- Entertainment


How To Write An Analytical Essay A Full Guide
Crafting an impeccable analytical essay is an art form that demands precision, insight, and a structured approach. Whether you’re delving into literature, dissecting historical events, or unraveling scientific theories, the ability to present a compelling analysis is pivotal. Here’s a comprehensive guide to navigate the intricate path of writing a flawless analytical essay.
What Is An Analytical Essay
An analytical essay is a type of academic writing that delves deeply into a topic, idea, or piece of literature. Unlike descriptive or narrative essays, which focus on providing a vivid description or telling a story, an analytical essay aims to examine and dissect its subject matter.
The primary objective of an analytical essay is to present a thorough analysis or interpretation of the subject, often breaking it down into its constituent parts and scrutinizing how they contribute to the whole.
Why Analytical Essay Is Important
Analytical essays play a pivotal role in developing critical thinking skills and fostering a deeper understanding of complex subjects. Through the meticulous examination and interpretation of information, these essays teach individuals how to dissect arguments, evaluate evidence, and form well-supported conclusions. They serve as a platform for honing analytical prowess, enabling individuals to engage with diverse perspectives, challenge assumptions, and articulate their insights effectively. Moreover, mastering the art of analytical essays equips individuals with invaluable skills applicable across various disciplines, fostering a capacity for logical reasoning, problem-solving, and persuasive communication—a skill set indispensable in academia, professional endeavors, and everyday life.
Tips For Writing A Good Analytical Essay
Understanding the essence.
To excel in analytical writing, one must comprehend the essence of analysis itself. It’s not merely about summarizing or narrating; it’s about deconstructing the core components, scrutinizing their significance, and synthesizing perspectives to derive insightful conclusions.
Devising a Strategic Blueprint
Begin with a comprehensive understanding of your subject matter. Formulate a thesis statement —a succinct encapsulation of your perspective—which serves as the guiding beacon throughout your essay. Craft an outline delineating key sections and their respective arguments, ensuring a logical flow that seamlessly connects each point.
The Pinnacle of Research
A sturdy analytical essay is built upon a foundation of rigorous research. Delve into reputable sources, be it scholarly articles, books, or credible online repositories. Gather diverse perspectives and data to fortify your arguments, but always uphold the standards of credibility and relevance.
Structure: The Backbone of Brilliance
A well-structured essay is akin to an architectural marvel. The introduction should entice readers with a gripping hook, provide context, and introduce the thesis statement. The body paragraphs, each beginning with a topic sentence, should expound on individual arguments supported by evidence and analysis. Finally, the conclusion should reaffirm the thesis while offering a nuanced synthesis of the essay’s core ideas.
The Art of Analysis
Here’s where the magic unfolds. Analyze, dissect, and interpret the data and evidence gathered. Scrutinize underlying themes, dissect intricate details, and juxtapose contrasting viewpoints. Employ analytical tools pertinent to your subject, such as literary devices for literature analyses, statistical methods for scientific inquiries, or historical frameworks for historical essays.
Precision in Language and Style
The language employed in an analytical essay should be precise, articulate, and tailored to convey complex ideas clearly. Utilize a formal tone, vary sentence structures, and employ transitions to ensure a seamless progression of ideas. Embrace clarity and coherence as your allies in elucidating intricate analyses.
Revisiting and Refining
Revision is the crucible wherein a good essay transforms into a great one. Review your work meticulously—check for coherence, refine arguments, ensure logical transitions, and verify the alignment of evidence with your thesis. Seek feedback from peers or mentors to gain diverse perspectives and refine your essay further.
Conclusion: A Culmination of Mastery
In conclusion, a perfect analytical essay isn’t merely a collection of facts and opinions; it’s an orchestrated symphony of critical thinking, analysis, and eloquent expression. Embrace the journey of discovery, relish the complexities, and let your essay resonate as a testament to your mastery of analytical prowess.
Best Place To Avail Analytical Essay Service
At Allessaywriter.com, excellence meets expertise in crafting exceptional analytical essay services . Our platform is your gateway to top-tier service, offering a seamless experience to elevate your academic journey. With a team of seasoned writers dedicated to precision and depth in analysis, we ensure tailored essays that reflect critical thinking and comprehensive understanding. Trust us for meticulous research, compelling arguments, and impeccable structure, all aimed at delivering the finest analytical essays that exceed expectations.
An analytical essay service encapsulates the culmination of rigorous analysis, insightful interpretation, and concise articulation. It serves as the pinnacle of intellectual prowess, combining critical thinking with eloquent expression to offer a profound understanding of complex subjects. So if you are still wondering about analytical essay writing then ask our writers and get our do my essay help services.

Meet Kathy, the mindful mind behind the words at minimalistfocus.com. With an innate ability to distill the essence of life down to its purest form, Kathy's writing resonates with those seeking clarity in a cluttered world.
Related Post
7 toys that can keep your kids quiet this mother’s day, exploring the best personalities of miniature schnauzers, eco-friendly waste management: how panama city residents can make a difference, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Type above and press Enter to search. Press Esc to cancel.
📕 Studying HQ
Guide to writing an analytical essay, carla johnson.
- June 13, 2023
- Essay Topics and Ideas , How to Guides
An analytical essay is a type of academic writing in which a complicated topic or idea is broken down into smaller parts, analyzed and looked at, and a well-structured argument or evaluation is given. The main purpose of an analytical essay is to show that the writer has a deep understanding of the topic and can also think critically about it. Analytical essays are important in many fields, such as literature, history, science, and sociology. They require a deep knowledge of the topic and the ability to think critically and objectively about the information given. Analytical essays include things like a literary analysis, a research paper , or an analysis of a piece of rhetoric. Writing an analytical essay is useful because it helps the writer improve their analytical and critical thinking skills. In analytical essays, students must look at and evaluate different sources, find patterns and relationships, and come to meaningful conclusions. When students write analytical essays, they also improve their research skills because they have to find relevant information from multiple sources and put it all together in a logical argument.
Also, analytical essays are important in academic writing because they help students understand ideas, theories, and concepts that are hard to understand. By breaking a topic down into smaller parts, students can better understand it and figure out what the main ideas and themes are. Analytical essays help students get better at writing by making them present their arguments in a way that is clear, concise, and well-organized. Writing an analytical essay is a skill that students need to learn if they want to do well in school and in their careers. For analytical essays, you need to be able to think critically , do research, and write well, all of which are important for success in many fields. By getting better at these skills, students can become better writers and thinkers, which will help them reach their academic and career goals.
What You'll Learn
Understanding the Basics of Analytical Essays
There are a few main things that set an analytical essay apart from other types of essays. One of the most important things about it is that it requires a thorough look at the subject. An analytical essay isn’t just a description of a topic or a point of view. Instead, it calls for a thorough look at the subject, breaking it down into its different parts and evaluating each one carefully.
Argumentative essays try to convince the reader to agree with a certain point of view. Descriptive essays, on the other hand, try to give a detailed description of a topic. Analytical essays, on the other hand, require the writer to look at the topic objectively and judge it, as well as use evidence from different sources to back up their claims. In an analytical essay, you can’t say enough about how important analysis is. Analysis is the process of breaking down big ideas or thoughts into smaller, more manageable pieces. By analyzing the topic, the writer can find the main ideas, patterns, and connections, which can then be used to back up their arguments.
Also, analysis lets the author draw conclusions that make sense based on the evidence given. If there wasn’t any analysis in an analytical essay, it would just be a list of facts and opinions. Analysis is what gives depth and substance to an analytical essay and lets the writer make a well-reasoned, evidence-based argument.
Analytical essays are different from other types of essays because they focus on analysis and evaluation. They require a thorough look at a subject, breaking it down into its different parts and judging each one objectively. Students can get the skills they need to do well in school and in the workplace by learning what makes an analytical essay unique and what role analysis plays in this type of writing.
Choosing a Topic for Your Analytical Essay
It can be hard to decide what to write about in an analytical essay, but there are several ways to come up with ideas. One way to do this is to make a list of possible topics based on your interests, your schoolwork, or what’s going on in the world right now. You can also find possible topics by reading articles, books, or other materials in your field of study. When choosing a topic for your analytical essay, you should think about a few things. First and foremost, the topic must fit with the needs of the course or assignment. It should also be narrow enough to allow for a detailed analysis while still having enough information for research . Also, the topic should be something you’re interested in as a writer. This will make the writing process more interesting and fun.
To help you get started, here are some examples of potential analytical essay topics:
1. The impact of social media on mental health
2. Analyzing the themes of race and identity in Toni Morrison’s “Beloved”
3. The role of technology in modern education
4. An analysis of the effectiveness of the Affordable Care Act
5. Examining the causes and consequences of income inequality in the United States
6. The portrayal of gender roles in Shakespeare’s plays
7. Analyzing the impact of climate change on global food production
8. A critical analysis of the role of the media in shaping public opinion
9. A comparison of different political ideologies and their impact on society
10. An analysis of the ethical implications of gene editing technology.
A topic for an analytical essay must be chosen with care, taking into account several factors such as relevance, scope, and personal interest. By brainstorming ideas, researching different sources, and applying these criteria, you can choose a topic that is both interesting and informative, allowing you to write a well-researched and well-argued analytical essay.
Conducting Research for Your Analytical Essay
In order to write an analytical essay, you need to do research. It lets the writer gather relevant information, find patterns and relationships, and come to conclusions that make sense. If you didn’t do research for your analytical essay, it wouldn’t have much substance or credibility, and the arguments you made would be weak and not backed up. You can gather information for your analytical essay from a number of different places. There are many examples, such as books, academic journals, online databases, government reports, and reputable news sources. When choosing sources, think about how relevant, reliable, and trustworthy they are. Academic sources like peer-reviewed journals and scholarly books are more reliable and credible than popular sources like blogs and social media posts.
To conduct effective research for your analytical essay, here are some tips to keep in mind:
1. Start early: Give yourself plenty of time to conduct research, as it can be a time-consuming process.
2. Use multiple sources: Gather information from a variety of sources to ensure you have a well-rounded understanding of the topic.
3. Take notes: Keep detailed notes on the information you gather, including the source and page number, to make it easier to cite your sources later.
4. Evaluate your sources: Assess the reliability and credibility of your sources, looking for biases or conflicts of interest that may affect the information presented.
5. Organize your research: Create a system for organizing your research, such as using annotated bibliographies or note-taking apps, to keep track of your sources and ideas.
You can conduct effective research for your analytical essay by following these tips, gathering reliable and credible information that supports your arguments and improves the overall quality of your writing.
Developing a Thesis Statement for Your Analytical Essay
A thesis statement is a short sentence that sums up the main argument or point of an essay. It gives the reader a clear idea of where the author stands on the subject and acts as a road map. In an analytical essay, the thesis statement is very important because it sets the tone for the whole essay and shows the writer how to analyze and evaluate the subject . In an analytical essay, you can’t say enough about how important a strong thesis statement is. A well-written thesis statement states the writer’s main point in a clear and concise way, making it easier for the reader to follow the writer’s thought process and understand the purpose of the essay. A strong thesis statement also helps the writer focus their analysis and evaluation, making sure that each paragraph supports the main point and builds on it.
To develop a strong thesis statement for your analytical essay, here are some tips to consider:
1. Start with a question: Ask yourself a question related to your topic and use the answer to develop your thesis statement.
2. Be specific: Your thesis statement should be specific and focused on the main argument of your essay .
3. Use evidence: Support your thesis statement with evidence from your research, such as quotes or statistics, to give it more credibility and strength.
4. Be original: Your thesis statement should be unique and original, providing a fresh perspective on the topic.
5. Revise as needed: As you write your essay , revisit your thesis statement and revise it if necessary to ensure it remains relevant and accurate.
By following these tips, you can develop a strong thesis statement for your analytical essay, providing a clear and concise statement of your main argument and guiding the reader through your analysis and evaluation of the topic.
Analytical Essay Structure
An analytical essay is made up of an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion, just like a regular essay. The purpose of the introduction is to give background on the topic, introduce the thesis statement, and get the reader interested. Through analysis and evaluation of the topic, the body paragraphs should support the thesis statement with evidence and examples . The conclusion should sum up the main points of the essay and restate the thesis statement in a new way that makes sense.
Here is a more detailed breakdown of the structure of an analytical essay:
1. Introduction: The introduction should set the tone for the essay by providing background information on the subject as well as a clear thesis statement. It should also engage the reader and convey the writer’s point of view on the subject.
2. Body paragraphs: The body of the essay should be divided into several paragraphs, each focusing on a different aspect of the topic. Each paragraph should start with a clear topic sentence that supports the thesis statement and then proceed to an analysis and evaluation of the subject matter, using evidence and examples to support the writer’s argument.
3. Conclusion: The conclusion should summarize the essay’s main points and restate the thesis statement in a new and meaningful way. It should also provide the reader with a sense of closure, leaving them with a clear understanding of the writer’s point of view on the subject.
To organize your ideas in an analytical essay, here are some tips to consider:
1. Create an outline: Before you start writing your essay , create an outline that organizes your ideas and supports your thesis statement. This will help you to organize your thoughts and ensure that each paragraph supports the main argument.
2. Use topic sentences: Each paragraph should begin with a clear topic sentence that supports the thesis statement and provides a roadmap for the reader.
3. Use evidence: Use evidence and examples to support each point you make in your essay , ensuring that each paragraph reinforces the main argument.
4. Use transitions: Use transitional phrases and sentences to connect your ideas and ensure that your essay flows smoothly from one paragraph to the next.
By following these tips, you can organize your ideas effectively in an analytical essay, producing a well-structured and well-supported piece of writing.
Writing the Introduction Paragraph
An analytical essay’s introduction paragraph serves as a road map for the reader, providing background information on the topic, introducing the thesis statement, and engaging the reader. The introduction’s purpose is to set the tone for the essay , grab the reader’s attention, and provide a clear understanding of the writer’s viewpoint on the topic.
To write an engaging introduction paragraph for your analytical essay, here are some tips to consider:
1. Start with a hook: Begin your introduction with a hook that captures the reader’s attention and makes them want to keep reading. This could be a surprising statistic, a provocative question, or a striking image.
2. Provide background information: Provide some context for the topic by providing background information and explaining why it is important.
3. Introduce the thesis statement: Clearly state your thesis statement in the introduction, providing a roadmap for the reader and guiding the rest of your essay.
4. Be concise: Keep your introduction concise and to the point, avoiding unnecessary information or tangents.
5. Revise as needed: As you write your essay, revisit your introduction and revise it as needed to ensure that it remains relevant and engaging.
Here are some examples of effective introduction paragraphs for an analytical essay:
1. “Throughout history, the concept of justice has been a subject of debate and controversy. From the ancient Greeks to modern-day philosophers, the definition and application of justice have been explored in depth. In this essay, I will examine the concept of justice in the context of criminal justice reform and argue that a more restorative approach is needed to address the root causes of crime and reduce recidivism.
2. The rise of social media has had a profound impact on our society, transforming the way we communicate, share information, and interact with the world around us. However, this transformation has not been without its challenges. In this essay, I will explore the impact of social media on mental health and argue that we need to take a more proactive approach to addressing the negative effects of social media on our well-being.
3. “Climate change is one of the most pressing issues of our time, affecting everything from the environment to the economy. Despite the overwhelming scientific evidence, there are still those who deny the reality of climate change or refuse to take action. In this essay, I will analyze the reasons for this denial and argue that we need to take urgent action to address the threat of climate change before it’s too late.”
Writing the Body Paragraphs
An analytical essay’s body paragraphs are where the writer presents their analysis and evaluation of the topic. The purpose of the body paragraphs is to provide evidence and examples to support the thesis statement, while using clear and concise language to make the argument as persuasive as possible.
To write clear and concise body paragraphs for your analytical essay, here are some tips to consider:
1. Use topic sentences: Each body paragraph should begin with a clear topic sentence that supports the thesis statement and provides a roadmap for the reader.
2. Provide evidence: Use evidence and examples to support each point you make in your essay , ensuring that each paragraph reinforces the main argument. The evidence should be relevant, reliable, and credible.
3. Use analysis and evaluation: Analyze and evaluate the evidence you present to demonstrate how it supports your argument. This shows the reader that you have thought deeply about the topic and considered multiple perspectives.
4. Be clear and concise: Use clear and concise language to make your argument as persuasive as possible. Avoid using jargon, complex sentences, or overly technical language that may confuse the reader.
5. Use transitions: Use transitional phrases and sentences to connect your ideas smoothly and ensure that your essay flows from one paragraph to the next.
Here are some examples of effective body paragraphs for an analytical essay:
1. The first reason why a restorative approach to criminal justice reform is necessary is that it addresses the root causes of crime. Rather than simply punishing offenders, restorative justice encourages dialogue between the offender and the victim, allowing both parties to understand the harm that has been caused and work together to find a solution. This approach has been shown to reduce recidivism rates and promote healing within communities.”
2. One of the most significant negative effects of social media on mental health is the increase in anxiety and depression. Studies have shown that social media use is associated with feelings of isolation, comparison, and low self-esteem, all of which contribute to poor mental health . In order to address this issue, we need to take a more proactive approach to promoting mental health and well-being, such as limiting social media use, encouraging face-to-face interactions, and providing mental health resources for those in need.
3. One of the main reasons why climate change denial persists is due to the influence of special interest groups and political ideology . These groups use their resources to spread misinformation and discredit the overwhelming scientific consensus on climate change. In order to combat this, we need to prioritize education and awareness, promote scientific literacy, and hold those who spread misinformation accountable for their actions.”
Writing the Conclusion Paragraph
The conclusion paragraph of an analytical essay summarizes the author’s main points and emphasizes the significance of the thesis statement. The conclusion’s goal is to leave a lasting impression on the reader by bringing the essay to a close and reinforcing the main argument .
To write a strong conclusion for your analytical essay, here are some tips to consider:
1. Restate the thesis statement: The conclusion should restate the thesis statement in a new and meaningful way, emphasizing its importance and relevance to the topic.
2. Summarize the main points: Summarize the main points of the essay, highlighting the evidence and examples that support the thesis statement .
3. Provide a final thought: End the essay with a final thought or reflection on the topic, leaving the reader with something to think about or consider.
4. Be concise: Keep the conclusion concise and to the point, avoiding any new information or arguments.
5. Make it memorable: Use language and phrasing that is memorable and impactful, leaving a lasting impression on the reader.
Here are some examples of effective conclusion paragraphs for an analytical essay:
1. “In conclusion, a restorative approach to criminal justice reform is not only necessary but essential. By addressing the root causes of crime, promoting dialogue and understanding, and fostering healing within communities, we can create a more just and equitable society for all.”
2. In order to address the negative effects of social media on mental health , we need to take a more proactive approach to promoting well-being. By limiting social media use, encouraging face-to-face interactions, and providing mental health resources, we can create a healthier and more connected society.
3. “Climate change is one of the most pressing issues of our time, and we must take urgent action to address it. By promoting education and awareness, prioritizing scientific literacy, and holding those who spread misinformation accountable, we can create a more sustainable and equitable future for generations to come.”
Editing and Proofreading Your Analytical Essay
The editing and proofreading stages of the essay writing process are critical. It ensures that the essay is clear, concise, and error-free, improving overall writing quality and the credibility of the arguments presented.
To edit and proofread your analytical essay, here are some tips to consider:
1. Take a break: After completing your essay, take a break before editing and proofreading it. This will allow you to approach the essay with fresh eyes and a clear mind.
2. Read it out loud: Reading the essay out loud can help you to identify awkward phrasing, grammatical errors, and other issues.
3. Be consistent: Ensure that you are consistent in your use of language, formatting, and citation styles throughout the essay.
4. Use a checklist: Use a checklist to ensure that you have addressed all the necessary components of the essay, such as the thesis statement, evidence, and analysis.
5. Get feedback: Ask a friend or colleague to read your essay and provide feedback on areas that need improvement.
Common mistakes to avoid in analytical essays include:
1. Using overly complicated language or jargon that may confuse the reader.
2. Failing to provide evidence or examples to support the thesis statement.
3. Neglecting to address counterarguments or alternative perspectives on the topic.
4. Making unsupported claims or presenting opinions as facts.
5. Failing to proofread and edit the essay thoroughly, leading to grammatical errors and typos.
By following these tips and avoiding common mistakes, you can edit and proofread your analytical essay effectively, producing a well-written and error-free piece of writing.
Analytical Essay Examples
Here are some examples of successful analytical essays:
1. “The Symbolism of the Green Light in The Great Gatsby” by F. Scott Fitzgerald: This essay analyzes the symbolism of the green light in the novel, arguing that it represents Gatsby’s hopes and dreams and his ultimate failure to achieve them.
2. “The Rhetoric of Malcolm X” by Malcolm X: In this essay, Malcolm X analyzes his own rhetorical strategies, explaining how he uses language and persuasion to achieve his goals.
3. “The Role of Women in Shakespeare’s Macbeth” by William Shakespeare: This essay analyzes the role of women in the play, arguing that they are often marginalized and oppressed by the male characters.
Each of these essays follows a clear and well-structured format, with a strong thesis statement, supporting evidence, and a clear conclusion. The writers use analysis and evaluation to present their arguments, using evidence and examples to support their claims.
When using analytical essay examples to improve your writing, here are some tips to consider:
1. Choose examples that are relevant to your topic or subject matter.
2. Read the example essays carefully, paying attention to the structure, language, and evidence used.
3. Identify the thesis statement and main arguments of the essay.
4. Analyze the evidence used to support the arguments, evaluating its relevance and credibility.
5. Consider how the writer uses language and rhetoric to persuade the reader.
6. Use The examples as a guide for structuring your own essay, but be sure to use your own unique ideas and perspective.
7. Practice writing your own analytical essays and seek feedback from others to improve your writing skills.
8. Avoid copying or plagiarizing the example essays, as this can lead to serious academic consequences.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. what is an analytical essay.
An analytical essay is a type of academic writing that requires the writer to analyze and evaluate a specific topic or subject matter. The writer presents an argument or thesis statement and supports it with evidence and examples, using analysis and evaluation to persuade the reader.
2. What are the main characteristics of an analytical essay?
The main characteristics of an analytical essay include:
– A clear and concise thesis statement that presents the writer’s argument
– Use of evidence and examples to support the argument
– Analysis and evaluation of the evidence presented
– Clear and logical structure, with well-developed paragraphs and transitions between them
– Use of formal and academic language
– Objective and impartial tone
3. What are some tips for writing an analytical essay?
Here are some tips for writing an analytical essay:
– Choose a topic that interests you and that you can analyze in depth
– Develop a clear and concise thesis statement that presents your argument
– Use evidence and examples to support your argument, ensuring that they are relevant, reliable, and credible
– Analyze and evaluate the evidence presented, demonstrating your critical thinking skills
– Use a clear and logical structure, with well-developed paragraphs and transitions between them
– Use formal and academic language, avoiding slang and colloquialisms
– Edit and proofread your essay thoroughly, ensuring that it is error-free and well-written.
To summarize, writing an effective analytical essay necessitates a thorough understanding of the subject matter, a well-developed thesis statement, strong evidence and analysis, and a clear and logical structure. To summarize the main points covered in this guide:
– The writer of an analytical essay must analyze and evaluate a specific topic or subject matter.
– A clear thesis statement, evidence and examples to support the argument, analysis and evaluation of the evidence, a clear and logical structure, formal and academic language, and an objective tone are the main characteristics of an analytical essay.
– Choosing a relevant topic, developing a clear thesis statement, using credible evidence and examples, analyzing and evaluating the evidence, using a clear and logical structure, using formal and academic language, and thoroughly editing and proofreading the essay are all tips for writing a successful analytical essay.
An effective analytical essay demonstrates critical thinking skills as well as the ability to analyze and evaluate complex issues. It is an important skill for both academic and professional success.
Finally, practicing writing on a regular basis, seeking feedback from others, and reading and analyzing examples of successful analytical essays can all help you improve your own writing skills.
Start by filling this short order form order.studyinghq.com
And then follow the progressive flow.
Having an issue, chat with us here
Cathy, CS.
New Concept ? Let a subject expert write your paper for You
Have a subject expert write for you now, have a subject expert finish your paper for you, edit my paper for me, have an expert write your dissertation's chapter, popular topics.
Business StudyingHq Essay Topics and Ideas How to Guides Samples
- Nursing Solutions
- Study Guides
- Free Study Database for Essays
- Privacy Policy
- Writing Service
- Discounts / Offers
Study Hub:
- Studying Blog
- Topic Ideas
- How to Guides
- Business Studying
- Nursing Studying
- Literature and English Studying
Writing Tools
- Citation Generator
- Topic Generator
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Conclusion Maker
- Research Title Generator
- Thesis Statement Generator
- Summarizing Tool
- Terms and Conditions
- Confidentiality Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Refund and Revision Policy
Our samples and other types of content are meant for research and reference purposes only. We are strongly against plagiarism and academic dishonesty.
Contact Us:
📞 +15512677917
2012-2024 © studyinghq.com. All rights reserved

