

Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Our Environment
Case study questions class 10 science chapter 15 our environment.
CBSE Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Our Environment. Term 2 Important Case Study Questions for Class 10 Board Exam Students. Here we have arranged some Important Case Base Questions for students who are searching for Paragraph Based Questions Our Environment.
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 15 marks.
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Our Environment
Case Study – 1
1.) Waste management is essential in today’s society. Due to an increase in population, the generation of waste is getting doubled day by day. Moreover, the increase in waste is affecting the lives of many people. Waste management is the managing of waste by disposal and recycling of it. Moreover, waste management needs proper techniques keeping in mind the environmental situations. For instance, there are various methods and techniques by which the waste is disposed of. You must have come across 5 R’s to save the environment: refuse, reduce, reuse, repurpose and recycle.
[ CBSE Academic Question Paper ]
1) Recycling of paper is a good practice but recycled paper should not be used as food packaging because
a) recycled papers take lots of space b) recycled papers can’t cover food properly c) recycled papers can cause infection d) recycled papers are costly
Answer – c) recycled papers can cause infection
2) Effective segregation of wastes at the point of generation is very important. Select the appropriate statements giving the importance of waste segregation.
- i) less waste goes to the landfills
- ii) better for public health and the environment
- iii) help in reducing the waste
- iv) resulting in deterioration of a waste picker’s health
a) both i) and ii) b) both i) and iii) c) both ii) and iii) d) both i) and iv)
Answer – a) both i) and ii)
Case Study – 2
1.) Food chains are very important for the survival of most species. When only one element is removed from the food chain it can result in extinction of a species in some cases. The foundation of the food chain consists of primary producers. Primary producers, or autotrophs, can use either solar energy or chemical energy to create complex organic compounds, whereas species at higher trophic levels cannot and so must consume producers or other life that itself consumes producers. Because the sun’s light is necessary for photosynthesis, most life could not exist if the sun disappeared. Even so, it has recently been discovered that there are some forms of life, chemotrophs, that appear to gain all their metabolic energy from chemosynthesis driven by hydrothermal vents, thus showing that some life may not require solar energy to thrive.
1) If 10,000 J solar energy falls on green plants in a terrestrial ecosystem, what percentage of solar energy will be converted into food energy?
- a) 10,000 J
- d) It will depend on the type of the terrestrial plant.
Answer – b) 100 J
2) Matter and energy are two fundamental inputs of an ecosystem. Movement of
- a) Energy is bidirectional and matter is repeatedly circulating.
- b) Energy is repeatedly circulation and matter is unidirectional.
- c) Energy is unidirectional and matter is repeatedly circulating.
- d) Energy is multidirectional and matter is bidirectional.
Answer – c) Energy is unidirectional and matter is repeatedly circulating
3) Mr. X is eating curd/yogurt. For this food intake in a food chain he should be considered as occupying
- a) First trophic level
- b) Second trophic level
- c) Third trophic level
- d) Fourth trophic level
Answer – c) Third Trophic level
4 Which of the following limits the number of trophic levels in a food chain?
- a) Decrease in energy at higher trophic levels
- b) Less availability of food
- c) Polluted air
Answer – a) Decrease in energy at higher trophic level
5) The decomposers are not included in the food chain. The correct reason for the same is because decomposers:
- a) Act at every trophic level of the food chain
- b) Do not breakdown organic compounds
- c) Convert organic material to inorganic forms
- d) Release enzymes outside their body to convert organic material to inorganic forms
Answer – a) Act at every trophic level of the food chain
Case Study – 3
Food chains are very important for the survival of most species.

