The marketplace for case solutions.

Case Study Solutions
Hundreds of case solutions at your fingertips! Case study answers written by top business students.

We are the marketplace for case study solutions
Save time and get inspired by our case solutions. We help you be a top student at your university!
High-quality only
Immediate access.

What Students Say About Us

I finished my assignment thanks to your solution. Thank you very much for this! Much better than what I expected. It was a great idea to let me sample it before I buy – many companies don’t do this, and what a wasted sale in my opinion! Best of luck! 🙂
How to Write a Business Case: Examples, Templates, and Checklists
By Joe Weller | April 24, 2019 (updated February 26, 2023)
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
This article presents expert tips on how to write a business case. We also provide a checklist to prepare for, write, and present a business case, along with free, easy-to-use Word and PowerPoint business case templates.
Included on this page, you'll find details on how to write a business case , sections to include in your business case , a business case checklist , and business case presentation examples .
What Is a Business Case?
A business case is a formal, structured document; an informal, short document; or a verbal exchange that defines the benefits of an initiative or project.
In addition, a business case forecasts the costs, benefits, and risks of an initiative, so decision makers — and even the project initiators — can decide whether a project is worthwhile and why to choose one approach over similar strategies.
Jim Maholic has over 20 years of experience with IT strategy and business case development, including two stints as a CIO, two management positions with the Big Four consulting firms, and leadership positions at several technology companies.
He describes a business case in this way: “A business case is the full story that explains the ROI for a capital project. It begins with a statement of a business problem, then explores how we can solve it or what the value of solving it is. For example, ‘Our revenues aren’t rising as fast as they should,’ or ‘Inventory isn't turning over as fast as it should,’ or ‘Costs are too high.’ That's where the business case starts.

“Then, we find out how big this problem is. We talk to people in the company and find out what they think the value of solving the problem is. All this information is packaged into a story that says, ‘Here's the problem. Here's the value of solving the problem. Here's what it costs in hardware, software, or whatever. Here are the benefits. And here’s the whole story.’”
Business Cases Explain Why You Should Invest
A business case explains why stakeholders should invest in a project. The purpose of a business case contrasts with that of a project proposal , which provides a high-level outline of what you want to initiate and its benefits to the company, or that of a project plan , which explains how you execute a project. You should create your business case during the earliest stages of project planning .
A business case can also become a key document for a project manager when planning, creating milestones, and evaluating progress.
Other names and uses for business cases are financial justification, cost-benefit analysis (CBA) , total cost of ownership (TCO) analysis , and return on investment (ROI) analysis . Nonprofits and government entities sometimes refer to business cases as case statements .
What Is Business Case Analysis (BCA)?
A business case analysis (BCA) looks not only at lowest costs, but also at technical value and other nonquantitative factors in what is known as a best-value analysis . The BCA addresses the triple constraints of time, money, and scope, and it can include measures such as performance, reliability, viability, and supportability.
Although business case analysis is used interchangeably with business case , some experts consider the analysis to be part of the business case as a whole.
What Is a Business Case Used For?
A business case helps a company or an organization prepare for new ventures or changes. This document is a crucial building block of project success and underpins the foundations of senior-level involvement and strong planning. Business cases summarize the benefits of an endeavor, clarifying a project’s business value to help stakeholders make decisions.
A good business case should focus less on the technology, domain knowledge, or specific deliverables and more on the users of a product and the goals of a project. In the same vein, a project manager should focus not only on creating output, but also on delivering value. An initiative can offer many types of value, including contributing to strategic aims, increasing efficiency, and supporting compliance. Insufficient attention to the details of a business case and the accompanying research can lead to poor project results.
Business cases usually describe these items:
- A business problem or opportunity
- Possible solutions and their benefits and disadvantages (sometimes known as disbenefits )
- Risks associated with the main solution
- Implementation timeline
- Consequences for implementing a solution and for retaining the status quo
- Resources required for the initiative or project
Advantages of a Business Case
A business case may seem like just another document destined for the shelf or the shredder, but it can offer real advantages:
- All stakeholders have similar expectations concerning the value and benefits of an initiative to an organization.
- You can convert a business case into a project plan with milestones. You increase the chances of a project’s success with planning.
- A business case becomes a gauge for determining whether an endeavor continues to offer value during execution and after a team produces a deliverable.
- Project planners can more easily establish objectives and goals.
- You can more easily discern success.
- Teams apply the right resources more efficiently.
Who Prepares a Business Case?
You might think that business cases are the purview of financial officers and accountants. In fact, people who have direct knowledge of processes and teams should be responsible for creating these documents.
Some pundits say that the individual who advocates change must enact the change, so anyone in any role could assume the responsibilities for producing a business case. This includes consultants, line managers, or IT managers. In some organizations, the project sponsor or project manager may guide the preparation of the business case and include input from relevant departments and SMEs.
When Do You Need a Business Case?
It’s no longer enough to complete a project and present a deliverable. In an economy that often seems as unstable as it was in 2008, stakeholders want to see that a deliverable creates value and benefits for an organization. This is particularly true for complex projects or those that require justification for enlisting external resources. Public sector projects frequently need business cases.
What's in a Business Case?
A business case outlines for a decision maker the benefits and business value of a proposed initiative. The term business case frequently refers to a written document that is submitted for review or presented at a meeting, but can also apply to an informal, spoken proposal.
What Should Be in a Business Case?
A well-written business case flows logically from presenting a problem or opportunity through the advantages and disadvantages of solutions to describing the recommended solution. When you require great detail, you can chunk text into sub-sections so that the content is easier to scan, as well as faster and less overwhelming to read. Following are the common sections of a business case in sequential order:
- Executive summary
- Problem statement
- Analysis and financial details
- Recommendation
Many organizations have pre-established templates for writing business cases. If your organization doesn’t, search online for free, easy-to-use business case templates for construction business cases, one-page business cases, and more. Depending on the narrative needs of the business case, it can contain many possible sections:
- Preface: A preface may indicate the intended audience and any related documents.
- Table of Contents: If your document is delivered as a PDF file, consider hyperlinking your table of contents to the appropriate sections.
- What is the problem?
- What do you believe is the value of solving the problem?
- How much are you asking for?
- When will we start seeing benefits?
“I’ve had some presentations that don't get beyond that first page,” Maholic muses.
- Description of the Product or Service: When proposing a new object or concept, detail what the deliverable is and how it works.
- A Problem Statement or Mission Statement: By describing the problem or the mission of the organization, you can contextualize the proposed initiative.
- Business Drivers for the Initiative: Indicate what benefits will contribute to the strategic aims of the organization.
- Finance Section: Explain how much the project will cost and whether it is affordable. Detail the cash flow. Describe the expenses to execute (or not execute) the project in a cost comparison against forecasted benefits. Conduct a sensitivity analysis , a technique for determining how the different values of an independent variable affect a dependent variable.
- Financial and nonfinancial benefits
- Quality improvements
- Cost savings through efficiencies
- Added revenue
- Competitiveness
- Improved customer services
- Options: What are the possible solutions to the problem? Usually, you narrow this list to 3 to 5 viable choices. Frequently, you include a “do nothing” option and a benchmark option. Some organizations require the do-nothing option; others require it only if the do-nothing option is a legitimate possibility. Quantify the benefits of each potential solution. Also, outline the risks, issues, and interdependencies for each solution.
- What is required?
- How is it done?
- Who does what?
- When will things happen?
- Assessments or Analysis: Your analysis should list assumptions and consider cash flow and costs. Describe the risks of the project and the plans to deal with them. Also, discuss how you will leverage opportunities. Describe the context of your undertaking using PESTLE (political, economic, sociological, technological, legal, and environmental) analysis.
- Project Approach: Detail the organization of the project, including governance and accountability, roles and responsibilities, and the schedule of progress reporting. Describe the purchasing strategy for completing the endeavor. Will you lease equipment? Rent office space? Hire contractors or employees?
- Recommendation and Next Steps: Note the recommended solution and immediate required action.
- Appendix: Add supporting documentation here, such as spreadsheets, charts, or drawings.
Considerations for Executive Presentations
The sections that comprise a business case may vary depending on your house style and the type of initiative. Jim Maholic says, “I package my business cases this way: I set up a one-hour meeting, so I have maybe 20 slides, but 10 to 15 slides are plenty. In reality, I might have 100 slides, but I add those in an appendix.” You may have credible supporting information, but you don’t want to bore your audience of decision makers by slogging through each slide.
“They might allocate an hour, but honestly, you're going to get their attention for 10 to 15 minutes, and then they'll start checking email and stuff,” Maholic adds. “You really have to be crisp in how you do this and know where you're going.
“Start with, ‘We have this problem,’ followed by, ‘Here are the people that we talked to who validated that this is a problem. They offered ideas about solving this problem, so we could see this substantial benefit,’” he notes.
“What matters in an executive meeting is that I answer the main questions: What is the problem? What is the cost of not solving it? What are the benefits of solving it? And when do we see the benefits? You may address additional questions later in the meeting or after the meeting, on an individual, offline basis,” Maholic says.
Business Case Templates
Using templates, you can more easily create business cases because you can focus on your research and fill in the blanks. The following free, downloadable templates are customizable for your organization’s needs.
Business Case Presentation Template

You can lengthen this short PowerPoint presentation template to accommodate more detail. The business case presentation template includes spaces for describing the following elements: the project name, the executive summary, the project description, the financials, the recommended solution, the assumptions and dependencies, the options, and the benefits.
Download Business Case Presentation Template - PowerPoint
Simple Business Case Template

A simple business case template serves a small project or a small organization. It can cover extensive details if necessary. It includes spaces for describing the following elements of the case: the title, the executive summary, the business objective, the target users, the financials and costs, the assumptions and dependencies, the implementation strategy, the required resources, and the project governance and reporting.
Download Simple Business Case Template
Word | PDF | Smartsheet
Healthcare Business Case Template