- Houston Community College
- Eagle Online

- Nicole Antoine
Checklist for Literary & Critical Analysis Essays
Checklist for Literary & Critical Analysis Essay
Please use this checklist when drafting your critical analysis essay!
The Ultimate Guide to Analytical Essay Writing: How to Craft an A-Grade Paper?
25 January, 2021
17 minutes read
Author: Kate Smith
An analytical essay is often considered the most challenging piece of writing. However, those who have dealt with it at least once are a step closer to calling themselves masters of essay writing. This type of paper requires plenty of analytical skills to carry out an in-depth analysis of the assigned topic. Yet, the main goal of an analytical essay is not only to demonstrate your ability to learn the basics of the theme.

You also need to think critically, analyze facts, express your standpoint, and clearly show a deep understanding of key concepts. In short, your main task as an author is to prove the validity of your views by coming up with strong arguments that do not beg any questions.

The given guide provides a full analytical essay definition, as well as specifies its features and structural aspects. The following information will help you properly start your paper, choose a relevant topic, and come up with compelling conclusions.
What is an Analytical Essay?
An analytical essay is a piece of writing aimed to provide a thorough analysis of a definite phenomenon using persuasive arguments and supporting assertions. Analysis in the analytical essay writing process stands for a method of research that allows one to study specific features of an object. Analytical papers also have to do with analysis of a specific problem; that is consideration of the problem itself and identification of its key patterns. The subject matter of analysis can be a well-known or little-studied scientific phenomenon, artistic work, historical event, social problem, etc.
The content of an analytical essay will totally depend on the object that has been chosen for analysis. Thus, when shedding light on any kind of scientific work, an analytical essay can be devoted to the analysis of research credibility, its relevance, or the adequacy of conclusions. When considering a work of art, an essay writer can focus on the analysis of the author’s artistic techniques or issues raised in the book. For this reason, it is essential to accurately determine the topic and subject matter of your future analytical essay.
Steps to Take Before Writing
The preparational stage of analytical essay writing cannot be omitted. It lays the basis for the A-grade paper and should be carefully completed. If you don’t know how to start an analytical essay, read a few handy tips that will ensure a solid foundation for your paper.
Define a subject matter
You first need to clearly understand the issue you will base your essay on. Since analytical essays imply an in-depth analysis of a specific problem, you need to define its core. Try to split the analysis into several components and provide arguments taken either from a book, a research, a scientific work, or a movie (depending on the subject matter of your analysis), and support your views comprehensively.
Decide on the content of your analytical essay
If you are a student who was given an analytical essay topic, read the task several times before you are 100% sure that you clearly understand the requirements as to the analytical essay format. In case you were lucky to choose the topic of the analytical paper by yourself, make sure the theme you will be dealing with is familiar or at least seems interesting to you.
Remember that different subject matters require a different approach to their analysis. If you examine some literature work, you can prove your opinion based on the deeds of a certain or several characters. But if you have been assigned the task to elaborate on some historic events, analyze their main causes, driving forces that have affected their course, and their global consequences.
Take care of the proper start
Don’t forget to start your analytical essay with a thesis statement. It is a sentence or a couple of sentences that aim to summarize the key statements of your paper. A thesis statement should provide readers with a preliminary idea of what your essay is all about.
Find extra reasoning
Make sure your thesis is supported by compelling arguments. To find enough evidence, you should carry out a thorough analysis of the assigned topic. List the crucial points of your research and ponder over the ways they can be used to prove your final opinion.
Elaborate the outline
A sound outline elaborated at the preparation stage will help you ensure a proper analytical essay structure and make the overall writing process easier. As a rule, an analytical essay consists of an introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Your outline plan should include the key arguments you want to discuss in each paragraph.
Analytical Essay Thesis
A thesis statement represents the central idea of your paper and must serve as strong proof of your standpoint. While elaborating your thesis statement, it is crucial to include it at the end of the first paragraph and thus set a direction for the overall paper.
Analytical Essay Outline
An outline is not a required element of analytical essays writing and should not be included in the text, but it can greatly facilitate the whole process of paper writing.
The analytical essay structure looks as follows:
Introduction
In the introduction of an analytical essay, you will need to identify your paper’s subject matter. Mention the purpose of your work and specify its scope of research. Don’t forget to include a thesis to let readers know what your work is about.
Body Section
As has already been mentioned, the body section covers three or more main paragraphs, each being supported with arguments and details. Besides, you need to provide a small conclusion to each statement to make your essay sound professional and persuasive.
At this stage, you need to summarize the points elucidated in your paper and make sure there is a smooth and logical transition from the body section to the concluding part of the text. If you don’t know how to conclude an analytical essay, try to restate the thesis statement without copying it word for word.
Analytical Essay Examples
Writing an analytical essay may seem to be a thorny way. If you are still not sure how to properly craft one, try to find some examples that will help you go in the right direction. Below, there are some great examples of analytical essays. Take a look at their structure and try to write something similar based on your views and ideas:
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1JeR4i4RIZIj448W3KVFyHP-eS3QPN7gW/view
https://stlcc.edu/docs/student-support/academic-support/college-writing-center/rhetorical-analysis-sample-essay.pdf
https://www.germanna.eduhttp://handmadewriting.com/wp-content/uploads/tutoring/handouts/Literary-Analysis-Sample-Paper.pdf
30 Analytical Essay Topics
If you were allowed to choose the theme for your paper by yourself, check on the following analytical essay topics. Each of them can bring you the highest score:
General topics
- The influence of social networks on the life of teens
- Are salaries of football players too high?
- Wearing uniforms in schools should be banned
- A person in society: the problems of loneliness and privacy
- Sociology of corporate relationships
- Does the observation of space need more investments?
- Should the voting age in the UK be decreased?
- Reasons why capital punishment should be brought back in the UK
- A world with no rules: a new human era or a road to the global collapse?
- Life without technologies: will modern people survive?
- Should scientists test drugs on animals to fight cancer?
- The problem of keeping the balance between career and family life
- The importance of listening to your body
- Problems caused by the lack of communication
- Food addiction and the problems it causes
- Problems of vaccination in the XXI century
- Does evil really rule the world?
- How does body size affect life quality?
- Pros and cons of video games
- The role of a family model in the life and career of a person
Analytical Essay Topics on Literature
- “Robinson Crusoe”: fantasy vs reality
- Observation of the artistic uniqueness in the comedy by W. Shakespeare “A Midsummer Night’s Dream”
- Observe the social problems in the novel by John Steinbeck “The Grapes of Wrath”
- Convulsions and death of the “little man” in the networks of impersonal, alienated forces in the novel “The Metamorphosis”
- Observation of the problems of a man on a plagued land in the novel “The Plague”
- Revolt of the protagonist in the novel by J. Salinger “The Catcher in the Rye”
- Observation of friendship and love in the fate of humanity in the XX century
- The triumph of immorality in the novel by F. Sagan “Hello Sadness”
- Observation of the personality of an American student in the novel by J. Salinger “The Catcher in the Rye”
- Eternal tragedies of humanity in the tragedy by W. Shakespeare “The Tragedy of Hamlet, Prince of Denmark”
How to Write a Well-Structured Analytical Essay With a Solid Argument
Writing an analytical essay with a clear structure might be challenging unless you are thoroughly prepared. We decided to help you out and create a detailed guide listing the main things to consider when creating an analytical essay outline. You need to explain your main idea in a concise way to bring your point across. As analytical writing has high requirements, it pays off to find an analytical essay example and analyze how this text was written. It will allow you to understand the analytical essay format better and learn how to provide substantive analysis on various topics. Read on to learn how to write a top-level analytical paper and submit it on time.
Main Tips for Writing an Analytical Essay
An analytical essay should provide a comprehensive analysis of a chosen topic. What makes an analysis essay different from other assignments is that it includes a personal opinion of an author. This is why analytical writing should be persuasive.
Below, we have rounded up the key tips you need to follow when producing an analytical essay outline and the main body of your text. Read on to learn more about the analytical essay format and create a text that will fully meet the requirements.
Select an Analytical Essay Topic
Before creating an analytical essay outline, make sure to pick a topic that you are interested in. It should be provocative enough to engage your readers. A widely-debated topic will help you write an analytical essay that grabs the attention of a wide audience.
Consider your goals and conduct thorough research to see if you have enough sources to support the main thesis of your analysis essay.
Come Up With a Strong Analytical Thesis Statement
When writing an analytical essay, start by formulating a thesis statement that includes the topic and the main goal of your text. It will help you create an analytical essay outline and show your readers what you will discuss in your analysis essay.
Add it to the last paragraph of your analytical essay introduction. Due to this, your analytical essay outline will look better structured. Look at any analytical essay example to see how you can introduce your subject. In most cases, one sentence will suffice to state your analysis essay’s goal. However, a complex analytical essay outline might require you to use two sentences for a thesis statement.
Write an Analytical Essay Body with a Clear Structure
Your analytical essay outline should include 3-4 paragraphs. However, a literary analysis essay usually consists of 5 paragraphs. When it comes to analytical writing, it is important to cover a different point in each section of the main body of an analysis paper.
After writing an analytical essay, check whether each paragraph contains an introduction and the main point. Besides, it should contain evidence. An expertly written analytical essay outline will help you reach out to your target audience more effectively.
Conduct Research Before Writing an Analytical Essay Outline
While this step is preparatory, it is a must for those who want to write a well-grounded analytical paper.
- First, select the best ideas for your essay
- Then, emphasize the problems with works written by other researchers
- Finally, write your analytical essay outline to demonstrate what approach you want to take
Examine the context and find examples to illustrate the scope of the issue. You may draw parallels to emphasize your point and make your topic more relatable.
Analyze the Implications of the Evidence
After listing your pieces of evidence and demonstrating how it is related to your thesis, show why it is important. You need to explore it deeply and use it to support your argument. It will make your analytical essay outline well-grounded facts.
Write an Analytical Essay Conclusion
Whether you write a literary analysis essay or other types of assignments, there is no need to add any new data at the end of your analysis paper. Instead, summarize the arguments you mentioned in your analytical essay outline. The conclusion of your analysis essay should be short and clear. Here, you need to demonstrate that you have achieved your goals.
Analytical Essay Writing Tips
If you want to get the highest grade for your analytical essay, you need to know a little bit more than just the basics of paper writing. Read these handy tips to write a perfect essay you will be proud of:
- Double-check your paper for spelling and grammar mistakes. In case your essay contains too many errors, neither an in-depth analysis nor the elaborate writing style will make it look any better. Situations when essays of great value in terms of research and a message they convey are poorly assessed because of the abundance of mistakes are not rare. Make sure you have enough time to proofread your paper before submission. Also, you may consider asking somebody to take a fresh look at your essay and check it for you.
- Reading your analytical essay out loud helps you discover all types of errors or weak phrases. This method might seem a bit uncomfortable, but it has proved to be very effective for many students. Note that silent reading of your paper isn’t even half as helpful as reading it aloud.
- Another great idea to check on the rhythm and flow of your paper is to ask someone to read it for you. While listening to the text, you could perceive it from another perspective and discover even more inconsistencies and mistakes.
- Double-check the facts you use in your analytical essay. The names of people, books, research, publications, as well as dates of historical events are too important to be misspelled. Things like these show your professionalism and the way you treat your readers.
Write an Analytical Essay with HandmadeWriting
Writing an analytical essay requires time, strong writing skills, great attention to detail, and a huge interest in the assigned topic. However, life can be unpredictable sometimes, and students might find themselves at risk of failing their creative assignments. Stress, family issues, poor health, and even unwillingness to work on a certain topic may become significant obstacles on their way to the A-grade work.
If you have similar problems, there is no need to compromise your reputation and grades. You can always refer to HandmadeWriting professionals who are ready to help you with a paper of any type and complexity. They will understand your individual style and totally devote themselv

A life lesson in Romeo and Juliet taught by death
Due to human nature, we draw conclusions only when life gives us a lesson since the experience of others is not so effective and powerful. Therefore, when analyzing and sorting out common problems we face, we may trace a parallel with well-known book characters or real historical figures. Moreover, we often compare our situations with […]

Ethical Research Paper Topics
Writing a research paper on ethics is not an easy task, especially if you do not possess excellent writing skills and do not like to contemplate controversial questions. But an ethics course is obligatory in all higher education institutions, and students have to look for a way out and be creative. When you find an […]

Art Research Paper Topics
Students obtaining degrees in fine art and art & design programs most commonly need to write a paper on art topics. However, this subject is becoming more popular in educational institutions for expanding students’ horizons. Thus, both groups of receivers of education: those who are into arts and those who only get acquainted with art […]
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Write a Perfect Analytical Paragraph

- 8-minute read
- 30th January 2023
If you are looking up how to write an analytical paragraph, you are most likely writing an argumentative or analytical essay. Analytical essays are similar to other essays, such as descriptive essays, in that you have a central idea, organize supporting ideas into body paragraphs, and make conclusions.
However, analytical essays differ from other essays because the writer must go further. They require the writer to interpret and analyze a given text or information using evidence to support their central idea or thesis statement. This analysis takes place in analytical paragraphs, or body paragraphs, if you are writing an analytical essay .
In this article, you’ll learn the components of a perfect analytical paragraph: the topic sentence, evidence, analysis, and conclusion. Keep reading to learn more.
What Is an Analytical Paragraph?
An analytical paragraph is a paragraph that breaks down a piece of literature, an idea, or a concept into smaller parts and analyzes each part to understand the whole. Being able to write an effective and successful analytical paragraph reflects a writer’s critical thinking and organizational writing skills. All in all, like any other type of writing, writing an analytical paragraph requires skill and practice.
Write the Topic Sentence
A topic sentence is usually the first, or sometimes second, sentence at the beginning of anybody paragraph. Your topic sentence should contain one main idea related to the thesis statement . If it is not related to your thesis statement, then you are likely off topic.
Pro Tip: If your topic sentence is the second sentence of your paragraph, then your first sentence should be a transitional sentence .
Let’s look at a thesis statement and some topic sentences to get a better idea.
Topic: Examine and analyze the marriages in George Eliot’s Middlemarch .
Thesis Statement: Eliot uses three different marriages to give depth to everyday people and show the reader the struggles of marriage within the nineteenth century’s societal standards of submissive roles, class range, and financial status.
Topic Sentence 1: Lydgate and Rosamond had a terrible marriage in Middlemarch , like all other marriages during this time.
This topic sentence is not effective because it is not specific enough and does not directly relate to the thesis statement. It does not mention how their “terrible” marriage is related to submissive roles, class range, or financial status. Additionally, the overly generalized language of “all” marriages being terrible marriages during this time is a weak argument.
Topic Sentence 2: Financial matters play a huge role in the Lydgate and Rosamond marriage, as Lydgate has no money and Rosamond is a big spender.
This topic sentence is effective because it directly supports the thesis statement. It is focused on the financial status of this marriage.
Provide Evidence
The type of evidence you use to support your topic sentence will largely depend on the topic of your analytical essay. For example, if you are writing an essay related to a work of literature, you will need to provide direct quotes, paraphrasing, specific details, or a summary from the work to support your main idea. If your topic is related to analyzing data, then you may use figures, statistics, or charts and graph evidence to support your topic sentence.
Regardless of what type of evidence you provide, it must be appropriate and directly relate to and support your topic sentence.
For example, if we take the above thesis and topic sentence, we might select direct quotes, paraphrases, or summaries from the novel Middlemarch that depict the marriage’s financial stress.
Pro Tip: When using direct quotes, make sure you always provide an in-text citation and use correct punctuation to ensure your essay is neat and clean.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Once you have provided evidence, you should analyze it to illustrate its significance and how it relates to the topic sentence. In your analysis, you can discuss how an author uses certain literary devices to emphasize character traits, themes, patterns, and connections in a literary work.
Be sure that your analysis always connects to the topic sentence/main idea of the paragraph. Avoid introducing new ideas in this section. Save those for later paragraphs or consider creating a new one to explore and analyze the new point.
Conclude Your Paragraph
When closing an analytical paragraph, you can consider doing two things:
● Briefly emphasize the main point your reader should take away after having read the paragraph.
● Begin a transition if the analysis continues into the next paragraph. (This strategy may be more suitable for longer, more in-depth analytical essays).
Using the above example topic sentence, we might conclude the paragraph as follows:
Notice how this concluding statement not only emphasizes the main points from the paragraph but also ties back into the thesis statement.
Writing Tips For Analytical Paragraphs
Leave out first person language.
Avoid using language such as “in my opinion,” “from my perspective,” or “I think.” While the analysis is your interpretation of a text or information, you should rely on and focus on using evidence to support your ideas. Overall, you should aim to maintain an objective tone .
Instead of saying “I think Rosamond is manipulative,” you should use evidence from the text to show that she was manipulative. For example, “Rosamond shows a pattern of manipulation throughout Middlemarch , specifically toward her husband. For instance, she says, ‘…’”
Do Writing Exercises
When writing, especially in the early drafts of an essay, it is typical to find the main idea of a paragraph at the end. This is a natural course for our thinking process. However, the main idea should be presented as your topic sentence at the beginning of this paragraph. Additionally, most students leave this main idea at the end because they do not identify it as the main idea.
To overcome this dilemma, try a looping prewriting exercise . In this exercise, you write continuously for a designated time (maybe 10 minutes, your choice). At the end of that time, read over what you’ve written and circle the main idea of the text (this is usually at the end). In the next cycle, you start with this main idea at the beginning and further examine and analyze it.
This is a wonderful exercise to help you pick out main ideas and delve deeper into your analysis.
Get Feedback
If you are a student, there are several options to get feedback for free. Ask a friend to read your essay. Go to your writing center to get feedback and help with your writing. Go to your professor’s office hours with your writing or questions to get detailed advice. More often than not, they are happy to see you take advantage of their expertise.
As a working professional, writer, or author, you can look to fellow authors or bookish friends to read your work. You can find free beta readers online from sites such as Goodreads to get feedback from your target audience. You can also find writing groups on social media platforms.
Proofread Your Work
It can be easy to finish writing an essay and think “Finally, I’m done!” Unfortunately, that is only half the process. Be sure to always read and reread your writing before hitting submit. Check for stray commas, spelling errors, or awkward sentences to make your main ideas and hard work shine. Learn about 6 Quick and Easy Tips for Proofreading you can do at home.
Writing an analytical paragraph doesn’t have to be stressful. Be sure to include a topic sentence at the beginning of your paragraph that connects to the thesis statement. Provide a variety of evidence to support your main idea, analyze the text by highlighting literary devices used, themes, and patterns, and end with a brief concluding statement.
If you need more help with writing analysis, descriptive essays, or any other type of essay, then Proofed is here to help. Try our free trial today!
What Is a Topic Sentence?
A topic sentence goes at the beginning of a body paragraph and clearly states the main idea of the paragraph.
How Do I Organize an Analytical Paragraph?
An analytical paragraph has four components: topic sentence, evidence, analysis, and conclusion. The topic sentence is the most important part of any body paragraph because it establishes the main idea of the paragraph and relates to the thesis statement.
What Makes a Good Analytical Paragraph?
A good analytical paragraph has a clear topic sentence, strong evidence, and a thorough analysis that reflects the writer’s critical thinking and writing skills. It should conclude by emphasizing the main idea of the paragraph and how it supports the essay overall.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
3-minute read
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...
2-minute read
How to Cite the CDC in APA
If you’re writing about health issues, you might need to reference the Centers for Disease...
5-minute read

