in the last 12 months) or potential confounder and mediator variables not available at baseline (e.g. number of GP visits).
Recruitment and data collection
Recruitment is currently underway. The sampling phase provided a list of potential participants for invitation, and recruitment for the follow-up survey uses the contact details from the NZHS interview (physical address, mobile/landline telephone, and email address if available). Recruitment will take place over three tranches to (1) manage fieldwork capacity and (2) allow tracking of response rates and adaptation of contact strategies if recruitment is sub-optimal.
To maximise response rates, we chose to use a multi-modal survey [ 45 ]. Participants are invited to respond by a paper questionnaire included with the initial invitation letter (questionnaire returned by pre-paid post), by self-completed online questionnaire, or by computer-assisted telephone interview (CATI, on mobile or landline.) A pen is included in the study invitation to improve initial engagement with the paper-based survey [ 46 ]. Participants completing the survey are offered a NZ$20 gift card to recognise their participation. The contact information contains instructions for opting out of the study.
Those participants not responding online or by post receive a reminder postcard mailed out two weeks after the initial letter, containing a link to the web survey and a note that the participant will be contacted by telephone in two weeks’ time.
Two weeks after the reminder postcard (four weeks post-invitation) remaining non-respondents are contacted using CATI processes. For those with mobile phone numbers or email addresses, a text (SMS) or email reminder is sent two days before the telephone contact phase. Once contact is made by telephone, the interviewer asks the participant to complete the survey over the telephone at that time or organises a subsequent appointment (interview duration approximately 15 min). Interviewers make up to seven telephone contact attempts for each participant, using all recorded telephone numbers. Respondents who decline to complete the full interview at telephone follow-up are asked to consider answering two priority questions (self-rated health and any unmet need for healthcare in the last 12 months: questions 1 and 8 in Table 3 and Additional file 1 ).
Past surveys conducted in NZ have frequently noted lower response rates and hence under-representation of Māori [ 47 , 48 ]. Drawing on Kaupapa Māori research principles, we are explicitly aiming for equitable response rates of Māori to ensure maximum power for ethnically stratified analysis. This involves providing culturally appropriate invitations and interviewers for participants, and actively monitoring response rates by ethnicity during data collection to allow longer and more frequent follow-up of Māori, Pacific and Asian participants if required [ 48 , 49 ]. The use of a multi-modal survey is also expected to minimise recruitment problems inherent to any single modality (e.g. lower phone ownership or internet access in some ethnic groups).
We have contracted an external research company to co-ordinate recruitment and data collection fieldwork under our supervision (covering all contact processes described here), which follows recruitment and data management protocols set by our research team.
Statistical analysis
Propensity score methods for the sampling stage are described above: this section focuses on causal analyses for health outcomes in the achieved sample. The sampling frame selects participants based on “ever” experience of racism, which is our exposure definition.
All analyses will account for both the complex survey sampling frame (weights, strata and clusters from the NZHS) and the secondary sampling phase (selection based on propensity scores). Complex survey data will be handled using software to account for these designs (e.g. survey package [ 50 ] in R); propensity scores will be handled in the main analysis by using inverse probability of treatment weights (IPTW) combined with the sampling weights [ 51 ].
Linear regression methods will be used to compare change in continuous outcome measures (e.g. K10 score) by estimating mean score at follow-up, adjusted for baseline. Analysis of dichotomous categorical outcomes (e.g. self-rated health) will use logistic regression methods, again adjusted for baseline (for health outcomes). We will conduct analyses stratified by ethnic group to explore whether the impact of racism differs by ethnic group. Models will adjust for confounders included in creating the propensity scores (doubly-robust estimation) to address residual confounding not fully covered by the propensity score approach [ 52 ]. Analysis for other outcomes will use similar methods.
As we hypothesise that some outcomes (e.g. self-reported mental distress) will be more strongly influenced by recent experience of racism, we will also examine our main outcomes restricted to those only reporting historical (more than 12 months ago) or recent (last 12 months) racism at baseline. These historical and recent experience groups (and corresponding unexposed individuals) form nested sub-groups of the total cohort, and so analysis will follow the same framework outlined above. Experience of racism in the last 12 months (measured at follow-up) will be examined in cross-sectional analyses and in combination with baseline measures of racism to create a measure to examine the cumulative impact of racism on outcomes.