A healthcare business case template helps you explain the current setup and how the proposed solution can create improvements. It provides space for a one-page executive summary, context for the problem or opportunity, a description of the current situation, an explanation of the proposed changes, and details of how the changes can affect your organization and any other entities.
Download Healthcare Business Case Template
Word | Google Docs
New Product Business Case Template
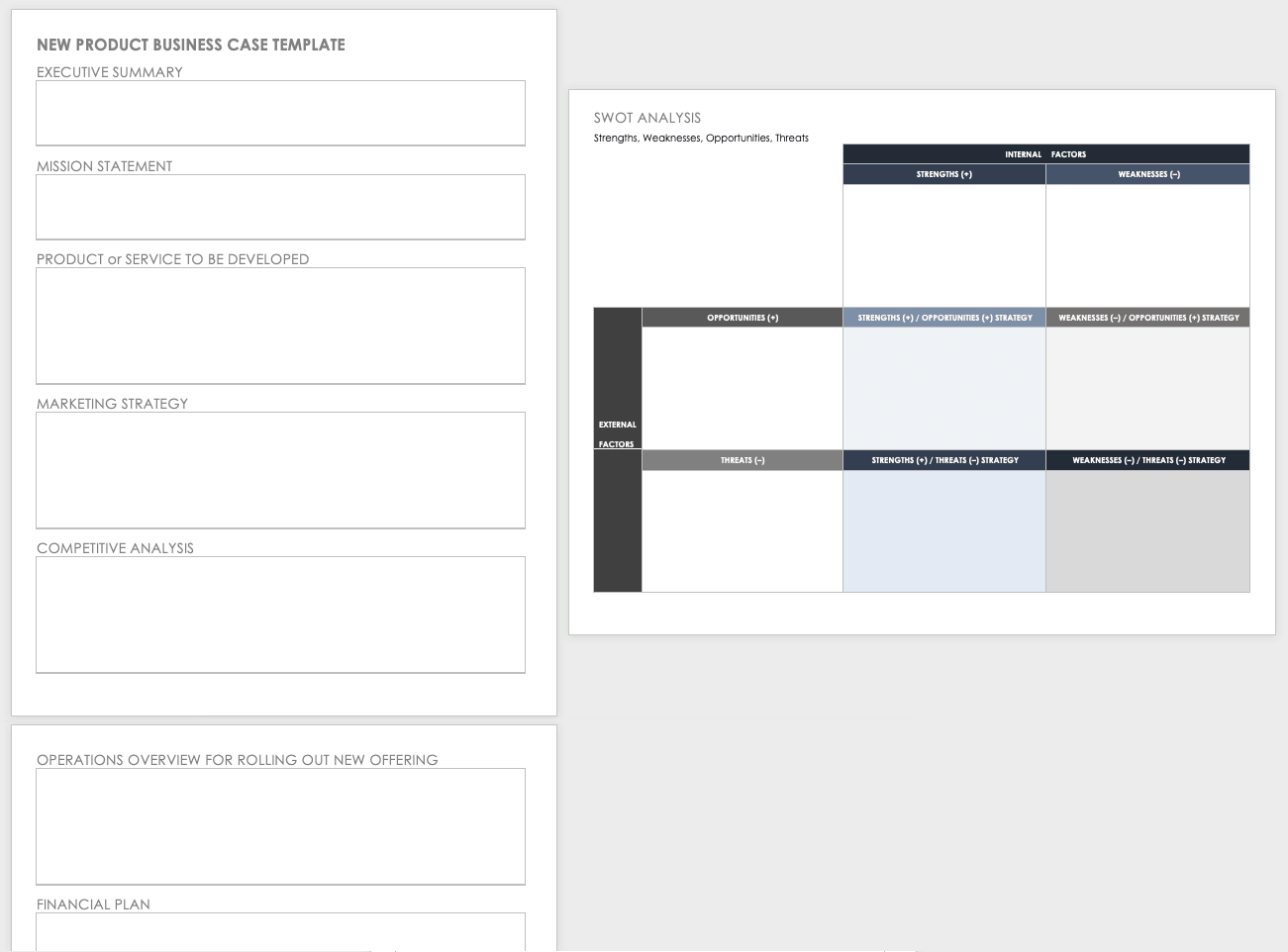
A new product business case template explores the business landscape for a new product or service. In addition to the meta information, such as the title, the author, and the executive summary, the template includes space to describe the current mission statement, the proposed product or service, the marketing strategy, an analysis of competitors, SWOT analysis , an overview of the implementation plan, and financial details.
Download New Product Business Case Template
Preparing to Write the Business Case
You can expedite your business process by understanding business case structure and using a template. In addition, having the correct perspective and following best practices can contribute to your success.
Why Are You Doing the Project?
Before you start researching and writing, understand why you want to initiate a project. The goal of a project is to solve problems. What is a problem? A problem prevents your organization from achieving its full potential. To begin, determine what problem the project is trying to solve.
Projects have deliverables, whether tangible or intangible. Think of an outcome as the result created by the deliverables. Benefits represent quantifiable improvements derived from an outcome. When a customer or team member can leverage these benefits, they become advantages.
Do Your Business Case Research
To start, review the mission statement(s) for the organization or the project. Identify the sources of data for your business case. One way to encourage the acceptance of your proposal is to discuss your rough estimates of the costs and resources with a project sponsor or customer before you embark on the business case. This helps you and the sponsor understand each other’s expectations and lessens the chance of sticker shock during the executive presentation. Then interview the people who conduct the day-to-day work and get their perspective on problems and possible solutions.
Do the Business Case Math
You must consider whether the returns justify the request. “If we're asking for $3 million, we've got to show that the project benefits far exceed that amount,” asserts Maholic. “With returns of $10, $15, or $20 million, you're going to get their attention. If you say the benefits are $300 million, they're going to think you've fallen off the truck somewhere, because that's not realistic. On the other hand, if you show benefits of $3.5 million for a cost of $3 million, that's probably not going to beat the projected return of any other project that comes across their desk.”
Consider Who the Business Case Is For
Whether the business case comes in document form or as a presentation, the project sponsor and key stakeholders will study it. Consider the key audience for each section of your document and write with that audience in mind.
The most convincing arguments for projects are those that your team can initiate and wrap up within six months, as well as produce considerable quantifiable results. Especially when big money is on the table, your proposal will compete with others from different departments. “No company has all the money it wants to invest in everything — it has to prioritize. The business case helps evaluate what the return will be for each of the projects that comes across the board's desk for approval,” explains Maholic.
Furthermore, a business case presents estimates. A business case should be built on sound research, but no one has a lock on certitude. “I think first-time business case writers in particular get caught up in building some great story. But seasoned executives get requests all the time, and they're not buffaloed by clever-sounding words or fancy spreadsheets,” Maholic cautions.
“Your ideas have to be rooted in something sensible, not just, ‘I bet we can raise revenues by 15 percent,’” he explains. Grand plans may be possible, but the key, according to Maholic, is to help decision makers understand how it is possible.
How Do You Write a Business Case?
When you have the main questions in mind and a sense of the required sections and format, you can begin to write. Consider limiting the number of authors to ensure an effective writing effort that’s consistent in style and voice. Then follow these tips:
- Concisely cover the core content with enough detail, so stakeholders can make an informed decision.
- Compare options, so decision makers understand the landscape.
- Be clear, concise, and captivating.
- Avoid jargon as much as possible.
- Demonstrate the value of the project to the business by creating a credible and accurate argument.
- Clearly describe the landscape for the initiative, including its dependencies. Enumerating these dependencies is crucial because contextual changes can alter the project parameters or eliminate the need for the project altogether.
- Focus on the business and the business value rather than the knowledge domain covered by the intended project deliverable.
How Do You Know You Have Enough Detail?
You determine the length of your business cases according to the scope and complexity of your proposed endeavour. A complex project means a long business case; a small, short project means a short business case.
However, Maholic cautions against adding too much detail — conciseness can be a challenge. “You may take 4 to 6 weeks to create a business. You might talk to 50 or 100 people. There's this gnawing urge in some people to show everything they've collected in the executive presentation. Look how hard we worked. Look how smart I am . That's just awful.
“You have enough data and slides when you can answer those 4 or 5 basic questions. There may be 100 other slides, but those are supporting detail,” he says.
Common Mistakes in Writing Business Cases
You can strengthen your business case by avoiding common mistakes:
- Forget What Your White Papers Say: Maholic finds that when salespeople create cases for customers, they frequently rely on the benefits outlined in a product’s white papers. He notes, “Saying your product cuts costs by Y percent is a great place to start, but it has to be balanced by what's in front of you regarding a particular customer.” He continues, “As a salesperson, you may say that your product can increase revenue by 5 percent. That may be true for past customers, but this particular customer may have three straight years of declining revenues. It's silly to say that a product is going to both arrest a decline and bump up revenue by 5 percent. You have to think things through. That’s the analysis part. You can't just mouth off.”
- Spreadsheets Are not the Main Show: "Too often, I think, people hear business case , and they jump right to building a spreadsheet,” Maholic says. “They're eager to build the mother of all spreadsheets and show how smart they are by demonstrating the mother of all spreadsheets. While certainly spreadsheets are necessary to show the math, the spreadsheet is only a small part of the solution. Spreadsheets don't really articulate the problem or indicate who you talked to or what you analyzed to get to that solution,” he adds.
- Arguments Do not Equal More Money: Sometimes, people believe that a strong case justifies a more generous price tag. Not so, says Maholic: “As a decision maker, having a better business case doesn't mean I'm going to roll over and say, ‘Sure, you can charge me an extra million dollars.’ A good business case means the project has the value to go forward. Now, we're going to start negotiating and I'm still going to work to get the best price I can. People who've done business cases before know that. But people who are new to them don't completely understand that.”
- Remember That It’s About Value, Not About Toys: For startups, the coolness factor of the technology or product may carry some weight, but for most organizations, a business case must focus on the business value without getting lost in the domain knowledge and technical details. Maholic explains: “Nobody at the executive level cares what the throughput ratio is of this process or that stack. What they want to know is, ‘Do I get revenue more quickly? Do I cut costs more deeply? Tell me what the value of doing X is, and then you can go off and buy whatever toys you want to in order to do X.’”
Steps to Produce a Business Case
Your organization may have a tribal understanding of the best process for creating a business case. Some employees may advocate for following the Ds , which refer to the steps to produce a business case. The Ds can include as many as six steps, but generally focus on these four:
- Discover your problem or opportunity.
- Design your solutions and alternatives.
- Develop the details that describe the pros and cons of each potential solution.
- Deploy the business case.
Some advocates add the Define step to the beginning of the process and the Deliver step to the end. For best results, create your business case in the following order:
- Determine your problem or opportunity.
- Research the context for your proposal as appropriate: When developing a new product, your research may focus on the market; when acquiring new training or software, you may review current internal processes; and when making a new purchase, you may interview dozens of team members who use current tools and procedures.
- Compare alternative approaches and recommend the most appropriate strategy.
- Gather supporting data and evidence for the recommended approach.
- Write the business case.
- Write the executive summary.
- Edit your business case draft.
- Present your business case to either the final authority or the personnel who will be instrumental in implementing the case plan.
Download Business Case Process Checklist
The Business Case in Project Development
Contrary to what you might imagine, the business case can be a living document. Starting with the review process, stakeholders may reject, cancel, postpone, accept, or adjust the business case. To some extent, the business case becomes the guidebook for your initiative. Stakeholders and the project manager should refer to the business case throughout the lifecycle of the project to ensure that efforts (and intentions) remain on track.
What Are the Features of a Project Business Case?
A well-considered business case offers the following characteristics: an easy-to-understand description of the business value of the initiative and the immediate benefits of the project, including details of the positive impact on organizational strategy.
How Do You Analyze a Business Case?
In university-level business schools, business case studies (or case studies) function as teaching tools to help students use their analytic skills. Case studies describe a company and how it employs a solution. Following is the suggested approach for students analyzing a case:
- Review the case in detail. Identify the key issues.
- Determine 2 to 5 essential problems.
- Look for solutions to those problems.
- Describe your recommended solution.
What Is a Full Business Case?
A business case is a structured, detailed document that presents the justification for the commitment of financial and other resources to an endeavor. Business cases help you gain the support of management and other stakeholders, as well as approval for projects and programs.
What Is a Business Case in Project Management?
An approved business case can have a long life. Although the project sponsor ultimately owns the business case, it is the project manager who uses the business case as the guidebook for expectations and dependencies. In addition, the business case becomes an important document in an organization’s project portfolio management process. During this process, a company balances its resources with its strategic objectives to determine the livelihood of all the projects it undertakes.
History and Origins of Business Cases
The formal business case has its roots in 19th-century Europe, particularly with the work of French-Italian engineer-economist Jules Dupuit. His contribution included statistical tools to identify, measure, and value the benefits beyond merely determining the lowest bidder. Specifically, Dupuit is credited with inventing what he called the benefit-cost analysis . Today, professionals recognize the value of business cases outside of public works and government. Both nonprofit and for-profit organizations regularly use business cases.
Resources and Examples for Creating Your Business Case
If you’re new to business cases, you don’t have to start empty-handed. We offer resources to help you begin writing. Please see the following examples and templates:
- Here’s an example of a business case in a classic document format . This particular business case argues against a capital investment.
- This example presents three business cases for one higher education department . The presentation comes in a slide format.
- In this article, Jim Maholic offers a template for creating your business case .
Improve Your Business Cases with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
Problem-Solving in Business: CASE STUDIES
- ABOUT THIS LIBGUIDE
- PROBLEM-SOLVING DEFINED AND WHY IT IS IMPORTANT
- SKILLS AND QUALIFICATIONS NEEDED IN PROBLEM-SOLVING
- PROBLEM-SOLVING STEPS
- CASE STUDIES
- MORE HELPFUL RESOURCES
- << Previous: PROBLEM-SOLVING STEPS
- Next: MORE HELPFUL RESOURCES >>
- Last Updated: Mar 23, 2024 4:47 PM
- URL: https://libguides.nypl.org/problem_solving_in_business
- Harvard Business School →
- Academic Experience
- Faculty & Research
- The Field Method
- A Global Experience
The HBS Case Method
- Joint Degree Programs
- The Section Experience
- The HBS Case Method →
Take a Seat in the MBA Classroom
- Harvard Business School
How the HBS Case Method Works

How the Case Method Works

- Read and analyze the case. Each case is a 10-20 page document written from the viewpoint of a real person leading a real organization. In addition to background information on the situation, each case ends in a key decision to be made. Your job is to sift through the information, incomplete by design, and decide what you would do.
- Discuss the case. Each morning, you’ll bring your ideas to a small team of classmates from diverse professional backgrounds, your discussion group, to share your findings and listen to theirs. Together, you begin to see the case from different perspectives, better preparing you for class.
- Engage in class. Be prepared to change the way you think as you debate with classmates the best path forward for this organization. The highly engaged conversation is facilitated by the faculty member, but it’s driven by your classmates’ comments and experiences. HBS brings together amazingly talented people from diverse backgrounds and puts that experience front and center. Students do the majority of the talking (and lots of active listening), and your job is to better understand the decision at hand, what you would do in the case protagonist’s shoes, and why. You will not leave a class thinking about the case the same way you thought about it coming in! In addition to learning more about many businesses, in the case method you will develop communication, listening, analysis, and leadership skills. It is a truly dynamic and immersive learning environment.
- Reflect. The case method prepares you to be in leadership positions where you will face time-sensitive decisions with limited information. Reflecting on each class discussion will prepare you to face these situations in your future roles.
Student Perspectives

“I’ve been so touched by how dedicated other people have been to my learning and my success.”
Faculty Perspectives

“The world desperately needs better leadership. It’s actually one of the great gifts of teaching here, you can do something about it.”
Alumni Perspectives

“You walk into work every morning and it's like a fire hose of decisions that need to be made, often without enough information. Just like an HBS case.”
Celebrating the Inaugural HBS Case

“How do you go into an ambiguous situation and get to the bottom of it? That skill – the skill of figuring out a course of inquiry, to choose a course of action – that skill is as relevant today as it was in 1921.”
Business growth
Marketing tips
16 case study examples (+ 3 templates to make your own)
I like to think of case studies as a business's version of a resume. It highlights what the business can do, lends credibility to its offer, and contains only the positive bullet points that paint it in the best light possible.
Imagine if the guy running your favorite taco truck followed you home so that he could "really dig into how that burrito changed your life." I see the value in the practice. People naturally prefer a tried-and-true burrito just as they prefer tried-and-true products or services.
To help you showcase your success and flesh out your burrito questionnaire, I've put together some case study examples and key takeaways.
What is a case study?
A case study is an in-depth analysis of how your business, product, or service has helped past clients. It can be a document, a webpage, or a slide deck that showcases measurable, real-life results.
For example, if you're a SaaS company, you can analyze your customers' results after a few months of using your product to measure its effectiveness. You can then turn this analysis into a case study that further proves to potential customers what your product can do and how it can help them overcome their challenges.
It changes the narrative from "I promise that we can do X and Y for you" to "Here's what we've done for businesses like yours, and we can do it for you, too."
16 case study examples
While most case studies follow the same structure, quite a few try to break the mold and create something unique. Some businesses lean heavily on design and presentation, while others pursue a detailed, stat-oriented approach. Some businesses try to mix both.
There's no set formula to follow, but I've found that the best case studies utilize impactful design to engage readers and leverage statistics and case details to drive the point home. A case study typically highlights the companies, the challenges, the solution, and the results. The examples below will help inspire you to do it, too.
1. .css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class]{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;cursor:pointer;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class]{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;cursor:pointer;-webkit-transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;outline-offset:1px;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;outline:1px solid transparent;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='ocean']{color:#3d4592;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='ocean']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='ocean']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='white']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='white']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='white']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='primary']{color:#3d4592;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='primary']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='primary']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='secondary']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='secondary']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='secondary']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-weight='inherit']{font-weight:inherit;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-weight='normal']{font-weight:400;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-weight='bold']{font-weight:700;} Volcanica Coffee and AdRoll

