
Popular Insights:
Best Project Management Software
Mind Mapping Software
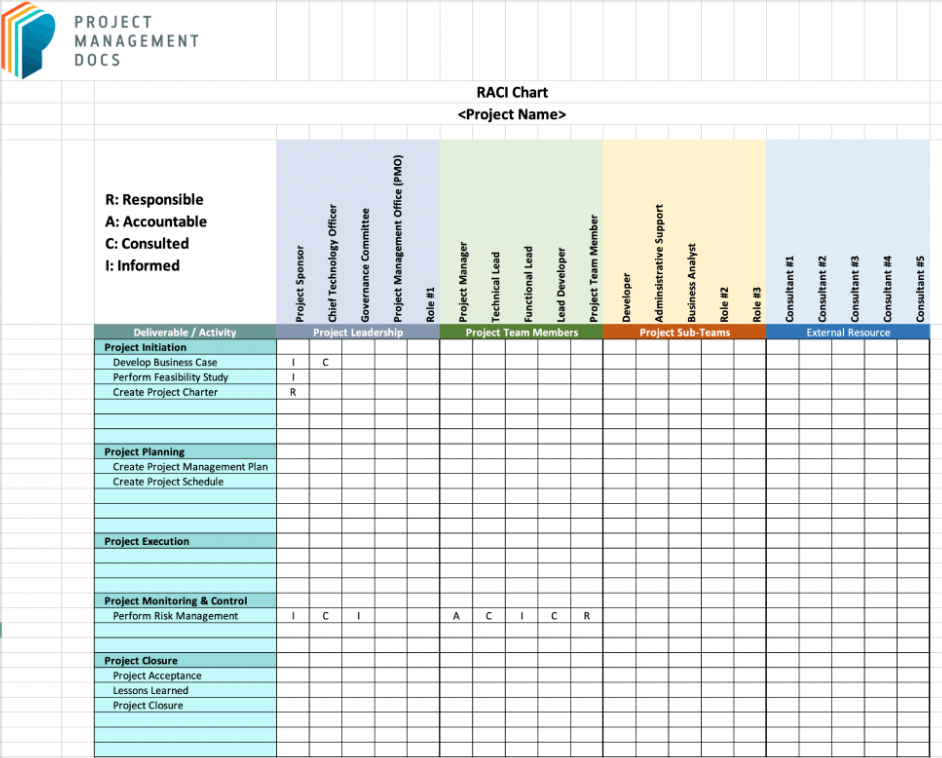
What Is a RACI Matrix?
Share this Article:
Our content and product recommendations are editorially independent. We may make money when you click links to our partners. Learn more in our Editorial & Advertising Policy .
A RACI matrix is a document that clarifies which individuals or groups are responsible for a project’s successful completion, and the roles that each will play throughout the project. The acronym RACI stands for the different responsibility types: Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed.
Successful project management depends on a team-wide understanding of roles and responsibilities. Using a RACI matrix to assign and define each role is a great way to keep a project on track and positioned for success. When designed correctly, the RACI matrix is a way for a project manager to help ensure the success of the project before it’s even begun.
Read more: What is Project Management?
Featured Partners
{{ POSITION }}. {{ TITLE }}
Video: Decoding the RACI Matrix for Effective Project Management
How Does a RACI Chart Help Project Managers?
Project managers use RACI charts to keep track of team roles and relay those responsibilities to the larger team. The matrix defines clear roles and responsibilities for individual team members across the various phases of the project, breaking each role down into four types of designation: those who are Responsible and Accountable for project deliverables, those who should be Consulted as work begins, and stakeholders who need to be Informed of ongoing progress, roadblocks, and updates.
Read more: Project Management Phases
RACI Matrix Definitions
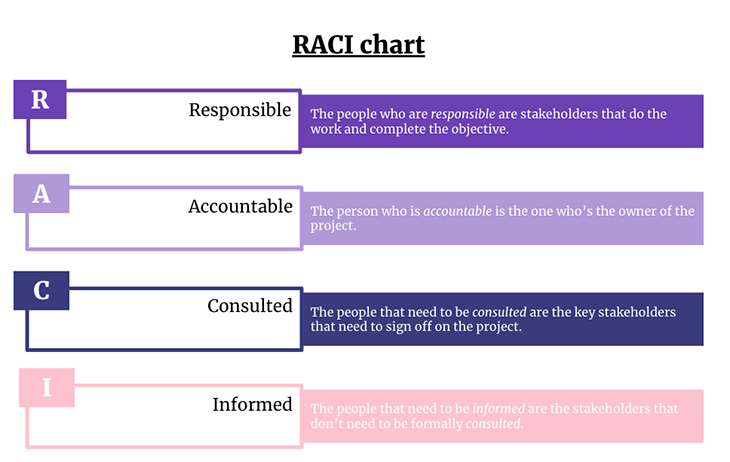
Responsible.
The individual(s) with responsibility for the task or deliverable is typically responsible for developing and completing the project deliverables themselves. The responsible parties are typically hands-on team members who make direct contributions toward the completion of the project. The responsible team is comprised of the project’s “doers”, working hands-on to ensure that each deliverable is completed.
Some examples of responsible parties are:
- Project Managers
- Business Analysts
- Graphic Designers
- Copywriters
Accountable
Accountable parties ensure accountability to project deadlines, and ultimately, accountability to project completion. This group frequently also falls under the informed category.
Some examples of accountable parties are:
- Product Owners
- Signature Authorities
- Business Owners
- Key Stakeholders
Consulted individuals’ opinions are crucial, and their feedback needs to be considered at every step of the game. These individuals provide guidance that is often a prerequisite to other project tasks, for example, providing legal guidance on a project throughout the process. If you are working on new product development or expansion, this could essentially be the entire organization.
Some examples of consulted parties are:
- Legal Experts
- Information Security and Cybersecurity Experts
- Compliance Consultants
Informed persons are those that need to stay in the loop of communication throughout the project. These individuals do not have to be consulted or be a part of the decision-making, but they should be made aware of all project updates. Typically, this party are business owners or stakeholders that are more interested in viewing the project at a 30,000-foot view. Keep this group on your cc list for awareness of topics, decisions, and progress – that includes making them part of the initial project kickoff and project demos as optional attendees. This group often also falls under the accountable group.
Some examples of informed parties are:
- Project Committee Members
- External Stakeholders
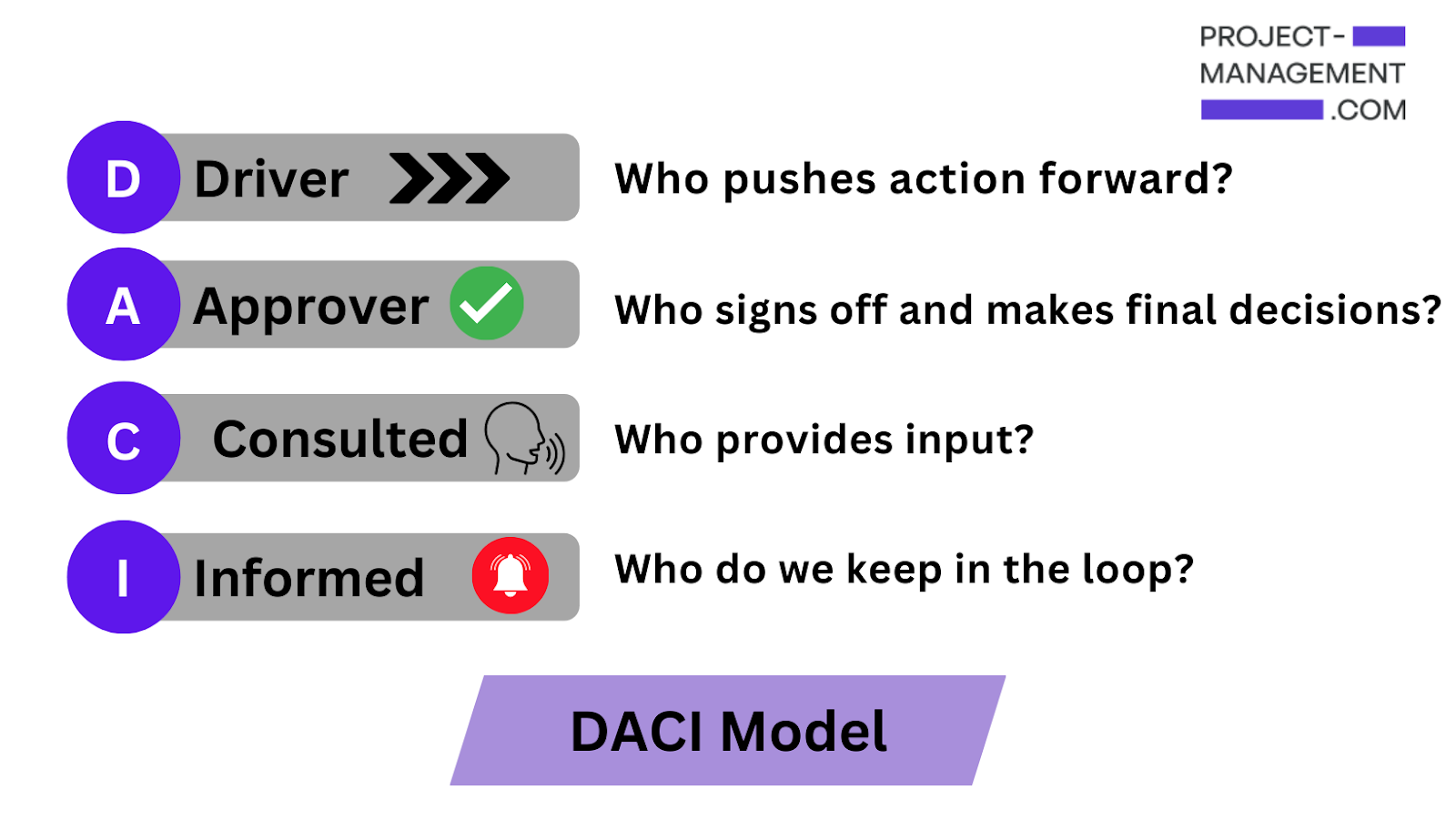
Read more: DACI vs RACI Model Guide
Why Are RACI Roles Important?
RACI roles provide a sense of organization and clarity for teams that are looking to divide roles and keep team members accountable for their contributions. Considering that 27% of projects go over budget, for reasons like scope creep and lack of defined roles, RACI roles help position a project for success and avoid common pitfalls.
Moreover, RACI roles help ensure that communication between all roles is ongoing. When you consider that nearly half of all project spending is at risk of being wasted due to a lack of effective team-based communication, it becomes all that more important to prioritize. Ultimately, teams who prioritize communication and well-defined roles are better off, and RACI roles help teams achieve that goal faster – while providing accountability for each team member’s unique contributions to the success of the project.
Read More: Top 10 Main Causes of Project Failure
How to Create a RACI Matrix
If you’re looking to implement a RACI matrix as part of your team’s project planning process, take these steps to create a RACI matrix.
Ensure that you have a thorough understanding of the project and its demands before outlining any further steps by communicating with key stakeholders and decision-makers.
Determine the list of key activities and deliverables from the director of program management or other leadership.
Determine who is needed to be a part of the project or initiative.
Determine the project roles and responsible job titles and persons for each activity and deliverable.
Hold review sessions with key members of the team for alignment, and if you haven’t already, host a kickoff meeting with the entirety of the team and key stakeholders to unveil the matrix, address questions, and more.
If the project has already started, it’s not too late to implement a RACI matrix.
- Outline the story. Using research from multiple sources, do a, b, c, and d.
- Utilize steps 2 and 3 (shown above). Ensure the right groups are assigned and engaged.
- Hold a review session. Ensure that the team acknowledges and discusses the plan and the roles assigned.
Read more: 8 Factors That Lead to Successful Projec ts
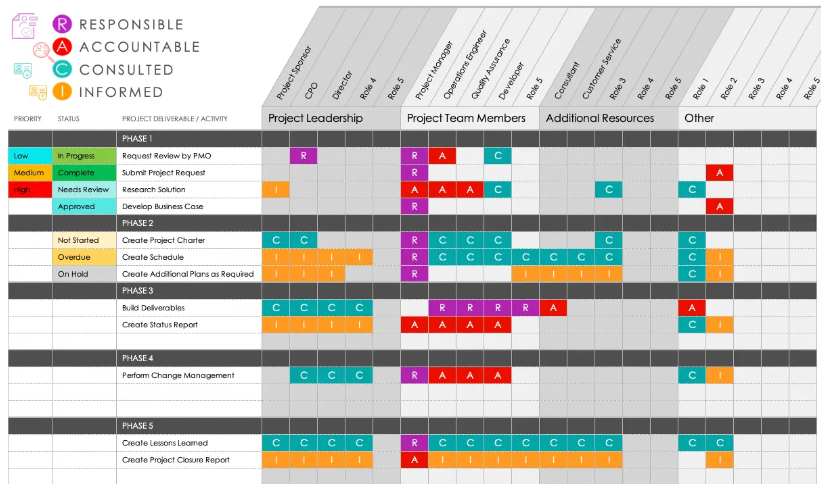
Examples of a RACI Matrix