Six Product Description Generator Tools for Your Product Copy
Introduction If you’re involved with ecommerce, you’re likely familiar with the often painstaking process of...
What Is a Content Editor?
Are you interested in learning more about the role of a content editor and the...
4-minute read
The Benefits of Using an Online Proofreading Service
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
8.5 Writing Process: Creating an Analytical Report
Learning outcomes.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Identify the elements of the rhetorical situation for your report.
- Find and focus a topic to write about.
- Gather and analyze information from appropriate sources.
- Distinguish among different kinds of evidence.
- Draft a thesis and create an organizational plan.
- Compose a report that develops ideas and integrates evidence from sources.
- Give and act on productive feedback to works in progress.
You might think that writing comes easily to experienced writers—that they draft stories and college papers all at once, sitting down at the computer and having sentences flow from their fingers like water from a faucet. In reality, most writers engage in a recursive process, pushing forward, stepping back, and repeating steps multiple times as their ideas develop and change. In broad strokes, the steps most writers go through are these:
- Planning and Organization . You will have an easier time drafting if you devote time at the beginning to consider the rhetorical situation for your report, understand your assignment, gather ideas and information, draft a thesis statement, and create an organizational plan.
- Drafting . When you have an idea of what you want to say and the order in which you want to say it, you’re ready to draft. As much as possible, keep going until you have a complete first draft of your report, resisting the urge to go back and rewrite. Save that for after you have completed a first draft.
- Review . Now is the time to get feedback from others, whether from your instructor, your classmates, a tutor in the writing center, your roommate, someone in your family, or someone else you trust to read your writing critically and give you honest feedback.
- Revising . With feedback on your draft, you are ready to revise. You may need to return to an earlier step and make large-scale revisions that involve planning, organizing, and rewriting, or you may need to work mostly on ensuring that your sentences are clear and correct.
Considering the Rhetorical Situation
Like other kinds of writing projects, a report starts with assessing the rhetorical situation —the circumstance in which a writer communicates with an audience of readers about a subject. As the writer of a report, you make choices based on the purpose of your writing, the audience who will read it, the genre of the report, and the expectations of the community and culture in which you are working. A graphic organizer like Table 8.1 can help you begin.
Summary of Assignment
Write an analytical report on a topic that interests you and that you want to know more about. The topic can be contemporary or historical, but it must be one that you can analyze and support with evidence from sources.
The following questions can help you think about a topic suitable for analysis:
- Why or how did ________ happen?
- What are the results or effects of ________?
- Is ________ a problem? If so, why?
- What are examples of ________ or reasons for ________?
- How does ________ compare to or contrast with other issues, concerns, or things?
Consult and cite three to five reliable sources. The sources do not have to be scholarly for this assignment, but they must be credible, trustworthy, and unbiased. Possible sources include academic journals, newspapers, magazines, reputable websites, government publications or agency websites, and visual sources such as TED Talks. You may also use the results of an experiment or survey, and you may want to conduct interviews.
Consider whether visuals and media will enhance your report. Can you present data you collect visually? Would a map, photograph, chart, or other graphic provide interesting and relevant support? Would video or audio allow you to present evidence that you would otherwise need to describe in words?
Another Lens. To gain another analytic view on the topic of your report, consider different people affected by it. Say, for example, that you have decided to report on recent high school graduates and the effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on the final months of their senior year. If you are a recent high school graduate, you might naturally gravitate toward writing about yourself and your peers. But you might also consider the adults in the lives of recent high school graduates—for example, teachers, parents, or grandparents—and how they view the same period. Or you might consider the same topic from the perspective of a college admissions department looking at their incoming freshman class.
Quick Launch: Finding and Focusing a Topic
Coming up with a topic for a report can be daunting because you can report on nearly anything. The topic can easily get too broad, trapping you in the realm of generalizations. The trick is to find a topic that interests you and focus on an angle you can analyze in order to say something significant about it. You can use a graphic organizer to generate ideas, or you can use a concept map similar to the one featured in Writing Process: Thinking Critically About a “Text.”
Asking the Journalist’s Questions
One way to generate ideas about a topic is to ask the five W (and one H) questions, also called the journalist’s questions : Who? What? When? Where? Why? How? Try answering the following questions to explore a topic:
Who was or is involved in ________?
What happened/is happening with ________? What were/are the results of ________?
When did ________ happen? Is ________ happening now?
Where did ________ happen, or where is ________ happening?
Why did ________ happen, or why is ________ happening now?
How did ________ happen?
For example, imagine that you have decided to write your analytical report on the effect of the COVID-19 shutdown on high-school students by interviewing students on your college campus. Your questions and answers might look something like those in Table 8.2 :
Asking Focused Questions
Another way to find a topic is to ask focused questions about it. For example, you might ask the following questions about the effect of the 2020 pandemic shutdown on recent high school graduates:
- How did the shutdown change students’ feelings about their senior year?
- How did the shutdown affect their decisions about post-graduation plans, such as work or going to college?
- How did the shutdown affect their academic performance in high school or in college?
- How did/do they feel about continuing their education?
- How did the shutdown affect their social relationships?
Any of these questions might be developed into a thesis for an analytical report. Table 8.3 shows more examples of broad topics and focusing questions.
Gathering Information
Because they are based on information and evidence, most analytical reports require you to do at least some research. Depending on your assignment, you may be able to find reliable information online, or you may need to do primary research by conducting an experiment, a survey, or interviews. For example, if you live among students in their late teens and early twenties, consider what they can tell you about their lives that you might be able to analyze. Returning to or graduating from high school, starting college, or returning to college in the midst of a global pandemic has provided them, for better or worse, with educational and social experiences that are shared widely by people their age and very different from the experiences older adults had at the same age.
Some report assignments will require you to do formal research, an activity that involves finding sources and evaluating them for reliability, reading them carefully, taking notes, and citing all words you quote and ideas you borrow. See Research Process: Accessing and Recording Information and Annotated Bibliography: Gathering, Evaluating, and Documenting Sources for detailed instruction on conducting research.
Whether you conduct in-depth research or not, keep track of the ideas that come to you and the information you learn. You can write or dictate notes using an app on your phone or computer, or you can jot notes in a journal if you prefer pen and paper. Then, when you are ready to begin organizing your report, you will have a record of your thoughts and information. Always track the sources of information you gather, whether from printed or digital material or from a person you interviewed, so that you can return to the sources if you need more information. And always credit the sources in your report.
Kinds of Evidence
Depending on your assignment and the topic of your report, certain kinds of evidence may be more effective than others. Other kinds of evidence may even be required. As a general rule, choose evidence that is rooted in verifiable facts and experience. In addition, select the evidence that best supports the topic and your approach to the topic, be sure the evidence meets your instructor’s requirements, and cite any evidence you use that comes from a source. The following list contains different kinds of frequently used evidence and an example of each.
Definition : An explanation of a key word, idea, or concept.
The U.S. Census Bureau refers to a “young adult” as a person between 18 and 34 years old.
Example : An illustration of an idea or concept.
The college experience in the fall of 2020 was starkly different from that of previous years. Students who lived in residence halls were assigned to small pods. On-campus dining services were limited. Classes were small and physically distanced or conducted online. Parties were banned.
Expert opinion : A statement by a professional in the field whose opinion is respected.
According to Louise Aronson, MD, geriatrician and author of Elderhood , people over the age of 65 are the happiest of any age group, reporting “less stress, depression, worry, and anger, and more enjoyment, happiness, and satisfaction” (255).
Fact : Information that can be proven correct or accurate.
According to data collected by the NCAA, the academic success of Division I college athletes between 2015 and 2019 was consistently high (Hosick).
Interview : An in-person, phone, or remote conversation that involves an interviewer posing questions to another person or people.
During our interview, I asked Betty about living without a cell phone during the pandemic. She said that before the pandemic, she hadn’t needed a cell phone in her daily activities, but she soon realized that she, and people like her, were increasingly at a disadvantage.
Quotation : The exact words of an author or a speaker.
In response to whether she thought she needed a cell phone, Betty said, “I got along just fine without a cell phone when I could go everywhere in person. The shift to needing a phone came suddenly, and I don’t have extra money in my budget to get one.”
Statistics : A numerical fact or item of data.
The Pew Research Center reported that approximately 25 percent of Hispanic Americans and 17 percent of Black Americans relied on smartphones for online access, compared with 12 percent of White people.
Survey : A structured interview in which respondents (the people who answer the survey questions) are all asked the same questions, either in person or through print or electronic means, and their answers tabulated and interpreted. Surveys discover attitudes, beliefs, or habits of the general public or segments of the population.
A survey of 3,000 mobile phone users in October 2020 showed that 54 percent of respondents used their phones for messaging, while 40 percent used their phones for calls (Steele).
- Visuals : Graphs, figures, tables, photographs and other images, diagrams, charts, maps, videos, and audio recordings, among others.
Thesis and Organization
Drafting a thesis.
When you have a grasp of your topic, move on to the next phase: drafting a thesis. The thesis is the central idea that you will explore and support in your report; all paragraphs in your report should relate to it. In an essay-style analytical report, you will likely express this main idea in a thesis statement of one or two sentences toward the end of the introduction.
For example, if you found that the academic performance of student athletes was higher than that of non-athletes, you might write the following thesis statement:
student sample text Although a common stereotype is that college athletes barely pass their classes, an analysis of athletes’ academic performance indicates that athletes drop fewer classes, earn higher grades, and are more likely to be on track to graduate in four years when compared with their non-athlete peers. end student sample text
The thesis statement often previews the organization of your writing. For example, in his report on the U.S. response to the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, Trevor Garcia wrote the following thesis statement, which detailed the central idea of his report:
student sample text An examination of the U.S. response shows that a reduction of experts in key positions and programs, inaction that led to equipment shortages, and inconsistent policies were three major causes of the spread of the virus and the resulting deaths. end student sample text
After you draft a thesis statement, ask these questions, and examine your thesis as you answer them. Revise your draft as needed.
- Is it interesting? A thesis for a report should answer a question that is worth asking and piques curiosity.
- Is it precise and specific? If you are interested in reducing pollution in a nearby lake, explain how to stop the zebra mussel infestation or reduce the frequent algae blooms.
- Is it manageable? Try to split the difference between having too much information and not having enough.
Organizing Your Ideas
As a next step, organize the points you want to make in your report and the evidence to support them. Use an outline, a diagram, or another organizational tool, such as Table 8.4 .
Drafting an Analytical Report
With a tentative thesis, an organization plan, and evidence, you are ready to begin drafting. For this assignment, you will report information, analyze it, and draw conclusions about the cause of something, the effect of something, or the similarities and differences between two different things.
Introduction
Some students write the introduction first; others save it for last. Whenever you choose to write the introduction, use it to draw readers into your report. Make the topic of your report clear, and be concise and sincere. End the introduction with your thesis statement. Depending on your topic and the type of report, you can write an effective introduction in several ways. Opening a report with an overview is a tried-and-true strategy, as shown in the following example on the U.S. response to COVID-19 by Trevor Garcia. Notice how he opens the introduction with statistics and a comparison and follows it with a question that leads to the thesis statement (underlined).
student sample text With more than 83 million cases and 1.8 million deaths at the end of 2020, COVID-19 has turned the world upside down. By the end of 2020, the United States led the world in the number of cases, at more than 20 million infections and nearly 350,000 deaths. In comparison, the second-highest number of cases was in India, which at the end of 2020 had less than half the number of COVID-19 cases despite having a population four times greater than the U.S. (“COVID-19 Coronavirus Pandemic,” 2021). How did the United States come to have the world’s worst record in this pandemic? underline An examination of the U.S. response shows that a reduction of experts in key positions and programs, inaction that led to equipment shortages, and inconsistent policies were three major causes of the spread of the virus and the resulting deaths end underline . end student sample text
For a less formal report, you might want to open with a question, quotation, or brief story. The following example opens with an anecdote that leads to the thesis statement (underlined).
student sample text Betty stood outside the salon, wondering how to get in. It was June of 2020, and the door was locked. A sign posted on the door provided a phone number for her to call to be let in, but at 81, Betty had lived her life without a cell phone. Betty’s day-to-day life had been hard during the pandemic, but she had planned for this haircut and was looking forward to it; she had a mask on and hand sanitizer in her car. Now she couldn’t get in the door, and she was discouraged. In that moment, Betty realized how much Americans’ dependence on cell phones had grown in the months since the pandemic began. underline Betty and thousands of other senior citizens who could not afford cell phones or did not have the technological skills and support they needed were being left behind in a society that was increasingly reliant on technology end underline . end student sample text
Body Paragraphs: Point, Evidence, Analysis
