
An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

- Digg
Latest Earthquakes | Chat Share Social Media

Measurable Performance Verbs for Writing Objectives
Do not use the following verbs in your objectives: Know, Comprehend, Understand, Appreciate, Familiarize, Study, Be Aware, Become Acquainted with, Gain Knowledge of, Cover, Learn, Realize. These are not measurable!
Knowledge Verbs
Count, Define, Draw, Identify, Indicate, List, Name, Point, Quote, recognize, Recall, Recite, Read, Record, Repeat, State, Tabulate, Trace, Write
Comprehension Verbs
Associate, Compare, Compute, Contrast, Describe, Differentiate, Discuss, Distinguish, Estimate, Interpret, Interpolate, Predict, Translate
Application Verbs
Apply, Calculate, Classify, Complete, Demonstrate, Employ, Examine, Illustrate, Practice, Relate, Solve, Use, Utilize
Analysis Verbs
Order, Group, Translate, Transform, Analyze, Detect, Explain, Infer, Separate, Summarize, Construct
Synthesis Verbs
Arrange, Combine, Construct, Create, Design, Develop, Formulate, Generalize, Integrate, Organize, Plan, Prepare, Prescribe, Produce, Propose, Specify
Evaluation Verbs
Appraise, Assess, Critique, Determine, Evaluate, Grade, Judge, Measure, Rank, Rate, Select, Test, Recommend
« Return to Training Developer's Tool Box
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
100+ Research Vocabulary Words & Phrases
The academic community can be conservative when it comes to enforcing academic writing style , but your writing shouldn’t be so boring that people lose interest midway through the first paragraph! Given that competition is at an all-time high for academics looking to publish their papers, we know you must be anxious about what you can do to improve your publishing odds.
To be sure, your research must be sound, your paper must be structured logically, and the different manuscript sections must contain the appropriate information. But your research must also be clearly explained. Clarity obviously depends on the correct use of English, and there are many common mistakes that you should watch out for, for example when it comes to articles , prepositions , word choice , and even punctuation . But even if you are on top of your grammar and sentence structure, you can still make your writing more compelling (or more boring) by using powerful verbs and phrases (vs the same weaker ones over and over). So, how do you go about achieving the latter?
Below are a few ways to breathe life into your writing.
1. Analyze Vocabulary Using Word Clouds
Have you heard of “Wordles”? A Wordle is a visual representation of words, with the size of each word being proportional to the number of times it appears in the text it is based on. The original company website seems to have gone out of business, but there are a number of free word cloud generation sites that allow you to copy and paste your draft manuscript into a text box to quickly discover how repetitive your writing is and which verbs you might want to replace to improve your manuscript.
Seeing a visual word cloud of your work might also help you assess the key themes and points readers will glean from your paper. If the Wordle result displays words you hadn’t intended to emphasize, then that’s a sign you should revise your paper to make sure readers will focus on the right information.
As an example, below is a Wordle of our article entitled, “ How to Choose the Best title for Your Journal Manuscript .” You can see how frequently certain terms appear in that post, based on the font size of the text. The keywords, “titles,” “journal,” “research,” and “papers,” were all the intended focus of our blog post.

2. Study Language Patterns of Similarly Published Works
Study the language pattern found in the most downloaded and cited articles published by your target journal. Understanding the journal’s editorial preferences will help you write in a style that appeals to the publication’s readership.
Another way to analyze the language of a target journal’s papers is to use Wordle (see above). If you copy and paste the text of an article related to your research topic into the applet, you can discover the common phrases and terms the paper’s authors used.
For example, if you were writing a paper on links between smoking and cancer , you might look for a recent review on the topic, preferably published by your target journal. Copy and paste the text into Wordle and examine the key phrases to see if you’ve included similar wording in your own draft. The Wordle result might look like the following, based on the example linked above.

If you are not sure yet where to publish and just want some generally good examples of descriptive verbs, analytical verbs, and reporting verbs that are commonly used in academic writing, then have a look at this list of useful phrases for research papers .
3. Use More Active and Precise Verbs
Have you heard of synonyms? Of course you have. But have you looked beyond single-word replacements and rephrased entire clauses with stronger, more vivid ones? You’ll find this task is easier to do if you use the active voice more often than the passive voice . Even if you keep your original sentence structure, you can eliminate weak verbs like “be” from your draft and choose more vivid and precise action verbs. As always, however, be careful about using only a thesaurus to identify synonyms. Make sure the substitutes fit the context in which you need a more interesting or “perfect” word. Online dictionaries such as the Merriam-Webster and the Cambridge Dictionary are good sources to check entire phrases in context in case you are unsure whether a synonym is a good match for a word you want to replace.
To help you build a strong arsenal of commonly used phrases in academic papers, we’ve compiled a list of synonyms you might want to consider when drafting or editing your research paper . While we do not suggest that the phrases in the “Original Word/Phrase” column should be completely avoided, we do recommend interspersing these with the more dynamic terms found under “Recommended Substitutes.”
A. Describing the scope of a current project or prior research
B. outlining a topic’s background, c. describing the analytical elements of a paper, d. discussing results, e. discussing methods, f. explaining the impact of new research, wordvice writing resources.
For additional information on how to tighten your sentences (e.g., eliminate wordiness and use active voice to greater effect), you can try Wordvice’s FREE APA Citation Generator and learn more about how to proofread and edit your paper to ensure your work is free of errors.
Before submitting your manuscript to academic journals, be sure to use our free AI proofreader to catch errors in grammar, spelling, and mechanics. And use our English editing services from Wordvice, including academic editing services , cover letter editing , manuscript editing , and research paper editing services to make sure your work is up to a high academic level.
We also have a collection of other useful articles for you, for example on how to strengthen your writing style , how to avoid fillers to write more powerful sentences , and how to eliminate prepositions and avoid nominalizations . Additionally, get advice on all the other important aspects of writing a research paper on our academic resources pages .

