
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 5: Presenting Your Speech Module

Four Types of Speeches
Speeches can be categorized into four broad areas depending on the amount of preparation that is undertaken and depending upon the nature of the occasion. The four types of speeches are manuscript, memorized, extemporaneous, and impromptu. Our aim is to acquaint you with these four different modes of delivery, to provide suggestions for when you are asked to make impromptu remarks, and then to focus most your time on the preparation, practice, and presentation of extemporaneous speeches.
Manuscript Speech
When you listen to the President deliver a State of the Union message, you listen to a well-crafted speech being read from a teleprompter. The speech has been polished by a staff of speechwriters and has been practiced many times. The President will know how to anticipate the reaction of the audience and will know when to pause for applause and when to expect laughter. This form of speaking is used when the exact words matter and when much time and energy is expended on getting everything just right. There are times when people who are not leaders of countries deliver manuscript speeches as well. They are used when people testify before Congress, when people read important statements in a public setting, or when people deliver reports at professional meetings. All call for exact words in the correct order.
While the President has access to a staff of speech writers and a teleprompter, most of us do not. If you were given this type of assignment, you would have to read your manuscript speech from printed notes. In that case, you would want to ensure that you had prepared your manuscript carefully, using large fonts so you could read it easily without burying your nose in the pages. Reading the speech does not allow you to skimp on the preparation. Practice the speech many times. This allows you to make changes, if needed, and to select the best words to communicate your exact meaning. Remember to speak clearly and naturally -strive for a conversational tone. It shouldn’t sound read -even if you are reading. Also, remember to speak slowly; there is a natural tendency to speed up when we speak in public. Delivering a speech is not a race; you do not receive bonus points for finishing early.
Unless you are specifically told by your instructor to prepare and deliver a manuscript speech, you should never write out the entire speech. Spend your time developing your outline, organizing your ideas, and determining where you can best insert your supports. Then practice using the outline while speaking.
Memorized Speech
When you were in elementary school, did you ever have to memorize a poem or a part of a speech? If you are like most students, the answer is “Yes. ” There is nothing wrong with memorization. But if you try to memorize a speech, you risk forgetting what you planned to say and coming across as completely unprepared. Memorizing your speech is even worse than reading it. All the objections that apply to the read speech also apply to the memorized speech. Spontaneity is gone. The speech can sound stilted. Often, delivery is too rapid. Concentration is on the words, not the ideas. Sometimes the speech sounds too formal, like a written essay. There is minimal feedback or other contact with the audience. And what happens if your mind goes completely blank or if an audience member interrupts? The entire presentation will likely fall apart. Memorizing a speech puts entirely too much pressure on the speaker.
That said, there are a couple of parts of the speech that you may want to have memorized -or practiced so well that you can deliver them almost as if memorized. These include:
Your introduction: It sets the stage for the entire speech. The words should be well chosen and rehearsed. You may find that as you repeat this portion of the speech during your rehearsals you do come to memorize it word for word. If so, this is fine. After all, once you have determined the best way of saying something, why not use it? Just make sure the presentation does not sound memorized. Your conclusion: The summary and call to action are the final words that your audience will hear. As with the introduction, if you practice this repeatedly you will develop the best way to say what you want and you will probably have perfected this portion of the speech.
Impromptu Speech
There will come a time for all of us when we are asked to “say a few words ” without much preparation. You haven’t prepared any notes, you haven’t practiced what you’ll say, and you’re being asked to “wing it. ” While this may seem incredibly scary, impromptu presentations are the most common type of public speaking. You’re in class and suddenly the professor wants to hear how group projects are going. You, as the leader of your group, are asked to stand and briefly discuss what the group is doing and how much you’ve completed so far. That’s an impromptu speech. You didn’t know when you headed to class that day that you’d be speaking in public, but you did it. No sweat! Or maybe you’re in a meeting at work and the boss announces that he wants you to brief everyone in the meeting on the new equipment being installed that afternoon. Again, no prior planning, no notes, you just do it. That’s impromptu speaking.
Extemporaneous Speech
The focus of most college courses in public speaking is the extemporaneous speech. This is because this is the type of speech used most in business, education, preaching, and political affairs. Few of us will ever have a professional staff of speechwriters or ever deliver a speech with the aid of a teleprompter. But when you do have a speech or presentation to deliver, you’ll want to sound prepared, authoritative, and clear.
Simply stated, an extemporaneous speech is one where you will have time for preparation and practice but will not be expected to read from a manuscript or to have the speech memorized. The question most students ask is, “How much time should be spent in preparation and practice? ” Perhaps Mark Twain said it best. When speaking about preparing for an impromptu speech, he noted, “It usually takes more than three weeks to prepare a good impromptu speech ” (King). While celebrated as a humorist, there is much truth in his words. To appear to be speaking off the cuff, and to do it well, you must prepare thoroughly and practice to perfection. When you speak extemporaneously, it means you’ve had ample time to prepare and research and that you have rehearsed your speech (many times) using an outline or notes to remind you of the progression of ideas you wish to present. You will follow all the normal steps outlined in the earlier chapters. Choose a topic, narrow appropriately, analyze your audience, choose your supports, and create an outline. You will know your speech so well and will amaze your audience!
Fundamentals of Public Speaking Copyright © by Lumen Learning is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
9 Different Types of Speeches (Plus Tips and Examples for Each)
Posted on Published: August 6, 2018 - Last updated: March 5, 2021

One of the most famous speeches is Dr. Martin Luther King’s “I Have a Dream.” It was delivered 55 years ago in Washington D.C. to an estimated 250,000 people who showed up in support of civil rights.
People might have never heard of the speech had the sound system not been fixed promptly. It was discovered that someone had sabotaged the sound system just before the event started.
As shown by Dr. King, speeches are powerful and can be used to move mountains. That’s why it’s important to know the different types of speeches and how you can harness them to your advantage.
Basic Types of Speeches
Demonstrative speech.

The purpose of a demonstrative speech is to educate the audience on something . It can include visual aids that add to the demonstration and describe in practical terms how to do something. Demonstrative speeches are similar to informative speeches but informative speeches normally do not include actual demonstrations.
If you give a talk on how to start a blog, how to write a cover letter, or even how to make money on the Internet, these can be considered demonstrative speeches. Asking yourself “how” and “why” questions is a great way to get this type of speech started and, of course, visual aids are a necessity for any type of demonstrative speech or presentation.
Entertaining Speech

If you’ve ever been to a wedding reception or banquet — and who hasn’t? — you are already familiar with an entertaining type of speech. The main purpose of a best man’s speech or an after-dinner speaker is to entertain the crowd and most speakers do that through illustrations, funny stories, and basic humor. Entertaining speeches are informal and usually very short; they are speeches that provide a lot of enjoyment and pleasure for the audience.
Informative Speech

People who give informative speeches are there to present the audience with new information on a particular subject. They present statistics and facts about topics such as social and economic changes in the community but they do not use visual aids in the speech.
Instead, they rely on educational information, facts, and various data so that the audience actually learns something. If you’ve ever been to a museum and had a tour guide, you’ve enjoyed the benefits of an informative speech. Any time that a talk is given to give the audience details and information on a certain topic, this is an example of an informative speech.
Persuasive Speech

Persuasive speeches are there to persuade the audience that an opinion expressed by the speaker is the right one. Whether you’re discussing what to eat for supper or which political point makes the most sense, these are examples of persuasive speeches. Most people, in an attempt to persuade the audience that their point of view is the right one, use solid facts to back up their argument. This is one of the best ways to make sure that your persuasive speech does the trick, which means that using research and statistics to develop your argument is always more likely to make people come to your side.
Other Types of Speeches
Oratorical speech.

Oratorical speeches are delivered in the style used by an orator. Its name is a little redundant because “orator” and “oratorical” both relate to the giving of speeches. These types of speeches are usually given at a special celebration such as an inauguration or ribbon-cutting ceremony. They can be long and formal, such as speeches used at a graduation, funeral, or inauguration, or short and informal, such as speeches delivered as toasts at special events.
Oratorical speeches can also be given at events such as birthday parties, going-away parties, retirement parties, and many others. Political speeches are usually considered oratorical speeches and they are better when they do not try and settle a complex argument but instead when they appeal to common virtues and basic truths. In oratorical speeches, the speaker is not trying to persuade someone to do something or believe a certain way but even though they are fairly general in purpose, the speaker can still address certain issues while giving the speech. Inauguration speeches are perhaps the most well-known oratorical speeches that exist today.
Special Occasion Speech

Speeches that don’t fall into any other category are usually classified as special occasion speeches and these can include speaker introduction speeches, designed to be short but interesting and to introduce an upcoming speaker; tribute speeches, which are designed to pay tribute to someone either dead or alive; and award acceptance speeches, which are meant to thank someone for an award and describe what the award means to you.
Special occasion speeches are designed to be short, usually ten minutes or less; succinct and to the point; and mood-setting. In other words, there are distinct purposes for special occasion speeches and whether the event they’re offered at includes something that is happy or somber, for someone still living or a posthumous occasion, or something large or small, they are often some of the easiest speeches to write. Most often, speeches for special occasions are fun and upbeat and if you research them online, it is easy to find out how to get started for your own special occasion speech.
Motivational Speech

A motivational speech is a unique type of speech and has the goal of self-improvement for the audience members. With a motivational speech, you can turn a negative situation into a positive one. These types of speeches are especially popular in business meetings with executives, to complete a certain task, or to encourage employees to sell more of your product or service. Motivational speeches can be found in elementary school to high school in order to motivate the students to do better on a test or in a sporting event. The speeches are great for inspiring people, lifting a person’s self-esteem, or even motivating an entire crowd of people.
Motivational speeches often use techniques to make the speeches more effective. These include:
- Starting with an activity –g., a breathing exercise — to demonstrate what the speaker’s goals are and which results are expected in the end
- Asking a question in order to pique the audience’s curiosity and interest
- Quoting a scientific study so that your motivational speech has some authority and trust
- Telling a story to get the audience more interested and involved; this can include a historical story, a personal story, or even a professional story, although a story from your own life is likely to work best
- Making sure that you address the audience’s problem so that you can then give them detailed suggestions on what can solve that problem, which will naturally increase their motivation
Debate Speech

In a formal debate, much verbal sparring is experienced and the debates come in various forms as well. These forms include Parliamentary, classical, extemporaneous, Lincoln-Douglas, impromptu, public forum, and mock trials, to name a few. As a general rule, in a debate, both sides get equal time to discuss the issue and explain why their view of the issue is the right one. Debates are somewhat different than persuasive speeches because you aren’t necessarily there to get the other side to switch to your side; instead you are there, in essence, to justify why you believe a certain thing.
Debates are arguments that have rules and regardless of which style you choose, each side receives the topic then has a certain amount of time to prepare to present it. Debate teams develop very valuable skills, including research skills, public speaking skills, leadership skills, initiative skills, developing grace under pressure, critical thinking skills, and developing arguments that are both logical and sound. Debaters also learn to think on their feet, which is why many people who join debate teams during high school and college go on to become professional mediators or lawyers.
There are many advantages to belonging to a debate team and some of those can be found here .
Forensic Speech

The term “forensic speech” merely refers to the practice and study of debate and public speaking. This is according to the American Forensic Association and this activity is practiced by millions of high school and college students each and every year. The reason why it is called forensics is that this practice is patterned after the competitions at public forums during the period of ancient Greece.
The speeches can take place inside a classroom, a national or international tournament, or even a regional event. During the activity, students learn to research and speech skills in order to learn all different types of speeches. Forensic speeches allow students to perfect their craft under the supervision of experienced public speakers and it can even be considered a type of “on-the-job training” because the students involved in this activity are continuously honing their craft while practicing it at the same time.
Examples of Speeches: Possible Speech Topics
If you’re looking for ideas when writing a demonstrative speech, check out websites such as this .
Examples of great ideas for entertaining speeches can be found here .
Some interesting topics to use for informative speeches are listed here .
Get more ideas on what to write about in a good persuasive speech by visiting websites such as this.
Tips to Make Speeches More Effective
- Choose an easy topic. This is the best way to make sure that your speech is both effective and interesting. Choosing a topic that is too complex or technical is a great way to lose the audience’s interest quickly because most people don’t enjoy topics that take too much concentration. In addition, many audiences are made up of people from many different walks of life so choosing an easy topic ensures that the audience will understand what you’re talking about without losing interest at some point.
- Know your audience . This is easier to do than it seems, especially because the people who hire you for the speech often help you familiarize yourself with your audience so that you can have this valuable information before you start writing the speech. One thing to look for is the mental level of the audience so if they are going to be within a certain age range, gender, or area of interest, you can easily cater your speech to this feature. Using innovative techniques to keep the speech uplifting and positive also helps so doing your due diligence on your audience is always a great first step when creating the perfect demonstrative speech.
- Keep your visual aids interesting. Visual aids are a very important part of a demonstrative speech and if you use a variety of visual aids, the speech is guaranteed to keep the audience’s attention. It’s best if you use visual aids such as drawings, photographs, 3-D items, and even flashcards for more emphasis. If you go back and forth between color and black-and-white pictures and visual aids of many different sizes and types, that will keep the audience’s interest throughout the speech. Furthermore, making your visual aids stand out is also important because during many speeches, the audience members pay more attention to the visual aids than they do to the speech itself.
- Add entertainment of some type. This can include a video, a sound clip, or even a funny cartoon. If you insert one of these items periodically throughout your speech, it not only keeps things more interesting and entertaining but it also enables it to be funnier, which means that it is going to be a speech that people will remember for a very long time.
- Tell jokes periodically. Many effective entertaining speeches have jokes inserted into them every now and then. If you’re delivering your speech, simply stop occasionally and say, “that reminds me of a joke…” Even entertaining speeches can have slow spots and a good joke can break up the monotony and keep the entertaining speech, well, entertaining.
- Tell funny stories. Funny stories go great with entertaining speeches because much as the speeches themselves, these stories are designed to help people relax and laugh a bit. Everyone enjoys a funny story and if you tell three to four of them in your speech, it can make the speech much more entertaining and something that is guaranteed to be enjoyed by everyone.
- Tell a scary story . As long as it isn’t too scary, this technique works every time. Everybody loves a good old-fashioned scary story and since both these stories and your speech will entertain people, they are the perfect two items to include together. Scary stories aren’t appropriate for every type of entertaining speech but for most of them, they will work just fine.
- Dramatize an anecdote. Anecdotes are perfect for entertaining speeches because they are amusing stories about real-life people. They make an already entertaining speech even more entertaining and they can easily relate to the topic you’ve chosen for your speech. Anecdotes also make the speech a little more light-hearted and since there are literally millions of subjects to choose from, it is easy to incorporate an anecdote into entertaining speeches of all types and subject matters.
- Include a theme. A theme that repeats itself throughout your speech is a good way to make it more memorable and also a lot funnier and more entertaining. A humorous theme works best because it fits perfectly within a speech meant to be entertaining. If you’ve researched your speech’s topic thoroughly enough, it will be easy to determine which theme to choose in the end.
- Include enough pieces of information throughout your speech. As a general rule, if you include one piece of information for every minute of the speech , it goes a long way in delivering the right amount of information. If you can, view a stand-up comic’s routine. Most of them go for a laugh every minute so in an average 30-minute routine, they aim to get at least 30 laughs.
- Organize, organize, organize. Your speech needs to be organized from start to finish, which means keeping in mind what you want to teach the audience and listing points that describe each of these things. Remember, this is a speech that is supposed to teach something to the audience so writing out your speech in bullet form is a great way to keep it organized. This organization takes a lot of pre-planning so keep all of this in mind while you’re writing your speech.
- Don’t recite your speech word for Instead, write it out with 30 to 60 points that you wish to get across to the audience members. Reciting it word for word makes it sound boring and as if you aren’t interested in the topic yourself but giving the speech in your own words makes it more interesting and does a better job of getting your points across to the audience. To make it more effective, write down your speech in outline form and bring that outline with you to the event.
- Make sure that your speech is long enough. Since most people tend to talk fast when they’re nervous, such as when they are giving a speech, it is a good idea to prepare 35 minutes worth of content for a 30-minute speech. Also, practicing the speech more than once helps you determine whether the content you’ve written will suffice. The more practice, the better, and always remember to include more content as related to the length of time that you hope to be speaking.
- Don’t stay stuck behind the podium. Informative speeches can easily be boring speeches so come out from behind the podium occasionally and make direct eye contact with audience members. This serves several purposes. First, it engages the audience more and makes them feel as though you are truly interested in them; second, it lets you know if what you’re conveying is actually getting across because you can more clearly see the expressions on their faces as you speak.
- Make your ending memorable. At the end of your speech, there are a few things that you can do to make it truly effective. These include thanking the audience, giving them your contact information in case they want to get in touch with you later on, encouraging them to ask questions, and, when questions are asked, making sure that you rephrase them so that everyone in the room will understand your answers.
- Choose something controversial. This may sound odd but the truth is that topics that everyone agrees on or is favorable to don’t need much persuasion. A controversial topic such as the death penalty or gun control usually has people on both sides pretty firm in their beliefs and if you can convince one of those people to change his or her mind or understand the other side’s beliefs, this says a lot about your speech-writing abilities. Of course, if you have passion when it comes to your topic, you are likely to be more effective; however, starting with a controversial topic is a great way to get started with your persuasive speech.
- Consider people’s perceptions of the topic. With controversial subjects, it is common for people on both sides to have certain inaccurate perceptions regarding the topic. If you specifically address some of these perceptions, it goes a long way in teaching the other side some facts that they may not have known about your side of the issue. The more they learn about your side, the more likely they are to agree with you in the end. Remember, for most people, perception is reality so addressing people’s perceptions is a great tactic for use in persuasive speeches.
- Use facts instead of emotions. Controversial topics are usually very emotional ones but trying to use emotions to bring people to your side is rarely effective. If you use straight facts and you are able to inform them which sources you used to get those facts, it will at least plant some fact-based ideas in the minds of the other side. This may not convince them to be on your side right now but it is much more likely to do so sometime in the future.
- Consider the other side’s sense of opposition. Regardless of what side you’re on regarding a controversial subject, you are liable to feel a certain amount of opposition from the other side. When you’re giving a persuasive speech, finding a way to eliminate this opposition or the perception of it can help your speech become more effective. Learn the obstacles the other side feels are associated with your view of the issue and find ways to convince them that they will not be ostracized or opposed in any way if they come over to your side. This is easy because once you determine what types of opposition they feel or sense, you can easily address the opposition specifically during your speech.

Informative Speeches — Types, Topics, and Examples

What is an informative speech?
An informative speech uses descriptions, demonstrations, and strong detail to explain a person, place, or subject. An informative speech makes a complex topic easier to understand and focuses on delivering information, rather than providing a persuasive argument.
Types of informative speeches
The most common types of informative speeches are definition, explanation, description, and demonstration.

A definition speech explains a concept, theory, or philosophy about which the audience knows little. The purpose of the speech is to inform the audience so they understand the main aspects of the subject matter.
An explanatory speech presents information on the state of a given topic. The purpose is to provide a specific viewpoint on the chosen subject. Speakers typically incorporate a visual of data and/or statistics.
The speaker of a descriptive speech provides audiences with a detailed and vivid description of an activity, person, place, or object using elaborate imagery to make the subject matter memorable.
A demonstrative speech explains how to perform a particular task or carry out a process. These speeches often demonstrate the following:
How to do something
How to make something
How to fix something
How something works

How to write an informative speech
Regardless of the type, every informative speech should include an introduction, a hook, background information, a thesis, the main points, and a conclusion.
Introduction
An attention grabber or hook draws in the audience and sets the tone for the speech. The technique the speaker uses should reflect the subject matter in some way (i.e., if the topic is serious in nature, do not open with a joke). Therefore, when choosing an attention grabber, consider the following:
What’s the topic of the speech?
What’s the occasion?
Who’s the audience?
What’s the purpose of the speech?

Common Attention Grabbers (Hooks)
Ask a question that allows the audience to respond in a non-verbal way (e.g., a poll question where they can simply raise their hands) or ask a rhetorical question that makes the audience think of the topic in a certain way yet requires no response.
Incorporate a well-known quote that introduces the topic. Using the words of a celebrated individual gives credibility and authority to the information in the speech.
Offer a startling statement or information about the topic, which is typically done using data or statistics. The statement should surprise the audience in some way.
Provide a brief anecdote that relates to the topic in some way.
Present a “what if” scenario that connects to the subject matter of the speech.
Identify the importance of the speech’s topic.
Starting a speech with a humorous statement often makes the audience more comfortable with the speaker.
Include any background information pertinent to the topic that the audience needs to know to understand the speech in its entirety.
The thesis statement shares the central purpose of the speech.
Demonstrate

Preview the main ideas that will help accomplish the central purpose. Typically, informational speeches will have an average of three main ideas.
Body paragraphs
Apply the following to each main idea (body) :
Identify the main idea ( NOTE: The main points of a demonstration speech would be the individual steps.)
Provide evidence to support the main idea
Explain how the evidence supports the main idea/central purpose
Transition to the next main idea

Review or restate the thesis and the main points presented throughout the speech.
Much like the attention grabber, the closing statement should interest the audience. Some of the more common techniques include a challenge, a rhetorical question, or restating relevant information:
Provide the audience with a challenge or call to action to apply the presented information to real life.
Detail the benefit of the information.
Close with an anecdote or brief story that illustrates the main points.
Leave the audience with a rhetorical question to ponder after the speech has concluded.
Detail the relevance of the presented information.

