Reference management. Clean and simple.

How to write a thesis statement + examples

What is a thesis statement?
Is a thesis statement a question, how do you write a good thesis statement, how do i know if my thesis statement is good, examples of thesis statements, helpful resources on how to write a thesis statement, frequently asked questions about writing a thesis statement, related articles.
A thesis statement is the main argument of your paper or thesis.
The thesis statement is one of the most important elements of any piece of academic writing . It is a brief statement of your paper’s main argument. Essentially, you are stating what you will be writing about.
You can see your thesis statement as an answer to a question. While it also contains the question, it should really give an answer to the question with new information and not just restate or reiterate it.
Your thesis statement is part of your introduction. Learn more about how to write a good thesis introduction in our introduction guide .
A thesis statement is not a question. A statement must be arguable and provable through evidence and analysis. While your thesis might stem from a research question, it should be in the form of a statement.
Tip: A thesis statement is typically 1-2 sentences. For a longer project like a thesis, the statement may be several sentences or a paragraph.
A good thesis statement needs to do the following:
- Condense the main idea of your thesis into one or two sentences.
- Answer your project’s main research question.
- Clearly state your position in relation to the topic .
- Make an argument that requires support or evidence.
Once you have written down a thesis statement, check if it fulfills the following criteria:
- Your statement needs to be provable by evidence. As an argument, a thesis statement needs to be debatable.
- Your statement needs to be precise. Do not give away too much information in the thesis statement and do not load it with unnecessary information.
- Your statement cannot say that one solution is simply right or simply wrong as a matter of fact. You should draw upon verified facts to persuade the reader of your solution, but you cannot just declare something as right or wrong.
As previously mentioned, your thesis statement should answer a question.
If the question is:
What do you think the City of New York should do to reduce traffic congestion?
A good thesis statement restates the question and answers it:
In this paper, I will argue that the City of New York should focus on providing exclusive lanes for public transport and adaptive traffic signals to reduce traffic congestion by the year 2035.
Here is another example. If the question is:
How can we end poverty?
A good thesis statement should give more than one solution to the problem in question:
In this paper, I will argue that introducing universal basic income can help reduce poverty and positively impact the way we work.
- The Writing Center of the University of North Carolina has a list of questions to ask to see if your thesis is strong .
A thesis statement is part of the introduction of your paper. It is usually found in the first or second paragraph to let the reader know your research purpose from the beginning.
In general, a thesis statement should have one or two sentences. But the length really depends on the overall length of your project. Take a look at our guide about the length of thesis statements for more insight on this topic.
Here is a list of Thesis Statement Examples that will help you understand better how to write them.
Every good essay should include a thesis statement as part of its introduction, no matter the academic level. Of course, if you are a high school student you are not expected to have the same type of thesis as a PhD student.
Here is a great YouTube tutorial showing How To Write An Essay: Thesis Statements .


Thesis Statements
What this handout is about.
This handout describes what a thesis statement is, how thesis statements work in your writing, and how you can craft or refine one for your draft.
Introduction
Writing in college often takes the form of persuasion—convincing others that you have an interesting, logical point of view on the subject you are studying. Persuasion is a skill you practice regularly in your daily life. You persuade your roommate to clean up, your parents to let you borrow the car, your friend to vote for your favorite candidate or policy. In college, course assignments often ask you to make a persuasive case in writing. You are asked to convince your reader of your point of view. This form of persuasion, often called academic argument, follows a predictable pattern in writing. After a brief introduction of your topic, you state your point of view on the topic directly and often in one sentence. This sentence is the thesis statement, and it serves as a summary of the argument you’ll make in the rest of your paper.
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement:
- tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion.
- is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper.
- directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself. The subject, or topic, of an essay might be World War II or Moby Dick; a thesis must then offer a way to understand the war or the novel.
- makes a claim that others might dispute.
- is usually a single sentence near the beginning of your paper (most often, at the end of the first paragraph) that presents your argument to the reader. The rest of the paper, the body of the essay, gathers and organizes evidence that will persuade the reader of the logic of your interpretation.
If your assignment asks you to take a position or develop a claim about a subject, you may need to convey that position or claim in a thesis statement near the beginning of your draft. The assignment may not explicitly state that you need a thesis statement because your instructor may assume you will include one. When in doubt, ask your instructor if the assignment requires a thesis statement. When an assignment asks you to analyze, to interpret, to compare and contrast, to demonstrate cause and effect, or to take a stand on an issue, it is likely that you are being asked to develop a thesis and to support it persuasively. (Check out our handout on understanding assignments for more information.)
How do I create a thesis?
A thesis is the result of a lengthy thinking process. Formulating a thesis is not the first thing you do after reading an essay assignment. Before you develop an argument on any topic, you have to collect and organize evidence, look for possible relationships between known facts (such as surprising contrasts or similarities), and think about the significance of these relationships. Once you do this thinking, you will probably have a “working thesis” that presents a basic or main idea and an argument that you think you can support with evidence. Both the argument and your thesis are likely to need adjustment along the way.
Writers use all kinds of techniques to stimulate their thinking and to help them clarify relationships or comprehend the broader significance of a topic and arrive at a thesis statement. For more ideas on how to get started, see our handout on brainstorming .
How do I know if my thesis is strong?
If there’s time, run it by your instructor or make an appointment at the Writing Center to get some feedback. Even if you do not have time to get advice elsewhere, you can do some thesis evaluation of your own. When reviewing your first draft and its working thesis, ask yourself the following :
- Do I answer the question? Re-reading the question prompt after constructing a working thesis can help you fix an argument that misses the focus of the question. If the prompt isn’t phrased as a question, try to rephrase it. For example, “Discuss the effect of X on Y” can be rephrased as “What is the effect of X on Y?”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? If your thesis simply states facts that no one would, or even could, disagree with, it’s possible that you are simply providing a summary, rather than making an argument.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? Thesis statements that are too vague often do not have a strong argument. If your thesis contains words like “good” or “successful,” see if you could be more specific: why is something “good”; what specifically makes something “successful”?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? If a reader’s first response is likely to be “So what?” then you need to clarify, to forge a relationship, or to connect to a larger issue.
- Does my essay support my thesis specifically and without wandering? If your thesis and the body of your essay do not seem to go together, one of them has to change. It’s okay to change your working thesis to reflect things you have figured out in the course of writing your paper. Remember, always reassess and revise your writing as necessary.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? If a reader’s first response is “how?” or “why?” your thesis may be too open-ended and lack guidance for the reader. See what you can add to give the reader a better take on your position right from the beginning.
Suppose you are taking a course on contemporary communication, and the instructor hands out the following essay assignment: “Discuss the impact of social media on public awareness.” Looking back at your notes, you might start with this working thesis:
Social media impacts public awareness in both positive and negative ways.
You can use the questions above to help you revise this general statement into a stronger thesis.
- Do I answer the question? You can analyze this if you rephrase “discuss the impact” as “what is the impact?” This way, you can see that you’ve answered the question only very generally with the vague “positive and negative ways.”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not likely. Only people who maintain that social media has a solely positive or solely negative impact could disagree.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? No. What are the positive effects? What are the negative effects?
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? No. Why are they positive? How are they positive? What are their causes? Why are they negative? How are they negative? What are their causes?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? No. Why should anyone care about the positive and/or negative impact of social media?
After thinking about your answers to these questions, you decide to focus on the one impact you feel strongly about and have strong evidence for:
Because not every voice on social media is reliable, people have become much more critical consumers of information, and thus, more informed voters.
This version is a much stronger thesis! It answers the question, takes a specific position that others can challenge, and it gives a sense of why it matters.
Let’s try another. Suppose your literature professor hands out the following assignment in a class on the American novel: Write an analysis of some aspect of Mark Twain’s novel Huckleberry Finn. “This will be easy,” you think. “I loved Huckleberry Finn!” You grab a pad of paper and write:
Mark Twain’s Huckleberry Finn is a great American novel.
You begin to analyze your thesis:
- Do I answer the question? No. The prompt asks you to analyze some aspect of the novel. Your working thesis is a statement of general appreciation for the entire novel.
Think about aspects of the novel that are important to its structure or meaning—for example, the role of storytelling, the contrasting scenes between the shore and the river, or the relationships between adults and children. Now you write:
In Huckleberry Finn, Mark Twain develops a contrast between life on the river and life on the shore.
- Do I answer the question? Yes!
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not really. This contrast is well-known and accepted.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? It’s getting there–you have highlighted an important aspect of the novel for investigation. However, it’s still not clear what your analysis will reveal.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? Not yet. Compare scenes from the book and see what you discover. Free write, make lists, jot down Huck’s actions and reactions and anything else that seems interesting.
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? What’s the point of this contrast? What does it signify?”
After examining the evidence and considering your own insights, you write:
Through its contrasting river and shore scenes, Twain’s Huckleberry Finn suggests that to find the true expression of American democratic ideals, one must leave “civilized” society and go back to nature.
This final thesis statement presents an interpretation of a literary work based on an analysis of its content. Of course, for the essay itself to be successful, you must now present evidence from the novel that will convince the reader of your interpretation.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Lunsford, Andrea A. 2015. The St. Martin’s Handbook , 8th ed. Boston: Bedford/St Martin’s.
Ramage, John D., John C. Bean, and June Johnson. 2018. The Allyn & Bacon Guide to Writing , 8th ed. New York: Pearson.
Ruszkiewicz, John J., Christy Friend, Daniel Seward, and Maxine Hairston. 2010. The Scott, Foresman Handbook for Writers , 9th ed. Boston: Pearson Education.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
- Skip to Content
- Skip to Main Navigation
- Skip to Search

Indiana University Bloomington Indiana University Bloomington IU Bloomington

- Mission, Vision, and Inclusive Language Statement
- Locations & Hours
- Undergraduate Employment
- Graduate Employment
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Newsletter Archive
- Support WTS
- Schedule an Appointment
- Online Tutoring
- Before your Appointment
- WTS Policies
- Group Tutoring
- Students Referred by Instructors
- Paid External Editing Services
- Writing Guides
- Scholarly Write-in
- Dissertation Writing Groups
- Journal Article Writing Groups
- Early Career Graduate Student Writing Workshop
- Workshops for Graduate Students
- Teaching Resources
- Syllabus Information
- Course-specific Tutoring
- Nominate a Peer Tutor
- Tutoring Feedback
- Schedule Appointment
- Campus Writing Program
Writing Tutorial Services
How to write a thesis statement, what is a thesis statement.
Almost all of us—even if we don’t do it consciously—look early in an essay for a one- or two-sentence condensation of the argument or analysis that is to follow. We refer to that condensation as a thesis statement.
Why Should Your Essay Contain a Thesis Statement?
- to test your ideas by distilling them into a sentence or two
- to better organize and develop your argument
- to provide your reader with a “guide” to your argument
In general, your thesis statement will accomplish these goals if you think of the thesis as the answer to the question your paper explores.
How Can You Write a Good Thesis Statement?
Here are some helpful hints to get you started. You can either scroll down or select a link to a specific topic.
How to Generate a Thesis Statement if the Topic is Assigned How to Generate a Thesis Statement if the Topic is not Assigned How to Tell a Strong Thesis Statement from a Weak One
How to Generate a Thesis Statement if the Topic is Assigned
Almost all assignments, no matter how complicated, can be reduced to a single question. Your first step, then, is to distill the assignment into a specific question. For example, if your assignment is, “Write a report to the local school board explaining the potential benefits of using computers in a fourth-grade class,” turn the request into a question like, “What are the potential benefits of using computers in a fourth-grade class?” After you’ve chosen the question your essay will answer, compose one or two complete sentences answering that question.
Q: “What are the potential benefits of using computers in a fourth-grade class?” A: “The potential benefits of using computers in a fourth-grade class are . . .”
A: “Using computers in a fourth-grade class promises to improve . . .”
The answer to the question is the thesis statement for the essay.
[ Back to top ]
How to Generate a Thesis Statement if the Topic is not Assigned
Even if your assignment doesn’t ask a specific question, your thesis statement still needs to answer a question about the issue you’d like to explore. In this situation, your job is to figure out what question you’d like to write about.
A good thesis statement will usually include the following four attributes:
- take on a subject upon which reasonable people could disagree
- deal with a subject that can be adequately treated given the nature of the assignment
- express one main idea
- assert your conclusions about a subject
Let’s see how to generate a thesis statement for a social policy paper.
Brainstorm the topic . Let’s say that your class focuses upon the problems posed by changes in the dietary habits of Americans. You find that you are interested in the amount of sugar Americans consume.
You start out with a thesis statement like this:
Sugar consumption.
This fragment isn’t a thesis statement. Instead, it simply indicates a general subject. Furthermore, your reader doesn’t know what you want to say about sugar consumption.
Narrow the topic . Your readings about the topic, however, have led you to the conclusion that elementary school children are consuming far more sugar than is healthy.
You change your thesis to look like this:
Reducing sugar consumption by elementary school children.
This fragment not only announces your subject, but it focuses on one segment of the population: elementary school children. Furthermore, it raises a subject upon which reasonable people could disagree, because while most people might agree that children consume more sugar than they used to, not everyone would agree on what should be done or who should do it. You should note that this fragment is not a thesis statement because your reader doesn’t know your conclusions on the topic.
Take a position on the topic. After reflecting on the topic a little while longer, you decide that what you really want to say about this topic is that something should be done to reduce the amount of sugar these children consume.
You revise your thesis statement to look like this:
More attention should be paid to the food and beverage choices available to elementary school children.
This statement asserts your position, but the terms more attention and food and beverage choices are vague.
Use specific language . You decide to explain what you mean about food and beverage choices , so you write:
Experts estimate that half of elementary school children consume nine times the recommended daily allowance of sugar.
This statement is specific, but it isn’t a thesis. It merely reports a statistic instead of making an assertion.
Make an assertion based on clearly stated support. You finally revise your thesis statement one more time to look like this:
Because half of all American elementary school children consume nine times the recommended daily allowance of sugar, schools should be required to replace the beverages in soda machines with healthy alternatives.
Notice how the thesis answers the question, “What should be done to reduce sugar consumption by children, and who should do it?” When you started thinking about the paper, you may not have had a specific question in mind, but as you became more involved in the topic, your ideas became more specific. Your thesis changed to reflect your new insights.
How to Tell a Strong Thesis Statement from a Weak One
1. a strong thesis statement takes some sort of stand..
Remember that your thesis needs to show your conclusions about a subject. For example, if you are writing a paper for a class on fitness, you might be asked to choose a popular weight-loss product to evaluate. Here are two thesis statements:
There are some negative and positive aspects to the Banana Herb Tea Supplement.
This is a weak thesis statement. First, it fails to take a stand. Second, the phrase negative and positive aspects is vague.
Because Banana Herb Tea Supplement promotes rapid weight loss that results in the loss of muscle and lean body mass, it poses a potential danger to customers.
This is a strong thesis because it takes a stand, and because it's specific.
2. A strong thesis statement justifies discussion.
Your thesis should indicate the point of the discussion. If your assignment is to write a paper on kinship systems, using your own family as an example, you might come up with either of these two thesis statements:
My family is an extended family.
This is a weak thesis because it merely states an observation. Your reader won’t be able to tell the point of the statement, and will probably stop reading.
While most American families would view consanguineal marriage as a threat to the nuclear family structure, many Iranian families, like my own, believe that these marriages help reinforce kinship ties in an extended family.
This is a strong thesis because it shows how your experience contradicts a widely-accepted view. A good strategy for creating a strong thesis is to show that the topic is controversial. Readers will be interested in reading the rest of the essay to see how you support your point.
3. A strong thesis statement expresses one main idea.
Readers need to be able to see that your paper has one main point. If your thesis statement expresses more than one idea, then you might confuse your readers about the subject of your paper. For example:
Companies need to exploit the marketing potential of the Internet, and Web pages can provide both advertising and customer support.
This is a weak thesis statement because the reader can’t decide whether the paper is about marketing on the Internet or Web pages. To revise the thesis, the relationship between the two ideas needs to become more clear. One way to revise the thesis would be to write:
Because the Internet is filled with tremendous marketing potential, companies should exploit this potential by using Web pages that offer both advertising and customer support.
This is a strong thesis because it shows that the two ideas are related. Hint: a great many clear and engaging thesis statements contain words like because , since , so , although , unless , and however .
4. A strong thesis statement is specific.
A thesis statement should show exactly what your paper will be about, and will help you keep your paper to a manageable topic. For example, if you're writing a seven-to-ten page paper on hunger, you might say:
World hunger has many causes and effects.
This is a weak thesis statement for two major reasons. First, world hunger can’t be discussed thoroughly in seven to ten pages. Second, many causes and effects is vague. You should be able to identify specific causes and effects. A revised thesis might look like this:
Hunger persists in Glandelinia because jobs are scarce and farming in the infertile soil is rarely profitable.
This is a strong thesis statement because it narrows the subject to a more specific and manageable topic, and it also identifies the specific causes for the existence of hunger.
Produced by Writing Tutorial Services, Indiana University, Bloomington, IN
Writing Tutorial Services social media channels