Best Active Verbs for Research Papers with Examples
What are active verbs.
Active verbs, often referred to as "action verbs," depict activities, processes, or occurrences. They energize sentences by illustrating direct actions, like "run," "write," or "discover." In contrast, linking verbs connect the subject of a sentence to its complement, offering information about the subject rather than denoting an action. The most common linking verb is the "be" verb (am, is, are, was, were, etc.), which often describes a state of being. While active verbs demonstrate direct activity or motion, linking and "be" verbs serve as bridges, revealing relations or states rather than actions.
While linking verbs are necessary to states facts or show connections between two or more items, subjects, or ideas, active verbs usually have a more specific meaning that can explain these connections and actions with greater accuracy. And they captivate the reader’s attention! (See what I did there?)
Why are active verbs important to use in research papers?
Using active verbs in academic papers enhances clarity and precision, propelling the narrative forward and making your arguments more compelling. Active verbs provide clear agents of action, making your assertions clearer and more vigorous. This dynamism ensures readers grasp the research's core points and its implications.
For example, using an active vs passive voice sentence can create more immediate connection and clarity for the reader. Instead of writing "The experiment was conducted by the team," one could write, "The team conducted the experiment."
Similarly, rather than stating "Results were analyzed," a more direct approach would be "We analyzed the results." Such usage not only shortens sentences but also centers the focus, making the statements about the research more robust and persuasive.
Best Active Verbs for Academic & Research Papers
When writing research papers , choose active verbs that clarify and energize writing: the Introduction section "presents" a hypothesis, the Methods section "describes" your study procedures, the Results section "shows" the findings, and the Discussion section "argues" the wider implications. Active language makes each section more direct and engaging, effectively guiding readers through the study's journey—from initial inquiry to final conclusions—while highlighting the researcher's active role in the scholarly exploration.
Active verbs to introduce a research topic
Using active verbs in the Introduction section of a research paper sets a strong foundation for the study, indicating the actions taken by researchers and the direction of their inquiry.
Stresses a key stance or finding, especially when referring to published literature.
Indicates a thorough investigation into a research topic.
Draws attention to important aspects or details of the study topic you are addressing.
Questions or disputes established theories or beliefs, especially in previous published studies.
Highlights and describes a point of interest or importance.
Inspects or scrutinizes a subject closely.
Sets up the context or background for the study.
Articulates
Clearly expresses an idea or theory. Useful when setting up a research problem statement .
Makes something clear by explaining it in more detail.
Active verbs to describe your study approach
Each of these verbs indicates a specific, targeted action taken by researchers to advance understanding of their study's topic, laying out the groundwork in the Introduction for what the study aims to accomplish and how.
Suggests a theory, idea, or method for consideration.
Investigates
Implies a methodical examination of the subject.
Indicates a careful evaluation or estimation of a concept.
Suggests a definitive or conclusive finding or result.
Indicates the measurement or expression of an element in numerical terms.
Active verbs to describe study methods
The following verbs express a specific action in the methodology of a research study, detailing how researchers execute their investigations and handle data to derive meaningful conclusions.
Implies carrying out a planned process or experiment. Often used to refer to methods in other studies the literature review section .
Suggests putting a plan or technique into action.
Indicates the use of tools, techniques, or information for a specific purpose.
Denotes the determination of the quantity, degree, or capacity of something.
Refers to the systematic gathering of data or samples.
Involves examining data or details methodically to uncover relationships, patterns, or insights.
Active verbs for a hypothesis or problem statement
Each of the following verbs initiates a hypothesis or statement of the problem , indicating different levels of certainty and foundations of reasoning, which the research then aims to explore, support, or refute.
Suggests a hypothesis or a theory based on limited evidence as a starting point for further investigation.
Proposes a statement or hypothesis that is assumed to be true, and from which a conclusion can be drawn.
Attempts to identify
Conveys an explicit effort to identify or isolate a specific element or relationship in the study.
Foretells a future event or outcome based on a theory or observation.
Theorizes or puts forward a consideration about a subject without firm evidence.
Proposes an idea or possibility based on indirect or incomplete evidence.
Active verbs used to interpret and explain study results
In the Discussion section , the findings of your study are interpreted and explained to the reader before moving on to study implications and limitations . These verbs communicate the outcomes of the research in a precise and assertive manner, conveying how the data aligns with the expectations and hypotheses laid out earlier in the paper.
Shows or unveils findings from the data.
Demonstrates
Clearly shows the result of an experiment or study, often implying evidence of a cause-and-effect relationship.
Illustrates
Shows or presentes a particular result or trend.
Provides evidence in favor of a theory or hypothesis.
Establishes the truth or validity of an anticipated outcome or theory.
Visually presents data, often implying the use of figures or tables.
Active verbs to discuss study implications
In the discussion of study implications, these verbs help to weave the results into a broader context, suggesting relevance, highlighting importance, and pointing out potential consequences within the respective field of research.
Proposes a possible interpretation or implication without making a definitive statement.
Points to broader consequences or significances hinted at by the results.
Indicates a logical consequence or a meaning that is not explicitly stated.
Strengthens the validity or importance of a concept or finding.
Emphasizes certain findings and their broader ramifications.
Underscores
Underlines or emphasizes the significance or seriousness of an implication.
Active verbs to discuss study limitations
Discussing study limitations with these verbs allows researchers to maintain transparency about their study's weaknesses, thus providing a clearer picture of the context and reliability of the research findings.
Acknowledges
Recognizes the existence of potential weaknesses or restrictions in the study.
Directly confronts a specific limitation and often discusses ways it has been mitigated.
Makes an observation of a limitation that could affect the interpretation of the results.
Reflects on or thinks about a limitation in the context of the study's impact or scope.
Points out and describes a specific limitation.
Makes known or reveals a limitation that could have an effect on the study's conclusions.
Active verbs for the Conclusion section
In the Conclusion section , these verbs are pivotal in crystallizing the core findings, implications, and the future trajectory of research initiated by the study.
Signifies drawing a final inference or judgement based on the results.
Provides a brief statement of the main points of the research findings.
States positively or asserts the validity of the findings.
Advises on a course of action based on the results obtained.
Highlights the importance or significance of the research outcomes.
Use an AI Grammar Checker to Correct Your Research Verbs
While lists like these will certainly help you improve your writing in any academic paper, it can still be a good idea to revise your paper using an AI writing assistant during the drafting process, and with professional editing services before submitting your work to journals.
Wordvice’s AI Proofreading Tool , AI Paraphrasing Tool , AI Summarizer , and AI Translator are ideal for enhancing your academic papers. And with our professional editing services, including academic proofreading and paper editing services, you get high-quality English editing from experts in your paper’s subject area.
Are You Using the Right Verbs in Your Research Paper?

Most researchers are focused on ensuring that their work not only gets the attention it deserves but is also published in leading international journals. However, this is a challenging task, given that journals often reject papers due to issues with language even if the research presented was groundbreaking. Writing an academic research paper is not just about conducting and reporting one’s work – the language one uses plays a significant role in how the research paper is received.
Academic writing needs to be formal and precise and researchers must possess the requisite language skills and knowledge about the correct words to use in scientific writing. This is a skill that early career researchers must acquire and perfect over time. Consistent writing will help you gain the experience you require to create error-free, submission ready research manuscripts. You will for example, learn that one proven way to make your manuscript more compelling is by using strong verbs for essays.
This article provides a brief overview of the different types of verbs to use in research papers. It also offers interesting insights into how verbs can be used effectively in academic writing.
What is a verb?
Let us first understand what a verb is. Verbs are words that convey an action, occurrence, or state of being. Given that most manuscripts contain explanations and descriptions of processes and methodologies, it is important to understand and choose the right kind of action verbs to be in for maximum impact.
Types of verbs
Broadly, verbs can be categorized into three different types.
- Action verbs – Action verbs verbs communicate precise actions
- Auxiliary verbs – Auxiliary verbs display the tense of the verb used. Sometimes referred to as helping verbs, they reveal if the verb is positive or negative
- Modal verbs – Modal verbs are auxiliary verbs that denote abilities
When using verbs in academic writing, it is very important for early career researchers and authors to ensure that colloquial or informal verbs should not make their way into their academic writing. Adhering to a formal structure of language with appropriate verbs is essential to maintaining the right tone and to accurately convey the author’s thoughts. For example, the use of action verbs in research objectives or strong verbs for thesis statements goes a long way in making the manuscript more impactful.
Usage of verbs
Researchers and authors must be careful in their selection of verbs to convey the proposed meaning. It is important to understand the context in which the verbs are to be used, and the way the language must be structured. Let us look at some examples of how verbs are used in academic writing.
If researchers want to present an analysis of the work that has been done, then verbs like analyze, appraise, define, diagnose, explore, identify, investigate, or observe may be a used effectively. Attest, confirm, contend, demonstrate, document, indicate or reveal are some verbs researchers can use when they discuss the findings of their research. When trying to convey that a researcher has taken a specific stand of their research findings, they can use words such as like , comment, convey, elaborate, establish, identify, or propose.
Phrasal verbs
It is important for early career researchers and authors to learn how to avoid phrasal verbs in academic writing. Phrasal verbs are words that we use to convey what we think or speak about, see, or experience. These kinds of phrasal verbs tend to be informal and out of place in an academic setting. Some common phrasal verbs and their alternative single verb that may be used are: Find out ( discover ), Looked at ( discovered ), Put into ( contribute ). However, phrasal verbs like carried out, consists of, discussed by, based on, or subjected to may be used while writing research articles or papers.
Contractions and abbreviations
Another aspect that early career researchers and authors must be mindful of when writing their manuscript is to avoid the use of contractions and abbreviations like “isn’t”, “won’t” or “don’t” as they have an informal flavor that is typically not accepted as formal writing. Academic writing demands that the expanded forms of these abbreviations must be used – so ‘is not,’ ‘will not,’ and ‘do not,’ are the correct versions to be used.
It is also highly recommended that researchers check the American or British style guides to make sure that the verbs they are using align with them.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- How and When to Use Active or Passive Voice in Research Papers
- What is the Oxford Comma and When Do You Use It?
- What is an Imperative Sentence?
- Defence vs. Defense: Let Us End the Confusion
Research Paper Writing: A 15-Point Academic Writing Checklist
Believe or beleive: how to remember the right spelling, you may also like, how to paraphrase research papers effectively, 4 types of transition words for research papers , paraphrasing in academic writing: answering top author queries, sentence length: how to improve your research paper..., navigating language precision: complementary vs. complimentary, climatic vs. climactic: difference and examples, language and grammar rules for academic writing, transitive and intransitive verbs in the world of..., led vs. lead: how to differentiate between the..., academic writing for esl students: 7 tips and strategies....