1) Which of the following limits the number of trophic levels in a food chain?
Answer – a) Decrease in energy at higher trophic level
2) If Ravi is consuming curd/yogurt for lunch , which trophic level in a food chain he should be considered as occupying ?
Answer – c) Third Trophic level
3) Matter and energy are two fundamental inputs of an ecosystem. Movement of
Answer – c) Energy is unidirectional and matter is repeatedly circulating.
4) If 10,000 J solar energy falls on green plants in a terrestrial ecosystem, what percentage of solar energy will be converted into food energy ?
Answer – a) Act at every trophic level of the food chain
Case study – 4
In Kunjpura village, located in Karnal district, Haryana, Aditya Aggarwal and his older brother Amit Aggarwal run Tee Cee Industries, a steel plant set up by their ancestors in 1984. Along with this, they also run a gaushala that houses 1,200 cows that can no longer produce milk. The cow shelter was manageable but running the steel plant was turning out to be expensive because they spent a whopping Rs 5 lakh every month on electricity. The brothers struck upon an idea. Why not run the factory with the biogas produced from cow dung from the shelter and other gaushalas, along with bio and agri led Aditya and Amit to start Amrit Fertilizers, a biogas project, in 2014, without any government support.
1) Raw material used in bio gas plant is
- (a) Animal dung
- (b) crop residue
- (c) Food waste
- (d) All of the above
Answer – (d) All of the above
2) Biogas is a better fuel than animal dung cake because
- (i) Biogas has lower calorific value.
- (ii) Animal dung cake has higher calorific value.
- (iii) Biogas has high heating capacity.
- (iv) Biogas burns without smoke.
(a) (i) only
(b) (ii) only
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (ii)
Answer – (c) (iii) and (iv)
3) Biogas is formed in the
(a) presence of air only.
(b) presence of water only.
(c) absence of air only.
(d) presence of water and absence of air.
Answer – (d) presence of water and absence of air.
4) Biogas is a mixture of the following gases.
(a) Ethane,Carbon monoxide, Nitrogen and Butane
(b) Methane,Hydrogen,Carbon dioxide and Nitrogen
(c) Butane,Carbon monoxide,Propane and Hydrogen
(d) Carbon monoxide,Sulphur dioxide and Hydrogen
Answer – (b) Methane, Hydrogen, Carbon dioxide and Nitrogen
CASE STUDY : 5
We are an integral part of the environment. Changes in the environment affect us and our activities change the environment around us
Ozone (O3 ) is a molecule formed by three atoms of oxygen. While O2 , which we normally refer to as oxygen, is essential for all aerobic forms of life. Ozone, is a deadly poison. However, at the higher levels of the atmosphere, ozone performs an essential function. It shields the surface of the earth from ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the Sun.
i) How does ozone is formed?
Ans: The UV radiations coming from the sun split the molecular oxygen into nascent oxygen. When these nascent oxygen combined to molecular oxygen, it forms ozone(O3).
ii) In which layer of atmosphere does ozone is present?
Ans: The ozone is present in the stratosphere layer of atmosphere just above troposphere.
iii) What are the causes for ozone depletion?
Ans: The synthetic chemicals like CFCs ( chlorofluorocarbons) which used as refrigerants amd in the fire extinguisher
iv) Write the chemical reaction for the formation of ozone?
Ans: O2 👉 [O] + [O]
[O] + O2 👉 O3 (ozone)
v) What are the effects of UV radiations?
Ans: It causes different types of cancer in human beings.
CASE STUDY : 6
In our daily activities, we generate a lot of material that are thrown away. What are some of these waste materials? What happens after we throw them away? Let us perform an activity to find answers to these questions.
- Collect waste material from your homes. This could include all the waste generated during a day, like kitchen waste (spoilt food, vegetable peels, used tea leaves, milk packets and empty cartons), waste paper, empty medicine bottles/strips/bubble packs, old and torn clothes and broken footwear.
- Bury this material in a pit in the school garden or if there is no space available, you can collect the material in an old bucket/ flower pot and cover with at least 15 cm of soil.
- Keep this material moist and observe at 15-day intervals.
- What are the materials that remain unchanged over long periods of time?
- What are the materials which change their form and structure over time?
- Of these materials that are changed, which ones change the fastest?
We have seen in the chapter on ‘Life Processes’ that the food we eat is digested by various enzymes in our body. Have you ever wondered why the same enzyme does not break-down everything we eat? Enzymes are specific in their action, specific enzymes are needed for the break-down of a particular substance. That is why we will not get any energy if we try to eat coal! Because of this, many human-made materials like plastics will not be broken down by the action of bacteria or other saprophytes. These materials will be acted upon by physical processes like heat and pressure, but under the ambient conditions found in our environment, these persist for a long time.
i) What is biodegradable substances?
Ans: The substances that are broken down by biological process are called as biodegradable substances.
Eg: Vegetables waste materials.
ii) What are the examples of non- biodegradable substances?
Ans: Plastic, rubber, foam, batteries etc.
iii) what are the ways through which we can reduce pollution especially the non- biodegradable waste?
Ans: •We can use RRR methods i.e reduce, reuse and recycle.
Reduce the use of plastic
iv) What are the effects of biodegradable substances on our environment?
Ans: • Release green house gases.
They are breeding ground for mosquitoes and houseflies causing various disease.
v) What are the non- biodegradable on environment?
Ans: • causes soil pollution and sometimes air pollution when burnt in air.
- death of cattles due to ingestion of these waste.
- choking of drainage system
CASE STUDY : 7
The food we eat acts as a fuel to provide us energy to do work. Thus the interactions among various components of the environment involves flow of energy from one component of the system to another. As we have studied, the autotrophs capture the energy present in sunlight and convert it into chemical energy. This energy supports all the activities of the living world. From autotrophs, the energy goes to the heterotrophs and decomposers.
i) What is food chain?
Ans: A series of organism feeding on one another and taking part in various biotic levels is called food chain.
ii) Give a example of one terrestrial food chain.
Ans: Sunlight 👉 plants (producers) 👉 Goat/ Deer (herbivores) 👉 Tiger (carnivores)
iii) What are the feature of food chain?
Ans: •It is unidirectional
The energy available at each level gets diminished due to loss at each level.
iv) What do you meant by biological magnification?
Ans: The gradual increase in the concentration of any substance ( generally toxic) in trophic levels is called as biological magnification.
v) What is the average value for the amount of organic matter that is present at each step and reaching the next level of consumers?
CASE STUDY : 8
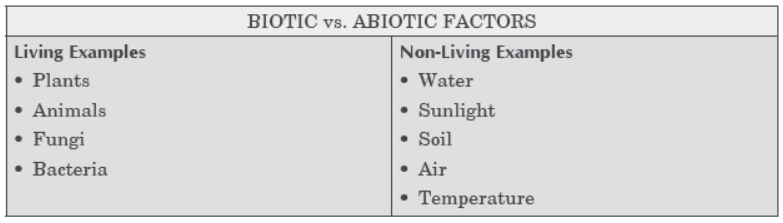
All organisms such as plants, animals, microorganisms and human beings as well as the physical surroundings interact with each other and maintain a balance in nature. All the interacting organisms in an area together with the non-living constituents of the environment form an ecosystem. Thus, an ecosystem consists of biotic components comprising living organisms and abiotic components comprising physical factors like temperature, rainfall, wind, soil and minerals.
i) What is natural ecosystem?
Ans: An environment where living organism and non- living interact with each other freely in nature is called as natural ecosystem.
ii) what are the examples of artificial ecosystem?
Ans: Gardens, crop- fields
iii) what are consumers?
Ans: Organism which consume food either directly or indirectly by feeding on one another animals are called as consumers.
iv) What are the type of consumers?
Ans: They are herbivores, carnivores, omnivores and parasites.
v) What are producers?
Ans: The green plants and some bacteria which make their food by using sunlight i.e photosynthesis are called as producers
We hope that above case study questions will help you for your upcoming exams. To see more click below –
- Class 10 Assertion & Reason
- CBSE Class 10 Sample Papers
- Important Difference between Class 10 Biology
- Important Difference between Class 10 Physics
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: class 10th
- Post comments: 0 Comments
Case study Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 15 are very important to solve for your exam. Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Case Study Questions have been prepared for the latest exam pattern. You can check your knowledge by solving case study-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Our Environment Case Study Questions With answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment
Case Study/Passage Based Questions
Question 1:
In any given ecosystem, all living organisms are linked in a systematic chain with respect to their mode of manufacturing food/feeding habits. This sequential interlinking of organisms involving the transfer of food energy from producers through a series of organisms with repeated eating and being eaten is called the food chain. A food chain may have 3-4 trophic levels.
(i) Which of the following statements regarding the food chain is incorrect? (a) It is a single straight pathway through which food energy travels in the ecosystem. (b) It adds adaptability and competitiveness to the organisms. (c) Presence of isolated food chains adds to the instability of the ecosystem. (d) Food chain binds up the inorganic nutrients of the ecosystem.
Answer: (b) It adds adaptability and competitiveness to the organisms.
(ii) Consider the following food chain. Grass ⟶⟶A ⟶⟶Frog ⟶⟶ Snake⟶⟶Eagle Which of the following can be placed at A?
Answer: (a) Grasshopper
(iii) Select the correct food chain. (a) Aquatic plants ⟶⟶ Tadpole ⟶⟶Water beetle⟶⟶Pike⟶⟶Perch (b) Grass⟶⟶Grasshopper⟶⟶Snake⟶⟶ Frog⟶⟶ Eagle (c) Grass⟶⟶ Rabbit⟶⟶ Wild cat⟶⟶ Tiger (d) Zooplankton ⟶⟶ Phytoplankton ⟶⟶Small fish⟶⟶Fish
Answer: (c) Grass⟶⟶ Rabbit⟶⟶ Wild cat⟶⟶ Tiger
(iv) Food chains are sustained by producers and _____________.
Answer: (d) decomposers
(v) Select the incorrect statement. (a) Food chain may terminate at level of herbivore (b) Food chain is always straight (c) Food chain may have 3-5 trophic levels (d) In a food chain, 80 to 90% of potential energy is lost as heat, at each transfer
Answer: (a) Food chain may terminate at level of herbivore
Question 2:
An ecosystem may be defined as a structural and functional unit of the biosphere comprising living organisms and their non-living environment which interact by means of food chains and biogeochemical cycles resulting in energy flow, biotic diversity, and material cycling to form a stable, self-supporting system.
2.1) The two basic processes involved in an ecosystem are : (a) cycling of materials and food chains (b) energy flow and self-sustainability (c) carbon cycle and biotic diversity (d) cycling of materials and flow of energy
Answer: (d) cycling of materials and flow of energy
2.2) Which among the following is not an artificial ecosystem? (a) Orchard (b) Lake (c) Aquarium (d) Cropland
Answer: (b) Lake
2.3) The role of fungi and bacteria in an ecosystem is to : (a) increase the supply of nutrients (b) increase the supply of energy (c) release nutrients from dead organic matter (d) increase the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere
Answer: (c) release nutrients from dead organic matter
2.4) What would be one of the likely results be if all decomposers in a particular ecosystem were wiped out? (a) The atmospheric reservoir of carbon dioxide would decline. (b) More food would be available for other consumers in the ecosystem. (c) The other organisms in the ecosystem would experience lower death rates. (d) There would be no significant impact, as dead organic matters would spontaneously decompose.
Answer: (a) The atmospheric reservoir of carbon dioxide would decline.
2.5) Which of the following holds true for an ecosystem? (a) Animals can live without plants. (b) Plants can live without animals. (c) Animals can survive for long without plants. (d) Plants can survive for long without animals.
Answer: (d) Plants can survive for long without animals
Question 3:
The ozone layer is present in the earth’s atmosphere. It is in the form of a protective shield. It contains three oxygen atoms (O3) which are formed as a consequence of photochemical reactions in the environment. Ozone absorbs harmful ultraviolet radiation from the sun. In this way, it protects all living beings on the earth. The thinning of the ozone layer due to various human activities allows more UV radiations to pass through it which leads to harmful effects on man, animals, and plants.
(i) Ozone layer is present in which layer of the atmosphere?
Answer: (c) Stratosphere
(ii) Enhanced UV radiations would affect humans and other animals causing (a) skin cancer (b) blindness and increased chances of cataracts in the eyes (c) malfunctioning of the immune system (d) all of these
Answer: (d) all of these
(iii) Read the given statements regarding ozone. I. Ozone hole was first discovered over Montreal in 1976. II. Ozone is a result of photochemical reactions in which starting molecule is oxygen. III. Harmful chemicals produce active chlorine in presence of UV radiations, that destroys ozone layers. IV. Ozone absorbs UV-radiations in the range of 800 – 1100 A. Select the option that correctly identifies them as true (T) and false (F).
Answer: (a)
(iv) Which of the following are related to depletion of ozone layer?
Answer: (d) All of these
(v) Refer to the given events regarding thinning of ozone layer and arrange them in a sequence. I. Active chlorine is produced in presence of UV radiations. II. CFCs are released in the air. III. Ozone layer in the stratosphere become thin. IV. CFCs enter from troposphere into stratosphere. V. Use of CFCs in refrigerators and air conditioners as coolants. VI. Active chlorine destroy ozone by converting it into oxygen.
Answer: (b) V →→ II →→ IV →→I →→VI →→ III
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries of CBSE Class 10 Science Our Environment Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible By Team Study Rate
You Might Also Like
Mcq class 10 social science history the making of global world questions with answers, class 10 science evergreen solutions pdf, mcq class 10 social science civics gender religion and caste quiz with answers, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment
- Last modified on: 1 year ago
- Reading Time: 2 Minutes
Question 1:
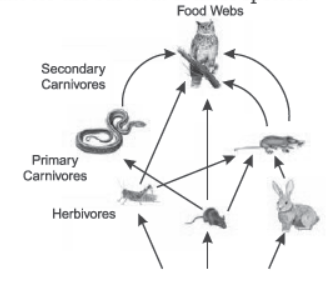
Food web is the interconnection of different food chains, which correlate at various trophic levels operating in an ecosystem.