As shown above, a RACI matrix helps break down what roles individuals will play as work is carried out and to what extent they will be involved in the project overall. The horizontal axis represents each person on the project team and the vertical axis represents each task.
Each square of the matrix represents an individual, a task, and that individual’s role within the project, either responsible, accountable, consulted, or informed. In this situation, for example, the project manager is accountable for accessing risk, defining performance requirements, creating designs, executing construction, and approving construction work. However, they are only informed about approving construction work and defining functional and aesthetic needs.
Read more: Understanding Different Types of Stakeholders and Their Roles
Our FREE Downloadable RACI Matrix Template
Who creates the raci matrix.
The RACI matrix — sometimes called RACI model, RACI diagram, or simply just RAC — is created by the project manager at the start of the project as a key part of establishing the initial human resources planning for the project. Because miscommunication is a common threat to any project, RACI charts are a great asset to teams dealing with any type of project, from very simple projects to extremely complex ones.
Common Mistakes When Creating a RACI Matrix
- Failure to plan ahead: Utilizing a RACI matrix should not be your first step in project planning. Having a fully assembled project team and at least a general idea of a task list and project plans is a better place to start before preparing a matrix.
- Working with too large a team: A RACI matrix is likely not the best bet for a large team, as it will make the matrix hard to understand and overly complex.
- Not communicating with the project team: A RACI matrix should help organize tasks and responsibilities that have already been introduced to the project team – no one likes to be blindsided. Be sure to host a kickoff meeting with the team first before creating a RACI matrix.
FAQ: How do I Implement a RACI matrix?
Implementing a RACI matrix takes more than just a few emails and sporadic conversations – it takes consistent communication and planning. You should host a kickoff meeting to introduce the matrix to the team and make a plan to continue meeting at predetermined times throughout the project lifecycle.
Here are a few more tips to keep in mind as you implement your RACI matrix within the team dynamic:
- Get everyone prepared. Send the document around to the meeting distribution as read-ahead material, requesting feedback if there are any major concerns.
- Roll out each role for the team . During the meeting, conduct a review of the tasks and responsible parties. Do not rush through this review, but rather ensure enough time in your project kickoff for this important aspect. (Be certain to clarify the definitions of RACI to avoid ambiguity.)
- Consider changes and update accordingly. After the meeting, send out the notes documenting acceptance or updates to the RACI. In addition to sending out the notes, request any corrections within a reasonable yet defined timeframe. Clarify that if no changes are requested, each person is acknowledging their role and committing to the project tasks as outlined.
- Stay in touch. Consider a quick review with the entire team each quarter or every six months for longer projects to ensure it remains up-to-date and not simply another document in the repository but a relied-upon artifact.
FAQ: What are RACI matrix best practices?
As you implement the raci matrix….
- Encourage teamwork and foster collaboration whenever possible.
- Don’t fear updates – make changes and adjustments as needed (but be sure to communicate those changes clearly to all parties).
- Earlier is better. Roll out your matrix plan to the team BEFORE you plan to implement it for the best results.
- Have a clear-cut understanding of the project scope and how each role connects to the overall project goal.
For “Responsible” Parties:
- Make sure your project’s definition of Responsible is clear on who holds the “decider” role for the project or project phase’s completion, and what the dimensions of that responsibility will be.
- Ensure that all parties are aware of their role and responsibilities within the matrix.
For “Accountable” Parties:
- When multiple Accountable team members must exist, use your definitions to make clear which individual is accountable for a given project element, and how that individual needs to interact with other Accountable team members.
- Ensure that there is only one “Accountable” party assigned per task.
- Be sure that the Accountable party has the authority and power to oversee the task as the accountable party.
For Consulted and Informed Parties:
- Consulted parties are often high-level decision-makers with heavy schedules. Make sure you’re clear on their availability ahead of time.
- Similar to Consulted parties, Informed parties are often less hands-on and have less understanding of day-to-day project operations. As the project goes on, make sure to keep detailed notes to keep the Informed party up-to-date on key information.
- Understand the ways that these parties like to communicate and create a plan to reach them early – whether that’s over phone calls, emails, video calls, or from within your project management system’s collaboration tools.
- Knowing the difference between who needs to be consulted versus informed can be a challenge if there is ambiguity about project roles. Consider what aspects of the project different team members need to know to do their jobs, and then bake those into your definitions.
RACI Matrix Pros & Cons
- Increased Engagement: RACI helps engage project participants in the project lifecycle.
- Enhanced Project Planning: Project managers make project planning more organized, efficient, and detailed.
- Identifiable Improvement Opportunities: Areas of improvement are more easily identified.
- Easier Collaboration: Use of a RACI matrix creates a clear path for leadership to sign off on project steps, as project documentation in the RACI model is heavily emphasized.
- Better Communication: Improves overall group communication as a whole.
- Group Accountability: Assists groups, especially larger project teams, stay connected and accountable to their roles and project goals
- Limitations on Role Scope: The RACI model does not provide details on role scope, especially for responsible parties. These gaps in detail also affect other team roles, for example, another gap in a RACI is the determination of who is responsible for verifier and signatory.
- Limits on Task Details and Scope: While a RACI matrix can provide an overview of who is responsible for different tasks, it will not state what needs to be done.
- Not Aligned to the Agile Methodology: Project managers using an agile methodology like scrum may find it redundant since accountability, ownership, and ongoing communication is built into the scrum framework (i.e., product owner, scrum master, and daily standups with the team). Additionally, agile focuses on team-based delivery and accountability, while the RACI framework and alternatives focus on individual responsibility and autonomous accountability.
Read more: Top 10 Causes of Project Failure
Free RACI Matrix Templates
A number of project management software solutions include a native RACI matrix template. Here are just a few we’ve found:
Colorful RACI Chart Template
We love this template from Smartsheet because it’s colorful, thorough, and includes room for every party involved in the project.
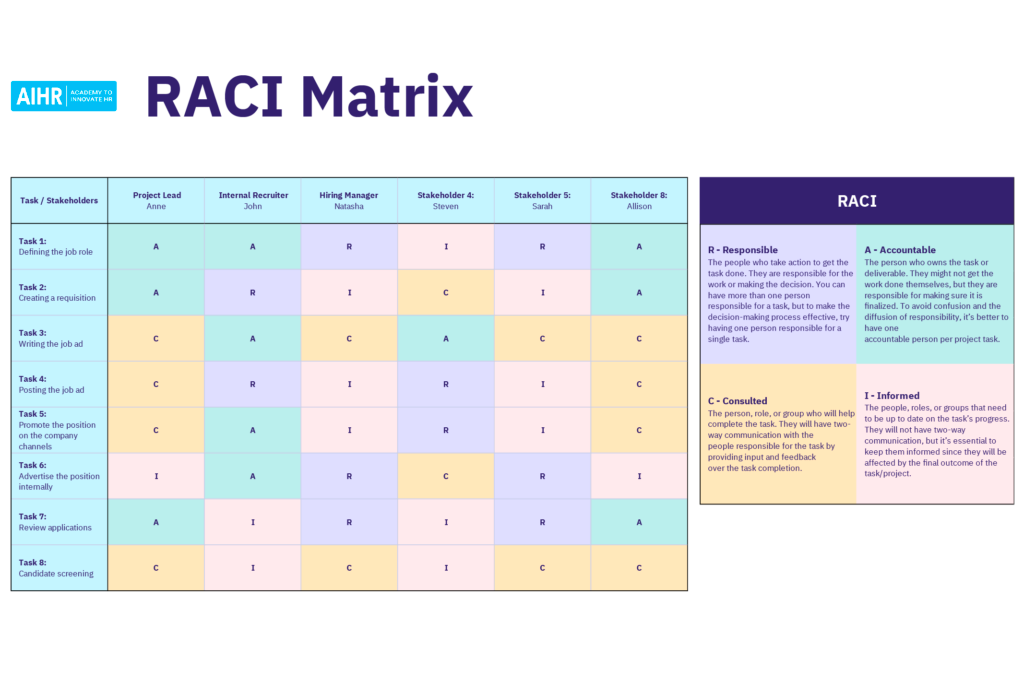
Pastel Colored RACI Matrix Template
This template from the Academy to Innovate HR is a great choice for project managers who want to organize their team roles with an easy-on-the-eyes chart that evolves beyond the simple spreadsheet.
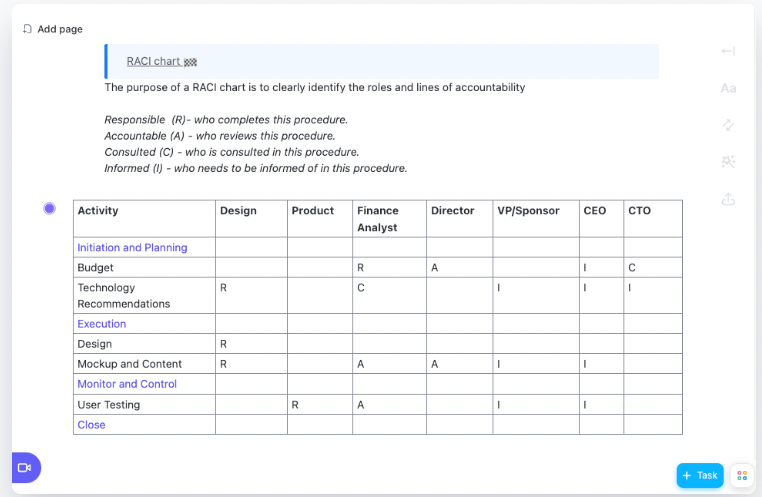
Simple RACI Chart from Clickup
These RACI templates from Clickup have enough variety to fit any of your project needs, but are simple enough for even beginner PMs to use.
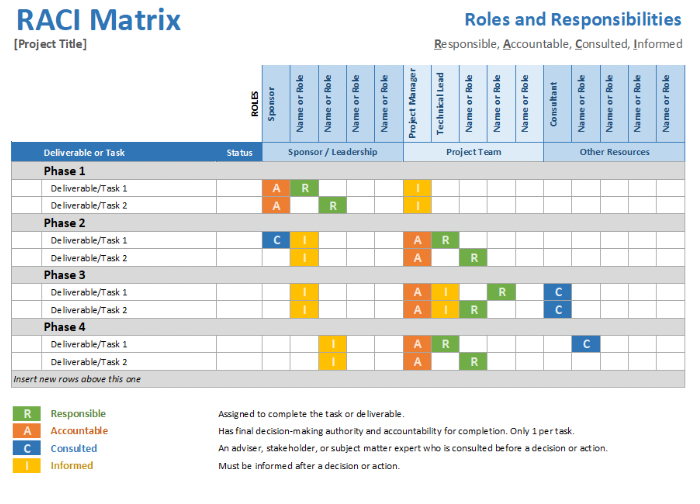
Detailed RACI Matrix Template
This template is a great starter template for anyone looking to explore RACI charts in their project management strategy. As an added bonus – it comes with the RACI definitions already built in!
Excel-Based RACI Chart Template
Are you an Excel or Google Sheets user looking to take advantage of the RACI matrix? An Excel-formatted template from Project Management Docs can be just the solution for you. This template is a great template for users who want a chart that comes in a pre-formatted structure.
Sign up for our emails and be the first to see helpful how-tos, insider tips & tricks, and a collection of templates & tools. Subscribe Now
{{ TITLE }}
You should also read.