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Writing a Paper: Thesis Statements
Basics of thesis statements.
The thesis statement is the brief articulation of your paper's central argument and purpose. You might hear it referred to as simply a "thesis." Every scholarly paper should have a thesis statement, and strong thesis statements are concise, specific, and arguable. Concise means the thesis is short: perhaps one or two sentences for a shorter paper. Specific means the thesis deals with a narrow and focused topic, appropriate to the paper's length. Arguable means that a scholar in your field could disagree (or perhaps already has!).
Strong thesis statements address specific intellectual questions, have clear positions, and use a structure that reflects the overall structure of the paper. Read on to learn more about constructing a strong thesis statement.
Being Specific
This thesis statement has no specific argument:
Needs Improvement: In this essay, I will examine two scholarly articles to find similarities and differences.
This statement is concise, but it is neither specific nor arguable—a reader might wonder, "Which scholarly articles? What is the topic of this paper? What field is the author writing in?" Additionally, the purpose of the paper—to "examine…to find similarities and differences" is not of a scholarly level. Identifying similarities and differences is a good first step, but strong academic argument goes further, analyzing what those similarities and differences might mean or imply.
Better: In this essay, I will argue that Bowler's (2003) autocratic management style, when coupled with Smith's (2007) theory of social cognition, can reduce the expenses associated with employee turnover.
The new revision here is still concise, as well as specific and arguable. We can see that it is specific because the writer is mentioning (a) concrete ideas and (b) exact authors. We can also gather the field (business) and the topic (management and employee turnover). The statement is arguable because the student goes beyond merely comparing; he or she draws conclusions from that comparison ("can reduce the expenses associated with employee turnover").
Making a Unique Argument
This thesis draft repeats the language of the writing prompt without making a unique argument:
Needs Improvement: The purpose of this essay is to monitor, assess, and evaluate an educational program for its strengths and weaknesses. Then, I will provide suggestions for improvement.
You can see here that the student has simply stated the paper's assignment, without articulating specifically how he or she will address it. The student can correct this error simply by phrasing the thesis statement as a specific answer to the assignment prompt.
Better: Through a series of student interviews, I found that Kennedy High School's antibullying program was ineffective. In order to address issues of conflict between students, I argue that Kennedy High School should embrace policies outlined by the California Department of Education (2010).
Words like "ineffective" and "argue" show here that the student has clearly thought through the assignment and analyzed the material; he or she is putting forth a specific and debatable position. The concrete information ("student interviews," "antibullying") further prepares the reader for the body of the paper and demonstrates how the student has addressed the assignment prompt without just restating that language.
Creating a Debate
This thesis statement includes only obvious fact or plot summary instead of argument:
Needs Improvement: Leadership is an important quality in nurse educators.
A good strategy to determine if your thesis statement is too broad (and therefore, not arguable) is to ask yourself, "Would a scholar in my field disagree with this point?" Here, we can see easily that no scholar is likely to argue that leadership is an unimportant quality in nurse educators. The student needs to come up with a more arguable claim, and probably a narrower one; remember that a short paper needs a more focused topic than a dissertation.
Better: Roderick's (2009) theory of participatory leadership is particularly appropriate to nurse educators working within the emergency medicine field, where students benefit most from collegial and kinesthetic learning.
Here, the student has identified a particular type of leadership ("participatory leadership"), narrowing the topic, and has made an arguable claim (this type of leadership is "appropriate" to a specific type of nurse educator). Conceivably, a scholar in the nursing field might disagree with this approach. The student's paper can now proceed, providing specific pieces of evidence to support the arguable central claim.
Choosing the Right Words
This thesis statement uses large or scholarly-sounding words that have no real substance:
Needs Improvement: Scholars should work to seize metacognitive outcomes by harnessing discipline-based networks to empower collaborative infrastructures.
There are many words in this sentence that may be buzzwords in the student's field or key terms taken from other texts, but together they do not communicate a clear, specific meaning. Sometimes students think scholarly writing means constructing complex sentences using special language, but actually it's usually a stronger choice to write clear, simple sentences. When in doubt, remember that your ideas should be complex, not your sentence structure.
Better: Ecologists should work to educate the U.S. public on conservation methods by making use of local and national green organizations to create a widespread communication plan.
Notice in the revision that the field is now clear (ecology), and the language has been made much more field-specific ("conservation methods," "green organizations"), so the reader is able to see concretely the ideas the student is communicating.
Leaving Room for Discussion
This thesis statement is not capable of development or advancement in the paper:
Needs Improvement: There are always alternatives to illegal drug use.
This sample thesis statement makes a claim, but it is not a claim that will sustain extended discussion. This claim is the type of claim that might be appropriate for the conclusion of a paper, but in the beginning of the paper, the student is left with nowhere to go. What further points can be made? If there are "always alternatives" to the problem the student is identifying, then why bother developing a paper around that claim? Ideally, a thesis statement should be complex enough to explore over the length of the entire paper.
Better: The most effective treatment plan for methamphetamine addiction may be a combination of pharmacological and cognitive therapy, as argued by Baker (2008), Smith (2009), and Xavier (2011).
In the revised thesis, you can see the student make a specific, debatable claim that has the potential to generate several pages' worth of discussion. When drafting a thesis statement, think about the questions your thesis statement will generate: What follow-up inquiries might a reader have? In the first example, there are almost no additional questions implied, but the revised example allows for a good deal more exploration.
Thesis Mad Libs
If you are having trouble getting started, try using the models below to generate a rough model of a thesis statement! These models are intended for drafting purposes only and should not appear in your final work.
- In this essay, I argue ____, using ______ to assert _____.
- While scholars have often argued ______, I argue______, because_______.
- Through an analysis of ______, I argue ______, which is important because_______.
Words to Avoid and to Embrace
When drafting your thesis statement, avoid words like explore, investigate, learn, compile, summarize , and explain to describe the main purpose of your paper. These words imply a paper that summarizes or "reports," rather than synthesizing and analyzing.
Instead of the terms above, try words like argue, critique, question , and interrogate . These more analytical words may help you begin strongly, by articulating a specific, critical, scholarly position.
Read Kayla's blog post for tips on taking a stand in a well-crafted thesis statement.
Related Resources
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Introductions
- Next Page: Conclusions
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
How to Write a Strong Thesis Statement: 4 Steps + Examples

What’s Covered:
What is the purpose of a thesis statement, writing a good thesis statement: 4 steps, common pitfalls to avoid, where to get your essay edited for free.
When you set out to write an essay, there has to be some kind of point to it, right? Otherwise, your essay would just be a big jumble of word salad that makes absolutely no sense. An essay needs a central point that ties into everything else. That main point is called a thesis statement, and it’s the core of any essay or research paper.
You may hear about Master degree candidates writing a thesis, and that is an entire paper–not to be confused with the thesis statement, which is typically one sentence that contains your paper’s focus.
Read on to learn more about thesis statements and how to write them. We’ve also included some solid examples for you to reference.
Typically the last sentence of your introductory paragraph, the thesis statement serves as the roadmap for your essay. When your reader gets to the thesis statement, they should have a clear outline of your main point, as well as the information you’ll be presenting in order to either prove or support your point.
The thesis statement should not be confused for a topic sentence , which is the first sentence of every paragraph in your essay. If you need help writing topic sentences, numerous resources are available. Topic sentences should go along with your thesis statement, though.
Since the thesis statement is the most important sentence of your entire essay or paper, it’s imperative that you get this part right. Otherwise, your paper will not have a good flow and will seem disjointed. That’s why it’s vital not to rush through developing one. It’s a methodical process with steps that you need to follow in order to create the best thesis statement possible.
Step 1: Decide what kind of paper you’re writing
When you’re assigned an essay, there are several different types you may get. Argumentative essays are designed to get the reader to agree with you on a topic. Informative or expository essays present information to the reader. Analytical essays offer up a point and then expand on it by analyzing relevant information. Thesis statements can look and sound different based on the type of paper you’re writing. For example:
- Argumentative: The United States needs a viable third political party to decrease bipartisanship, increase options, and help reduce corruption in government.
- Informative: The Libertarian party has thrown off elections before by gaining enough support in states to get on the ballot and by taking away crucial votes from candidates.
- Analytical: An analysis of past presidential elections shows that while third party votes may have been the minority, they did affect the outcome of the elections in 2020, 2016, and beyond.
Step 2: Figure out what point you want to make
Once you know what type of paper you’re writing, you then need to figure out the point you want to make with your thesis statement, and subsequently, your paper. In other words, you need to decide to answer a question about something, such as:
- What impact did reality TV have on American society?
- How has the musical Hamilton affected perception of American history?
- Why do I want to major in [chosen major here]?
If you have an argumentative essay, then you will be writing about an opinion. To make it easier, you may want to choose an opinion that you feel passionate about so that you’re writing about something that interests you. For example, if you have an interest in preserving the environment, you may want to choose a topic that relates to that.
If you’re writing your college essay and they ask why you want to attend that school, you may want to have a main point and back it up with information, something along the lines of:
“Attending Harvard University would benefit me both academically and professionally, as it would give me a strong knowledge base upon which to build my career, develop my network, and hopefully give me an advantage in my chosen field.”
Step 3: Determine what information you’ll use to back up your point
Once you have the point you want to make, you need to figure out how you plan to back it up throughout the rest of your essay. Without this information, it will be hard to either prove or argue the main point of your thesis statement. If you decide to write about the Hamilton example, you may decide to address any falsehoods that the writer put into the musical, such as:
“The musical Hamilton, while accurate in many ways, leaves out key parts of American history, presents a nationalist view of founding fathers, and downplays the racism of the times.”
Once you’ve written your initial working thesis statement, you’ll then need to get information to back that up. For example, the musical completely leaves out Benjamin Franklin, portrays the founding fathers in a nationalist way that is too complimentary, and shows Hamilton as a staunch abolitionist despite the fact that his family likely did own slaves.
Step 4: Revise and refine your thesis statement before you start writing
Read through your thesis statement several times before you begin to compose your full essay. You need to make sure the statement is ironclad, since it is the foundation of the entire paper. Edit it or have a peer review it for you to make sure everything makes sense and that you feel like you can truly write a paper on the topic. Once you’ve done that, you can then begin writing your paper.
When writing a thesis statement, there are some common pitfalls you should avoid so that your paper can be as solid as possible. Make sure you always edit the thesis statement before you do anything else. You also want to ensure that the thesis statement is clear and concise. Don’t make your reader hunt for your point. Finally, put your thesis statement at the end of the first paragraph and have your introduction flow toward that statement. Your reader will expect to find your statement in its traditional spot.
If you’re having trouble getting started, or need some guidance on your essay, there are tools available that can help you. CollegeVine offers a free peer essay review tool where one of your peers can read through your essay and provide you with valuable feedback. Getting essay feedback from a peer can help you wow your instructor or college admissions officer with an impactful essay that effectively illustrates your point.

