

Gujarat Earthquake 2001: Case Study
Introduction
Gujarat is a state in the north western part of India. Beneath India, the Indo-Australian and the Eurasian Plate are moving towards each other at about 2cm per year. Both plates are continental, so this is a compressional boundary where both the plates are pushed up to form fold mountains The Himalayas are the most obvious result of this collision. Along with the creation of fold mountains, the movement of the plates creates stress within the rocks. When the stress is suddenly released by rocks slipping past each other, we experience an earthquake.
The epicentre of the Gujarat earthquake was a small town called Bhuj. At 08:46 local time, on Friday 26th January 2001 it was struck by an earthquake that measured 7.9 on the Richter Scale It turned out to be one of the two most deadly earthquakes in the recorded history of India, with almost 20,000 people confirmed as dead, and another 166,000 injured. Add to that a further 600,000 left homeless, almost 350,000 homes destroyed and another 844,000 damaged and it becomes obvious that this was a major humanitarian disaster. The Indian government has calculated that in one way or another, the ‘quake had an effect on 15.9 million people – nearly half the population of India!
The cost of the damage varies depending upon who’s figures you use, but it was between 1.3 billion and 5 billion US dollars. In built up areas modern buildings were shaken but mostly survived. Others, however, including several multistory concrete buildings collapsed. Because only some of the new buildings collapsed, the government suspected that dodgy building methods may have been the cause. Investigations led to a number of builders, architects and engineers being charged with culpable murder and criminal conspiracy.
Before the quake this was a rather dry area often affected by drought. After the quake there were many reports of the water table rising, sometimes to surface level. In a number of places new springs appeared, some with fresh water and others, more surprisingly, with salt water. Some desert rivers, that had been dry for over a century, began to flow again, and there was evidence of liquefaction in many places.
Transport and Communications
Access to the sites of earthquakes is always likely to be restricted by the damage caused by the quake, because ground movements damage roads and railways. Damage to roads affected the transportation of goods to the 40 or so ports along the Gujarat coastline.
Bhuj was no exception and suffered from very limited transport after the earthquake. Even days after the quake, the rescue services had not managed to gain access to all the remote villages that suffered during the earthquake. Roads were cracked, lifted and warped, but most obstructions in built up areas were caused by debris that fell onto roads. Where there was a possibility of survivors under the debris, it was out of the question to just bulldoze the rubble out of the way; it had to be carefully and slowly removed, leaving roads blocked until there was no hope of finding survivors.
Telephone lines were broken, exchanges damaged and power lost to the telephone system. In many remote areas mobile telephones don’t work, so all forms of communication with ‘difficult to reach’ places were out of order. Repairing phone lines took time, and the process wasn’t helped by blocked roads, damaged buildings and the loss of workers killed or injured in the event.
Gujarat was the second most industrialised state in India, with well developed diamond, pharmaceutical, chemical, textile and steel industries. Although most survived the quake with little or no major structural damage, they were disrupted by the destruction of communications, transportation and electricity / gas supplies. Immediately after the quake, industry was losing about 200 million dollars every day.
The huge loss of life also had an impact on industry because many of the dead were workers in local businesses.
” The lives lost would impact the (businesses) as many employees would have been a victim of the tragedy,” the Confederation of Indian Industry said in a statement.
General Services
As with many large earthquakes, services like water, gas, electricity and sewerage provided through a network of underground pipes and cables were damaged when the ground flexed and moved. Broken pipes and cables led to loss of fresh water, sewerage discharges and no power in many areas. At the epicentre, in Bhuj, 95 percent of the town was left uninhabitable, with no water, electricity or shelter.

Bhuj Earthquake India 2001 – A Complete Study
Bhuj earthquake india.

Gujarat : Disaster on a day of celebration : 51st Republic Day on January 26, 2001
- 7.9 on the Richter scale.
- 8.46 AM January 26th 2001
- 20,800 dead
Basic Facts
- Earthquake: 8:46am on January 26, 2001
- Epicenter: Near Bhuj in Gujarat, India
- Magnitude: 7.9 on the Richter Scale
Geologic Setting
- Indian Plate Sub ducting beneath Eurasian Plate
- Continental Drift
- Convergent Boundary
Specifics of 2001 Quake
Compression Stress between region’s faults
Depth: 16km
Probable Fault: Kachchh Mainland
Fault Type: Reverse Dip-Slip (Thrust Fault)
The earthquake’s epicentre was 20km from Bhuj. A city with a population of 140,000 in 2001. The city is in the region known as the Kutch region. The effects of the earthquake were also felt on the north side of the Pakistan border, in Pakistan 18 people were killed.
Tectonic systems
The earthquake was caused at the convergent plate boundary between the Indian plate and the Eurasian plate boundary. These pushed together and caused the earthquake. However as Bhuj is in an intraplate zone, the earthquake was not expected, this is one of the reasons so many buildings were destroyed – because people did not build to earthquake resistant standards in an area earthquakes were not thought to occur. In addition the Gujarat earthquake is an excellent example of liquefaction, causing buildings to ‘sink’ into the ground which gains a consistency of a liquid due to the frequency of the earthquake.
India : Vulnerability to earthquakes
- 56% of the total area of the Indian Republic is vulnerable to seismic activity .
- 12% of the area comes under Zone V (A&N Islands, Bihar, Gujarat, Himachal Pradesh, J&K, N.E.States, Uttaranchal)
- 18% area in Zone IV (Bihar, Delhi, Gujarat, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, J&K, Lakshadweep, Maharashtra, Punjab, Sikkim, Uttaranchal, W. Bengal)
- 26% area in Zone III (Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Goa, Gujarat, Haryana, Kerala, Maharashtra, Orissa, Punjab, Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu, Uttaranchal, W. Bengal)
- Gujarat: an advanced state on the west coast of India.
- On 26 January 2001, an earthquake struck the Kutch district of Gujarat at 8.46 am.
- Epicentre 20 km North East of Bhuj, the headquarter of Kutch.
- The Indian Meteorological Department estimated the intensity of the earthquake at 6.9 Richter. According to the US Geological Survey, the intensity of the quake was 7.7 Richter.
- The quake was the worst in India in the last 180 years.
What earthquakes do
- Casualties: loss of life and injury.
- Loss of housing.
- Damage to infrastructure.
- Disruption of transport and communications.
- Breakdown of social order.
- Loss of industrial output.
- Loss of business.
- Disruption of marketing systems.
- The earthquake devastated Kutch. Practically all buildings and structures of Kutch were brought down.
- Ahmedabad, Rajkot, Jamnagar, Surendaranagar and Patan were heavily damaged.
- Nearly 19,000 people died. Kutch alone reported more than 17,000 deaths.
- 1.66 lakh people were injured. Most were handicapped for the rest of their lives.
- The dead included 7,065 children (0-14 years) and 9,110 women.
- There were 348 orphans and 826 widows.
Loss classification
Deaths and injuries: demographics and labour markets
Effects on assets and GDP
Effects on fiscal accounts
Financial markets
Disaster loss
- Initial estimate Rs. 200 billion.
- Came down to Rs. 144 billion.
- No inventory of buildings
- Non-engineered buildings
- Land and buildings
- Stocks and flows
- Reconstruction costs (Rs. 106 billion) and loss estimates (Rs. 99 billion) are different
- Public good considerations
Human Impact: Tertiary effects
- Affected 15.9 million people out of 37.8 in the region (in areas such as Bhuj, Bhachau, Anjar, Ganhidham, Rapar)
- High demand for food, water, and medical care for survivors
- Humanitarian intervention by groups such as Oxfam: focused on Immediate response and then rehabilitation
- Of survivors, many require persistent medical attention
- Region continues to require assistance long after quake has subsided
- International aid vital to recovery
Social Impacts