How to Take Meeting Minutes Effectively (+ Example and Templates)

How to Manage Time Constraints: Top 7 Expert Tips
6 RACI Matrix Alternatives to Help Define Project Roles
Join our newsletter.
Subscribe to Project Management Insider for best practices, reviews and resources.
By clicking the button you agree of the privacy policy

Get the Newsletter
You might also like.

10 Benefits of Project Management Software for Business

Risk Identification Techniques and Methods for Projects
How to Measure the Success of a Project: 5 Steps (+ Examples)

The Defense Acquisition Encyclopedia
Program Management
A Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) describes the participation of various organizations, people, and their roles in completing tasks or deliverables for a project. The Program Manager (PM) uses it to clarify roles and responsibilities in a cross-functional team , projects, and processes. A RAM has four primary assignments: Responsible , Accountable , Consulted , and Informed (also called a RACI matrix).
Definition: A Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) describes the role and responsibilities of various people and/or organizations in completing specific tasks for a project.
Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed (RACI) Matrix
A RAM is called a Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed (RACI) matrix. The PMBOK Guide 4th Edition defines RACI as a RAM that illustrates the connections between work packages or activities and project team members. In fundamental terms, RAM refers to the framework in place to distribute duties to individuals where, in a RACI, each team member is assigned a role based on one of the four roles. On larger projects, RAMs can be developed at various levels.
- Responsible (R): Those who do the work to achieve the task. There is typically one role with a participation type of responsibility, although others can be delegated to assist in the work required.
- Accountable (A): The one ultimately accountable for the correct and thorough completion of the deliverable or task, and the one to whom Responsible is accountable. In other words, an Accountable must sign off (Approve) on work that Responsible provides. There must be only one Accountable specified for each task or deliverable.
- Consulted (C): Those whose opinions are sought and with whom there is two-way communication.
- Informed (I): Those who are kept up-to-date on progress, often only on completion of the task or deliverable, and with whom there is just one-way communication.
Benefit of Utilizing a Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM)
The RAM holds substantial advantages for project managers by clarifying the importance of their processes within the team. It fosters a sense of collective contribution among all employees, eliminating the sense of isolation. This project management technique, the RAM, empowers every team member to grasp the broader context of their work. Instead of simply instructing an administrative assistant to collect phone numbers without context, you can refer them to this valuable resource. By using the RAM, employees become more engaged in achieving positive results as they comprehend the alignment of their contributions with the company’s overall operations.
Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) Goal in Project Management
A RAM is used in project management as a communication tool to ensure that work tasks are designated as a responsible agent. A RAM can define what a project team is responsible for within each component of the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) . It could also be used within a working group to designate roles, responsibilities, and levels of authority for specific activities. The matrix format shows all activities associated with one person and all people associated with one activity. This ensures that only one person is accountable for any task to avoid confusion.
Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) Tutorial
Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) Standard Format
A RAM is displayed as a chart that illustrates the interaction between work packages that need to be done and project team members. Typically, the list of objectives is on the left-hand column with the project team member names across the top. Each work package will be assigned to the appropriate project team member. The chart aids in communication among the project team members.
No one should typically have more than one degree of responsibility for any given deliverable or activity group in the RAM chart. To simplify things, we’ve assigned each participant in this scenario a certain amount of commitment. However, there is frequently white space when you create a genuine model for more than four people. In some situations, it’s okay to have someone with secondary responsibility but not primary.
Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) Template
Template: responsibility assignment matrix (ram) (excel), 6 steps to developing a responsibility assignment matrix (ram).
Below is a list of the 6 (six) most common steps in developing a Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM).
- Step 1: List all project tasks and deliverables
- Step 2: Identify all project stakeholders
- Step 3: Determine the responsibility and accountability level for each task and deliverable
- Step 4: Assign stakeholders to each task
- Step 5: Assign overall stakeholder
- Step 6: Ensure all stakeholder know their responsibility
Developing Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) Matrix Best Practices
Below is a list of best practice topics that can help Program Managers effectively build and use a Responsibility Assignment Matrix.
- One stakeholder is in charge per task.
- The least amount of people accountable, the better.
- Be Efficient with Meetings.
- Constant Communication.
- Stakeholders agree on final RAM
Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) Lessons Learned
A Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) is a tool used in project management to identify and clarify the roles and responsibilities of the different people or groups working on a project. The goal of making a RAM is to make sure that all tasks are done and that responsibilities don’t overlap or get missed. Here are some things you can learn to make sure your RAM is built right:
- Define the project’s goals and scope in detail: Before making a RAM, it’s important to have a clear idea of the project’s goals and scope. This will help make sure that all necessary tasks are included and that the responsibilities are in line with the overall project goals.
- Find out who all the stakeholders are and what their roles are: A RAM should have a list of all the people or groups involved in the project, such as internal team members, external partners, and customers. There should be roles and responsibilities for each stakeholder.
- Give each stakeholder specific tasks and responsibilities: Instead of giving each stakeholder a general role, it is important to give them specific tasks and responsibilities. This will help make sure that no one’s responsibilities get mixed up or left out.
- Make sure that all stakeholders know about and understand the RAM: It is important to make sure that all stakeholders know about and understand the RAM. This can be done by having regular meetings and giving updates, as well as by putting the RAM in writing.
- Review and update the RAM often: As the project moves forward, it may be necessary to review and update the RAM. This can help make sure that the RAM stays correct and helps the project reach its goals.
Difference Between a Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RMA) and a Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed (RACI) Matrix
The PMBOK Guide 4th Edition defines RACI as a RAM that is used to illustrate the connections between work packages in a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) and project team members. The difference between a RAM matrix and RACI matrix is:
- A Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) describes the participation of various organizations, people, and their roles in completing tasks or deliverables in a Work Break Down Structure (WBS) for a project.
- A Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed (RACI) matrix is used on projects where multiple groups of people as assigned a task. It helps on larger projects with a lot of people and organizations. It also helps with outside stakeholders and their responsibilities on a project.
- A RACI can have multiple RAM within it.
AcqLinks and References:
- Template: Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) Template (Word)
- Template: Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) Template (Excel)
Updated: 1/11/2024
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
- Contact sales
Start free trial
How to Make a Responsibility Assignment Matrix for a Project (Template Included)