Related CollegeVine Blog Posts

While Sandel argues that pursuing perfection through genetic engineering would decrease our sense of humility, he claims that the sense of solidarity we would lose is also important.
This thesis summarizes several points in Sandel’s argument, but it does not make a claim about how we should understand his argument. A reader who read Sandel’s argument would not also need to read an essay based on this descriptive thesis.
Broad thesis (arguable, but difficult to support with evidence)
Michael Sandel’s arguments about genetic engineering do not take into consideration all the relevant issues.
This is an arguable claim because it would be possible to argue against it by saying that Michael Sandel’s arguments do take all of the relevant issues into consideration. But the claim is too broad. Because the thesis does not specify which “issues” it is focused on—or why it matters if they are considered—readers won’t know what the rest of the essay will argue, and the writer won’t know what to focus on. If there is a particular issue that Sandel does not address, then a more specific version of the thesis would include that issue—hand an explanation of why it is important.
Arguable thesis with analytical claim
While Sandel argues persuasively that our instinct to “remake” (54) ourselves into something ever more perfect is a problem, his belief that we can always draw a line between what is medically necessary and what makes us simply “better than well” (51) is less convincing.
This is an arguable analytical claim. To argue for this claim, the essay writer will need to show how evidence from the article itself points to this interpretation. It’s also a reasonable scope for a thesis because it can be supported with evidence available in the text and is neither too broad nor too narrow.
Arguable thesis with normative claim
Given Sandel’s argument against genetic enhancement, we should not allow parents to decide on using Human Growth Hormone for their children.
This thesis tells us what we should do about a particular issue discussed in Sandel’s article, but it does not tell us how we should understand Sandel’s argument.
Questions to ask about your thesis
- Is the thesis truly arguable? Does it speak to a genuine dilemma in the source, or would most readers automatically agree with it?
- Is the thesis too obvious? Again, would most or all readers agree with it without needing to see your argument?
- Is the thesis complex enough to require a whole essay's worth of argument?
- Is the thesis supportable with evidence from the text rather than with generalizations or outside research?
- Would anyone want to read a paper in which this thesis was developed? That is, can you explain what this paper is adding to our understanding of a problem, question, or topic?
- picture_as_pdf Thesis
Home / Guides / Writing Guides / Parts of a Paper / How to Write a Strong Thesis Statement
How to Write a Strong Thesis Statement
A thesis can be found in many places—a debate speech, a lawyer’s closing argument, even an advertisement. But the most common place for a thesis statement (and probably why you’re reading this article) is in an essay.
Whether you’re writing an argumentative paper, an informative essay, or a compare/contrast statement, you need a thesis. Without a thesis, your argument falls flat and your information is unfocused. Since a thesis is so important, it’s probably a good idea to look at some tips on how to put together a strong one.
Guide Overview
What is a “thesis statement” anyway.
- 2 categories of thesis statements: informative and persuasive
- 2 styles of thesis statements
- Formula for a strong argumentative thesis
- The qualities of a solid thesis statement (video)
You may have heard of something called a “thesis.” It’s what seniors commonly refer to as their final paper before graduation. That’s not what we’re talking about here. That type of thesis is a long, well-written paper that takes years to piece together.
Instead, we’re talking about a single sentence that ties together the main idea of any argument . In the context of student essays, it’s a statement that summarizes your topic and declares your position on it. This sentence can tell a reader whether your essay is something they want to read.
2 Categories of Thesis Statements: Informative and Persuasive
Just as there are different types of essays, there are different types of thesis statements. The thesis should match the essay.
For example, with an informative essay, you should compose an informative thesis (rather than argumentative). You want to declare your intentions in this essay and guide the reader to the conclusion that you reach.
To make a peanut butter and jelly sandwich, you must procure the ingredients, find a knife, and spread the condiments.
This thesis showed the reader the topic (a type of sandwich) and the direction the essay will take (describing how the sandwich is made).
Most other types of essays, whether compare/contrast, argumentative, or narrative, have thesis statements that take a position and argue it. In other words, unless your purpose is simply to inform, your thesis is considered persuasive. A persuasive thesis usually contains an opinion and the reason why your opinion is true.
Peanut butter and jelly sandwiches are the best type of sandwich because they are versatile, easy to make, and taste good.
In this persuasive thesis statement, you see that I state my opinion (the best type of sandwich), which means I have chosen a stance. Next, I explain that my opinion is correct with several key reasons. This persuasive type of thesis can be used in any essay that contains the writer’s opinion, including, as I mentioned above, compare/contrast essays, narrative essays, and so on.
2 Styles of Thesis Statements
Just as there are two different types of thesis statements (informative and persuasive), there are two basic styles you can use.
The first style uses a list of two or more points . This style of thesis is perfect for a brief essay that contains only two or three body paragraphs. This basic five-paragraph essay is typical of middle and high school assignments.
C.S. Lewis’s Chronicles of Narnia series is one of the richest works of the 20th century because it offers an escape from reality, teaches readers to have faith even when they don’t understand, and contains a host of vibrant characters.
In the above persuasive thesis, you can see my opinion about Narnia followed by three clear reasons. This thesis is perfect for setting up a tidy five-paragraph essay.
In college, five paragraph essays become few and far between as essay length gets longer. Can you imagine having only five paragraphs in a six-page paper? For a longer essay, you need a thesis statement that is more versatile. Instead of listing two or three distinct points, a thesis can list one overarching point that all body paragraphs tie into.
Good vs. evil is the main theme of Lewis’s Narnia series, as is made clear through the struggles the main characters face in each book.
In this thesis, I have made a claim about the theme in Narnia followed by my reasoning. The broader scope of this thesis allows me to write about each of the series’ seven novels. I am no longer limited in how many body paragraphs I can logically use.
Formula for a Strong Argumentative Thesis
One thing I find that is helpful for students is having a clear template. While students rarely end up with a thesis that follows this exact wording, the following template creates a good starting point:
___________ is true because of ___________, ___________, and ___________.
Conversely, the formula for a thesis with only one point might follow this template:
___________________ is true because of _____________________.
Students usually end up using different terminology than simply “because,” but having a template is always helpful to get the creative juices flowing.
The Qualities of a Solid Thesis Statement
When composing a thesis, you must consider not only the format, but other qualities like length, position in the essay, and how strong the argument is.
Length: A thesis statement can be short or long, depending on how many points it mentions. Typically, however, it is only one concise sentence. It does contain at least two clauses, usually an independent clause (the opinion) and a dependent clause (the reasons). You probably should aim for a single sentence that is at least two lines, or about 30 to 40 words long.
Position: A thesis statement always belongs at the beginning of an essay. This is because it is a sentence that tells the reader what the writer is going to discuss. Teachers will have different preferences for the precise location of the thesis, but a good rule of thumb is in the introduction paragraph, within the last two or three sentences.
Strength: Finally, for a persuasive thesis to be strong, it needs to be arguable. This means that the statement is not obvious, and it is not something that everyone agrees is true.
Example of weak thesis:
Peanut butter and jelly sandwiches are easy to make because it just takes three ingredients.
Most people would agree that PB&J is one of the easiest sandwiches in the American lunch repertoire.
Example of a stronger thesis:
Peanut butter and jelly sandwiches are fun to eat because they always slide around.
This is more arguable because there are plenty of folks who might think a PB&J is messy or slimy rather than fun.
Composing a thesis statement does take a bit more thought than many other parts of an essay. However, because a thesis statement can contain an entire argument in just a few words, it is worth taking the extra time to compose this sentence. It can direct your research and your argument so that your essay is tight, focused, and makes readers think.
EasyBib Writing Resources
Writing a paper.
- Academic Essay
- Argumentative Essay
- College Admissions Essay
- Expository Essay
- Persuasive Essay
- Research Paper
- Thesis Statement
- Writing a Conclusion
- Writing an Introduction
- Writing an Outline
- Writing a Summary
EasyBib Plus Features
- Citation Generator
- Essay Checker
- Expert Check Proofreader
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tools
Plagiarism Checker
- Spell Checker
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Grammar and Plagiarism Checkers
Grammar Basics
Plagiarism Basics
Writing Basics
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples
What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples
Published on September 14, 2022 by Tegan George . Revised on November 21, 2023.
A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a master’s program or a capstone to a bachelor’s degree.
Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation , it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete. It relies on your ability to conduct research from start to finish: choosing a relevant topic , crafting a proposal , designing your research , collecting data , developing a robust analysis, drawing strong conclusions , and writing concisely .
Thesis template
You can also download our full thesis template in the format of your choice below. Our template includes a ready-made table of contents , as well as guidance for what each chapter should include. It’s easy to make it your own, and can help you get started.
Download Word template Download Google Docs template
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Thesis vs. thesis statement, how to structure a thesis, acknowledgements or preface, list of figures and tables, list of abbreviations, introduction, literature review, methodology, reference list, proofreading and editing, defending your thesis, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about theses.
You may have heard the word thesis as a standalone term or as a component of academic writing called a thesis statement . Keep in mind that these are two very different things.
- A thesis statement is a very common component of an essay, particularly in the humanities. It usually comprises 1 or 2 sentences in the introduction of your essay , and should clearly and concisely summarize the central points of your academic essay .
- A thesis is a long-form piece of academic writing, often taking more than a full semester to complete. It is generally a degree requirement for Master’s programs, and is also sometimes required to complete a bachelor’s degree in liberal arts colleges.
- In the US, a dissertation is generally written as a final step toward obtaining a PhD.
- In other countries (particularly the UK), a dissertation is generally written at the bachelor’s or master’s level.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
The final structure of your thesis depends on a variety of components, such as:
- Your discipline
- Your theoretical approach
Humanities theses are often structured more like a longer-form essay . Just like in an essay, you build an argument to support a central thesis.
In both hard and social sciences, theses typically include an introduction , literature review , methodology section , results section , discussion section , and conclusion section . These are each presented in their own dedicated section or chapter. In some cases, you might want to add an appendix .
Thesis examples
We’ve compiled a short list of thesis examples to help you get started.
- Example thesis #1: “Abolition, Africans, and Abstraction: the Influence of the ‘Noble Savage’ on British and French Antislavery Thought, 1787-1807” by Suchait Kahlon.
- Example thesis #2: “’A Starving Man Helping Another Starving Man’: UNRRA, India, and the Genesis of Global Relief, 1943-1947″ by Julian Saint Reiman.
The very first page of your thesis contains all necessary identifying information, including:
- Your full title
- Your full name
- Your department
- Your institution and degree program
- Your submission date.
Sometimes the title page also includes your student ID, the name of your supervisor, or the university’s logo. Check out your university’s guidelines if you’re not sure.
Read more about title pages
The acknowledgements section is usually optional. Its main point is to allow you to thank everyone who helped you in your thesis journey, such as supervisors, friends, or family. You can also choose to write a preface , but it’s typically one or the other, not both.
Read more about acknowledgements Read more about prefaces
An abstract is a short summary of your thesis. Usually a maximum of 300 words long, it’s should include brief descriptions of your research objectives , methods, results, and conclusions. Though it may seem short, it introduces your work to your audience, serving as a first impression of your thesis.
Read more about abstracts
A table of contents lists all of your sections, plus their corresponding page numbers and subheadings if you have them. This helps your reader seamlessly navigate your document.
Your table of contents should include all the major parts of your thesis. In particular, don’t forget the the appendices. If you used heading styles, it’s easy to generate an automatic table Microsoft Word.
Read more about tables of contents
While not mandatory, if you used a lot of tables and/or figures, it’s nice to include a list of them to help guide your reader. It’s also easy to generate one of these in Word: just use the “Insert Caption” feature.
Read more about lists of figures and tables
If you have used a lot of industry- or field-specific abbreviations in your thesis, you should include them in an alphabetized list of abbreviations . This way, your readers can easily look up any meanings they aren’t familiar with.
Read more about lists of abbreviations
Relatedly, if you find yourself using a lot of very specialized or field-specific terms that may not be familiar to your reader, consider including a glossary . Alphabetize the terms you want to include with a brief definition.
Read more about glossaries
An introduction sets up the topic, purpose, and relevance of your thesis, as well as expectations for your reader. This should:
- Ground your research topic , sharing any background information your reader may need
- Define the scope of your work
- Introduce any existing research on your topic, situating your work within a broader problem or debate
- State your research question(s)
- Outline (briefly) how the remainder of your work will proceed
In other words, your introduction should clearly and concisely show your reader the “what, why, and how” of your research.
Read more about introductions
A literature review helps you gain a robust understanding of any extant academic work on your topic, encompassing:
- Selecting relevant sources
- Determining the credibility of your sources
- Critically evaluating each of your sources
- Drawing connections between sources, including any themes, patterns, conflicts, or gaps
A literature review is not merely a summary of existing work. Rather, your literature review should ultimately lead to a clear justification for your own research, perhaps via:
- Addressing a gap in the literature
- Building on existing knowledge to draw new conclusions
- Exploring a new theoretical or methodological approach
- Introducing a new solution to an unresolved problem
- Definitively advocating for one side of a theoretical debate
Read more about literature reviews
Theoretical framework
Your literature review can often form the basis for your theoretical framework, but these are not the same thing. A theoretical framework defines and analyzes the concepts and theories that your research hinges on.
Read more about theoretical frameworks
Your methodology chapter shows your reader how you conducted your research. It should be written clearly and methodically, easily allowing your reader to critically assess the credibility of your argument. Furthermore, your methods section should convince your reader that your method was the best way to answer your research question.
A methodology section should generally include:
- Your overall approach ( quantitative vs. qualitative )
- Your research methods (e.g., a longitudinal study )
- Your data collection methods (e.g., interviews or a controlled experiment
- Any tools or materials you used (e.g., computer software)
- The data analysis methods you chose (e.g., statistical analysis , discourse analysis )
- A strong, but not defensive justification of your methods
Read more about methodology sections
Your results section should highlight what your methodology discovered. These two sections work in tandem, but shouldn’t repeat each other. While your results section can include hypotheses or themes, don’t include any speculation or new arguments here.
Your results section should:
- State each (relevant) result with any (relevant) descriptive statistics (e.g., mean , standard deviation ) and inferential statistics (e.g., test statistics , p values )
- Explain how each result relates to the research question
- Determine whether the hypothesis was supported
Additional data (like raw numbers or interview transcripts ) can be included as an appendix . You can include tables and figures, but only if they help the reader better understand your results.
Read more about results sections
Your discussion section is where you can interpret your results in detail. Did they meet your expectations? How well do they fit within the framework that you built? You can refer back to any relevant source material to situate your results within your field, but leave most of that analysis in your literature review.
For any unexpected results, offer explanations or alternative interpretations of your data.
Read more about discussion sections
Your thesis conclusion should concisely answer your main research question. It should leave your reader with an ultra-clear understanding of your central argument, and emphasize what your research specifically has contributed to your field.
Why does your research matter? What recommendations for future research do you have? Lastly, wrap up your work with any concluding remarks.
Read more about conclusions
In order to avoid plagiarism , don’t forget to include a full reference list at the end of your thesis, citing the sources that you used. Choose one citation style and follow it consistently throughout your thesis, taking note of the formatting requirements of each style.
Which style you choose is often set by your department or your field, but common styles include MLA , Chicago , and APA.
Create APA citations Create MLA citations
In order to stay clear and concise, your thesis should include the most essential information needed to answer your research question. However, chances are you have many contributing documents, like interview transcripts or survey questions . These can be added as appendices , to save space in the main body.
Read more about appendices
Once you’re done writing, the next part of your editing process begins. Leave plenty of time for proofreading and editing prior to submission. Nothing looks worse than grammar mistakes or sloppy spelling errors!
Consider using a professional thesis editing service or grammar checker to make sure your final project is perfect.
Once you’ve submitted your final product, it’s common practice to have a thesis defense, an oral component of your finished work. This is scheduled by your advisor or committee, and usually entails a presentation and Q&A session.
After your defense , your committee will meet to determine if you deserve any departmental honors or accolades. However, keep in mind that defenses are usually just a formality. If there are any serious issues with your work, these should be resolved with your advisor way before a defense.
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Survivorship bias
- Self-serving bias
- Availability heuristic
- Halo effect
- Hindsight bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
The conclusion of your thesis or dissertation shouldn’t take up more than 5–7% of your overall word count.
If you only used a few abbreviations in your thesis or dissertation , you don’t necessarily need to include a list of abbreviations .
If your abbreviations are numerous, or if you think they won’t be known to your audience, it’s never a bad idea to add one. They can also improve readability, minimizing confusion about abbreviations unfamiliar to your reader.
When you mention different chapters within your text, it’s considered best to use Roman numerals for most citation styles. However, the most important thing here is to remain consistent whenever using numbers in your dissertation .
A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical first steps in your writing process. It helps you to lay out and organize your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding what kind of research you’d like to undertake.
Generally, an outline contains information on the different sections included in your thesis or dissertation , such as:
- Your anticipated title
- Your abstract
- Your chapters (sometimes subdivided into further topics like literature review , research methods , avenues for future research, etc.)
A thesis is typically written by students finishing up a bachelor’s or Master’s degree. Some educational institutions, particularly in the liberal arts, have mandatory theses, but they are often not mandatory to graduate from bachelor’s degrees. It is more common for a thesis to be a graduation requirement from a Master’s degree.
Even if not mandatory, you may want to consider writing a thesis if you:
- Plan to attend graduate school soon
- Have a particular topic you’d like to study more in-depth
- Are considering a career in research
- Would like a capstone experience to tie up your academic experience
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. (2023, November 21). What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 15, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/thesis/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, dissertation & thesis outline | example & free templates, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, 10 research question examples to guide your research project, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Jump to navigation