People love a good farm-to-table coffee story, and boy am I one of them. But I've shared this case study with you for more reasons than my love of coffee. I enjoyed this study because it was written as though it was a letter.
In this case study, the founder of Volcanica Coffee talks about the journey from founding the company to personally struggling with learning and applying digital marketing to finding and enlisting AdRoll's services.
It felt more authentic, less about AdRoll showcasing their worth and more like a testimonial from a grateful and appreciative client. After the story, the case study wraps up with successes, milestones, and achievements. Note that quite a few percentages are prominently displayed at the top, providing supporting evidence that backs up an inspiring story.
Takeaway: Highlight your goals and measurable results to draw the reader in and provide concise, easily digestible information.
2. Taylor Guitars and Airtable

This Airtable case study on Taylor Guitars comes as close as one can to an optimal structure. It features a video that represents the artistic nature of the client, highlighting key achievements and dissecting each element of Airtable's influence.
It also supplements each section with a testimonial or quote from the client, using their insights as a catalyst for the case study's narrative. For example, the case study quotes the social media manager and project manager's insights regarding team-wide communication and access before explaining in greater detail.
Takeaway: Highlight pain points your business solves for its client, and explore that influence in greater detail.
3. EndeavourX and Figma

My favorite part of Figma's case study is highlighting why EndeavourX chose its solution. You'll notice an entire section on what Figma does for teams and then specifically for EndeavourX.
It also places a heavy emphasis on numbers and stats. The study, as brief as it is, still manages to pack in a lot of compelling statistics about what's possible with Figma.
Takeaway: Showcase the "how" and "why" of your product's differentiators and how they benefit your customers.
4. ActiveCampaign and Zapier

Zapier's case study leans heavily on design, using graphics to present statistics and goals in a manner that not only remains consistent with the branding but also actively pushes it forward, drawing users' eyes to the information most important to them.
The graphics, emphasis on branding elements, and cause/effect style tell the story without requiring long, drawn-out copy that risks boring readers. Instead, the cause and effect are concisely portrayed alongside the client company's information for a brief and easily scannable case study.
Takeaway: Lean on design to call attention to the most important elements of your case study, and make sure it stays consistent with your branding.
5. Ironclad and OpenAI
In true OpenAI fashion, this case study is a block of text. There's a distinct lack of imagery, but the study features a narrated video walking readers through the product.
The lack of imagery and color may not be the most inviting, but utilizing video format is commendable. It helps thoroughly communicate how OpenAI supported Ironclad in a way that allows the user to sit back, relax, listen, and be impressed.
Takeaway: Get creative with the media you implement in your case study. Videos can be a very powerful addition when a case study requires more detailed storytelling.
6. Shopify and GitHub

GitHub's case study on Shopify is a light read. It addresses client pain points and discusses the different aspects its product considers and improves for clients. It touches on workflow issues, internal systems, automation, and security. It does a great job of representing what one company can do with GitHub.
To drive the point home, the case study features colorful quote callouts from the Shopify team, sharing their insights and perspectives on the partnership, the key issues, and how they were addressed.
Takeaway: Leverage quotes to boost the authoritativeness and trustworthiness of your case study.
7 . Audible and Contentful

Contentful's case study on Audible features almost every element a case study should. It includes not one but two videos and clearly outlines the challenge, solution, and outcome before diving deeper into what Contentful did for Audible. The language is simple, and the writing is heavy with quotes and personal insights.
This case study is a uniquely original experience. The fact that the companies in question are perhaps two of the most creative brands out there may be the reason. I expected nothing short of a detailed analysis, a compelling story, and video content.
Takeaway: Inject some brand voice into the case study, and create assets that tell the story for you.
8 . Zoom and Asana
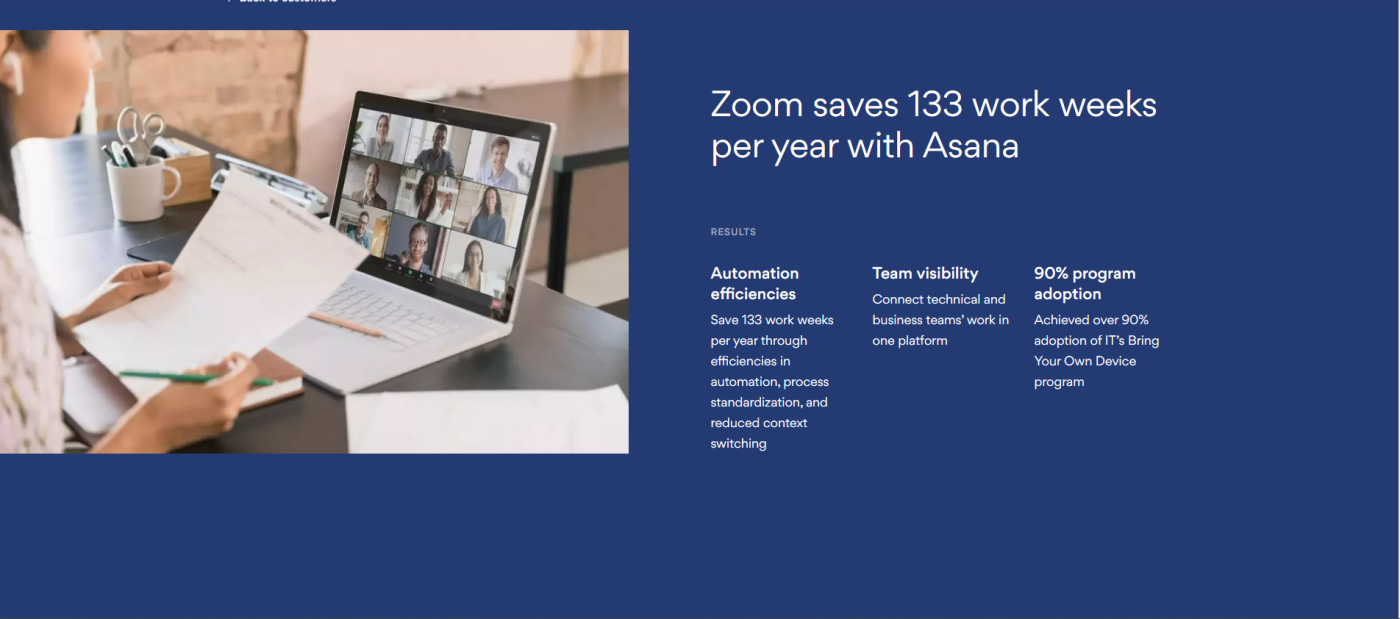
Asana's case study on Zoom is longer than the average piece and features detailed data on Zoom's growth since 2020. Instead of relying on imagery and graphics, it features several quotes and testimonials.
It's designed to be direct, informative, and promotional. At some point, the case study reads more like a feature list. There were a few sections that felt a tad too promotional for my liking, but to each their own burrito.
Takeaway: Maintain a balance between promotional and informative. You want to showcase the high-level goals your product helped achieve without losing the reader.
9 . Hickies and Mailchimp

I've always been a fan of Mailchimp's comic-like branding, and this case study does an excellent job of sticking to their tradition of making information easy to understand, casual, and inviting.
It features a short video that briefly covers Hickies as a company and Mailchimp's efforts to serve its needs for customer relationships and education processes. Overall, this case study is a concise overview of the partnership that manages to convey success data and tell a story at the same time. What sets it apart is that it does so in a uniquely colorful and brand-consistent manner.
Takeaway: Be concise to provide as much value in as little text as possible.
10. NVIDIA and Workday
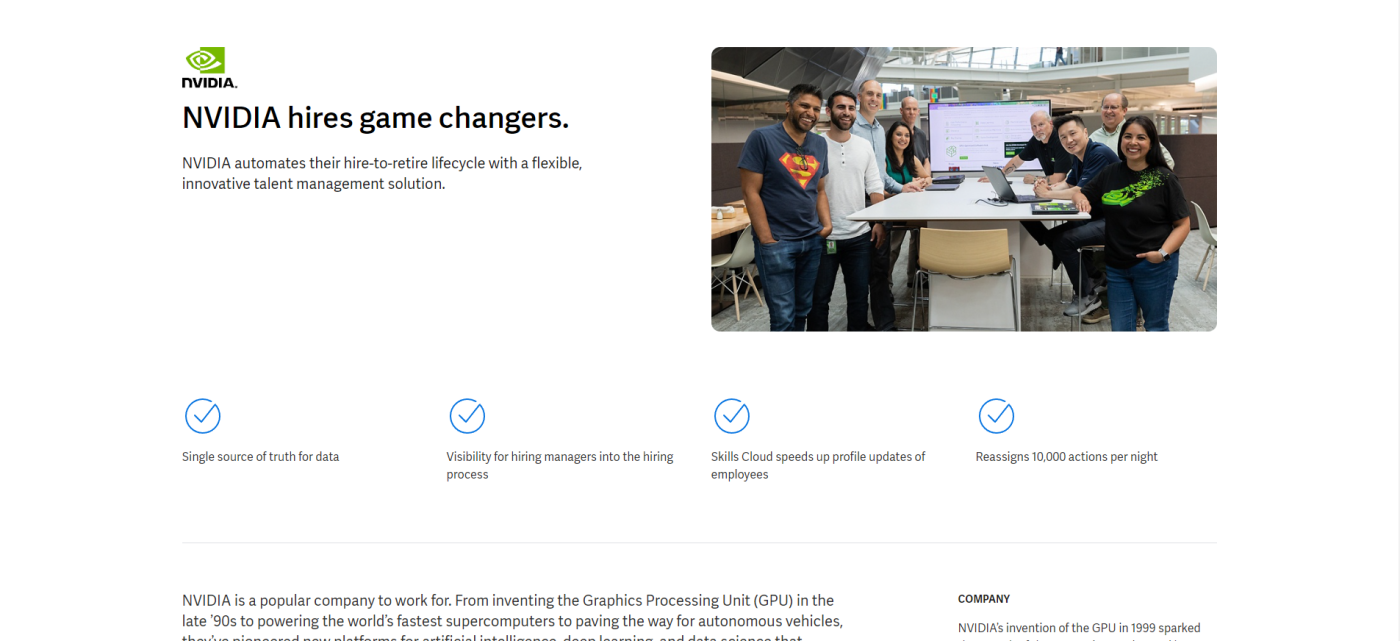
The gaming industry is notoriously difficult to recruit for, as it requires a very specific set of skills and experience. This case study focuses on how Workday was able to help fill that recruitment gap for NVIDIA, one of the biggest names in the gaming world.
Though it doesn't feature videos or graphics, this case study stood out to me in how it structures information like "key products used" to give readers insight into which tools helped achieve these results.
Takeaway: If your company offers multiple products or services, outline exactly which ones were involved in your case study, so readers can assess each tool.
11. KFC and Contentful
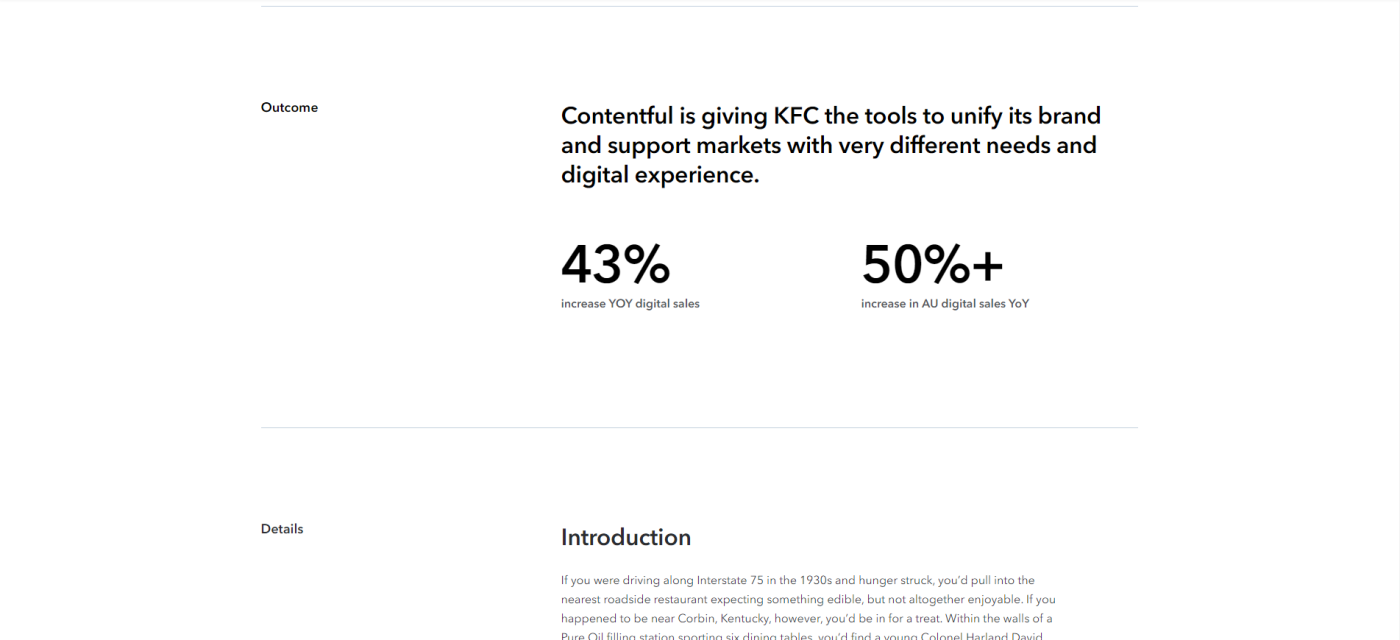
I'm personally not a big KFC fan, but that's only because I refuse to eat out of a bucket. My aversion to the bucket format aside, Contentful follows its consistent case study format in this one, outlining challenges, solutions, and outcomes before diving into the nitty-gritty details of the project.
Say what you will about KFC, but their primary product (chicken) does present a unique opportunity for wordplay like "Continuing to march to the beat of a digital-first drum(stick)" or "Delivering deep-fried goodness to every channel."
Takeaway: Inject humor into your case study if there's room for it and if it fits your brand.
12. Intuit and Twilio

Twilio does an excellent job of delivering achievements at the very beginning of the case study and going into detail in this two-minute read. While there aren't many graphics, the way quotes from the Intuit team are implemented adds a certain flair to the study and breaks up the sections nicely.
It's simple, concise, and manages to fit a lot of information in easily digestible sections.
Takeaway: Make sure each section is long enough to inform but brief enough to avoid boring readers. Break down information for each section, and don't go into so much detail that you lose the reader halfway through.
13. Spotify and Salesforce