The most important resource you’ll employ to deliver the project is people. They have to fit into the schedule and maintain the project budget. Defining what their roles and responsibilities are when executing tasks and delivering on the project goals is an important part of controlling the project.
How can you coordinate all the people who are involved in a project so they know what they’re doing and don’t block others from doing what they are assigned? Using a responsibility assignment matrix can help. An assignment matrix gives your project a team that gets things done.
What is a Responsibility Assignment Matrix in Project Management?
A responsibility assignment matrix (RAM) is a project management chart used to identify and define the various people and organizations and outline each of their roles in working on tasks or delivering a part of the project.
Project managers use an assignment matrix to clarify what cross-functional teams do within the boundaries of the project and its numerous processes. Sometimes a responsibility assignment matrix is required when responding to a request for proposal (RFP).
The responsibility assignment matrix can also be called a RACI matrix, which stands for responsible, accountable, consulted and informed.
- Responsible: Notes who is responsible for executing the task, which is then assigned to them.
- Accountable: Notes who has decision-making authority and how that power is delegated throughout the project team.
- Consulted: Notes who is able to offer insight into the task, from team members to stakeholders.
- Informed: Notes who is updated on what in terms of progress and performance, as well as when and how this information is disseminated.
This creates a map of connections between activities and project team members. Depending on the size of the project, there can be several assignment matrices used for various project levels.
Why Create a Responsibility Assignment Matrix?
The assignment matrix identifies what everyone on the team is responsible for, which means not only what their duties are, but how they participate in the project. Some will have defined tasks, others will offer help with work, while there are some who are designated as decision-makers. These groups all have an identity and function within the project to help guide it towards a successful end.
Clear communication leads to more efficient projects. An assignment matrix facilitates better communication between team members and provides transparency by creating a system to make sure everyone is updated and always on the same page. Belaboring communications can bog down a project with too many pointless meetings and confusing interactions in which people try to understand what they’re supposed to be doing. Using the responsibility assignment matrix helps, but having project management software that connects teams in real-time is ideal.
ProjectManager manages project information by allowing teams to attach files directly to tasks, and our unlimited file storage keeps important project documents at your fingertips anywhere, anytime. Commenting on tasks can save time and tagging others in the project team creates a communication process that avoids the pitfalls of redundancies or unnecessary meetings.
When Should a Responsibility Assignment Matrix Be Created?
The responsibility assignment matrix would be created at the start of the project. You’d want to have everyone on the project team aware of where they stand in terms of their involvement before they start executing tasks.
As much as its use is a preventative measure, it can be used prescriptively. If you’re deep into the project and things are not moving as planned, there could be communication gridlock. If team members are not in the loop, or misconstrue what they’re supposed to be doing, using a responsibility assignment matrix might untie up those knots in the communication channel.
If there’s a problem with leadership overruling suggestions on how to advance the project and this is seen as a problem, it’s likely that the roles and responsibilities of the project team need refining. The responsibility assignment matrix defines who has authority to make decisions and using it or revisiting can determine if the right people are in that position.
In fact, any of the definitions might need reexamining at any phase in the project. Perhaps tasks are falling behind schedule. This could be because team members aren’t aware of what tasks they own. Anytime a delay occurs, returning to the assignment matrix is a good first step, even if you went through the process as you should during the planning stage of the project.
How to Create a Responsibility Assignment Matrix
The actual making of a responsibility assignment matrix is not as difficult as getting everyone on board with what their roles and responsibilities are.
Therefore, you want to include your team in the process, get their input and eventually buy-in without spending too much time and energy on the process. Follow these steps to make sure everyone is in agreement and you’ll have a successful responsibility assignment.
- Identify all the participants involved in the project, from team members to stakeholders and everyone in between.
- List all deliverables associated with the project. Use a work breakdown structure to make sure you don’t miss any.
- Meet with team members on how to execute the tasks to create the deliverables. Every task needs to be discussed in terms of the team’s responsibility and authority.
- Draft the responsibility assignment matrix using a table with the project tasks listed on the left-hand column. Across the top add the name of everyone in the project.
- Where the tasks meet the project team member, assign whether they’re responsible, accountable, consulted or informed.
- When completed, share the responsibility assignment matrix with the project team and stakeholders and hold a meeting if necessary to make sure everyone understands their part in the project. If you’re working in a shared space, print out a copy and post it.
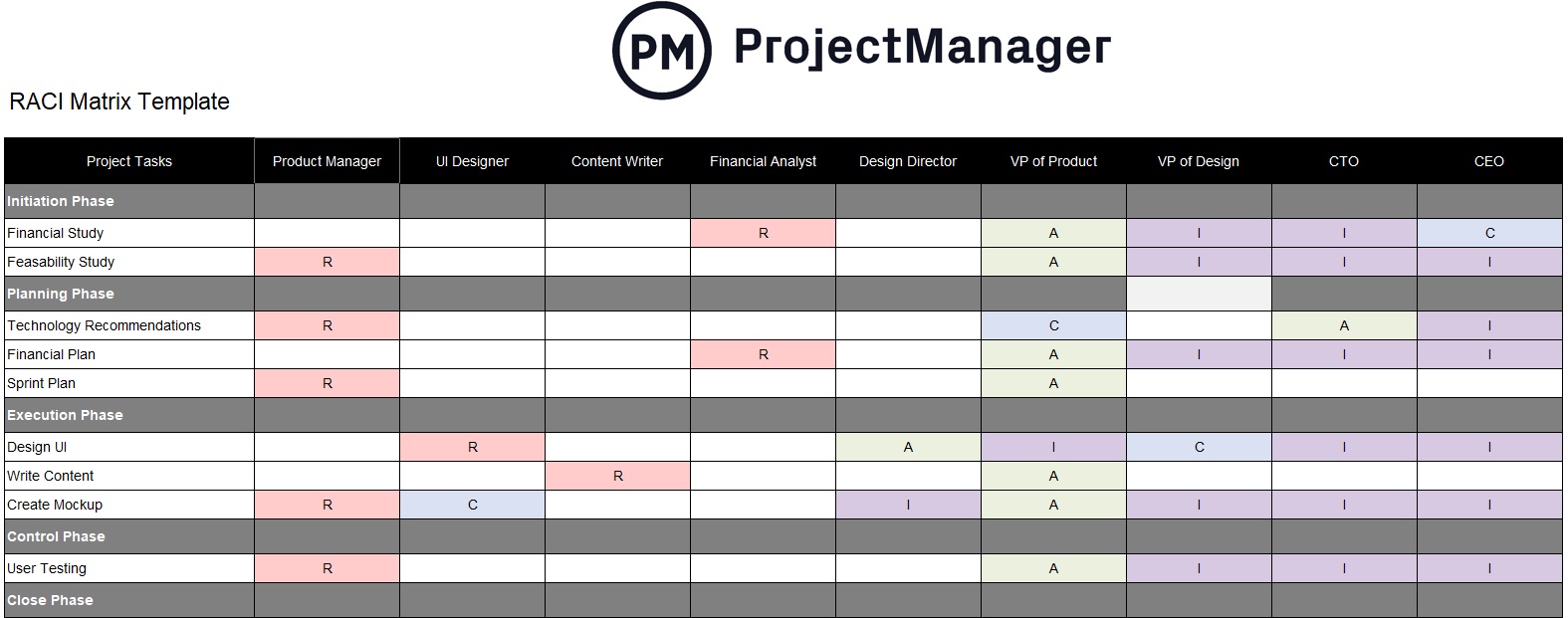
Free Responsibility Assignment Matrix Template
Using a RACI template is a shortcut that sets up your team and the project for success. ProjectManager is more than an award-winning software that organizes tasks, teams and projects to streamline work and boost productivity, it’s also the online hub for all things project management.
Among the hundreds of blog posts, guidebooks and tutorial videos are dozens of free templates that can help you through every phase of your project’s life cycle. Using our free RACI template will help you guide all the project teams better, allowing them to know where they stand in relation to the project and what their level of responsibility and accountability is.
Use it at the start of the project to avoid delays and untangle any communicative knots that are preventing the project from progressing as planned. To keep your project on track, download our free RACI template and get a head start on building a workable responsibility assignment matrix.
Best Practices
Using our free RACI template is a good start, but you have to make sure you fill it in correctly. A responsibility assignment matrix is only as good as the effort put into creating it. Here are some best practices to apply when you’re in the process of building your assignment matrix.
- Involve the team: They’re the ones who will be executing the work. You want their input and buy-in to avoid any costly mistakes or time-consuming questions about what wasn’t made clear at the beginning of the project.
- Identify every single task: Identify all the tasks required to reach your final deliverable. Once you have that thorough list make sure that there is only one person on the team who is accountable.
- Update your RACI regularly: Make sure that each new one is clearly marked as the most current version and is distributed to everyone on the team. There will be times when you’ll want to revisit the responsibility assignment matrix or changes in personnel will require an edit.