Sensitivity analyses
While the sampling invitation lists are based on matched samples, we have no control about specific individuals choosing to participate in the follow-up survey, and so the original matching is unlikely to be maintained in the achieved sample. We will conduct sensitivity analyses using re-matched data (based on propensity scores for those participating in follow-up) to allow for re-calibration of exposed and unexposed groups in the achieved sample.
To consider potential for bias due to non-response in our follow-up sample, we will compare NZHS 2016/17 cross-sectional data for responders and non-responders on baseline sociodemographic, socioeconomic, and baseline health variables.
Sample size
Based on NZHS 2011/12 responses, we anticipated a total pool of 2100 potential participants with “ever” experience of racism, with approximately 1100 expected to be Māori/Pacific/Asian ethnicity, and 10,000 with no report of racism (at least 2 unexposed per exposed individual in each ethnic group).
For the main analyses (based on “ever” experience of racism) we assumed a conservative follow-up rate of 40%, giving a final sample size of at least 840 exposed individuals. This response rate includes re-contact and agreement to participate, based on past experience recruiting NZHS participants for other studies and the relative length of the current survey questionnaire.
Initial projections (based on NZHS2011/12 data) indicated sufficient numbers of unexposed individuals for 1:1 matching based on ethnicity and propensity scores. This gives a feasible total sample size of n = 1680, providing substantial power for the K10 mental health outcome (standard deviation = 6.5: > 95% power to detect difference in change of 2 units of K10 between groups.) For the second main health outcome (change in self-rated health), this sample size will have > 85% power for a difference between 8% of those exposed to racism having worse self-reported health at follow-up (relative to baseline) compared to 5% of unexposed individuals.
For analyses of effects stratified by ethnicity, we expect > 95% power for Māori participants ( n = 280 each exposed and unexposed) for the K10 outcome (assumptions as above); change in self-rated health will have 80% power for a difference between 12% of exposed individuals having worse self-reported health at follow-up (relative to baseline) compared to 5% of unexposed individuals. Stratified estimates for Pacific and Asian groups will have poorer precision, but should still provide valid comparisons.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
The study involves recruiting participants who have already completed the NZHS interview (including questions on racial discrimination) The NZHS as conducted by the Ministry of Health has its own ethical approval (MEC/10/10/103) and participants are only invited onto the present study if they explicitly consented (at the time of completing the NZHS) to re-contact for future health research. The current study was reviewed and approved by the University of Otago’s Human Ethics (Health) Committee prior to commencement of fieldwork (reference: H17/094). Participants provided informed consent to participate at the time of completing the follow-up survey depending on response modality: implicitly through completion and return of the paper survey which stated “By completing this survey, you indicate that you understand the research and are willing to participate” (see Additional file 1 : a separate written consent document was not required by the ethics committee); in the online survey by responding “yes” to a similarly worded question that they understood the study and agreed to take part (recorded as part of data collection, and participation could not continue unless ticked), or by verbal consent in a similar initial question in the telephone interview (since written consent could not be collected in this setting). These consent methods were approved by the reviewing Ethics committee [ 53 ]. Ethical approval for the study included using the same consent processes for those participants aged 16 to 18 as for older participants.
This study will contribute robust evidence to the limited national and international literature from prospective studies on the causal links between experience of racism and subsequent health. The use of the NZHS as the baseline for the prospective study capitalises on the inclusion of racism questions in that survey to provide a unique and important opportunity to build on and substantially strengthen the current evidence base for the impact of racism on health using data spanning the entire New Zealand adult population. In addition, our use of propensity scores in the sampling phase is a novel approach to prospective recruitment of participants from the NZHS. This approach should manage confounding while reducing the need (and cost) of following up all NZHS participants, without compromising the internal validity of the results. The novel methods developed for using the NZHS as the base for a prospective cohort study will have wider application to other health priority areas. One general limitation of this approach is that baseline data (for both propensity score development and baseline health measures) is limited to the data captured in the existing larger survey. We anticipate that this study will assist in prioritising racism as a health determinant and inform the development of anti-racism interventions in health service delivery and policy making.