Before speech writing, brainstorm a list of informative speech topic ideas. The right topic depends on the type of speech, but good topics can range from video games to disabilities and electric cars to healthcare and mental health.
Informative speech topics
Some common informative essay topics for each type of informational speech include the following:
Informative speech examples
The following list identifies famous informational speeches:
“Duties of American Citizenship” by Theodore Roosevelt
“Duty, Honor, Country” by General Douglas MacArthur
“Strength and Dignity” by Theodore Roosevelt
Explanation
“Give Me Liberty or Give Me Death” by Patrick Henry
“The Decision to Go to the Moon” by John F. Kennedy
“We Shall Fight on the Beaches” by Winston Churchill
Description
“I Have a Dream” by Martin Luther King, Jr.
“Pearl Harbor Address” by Franklin Delano Roosevelt
“Luckiest Man” by Lou Gehrig
Demonstration
The Way to Cook with Julia Child
This Old House with Bob Vila
Bill Nye the Science Guy with Bill Nye
Speech Structure: The Complete OBC Guide
What makes a great speech? The content, of course, but also the structure. All great speakers overlay their content on a well-known structure.
Your speech structure is the glue that binds your points together. Without it, you cannot really have the impact you desire to have on the audience.
The beauty of this is that a good structure is so subtle it is almost invisible. Its effectiveness is only evident in its impact.
Speech writing can be intimidating for some, however, we have incorporated plenty of speech examples to get a complete understanding. We aim to explain a proper structure that can be applied to any of your speeches.
There are four things you need to keep in mind about this:

Table of Contents
What is the purpose of your speech?
Can too much content be harmful, who is the audience, informative speech, persuasive speech, argumentative speech, demonstration speech, humorous speech, strong statement, visual prop or demonstration, personal anecdote, problem or strong statement, summary on writing your introduction:, credibility, cause and effect:, problems and solutions:, lucky number three, summary on writing your body:, call to action, inspirational, key takeaway, summary of writing your conclusion:, meta description:, picking the right topic.
The content of a speech can largely determine how the audience receives it. For this, you will need to accurately assess who is going to be listening to your speech. There are some questions you need to ask before sitting down to write this speech.
Do you intend to introduce a concept or argue on a controversial topic? Is your purpose of imparting knowledge or guiding the audience through a demonstration? It is essential to have your intentions cleared; otherwise, you can risk creating a speech with no direction.
We understand that as daunting as speaking can be, it is, at the same time, fascinating. When you pick a topic that you are passionate about, it is easy to find yourself packing the speech with all kinds of information. However, in doing so, you can overwhelm your audience.
There is such a thing as too much information. You need to make sure that whatever information you do include is impactful and influential. Aim for something short but memorable. Pick one takeaway message and gear your speech towards that objective.
While it is vital to pick a topic that interests you, it is equally important to make sure that it can grab the audience’s attention. What is the target demographic for your speech? What is the setting for this speech? Is it a particularly controversial topic?
This is important because as humans, most people are likely to be more interested in your presentation if it benefits them somehow. At the same time, you have to consider the setting.
For instance: an office setting would not be the right setting for a controversial social speech. If your speech includes demonstration and requires volunteers, you need to ensure that this is an audience willing to participate.
Do you understand the various types of speeches?
Before you pen down your presentation, stop to wonder whether you understand the different types of speeches. Understanding what kind of speech you are going for can help you better structure it for maximum efficiency:
An informative speech intends to explain complex topics to your audience by providing engaging information. This can include objects, events, procedures, and more. It is better if you pick a topic that you are interested in so that your enthusiasm shines through.
When you give an informative speech, you are merely trying to educate your audiences about a particular topic. You refrain from becoming too argumentative as it might come across too strong for your listeners. If this is the type of speech you intend to give, you can check out 100 Informative Speech Topics and Ideas to make your job easier.
A persuasive speech intends to convince the audiences of your viewpoint. It uses compelling points to sway the listener’s opinions. The primary purpose of this type of speech is to affect the audiences’ thought process and persuade them to think about changing how they feel about a topic.
Some examples of a persuasive speech can be a politician’s speech, an animal activist’s speech, and so on. As you can see, the goal here is to persuade and obtain something ultimately. A politician might want to sway your vote in their favor, whereas ani activist has a cause that they’d like to advocate for.
If this is the type of speech you intend to give, you can check out 237 Easy Persuasive Speech Topics and Guide to better plan your speech.
An argumentative speech is more or less a persuasive speech. However, a persuasive speech does not always have to be argumentative. The purpose of an argumentative is to alter how the audience views a subject.
Changing the audience’s opinion is not an easy job. This is why you need to not only pick a persuasive topic but also believe in it. You need a strong claim along with irrefutable points to support it.
The best argumentative speeches utilize issues relating to current events. You can see this in the media in the form of mostly social, ethical, political, or religious arguments. Your arguments should make use of logic and realistic examples. Some examples of this type of speech can be: Dress codes shouldn’t be mandatory, Space exploration is a waste of money, etc.
If you’d like to see more topic ideas for an argumentative speech, you can browse the 200 Argumentative Speech Topics and ideas: A Complete Guide .
A demonstration speech, true to its name, demonstrates to the audience how something works. This type of presentation is more common for high school or college students. It makes use of props and useful body language to properly guide the audience through an activity.
This type of speech can fall under informative speech as you are informing the listeners on a task. While this type of speech is considered a basic speech, it is an excellent way to practice your expository speaking.
If this is the type of speech you’d like to give, here’s a list of 279 Demonstration Speech Topics and Ideas: A Complete Guide , so that you can better perfect your speech.
A humorous speech is the perfect light-hearted solution for adding a fun twist to your speech. This type of presentation aims to entertain the audience. A humorous speech can incorporate any of the above examples. It is, thus, very versatile. And what’s more? You get to have just as much fun delivering it!
The thing to keep in mind with this kind of speech is that you need to pick a proper topic. You intend to garner a joyful response to its best not to pick a sensitive topic. To help you out, you can browse the 300 Funny Speech Topics to Tickle Some Funny Bones! to structure your humorous speech.
Writing the Introduction (Opening)
The introduction of your speech is vital to the success of your speech. It is what sets the tone of your entire speech. It determines whether or not you grab the attention of the listeners. You will get only one chance to charm your audience and make sure they follow the rest of your speech.
So, how can you make this happen? There are a few different ways you can approach this:
Asking a question is an excellent way to grab your audience’s attention. It piques their curiosity and ensures that they will listen to get an answer to said question. The question can be either rhetorical or literal. For instance, “Have you ever wondered what it’d be like to live in a world without technology?” or “Have you ever felt broken-hearted?”.
Either the audience resonates with your question, or it generates curiosity. This is also a great way to get some audience participation. If you say, “With a show of hands, how many of us here have tried to change our habits and failed?” you can not only garner interest but also physically get the audience invested in your speech.
A question is a great way to get your listeners thinking about your topic while introducing your topic, all in a matter of seconds!
A strong statement is also an excellent way to create a compelling introduction. You must know Martin Luther King’s iconic, “I have a dream.” The intensity that radiates from that sentence immediately captures an audiences’ attention and creates a commanding presence.
Similarly, an excellent example of this type of opening is from Larry Smith’s speech. “I want to discuss with you this afternoon why you’re going to fail to have a great career.” This immediately generates intrigue and curiosity. That’s what you’re going for.
This statement does not have to just be cold facts. It can be a part of a personal story as well. For instance, the statement “Last week, I found out that my childhood friend got in a car accident” is bound to create a powerful silence. If your speech has such a strong emotive statement, you can use it in your introduction to engage your audience better.
Another helpful tip that goes with a strong statement in silence. Give your listener’s a chance to absorb the statement that you have put in front of them with a couple of seconds of silence before diving in further.
A prop can be a fantastic addition to your speech. Not only does it help emphasize your point, but it also helps the audience stay focused on your speech. Props are especially good for a demonstrative speech. Or you can simply incorporate demonstrations as part of your speech.
Body language speaks much louder than words can for us humans. This is why using colorful bags, a deck of cards, colored papers, etc. can be so effective as an opener for your speech. Once, I attended a speech where the speaker brought a heavy bag and simply set it on the table, talking about the bag. The audience was hooked, waiting eagerly till the end to find out what was in the bag.
A quotation can be the perfect way to capture your audience’s attention. It also helps set a tone for the speech that is to come. The quote you pick can be a well-known saying such as “They say all that glitters is not gold, well I beg to differ.” Doing so, you can ignite curiosity.
Similarly, you can also quote a person or a publication and tie it to your speech. For instance, for a motivational speech, you can take the example of someone like Bill Gates- “Your most unhappy customers are your greatest source of learning.” When you use a quote from a big name, you will definitely get people wanting to hear and learn more.
Humor is always a great tool to have in your arsenal. A good icebreaker can warm the listeners up to you and make them more receptive to the rest of your speech. Humor is a very endearing trait for a skilled speaker. Some ideas for your opening can be:
“It’s the funniest thing. As I was coming up to the stage, I began thinking we actually have quite a lot in common. None of us have a clue about what I’m going to say!”
“I know we are all busy, and I want to honor your time. So I will make sure to be accurate and brief, no matter long it takes me.”
The great thing about using humor is that it works on your audience subconsciously. You seem at ease with yourself and radiate confidence. You have to remember that for humor to be effective; it has to be effortless. If you seem unsure about your lines, the audience is sure to pick up on it.
A strong statistic will always add validity to your speeches. Presenting the audience with irrefutable facts backed up by a strong source is a surefire way to gain credibility. It can also add gravity to the scale of the issue that you want to draw attention to.
However, it is easy to overdo things when it comes to numbers. It can be tempting to add strong statistics to the rest of your speech as well. But remember, the strongest points are ones that linger in an audience’s mind. If you give them too many numbers, none of them will stick out in their heads, and they are bound to feel lost.
Some examples can be: “Look to your right. Now, look to your left. One in three women and one in four women are known to have suffered physical violence. A statement like this not only ignites awareness but also physically makes your listener feel involved in your speech.
An anecdote is a short story taken from your life itself. The story usually adds to the theme of your story. Short and light-hearted anecdotes can add a lot of enthusiasm and charm to your speech. However, you don’t have to make them humorous. Even more, touching stories can be equally, if not more engaging.
When used correctly, a personal anecdote makes for the perfect introduction that draws your listeners towards your central message. Not only does it create empathy, but it also sparks interest. If you don’t have a personal anecdote itself, you can go for a third-person anecdote that speaks to you as well.
Opening with a problem can make for a strong opening. This method generates interest and keeps the audience listening with the promise of an upcoming solution. Try to aim for a problem that caters to a wider demographic for a higher relatability.
Problems that relate to current events can have a better draw. For instance: “Why should remote working be implemented even after quarantine?”
In a similar vein, a powerful statement can be an excellent way to capture your audience’s attention. A statement, when paired with silence, can make for an effective tool. Example: “The top 20% of our society makes 80% of all the money. Would you like to be part of this 20%? If so, I’m going to give you some pointers on how you can align yourself in that direction. Does that sound like something you might be interested in?”
- Your opening plays a big role in whether or not you can grab your listener’s attention straight off the bat.
- Give your audience a reason to pay attention by clearly stating the purpose of your speech.
- If you are giving a speech regarding a field you have some experience with, remember to establish credibility early on.
- Give a short highlight reel of your main points.
- Quotations or powerful statements are a great way to catch the audience’s attention.
- Including current events or statistics will make your speech seem more relevant to a wider range of listeners.
- Asking a question will get your audience more involved and add intrigue to the rest of your presentation.
Structuring your content (Body)
The body of your speech will hold all of your main points. Since this is the longest section of your speech, you need to ensure that it is interesting enough to keep everyone’s attention. Depending on the objective of your speech, you will need to add examples, opinions, and facts to back up your points. What helps during this time is proper organization.
Here are some things you want to keep in mind while drafting the body of your speech:
No matter how much you believe in your point, you still need to give your audience a credible reason to take your word for it. This can be done by adding examples, detailed descriptions, statistics, and so on. Always remember to credit the source when using a statistic. You can also add a strong testimonial to add a touch of personalized support if that applies to your objective.
Transitions
When you have a lot of content packed into your speech, transitions become vital to the effectiveness of your speech. You can consider these as points of a refresh in your speech. Here, the audience can reengage and follow along more attentively.
The best transitions are always invisible. They can seamlessly add flow to your speech without giving any indication of such to your audience. There are many ways to incorporate this into your speech.
Some examples can be:
A connective transition is where you reiterate a previous point and introduce a connecting point. The way this method works is that it rehashes an important aspect while relating it to what’s next.
The most effective way to use this is in a problem/solution module. This is where you begin by stating a problem and transition towards a solution.
Example: Now that we’ve understood the various negative effects of junk food, let me tell you how we can plan a better diet to combat obesity.
When you do this, you are providing a summary of the problem and swiftly leading them towards a solution. If you jump straight to the next section, it can feel rushed. Besides, pauses are another important element of speech delivery.
Keywords, as the name suggests, have a certain draw to them. These are words that are central to the theme of your speech. Repetition is a very effective tool in conveying your message.
For instance: If your speech is about the scarcity of running water in rural communities, you can draw attention by repeating the factors that cause this issue. Doing so will also let you explain in better detail these factors while keeping your audience hooked to the main theme.
Content Approach
Depending on your speech, there are various ways to approach how you frame your content. We all know that content is king; however, without the right approach, it’s easy for your message to get lost along the way. This is why it’s so important to keep your subject matter relevant and interesting. Make sure the content is as compact and concise as you can make it. Some of the methods by which you can ensure this is as follows:
Cause and effect is a great way to present your ideas. This method works best for explaining events and consequences or results. Make sure to include all the appropriate details to add emphasis. The element of ‘what’s next’ is what keeps the audience hooked to your speech. As you unfold a cause and follow it with the effects, it will feel both interesting as well as rewarding to your audience.
Problem and solution is a speech method as old as time. But it is so because of its reliability. This approach works best for a motivational speech. This type of speech intends to address a problem and offer a systematic solution that benefits the listeners. It is also a common approach for pushing an audience to buy into a service or product. You pose a problem and then offer a solution, including a whole package. Make sure the solution you offer is versatile so that it applies to a wider range of people, thereby increasing appeal.
A narrative approach is excellent for anybody who wants to sharpen their storytelling skills. The important ingredients for a narrative speech are chronology and a simple organization pattern. Typically, any story will have a beginning, middle, and end. Going in order, with smooth transitions will make your story easy to follow.
This type of speech is most effective for presenting events, life lessons, experiences, rituals, and personal beliefs. Try to stick to the core of the story without too many unnecessary details. Just because a narrative includes storytelling does not mean it can’t have an end goal. For instance: a personal experience of failure might be a great story of caution for the listeners.
The most important thing for a successful narrative speech is build-up. You want your audience to be invested, to care about what comes next, to raise the stakes so that when you provide the conclusion, it is that much more effective. You must always ask yourself, “What do I want the audience to remember after this speech?”.
The best way to write this would be to outline a sketch of events that are relevant to your narrative. After that, you can think about the best way to escalate the stakes. Remember that eye contact is an important visual medium in a narrative speech. It will help your audience connect better to your story.
The number three is impactful. Even the general structure of a speech is divided into three parts: Opening, Body, and Conclusion. When you want to make a point that people remember, you should consider splitting it into three, where the first two act as a build-up while your final point brings the unexpected impact.
The best thing about this method is that you can apply it to just about any kind of speech. This, in fact, adds more structure to your speech and makes it more easily digestible. The key ingredient here becomes balance and transition. Make sure you focus on all three elements of your story equally, so it does not feel rushed. Add in a seamless transition to make your story structure seem effortless.
- Make sure you have designed your content to suit your audience.
- Divide your body into easily digestible sections so that your main points come across clearly.
- Stress on keywords and clever repetitions to drive your point home.
- Work on your transitions to establish clear sections but a seamless switch to keep your listeners hooked.
- When using facts or statistics, always back it up with a credible source.
Closing your speech (Conclusion)
The conclusion is vital to the success of your speech. This is the parting thought that you will be leaving your audience with, so you have to make sure that it’s a good one. The conclusion is where you reiterate your key point. This is why there is so much importance put on a conclusion to be powerful enough to stay in your memory.
Here are some possible ways you can approach your conclusion:
A call-to-action refers to a statement or material that intends to encourage the listener or viewer to take the initiative. It can also be considered as instruction as it usually directs the audience towards something.
The most effective way to approach this is to manage both your energy as well as your tempo. While it is essential to maintain a clear and well-enunciated speech throughout, when you reach a conclusion, you are going to want to speed up just a little bit.
What this does is add a sense of urgency to the message that you are giving. Similarly, higher energy makes the audience resonate and respond equally. They will associate this high energy with your message and remember your speech for longer.
Some examples of this can be: “As we can see, the effects of depression can be life-threatening. So I encourage each and every one of you to go home today and reach out to your friends, talk to them and open up a platform where they know they can come to talk to you for anything. Because you’d rather hear their problems than hear about their death.”
For speeches that are over 5-6 minutes long, the audience can sometimes lose track of the earlier points. This is why it is necessary to summarize your main points before you leave the stage. You don’t have to take them through the entire story, but make sure you include the keywords that trigger in them the memory of that portion.
You can do this by saying something along the lines of “Let me briefly run you through what we discussed” or “So, we talked about three main things today.” This not only does a great job of reiterating and reconfirming your main points but also signals to the audience that you are drawing towards the end of your presentation.
Repetition. Repetition. Repetition.
Even though you might be well familiarized with your speech, it is safe to assume that most of the audience is hearing it for the first time. For this reason, you need to drive your point home by essentially drilling it into their minds. Now, you can’t simply repeat the central theme over and over as that isn’t an effective strategy. But there can be an art to repetition as well.
You should aim to rephrase and reinforce your central idea as you conclude your speech. Don’t go for a word-for-word repetition, but aim to reframe your key themes and arguments. Paraphrasing, in this way, makes sure that you capture the essence of your speech without running the risk of boring your listeners with identical sentences.
We don’t even need to look too far for examples of this method. In Martin Luther King’s famous “I have a dream” speech at the Lincoln Memorial, he used this method of repetition paired with a rising momentum to create impact. Repetition works best when it is subtle and works on the listeners subconsciously.
Ending your speech on a light note is a great way to brighten moods and make sure the audience remembers your message. Your joke can also be a good way to repeat your central message. If you do decide to end with a humorous story, remember to carve out more time for it. Make sure your conclusion doesn’t distract from your main message.
Some people tend to get too excited and give away the upcoming punchline. Remember that the most effective humor approach is one you don’t see coming. How you can add the subtlety to your conclusion is by following this formula:
Set up – pause – Build up – pause – Punchline
Motivational conclusions are always an upbeat way to close your speech. You will be leaving the stage on high energy that is sure to be contagious. This also ensures that your audience will be taking a piece of your conclusion with them, making sure that it is not only memorable but also useful.
There are many ways to approach an inspirational closing. You can go with an anecdote, a quote, a poem, and so on. The purpose is to give a push, to add strength, to ignite a can-do attitude.
The trick to a powerful inspirational speech is emotion. Humans are excellent at empathizing. If you can adequately emote throughout your story, adding drama into your storytelling, then it is bound to have a more substantial effect. Vocal variety can also be an excellent element for this. Alter your tempo to weave excitement into your story. You can also use smart pauses to add more intrigue.
Your facial expressions play a significant role in how the audience receives your speech. Whether it is a sad or happy story, make sure that your face conveys it. It can be addictive to have the audience’s attention like this, but don’t get too greedy. Remember to end on your highest note, leaving a lasting impression.
There are many types of speeches out there. For instance: you might think that a humorous speech is just that: humorous. But think again. All the best speeches have at least one key takeaway.
A takeaway message is quite similar to an inspirational conclusion. The question you have to ask yourself is this: What is the purpose of my speech? Even if you’ve got a fantastic anecdotal story to share, you have to remember that the audience will always wonder what they are getting from the speech. That will be your takeaway.
For an effective conclusion, you have to step back and overview your speech. From your introduction to the body, what is the message you are trying to convey? Make sure your conclusion reflects it. For example: if your speech is about a drowning story, you can probably try to include what you could’ve done and how the audience can avoid being in a similar situation.
A call-back is a fun twist to add to your conclusion. There is a reason why a circle is one of the most pleasing shapes; it gives you a sense of completion. Even if you aren’t aware of it, it works on your mind subliminally. An effective way to conduct this method is to find a way to tie your ending to your introduction.
You can understand a call-back as a reference. It doesn’t have to be limited to just the introduction; you can reference the body of your speech as well. This not only makes for a great repetition tool but also adds a feeling of completion into your presentation.
However, you should pick something that the audience can connect to. This helps create a special and unique bond as if it were an inside joke just between you two.
- Signal your audience when you’re drawing to your conclusion.
- Add trigger transitions like “In conclusion,” “In summary,” “That brings us towards the end,” and so on.
- Try to end on a high note with something memorable.
- Write your conclusion last so that it complements your introduction.
- Try to paraphrase your words without repeating the same words over and over.
- Your audience is more likely to remember your speech if you end with something useful to them or with a call to action.
- Leave on an attention-grabbing note.
Wrapping Up:
A speech typically has one of four purposes: to inform, to entertain, to instruct, or to persuade. To deliver an effective speech, you need to first make sure you understand what your objective is. Then, you can follow our guidelines to construct a solid structure and deliver a well-rounded and impactful presentation. Now that you know how to create an effective speech structure, you are ready to dominate the stage!
The best speech structures are invisible and effective. Learn the tips and tricks to deliver the perfect opening, body, and conclusion and wow the stage.
Speech Writing
Types Of Speeches
Common Types of Speeches that Every Speechwriter Should Know
12 min read
People also read
The 10 Key Steps for Perfect Speech Writing
Understanding the Speech Format - Detailed Guide & Examples
How to Start A Speech - 13 Interesting Ideas & Examples
20+ Outstanding Speech Examples for Your Help
Good Impromptu Speech Topics for Students
Entertaining Speech Topics for Your Next Debate
How to Write a Special Occasion Speech: Types, Tips, and Examples
Introduction Speech - A Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
How to Write the Best Acceptance Speech for Your Audience?
Presentation Speech - An Ultimate Writing Guide
Commemorative Speech - Writing Guide, Outline & Examples
Farewell Speech - Writing Tips & Examples
How to Write an Extemporaneous Speech? A Step-by-Step Guide
Crafting the Perfect Graduation Speech: A Guide with Examples
Going back in history, a powerful speech backed up many significant events. Such speeches were delivered by people with speech-giving skills of the highest order.
Public speaking is an art, and to master it, the speaker should have a clear objective in mind. The presenter has to understand and tailor the speech to the nature of the audience.
That being said, having a clear objective and purpose of speech in mind makes the speech writing process simpler and more manageable.
But the question comes to mind: “ How many types of speeches are there? ”
Worry not, as in this blog, we will understand the different types of speeches with examples. At the end, there are some handy tips for you to ease your speech-writing process!
Carry on reading!
- 1. What are The Different Types of Speeches in English?
- 2. Types of Speeches According to the Purpose
- 3. Types of Speeches According to the Delivery
- 4. Types of Speeches According to Special Occasion
- 5. Other Types of Speeches
- 6. Tips to Conduct Effective Research for Your Speech
What are The Different Types of Speeches in English?
Although there is a variety of speech types, we generally look at speeches in three different ways.
- Types of speeches according to the purpose
- Types of speeches according to the delivery
- Types of speeches according to special occasion
Apart from the above types, there are some other types of speeches as well, which we will address later!
Now, let’s set sail for the types of speeches according to the purpose.
Types of Speeches According to the Purpose
Each and every speech has a specific purpose, i.e., some are delivered to entertain the audience, and others might be delivered to inform the audience.
When a speaker delivers a speech, he has a clear purpose in his mind for why he wants to convey this message to the audience.
The principal purpose of delivering a speech falls into four basic categories:
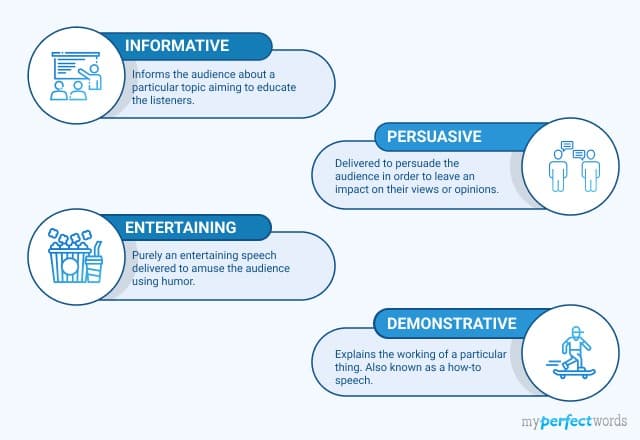
1. Informative Speech
When a speaker tries to inform a particular group or audience about a particular subject, they’re delivering an informative speech. The sole aim of an informative speech is to educate the audience on a topic.
The presenter may make use of facts and statistics to deliver an impactful informative speech. Such speeches deliver new information on a specific place, person, issue, or occasion by describing, explaining, and defining.
These are some common types of informative speeches:
- Explanatory Speech : Delivered to clarify a complex topic, process, or concept by breaking it down into understandable elements, making it easier for the audience to grasp.
- Descriptive Speech : It is a kind of informative speech that creates an accurate picture of a certain individual, place, or thing in the mind of the audience.
- Definition Speech : A definition speech provides clear explanations of terms, concepts, or ideas, allowing the audience to understand the meaning of the subject.
Possible scenarios of informative speeches could be:
- A CEO’s reporting on the company's financial performance for the past month, highlighting revenue, expenses, and net profit.
Here is a more detailed example of a compelling informative speech and a sample speech for students:
Informative Speech Example
Speech Example for Students
2. Persuasive Speech
In a persuasive speech , the speaker aims to persuade the audience with their opinion. Using persuasive language, the orator tries to reinforce the listeners' perspectives, or feelings about a particular subject.
Including factual evidence is necessary in a persuasive speech. With concrete details, there is a higher chance of persuading the audience to agree with what you make claims about.
This genre of speech is the hardest because it is difficult to convince people of anything. And it becomes more difficult if you ask them to challenge their current belief and think out of that perspective.
Some common persuasive speech types are:
- Policy Persuasion: Urges for specific actions or policies, aiming to influence the audience's decision-making.
- Value Persuasion: Seeks to modify or fortify the audience's beliefs, values, or attitudes about a particular theme or topic.
- Fact Persuasion: Focuses on presenting facts and evidence to persuade the audience to accept a certain point of view.
An example of a persuasive speech could be:
- Encouraging the audience to vote in the upcoming election to have a say in shaping our community's future.
Here is a complete example of a persuasive speech:
Persuasive Speech Example
3. Entertaining Speech
Have you ever been to an employee’s promotional party or even a standup comedy session? If the speaker managed to entertain you or make you laugh, they delivered an entertaining speech!
In the most simple words, entertainment speeches are intended to entertain the audience. The basic purpose of such kinds of speeches is to provide pleasure and enjoyment that make the audience laugh.
Although this speech is meant to make the audience laugh and enjoy the occasion, it should have a lighter moment as well.
Here are some types of entertaining speeches:
- Humorous Speech: Makes use of humor, jokes, and comedy to amuse and entertain the audience.
- Storytelling Speech: Aims to engage the listeners by sharing a relatable story to convey a message or illustrate a point. Quite often, the presenter uses vivid details and emotions.
- Roast or Toast: In such a speech, an individual is targeted and teased with the help of humor in a lighthearted way. In a toast, the speaker celebrates or honors someone’s success, typically on a positive note.
Let’s see what an example of an entertaining speech could be:
- A standup comedy session in your college, organized by some society members!
For a detailed insight on entertaining speeches, take a look at this example:
Entertaining Speech Example
4. Demonstrative Speech
Also known as a how-to speech, a demonstrative speech is given to demonstrate the working of a particular thing. Typically, a demonstrative speech makes use of visual aids for a clear understanding.
A little detail to notice is that you shouldn’t confuse a demonstrative speech with an informative speech. Although both types of speeches provide new information to the audience, demonstrative speeches demonstrate how to do or perform something.
Here are some types of demonstrative speech:
- Process Demonstrative Speech: Guides the audience through a series of steps or a sequence of actions to achieve a specific outcome or create something.
- Object Demonstrative Speech: Provides detailed information about a specific object, focusing on its characteristics, features, and uses.
- Activity Demonstrative Speech: Demonstrates how to perform a particular activity or task, offering practical instructions and insights to the audience.
See this accurate example of a demonstrative speech topic:
- Cooking a classic spaghetti carbonara, step by step, for a delicious Italian meal.
For a more in-depth demonstrative speech, see the example below:
Demonstrative Speech Example
Head over to our demonstrative speech ideas blog if you need great ideas for your next demonstrative speech!
Well, we just covered what are the types of speeches according to the purpose. Now we will jump to different speech types according to their delivery!
Types of Speeches According to the Delivery
The easiest way to start your speech is not always the best one. A substantial amount of work goes into the preparation of delivering a compelling message. So, when you are asked to deliver a speech, get familiar with the type of speech and your target audience.
Always think of the delivery method that is suitable for delivering a particular message. There are four ways that can help you understand how to balance the formality while delivering the speech.
1. Impromptu Speaking
Consider yourself in an urgent situation where you’re asked to deliver a brief presentation on your semester project updates. You’ve been urgently contacted by your supervisor, and you’ve not even prepared the presentation.
Obviously, you will present your project without any preparation.
Well, that’s when you’ll deliver an impromptu speech without any prior planning. In short, an impromptu speech is the presentation of a brief and concise message without preparation.
Here is a great example of a well-written impromptu speech:
Impromptu Speech Example
Visit our impromptu speech topics blog to get amazing ideas!
2. Extemporaneous Speaking
Extemporaneous speaking is the opposite of impromptu speaking, as it’s planned, well-prepared, and rehearsed properly. It is a perfect balance as it allows the speaker to use notes and give time to prepare well to deliver the speech.
Extemporaneous speeches are not meant to be memorized, and as a result, the delivery is quite natural and follows a conversational style.
See this example of a comprehensive extemporaneous speech:
Extemporaneous Speech Example
3. Manuscript Speaking
It is the word-for-word iteration of a written message. The speaker keeps his attention on the printed page while delivering a manuscript message. Such speeches work well where the exact repetition of original words is required, i.e., reading the organization’s mission statement.
This is the easiest type of public speaking, but it is not as effective as others. The audience might lose their interest soon, as the speaker is just reading the manuscript.
Take a look at this compelling example of a manuscript speech for a better understanding:
Manuscript Speech Example
4. Memorized Speaking
When a speaker has to deliver a speech relying on their memory, without the use of any notes, they’re delivering a memorized speech. The spokesperson must thoroughly research the speech until they can recite it from memory.
Memorized speaking is performed in situations where precision, effective delivery, and a positive engagement with the audience are required. Most commonly, this speaking style is practiced in formal speeches, academic competitions, theatrical performances, etc.
For an even better understanding, see this example of memorized speech:
Memorized Speech Example
5. Oratorical Speech
Oratorical speech is a subcategory of memorized speaking. Although oratorical literally means “ relating to the art of speech giving ”, oratorical speaking is a very specific type of speech.
Such speeches are often quite long and formal. They’re typically known for their eloquence, use of persuasive and rhetorical style of delivery. To deliver an impactful speech, the speaker has to perform a high degree of practice and memorization.
Below is a great example of a comprehensive oratorical speech:
Oratorical Speech Example
Types of Speeches According to Special Occasion
Special occasion speeches are intended to entertain or commemorate the audience. They have no set format and are designed to fit the particular occasion. The special occasion could be a birthday party, a graduation ceremony, or someone’s funeral.
Here are eight common types of special occasion speeches:
1. Introduction Speech
The introduction speeches are given to introduce the speaker who is going to give a speech. It is given to inspire or persuade the audience to listen to that speaker. It is generally small and brief speeches.
2. Presentation Speech
These speeches are usually given at award ceremonies, where an individual presents an award or prize to a person. The main purpose of the presentation speech is to provide recognition of the recipient’s accomplishments.
A toast is a brief tribute to a particular person or an event. The toasts are given on a special occasion to honor or acknowledge someone. It is given to express best wishes to someone for the future.
A roast is a kind of toast where the speaker praises and humorously pokes the person being honored. It might be given to a person who has achieved noteworthy success or moving away. It contains administration, appreciation, comedic insult, or tribute to someone.
5. Acceptance
These types of speeches are given by the person who has just received a prize or an award. Acceptance speech allows the recipient to show humility and grace for the award and say a few words of appreciation.
6. Commemorative Speech
These types of speeches are given at conventions, conferences, or graduation ceremonies. The commemorative speech is the summary of the central message around which the whole meeting or conference revolves.
7. Farewell Speech
Farewell speeches are like keynote addresses. These speeches are usually given at graduation ceremonies, or when someone leaves an organization, or at farewell parties. It is celebratory in nature and emphasizes looking ahead to the future.
Eulogies are given at funeral and memorial ceremonies to praise the person who has just died. The basic purpose is to reflect the audience’s emotions and offer condolences to the dead person’s relatives.
Below is a special occasion speech example:
Special Occasion Speech Example
Other Types of Speeches
Here are some different types of speeches that are quite common.
- Motivational Speech Being a special kind of speech, a motivational speech motivates the audience to pursue their betterment. The speaker uses strong and impactful words to encourage the listeners to push themselves to do something better
Want to know some great motivational speech ideas ? Head over to our blog! ?
- Forensic Speech Forensic speech is practiced in a competitive setting, where students take part in speech competitions. The speakers delivering a forensic speech are typically judged on their presentation, argumentation, communication skills, etc.
Debate Speech Debate speeches typically follow a certain set of rules and take place in a debating event. We can say that debate speech is a form of persuasive speech but includes plenty of facts and figures.
In a debate speech, you only have to back your claims with plenty of strong facts, but your aim is not to convince the audience to support you.
Tips to Conduct Effective Research for Your Speech
To make sure you research and deliver your speech in the best way possible, take a look at the tips mentioned below:
- Research Your Audience : Understand their opinions and thoughts and identify the best way to reach and engage them.
- Consider the Occasion or Location : Tailor your speech to the specific setting or event
- Focus on Your Expertise : Concentrate on your area of knowledge and gather comprehensive information on your topic
- Stay on Topic: Avoid getting off track and maintain a clear focus on your specific subject
- Present Balanced Evidence: Provide a balanced set of evidence for the audience to draw their own conclusions
- Keep It Concise: Avoid overwhelming the audience with excessive information. Just focus on delivering key points and takeaways effectively.
- Be Yourself: Convey passion and enthusiasm for your topic and connect with the audience on a personal level.
- Use Visual Aids: Make the speech more engaging by incorporating visual elements
- Use Reliable Sources: Utilize trustworthy and credible sources for data and statistics
- Properly Cite Sources: Build trust and credibility by citing your sources appropriately
In conclusion , for the various types of speeches, you have to tailor your preparation accordingly. With an abundance of speech types out there, one can get confused between them.
That’s why in this blog, we covered various types of speeches, covering all the essential details about each one. With the included examples, you can have an idea about how to pen down and deliver a wonderful speech.
If you require assistance with crafting any speech, feel free to reach out to our professional essay writing service . Our writers are exceptionally skilled, providing top-quality services 24/7.
Don't hesitate, buy speech and secure support from our top essay writers!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the various speech style categories.
The various speech styles include:
- Formal style
- Frozen style
- Casual style
- Consultative style
Can you explain the difference between informative and persuasive speeches?
Informative speeches aim to educate or provide information to the audience. Persuasive speeches aim to convince or persuade the audience to adopt a specific viewpoint or take action.
What is an oratory or rhetorical speech?
Oratory speeches are characterized by eloquence and persuasive language. They often use rhetorical devices and are designed to inspire or move the audience emotionally.
What is an acceptance speech?
An acceptance speech is given when someone receives an award or recognition. It expresses gratitude and often includes acknowledgments and thanks.
How do I choose the right type of speech for a specific occasion?
The choice depends on the event's purpose, the nature of the audience, and the goals of the speech. Consider what you want to achieve and the message you want to convey.
How do you adapt your speech style for a formal versus a casual setting?
In a formal setting, use more structured language and adhere to conventions. In a casual setting, you can be more relaxed and conversational.