- Aims and Objectives – A Guide for Academic Writing
- Doing a PhD
One of the most important aspects of a thesis, dissertation or research paper is the correct formulation of the aims and objectives. This is because your aims and objectives will establish the scope, depth and direction that your research will ultimately take. An effective set of aims and objectives will give your research focus and your reader clarity, with your aims indicating what is to be achieved, and your objectives indicating how it will be achieved.
Introduction
There is no getting away from the importance of the aims and objectives in determining the success of your research project. Unfortunately, however, it is an aspect that many students struggle with, and ultimately end up doing poorly. Given their importance, if you suspect that there is even the smallest possibility that you belong to this group of students, we strongly recommend you read this page in full.
This page describes what research aims and objectives are, how they differ from each other, how to write them correctly, and the common mistakes students make and how to avoid them. An example of a good aim and objectives from a past thesis has also been deconstructed to help your understanding.
What Are Aims and Objectives?
Research aims.
A research aim describes the main goal or the overarching purpose of your research project.
In doing so, it acts as a focal point for your research and provides your readers with clarity as to what your study is all about. Because of this, research aims are almost always located within its own subsection under the introduction section of a research document, regardless of whether it’s a thesis , a dissertation, or a research paper .
A research aim is usually formulated as a broad statement of the main goal of the research and can range in length from a single sentence to a short paragraph. Although the exact format may vary according to preference, they should all describe why your research is needed (i.e. the context), what it sets out to accomplish (the actual aim) and, briefly, how it intends to accomplish it (overview of your objectives).
To give an example, we have extracted the following research aim from a real PhD thesis:
Example of a Research Aim
The role of diametrical cup deformation as a factor to unsatisfactory implant performance has not been widely reported. The aim of this thesis was to gain an understanding of the diametrical deformation behaviour of acetabular cups and shells following impaction into the reamed acetabulum. The influence of a range of factors on deformation was investigated to ascertain if cup and shell deformation may be high enough to potentially contribute to early failure and high wear rates in metal-on-metal implants.
Note: Extracted with permission from thesis titled “T he Impact And Deformation Of Press-Fit Metal Acetabular Components ” produced by Dr H Hothi of previously Queen Mary University of London.
Research Objectives
Where a research aim specifies what your study will answer, research objectives specify how your study will answer it.
They divide your research aim into several smaller parts, each of which represents a key section of your research project. As a result, almost all research objectives take the form of a numbered list, with each item usually receiving its own chapter in a dissertation or thesis.
Following the example of the research aim shared above, here are it’s real research objectives as an example:
Example of a Research Objective
- Develop finite element models using explicit dynamics to mimic mallet blows during cup/shell insertion, initially using simplified experimentally validated foam models to represent the acetabulum.
- Investigate the number, velocity and position of impacts needed to insert a cup.
- Determine the relationship between the size of interference between the cup and cavity and deformation for different cup types.
- Investigate the influence of non-uniform cup support and varying the orientation of the component in the cavity on deformation.
- Examine the influence of errors during reaming of the acetabulum which introduce ovality to the cavity.
- Determine the relationship between changes in the geometry of the component and deformation for different cup designs.
- Develop three dimensional pelvis models with non-uniform bone material properties from a range of patients with varying bone quality.
- Use the key parameters that influence deformation, as identified in the foam models to determine the range of deformations that may occur clinically using the anatomic models and if these deformations are clinically significant.
It’s worth noting that researchers sometimes use research questions instead of research objectives, or in other cases both. From a high-level perspective, research questions and research objectives make the same statements, but just in different formats.
Taking the first three research objectives as an example, they can be restructured into research questions as follows:
Restructuring Research Objectives as Research Questions
- Can finite element models using simplified experimentally validated foam models to represent the acetabulum together with explicit dynamics be used to mimic mallet blows during cup/shell insertion?
- What is the number, velocity and position of impacts needed to insert a cup?
- What is the relationship between the size of interference between the cup and cavity and deformation for different cup types?
Difference Between Aims and Objectives
Hopefully the above explanations make clear the differences between aims and objectives, but to clarify:
- The research aim focus on what the research project is intended to achieve; research objectives focus on how the aim will be achieved.
- Research aims are relatively broad; research objectives are specific.
- Research aims focus on a project’s long-term outcomes; research objectives focus on its immediate, short-term outcomes.
- A research aim can be written in a single sentence or short paragraph; research objectives should be written as a numbered list.
How to Write Aims and Objectives
Before we discuss how to write a clear set of research aims and objectives, we should make it clear that there is no single way they must be written. Each researcher will approach their aims and objectives slightly differently, and often your supervisor will influence the formulation of yours on the basis of their own preferences.
Regardless, there are some basic principles that you should observe for good practice; these principles are described below.
Your aim should be made up of three parts that answer the below questions:
- Why is this research required?
- What is this research about?
- How are you going to do it?
The easiest way to achieve this would be to address each question in its own sentence, although it does not matter whether you combine them or write multiple sentences for each, the key is to address each one.
The first question, why , provides context to your research project, the second question, what , describes the aim of your research, and the last question, how , acts as an introduction to your objectives which will immediately follow.
Scroll through the image set below to see the ‘why, what and how’ associated with our research aim example.

Note: Your research aims need not be limited to one. Some individuals per to define one broad ‘overarching aim’ of a project and then adopt two or three specific research aims for their thesis or dissertation. Remember, however, that in order for your assessors to consider your research project complete, you will need to prove you have fulfilled all of the aims you set out to achieve. Therefore, while having more than one research aim is not necessarily disadvantageous, consider whether a single overarching one will do.
Research Objectives
Each of your research objectives should be SMART :
- Specific – is there any ambiguity in the action you are going to undertake, or is it focused and well-defined?
- Measurable – how will you measure progress and determine when you have achieved the action?
- Achievable – do you have the support, resources and facilities required to carry out the action?
- Relevant – is the action essential to the achievement of your research aim?
- Timebound – can you realistically complete the action in the available time alongside your other research tasks?
In addition to being SMART, your research objectives should start with a verb that helps communicate your intent. Common research verbs include:
Table of Research Verbs to Use in Aims and Objectives
Last, format your objectives into a numbered list. This is because when you write your thesis or dissertation, you will at times need to make reference to a specific research objective; structuring your research objectives in a numbered list will provide a clear way of doing this.
To bring all this together, let’s compare the first research objective in the previous example with the above guidance:

Checking Research Objective Example Against Recommended Approach
Research Objective:
1. Develop finite element models using explicit dynamics to mimic mallet blows during cup/shell insertion, initially using simplified experimentally validated foam models to represent the acetabulum.
Checking Against Recommended Approach:
Q: Is it specific? A: Yes, it is clear what the student intends to do (produce a finite element model), why they intend to do it (mimic cup/shell blows) and their parameters have been well-defined ( using simplified experimentally validated foam models to represent the acetabulum ).
Q: Is it measurable? A: Yes, it is clear that the research objective will be achieved once the finite element model is complete.
Q: Is it achievable? A: Yes, provided the student has access to a computer lab, modelling software and laboratory data.
Q: Is it relevant? A: Yes, mimicking impacts to a cup/shell is fundamental to the overall aim of understanding how they deform when impacted upon.
Q: Is it timebound? A: Yes, it is possible to create a limited-scope finite element model in a relatively short time, especially if you already have experience in modelling.
Q: Does it start with a verb? A: Yes, it starts with ‘develop’, which makes the intent of the objective immediately clear.
Q: Is it a numbered list? A: Yes, it is the first research objective in a list of eight.
Mistakes in Writing Research Aims and Objectives
1. making your research aim too broad.
Having a research aim too broad becomes very difficult to achieve. Normally, this occurs when a student develops their research aim before they have a good understanding of what they want to research. Remember that at the end of your project and during your viva defence , you will have to prove that you have achieved your research aims; if they are too broad, this will be an almost impossible task. In the early stages of your research project, your priority should be to narrow your study to a specific area. A good way to do this is to take the time to study existing literature, question their current approaches, findings and limitations, and consider whether there are any recurring gaps that could be investigated .
Note: Achieving a set of aims does not necessarily mean proving or disproving a theory or hypothesis, even if your research aim was to, but having done enough work to provide a useful and original insight into the principles that underlie your research aim.
2. Making Your Research Objectives Too Ambitious
Be realistic about what you can achieve in the time you have available. It is natural to want to set ambitious research objectives that require sophisticated data collection and analysis, but only completing this with six months before the end of your PhD registration period is not a worthwhile trade-off.
3. Formulating Repetitive Research Objectives
Each research objective should have its own purpose and distinct measurable outcome. To this effect, a common mistake is to form research objectives which have large amounts of overlap. This makes it difficult to determine when an objective is truly complete, and also presents challenges in estimating the duration of objectives when creating your project timeline. It also makes it difficult to structure your thesis into unique chapters, making it more challenging for you to write and for your audience to read.
Fortunately, this oversight can be easily avoided by using SMART objectives.
Hopefully, you now have a good idea of how to create an effective set of aims and objectives for your research project, whether it be a thesis, dissertation or research paper. While it may be tempting to dive directly into your research, spending time on getting your aims and objectives right will give your research clear direction. This won’t only reduce the likelihood of problems arising later down the line, but will also lead to a more thorough and coherent research project.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.
Frequently asked questions
How do i write a research objective.
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement.
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
Ask our team
Want to contact us directly? No problem. We are always here for you.
- Chat with us
- Email [email protected]
- Call +44 (0)20 3917 4242
- WhatsApp +31 20 261 6040