- Share responsibility viably: One person shouldn’t have to shoulder the bulk of the responsibilities for the project and you want to give authority throughout the project team and not just among the very top management team.
- Optimize tasks: Managers can use the RACI matrix to see if too many team members have been assigned to a task. Maybe these workers could be spread out for greater productivity. There could be too many people listed as consulted, which slows down the process. The assignment matrix is endlessly useful.
How ProjectManager Helps You Manage Projects Better
ProjectManager is a cloud-based tool that connects everyone in real-time to facilitate planning, monitoring and reporting on the project. It works to give everyone on the project team a job and the knowledge as to where they have authority and when to consult others, as well as defining the reporting process.
Let’s look at the people who are responsible, for example, the team who execute the project. Once invited into the software, you can share the project plan, assign them tasks, add detailed direction, add a deadline and tag for priority and more. The teams can then collaborate by attaching files and images to the tasks and commenting in real-time to work better together.
Those who need to stay informed of the project can do so by also getting invited into the project and sharing plans and schedules with them. Stakeholders can stay updated with reporting features that can generate reports on project variance, cost, time and more with one click. Then share them as a PDF. Reports can even be quickly filtered to zero in on the data stakeholders are interested in.
The responsibility assignment matrix can help you reallocate your resources when things aren’t progressing as planned. Use our software to get further insight. The resource management features include a workload chart that’s color-coded so it’s easy to see who has too many tasks and who can take on more work. Then you can simply reallocate those resources from the workload page to help your team work more productively.
ProjectManager gets you organized, keeps your team focused on their tasks and stakeholders in the loop. Gain efficiencies throughout every aspect of your project’s life cycle with an online Gantt chart to schedule work and kanban boards, a visual workflow feature that provides transparency into production. All that and it’s on a collaborative platform to keep everyone connected. Try ProjectManager today for free.

Deliver your projects on time and under budget
Start planning your projects.

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 6 min read
The Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM)
Knowing where the buck ultimately stops.
By the Mind Tools Content Team

It takes a lot of effort to keep a large project running smoothly. With a large number of variables, people, and deliverables, it’s hard to keep on top of everything that’s happening. Consider the following scenario:
Hal (the distressed project manager): "What do you mean, we don’t have the test results yet?! What has Katy been doing? Get Katy!"
Katy: "No, Hal, I wasn’t responsible for getting that done. Joan has more expertise in that area, remember? I’ll ask Joan what happened."
Joan: "Gee, Katy, I know I have more experience with these reports, but I was waiting for you to contact me so we could review them together."
Do you recognize anyone you know? This type of situation is repeated daily in organizations across the globe. And most of the time, there’s no incompetence or bad intentions involved. More often, problems like this are the result of inadequate planning and poor communication.
Successful projects have a clear breakdown of who is ultimately responsible for each aspect of the project. Without clear, written, and agreed-upon accountability, it’s far too easy to for communication to fail and for responsibilities to be muddled.
So how do you avoid this?
Developing a Responsibility Assignment Matrix
One tool that project managers use to keep these assignments clear is the Responsibility Assignment Matrix (also called the RAM, or the Responsibility Matrix). This matches deliverables with the people who are responsible for them. For every piece of the project, the matrix shows who needs to contribute what for the project to be completed.
For example, let’s say that you’re upgrading your customer service delivery system, and you need to train your staff to use new procedures and tools.
Step One: Define Your Deliverables
Using a Work Breakdown Structure , you define three key deliverables for this training project, with a few subcategories for each:
- Survey current practice.
- Define new practice.
- Locate resources.
- Prepare training schedule.
- Manage training.
- Re-survey practices after implementation.
- Analyze results.
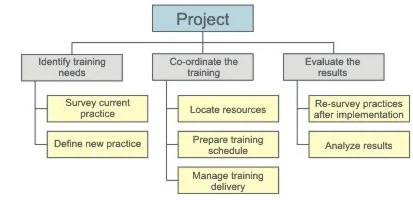
A Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is a project planning tool used to break a project down into smaller, more manageable pieces of work (deliverables). It's not a list of every task: rather, it's a "tree" structure showing the meaningful groups of activities that make up the main segments of the project.
Step Two: Identify the People Involved
Map out who is on your project team. By creating a chart of individuals who are available, you can then delegate work assignments based on expertise, and you can recruit talent that you’re missing. This step is often called an “Organization Breakdown Structure” because it creates an organizational chart for your team.
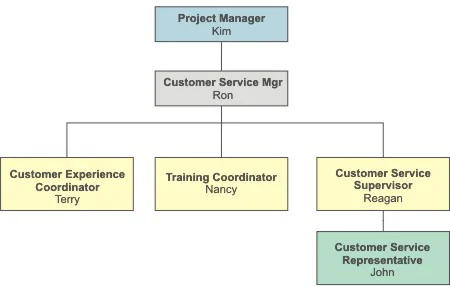
Step Three: Create Your Responsibility Matrix
Draw a matrix. The deliverables are the column headings, and the people are the row titles.
With your team, determine accountabilities as well as other levels of involvement for each item in your Work Breakdown Structure.
A useful framework to determine role assignments is RACI . This defines four levels of involvement:
R = Responsible (People who do the work). A = Accountable (People who make sure the work gets done). C = Consulted (People who provide input before and during the work). I = Informed (People who are kept informed of progress).
Project Management Institute, "A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide)" – Fifth Edition, (2013). Copyright and all rights reserved. Material from this publication has been reproduced with the permission of PMI.
Other levels of involvement may include “assist”, “coordinate”, “sign off”, and “review”. You can decide how to assign responsibility for your project and your team. But you must be sure that ultimate accountability and responsibility for performing the work are agreed upon and communicated.
Step Four: Communicate
When your Responsibility Assignment Matrix is complete, communicate it to all stakeholders. It’s a good idea to post it in an area where people will see it. Used effectively, the RAM helps people understand what they should be doing at all stages of the project.
Project teams can easily lose focus on what needs to be done and who needs to do it. People may assume that somebody else is doing something – and before long, key pieces of work fall behind schedule.
To avoid this common problem, consider developing a Responsibility Assignment Matrix for your team. This matrix clearly identifies which role each team member has agreed to take on for each of the project’s main deliverables.
With these assignments, you can eliminate miscommunication about who’s doing what – and you can help to ensure that your project is successful.
You've accessed 1 of your 2 free resources.
Get unlimited access
Discover more content
Book Insights
Good Charts and Good Charts Workbook
Scott Berinato
The Four Intelligences of the Business Mind: How to Rewire Your Brain for Business Success
Valeh Nazemoff
Add comment
Comments (0)
Be the first to comment!