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Dr. Barbara is a highly experienced writer and author who holds a Ph.D. degree in public health from an Ivy League school. She has worked in the medical field for many years, conducting extensive research on various health topics. Her writing has been featured in several top-tier publications.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading


Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
17.2 Types of Persuasive Speeches
Learning objectives.
- Differentiate among the four types of persuasive claims.
- Understand how the four types of persuasive claims lead to different types of persuasive speeches.
- Explain the two types of policy claims.

Burns Library, Boston College – Maya Angelou – CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
Obviously, there are many different persuasive speech topics you could select for a public speaking class. Anything from localized claims like changing a specific college or university policy to larger societal claims like adding more enforcement against the trafficking of women and children in the United States could make for an interesting persuasive speech. You’ll notice in the previous sentence we referred to the two topics as claims. In this use of the word “claim,” we are declaring the goodness or positivity of an attitude, value, belief, or behavior that others may dispute. As a result of the dispute between our perceptions of the goodness of an attitude, value, belief, or behavior and the perceptions of others, we attempt to support the claim we make using some sort of evidence and logic as we attempt to persuade others. There are four common claims that can be made: definitional, factual, policy, and value.
Definitional Claims
The first common types of claims that a persuasive speaker can make are definitional or classification claims. Definitional claims are claims over the denotation or classification of what something is. In essence, we are trying to argue for what something is or what something is not. Most definitional claims falling to a basic argument formula:
X is (or is not) a Y because it has (or does not have) features A , B , or C .
For example, maybe you’re trying to persuade your class that while therapeutic massage is often performed on nude clients, it is not a form of prostitution. You could start by explaining what therapeutic massage is and then what prostitution is. You could even look at the legal definition of prostitution and demonstrate to your peers that therapeutic massage does not fall into the legal definition of prostitution because it does not involve the behaviors characterized by that definition.
Factual Claims
Factual claims set out to argue the truth or falsity of an assertion. Some factual claims are simple to answer: Barack Obama is the first African American President; the tallest man in the world, Robert Wadlow, was eight feet and eleven inches tall; Facebook wasn’t profitable until 2009. All these factual claims are well documented by evidence and can be easily supported with a little research.
However, many factual claims cannot be answered absolutely. Some factual claims are simply hard to determine the falsity or trueness of because the final answer on the subject has not been discovered (e.g., when is censorship good, what rights should animals have, when does life begin). Probably the most historically interesting and consistent factual claim is the existence of a higher power, God, or other religious deity. The simple fact of the matter is that there is not enough evidence to clearly answer this factual claim in any specific direction, which is where the notion of faith must be involved in this factual claim.
Other factual claims that may not be easily answered using evidence are predictions of what may or may not happen. For example, you could give a speech on the future of climate change or the future of terrorism in the United States. While there may be evidence that something will happen in the future, unless you’re a psychic, you don’t actually know what will happen in the future.
When thinking of factual claims, it often helps to pretend that you’re putting a specific claim on trial and as the speaker your job is to defend your claim as a lawyer would defend a client. Ultimately, your job is to be more persuasive than your audience members who act as both opposition attorneys and judges.
Policy Claims
The third common claim that is seen in persuasive speeches is the policy claim —a statement about the nature of a problem and the solution that should be implemented. Policy claims are probably the most common form of persuasive speaking because we live in a society surrounded by problems and people who have ideas about how to fix these problems. Let’s look at a few examples of possible policy claims:
- The United States should stop capital punishment.
- The United States should become independent from the use of foreign oil.
- Human cloning for organ donations should be legal.
- Nonviolent drug offenders should be sent to rehabilitation centers and not prisons.
- The tobacco industry should be required to pay 100 percent of the medical bills for individuals dying of smoking-related cancers.
- The United States needs to invest more in preventing poverty at home and less in feeding the starving around the world.
Each of these claims has a clear perspective that is being advocated. Policy claims will always have a clear and direct opinion for what should occur and what needs to change. When examining policy claims, we generally talk about two different persuasive goals: passive agreement and immediate action.
Gain Passive Agreement
When we attempt to gain the passive agreement of our audiences, our goal is to get our audiences to agree with what we are saying and our specific policy without asking the audience to do anything to enact the policy. For example, maybe your speech is on why the Federal Communications Commission should regulate violence on television like it does foul language (i.e., no violence until after 9 p.m.). Your goal as a speaker is to get your audience to agree that it is in our best interest as a society to prevent violence from being shown on television before 9 p.m., but you are not seeking to have your audience run out and call their senators or congressmen or even sign a petition. Often the first step in larger political change is simply getting a massive number people to agree with your policy perspective.
Let’s look at a few more passive agreement claims:
- Racial profiling of individuals suspected of belonging to known terrorist groups is a way to make America safer.
- Requiring American citizens to “show their papers” is a violation of democracy and resembles tactics of Nazi Germany and communist Russia.
- Colleges and universities should voluntarily implement a standardized testing program to ensure student learning outcomes are similar across different institutions.
In each of these claims, the goal is to sway one’s audience to a specific attitude, value, or belief, but not necessarily to get the audience to enact any specific behaviors.
Gain Immediate Action
The alternative to passive agreement is immediate action, or persuading your audience to start engaging in a specific behavior. Many passive agreement topics can become immediate action-oriented topics as soon as you tell your audience what behavior they should engage in (e.g., sign a petition, call a senator, vote). While it is much easier to elicit passive agreement than to get people to do something, you should always try to get your audience to act and do so quickly. A common mistake that speakers make is telling people to enact a behavior that will occur in the future. The longer it takes for people to engage in the action you desire, the less likely it is that your audience will engage in that behavior.
Here are some examples of good claims with immediate calls to action:
- College students should eat more fruit, so I am encouraging everyone to eat the apple I have provided you and start getting more fruit in your diet.
- Teaching a child to read is one way to ensure that the next generation will be stronger than those that have come before us, so please sign up right now to volunteer one hour a week to help teach a child to read.
- The United States should reduce its nuclear arsenal by 20 percent over the next five years. Please sign the letter provided encouraging the president to take this necessary step for global peace. Once you’ve signed the letter, hand it to me, and I’ll fax it to the White House today.
Each of these three examples starts with a basic claim and then tags on an immediate call to action. Remember, the faster you can get people to engage in a behavior the more likely they actually will.
Value Claims
The final type of claim is a value claim , or a claim where the speaker is advocating a judgment claim about something (e.g., it’s good or bad, it’s right or wrong, it’s beautiful or ugly, moral or immoral).
Let’s look at three value claims. We’ve italicized the evaluative term in each claim:
- Dating people on the Internet is an immoral form of dating.
- SUVs are gas guzzling monstrosities .
- It’s unfair for pregnant women to have special parking spaces at malls, shopping centers, and stores.
Each of these three claims could definitely be made by a speaker and other speakers could say the exact opposite. When making a value claim, it’s hard to ascertain why someone has chosen a specific value stance without understanding her or his criteria for making the evaluative statement. For example, if someone finds all forms of technology immoral, then it’s really no surprise that he or she would find Internet dating immoral as well. As such, you need to clearly explain your criteria for making the evaluative statement. For example, when we examine the SUV claim, if your criteria for the term “gas guzzling monstrosity” are ecological impact, safety, and gas consumption, then your evaluative statement can be more easily understood and evaluated by your audience. If, however, you state that your criterion is that SUVs are bigger than military vehicles and shouldn’t be on the road, then your statement takes on a slightly different meaning. Ultimately, when making a value claim, you need to make sure that you clearly label your evaluative term and provide clear criteria for how you came to that evaluation.
Key Takeaways
- There are four types of persuasive claims. Definition claims argue the denotation or classification of what something is. Factual claims argue the truth or falsity about an assertion being made. Policy claims argue the nature of a problem and the solution that should be taken. Lastly, value claims argue a judgment about something (e.g., it’s good or bad, it’s right or wrong, it’s beautiful or ugly, moral or immoral).
- Each of the four claims leads to different types of persuasive speeches. As such, public speakers need to be aware what type of claim they are advocating in order to understand the best methods of persuasion.
- In policy claims, persuaders attempt to convince their audiences to either passively accept or actively act. When persuaders attempt to gain passive agreement from an audience, they hope that an audience will agree with what is said about a specific policy without asking the audience to do anything to enact the policy. Gaining immediate action, on the other hand, occurs when a persuader gets the audience to actively engage in a specific behavior.
- Look at the list of the top one hundred speeches in the United States during the twentieth century compiled by Stephen E. Lucas and Martin J. Medhurst ( http://www.americanrhetoric.com/top100speechesall.html ). Select a speech and examine the speech to determine which type of claim is being made by the speech.
- Look at the list of the top one hundred speeches in the United States during the twentieth century compiled by Stephen E. Lucas and Martin J. Medhurst and find a policy speech ( http://www.americanrhetoric.com/top100speechesall.html ). Which type of policy outcome was the speech aimed at achieving—passive agreement or immediate action? What evidence do you have from the speech to support your answer?
Stand up, Speak out Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 9 Public Speaking
9.2 Types of Speeches