Our support team is here to help you daily via chat, WhatsApp, email, or phone between 9:00 a.m. to 11:00 p.m. CET.
Our APA experts default to APA 7 for editing and formatting. For the Citation Editing Service you are able to choose between APA 6 and 7.
Yes, if your document is longer than 20,000 words, you will get a sample of approximately 2,000 words. This sample edit gives you a first impression of the editor’s editing style and a chance to ask questions and give feedback.
How does the sample edit work?
You will receive the sample edit within 24 hours after placing your order. You then have 24 hours to let us know if you’re happy with the sample or if there’s something you would like the editor to do differently.
Read more about how the sample edit works
Yes, you can upload your document in sections.
We try our best to ensure that the same editor checks all the different sections of your document. When you upload a new file, our system recognizes you as a returning customer, and we immediately contact the editor who helped you before.
However, we cannot guarantee that the same editor will be available. Your chances are higher if
- You send us your text as soon as possible and
- You can be flexible about the deadline.
Please note that the shorter your deadline is, the lower the chance that your previous editor is not available.
If your previous editor isn’t available, then we will inform you immediately and look for another qualified editor. Fear not! Every Scribbr editor follows the Scribbr Improvement Model and will deliver high-quality work.
Yes, our editors also work during the weekends and holidays.
Because we have many editors available, we can check your document 24 hours per day and 7 days per week, all year round.
If you choose a 72 hour deadline and upload your document on a Thursday evening, you’ll have your thesis back by Sunday evening!
Yes! Our editors are all native speakers, and they have lots of experience editing texts written by ESL students. They will make sure your grammar is perfect and point out any sentences that are difficult to understand. They’ll also notice your most common mistakes, and give you personal feedback to improve your writing in English.
Every Scribbr order comes with our award-winning Proofreading & Editing service , which combines two important stages of the revision process.
For a more comprehensive edit, you can add a Structure Check or Clarity Check to your order. With these building blocks, you can customize the kind of feedback you receive.
You might be familiar with a different set of editing terms. To help you understand what you can expect at Scribbr, we created this table:
View an example
When you place an order, you can specify your field of study and we’ll match you with an editor who has familiarity with this area.
However, our editors are language specialists, not academic experts in your field. Your editor’s job is not to comment on the content of your dissertation, but to improve your language and help you express your ideas as clearly and fluently as possible.
This means that your editor will understand your text well enough to give feedback on its clarity, logic and structure, but not on the accuracy or originality of its content.
Good academic writing should be understandable to a non-expert reader, and we believe that academic editing is a discipline in itself. The research, ideas and arguments are all yours – we’re here to make sure they shine!
After your document has been edited, you will receive an email with a link to download the document.
The editor has made changes to your document using ‘Track Changes’ in Word. This means that you only have to accept or ignore the changes that are made in the text one by one.
It is also possible to accept all changes at once. However, we strongly advise you not to do so for the following reasons:
- You can learn a lot by looking at the mistakes you made.
- The editors don’t only change the text – they also place comments when sentences or sometimes even entire paragraphs are unclear. You should read through these comments and take into account your editor’s tips and suggestions.
- With a final read-through, you can make sure you’re 100% happy with your text before you submit!
You choose the turnaround time when ordering. We can return your dissertation within 24 hours , 3 days or 1 week . These timescales include weekends and holidays. As soon as you’ve paid, the deadline is set, and we guarantee to meet it! We’ll notify you by text and email when your editor has completed the job.
Very large orders might not be possible to complete in 24 hours. On average, our editors can complete around 13,000 words in a day while maintaining our high quality standards. If your order is longer than this and urgent, contact us to discuss possibilities.
Always leave yourself enough time to check through the document and accept the changes before your submission deadline.
Scribbr is specialised in editing study related documents. We check:
- Graduation projects
- Dissertations
- Admissions essays
- College essays
- Application essays
- Personal statements
- Process reports
- Reflections
- Internship reports
- Academic papers
- Research proposals
- Prospectuses
Calculate the costs
The fastest turnaround time is 24 hours.
You can upload your document at any time and choose between three deadlines:
At Scribbr, we promise to make every customer 100% happy with the service we offer. Our philosophy: Your complaint is always justified – no denial, no doubts.
Our customer support team is here to find the solution that helps you the most, whether that’s a free new edit or a refund for the service.
Yes, in the order process you can indicate your preference for American, British, or Australian English .
If you don’t choose one, your editor will follow the style of English you currently use. If your editor has any questions about this, we will contact you.

Research Aims and Objectives: The dynamic duo for successful research
Picture yourself on a road trip without a destination in mind — driving aimlessly, not knowing where you’re headed or how to get there. Similarly, your research is navigated by well-defined research aims and objectives. Research aims and objectives are the foundation of any research project. They provide a clear direction and purpose for the study, ensuring that you stay focused and on track throughout the process. They are your trusted navigational tools, leading you to success.
Understanding the relationship between research objectives and aims is crucial to any research project’s success, and we’re here to break it down for you in this article. Here, we’ll explore the importance of research aims and objectives, understand their differences, and delve into the impact they have on the quality of research.
Understanding the Difference between Research Aims and Objectives
In research, aims and objectives are two important components but are often used interchangeably. Though they may sound similar, they are distinct and serve different purposes.
Research Aims:
Research aims are broad statements that describe the overall purpose of your study. They provide a general direction for your study and indicate the intended achievements of your research. Aims are usually written in a general and abstract manner describing the ultimate goal of the research.
Research Objectives:
Research objectives are specific, measurable, and achievable goals that you aim to accomplish within a specified timeframe. They break down the research aims into smaller, more manageable components and provide a clear picture of what you want to achieve and how you plan to achieve it.
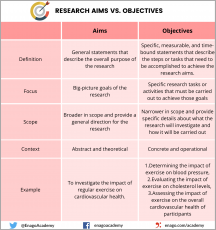
In the example, the objectives provide specific targets that must be achieved to reach the aim. Essentially, aims provide the overall direction for the research while objectives provide specific targets that must be achieved to accomplish the aims. Aims provide a broad context for the research, while the objectives provide smaller steps that the researcher must take to accomplish the overall research goals. To illustrate, when planning a road trip, your research aim is the destination you want to reach, and your research objectives are the specific routes you need to take to get there.
Aims and objectives are interconnected. Objectives play a key role in defining the research methodology, providing a roadmap for how you’ll collect and analyze data, while aim is the final destination, which represents the ultimate goal of your research. By setting specific goals, you’ll be able to design a research plan that helps you achieve your objectives and, ultimately, your research aim.
Importance of Well-defined Aims and Objectives
The impact of clear research aims and objectives on the quality of research cannot be understated. But it’s not enough to simply have aims and objectives. Well-defined research aims and objectives are important for several reasons:
- Provides direction: Clear aims and well-defined objectives provide a specific direction for your research study, ensuring that the research stays focused on a specific topic or problem. This helps to prevent the research from becoming too broad or unfocused, and ensures that the study remains relevant and meaningful.
- Guides research design: The research aim and objectives help guide the research design and methodology, ensuring that your study is designed in a way that will answer the research questions and achieve the research objectives.
- Helps with resource allocation: Clear research aims and objectives helps you to allocate resources effectively , including time, financial resources, human resources, and other required materials. With a well-defined aim and objectives, you can identify the resources required to conduct the research, and allocate them in a way that maximizes efficiency and productivity.
- Assists in evaluation: Clearly specified research aims and objectives allow for effective evaluation of your research project’s success. You can assess whether the research has achieved its objectives, and whether the aim has been met. This evaluation process can help to identify areas of the research project that may require further attention or modification.
- Enhances communication: Well-defined research aims and objectives help to enhance communication among the research team, stakeholders, funding agencies, and other interested parties. Clear aims and objectives ensure that everyone involved in your research project understands the purpose and goals of the study. This can help to foster collaboration and ensure that everyone is working towards the same end goal.
How to Formulate Research Aims and Objectives
Formulating effective research aims and objectives involves a systematic process to ensure that they are clear, specific, achievable, and relevant. Start by asking yourself what you want to achieve through your research. What impact do you want your research to have? Once you have a clear understanding of your aims, you can then break them down into specific, achievable objectives. Here are some steps you can follow when developing research aims and objectives:
- Identify the research question : Clearly identify the questions you want to answer through your research. This will help you define the scope of your research. Understanding the characteristics of a good research question will help you generate clearer aims and objectives.
- Conduct literature review : When defining your research aim and objectives, it’s important to conduct a literature review to identify key concepts, theories, and methods related to your research problem or question. Conducting a thorough literature review can help you understand what research has been done in the area and what gaps exist in the literature.
- Identify the research aim: Develop a research aim that summarizes the overarching goal of your research. The research aim should be broad and concise.
- Develop research objectives: Based on your research questions and research aim, develop specific research objectives that outline what you intend to achieve through your research. These objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
- Use action verbs: Use action verbs such as “investigate,” “examine,” “analyze,” and “compare” to describe your research aims and objectives. This makes them more specific and measurable.
- Ensure alignment with research question: Ensure that the research aim and objectives are aligned with the research question. This helps to ensure that the research remains focused and that the objectives are specific enough to answer your research question.
- Refine and revise: Once the research aim and objectives have been developed, refine and revise them as needed. Seek feedback from your colleagues, mentors, or supervisors to ensure that they are clear, concise, and achievable within the given resources and timeframe.
- Communicate: After finalizing the research aim and objectives, they should be communicated to the research team, stakeholders, and other interested parties. This helps to ensure that everyone is working towards the same end goal and understands the purpose of the study.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid While Formulating Aims and Objectives
There are several common mistakes that researchers can make when writing research aims and objectives. These include:
- Being too broad or vague: Aims and objectives that are too general or unclear can lead to confusion and lack of focus. It is important to ensure that the aims and objectives are concise and clear.
- Being too narrow or specific: On the other hand, aims and objectives that are too narrow or specific may limit the scope of the research and make it difficult to draw meaningful conclusions or implications.
- Being too ambitious: While it is important to aim high, being too ambitious with the aims and objectives can lead to unrealistic expectations and can be difficult to achieve within the constraints of the research project.
- Lack of alignment: The aims and objectives should be directly linked to the research questions being investigated. Otherwise, this will lead to a lack of coherence in the research project.
- Lack of feasibility: The aims and objectives should be achievable within the constraints of the research project, including time, budget, and resources. Failing to consider feasibility may cause compromise of the research quality.
- Failing to consider ethical considerations: The aims and objectives should take into account any ethical considerations, such as ensuring the safety and well-being of study participants.
- Failing to involve all stakeholders: It’s important to involve all relevant stakeholders, such as participants, supervisors, and funding agencies, in the development of the aims and objectives to ensure they are appropriate and relevant.
To avoid these common pitfalls, it is important to be specific, clear, relevant, and realistic when writing research aims and objectives. Seek feedback from colleagues or supervisors to ensure that the aims and objectives are aligned with the research problem , questions, and methodology, and are achievable within the constraints of the research project. It’s important to continually refine your aims and objectives as you go. As you progress in your research, it’s not uncommon for research aims and objectives to evolve slightly, but it’s important that they remain consistent with the study conducted and the research topic.
In summary, research aims and objectives are the backbone of any successful research project. They give you the ability to cut through the noise and hone in on what really matters. By setting clear goals and aligning them with your research questions and methodology, you can ensure that your research is relevant, impactful, and of the highest quality. So, before you hit the road on your research journey, make sure you have a clear destination and steps to get there. Let us know in the comments section below the challenges you faced and the strategies you followed while fomulating research aims and objectives! Also, feel free to reach out to us at any stage of your research or publication by using #AskEnago and tagging @EnagoAcademy on Twitter , Facebook , and Quora . Happy researching!
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Reporting Research
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for data interpretation
In research, choosing the right approach to understand data is crucial for deriving meaningful insights.…

Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right approach
The process of choosing the right research design can put ourselves at the crossroads of…

- Career Corner
Unlocking the Power of Networking in Academic Conferences
Embarking on your first academic conference experience? Fear not, we got you covered! Academic conferences…

Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making
Research recommendations play a crucial role in guiding scholars and researchers toward fruitful avenues of…

- Promoting Research
Concept Papers in Research: Deciphering the blueprint of brilliance
Concept papers hold significant importance as a precursor to a full-fledged research proposal in academia…
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for…
Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right…
8 Effective Strategies to Write Argumentative Essays

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What should universities' stance be on AI tools in research and academic writing?
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Verbs for Research Objectives

Related Papers
DG Farnsworth
Jabulani Msamala
Stella Atter
Western journal of nursing research
Nancy Fahrenwald
The National Institutes of Health has implemented new grant application guidelines that include a substantial reduction in the number of pages allowed for project descriptions. Shorter proposals will potentially decrease reviewer burden, but investigators may find the new page limits challenging. Writing more concisely while still presenting a persuasive argument requires honing certain skills with regard to preparation, construction, and editing of proposals. This article provides strategies from the Western Journal of Nursing Research editorial board for preparing competitive shorter research proposals. Two key strategies for success are fully conceptualizing the study prior to writing and obtaining assistance from experienced colleagues during the editing process.
Medical Education
Beth Dawson
Rebekka Tunombili
Md. Muddasir
Muhammad Umair
gharbi amira
Weed Technology
Stephen Powles
RELATED PAPERS
Management Science
Marcelo Osvaldo Olivares
Using Old Solutions to New Problems - Natural Drug Discovery in the 21st Century
Yanwen Wang
Principles and Practice of …
Thibaut Feydy
Geomorphology
Michael A Fullen
James Dunnett
Stefanos Kaxiras
SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2004
Scott W Singleton
Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment
Muhsiung Chang
Revista Mexicana de Análisis Político y Administración Pública
Bernardo Zamichiei
Gerrit Lohmann
Journal of Endourology Case Reports
Joey El Khoury
The Journal of Engineering and Exact Sciences
Raimundo Passos
Bushan kumar
Journal of Medicinal Chemistry
Alessandro Casnati
Journal of Global Initiatives: Policy, Pedagogy, Perspective
Grace Oloukoi
Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety
Sohail Akram
2012 IEEE 3rd Latin American Symposium on Circuits and Systems (LASCAS)
Pedro Julian
Artyushkina Olga
Emilio Pecora
Leyshon, Michael
American Journal of Public Health
luis falcon
Chemistry - A European Journal
Elisabeth Irran
Revista de la Academia Colombiana de Ciencias Exactas, Físicas y Naturales
Juan Armando Sánchez
BRILL eBooks
Kazimierz J Bem
See More Documents Like This
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Research Objectives – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Research Objectives – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Objectives
Research objectives refer to the specific goals or aims of a research study. They provide a clear and concise description of what the researcher hopes to achieve by conducting the research . The objectives are typically based on the research questions and hypotheses formulated at the beginning of the study and are used to guide the research process.
Types of Research Objectives
Here are the different types of research objectives in research:
- Exploratory Objectives: These objectives are used to explore a topic, issue, or phenomenon that has not been studied in-depth before. The aim of exploratory research is to gain a better understanding of the subject matter and generate new ideas and hypotheses .
- Descriptive Objectives: These objectives aim to describe the characteristics, features, or attributes of a particular population, group, or phenomenon. Descriptive research answers the “what” questions and provides a snapshot of the subject matter.
- Explanatory Objectives : These objectives aim to explain the relationships between variables or factors. Explanatory research seeks to identify the cause-and-effect relationships between different phenomena.
- Predictive Objectives: These objectives aim to predict future events or outcomes based on existing data or trends. Predictive research uses statistical models to forecast future trends or outcomes.
- Evaluative Objectives : These objectives aim to evaluate the effectiveness or impact of a program, intervention, or policy. Evaluative research seeks to assess the outcomes or results of a particular intervention or program.
- Prescriptive Objectives: These objectives aim to provide recommendations or solutions to a particular problem or issue. Prescriptive research identifies the best course of action based on the results of the study.
- Diagnostic Objectives : These objectives aim to identify the causes or factors contributing to a particular problem or issue. Diagnostic research seeks to uncover the underlying reasons for a particular phenomenon.
- Comparative Objectives: These objectives aim to compare two or more groups, populations, or phenomena to identify similarities and differences. Comparative research is used to determine which group or approach is more effective or has better outcomes.
- Historical Objectives: These objectives aim to examine past events, trends, or phenomena to gain a better understanding of their significance and impact. Historical research uses archival data, documents, and records to study past events.
- Ethnographic Objectives : These objectives aim to understand the culture, beliefs, and practices of a particular group or community. Ethnographic research involves immersive fieldwork and observation to gain an insider’s perspective of the group being studied.
- Action-oriented Objectives: These objectives aim to bring about social or organizational change. Action-oriented research seeks to identify practical solutions to social problems and to promote positive change in society.
- Conceptual Objectives: These objectives aim to develop new theories, models, or frameworks to explain a particular phenomenon or set of phenomena. Conceptual research seeks to provide a deeper understanding of the subject matter by developing new theoretical perspectives.
- Methodological Objectives: These objectives aim to develop and improve research methods and techniques. Methodological research seeks to advance the field of research by improving the validity, reliability, and accuracy of research methods and tools.
- Theoretical Objectives : These objectives aim to test and refine existing theories or to develop new theoretical perspectives. Theoretical research seeks to advance the field of knowledge by testing and refining existing theories or by developing new theoretical frameworks.
- Measurement Objectives : These objectives aim to develop and validate measurement instruments, such as surveys, questionnaires, and tests. Measurement research seeks to improve the quality and reliability of data collection and analysis by developing and testing new measurement tools.
- Design Objectives : These objectives aim to develop and refine research designs, such as experimental, quasi-experimental, and observational designs. Design research seeks to improve the quality and validity of research by developing and testing new research designs.
- Sampling Objectives: These objectives aim to develop and refine sampling techniques, such as probability and non-probability sampling methods. Sampling research seeks to improve the representativeness and generalizability of research findings by developing and testing new sampling techniques.
How to Write Research Objectives
Writing clear and concise research objectives is an important part of any research project, as it helps to guide the study and ensure that it is focused and relevant. Here are some steps to follow when writing research objectives:
- Identify the research problem : Before you can write research objectives, you need to identify the research problem you are trying to address. This should be a clear and specific problem that can be addressed through research.
- Define the research questions : Based on the research problem, define the research questions you want to answer. These questions should be specific and should guide the research process.
- Identify the variables : Identify the key variables that you will be studying in your research. These are the factors that you will be measuring, manipulating, or analyzing to answer your research questions.
- Write specific objectives: Write specific, measurable objectives that will help you answer your research questions. These objectives should be clear and concise and should indicate what you hope to achieve through your research.
- Use the SMART criteria: To ensure that your research objectives are well-defined and achievable, use the SMART criteria. This means that your objectives should be Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
- Revise and refine: Once you have written your research objectives, revise and refine them to ensure that they are clear, concise, and achievable. Make sure that they align with your research questions and variables, and that they will help you answer your research problem.
Example of Research Objectives
Examples of research objectives Could be:
Research Objectives for the topic of “The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Employment”:
- To investigate the effects of the adoption of AI on employment trends across various industries and occupations.
- To explore the potential for AI to create new job opportunities and transform existing roles in the workforce.
- To examine the social and economic implications of the widespread use of AI for employment, including issues such as income inequality and access to education and training.
- To identify the skills and competencies that will be required for individuals to thrive in an AI-driven workplace, and to explore the role of education and training in developing these skills.
- To evaluate the ethical and legal considerations surrounding the use of AI for employment, including issues such as bias, privacy, and the responsibility of employers and policymakers to protect workers’ rights.
When to Write Research Objectives
- At the beginning of a research project : Research objectives should be identified and written down before starting a research project. This helps to ensure that the project is focused and that data collection and analysis efforts are aligned with the intended purpose of the research.
- When refining research questions: Writing research objectives can help to clarify and refine research questions. Objectives provide a more concrete and specific framework for addressing research questions, which can improve the overall quality and direction of a research project.
- After conducting a literature review : Conducting a literature review can help to identify gaps in knowledge and areas that require further research. Writing research objectives can help to define and focus the research effort in these areas.
- When developing a research proposal: Research objectives are an important component of a research proposal. They help to articulate the purpose and scope of the research, and provide a clear and concise summary of the expected outcomes and contributions of the research.
- When seeking funding for research: Funding agencies often require a detailed description of research objectives as part of a funding proposal. Writing clear and specific research objectives can help to demonstrate the significance and potential impact of a research project, and increase the chances of securing funding.
- When designing a research study : Research objectives guide the design and implementation of a research study. They help to identify the appropriate research methods, sampling strategies, data collection and analysis techniques, and other relevant aspects of the study design.
- When communicating research findings: Research objectives provide a clear and concise summary of the main research questions and outcomes. They are often included in research reports and publications, and can help to ensure that the research findings are communicated effectively and accurately to a wide range of audiences.
- When evaluating research outcomes : Research objectives provide a basis for evaluating the success of a research project. They help to measure the degree to which research questions have been answered and the extent to which research outcomes have been achieved.
- When conducting research in a team : Writing research objectives can facilitate communication and collaboration within a research team. Objectives provide a shared understanding of the research purpose and goals, and can help to ensure that team members are working towards a common objective.
Purpose of Research Objectives
Some of the main purposes of research objectives include:
- To clarify the research question or problem : Research objectives help to define the specific aspects of the research question or problem that the study aims to address. This makes it easier to design a study that is focused and relevant.
- To guide the research design: Research objectives help to determine the research design, including the research methods, data collection techniques, and sampling strategy. This ensures that the study is structured and efficient.
- To measure progress : Research objectives provide a way to measure progress throughout the research process. They help the researcher to evaluate whether they are on track and meeting their goals.
- To communicate the research goals : Research objectives provide a clear and concise description of the research goals. This helps to communicate the purpose of the study to other researchers, stakeholders, and the general public.
Advantages of Research Objectives
Here are some advantages of having well-defined research objectives:
- Focus : Research objectives help to focus the research effort on specific areas of inquiry. By identifying clear research questions, the researcher can narrow down the scope of the study and avoid getting sidetracked by irrelevant information.
- Clarity : Clearly stated research objectives provide a roadmap for the research study. They provide a clear direction for the research, making it easier for the researcher to stay on track and achieve their goals.
- Measurability : Well-defined research objectives provide measurable outcomes that can be used to evaluate the success of the research project. This helps to ensure that the research is effective and that the research goals are achieved.
- Feasibility : Research objectives help to ensure that the research project is feasible. By clearly defining the research goals, the researcher can identify the resources required to achieve those goals and determine whether those resources are available.
- Relevance : Research objectives help to ensure that the research study is relevant and meaningful. By identifying specific research questions, the researcher can ensure that the study addresses important issues and contributes to the existing body of knowledge.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Thesis Outline – Example, Template and Writing...