Current stage of research
Funding for this project began October 1st 2017. The first set of respondent invitations was mailed out on July 12th 2018; fieldwork for the final tranche of invitations was underway at the time of submission and is expected to be completed by 31 December 2018. Analysis and reporting will take place in mid-to-late 2019.
Abbreviations
Computer Assisted Telephone Interview
General Practitioner
General Social Survey
Index of Multiple Deprivation
Inverse Probability of Treatment Weights
- New Zealand
New Zealand Deprivation Index
New Zealand Health Survey
12/36-Item Short Form Survey
short message service
Commission on Social Determinants of Health. Closing the gap in a generation: health equity through actions on the social determinants of health. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2008.
Google Scholar
Ministry of Health. Annual Update of Key Results 2016/17: New Zealand Health Survey 2017 [Available from: https://www.health.govt.nz/publication/annual-update-key-results-2016-17-new-zealand-health-survey . accessed 13/09/2018].
Ministry of Social Development. The Social Report 2016: Te pūrongo oranga tangata. Wellington: Ministry of Social Development; 2016.
Williams DR, Mohammed SA. Racism and health I: pathways and scientific evidence. Am Behav Sci. 2013;57(8). https://doi.org/10.1177/0002764213487340 .
Reid P, Robson B. Understanding health inequities. In: Robson B, Harris R, editors. Hauora: Maori standards of health IV a study of the years 2000–2005. Wellington: Te Ropu Rangahau Hauora a Eru Pomare; 2007. p. 3–10.
Jones C. Confronting institutionalized racism. Phylon. 2002;50:7–22.
Article Google Scholar
Garner S. Racisms: An introduction. London/Thousand Oaks CA: Sage; 2010.
Book Google Scholar
Becares L, Cormack D, Harris R. Ethnic density and area deprivation: neighbourhood effects on Maori health and racial discrimination in Aotearoa/New Zealand. Soc Sci Med. 2013;88:76–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2013.04.007 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Paradies YC. Defining, conceptualizing and characterizing racism in health research. Crit Public Health. 2006;16(2):143–57. https://doi.org/10.1080/09581590600828881 .
Krieger N. Methods for the scientific study of discrimination and health: an ecosocial approach. Am J Public Health. 2012;102(5):936–44. https://doi.org/10.2105/AJPH.2011.300544 .
Jones CP. Invited commentary: "race," racism, and the practice of epidemiology. Am J Epidemiol. 2001;154(4):299–304; discussion 05-6.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Paradies Y, Ben J, Denson N, et al. Racism as a determinant of health: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2015;10(9):e0138511. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0138511 .
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Lewis TT, Cogburn CD, Williams DR. Self-reported experiences of discrimination and health: scientific advances, ongoing controversies, and emerging issues. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. 2015;11:407–40. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-032814-112728 .
Gee GC, Ro A, Shariff-Marco S, et al. Racial discrimination and health among Asian Americans: evidence, assessment, and directions for future research. Epidemiol Rev. 2009;31:130–51. https://doi.org/10.1093/epirev/mxp009 .
Williams DR, Mohammed SA. Discrimination and racial disparities in health: evidence and needed research. J Behav Med. 2009;32(1):20–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10865-008-9185-0 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Ben J, Cormack D, Harris R, et al. Racism and health service utilisation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2017;12(12):e0189900. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0189900 published Online First: 2017/12/19.
Harris R, Cormack D, Tobias M, et al. The pervasive effects of racism: experiences of racial discrimination in New Zealand over time and associations with multiple health domains. Soc Sci Med. 2012;74(3):408–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2011.11.004 .
Ministry of Health. Methodology report 2016/17: New Zealand health survey. Wellington: Ministry of Health; 2017.
Ministry of Health. Content guide 2016/17: New Zealand health survey. Wellington: Ministry of Health; 2017.