Salesforce created a video that accurately summarizes the key points of the case study. Beyond that, the page itself is very light on content, and sections are as short as one paragraph.
I especially like how information is broken down into "What you need to know," "Why it matters," and "What the difference looks like." I'm not ashamed of being spoon-fed information. When it's structured so well and so simply, it makes for an entertaining read.
Takeaway: Invest in videos that capture and promote your partnership with your case study subject. Video content plays a promotional role that extends beyond the case study in social media and marketing initiatives .
14. Benchling and Airtable

Benchling is an impressive entity in its own right. Biotech R&D and health care nuances go right over my head. But the research and digging I've been doing in the name of these burritos (case studies) revealed that these products are immensely complex.
And that's precisely why this case study deserves a read—it succeeds at explaining a complex project that readers outside the industry wouldn't know much about.
Takeaway: Simplify complex information, and walk readers through the company's operations and how your business helped streamline them.
15. Chipotle and Hubble

The concision of this case study is refreshing. It features two sections—the challenge and the solution—all in 316 words. This goes to show that your case study doesn't necessarily need to be a four-figure investment with video shoots and studio time.
Sometimes, the message is simple and short enough to convey in a handful of paragraphs.
Takeaway: Consider what you should include instead of what you can include. Assess the time, resources, and effort you're able and willing to invest in a case study, and choose which elements you want to include from there.
16. Hudl and Zapier
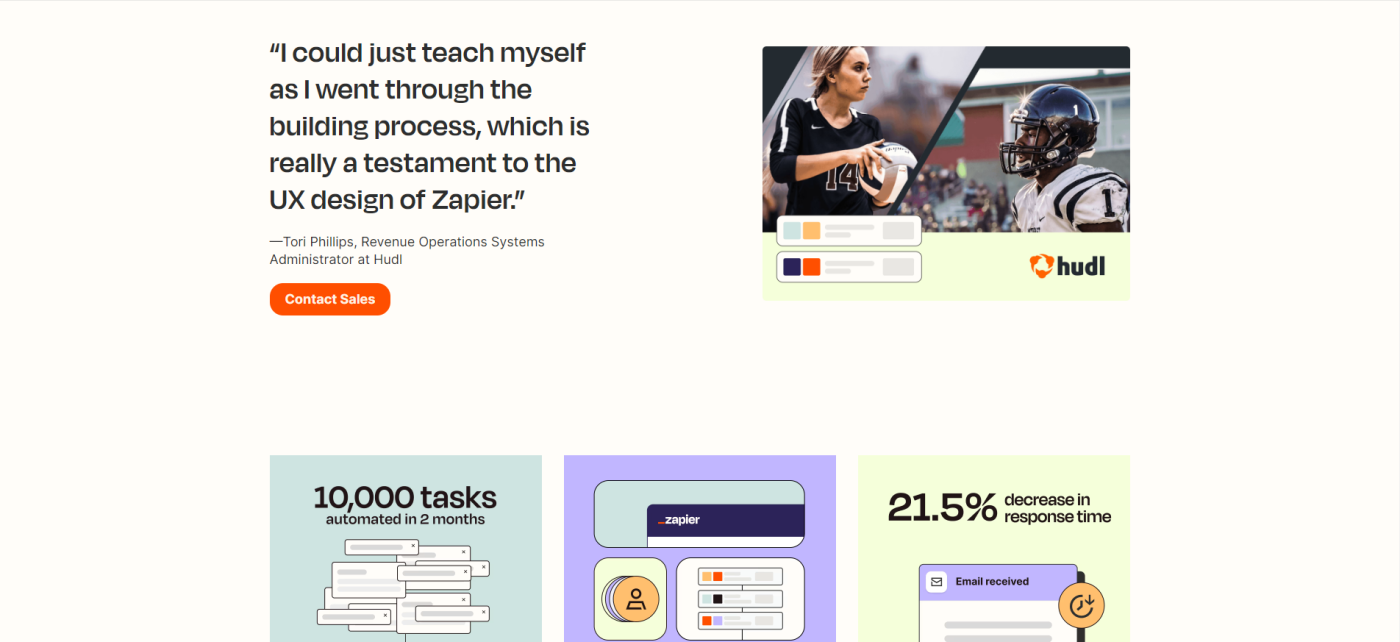
I may be biased, but I'm a big fan of seeing metrics and achievements represented in branded graphics. It can be a jarring experience to navigate a website, then visit a case study page and feel as though you've gone to a completely different website.
The Zapier format provides nuggets of high-level insights, milestones, and achievements, as well as the challenge, solution, and results. My favorite part of this case study is how it's supplemented with a blog post detailing how Hudl uses Zapier automation to build a seamless user experience.
The case study is essentially the summary, and the blog article is the detailed analysis that provides context beyond X achievement or Y goal.
Takeaway: Keep your case study concise and informative. Create other resources to provide context under your blog, media or press, and product pages.
3 case study templates
Now that you've had your fill of case studies (if that's possible), I've got just what you need: an infinite number of case studies, which you can create yourself with these case study templates.
Case study template 1

If you've got a quick hit of stats you want to show off, try this template. The opening section gives space for a short summary and three visually appealing stats you can highlight, followed by a headline and body where you can break the case study down more thoroughly. This one's pretty simple, with only sections for solutions and results, but you can easily continue the formatting to add more sections as needed.
Case study template 2

For a case study template with a little more detail, use this one. Opening with a striking cover page for a quick overview, this one goes on to include context, stakeholders, challenges, multiple quote callouts, and quick-hit stats.
Case study template 3

Whether you want a little structural variation or just like a nice dark green, this template has similar components to the last template but is designed to help tell a story. Move from the client overview through a description of your company before getting to the details of how you fixed said company's problems.
Tips for writing a case study
Examples are all well and good, but you don't learn how to make a burrito just by watching tutorials on YouTube without knowing what any of the ingredients are. You could , but it probably wouldn't be all that good.
Writing a good case study comes down to a mix of creativity, branding, and the capacity to invest in the project. With those details in mind, here are some case study tips to follow:
Have an objective: Define your objective by identifying the challenge, solution, and results. Assess your work with the client and focus on the most prominent wins. You're speaking to multiple businesses and industries through the case study, so make sure you know what you want to say to them.
Focus on persuasive data: Growth percentages and measurable results are your best friends. Extract your most compelling data and highlight it in your case study.
Use eye-grabbing graphics: Branded design goes a long way in accurately representing your brand and retaining readers as they review the study. Leverage unique and eye-catching graphics to keep readers engaged.
Simplify data presentation: Some industries are more complex than others, and sometimes, data can be difficult to understand at a glance. Make sure you present your data in the simplest way possible. Make it concise, informative, and easy to understand.
Use automation to drive results for your case study
A case study example is a source of inspiration you can leverage to determine how to best position your brand's work. Find your unique angle, and refine it over time to help your business stand out. Ask anyone: the best burrito in town doesn't just appear at the number one spot. They find their angle (usually the house sauce) and leverage it to stand out.
In fact, with the right technology, it can be refined to work better . Explore how Zapier's automation features can help drive results for your case study by making your case study a part of a developed workflow that creates a user journey through your website, your case studies, and into the pipeline.
Case study FAQ
Got your case study template? Great—it's time to gather the team for an awkward semi-vague data collection task. While you do that, here are some case study quick answers for you to skim through while you contemplate what to call your team meeting.
What is an example of a case study?
An example of a case study is when a software company analyzes its results from a client project and creates a webpage, presentation, or document that focuses on high-level results, challenges, and solutions in an attempt to showcase effectiveness and promote the software.
How do you write a case study?
To write a good case study, you should have an objective, identify persuasive and compelling data, leverage graphics, and simplify data. Case studies typically include an analysis of the challenge, solution, and results of the partnership.
What is the format of a case study?
While case studies don't have a set format, they're often portrayed as reports or essays that inform readers about the partnership and its results.
Related reading:
How Hudl uses automation to create a seamless user experience
How to make your case studies high-stakes—and why it matters
How experts write case studies that convert, not bore
Get productivity tips delivered straight to your inbox
We’ll email you 1-3 times per week—and never share your information.

Hachem Ramki
Hachem is a writer and digital marketer from Montreal. After graduating with a degree in English, Hachem spent seven years traveling around the world before moving to Canada. When he's not writing, he enjoys Basketball, Dungeons and Dragons, and playing music for friends and family.
- Content marketing
Related articles
10 examples of ethos in advertising to inspire your next campaign
10 examples of ethos in advertising to...

17 testimonial advertising examples to inspire your next campaign
17 testimonial advertising examples to...

B2B email marketing: Proven strategies and examples
B2B email marketing: Proven strategies and...

10 social media advertising examples to inspire your next campaign
10 social media advertising examples to...
Improve your productivity automatically. Use Zapier to get your apps working together.


Top 40 Most Popular Case Studies of 2021
Two cases about Hertz claimed top spots in 2021's Top 40 Most Popular Case Studies
Two cases on the uses of debt and equity at Hertz claimed top spots in the CRDT’s (Case Research and Development Team) 2021 top 40 review of cases.
Hertz (A) took the top spot. The case details the financial structure of the rental car company through the end of 2019. Hertz (B), which ranked third in CRDT’s list, describes the company’s struggles during the early part of the COVID pandemic and its eventual need to enter Chapter 11 bankruptcy.
The success of the Hertz cases was unprecedented for the top 40 list. Usually, cases take a number of years to gain popularity, but the Hertz cases claimed top spots in their first year of release. Hertz (A) also became the first ‘cooked’ case to top the annual review, as all of the other winners had been web-based ‘raw’ cases.
Besides introducing students to the complicated financing required to maintain an enormous fleet of cars, the Hertz cases also expanded the diversity of case protagonists. Kathyrn Marinello was the CEO of Hertz during this period and the CFO, Jamere Jackson is black.
Sandwiched between the two Hertz cases, Coffee 2016, a perennial best seller, finished second. “Glory, Glory, Man United!” a case about an English football team’s IPO made a surprise move to number four. Cases on search fund boards, the future of malls, Norway’s Sovereign Wealth fund, Prodigy Finance, the Mayo Clinic, and Cadbury rounded out the top ten.
Other year-end data for 2021 showed:
- Online “raw” case usage remained steady as compared to 2020 with over 35K users from 170 countries and all 50 U.S. states interacting with 196 cases.
- Fifty four percent of raw case users came from outside the U.S..
- The Yale School of Management (SOM) case study directory pages received over 160K page views from 177 countries with approximately a third originating in India followed by the U.S. and the Philippines.
- Twenty-six of the cases in the list are raw cases.
- A third of the cases feature a woman protagonist.
- Orders for Yale SOM case studies increased by almost 50% compared to 2020.
- The top 40 cases were supervised by 19 different Yale SOM faculty members, several supervising multiple cases.
CRDT compiled the Top 40 list by combining data from its case store, Google Analytics, and other measures of interest and adoption.
All of this year’s Top 40 cases are available for purchase from the Yale Management Media store .
And the Top 40 cases studies of 2021 are:
1. Hertz Global Holdings (A): Uses of Debt and Equity
2. Coffee 2016
3. Hertz Global Holdings (B): Uses of Debt and Equity 2020
4. Glory, Glory Man United!
5. Search Fund Company Boards: How CEOs Can Build Boards to Help Them Thrive
6. The Future of Malls: Was Decline Inevitable?
7. Strategy for Norway's Pension Fund Global
8. Prodigy Finance
9. Design at Mayo
10. Cadbury
11. City Hospital Emergency Room
13. Volkswagen
14. Marina Bay Sands
15. Shake Shack IPO
16. Mastercard
17. Netflix
18. Ant Financial
19. AXA: Creating the New CR Metrics
20. IBM Corporate Service Corps
21. Business Leadership in South Africa's 1994 Reforms
22. Alternative Meat Industry
23. Children's Premier
24. Khalil Tawil and Umi (A)
25. Palm Oil 2016
26. Teach For All: Designing a Global Network
27. What's Next? Search Fund Entrepreneurs Reflect on Life After Exit
28. Searching for a Search Fund Structure: A Student Takes a Tour of Various Options
30. Project Sammaan
31. Commonfund ESG
32. Polaroid
33. Connecticut Green Bank 2018: After the Raid
34. FieldFresh Foods
35. The Alibaba Group
36. 360 State Street: Real Options
37. Herman Miller
38. AgBiome
39. Nathan Cummings Foundation
40. Toyota 2010
7 Favorite Business Case Studies to Teach—and Why
Explore more.
- Case Teaching
- Course Materials
FEATURED CASE STUDIES
The Army Crew Team . Emily Michelle David of CEIBS
ATH Technologies . Devin Shanthikumar of Paul Merage School of Business
Fabritek 1992 . Rob Austin of Ivey Business School
Lincoln Electric Co . Karin Schnarr of Wilfrid Laurier University
Pal’s Sudden Service—Scaling an Organizational Model to Drive Growth . Gary Pisano of Harvard Business School
The United States Air Force: ‘Chaos’ in the 99th Reconnaissance Squadron . Francesca Gino of Harvard Business School
Warren E. Buffett, 2015 . Robert F. Bruner of Darden School of Business
To dig into what makes a compelling case study, we asked seven experienced educators who teach with—and many who write—business case studies: “What is your favorite case to teach and why?”
The resulting list of case study favorites ranges in topics from operations management and organizational structure to rebel leaders and whodunnit dramas.
1. The Army Crew Team
Emily Michelle David, Assistant Professor of Management, China Europe International Business School (CEIBS)