Research Paper Conclusion – Writing Guide and...

Appendices – Writing Guide, Types and Examples

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Research Report – Example, Writing Guide and...

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...
Frequently asked questions
How do i write a research objective.
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement .
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
Frequently asked questions: Writing a research paper
A research project is an academic, scientific, or professional undertaking to answer a research question . Research projects can take many forms, such as qualitative or quantitative , descriptive , longitudinal , experimental , or correlational . What kind of research approach you choose will depend on your topic.
The best way to remember the difference between a research plan and a research proposal is that they have fundamentally different audiences. A research plan helps you, the researcher, organize your thoughts. On the other hand, a dissertation proposal or research proposal aims to convince others (e.g., a supervisor, a funding body, or a dissertation committee) that your research topic is relevant and worthy of being conducted.
Formulating a main research question can be a difficult task. Overall, your question should contribute to solving the problem that you have defined in your problem statement .
However, it should also fulfill criteria in three main areas:
- Researchability
- Feasibility and specificity
- Relevance and originality
Research questions anchor your whole project, so it’s important to spend some time refining them.
In general, they should be:
- Focused and researchable
- Answerable using credible sources
- Complex and arguable
- Feasible and specific
- Relevant and original
All research questions should be:
- Focused on a single problem or issue
- Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources
- Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints
- Specific enough to answer thoroughly
- Complex enough to develop the answer over the space of a paper or thesis
- Relevant to your field of study and/or society more broadly

A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
Your research objectives indicate how you’ll try to address your research problem and should be specific:
Research objectives describe what you intend your research project to accomplish.
They summarize the approach and purpose of the project and help to focus your research.
Your objectives should appear in the introduction of your research paper , at the end of your problem statement .
The main guidelines for formatting a paper in Chicago style are to:
- Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman
- Use 1 inch margins or larger
- Apply double line spacing
- Indent every new paragraph ½ inch
- Include a title page
- Place page numbers in the top right or bottom center
- Cite your sources with author-date citations or Chicago footnotes
- Include a bibliography or reference list
To automatically generate accurate Chicago references, you can use Scribbr’s free Chicago reference generator .
The main guidelines for formatting a paper in MLA style are as follows:
- Use an easily readable font like 12 pt Times New Roman
- Set 1 inch page margins
- Include a four-line MLA heading on the first page
- Center the paper’s title
- Use title case capitalization for headings
- Cite your sources with MLA in-text citations
- List all sources cited on a Works Cited page at the end
To format a paper in APA Style , follow these guidelines:
- Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman or 11 pt Arial
- If submitting for publication, insert a running head on every page
- Apply APA heading styles
- Cite your sources with APA in-text citations
- List all sources cited on a reference page at the end
No, it’s not appropriate to present new arguments or evidence in the conclusion . While you might be tempted to save a striking argument for last, research papers follow a more formal structure than this.
All your findings and arguments should be presented in the body of the text (more specifically in the results and discussion sections if you are following a scientific structure). The conclusion is meant to summarize and reflect on the evidence and arguments you have already presented, not introduce new ones.
The conclusion of a research paper has several key elements you should make sure to include:
- A restatement of the research problem
- A summary of your key arguments and/or findings
- A short discussion of the implications of your research
Don’t feel that you have to write the introduction first. The introduction is often one of the last parts of the research paper you’ll write, along with the conclusion.
This is because it can be easier to introduce your paper once you’ve already written the body ; you may not have the clearest idea of your arguments until you’ve written them, and things can change during the writing process .
The way you present your research problem in your introduction varies depending on the nature of your research paper . A research paper that presents a sustained argument will usually encapsulate this argument in a thesis statement .
A research paper designed to present the results of empirical research tends to present a research question that it seeks to answer. It may also include a hypothesis —a prediction that will be confirmed or disproved by your research.
The introduction of a research paper includes several key elements:
- A hook to catch the reader’s interest
- Relevant background on the topic
- Details of your research problem
and your problem statement
- A thesis statement or research question
- Sometimes an overview of the paper
Ask our team
Want to contact us directly? No problem. We are always here for you.
- Email [email protected]
- Start live chat
- Call +1 (510) 822-8066
- WhatsApp +31 20 261 6040