(i) How many food chains are present in the given food web?
(ii) Name the primary consumer in the given food web.
(iii) How much percentage of energy is less at each trophic level?
(iv) If all the foxes are killed due to a disease, what will be your observations about food web?
(v) Name the organism in which accumulation of toxic non-biodegradable substances is the lowest.
Related Posts
Category lists (all posts).
All categories of this website are listed below with number of posts in each category for better navigation. Visitors can click on a particular category to see all posts related to that category.
- Full Form (1)
- Biography of Scientists (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions in Biology (37)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Biology (14)
- DPP Biology for NEET (12)
- Blog Posts (35)
- Career Guidance (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 10 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 10 Maths (15)
- Extra Questions for Class 10 Maths (12)
- Maths Formulas for Class 10 (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Maths (15)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths (4)
- Quick Revision Notes for Class 10 Maths (14)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 10 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science (14)
- Evergreen Science Book Solutions for Class 10 (17)
- Extra Questions for Class 10 Science (23)
- HOTS for Class 10 Science (17)
- Important Questions for Class 10 Science (10)
- Lakhmir Singh Class 10 Biology Solutions (4)
- Lakhmir Singh Class 10 Chemistry Solutions (5)
- Lakhmir Singh Class 10 Physics Solutions (5)
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science (20)
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science (16)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science (15)
- Quick Revision Notes for Class 10 Science (4)
- Study Notes for Class 10 Science (17)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 10 Social Science (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 10 Social Science (24)
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Social Science (3)
- Topicwise Notes for Class 10 Social Science (4)
- CBSE CLASS 11 (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (11)
- Free Assignments for Class 11 Chemistry (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (8)
- Very Short Answer Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (7)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Entrepreneurship (8)
- Important Questions for CBSE Class 11 Entrepreneurship (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Geography (24)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Geography (24)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 History (12)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 History (12)
- Assertion and Reason Questions for Class 11 Maths (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Maths (16)
- Formulas for Class 11 Maths (6)
- MCQ Questions for Class 11 Maths (17)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths (8)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Physical Education (11)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Physics (15)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Physics (12)
- Class 11 Physics Study Notes (5)
- Concept Based Notes for Class 11 Physics (2)
- Conceptual Questions for Class 11 Physics (10)
- Derivations for Class 11 Physics (3)
- Extra Questions for Class 11 Physics (13)
- MCQ Questions for Class 11 Physics (16)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics (16)
- Numerical Problems for Class 11 Physics (4)
- Physics Formulas for Class 11 (7)
- Revision Notes for Class 11 Physics (11)
- Very Short Answer Questions for Class 11 Physics (11)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Political Science (20)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Political Science (20)
- CBSE CLASS 12 (8)
- Extra Questions for Class 12 Biology (14)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Biology (13)
- Case Studies for CBSE Class 12 Business Studies (13)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Business Studies (1)
- Revision Notes for Class 12 Business Studies (10)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (15)
- Case Study Based Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (14)
- Extra Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (5)
- Important Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (15)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (8)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry (16)
- Revision Notes for Class 12 Chemistry (7)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Economics (9)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Economics (9)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Economics (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 English (2)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Entrepreneurship (7)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Entrepreneurship (7)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Geography (18)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 History (8)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 History (13)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Informatics Practices (13)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Informatics Practices (11)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Informatics Practices (5)
- Assertion and Reason Questions for Class 12 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Maths (13)
- Maths Formulas for Class 12 (5)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Maths (14)
- Problems Based on Class 12 Maths (1)
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 12 Maths (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Physical Education (11)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Physical Education (11)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Physical Education (10)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Physics (16)
- Case Study Based Questions for Class 12 Physics (14)
- Class 12 Physics Conceptual Questions (16)
- Class 12 Physics Discussion Questions (1)
- Class 12 Physics Latest Updates (2)
- Derivations for Class 12 Physics (8)
- Extra Questions for Class 12 Physics (4)
- Important Questions for Class 12 Physics (8)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Physics (14)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics (18)
- Numerical Problems Based on Class 12 Physics (16)
- Physics Class 12 Viva Questions (1)
- Revision Notes for Class 12 Physics (7)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Political Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Political Science (16)
- Notes for Class 12 Political Science (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 6 Maths (13)
- Case Study Questions for Class 6 Maths (13)
- Extra Questions for Class 6 Maths (1)
- Worksheets for Class 6 Maths (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 6 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 6 Science (16)
- Extra Questions for Class 6 Science (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 6 Science (9)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 6 Social Science (1)
- Case Study Questions for Class 6 Social Science (26)
- NCERT Exemplar for Class 7 Maths (13)
- NCERT Exemplar for Class 7 Science (19)
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 7 Maths (12)
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 7 Science (18)
- NCERT Notes for Class 7 Science (18)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 7 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 7 Maths (14)
- Extra Questions for Class 7 Maths (5)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 7 Science (18)
- Case Study Questions for Class 7 Science (17)
- Extra Questions for Class 7 Science (19)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 7 Social Science (1)
- Case Study Questions for Class 7 Social Science (30)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 8 Maths (7)
- Case Study Questions for Class 8 Maths (17)
- Extra Questions for Class 8 Maths (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 8 Maths (6)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 8 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 8 Science (11)
- Extra Questions for Class 8 Science (2)
- MCQ Questions for Class 8 Science (4)
- Numerical Problems for Class 8 Science (1)
- Revision Notes for Class 8 Science (11)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 8 Social Science (27)
- Case Study Questions for Class 8 Social Science (23)
- CBSE Class 9 English Beehive Notes and Summary (2)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 9 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 9 Maths (14)
- MCQ Questions for Class 9 Maths (11)
- NCERT Notes for Class 9 Maths (6)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths (12)
- Revision Notes for Class 9 Maths (3)
- Study Notes for Class 9 Maths (10)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 9 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science (14)
- Evergreen Science Book Solutions for Class 9 (15)
- Extra Questions for Class 9 Science (22)
- MCQ Questions for Class 9 Science (11)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science (15)
- Revision Notes for Class 9 Science (1)
- Study Notes for Class 9 Science (15)
- Topic wise MCQ Questions for Class 9 Science (2)
- Topicwise Questions and Answers for Class 9 Science (15)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 9 Social Science (15)
- Case Study Questions for Class 9 Social Science (19)
- CHEMISTRY (8)
- Chemistry Articles (2)
- Daily Practice Problems (DPP) (3)
- Books for CBSE Class 9 (1)
- Books for ICSE Class 10 (3)
- Editable Study Materials (8)
- Exam Special for CBSE Class 10 (3)
- H. C. Verma (Concepts of Physics) (13)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Biology (14)
- Extra Questions for ICSE Class 10 Chemistry (1)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Chemistry (5)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Maths (16)
- Important Questions for ICSE Class 10 Physics (13)
- MCQ Questions for ICSE Class 10 Physics (4)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Physics (8)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 9 Maths (7)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 9 Physics (10)
- Topicwise Problems for IIT Foundation Mathematics (4)
- Challenging Physics Problems for JEE Advanced (2)
- Topicwise Problems for JEE Physics (1)
- DPP for JEE Main (1)
- Integer Type Questions for JEE Main (1)
- Integer Type Questions for JEE Chemistry (6)
- Chapterwise Questions for JEE Main Physics (1)
- Integer Type Questions for JEE Main Physics (8)
- Physics Revision Notes for JEE Main (4)
- JEE Mock Test Physics (1)
- JEE Study Material (1)
- JEE/NEET Physics (6)
- CBSE Syllabus (1)
- Maths Articles (2)
- NCERT Books for Class 12 Physics (1)
- NEET Chemistry (13)
- Important Questions for NEET Physics (17)
- Topicwise DPP for NEET Physics (5)
- Topicwise MCQs for NEET Physics (32)
- NTSE MAT Questions (1)
- Physics (1)
- Alternating Current (1)
- Electrostatics (6)
- Fluid Mechanics (2)
- PowerPoint Presentations (13)
- Previous Years Question Paper (3)
- Products for CBSE Class 10 (15)
- Products for CBSE Class 11 (10)
- Products for CBSE Class 12 (6)
- Products for CBSE Class 6 (2)
- Products for CBSE Class 7 (5)
- Products for CBSE Class 8 (1)
- Products for CBSE Class 9 (3)
- Products for Commerce (3)
- Products for Foundation Courses (2)
- Products for JEE Main & Advanced (10)
- Products for NEET (6)
- Products for ICSE Class 6 (1)
- Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance (1)
- Topic Wise Study Notes (Physics) (2)
- Topicwise MCQs for Physics (2)
- Uncategorized (138)
Test series for students preparing for Engineering & Medical Entrance Exams are available. We also provide test series for School Level Exams. Tests for students studying in CBSE, ICSE or any state board are available here. Just click on the link and start test.
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online JEE Test Series for 499/- Only (Web + App) for 1 Year
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
- New QB365-SLMS
- NEET Materials
- JEE Materials
- Banking first yr Materials
- TNPSC Materials
- DIPLOMA COURSE Materials
- 5th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard Materials
- 11th Standard Materials
- 10th Standard Materials
- 9th Standard Materials
- 8th Standard Materials
- 7th Standard Materials
- 6th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard CBSE Materials
- 11th Standard CBSE Materials
- 10th Standard CBSE Materials
- 9th Standard CBSE Materials
- 8th Standard CBSE Materials
- 7th Standard CBSE Materials
- 6th Standard CBSE Materials
- Tamilnadu Stateboard
- Scholarship Exams
- Scholarships

CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Our Environment Chapter Case Study Questions With Solution 2021
By QB365 on 21 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 10 , and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
Cbse 10th standard science subject our environment case study questions with solution 2021.
10th Standard CBSE
Final Semester - June 2015
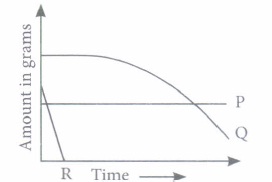
(ii) Which of the following statements regarding solid wastes is correct? (a) Change in the packaging technology has resulted in generation of lot of solid wastes. (b) Dumping of solid wastes could reduce the fertility of the soil leading to reduction in crop yield. (c) Accumulation of solid waste could cause increased incidents of disease in a locality. (d) All of these (iii) Teacher kept few solid wastes in her class as given
She asked students to arrange them in group A (Biodegradable) and group B (Non-biodegradable). Select the student that has grouped the items correctly.
In any given ecosystem, all living organisms are linked in a systematic chain with respect to their mode of manufacturing food/feeding habits. This sequential interlinking of organisms involving transfer of food energy from producers through a series of organisms with repeated eating and being eaten is called the food chain. A food chain may have 3-4 trophic levels. (i) Which of the following statements regarding food chain is incorrect? (a) It is a single straight pathway through which food energy travels in the ecosystem. (b) It adds adaptability and competitiveness to the organisms. (c) Presence of isolated food chains adds to instability of the ecosystem. (d) Food chain binds up inorganic nutrients of the ecosystem. (ii) Consider the following food chain. Grass \(\longrightarrow\) A \(\longrightarrow\) Frog \(\longrightarrow\) Snake \(\longrightarrow\) Eagle Which of the following can be placed at A?
(iii) Select the correct food chain. (a) Aquatic plants \(\longrightarrow\) Tadpole \(\longrightarrow\) Water beetle \(\longrightarrow\) Pike \(\longrightarrow\) Perch (b) Grass \(\longrightarrow\) Grasshopper \(\longrightarrow\) Snake \(\longrightarrow\) Frog \(\longrightarrow\) Eagle (c) Grass \(\longrightarrow\) Rabbit \(\longrightarrow\) Wild cat \(\longrightarrow\) Tiger (d) Zooplankton \(\longrightarrow\) Phytoplankton \(\longrightarrow\) Small fish \(\longrightarrow\) Fish (iv) Food chains are sustained by producers and _____________.
(v) Select the incorrect statement. (a) Food chain may terminate at level of herbivore (b) Food chain is always straight (c) Food chain may have 3-5 trophic levels (d) In a food chain, 80 to 90% of potential energy is lost as heat, at each transfer
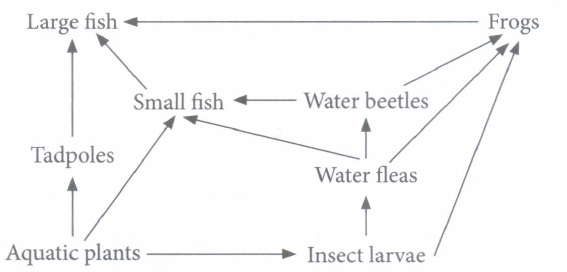
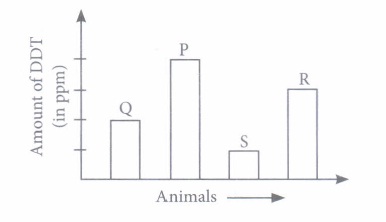
Some harmful non-biodegradable chemicals, i.e., pesticides (e.g., DDT) and heavy metals (e.g., mercury, arsenic cadmium, etc.) enter the bodies of organism through the food chain and go on concentrating at each trophic level. This phenomenon is called bio-magnification or biological magnification. (i) Refer to the given food chain Phytoplankton \(\longrightarrow\) Zooplankton \(\longrightarrow\) Small fish \(\longrightarrow\) Large fish \(\longrightarrow\) Fish eating birds If concentration of DDT in small fish is estimated to be 0.5 ppm, then amount of DDT in zooplankton and large fish would respectively be
(ii) Refer to the given table.
According to the given data. The correct order in a food chain will be
(iv) Higher amount of DDT disturb calcium metabolism of birds. This results in
(v) When animals are sprayed with poisons, they may die immediately, but their bodies still contain the poison. The poison in their bodies will then be passed on to the animals which eat them. What would be the consequence of a mass poisoning of the rabbit population in a grazing food chain and why? (a) Plants would die quickly as they are eaten by rabbits (b) Grasshopper would die quickly as all the animals in the food web would be affected (c) Western rattlesnakes would quickly become poisoned as they eat rabbits (d) Hawk would become poisoned as they feed on rabbits
Ozone layer is present in the earth's atmosphere. It is in the form of a protective shield. It contains three oxygen atoms (O 3 ) which are formed as a consequence of photochemical reactions in the environment. Ozone absorbs harmful ultraviolet radiations of the sun. In this way, it protects all living beings on the earth. The thinning of ozone layer due to various human activities allows more UV radiations to pass through it which leads to harmful effects on man, animals and plants. (i) Ozone layer is present in which layer of the atmosphere?
(ii) Enhanced UV-radiations would affect humans and other animals causing (a) skin cancer (b) blindness and increased chances of cataract in eyes (c) malfunctioning of the immune system (d) all of these (iii) Read the given statements regarding ozone. I. Ozone hole was first discovered over Montreal in 1976. II. Ozone is a result of photochemical reactions in which starting molecule is oxygen. III. Harmful chemicals produce active chlorine in presence of UV radiations, that destroys ozone layers. IV. Ozone absorbs UV-radiations in the range of 800 - 1100 A. Select the option that correctly identifies them as true (T) and false (F).
(iv) Which of the following are related to depletion of ozone layer?
(v) Refer to the given events regarding thinning of ozone layer and arrange them in a sequence. I. Active chlorine is produced in presence of UV radiations. II. CFCs are released in the air. III. Ozone layer in the stratosphere become thin. IV. CFCs enter from troposphere into stratosphere. V. Use of CFCs in refrigerators and air conditioners as coolants. VI. Active chlorine destroy ozone by converting it into oxygen.
*****************************************
Cbse 10th standard science subject our environment case study questions with solution 2021 answer keys.
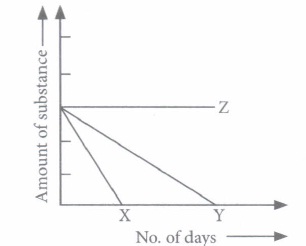
(i) (a) : According to the given graph, P is a waste that is not decomposed with the time. Hence, it can be a non-biodegradable waste such as glass and plastic wastes, synthetic polymers, pesticides, etc. Q took sometime for decomposing, hence it can be a waste made up of biodegradable material such as leather bag. As R starts decomposing in a very short span of time, this means it is a biodegradable waste such as fruit peel, cow dung, human excreta, etc. (ii) (d): Increased use of plastic material in packaging has resulted in generation of lot of solid wastes. Dumping industrial chemical waste affects the soil fertility and subsequently reduces crop yield. Solid waste can block drains creating pools of water which can become breeding ground for mosquitoes and therefore, could increase the incidents of disease in the locality. (iii) (a) (iv) (c) : Used syringes and needles should not be reused as they may be contaminated. They must be burned at high temperature inside a closed chamber to prevent cross contamination. (v) (c) : Both substances X and Y decompose so they both are biodegradable materials. Substance Z does not decompose at all. Hence, it could be a non-biodegradable material.
(i) (b): Since a food chain is a sequential flow of food energy, it does not add to the adaptability and competitiveness of the organism. (ii) (a) : In the given food chain, A is a primary consumer that feeds on grass and being eaten by frog. Therefore, among the given organisms, A should be grasshopper. (iii) (c) (iv) (d) (v) (a): In a food chain, there is repeated eating in which each group eats the smaller one and is eaten by the larger one.
(i) (c) : In the given food web, water fleas feed on insect larvae and are in turn fed by water beetles. So, if water fleas get eliminated then population of insect larvae will increase and that of water beetles will decrease. As small fish are dependent on water beetles for food, a decrease in population of water fleas will cause a decrease in their population as well. Population of frogs remain unaffected as frog also depend upon insect larvae for food. (ii) (a) : Small fish operates at both primary and tertiary consumer level in the given food web Aquatic plant \(\longrightarrow\) Small fish \(\longrightarrow\) Large fish Aquatic plant \(\longrightarrow\) Insect larvae \(\longrightarrow\) Water fleas \(\longrightarrow\) Small fish \(\longrightarrow\) Large fishes (iii) (c) (iv) (d) (v) (b): Food webs make a natural ecosystem stable than a man-made ecosystem.
(i) (a): Due to bio-rnagnification, the concentration of DDT will always be less in zooplanktons than large fish (ii) (c) (iii) (b) : Due to bio-rnagnification the nonbio-degradable chemicals such as DDT accumulate and go on concentrating at each trophic level. (iv) (d) : Higher amounts of DDT disturb calcium metabolism of birds resulting in thinning of egg shells and their prematllre breaking that kills the embryos. (v) (d)
(i) (c) : Ozone is present in the stratosphere of the earth's atmosphere between 20 to 26 km above sea level. (ii) (d) (iii) (a) : Ozone hole was first discovered over Antarctica in 1985. Ozone absorbs UV-radiations in the range 2000-2900A. (iv) (d) : The substances that depletes the ozone layer are called ozone depleting substances (ODS). The main ODS are chlorofluorocarbons, halons, methane, nitrous oxide, carbon tetrachloride and chlorine. (v) (b)
Related 10th Standard CBSE Science Materials
10th standard cbse syllabus & materials, cbse 10th maths probability chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths statistics chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths surface areas and volumes chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths areas related to circles chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths circles chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths some applications of trigonometry chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths introduction to trigonometry chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths coordinate geometry chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths triangles chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths arithmetic progressions chapter case study questions with answers, cbse 10th maths quadratic equations chapter case study questions with answers, cbse 10th social science the making of a global world chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th social science nationalism in india chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th social science the rise of nationalism in europe chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths pair of linear equation in two variables chapter case study question with answers.

Class VI to XII
Tn state board / cbse, 3000+ q&a's per subject, score high marks.