- 80% of water and food sources were destroyed.
- The obvious social impacts are that around 20,000 people were killed and near 200,000 were injured.
- However at the same time, looting and violence occurred following the quake, and this affected many people too.
- On the other hand, the earthquake resulted in millions of USD in aid, which has since allowed the Bhuj region to rebuild itself and then grow in a way it wouldn’t have done otherwise.
- The final major social effect was that around 400,000 Indian homes were destroyed resulting in around 2 million people being made homeless immediately following the quake.
Social security and insurance
- Ex gratia payment: death relief and monetary benefits to the injured
- Major and minor injuries
- Cash doles
- Government insurance fund
- Group insurance schemes
- Claim ratio
Demographics and labour market
- Geographic pattern of ground motion, spatial array of population and properties at risk, and their risk vulnerabilities.
- Low population density was a saving grace.
- Extra fatalities among women
- Effect on dependency ratio
- Farming and textiles

Economic Impacts
- Total damage estimated at around $7 billion. However $18 billion of aid was invested in the Bhuj area.
- Over 15km of tarmac road networks were completely destroyed.
- In the economic capital of the Gujarat region, Ahmedabad, 58 multi storey buildings were destroyed, these buildings contained many of the businesses which were generating the wealth of the region.
- Many schools were destroyed and the literacy rate of the Gujarat region is now the lowest outside southern India.
Impact on GDP
- Applying ICOR
- Rs. 99 billion – deduct a third as loss of current value added.
- Get GDP loss as Rs. 23 billion
- Adjust for heterogeneous capital, excess capacity, loss Rs. 20 billion.
- Reconstruction efforts.
- Likely to have been Rs. 15 billion.
Fiscal accounts
- Differentiate among different taxes: sales tax, stamp duties and registration fees, motor vehicle tax, electricity duty, entertainment tax, profession tax, state excise and other taxes. Shortfall of Rs. 9 billion of which about Rs. 6 billion unconnected with earthquake.
- Earthquake related other flows.
- Expenditure:Rs. 8 billion on relief. Rs. 87 billion on rehabilitation.
Impact on Revenue Continue Reading
Comments are closed.
Privacy Overview
- 0 Shopping Cart

Gujurat Earthquake 2001
Gujurat earthquake.
An earthquake measuring 7.9 on the Richter Scale.
Friday 26th January 2001 at 08:46 local time.
The earthquake occurred in north-western India. The epicentre was close to the small desert town of Bhuj in the north-western state of Gujarat.
India lies on a collision margin. The Indo-Australian and the Eurasian Plate collide into each other at the rate of around 2cm per year. As neither can subduct (both plates are continental) the land where the two plate meet is forced upwards. Over the last 60 million years this process has formed The Himalayas
As the two continental plates move towards each other pressure builds up. Eventually this pressure is released. This caused the earthquake in India
Latest Blog Entries
Related Topics
Use the images below to explore related GeoTopics.
Previous Topic Page
Topic home, christchurch earthquake 2011, share this:.
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
Please Support Internet Geography
If you've found the resources on this site useful please consider making a secure donation via PayPal to support the development of the site. The site is self-funded and your support is really appreciated.
Search Internet Geography
Top posts and pages.
Pin It on Pinterest
- Click to share
- Print Friendly
Gujarat Earthquake in 2001
Introduction
We value your ideas and suggestions. Please contact the maintainer of this site. This site can be found at: http://www.geography-site.co.uk Last Modified on: March 17, 2011 © Geography Site
- Differences
- Niche Topics
- Tools & Equip.

✔ Humans are the superior social animals instilled with emotions, feelings, and, most importantly, wisdom. The world has dramatically evolved from the primitive Stone Age to the modern world. The credit for this drastic change solely goes to humans and their broad horizons of knowledge.
✔ With the advancement of technology, it seems that there is nothing humans cannot achieve. Despite all the development and improvement, one aspect of nature still exists beyond humans’ control, i.e., natural disasters.
✔ Natural disasters are unpredictable events of nature, primarily resulting in catastrophic damage. An earthquake is a natural disaster that humans still do not have any hold of .
✔ An earthquake is a sudden movement of the Earth’s surface or ground resulting from the passage of seismic waves.
✔ It is unpredictable and can occur any day of the year, any second time, causing a lot of negative impacts and suffering.
✔ The world has witnessed many devastating quakes that caused significant destruction and losses, and one such earthquake is the Bhuj Earthquake.
2. Bhuj Earthquake: The Event
✔ On January 26, 2001 , India was all set to celebrate the 52nd Republic Day, so a massive earthquake struck Gujarat.