Harris R, Cormack D, Tobias M, et al. Self-reported experience of racial discrimination and health care use in New Zealand: results from the 2006/07 New Zealand health survey. Am J Public Health. 2012;102(5):1012–9. https://doi.org/10.2105/AJPH.2011.300626 .
Harris RB, Cormack DM, Stanley J. Experience of racism and associations with unmet need and healthcare satisfaction: the 2011/12 adult New Zealand health survey. Aust N Z J Public Health. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1111/1753-6405.12835 published Online First: 2018/10/09.
Harris RB, Stanley J, Cormack DM. Racism and health in New Zealand: prevalence over time and associations between recent experience of racism and health and wellbeing measures using national survey data. PLoS One. 2018;13(5):e0196476. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0196476 published Online First: 2018/05/04.
Dyall L, Kepa M, Teh R, et al. Cultural and social factors and quality of life of Maori in advanced age. Te puawaitanga o nga tapuwae kia ora tonu - life and living in advanced age: a cohort study in New Zealand (LiLACS NZ). N Z Med J. 2014;127(1393):62–79.
PubMed Google Scholar
Crengle S, Robinson E, Ameratunga S, et al. Ethnic discrimination prevalence and associations with health outcomes: data from a nationally representative cross-sectional survey of secondary school students in New Zealand. BMC Public Health. 2012;12:45. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-12-45 .
Thayer ZM, Kuzawa CW. Ethnic discrimination predicts poor self-rated health and cortisol in pregnancy: insights from New Zealand. Soc Sci Med. 2015;128:36–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2015.01.003 .
Stronge S, Sengupta NK, Barlow FK, et al. Perceived discrimination predicts increased support for political rights and life satisfaction mediated by ethnic identity: a longitudinal analysis. Cult Divers Ethn Minor Psychol. 2016;22(3):359–68. https://doi.org/10.1037/cdp0000074 .
Becares L, Atatoa-Carr P. The association between maternal and partner experienced racial discrimination and prenatal perceived stress, prenatal and postnatal depression: findings from the growing up in New Zealand cohort study. Int J Equity Health. 2016;15(1):155. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12939-016-0443-4 .
Robson B, Harris R, editors. Hauora : Maori standards of health IV : a study of the years 2000–2005. Wellington: Te Rōpū Rangahau Hauora a Eru Pōmare; 2007.
UN General Assembly. United Nations Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples : resolution / adopted by the General Assembly 2007. Available from: https://undocs.org/A/RES/61/295 . Accessed 1 Nov 2018.
Smith L. Decolonizing methodologies: research and indigenous peoples. 2nd ed. London and New York: Zed Books; 2012.
Harris R, Tobias M, Jeffreys M, et al. Racism and health: the relationship between experience of racial discrimination and health in New Zealand. Soc Sci Med. 2006;63(6):1428–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2006.04.009 .
Sturmer T, Joshi M, Glynn RJ, et al. A review of the application of propensity score methods yielded increasing use, advantages in specific settings, but not substantially different estimates compared with conventional multivariable methods. J Clin Epidemiol. 2006;59(5):437–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2005.07.004 .
Luo Z, Gardiner JC, Bradley CJ. Applying propensity score methods in medical research: pitfalls and prospects. Med Care Res Rev. 2010;67(5):528–54. https://doi.org/10.1177/1077558710361486 .
Weitzen S, Lapane KL, Toledano AY, et al. Principles for modeling propensity scores in medical research: a systematic literature review. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2004;13(12):841–53. https://doi.org/10.1002/pds.969 .
Shah BR, Laupacis A, Hux JE, et al. Propensity score methods gave similar results to traditional regression modeling in observational studies: a systematic review. J Clin Epidemiol. 2005;58(6):550–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2004.10.016 .
Stuart EA. Matching methods for causal inference: a review and a look forward. Stat Sci. 2010;25(1):1–21. https://doi.org/10.1214/09-STS313 published Online First: 2010/09/28.
Stuart EA, Ialongo NS. Matching methods for selection of subjects for follow-up. Multivariate Behav Res. 2010;45(4):746–65. https://doi.org/10.1080/00273171.2010.503544 [published Online First: 2011/01/12].