- Undergraduate Admissions
- Transfer Admissions
- Graduate Admissions
- Honors and Scholars Admissions
- International Admissions
- Law Admissions
- Office of Financial Aid
- Orientation
- Pre-College Programs
- Scholarships
- Tuition & Fees
- Academic Calendar
- Academic Colleges
- Degree Programs
- Online Programs
- Class Schedule
- Workforce Development
- Sponsored Programs and Research Services
- Technology Transfer
- Faculty Expertise Database
- Research Centers
- College of Graduate Studies
- Institutional Research and Analysis
- At a Glance
- Concerned Vikes
- Free Speech on Campus
- Policies and Procedures
- Messages & Updates
- In the News
- Board of Trustees
- Senior Leadership Team
- Services Near CSU

Cleveland State University
Search this site
Thesis statement.
Definition:
The thesis is usually considered the most important sentence of your essay because it outlines the central purpose of your essay in one place. A good thesis will link the subject of an essay with a controlling idea. Consider, for example, the following thesis:
People in the past spent a great deal of effort protecting themselves from witches. Subject: people feared witches Controlling Idea: people spent a great deal of effort protecting themselves
In a short essay, a thesis statement appears at, or near, the end of the introductory paragraph of the paper so that readers know the topic of the essay before they see the writer's statement of the central purpose of the essay. This way the first paragraph helps the reader understand why the writer is writing.
A thesis should be narrow in focus in order to allow the fullest exploration of its issues as possible, and it should reflect the type of paper that follows, whether it be persuasive or informative. Narrowing the focus of the thesis may require posing questions about it to yourself before committing to a final version.
What follows is a method for writing thesis statements that many writers have found useful (we found it in Chapter 3 of The Allyn & Bacon Handbook ).
1. Decide what you are writing about:
A clear, concise thesis statement does more than outline the subject in question; it makes the reader aware of the writer's stand on the subject in question, connecting a subject with a controlling idea.
2. Think about all the elements your paper will deal with:
A thesis generally consists of a subject that contains within itself a number of smaller facts; the topic sentence of each paragraph that makes up the body of the paper should refer (in some clear way) back to the ideas contained within the thesis statement in order to keep the paper from digressing.
3. Think about the purpose and tone of your paper:
A thesis statement should contain the main point of the paper and suggest to the reader a direction that the paper will take in exploring, proving, or disproving that main point.
4. State your main point in a sentence or two:
A good writer can assert the main idea of a short, coherent essay briefly. Instead of rambling, be as straightforward as possible.
5. Revise your thesis as you develop your paper:
A final version of a thesis statement will only be available after a draft of the paper it is a part of has been completed. The focus of the paper may change and evolve over the period it is written in; necessarily, the thesis statement should be revised to reflect the alterations in the paper.
Few writers finish a paper writing about the exact topic they begin with. While you write a paper, your main point may change. As you're finishing, make sure your thesis statement has changed along with the subject and controlling ideas of your paper.
Questions, comments, and other sundry things may be sent to [email protected]
[Top of Page]
©2024 Cleveland State University | 2121 Euclid Avenue, Cleveland, OH 44115-2214 | (216) 687-2000. Cleveland State University is an equal opportunity educator and employer. Affirmative Action | Diversity | Employment | Tobacco Free | Non-Discrimination Statement | Web Privacy Statement | Accreditations
It appears you have javascript disabled. Please enable javascript to get the full experience of gustavus.edu
Tips on writing a thesis statement: composing compelling thesis statements.
College-level courses demand a solid grasp of writing concepts, and some students arrive at Intro to Composition unprepared to write a high-quality essay. Teachers tend to give a bit more slack at the high school level, but college professors are often much more exacting. That’s why excellent writing skills are crucial to the majority of college courses — even outside the English department.
One of the most important elements to master is the thesis statement. A strong thesis statement is at the root of all writing, from op-eds to research papers. It’s an essential element of any persuasive piece; something we look for without even thinking about it. A convincing, attention-grabbing thesis statement keeps the reader engaged — and lets them know where the piece is headed.
Having a few tips and tricks in your toolbox can help you to make a convincing academic argument every time.
What is a Thesis Statement?
First, the basics. A thesis statement is a sentence or two that states the main idea of a writing assignment. It also helps to control the ideas presented within the paper. However, it is not merely a topic. It often reflects a claim or judgment that a writer has made about a reading or personal experience. For instance: Tocqueville believed that the domestic role most women held in America was the role that gave them the most power, an idea that many would hotly dispute today.
Every assignment has a question or prompt. It’s important that your thesis statement answers the question. For the above thesis statement, the question being answered might be something like this: Why was Tocqueville wrong about women? If your thesis statement doesn’t answer a question, you’ll need to rework your statement.
Where Will I Use Thesis Statements?
Writing an exceptional thesis statement is a skill you’ll need both now and in the future, so you’ll want to be confident in your ability to create a great one. Whether in academic, professional, or personal writing, a strong thesis statement enhances the clarity, effectiveness, and impact of the overall message. Here are some real-world examples that demonstrate the importance of composing an outstanding thesis statement:
- Academic writing. The success of academic research papers depends on an exceptional thesis statement. Along with establishing the focus of the paper, it also provides you with direction in terms of research. The thesis sets a clear intention for your essay, helping the reader understand the argument you’re presenting and why the evidence and analysis support it.
- Persuasive writing. Persuasive writing depends on an excellent thesis statement that clearly defines the author’s position. Your goal is to persuade the audience to agree with your thesis. Setting an explicit stance also provides you with a foundation on which to build convincing arguments with relevant evidence.
- Professional writing. In the business and marketing world, a sound thesis statement is required to communicate a project’s purpose. Thesis statements not only outline a project’s unique goals but can also guide the marketing team in creating targeted promotional strategies.
Where Do Thesis Statements Go?
A good practice is to put the thesis statement at the end of your introduction so you can use it to lead into the body of your paper. This allows you, as the writer, to lead up to the thesis statement instead of diving directly into the topic. Placing your thesis here also sets you up for a brief mention of the evidence you have to support your thesis, allowing readers a preview of what’s to come.
A good introduction conceptualizes and anticipates the thesis statement, so ending your intro with your thesis makes the most sense. If you place the thesis statement at the beginning, your reader may forget or be confused about the main idea by the time they reach the end of the introduction.
What Makes a Strong Thesis Statement?
A quality thesis statement is designed to both inform and compel. Your thesis acts as an introduction to the argument you’ll be making in your paper, and it also acts as the “hook”. Your thesis should be clear and concise, and you should be ready with enough evidence to support your argument.
There are several qualities that make for a powerful thesis statement, and drafting a great one means considering all of them:
A strong thesis makes a clear argument .
A thesis statement is not intended to be a statement of fact, nor should it be an opinion statement. Making an observation is not sufficient — you should provide the reader with a clear argument that cohesively summarizes the intention of your paper.
Originality is important when possible, but stick with your own convictions. Taking your paper in an already agreed-upon direction doesn’t necessarily make for compelling reading. Writing a thesis statement that presents a unique argument opens up the opportunity to discuss an issue in a new way and helps readers to get a new perspective on the topic in question. Again, don’t force it. You’ll have a harder time trying to support an argument you don’t believe yourself.
A strong thesis statement gives direction .
If you lack a specific direction for your paper, you’ll likely find it difficult to make a solid argument for anything. Your thesis statement should state precisely what your paper will be about, as a statement that’s overly general or makes more than one main point can confuse your audience.
A specific thesis statement also helps you focus your argument — you should be able to discuss your thesis thoroughly in the allotted word count. A thesis that’s too broad won’t allow you to make a strong case for anything.
A strong thesis statement provides proof.
Since thesis statements present an argument, they require support. All paragraphs of the essay should explain, support, or argue with your thesis. You should support your thesis statement with detailed evidence that will interest your readers and motivate them to continue reading the paper.
Sometimes it is useful to mention your supporting points in your thesis. An example of this could be: John Updike's Trust Me is a valuable novel for a college syllabus because it allows the reader to become familiar with his writing and provides themes that are easily connected to other works. In the body of your paper, you could write a paragraph or two about each supporting idea. If you write a thesis statement like this, it will often help you to keep control of your ideas.
A strong thesis statement prompts discussion .
Your thesis statement should stimulate the reader to continue reading your paper. Many writers choose to illustrate that the chosen topic is controversial in one way or another, which is an effective way to pull in readers who might agree with you and those who don’t!
The ultimate point of a thesis statement is to spark interest in your argument. This is your chance to grab (and keep) your reader’s attention, and hopefully, inspire them to continue learning about the topic.
Testing Your Thesis Statement
Because your thesis statement is vital to the quality of your paper, you need to ensure that your thesis statement posits a cohesive argument. Once you’ve come up with a working thesis statement, ask yourself these questions to further refine your statement:
- Is it interesting ? If your thesis is dull, consider clarifying your argument or revising it to make a connection to a relatable issue. Again, your thesis statement should draw the reader into the paper.
- Is it specific enough ? If your thesis statement is too broad, you won’t be able to make a persuasive argument. If your thesis contains words like “positive” or “effective”, narrow it down. Tell the reader why something is “positive”. What in particular makes something “effective”?
- Does it answer the question ? Review the prompt or question once you’ve written your working thesis and be sure that your thesis statement directly addresses the given question.
- Does my paper successfully support my thesis statement ? If you find that your thesis statement and the body of your paper don’t mesh well, you’re going to have to change one of them. But don’t worry too much if this is the case — writing is intended to be revised and reworked.
- Does my thesis statement present the reader with a new perspective? Is it a fresh take on an old idea? Will my reader learn something from my paper? If your thesis statement has already been widely discussed, consider if there’s a fresh angle to take before settling.
- Finally, am I happy with my thesis ? If not, you may have difficulty writing your paper. Composing an essay about an argument you don’t believe in can be more difficult than taking a stand for something you believe in.
Quick Tips for Writing Thesis Statements
If you’re struggling to come up with a thesis statement, here are a few tips you can use to help:
- Know the topic. The topic should be something you know or can learn about. It is difficult to write a thesis statement, let alone a paper, on a topic that you know nothing about. Reflecting on personal experience and/or researching your thesis topic thoroughly will help you present more convincing information about your statement.
- Brainstorm. If you are having trouble beginning your paper or writing your thesis, take a piece of paper and write down everything that comes to mind about your topic. Did you discover any new ideas or connections? Can you separate any of the things you jotted down into categories? Do you notice any themes? Think about using ideas generated during this process to shape your thesis statement and your paper.
- Phrase the topic as a question. If your topic is presented as a statement, rephrasing it as a question can make it easier to develop a thesis statement.
- Limit your topic. Based on what you know and the required length of your final paper, limit your topic to a specific area. A broad scope will generally require a longer paper, while a narrow scope can be sufficiently proven by a shorter paper.
Writing Thesis Statements: Final Thoughts
The ability to compose a strong thesis statement is a skill you’ll use over and over again during your college days and beyond. Compelling persuasive writing is important, whether you’re writing an academic essay or putting together a professional pitch.
If your thesis statement-writing skills aren’t already strong, be sure to practice before diving into college-level courses that will test your skills. If you’re currently looking into colleges, Gustavus Adolphus offers you the opportunity to refine your writing skills in our English courses and degree program . Explore Gustavus Adolphus’ undergraduate majors here .