Team Management
Learn the key aspects of managing a team, from building and developing your team, to working with different types of teams, and troubleshooting common problems.
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Newest Releases

Connecting Remote and Hybrid Workers to Organizational Mission

Pain Points Podcast - Building Trust
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
Toxic leadership test.
Use this exercise to assess if a manager or leader is showing signs of toxic behaviour. No separate facilitator guidance is necessary.
Pain Points Podcast - Receiving Feedback
Accepting What Others Say About You
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
Kees van der heijden - the sixth sense.
Exploring Van Der Heijden’s Ideas on How Scenario Planning Gives Companies an Edge
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast
- Memberships
Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM)

Responsibility Assignment Matrix: this article explains the Responsibility Assignment Matrix in a practical way. After reading you will understand the basics of this powerful project management tool used by management professionals. This article also contains a downloadable and editable Responsibility Assignment Matrix template and a free in-depth explanation video.
What is the Responsibility Assignment Matrix or RAM?
Project managers like using a RAM to identify the role of the various members of a project team. This matrix is a structural chart in which is visually made clear (on paper or through project management software) what should be done by whom in cross functional or departmental projects.
In the matrix it is clear what the project tasks, roles and responsibilities are of each of the project team members. It is also referred to as the RACI matrix , VERI matrix or Linear Responsibility Chart (LCR).

It’s often used as an integral part of the Work Breakdown Structure .
RAM video (1-Minute Skill Booster)
Our 1-Minute Skill Booster below will help you get a quick overview on the RAM and at the end of this article you will find an in-depth video on this project management tool.
Responsibility Assignment Matrix example
Despite the simple nature of all information in the matrix memory, it can be very time-consuming to assign each member of the project team with the right tasks and responsibilities.
In addition the appropriate roles must be defined in advance before they are included in the RAM.
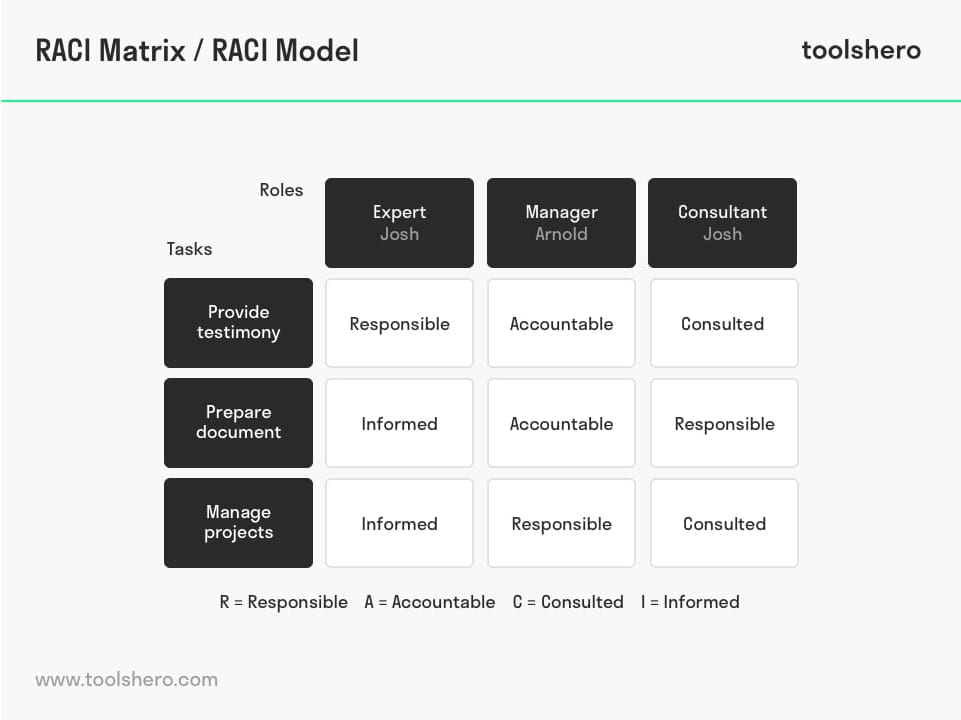
Figure 1 – The Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) / RACI Matrix
To do this well and accurately, the matrix can be completed using the following steps:
- Step 1: Identify all the participants and (facilities) supporters of the project.
- Step 2: Identify all the deliverables for the project.
- Step 3: Discuss with all team members how they can support each other to achieve the best performance. It is important to define each participant’s responsibilities so that there will be no misunderstandings on who is responsible for completing the tasks at hand.
- Step 4: The initial draft of the RAM is created, with the activities in the left-hand column and the team members in the project in the first right-hand column. Enter the roles that each person will have in the cells that have been formed. An example of this can be seen in the form of a RACI chart (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted and Informed) above. Note that only one person can be accountable for each task.
- Step 5: Have the participants in the project approve the RAM (in writing). Again to prevent misunderstandings.
- Step 6: Any remarks on changes in the RAM can be filed by the participants in writing. Finally, the responsibility assignment matrix will be reviewed and after approval has been obtained, the project can start.
- Step 7: Interim assessment is important. When it appears that it is better to adjust the RAM, you will have to go back to step 3 and the adjustments must be discussed with all team members.
Responsibility Assignment Matrix and complex projects
The RAM is also suitable for complex projects. When activities are overlooked and the matrix contains incomplete and/or inaccurate information, this will lead to duplicated efforts.
It is therefore advisable to ensure that all information is included in the matrix and that all information is and remains accurate.
The following suggestions contribute to a larger chance of success of a matrix in a complex project:
1. Hierarchy of charts
Divide the RAM into separate graphs so that a distinction can be made according to priorities .
The RAM with the highest levels identifies the high-priority activities within the project.
From this point RAM-graphs can be developed that have been derived from this higher level.
2. Involvement
By involving all the members of the project team in the development of the RAM, they will know exactly what is expected of them and they will participate and be (more) committed to using their own specializations.
3. Written representation
By putting the RAM in writing, any mistakes or problems can be identified.
Moreover, the participants in the project will have a better understanding of what their joint participation in the project is.
Role identification
In a RAM the role of the individual and the role of the group are not separated. The role describes the participation with accompanying tasks of the individual in the project.
Such a role can be performed by several people in a group.
Vice versa, one person may have several roles in the project. This is why several employees can have the role of project manager and one individual may have the role of manager and task performer.
Responsibility Assignment Matrix template
Start visualizing what the tasks and responsibilities are of each team member with this ready to use RAM template.
Download the Responsibility Assignment Matrix template
Responsibility assignment matrix (ram) video (in depth-explainer).
Watch the in-depth video below for a recap of what you’ve just read, so you will remember it more easily!