✔ The Bhuj Earthquake, also known as the 2001 Gujarat Earthquake, occurred at 8:46 a.m.
✔ The epicenter was at Bhuj, which is the District headquarters of Kutch district in the state of Gujarat.
✔ The earthquake was mighty and recorded 6.9 Mb on the Richter scale (Mw 7.6) .
✔ It lasted over two minutes, and what happened next was unimaginable and catastrophic.
✔ The shakes induced were felt in about 70% of the country’s regions, and the tremors were felt even in Nepal and Pakistan.
✔ It resulted in a loss of over 20,000 lives and left behind around 1.7 lakh people injured .
✔ Moreover, it caused severe damage to the physical infrastructure and left over 229 villages damaged beyond repair .
✔ About 600 aftershocks of magnitude ranging from 2.8 to 5.9 have been recorded so far.
3. Seismic Zone of Bhuj Earthquake
✔ On January 26, 2001, the Kutch district of Gujarat, India, was struck by the Bhuj earthquake, which resulted in across-the-board obliteration and loss of life. This area has a chronology of seismic activity.
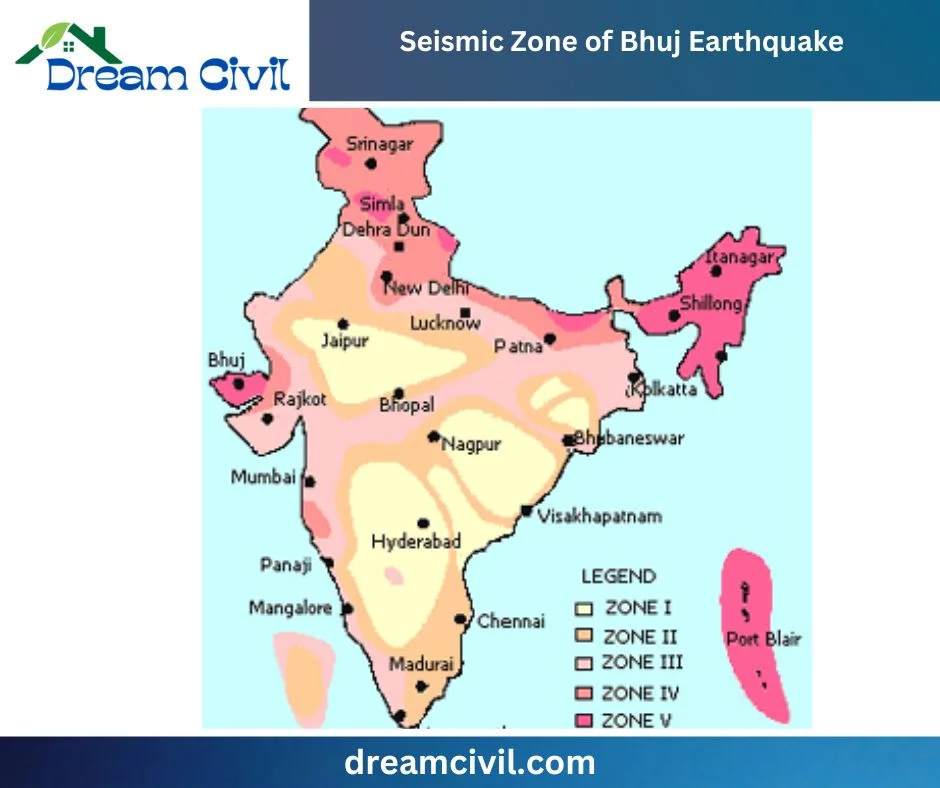
✔ The earthquake, which enlisted 7.7 on the Richter scale, emerged along the Kutch Rift – a geological feature between the Indian and Arabian plates. This rift is delicate in the Earth’s crust, making it more sensitive to tremors.
✔ Regrettably, the Bhuj earthquake remains one of India’s most toxic natural disasters, proclaiming the lives of more than 13,000 people and wounding over 167,000. Also, the earthquake caused consequential damage to buildings and infrastructure.
✔ This is a stark reminder of the seismic hazard in Gujarat and other regions of India. It accentuates the importance of taking benchmarks to downsize the impact of earthquakes. Attention to the risks to defend lives and property is crucial.
4. Memorial Sites of Bhuj Earthquake
5. causes of the bhuj earthquake .
✔ Gujarat is located 300-400 km from the boundary of the Indian and Eurasian plates.

✔ Geologists say the earthquake occurred at the convergent boundary between the two tectonic plates, making Gujarat the quake’s epicenter.
✔ Even today, the continuous continental collision of the plate boundary between the Indian Plate and the Eurasian Plate governs the plate tectonics of the region.
✔ This area faced a roughly west-east rifting trend during the break-up of Gondwana in the Jurassic.
✔ The area has also undergone shortening during the collision with the Eurasian plate, thereby reactivating the existing rift faults and developing new low-angle thrust faults.
✔ Hence, the Bhuj Earthquake occurred due to the movement on the previously unknown south-dipping fault tending parallel to the deduced rift formations.
6. Parameters of the Bhuj Earthquake
✔ According to the teleseismic data, the epicentral coordinates of the mainshock were 23.36 degrees north and 70.34 degrees east .
✔ The seismic moment of the event is estimated to be about 6.2*10^28 dyne-cm .
✔ The uplift was 2m, 15 km west of the epicenter .
✔ The shake had reverse motion with severe shakes that lasted about 85 seconds and minor shakes that lasted several minutes.
✔ As per the reports of the survivors, two different distinctive pulses were felt, which may be due to the separate arrivals of the P wave and S wave.
7. Areas Affected by the Bhuj Earthquake
✔ The post-earthquake reports suggest that the areas as far as 300km from the epicenter were affected.
✔ Among the 25 districts of the state of Gujarat, 22 districts suffered severe damage .
✔ The Kutch district was the most severely damaged one.
✔ This district’s four major areas, Bhuj, Anjar, Bachau, and Rapar, were almost destroyed.
✔ In rural regions, almost 229 villages were severely damaged .
✔ Ahmedabad, about 300km from the epicenter, also suffered considerable destruction.