In today’s world, we are constantly bombarded with messages both good and bad. No matter where you live, where you work or go to school, or what kinds of media you use, you are probably exposed to hundreds. if not thousands, of advertising messages every day. Researcher Norman W. Edmund estimates that by 2020 the amount of knowledge in the world will double every seventy-three days (Edmund, 2005).
Christian Pierret – Leader – CC BY 2.0.
Because we live in a world where we are overwhelmed with content, communicating information in a way that is accessible to others is more important today than ever before. To help us further understand why public speaking is important, we will first examine public speaking in everyday life. We will then discuss how public speaking can benefit you personally.
Everyday Public Speaking
Every single day people across the United States and around the world stand up in front of some kind of audience and speak. In fact, there’s even a monthly publication that reproduces some of the top speeches from around the United States called Vital Speeches of the Day ( http://www.vsotd.com ). Although public speeches are of various types, they can generally be grouped into three categories based on their intended purpose: informative, persuasive, and entertaining.
Informative Speaking
One of the most common types of public speaking is informative speaking . The primary purpose of informative presentations is to share one’s knowledge of a subject with an audience. Reasons for making an informative speech vary widely. For example, you might be asked to instruct a group of coworkers on how to use new computer software or to report to a group of managers how your latest project is coming along. A local community group might wish to hear about your volunteer activities in New Orleans during spring break, or your classmates may want you to share your expertise on Mediterranean cooking. What all these examples have in common is the goal of imparting information to an audience.
Informative speaking is integrated into many different occupations. Physicians often lecture about their areas of expertise to medical students, other physicians, and patients. Teachers find themselves presenting to parents as well as to their students. Firefighters give demonstrations about how to effectively control a fire in the house. Informative speaking is a common part of numerous jobs and other everyday activities. As a result, learning how to speak effectively has become an essential skill in today’s world.
Persuasive Speaking
A second common reason for speaking to an audience is to persuade others. In our everyday lives, we are often called on to convince, motivate, or otherwise persuade others to change their beliefs, take an action, or reconsider a decision. Advocating for music education in your local school district, convincing clients to purchase your company’s products, or inspiring high school students to attend college all involve influencing other people through public speaking.
For some people, such as elected officials, giving persuasive speeches is a crucial part of attaining and continuing career success. Other people make careers out of speaking to groups of people who pay to listen to them. Motivational authors and speakers, such as Les Brown ( http://www.lesbrown.com ), make millions of dollars each year from people who want to be motivated to do better in their lives. Brian Tracy, another professional speaker and author, specializes in helping business leaders become more productive and effective in the workplace ( http://www.briantracy.com ).
Whether public speaking is something you do every day or just a few times a year, persuading others is a challenging task. If you develop the skill to persuade effectively, it can be personally and professionally rewarding.
Entertaining Speaking
Entertaining speaking involves an array of speaking occasions ranging from introductions to wedding toasts, to presenting and accepting awards, to delivering eulogies at funerals and memorial services in addition to after-dinner speeches and motivational speeches. Entertaining speaking has been important since the time of the ancient Greeks, when Aristotle identified epideictic speaking (speaking in a ceremonial context) as an important type of address. As with persuasive and informative speaking, there are professionals, from religious leaders to comedians, who make a living simply from delivering entertaining speeches. As anyone who has watched an awards show on television or has seen an incoherent best man deliver a wedding toast can attest, speaking to entertain is a task that requires preparation and practice to be effective.
Personal Benefits of Public Speaking
Oral communication skills were the number one skill that college graduates found useful in the business world, according to a study by sociologist Andrew Zekeri (Zekeri, 2004). That fact alone makes learning about public speaking worthwhile. However, there are many other benefits of communicating effectively for the hundreds of thousands of college students every year who take public speaking courses. Let’s take a look at some of the personal benefits you’ll get both from a course in public speaking and from giving public speeches.
Benefits of Public Speaking Courses
In addition to learning the process of creating and delivering an effective speech, students of public speaking leave the class with a number of other benefits as well. Some of these benefits include
- developing critical thinking skills,
- fine-tuning verbal and nonverbal skills,
- overcoming fear of public speaking.
Developing Critical Thinking Skills
One of the very first benefits you will gain from your public speaking course is an increased ability to think critically. Problem solving is one of many critical thinking skills you will engage in during this course. For example, when preparing a persuasive speech, you’ll have to think through real problems affecting your campus, community, or the world and provide possible solutions to those problems. You’ll also have to think about the positive and negative consequences of your solutions and then communicate your ideas to others. At first, it may seem easy to come up with solutions for a campus problem such as a shortage of parking spaces: just build more spaces. But after thinking and researching further you may find out that building costs, environmental impact from loss of green space, maintenance needs, or limited locations for additional spaces make this solution impractical. Being able to think through problems and analyze the potential costs and benefits of solutions is an essential part of critical thinking and of public speaking aimed at persuading others. These skills will help you not only in public speaking contexts but throughout your life as well. As we stated earlier, college graduates in Zekeri’s study rated oral communication skills as the most useful for success in the business world. The second most valuable skill they reported was problem-solving ability, so your public speaking course is doubly valuable!
Another benefit to public speaking is that it will enhance your ability to conduct and analyze research. Public speakers must provide credible evidence within their speeches if they are going to persuade various audiences. So your public speaking course will further refine your ability to find and utilize a range of sources.
Fine-Tuning Verbal and Nonverbal Skills
A second benefit of taking a public speaking course is that it will help you fine-tune your verbal and nonverbal communication skills. Whether you competed in public speaking in high school or this is your first time speaking in front of an audience, having the opportunity to actively practice communication skills and receive professional feedback will help you become a better overall communicator. Often, people don’t even realize that they twirl their hair or repeatedly mispronounce words while speaking in public settings until they receive feedback from a teacher during a public speaking course. People around the United States will often pay speech coaches over one hundred dollars per hour to help them enhance their speaking skills. You have a built-in speech coach right in your classroom, so it is to your advantage to use the opportunity to improve your verbal and nonverbal communication skills.
Overcoming Fear of Public Speaking
An additional benefit of taking a public speaking class is that it will help reduce your fear of public speaking. Whether they’ve spoken in public a lot or are just getting started, most people experience some anxiety when engaging in public speaking. Heidi Rose and Andrew Rancer evaluated students’ levels of public speaking anxiety during both the first and last weeks of their public speaking class and found that those levels decreased over the course of the semester (Rose & Rancer, 1993). One explanation is that people often have little exposure to public speaking. By taking a course in public speaking, students become better acquainted with the public speaking process, making them more confident and less apprehensive. In addition, you will learn specific strategies for overcoming the challenges of speech anxiety.
Comm 101 (Dutton) by [author removed at request of original publisher] is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
- Games, topic printables & more
- The 4 main speech types
- Example speeches
- Commemorative
- Declamation
- Demonstration
- Informative
- Introduction
- Student Council
- Speech topics
- Poems to read aloud
- How to write a speech
- Using props/visual aids
- Acute anxiety help
- Breathing exercises
- Letting go - free e-course
- Using self-hypnosis
- Delivery overview
- 4 modes of delivery
- How to make cue cards
- How to read a speech
- 9 vocal aspects
- Vocal variety
- Diction/articulation
- Pronunciation
- Speaking rate
- How to use pauses
- Eye contact
- Body language
- Voice image
- Voice health
- Public speaking activities and games
- About me/contact
- Activities and games
- 5 fun speech games
Public Speaking Activities
5 fun speech games to build skills and confidence.
By: Susan Dugdale | Last modified: 10-26-2023
There are five public speaking activities on this page, along with numerous spinoffs.
Their principal purpose is to develop speech fluency and confidence through fun!
You'll find they are easily adaptable to groups of all ages and skill levels: from newcomers to advanced.
I've used them all and know they work. People become so enjoyably engrossed in them, they forget to be fearful!
1. Interview Introductions
Interview Introductions are a great way to break the ice with a new group of people. The exercise has them finding out about each other and then introducing the person they interviewed to the whole group.
As it's a lot less threatening or scary to talk about someone else rather than yourself, you'll find people respond really positively as they're generally eager to represent the person they interviewed well.

Instructions
- Divide your group into pairs.
- Each person interviews the other in turn. The information gained forms the basis of a brief introduction speech they'll give to the whole group when the interviewing process is complete.
- Ask them to find out their partner's name, where they live/work, what hobbies they have, what their favorite book, film, song...is, what they're most proud of (an achievement perhaps), what they hope for from the class, something funny that happened in their childhood, where they go for holidays, what they think about the latest local issue ... Obviously they can't expect to cover all of that in detail inside the brief time they spend talking with each other. One or two interesting points is enough!
- Establish a time limit for the interviews. I've found 10 minutes works well. Keep track of the time and call change at the halfway point, 5 minutes, to ensure both people get an opportunity to be interviewed and to interview.
- When the group comes back together the introductions begin: "This is Mary from Taupo. When she's not working for the Social Welfare Department as a community social worker she's collecting stamps. She says part of their charm is that they don't answer back and are quiet!"
2. Image Starters

Picture prompts or image starters are great for sparking imaginative storytelling and conversations.
Either use my ready-made printable file of 40 picture prompts , (which you can find out more about by clicking the link), or gather up a collection of your own to use.
You'll need interesting images/photos from magazines or newspapers - enough for everybody to have one each and then a few spare.
Place them face down and have everybody pick one.
Using the image as a prompt, what can they share about it?

Questions to get started are:
- Where is this photo/image from? (And the answer doesn't have to be true - merely plausible! Encourage imaginative creativity.)
- What's happening in this photo/picture?
- What feelings does the image evoke?
- Is there a season or time associated with it?
- What happened after or before the photo was taken?
5 activities using image starters
If you'd like specific instructions for five different activities based around images you'll find them here: picture prompts for impromptu speeches .
They range from introductory 'show and tell', like the starter questions above, to more advanced. There are solo as well as group activities.
3. For and Against

'For and Against' encourages flexibility: the ability to see a topic from opposing sides.
A speaker has 30 seconds to talk 'for' a topic and then another 30 seconds to speak 'against' it.
Prepare and print out a selection of controversial speech topics. You'll need one per person.
Put the topics into a non-see through bag. Have each speaker select their topic when it's their turn to speak.
Ideally what's wanted is at least two or three good points supporting both sides: for and against.
Time the speech. Call start, the half way point and, stop.
Sample topics:
- money is the root of all evil
- a country gets the government it deserves
- ' green ' politics are just the current fashion
- pets in apartments should be banned
- marriage is essentially a business contract
- 'Religion is the opiate of the masses' : Karl Marx
- poverty is a state of mind
- euthanasia is unjustifiable
- global warming is media hype
- cloning animals should be banned
- animal testing is immoral
For variation split your group into pairs and extend the time limit to 1 - 2 minutes. One person takes the 'for' position, and other takes the 'against'.
More 1 minute speech practice

For 150 1 minute speech topics with 3 example speech outlines following the PREP (Point, Reason, Example, Point) format, the full text of three speeches plus audio, visit: 1 minute speech topics .
Get instant organizers for impromptu speeches
For more on structuring impromptu speeches quickly and effectively go to impromptu speaking templates . You'll find 7 useful speech outline organizers explained (including PREP), alongside suggestions to banish impromptu speaking blues.
4. The Object of my Affection

Gather up a collection of small objects, enough for one per speaker. For example: a vintage toy car, a can of sardines, a hair ribbon, an old black and white photographic portrait, a pair of baby shoes ....
Put all of them into a non-see through bag.
Each speaker puts their hand into the bag and pulls out an object. Whatever they get forms the basis of their 1 - 2 minute speech.
Ideas to help the speakers get started:
- This ... { insert the name of whatever it is the speaker has in their hand } saved my life. It happened like this...
- Whenever I see a ...{ insert the name of whatever it is the speaker has in their hand } it reminds me of the time I...
- I collect ...{i nsert the name of whatever it is the speaker has in their hand } and this one is the prize of my collection. It used to belong to ...
5. Conducted Speech

This is a group public speaking activity. It is noisy, effective and outrageously good fun!
Select a tongue twister from this page of diction exercises eg. " Sister Susie sat on the seashore sewing shirts for soldiers ".
Divide your class into groups of four. Three in each group will be the speakers and the fourth, the conductor.
The speakers repeat the tongue twister responding to the conductor's direction. He/she can make them go faster or slower, louder or quieter. The conductor could even decide to make it a round by staggering when each person begins!
The goal of the exercise is to practice articulation coupled with vocal variety ie. speech rate and volume.
It also teaches cooperation and focus, or concentration. Let your mind wander, and it's game over! You've lost it, not only for yourself but your group as well.
Swap the conductor role around to give everybody a turn.
Once everybody is familiar with the activity, give the groups turns at demonstrating their prowess to the whole class. They'll love seeing and hearing each other perform. ☺
If you liked these speech activities ...

You'll love my ebook!
28 public speaking games (with many more variations and extensions), full instructions, PLUS printable topic, tongue twister, poem and image sheets.
A complete one-stop-select-print-go public speaking resource for busy people.
Find out more >>
For more freebie public speaking activities:
- 10 activities for public speaking - a collection of tried and tested speech class activities for middle school upwards
- Another 7 fun-filled public speaking games for groups
- Improv games - a collection of 5 excellent drama games for groups
- Public speaking exercises - these focus on the individual speaker- how to breathe well, stand, use eye contact effectively...
What's the difference between these freebie activities and your ebook?
My ebook contains the best of all the games from these pages and then some more strictly Susan specials, PLUS detailed instructions on how to use them.
You'll find out how to select games for a class, introduce them for maximum effect, integrate them into your lesson plans, and so on.
It also has all the topics, tongue twisters, images etc you need to play available as printables.
It's a one-stop, time saving resource that you'll return to time, and time again. Why not check it out?

Your students will thank you for it!
- Return to the top of the public speaking activities page
speaking out loud
Subscribe for FREE weekly alerts about what's new For more see speaking out loud

Top 10 popular pages
- Welcome speech
- Demonstration speech topics
- Impromptu speech topic cards
- Thank you quotes
- Impromptu public speaking topics
- Farewell speeches
- Phrases for welcome speeches
- Student council speeches
- Free sample eulogies
From fear to fun in 28 ways
A complete one stop resource to scuttle fear in the best of all possible ways - with laughter.

Useful pages
- Search this site
- About me & Contact
- Blogging Aloud
- Free e-course
- Privacy policy
©Copyright 2006-24 www.write-out-loud.com
Designed and built by Clickstream Designs
Module 2: Informative Speaking
Types of informative speeches.
In the last section we examined how informative speakers need to be objective, credible, knowledgeable, and how they need to make the topic relevant to their audience. This section discusses the four primary types of informative speeches. These include definitional speeches, descriptive speeches, explanatory speeches, and demonstration speeches.
Definitional Speeches
In definitional speeches the speaker attempts to set forth the meaning of concepts, theories, philosophies, or issues that may be unfamiliar to the audience. In these types of speeches, speakers may begin by giving the historical derivation, classification, or synonyms of terms or the background of the subject. In a speech on “How to identify a sociopath,” the speaker may answer these questions: Where did the word ‘sociopath’ come from? What is a sociopath? How many sociopaths are there in the population? What are the symptoms? Carefully define your terminology to give shape to things the audience cannot directly sense. Describing the essential attributes of one concept compared to another (as through use of analogies) can increase understanding as well. For a speech on “Elderly Abuse,” the speaker may compare this type of abuse to child or spousal abuse for contrast.
Regardless of the listeners’ level of knowledge about the subject, it is very important in these types of speeches to show the relevance of the topic to their lives. Often the topics discussed in definitional speeches are abstract—distanced from reality. So provide explicit, real-life examples and applications of the subject matter. If you were going to give a speech about civil rights, you would need to go beyond commonly held meanings and show the topic in a new light. In this type of speech, the speaker points out the unique and distinguishing properties or boundaries of a concept in a particular context (Rinehart, 2002). The meaning of “civil rights” has changed significantly over time. What does it mean today compared to the 1960s? How will knowing this distinction help audience members? What are some specific incidents involving civil rights issues in current news? What changes in civil rights legislation might listeners see in their lifetimes?
Sample Definitional Speech Outline
Title: “Life is suffering,” and Other Buddhist Teachings (Thompson, 1999)
Specific Purpose: At the end of my speech, my audience will understand the Four Noble Truths and the Eightfold Path in Buddhism
Central Idea: Regardless of your religious beliefs, Buddhist philosophy teaches a number of useful lessons you can apply to your own life.
- All life involves dukkha (suffering)
- Suffering is caused by tanha (longing for things to be other than they are)
- If this longing stops ( nirodha ), suffering will cease
- The way to eliminate longing is to follow the Eightfold Path
- Right intention
- Right speech
- Right action
- Right livelihood
- Right effort
- Right mindfulness
- Right contemplation
Descriptive Speeches

To gaze in wonder at that magnificent dome and elegant gardens will be a moment that you remember for the rest of your life. The Taj Mahal just takes your breath away. What is immediately striking is its graceful symmetry—geometric lines run through formal gardens ending in a white marble platform. Atop this platform is great white bulbous dome complemented by four towering minarets in each corner. The whole image shimmers in a reflecting pool flanked by beautiful gardens—the effect is magical. The first stretch by the reflecting pool is where most people pose for their photos. But we were impressed by the fresh, green gardens. As you approach through the gardens two mosques come into view flanking the Taj—both exquisitely carved and built of red sandstone.
In the descriptive speech, determine the characteristics, features, functions, or fine points of the topic. What makes the person unique? How did the person make you feel? What adjectives apply to the subject? What kind of material is the object made from? What shape is it? What color is it? What does it smell like? Is it part of a larger system? Can it be seen by the naked eye? What is its geography or location in space? How has it changed or evolved over time? How does it compare to a similar object? When preparing for the speech, try to think of ways to appeal to as many of the senses as possible. As an example, in a speech about different types of curried dishes, you could probably verbally describe the difference between yellow, red, and green curry, but the speech will have more impact if the audience can see, smell, and taste samples.
Sample Descriptive Speech Outline