“I love teaching The Army Crew Team case because it beautifully demonstrates how a team can be so much less than the sum of its parts.
I deliver the case to executives in a nearby state-of-the-art rowing facility that features rowing machines, professional coaches, and shiny red eight-person shells.
After going through the case, they hear testimonies from former members of Chinese national crew teams before carrying their own boat to the river for a test race.
The rich learning environment helps to vividly underscore one of the case’s core messages: competition can be a double-edged sword if not properly managed.
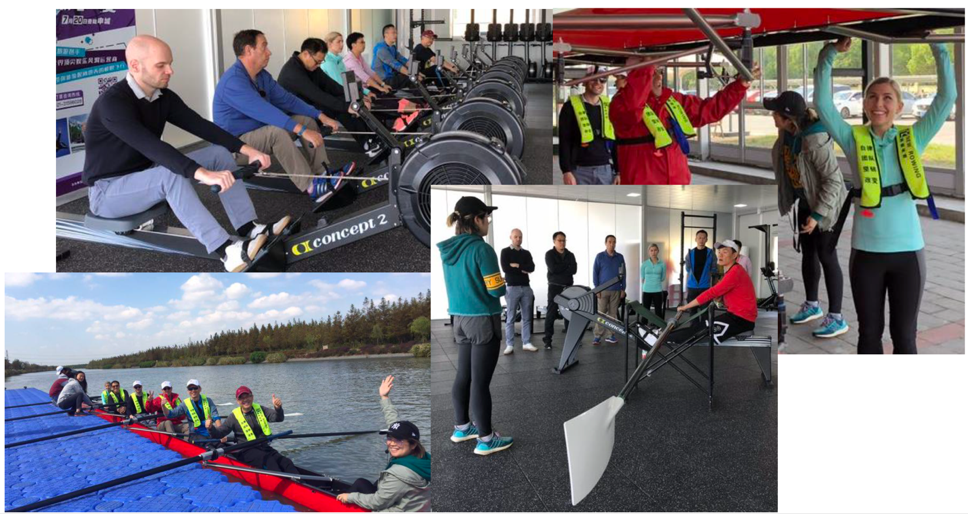

Executives in Emily Michelle David’s organizational behavior class participate in rowing activities at a nearby facility as part of her case delivery.
Despite working for an elite headhunting firm, the executives in my most recent class were surprised to realize how much they’ve allowed their own team-building responsibilities to lapse. In the MBA pre-course, this case often leads to a rich discussion about common traps that newcomers fall into (for example, trying to do too much, too soon), which helps to poise them to both stand out in the MBA as well as prepare them for the lateral team building they will soon engage in.
Finally, I love that the post-script always gets a good laugh and serves as an early lesson that organizational behavior courses will seldom give you foolproof solutions for specific problems but will, instead, arm you with the ability to think through issues more critically.”
2. ATH Technologies
Devin Shanthikumar, Associate Professor of Accounting, Paul Merage School of Business

“As a professor at UC Irvine’s Paul Merage School of Business, and before that at Harvard Business School, I have probably taught over 100 cases. I would like to say that my favorite case is my own, Compass Box Whisky Company . But as fun as that case is, one case beats it: ATH Technologies by Robert Simons and Jennifer Packard.
ATH presents a young entrepreneurial company that is bought by a much larger company. As part of the merger, ATH gets an ‘earn-out’ deal—common among high-tech industries. The company, and the class, must decide what to do to achieve the stretch earn-out goals.
ATH captures a scenario we all want to be in at some point in our careers—being part of a young, exciting, growing organization. And a scenario we all will likely face—having stretch goals that seem almost unreachable.
It forces us, as a class, to really struggle with what to do at each stage.
After we read and discuss the A case, we find out what happens next, and discuss the B case, then the C, then D, and even E. At every stage, we can:
see how our decisions play out,
figure out how to build on our successes, and
address our failures.
The case is exciting, the class discussion is dynamic and energetic, and in the end, we all go home with a memorable ‘ah-ha!’ moment.
I have taught many great cases over my career, but none are quite as fun, memorable, and effective as ATH .”
3. Fabritek 1992
Rob Austin, Professor of Information Systems, Ivey Business School

“This might seem like an odd choice, but my favorite case to teach is an old operations case called Fabritek 1992 .
The latest version of Fabritek 1992 is dated 2009, but it is my understanding that this is a rewrite of a case that is older (probably much older). There is a Fabritek 1969 in the HBP catalog—same basic case, older dates, and numbers. That 1969 version lists no authors, so I suspect the case goes even further back; the 1969 version is, I’m guessing, a rewrite of an even older version.
There are many things I appreciate about the case. Here are a few:
It operates as a learning opportunity at many levels. At first it looks like a not-very-glamorous production job scheduling case. By the end of the case discussion, though, we’re into (operations) strategy and more. It starts out technical, then explodes into much broader relevance. As I tell participants when I’m teaching HBP's Teaching with Cases seminars —where I often use Fabritek as an example—when people first encounter this case, they almost always underestimate it.
It has great characters—especially Arthur Moreno, who looks like a troublemaker, but who, discussion reveals, might just be the smartest guy in the factory. Alums of the Harvard MBA program have told me that they remember Arthur Moreno many years later.
Almost every word in the case is important. It’s only four and a half pages of text and three pages of exhibits. This economy of words and sparsity of style have always seemed like poetry to me. I should note that this super concise, every-word-matters approach is not the ideal we usually aspire to when we write cases. Often, we include extra or superfluous information because part of our teaching objective is to provide practice in separating what matters from what doesn’t in a case. Fabritek takes a different approach, though, which fits it well.
It has a dramatic structure. It unfolds like a detective story, a sort of whodunnit. Something is wrong. There is a quality problem, and we’re not sure who or what is responsible. One person, Arthur Moreno, looks very guilty (probably too obviously guilty), but as we dig into the situation, there are many more possibilities. We spend in-class time analyzing the data (there’s a bit of math, so it covers that base, too) to determine which hypotheses are best supported by the data. And, realistically, the data doesn’t support any of the hypotheses perfectly, just some of them more than others. Also, there’s a plot twist at the end (I won’t reveal it, but here’s a hint: Arthur Moreno isn’t nearly the biggest problem in the final analysis). I have had students tell me the surprising realization at the end of the discussion gives them ‘goosebumps.’
Finally, through the unexpected plot twist, it imparts what I call a ‘wisdom lesson’ to young managers: not to be too sure of themselves and to regard the experiences of others, especially experts out on the factory floor, with great seriousness.”
4. Lincoln Electric Co.
Karin Schnarr, Assistant Professor of Policy, Wilfrid Laurier University

“As a strategy professor, my favorite case to teach is the classic 1975 Harvard case Lincoln Electric Co. by Norman Berg.
I use it to demonstrate to students the theory linkage between strategy and organizational structure, management processes, and leadership behavior.
This case may be an odd choice for a favorite. It occurs decades before my students were born. It is pages longer than we are told students are now willing to read. It is about manufacturing arc welding equipment in Cleveland, Ohio—a hard sell for a Canadian business classroom.
Yet, I have never come across a case that so perfectly illustrates what I want students to learn about how a company can be designed from an organizational perspective to successfully implement its strategy.
And in a time where so much focus continues to be on how to maximize shareholder value, it is refreshing to be able to discuss a publicly-traded company that is successfully pursuing a strategy that provides a fair value to shareholders while distributing value to employees through a large bonus pool, as well as value to customers by continually lowering prices.
However, to make the case resonate with today’s students, I work to make it relevant to the contemporary business environment. I link the case to multimedia clips about Lincoln Electric’s current manufacturing practices, processes, and leadership practices. My students can then see that a model that has been in place for generations is still viable and highly successful, even in our very different competitive situation.”
5. Pal’s Sudden Service—Scaling an Organizational Model to Drive Growth
Gary Pisano, Professor of Business Administration, Harvard Business School

“My favorite case to teach these days is Pal’s Sudden Service—Scaling an Organizational Model to Drive Growth .
I love teaching this case for three reasons:
1. It demonstrates how a company in a super-tough, highly competitive business can do very well by focusing on creating unique operating capabilities. In theory, Pal’s should have no chance against behemoths like McDonalds or Wendy’s—but it thrives because it has built a unique operating system. It’s a great example of a strategic approach to operations in action.
2. The case shows how a strategic approach to human resource and talent development at all levels really matters. This company competes in an industry not known for engaging its front-line workers. The case shows how engaging these workers can really pay off.
3. Finally, Pal’s is really unusual in its approach to growth. Most companies set growth goals (usually arbitrary ones) and then try to figure out how to ‘backfill’ the human resource and talent management gaps. They trust you can always find someone to do the job. Pal’s tackles the growth problem completely the other way around. They rigorously select and train their future managers. Only when they have a manager ready to take on their own store do they open a new one. They pace their growth off their capacity to develop talent. I find this really fascinating and so do the students I teach this case to.”
6. The United States Air Force: ‘Chaos’ in the 99th Reconnaissance Squadron
Francesca Gino, Professor of Business Administration, Harvard Business School

“My favorite case to teach is The United States Air Force: ‘Chaos’ in the 99th Reconnaissance Squadron .
The case surprises students because it is about a leader, known in the unit by the nickname Chaos , who inspired his squadron to be innovative and to change in a culture that is all about not rocking the boat, and where there is a deep sense that rules should simply be followed.
For years, I studied ‘rebels,’ people who do not accept the status quo; rather, they approach work with curiosity and produce positive change in their organizations. Chaos is a rebel leader who got the level of cultural change right. Many of the leaders I’ve met over the years complain about the ‘corporate culture,’ or at least point to clear weaknesses of it; but then they throw their hands up in the air and forget about changing what they can.
Chaos is different—he didn’t go after the ‘Air Force’ culture. That would be like boiling the ocean.
Instead, he focused on his unit of control and command: The 99th squadron. He focused on enabling that group to do what it needed to do within the confines of the bigger Air Force culture. In the process, he inspired everyone on his team to be the best they can be at work.
The case leaves the classroom buzzing and inspired to take action.”
7. Warren E. Buffett, 2015
Robert F. Bruner, Professor of Business Administration, Darden School of Business

“I love teaching Warren E. Buffett, 2015 because it energizes, exercises, and surprises students.
Buffett looms large in the business firmament and therefore attracts anyone who is eager to learn his secrets for successful investing. This generates the kind of energy that helps to break the ice among students and instructors early in a course and to lay the groundwork for good case discussion practices.
Studying Buffett’s approach to investing helps to introduce and exercise important themes that will resonate throughout a course. The case challenges students to define for themselves what it means to create value. The case discussion can easily be tailored for novices or for more advanced students.
Either way, this is not hero worship: The case affords a critical examination of the financial performance of Buffett’s firm, Berkshire Hathaway, and reveals both triumphs and stumbles. Most importantly, students can critique the purported benefits of Buffett’s conglomeration strategy and the sustainability of his investment record as the size of the firm grows very large.
By the end of the class session, students seem surprised with what they have discovered. They buzz over the paradoxes in Buffett’s philosophy and performance record. And they come away with sober respect for Buffett’s acumen and for the challenges of creating value for investors.
Surely, such sobriety is a meta-message for any mastery of finance.”
More Educator Favorites

Emily Michelle David is an assistant professor of management at China Europe International Business School (CEIBS). Her current research focuses on discovering how to make workplaces more welcoming for people of all backgrounds and personality profiles to maximize performance and avoid employee burnout. David’s work has been published in a number of scholarly journals, and she has worked as an in-house researcher at both NASA and the M.D. Anderson Cancer Center.

Devin Shanthikumar is an associate professor and the accounting area coordinator at UCI Paul Merage School of Business. She teaches undergraduate, MBA, and executive-level courses in managerial accounting. Shanthikumar previously served on the faculty at Harvard Business School, where she taught both financial accounting and managerial accounting for MBAs, and wrote cases that are used in accounting courses across the country.

Robert D. Austin is a professor of information systems at Ivey Business School and an affiliated faculty member at Harvard Medical School. He has published widely, authoring nine books, more than 50 cases and notes, three Harvard online products, and two popular massive open online courses (MOOCs) running on the Coursera platform.

Karin Schnarr is an assistant professor of policy and the director of the Bachelor of Business Administration (BBA) program at the Lazaridis School of Business & Economics at Wilfrid Laurier University in Waterloo, Ontario, Canada where she teaches strategic management at the undergraduate, graduate, and executive levels. Schnarr has published several award-winning and best-selling cases and regularly presents at international conferences on case writing and scholarship.

Gary P. Pisano is the Harry E. Figgie, Jr. Professor of Business Administration and senior associate dean of faculty development at Harvard Business School, where he has been on the faculty since 1988. Pisano is an expert in the fields of technology and operations strategy, the management of innovation, and competitive strategy. His research and consulting experience span a range of industries including aerospace, biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, specialty chemicals, health care, nutrition, computers, software, telecommunications, and semiconductors.

Francesca Gino studies how people can have more productive, creative, and fulfilling lives. She is a professor at Harvard Business School and the author, most recently, of Rebel Talent: Why It Pays to Break the Rules at Work and in Life . Gino regularly gives keynote speeches, delivers corporate training programs, and serves in advisory roles for firms and not-for-profit organizations across the globe.

Robert F. Bruner is a university professor at the University of Virginia, distinguished professor of business administration, and dean emeritus of the Darden School of Business. He has also held visiting appointments at Harvard and Columbia universities in the United States, at INSEAD in France, and at IESE in Spain. He is the author, co-author, or editor of more than 20 books on finance, management, and teaching. Currently, he teaches and writes in finance and management.
Related Articles

We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience, including personalizing content. Learn More . By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .

- Testimonial
- Web Stories
Learning Home

Not Now! Will rate later

MBA Case Studies - Solved Examples


Need of MBA Case Studies
Case i: chemco case.
- ChemCo is a quality leader in the U.K. car batteries market.
- Customer battery purchases in the automobile market are highly seasonal.
- The fork-lift business was added to utilize idle capacity during periods of inactivity.
- This is a low-growth industry (1% annual growth over the last two years)
- Large customers are sophisticated and buy based on price and quality. Smaller customers buy solely on price.
- There is a Spanish competitor in the market who offers low priced batteries of inferior quality.