What Makes a Thesis Statement Spectacular? — 5 things to know
Table of Contents
What Is a Thesis Statement?
A thesis statement is a declarative sentence that states the primary idea of an essay or a research paper . In this statement, the authors declare their beliefs or what they intend to argue in their research study. The statement is clear and concise, with only one or two sentences.
Thesis Statement — An Essential in Thesis Writing
A thesis statement distills the research paper idea into one or two sentences. This summary organizes your paper and develops the research argument or opinion. The statement is important because it lets the reader know what the research paper will talk about and how the author is approaching the issue. Moreover, the statement also serves as a map for the paper and helps the authors to track and organize their thoughts more efficiently.
A thesis statement can keep the writer from getting lost in a convoluted and directionless argument. Finally, it will also ensure that the research paper remains relevant and focused on the objective.
Where to Include the Thesis Statement?
The thesis statement is typically placed at the end of the introduction section of your essay or research paper. It usually consists of a single sentence of the writer’s opinion on the topic and provides a specific guide to the readers throughout the paper.
6 Steps to Write an Impactful Thesis Statement
Step 1 – analyze the literature.
Identify the knowledge gaps in the relevant research paper. Analyze the deeper implications of the author’s research argument. Was the research objective mentioned in the thesis statement reversed later in the discussion or conclusion? Does the author contradict themselves? Is there a major knowledge gap in creating a relevant research objective? Has the author understood and validated the fundamental theories correctly? Does the author support an argument without having supporting literature to cite? Answering these or related questions will help authors develop a working thesis and give their thesis an easy direction and structure.
Step 2 – Start with a Question
While developing a working thesis, early in the writing process, you might already have a research question to address. Strong research questions guide the design of studies and define and identify specific objectives. These objectives will assist the author in framing the thesis statement.
Step 3 – Develop the Answer
After initial research, the author could formulate a tentative answer to the research question. At this stage, the answer could be simple enough to guide the research and the writing process. After writing the initial answer, the author could elaborate further on why this is the chosen answer. After reading more about the research topic, the author could write and refine the answers to address the research question.
Step 4 – Write the First Draft of the Thesis Statement
After ideating the working thesis statement, make sure to write it down. It is disheartening to create a great idea for a thesis and then forget it when you lose concentration. The first draft will help you think clearly and logically. It will provide you with an option to align your thesis statement with the defined research objectives.

Step 5 – Anticipate Counter Arguments Against the Statement
After developing a working thesis, you should think about what might be said against it. This list of arguments will help you refute the thesis later. Remember that every argument has a counterargument, and if yours does not have one, what you state is not an argument — it may be a fact or opinion, but not an argument.
Step 6 – Refine the Statement
Anticipating counterarguments will help you refine your statement further. A strong thesis statement should address —
- Why does your research hold this stand?
- What will readers learn from the essay?
- Are the key points of your argumentative or narrative?
- Does the final thesis statement summarize your overall argument or the entire topic you aim to explain in the research paper?

5 Tips to Create a Compelling Thesis Statement
A thesis statement is a crucial part of any academic paper. Clearly stating the main idea of your research helps you focus on the objectives of your paper. Refer to the following tips while drafting your statement:
1. Keep it Concise
The statement should be short and precise. It should contain no more than a couple of sentences.
2. Make it Specific
The statement should be focused on a specific topic or argument. Covering too many topics will only make your paper weaker.
3. Express an Opinion
The statement should have an opinion on an issue or controversy. This will make your paper arguable and interesting to read.
4. Be Assertive
The statement should be stated assertively and not hesitantly or apologetically. Remember, you are making an argument — you need to sound convincing!
5. Support with Evidence
The thesis should be supported with evidence from your paper. Make sure you include specific examples from your research to reinforce your objectives.
Thesis Statement Examples *
Example 1 – alcohol consumption.
High levels of alcohol consumption have harmful effects on your health, such as weight gain, heart disease, and liver complications.
This thesis statement states specific reasons why alcohol consumption is detrimental. It is not required to mention every single detriment in your thesis.
Example 2 – Benefits of the Internet
The internet serves as a means of expediently connecting people across the globe, fostering new friendships and an exchange of ideas that would not have occurred before its inception.
While the internet offers a host of benefits, this thesis statement is about choosing the ability that fosters new friendships and exchange ideas. Also, the research needs to prove how connecting people across the globe could not have happened before the internet’s inception — which is a focused research statement.
*The following thesis statements are not fully researched and are merely examples shown to understand how to write a thesis statement. Also, you should avoid using these statements for your own research paper purposes.
A gripping thesis statement is developed by understanding it from the reader’s point of view. Be aware of not developing topics that only interest you and have less reader attraction. A harsh yet necessary question to ask oneself is — Why should readers read my paper? Is this paper worth reading? Would I read this paper if I weren’t its author?
A thesis statement hypes your research paper. It makes the readers excited about what specific information is coming their way. This helps them learn new facts and possibly embrace new opinions.
Writing a thesis statement (although two sentences) could be a daunting task. Hope this blog helps you write a compelling one! Do consider using the steps to create your thesis statement and tell us about it in the comment section below.
Great in impactation of knowledge
An interesting expository. Thanks for the concise explanation.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Publishing Research
- Reporting Research
How to Optimize Your Research Process: A step-by-step guide
For researchers across disciplines, the path to uncovering novel findings and insights is often filled…

- Industry News
- Trending Now
Breaking Barriers: Sony and Nature unveil “Women in Technology Award”
Sony Group Corporation and the prestigious scientific journal Nature have collaborated to launch the inaugural…

Achieving Research Excellence: Checklist for good research practices
Academia is built on the foundation of trustworthy and high-quality research, supported by the pillars…

- Promoting Research
Plain Language Summary — Communicating your research to bridge the academic-lay gap
Science can be complex, but does that mean it should not be accessible to the…

Science under Surveillance: Journals adopt advanced AI to uncover image manipulation
Journals are increasingly turning to cutting-edge AI tools to uncover deceitful images published in manuscripts.…
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for…
Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right…
Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What should universities' stance be on AI tools in research and academic writing?
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Tips and Examples for Writing Thesis Statements

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
This resource provides tips for creating a thesis statement and examples of different types of thesis statements.
Tips for Writing Your Thesis Statement
1. Determine what kind of paper you are writing:
- An analytical paper breaks down an issue or an idea into its component parts, evaluates the issue or idea, and presents this breakdown and evaluation to the audience.
- An expository (explanatory) paper explains something to the audience.
- An argumentative paper makes a claim about a topic and justifies this claim with specific evidence. The claim could be an opinion, a policy proposal, an evaluation, a cause-and-effect statement, or an interpretation. The goal of the argumentative paper is to convince the audience that the claim is true based on the evidence provided.
If you are writing a text that does not fall under these three categories (e.g., a narrative), a thesis statement somewhere in the first paragraph could still be helpful to your reader.
2. Your thesis statement should be specific—it should cover only what you will discuss in your paper and should be supported with specific evidence.
3. The thesis statement usually appears at the end of the first paragraph of a paper.
4. Your topic may change as you write, so you may need to revise your thesis statement to reflect exactly what you have discussed in the paper.
Thesis Statement Examples
Example of an analytical thesis statement:
The paper that follows should:
- Explain the analysis of the college admission process
- Explain the challenge facing admissions counselors
Example of an expository (explanatory) thesis statement:
- Explain how students spend their time studying, attending class, and socializing with peers
Example of an argumentative thesis statement:
- Present an argument and give evidence to support the claim that students should pursue community projects before entering college

Home » How to Craft a Powerful Thesis Statement for Your Essay
How to Craft a Powerful Thesis Statement for Your Essay