Specific Purpose: At the end of my speech, my audience will be able to visualize some of the main attractions on Easter Island.
Central Idea: Easter Island hosts a number of ancient, mysterious, and beautiful attractions that make it an ideal vacation destination.
- Average 13 feet high; 14 tons
- Play sacred role for Rapa Nui (native inhabitants)
- Central Ahu ceremonial sites
- Snorkeling & Scuba
- Giant crater
- Sheer cliffs to ocean
Be able to describe anything visual, such as a street scene, in words that convey your meaning. ~ Marilyn vos Savant
Explanatory Speeches
An explanatory speech (also known as a briefing) is similar to the descriptive speech in that they both share the function of clarifying the topic. But explanatory speeches focus on reports of current and historical events, customs, transformations, inventions, policies, outcomes, and options. Whereas descriptive speeches attempt to paint a picture with words so that audiences can vicariously experience it, explanatory speeches focus on the how or why of a subject and its consequences. Thus, a speaker might give a descriptive speech on the daily life of Marie Antoinette, or an explanatory speech on how she came to her death. Recall that definitional speeches focus on delineating concepts or issues. In this case, a speaker might give a definitional speech about the Emergency Economic Stabilization Act of 2008, or an explanatory speech on why the financial bailout was necessary for U.S. financial stability.
If a manager wanted to inform employees about a new workplace internet use policy, s/he might cover questions like: Why was a policy implemented? How will it help? What happens if people do not follow established policies? Explanatory speeches are less concerned with appealing to the senses than connecting the topic to a series of related other subjects to enhance a deep understanding (McKerrow, Gronbeck, Ehninger, & Monroe, 2000). For example, to explain the custom of the Thai wai greeting (hands pressed together as in prayer), you also need to explain how it originated to show one had no weapons, and the ways it is tied to religion, gender, age, and status.
Sample Explanatory Speech Outline
Title: Giant Waves, Death, and Devastation: The 2004 Indian Ocean Tsunami (National Geographic, 2006)
Specific Purpose: At the end of my speech, my audience will be aware of the nature of the 2004 Tsunami and the destruction it caused.
Central Idea: The 2004 Asian Tsunami was one of the worst natural disasters in human history in terms of magnitude, loss of human life, and enduring impact.
- Earthquake epicenter and magnitude
- Tsunami forms (waves reach up to 100 feet)
- Tsunami strikes land of various countries with no warning
- The countries and people involved
- Loss of food, water, hospitals, housing, electricity, and plumbing
- Threat of disease
- Environmental destruction
- Economic devastation
- Psychological trauma
I hear and I forget. I see and I remember. I do and I understand. – Confucious
Demonstration Speeches
The most practical of all informative speeches, a demonstration speech shows listeners how some process is accomplished or how to perform it themselves. The focus is on a chronological explanation of some process (how potato chips are made), procedure (how to fight fires on a submarine), application (how to use the calendar function in Outlook), or course of action (how court cases proceed to Supreme Court status). Speakers might focus on processes that have a series of steps with a specific beginning and end (how to sell a home by yourself) or the process may be continuous (how to maintain the hard drive on your computer to prevent crashes). Demonstration speeches can be challenging to write due to the fact that the process may involve several objects, a set of tools, materials, or a number of related relationships or events (Rinehart, 2002). Nevertheless, these types of speeches provide the greatest opportunity for audience members to get involved or apply the information later.
When preparing this speech, remember first to keep the safety of the audience in mind. One speaker severely burned his professor when he accidently spilled hot oil from a wok on her. Another student nearly took the heads off listeners when he was demonstrating how to swing a baseball bat. Keep in mind also that you may need to bring in examples or pictures of completed steps in order to make efficient use of your time. Just think of the way that cooking demonstrations are done on TV—the ingredients are premeasured, the food is premixed, and the mixture magically goes from uncooked to cooked in a matter of seconds. Finally, if you are having your audience participate during your presentation (making an origami sculpture), know what their knowledge level is so that you don’t make them feel unintelligent if they are not successful. Practice your speech with friends who know nothing about the topic to gauge if listeners can do what you are asking them to do in the time allotted.
Sample Demonstration Speech Outline
Title: How to Survive if You Get Stranded in the Wilderness (U.S. Department of Defense, 2006).
Specific Purpose: At the end of my speech my audience will understand what to do if they unexpectedly become stranded in the wilderness.
Central Idea: You can greatly improve your ability to stay alive and safe in the wilderness by learning a few simple survival techniques.
- Size up the surroundings
- Size up your physical and mental states
- Size up your equipment (handout “What to Include in a Survival Kit”)
- Obtaining water
- Acquiring food
- Building a fire
- Locating shelter
- Call or signal rescue personnel
- Wilderness navigation
- Leaving “bread crumb” trail
- Chapter 15 Types of Informative Speeches. Authored by : Lisa Schreiber, Ph.D.. Provided by : Millersville University, Millersville, PA. Located at : http://publicspeakingproject.org/psvirtualtext.html . Project : Public Speaking Project. License : CC BY-NC-ND: Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives
- Taj Mahal, Agra, India. Authored by : Yann. Located at : https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Taj_Mahal,_Agra,_India.jpg . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Maoi at Rano Raraku. Authored by : Aurbina. Located at : https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Moai_Rano_raraku.jpg . License : Public Domain: No Known Copyright

Privacy Policy

6 Types of Speeches
Learning objectives.
- Differentiate between speaking to inform and speaking to persuade.
- Watch an informative and persuasive speech.
General Purposes of Speaking
The two general purposes of speeches this section will discuss are speaking to inform and speaking to persuade. Public speaking students will write and deliver these two types of speeches in this class. It is important to understand the differences before we begin our first LIVE speech, the informative speech. While any topic can be informative or persuasive, the difference is in the speaker’s purpose.
Simply put, this is about helping audience members acquire information that they do not already possess. The most important characteristic of informative topics is that the goal is to share knowledge . The goal is not to encourage people to use that knowledge in any specific way. When a speaker starts encouraging people to use knowledge in a specific way, they are no longer informing but persuading. Let’s say you are assigned to inform an audience about a new vaccination program. In an informative speech, the purpose of the speech is to explain to your audience what the program is and how it works. If, however, you start encouraging your audience to participate or not in the vaccination program, you are no longer informing them about the program but rather persuading them to do something.
One of the most common mistakes new public speaking students make is to blur the line between informing and persuading. Often times it is difficult for us to just share information without trying to convince others to agree with us or change their behaviors. People are typically opinionated and we like our opinions and want others to agree with us. However, knowledge sharing is an important part of every society. You may be asked to share your knowledge in a class or deliver a presentation to inform colleagues in the workplace. Learning how to deliver informative speeches is a valuable skill.
Example Informative Speech
The following video is an example of an informative speech. Take note of the strategies Andrea Ambam uses to share knowledge about bias in the judicial system. She shares research to support her points. Her opinion is apparent, based on her approach; yet, she does not ask the audience to do anything with the information she shares (a call to action). Additionally, she does not offer a solution to the issue. She simply shares researched information (facts, stats, examples, anecdotes) with her audience.
To Persuade
When we speak to persuade, we attempt to get listeners to embrace a point of view or to adopt a behavior that they may not have done otherwise. While persuasive speaking includes informing the audience about a topic, a persuasive speech is distinguished by the fact that it includes a call to action for the audience to make some change in their behavior or thinking. Persuasion can address behaviors—observable actions on the part of listeners—and it can also address intangible thought processes in the form of attitudes, values, and beliefs.
Behavior change: When the speaker attempts to persuade an audience to change behavior. This may be asking your audience to donate money to a cause, to participate in a recycling program, or to adopt a cat. In these examples, the speaker is asking the audience to do something.
Attitude change: An attitude is defined as an individual’s general predisposition toward something as being good or bad, right or wrong, negative or positive. If you believe that dress codes on college campuses are a good idea, you want to give a speech persuading others to adopt a positive attitude toward campus dress codes.
Value change: A value refers to an individual’s perception of the usefulness, importance, or worth of something. We can value a college education, we can value technology, and we can value freedom. Values, as a general concept, are fairly ambiguous and tend to be very lofty ideas. Ultimately, what we value in life actually motivates us to engage in a range of behaviors. For example, if you value protecting the environment, you may recycle more of your trash than someone who does not hold this value. If you value family history and heritage, you may be more motivated to spend time with your older relatives and ask them about their early lives than someone who does not hold this value.
Belief change: Beliefs are propositions or positions that an individual holds as true or false without positive knowledge or proof. Core beliefs are beliefs that people have actively engaged in and created over the course of their lives (e.g., belief in a higher power, belief in extraterrestrial life forms). Dispositional beliefs the other hand, are beliefs that people have not actively engaged in; they are judgments based on related subjects, which people make when they encounter a proposition. Persuading audiences to change core beliefs is more difficult than persuading audiences to change dispositional beliefs. If you find a topic related to dispositional beliefs, using your speech to help listeners alter their processing of the belief is a realistic possibility. But as a novice public speaker, you are probably best advised to avoid core beliefs. Although core beliefs often appear to be more exciting and interesting than dispositional ones, you are very unlikely to alter anyone’s core beliefs in a five- to ten-minute classroom speech.
Example Persuasive Speech
The following video is an example of a persuasive speech. Ron Finley uses persuasive strategies to convince the audience that planting community gardens can have a positive impact on health and hunger in South Central LA.
Key Takeaways
- Speaking to inform is sharing knowledge with your audience.
- Speaking to persuade is attempting to convince your audience to change a behavior, attitude, value, or belief.
- Any topic can be informative or persuasive. The difference is in the speaker’s purpose and approach.
Atwood, C. G. (2009). Knowledge management basics . Alexandria, VA: ASTD Press.
Hendriks, P. (1999). Why share knowledge? The influence of ICT on the motivation for knowledge sharing. Knowledge and Process Management, 6 , 91–100.
O’Hair, D., Stewart, R., & Rubenstein, H. (2007). A speaker’s guidebook: Text and reference (3rd ed.). Boston, MA: Bedford/St. Martins.
Roye, S. (2010). Austan Goolsbee a funny stand-up comedian? Not even close… [Web log post]. Retrieved from http://www.realfirststeps.com/1184/austan-goolsbee-funny-standup-comedian-close
Public Speaking Copyright © by Dr. Layne Goodman; Amber Green, M.A.; and Various is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

15.2 Types of Special Occasion Speeches

Unlike the informative and persuasive speeches, special occasion speeches are much broader and allow for a wider range of topics, events, and approaches to be employed. However, while the following list of special occasion speeches is long, your instructor will have specific types of special occasion speeches that you will be allowed (or required) to do for class. Since you are likely to give many special occasion speeches in your life, we want to cover everything you might need to know to give a good one.
Speeches of Introduction
The first type of special occasion speech is the speech of introduction , which is a mini speech given by the host of a ceremony that introduces another speaker and their speech. Few things are worse than when the introducer of a speaker stands up and says, “This is Wyatt Ford. He’s going to talk about stress.” While we did learn the speaker’s name and the topic, the introduction falls flat. Audiences won’t be the least bit excited about listening to Wyatt’s speech.
Just like any other speech, a speech of introduction should have a clear introduction, body, and conclusion—and should be brief. As a speech of introduction, it is important to focus on the person being introduced; the speech should be about them.
For an introduction, think of a hook that will make your audience interested in the upcoming speaker. You need to find something that can grab the audience’s attention and make them excited about hearing the main speaker.
The body of your speech of introduction should be devoted to telling the audience about the speaker’s topic, why the speaker is qualified, and why the audience should listen (notice we now have our three main points). First, tell your audience in general terms about the overarching topic of the speech. Next, you need to tell the audience why the speaker is a credible presenter on the topic. Has the speaker written books or articles on the subject? Has the speaker had special life events that make him or her qualified? Lastly, you need to briefly explain to the audience why they should care about the upcoming speech. The outline can be adjusted; for example, you can give the biographical information first, but these three areas should be covered.
The final part of a good introduction is the conclusion, which is generally designed to welcome the speaker to the platform. Many introducers will conclude by saying something like, “I am looking forward to hearing Wyatt Ford’s advice; please join me in welcoming Dr. Wyatt Ford.” At this point, you as the person introducing the speaker are “handing off” the speaking duties to someone else, so it is not uncommon to end your speech of introduction by clapping as the speaker comes on stage or shaking the speaker’s hand.
Speeches of Presentation
The second type of special occasion speech is the speech of presentation . A speech of presentation is a brief speech given to accompany a prize or honor.
The introduction in a speech of presentation needs to let the audience know what award is being presented, just a brief statement about the award is enough to begin the speech. In the body of the speech, you want to make sure you explain what the award or honor is and why the presentation is important. Next, you can explain what the recipient has accomplished in order for the award to be bestowed. Did the person win a race? Did the person write an important piece of literature? Did the person mediate conflict? Whatever the recipient has done, you need to clearly highlight his or her work. Lastly, if the race or competition was conducted in a public forum and numerous people didn’t win, you may want to recognize those people for their efforts as well. While you don’t want to steal the show away from the winner, you may want to highlight the work of the other competitors or nominees.
Speeches of Acceptance
The complement to a speech of presentation is the speech of acceptance. The speech of acceptance is a speech given by the recipient of a prize or honor. In the introduction for this speech, you want to acknowledge the award, then the body of the speech usually shares these three typical components of a speech of acceptance: 1) put the award or honor into perspective, 2) thank those who helped you achieve your goal and tell stories of their contributions, and 3) discuss the work you did to achieve the award. First, you want to put the award in perspective. Tell the people listening to your speech why the award is meaningful to you.
Second, you want to give credit to those who helped you achieve the award or honor. No person accomplishes things in life on his or her own. We all have family members, friends, and colleagues who support us and help us achieve what we do in life, and a speech of acceptance is a great time to graciously recognize those individuals. Lastly, you want to share the work you put in to achieve this award. If you know you are up for an award, have a speech ready. A good rule to remember is: Be thankful, be gracious, be short.
Speeches of Dedication
A fourth special occasion speech is the speech of dedication . A speech of dedication is delivered when a new store opens, a building is named after someone, a plaque is placed on a wall, a new library is completed, and so on. These speeches are designed to highlight the importance of the project and possibly those to whom the project has been dedicated.
When preparing a speech of dedication, start by explaining how you are involved in the dedication. If the person to whom the dedication is being made is a relative, tell the audience about your relationship and your relative’s accomplishments. Second, you want to explain what is being dedicated. If the dedication is a new building or a pre-existing building, you want to explain the importance of the structure. You should then explain who was involved in the project.
If the project is a new structure, talk about the people who built the structure or designed it. If the project is a pre-existing structure, talk about the people who put together and decided on the dedication. Lastly, explain why the structure is important for the community in which it is located. If the dedication is for a new store, talk about how the store will bring in new jobs and new shopping opportunities. If the dedication is for a new wing of a hospital, talk about how patients will be served and the advances in medicine the new wing will provide the community.
At one time or another, almost everyone is going to be asked to deliver a toast . A toast is a speech designed to congratulate, appreciate, or remember. First, toasts can be delivered for the purpose of congratulating someone for an honor, a new job, or getting married. You can also toast someone to show your appreciation for something he or she has done. Lastly, we toast people to remember them and what they have accomplished.
When preparing a toast, the first goal is always to keep your remarks brief. Toasts are generally given during the middle of festivities (e.g., wedding, retirement party, farewell party), and you don’t want your toast to take away from those festivities for too long. Second, the goal of a toast is to focus attention on the person or persons being toasted—not on the speaker.
As such, you need to focus your attention toward the people being toasted, both by physically looking at them and by keeping your message about them. The body of the speech should share stories or fun information about the people being toasted and should be appropriate to the occasion. You should avoid any inside jokes between you and the people being toasted because toasts are public and should be accessible for everyone who hears them. To conclude a toast, simply say something like “Please join me in recognizing Gina for her achievement,” and lift your glass. When you lift your glass, this will signal to others to do the same, and then you can all take a drink, which is the end of your speech.
A roast is a very interesting and peculiar speech because it is designed to both praise and good-naturedly insult a person being honored. Because of this combination of purposes, it is not hard to argue that the roast is a challenging type of speech to write given the difficult task of simultaneously praising and insulting the person. Generally, roasts are given at the conclusion of a banquet in honor of someone’s life achievements. The television station Comedy Central has been conducting roasts of various celebrities for a few years, and if you’ve ever watched one, you know that the “roasters” say some harsh things about the “roastees” even though they are friends.
How does one prepare for a roast? First, you want to really think about the person who is being roasted. Does he or she have any strange habits or amusing stories in their past that you can discuss? When you think through these questions, you want to make sure that you cross anything off your list that is truly private information or will really hurt the person. The goal of a roast is to poke at them in a good-natured manner.
Second, when selecting which aspects to poke fun at, you need to make sure that the items you choose are widely known by your audience. Roasts work when many people in the audience can relate to the jokes being made. If you have an inside joke with the roastee, bringing it up during the roast may be great fun for the two of you, but it will leave your audience unimpressed. Lastly, end on a positive note. While the jokes are definitely the fun part of a roast, you should leave the roastee and the audience knowing that you truly do care about and appreciate the person.
A eulogy is a speech given in honor of someone who has died. Not to sound depressing, but since everyone who is alive will someday die, the chance of your being asked to give a eulogy someday for a friend or family member is significant. However, when the time comes to deliver a eulogy, it’s good to know what you’re doing and to adequately prepare your remarks.
When preparing a eulogy, first you need to know that you were asked because you are an important person in their lives and know about the deceased. The eulogy should be personal and help the audience to appreciate and celebrate the person who passed. Although eulogies are delivered on the serious and sad occasion, it is very helpful to look for at least one point to be lighter or humorous. In some cultures, in fact, the friends and family attending the funeral expect the eulogy to be highly entertaining and amusing.
Knowing the deceased and the audience is vital when deciding on the type and amount of humor to use in a eulogy. It would be appropriate to tell a funny story about Uncle Joe’s love for his car or Aunt Mary’s love of tacky Christmas sweaters. Ultimately, the goal of the humor or lighter aspects of a eulogy is to relieve the tension that is created by the serious nature of the occasion and to celebrate the person who has passed.
If you are ever asked to give a eulogy, here are three parts of a eulogy (i.e., main points) you can use to write one: praise, lament, and consolation.
The first thing you want to do when remembering someone who has passed away is remind the audience what made that person so special. So you will want to praise them and their accomplishments. This can include notable achievements (being an award winner; helping with charities), personal qualities (“she was always willing to listen to your problems and help in any way she could”), or anecdotes and stories (being a great mother; how she drove to college to visit you when you were homesick).
The second thing you want to do in a eulogy is to lament the loss. To lament means to express grief or sorrow, which is what everyone at a funeral has gathered to do. You will want to acknowledge that everyone is sad and that the deceased’s passing will be difficult to get through. Here you might mention all the things that will no longer happen because of the death. “Now that Grandpa is gone, there won’t be any more Sunday dinners where he cooks chicken on the grill or bakes his famous macaroni and cheese.”
The final step in a eulogy is to console the audience, or to offer comfort in a time of grief. What you must remember is that a eulogy is not a speech for the person who has died; it is a speech for the people who are still living to try to help them deal with the loss. You will want to end your eulogy on a positive note. Offer some hope that someday, things will get better.
“We may miss Aunt Linda deeply, but our memories of her will live on forever, and her impact on this world will not soon be forgotten.”
Using the Praise-Lament-Console format for eulogies gives you a simple system where you can fill in the sections with 1) why was the person good, 2) why you will miss him or her, and 3) how you and the audience will get through this loss. It sometimes also helps to think of the three points in terms of Past-Present-Future: you will praise the deceased for what he did when he was alive (the past), lament the loss you are feeling now (the present), and console your audience by letting them know that things will be all right (the future).
With regard to a eulogy you might give in class, you generally have two options for how to proceed: you can eulogize a real person who has passed away, or you can eulogize a fictional character (if your instructor permits that). If you give a eulogy in class on someone in your life who has passed away, be aware that it is very common for students to become emotional and have difficulty giving their speech. Even though you may have been fine practicing at home and feel good about giving it, the emotional impact of speaking about a deceased loved one in front of others can be surprisingly powerful.
Speeches for Commencements
A speech of commencement (or commencement speech) is designed to recognize and celebrate the achievements of a graduating class or other group of people. These typically take place at graduation ceremonies. Nearly every one of us has sat through commencement speeches at some point in our lives. Numerous celebrities and politicians have been asked to deliver commencement speeches at colleges and universities.
If you’re ever asked to deliver a commencement speech, there are some key points to think through when deciding on your speech’s content.
- If there is a specific theme for the graduation, make sure that your commencement speech addresses that theme. If there is no specific theme, come up with one for your speech. Some common commencement speech themes are commitment, competitiveness, competence, confidence, decision making, discipline, ethics, failure (and overcoming failure), faith, generosity, integrity, involvement, leadership, learning, persistence, personal improvement, professionalism, reality, responsibility, and self-respect.
- Talk about your life and how graduates can learn from your experiences to avoid pitfalls or take advantage of life. How can your life inspire the graduates in their future endeavors?
- Make the speech humorous. Commencement speeches should be entertaining and make an audience laugh.
- Be brief! Nothing is more painful than a commencement speaker who drones on and on. Remember, the graduates are there to get their diplomas; their families are there to watch the graduates walk across the stage.
- Remember, while you may be the speaker, you’ve been asked to impart wisdom and advice for the people graduating and moving on with their lives, so keep it focused on them.
- Place the commencement speech into the broader context of the graduates’ lives. Show the graduates how the advice and wisdom you are offering can be utilized to make their own lives better.
Overall, it’s important to make sure that you have fun when delivering a commencement speech. Remember, it’s a huge honor and responsibility to be asked to deliver a commencement speech, so take the time to really think through and prepare your speech.
After-Dinner Speeches
After-dinner speeches are humorous speeches that make a serious point. These speeches get their name from the fact that they historically follow a meal of some kind. After-dinner speakers are generally asked to speak because they have the ability both to speak effectively and to make people laugh. All the basic conventions of public speaking previously discussed in this text apply to after-dinner speeches, but the overarching goal of these speeches is to be entertaining and to create an atmosphere of amusement. The speech should have a theme, such as celebrating the accomplishments of the last year, or connecting the audience to a special event that is important to the group.
When creating the speech, go back through and look for opportunities to insert humorous remarks. Once you’ve looked through your speech and examined places for verbal humor, think about any physical humor or props that would enhance your speech. The goal for a funny prop is that it adds to the humor of the speech without distracting from its message.
Just because you find something unbelievably funny in your head doesn’t mean that it will make anyone else laugh. Often, humor that we have written down on paper just doesn’t translate when orally presented. You may have a humorous story that you love reading on paper, but find that it just seems to be too long once you start telling it out loud. You also need to make sure the humor you choose will be appropriate for a specific audience. What one audience finds funny another may find offensive. Humor is the double-edged sword of public speaking. On one side, it is an amazing and powerful speaking tool, but on the other side, few things will alienate an audience more than offensive humor. If you’re ever uncertain about whether a piece of humor will offend your audience, don’t use it.
So you may now be asking, “What kind of topics are serious that I can joke about?” The answer to that, like the answer to most everything else in the book, is dependent on your audience and the speaking situation, which is to say any topic will work, while at the same time you need to be very careful about how you choose your topic.
Take, for example, the experience one of your authors had while he was attending a large university. One of the major problems that any large university faces is parking: the ratio of parking spaces to students at some of these schools can be 1:7 (one parking space for every seven students). In addressing this topic at a banquet, a student gave an after-dinner speech that addressed the problem of the lack of student parking. To do so, he camouflaged his speech as a faux-eulogy (fake eulogy) for the yellow and black board on the parking lot gates that was constantly and consistently driven through by students wanting to access restricted parking. The student personified the board by noting how well it had done its job and lamented that it would never get to see its little toothpick children grow up to guard the White House. But underneath the humor incorporated into the speech was a serious message: this wouldn’t keep happening if adequate parking was provided for students on campus.
Motivational Speeches
A motivational speech is designed not only to make an audience experience emotional arousal (fear, sadness, joy, excitement) but also to motivate the audience to do something with that emotional arousal. A motivational speech helps to inspire people in a broader fashion, often without a clearly articulated end result in mind. As such, motivational speaking is a highly specialized form of persuasive speaking commonly delivered in schools, businesses, religious houses of worship, and club or group contexts.
The hero speech is a motivational speech given by someone who is considered a hero in society (e.g., military speakers, political figures, and professional athletes).
The survivor speech is a speech given by someone who has survived a personal tragedy or who has faced and overcome serious adversity.
The religious speech is self-explanatory; it is designed to incorporate religious ideals into a motivational package to inspire an audience into thinking about or changing aspects of their religious lives. The final type of motivational speech is the success speech, which is given by someone who has succeeded in some aspect of life and is giving back by telling others how they too can be successful.
As stated at the beginning of this section, you will almost certainly be limited by your professor with regards to which of these types of speeches you can give for your special occasion speech in class, but it is not unrealistic to think that you will be called upon at various points in your life to give one or more of these speeches. Knowing the types and basic structures will help when those moments arise.
a mini-speech given by the host of a ceremony that introduces another speaker and his or her speech
a brief speech given to accompany a prize or honor
a speech given by the recipient of a prize or honor
a speech delivered to mark the unveiling, opening, or acknowledging of some landmark or structure
a speech designed to congratulate, appreciate, or remember
a humorous speech designed to both praise and good-naturedly insult a person being honored
a speech given in honor of someone who has died
a speech designed to recognize and celebrate the achievements of a graduating class or other group of people
a humorous speech that makes a serious point
a speech designed not only to make an audience experience emotional arousal (fear, sadness, joy, excitement) but also to motivate the audience to do something with that emotional arousal
a motivational speech given by someone who is considered a hero in society
a speech given by someone who has survived a personal tragedy or who has faced and overcame serious adversity
a speech designed to incorporate religious ideals into a motivational package to inspire an audience into thinking about or changing aspects of their religious lives
It’s About Them: Public Speaking in the 21st Century Copyright © 2022 by LOUIS: The Louisiana Library Network is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Different Types Of Speeches
When you think of impressive speeches, you might think of pieces that have the power to inspire and motivate entire…