Essential MBA GD Guide: Key Topics with Strategies Free
- Importance of Group Discussions
- Tips and Strategies to handle a GD
- Top 25 GD topics
- Free Download
- Established player in car batteries
- Losing heavily in fork-lift truck batteries
- Old fashioned owner resistance to change
- Low priced competitors
- Foreign competitors gaining market share
- Decisive Interview, GD & Essay prep
- GD: Topics 2021
- GD: Approach
- GD: Do's and Don'ts
- GD: Communications
- Solved GDs Topics
GD Introduction
- Types of GD topics: Techniques
- GD: Ettiquette
- GD: Content
- Solved Case Studies
- High quality product, but low end customers care more about price than quality
- Mismanaged product diversification in a price sensitive market
- Alternative 1: Establish an Off-Brand for the fork-lift business
- Alternative 2: Educate the customer market about product quality
- Alternative 3: Exit the fork-lift battery business
- Establishing the firm's quality image
- Increase in market share
- Increase in sales
- Cost of the product
- Protect firm's quality image in the automobile industry
- Redesigned product to reduce the cost of manufacture
- Low price to enable it to compete with Spanish producer
- Make use of the quality leadership in car batteries market
- Offer reliability testing, extended warranties etc. to promote quality image
- Set higher prices to extract surplus from these advantages
- A passive strategy, not proactive
- Recommendations: Alternative 1 is recommended in this case. Since the firm operates in an industry which has low growth, hence it can expand market share and sales only by taking the customers from other players. Hence, it needs to tackle the Spanish competitor head-on by aggressively pricing its product. At the same time, launching a low-priced product under the same brand name erodes the high quality image in the car batteries market. Hence, the best option is to go for an off-brand to target the fork-lift customers who are increasingly becoming price sensitive. This will enable the company to ward off the threat in short-term and build its position strongly in the long-term.

Case II: NAKAMURA LACQUER COMPANY
- The Nakamura Lacquer Company: The Nakamura Lacquer Company based in Kyoto, Japan was one of the many small handicraft shops making lacquerware for the daily table use of the Japanese people.
- Mr. Nakamura- the personality: In 1948, a young Mr. Nakamura took over his family business. He saw an opportunity to cater to a new market of America, i.e. GI's of the Occupation Army who had begun to buy lacquer ware as souvenirs. However, he realized that the traditional handicraft methods were inadequate. He was an innovator and introduced simple methods of processing and inspection using machines. Four years later, when the Occupation Army left in 1952, Nakamura employed several thousand men, and produced 500,000 pieces of lacquers tableware each year for the Japanese mass consumer market. The profit from operations was $250,000.
- The Brand: Nakamura named his brand “Chrysanthemum” after the national flower of Japan, which showed his patriotic fervor. The brand became Japan's best known and best selling brand, being synonymous with good quality, middle class and dependability.
- The Market: The market for lacquerware in Japan seems to have matured, with the production steady at 500,000 pieces a year. Nakamura did practically no business outside of Japan. However, early in 1960, when the American interest in Japanese products began to grow, Nakamura received two offers
- The Rose and Crown offer: The first offer was from Mr. Phil Rose, V.P Marketing at the National China Company. They were the largest manufacturer of good quality dinnerware in the U.S., with their “Rose and Crown” brand accounting for almost 30% of total sales. They were willing to give a firm order for three eyes for annual purchases of 400,000 sets of lacquer dinnerware, delivered in Japan and at 5% more than what the Japanese jobbers paid. However, Nakamura would have to forego the Chrysanthemum trademark to “Rose and Crown” and also undertaken to sell lacquer ware to anyone else the U.S. The offer promised returns of $720,000 over three years (with net returns of $83,000), but with little potential for the U.S. market on the Chrysanthemum brand beyond that period.
- The Semmelback offer: The second offer was from Mr. Walter Sammelback of Sammelback, Sammelback and Whittacker, Chicago, the largest supplier of hotel and restaurant supplies in the U.S. They perceived a U.S. market of 600,000 sets a year, expecting it to go up to 2 million in around 5 years. Since the Japanese government did not allow overseas investment, Sammelback was willing to budget $1.5 million. Although the offer implied negative returns of $467,000 over the first five years, the offer had the potential to give a $1 million profit if sales picked up as anticipated.
- Meeting the order: To meet the numbers requirement of the orders, Nakamura would either have to expand capacity or cut down on the domestic market. If he chose to expand capacity, the danger was of idle capacity in case the U.S. market did not respond. If he cut down on the domestic market, the danger was of losing out on a well-established market. Nakamura could also source part of the supply from other vendors. However, this option would not find favor with either of the American buyers since they had approached only Nakamura, realizing that he was the best person to meet the order.
- Decision problem: Whether to accept any of the two offers and if yes, which one of the two and under what terms of conditions?
- To expand into the U.S. market.
- To maintain and build upon their reputation of the “Chrysanthemum” brand
- To increase profit volumes by tapping the U.S. market and as a result, increasing scale of operations.
- To increase its share in the U.S. lacquerware market.
- Profit Maximization criterion: The most important criterion in the long run is profit maximization.
- Risk criterion: Since the demand in the U.S. market is not as much as in Japan.
- Brand identity criterion: Nakamura has painstakingly built up a brand name in Japan. It is desirable for him to compete in the U.S. market under the same brand name
- Flexibility criterion: The chosen option should offer Nakamura flexibility in maneuvering the terms and conditions to his advantage. Additionally, Nakamura should have bargaining power at the time of renewal of the contract.
- Short term returns: Nakamura should receive some returns on the investment he makes on the new offers. However, this criterion may be compromised in favor of profit maximization in the long run.?
- Reject both: React both the offers and concentrate on the domestic market
- Accept RC offer: Accept the Rose and Crown offer and supply the offer by cutting down on supplies to the domestic market or through capacity expansion or both
- Accept SSW: offer; accept the SSW offer and meet it through cutting down on supply to the domestic market or through capacity expansion or both. Negotiate term of supply.
- Reject both: This option would not meet the primary criterion of profit maximization. Further, the objective of growth would also not be met. Hence, this option is rejected.
- Accept RC offer: The RC offer would assure net returns of $283,000 over the next three yeas. It also assures regular returns of $240,000 per year. However, Nakamura would have no presence in the U.S. with its Chrysanthemum brand name The RC offer would entail capacity expansion, as it would not be possible to siphon of 275,000 pieces from the domestic market over three years without adversely affecting operations there. At the end of three years, Nakamura would have little bargaining power with RC as it would have an excess capacity of 275,000 pieces and excess labor which it would want to utilize. In this sense the offer is risky. Further, the offer is not flexible. Long-term profit maximization is uncertain in this case a condition that can be controlled in the SSW offer. Hence, this offer is rejected.
- Accept SSW offer: The SSW offer does not assure a firm order or any returns for the period of contract. Although, in its present form the offer is risky if the market in the U.S. does not pick up as expected, the offer is flexible. If Nakamura were to exhibit caution initially by supplying only 300,000 instead of the anticipated 600,000 pieces, it could siphon off the 175,000 required from the domestic market. If demand exists in the U.S., the capacity can be expanded. With this offer, risk is minimized. Further, it would be competing on its own brand name. Distribution would be taken care of and long-term profit maximization criterion would be satisfied as this option has the potential of $1 million in profits per year. At the time of renewal of the contract, Nakamura would have immense bargaining power.
- Negotiate terms of offer with SSW: The terms would be that NLC would supply 300,000 pieces in the first year. If market demand exists, NLC should expand capacity to provide the expected demand.
- Action Plan: In the first phase, NLC would supply SSW with 300,000 pieces. 125,000 of these would be obtained by utilizing excess capacity, while the remaining would be obtained from the domestic market. If the expected demand for lacquer ware exists in the U.S., NLC would expand capacity to meet the expected demand. The debt incurred would be paid off by the fifth year.
- Contingency Plan: In case the demand is not as expected in the first year, NLC should not service the U.S. market and instead concentrate on increasing penetration in the domestic market.
FAQs about MBA Case Studies
- Group Discussions
- Personality
- Past Experiences
Most Popular Articles - PS

100 Group Discussion (GD) Topics for MBA 2024

Solved GDs Topic

Top 50 Other (Science, Economy, Environment) topics for GD
5 tips for starting a GD

GD FAQs: Communication

GD FAQs: Content

Stages of GD preparation

Group Discussion Etiquettes

Case Study: Tips and Strategy

Practice Case Studies: Long

Practice Case Studies: Short
5 tips for handling Abstract GD topics
5 tips for handling a fish market situation in GD
5 things to follow: if you don’t know much about the GD topic

Do’s and Don’ts in a Group Discussion
5 tips for handling Factual GD topics

How to prepare for Group Discussion
Download our app.
- Learn on-the-go
- Unlimited Prep Resources
- Better Learning Experience
- Personalized Guidance
Get More Out of Your Exam Preparation - Try Our App!
Business Case Studies
- Getting Started
- Case Analysis
- Finding Case Studies in the Library
Free Case Studies
- Buying Cases
- Writing Case Studies
- Case Competitions
- Case Interviews
- Case Method (Teaching)
Many academic and business institutions develop and publish case studies. Some of these organizations provide free access to their case studies:
- Acadia Institute of Case Studies Focuses on entrepreneurship and small business operations.
- Business Case Studies by Company
- Business Ethics Case Analyses
- Canadian Centre for Occupational Health & Safety: Workplace Health Case Studies
- Case Centre Available for a fee.
- Daniels Fund Ethics Initiative Case Studies
- Give to Get Marketing. Marketing and Advertising Case Studies
- HR Open Source Case Studies
- MarketingSherpa Choose "Case Studies" as the content type in the filters.
- MaRS Search for "case study" in the top right search box.
- MERLOT Business Cases
- MIT LearningEdge Case Studies Free case studies by MIT Sloan School of Management.
- Penske. Logistics Case Studies
- Society of Human Resources Management.
- Open Case Studies Project by UBC The Open Case Studies project at UBC brings together faculty and students from different disciplines to write, edit, and learn with case studies that are free and open.
- World's Best Case Studies Short video case studies covering topics including consumer goods, services, and technology.
- << Previous: Finding Case Studies in the Library
- Next: Buying Cases >>
- Last Updated: Jan 17, 2024 11:02 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.ubc.ca/businesscases
- Boston University Libraries
Business Case Studies
Open access cases.
- Getting Started
- Harvard Business School Cases
- Diverse Business Cases
- Databases with Cases
- Journals with Cases
- Books with Cases
- Case Analysis
- Case Interviews
- Case Method (Teaching)
- Writing Case Studies
- Citing Business Sources

A number of universities and organizations provide access to free business case studies. Below are some of the best known sources.

- << Previous: Books with Cases
- Next: Case Analysis >>
- Last Updated: Nov 17, 2023 12:09 PM
- URL: https://library.bu.edu/business-case-studies
- Contact sales
Start free trial
How to Write a Business Case (Template Included)

Table of Contents
What is a business case, how to write a business case, business case template, watch our business case training video, key elements of a business case, how projectmanager helps with your business case.
A business case is a project management document that explains how the benefits of a project overweigh its costs and why it should be executed. Business cases are prepared during the project initiation phase and their purpose is to include all the project’s objectives, costs and benefits to convince stakeholders of its value.
A business case is an important project document to prove to your client, customer or stakeholder that the project proposal you’re pitching is a sound investment. Below, we illustrate the steps to writing one that will sway them.
The need for a business case is that it collects the financial appraisal, proposal, strategy and marketing plan in one document and offers a full look at how the project will benefit the organization. Once your business case is approved by the project stakeholders, you can begin the project planning phase.
Projects fail without having a solid business case to rest on, as this project document is the base for the project charter and project plan. But if a project business case is not anchored to reality, and doesn’t address a need that aligns with the larger business objectives of the organization, then it is irrelevant.