Ministry of Health. Ethnicity Data Protocols Wellington: Ministry of Health; 2017. Available from: https://www.health.govt.nz/system/files/documents/publications/hiso-10001-2017-ethnicity-data-protocols-v2.pdf . Accessed 1 Nov 2018.
Austin PC. An introduction to propensity score methods for reducing the effects of confounding in observational studies. Multivariate Behav Res. 2011;46(3):399–424. https://doi.org/10.1080/00273171.2011.568786 .
Caliendo M, Kopeinig S. Some practical guidance for the implementation of propensity score matching. J Econ Surv. 2008;22(1):31–72. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-6419.2007.00527.x .
Ho DE, Imai K, King G, et al. Matching as nonparametric preprocessing for reducing model dependence in parametric causal inference. Polit Anal. 2017;15(03):199–236. https://doi.org/10.1093/pan/mpl013 .
Ho DE, Imai K, King G, et al. MatchIt: nonparametric preprocessing for parametric causal inference. J Stat Softw. 2011;42(8):1–28.
Sarnyai Z, Berger M, Jawan I. Allostatic load mediates the impact of stress and trauma on physical and mental health in indigenous Australians. Australas Psychiatry. 2016;24(1):72–5. https://doi.org/10.1177/1039856215620025 published Online First: 2015/12/10.
Kaholokula J. Mauli Ola: Pathways toward Social Justice for Native Hawaiians. Townsville: LIME Network Conference; 2015.
Fowler FJ, Roman AM, Mahmood R, et al. Reducing nonresponse and nonresponse error in a telephone survey: an informative case study. J Survey Stat Methodol. 2016;4(2):246–62. https://doi.org/10.1093/jssam/smw004 .
White E, Carney PA, Kolar AS. Increasing response to mailed questionnaires by including a pencil/pen. Am J Epidemiol. 2005;162(3):261–6. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwi194 [published Online First: 2005/06/24].
Fink JW, Paine SJ, Gander PH, et al. Changing response rates from Maori and non-Maori in national sleep health surveys. N Z Med J. 2011;124(1328):52–63.
Paine SJ, Priston M, Signal TL, et al. Developing new approaches for the recruitment and retention of Indigenous participants in longitudinal research: Lessons from E Moe, Māmā: Maternal Sleep and Health in Aotearoa/New Zealand. MAI Journal: A New Zealand Journal of Indigenous Scholarship. 2013;2(2):121–32.
Selak V, Crengle S, Elley CR, et al. Recruiting equal numbers of indigenous and non-indigenous participants to a 'polypill' randomized trial. Int J Equity Health. 2013;12:44. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-9276-12-44 .
Lumley T. survey: analysis of complex survey samples v3.32 2017 [R package]. Available from: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/survey/index.html . Accessed 1 Nov 2018.
Lenis D, Nguyen TQ, Dong N, et al. It's all about balance: propensity score matching in the context of complex survey data. Biostatistics. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1093/biostatistics/kxx063 [published Online First: 2018/01/03].
Funk MJ, Westreich D, Wiesen C, et al. Doubly robust estimation of causal effects. Am J Epidemiol. 2011;173(7):761–7. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwq439 [published Online First: 2011/03/10].
National Ethics Advisory Committee. Ethical guidelines for observational studies: observational research, audits and related activities. Revised edition. Wellington: Ministry of Health; 2012.
Atkinson J, Salmond C, Crampton P. NZDep2013 index of deprivation. Dunedin: University of Otago; 2014.
Exeter DJ, Zhao J, Crengle S, et al. The New Zealand indices of multiple deprivation (IMD): a new suite of indicators for social and health research in Aotearoa, New Zealand. PLoS One. 2017;12(8):e0181260. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0181260 [published Online First: 2017/08/05].
Kessler RC, Andrews G, Colpe LJ, et al. Short screening scales to monitor population prevalences and trends in non-specific psychological distress. Psychol Med. 2002;32(6):959–76.
Ware J Jr, Kosinski M, Keller SD. A 12-item short-form health survey: construction of scales and preliminary tests of reliability and validity. Med Care. 1996;34(3):220–33.