8. Effects of the Bhuj Earthquake
✔ The Bhuj Earthquake directly affected the existing geographical formations, physical infrastructures, human settlements and lives, livestock and other animals, and other country assets .
✔ Some of the effects of the earthquake can be summarized as follows:
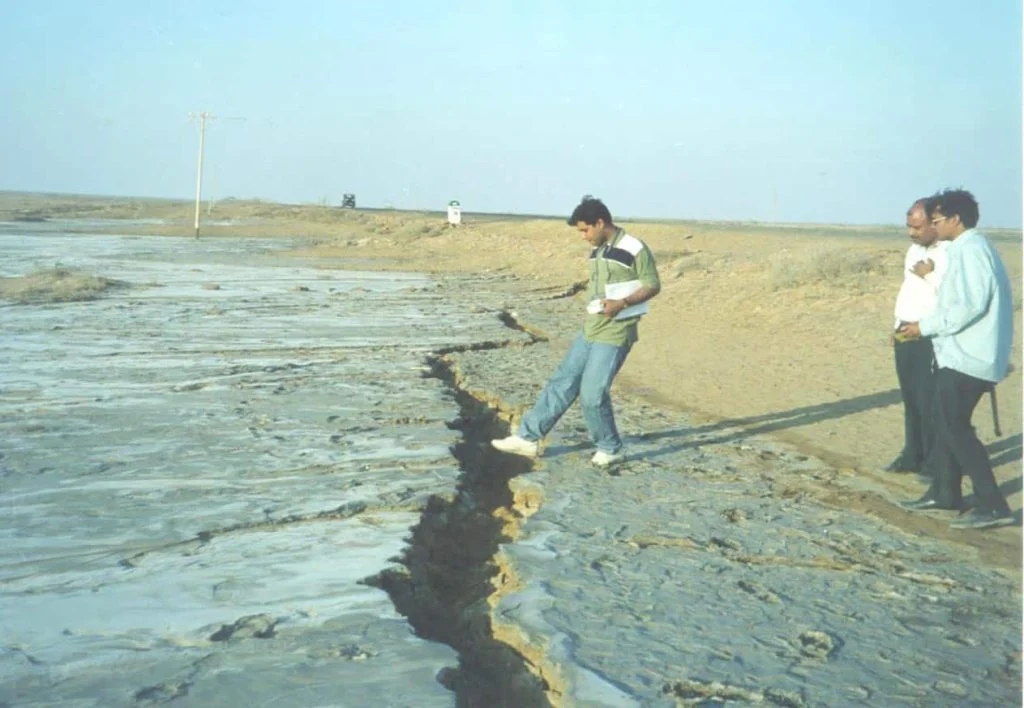

I. Fault Rupture: ✔ Though no significant evidence of fault rupture has been found in the earthquake, ground deformations and cracks were prominent in the severely affected areas.
✔ The reports suggest these originated due to liquefaction and lateral spreading during the quake.
II. Liquefaction:
✔ Generally, liquefaction can be understood as a loss of strength and stiffness of soil, particularly saturated, due to excessive stress such as seismic forces.
✔ The Gujarat earthquake resulted in widespread liquefaction in the Rann area, Gulf of Kutch, and Kandla River.
III. Slope Failure:
✔ Extensive slope failure occurred in several regions. Rock slope failure could be observed in an area over 10,000 km.
✔ The regions near Bhuj and Bhachau suffered major slope failures.
IV. Effect on Infrastructures:
✔ The Bhuj Earthquake destroyed 300,000 homes.
✔ On top of that, over 700,000 homes were partially destroyed.
✔ The monuments, pagodas, historical places, and Kutch and Saurashtra’s tombs also collapsed or suffered severe damage.
✔ According to the Indian National Trust for Art and Cultural Heritage (INTACH), about 40% of the heritage was collapsed or severely damaged .
✔ Bridges and railways of the affected area were also destructed.
✔ Fibre optics providing communications to the areas became unfunctional.
V. Effect on Human lives and Death tolls:
✔ The Gujarat Earthquake took thousands of lives and left thousands homeless.
✔ According to the sources, the earthquake killed about 20,000 people, among which 18 were from southeastern Pakistan.
✔ About 1,67,000 people were injured .
✔ The death toll in the Kutch region alone reached 12,300.
✔ The settlement of Bhuj was devastated.
✔ Several hundred people were also killed in Ahmedabad.
9. Rescue and Relief Efforts
✔ Since the earthquake occurred on Republic Day , most government machinery was occupied; thus, an immediate response was impossible.
✔ Only the emergency control room of the capital state of Gandhinagar became operational by 9:30 a.m .
✔ The destruction was so massive that the relief operations could not be carried out immediately.
✔ Relief operations began 72 hours after the earthquake from within and outside the country.
✔ The Indian Air Force distributed relief materials such as blankets, packed foods, tents, and medicine.
Soot to mm Conversion Calculator
Standard brick size | india, us, uk, singapore, pakistan, nepal, hongkong, japan, australia, romania, etc., 15+ safety equipment and tools in construction : with images and uses, blueprint symbols: floor plan, hvac, plumbing and architectural floor plan symbols, construction accident law firm: 15+ most asked questions, road safety barriers: where to use, construction injury law firm, what are traffic delineator posts : importances & 5+ types of delineator post.
- Privacy & Terms
©Dream Civil International 2019-2023

Provide details on what you need help with along with a budget and time limit. Questions are posted anonymously and can be made 100% private.

Studypool matches you to the best tutor to help you with your question. Our tutors are highly qualified and vetted.

Your matched tutor provides personalized help according to your question details. Payment is made only after you have completed your 1-on-1 session and are satisfied with your session.

- Homework Q&A
- Become a Tutor
All Subjects
Mathematics
Programming
Health & Medical
Engineering
Computer Science
Foreign Languages
Access over 20 million homework & study documents
Case study: gujarat earthquake.
Sign up to view the full document!