When you think of impressive speeches, you might think of pieces that have the power to inspire and motivate entire nations of people to greatness. Speeches such as Jawaharlal Nehru’s “Tryst with Destiny”, or John F. Kennedy’s “We choose to go to the moon” have been studied by students and communicators for decades.
In the corporate realm too, speeches can have great power. Steve Jobs’s keynote presentation announcing the iPhone in 2007, for example, is the stuff of legend.
While you might not be addressing millions around the world anytime soon, there are many platforms on which you’ll have to use types of public speaking in the professional arena. By studying different types of speeches, you can learn a lot about impactful communication.
What Are The Types Of Speeches?
The purpose of the speech, how to prepare for your speech, how to make a speech impactful, tips for delivery, hone your speech skills.
While political speeches at historical moments are brilliant oratorical examples we can all learn from, we’ll be taking a closer look at the types of public speech in a business context. We can broadly divide these into three types of public speaking: speeches, lectures and seminars or workshops. These aren’t the only categories, but they’re the most common ones you’ll encounter in your professional life.
Public speaking types: Motivational or inspirational
Speeches are typically “big” talks that are meant to be heavily persuasive and informative to large crowds—usually comprising several hundred people or more. Most speeches will include at least one focal point you want your audience to remember after they leave. Top management might give speeches to commemorate an important milestone such as a centenary celebration, or to announce a new product.
Public speaking types: Informative or inspirational
Lectures are also considered a form of public speaking, meant for smaller groups or classes of people. You’ll probably use lectures in a workplace setting more often, because speeches are usually reserved for special events. They are typically more of an explanation of something the speaker is an expert at. Organizational leadership and management might be invited to share their knowledge at an industry forum or at an internal meet.
Seminars Or Workshops
Public speaking types: Demonstrative or informational
Seminars are also considered public speaking, but they’re usually for smaller, more intimate groups of people—though some seminars can have large attendance as well. Most workplaces conduct seminars or workshops throughout the year, and they’re very useful for explaining information and processes the business needs employees to know. Training meetings and inductions are examples of this type of speech.
Different forums, audiences and venues call for different types of speeches. By understanding your audience, you can create maximum effect.
To determine the kind of speech you need to deliver, you need to define the purpose of the speech.
Often, when people need inspiration, they’ll either turn to a motivational speaker or attend a seminar. A motivational speaker needs to quickly establish rapport and credibility. Think of online talks by management gurus Tony Robbins or Simon Sinek, who do this so effectively. They are viewed by millions for a reason. .
Whether that’s the sort of speech you’d like to make, or if you’re attempting something more casual, here are three critical components that will help you connect to the audience:
A professional speech needs to be interesting for the audience. For this, it must be relevant. The speaker must have established their expertise, and the audience must be keen to hear what they bring to the table.
Research your subject as much as you can. It’s very important that a good professional speech needs to be logical and orderly. Express a simple idea clearly and concisely, backed up with data where necessary.
As we’ve seen, it’s very important for a good professional speech to motivate the audience. It isn’t just about wizardry with words, it’s also about content. What do you want the audience to take away from the talk? Tell them how it’s possible and inspire them to go out and do it. ( https://mclaneedgers.com )
Identifying the purpose of your speech will help you connect with your audience and deliver an impactful message.
If you’ve worked out the kind of speech you’re delivering, its purpose and have put together ideas for content, you’ll need to work out the logistics. Here are few areas to address:
Time Is Of The Essence
Know how much time you’ll get for your speech. Depending on the organization, the venue, and even the audience, there are maximum time limits for speeches. Knowing the time available will help you get your thoughts down and rehearse.
Visual Aids
Depending on what your topic is, use visual aids to show your audience what you’re talking about. These should always apply to the speech and help with understanding your material.
Prepare Handouts
Decide if your talk calls for a handout. Are you presenting a lot of data? A handout will help your audience process and remember it. A handout could be a copy of your presentation slides, or you could prepare something specifically for the purpose. Make sure all necessary materials are ready beforehand.
Most people are nervous about public speaking and are afraid they aren’t good at it. That’s okay! You don’t have to be a brilliant speaker to make your speech effective—and preparation and the right tools can go a long way.
Once you’ve decided what type of speech you’re going to give, you can work on making your content as impactful as possible.
Your speech should cover all the information and it must follow a logical flow. Here are a few tips for structuring your speech or presentation:
Introduce Your Speech
Make sure you introduce yourself and where you’re coming from. This is a good chance to share a little about yourself. It helps establish a connection with your audience.
Give Background Information
Now give some background information about the topic itself. If your speech is persuasive, you’ll want to be straightforward about it. Clear and concise language makes for the most impact.
Make Your Point
Now that you’ve shared the information, it’s time to drive home the main point. Finishing strong will make your message stick.
Different types of speeches have unique characteristics—but they also have much in common. Organization and practice will help you get past your stage fright.
There are many ways of learning to improve one’s voice and ability in public speaking. Writing down your thoughts and rehearsing are crucial—no matter how much you think you can speak off the cuff, it’s usually a bad idea. Here are some strategies used by public speakers:
Voice modulation
Working on your voice modulation can make a big difference when giving all types of speeches. Varying loudness, pitch and tempo are some skills to practice. Amplification is also important for a speech, so your voice doesn’t fade out. Voice modulation improves speech clarity by eliminating the problem of shouting and muffled sounds. Voice amplification is a necessity when speaking in large spaces.
No speech can be effective if the words are unclear. Above all, you must be easy to understand. If you’re having trouble, try to speak slower at first and then increase your speed as you get more comfortable.
Build Connection
There are two parts to an excellent speech—the person delivering the speech and the listener. There are many ways of connecting with the audience and making them really feel what you’re saying. Storytelling skills come into play here—drawing from your own life experience usually makes for an impactful presentation. Humor, if appropriate, can be effective, too. Inject emotion and energy into your delivery.
Remember that no matter what public speaking types you’d like to master, you can improve your delivery through preparation and practice.
With Harappa’s Speaking Effectively course, you can increase the impact of your verbal communication. Whether you’re delivering a speech to thousands of people or making a presentation to a prospective client, public speaking is a core skill for so many professionals today. If you’re in a client-facing role and would like to learn how to make your point clearly, concisely and persuasively, this is the course for you. Sign up to take your career to the next level!
Explore Harappa Diaries to learn more about topics such as the Principles of Communication , How To Improve Communication Skills , What Is Internal Communication & The Art Of Storytelling to communicate with impact.


4 Main Types of Speeches in Public Speaking (With Examples)

We live in a world where communication is king.
With social media and all the digital stuff, we’re bombarded with information constantly, and everyone is fighting for our attention.
Research shows that our attention spans have declined from 12 seconds to just 8.25 seconds in the past 15 years, even shorter than a goldfish’s attention span.
So, the point is being able to get your point across quickly and effectively is a big deal. That’s where the invaluable skill of public speaking comes in handy.
But being a great speaker goes beyond just having confidence. It’s about understanding different kinds of speeches and knowing which one works best for your audience and purpose.
In this blog, we will explore four main types of speeches (or types of public speaking), each with its own purpose and impact. By understanding these types, you can connect with your audience , cater to their needs, and deliver a message that resonates.
So, let’s dive right in:

What is Speech?
Importance of public speaking (7 benefits).
- 4 Main Types of Public Speeches (With Examples)
Other Types of Speeches
Final thoughts.
A speech is a formal or informal presentation in which a person communicates their thoughts, ideas, or information to an audience. It is a spoken expression of thoughts, often delivered in a structured and organized manner.
Speeches can be delivered to serve various purposes, such as to persuade , educate, motivate, or entertain the audience.
People usually give speeches in public places, like meetings, conferences, classrooms, or special events, aiming to connect with and influence the listeners through their words.

A public speech may involve the use of supporting materials, such as visual aids, slides , or props, to enhance understanding and engagement.
The delivery of a speech encompasses not only the words spoken but also factors like the tone of voice, body language , and timing, which can greatly impact the overall effectiveness and reception of the message.
You may want to check out our short video on how to speak without hesitation.
Public speaking is a superpower that transforms your life in more ways than you can imagine.
Here are 7 reasons why Public speaking is an invaluable skill:
- Effective Communication: Being a good public speaker helps you express yourself clearly and confidently. It allows you to share your knowledge, opinions, and ideas in a captivating manner.
- Professional Growth: Mastering public speaking gives you a competitive edge in the job market. It allows you to lead meetings , present ideas, negotiate deals, and pitch projects with confidence.

- Building Confidence: Overcoming the fear of public speaking and delivering successful presentations significantly boosts your self-confidence . With experience, you become more self-assured in various situations, both inside and outside of public speaking.
- Influence and Persuasion: A strong public speaker can inspire, motivate, and influence others. By effectively conveying your message, you can sway opinions, change attitudes, and drive positive change in your personal and professional circles.

- Leadership Development: Public speaking is a crucial skill for effective leadership. It enables you to inspire and guide others, lead meetings and presentations, and rally people around a common goal.
- Personal Development: Public speaking encourages personal growth and self-improvement. It pushes you out of your comfort zone, enhances your critical thinking and problem-solving skills, and helps you become a more well-rounded individual.
- Increased Visibility: The ability to speak confidently in public attracts attention and raises your visibility among peers, colleagues, and potential employers. This can lead to new opportunities, collaborations, and recognition for your expertise.

Public speaking is a vital tool for social change. History has shown us how influential speeches have shaped the world we live in. From Martin Luther King Jr.’s “ I Have a Dream ” speech to Malala Yousafzai’s advocacy for girls’ education, public speaking has been at the forefront of inspiring change. Your words have the power to challenge beliefs, ignite passion, and rally others around a cause. So, if you have a message you want to share or a mission you want to pursue, mastering the art of public speaking is essential.
1. Informative Speech
An informative speech is a type of public speaking that aims to educate or provide information to the audience about a specific topic. The main purpose of this speech is to present facts, concepts, or ideas in a clear and understandable manner.

Delivering an Informative Speech
In an informative speech, the speaker’s objective is to provide knowledge, increase awareness, or explain a subject in detail.
To be informative, you need to structure your content in a way that’s clear and easy to follow. The structure of an informative speech typically includes:
- an introduction where you grab the audience’s attention and introduce the topic
- the body where you present the main points and supporting evidence
- a conclusion where you summarize the key information and emphasize your message.
- a Q&A session or a brief discussion to further deepen their understanding.
Informative speech could be formal or informal speech, depending on the context. However, it is helpful to maintain a conversational tone.
Use relatable examples, anecdotes, or even a touch of humor to keep your audience engaged and interested. Think of it as having a friendly chat with a group of curious friends.
Examples of Informative Speeches:
An Example of Informative Speech
- Academic Settings : Students may deliver presentations to educate their classmates. Teachers or instructors may explain a specific subject to students in schools, colleges, and universities.
- Business and Professional Presentations: In the corporate world, professionals may present information about industry trends, new technologies, market research, or company updates to inform and educate their colleagues or clients.
- Public Events and Conferences: Informative speeches are prevalent in public events and conferences where experts and thought leaders share their knowledge and insights with a broader audience.
- Ted Talks and Similar Platforms: TED speakers design their speeches to educate, inspire, and spread ideas that have the potential to make a positive impact on society.
- Community Gatherings: Informative speeches can be delivered at community gatherings where speakers may inform the community about local issues, government policies, or initiatives aimed at improving the community’s well-being.
The beauty of informative speeches is their versatility; they can be adapted to different settings and tailored to suit the needs and interests of the audience.
2. Demonstrative Speech
In a demonstrative speech, the main goal is to show how to do something or how something works. It is like giving a step-by-step guide or providing practical instructions.
The purpose of a demonstrative speech is to educate or inform the audience about a specific process, task, or concept.
It can be about anything that requires a demonstration, such as cooking a recipe, performing a science experiment, using a software program, or even tying a tie.

The key to a successful demonstrative speech is to be organized and concise.
When preparing for a demonstrative speech, you need to break down the process or technique into clear and easy-to-follow steps.
You need to make sure that your audience can grasp the concepts and replicate the actions themselves. Visual aids like props, slides, or even live demonstrations are incredibly helpful in illustrating your points.
A great demonstrative speech not only teaches but also inspires.
You need to ignite a sense of enthusiasm and curiosity in your audience . Encourage them to try it out themselves and apply what they’ve learned in their own lives.
Examples of Demonstrative Speeches:
An Example of Demonstrative Speech
- Educational Settings: Demonstrative speeches are often used in classrooms, workshops, or training sessions to teach students or participants how to perform specific activities. For instance, a teacher might give a demonstrative speech on how to conduct a science experiment, play a musical instrument, or solve a math problem.
- Professional Training: In the workplace, a trainer might give a demonstrative speech on how to use a new software application, operate a piece of machinery, or follow safety protocols.
- DIY and Home Improvement: Demonstrative speeches are commonly seen in DIY (do-it-yourself) videos, TV shows, or workshops where experts demonstrate how to complete tasks like painting a room, fixing plumbing issues, or building furniture.
- Culinary Demonstrations: Demonstrative speeches are prevalent in the culinary world, where chefs or cooking experts showcase recipes and cooking techniques.
Overall, a demonstrative speech is a practical and hands-on type of speech that aims to educate, inform, and empower the audience by teaching them how to perform a particular task or skill.
3. Persuasive Speech
A persuasive speech is when the speaker tries to convince the audience to adopt or support a particular point of view, belief, or action. In a persuasive speech, the speaker aims to influence the audience’s opinions, attitudes, or behaviors.
You may present arguments and evidence to support your viewpoint and try to persuade the listeners to take specific actions or simply agree with you.
You have to use persuasive techniques such as logical reasoning, emotional appeals, and credibility to make your case.

Let me break it down for you.
- First, you need a clear and persuasive message. Identify your objective and what you want to achieve with your speech. Once you have a crystal-clear goal, you can shape your arguments and craft your speech accordingly.
- Secondly, you need to connect with your audience on an emotional level. You may use stories , anecdotes, and powerful examples to evoke emotions that resonate with your audience.
- Thirdly, you need to present compelling evidence, facts, and logical reasoning to support your arguments. Back up your claims with credible sources and statistics.
- Additionally, the delivery of your speech plays a crucial role in persuasion. Your body language, tone of voice , and overall presence should exude confidence and conviction.
- Lastly, end your persuasive speech with a call to action. Whether it’s signing a petition, donating to a cause, or changing a behavior, make it clear what steps you want your audience to take.

Examples of Persuasive speeches:
An Example of Persuasive Speech
- Political speeches: Politicians ****often deliver persuasive speeches to win support for their policies or convince people to vote for them.
- Sales and marketing presentations: Advertisements ****use persuasive techniques to persuade consumers to buy their products.
- Social issue speeches: Activists, advocates, or community leaders often give persuasive speeches to raise awareness about social issues and mobilize support for a cause.

Effective persuasion helps you win over clients, close deals, and secure promotions.
However, it’s important to note that persuasion should always be used ethically and with integrity. It’s not about manipulating people but rather about creating win-win situations.
4. Entertaining Speech
An entertaining speech is a type of public presentation that aims to captivate and amuse the audience while providing enjoyment and laughter. Unlike other types of speeches, entertaining speeches prioritize humor, storytelling , and engaging content to entertain and delight the listeners.
In an entertaining speech, the speaker uses various techniques such as jokes, anecdotes, funny stories, witty observations, humorous examples, and clever wordplay to engage the audience and elicit laughter.
The primary objective is to entertain and create a positive, lighthearted atmosphere.