Fleishman JA, Selim AJ, Kazis LE. Deriving SF-12v2 physical and mental health summary scores: a comparison of different scoring algorithms. Qual Life Res. 2010;19(2):231–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-009-9582-z .
Bastos JL, Harnois CE, Paradies YC. Health care barriers, racism, and intersectionality in Australia. Soc Sci Med. 2018;199:209–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2017.05.010 [published Online First: 2017/05/16].
Australian Bureau of Statistics. General Social Survey 2014: Household questionnaire. Canberra: Australian Bureau of Statistics; 2014.
Ministry of Health. The New Zealand Health Survey: Content Guide and questionnaires 2011–2012 Wellington: Ministry of Health; 2012 [Available from: http://www.health.govt.nz/publication/new-zealand-health-survey-content-guide-and-questionnaires-2011-2012 . accessed 31/10/2016 2016].
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the assistance of the Ministry of Health’s New Zealand Health Survey Team for facilitating access to the NZHS data and respondent lists, and for help with constructing the questionnaire (including providing the Helpline contact template).
We would also like to acknowledge the expertise and input of our project advisory team: Natalie Talamaivao (Senior Advisor, Māori Health Research, Ministry of Health), Associate Professor Bridget Robson (Director, Eru Pōmare Māori Health Research Centre, University of Otago, Wellington), and Dr. Sarah-Jane Paine (Senior Research Fellow, University of Auckland and University of Otago, Wellington). Thanks also to Ms. Ruruhira Rameka (Eru Pōmare Māori Health Research Centre, University of Otago, Wellington) for providing administrative support. Research New Zealand was contracted to undertake the data collection and other fieldwork for the follow-up survey.
This project was funded by the Health Research Council of New Zealand (HRC 17–066). The funding body approved the study but has no further role in the study design or outputs from the study.
Availability of data and materials
Data from the follow-up study is not available to other researchers as participants did not provide their consent for data sharing. The NZHS 2016/17 data used as the baseline for the study described in this protocol is available to approved researchers subject to the New Zealand Ministry of Health’s Survey Microdata Access agreement https://www.health.govt.nz/nz-health-statistics/national-collections-and-surveys/surveys/access-survey-microdata .
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Public Health, University of Otago, Wellington, 23a Mein Street, Newtown, Wellington, New Zealand
James Stanley & Richard Edwards
Eru Pōmare Māori Health Research Centre, University of Otago, Wellington, 23a Mein Street, Newtown, Wellington, New Zealand
Ricci Harris, Donna Cormack & Andrew Waa
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
JS and RH initiated the project and are co-principal investigators of the study, and jointly led writing of the grant application and this protocol paper. JS designed the sampling plan, led the development of the contact protocol, led the development of the statistical analysis plan, contributed to revising the questionnaire, and is guarantor of the paper. RH designed the questionnaire, contributed to development of the sampling and contact protocol, and co-led the statistical analysis plan. DC led the conceptual plan with support from RH. AW and RE contributed to the contact protocol. DC, AW and RE all contributed to writing the grant application, revising the questionnaire and sampling plans, and revising the draft protocol paper. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to James Stanley .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The follow-up study protocol and questionnaire were approved by the University of Otago’s Human Ethics (Health) Committee prior to commencement of fieldwork (reference: H17/094). The NZHS has its own ethical approval as granted to the New Zealand Ministry of Health (NZ Multi-Region Ethics Committee, MEC/10/10/103), and consent for re-contact was gained from participants at the time of their NZHS interview. Participants provided informed consented to participate at the time of completing the follow-up survey: implicitly through completion and return of the paper survey which stated “By completing this survey, you indicate that you understand the research and are willing to participate”; in the online survey by responding “yes” to a similarly worded question that they understood the study and agreed to take part, or by verbal consent in a similar initial question in the telephone interview.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
JS, RH, DC, AW, and RE report funding from the Health Research Council of New Zealand to complete this work. JS and RH report personal fees from the Health Research Council of New Zealand for service as external members on committees (neither are employees of the HRC), outside the scope of the current work.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Additional file
Additional file 1:.