10th Standard CBSE Study Materials


10th Standard CBSE Subjects
CBSE NCERT Solutions
NCERT and CBSE Solutions for free
Case Study Chapter 15 Our Environment
Please refer to Chapter 15 Our Environment Case Study Questions with answers provided below. We have provided Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science for all chapters as per CBSE, NCERT and KVS examination guidelines. These case based questions are expected to come in your exams this year. Please practise these case study based Class 10 Science Questions and answers to get more marks in examinations.
Case Study Questions Chapter 15 Our Environment
Case/Passage – 1 Food chains are very important for the survival of most species. When only one element is removed from the food chain it can result in extinction of a species in some cases. The foundation of the food chain consists of primary producers. Primary producers, or autotrophs, can use either solar energy or chemical energy to create complex organic compounds, whereas species at higher trophic levels cannot and so must consume producers or other life that itself consumes producers. Because the sun’s light is necessary for photosynthesis, most life could not exist if the sun disappeared. Even so, it has recently been discovered that there are some forms of life, chemotrophs, that appear to gain all their metabolic energy from chemosythesis driven by hydrothermal vents, thus showing that some life may not require solar energy to thrive.
Question: If 10,000 J solar energy falls on green plants in a terrestrial ecosystem, what percentage of solar energy will be converted into food energy? (a) 10,000 J (b) 100 J (c) 1000 J (d) It will depend on the type of the terrestrial plant.
Question: If Ravi is consuming curd/yogurt for lunch, which trophic level in a food chain he should be considered as occupying ? (a) First trophic level (b) Second trophic level (c) Third trophic level (d) Fourth trophic level
Question: The decomposers are not included in the food chain.The correct reason for the same is because decomposers: (a) Act at every trophic level of the food chain (b) Do not breakdown organic compounds (c) Convert organic material to inorganic forms (d) Release enzymes outside their body to convert organic material to inorganic forms
Question: Matter and energy are two fundament al inputs of an ecosystem. Movement of (a) Energy is bidirectional and matter is repeatedly circulating. (b) Energy is repeatedly circulation and matter is unidirectional. (c) Energy is unidirectional and matter is repeatedly circulating. (d) Energy is multidirectional and matter is bidirectional.
Question: Which of the following limits the number of trophic levels in a food chain? (a) Decrease in energy at higher trophic levels (b) Less availability of food (c) Polluted air (d) Water
Case/Passage – 2
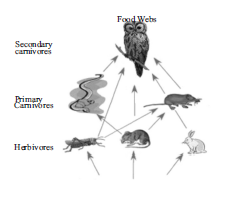
The diagram below shows a food web from the sea shore
Question: The mussel can be described as (a) Producer (b) Primary consumer (c) Secondary consumer (d) decomposer
Question: Which trophic level is incorrectly defined? (a) Carnivores – secondary or tertiary consumers (b) Decomposers – microbial heterotrophs (c) Herbivores – primary consumers (d) Omnivores – molds, yeast and mushrooms
Question: The given figure best represents:
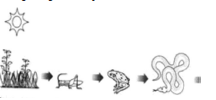
(a) Grassland food chain (b) Parasitic food chain (c) Forest food chain (d) Aquatic food chain
Question: Why do all food chains start with plants? (a) Because plants are easily grown (b) Because plants are nutritious (c) Because plants can produce its own energy (d) Because plants do not require energy
Question: In the food web, what two organisms are competing for food?

(a) A and B (c) A and C (b) D and F (d) B and D
Question: Consider the following statements concerning food chains: (i) Removal of 80% tigers from an area resulted in greatly increased growth of vegetation (ii) Removal of most of the carnivores resulted in an increased population of herbivores. (iii) The length of the food chains is generally limited to 3 – 4 trophic levels due to energy loss (iv) The length of the food chains may vary from 2 to 8 trophic levels Which two of the above statements are correct? (a) (i), (iv) (b) (i), (ii) (c) (ii), (iii) (d) (iii), (iv)
Question: Which of the following group of organisms are not included in ecological food chain? (a) Carnivores (b) Saprophytes (c) Herbivores (d) Predators
Case/Passage – 3
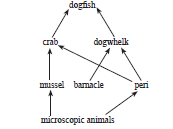
Biosphere is a global ecosystem composed of living organisms and abiotic factors from which they derive energy and nutrients. And ecosystem is defined as structural and functional unit of the biosphere comprising of living and non-living environment that interact by means of food chains and chemical cyclesresulting in energy flow, biotic diversity and material cycling to form a stable, self-supporting system

The diagram below shows a food web from the sea shore
Question: The mussel can be described as (a) Producer (b) Primary consumer (c) Secondary consumer (d) decomposer
Question: The given figure best represents:
Case/Passage – 4
Food chains are very important for the survival of most species.
Question. Matter and energy are two fundamental inputs of an ecosystem. Movement of (a) Energy is bidirectional and matter is repeatedly circulating. (b) Energy is repeatedly circulation and matter is unidirectional. (c) Energy is unidirectional and matter is repeatedly circulating. (d) Energy is multidirectional and matter is bidirectional.
Question. Which of the following limits the number of trophic levels in a food chain? (a) Decrease in energy at higher trophic levels (b) Less availability of food (c) Polluted air (d) Water
Question. If 10,000 J solar energy falls on green plants in a terrestrial ecosystem, what percentage of solar energy will be converted into food energy? (a) 10,000 J (b) 100 J (c) 1000 J (d) It will depend on the type of the terrestrial plant.
Question. If Ravi is consuming curd/yogurt for lunch , which trophic level in a food chain he should be considered as occupying ? (a) First trophic level (b) Second trophic level (c) Third trophic level (d) Fourth trophic level
Question. The decomposers are not included in the food chain.The correct reason for the same is because decomposers: (a) Act at every trophic level of the food chain (b) Do not breakdown organic compounds (c) Convert organic material to inorganic forms (d) Release enzymes outside their body to convert organic material to inorganic forms
Case/Passage – 5
Observe the following diagram and answer the questions any four from (i) and (v)
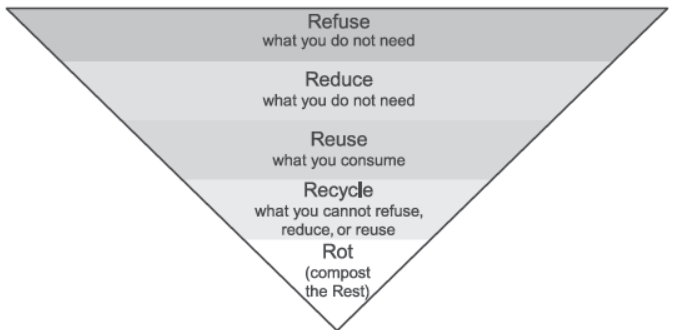
Question. Effective segregation of wastes at the point of generation is very important. Select the appropriate statements giving the importance of waste segregation. I. less waste goes to the landfills II. better for public health and the environment III. help in reducing the waste IV. resulting in deterioration of a waste picker’s health (a) both I and II (b) both I and III (c) both II and III (d) both I and IV
Question. The given graph shows the amount of waste generated, dumped and treated in percentage. Identify the reason of low success rate of waste management process.

(a) only 15% of urban India’s waste is processed (b) less than 60% of waste is collected from households (c) more than 60% of waste is collected from households (d) both (a) and (b)
Question. Choose the waste management strategy that is matched with correct example. (a) Refuse Choose products that use less packaging (b) Reduce Give unwanted toys and books to hospitals or schools (c) Reuse Not using single use plastic (d) Repurpose Making flower pot from used plastic bottle
Question. Recycling of paper is a good practice but recycled paper should not be used as food packaging because (a) recycled papers may release color /dyes on food items (b) recycled papers are not absorbent (c) recycled papers can cause infection due to release of methane (d) recycled papers are costly
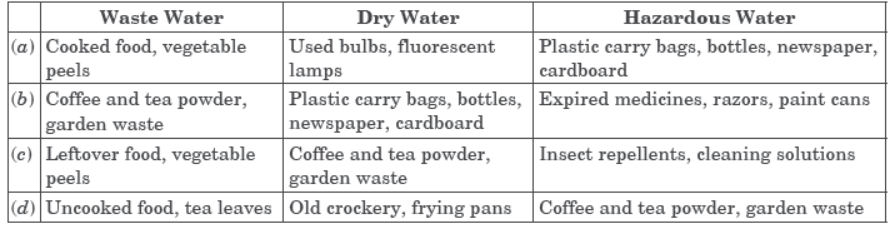
Question. According to the ‘Solid Waste Management Rule 2016’, the waste should be segregated into three categories. Observe the table below and select the row that has correct information
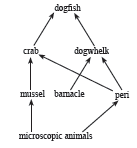
Case/Passage – 6
Biosphere is a global ecosystem composed of living organisms and abiotic factors from which they derive energy and nutrients. And ecosystem is defined as structural and functional unit of the biosphere comprising of living and non-living environment that interact by means of food chains and chemical cycles resulting in energy flow, biotic diversity and material cycling to form a stable, self-supporting system
Question. The given figure best represents:

(a) Grassland food chain (b) Parasitic food chain (c) Forest food chain (d) Aquatic food chain
Question. Consider the following statements concerning food chains: (i) Removal of 80% tigers from an area resulted in greatly increased growth of vegetation (ii) Removal of most of the carnivores resulted in an increased population of herbivores. (iii) The length of the food chains is generally limited to 3 – 4 trophic levels due to energy loss (iv) The length of the food chains may vary from 2 to 8 trophic levels Which two of the above statements are correct? (a) (i), (iv) (b) (i), (ii) (c) (ii), (iii) (d) (ii), (iv)
Question. Which trophic level is incorrectly defined? (a) Carnivores – secondary or tertiary consumers (b) Decomposers – microbial heterotrophs (c) Herbivores – primary consumers (d) Omnivores – molds, yeast and mushrooms
Question. The diagram below shows a food web from the sea shore
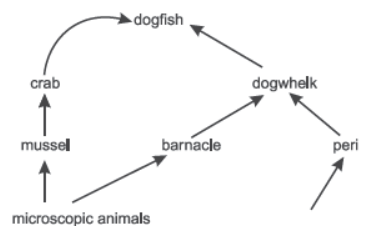
The mussel can be described as (a) Producer (b) Primary consumer (c) Secondary consumer (d) Decomposer
Question. Which of the following group of organisms are not included in ecological food chain? (a) Carnivores (b) Saprophytes (c) Herbivores (d) Predators
Class 10 Science Our Environment… Exam Questions
Question. List two items that can be easily recycled but we throw them in the dustbin. Answer : Glass and plastic items can be easily recycled.
Question. State a way to prevent accumulation of harmful chemicals in our bodies. Answer : To minimize use of pesticides in agriculture.
Question. During heavy rain in a village the rainwater carried excessive fertilizers to a pond. How will it affect the fish population in the pond in the long run? Answer : The growth of fish will decrease as water gets polluted due to excessive algae growth.
Question. Write any two consequences if decomposers are removed from the ecosystem. Answer : (i) Dead organisms will pile up. (ii) There will be no replenishment of soil.
Question. State 10 percent law. Answer : The energy available at any trophic level is only 10% of energy from previous trophic level.
Question. What will be the impact on ecosystems if bacteria,fungi/microorganism are removed from the environment? Answer : Complex organic molecules will not breakdown into simple inorganic substances, preventing replenishment of soil.
Question. How is ozone layer important for human kind? Answer : Ozone layer checks the entry of ultra violet rays of sun from reaching the earth. These rays otherwise can cause skin and blood cancer as well as defects in vision in human beings.
Question. A primary consumer in the food chain has 10000 J energy available. How much energy will be provided for tertiary consumer in this food chain? Answer : 100 J.
Question. Name the two components of an ecosystem. Answer : Biotic and abiotic are two components of an ecosystem.
Question. In a food chain of frog, grass, insect and snake, assign trophic level to frog. Answer : Grass$ Insect$ Frog$ Snake Frog is in 3rd trophic level i.e., secondary consumer.
Question. In a food chain of rabbit, grass and fox, assign trophic level to rabbit. Answer : Grass$ rabbit$ fox Rabbit is a primary consumer or a herbivore or 1st trophic level.
Question. Name two decomposers operating in our ecosystem. Answer : Bacteria and fungi.
Question. How do bacteria and fungi able to decompose some of the wastes in our ecosystem? Answer : Bacteria and fungi have enzymes to break down complex organic substances to simple and smaller ones.
Question. Which chemical is used in fire extinguishers? How is it harmful? Answer : Fire extinguishers use Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs). It depletes ozone layer.
Question. What are the two main components of our environment? Answer : Two main components of our environment are: a. Biotic (e.g., plants, animals etc.) b. Abiotic (e.g., soil, air, water etc.)
Question. In a certain study conducted on occurrence of DDT along food chains in an ecosystem, the concentration of DDT in grass was found to be 0.5 ppm (parts per million), in sheep it was 2 ppm and in man it was 10 ppm. Why was the concentration of DDT maximum in case of man? Answer : DDT is non-biodegradable substance which accumulates at each trophic level. Since man is at the highest trophic level, there is maximum accumulation of DDT in him (biological magnification).
Question. Ozone is deadly poisonous, still it performs an essential function. How? Answer : Ozone layer shields the surface of the earth and blocks the entry of UV rays from the sun.
Question. What is depicted in the below mentioned scheme? Answer : Food chain/10% law.
Question. Why are plastics non-biodegradable substances? Answer : Plastics cannot be broken down by the action of enzymes/bacteria/saprophyte.
Question. What is meant non-biodegradable waste? Identify biodegradable waste from the following: Empty packet of chips, empty plastic bottle of mineral water, empty paper box of sweets, empty tin of a cold drink. Answer : Substances that do not break down by biological process are called non¬biodegradable waste. Empty paper box of sweets.
Question. Consider a food chain consisting of: wheat, rat, snakes, peacock: What will happen if all the snakes are killed? Answer : If all snakes of food chain are killed the peacocks belonging to the next level will also die. Also the population of rats in the preceding level will highly increase.
Question. Choose one consumer each that belongs to the second and third trophic levels from the organisms given below: Eagle, frog, tiger, rabbit, fox Answer : (i) Second trophic level$ Rabbit (ii) Third trophic level$ Frog and fox.
Question. What happens during the first step of ozone formation in the atmosphere? Answer : Oxygen in the presence of UV rays splits oxygen molecule into 2 oxygen atoms. (Image 55)
Question. Why are non-biodegradable substances not broken down by microbes? Answer : Microbes are highly specific enzymes which can breakdown natural materials.
Question. What is an ecosystem? Answer : Ecosystem is an interaction of physical and biotic factors present in an area among each other.
Question. Why is forest/lake considered a natural ecosystem? Answer : Forests and lakes have both biotic and abiotic components which are present naturally and are interacting without man’s interference.
Question. If the energy available in phytoplanktons is 10,000 KJ, how much energy would a whale get on consuming them? Answer : 1000 J.
Question. List two man-made ecosystems. Answer : Aquarium, crop land, park are man made ecosystem.
Question. ‘Save the Tiger’ campaign is being over¬emphasised these days by our government. What may be the possible reason? Answer : Tiger stands at the top trophic level. To maintain ecological balance in nature and to preserve gene pool. Tiger is a threatened species. To help its survival, the Save the Tiger’ campaign is emphasized.
Question. When plants are eaten by primary consumers, a great deal of energy is lost as heat to the environment and some amount goes in carrying out various life processes. State the average percentage of energy lost in this manner. Answer : 90%.
Short Answer Questions
Question. a. What is the height of ozone from the equator? b. Name the rays against which ozone layer provides protection. c. Name one effect of depletion of ozone. Answer : i. 10 to 16 km. ii. UV rays. iii. Global wanning.
Question. Within the school premises while playing some students observed that some people are burning dry leaves. They knew that it would cause harm to the environment. They immediately went and to these people requested them to stop it. (i) How can the above activity be changed to make it environment friendly? (ii) ‘Students took initiative to stop the practice’. What values are displayed by them in this situation? (iii) How can we spread awareness among people about being environment friendly? Answer : (i) Dry leaves can be put in the cojnpost pit to make manure. (ii) Concern for environment, scientific temperament. (iii) Counselling, posters, print and audio visual media.
Question. What is wild life? How is it important? How is it being protected by government of India? Answer : Wild life means our flora and fauna. It is important: a. to preserve bio-diversity. b. as each species has a position in the food chain so wildlife helps in balancing the nature. Various species of plants and animals are preserved in botanical gardens, national parks, zoological parks and wildlife sanctuaries.
Question. List three environmental friendly practices which you would like to form a part of your daily habits giving justification for each. Answer : Three environmental friendly activities are: a. Should walk short distance to reduce use of vehicle running on fossil fuels. b. Use both sides of papers to reduce its use. Less trees will be cut to make more paper. c. Packing the gifts should not be practiced. It will reduce the use of shiny but non- biodegradable packing paper. Instead use the boxes and envelopes in which the gifts was received.
Question. State one important function of ozone layer in the atmosphere. How is it formed there? Which compounds are responsible for the depletion of ozone layer? How do these compounds enter into the atmosphere? Answer : Ozone present in the upper regions of the atmosphere protects us from dangerous UV radiations. Formation of ozone layer : Ozone at the higher levels of the atmosphere is a product of UV radiations acting on oxygen (O2) molecule. The higher energy UV radiations split apart some molecular oxygen (O2) into free oxygen (O) atoms. These atoms then combine with the molecular oxygen to form ozone as shown: (Image 100) Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) are responsible for the depletion of ozone layer. These compounds enter the atmosphere.
Question. State two advantages of conserving (i) forests (ii) wild life Answer : (i) Advantages of conserving forest are termed as ‘biodiversity hotspots’. They have large number of species of plants and animals. (a) They purify air, help in recharging groundwater, bring rains and maintain the fertility of soil. (b) They are also a source of income for tribal people. (ii) Wild life is important (a) To preserve bio-diversity. (b) As each species has a position in the food chain so wildlife helps in balancing the nature.
Question. What are ozone holes? How do they form? Answer : The coolants of Refrigerators and A/Cs use CFCs which release fluorine which react with ozone gas and break it into oxygen and a very reactive form of atomic oxygen which in turn can break another ozone molecule. Thus a chain reaction starts and layer of ozone becomes thinner at some places in upper atmosphere. These are called ozone holes.
Question. Distinguish between biodegradable , and nonbiodegradable substances. List two effects of each of them on our environment. Answer :
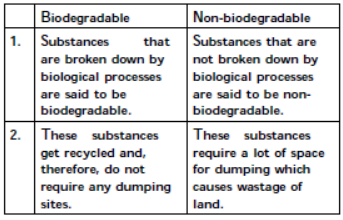
Effects of biodegradable substances: a. They release harmful gases like methane, ammonia, carbon dioxide, hydrogen sulphide, etc., during decomposition process. b. They release foul smell only during decomposition process but they do not cause any type of soil pollution. Effects of non-biodegradable substances: a. They persist in the environment for a long time and, thus, harm the various members of the ecosystem. b. They release very harmful gases when they are acted upon by physical processes like heat and pressure. c. They cause pollution of air, soil and water.
Question. Make an aquatic food chain up to tertiary consumer level. State the trophic level at which concentration of pesticide is maximum and why? Answer : Phytoplankton > Zooplankton -> Small fish > Bird. Tertiary consumer, E.g., Bird. Pesticides are not degradable and get progressively accumulated at each trophic level.