Our team helps students graduate by offering:
- A world-class citation generator
- Plagiarism Checker software powered by Turnitin
- Innovative Citation Checker software
- Professional proofreading services
- Over 300 helpful articles about academic writing, citing sources, plagiarism, and more
Scribbr specializes in editing study-related documents . We proofread:
- PhD dissertations
- Research proposals
- Personal statements
- Admission essays
- Motivation letters
- Reflection papers
- Journal articles
- Capstone projects
Scribbr’s Plagiarism Checker is powered by elements of Turnitin’s Similarity Checker , namely the plagiarism detection software and the Internet Archive and Premium Scholarly Publications content databases .
The add-on AI detector is powered by Scribbr’s proprietary software.
The Scribbr Citation Generator is developed using the open-source Citation Style Language (CSL) project and Frank Bennett’s citeproc-js . It’s the same technology used by dozens of other popular citation tools, including Mendeley and Zotero.
You can find all the citation styles and locales used in the Scribbr Citation Generator in our publicly accessible repository on Github .
- Bloom’s Taxonomy
- Knowledge Hub
- Learning Theories
Are you trying to teach people without identifying educational objectives? If you keep doing that, your learners may waste their time succeeding in things that are of no use to them. To avoid that, clarify your instructional goals using Bloom’s Taxonomy.
This article will help you learn:
What is Bloom’s Taxonomy?
Original bloom’s taxonomy, revised bloom’s taxonomy, bloom’s taxonomy levels.
- Why Bloom’s Taxonomy is important?
Bloom’s Taxonomy verbs
Bloom’s Taxonomy attempts to classify learning stages from remembering facts to creating new ideas based on the acquired knowledge.
The idea of Bloom’s Taxonomy is that learning is a consecutive process. Before applying a concept in real life, we must understand it. Before we understand a concept, we must remember the key facts related to it.
Although initially described as a framework, it is now often depicted as a pyramid.
The basis of the pyramid is Knowledge , the first level of learning. Above it lies Comprehension , Application , Analysis , Synthesis and Evaluation . Each level above builds upon the one below, so you can only move up the pyramid one step at a time.
In teh cotext of employee learning and development , Bloom’s Taxonomy guides corporate training by focusing on critical thinking over simple memorization. Created in 1956 and updated in 2001, it helps trainers design programs that teach employees to think deeply and solve problems effectively, matching today’s fast-paced work environments.
Now, we are diving into both versions and see how they apply to our learning strategies.
The original taxonomy was first described in 1956 in the book Taxonomy of Educational Objectives by American educational psychologist Benjamin Bloom and his coauthors Max Englehart, Edward Furst, Walter Hill, and David Krathwohl. Their book classifies learning goals into one of the categories mentioned above (from Knowledge to Evaluation).
Their goal was to provide teachers with a common vocabulary to discuss curricular and evaluation problems with greater precision.

The taxonomy of educational objectives was supposed to help teachers speak the same language and thus “facilitate the exchange of information about their curricular developments and evaluation devices.”
Though it was designed primarily for college professors, it finally became popular among educators, from K-12 teachers to corporate trainers.
Since its publication, the book has been translated into more than twenty languages and is now used for instructional design worldwide. However, it is currently more often applied in its revised version.
Comparison image of the original vs. revised Bloom’s Taxonomies
To provide learners with clearer instructional goals, a group of researchers led by Bloom’s colleague David Krathwohl and one of Bloom’s students, Lorin Anderson, revised the taxonomy in 2001.
In the new variant, nouns were replaced by action verbs. Also, the two highest levels of the taxonomy were swapped. The new learning stages are Remember , Understand , Apply , Analyze , Evaluate and Create . The authors also defined cognitive processes associated with these instructional goals. For example, the ability to remember requires recognizing and recalling .
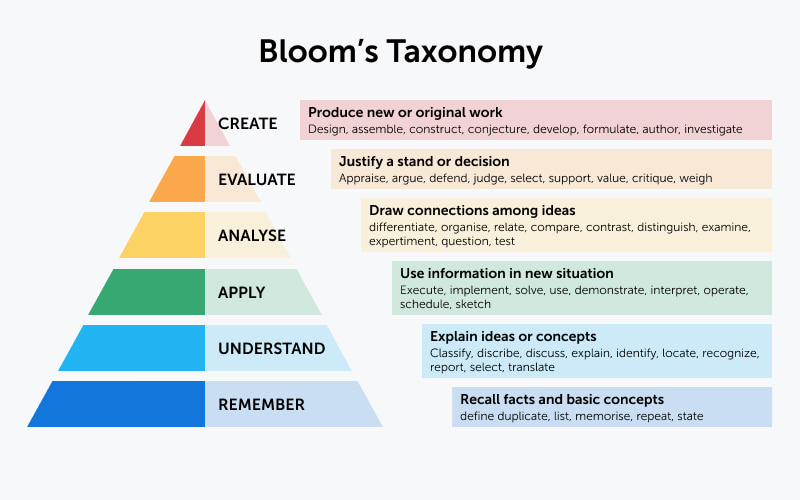
Let’s take a closer look at each learning stage, based on the book describing the revised framework A Taxonomy For Learning, Teaching and Assessing by Krahtwohl and Anderson. The authors recommend reading the name of each learning category as though preceded by the phrase “The student is able to…” or “The student learns to…”
1. Remember
This stage of learning is about memorizing basic facts, dates, events, persons, places, concepts and patterns.
In corporate training, remembering is about memorizing key company facts, product details, compliance rules, or standard operating procedures. For example, learners might be asked to recall:
- The core values of the company.
- Safety protocols for their work environment.
- Key product features and benefits.
This stage involves recognizing (product names, or safety signs from memory) and recalling (memorizing and retrieving important company policies or product information).
2. Understand
Understanding in a corporate setting moves learners beyond rote memorization, encouraging them to explain concepts in their own words or interpret data. Examples include:
- Describing the impact of a new policy on daily operations.
- Interpreting a sales graph to summarize quarterly performance.
Key processes here include:
- interpreting data,
- exemplifying through case studies,
- classifying types of customer feedback,
- summarizing project reports,
- inferring conclusions from meeting discussions,
- comparing different leadership styles,
- and explaining the rationale behind strategic decisions.
Now, it’s time to use learned information in new but related contexts, such as solving problems or executing tasks based on training.
Corporate learners might be tasked with:
- Applying a new sales technique in a role-play scenario.
- Using a software tool to manage customer relationships.
This stage emphasizes executing (following a procedure for a familiar task) and implementing (applying a procedure in a new context).
Analysis in corporate training entails breaking down complex information or processes to understand their components and relationships.
Learners might:
- Analyze sales data to identify trends.
- Examine a project’s failure to pinpoint contributing factors.
Activities focus on differentiating between relevant and irrelevant data, organizing parts of a project to outline its structure, and attributing causes to an outcome, such as determining the factors leading to a successful product launch.
5. Evaluate
Evaluation requires judgment and critical thinking to assess the value or effectiveness of something, based on criteria and standards. In a corporate environment, this could involve:
- Assessing the feasibility of a new market expansion plan.
- Critiquing a proposed project management approach.
Learners engage in checking (evaluating the consistency of an argument) and critiquing (judging a proposal against set criteria).
Creation, the pinnacle of Bloom’s Taxonomy, entails producing something new or original. This stage is vital for innovation within the company. Examples include:
- Designing a marketing strategy for a new product.
- Developing a training program for new hires.
Key cognitive processes are generating (coming up with a new business strategy), planning (outlining a project plan), and producing (creating a new product design).
Why Bloom’s Taxonomy is important
Bloom’s Taxonomy can help educators map learning within a single lesson or even a whole course.
Using the taxonomy as a guide, trainers can identify clear instructional goals corresponding to each taxonomy level and create plans to achieve them.
By setting achievable objectives for learners, instructors make them more active and responsible for their education.
The taxonomy can also be useful for evaluating learners correctly.
For L&D professionals and instructional designers, applying Bloom’s Taxonomy to corporate training programs ensures not just the acquisition of knowledge, but the development of skills that enhance employees’ ability to innovate, solve problems, and make informed decisions, driving business success and personal growth.
When talking about Bloom’s taxonomy, action verbs associated with the categories and cognitive processes are often mentioned. Instructors use these verbs to describe activities required for achieving educational objectives corresponding to each level.
For instance, at the analyzing level, the Azusa Pacific University recommends using verbs like “compare” , “distinguish” , and “simplify” when formulating instructional tasks.
There is a list of Bloom’s taxonomy verbs , created by the University of Arkansas . Using these verbs can help learners explicitly navigate what they must do to demonstrate their mastery of the objective.
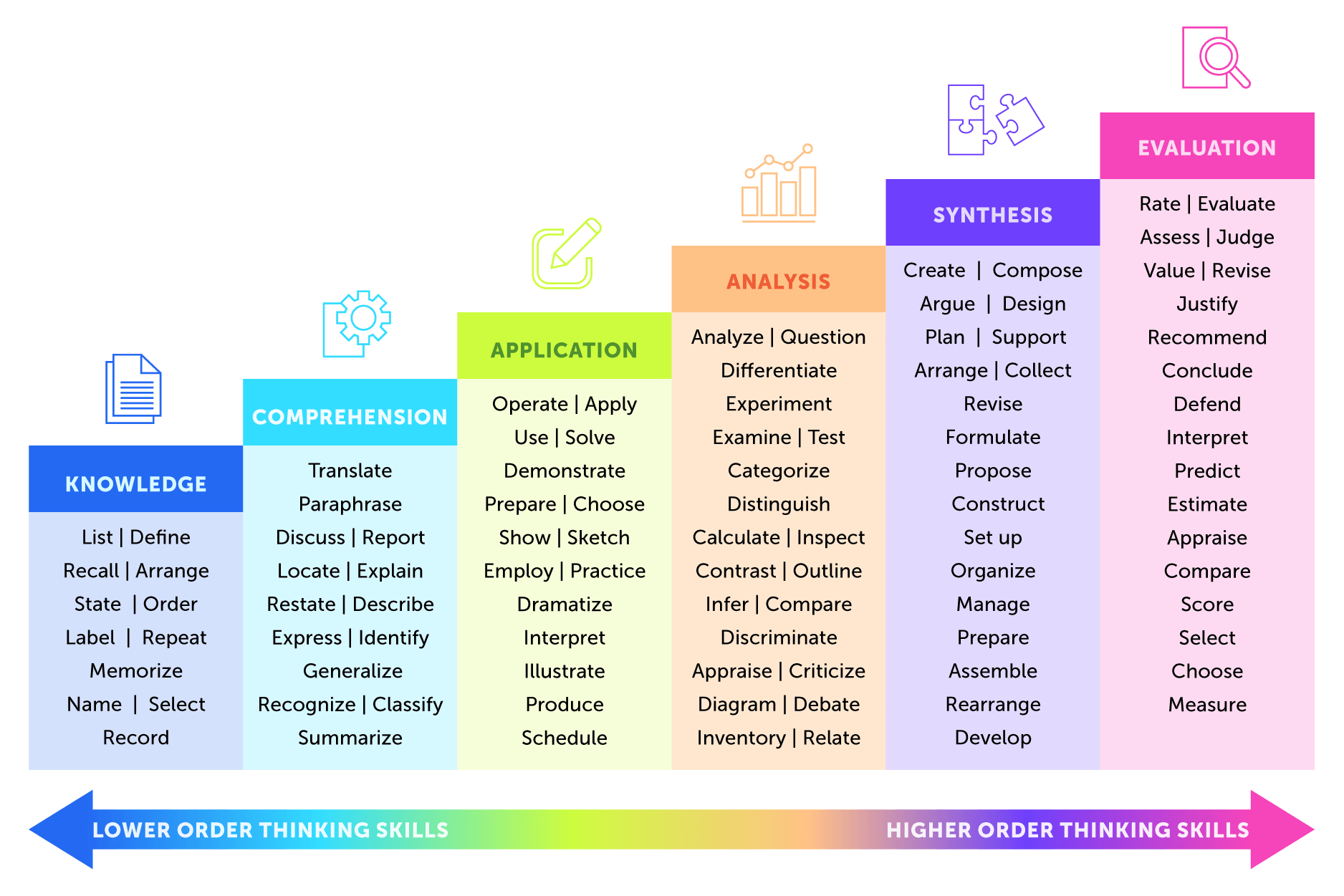
However, neither Bloom’s original book nor his followers’ book contains a list of such verbs. The authors of a study of 47 verb lists collected from 35 universities and textbooks note: “There was very little agreement between these lists, most of which were not supported by evidence explaining where the verbs came from.”
Nevertheless, given that such lists of verbs are being created anyway, the authors identified verbs that appeared in more than 50% of the listings. Then they identified verbs for which 50% of their appearances were in one specific tier. Using these verbs, the authors constructed “A Master List of Action Verbs for Learning Outcomes.”
Learn strategies to ensure learning effectiveness and efficiency
Call for L&D decision-makers, HR professionals, and business leaders struggling with change, alignment, or resource management
- Learn to adapt to regulation changes, global events, and tech advancement disruptions.
- Discover how to make every learning opportunity count towards the success of your business.
- Learn how to achieve impact with fewer resources.