24/7 Homework Help
Stuck on a homework question? Our verified tutors can answer all questions, from basic math to advanced rocket science !

Similar Documents
working on a homework question?
Studypool is powered by Microtutoring TM
Copyright © 2024. Studypool Inc.
Studypool is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university.
Ongoing Conversations

Access over 20 million homework documents through the notebank
Get on-demand Q&A homework help from verified tutors
Read 1000s of rich book guides covering popular titles

Sign up with Google
Sign up with Facebook
Already have an account? Login
Login with Google
Login with Facebook
Don't have an account? Sign Up

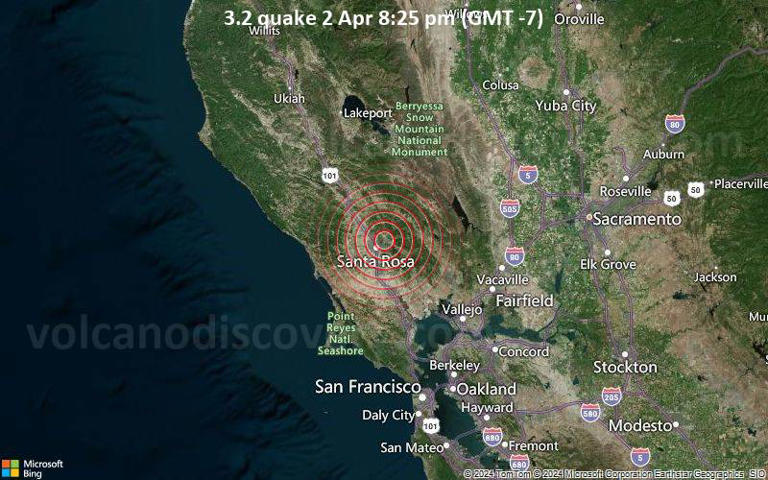
Understanding the Impact of Minor Earthquakes A Case Study of the 2024 Santa Rosa, California, Event
O n April 2nd, 2024, the city of Santa Rosa, California, experienced a minor earthquake with a magnitude of 3.2. While the seismic event did not cause significant damage, it serves as a reminder of the ongoing seismic activity in California and the potential risks associated with living in earthquake-prone regions. This article examines the impact of the 2024 Santa Rosa earthquake, delving into the science behind minor earthquakes, the response of local communities, and the lessons learned from the event.
Understanding Minor Earthquakes
Minor earthquakes, such as the one experienced in Santa Rosa, are relatively common occurrences in seismically active regions like California. These events are typically characterized by low magnitudes and shallow depths, resulting in minimal damage to infrastructure and property. However, despite their relatively benign nature, minor earthquakes serve as important reminders of the underlying tectonic forces at work beneath the Earth’s surface.
The 2024 Santa Rosa Earthquake: Magnitude and Impact
The earthquake that struck Santa Rosa on April 2nd, 2024, had a magnitude of 3.2 and occurred at a very shallow depth of 6 miles beneath the epicenter. While the quake was not strong enough to cause significant damage, it was widely felt in the area surrounding Santa Rosa. Residents reported light vibrations and shaking, but no reports of injuries or structural damage were recorded.
Response and Preparedness
In the aftermath of the earthquake, local authorities and emergency responders in Santa Rosa activated response protocols to ensure the safety and well-being of residents. While the event did not require extensive search and rescue efforts, it served as a valuable opportunity for communities to review and reinforce their preparedness measures. Public education campaigns, seismic retrofitting initiatives, and community drills play a crucial role in enhancing resilience and mitigating the impact of future seismic events.
Lessons Learned and Future Mitigation Efforts
The 2024 Santa Rosa earthquake provides valuable insights into the importance of ongoing monitoring, preparedness, and response efforts in earthquake-prone regions. While minor earthquakes may not cause widespread damage, they serve as important reminders of the need for vigilance and resilience. Moving forward, investments in early warning systems, infrastructure resilience, and public awareness campaigns will be crucial in minimizing the impact of future seismic events on communities in California and beyond.
The 2024 Santa Rosa earthquake serves as a testament to the dynamic nature of Earth’s geology and the ongoing threat of seismic activity in California. While minor earthquakes may not garner the same level of attention as major events, they nonetheless highlight the importance of preparedness, response, and mitigation efforts in earthquake-prone regions. By understanding the impact of minor earthquakes and taking proactive measures to enhance resilience, communities can better prepare for the inevitable challenges posed by seismic events in the future.
share this!
April 3, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
reputable news agency
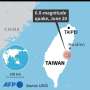
Fierce earthquake rattles Taiwan, killing 9 and injuring more than 1,000
by JOHNSON LAI, CHRISTOPHER BODEEN and SIMINA MISTREANU
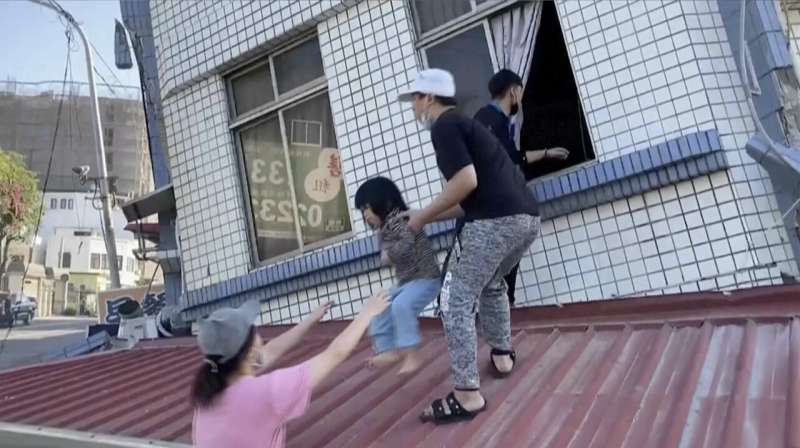