Related Posts

Minerals and Energy Resources Class 10 Social Science Notes and Questions

Office Tools Class 10 Computer Science Notes and Questions

Coordinate Geometry Class 10 Mathematics Notes And Questions
Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Case Based Questions - Our Environment
Case study - 1.
All organisms such as plants, animals, microorganisms and human beings as well as the physical surroundings interact with each other and maintain a balance in nature. All the interacting organisms in an area together with the non-living constituents of the environment form an ecosystem. Thus, an ecosystem consists of biotic components comprising living organisms and abiotic components comprising physical factors like temperature, rainfall, wind, soil and minerals.
Q1: What is natural ecosystem? Ans: An environment where living organism and non- living interact with each other freely in nature is called as natural ecosystem. Q2: what are the examples of artificial ecosystem? Ans: Gardens, crop- fields Q3: What are consumers? Ans: Organism which consume food either directly or indirectly by feeding on one another animals are called as consumers. Q4: What are the type of consumers? Ans: They are herbivores, carnivores, omnivores and parasites. Q5: What are producers? Ans: The green plants and some bacteria which make their food by using sunlight i.e photosynthesis are called as producers.
Case Study - 2
The food we eat acts as a fuel to provide us energy to do work. Thus the interactions among various components of the environment involves flow of energy from one component of the system to another. As we have studied, the autotrophs capture the energy present in sunlight and convert it into chemical energy. This energy supports all the activities of the living world. From autotrophs, the energy goes to the heterotrophs and decomposers.
Q1: What is food chain? Ans: A series of organism feeding on one another and taking part in various biotic levels is called food chain. Q2: Give a example of one terrestrial food chain. Ans: Sunlight ⇒ plants (producers) ⇒ Goat/ Deer (herbivores) ⇒ Tiger (carnivores) Q3: What are the feature of food chain? Ans: It is unidirectional The energy available at each level gets diminished due to loss at each level. Q4: What do you meant by biological magnification? Ans: The gradual increase in the concentration of any substance ( generally toxic) in trophic levels is called as biological magnification. Q5: What is the average value for the amount of organic matter that is present at each step and reaching the next level of consumers? Ans: 10%
Case Study - 3
In our daily activities, we generate a lot of material that are thrown away. What are some of these waste materials? What happens after we throw them away? Let us perform an activity to find answers to these questions.
- Collect waste material from your homes. This could include all the waste generated during a day, like kitchen waste (spoilt food, vegetable peels, used tea leaves, milk packets and empty cartons), waste paper, empty medicine bottles/strips/bubble packs, old and torn clothes and broken footwear.
- Bury this material in a pit in the school garden or if there is no space available, you can collect the material in an old bucket/ flower pot and cover with at least 15 cm of soil.
- Keep this material moist and observe at 15-day intervals.
- What are the materials that remain unchanged over long periods of time?
- What are the materials which change their form and structure over time?
- Of these materials that are changed, which ones change the fastest?
We have seen in the chapter on ‘Life Processes’ that the food we eat is digested by various enzymes in our body. Have you ever wondered why the same enzyme does not break-down everything we eat? Enzymes are specific in their action, specific enzymes are needed for the break-down of a particular substance. That is why we will not get any energy if we try to eat coal! Because of this, many human-made materials like plastics will not be broken down by the action of bacteria or other saprophytes. These materials will be acted upon by physical processes like heat and pressure, but under the ambient conditions found in our environment, these persist for a long time.
Q1: What is biodegradable substances? Ans: The substances that are broken down by biological process are called as biodegradable substances. Example: Vegetables waste materials. Q2: What are the examples of non- biodegradable substances? Ans: Plastic, rubber, foam, batteries etc. Q3: What are the ways through which we can reduce pollution especially the non- biodegradable waste? Ans:
- We can use RRR methods i.e reduce, reuse and recycle.
- Reduce the use of plastic.
Q4: What are the effects of biodegradable substances on our environment? Ans:
- Release green house gases.
- They are breeding ground for mosquitoes and houseflies causing various disease.
Q5: What are the non- biodegradable on environment? Ans:
- causes soil pollution and sometimes air pollution when burnt in air.
- death of cattles due to ingestion of these waste.
- choking of drainage system.
Case Study - 4
We are an integral part of the environment. Changes in the environment affect us and our activities change the environment around us Ozone (O3 ) is a molecule formed by three atoms of oxygen. While O2 , which we normally refer to as oxygen, is essential for all aerobic forms of life. Ozone, is a deadly poison. However, at the higher levels of the atmosphere, ozone performs an essential function. It shields the surface of the earth from ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the Sun.
Q1: How does ozone is formed? Ans: The UV radiations coming from the sun split the molecular oxygen into nascent oxygen. When these nascent oxygen combined to molecular oxygen, it forms ozone(O3). Q2: In which layer of atmosphere does ozone is present? Ans: The ozone is present in the stratosphere layer of atmosphere just above troposphere. Q3: What are the causes for ozone depletion? Ans: The synthetic chemicals like CFCs (chlorofluorocarbons) which used as refrigerants amd in the fire extinguisher. Q4: Write the chemical reaction for the formation of ozone? Ans: O2 ⇒ [O] + [O] [O] + O2 ⇒ O3 (ozone) Q5: What are the effects of UV radiations? Ans: It causes different types of cancer in human beings.
Case study – 5
In Kunjpura village, located in Karnal district, Haryana, Aditya Aggarwal and his older brother Amit Aggarwal run Tee Cee Industries, a steel plant set up by their ancestors in 1984. Along with this, they also run a gaushala that houses 1,200 cows that can no longer produce milk. The cow shelter was manageable but running the steel plant was turning out to be expensive because they spent a whopping Rs 5 lakh every month on electricity. The brothers struck upon an idea. Why not run the factory with the biogas produced from cow dung from the shelter and other gaushalas, along with bio and agri led Aditya and Amit to start Amrit Fertilizers, a biogas project, in 2014, without any government support.
Q1: Raw material used in bio gas plant is (a) Animal dung (b) Crop residue (c) Food waste (d) All of the above Ans: (d) Explanation: Biogas is produced through a process called anaerobic digestion, in which organic materials are broken down by microorganisms in the absence of oxygen. Various organic materials can be used as raw materials in a biogas plant, including animal dung, crop residues, and food waste. All of these materials are rich in organic matter, which serves as a source of energy for the microorganisms to produce biogas. Therefore, the correct answer is (d) All of the above. Q2: Biogas is a better fuel than animal dung cake because (i) Biogas has lower calorific value. (ii) Animal dung cake has higher calorific value. (iii) Biogas has high heating capacity. (iv) Biogas burns without smoke. (a) (i) only (b) (ii) only (c) (iii) and (iv) (d) (i) and (ii) Ans: (c) Explanation: Biogas is a better fuel than animal dung cake for several reasons. Biogas has a higher calorific value compared to animal dung cake, meaning it releases more energy when burned. Additionally, biogas burns without producing smoke, making it a cleaner fuel option. The statements (iii) and (iv) are correct, as biogas indeed has a high heating capacity and burns without smoke. Therefore, the correct answer is (c) (iii) and (iv). Q3: Biogas is formed in the (a) presence of air only. (b) presence of water only. (c) absence of air only. (d) presence of water and absence of air. Ans: (d) Explanation: Biogas is formed through the process of anaerobic digestion, which occurs in the absence of air (oxygen). The microorganisms that produce biogas thrive in an oxygen-free environment. However, the presence of water is also important for the process to take place. Water helps maintain the right conditions for the microorganisms to break down organic materials and produce biogas. Therefore, the correct answer is (d) presence of water and absence of air. Q4: Biogas is a mixture of the following gases. (a) Ethane, Carbon monoxide, Nitrogen and Butane (b) Methane, Hydrogen, Carbon dioxide and Nitrogen (c) Butane, Carbon monoxide, Propane and Hydrogen (d) Carbon monoxide, Sulphur dioxide and Hydrogen Ans: (b) Explanation: Biogas is primarily composed of methane (CH4), which is the main combustible component and provides the energy content. It also contains smaller amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2), some traces of hydrogen (H2), and in some cases, small quantities of nitrogen (N2) and other gases. The option (b) correctly lists the main components of biogas, which are methane, hydrogen, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen. Therefore, the correct answer is (b) Methane, Hydrogen, Carbon dioxide and Nitrogen.
Case Study – 6
Food chains are very important for the survival of most species. When only one element is removed from the food chain it can result in extinction of a species in some cases. The foundation of the food chain consists of primary producers. Primary producers, or autotrophs, can use either solar energy or chemical energy to create complex organic compounds, whereas species at higher trophic levels cannot and so must consume producers or other life that itself consumes producers. Because the sun’s light is necessary for photosynthesis, most life could not exist if the sun disappeared. Even so, it has recently been discovered that there are some forms of life, chemotrophs, that appear to gain all their metabolic energy from chemosynthesis driven by hydrothermal vents, thus showing that some life may not require solar energy to thrive.
Q1: If 10,000 J solar energy falls on green plants in a terrestrial ecosystem, what percentage of solar energy will be converted into food energy? (a) 10,000 J (b) 100 J (c) 1000 J (d) It will depend on the type of the terrestrial plant Ans: (b) Explanation: The efficiency of energy conversion from solar energy to food energy in plants is generally low. Only a small fraction of the solar energy is converted through photosynthesis into food energy (organic matter). It's estimated that, on average, about 1% to 3% of the solar energy is converted into chemical energy in plants. Therefore, in this case, if 10,000 J of solar energy falls on green plants, approximately 100 J (1% of 10,000 J) would be converted into food energy. The correct answer is (b) 100 J. Q2: Matter and energy are two fundamental inputs of an ecosystem. Movement of (a) Energy is bidirectional and matter is repeatedly circulating. (b) Energy is repeatedly circulation and matter is unidirectional. (c) Energy is unidirectional and matter is repeatedly circulating. (d) Energy is multidirectional and matter is bidirectional. Ans: (c) Explanation: In an ecosystem, energy flows in a unidirectional manner, usually from the Sun through producers (plants), consumers, and ultimately decomposers. Matter, on the other hand, circulates within the ecosystem through various biogeochemical cycles (such as the carbon cycle, nitrogen cycle, etc.), which involve the uptake, use, and recycling of elements like carbon, nitrogen, and other nutrients. Therefore, the correct answer is (c) Energy is unidirectional and matter is repeatedly circulating. Q3: Mr. X is eating curd/yogurt. For this food intake in a food chain he should be considered as occupying (a) First trophic level (b) Second trophic level (c) Third trophic level (d) Fourth trophic level Ans: (c) Explanation: When Mr. X eats curd/yogurt, he is consuming a product derived from milk, which is obtained from animals such as cows. Since he is consuming a product derived from primary consumers (herbivores), he should be considered as occupying the third trophic level in the food chain. The primary producers (plants) form the first trophic level, the herbivores (consumers that eat plants) form the second trophic level, and the carnivores or omnivores that eat herbivores occupy higher trophic levels. Therefore, the correct answer is (c) Third trophic level. Q4: Which of the following limits the number of trophic levels in a food chain? (a) Decrease in energy at higher trophic levels (b) Less availability of food (c) Polluted air (d) Water Ans: (a) Explanation: The decrease in energy at higher trophic levels is a key factor that limits the number of trophic levels in a food chain. As energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next, there is a significant loss of energy, usually in the form of heat, due to metabolic processes and inefficiencies in energy conversion. This decrease in available energy limits the amount of energy that can sustain organisms at higher trophic levels. As a result, there is typically a decrease in the number of trophic levels in a food chain, with fewer organisms occupying higher trophic levels. Therefore, the correct answer is (a) Decrease in energy at higher trophic levels. Q5: The decomposers are not included in the food chain. The correct reason for the same is because decomposers: (a) Act at every trophic level of the food chain (b) Do not breakdown organic compounds (c) Convert organic material to inorganic forms (d) Release enzymes outside their body to convert organic material to inorganic forms Ans: (a) Explanation: The decomposers, such as bacteria and fungi, play a crucial role in breaking down organic matter and recycling nutrients in ecosystems. However, they do not occupy specific trophic levels in a linear food chain like producers and consumers do. Instead, decomposers act at every trophic level of the food chain and ecosystem by breaking down dead organic matter and returning nutrients to the soil, which are then taken up by plants. This cycling of nutrients is essential for the functioning of ecosystems but does not fit into the traditional linear structure of a food chain. Therefore, the correct reason is (a) Decomposers act at every trophic level of the food chain.
Top Courses for Class 10
Sample paper, practice quizzes, extra questions, video lectures, study material, objective type questions, mock tests for examination, shortcuts and tricks, important questions, previous year questions with solutions, viva questions, semester notes, past year papers.