Use the body paragraphs of your report to present evidence that supports your thesis. A reliable pattern to keep in mind for developing the body paragraphs of a report is point , evidence , and analysis :
- The point is the central idea of the paragraph, usually given in a topic sentence stated in your own words at or toward the beginning of the paragraph. Each topic sentence should relate to the thesis.
- The evidence you provide develops the paragraph and supports the point made in the topic sentence. Include details, examples, quotations, paraphrases, and summaries from sources if you conducted formal research. Synthesize the evidence you include by showing in your sentences the connections between sources.
- The analysis comes at the end of the paragraph. In your own words, draw a conclusion about the evidence you have provided and how it relates to the topic sentence.
The paragraph below illustrates the point, evidence, and analysis pattern. Drawn from a report about concussions among football players, the paragraph opens with a topic sentence about the NCAA and NFL and their responses to studies about concussions. The paragraph is developed with evidence from three sources. It concludes with a statement about helmets and players’ safety.
student sample text The NCAA and NFL have taken steps forward and backward to respond to studies about the danger of concussions among players. Responding to the deaths of athletes, documented brain damage, lawsuits, and public outcry (Buckley et al., 2017), the NCAA instituted protocols to reduce potentially dangerous hits during football games and to diagnose traumatic head injuries more quickly and effectively. Still, it has allowed players to wear more than one style of helmet during a season, raising the risk of injury because of imperfect fit. At the professional level, the NFL developed a helmet-rating system in 2011 in an effort to reduce concussions, but it continued to allow players to wear helmets with a wide range of safety ratings. The NFL’s decision created an opportunity for researchers to look at the relationship between helmet safety ratings and concussions. Cocello et al. (2016) reported that players who wore helmets with a lower safety rating had more concussions than players who wore helmets with a higher safety rating, and they concluded that safer helmets are a key factor in reducing concussions. end student sample text
Developing Paragraph Content
In the body paragraphs of your report, you will likely use examples, draw comparisons, show contrasts, or analyze causes and effects to develop your topic.
Paragraphs developed with Example are common in reports. The paragraph below, adapted from a report by student John Zwick on the mental health of soldiers deployed during wartime, draws examples from three sources.
student sample text Throughout the Vietnam War, military leaders claimed that the mental health of soldiers was stable and that men who suffered from combat fatigue, now known as PTSD, were getting the help they needed. For example, the New York Times (1966) quoted military leaders who claimed that mental fatigue among enlisted men had “virtually ceased to be a problem,” occurring at a rate far below that of World War II. Ayres (1969) reported that Brigadier General Spurgeon Neel, chief American medical officer in Vietnam, explained that soldiers experiencing combat fatigue were admitted to the psychiatric ward, sedated for up to 36 hours, and given a counseling session with a doctor who reassured them that the rest was well deserved and that they were ready to return to their units. Although experts outside the military saw profound damage to soldiers’ psyches when they returned home (Halloran, 1970), the military stayed the course, treating acute cases expediently and showing little concern for the cumulative effect of combat stress on individual soldiers. end student sample text
When you analyze causes and effects , you explain the reasons that certain things happened and/or their results. The report by Trevor Garcia on the U.S. response to the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 is an example: his report examines the reasons the United States failed to control the coronavirus. The paragraph below, adapted from another student’s report written for an environmental policy course, explains the effect of white settlers’ views of forest management on New England.
student sample text The early colonists’ European ideas about forest management dramatically changed the New England landscape. White settlers saw the New World as virgin, unused land, even though indigenous people had been drawing on its resources for generations by using fire subtly to improve hunting, employing construction techniques that left ancient trees intact, and farming small, efficient fields that left the surrounding landscape largely unaltered. White settlers’ desire to develop wood-built and wood-burning homesteads surrounded by large farm fields led to forestry practices and techniques that resulted in the removal of old-growth trees. These practices defined the way the forests look today. end student sample text
Compare and contrast paragraphs are useful when you wish to examine similarities and differences. You can use both comparison and contrast in a single paragraph, or you can use one or the other. The paragraph below, adapted from a student report on the rise of populist politicians, compares the rhetorical styles of populist politicians Huey Long and Donald Trump.
student sample text A key similarity among populist politicians is their rejection of carefully crafted sound bites and erudite vocabulary typically associated with candidates for high office. Huey Long and Donald Trump are two examples. When he ran for president, Long captured attention through his wild gesticulations on almost every word, dramatically varying volume, and heavily accented, folksy expressions, such as “The only way to be able to feed the balance of the people is to make that man come back and bring back some of that grub that he ain’t got no business with!” In addition, Long’s down-home persona made him a credible voice to represent the common people against the country’s rich, and his buffoonish style allowed him to express his radical ideas without sounding anti-communist alarm bells. Similarly, Donald Trump chose to speak informally in his campaign appearances, but the persona he projected was that of a fast-talking, domineering salesman. His frequent use of personal anecdotes, rhetorical questions, brief asides, jokes, personal attacks, and false claims made his speeches disjointed, but they gave the feeling of a running conversation between him and his audience. For example, in a 2015 speech, Trump said, “They just built a hotel in Syria. Can you believe this? They built a hotel. When I have to build a hotel, I pay interest. They don’t have to pay interest, because they took the oil that, when we left Iraq, I said we should’ve taken” (“Our Country Needs” 2020). While very different in substance, Long and Trump adopted similar styles that positioned them as the antithesis of typical politicians and their worldviews. end student sample text
The conclusion should draw the threads of your report together and make its significance clear to readers. You may wish to review the introduction, restate the thesis, recommend a course of action, point to the future, or use some combination of these. Whichever way you approach it, the conclusion should not head in a new direction. The following example is the conclusion from a student’s report on the effect of a book about environmental movements in the United States.
student sample text Since its publication in 1949, environmental activists of various movements have found wisdom and inspiration in Aldo Leopold’s A Sand County Almanac . These audiences included Leopold’s conservationist contemporaries, environmentalists of the 1960s and 1970s, and the environmental justice activists who rose in the 1980s and continue to make their voices heard today. These audiences have read the work differently: conservationists looked to the author as a leader, environmentalists applied his wisdom to their movement, and environmental justice advocates have pointed out the flaws in Leopold’s thinking. Even so, like those before them, environmental justice activists recognize the book’s value as a testament to taking the long view and eliminating biases that may cloud an objective assessment of humanity’s interdependent relationship with the environment. end student sample text
Citing Sources
You must cite the sources of information and data included in your report. Citations must appear in both the text and a bibliography at the end of the report.
The sample paragraphs in the previous section include examples of in-text citation using APA documentation style. Trevor Garcia’s report on the U.S. response to COVID-19 in 2020 also uses APA documentation style for citations in the text of the report and the list of references at the end. Your instructor may require another documentation style, such as MLA or Chicago.
Peer Review: Getting Feedback from Readers
You will likely engage in peer review with other students in your class by sharing drafts and providing feedback to help spot strengths and weaknesses in your reports. For peer review within a class, your instructor may provide assignment-specific questions or a form for you to complete as you work together.
If you have a writing center on your campus, it is well worth your time to make an online or in-person appointment with a tutor. You’ll receive valuable feedback and improve your ability to review not only your report but your overall writing.
Another way to receive feedback on your report is to ask a friend or family member to read your draft. Provide a list of questions or a form such as the one in Table 8.5 for them to complete as they read.
Revising: Using Reviewers’ Responses to Revise your Work
When you receive comments from readers, including your instructor, read each comment carefully to understand what is being asked. Try not to get defensive, even though this response is completely natural. Remember that readers are like coaches who want you to succeed. They are looking at your writing from outside your own head, and they can identify strengths and weaknesses that you may not have noticed. Keep track of the strengths and weaknesses your readers point out. Pay special attention to those that more than one reader identifies, and use this information to improve your report and later assignments.
As you analyze each response, be open to suggestions for improvement, and be willing to make significant revisions to improve your writing. Perhaps you need to revise your thesis statement to better reflect the content of your draft. Maybe you need to return to your sources to better understand a point you’re trying to make in order to develop a paragraph more fully. Perhaps you need to rethink the organization, move paragraphs around, and add transition sentences.
Below is an early draft of part of Trevor Garcia’s report with comments from a peer reviewer:
student sample text To truly understand what happened, it’s important first to look back to the years leading up to the pandemic. Epidemiologists and public health officials had long known that a global pandemic was possible. In 2016, the U.S. National Security Council (NSC) published a 69-page document with the intimidating title Playbook for Early Response to High-Consequence Emerging Infectious Disease Threats and Biological Incidents . The document’s two sections address responses to “emerging disease threats that start or are circulating in another country but not yet confirmed within U.S. territorial borders” and to “emerging disease threats within our nation’s borders.” On 13 January 2017, the joint Obama-Trump transition teams performed a pandemic preparedness exercise; however, the playbook was never adopted by the incoming administration. end student sample text
annotated text Peer Review Comment: Do the words in quotation marks need to be a direct quotation? It seems like a paraphrase would work here. end annotated text
annotated text Peer Review Comment: I’m getting lost in the details about the playbook. What’s the Obama-Trump transition team? end annotated text
student sample text In February 2018, the administration began to cut funding for the Prevention and Public Health Fund at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; cuts to other health agencies continued throughout 2018, with funds diverted to unrelated projects such as housing for detained immigrant children. end student sample text
annotated text Peer Review Comment: This paragraph has only one sentence, and it’s more like an example. It needs a topic sentence and more development. end annotated text
student sample text Three months later, Luciana Borio, director of medical and biodefense preparedness at the NSC, spoke at a symposium marking the centennial of the 1918 influenza pandemic. “The threat of pandemic flu is the number one health security concern,” she said. “Are we ready to respond? I fear the answer is no.” end student sample text
annotated text Peer Review Comment: This paragraph is very short and a lot like the previous paragraph in that it’s a single example. It needs a topic sentence. Maybe you can combine them? end annotated text
annotated text Peer Review Comment: Be sure to cite the quotation. end annotated text
Reading these comments and those of others, Trevor decided to combine the three short paragraphs into one paragraph focusing on the fact that the United States knew a pandemic was possible but was unprepared for it. He developed the paragraph, using the short paragraphs as evidence and connecting the sentences and evidence with transitional words and phrases. Finally, he added in-text citations in APA documentation style to credit his sources. The revised paragraph is below:
student sample text Epidemiologists and public health officials in the United States had long known that a global pandemic was possible. In 2016, the National Security Council (NSC) published Playbook for Early Response to High-Consequence Emerging Infectious Disease Threats and Biological Incidents , a 69-page document on responding to diseases spreading within and outside of the United States. On January 13, 2017, the joint transition teams of outgoing president Barack Obama and then president-elect Donald Trump performed a pandemic preparedness exercise based on the playbook; however, it was never adopted by the incoming administration (Goodman & Schulkin, 2020). A year later, in February 2018, the Trump administration began to cut funding for the Prevention and Public Health Fund at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, leaving key positions unfilled. Other individuals who were fired or resigned in 2018 were the homeland security adviser, whose portfolio included global pandemics; the director for medical and biodefense preparedness; and the top official in charge of a pandemic response. None of them were replaced, leaving the White House with no senior person who had experience in public health (Goodman & Schulkin, 2020). Experts voiced concerns, among them Luciana Borio, director of medical and biodefense preparedness at the NSC, who spoke at a symposium marking the centennial of the 1918 influenza pandemic in May 2018: “The threat of pandemic flu is the number one health security concern,” she said. “Are we ready to respond? I fear the answer is no” (Sun, 2018, final para.). end student sample text
A final word on working with reviewers’ comments: as you consider your readers’ suggestions, remember, too, that you remain the author. You are free to disregard suggestions that you think will not improve your writing. If you choose to disregard comments from your instructor, consider submitting a note explaining your reasons with the final draft of your report.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Authors: Michelle Bachelor Robinson, Maria Jerskey, featuring Toby Fulwiler
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Writing Guide with Handbook
- Publication date: Dec 21, 2021
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/8-5-writing-process-creating-an-analytical-report
© Dec 19, 2023 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
- Increase Font Size
What is Exposition Writing
12.6 Analytical Essay Checklist Exercise
For each essay, answer the following questions in groups of 3-4 people. One person should record the answers. One person should keep the group on task. One person should keep track of time. Be prepared to explain your answers.
- Structure: Was there an introduction, 3-5 body paragraphs, and a conclusion? Was each distinguishable?
- Could you easily identify a thesis? Was it a strong or weak thesis? Explain your answer.
- Could you easily identify topic sentences?
- Was support provided for each main point? Was it effective support?
- Were outside sources cited with in the essay? (internal documentation)
- Were outside sources cited on a Works Cited page? (external documentation)
- Was the introduction engaging and did it provide information helpful in following the essays? Why/why not?
Was the conclusion effective? Why/why not?