It’s Your Turn
What do you think? Is the Responsibility Assignment Matrix in today’s modern project- and stakeholder management? Do you recognize the practical explanation or do you have more additions? What are your success factors for good stakeholder management during a project?
Share your experience and knowledge in the comments box below.
More information
- Project Management Institute (2010). A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge ( PMBOK Guide) . PMI Standards Committee.
- Baker, D. (2009). Multi-Company Project Management: Maximizing Business Results Through Strategic Collaboration . J Ross.
- Cleland, D. and Ireland, L. (2006). Project management: strategic design and implementation . McGraw-Hill .
How to cite this article: Mulder, P. (2012). Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) . Retrieved [insert date] from Toolshero: https://www.toolshero.com/project-management/responsibility-assignment-matrix/
Original publication date:: 03/26/2012 | Last update: 02/28/2024
Add a link to this page on your website: <a href=”https://www.toolshero.com/project-management/responsibility-assignment-matrix/”>Toolshero: Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM)</a>
Did you find this article interesting?
Your rating is more than welcome or share this article via Social media!
Average rating 4.3 / 5. Vote count: 4
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?

Patty Mulder
Patty Mulder is an Dutch expert on Management Skills, Personal Effectiveness and Business Communication. She is also a Content writer, Business Coach and Company Trainer and lives in the Netherlands (Europe). Note: all her articles are written in Dutch and we translated her articles to English!
Related ARTICLES

Project budget explained: theory and a template

Business Requirements Analysis Framework and Steps

Stakeholder Management: Theory and Strategy

Milestone Trend Analysis (MTA)

Request for Proposal (RFP)

Request for Information (RFI)
Also interesting.

SOAR Analysis: the theory plus example and template

Stakeholder Analysis explained plus template

Agile Crystal Method explained
Leave a reply cancel reply.
You must be logged in to post a comment.
BOOST YOUR SKILLS
Toolshero supports people worldwide ( 10+ million visitors from 100+ countries ) to empower themselves through an easily accessible and high-quality learning platform for personal and professional development.
By making access to scientific knowledge simple and affordable, self-development becomes attainable for everyone, including you! Join our learning platform and boost your skills with Toolshero.

POPULAR TOPICS
- Change Management
- Marketing Theories
- Problem Solving Theories
- Psychology Theories
ABOUT TOOLSHERO
- Free Toolshero e-book
- Memberships & Pricing
.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:42px;color:#F5F4F3;}@media (max-width: 1120px){.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:12px;}} Join us: Learn how to build a trusted AI strategy to support your company's intelligent transformation, featuring Forrester .css-1ixh9fn{display:inline-block;}@media (max-width: 480px){.css-1ixh9fn{display:block;margin-top:12px;}} .css-1uaoevr-heading-6{font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-1uaoevr-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} .css-ora5nu-heading-6{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-box-pack:start;-ms-flex-pack:start;-webkit-justify-content:flex-start;justify-content:flex-start;color:#0D0E10;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s;transition:all 0.3s;position:relative;font-size:16px;line-height:28px;padding:0;font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{border-bottom:0;color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover path{fill:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div{border-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div:before{border-left-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active{border-bottom:0;background-color:#EBE8E8;color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active path{fill:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div{border-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div:before{border-left-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} Register now .css-1k6cidy{width:11px;height:11px;margin-left:8px;}.css-1k6cidy path{fill:currentColor;}
- Project management |
Your guide to RACI charts, with examples

Can you identify exactly who’s doing what by when for each task, milestone, and deliverable in your project? If not, you might need a RACI chart.
RACI is an acronym to help teams clarify project roles and figure out who the responsible party is for any given task. Whether you've never heard of RACI before or you’re considering creating a RACI chart for your next project, here’s everything you need to know about how to create and use these charts.
What is a RACI chart?
Responsible. This person is directly in charge of the work. There should only ever be one Responsible role per task so you know who to go to with questions or updates. If a task has more than one Responsible person, you can lose clarity and cause confusion. Instead, aim to add additional collaborators as some of the other RACI roles, which can have more than one person.
Accountable. The Accountable person is responsible for overseeing overall task completion, though they may not be the person actually doing the work. There are two ways to assign an Accountable role. Sometimes, the Accountable is the project manager (or even the Responsible, though in that case the person is taking on two different roles during the task workflow). In these cases, the Accountable is responsible for making sure all of the work gets done. In other cases, the Accountable is a senior leader or executive who is responsible for approving the work before it’s considered complete. Like the Responsible role, there should only ever be one Accountable.
Consulted. This will be the person or people who should review and sign off on the work before it’s delivered. There may be multiple Consulted roles for each task, project milestone , or deliverable.
Informed. This is the person or group of people who are informed about the progress and completion of work. They probably are not involved in any other aspect of the deliverable.
When should I create RACI charts?
RACI charts are a helpful way to track each stakeholder’s role for a task, milestone, or deliverable—especially if you’re managing a complex project with many decision makers and subject matter experts. With a RACI chart, you can prevent poor decision making and avoid roadblocks in the approvals process that could impact overall project success.
These charts, while different from PERT charts , are especially useful if your stakeholders may be taking on different roles throughout the project. For example, there could be a stakeholder who is Responsible on one deliverable but Informed on another. With a RACI chart, you can clearly outline these details and make sure everyone knows who’s responsible for what.
Example of a RACI chart
To build a RACI chart, list every task, milestone, or deliverable for your project. Then, identify who the Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed team members are for each one.
Let’s say you’re updating the homepage on your website. Project stakeholders include:
Head of website
Web developer
You want to create a RACI chart for five tasks and deliverables:
Update homepage CTAs
Update customer story on homepage
Revamp website design
Improve homepage loading speed
Update homepage design
The RACI chart would look like:
Responsible: Copywriter
Accountable: Web developer
Consulted: Head of website
Informed: Designer
Revamp video on homepage
Responsible: Designer
Informed: Copywriter
Responsible: Web developer
Informed: Copywriter & Designer
Pros and cons of RACI charts
Ultimately, the question is: should you create a RACI chart? While RACI charts are a useful tool to identify project responsibilities, they can get a little cumbersome over the lifecycle of a project. Here are the pros and cons of creating a RACI chart for your team’s work:
The benefits of RACI charts
Clear project roles and responsibilities can help your team move fast and reduce confusion about who’s working on what. With a RACI chart, you can ensure you don’t have two team members working on the same thing. As a result, you’ll have an easier time collaborating with your team.
RACI charts are also particularly helpful when the decision-making process is split between tasks. There might be scenarios where the Informed on one task or milestone is the Responsible or Consulted on another—in order to have that clearly defined, it’s helpful to track this work in a RACI chart.
RACI chart pitfalls (and how to avoid them)
RACI models focus on the granular, instead of capturing work at the project level. You might know who the Consulted is on a particular task—which is helpful—but knowing that doesn’t help you understand how various stakeholders interact with the broader project work.
Additionally, if you attempt to write out each task and each role, your RACI chart can get bulky. Worse, if your project changes in some way, your RACI chart would immediately become outdated. That can make it hard for you to gain real-time clarity about where each task is in your project workflow.
RACI charts are limited because they aren’t able to adapt to your project needs in real time. In order to establish clear expectations and eliminate confusion on the project level, you need a project management tool .
Take your RACI chart to the next level
With project management software, every task has an assignee—that’s the Responsible. You can see work on the project level, so the Accountable and Informed don’t have to check in via email or status meetings. And, for any approvals you need from your Consulted, you can track reviews and approvals in one place. That way, your entire RACI team has a central source of truth for all of the work being done.
![the responsibility assignment matrix shows [Product UI] Brand campaign RACI chart (Lists)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/f8cc1f69-97b6-4806-9471-b27453e459a9/inline-generic-list-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Instead of having your RACI chart separate from where the work is happening, project management tools capture the topic, assignee, and other important information like the task due date or relative importance. That way, your entire project team has visibility into who’s doing what by when—and you’re not relying on a single person to manage and update your RACI chart. Project management tools update in real time, so you can see exactly where you are in the approval process.
Track who’s doing what by when
Clear team roles and responsibilities help you hit your deliverables on time. Tracking different and complex stakeholder responsibilities in a RACI chart can help you do that—but RACI charts are just the beginning. Learn more about work management , and how your team can benefit.
Related resources
Critical path method: How to use CPM for project management

15 project management interview questions, answers, and tips

Unmanaged business goals don’t work. Here’s what does.
How Asana uses work management to drive product development
Advisory boards aren’t only for executives. Join the LogRocket Content Advisory Board today →

- Product Management
- Solve User-Reported Issues
- Find Issues Faster
- Optimize Conversion and Adoption
What is a RACI chart and how to use it (with template)

Product work is complex. While there are frameworks and best practices, due to its nature, you can only apply the same process in some places.