Case Based Questions: Our Environment Free PDF Download
Importance of case based questions: our environment, case based questions: our environment notes, case based questions: our environment class 10, study case based questions: our environment on the app, welcome back, create your account for free.
Forgot Password
Unattempted tests, change country.
CBSE Expert
Class 10 Science: Case Study Chapter 15 Our Environment PDF Download
In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given.

Here we are providing you with Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment Case Study Questions, by practicing these Case Study and Passage Based Questions will help you in your Class 10th Board Exam.
Case Study Chapter 15 Our Environment
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment
Case Study/Passage Based Questions
Question 1:
In any given ecosystem, all living organisms are linked in a systematic chain with respect to their mode of manufacturing food/feeding habits. This sequential interlinking of organisms involving the transfer of food energy from producers through a series of organisms with repeated eating and being eaten is called the food chain. A food chain may have 3-4 trophic levels.
(i) Which of the following statements regarding the food chain is incorrect? (a) It is a single straight pathway through which food energy travels in the ecosystem. (b) It adds adaptability and competitiveness to the organisms. (c) Presence of isolated food chains adds to the instability of the ecosystem. (d) Food chain binds up the inorganic nutrients of the ecosystem.
Answer: (b) It adds adaptability and competitiveness to the organisms.
(ii) Consider the following food chain. Grass ⟶⟶A ⟶⟶Frog ⟶⟶ Snake⟶⟶Eagle Which of the following can be placed at A?
Answer: (a) Grasshopper
(iii) Select the correct food chain. (a) Aquatic plants ⟶⟶ Tadpole ⟶⟶Water beetle⟶⟶Pike⟶⟶Perch (b) Grass⟶⟶Grasshopper⟶⟶Snake⟶⟶ Frog⟶⟶ Eagle (c) Grass⟶⟶ Rabbit⟶⟶ Wild cat⟶⟶ Tiger (d) Zooplankton ⟶⟶ Phytoplankton ⟶⟶Small fish⟶⟶Fish
Answer: (c) Grass⟶⟶ Rabbit⟶⟶ Wild cat⟶⟶ Tiger
(iv) Food chains are sustained by producers and _____________.
Answer: (d) decomposers
(v) Select the incorrect statement. (a) Food chain may terminate at level of herbivore (b) Food chain is always straight (c) Food chain may have 3-5 trophic levels (d) In a food chain, 80 to 90% of potential energy is lost as heat, at each transfer
Answer: (a) Food chain may terminate at level of herbivore
Question 2:
An ecosystem may be defined as a structural and functional unit of the biosphere comprising living organisms and their non-living environment which interact by means of food chains and biogeochemical cycles resulting in energy flow, biotic diversity, and material cycling to form a stable, self-supporting system.
2.1) The two basic processes involved in an ecosystem are : (a) cycling of materials and food chains (b) energy flow and self-sustainability (c) carbon cycle and biotic diversity (d) cycling of materials and flow of energy
Answer: (d) cycling of materials and flow of energy
2.2) Which among the following is not an artificial ecosystem? (a) Orchard (b) Lake (c) Aquarium (d) Cropland
Answer: (b) Lake
2.3) The role of fungi and bacteria in an ecosystem is to : (a) increase the supply of nutrients (b) increase the supply of energy (c) release nutrients from dead organic matter (d) increase the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere
Answer: (c) release nutrients from dead organic matter
2.4) What would be one of the likely results be if all decomposers in a particular ecosystem were wiped out? (a) The atmospheric reservoir of carbon dioxide would decline. (b) More food would be available for other consumers in the ecosystem. (c) The other organisms in the ecosystem would experience lower death rates. (d) There would be no significant impact, as dead organic matters would spontaneously decompose.
Answer: (a) The atmospheric reservoir of carbon dioxide would decline.
2.5) Which of the following holds true for an ecosystem? (a) Animals can live without plants. (b) Plants can live without animals. (c) Animals can survive for long without plants. (d) Plants can survive for long without animals.
Answer: (d) Plants can survive for long without animals
You can also practice Class 10 Science MCQ Questions for Board Exams.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Download India's best Exam Preparation App Now.
Key Features
- Revision Notes
- Important Questions
- Previous Years Questions
- Case-Based Questions
- Assertion and Reason Questions
No thanks, I’m not interested!

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- DK Goel Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- ML Aggarwal Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Sandeep Garg Textbook Solution
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- HOTS Question
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- Important Info
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Sample Papers
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam

SHARING IS CARING If our Website helped you a little, then kindly spread our voice using Social Networks. Spread our word to your readers, friends, teachers, students & all those close ones who deserve to know what you know now.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences
- Chemical Reactions and Equations 14 April, 2021, 6:02 pm
- Acids, Bases, and Salts 14 April, 2021, 6:02 pm
- Metals and Non-Metals 14 April, 2021, 6:02 pm
- Carbon and its Compounds 14 April, 2021, 6:02 pm
- Periodic Classification of Elements 14 April, 2021, 6:02 pm
- Life Processes 14 April, 2021, 6:02 pm
- How Do Organisms Reproduce 14 April, 2021, 6:02 pm
- Heredity and Evolution 14 April, 2021, 6:02 pm
- Light Reflection and Refraction 14 April, 2021, 6:02 pm

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here we have arranged some Important Case Base Questions for students who are searching for Paragraph Based Questions Our Environment. At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 15 ...
Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Case Study Questions have been prepared for the latest exam pattern. You can check your knowledge by solving case study-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment. Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th. In CBSE ...
Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment Question 1: Food web is the interconnection of different food chains, which correlate at various trophic levelsoperating in an ecosystem. (i) How many food chains are present in the given food web? (ii) Name the primary consumer in the given food web. (iii) How … Continue reading Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science ...
CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Our Environment Case Study Questions With Solution 2021. 10th Standard CBSE. Reg.No. : Science. Time : 00:30:00 Hrs. Total Marks : 20. Advancement of the technology has resulted in improvement of our lifestyle and has also changed our attitude. When the human population was low and technology was in its ...
Students should follow some basic tips to solve Our Environment Case Study Based Questions. These tips can help students to score good marks in CBSE Class 10 Science. Generally, the case based questions are in the form of Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs). Students should start solving the case based questions through reading the given passage.
These case based questions are expected to come in your exams this year. Please practise these case study based Class 10 Science Questions and answers to get more marks in examinations. Case Study Questions Chapter 15 Our Environment. Case/Passage – 1 Food chains are very important for the survival of most species.
The Case Based Questions: Our Environment is an invaluable resource that delves deep into the core of the Class 10 exam. These study notes are curated by experts and cover all the essential topics and concepts, making your preparation more efficient and effective.
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment. Case Study/Passage Based Questions. Question 1: In any given ecosystem, all living organisms are linked in a systematic chain with respect to their mode of manufacturing food/feeding habits. This sequential interlinking of organisms ...
Hello Students!!!"Today, we're looking at the top 5 case-based study questions from the chapter ""Our Environment"". Grade: 10Subject: Science, Biology Chapt... CBSE Exam, class 10
Our Environment Case Study: Here, Students can read Class 10 Our Environment Case Based Questions with Answers in PDF File format. Apart from this, You can download ...