Expression and Inquiry by Christopher Manning; Sally Pierce; and Melissa Lucken is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

13.6: Analytical Essay Checklist Exercise
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 50422

- Chris Manning, Sally Pierce, & Melissa Lucken
- Lansing Community College
For each essay, answer the following questions in groups of 3-4 people. One person should record the answers. One person should keep the group on task. One person should keep track of time. Be prepared to explain your answers.
- Structure: Was there an introduction, 3-5 body paragraphs, and a conclusion? Was each distinguishable?
- Could you easily identify a thesis? Was it a strong or weak thesis? Explain your answer.
- Could you easily identify topic sentences?
- Was support provided for each main point? Was it effective support?
- Were outside sources cited with in the essay? (internal documentation)
- Were outside sources cited on a Works Cited page? (external documentation)
- Was the introduction engaging and did it provide information helpful in following the essays? Why/why not?
Was the conclusion effective? Why/why not?

The Ultimate Essay Checklist
#scribendiinc
Getting Started
Essay writing: it might not be your favorite thing in the world, but the essay editing experts at Scribendi are here to change that by making it a little less scary and a lot more fun! (Okay—perhaps "fun" is a bit strong. How about "bearable"?)
While there are four main types of essays—expository, persuasive, analytical, and argumentative—the basic structure of any essay is the same:
- An introductory paragraph
- At least three body paragraphs
- A concluding paragraph
- A bibliography
Generally, the higher your level of education, the more complex your essay structure will be. While high school students typically stick with the five-paragraph essay, university and graduate students are expected to discuss topics that require more than five paragraphs to flesh out. Whatever type of essay you're writing, following this basic format will help you accomplish your intended goal.
This ultimate essay checklist will provide you with everything you need to unleash your knowledge and express your creativity while following standard essay-writing conventions. This essay checklist will show you how to write a stellar essay of any style, and it will give you the confidence to explore and write about any topic.
General Tips
- Get an early start. It's much easier to come up with and organize your ideas when you're not pressed for time and are able to conduct proper research. The earlier you start, the easier it will be . . . so don't procrastinate!
- Choose a topic. Your instructor will likely give you a handful of topics to choose from or a general topic area. Depending on the instructions you're given, you will have to select and refine the topic. You can choose something you're already interested in or something you know nothing about—either way, you'll be doing your research and learning along the way.
- Use various sources of information. With the vast amount of information available today, you're far from limited when it comes to choosing your sources. Use books, websites, journal articles, research studies, interviews—the world is your oyster! Just remember to keep track of your sources so that you can cite them properly and add them to your bibliography. Also check what kinds of sources your professor wants: primary, secondary, or both?
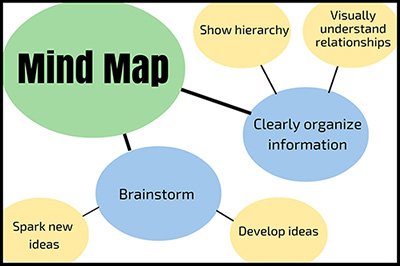
- Do not plagiarize. Cite your work and give credit where it's due. Do not take credit for others' thoughts or ideas, and make yourself aware of the basic rules for avoiding plagiarism .
- Create an outline. Make a rough outline of the sections and points of your essay. Writing your ideas down will help you organize your thoughts and see what you need to add, change, or rearrange.
- Provide evidence. Use evidence from your research to support your ideas. Each body paragraph will contain an original idea, but you will need to back it up with evidence to make it credible.
- Don't use "I" statements or make sweeping generalizations. Stay objective, and be specific.
- Grab your audience's attention. Come up with an attention-grabbing title and introduction that will make your reader want more.
- Use logic. Within each paragraph and throughout your essay, keep your ideas coherent and linear.
- Use an essay style that complements your content (and is in accordance with your professor's guidelines). There are four main types of essays:
- Expository : The writer explains an idea or issue to the reader.
- Persuasive : The writer tries to convince the reader to take his or her position on an idea, issue, or topic.
- Analytical : The writer examines and analyzes an idea, issue, or topic.
- Argumentative : The writer tries to prove that his or her position is correct.
- Answer what , why , and how . Regardless of the type of essay you write, it should answer each of these questions.
- Don't feel obliged to write your first draft in order, from introduction to bibliography. It can be difficult to write a completely linear essay when you have lots of different ideas, so start by writing whatever you're ready to write—you can put all the pieces together later. This will make the process easier and less stressful.
Introduction
The introductory paragraph broadly introduces your topic by giving your reader an overview of what your essay will be about and the points that will be discussed. It often starts with a general statement that acts as the topic sentence for the paragraph, and it provides a general discussion that leads to a specific thesis statement at the end of the paragraph.
- Do not explicitly explain your intentions. For example, do not say, "The purpose of this essay is to . . ." Instead, allow the topic sentence to help your reader identify and determine your purpose. By the time readers get to the end, they will have a comprehensive understanding of your essay and its intent.
- Choose a thesis statement that the body of your essay will be able to support. This thesis will be the "hook" of your essay, and it is often one of the last sentences in the introductory paragraph. A hook is a line that grabs the reader's attention—it "hooks" them, just like a fishing hook grabs a fish. The goal of the hook is to keep your reader interested and to clearly indicate the purpose of the essay.
The body of the essay develops the argument that was outlined in the introduction.
- Use topic sentences. The topic sentence of each paragraph provides a brief summary of what the paragraph is about.