Get your free
Use this free Business Case Template for Word to manage your projects better.
The research you’ll need to create a strong business case is the why, what, how and who of your project. This must be clearly communicated. The elements of your business case will address the why but in greater detail. Think of the business case as a document that is created during the project initiation phase but will be used as a reference throughout the project life cycle.
Whether you’re starting a new project or mid-way through one, take time to write up a business case to justify the project expenditure by identifying the business benefits your project will deliver and that your stakeholders are most interested in reaping from the work. The following four steps will show you how to write a business case.
Step 1: Identify the Business Problem
Projects aren’t created for projects’ sake. They should always be aligned with business goals . Usually, they’re initiated to solve a specific business problem or create a business opportunity.
You should “Lead with the need.” Your first job is to figure out what that problem or opportunity is, describe it, find out where it comes from and then address the time frame needed to deal with it.
This can be a simple statement but is best articulated with some research into the economic climate and the competitive landscape to justify the timing of the project.
Step 2: Identify the Alternative Solutions
How do you know whether the project you’re undertaking is the best possible solution to the problem defined above? Naturally, prioritizing projects is hard, and the path to success is not paved with unfounded assumptions.
One way to narrow down the focus to make the right solution clear is to follow these six steps (after the relevant research, of course):
- Note the alternative solutions.
- For each solution, quantify its benefits.
- Also, forecast the costs involved in each solution.
- Then figure out its feasibility .
- Discern the risks and issues associated with each solution.
- Finally, document all this in your business case.
Step 3: Recommend a Preferred Solution
You’ll next need to rank the solutions, but before doing that it’s best to set up criteria, maybe have a scoring mechanism such as a decision matrix to help you prioritize the solutions to best choose the right one.
Some methodologies you can apply include:
- Depending on the solution’s cost and benefit , give it a score of 1-10.
- Base your score on what’s important to you.
- Add more complexity to your ranking to cover all bases.
Regardless of your approach, once you’ve added up your numbers, the best solution to your problem will become evident. Again, you’ll want to have this process also documented in your business case.
Step 4: Describe the Implementation Approach
So, you’ve identified your business problem or opportunity and how to reach it, now you have to convince your stakeholders that you’re right and have the best way to implement a process to achieve your goals. That’s why documentation is so important; it offers a practical path to solve the core problem you identified.
Now, it’s not just an exercise to appease senior leadership. Who knows what you might uncover in the research you put into exploring the underlying problem and determining alternative solutions? You might save the organization millions with an alternate solution than the one initially proposed. When you put in the work on a strong business case, you’re able to get your sponsors or organizational leadership on board with you and have a clear vision as to how to ensure the delivery of the business benefits they expect.
Our business case template for Word is the perfect tool to start writing a business case. It has 9 key business case areas you can customize as needed. Download the template for free and follow the steps below to create a great business case for all your projects.
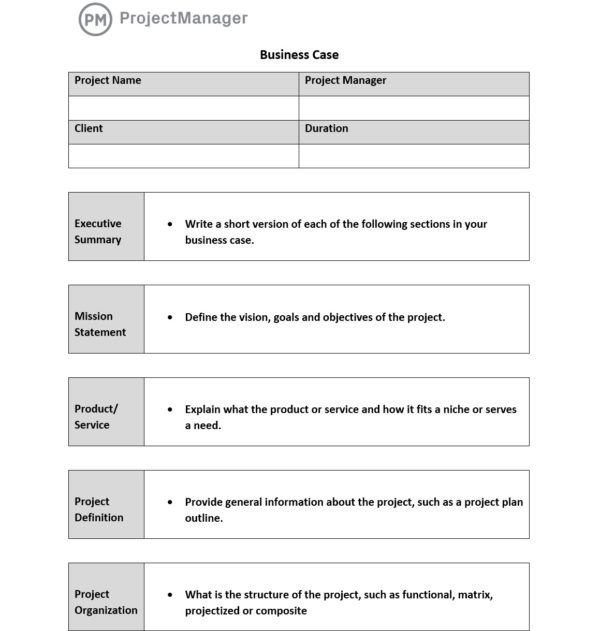
One of the key steps to starting a business case is to have a business case checklist. The following is a detailed outline to follow when developing your business case. You can choose which of these elements are the most relevant to your project stakeholders and add them to our business case template. Then once your business case is approved, start managing your projects with a robust project management software such as ProjectManager.
1. Executive Summary
The executive summary is a short version of each section of your business case. It’s used to give stakeholders a quick overview of your project.
2. Project Definition
This section is meant to provide general information about your projects, such as the business objectives that will be achieved and the project plan outline.
3. Vision, Goals and Objectives
First, you have to figure out what you’re trying to do and what is the problem you want to solve. You’ll need to define your project vision, goals and objectives. This will help you shape your project scope and identify project deliverables.
4. Project Scope
The project scope determines all the tasks and deliverables that will be executed in your project to reach your business objectives.
5. Background Information
Here you can provide a context for your project, explaining the problem that it’s meant to solve, and how it aligns with your organization’s vision and strategic plan.
6. Success Criteria and Stakeholder Requirements
Depending on what kind of project you’re working on, the quality requirements will differ, but they are critical to the project’s success. Collect all of them, figure out what determines if you’ve successfully met them and report on the results .
7. Project Plan
It’s time to create the project plan. Figure out the tasks you’ll have to take to get the project done. You can use a work breakdown structure template to make sure you are through. Once you have all the tasks collected, estimate how long it will take to complete each one.
Project management software makes creating a project plan significantly easier. ProjectManager can upload your work breakdown structure template and all your tasks are populated in our tool. You can organize them according to your production cycle with our kanban board view, or use our Gantt chart view to create a project schedule.
8. Project Budget
Your budget is an estimate of everything in your project plan and what it will cost to complete the project over the scheduled time allotted.
9. Project Schedule
Make a timeline for the project by estimating how long it will take to get each task completed. For a more impactful project schedule , use a tool to make a Gantt chart, and print it out. This will provide that extra flourish of data visualization and skill that Excel sheets lack.
10. Project Governance
Project governance refers to all the project management rules and procedures that apply to your project. For example, it defines the roles and responsibilities of the project team members and the framework for decision-making.
11. Communication Plan
Have milestones for check-ins and status updates, as well as determine how stakeholders will stay aware of the progress over the project life cycle.
12. Progress Reports
Have a plan in place to monitor and track your progress during the project to compare planned to actual progress. There are project tracking tools that can help you monitor progress and performance.
Again, using a project management tool improves your ability to see what’s happening in your project. ProjectManager has tracking tools like dashboards and status reports that give you a high-level view and more detail, respectively. Unlike light-weight apps that make you set up a dashboard, ours is embedded in the tool. Better still, our cloud-based software gives you real-time data for more insightful decision-making. Also, get reports on more than just status updates, but timesheets, workload, portfolio status and much more, all with just one click. Then filter the reports and share them with stakeholders to keep them updated.

13. Financial Appraisal
This is a very important section of your business case because this is where you explain how the financial benefits outweigh the project costs . Compare the financial costs and benefits of your project. You can do this by doing a sensitivity analysis and a cost-benefit analysis.
14. Market Assessment
Research your market, competitors and industry, to find opportunities and threats
15. Competitor Analysis
Identify direct and indirect competitors and do an assessment of their products, strengths, competitive advantages and their business strategy.
16. SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis helps you identify your organization’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. The strengths and weaknesses are internal, while the opportunities and threats are external.
17. Marketing Strategy
Describe your product, distribution channels, pricing, target customers among other aspects of your marketing plan or strategy.
18. Risk Assessment
There are many risk categories that can impact your project. The first step to mitigating them is to identify and analyze the risks associated with your project activities.
ProjectManager , an award-winning project management software, can collect and assemble all the various data you’ll be collecting, and then easily share it both with your team and project sponsors.
Once you have a spreadsheet with all your tasks listed, you can import it into our software. Then it’s instantly populated into a Gantt chart . Simply set the duration for each of the tasks, add any dependencies, and your project is now spread across a timeline. You can set milestones, but there is so much more you can do.
You have a project plan now, and from the online Gantt chart, you can assign team members to tasks. Then they can comment directly on the tasks they’re working on, adding as many documents and images as needed, fostering a collaborative environment. You can track their progress and change task durations as needed by dragging and dropping the start and end dates.
But that’s only a taste of what ProjectManager offers. We have kanban boards that visualize your workflow and a real-time dashboard that tracks six project metrics for the most accurate view of your project possible.
Try ProjectManager and see for yourself with this 30-day free trial .
If you want more business case advice, take a moment to watch Jennifer Bridges, PMP, in this short training video. She explains the steps you have to take in order to write a good business case.
Here’s a screenshot for your reference.

Transcription:
Today we’re talking about how to write a business case. Well, over the past few years, we’ve seen the market, or maybe organizations, companies or even projects, move away from doing business cases. But, these days, companies, organizations, and those same projects are scrutinizing the investments and they’re really seeking a rate of return.
So now, think of the business case as your opportunity to package your project, your idea, your opportunity, and show what it means and what the benefits are and how other people can benefit.
We want to take a look today to see what’s in the business case and how to write one. I want to be clear that when you look for information on a business case, it’s not a briefcase.
Someone called the other day and they were confused because they were looking for something, and they kept pulling up briefcases. That’s not what we’re talking about today. What we’re talking about are business cases, and they include information about your strategies, about your goals. It is your business proposal. It has your business outline, your business strategy, and even your marketing plan.
Why Do You Need a Business Case?
And so, why is that so important today? Again, companies are seeking not only their project managers but their team members to have a better understanding of business and more of an idea business acumen. So this business case provides the justification for the proposed business change or plan. It outlines the allocation of capital that you may be seeking and the resources required to implement it. Then, it can be an action plan . It may just serve as a unified vision. And then it also provides the decision-makers with different options.
So let’s look more at the steps required to put these business cases together. There are four main steps. One, you want to research your market. Really look at what’s out there, where are the needs, where are the gaps that you can serve? Look at your competition. How are they approaching this, and how can you maybe provide some other alternatives?
You want to compare and finalize different approaches that you can use to go to market. Then you compile that data and you present strategies, your goals and other options to be considered.
And then you literally document it.
So what does the document look like? Well, there are templates out there today. The components vary, but these are the common ones. And then these are what I consider essential. So there’s the executive summary. This is just a summary of your company, what your management team may look like, a summary of your product and service and your market.
The business description gives a little bit more history about your company and the mission statement and really what your company is about and how this product or service fits in.
Then, you outline the details of the product or service that you’re looking to either expand or roll out or implement. You may even include in their patents may be that you have pending or other trademarks.
Then, you want to identify and lay out your marketing strategy. Like, how are you gonna take this to your customers? Are you going to have a brick-and-mortar store? Are you gonna do this online? And, what are your plans to take it to market?
You also want to include detailed information about your competitor analysis. How are they doing things? And, how are you planning on, I guess, beating your competition?
You also want to look at and identify your SWOT. And the SWOT is your strength. What are the strengths that you have in going to market? And where are the weaknesses? Maybe some of your gaps. And further, where are your opportunities and maybe threats that you need to plan for? Then the overview of the operation includes operational information like your production, even human resources, information about the day-to-day operations of your company.
And then, your financial plan includes your profit statement, your profit and loss, any of your financials, any collateral that you may have, and any kind of investments that you may be seeking.
So these are the components of your business case. This is why it’s so important. And if you need a tool that can help you manage and track this process, then sign up for our software now at ProjectManager .

Deliver your projects on time and under budget
Start planning your projects.

Business Case Studies
Case studies are written by professors at HBS and at renowned business programs worldwide and offer slices of business life, focusing on actual problems and decisions companies face.

Global Wine War 2015: New World Versus Old

The case contrasts the tradition-bound Old World wine industry with the market-oriented New World producers in the battle for the Chinese wine market in 2015. China's wine consumption growth presented a large and fast growing export target that was...
Copyright Permissions
If you'd like to share this PDF, you can purchase copyright permissions by increasing the quantity.
Order for your team and save!
- +91- 9640901313 [email protected]
- Search for a Case
- Publications

4 th International Case Study Conference (December 14-15, 2023)
Theme: the future of case method.
⇨Deliberations on The Future of Case Method ⇨Cash prizes for Top 3 case studies ⇨Editorial and mentoring support to selected case authors ⇨Opportunity to publish case studies in reputed indexed journals and case repositories ⇨Networking opportunity with experts in case teaching and case writing Contact Us Email: [email protected] Register here: https://www.ifheindia.org/conference/ICSC2023/ Tel: +91 96409 01313

ICMR (IBS Center for Management Research)
Asia Pacific's largest case study repository for management students, faculties, trainers and corporate executives

ICMR is Asia's most popular repository of management case studies. ICMR Case Collection provides Teachers, Corporate Trainers, and Management Professionals with a variety of teaching and reference material. The collection consists of case studies on a wide range of companies and industries - both Indian and international. ICMR is involved in business research, management consulting, and the development of case studies and courseware in management. ICMR also provides knowledge process outsourcing services to international clients. Over 10 million copies of ICMR case studies have been printed in international and Indian textbooks, workbooks and case study volumes. More than 200,000 individual copies of our case studies have been purchased by many of the leading business schools and universities around the world. Our case studies have won prizes in several global case writing competitions, and also appear in many international management textbooks. More than 5500 case studies, short case studies, and business reports are available for immediate download from this site. The material is available for download as pdf files, with a 'Do Not Copy' watermark.
Case Study Categories
Varieties and numbers of case studies are available in our repository in different management subject categories. Below are the most popular categories in management areas:

Business Strategy
Human resource management, it and systems, leadership and entrepreneurship, business ethics, awards and achievements.
ICMR cases have won awards in some of the most prestigious global case writing competitions such as EFMD, oikos, John Molson, CEIBS, The Case Centre, E-PARCC and many more...

New Arrivals
Please check our recent case studies

Corporate Governance Crisis at Startups: The Zilingo Story
The case discusses how Zilingo Pte Ltd (Zilingo), a Singapore-based B2B fashion tech platform, ended up in liquidation after a protracted crisis due to issues that led to corporate governance failure. Founded in 2016 by Ankiti Bose (Bose) and Dhruv Kapoor, Zilingo was an online fashion and beauty startup company that empowered apparel supply chain players to produce, source, and trade efficiently through its technology platform. It was one of Southeast Asia’s vaunted startups...
Amazon's Private Label Brands: An Ethical Perspective
The case “Amazon’s Private Label Brands: An Ethical Perspective” discusses the ethical implications surrounding the promotion of US-based multinational technology company Amazon.com, Inc. (Amazon) of Amazon Private Label (APL) products on its online marketplace. The case starts out with a brief look at– the world's largest e-commerce platform's launch of various APL products from the late 2000s. It then delves into the various controversies surrounding APL products through the years...
Twitter under Elon Musk: Present Tense, Future Perfect?
The case discusses the problems faced by social media platform Twitter and its future under the ownership of Elon Musk. After he acquired Twitter for US$44 billion in October 2022, Musk primarily known for his innovative efforts, introduced a list of controversial policy and feature changes to the platform. These included rebranding Twitter to ‘X’, making policy changes and sweeping layoffs, resorting to cost cutting, reinstating accounts, and introducing paid verification...
Google's Post-Pandemic Multi-Purpose Workplace Design
The case touches upon the early office design initiatives at Google including at its headquarters Googolplex. Next, it describes in detail how Google’s Real Estate and Workplace Services team (REWS) focused on redesigning the existing office spaces in 2022 and creating and testing new multi-purpose offices and private workspaces to enable employees to collaborate effectively across work environments. Google designed Team Pods with chairs, desks, white boards, and storage units on casters that could be shifted based...
Reliance's Foreign Currency Bond
The case study is about Reliance Industries Ltd (RIL)'s foreign currency bond issuance and listing on international stock exchanges. The case starts with a brief history of the company, from the founding of RIL by Dhirubhai Ambani in 1966 to being led by Mukesh Ambani in 2022.The case then moves on to the details of RIL's financials, showcasing how the company has grown over the years, and how efficiently it has raised funds from the global capital market and utilized these funds for expansion. Finally, it delves into the details of foreign currency bonds issued by RIL...
Enbridge: A Diversity, Equity & Inclusion (DEI) Leader in the Energy Industry
The case describes the various initiatives taken by Enbridge, a Canadian energy company, to create a diverse and inclusive culture where employees would feel good coming to work, collaborate across teams, and be successful and grow their careers. The case first touches upon the main goals of the D&I strategy put in place at Enbridge. It then describes how Enbridge decided to encourage its employee community through various initiatives that included activities, education, and networking...
ICMR Books Collections
ICMR books are ideal resources designed to help deepen knowledge on the management theories and concepts helping to enhance decision-making skills