Introduction
In the realm of academic writing, a powerful thesis statement serves as the bedrock upon which your entire essay rests. It is the linchpin that holds your arguments together, the guiding star that illuminates the path of your exploration, and the foundation upon which you build a persuasive and coherent piece of work. Crafting a strong thesis statement is no mere triviality; it is a skill that can elevate your writing and captivate your readers. In this blog post, we will delve into the art of crafting a powerful thesis statement for your essay, exploring the strategies that can help you master this essential aspect of academic writing.
Picture this: you’ve been assigned an essay prompt, and you sit down to begin the writing process. As you ponder over your topic, ideas start to flood your mind, but where do you begin? How do you channel those thoughts into a concise, impactful, and memorable thesis statement? This is where our journey begins.
The thesis statement is the compass that guides your essay, providing direction and focus. It encapsulates the central argument or main idea of your piece, presenting it to your readers in a clear, assertive, and concise manner. A well-crafted thesis statement not only sets the stage for your essay but also entices your readers to delve deeper into your analysis.
Understanding the purpose of a thesis statement is paramount. It serves as a roadmap for both you and your readers, outlining the scope and purpose of your essay. A strong thesis statement establishes the tone, sets expectations, and creates a framework for your arguments, ensuring that your essay remains coherent and organized. It helps you avoid the pitfalls of wandering off-topic or losing sight of your main argument, providing a solid anchor to keep your writing on track.
To craft a compelling thesis statement, it is crucial to carefully analyze the essay prompt. Take the time to decipher its intricacies, unravel its underlying themes, and discern the key ideas it presents. By thoroughly understanding the prompt, you can identify the main focus of your essay and tailor your thesis statement accordingly. The prompt serves as your guiding light, illuminating the path you must take to develop a robust thesis statement.
When brainstorming ideas for your thesis statement, explore multiple avenues and consider different perspectives. Allow your thoughts to flow freely, employing techniques such as mind-mapping or freewriting to uncover connections and possibilities. This creative process enables you to generate unique insights and uncover potential arguments that will strengthen your thesis statement.
Once you have a pool of ideas, it is time to refine and distill them into a clear and concise thesis statement. Precision is key here. A strong thesis statement should be specific, avoiding vague or general statements. It should present a clear argument or position that you will support throughout your essay. Refining your thesis statement is an iterative process that requires revision, reflection, and a keen eye for precision.
Incorporating your thesis statement effectively within your essay is equally important. The placement of your thesis statement within the introduction sets the tone for the entire piece. It should seamlessly lead readers into your arguments, captivating their attention and motivating them to continue reading. Integrating the thesis statement throughout your essay helps maintain a sense of unity and coherence, ensuring that each paragraph aligns with and supports your central argument.
In the following sections, we will explore each step in detail, offering practical tips, techniques, and examples to guide you on your journey to crafting a powerful thesis statement for your essay. By following these strategies, you will not only enhance your writing skills but also engage your readers and leave a lasting impression. So, let us embark on this transformative adventure and unlock the true potential of your academic writing.
1: Understanding the Purpose of a Thesis Statement
A thesis statement is the heart and soul of any well-crafted essay. In this section, we will delve into the purpose of a thesis statement and its significance in guiding the direction of your writing.
At its core, a thesis statement serves as a concise summary of the main argument or central idea that you aim to convey in your essay. It is a declaration that encapsulates the essence of your work and presents it to your readers in a clear and assertive manner. Think of it as the North Star that guides both you and your audience throughout the essay, providing a sense of direction and focus.
The primary purpose of a thesis statement is to establish the purpose and scope of your essay. It acts as a roadmap, informing your readers about what they can expect from your writing. A well-crafted thesis statement sets the stage, defines the boundaries, and prepares the groundwork for the subsequent analysis and argumentation in your essay.
Clarity is of utmost importance when it comes to a thesis statement. It should convey your main point with precision and eliminate any ambiguity. By doing so, you ensure that your readers understand the central message you are trying to convey, enabling them to engage with your ideas more effectively.
Moreover, a strong thesis statement helps maintain the coherence and organization of your essay. It serves as a unifying thread that connects the different elements of your writing, ensuring that every paragraph and argument aligns with the overarching message. This cohesive structure enhances the readability and logical flow of your essay, making it easier for readers to follow and comprehend your ideas.
Crafting a powerful thesis statement involves careful consideration of the key components that make it effective. First and foremost, it should be specific and focused. Avoid vague or general statements that lack depth and fail to provide a clear direction for your essay. Instead, zero in on a particular aspect or argument that you will explore in your writing.
Additionally, a thesis statement should be assertive. It should present a strong and confident position or claim that you will support and defend throughout your essay. By taking a clear stance, you engage your readers and prompt them to consider your perspective.
It’s important to note that a thesis statement is not a mere statement of fact. It goes beyond stating the obvious and delves into the realm of analysis, interpretation, and argumentation. It should be thought-provoking and invite discussion, encouraging readers to explore the complexities of the topic at hand.
As you develop your thesis statement, keep in mind that it is not set in stone. It can evolve and adapt as you delve deeper into your research and writing process. Don’t be afraid to refine and revise your thesis statement as your understanding of the topic expands. This flexibility allows you to incorporate new insights and perspectives, enhancing the overall quality and depth of your essay.
2. Analyzing the Essay Prompt
When you receive an essay prompt, it is crucial to take the time to dissect and comprehend its nuances. The essay prompt provides valuable insights into the main ideas, themes, and objectives of your assignment. By carefully analyzing the prompt, you can identify the key elements that should be addressed in your essay.
The first step in analyzing the essay prompt is to read it thoroughly. Pay close attention to the wording and structure of the prompt. Look for keywords or phrases that provide clues about the specific focus or approach required. These keywords might include “analyze,” “compare and contrast,” “evaluate,” or “discuss.” Understanding these instructions will help you shape your thesis statement accordingly.
Next, identify the main ideas or concepts presented in the essay prompt. These are the building blocks of your essay and should be reflected in your thesis statement. Consider the central question or problem that the prompt poses and how it relates to the broader context of your subject or course.
As you analyze the essay prompt, be mindful of any subtopics or specific areas of emphasis that are mentioned. These can guide your thinking and influence the direction of your thesis statement. Take note of any limitations or constraints mentioned in the prompt, such as a specific time period, geographical context, or theoretical framework, as these factors will shape the scope of your thesis statement.
It is also essential to consider the target audience of your essay. The prompt may indicate whether the essay should be geared towards a general audience or a specific group of readers, such as experts in the field. Understanding your audience will help you tailor your thesis statement to meet their needs and expectations.
Another aspect to consider when analyzing the prompt is the desired outcome or objective of your essay. What is the purpose of your writing? Are you expected to present an argument, provide an analysis, or propose a solution? By understanding the intended outcome, you can ensure that your thesis statement aligns with the goals of the assignment.
Furthermore, take note of any additional guidelines or formatting requirements outlined in the prompt. These might include citation styles, word limits, or specific sources to be referenced. Adhering to these guidelines will ensure that your thesis statement and subsequent essay meet the specific criteria set by your instructor.
3. Brainstorming and Generating Ideas
In this section, we will explore effective techniques for brainstorming and generating ideas to support the development of a powerful thesis statement. By tapping into your creativity and employing various strategies, you can uncover compelling arguments and perspectives for your essay.
(i) Mind Mapping:
Begin by creating a mind map, a visual representation of your thoughts and ideas. Start with the main topic or concept in the center and branch out to related subtopics or supporting arguments. This technique allows you to explore different angles and connections, helping you generate a range of ideas that can contribute to your thesis statement.
(ii) Freewriting:
Set a timer for a designated period, such as 10 or 15 minutes, and write continuously without worrying about grammar, punctuation, or coherence. Let your thoughts flow freely, allowing unexpected ideas and associations to emerge. Freewriting enables you to bypass self-censorship and access your subconscious, leading to unique insights and potential thesis statement concepts.
(iii) Research and Reading:
Engage in extensive research and reading on your topic. Explore scholarly articles, books, reputable websites, and other relevant sources. As you gather information, jot down interesting ideas, arguments, or quotes that resonate with you. These can serve as inspiration for your thesis statement and provide a solid foundation for your essay.
(iv) Discussion and Collaboration:
Engage in discussions with peers, instructors, or experts in the field. Share your ideas, listen to different perspectives, and ask thought-provoking questions. Collaborative brainstorming sessions can stimulate creativity and offer valuable insights that you may not have considered on your own.
(v) Questioning Techniques:
Use questioning techniques to prompt deeper thinking and generate ideas. Ask yourself open-ended questions such as “What are the underlying causes of this issue?” or “How does this concept relate to other aspects of the topic?” These questions can help you explore different dimensions and uncover potential arguments for your thesis statement.
(vi) Reviewing Notes and Outlines:
Review any notes, outlines, or previous drafts you may have on the topic. Look for key points, supporting evidence, or connections that can contribute to your thesis statement. This review process allows you to build upon your existing knowledge and refine your understanding of the topic.
(vii) Considering Counterarguments:
Challenge your own assumptions and consider potential counterarguments. By exploring opposing viewpoints, you can strengthen your thesis statement by addressing possible objections or alternative perspectives. This approach adds depth and credibility to your argumentation.
Remember, during the brainstorming phase, quantity is more important than quality. Allow yourself to explore a wide range of ideas without judgment. Once you have generated a substantial list of potential arguments, evaluate and prioritize them based on their relevance, strength, and alignment with the essay prompt.
4. Refining Your Thesis Statement
Now that we have explored the initial steps of brainstorming and generating ideas, it’s time to shift our focus to the crucial process of refining your thesis statement. This stage involves honing in on the most compelling and precise expression of your main argument or position. By following the strategies outlined below, you can refine your thesis statement to ensure it effectively communicates the central theme of your essay.
(i) Review and Reflect:
Take a step back and carefully review your initial thesis statement. Reflect on its alignment with the essay prompt and its ability to capture the essence of your argument. Consider its clarity, relevance, and specificity. Identify any areas that may require further development or clarification.
(ii) Be Specific and Concise:
One of the key aspects of refining your thesis statement is to ensure it is specific and concise. Avoid general or vague statements that lack depth and fail to provide a clear direction for your essay. Instead, focus on a particular aspect or argument that you will explore in your writing. Use precise language and avoid broad claims that may dilute the impact of your thesis statement.
(iii) Incorporate Keywords:
Refer back to the keywords or key phrases from the essay prompt. Incorporate these words or concepts into your refined thesis statement to demonstrate a clear connection between your argument and the essay prompt. This helps to establish the relevance and coherence of your thesis statement within the context of your assignment.
(iv) Seek Precision and Clarity:
Refining your thesis statement involves striving for precision and clarity in your expression. Make sure your statement accurately reflects the main idea or argument of your essay, leaving no room for misinterpretation. Use specific language that leaves no doubt about the focus of your analysis.
(v) Evaluate and Eliminate Redundancy:
Scan your thesis statement for any redundant or unnecessary words or phrases. Streamline your statement to make it more concise and impactful. Remove any repetition or excessive wording that may detract from the clarity and strength of your thesis statement.
(vi) Test for Relevance:
As you refine your thesis statement, test it against the main body of your essay. Ensure that every argument, piece of evidence, or analysis you present directly supports and aligns with your thesis statement. This coherence ensures that your essay remains focused and cohesive throughout.
(vii) Solicit Feedback:
Don’t hesitate to seek feedback from peers, instructors, or writing tutors. Share your refined thesis statement and ask for their input and suggestions. Others may provide valuable insights or identify areas that require further refinement.
Remember, refining your thesis statement is an iterative process. Be open to revision and be willing to make adjustments as necessary. Keep in mind the overall purpose and scope of your essay, ensuring that your refined thesis statement effectively captures the essence of your argument.
By employing these strategies, you can refine your thesis statement to a clear, concise, and powerful statement that sets the stage for the rest of your essay. The refined thesis statement will act as a guiding beacon, directing your writing and captivating your readers’ attention.
5. Crafting a Clear and Concise Thesis Statement
Crafting a clear and concise thesis statement is crucial for effectively conveying the main argument or position of your essay. In this section, we will delve into the essential elements and strategies for creating a thesis statement that is both clear and concise.
(i) Identify the Main Argument:
Start by identifying the main argument or central idea that you want to convey in your essay. This should be a specific and focused statement that encapsulates the core message of your writing. Clearly articulate the position you will take or the perspective you will present.
(ii) Use Precise and Specific Language:
Choose your words carefully to ensure precision and clarity in your thesis statement. Avoid vague or general terms that lack specificity and depth. Instead, opt for specific and concrete language that clearly communicates your intentions and avoids ambiguity.
(iii) Keep it Concise:
Aim for brevity in your thesis statement. It should be concise and to the point, expressing your main argument in a succinct manner. Avoid lengthy or convoluted statements that may confuse or overwhelm your readers. By keeping it concise, you maintain focus and enhance the impact of your thesis statement.
(iv) One Main Idea:
Your thesis statement should convey one main idea or argument. Avoid introducing multiple ideas or topics within a single thesis statement, as this can lead to a lack of clarity and dilution of your main message. Stay focused on a single central point to ensure a clear and coherent thesis statement.
(v) Make it Debatable:
A strong thesis statement is one that invites discussion and presents a debatable claim. Avoid stating obvious or universally accepted facts. Instead, aim to present an argument or perspective that can be supported, challenged, or explored further within your essay. A debatable thesis statement stimulates critical thinking and engages your readers.
(vi) Consider the Scope:
Consider the scope of your essay when crafting your thesis statement. Ensure that your statement reflects the breadth and depth of your analysis, while still remaining concise. Strike a balance between providing enough information to convey your main argument and avoiding unnecessary details that can clutter your thesis statement.
(vii) Revise and Refine:
Crafting a clear and concise thesis statement often requires revision and refinement. After drafting your initial statement, review it carefully and assess its effectiveness. Consider whether it adequately captures your main argument and if there are any areas that can be further clarified or tightened. Revise as necessary to achieve the desired clarity and conciseness.
Remember, your thesis statement serves as the foundation of your essay, guiding your writing and providing a clear roadmap for your readers. By crafting a clear and concise thesis statement, you enable your audience to grasp your main argument from the outset and set the stage for a focused and coherent essay.
Take the time to carefully craft and refine your thesis statement, ensuring it captures the essence of your argument while maintaining clarity and conciseness. A well-crafted thesis statement enhances the overall quality of your essay and paves the way for a compelling and engaging piece of writing.
6. Incorporating the Thesis Statement into Your Essay
In this section, we will explore how to effectively incorporate your thesis statement into your essay. The thesis statement serves as the guiding principle of your writing, and integrating it seamlessly into your essay is essential for maintaining focus and coherence throughout your work.
(i) Introduce the Thesis Statement:
Begin your essay by introducing your thesis statement in a clear and concise manner. Provide a brief overview of the main argument or position you will be discussing in your essay. This introduction should set the tone and context for the rest of your writing, ensuring that your readers understand the purpose and direction of your essay from the very beginning.
(ii) Use Topic Sentences:
Each paragraph of your essay should align with and support your thesis statement. Begin each paragraph with a topic sentence that relates directly to your thesis. This topic sentence acts as a mini-thesis for the paragraph, outlining the main point or argument that will be discussed. By connecting each paragraph to your thesis statement, you maintain a cohesive and focused essay structure.
(iii) Provide Supporting Evidence:
As you develop your essay, provide supporting evidence, examples, or data that reinforce your thesis statement. These pieces of evidence should directly support the main argument you are making. By incorporating relevant and persuasive evidence, you strengthen the credibility and persuasiveness of your thesis statement.
(iv) Offer Analysis and Explanation:
In addition to presenting evidence, analyze and explain how each piece of evidence connects to your thesis statement. Clearly demonstrate the significance of the evidence in relation to your main argument. This analysis helps to deepen your readers’ understanding of your thesis statement and its relevance to the broader context of your essay.
(v) Address Counterarguments:
Acknowledge and address potential counterarguments to your thesis statement. Anticipate objections or alternative viewpoints and offer counterpoints or explanations to refute them. This shows that you have considered different perspectives and strengthens the overall validity of your thesis statement.
(vi) Reiterate the Thesis Statement in the Conclusion:
In your conclusion, restate your thesis statement in a slightly different way, emphasizing its importance and summarizing the main arguments you have presented in your essay. This helps to reinforce the central message of your essay and leave a lasting impression on your readers.
(vii) Revise and Edit:
As you review and edit your essay, ensure that your thesis statement remains consistent and well-integrated throughout. Check that each paragraph aligns with your thesis and contributes to the overall coherence of your essay. Make any necessary revisions to strengthen the connection between your thesis statement and the supporting content of your essay.
By effectively incorporating your thesis statement into your essay, you create a strong and cohesive piece of writing. The thesis statement acts as the backbone of your essay, guiding the content and providing a clear direction for your readers. Through thoughtful integration, you ensure that your essay remains focused, logical, and persuasive, ultimately leading to a compelling and impactful piece of work.
Crafting a powerful thesis statement is an essential skill in academic writing, as it sets the stage for a well-structured and persuasive essay. Throughout this blog, we have explored the process of understanding the purpose of a thesis statement, analyzing the essay prompt, brainstorming and generating ideas, refining the thesis statement, and incorporating it into your essay. By following these steps, you can enhance the quality of your academic writing and make a compelling impact on your readers.
As you embark on your academic journey, academiawriting.com stands as a reliable and professional resource to assist you with your writing needs. Our team of experienced writers understands the intricacies of crafting a powerful thesis statement and can help you develop an essay that meets your specific requirements. Whether you need assistance with brainstorming ideas, refining your thesis statement, or structuring your essay, academiawriting.com is here to provide expert guidance and support.
Ordering at academiawriting.com guarantees you access to a range of benefits. Our dedicated writers are well-versed in various academic disciplines and can tailor their expertise to meet your specific needs. With our commitment to delivering high-quality, original content and adhering to strict deadlines, you can trust us to provide you with a custom essay that meets the highest academic standards.
Don’t let the challenges of crafting a powerful thesis statement and writing an impactful essay hold you back. Place your order at academiawriting.com and let our experienced professionals help you succeed in your academic endeavors. We are dedicated to supporting your academic growth and ensuring your satisfaction with our services.
Take the next step towards achieving your academic goals by ordering at academiawriting.com today. Let us assist you in creating a compelling, well-structured essay that showcases your knowledge and critical thinking skills. Trust Academia Writing to be your partner in academic excellence.
By Erin Cross
You might also like:.