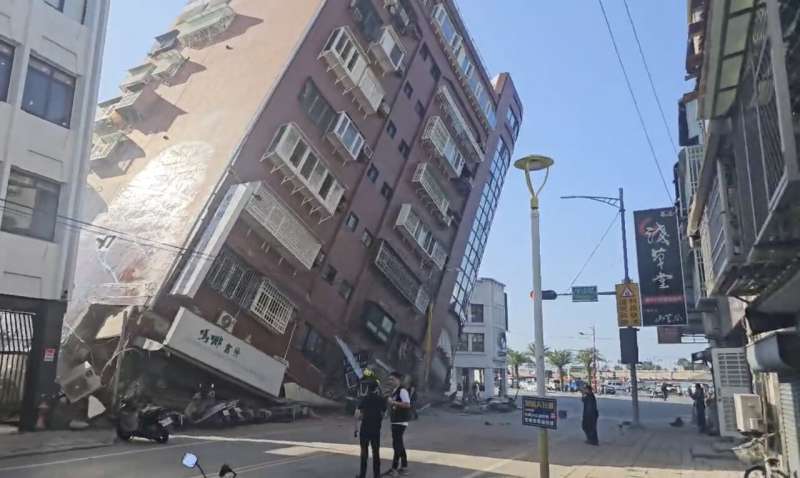
The strongest earthquake in a quarter-century rocked Taiwan Wednesday morning, killing nine people, stranding dozens at quarries and a national park, and sending some residents scrambling out the windows of damaged buildings.
The quake, which injured more than 1,000, struck just before 8 a.m. and was centered off the coast of rural, mountainous Hualien County, where some buildings leaned at severe angles, their ground floors crushed. Just over 150 kilometers (93 miles) away in the capital of Taipei, tiles fell from older buildings, and schools evacuated students to sports fields as aftershocks followed.
Rescuers fanned out in Hualien, looking for people who may be trapped and using excavators to stabilize damaged buildings. The numbers of people missing, trapped or stranded fluctuated as authorities learned of more in trouble and worked to locate or free them.
Some 70 workers who were stranded at two rock quarries were safe, according to Taiwan's national fire agency, but the roads to reach them were damaged by falling rocks. Six workers were going to be airlifted on Thursday.
In the hours after the quake, TV showed neighbors and rescue workers lifting residents, including a toddler, through windows and onto the street. Some doors had fused shut in the shaking.
Taiwan is regularly jolted by quakes and its population is among the best prepared for them. But authorities expected a relatively mild earthquake and did not send out alerts. The eventual quake was strong enough to scare even people who are used to such shaking.
"I've grown accustomed to (earthquakes). But today was the first time I was scared to tears by an earthquake," said Hsien-hsuen Keng, who lives in a fifth-floor apartment in Taipei. "I was awakened by the earthquake. I had never felt such intense shaking before."

At least nine people died in the quake, according to Taiwan's fire agency. Most of the fatalities were caused by falling rocks, including four people who were struck inside Taroko National Park, according to the state Central News Agency. One died in a residential building that was damaged, the news agency said.
A small tsunami washed ashore on southern Japanese islands but caused no damage.
At least 1,011 people were reported injured. Authorities initially lost contact with 50 hotel employees in minibuses in the park after the quake downed phone networks; three employees walked to the hotel, while the others remained stranded. About two dozen tourists were also stranded in the park, the state news agency said.
The quake and aftershocks caused many landslides and damaged roads, bridges and tunnels. The national legislature, a converted school built before World War II, and sections of the main airport in Taoyuan, just south of Taipei, also saw minor damage.
Hualien Mayor Hsu Chen-wei said 48 residential buildings were damaged in the city, which shares a name with the county. Hsu said water and electricity supplies were in the process of being restored.
Taiwan's earthquake monitoring agency said the quake was 7.2 magnitude while the U.S. Geological Survey put it at 7.4. It struck about 18 kilometers (11 miles) from Hualien and was about 35 kilometers (21 miles) deep. Multiple aftershocks followed.
Traffic along the east coast was at a virtual standstill after the earthquake, with landslides and falling debris hitting tunnels and highways. Train service was suspended across the island of 23 million people, with some tracks twisted by the stress of the quake, as was subway service in Taipei, where sections of a newly constructed elevated line split apart but did not collapse.
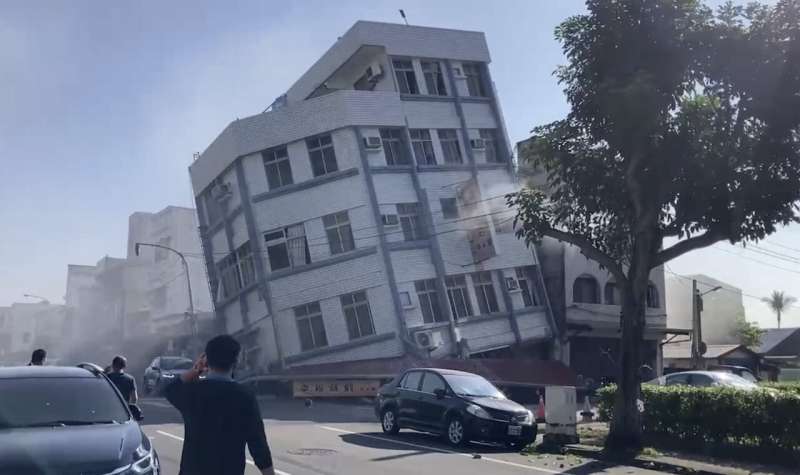