- Set up the transition to your next point. The concluding sentence of each paragraph should function as a hook and transition into the next paragraph.
- Discuss and support a different idea in each paragraph. Limit each paragraph to one main idea. The topic sentence of each paragraph will help you organize your own thoughts and let the reader know what that paragraph is about. If you're writing a five-paragraph essay, follow this general outline:
- The first paragraph contains the strongest argument and ties into the hook at the end of the introductory paragraph. Discuss your first point, elaborate on it, and provide evidence in support of it. Close with a transitional hook.
- The second paragraph contains a more neutral argument, and it ties into the hook at the end of the first paragraph. Discuss your second point, elaborate on it, and provide evidence to support it. Close with a transitional hook.
- The third paragraph contains another strong argument and ties into the hook at the end of the second paragraph. Discuss your third point, elaborate on it, and provide evidence to support it. Close with a transitional sentence that leads smoothly into the concluding paragraph.
In contrast to the introductory paragraph, the concluding paragraph starts out specific (by reintroducing the thesis) and becomes more general. It ties your ideas together and brings your paper to a culmination.
The concluding paragraph provides a general discussion of your findings and shows the reader that you have accomplished what you intended to at the outset.
- Restate your thesis (though not necessarily using the exact same words). In contrast to the introductory paragraph, the concluding paragraph starts out specific (by reintroducing the thesis) and becomes more general. It ties your ideas together and brings your paper to a close.
- Discuss your findings based on your research and evidence. Has your thesis been proven?
- Don't introduce any new ideas. The point here is to sum up and wrap up your essay, not to confuse readers by providing new information.
- End on a high note. You can finish the essay in a variety of ways. For example, you might provide suggestions for future research, state a call to action, share a quote, or ask a question. Depending on the topic and purpose of your essay, choose a closing line that will fit well with the rest of your essay's structure and leave readers thinking " Wow! "
Bibliography/Works Cited
The Bibliography or Works Cited page is a list of all the references you used throughout the paper. It can be alphabetized or numbered depending on the style guide you are using. While a Bibliography includes every resource you consulted when preparing your essay, a Works Cited page includes only the resources cited in your essay. Find out which is required by consulting the style guide assigned by your professor.

- To make creating your reference list easier, use citation software . There are many different options out there, and several of the software programs are free (especially if you're enrolled in a university that has a subscription to one of the services). These citation software programs essentially create your bibliography for you, making the process fast, easy, and accurate.
Review, Revise, Rework
- Give yourself a day or two before rereading and revising your essay. This way, you will have a fresh set of eyes, making it easier to catch any mistakes.
- Don't be afraid to rearrange paragraphs, delete sentences, or add information. Reading through your essay a few days after writing it makes it much easier to see where and how the structure needs to be changed.
- Correct any errors in spelling, grammar, and punctuation. Check the essay yourself, have a friend review it, or better yet, have your essay edited by a professional editing service .
- Avoid colloquialisms and contractions. ('Cause it just ain't professional in an academic setting. Lol.)
- Analyze the flow of your essay , and make sure that your ideas and paragraphs flow smoothly from one to the next.
- Cut out any extraneous information or fluff. We've all done it, but adding extra words to make a word count requirement doesn't fly with most professors, and it will definitely detract from the strength of your essay.
Now, it's Time to Write!
It may seem overwhelming, but writing an essay doesn't have to be stressful. After coming up with a topic, doing some research, and creating a basic outline, you're ready to start filling in the gaps. Using primary and/or secondary research, back up your ideas and support them with credible sources. Just don't forget to cite those sources! Once you've written your first draft, take a day or two away from your paper so you will have a clear head when you come back to revise it. As suggested, you may even want to have your paper edited by the professionals at Scribendi , who will not only correct any surface-level errors but will also check for consistency, clarity, and cohesiveness, providing comments and suggestions along the way.
Essay writing is so much easier if you're equipped with the right tools, and that's what we hope we've given you with this ultimate essay checklist. Now that you know how to write an essay (regardless of the style), we're confident in your ability to write an essay about any topic that your instructor might have in store for you. Happy writing!
Image sources: Foundry/Pixabay.com, succo/Pixabay.com, ClkerFreeVectorImages/Pixabay.com
Ask a Professional to Edit Your Essay
Hire one of our expert editors , or get a free sample.
Have You Read?
"The Complete Beginner's Guide to Academic Writing"
Related Posts

Escape the Five-Paragraph Essay

Essay Writing Help

How to Write a Great Thesis Statement
Upload your file(s) so we can calculate your word count, or enter your word count manually.
We will also recommend a service based on the file(s) you upload.
English is not my first language. I need English editing and proofreading so that I sound like a native speaker.
I need to have my journal article, dissertation, or term paper edited and proofread, or I need help with an admissions essay or proposal.
I have a novel, manuscript, play, or ebook. I need editing, copy editing, proofreading, a critique of my work, or a query package.
I need editing and proofreading for my white papers, reports, manuals, press releases, marketing materials, and other business documents.
I need to have my essay, project, assignment, or term paper edited and proofread.
I want to sound professional and to get hired. I have a resume, letter, email, or personal document that I need to have edited and proofread.
Prices include your personal % discount.
Prices include % sales tax ( ).

Know Your Terms: Holistic, Analytic, and Single-Point Rubrics
May 1, 2014
Can't find what you are looking for? Contact Us

Whether you’re new to rubrics, or you just don’t know their formal names, it may be time for a primer on rubric terminology.
So let’s talk about rubrics for a few minutes. What we’re going to do here is describe two frequently used kinds of rubrics, holistic and analytic , plus a less common one called the single-point rubric (my favorite, for the record). For each one, we’ll look at an example and explore its pros and cons.
Holistic Rubrics
A holistic rubric is the most general kind. It lists three to five levels of performance, along with a broad description of the characteristics that define each level. The levels can be labeled with numbers (such as 1 through 4), letters (such as A through F) or words (such as Beginning through Exemplary ). What each level is called isn’t what makes the rubric holistic — it’s the way the characteristics are all lumped together.
Suppose you’re an unusually demanding person. You want your loved ones to know what you expect if they should ever make you breakfast in bed. So you give them this holistic rubric:
When your breakfast is done, you simply gather your loved ones and say, “I’m sorry my darlings, but that breakfast was just a 2. Try harder next time.”
The main advantage of a holistic rubric is that it’s easy on the teacher — in the short run, anyway. Creating a holistic rubric takes less time than the others, and grading with one is faster, too. You just look over an assignment and give one holistic score to the whole thing.
The main disadvantage of a holistic rubric is that it doesn’t provide targeted feedback to students , which means they’re unlikely to learn much from the assignment. Although many holistic rubrics list specific characteristics for each level, the teacher gives only one score, without breaking it down into separate qualities. This often leads the student to approach the teacher and ask, “Why did you give me a 2?” If the teacher is the explaining kind, he will spend a few minutes breaking down the score. If not, he’ll say something like, “Read the rubric.” Then the student has to guess which factors had the biggest influence on her score. For a student who really tries hard, it can be heartbreaking to have no idea what she’s doing wrong.
Holistic rubrics are most useful in cases when there’s no time (or need, though that’s hard to imagine) for specific feedback. You see them in standardized testing — the essay portion of the SAT is scored with a 0-6 holistic rubric. When hundreds of thousands of essays have to be graded quickly, and by total strangers who have no time to provide feedback, a holistic rubric comes in handy.
Analytic Rubrics
An analytic rubric breaks down the characteristics of an assignment into parts, allowing the scorer to itemize and define exactly what aspects are strong, and which ones need improvement.
So for the breakfast in bed example, an analytic rubric would look like this:
In this case, you’d give your loved ones a separate score for each category. They might get a 3 on Presentation , but a 2 on Food and just a 1 on Comfort . To make feedback even more targeted, you could also highlight specific phrases in the rubric, like, “the recipient is crowded during the meal” to indicate exactly what went wrong.
This is where we see the main advantage of the analytic rubric: It gives students a clearer picture of why they got the score they got. It is also good for the teacher, because it gives her the ability to justify a score on paper, without having to explain everything in a later conversation.
Analytic rubrics have two significant disadvantages , however: (1) Creating them takes a lot of time . Writing up descriptors of satisfactory work — completing the “3” column in this rubric, for example — is enough of a challenge on its own. But to have to define all the ways the work could go wrong, and all the ways it could exceed expectations, is a big, big task. And once all that work is done, (2) students won’t necessarily read the whole thing. Facing a 36-cell table crammed with 8-point font is enough to send most students straight into a nap. And that means they won’t clearly understand what’s expected of them.
Still, analytic rubrics are useful when you want to cover all your bases, and you’re willing to put in the time to really get clear on exactly what every level of performance looks like.
Single-Point Rubrics
A single-point rubric is a lot like an analytic rubric, because it breaks down the components of an assignment into different criteria. What makes it different is that it only describes the criteria for proficiency ; it does not attempt to list all the ways a student could fall short, nor does it specify how a student could exceed expectations.
A single-point rubric for breakfast in bed would look like this:
Notice that the language in the “Criteria” column is exactly the same as the “3” column in the analytic rubric. When your loved ones receive this rubric, it will include your written comments on one or both sides of each category, telling them exactly how they fell short (“runny eggs,” for example) and how they excelled (“vase of flowers”). Just like with the analytic rubric, if a target was simply met, you can just highlight the appropriate phrase in the center column.
If you’ve never used a single-point rubric, it’s worth a try. In 2010, Jarene Fluckiger studied a collection of teacher action research studies on the use of single-point rubrics. She found that student achievement increased with the use of these rubrics, especially when students helped create them and used them to self-assess their work.
The single-point rubric has several advantages : (1) It contains far less language than the analytic rubric, which means students are more likely to read it and it will take less time to create , while still providing rich detail about what’s expected. (2) Areas of concern and excellence are open-ended . When using full analytic rubrics, I often find that students do things that are not described on the rubric, but still depart from expectations. Because I can’t find the right language to highlight, I find myself hand-writing justifications for a score in whatever space I can find. This is frustrating, time-consuming and messy. With a single-point rubric, there’s no attempt to predict all the ways a student might go wrong. Similarly, the undefined “Advanced” column places no limits on how students might stretch themselves. “If the highest level is already prescribed then creativity may be limited to that pre-determined level,” says Fluckiger. “Students may surprise us if we leave quality open-ended.”
The main disadvantage of single-point rubrics is that using them requires more writing on the teacher’s part. If a student has fallen short in many areas, completing that left-hand column will take more time than simply highlighting a pre-written analytic rubric.
Need Ready-Made Rubrics?
My Rubric Pack gives you four different designs in Microsoft Word and Google Docs formats. It also comes with video tutorials to show you how to customize them for any need, plus a Teacher’s Manual to help you understand the pros and cons of each style. Check it out here:

Fluckiger, J. (2010). Single point rubric: A tool for responsible student self-assessment. Teacher Education Faculty Publications. Paper 5. Retrieved April 25, 2014 from http://digitalcommons.unomaha.edu/tedfacpub/5 .
Mertler, C. A. (2001). Designing scoring rubrics for your classroom. Practical Assessment, Research & Evaluation , 7(25). Retrieved April 30, 2014 from http://PAREonline.net/getvn.asp?v=7&n=25 .
Know Your Terms is my effort to build a user-friendly knowledge base of terms every educator should know. New items will be added on an ongoing basis. If you heard some term at a PD and didn’t want to admit you didn’t know what it meant, send it to me via the contact form and I’ll research it for you.
What to Read Next
Categories: Instruction , Learning Theory
Tags: assessment , college teaching , Grades 3-5 , Grades 6-8 , Grades 9-12 , Grades K-2 , know your terms , rubrics
69 Comments
Jen, This is an awesome, thoughtful post and idea. I’m using this in my class with a final project the kids are turning in this morning. I’m excited about the clarity with which I can evaluate their projects.
I’m so glad to hear it. If you’re willing to share what you made and tell me how it all went later on, I would be thrilled to hear it.
So appreciated! These practical, detailed applications are helpful! Mahalo from Kauai, Hi.
Rubrics are great tools for making expectations explicit. Thanks for this post which gives me some vocabulary to discuss rubrics. Though, I could use some resources on rubric scoring, b/c I see a lot of teachers simply adding up the number of squares and having that be the total point value of an assignment, which leads to incorrect grades on assignments. I’ve found some converters, but haven’t found a resource that has the math broken out.
Thanks for the feedback, Jeremey! You are not the first person to request a clearer breakdown on the math for this rubric (or others), and you’re right, teachers definitely have different approaches to this. I have some good ideas on this, so I will plan a post on it for the near future.
Did you do a post regarding grading a single rubric?
Yup! Here’s Meet the Single Point Rubric . You might also be interested in How To Turn Rubric Scores into Grades . Hope this helps!
Really rubric is a very useful tool when assessing students in class
There is no such thing as an appropriate converter. Levels are levels and points and percentages are points and percentages and never the twain should meet.
(I’m very late to the discussion.)
Years ago, Ken O’Connor was the person who turned my grading around. For that reason, I would be against using the “0-80%” or “0-80 points” piece. O’Connor is very clear about how grades below 50 ruin a grade average.
I would love to be able to grade with standards only, but what I do instead, to fit into our district grading software, is to grade by standards (using letters, where “proficient” is a “B”), and the traditional letters are equal to 95/85/75/65/55. That gives kids a chance if they ever somehow earn only a F. It doesn’t kill the rest of their grade.
(I forgot to say that I absolutely love the one-column rubric. It is going to be a huge help to me this year.)
This post was so helpful! I am struggling right now with assigning Habits of Work grades to my Spanish students in middle and high school. I was using an analytic rubric for both my assessment and the students’ self-assessment, but it’s possible the quantity of words was exacerbating the problem of students scoring themselves in the best column out of reflex or habit. I’m going to try a single-point rubric to see if that can lead us to some more reflective thought.
This website was very helpful. Thank you.
LOVELY post. So didactic and useful. After reading some quite dense posts on rubrics, I’ve enjoyed this a lot. You have now convinced me to use rubrics! THANK YOU Jenny and CONGRATS!!!
SINGLE-POINT rubrics
I have not seen or heard of single point rubrics. I’m really excited to try that out. Less wordy and easier for students to see what is expected of them and get meaningful feedback.
Oooh! I never thought I’d like a post on rubrics, but this was awesome! Thanks for your great explanations. I’m currently working my way through your Teacher’s Guide to Tech/Jumpstart program and I wanted to take a minute and tell you how much I appreciate your site and podcasts too. Everything is so concise, interesting and helpful!
Sariah, thank you!! I haven’t gotten a ton of feedback on the JumpStart program, so it’s really nice to hear that! Let me know if you have any questions!
I am Master of Mathematics Education student and I am busy compiling my assignments on rubrics. Your notes are well explained and straight to the point. However, my Professor have instructed as to look up on primarily rubrics and multi-trait rubrics that i seems not to get. Do you care to differentiate them for me? Thank you.
Hi Martha. I was not familiar with those two terms, so I did a bit of reading in this post: http://carla.umn.edu/assessment/vac/improvement/p_5.html It seems to me that a primary trait rubric focuses on a single, somewhat broad description of how well the student achieved a certain goal. Multi-trait rubrics allow teachers to assess a task on a variety of descriptors. To me, the primary trait seems very much like the holistic rubric, and the multi-trait rubric seems a lot like an analytic rubric. If anyone else reading this knows the finer points of the differences among these four, I would love to hear them!
How to better calculate a grade with a rubric. Please see: http://tinypic.com/r/2dl6d5c/9 .
Thank you so much for this humorous and informative approach to rubrics. It seems to me that the single-point rubric, which I agree makes the most sense for assignment specific rubrics, is really just a clear set of assignment instructions / expectations with the addition of over/under columns to make it rubric-ish.
I love to have students help create rubrics. By the end of the year, we often create the entire rubric together as a class, but often I allow them to start by assigning one “open” section that they think I should grade on for which I help them write “exceeds, meets, doesn’t meet” standards. Then we move on to them assigning points for each standard that I’ve written (this is fascinating for me to see what they weight more heavily), and finally on to writing their own categories for which I write the standards, and then we reverse so that I write the categories and they write the standards. I give a lot of writing and speaking assignments and they really like being involved in how and what and how much we grade. (I never find they are too easy on themselves, either.) I love the single-point rubric especially for assignments I come up with off the cuff and don’t have time to write an elaborate rubric for!
If you’re moving away from traditional grades, the single-point rubric is a perfect instrument for delivering specific feedback.
This is a great site and I really liked the one example used with the multiple rubric styles so we could really understand the difference in them. I am confused about the difference between a Single Point rubric and a Primary Trait rubric. You didn’t mention the Primary Trait rubric so I am wondering if they are the same. Thank you, Karen
Thanks for writing in and for your kind words! I work for Cult of Pedagogy, and in answering your question, I started scrolling myself. Jenn responded to another reader, and I think you might find her response helpful as well as the link:
http://carla.umn.edu/assessment/vac/improvement/p_5.html
“It seems to me that a primary trait rubric focuses on a single, somewhat broad description of how well the student achieved a certain goal. Multi-trait rubrics allow teachers to assess a task on a variety of descriptors. To me, the primary trait seems very much like the holistic rubric, and the multi-trait rubric seems a lot like an analytic rubric.”
Hope this helps!
I do a sort of analytic + single point. I don’t include lots of writing on an analytic rubric. I give them the thick descriptions printed out earlier and I go over them (so each category actually does have detailed descriptions), but the rubric I mark is made up of lots of space and numbers 1-10. I keep it to ten categories. I leave lots of space for comments and comment on every category (even if it’s just one word). I conference with each student briefly when I hand back the rubrics. Each student is given two attempts – first for feedback, second for growth and a final score. (I taught high school theatre, so this method worked the best for me.)
Jen, Thank you for succinctly explaining the types of rubrics and THANK YOU for the free downloadable templates. I will share them with my education senior students!!! AWEsome work you have done.
You are very welcome, Alberta!
Dear Jennifer,
Thank you for the detailed information. I have been using single point rubrics from last year and I love them, but do you think we should give students a checklist as well? If so, what should it look like? I don’t want to kill their creativity, though.
I think the rubric can contain a checklist if you want students to include specific things in their end product, or you could do a separate checklist, then add something like “all items from checklist are included” in your rubric language. There is definitely a gray area here: Defining requirements too narrowly could stifle creativity, but it’s also important to be clear about expectations.
I have been working on a variation of the single-point rubric that I think might be even more useful for communicating expectations and feedback to students. Check it out here: https://docs.google.com/document/d/12JBIcpjeDYuTbQhEgJg2LKC5YPMDwTcIYCtl6jSGTeE/edit?usp=sharing
Really appreciate this post! Thank you. I have used the analytic approach, but I can really see the benefits of a single-point system. Thanks for your clear explanation.
Saying that ‘analytical’ rubrics are difficult and time consuming to write is true, but is also a cop-out. Taking the time to clearly define and articulate student behaviours at each level promotes student independence and self-assessment, and results in better outcomes. The fact that students have departed from what’s written on your rubric suggests that either the assessment wasn’t explained well enough or the rubric itself is of poor quality.
The analytical rubrics provided here fall well short of quality rubric standards. I would suggest reading Patrick griffin’s Assessment for Teaching, and visit the ReliableRubrics websites for good examples.
Thanks for the book and website suggestions, Martin. I do think it’s possible to construct a clear 4-column analytical rubric, but I have rarely seen one that manages to cover all the bases. The ones that DO cover every possible outcome are often insanely long. I’m thinking of some I got in grad school that were–I kid you not–several pages long and written in 9-point font. Despite the fact that I am a diligent student, even I got to the point where I threw in the towel and stopped reading the whole thing. Instead, I just gave my attention to the “3” and “4” columns. I’m guessing that other students do the same thing. If our goal is to have students understand what’s being asked of them and to pay attention to the details, why spend so much time on defining what NOT to do?
Thank you Jennifer, I have shared this with fellow colleagues in Costa Rica. I know this will be of great use!!
Thank you for this work. Your site has been very helfpul to me.
Thank you so much Jennifer! You seem to be an expert in making rubrics! I really appreciate the simplicity of the delivery of your thoughts about rubrics. I just want to ask if there is such a rubric for a cooperative activity? I am Geraldine, by the way, and me and my classmates are planning to conduct cooperative listening activities among Grade 8 students. We are having a hard time looking for a rubric that will assess their outputs as a group. Can you suggest one? Your response will be of great help. Thank you so much. May God bless you more and always!
Hi Geraldine, I work with Cult of Pedagogy and although we can’t think of anything specific to what you’re looking for, I’m thinking you might want to check out our Assessment & Feedback Pinterest board — there are a ton or resources that might help you create a rubric that would be specific to your needs. The most important thing is to identify what you want students to be able to do in the end. For example: listen to others with eye contact. (Be sure to check out Understanding by Design .) Then you can choose a rubric structure that will best fit your needs and provide effective feedback. Other than that, you might be able to find some great ideas through a Google search.
Well, thank you so much! May God bless you!
Great information. Can you tell me how you come to a total/final score on an analytic rubric if the student receives a variety of scores in the different categories? Thanks.
This is a great question! I’d check out Jenn’s post, Speed Up Grading with Rubric Codes . Even if you don’t use the codes, you’ll see in the video how an overall score can be given to a paper, even when scores in indivual categories vary. Basically the overall score reflects where most criteria have been met, along with supportive feedback. Hope this helps!
I loved the all of the rubrics you created for “Breakfast In Bed”. Your topic was an awesome analogy for teacher created tasks. I personally prefer the analytic rubric because I believe it gives the most accurate feedback to the student. If you feel more information is needed, you could expand the categories in the rubric, for example in this case, you could add a column called “sensory enhancements” , such as music or table setting. If you want to add a more personal comment you can always add it in the margin.
This issue has always frustrated me. I have recently been a HUGE proponent of holistic rubrics, but I do see the disadvantage of the feedback issue. For my first time teaching college composition, I used analytic rubrics–and hated them. It wasn’t the making rubrics that was time consuming, but determining how to break up the points and how to assign earned points for a paper. I would score a paper, add up all the points, and realized the paper got a B when, in reality, I knew it was a C-level paper. So I would erase and recalculate until I got the points I thought were more accurate. It took FOREVER!!! After some research, I decided to move to a holistic rubric, and it made grading way faster, but more importantly, I thought the numerical grade was much more accurate and consistent. (Score 6 would get a 95, 5 would be 85, etc., and I would give + or – for 3 more or less points). For feedback, I would annotate and underline/circle the parts of the criteria that they struggled in or did well in and left an end comment. And while I had them turn in a draft that I would give feedback on, I didn’t use the rubric for the draft feedback. Just comments on the paper.
I’m willing to try to single-point, but to get to that final numerical grade (since a no-grade classroom isn’t allowed, unfortunately) you’d still have to break down the points arbitrarily like an analytic rubric. Who’s to say that “structure” should be 30 points while “grammar” should be 10? What’s the actual difference between a 40/50 in “analysis” and a 42/50? My grading PTSD is resurfacing just thinking about grading essays that way. But at the same time, I also don’t like the limited feedback of the holistic rubric.
This is a link to a site where you can download a PDF that talks about a lot of composition issues, but pages 74-76 is about rubrics. Curious to know everyone’s thoughts. https://community.macmillan.com/docs/DOC-1593
Thank you so much 🙂 I learned a lot from this kind of Rubrics 🙂 (y)
Thank you very much for the breakdown of the the types of rubrics. This was very informational!
Thank you for the fantastic article. I came here from the Single Point Rubric post, and I feel so much better equipped to grade my next assignment. Thank you again!
Radhika, Yay! We are glad you found what you needed for your next assignment!
Jennifer, the clear, concise explanations of three types of rubrics are very refreshing. I teach a course called “Assessment and Measurement” to pre-service teachers and I introduce the analytic and holistic rubrics for them to use in performance assessments. The pre-service teachers spend a lot of time with just the language they want to use and, although I think rubrics are the path to more accuracy in grading, I find the idea is overwhelming to novice teachers. May I share this with my students? Of course giving you due credit. This is excellent.
Hi Hazel! Thanks for the positive feedback. You are welcome to share this post with your students!
Thank you! Your picture at the very beginning (and your examples) made the difference between holistic and analytical instantly click for me! Also, I have never heard of single point rubrics before, so I am excited to try them out this fall with an assignment or two that I think they would go perfectly with! Lastly, thanks for the templates!
I’ve been using rubrics for a long time. I started with the most complex, comprehensive things you cannot even imagine. It drove the kids crazy, and me too. Now I teach English to adults (as a 2nd or nth language) and I write much simpler rubrics. But they still have too much information. You are brilliant here with the single point rubric. What do you need to do to get it right? Write in the ways they didn’t match it, which is what you need to do anyways. I’m changing immediately to single point rubrics. I’ll also read your other posting about single point rubrics to see if you have any other ideas. I just met your blog this week (Online Global Academy) and will return, I’m sure. Many thanks. Lee
This is great to hear, Lee! Thanks for sharing.
I’ve always used rubrics but especially appreciate the single point rubric.
Hi My name is Andrena Weir, I work at the American School of Marrakech. Thank you so much for your information. As a Physical Ed teacher these rubrics are great. I like the one column rubric. I feel I spent too much time grading in ways that consume too much time. This is so much appreciated. I need someone like you to be in-contact with if I’m struggling to retrieve new Ideas. Thank you so very much, have the best day.
How about this type of rubric. Al the benefits of analytic but without the verbiage.
The food is raw/burned under/over cooked perfectly cooked
The tray is missing missing some items complete and utensils are dirty clean well presented
You get the idea
e.g. For Maths projects
https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/19MXAjBdiEHXwuxg0w7NkRIKuc4X7VNj1qOE74o_vNss/edit?usp=sharing
The blog destroyed my formatting.
The food is || raw/burned || under/over cooked || perfectly cooked
The tray is || missing || missing some items || complete and utensils are || dirty || clean || well presented
or check the linked example
I use rubrics with most of my practical assignments and yes they are very time consuming. After reading this post I’m very excited to try the single-point rubric. Most of the time my students just want to know what is needed. This way they can identify what I want them to be able to do. Thanks so much for this information about rubrics.
So glad this was helpful, Amy! I’ll be sure to let Jenn know.
Want to use analytical rubric
Thanks so much for all of the information. This is great to have as a resource!
I’ve never heard of a single-point rubric before but I love the idea! Your article totally spoke my language and touched on all of my concerns. Thanks for the tips!
Hi, Jennifer, I always come away with actionable tips. I am a faculty developer and Instructional Coach. Rubrics pose challenges for teachers, novice and seasoned alike, so thank you for these discussions to shine a light on rubrics, good and bad.
Meg, I am glad this post was helpful for you in your role! I will be sure to pass on your comments to Jenn.
Being in a rubricade, a crusade of rubrics, against the powers that might be from my school… I’m glad to read what you’ve made.
Neither the academic coordinator nor the headmaster seems to know anything about having more than four levels of achievement. Nothing about having single point rubrics or the ones needed for my laboratory reports which go up to 7 with numbers not correlative.
I’m a high (and middle) school natural sciences teacher, my specialty field is physics.
The rubric in question (rejected by my superiors) has been developped since my first days in the classroom, about 2 thousand eleven. I’ve been modifying it from time to time according to the new breakthroughs experienced in practice.
Maybe your really nice webpage will help me out in going past this nonsense.
Thanks a lot!
Glad you found this helpful!
A holistic rubric is only easier if the faculty are just slapping grades on assignments, which they shouldn’t be doing with any rubric, including a very detailed analytic one. There should be summary comments that explain how the student’s specific response to the assignment meets the descriptor for each score level and then suggestions for what they could do to improve (even if they got an A).
Thanks for your comment- as Jenn mentions in the post, holistic rubrics are limited in their space for feedback. Many teachers prefer the Single Point Rubric for personalized feedback. If the point of rubrics is to set students up with their next steps, this is one you might want to try!
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published.
literary analysis essay checklist
All Formats
Resource types, all resource types.
- Rating Count
- Price (Ascending)
- Price (Descending)
- Most Recent
Literary analysis essay checklist

Revising & Peer Editing Checklist : Argument, Narrative, Literary Analysis Essay

Five Paragraph Literary Analysis Essay Grading & Editing Checklist

- Word Document File
Literary Analysis Essay Peer Editing Checklist

The Outsiders Literary Analysis Essay , Organizer, Checklist , and Rubric

- Google Drive™ folder

Literary Analysis Essay editing checklist (self and peer)

Self-Editing Guide/ Checklist for Literary Analysis Essay

Writing and Revision Checklist for a Literary Analysis Essay

Literary Analysis Essay : Editing /Proofreading Checklists and Rubric (editable)

Writing Checklist or Rubric for Literary Analysis Essay

Literary Analysis Essay Graphic Organizer + Checklist

Literary Analysis Essay : Student Self-Edit Checklist

- Google Docs™
Literary Analysis Essay Checklist : 5 Paragraphs

Literary Analysis Essay Checklist : 4 Paragraphs
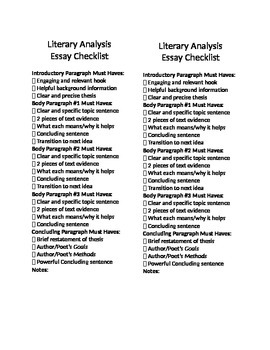
Literary Analysis Essay Checklist

Literary Essay Analysis Writing About Reading 3rd 4th Grade ELA Test Prep

- Google Apps™

Literary Analysis Unit and Literary Analysis Essay Writing in Middle School

An Example of a Literary Analysis Essay and Unit

Lord of the Flies Essay Unit for Literary Analysis Writing With Lesson Plans

- Easel Activity

PARCC / NJSLA Research Simulation and Literary Analysis : Format & Sample Essays

Romeo and Juliet Essay 1-Week of Literary Analysis Lesson Plans, Rubric, Etc.