Understanding Plagiarism: Types, Consequences, and Prevention

The Renaissance Writer: Inspiring Brilliance in Academic Prose

How to Write a Captivating Introduction for Your Academic Paper
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Enjoy this blog? Please spread the word :)
Academic & Employability Skills
Subscribe to academic & employability skills.
Enter your email address to subscribe to this blog and receive notifications of new posts by email.
Join 397 other subscribers.
Email Address
Why you should include a thesis statement in your essay
Posted in: essay-writing

If you're writing a 'show what you think' essay (i.e. discussion, argument, or problem-solution type essays), you should include a thesis, or problem, statement .
A thesis statement is a short, simple, one to two sentence summary of the position, argument or problem that you're going to develop in your assignment.
It forms part of your introduction, which should include:
- An attention-grabbing statement
- Definitions
- Information that sets the scene
- A very brief introduction to key ideas/arguments/research
- A thesis (or problem) statement
- What the essay will do, i.e. the route-map - what comes first, second, third etc.
As you can see, a thesis statement should usually come at the end of the introduction.
Why write a thesis statement?
A thesis statement:
- Provides the reader with a ‘guide’ to your argument.
- Tests your ideas by distilling them into a sentence or two. If your thesis statement is difficult to create and is unfocused, then your argument may be difficult and unfocused too!
- Helps you organise and develop your argument - and stay focused.
Your thesis statement therefore acts like an anchor that keeps your ideas pinned down. The themes of the paragraphs that follow in the main body should directly relate to the thesis, to build a convincing and reasoned response to the assignment question. Any content that doesn't relate to your thesis statement is irrelevant and should be removed.
The 'Fish Bone Essay Plan' below shows how the thesis statement controls the flow of ideas in your essay:
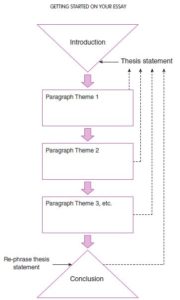
Here are a couple of examples of effective thesis/problem statements:
1. Although people may believe that modern democratic societies have achieved gender equality, the paper will show that this is in fact not the case, and that continuing inequality may be related to women's biology.
2. This essay will argue that there is a measurable correlation between increasing levels of childhood obesity and the number of targeted marketing campaigns launched by leading confectionary companies in the last ten years.
Adapted from: Hopkins, D. and Reid, T., 2018. The Academic Skills Handbook: Your Guid e to Success in Writing, Thinking and Communicating at University . Sage.
Share this:.
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
Click here to cancel reply.
- Email * (we won't publish this)
Write a response
How to navigate Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) tools with confidence and integrity
Artificial intelligence (AI) is advancing rapidly, and new Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) tools like ChatGPT, Claude, Elicit, Perplexity, Bard and Bing are now easily accessible online. As university students, how can you incorporate these emerging technologies into your studies and campus...

8 ways to beat procrastination
Whether you’re writing an assignment or revising for exams, getting started can be hard. Fortunately, there’s lots you can do to turn procrastination into action.

What I learnt from a skills enrichment workshop on feedback
If your course is largely essay-based (like mine is with Politics and International Relations) you’ll understand the frustration of receiving the same feedback on your assignments – over and over and over again.

- Translators
- Graphic Designers
Please enter the email address you used for your account. Your sign in information will be sent to your email address after it has been verified.
25 Thesis Statement Examples That Will Make Writing a Breeze

Understanding what makes a good thesis statement is one of the major keys to writing a great research paper or argumentative essay. The thesis statement is where you make a claim that will guide you through your entire paper. If you find yourself struggling to make sense of your paper or your topic, then it's likely due to a weak thesis statement.
Let's take a minute to first understand what makes a solid thesis statement, and what key components you need to write one of your own.

A thesis statement always goes at the beginning of the paper. It will typically be in the first couple of paragraphs of the paper so that it can introduce the body paragraphs, which are the supporting evidence for your thesis statement.
Your thesis statement should clearly identify an argument. You need to have a statement that is not only easy to understand, but one that is debatable. What that means is that you can't just put any statement of fact and have it be your thesis. For example, everyone knows that puppies are cute . An ineffective thesis statement would be, "Puppies are adorable and everyone knows it." This isn't really something that's a debatable topic.
Something that would be more debatable would be, "A puppy's cuteness is derived from its floppy ears, small body, and playfulness." These are three things that can be debated on. Some people might think that the cutest thing about puppies is the fact that they follow you around or that they're really soft and fuzzy.
All cuteness aside, you want to make sure that your thesis statement is not only debatable, but that it also actually thoroughly answers the research question that was posed. You always want to make sure that your evidence is supporting a claim that you made (and not the other way around). This is why it's crucial to read and research about a topic first and come to a conclusion later. If you try to get your research to fit your thesis statement, then it may not work out as neatly as you think. As you learn more, you discover more (and the outcome may not be what you originally thought).
Additionally, your thesis statement shouldn't be too big or too grand. It'll be hard to cover everything in a thesis statement like, "The federal government should act now on climate change." The topic is just too large to actually say something new and meaningful. Instead, a more effective thesis statement might be, "Local governments can combat climate change by providing citizens with larger recycling bins and offering local classes about composting and conservation." This is easier to work with because it's a smaller idea, but you can also discuss the overall topic that you might be interested in, which is climate change.
So, now that we know what makes a good, solid thesis statement, you can start to write your own. If you find that you're getting stuck or you are the type of person who needs to look at examples before you start something, then check out our list of thesis statement examples below.
Thesis statement examples
A quick note that these thesis statements have not been fully researched. These are merely examples to show you what a thesis statement might look like and how you can implement your own ideas into one that you think of independently. As such, you should not use these thesis statements for your own research paper purposes. They are meant to be used as examples only.
- Vaccinations Because many children are unable to vaccinate due to illness, we must require that all healthy and able children be vaccinated in order to have herd immunity.
- Educational Resources for Low-Income Students Schools should provide educational resources for low-income students during the summers so that they don't forget what they've learned throughout the school year.
- School Uniforms School uniforms may be an upfront cost for families, but they eradicate the visual differences in income between students and provide a more egalitarian atmosphere at school.
- Populism The rise in populism on the 2016 political stage was in reaction to increasing globalization, the decline of manufacturing jobs, and the Syrian refugee crisis.
- Public Libraries Libraries are essential resources for communities and should be funded more heavily by local municipalities.
- Cyber Bullying With more and more teens using smartphones and social media, cyber bullying is on the rise. Cyber bullying puts a lot of stress on many teens, and can cause depression, anxiety, and even suicidal thoughts. Parents should limit the usage of smart phones, monitor their children's online activity, and report any cyber bullying to school officials in order to combat this problem.
- Medical Marijuana for Veterans Studies have shown that the use of medicinal marijuana has been helpful to veterans who suffer from Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). Medicinal marijuana prescriptions should be legal in all states and provided to these veterans. Additional medical or therapy services should also be researched and implemented in order to help them re-integrate back into civilian life.
- Work-Life Balance Corporations should provide more work from home opportunities and six-hour workdays so that office workers have a better work-life balance and are more likely to be productive when they are in the office.
- Teaching Youths about Consensual Sex Although sex education that includes a discussion of consensual sex would likely lead to less sexual assault, parents need to teach their children the meaning of consent from a young age with age appropriate lessons.
- Whether or Not to Attend University A degree from a university provides invaluable lessons on life and a future career, but not every high school student should be encouraged to attend a university directly after graduation. Some students may benefit from a trade school or a "gap year" where they can think more intensely about what it is they want to do for a career and how they can accomplish this.
- Studying Abroad Studying abroad is one of the most culturally valuable experiences you can have in college. It is the only way to get completely immersed in another language and learn how other cultures and countries are different from your own.
- Women's Body Image Magazines have done a lot in the last five years to include a more diverse group of models, but there is still a long way to go to promote a healthy woman's body image collectively as a culture.
- Cigarette Tax Heavily taxing and increasing the price of cigarettes is essentially a tax on the poorest Americans, and it doesn't deter them from purchasing. Instead, the state and federal governments should target those economically disenfranchised with early education about the dangers of smoking.
- Veganism A vegan diet, while a healthy and ethical way to consume food, indicates a position of privilege. It also limits you to other cultural food experiences if you travel around the world.
- University Athletes Should be Compensated University athletes should be compensated for their service to the university, as it is difficult for these students to procure and hold a job with busy academic and athletic schedules. Many student athletes on scholarship also come from low-income neighborhoods and it is a struggle to make ends meet when they are participating in athletics.
- Women in the Workforce Sheryl Sandberg makes a lot of interesting points in her best-selling book, Lean In , but she only addressed the very privileged working woman and failed to speak to those in lower-skilled, lower-wage jobs.
- Assisted Suicide Assisted suicide should be legal and doctors should have the ability to make sure their patients have the end-of-life care that they want to receive.
- Celebrity and Political Activism Although Taylor Swift's lyrics are indicative of a feminist perspective, she should be more politically active and vocal to use her position of power for the betterment of society.
- The Civil War The insistence from many Southerners that the South seceded from the Union for states' rights versus the fact that they seceded for the purposes of continuing slavery is a harmful myth that still affects race relations today.
- Blue Collar Workers Coal miners and other blue-collar workers whose jobs are slowly disappearing from the workforce should be re-trained in jobs in the technology sector or in renewable energy. A program to re-train these workers would not only improve local economies where jobs have been displaced, but would also lead to lower unemployment nationally.
- Diversity in the Workforce Having a diverse group of people in an office setting leads to richer ideas, more cooperation, and more empathy between people with different skin colors or backgrounds.
- Re-Imagining the Nuclear Family The nuclear family was traditionally defined as one mother, one father, and 2.5 children. This outdated depiction of family life doesn't quite fit with modern society. The definition of normal family life shouldn't be limited to two-parent households.
- Digital Literacy Skills With more information readily available than ever before, it's crucial that students are prepared to examine the material they're reading and determine whether or not it's a good source or if it has misleading information. Teaching students digital literacy and helping them to understand the difference between opinion or propaganda from legitimate, real information is integral.
- Beauty Pageants Beauty pageants are presented with the angle that they empower women. However, putting women in a swimsuit on a stage while simultaneously judging them on how well they answer an impossible question in a short period of time is cruel and purely for the amusement of men. Therefore, we should stop televising beauty pageants.
- Supporting More Women to Run for a Political Position In order to get more women into political positions, more women must run for office. There must be a grassroots effort to educate women on how to run for office, who among them should run, and support for a future candidate for getting started on a political career.
Still stuck? Need some help with your thesis statement?
If you are still uncertain about how to write a thesis statement or what a good thesis statement is, be sure to consult with your teacher or professor to make sure you're on the right track. It's always a good idea to check in and make sure that your thesis statement is making a solid argument and that it can be supported by your research.
After you're done writing, it's important to have someone take a second look at your paper so that you can ensure there are no mistakes or errors. It's difficult to spot your own mistakes, which is why it's always recommended to have someone help you with the revision process, whether that's a teacher, the writing center at school, or a professional editor such as one from ServiceScape .
Related Posts

Need to Make Your Essay Longer? Here's How

How to Turn Your Dissertation Into a Book: A Step-By-Step Guide for New Authors
- Academic Writing Advice
- All Blog Posts
- Writing Advice
- Admissions Writing Advice
- Book Writing Advice
- Short Story Advice
- Employment Writing Advice
- Business Writing Advice
- Web Content Advice
- Article Writing Advice
- Magazine Writing Advice
- Grammar Advice
- Dialect Advice
- Editing Advice
- Freelance Advice
- Legal Writing Advice
- Poetry Advice
- Graphic Design Advice
- Logo Design Advice
- Translation Advice
- Blog Reviews
- Short Story Award Winners
- Scholarship Winners

Need an academic editor before submitting your work?

What Should a Thesis Statement on an Essay About a Short Story Look Like?