Questionnaire used in follow-up survey. (PDF 919 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Stanley, J., Harris, R., Cormack, D. et al. The impact of racism on the future health of adults: protocol for a prospective cohort study. BMC Public Health 19 , 346 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-019-6664-x
Download citation
Received : 28 November 2018
Accepted : 15 March 2019
Published : 28 March 2019
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-019-6664-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Prospective cohort study
- Health service utilisation
- Health inequities
BMC Public Health
ISSN: 1471-2458
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]

University of Warwick Publications service & WRAP
Highlight your research.
- Search WRAP
- Browse by Warwick Author
- Browse WRAP by Year
- Browse WRAP by Subject
- Browse WRAP by Department
- Browse WRAP by Funder
- Browse Theses by Department
- Search Publications Service
- Browse Publications service by Year
- Browse Publications service by Subject
- Browse Publications service by Department
- Browse Publications service by Funder
- Help & Advice
The Library
Institutional racism, the police and stop and search: a comparative study of stop and search in the uk and usa.

Delsol, Rebekah (2006) Institutional racism, the police and stop and search: a comparative study of stop and search in the UK and USA. PhD thesis, University of Warwick.
Request Changes to record. --> Request Changes to record.
This research examines the utility of the concept of institutional racism in explaining racial disparities in stop and search practice in the UK and US. The concept of institutional racism was introduced in 1960s America. The concept was politically powerful in expanding existing understandings of racial inequalities which focused on individual prejudice and cultural pathology, to showing how racist discourses can become embedded in the structures of social formation. There were a number of analytical weaknesses inherent in the term at its conception. The concept has been utilized at various points of history in the US and UK. The 1999 Macpherson Report brought the concept of institutional racism back to popular usage in the UK, particularly in discussions around discrimination and policing. Macpherson took as evidence of the existence of institutional racism the continued disparities in stop and search use. The power to stop and search people in the street suspected of criminal activity has long been a feature of British and American policing. Research in both countries has continually shown that these powers are being disproportionately exercised against ethnic minorities. Thus this thesis explores whether the concept is useful in explaining disproportionate stop and search outcomes. The research is based on a study of police officers from two forces in the UK and two police departments in the US. It uses semi-structured interviews, observations and draws on official policy documents and statistics. The purpose of the research is to gain an understanding of the circumstances and decision-making by officers as they conduct stop and search and to understand the context in which these decisions take place. The findings reveal that discriminatory outcomes in stop and search are the product of not only the actions of individual officers but also national and local policies and practices. These policies and practices are devised and implemented by social actors. The disproportionate outcomes not only result from racism but also prejudice based on class and gender. The concept of institutional racism reifies individual institutions and obscures the role of social actors in institutions, who shape the policies and practices of an institution. Without an understanding of the contexts in which people draw on race ideas and what features of their social position allows them to assert these ideas into the policies and practices of an institution we are unable to apportion responsibility and build reform agendas. Thus institutional racism fails to explain the disparities in stop and search use in the UK and US.
Request changes or add full text files to a record --> Request changes or add full text files to a record
Repository staff actions (login required)
Downloads per month over past year
View more statistics
Email us: [email protected] Contact Details About Us

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Institutional racism can be defined as differential access to power, resources, and opportunities by race that further entrenches privilege and oppression (Paradies 2016).Along with similar concepts such as systemic, structural, cultural, and societal racism, this form of racism profoundly shapes almost all aspects of our lives, including health and healthcare (Williams, Lawrence, and Davis 2019).
There is no "official" definition of structural racism — or of the closely related concepts of systemic and institutional racism — although multiple definitions have been offered. 3-7 All ...
Theory and research in cultural psychology highlight the need to examine racism not only "in the head" but also "in the world." Racism is often defined as individual prejudice, but racism is also systemic, existing in the advantages and disadvantages imprinted in cultural artifacts, ideological discourse, and institutional realities that work together with individual biases.
Racism in the United States. Although racism at individual, institutional, and structural levels has persisted for centuries in the United States, a new civil rights movement championed by Black Lives Matter has motivated Americans of all racialized groups and ethnicities to be antiracist and to examine and change behaviors that contribute to racism, social injustice, inequities, and ...