The initial panic quickly faded on the island, which prepares for such events with drills at schools and notices issued via public media and mobile phone. Stephen Gao, a seismologist and professor at Missouri University of Science and Technology, said Taiwan's readiness is among the most advanced in the world and includes strict building codes and a world-class seismological network.
By noon, the metro station in the busy northern Taipei suburb of Beitou was again buzzing with people commuting to jobs and people arriving to visit the hot springs or travel the mountain paths at the base of an extinct volcano.
The earthquake was felt in Shanghai and provinces along China's southeastern coast, according to Chinese media. China and Taiwan are about 160 kilometers (100 miles) apart.
The Japan Meteorological Agency said a tsunami of 30 centimeters (about 1 foot) was detected on the coast of Yonaguni island about 15 minutes after the quake struck. Smaller waves were measured in Ishigaki and Miyako islands. All alerts in the region had been lifted by Wednesday afternoon.
Taiwan lies along the Pacific "Ring of Fire," the line of seismic faults encircling the Pacific Ocean where most of the world's earthquakes occur.
Hualien was last struck by a deadly quake in 2018 that killed 17 people and brought down a historic hotel. Taiwan's worst quake in recent years struck on Sept. 21, 1999, with a magnitude of 7.7, causing 2,400 deaths, injuring around 100,000 and destroying thousands of buildings.
The economic fallout from the quake has yet to be calculated. Taiwan is the leading manufacturer of the world's most sophisticated computer chips and other high-technology items that are highly sensitive to seismic events. Parts of the electricity grid were shut down, possibly leading to disruptions in the supply chain and financial losses.
Taiwanese chipmaker TSMC, which supplies semiconductors to companies such as Apple, said it evacuated employees from some of its factories in Hsinchu, southwest of Taipei. Hsinchu authorities said water and electricity supplies for all the factories in the city's science park were functioning as normal.
© 2024 The Associated Press. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed without permission.
Explore further
Feedback to editors
Propelling atomically layered magnets toward green computers
4 hours ago

Researchers envision sci-fi worlds involving changes to atmospheric water cycle
13 hours ago

New fossil dolphin identified
14 hours ago

Pacific rock samples offer glimpse of active Earth 2.5 billion years ago

What four decades of canned salmon reveal about marine food webs


Study reports that people and environment both benefit from diversified farming, while bottom lines also thrive

New research traces the fates of stars living near the Milky Way's central black hole
15 hours ago

How NASA's Roman Telescope will measure the ages of stars

Rusty-patched bumblebee's struggle for survival found in its genes
Click chemistry: Research team creates 150 new compounds
Relevant physicsforums posts, unlocking the secrets of prof. verschure's rosetta stones.
2 hours ago
Major Earthquakes - 7.4 (7.2) Mag and 6.4 Mag near Hualien, Taiwan
17 hours ago
Iceland warming up again - quakes swarming
Mar 30, 2024
‘Our clouds take their orders from the stars,’ Henrik Svensmark on cosmic rays controlling cloud cover and thus climate
Mar 27, 2024
Higher Chance to get Lightning Strike by Large Power Consumption?
Mar 20, 2024
A very puzzling rock or a pallasite / mesmosiderite or a nothing burger
Mar 16, 2024
More from Earth Sciences
Related Stories

Offshore earthquake shakes Taiwan; no danger of tsunami
May 9, 2022

A strong earthquake shakes Indonesia's Java Island but no reports of casualties
Mar 22, 2024

Rattled Taiwan hit by more aftershocks
Sep 19, 2022
Strong quake hits eastern Taiwan: USGS
Jun 20, 2022

Strong quake hits off Taiwan's eastern coast
Jan 3, 2022

Strong 6.1-magnitude quake hits Taiwan, injuring 17 people
Apr 18, 2019
Recommended for you

Electric vehicles may be lowering Bay Area's carbon footprint: Monitors record small decrease in CO₂ emissions

Researchers find the link between human activity and shifting weather patterns in western North America
Ancient ocean oxygenation timeline revealed
18 hours ago

Unlocking Arctic mysteries: How melting ice shapes our climate
With the planet facing a 'polycrisis,' biodiversity researchers uncover major knowledge gaps
20 hours ago
Let us know if there is a problem with our content
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
- Education News
Gujarat Police Recruitment 2024: Check direct link to apply for 12,472 posts
Visual Stories

- THE WEEK TV
- ENTERTAINMENT
- WEB STORIES
- JOBS & CAREER
- Home Home -->
- wire updates wire updates -->
- SPORTS SPORTS -->
Shashank Singh guides PBKS to thrilling win against Gujarat Titans
Ahmedabad, Apr 4 (PTI) A cracking unbeaten half-century by all-rounder Shashank Singh and his fruitful 43-run partnership with an equally aggressive Ashutosh Sharma helped Punjab Kings defeat Gujarat Titans by three wickets in an Indian Premier League match here on Thursday. Shashank smashed an unbeaten 61 off 29 deliveries, while Ashutosh slammed a 17-ball 31 as PBKS chased down the 200-run target with one ball to spare after the team from Punjab had an inauspicious start, losing skipper Shikhar Dhawan for just one run. GT skipper Shubman Gill's unbeaten 89 off just 48 deliveries in the team's total of 199 for 4 went in vain. Gill was in sublime form as he took GT to an imposing total, hitting six boundaries and four maximums. He was assisted by Sai Sudarshan, who slammed a 19-ball 33 at the Narendra Modi Stadium. Gill and Sudarshan also shared a 53-run stand for the third wicket. Brief Scores: Gujarat Titans: 199 for 4 in 20 overs (Shubman Gill 89, Kane Williamson 26, Sai Sudharsan 33; Kagiso Rabada 2/44) lost to Punjab Kings 200 for 7 in 19.5 overs (Prabhsimran Singh 35, Shashank Singh 61 not out, Ashutosh Sharma 31; Noor Ahmad 2/32) by three wickets.
(This story has not been edited by THE WEEK and is auto-generated from PTI)

Taiwan earthquake: 'Missing' Indians safe, says MEA

Israel military on high alert after Iran’s revenge threat, cancels leave for combat units

WATCH: Kollywood star Ajith meets with accident during shooting of 'Vidaa Muyarchi'