How to Start a Good Book Report
A literary analysis of short stories allows writers to explain the basic elements of the story and make a deeper statement about the plot, characters, symbolism or theme. Writing such an analysis allows students to learn more about the story and gain an appreciation of literature in general. One of the most significant elements of the literary analysis is the thesis statement.
In any essay, the thesis statement establishes the purpose of the essay for the reader. A good thesis fits the assignment length, makes a statement about your overall point and includes the specific points you will give to support that idea about the story. The thesis must relate to a specific point about the short story such as the argumentative point you want to explain or defend. Place the thesis at the end of the introductory paragraph of the analysis.
When writing your thesis statement, make sure to clearly state the purpose of your essay to the reader. Narrow your focus to aspects of the story that fits the scope of the assignment, both in terms of the depth of your discussion as well as the minimum word count. For instance, saying a character is "interesting" or that many symbols appear in the story does not give your reader a clear idea of what you will discuss. Instead, choose words that emphasize your point, such as how a character's flaw causes his downfall or how a particular set of symbols illustrate the theme of the story.
The thesis for a literary analysis will determine the organization you will use in the body of the paper. Consider comparing or contrasting characters or situations, explaining a causal relationship between events in the plot, relating how a character fulfills a certain role or discussing how elements, such as the setting, illustrate the theme. Write your thesis with language like "differences," "similar," "cause," "effects" and the element or elements you will cover such as "theme," "character" and "setting."
Add subpoints to your thesis to preview the specifics you will provide in support of your thesis. These may list the characters, symbols, plot elements, similarities, differences, causes or effects you will discuss. Write these subpoints in the same order in your thesis that you will present them in the body of the paper and list them after your main idea in your thesis. For example, a good thesis might be, "The man in Jack London's 'To Build a Fire' fails in his mission due to his overconfidence in himself, his disdain toward nature’s power and his inability to retain his composure."
Related Articles

Tips on Writing an Explication Paper on a Short Story

How to Write a College Character Analysis Essay

How to Write an Essay Explaining a Concept

How to Write a Thesis Statement for "Robinson Crusoe"

How to Write a Motif Paper

How to Write an Introduction to a Reflective Essay

How to Write a Review of a Poetry Book
How to write a definition essay.
- Gwynedd-Mercy College: How to Write a Literary Analysis Essay
- Purdue Online Writing Lab: Tips and Examples for Writing Thesis Statements
- Purdue Online Writing Lab: Writing in Literature: Overview
- Purdue Online Writing Lab: Developing a Thesis
Kristie Sweet has been writing professionally since 1982, most recently publishing for various websites on topics like health and wellness, and education. She holds a Master of Arts in English from the University of Northern Colorado.
- Middle East
- Eastern Europe
- Southeast Asia
- Central Asia
- International Law
- New Social Compact
- Green Planet
- Urban Development
- African Renaissance
- Video & Podcasts
- Science & Technology
- Intelligence
- Energy News
- Environment
- Health & Wellness
- Arts & Culture
- Travel & Leisure
- Hotels & Resorts
- Publications
- Advisory Board
- Write for Us

This essay intends to analyze how Ethiopianism (Synthesis) is impossible without the ideological, philosophical, and practical struggle between Amhara (thesis) and anti-Amhara (anti-thesis).
Concerning this, by borrowing the ideas of dialectical idealism from George Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel (1770–1831) and dialectical materialism from Karl Marx (1818–1833) , this essay argues that the dialectical struggle for the march to Ethiopianism has been getting ethnic rather than spiritual and economic base.
Ethiopia has been operating under an ethnic federalist political system since 1991. Article 39 of the 1995 FDRE constitution grants ethnic groups the right to self-determination, including the ability to secede. After this, there are doubts about Ethiopia’s stability as an integrated state. Ethnicity turns into a battleground for Ethiopia’s integration or disintegration.
Relating to that, Ethiopian ethnic groups and ethnic elites have been in condemnation and quarrel. Ethnic groups and any ethnic elites who have been condemning ethnic federalism , anti-ethnic narration, and the continuity of the Ethiopian state can be enunciated under the Amhara thesis.
Ethnic groups and any ethnic elites who portray Amhara as dominant in politics, economy, or culture and wish the disintegration of the old, civilized state Ethiopia and wait for the political landscape to open up in order to form their sovereign states are stated under anti-Amhara anti-thesis.
Thus, the Ethiopian movement is unyielding on its own and requires Amhara as a thesis and anti-Amhara as an antithesis for realization. However, if the Amhara thesis has been growing weaker to prevail over the anti-Amhara thesis, the conflict between thesis and antithesis may fail to bring Ethiopianism back and would result in long-lasting material and humanitarian losses.
This essay contends that in the current situation, the march to reach Ethiopiansim has been facing barriers since there have been more than a century of conspiracy and ahistorical narration against the North Ethiopian ethnic groups (Tigray and Amhara-Agaw), more specifically Amhara, which take charge of crafting a civilized Ethiopia.
Thereby, the anti-Amhara thesis has been defusing in the minds of Ethiopian peoples for an extended period of time, and this has caused a number of Ethiopian peoples to be reluctant and cowardly to defend Ethiopia from European colonial thinking .
Concerning this, since the 1960s , most Ethiopian elites have been starting to accept colonial thinking and developing anti-Amhara theories. Sharing of the advanced living style, culture, literature, and arts from the North Ethiopian ethnic groups was taken as oppressive and assimilation, although ruling elites had the opportunity to manipulate the Northern culture for their political gain.
Anyway, such a phenomenon can be supported by Althusser’s idea. As Louis Althusser (1918–1990) , a French Marxist philosopher, argued in his essay “Ideology and Ideological State Apparatuses: Notes towards an Investigation,” capitalists use education as ideological state apparatuses to generate Marxist ideology-oriented generations.
This Althusser’s statement can be applied to the Ethiopian case. During the end of the monarchy political system and after the fall of the regime of Emperor Haile Selassie, Western educated Ethiopian elites with the left-wing military of the emperor have been starting to implement anti-Amhara thesis as ideology in the education sector and political apparatus to dismantle Ethiopia through process by taking the state craft of Ethiopia as architected by Northern and Southern-exclusive.
Ethiopia has been on the verge of fragility. Existing anti-Amhara and fake historical narratives will inevitably lead Ethiopia to collapse and the halt of Ethiopianism. There is no time to fix the current political crisis through national reconciliation and education. National reconciliation and education take a long time, although the country has had time to survive.
To save the country, the following short-range plan must be practical. Power balance is in need. For the anti-thesis of Amhara, the country needs to adopt the thesis of Amhara as a defense mechanism. For the purpose of this writing, the Amhara thesis or thesis of Amhara refers to thinking and ideology that lead to the continuity of the Ethiopian state with ethnic equality, equal and equitable distribution of resources, and political position for all ethnic groups rather than the hegemony or domination of Amhara ethnic groups and Amhara elites in the political and economic arena of Ethiopia.
Ethiopians who value their country must embrace the Amhara thesis and participate in all political, social, and intellectual battles in order to remake Ethiopia’s history—that is, to reconstruct Ethiopia for all. However, achieving the ideological superiority of “all to one Ethiopia” is necessary to ensure thesis hegemony over antithesis since it enables the transition to Ethiopiansm (synthesis).
For this, a good reference is Gramsci. Antonio Gramsci (1891–1937) , who was a leader of the Italian Communist Party, stated that to be a hegemon, ideological superiority must prevail. Accordingly, the ideology of “all to one Ethiopia” should be described on earth.
The Amhara elites and other ethnic group elites who need Ethiopia to survive must work together with an inclusive, democratic, and humanitarian political base . Ethnic groups who have been affected and victimized by political groups that have been under the category of antithesis and disintegration need to be represented in politics, and their rights need to be of great concern.
In addition to this, Ethiopian elites and politicians who have been on the side of this thesis have to work to foster positive diplomatic relations and political alliances for mutual benefit with the sovereign countries of all Horn of Africa countries . Related to this, elites should take care to not fail in conspiracy by interfering with the political issues of countries in the Horn of Africa and pronouncing the issue of port early, since this can cut off alliances and leave synthesis in danger.
In Ethiopian political history, the source of problems and solutions is the elite . It is the elite who developed anti-thesis and tried to create the sovereign state of Tigray and the sovereign state of Oromia in disintegrated Ethiopia. Similar, it is elites who can mobilize peoples to unite on the thesis for the journey to Ethiopanism. Accordingly, it is time to fill the playing field of the thesis, even though it is a complication to be sure, as if the Prosperity Party, rebel groups, or this and that ethnic groups have stood on the thesis for Ethiopian achievement.

Digital Minimalism: Strategies for a healthier balance between technology and real-world
Choosing a career: top 5 factors to consider for college students, guterres: ‘step back from the brink,’ to avert full-scale middle east conflict, unravelling pakistan’s data protection framework, terrorism and extremism: threat to the security of pakistan.
MD does not stand behind any specific agenda, narrative, or school of thought. We aim to expose all ideas, thinkers, and arguments to the light and see what remains valid and sound.
- Fine Living
© 2023 moderndiplomacy.eu. All Rights Reserved.
Privacy Overview

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Step 2: Write your initial answer. After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process. The internet has had more of a positive than a negative effect on education.
A thesis statement is a sentence in a paper or essay (in the opening paragraph) that introduces the main topic to the reader. As one of the first things your reader sees, your thesis statement is one of the most important sentences in your entire paper—but also one of the hardest to write! In this article, we explain how to write a thesis ...
It is a brief statement of your paper's main argument. Essentially, you are stating what you will be writing about. Organize your papers in one place. Try Paperpile. No credit card needed. Get 30 days free. You can see your thesis statement as an answer to a question. While it also contains the question, it should really give an answer to the ...
A thesis statement: tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion. is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper. directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself.
Hint: a great many clear and engaging thesis statements contain words like because, since, so, although, unless, and however. 4. A strong thesis statement is specific. A thesis statement should show exactly what your paper will be about, and will help you keep your paper to a manageable topic.
The thesis statement is the brief articulation of your paper's central argument and purpose. You might hear it referred to as simply a "thesis." Every scholarly paper should have a thesis statement, and strong thesis statements are concise, specific, and arguable. Concise means the thesis is short: perhaps one or two sentences for a shorter paper.
Read the following examples of strong thesis statements, from essays and book chapters, and see if you can identify the different elements of a strong thesis and of the MTS within them. Example 1: from "University Gothic, c. 1880-1910" by Minna Vuohelainen in Gothic Britain: Dark Places in the Provinces and Margins of the British Isles :
After reading your thesis statement, the reader should think, "This essay is going to try to convince me of something. I'm not convinced yet, but I'm interested to see how I might be." ... A good, standard place for your thesis statement is at the end of an introductory paragraph, especially in shorter (5-15 page) essays. Readers are used to ...
Step 4: Revise and refine your thesis statement before you start writing. Read through your thesis statement several times before you begin to compose your full essay. You need to make sure the statement is ironclad, since it is the foundation of the entire paper. Edit it or have a peer review it for you to make sure everything makes sense and ...
Thesis. Your thesis is the central claim in your essay—your main insight or idea about your source or topic. Your thesis should appear early in an academic essay, followed by a logically constructed argument that supports this central claim. A strong thesis is arguable, which means a thoughtful reader could disagree with it and therefore ...
In short, a thesis statement is a short statement which offers the reader information on what the essay is about, stating its main point or argument. A thesis statement should appear in both the introduction paragraph as well as the conclusion paragraph of the essay .
It does contain at least two clauses, usually an independent clause (the opinion) and a dependent clause (the reasons). You probably should aim for a single sentence that is at least two lines, or about 30 to 40 words long. Position: A thesis statement always belongs at the beginning of an essay.
Step 2: Do Your Research. A strong thesis statement will be clear and specific, and it will be later supported by evidence from your research. You won't be able to write a statement like this until you do your research. The research will look different depending on your task.
A thesis statement is a very common component of an essay, particularly in the humanities. It usually comprises 1 or 2 sentences in the introduction of your essay, and should clearly and concisely summarize the central points of your academic essay. A thesis is a long-form piece of academic writing, often taking more than a full semester to ...
Think about the purpose and tone of your paper: A thesis statement should contain the main point of the paper and suggest to the reader a direction that the paper will take in exploring, proving, or disproving that main point. 4. State your main point in a sentence or two: A good writer can assert the main idea of a short, coherent essay briefly.
The thesis sets a clear intention for your essay, helping the reader understand the argument you're presenting and why the evidence and analysis support it. Persuasive writing. Persuasive writing depends on an excellent thesis statement that clearly defines the author's position. ... Your thesis statement should state precisely what your ...
A thesis statement should appear in the introduction of the essay to layout the main topic and the author's stance on it. It should also appear in the conclusion of the essay, where the author can refer back to it. A thesis statement should be a short statement of only one or two sentences that delivers clear and concise information.
The thesis statement is typically placed at the end of the introduction section of your essay or research paper. It usually consists of a single sentence of the writer's opinion on the topic and provides a specific guide to the readers throughout the paper. ... A strong thesis statement should address — ... The statement should be short and ...
Using paper checkers responsibly. 2. Your thesis statement should be specific—it should cover only what you will discuss in your paper and should be supported with specific evidence. 3. The thesis statement usually appears at the end of the first paragraph of a paper. 4. Your topic may change as you write, so you may need to revise your ...
The first step in analyzing the essay prompt is to read it thoroughly. Pay close attention to the wording and structure of the prompt. Look for keywords or phrases that provide clues about the specific focus or approach required. These keywords might include "analyze," "compare and contrast," "evaluate," or "discuss.".
A thesis statement is a short, simple, one to two sentence summary of the position, argument or problem that you're going to develop in your assignment. It forms part of your introduction, which should include: An attention-grabbing statement. Definitions. Information that sets the scene. A very brief introduction to key ideas/arguments/research.
What that means is that you can't just put any statement of fact and have it be your thesis. For example, everyone knows that puppies are cute. An ineffective thesis statement would be, "Puppies are adorable and everyone knows it." This isn't really something that's a debatable topic. Something that would be more debatable would be, "A puppy's ...
In any essay, the thesis statement establishes the purpose of the essay for the reader. A good thesis fits the assignment length, makes a statement about your overall point and includes the specific points you will give to support that idea about the story. The thesis must relate to a specific point about the short story such as the ...
This essay intends to analyze how Ethiopianism (Synthesis) is impossible without the ideological, philosophical, and practical struggle between Amhara (thesis) and anti-Amhara (anti-thesis).. Concerning this, by borrowing the ideas of dialectical idealism from George Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel (1770-1831) and dialectical materialism from Karl Marx (1818-1833), this essay argues that the ...