Given growing interest in research on institutional racism in recent years, we conducted an updated search using the methods described in Groos et al. . As shown in Figure S1, we identified 36 additional papers published between January 1, 2018 and December 15, 2020 that met the authors' inclusion criteria.
Bioethics has the potential to make important contributions to anti-racist programmes and strategies addressing institutional racism, yet as scholars have argued, the "whiteness" of bioethics undermines its capacity to attend to institutionalized forms of racism (Mayes 2020; Russell 2016; Danis, Wilson, and White 2016).Catherine Myser argues that bioethics depends on social and ethical ...
Racism is a deep and persistent problem in education. Researchers from across the social sciences have shown that educational policies and practices in the United States have institutionalized racism (Brooks & Theoharis, 2018), creating an inequitable and hostile system that normalizes whiteness 1 and disadvantages people and communities of color (Horsford, 2011; Ladson-Billings, 2004).
Lived experience grounds an understanding and recognition of structural racism. African Americans who say they have personally experienced discrimination are equally divided over whether institutional racism or individual prejudice is the bigger problem for Black people today (44% each; Pew Research Center, 2016). African Americans who say they ...
June 2, 2020 Stanford scholars examine racism, social change and how to build a more just future. The recent acts of violence perpetrated against Black communities has led many to question racism ...
Definition. Systemic racism is said to occur when racially unequal opportunities and outcomes are inbuilt or intrinsic to the operation of a society's structures. Simply put, systemic racism refers to the processes and outcomes of racial inequality and inequity in life opportunities and treat-ment. Systemic racism permeates a society's (a ...
Richard A Powell and colleagues set out the barriers and solutions to eliminating inequalities embedded in the UK health research system Seismic forces are challenging the UK's ethno-racial status quo.12 As a result, many organisations have made public commitments to listen to, learn from, and act on factors sustaining historical and current ethno-racial injustices and inequalities. The UK ...
A third focus in the literature that examined institutional racism in K-12 schools was a critique of policies and practices that label and serve two frequently marginalized student groups—dual-language learners (DLLs), often referred to as English Learners; and students labeled with disabilities. There is a body of literature that ...
Systemic racism is a scientifically tractable phenomenon, urgent for cognitive scientists to address. This tutorial reviews the built-in systems that undermine life opportunities and outcomes by racial category, with a focus on challenges to Black Americans. From American colonial history, explicit practices and policies reinforced disadvantage across all domains of life, beginning with ...
Racial discrimination is recognised as a key social determinant of health and driver of racial/ethnic health inequities. Studies have shown that people exposed to racism have poorer health outcomes (particularly for mental health), alongside both reduced access to health care and poorer patient experiences. Most of these studies have used cross-sectional designs: this prospective cohort study ...
This research examines the utility of the concept of institutional racism in explaining racial disparities in stop and search practice in the UK and US. The concept of institutional racism was introduced in 1960s America. The concept was politically powerful in expanding existing understandings of racial inequalities which focused on individual prejudice and cultural pathology, to showing how ...
institutional racism, the perpetuation of discrimination on the basis of "race" by political, economic, or legal institutions and systems. According to critical race theory, an offshoot of the critical legal studies movement, institutional racism reinforces inequalities between groups—e.g., in wealth and income, education, health care, and civil rights—on the basis of the groups ...
The authors argue that sociologists use racism to refer to four constructs: (1) individual attitudes, (2) cultural schema, and two constructs associated with structural racism: (3) preexisting consequential inequalities, that is, racial dominance, and (4) processes that create or maintain racial dominance. The article compares this framework ...
Research should focus on the etiology of racism among European Americans and the central role played by White elites and the media in maintaining historic cultural and institutional arrangements ...
Clark and colleagues' (1999) biopsychosocial model of racism posits that racism results in psychological and physiological stress responses that can be linked to negative psychological wellbeing, and Jones' (2000) model categorizes internalized racism as a stressor for African Americans. While recent empirical research has documented the impact of racial discrimination on the psychological ...