Infosys founder Narayana Murthy recalls going hungry for 120 hours in Europe

AI study uncovers how personality shapes our genes and health

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The 2001 Gujarat earthquake, also known as the Bhuj earthquake, occurred on 26 January at 08:46 am IST.The epicentre was about 9 km south-southwest of the village of Chobari in Bhachau Taluka of Kutch (Kachchh) District of Gujarat, India.. The intraplate earthquake measured 7.6 on the moment magnitude scale and occurred at 17.4 km (10.8 mi) depth. It had a maximum felt intensity of X (Extreme ...
The earthquake struck near the town of Bhuj on the morning of India's annual Republic Day (celebrating the creation of the Republic of India in 1950), and it was felt throughout much of northwestern India and parts of Pakistan.The moment magnitude of the quake was 7.7 (6.9 on the Richter scale).In addition to killing more than 20,000 people and injuring more than 150,000 others, the quake ...
Gujarat Earthquake 2001: Case Study. Introduction. Gujarat is a state in the north western part of India. Beneath India, the Indo-Australian and the Eurasian Plate are moving towards each other at about 2cm per year. Both plates are continental, so this is a compressional boundary where both the plates are pushed up to form fold mountains The ...
US$920,000 as emergency aid and reconstruction. $2 million in aid -- $1.3 million to help furnish basic necessities to quake victims and $660,000 to Canadian and Indian relief organizations and the Red Cross. $602,000 in disaster relief; separately, China's Red Cross offered $50,000.
On 26 January 2001, an earthquake struck the Kutch district of Gujarat at 8.46 am. Epicentre 20 km North East of Bhuj, the headquarter of Kutch. The Indian Meteorological Department estimated the intensity of the earthquake at 6.9 Richter. According to the US Geological Survey, the intensity of the quake was 7.7 Richter.
As India celebrated its 52nd Republic Day on 26 January 2001, a massive earthquake measuring 7.9 on the Richter Scale struck Kutch district of western Gujarat at 8:46 am. Over 37.8 million people were affected as the devastating earthquake with an epicenter north-east of Bhuj city, destroyed homes, schools, roads, communication systems and ...
This Gujarat earthquake was considered to be the largest intraplate earthquake, not associated with a sub-duction zone, since the 1811-1812 events. ... 2001 earthquake was a case of history repeating itself 182 years later. Captain McMerdo described in his letter how the ground water level rose in most places and how the under-ground water ...
The 1999 Turkish Earthquake; Earthquakes in California; Gujarat Earthquake 2001; L'Aquila Earthquake 2009; Haiti Earthquake 2010; Japan Earthquake 2011; Christchurch Earthquake Case Study; Nepal Earthquake 2015; Amatrice Earthquake Case Study; Lombok Indonesia Earthquake 2018 Case Study; 2018 Sulawesi Indonesia Earthquake and Tsunami Case Study;
26 January 2001, India's 51st Republic Day, took on a different significance as a massive earthquake struck the state of Gujarat. The 6.9-magnitude earthquake was the worst to hit the state in the last half century. ... Project Results and Case Studies; PRODUCTS AND SERVICES. Public Sector Financing; Private Sector Financing; Financing ...
At 08:53 hours on 26 January 2001, an earthquake measuring 6.9 on the Richter scale devastated a large, drought-affected area of northwestern India, the state of Gujarat. The known number killed by the earthquake is 20,005, with 166,000 injured, of whom 20,717 were "seriously" injured.
PDF | On Nov 6, 2015, Dr. B Sairam and others published Site Effects: Case Study of the 2001 Bhuj Earthquake damages in the Ahmedabad city, Gujarat, India | Find, read and cite all the research ...
Particle motion of P and S waves suggest near-vertical ray paths. We present a preliminary analysis of aftershocks of the Mw=7.7 Republic Day (26 January) 2001 earthquake in Gujarat, India ...
Teja Malladi, Garima Jain, in Case Studies in Disaster Mitigation and Prevention, 2023. Case Summary. India has suffered many extreme events in the past, both climatic and non-climatic, but it was only after the 1999 Super cyclone, 2001 Gujarat earthquake, and 2004 Tsunami that institutional action for long-term risk reduction was orchestrated.
The epicentre of the Gujarat earthquake was a small town called Bhuj. At 08:46 local time, on Friday 26th January 2001 it was struck by an earthquake that measured 7.9 on the Richter Scale. It turned out to be one of the two most deadly earthquakes in the recorded history of India, with almost 20,000 people confirmed as dead, and another ...
Armenia: A case study. A nn Emerg Med 1990; 19:891-897. 9. Nakayama S, Okada N, ... Several earthquakes such as the Gujarat earthquake 2001 with magnitude 6.9 [1], Kashmir earthquake 2005 with ...
2001 Gujarat Earthquake:case study - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .ppsx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. This document divides India into 5 earthquake hazard zones based on expected damage, with Zone 5 being the highest risk of severe damage. Zone 5 includes Kashmir, the Western Himalayas, Central Himalayas, the North-East Indian ...
2. Bhuj Earthquake: The Event On January 26, 2001, India was all set to celebrate the 52nd Republic Day, so a massive earthquake struck Gujarat.. The Bhuj Earthquake, also known as the 2001 Gujarat Earthquake, occurred at 8:46 a.m.. The epicenter was at Bhuj, which is the District headquarters of Kutch district in the state of Gujarat.. The earthquake was mighty and recorded 6.9 Mb on the ...
case study of gujarat earthquake 2001.docx - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. Scribd is the world's largest social reading and publishing site. ...
Case Study: Gujarat Earthquake 2001 Bhuj Earthquake: Preliminary Report from IIT Kanpur A Powerful Earthquake of magnitude 6.9 on Richter-Scale rocked the Western Indian State of Gujarat on the 26th of January, 2001. It caused extensive damage to life & property. This earthquake was so devastating in its scale and suffering that the likes of ...
The earthquake that struck Santa Rosa on April 2nd, 2024, had a magnitude of 3.2 and occurred at a very shallow depth of 6 miles beneath the epicenter. While the quake was not strong enough to ...
Hualien was last struck by a deadly quake in 2018 that killed 17 people and brought down a historic hotel. Taiwan's worst quake in recent years struck on Sept. 21, 1999, with a magnitude of 7.7 ...
Here are the steps to apply online for Gujarat Police Recruitment 2024: • Visit the Official Website: Go to ojas.gujarat.gov.in, the official website of the Gujarat Police Recruitment Board ...
Shashank Singh guides PBKS to thrilling win against Gujarat Titans. Ahmedabad, Apr 4 (PTI) A cracking unbeaten half-century by all-rounder Shashank Singh and his fruitful 43-run partnership with an equally aggressive Ashutosh Sharma helped Punjab Kings defeat Gujarat Titans by three wickets in an Indian Premier League match here on Thursday ...