An entertaining speech is a powerful tool for building a connection with the audience. It isn’t just about cracking jokes. It’s about using humor strategically to reinforce the main message.
When we’re entertained, our guards come down, and we become more receptive to the speaker’s message. It’s like a spoonful of sugar that helps the medicine go down.
An entertaining speech can be particularly effective when the topic at hand is traditionally considered dull, serious, or sensitive. By infusing humor, you can bring life to the subject matter and help the audience connect with it on a deeper level.
With entertainment, you can make complex concepts more accessible. And also break down barriers that might otherwise discourage people from paying attention.
Delivery and timing are crucial elements in entertaining speeches.
The speaker’s tone, facial expressions, gestures , and voice modulation play a significant role in enhancing the comedic effect.
Effective use of pauses , punchlines, and comedic timing can heighten the audience’s anticipation and result in laughter and amusement.
Examples of Entertaining Speech:
An Example of Entertaining Speech
- Social Events: Entertaining speeches are often seen at social gatherings such as weddings, birthday parties, or anniversary celebrations.
- Conferences or Conventions: In professional conferences or conventions, an entertaining speech can be a refreshing break from the more serious and technical presentations. A speaker may use humor to liven up the atmosphere.
- Stand-up Comedy: Stand-up comedians are prime examples of entertaining speeches. They perform in comedy clubs, theaters, or even on television shows, aiming to make the audience laugh and enjoy their performance.
The content and style of an entertaining speech should be tailored to the audience and the occasion. While humor is subjective, the skilled entertaining speaker knows how to adapt their speech to suit the preferences and sensibilities of the specific audience. By carefully selecting appropriate humor, you can transform a dull or serious setting into an enjoyable experience for the audience.
Beyond the four main types of public speeches we mentioned, there are a few other different types of speeches worth exploring.
- Special Occasion Speeches: These speeches are delivered during specific events or occasions, such as weddings, graduation ceremonies, or award ceremonies. They are meant to honor or celebrate individuals, express congratulations, or provide inspiration and encouragement.
- Motivational Speeches: Motivational speeches aim to inspire and are commonly delivered by coaches, entrepreneurs, or motivational speakers. They often focus on personal development, goal-setting, overcoming obstacles, and achieving success.
- Commemorative Speeches: These speeches are delivered on anniversaries, memorial services, or dedications. These speeches express admiration, highlight achievements, and reflect on the impact of the person or event being commemorated.
- Debate Speeches: Debate speeches involve presenting arguments and evidence to support a particular viewpoint on a topic. They require logical reasoning, persuasive language, and the ability to counter opposing arguments effectively.
- Impromptu Speeches: Impromptu speeches are delivered without prior preparation or planning. You are given a topic or a question on the spot and must quickly organize your thoughts and deliver a coherent speech. These speeches test the speaker’s ability to think on their feet and communicate effectively in spontaneous situations.
- Oratorical Speech: An oratorical speech is a formal and eloquent speech delivered with great emphasis and rhetorical flair. It aims to inspire, persuade, or inform the audience through the skilled use of language and powerful delivery techniques. Oratorical speeches are typically given on significant occasions, such as political rallies, commemorative events, or public ceremonies.
No matter what kind of speech you are giving, pauses play a key role in making it captivating.
Check out our video on how pausing can transform your speeches.
Public speaking is a powerful skill that holds tremendous value in various aspects of our lives. Whether you’re aiming to inform, demonstrate, persuade, or entertain, mastering the art of public speaking can open doors to new opportunities and personal growth.
Growth happens when you push beyond your comfort zones. Public speaking may seem daunting at first, but remember that every great speaker started somewhere. Embrace the challenge and take small steps forward.
Start with speaking in front of friends or family, join a local speaking club, or seek opportunities to present in a supportive environment . Each time you step out of your comfort zone, you grow stronger and more confident.
Seek resources like TED Talks, workshops, books , and podcasts to learn from experienced speakers and improve your skills.
Just like any skill, public speaking requires practice. The more you practice, the more comfortable and confident you will become.
Seek opportunities to speak in public, such as volunteering for presentations or joining public speaking clubs. Embrace every chance to practice and refine your skills.
If you are looking for a supportive environment to practice and hone your public speaking skills, try out BBR English.
Our 1:1 live sessions with a corporate expert are designed to help you improve your communication skills. You’ll gain the confidence and skills you need to communicate effectively in any situation.
Don’t let fear or insecurity hold you back from achieving your goals.
Book your counseling session now and take the first step towards becoming a more confident and effective communicator.
Your future self will thank you!
To get a peek into our results, check out How A Farmer’s Son Faced His Fear Of Public Speaking To Climb Up The Leadership Roles In An MNC.
Happy Speaking!
Team BBR English
who needs to see our story? Share this content
- Opens in a new window
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
- 🌟 Expert advice on improving your spoken skills
- 📚 Engaging language learning resources
- 📆 Weekly tips to boost your spoken English
- 🎉 Exciting updates about our courses and events
- I agree to receiving marketing emails and special deals
My Speech Class
Public Speaking Tips & Speech Topics
Types of Public Speaking

Amanda Green was born in a small town in the west of Scotland, where everyone knows everyone. I joined the Toastmasters 15 years ago, and I served in nearly every office in the club since then. I love helping others gain confidence and skills they can apply in every day life.
When it comes to being a public speaker, the type of speech to give depends on what you’re trying to accomplish. The different types of public speaking are:
- Speaking to Inform (informative, argumentative speech)
- Speaking to Persuade, Motivate, or Take Action (persuasive, argumentative, controversial, policy speeches)
- Speaking to Entertain (funny, special occasion speeches)
In this article:
The 3 Basic Types of Public Speaking
Informative, special occasion, tips for writing an engaging speech.

- To Inform – when the speaker is presenting interesting facts or lessons to the audience, or explain how to go about doing something. This could be a teaching lecturing about the Civil War, a student giving an oral report or showing how to decorate a cake or set up a blog, a museum docent explaining the history of painting, or a doctor explaining a procedure.
- To persuade, Motivate, or Take Action – this is when the speaker will try influencing the audience in some way. The speaker might be trying to change your mind about something, to persuade you to change your opinion, to motivate to change a behavior, or to take action. Some examples are explaining the benefits of a non-profit for the purpose of eliciting donations, trying to get people to change bad eating habits by explaining all the benefits of eating healthily or attempting to convince people to vote against a candidate in an election.
- To Entertain – this type of speaking is often found at events like banquets, weddings, or dinners. The speaker is usually sharing a funny story or other anecdotal information. Some examples of this would be the best man speech at a wedding or an after-dinner speech given by a host of a party to thank guests for coming. They could also be planned as entertainment at an event. Topics are usually humorous and light and could serve a very specific purpose, like introducing a featured guest or giving a toast.
Different Types of Public Speeches
When making a speech, choosing an appropriate topic is obviously the first and most vital step of the process. This is never more true than when a persuasive speech must be constructed. It is important for the speaker to realize that the audience may already have an opinion on the topic, or may form an instant opinion during the opening lines of the presentation. This puts the speaker at somewhat of an instant disadvantage if he or she wishes to persuade those listening to alter their own viewpoints.
When choosing a persuasive speech topic , the speaker should choose a subject area about which they are passionate. This passion will come through in the delivery of the speech and will aid the audience in identifying with the speaker. On the other hand, if the speaker feels apathetic about their chosen topic, that will show as well. It will be difficult for the audience to care about the topic if the speaker obviously does not.
In order to hold the attention of the audience , the speaker should remember several things.
Can We Write Your Speech?
Get your audience blown away with help from a professional speechwriter. Free proofreading and copy-editing included.
- using descriptive language to create vivid mental pictures will keep the audience entertained.
- stirring emotion in the audience will provoke them to care about the subject. After all, if listeners don’t care about a topic they’re unlikely to stay focused or form an opinion on it.
- it’s important to find an angle for the chosen topic which has not been overdone in the past. For example, most people agree that smoking cigarettes is bad for their health, and will most likely be bored by a speech on this topic. If the speaker wishes to address a tobacco topic, perhaps they should narrow the focus of the speech to controversial laws, higher taxes, or methods to prevent smoking in youth. Choosing a fresh, new angle on a familiar topic will help the speaker to create a captive audience.
Speakers should always remember that the point of a persuasive speech is to convince the audience to consider a particular point of view. Therefore, it is vitally important that the speaker diligently research their topic, because a fully informed speaker will come across as much more convincing. A question-and-answer session at the end of the speech is the perfect way for the speaker to close his argument. This will demonstrate to the audience that the speaker genuinely cares about their concerns, and it gives the speaker a chance to clarify any lingering misconceptions that may exist within the minds of the audience. When choosing a topic for a persuasive speech, speakers should keep this in mind and select a subject area with which they feel comfortable and knowledgeable.
Writing the text for Persuasive Speech
There are three main components of persuasive speech structure:
Introduction
You can also include
- Questions and answers session at the end of your speech but this is optional.
- Grab attention . Do or say something shocking, intriguing, or dramatic to get attention of the audience from the very first minutes.
- State your topic . Announce what your speech is about, and your position.
- Preview statement . Introduce main points of your speech.
Further information on writing the introduction .
- Introduce your topic . You need to explain your topic to those people who do not know about it. Do not go into the details, simple definition is enough. This speech element is required.
- State your point
- State a Reason
- Give an Example
- Restate the Point
Further information on writing the speech body .
- Summary . Restate thesis and main points.
- Call to action .
Further information on writing the speech conclusion .
First, you need to pick a topic that will appeal to your audience members. To be appealing to audience members, a topic must be:
- Dealt with at a stimulating level : If you are merely teaching the audience information that they already know, you will certainly bore them. If you teach them information that is “over their heads”, you will lose their attention and interest. The key is to find a happy medium, new information that they will readily grasp.
- Dealt with creatively : Surprise your audience. Think about your topic in unexpected ways. Don’t merely step behind the podium with a modified version of an essay you wrote in another class. Be an entertainer. When an audience is entertained, they pay closer attention.
Your audience will also appreciate it if you pick a topic that is relevant to their lives. Whether we care to admit it or not, deep down, we all have one primary interest: ourselves. If your audience does not see a personal benefit that they will receive by listening to your speech, the speech will not be very appealing. When presenting an informative speech, it is important to have proper supporting material to enhance your audience’s understanding of your topic. Some forms of support include:
- Examples – It’s difficult to listen to someone speaking about an abstract idea with which you have little familiarity. As a listener in this situation, you are forced to do a lot of mental work and you may or may not fully grasp what the speaker is trying to say. It’s a whole different experience when the speaker uses an example that illustrates the abstract idea. For example (ha-ha), a speaker might be talking about poor economic conditions in a certain area of the country. Rather than just leaving the concept of a “poor economy” as an idea, they should speak about the specific struggles of real live people with names and anecdotes.
- Statistics – People tend to avoid statistics in a speech because they are afraid that people will find them boring. To the contrary, statistics can be interesting and informative if used correctly. The key is to pick statistics that are particularly startling or shocking. You can’t build an entire speech around statistics, of course. However, as long as the statistics add to the quality of the speech, and they don’t misrepresent the situation, they can be used liberally.
- Facts – A good informative speech is filled with facts. A “fact” is any bit of information that be verified as being “true”. Whenever you present facts in a speech, you should cite the source of those facts so that the audience believes them (and you) to be credible.
- Expert Opinion – An informative speech is not the time for your personal opinion, that time will come on the persuasive speech. Expert opinion, however, can and should be used in an informative speech. Expert opinion involves using excerpts and quotations from people who are highly respected in the field about which you are speaking. It is important to state the credentials of the person whom you are quoting, if the audience is not familiar with this person. Otherwise, your quote will not have much impact.
Whatever forms of support you may be using in your informative speech, it is important to select those sources carefully. Make sure that you are using up-to-date information. Make sure you are using unbiased sources (these can be especially hard to find on the Internet). And finally, make sure that you are working from a broad base of information. Do not base your entire speech on information found in a single source.
There are a number of social situations in which you might find yourself asked to make a speech. This page examines some of those situations and offers some advice on how to handle them. Speech of Introduction: A speech of introduction is when you are asked to introduce the “main” speaker at the function. Your speech should answer the following questions for the audience:
- Who is the speaker?- Talk about the speaker’s credentials and expertise and why they were chosen to speak.
- What will the speaker be discussing?- Give a short preview of the upcoming speech.
It’s critically important when giving a Speech of Introduction to get the speaker’s name and speech topic correct, naturally. Whenever possible, go over your introduction with the speaker beforehand to avoid potential embarrassment for both of you. Welcoming Speech: The goal of a welcoming speech is to bring people or groups of people together. For example, you might deliver a Welcoming Speech about a new employee in your company. The purpose is to formally introduce the newcomer(s) to the others. This involves telling the audience who the newcomer(s) is/are, where they came from, what they will be doing. Award Presentation Speech : When you are presenting someone with a gift or an award you have two goals to accomplish:
- Discuss the award itself- Who sponsors it, who it is named after, the history of the award, and the requirements to earn it.
- Discuss the winner of the award- Who they are, what they have done to earn the award.
When presenting an award, hand the award off with your left hand and shake hands with recipient with your right hand. Award Acceptance Speech: When receiving an award, your audience will most likely expect you to be gracious and humble. To this end, a good award acceptance speech involves thanking others who made your receiving the award possible. Be sure to thank those involved in helping you get the award, and the giver of the award. Tribute Speech: Situations for a Tribute Speech might be a eulogy at a funeral, or a speech given at a retirement party, or any other occasion where a person is being honored. Basically, sincerity is the key to a good Tribute Speech. You should focus on the positive aspects of the person, tell humorous or otherwise interesting stories about the person, and speak of the person’s accomplishments and admirable qualities. Toast: In most toasting situations (weddings, retirement parties, birthday parties) the person delivering the toast can anticipate that they will be asked to do so. Because of this, and because toasts are usually quite short, a good toast is often written in advance. A toast needs to be positive, and to include words of praise or encouragement for those to whom it is directed.
Preparing a speech is more than just getting the words down on paper and then reading them to an audience. The most important part of a speech is how it affects the audience and the only way it can affect the audience is if they’re actually listening. Engaging your audience is the key to having a successful speech.
How can you write a speech people will actually pay attention to? Here are some tips:
- Make the speech about the audience . Depending on what kind of speech you’re giving, you want the audience to gain a thorough understanding of what you’re speaking about or you’re trying to persuade them to take action. You might even just be trying to make them laugh. All your efforts should be aimed at making sure they understand what you’re saying.
- Write for your ear . Remember, what you’re writing is going to be said out loud. Sometimes, the way things look best on paper is not the way they’re going to sound best. Practice reading your speech out loud so you can make sure it sounds right. You can even record yourself and make necessary changes after you hear it out loud.
- Work through a rough draft of the whole thing and make edits and polish it later. Your speech will not be perfect at first. Writing the whole thing out first will often help you work out any writer’s block or could even make you see something a little clearer and find a better way to say it.
- Put a little bit of yourself into your speech . Don’t worry about being groundbreaking or unique, but make sure you feel a bit of yourself in your writing.
- Start preparing early . Sometimes, you might have no idea what you’re going to talk about. The more research you do, the more likely it is that you’ll find something really interesting about your topic that can grab your audience’s attention. You’ll also find it’s easier to structure and organize your speech the more you know about your topic.
- Limit the information . You can’t cover everything about a topic in a speech and, if you could, you’d lose the audience’s attention before too long. Try to stick to three main points so your speech is a little easier to follow.
- Write your speech as if it’s meant for one person to hear . This will make it sound more conversational and your audience will feel like you’re really trying to make a connection.
- Try to get the audience involved . There are a lot of ways to do this. You can ask simple questions, ask for volunteers for role playing exercises, or have someone help you demonstrate a concept presented in your speech.
- Pace your speech . Vary sentence and word length so it doesn’t become boring.
- Repeat key words and points effectively . This helps the audience understand what the main take away from your speech should be.
- Ask rhetorical questions as a way of attracting the listener’s attention.
- Tell personal stories and anecdotes that fit into the topic of your speech when applicable. This will make your speech a little more personal and can help you make a better connection with the audience.
- Use quotes when you can. It breaks up your speech and makes it more interesting. Bonus points if the quote is from a famous person that your audience will recognize.
Remember, the most important part of giving a speech is getting your audience to listen to what you’re saying. You want to be interesting enough that they’re actually going to want to hear what you have to say. Just as importantly, you want to make sure that they remember the key parts of your speech. The most effective way to achieve this is through an engaging speech.
206 Great Speech Topics for Teens [Persuasive, Informative]
Entertaining Speech Topics [195 Ideas To Keep Audience Engaged]
Leave a Comment
I accept the Privacy Policy
Reach out to us for sponsorship opportunities
Vivamus integer non suscipit taciti mus etiam at primis tempor sagittis euismod libero facilisi.
© 2024 My Speech Class
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Parts of speech
The 8 Parts of Speech | Chart, Definition & Examples

A part of speech (also called a word class ) is a category that describes the role a word plays in a sentence. Understanding the different parts of speech can help you analyze how words function in a sentence and improve your writing.
The parts of speech are classified differently in different grammars, but most traditional grammars list eight parts of speech in English: nouns , pronouns , verbs , adjectives , adverbs , prepositions , conjunctions , and interjections . Some modern grammars add others, such as determiners and articles .
Many words can function as different parts of speech depending on how they are used. For example, “laugh” can be a noun (e.g., “I like your laugh”) or a verb (e.g., “don’t laugh”).
Table of contents
- Prepositions
- Conjunctions
- Interjections
Other parts of speech
Interesting language articles, frequently asked questions.
A noun is a word that refers to a person, concept, place, or thing. Nouns can act as the subject of a sentence (i.e., the person or thing performing the action) or as the object of a verb (i.e., the person or thing affected by the action).
There are numerous types of nouns, including common nouns (used to refer to nonspecific people, concepts, places, or things), proper nouns (used to refer to specific people, concepts, places, or things), and collective nouns (used to refer to a group of people or things).
Ella lives in France .
Other types of nouns include countable and uncountable nouns , concrete nouns , abstract nouns , and gerunds .
Check for common mistakes
Use the best grammar checker available to check for common mistakes in your text.
Fix mistakes for free
A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun. Pronouns typically refer back to an antecedent (a previously mentioned noun) and must demonstrate correct pronoun-antecedent agreement . Like nouns, pronouns can refer to people, places, concepts, and things.
There are numerous types of pronouns, including personal pronouns (used in place of the proper name of a person), demonstrative pronouns (used to refer to specific things and indicate their relative position), and interrogative pronouns (used to introduce questions about things, people, and ownership).
That is a horrible painting!
A verb is a word that describes an action (e.g., “jump”), occurrence (e.g., “become”), or state of being (e.g., “exist”). Verbs indicate what the subject of a sentence is doing. Every complete sentence must contain at least one verb.
Verbs can change form depending on subject (e.g., first person singular), tense (e.g., simple past), mood (e.g., interrogative), and voice (e.g., passive voice ).
Regular verbs are verbs whose simple past and past participle are formed by adding“-ed” to the end of the word (or “-d” if the word already ends in “e”). Irregular verbs are verbs whose simple past and past participles are formed in some other way.
“I’ve already checked twice.”
“I heard that you used to sing .”
Other types of verbs include auxiliary verbs , linking verbs , modal verbs , and phrasal verbs .
An adjective is a word that describes a noun or pronoun. Adjectives can be attributive , appearing before a noun (e.g., “a red hat”), or predicative , appearing after a noun with the use of a linking verb like “to be” (e.g., “the hat is red ”).
Adjectives can also have a comparative function. Comparative adjectives compare two or more things. Superlative adjectives describe something as having the most or least of a specific characteristic.
Other types of adjectives include coordinate adjectives , participial adjectives , and denominal adjectives .
An adverb is a word that can modify a verb, adjective, adverb, or sentence. Adverbs are often formed by adding “-ly” to the end of an adjective (e.g., “slow” becomes “slowly”), although not all adverbs have this ending, and not all words with this ending are adverbs.
There are numerous types of adverbs, including adverbs of manner (used to describe how something occurs), adverbs of degree (used to indicate extent or degree), and adverbs of place (used to describe the location of an action or event).
Talia writes quite quickly.
Other types of adverbs include adverbs of frequency , adverbs of purpose , focusing adverbs , and adverbial phrases .
A preposition is a word (e.g., “at”) or phrase (e.g., “on top of”) used to show the relationship between the different parts of a sentence. Prepositions can be used to indicate aspects such as time , place , and direction .
I left the cup on the kitchen counter.
A conjunction is a word used to connect different parts of a sentence (e.g., words, phrases, or clauses).
The main types of conjunctions are coordinating conjunctions (used to connect items that are grammatically equal), subordinating conjunctions (used to introduce a dependent clause), and correlative conjunctions (used in pairs to join grammatically equal parts of a sentence).
You can choose what movie we watch because I chose the last time.
An interjection is a word or phrase used to express a feeling, give a command, or greet someone. Interjections are a grammatically independent part of speech, so they can often be excluded from a sentence without affecting the meaning.
Types of interjections include volitive interjections (used to make a demand or request), emotive interjections (used to express a feeling or reaction), cognitive interjections (used to indicate thoughts), and greetings and parting words (used at the beginning and end of a conversation).
Ouch ! I hurt my arm.
I’m, um , not sure.
The traditional classification of English words into eight parts of speech is by no means the only one or the objective truth. Grammarians have often divided them into more or fewer classes. Other commonly mentioned parts of speech include determiners and articles.
- Determiners
A determiner is a word that describes a noun by indicating quantity, possession, or relative position.
Common types of determiners include demonstrative determiners (used to indicate the relative position of a noun), possessive determiners (used to describe ownership), and quantifiers (used to indicate the quantity of a noun).
My brother is selling his old car.
Other types of determiners include distributive determiners , determiners of difference , and numbers .
An article is a word that modifies a noun by indicating whether it is specific or general.
- The definite article the is used to refer to a specific version of a noun. The can be used with all countable and uncountable nouns (e.g., “the door,” “the energy,” “the mountains”).
- The indefinite articles a and an refer to general or unspecific nouns. The indefinite articles can only be used with singular countable nouns (e.g., “a poster,” “an engine”).
There’s a concert this weekend.
If you want to know more about nouns , pronouns , verbs , and other parts of speech, make sure to check out some of our language articles with explanations and examples.
Nouns & pronouns
- Common nouns
- Proper nouns
- Collective nouns
- Personal pronouns
- Uncountable and countable nouns
- Verb tenses
- Phrasal verbs
- Types of verbs
- Active vs passive voice
- Subject-verb agreement
A is an indefinite article (along with an ). While articles can be classed as their own part of speech, they’re also considered a type of determiner .
The indefinite articles are used to introduce nonspecific countable nouns (e.g., “a dog,” “an island”).
In is primarily classed as a preposition, but it can be classed as various other parts of speech, depending on how it is used:
- Preposition (e.g., “ in the field”)
- Noun (e.g., “I have an in with that company”)
- Adjective (e.g., “Tim is part of the in crowd”)
- Adverb (e.g., “Will you be in this evening?”)
As a part of speech, and is classed as a conjunction . Specifically, it’s a coordinating conjunction .
And can be used to connect grammatically equal parts of a sentence, such as two nouns (e.g., “a cup and plate”), or two adjectives (e.g., “strong and smart”). And can also be used to connect phrases and clauses.
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked, what is a collective noun | examples & definition.
- What Is an Adjective? | Definition, Types & Examples
- Using Conjunctions | Definition, Rules & Examples
More interesting articles
- Definite and Indefinite Articles | When to Use "The", "A" or "An"
- Ending a Sentence with a Preposition | Examples & Tips
- What Are Prepositions? | List, Examples & How to Use
- What Is a Determiner? | Definition, Types & Examples
- What Is an Adverb? Definition, Types & Examples
- What Is an Interjection? | Examples, Definition & Types
"I thought AI Proofreading was useless but.."
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

Will Paxton To Be Featured On 2024 NSAA Speech Championships: Best of the Best on Nebraska Public Media

LINCOLN, Neb. (April 4, 2024) – Nebraska’s finest high school orators will take the stage for the “2024 NSAA Speech Championships: Best of the Best” at 2 p.m. CT, Sunday, April 21, on Nebraska Public Media.
Produced at the Lincoln Northwest High School Performing Arts Center in Lincoln, the two-hour program showcases high school students performing their winning state championships speeches. It is hosted by Lincoln media personality D-Wayne Taylor, a high-energy MC, host, DJ, beatboxer and voiceover artist.
Will Paxton, a senior from Stuart Public School, won 2 Gold Medals at State Speech and will be featured in this program. He won Entertainment Speaking and Extemporaneous Speaking. The Stuart team was also the D2 Runner-Up. On the “Best of the Best” program Will will present his gold medal-winning Extemporaneous Speech entitled “Should the U.S. Postal Service be Privatized?” Will’s speech coach is Brenda Larabee.
The annual Nebraska School Activities Association event was held March 20-22 at Kearney High School and included students from Nebraska schools competing in classes A, B, C1, C2, D1 and D2.
“2024 NSAA Speech Championships: Best of the Best” can also be viewed at NebraskaPublicMedia.org .


- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.5: Types of Speeches and Speaking Occasions
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 136142

- Lisa Schreiber and Morgan Hartranft
- Millersville University via Public Speaking Project
There are three general purposes for speaking in public. The general purpose of a speech is usually determined by the occasion in which the speech will be presented. The first general purpose is to inform your audience. In an informative speech, the presenter will share information about a particular person, place, object, process, concept, or issue by defining, describing, or explaining. Occasions for which an informative speech would be presented include a report presented to coworkers, a teacher presenting information to his or her class, and a training session for a job. The second purpose for public speaking is to persuade. In a persuasive speech, the presenter will attempt to reinforce or change their audiences’ beliefs, attitudes, feelings, or values. Several occasions where persuasion is used include a sales pitch to potential customers, a politician’s campaign speech, or a debate during a public forum. The last general purpose is to commemorate or entertain. These types of speeches often strengthen the bonds between audience members from recalling a shared experience or intend to amuse audiences through humor, stories, or illustrations. Examples of this purpose include a toast, such as a best man’s speech at a wedding reception; a eulogy to praise the dead; a commencement speech at graduation; or presenting an award. It is important to note that these general purposes may overlap one another. One might wish to use some forms of entertainment while informing or persuading his or her audience.

A desire presupposes the possibility of action to achieve it; action presupposes a goal which is worth achieving. ~ Ayn Rand

Paul Heyman Declares His Speech At The WWE Hall Of Fame To Be The Greatest Speech Of All Time
R oman Reigns, Paul Heyman’s tribal chief, introduced the master of the microphone in professional wrestling during the WWE Hall of Fame induction event for the class of 2024. In the center of Philadelphia, Heyman gave one of the most open and impassioned speeches anyone had ever heard.
It seemed appropriate to pay honor to Heyman’s ground-breaking accomplishments to the wrestling profession by having him inducted in the same city where he transformed the sport with ECW in the 1990s.
A Raw and Historic WWE Hall of Fame Speech
Legends like Bully Ray and Rob Van Dam, to whom Heyman gave great opportunities, were present to witness this momentous occasion.
Heyman raised the ante at the event by donning his signature ECW gear, making jokes about certain celebrities, and thanking the supporters who helped him along the way.
More than a week later, The Bloodline’s Wiseman hailed Heyman’s speech as the greatest in WWE Hall of Fame history. He took to his platform to declare it as such, jokingly suggesting that it even surpassed monumental historical speeches like the Emancipation Proclamation.
For Paul Heyman, the evening was a pinnacle achievement, being honored in the city where his wrestling journey began. Surrounded by peers and predecessors, his induction into the WWE Hall of Fame marked the culmination of his impactful legacy that continues to resonate today.
- Explained Why Steve Austin Was Not There At Wrestlemania 40
- Samantha Irvin Received An Apology From Ricochet

Language selection
- Français fr
Remarks by the Deputy Prime Minister on putting homeownership back within reach and supporting Canadian homeowners
From: Department of Finance Canada
Our focus today is unlocking the door to the middle class for millions of younger Canadians. In all we do, we dedicate ourselves to making a better life within reach for our younger generations. Because it is what you deserve. And it is what your parents and grandparents want for you, too.
April 11, 2024 – Toronto, ON
Check against delivery
Good morning, everyone.
I would like to start by acknowledging that we are gathered on the traditional territories of many nations, including the Mississaugas of the Credit, the Anishinaabeg, the Chippewa, the Haudenosaunee, and the Wendat Peoples.
Today, too many younger Canadians feel as though the deck is stacked against them. They can get a good job, they can work hard, but far too often, the reward of a secure, prosperous middle class life remains out of reach.
We want their hard work to be rewarded. And we have a plan to help every generation—especially younger Canadians—get ahead.
One of the biggest pressures on Canadians right now is housing. And we know that this is especially true for younger Canadians.
Faced with a shortage of housing options and increasingly high rent and home prices, many younger Canadians feel that the dream of homeownership is just that—a dream.
Our government is changing that. We want homeownership to be a reality for younger Canadians. And the measures I am announcing today will help set them up for success.
One of the first steps to getting those first keys of your own is saving for a downpayment. We know this step is also one of the biggest hurdles to homeownership.
That’s why, in the spring of last year, our government introduced the Tax-Free First Home Savings Account. The Tax-Free First Home Savings Account allows Canadians to contribute up to $40,000 towards the purchase of their first home. Like an RRSP, contributions are tax deductible, and like a TFSA, withdrawals to purchase a first home are non-taxable. It’s tax-free in, and tax-free out.
Today, only a year after the launch, I am really glad to announce that more than 750,000 Canadians have opened a Tax-Free First Home Savings Account. This account is making a real difference for Canadians and it’s clear that younger Canadians want to buy a first home of their own. And they are saving their hard-earned dollars to turn that dream into a reality.
Another program our government has in place to help Canadians pull together a downpayment is the Home Buyers’ Plan. It allows Canadians to withdraw funds from their RRSP to buy their first home. Like the Tax-Free First Home Savings Account, RRSPs are great vehicles to save for a downpayment because contributions are tax deductible and any income earned in the RRSP is tax exempt.
Right now, you can withdraw up to $35,000 from your RRSP to use toward a downpayment. In many cities in Canada, though, that’s not enough. Younger Canadians know they need to save more, for longer, to afford that first downpayment.
So, to help Canadians purchase their first home, today I am announcing that we are increasing the withdrawal limit for the Home Buyers’ Plan from $35,000 to $60,000, effective April 16th this year.
This, plus the Tax-Free First Home Savings Account, can be combined, which will give younger Canadians more tools to save what is actually needed for a downpayment.
We are also giving Canadians an extra three years to repay the amount they withdraw under the Home Buyers’ Plan. Canadians who made withdrawals any time between January 1st, 2022 through to December 31st, 2025 will now have a full five years before they need to start repayment—so they can focus on their mortgage payments and other costs.
Once you’ve saved for that first downpayment, the next step to owning a home is qualifying for a mortgage. A big part of qualifying for a mortgage is ensuring you can pay the monthly costs that come with it. For many younger Canadians, these costs are a significant barrier to homeownership.
That is why today we are announcing new enhancements to the Canadian Mortgage Charter.
The Charter details the tailored mortgage relief that Canadians can expect from their banks if they are in a challenging financial situation.
Effective August 1st this year, we are allowing 30-year amortizations on insured mortgages for first-time home buyers purchasing newly built homes. That, of course, includes condos and townhouses. First-time home buyers will now have 30 years to pay off their mortgage instead of 25 years. That translates to lower monthly payments—so more younger Canadians can afford to pay that monthly mortgage on a new home.
After you get those first keys of your own, we also want to make sure Canadians who own their home are protected.
We know that some homeowners are concerned about their mortgage payments and about renewing their mortgages at a higher rate.
To further support these Canadians, we are announcing stronger measures through the Canadian Mortgage Charter that include making sure lenders contact borrowers up to 24 months in advance of a homeowner’s mortgage renewal, so that homeowners have ample time to learn about the options available to them and to make informed decisions.
The new, stronger measures in the Canadian Mortgage Charter also include providing permanent amortization relief to all homeowners—including insured homeowners at risk—without any fees or penalties.
For example, let’s say a homeowner with an insured, 25-year mortgage is experiencing financial hardship. Last year, that homeowner worked with their bank to have their mortgage amortization temporarily extended to 35 years to lower their monthly mortgage payments. Now, with the strengthened Canadian Mortgage Charter, depending on the homeowner’s circumstances, this extension can be made permanent—so that their monthly costs stay low for as long as they need.
Because Canadians work really hard to be able to buy and afford their homes. It is only fair that mortgage lenders should help Canadians do everything they can to afford their homes at a time of higher interest rates.
These are all real, tangible measures that are going to help more Canadians get into the housing market and buy their first home, while protecting Canadians who already own their home.
Our government first came to office with a vow to strengthen and expand the middle class. We delivered on that pledge by reducing poverty, especially for children and seniors, and creating millions of good jobs for Canadians. Our work isn’t over.
Thank you very much.
Page details
A UC Berkeley law professor confronts a pro-Palestinian student during a backyard dinner
A dinner for graduating law students at the University of California, Berkeley, has become the latest flashpoint over free speech and concerns about Islamophobia and antisemitism on college campuses as the war in Gaza rages on.
Video shot by a law student and shared with NBC News shows law professor Catherine Fisk trying to grab a microphone out of the hands of a Palestinian student during a protest at an invitation-only event this week.
Fisk and her spouse, law school dean Erwin Chemerinsky, hosted the event at a dinner in their home’s backyard Tuesday.
Malak Afaneh was one of 60 students invited to what was supposed to be a quiet evening before graduation next month. But it took a turn when Afaneh stood up and started delivering an unsanctioned speech through a cordless microphone she had brought with her.
“Peace and blessings upon you all,” she began. “Tonight we are gathered here in the name of commemorating our final few weeks as law students.”
The video shows Chemerinsky immediately interjecting and asking Afaneh to leave.
“Please leave. No. Please leave. Please leave,” he says.
Afaneh continues, and Fisk walks down the steps toward her. Fisk puts an arm around Afaneh’s shoulder and grabs the microphone with her other hand. The two appear to briefly jostle for the microphone before Fisk releases her grip.
Afaneh, the leader of Berkeley Law Students for Justice in Palestine, and a group of nine other protesters eventually left. She said the interaction was an “assault” and discrimination against Palestinian students. She did not file a police report, she said, because she is considering all her legal options.
“It was clear Islamophobia,” she said Thursday. “Assault is assault. No way should a law professor have put their hands on a student, period.”
Chemerinsky, who is Jewish, called the disruption “ugly and divisive.”
“I am enormously sad that we have students who are so rude as to come into my home, in my backyard, and use this social occasion for their political agenda,” he said in a statement.
At the end of a different video, Fisk says, “We agree with you about what’s going on in Palestine.”
Fisk did not respond to a request for comment.
Asked whether legal or disciplinary action would be taken against Afaneh, Chemerinsky or Fisk, Dan Mogulof, a spokesman for the university, said he could not comment on matters pertaining to students and personnel.
In an emailed statement, university Chancellor Carol Christ said she has been in touch with Chemerinsky to offer her “support and sympathy.”
“I am appalled and deeply disturbed by what occurred at Dean Chemerinsky’s home last night,” the statement read in part. “While our support for Free Speech is unwavering, we cannot condone using a social occasion at a person’s private residence as a platform for protest.”
Afaneh said the chancellor has not contacted her.
Afaneh, a law clerk at the Council on American-Islamic Relations’ Bay Area office, had encouraged students to boycott the dinner because the university has investments in companies with ties to Israel.
Chemerinsky said in his statement that students had circulated a poster on campus and social media with a caricature of him holding a bloody knife and fork, with the words “No dinner with Zionist Chem while Gaza starves.”
“I never thought I would see such blatant antisemitism, with an image that invokes the horrible antisemitic trope of blood libel and that attacks me for no apparent reason other than I am Jewish,” he said.
Afaneh said the boycott targeted Chemerinsky because he is a representative of the university and has influence with school officials.
She and the nine other students agreed about two weeks ago to disrupt the dinner by giving a speech and then walking out, Afaneh said. They consulted attorneys beforehand to understand their free speech rights and what legal fallout they could expect, she said.
The Foundation for Individual Rights and Expression, a watchdog group, said on X : “Peaceful protest on public campuses is protected speech. Disruptive protest and trespassing on private property is not.
“The First Amendment doesn’t protect seriously disrupting events on public college campuses, much less at someone’s backyard dinner party.”
The UC Berkeley School of Law said in a statement Thursday that it paid for the dinner at the private residence, “as it does for all the student dinners.”
“There is not a First Amendment right to use private property for speech,” it said. “Even if the event had been held on the legal equivalent of government property, it still would be what is known as a ‘limited public forum,’ where there are allowable limits on who can attend the event, and what can be expressed.
“The source of funding for the event has no bearing on either,” it said.
UC Berkeley, the birthplace of the Free Speech Movement in the 1960s, adopted guidelines in 1966 to help students and administrators navigate First Amendment issues, which included creating “time, place and manner” policies.
Some students have recently been ignoring the guidelines, insisting they are being used as a tool to suppress their free speech, said law student Maryam Alhakim, a protester who attended the dinner.
“It’s being used against us in a way to curtail our activism,” Alhakim said.
Zahra Billoo, executive director of CAIR Bay Area, said she was more concerned about how a student was treated by a faculty member.
“It says something deeper about the racist way in which they perceive Palestinian students and those who stand in solidarity with them,” she said. “How would it have hurt for her to have made her speech?”
The confrontation is the latest in a spate of heated exchanges on college campuses across the county since the Israel-Hamas war started on Oct. 7.
UC Berkeley graduate students have spent months protesting beneath the school’s iconic Sather Gate, sometimes clashing with pro-Israel student groups. In February, a protest turned violent at an event featuring a former member of the Israeli army.
Last Friday, 20 students at Pomona College in Southern California were arrested after they stormed and occupied the college president’s office.
Several students were suspended from Columbia University in New York this month after they hosted an unsanctioned event on campus featuring a speaker linked to a terrorist organization.
Alicia Victoria Lozano is a California-based reporter for NBC News focusing on climate change, wildfires and the changing politics of drug laws.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Informative speech. Informative speeches aim to educate an audience on a particular topic or message. Unlike demonstrative speeches, they don't use visual aids. They do, however, use facts, data and statistics to help audiences grasp a concept. These facts and statistics help back any claims or assertions you make.
Manuscript Speech. Memorized Speech. Impromptu Speech. Extemporaneous Speech. Speeches can be categorized into four broad areas depending on the amount of preparation that is undertaken and depending upon the nature of the occasion. The four types of speeches are manuscript, memorized, extemporaneous, and impromptu.
Resources for demonstration speeches. 1. How to write a demonstration speech Guidelines and suggestions covering:. choosing the best topic: one aligning with your own interests, the audience's, the setting for the speech and the time available to you; how to plan, prepare and deliver your speech - step by step guidelines for sequencing and organizing your material plus a printable blank ...
Four Types of Speeches. Speeches can be categorized into four broad areas depending on the amount of preparation that is undertaken and depending upon the nature of the occasion. The four types of speeches are manuscript, memorized, extemporaneous, and impromptu. Our aim is to acquaint you with these four different modes of delivery, to provide ...
Oratorical Speech. Oratorical speeches are delivered in the style used by an orator. Its name is a little redundant because "orator" and "oratorical" both relate to the giving of speeches. These types of speeches are usually given at a special celebration such as an inauguration or ribbon-cutting ceremony. They can be long and formal ...
The most common types of informative speeches are definition, explanation, description, and demonstration. A definition speech explains a concept, theory, or philosophy about which the audience knows little. The purpose of the speech is to inform the audience so they understand the main aspects of the subject matter.
In a persuasive speech, the presenter will attempt to reinforce or change their audiences' beliefs, attitudes, feelings, or values. Several occasions where persuasion is used include a sales pitch to potential customers, a politician's campaign speech, or a debate during a public forum. The last general purpose is to commemorate or entertain.
The content, of course, but also the structure. All great speakers overlay their content on a well-known structure. Your speech structure is the glue that binds your points together. Without it, you cannot really have the impact you desire to have on the audience. The beauty of this is that a good structure is so subtle it is almost invisible.
Occasions for which an informative speech would be presented include a report presented to coworkers, a teacher presenting information to his or her class, and a training session for a job. The second purpose for public speaking is to persuade. In a persuasive speech, the presenter will attempt to reinforce or change their audiences' beliefs ...
Writing the Speech. After you have analyzed your audience, selected the topic, collected supporting materials, and written an outline, it is time to write the speech with an introduction, body and conclusion. These major parts follow the broadcaster's maxim: (1) Tell them what you are going to tell them. (2) Tell them.
2. Presentation Speech. These speeches are usually given at award ceremonies, where an individual presents an award or prize to a person. The main purpose of the presentation speech is to provide recognition of the recipient's accomplishments. 3. Toast. A toast is a brief tribute to a particular person or an event.
Obviously, there are many different persuasive speech topics you could select for a public speaking class. Anything from localized claims like changing a specific college or university policy to larger societal claims like adding more enforcement against the trafficking of women and children in the United States could make for an interesting persuasive speech.
Informative Speaking. One of the most common types of public speaking is informative speaking. The primary purpose of informative presentations is to share one's knowledge of a subject with an audience. Reasons for making an informative speech vary widely. For example, you might be asked to instruct a group of coworkers on how to use new ...
There are solo as well as group activities. 3. For and Against. 'For and Against' encourages flexibility: the ability to see a topic from opposing sides. A speaker has 30 seconds to talk 'for' a topic and then another 30 seconds to speak 'against' it. Prepare and print out a selection of controversial speech topics.
Identify the four types of speech delivery methods and when to use them. There are four basic methods of speech delivery: manuscript, memorized, impromptu, and extemporaneous. ... In your public speaking class, most of your speeches will probably be delivered extemporaneously. Try It . As per the Oxford English Dictionary's entry for "Off the ...
Types of Informative Speeches. In the last section we examined how informative speakers need to be objective, credible, knowledgeable, and how they need to make the topic relevant to their audience. This section discusses the four primary types of informative speeches. These include definitional speeches, descriptive speeches, explanatory ...
The two general purposes of speeches this section will discuss are speaking to inform and speaking to persuade. Public speaking students will write and deliver these two types of speeches in this class. It is important to understand the differences before we begin our first LIVE speech, the informative speech. While any topic can be informative ...
The first type of special occasion speech is the speech of introduction, which is a mini speech given by the host of a ceremony that introduces another speaker and their speech. Few things are worse than when the introducer of a speaker stands up and says, "This is Wyatt Ford. He's going to talk about stress.".
Speeches. Public speaking types: Motivational or inspirational. Speeches are typically "big" talks that are meant to be heavily persuasive and informative to large crowds—usually comprising several hundred people or more. Most speeches will include at least one focal point you want your audience to remember after they leave.
Demonstrative. Persuasive. Entertaining. 1. Informative Speech. An informative speech is a type of public speaking that aims to educate or provide information to the audience about a specific topic. The main purpose of this speech is to present facts, concepts, or ideas in a clear and understandable manner. . .
The different types of public speaking are: Speaking to Inform (informative, argumentative speech) Speaking to Persuade, Motivate, or Take Action (persuasive, argumentative, controversial, policy speeches) Speaking to Entertain (funny, special occasion speeches) In this article: The 3 Basic Types of Public Speaking.
A part of speech (also called a word class) is a category that describes the role a word plays in a sentence.Understanding the different parts of speech can help you analyze how words function in a sentence and improve your writing. The parts of speech are classified differently in different grammars, but most traditional grammars list eight parts of speech in English: nouns, pronouns, verbs ...
Will's speech coach is Brenda Larabee. The annual Nebraska School Activities Association event was held March 20-22 at Kearney High School and included students from Nebraska schools competing in classes A, B, C1, C2, D1 and D2. "2024 NSAA Speech Championships: Best of the Best" can also be viewed at NebraskaPublicMedia.org.
Occasions for which an informative speech would be presented include a report presented to coworkers, a teacher presenting information to his or her class, and a training session for a job. The second purpose for public speaking is to persuade. In a persuasive speech, the presenter will attempt to reinforce or change their audiences' beliefs ...
Democracy is not inevitable. It has succeeded and succeeds because it has delivered a good life for the middle class. When democracy fails to deliver on that most fundamental social contract, we should not be surprised if the middle class loses faith in democracy itself. Tax policy is not only, or chiefly, the province of accountants or economists.
More than a week later, The Bloodline's Wiseman hailed Heyman's speech as the greatest in WWE Hall of Fame history. He took to his platform to declare it as such, jokingly suggesting that it ...
Today, too many younger Canadians feel as though the deck is stacked against them. They can get a good job, they can work hard, but far too often, the reward of a secure, prosperous middle class life remains out of reach. We want their hard work to be rewarded. And we have a plan to help every generation—especially younger Canadians—get ahead.
UC Berkeley, the birthplace of the Free Speech Movement in the 1960s, adopted guidelines in 1966 to help students and administrators navigate First Amendment issues, which included creating ...