Ivan Andreev
Demand Generation & Capture Strategist
Ivan Andreev is a dedicated marketing professional with a proven track record of driving growth and efficiency in various marketing domains, especially SEO. With a career spanning over a decade, Ivan has developed a deep understanding of marketing strategies, project management, data analysis, and team leadership. His strong commitment to knowledge sharing, passion for process optimization, and turning challenges into opportunities have solidified his reputation as a pivotal player in the marketing team.
Join online event
Turn market challenges into opportunities
Learn L&D strategies that help you deal with change, alignment, or resource management

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Measurable Performance Verbs for Writing Objectives By Human Capital Do not use the following verbs in your objectives: Know, Comprehend, Understand, Appreciate, Familiarize, Study, Be Aware, Become Acquainted with, Gain Knowledge of, Cover, Learn, Realize. These are not measurable! Knowledge Verbs
Research objective: To investigate the clinical efficacy of LIPUS in the management of patellar tendinopathy symptoms. This article discusses the importance of clear, well-thought out objectives and suggests methods to write them clearly. What is the introduction in research papers?
If you are not sure yet where to publish and just want some generally good examples of descriptive verbs, analytical verbs, and reporting verbs that are commonly used in academic writing, then have a look at this list of useful phrases for research papers. 3. Use More Active and Precise Verbs Have you heard of synonyms? Of course you have.
ACTION VERBS FOR USE IN DEVELOPING OBJECTIVES THESE VERBS ARE BETTER AVOIDED Those that are often used but are open to many interpretations: appreciate, have faith in, know, learn, understand, believe LEVEL OF LEARNING COGNITIVE LEARNING The participant should be able to... Knowledge (remember information)
What verbs could you use? Gain knowledge/ understanding Identify Measure, Determine, Describe, Compare, Assess Explore or test a theory Measure, Test, Calculate, Determine, Investigate, Discover, Demonstrate, Examine Analyse or connect existing data/ research/ theories Examine, Contrast, Analyse, Relate, Compare, Determine
When writing research papers, choose active verbs that clarify and energize writing: the Introduction section "presents" a hypothesis, the Methods section "describes" your study procedures, the Results section "shows" the findings, and the Discussion section "argues" the wider implications.
A vital tool for this is the effective use of verbs. Research papers often involve the description of processes and methodologies, which makes it even more important for the specific action word to be used. This article provides recommendations on how you can select suitable verbs for your writing project. First, let us briefly review what ...
Published on July 12, 2022 by Eoghan Ryan . Revised on November 20, 2023. Research objectives describe what your research is trying to achieve and explain why you are pursuing it. They summarize the approach and purpose of your project and help to focus your research.
Using the right verbs for academic writing is very important for researchers. Learn about the kinds of verbs used in academic writing and understand via examples the right way to use them. ... For example, the use of action verbs in research objectives or strong verbs for thesis statements goes a long way in making the manuscript more impactful ...
research and the writing process and the importance of verbs. With respect to academic writing, the verb find―and its derivative found―are the most frequently used verbs and represent the basic and central core of academia (Meyer, 1997). Authors of The Concise Oxford English Dictionary (2008) defined the verb find as "discover by chance ...
Verbsforresearchobjectives©BCChew2017 Verbs Used to Write Research Objectives *Kindly cite me and put my work in your references if you have used this material please. I appreciate if you do it and wish you all the best. Thank you. Chew, B.C. (2017). Verbs Used to Write Research Objectives, Lecture Notes Distributed in Research Methods ...
Verbs for Writing Measurable Objectives Action Verbs for Cognitive Domain Knowledge Comprehension Application Analysis Synthesis Evaluation Reproduce Restate Translate Distinguish Compose Judge ... Choose React Build Write Conduct Adapt Make Isolate Respond Calibrate Sets Up Show Alter Construct Select Show Construct Operate Operate Change ...
Summary One of the most important aspects of a thesis, dissertation or research paper is the correct formulation of the aims and objectives. This is because your aims and objectives will establish the scope, depth and direction that your research will ultimately take.
Once you've decided on your research objectives, you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement. Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one. Example: Verbs for research objectives I will assess … I will compare …
Use action verbs: Use action verbs such as "investigate," "examine," "analyze," and "compare" to describe your research aims and objectives. This makes them more specific and measurable. ... To avoid these common pitfalls, it is important to be specific, clear, relevant, and realistic when writing research aims and objectives ...
Key Verbs for Writing Objectives Cognitive Domain Some verbs may be used in more than one category.
This article provides strategies from the Western Journal of Nursing Research editorial board for preparing competitive shorter research proposals. Two key strategies for success are fully conceptualizing the study prior to writing and obtaining assistance from experienced colleagues during the editing process. Download Free PDF.
January 5, 2024 by Muhammad Hassan Table of Contents Research Objectives Research objectives refer to the specific goals or aims of a research study. They provide a clear and concise description of what the researcher hopes to achieve by conducting the research.
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one. Example: Verbs for research objectives I will assess … I will compare … I will calculate … Frequently asked questions: Writing a research paper What is a research project?
The idea of Bloom's Taxonomy is that learning is a consecutive process. Before applying a concept in real life, we must understand it. Before we understand a concept, we must remember the key facts related to it. Although initially described as a framework, it is now often depicted as a pyramid. The basis of the pyramid is Knowledge, the ...
What behavioral objectives are NOT: a. Verbs that describe feelings, emotions, thoughts or similar things are not behavioral, because they are not observable or measurable. Verbs in this category include "appreciate, believe, know, learn, realize, think, understand", and so on. Steer clear of these types of words when writing your objectives. b.
For example, your course level verb might be an Applying level verb, "illustrate." Your lesson level verbs can be from any Bloom's level that is equal or below this level (applying, understanding, or remembering). Steps towards writing effective learning outcomes: Make sure there is one measurable verb in each objective.
Behavioral Objectives Are Not: • Started with verbs that describe feelings, emotions or thoughts. These verbs are not observable or measurable. • What the trainer / presenter intends to do during the PD offering. Write learning objectives from the perspective of what the participant / learner will be able to do after attending the PD ...