Strategic management consists of a set of decisions and actions resulting in the formulation and implementation of strategies designed to achieve the objectives of an organization. It involves taking decisions about the products, location, and the organization's structure-decisions that determine the survival of the organization in the short and long term.....
Business Communication
Communication is an essential aspect of business life. Everyday, business persons have to communicate with people at different levels of the organization or with people external to the organization. And in this globalized environment they also have to communicate with people from different countries, with different cultural backgrounds....
Economics For Managers
Economics is the study of how economic agents or societies choose to use scarce resources to satisfy unlimited wants. It examines how resources can be optimally distributed to satisfy the needs of individuals and society as a whole. Knowledge of economics helps businesses become more profitable through proper allocation of resources....
Testimonials
Case studies are an important tool to highlight managerial dilemmas. The ICMR case studies are of highest quality and tackle important managerial issues, including social and environmental sustainability. The case studies have repeatedly won international case study contests and have been tested around the globe with much success.
-Dr. Michael Pirson, Assistant Professor of Management, Fordham University; Research Fellow in Psychology; Harvard University; Co-founder and Academic Director, Humanet
I am impressed about the quality of ICMR cases, combining relevant issues, innovative organizationa and excellent case writing handcraft. In recent years, ICMR cases have performed extraordinarily well within the double-blind reviewed annual oikos Global Case Writing Competition.
-Dr. Jost Hamschmidt, Managing Director, oikos Foundation, St. Gallen, Switzerland; Head, oikos Global Case Writing Competition Program
Our Premium Services
ICMR provides knowledge partnership services as well as training services

- February 07, 2020
IBS Center for Management Research (ICMR) offers a subscription model for the purchase of case studies. At present, we are offering two subscription options…
Read More »

While ICMR regularly comes out with casebooks, case packs, and e-books comprising our cases, we have witnessed a high demand for our cases for…

ICMR India conducts workshops to train all the interested individuals in case research and writing. For more details, please write a mail to…
Copyright © 2020 - All Rights Reserved - ICMR India
- BA Bootcamp
- Data Analysis Bootcamp
- Skill Training
- BA Mentoring Support
- Certifications
Business Analyst Case Study | Free Case Study Template
Business analyst case studies blog describes an actual business analyst case study. This provides real-world exposure to new business analysts.
In this blog, we will be discussing what is business analysis case study, why develop them, when to develop them and how to develop them. We will provide a real business case analysis case study for better understanding.
Let’s start with understanding what is business analysis before we go to analyst case studies.
Topics Below
What is a business analysis case study
Why prepare business analysis case study
When to prepare business analysis case study
How to prepare business analysis case study
Example Business Analysis Case Studies
What is Business Analysis Case Study?
Before we try to understand, Business Analysis Case Study, let's understand the term case study and business analysis.
As per Wikipedia, a case study is:
"A case study is an in-depth, detailed examination of a particular case (or cases) within a real-world context."
For example, case studies in medicine may focus on an individual patient or ailment; case studies in business might cover a particular firm's strategy or a broader market; similarly, case studies in politics can range from a narrow happening over time like the operations of a specific political campaign, to an enormous undertaking like, world war, or more often the policy analysis of real-world problems affecting multiple stakeholders.
So, we can define Business Analysis Case Study as
"A Business Analysis case study is an in-depth, detailed examination of a particular business analysis initiative."
What is Business Analysis?
The BABOK guide defines Business Analysis as the “Practice of enabling change in an enterprise by defining needs and recommending solutions that deliver value to stakeholders”. Business Analysis helps in finding and implementing changes needed to address key business needs, which are essentially problems and opportunities in front of the organization.
Business analysis can be performed at multiple levels, such as at:
- The enterprise level, analyzing the complete business, and understanding which aspects of the business require changes.
- The organization level, analyzing a part of the business, and understanding which aspects of the organization require changes.
- The process level, analyzing a specific process, understanding which aspects of the process require changes.
- The product level, analyzing a specific product, and understanding which aspects of the product require changes.
Why Develop Business Analyst Case Study
Business analysis case studies can be useful for multiple purposes. One of the purpose can be to document business analysis project experiences which can be used in future by other business analysts.
This also can be used to showcase an organizations capabilities in the area of business analysis. For example, as Adaptive is a business analysis consulting organization, it develops multiple business analysis case studies which show cases the work done by Adaptive business analysts for the client. You can read one such case study for a manufacturing client .
When To Develop Business Analyst Case Study
Business analysis case studies are typically prepared after a project or initiative is completed. It is good to give a little time gap before we develop the case study because the impact of a change may take a little while after the change is implemented.
Most professionals prepare business analysis case studies for projects which are successful. But it is also important to remember that not all changes are going to be successful. There are definitely failures in an organizations project history.
It is also important to document the failure case studies because the failures can teach us about what not to do in future so that risks of failures are minimized.
How To Develop A Business Analyst Case Study
Document business problem / opportunity.
In this section of the business analyst case studies, we discuss the actual problem of the business case analysis example.
ABC Technologies has grown rapidly from being a tiny organization with less than 5 projects to one running 200 projects at the same time. The number of customer escalations has gone up significantly. Profitability is getting eroded over a period of time. Significant management time is spent in fire-fighting than improving the business.
Top management estimated a loss of 10% profitability due to poor management of projects which is estimated at about 10 Million USD per annum.
Document Problem / Opportunity Analysis
For our above business problem, we captured the following analysis details.
Discussions with key stakeholders revealed the following challenges in front of ABCT management:
- There is very little visibility of project performances to top management
- Non-standard project reporting by various projects makes it harder for top management to assess the correct health of the project
- Practically there is no practice of identifying risks and mitigating them
- Project practices are largely non-standardized. Few project managers do run their projects quite well because of their personal abilities, but most struggle to do so.
- Due to rapid growth, management has no option but to assign project management responsibilities to staff with little or no project management experience.
Document Identified Solutions
Based on root cause analysis, management decided to initiate a project to standardize management reporting. This required the organization to implement a project management system. The organization initially short-listed 10 project management tools. After comparing the business needs, tools, their costs, management decided to go with a specific tool.
Document Implementation Plan
The purchased tool lacked integration into the organizations existing systems. The vendor and organization’s IT team developed a project plan to integrate the new system with the existing systems.
Document Performance Improvements
After a year, the effectiveness of the project was assessed. Projects showed remarkable improvement wrt reduced customer escalations, better on-time billing, and better risk management. The system also allowed the organization to bid for larger contracts as the prospective customers demanded such a system from their suppliers. The application was further enhanced to cater to the needs of other businesses in the enterprise as they were different legal entities, and their policies were different.
Document lessons learnt
Some of the key lessons learnt during this business analysis initiative were:
1. Stakeholder buy-in in extremely important to the success of the project
2. It is always better to go with iterative approach achieve smaller milestones and then go for larger milestones

Other articles of interest
No more cold feet, be best prepared to ace the Business analyst job Interview with Business Analyst Interview Questions . Join Adaptive Inner Circle and get '1000 BA Interview Questions' book for free. Checkout the more information about CBAP Training from Adaptive US
You May Also Like
These Related Stories

How to conquer your CBAP exam anxiety

User Story vs. Use Case - How They Stack Up

CBAP Certification Exam Preparation in 10 Simple steps
Get email notifications, comments (25).
What caused Dubai floods? Experts cite climate change, not cloud seeding
- Medium Text
DID CLOUD SEEDING CAUSE THE STORM?

CAN'T CREATE CLOUDS FROM NOTHING
Sign up here.
Reporting by Alexander Cornwell; editing by Maha El Dahan and Alexandra Hudson
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

World Chevron
Turkey's justice minister warned the country's main pro-Kurdish DEM party on Wednesday that it would face the risk of legal action, and even a closure case like its predecessor, if it did not distance itself from Kurdish militants.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Share a brief explanation of your company and the products or services you provide. 7. Call-to-action (CTA) Add a call to action with the appropriate contact information (or a contact button, if this is a web-based case study) so that users can get in touch for additional information after reading the case study.
Case study examples. Case studies are proven marketing strategies in a wide variety of B2B industries. Here are just a few examples of a case study: Amazon Web Services, Inc. provides companies with cloud computing platforms and APIs on a metered, pay-as-you-go basis.
Business analysis case study examples correspond to the various aspects of business like management, marketing, competition, or research and development. ... Glenn had created a presentation that provided an overview of the solution scope for the MVP release. He had started his Stakeholder Map, adding the stakeholders and technology team ...
A case study is a real-life scenario where your company helped a person or business solve their unique challenges. It provides a detailed analysis of the positive outcomes achieved as a result of implementing your solution. Case studies are an effective way to showcase the value of your product or service to potential customers without overt ...
The Case Analysis Coach is an interactive tutorial on reading and analyzing a case study. The Case Study Handbook covers key skills students need to read, understand, discuss and write about cases. The Case Study Handbook is also available as individual chapters to help your students focus on specific skills.
In this classic case from the early 2000s, Colombian coffee entrepreneurs attempt to revive Colombia's famous Juan Valdez brand in the age of Starbucks. Published: February 22, 2013
Case study answers written by top business students. We are the marketplace for case study solutions. Save time and get inspired by our case solutions. We help you be a top student at your university! High-quality only. We manually review all case study submissions being sent to us.
A business case is a formal, structured document; an informal, short document; or a verbal exchange that defines the benefits of an initiative or project.. In addition, a business case forecasts the costs, benefits, and risks of an initiative, so decision makers — and even the project initiators — can decide whether a project is worthwhile and why to choose one approach over similar ...
Business case studies serve as practical models of how to explore, understand, and analyze a problem and to develop the best solution strategy. WHY CASE STUDIES ARE GOOD FOR BUSINESS : ANATOMY OF A CASE STUDY -- PROBLEM-ORIENTED METHOD: 1. Case studies allow a company to use storytelling to bring their product to life
6 QUALITIES OF GREAT CASE WRITERS. Curiosity. Comfort with ambiguity, since cases may have more than one "right" answer. Command of the topic or subject at hand. Ability to relate to the case protagonists. Enthusiasm for the case teaching method. Capacity for finding the drama in a business situation and making it feel personal to students.
A case library of 600+ case study examples to get you ready for your case interview! McKinsey, BCG, Bain & 20+ other firm styles represented! Skip to primary navigation; ... Business School Journal : Kearney: Market Study - Market Entry: N: 2: TMT: Marketing: Cable Operations in AZ and NM : Strategy& Profitability - Decline: N: 1: TMT:
That skill - the skill of figuring out a course of inquiry, to choose a course of action - that skill is as relevant today as it was in 1921.". Pioneered by HBS faculty, the case method presents the greatest challenges confronting organizations and places the student in the role of the decision maker.
For example, the case study quotes the social media manager and project manager's insights regarding team-wide communication and access before explaining in greater detail. Takeaway: Highlight pain points your business solves for its client, and explore that influence in greater detail. 3. EndeavourX and Figma.
Fifty four percent of raw case users came from outside the U.S.. The Yale School of Management (SOM) case study directory pages received over 160K page views from 177 countries with approximately a third originating in India followed by the U.S. and the Philippines. Twenty-six of the cases in the list are raw cases.
1. The Army Crew Team. Emily Michelle David, Assistant Professor of Management, China Europe International Business School (CEIBS) EMILY MICHELLE DAVID Assistant Professor, CEIBS. "I love teaching The Army Crew Team case because it beautifully demonstrates how a team can be so much less than the sum of its parts.
Prepare for B-school admission rounds, with these MBA case study examples. It is common for B-schools to incorporate a case-based discussion in the group exercise round or give a case study in a personal interview. So, here we have presented two popular MBA case study examples, with analysis and solution.
Free Case Studies. Many academic and business institutions develop and publish case studies. Some of these organizations provide free access to their case studies: Focuses on entrepreneurship and small business operations. Available for a fee. Give to Get Marketing. Marketing and Advertising Case Studies.
Ethics Unwrapped - McCombs School of Business, The University of Texas at Austin More than 50 case studies match ethics concepts to real world situations. From journalism to performing arts to foreign policy to scientific research to social work, these cases explore a range of current and historic ethical dilemmas, their motivating biases, and their consequences.
Our business case template for Word is the perfect tool to start writing a business case. It has 9 key business case areas you can customize as needed. Download the template for free and follow the steps below to create a great business case for all your projects. ProjectManager's free business case template.
By Christopher A. Bartlett and Sarah McAra. and. June 17, 2016. $11.95. Quick view. 1. Case studies written by professors at HBS and other leading business programs worldwide, focusing on real-world problems and decisions companies face.
ICMR is a premier case development center developing high-quality teaching cases with solutions in Management area. Business research, management consulting +91- 9640901313 [email protected]; Search for a Case ... More than 5500 case studies, short case studies, and business reports are available for immediate download from this site ...
Develop a plan. Follow through with your project. Review results and produce insights. Your business case development provides the core elements required to solve a problem, including metrics and ...
How To Develop A Business Analyst Case Study Document Business Problem / Opportunity. In this section of the business analyst case studies, we discuss the actual problem of the business case analysis example. ABC Technologies has grown rapidly from being a tiny organization with less than 5 projects to one running 200 projects at the same time.
BI Case Study—Overview The term business intelligence refers to a range of tools that provides easy-to-understand insights about an organization's past, present, and future states for informed decision-making. ... Instead, the case studies give you a look at the way business solutions such as BI software work to cover key processes through ...
5. LocaliQ's Website Grader for free SEO audits. If you need a quick, easy-to-understand website audit, LocaliQ's Free Website Grader will do the trick. Even though it's a free tool, you get a lot of information. For example, in your report you'll see: Technical SEO: Site security, site speed, mobile optimization.
A storm hit the United Arab Emirates and Oman this week bringing record rainfall that flooded highways, inundated houses, grid-locked traffic and trapped people in their homes.
Under the proposal, the inclusion rate for annual capital gains realized above $250,000 for individuals would be taxed at a rate of two-thirds, up from the current 50 per cent. Any gains under ...