Baby Literary Essay Analysis Graphic Organizers Templates Writing About Reading

Editable Middle School Literary Analysis Essay Rubrics for 6th 7th and 8th Grade

Essay Format Notes for Literary Analysis Writing

The Crucible Essay Unit for Literary Analysis Writing - Lesson Plans & Materials
- We're hiring
- Help & FAQ
- Privacy policy
- Student privacy
- Terms of service
- Tell us what you think
More From Forbes
How to choose participants for your emerging leader program.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Emerging leader programs hinge on your selection process. Here's everything you need to know to get ... [+] it right.
Let’s start with a real story of how not to choose participants for your emerging leader program. This pharmaceutical company had such a bad selection process that you can use it as a map of the mistakes you should avoid.
For context, this company has 1,000 sales reps and 100 sales managers. Here’s what the sales leader development team did:
- They asked each sales manager to nominate one high-potential sales rep.
- They whittled those 100 selections down to 12 nominees.
- They hired an outside talent selection I/O psychologist.
- The psychologist designed a rigorous, four-month selection process.
- Candidates took personality assessments, went through interviews, completed assignments, and finished by preparing and presenting projects to a panel.
- Then, after all that, the leadership development team selected eight of those 12 sales reps.
- Four sales reps returned to their jobs, unable to participate (and probably pretty peeved).
Here’s the biggest problem with this approach: It’s too selective. This poor leadership development team spent a huge chunk of their budget to weed out and disengage 88 of their top performers. Then, they demanded a significant amount of time and energy from four of their absolute best sales reps (we’re talking top 1%), only to tell them that they weren’t quite good enough. Yikes.
Open AI Gets Better Memory, New Lawsuits, And Sora’s First Music Video
Russian military personnel move into niger air base housing some us troops, madden 25 hall of famer will discontinue his relationship with ea, quantity: how do you decide how many emerging leaders to select.
I recommend that you think about this number in terms of two main categories of emerging leaders:
- Top talent to engage and retain. In the Pharma example, there’s a good chance that the eight leaders they chose went on to become great leaders. But, what about the 92 top sales reps they turned away? I cringe to think that they disengaged such a big portion of the top 10% of sales reps. Ideally, you want to engage and retain as large a percentage of that population as possible. Your emerging leader program is a great way to do so. Instead, this company poured hundreds of thousands of dollars into selecting and training only eight people. If retention is a key goal, expand your pool.
- Leaders to promote (replace manager attrition). Eight people does not cover this company’s average manager attrition rate of 20%. As managers leave or are promoted, about 20 seats will open up each year. At a bare minimum, you want 20 emerging leaders to choose from. Some will likely not be ready, and that’s okay because you don’t necessarily want all of your leaders to come up internally.
Generally speaking, both of the goals above point to the same solution: Broaden your pool. Even if many of your emerging leaders don’t siphon up into manager positions, development will help engage and retain them. In fact, emerging leadership development programs often help managers realize that they do not want to take a leadership role. And that is incredibly valuable.
Three Ways to Choose Your Participants
Here are three effective ways to consider handling your selection process:
- Have managers select, but don’t eliminate selections. Odds are, managers have a good grasp on who performs well and who would do well as a manager. Instead of weeding through their 100 selections to choose 12, take all 100 and develop them.
- Have employees self-select. If you want some checks and balances in place, you might ask your managers to confirm that those employees are a good fit for the emerging leader program and are at a good time in the year to handle the extra workload. But I’ve seen this work well with zero checks and balances.
- Select the top 10% or more of talent. Another way to select is to just take the top 10% of talent. No nominations, no weeding. Though, of course, there’s the whole debate about “what exactly makes a top 10% performer.”
All of these methods have something in common: They all seek to let more people in. Instead of spending your budget on selection, spend it on development. Imagine what the first pharma company could have done with all the money they spent weeding people out. They probably could have at least added the leaders they paid to eliminate (ironic!).
Regardless of your method, stay aware of how selection may interfere with diversity and equitable opportunity. Managers often carry biases. And, when team members know they weren’t selected by their manager, they can disengage. For these reasons, I tend to highly recommend self-selection.
Struggling to Choose One of the Above? Split Your Emerging Leader Program into Two Audiences
If you’re struggling to choose one of the above selection methods, it’s likely for the following reason (which I hear all the time):
“I want to have a big, equitable program that will develop anyone interested, but I also want a narrow ‘feeder’ program that pushes a select group of emerging leaders into management.”
There’s actually a simple, highly effective solution here: Split your audience. Do both.
At Ferring Pharmaceuticals, the Director of Commercial Leadership Development, Rob Daniel, did exactly this. He split emerging leaders into two main groups:
- Self-selected individual contributors: For the first program, Daniel allowed any sales rep to self-select. The program was six months long and focused on self-leadership topics like self-awareness, growth mindset, and emotional intelligence. This program helped Daniel’s team see who was interested in progressing and who was taking leadership development seriously.
- High-potential emerging leaders: This group of emerging leaders is already on track for a leadership position. They have a formalized individual development plan, have had serious conversations about becoming a leader, and have expressed a desire to lead people. This was a smaller audience (though still big enough to fill in for attrition). This program is a 12-month deep dive into leadership skills. It focuses on job shadowing and experiential learning. The goal of this program is to set emerging leaders up to thrive once they get promoted.
By building the program in this way, Daniel had his cake and ate it too. He engaged all talented sales reps while still getting selective as people progressed through the pipeline.
The number one objection to this style of program is price. But, Daniel actually ran both of these programs for less than the price of the failed emerging leader program at the beginning of this article. To do so, he leveraged self-driven learning, a behavior change platform, and group coaching. This made for a high-touch, expert-driven program that was still very cheap relative to the industry standard.
You can read more about Ferring’s approach here .
How to Evaluate and Select Your Candidates (If Not Self-Selected)
If you aren’t doing self-selection, then you need to determine your selection and evaluation criteria. Important things to consider include:
- Minimum tenure
- Minimum performance (and how to measure this)
- Essay questions (do you have them, and what are they?)
- Manager recommendation (beware of disengagement from those not selected)
- Live interview (how do you do this, and who conducts it?)
- Diversity (how do you ensure diversity and minimize bias?)
- Selection committee (who will be on it?)
Here’s a sample checklist:
Sample set of selection criteria. Each checkbox could have its own set of criteria.
At Olympus, for example, their emerging leader program used a selection committee to choose 20 participants from 40 applicants. With 80 first-line leaders across the organization, the target audience size would easily fill in for attrition. Olympus’s application process included a variety of criteria, such as:
- Modeling Olympus values.
- High performance: Set by each business unit, based on the 9-box model.
- Diversity in geography.
- Sales results.
- Achievements (e.g., field trainer responsibilities, national impact, and elite/quota performance).
- A letter of recommendation from your manager. A panel then reviewed and rated each essay.
- An essay assignment based on leadership competencies.
- A panel interview of each candidate’s manager.
For an in-depth look at a more intensive selection process, check out how Olympus does it here .
Promote Your Program Internally: A Story-Based Approach
Regardless of how big or small your audience is, you need to promote your program. If it’s open enrollment, you want to draw as many people as possible. And if it’s application-based, you want it to be as competitive as possible. Here are five guideposts to market your program.
- Make your audience the “hero” of your messaging. Show them what they have to gain by going through your program. Don’t get caught up in all the details, topics, and assessments that you personally geek out on. Focus on emerging leader success stories.
- Bring up the challenges your emerging leaders will face and how your program will help them rise above those challenges. For example, you might point out how tough it can be to transition from being great at sales to being great at leading a sales team, or how it can be difficult to know whether or not you want to lead people.
- Present your program as the answer to their challenge. Show how your program will help solve their challenge and guide them through it. Now is when you can geek out a bit and talk about how different topics and activities will help them overcome those challenges. For example, “By shadowing our best current manager, you will see first-hand what it takes to succeed as a manager.”
- Show your audience what they might lose by not joining your program. For example, you might point out that they may never know whether they want to take on a leadership role. Or, they may never be considered for the role.
- Be clear and concise. Make it easy for people to understand what they have to gain from your program.
Be sure to include testimonials if your program is already up and running. A great testimonial from an alumni may even touch on all of the above points.
Putting It All Together: When In Doubt, Expand Your Pool
Selection is daunting. But it’s worth being intentional about your process. Your audience is your program. My sweeping advice: If you’re unsure, expand your pool. You’ll regret passing up a potentially great leader more than you’ll regret developing a high-performer who never progresses into a leadership position.
Kevin Kruse is the Founder + CEO of LEADx , a leadership development company that specializes in emerging leader programs. Kevin is also a New York Times bestselling author of Great Leaders Have No Rules , 15 Secrets Successful People Know About Time Management , and Employee Engagement 2.0 .
- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Table of contents. Step 1: Reading the text and identifying literary devices. Step 2: Coming up with a thesis. Step 3: Writing a title and introduction. Step 4: Writing the body of the essay. Step 5: Writing a conclusion. Other interesting articles.
An analytical essay is a type of academic writing that delves deeply into a topic, idea, or piece of literature. Unlike descriptive or narrative essays, which focus on providing a vivid description or telling a story, an analytical essay aims to examine and dissect its subject matter. The primary objective of an analytical essay is to present a ...
An analytical essay is a type of academic writing in which a complicated topic or idea is broken down into smaller parts, analyzed and looked at, and a well-structured argument or evaluation is given. ... and citation styles throughout the essay. 4. Use a checklist: Use a checklist to ensure that you have addressed all the necessary components ...
The checklist for a literary & critical analysis essay is a tool that students can use to assess the development of five major components of their essay: Conceptual, Thesis, Development & Support, Structuring, and Language. Checklist for Literary & Critical Analysis Essay. Please use this checklist when drafting your critical analysis essay!
Analytical Essay - Handout 2022. Peay APSU Writing Center Analytical Essay Analytical Essay Resources: Website of Mrs. Maio and Cynthia Clumneck Muchnik's "Base FiveParagraph Structure" An analytical essay Begins with a main object, such as a poem, novel, short story, or play. Should examine how the selection establishes itself.
ANALYTICAL WRITING 1. Introduction ... Checklist for evaluation Choose the best answer for each of these items: ESSAY A ESSAY B 1. This type of essay is ... This essay seems to be developed by alternating the main characters and their role in furthering the narrative - there is some insight into the characters and their motives, but the essay ...
Writing Analytical Essays GETTING STARTED 1. Turn OFF your computer. Go into another room with a pen, the prompt, and some scratch paper. 2. Acknowledge the existence of the question. Do you know not only what the question is ... Here's a checklist: 3 a. Read aloud ONLY the topic sentences of every paragraph. If you (or someone
An analytical essay is a piece of writing aimed to provide a thorough analysis of a definite phenomenon using persuasive arguments and supporting assertions. Analysis in the analytical essay writing process stands for a method of research that allows one to study specific features of an object. Analytical papers also have to do with analysis of ...
with a strong analytical question that you will try to answer in your essay. Your answer to that question will be your essay's thesis. You may have many questions as you consider a source or set of sources, but not all of your questions will form the basis of a strong essay. For example, your initial questions
However, analytical essays differ from other essays because the writer must go further. They require the writer to interpret and analyze a given text or information using evidence to support their central idea or thesis statement. This analysis takes place in analytical paragraphs, or body paragraphs, if you are writing an analytical essay.
ENG 105: Composition I Learning Unit 8: Checklist Page 1 of 4 Textual Analysis Essay Checklist Instructions: Please read through this checklist before beginning your rough draft and then use it as a final revision checklist before turning in the final draft. You will not be required to turn in this checklist,
Essay Editing and Review Checklist: ... Has the essay topic been answered explicitly and fully? Is the essay analytical (i.e. Has it focused on `why', `how', `to what extent' and minimised description (the response to `what', 'when' 'who')
Analysis essay writing checklist. Your essay is almost finished! Now read your paper once again, checking whether you included all of the following in your analytical essay. Try not to read the text thoroughly, use purposeful reading instead. For example, in the first of the following points you need to look for the source and topic in the ...
Whenever you choose to write the introduction, use it to draw readers into your report. Make the topic of your report clear, and be concise and sincere. End the introduction with your thesis statement. Depending on your topic and the type of report, you can write an effective introduction in several ways.
For each essay, answer the following questions in groups of 3-4 people. One person should record the answers. One person should keep the group on task. One person should keep track of time. Be prepared to explain your answers.
13.6: Analytical Essay Checklist Exercise. Page ID. Chris Manning, Sally Pierce, & Melissa Lucken. Lansing Community College. For each essay, answer the following questions in groups of 3-4 people. One person should record the answers. One person should keep the group on task. One person should keep track of time.
While there are four main types of essays—expository, persuasive, analytical, and argumentative—the basic structure of any essay is the same: An introductory paragraph; At least three body paragraphs; ... This essay checklist will show you how to write a stellar essay of any style, and it will give you the confidence to explore and write ...
The Conclusion Paragraph: Strategies, Checklist, & Samples. The conclusion paragraph in a literary analysis essay functions as follows: It finishes off the essay and tells readers where the writer has brought them. It restates the thesis and contains echoes of the introduction and body paragraphs without listing the points covered in the essay
Planning Your Analytical Essay. To best succeed, we'll start from the planning stage, something you should do well before writing your essay. Make sure that you scribble down the point of each of your three paragraphs briefly, including 1-2 example quotes. Most importantly, be sure to write underneath the type of literary technique that said ...
The single-point rubric has several advantages: (1) It contains far less language than the analytic rubric, which means students are more likely to read it and it will take less time to create, while still providing rich detail about what's expected. (2) Areas of concern and excellence are open-ended.
4.9. (18) $32.99. Zip. Teaching Literary Analysis in middle school is finally broken down with this complete reading and essay writing unit. This unit includes 24 done-for-you lesson plans, reference pages, completed essays, and 40 literary analysis reading response examples with explanations and teaching for students.
At Olympus, for example, their emerging leader program used a selection committee to choose 20 participants from 40 applicants. With 80 first-line leaders across the organization, the target ...