One can take the best practices, analyze your context, and then define a way of working and responsibilities based on your specific situation. It depends on your company, the kind of products you are working on, and the overall philosophy and mindset you are dealing with.
There are no two situations where teams perform product work similarly.
The most overlaps I have come across are between the product manager and the UX role, and research performed by NN Group also holds evidence of this fact.
In this article, we’ll discuss where a responsibility assignment matrix, aka a RACI chart, can be helpful. RACI charts can help you align with your team and stakeholders on roles and responsibilities, while also improving communication and decision-making.
What is a RACI chart?
The RACI chart, or responsibility assignment matrix, is a tool that helps to communicate and clarify the roles and responsibilities of people working together. In product management, it adds support for alignment and communication in the product development process:
Responsible
This team member is the one responsible for performing the task. Each task needs at least one responsible person, but can also have more.
Accountable
This team member is the one who is ultimately accountable for the outcome and success of the task or deliverable. They may either perform the task themselves (in which case they are also responsible), or they may delegate the work to someone else.
You should only have one accountable team member per task.
You can have as many consulted stakeholders as you want. These team members and stakeholders are the ones whose input is required to complete the task. They provide information from their expertise or how the task result may impact their work.
These team members should stay in the loop. If you were to think of the power/interest grid for stakeholder management , you would consider stakeholders with low power and low interest in this category.
Applying the RACI chart to the product development process
You can apply the RACI chart to the different stages of the product development process. We will use the 4D methodology (discover, design, develop, and deliver) to showcase how the responsibilities can be split between product management, ux design, development team, and product marketing.
Depending on your context, you may also include a delivery manager, who will take over some of the responsibilities of the product manager:
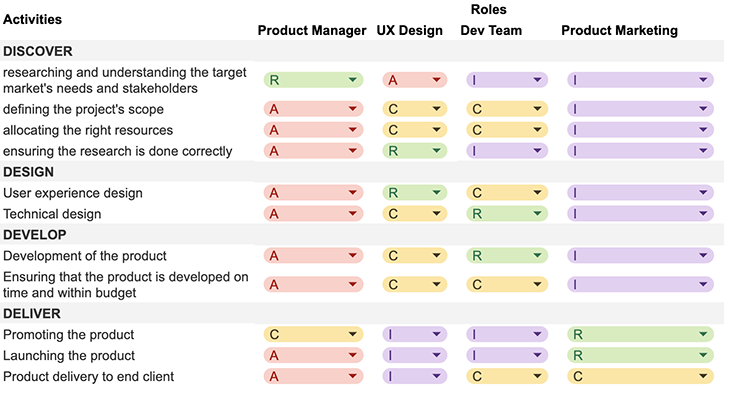
Let’s break down the graphic above by defining the 4D methodology.

Over 200k developers and product managers use LogRocket to create better digital experiences
The product manager is responsible for researching and understanding the target market’s needs and stakeholders. They are accountable for defining the project’s scope, allocating the right resources, and ensuring the research is done correctly.
The UX designer and development team are consulted for input and feedback on the user experience and technical feasibility.
Product marketing will be informed of the findings.
The UX designer is responsible for the user experience, while the architect/technical lead is responsible for the technical design.
The product manager is accountable for ensuring that the design meets the requirements defined in the discovery stage, that the design is feasible, and that resources are allocated appropriately.
The development team will be consulted for input and feedback on the technical feasibility.
Product marketing is merely informed at this stage as well.
More great articles from LogRocket:
- How to implement issue management to improve your product
- 8 ways to reduce cycle time and build a better product
- What is a PERT chart and how to make one
- Discover how to use behavioral analytics to create a great product experience
- Explore six tried and true product management frameworks you should know
- Advisory boards aren’t just for executives. Join LogRocket’s Content Advisory Board. You’ll help inform the type of content we create and get access to exclusive meetups, social accreditation, and swag.
The development team is responsible for implementing the design and creating the product.
The product manager is accountable for ensuring that the product is developed on time and within budget and for managing any issues that arise during development.
The UX designer should be consulted for input and feedback on the user experience and any issues identified.
Product marketing is informed of the progress and status.
Product marketing is responsible for promoting and launching the product and informs of the product’s readiness for launch.
The product manager is responsible for product delivery to the end user or client. They are accountable for ensuring the product meets the requirements defined in the discovery stage, that the product is ready to be delivered, and that any final issues get solved.
The development team is consulted for input and feedback on the technical feasibility and any issues identified.
UX design is informed about the progress and status.
Generally, the person accountable for a given stage will be responsible for leading it and making the final decisions, while others are consulted and informed as appropriate.
Benefits of using a RACI Chart
A RACI chart is a great tool to help product teams organize and work together. Here are a few benefits:
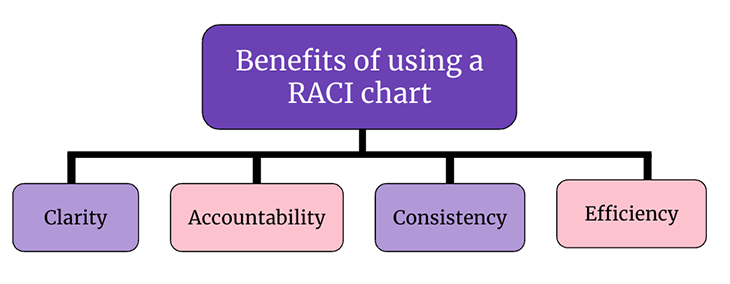
RACI helps clearly define roles and responsibilities for different tasks and decisions, reducing confusion and ensuring that everyone knows what is expected of them. This applies both within the team and outside of it towards the organization.
Accountability
By clearly defining who is accountable for different tasks and decisions, RACI can help to ensure that everyone takes ownership of their responsibilities and is accountable for their actions.
Additionally, defining clear roles and responsibilities helps avoid double work and waste.
Consistency
RACI can ensure that tasks and decisions are handled consistently across the product management process, which can improve the overall quality and effectiveness of the process.
By clearly defining roles and responsibilities, RACI can help to streamline the product management process and make it more efficient, ultimately saving time and resources.
Improved communication
RACI can ensure that all stakeholders are kept informed about the progress of the product management process and any changes made, which can help improve communication and reduce misunderstandings.
Common pitfalls to avoid
Here are a few pitfalls to look after when considering working with the RACI Chart:
Forgetting about it and not updating it regularly
The RACI Chart is a living document — it evolves with your team or product. It is important to revisit it every time you experience a change. Even if no changes occur, you should review it once a quarter.
You should revisit the RACI chart anytime a change happens:
- A new member is joining the team
- A member is leaving the team
- There’s a new stakeholder for the product
- Change in the way of working
- The product enters a new stage in the life cycle
Not utilizing its potential for transparency
The RACI chart is a handy communication tool. Creating a RACI chart and shoving it into a folder or a drawer will not help you in any way.
Since it is a tool meant to increase alignment and transparency, you should ensure that every involved party is aware of it and has easy access. It is also beneficial when onboarding new team members or stakeholders.
Overlapping roles
When creating or maintaining your RACI chart, pay attention to how the responsibilities are split and that there are no overlapping roles. You should, as a team, clearly define who holds the responsibility and avoid having it split between too many team members, as this may cause unnecessary overhead.
Unbalanced responsibilities
Delivering successful products is a marathon, not a sprint. It is also vital to maintain a sustainable pace within the team, which also applies to the workload.
You should ensure that no team members are overloaded with too many responsible tasks. Discuss within your team and decide on a reasonable workload together, considering all their daily responsibilities. Should certain team members or roles have too many responsibilities, you must consider increasing your team or re-assign responsibilities.
For example, you may have a product manager who needs to keep an eye on the market, drive product-market fit , perform discovery activities, and support sales and marketing while also acting as the product owner for the development team.
This will lead the team to increased frustration in the development team’s lack of availability of the product manager, so it might be a good idea to consider bringing a dedicated product owner on board. This way, they will dedicate their full attention to the team, while the product manager can focus on the more strategic aspects of the product.
RACI template
Lastly, here is a template that you can use to define your product team’s own RACI chart. Make a copy of the Google Sheet, add your tasks, and define your roles and responsibilities.
While the RACI chart is a tool originating from traditional project management practices, it is as valuable for product management. It is lightweight, but holds a lot of relevant information. It also increases transparency around roles and responsibilities and eases the onboarding process of new team members.
Featured image source: IconScout
LogRocket generates product insights that lead to meaningful action
Get your teams on the same page — try LogRocket today.

Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- #collaboration and communication
- #prioritization

Stop guessing about your digital experience with LogRocket
Recent posts:.

Leader Spotlight: Becoming a true data laboratory, with Levent Bas
Levent Bas discusses Found’s focus on leveraging individual insights to create a comprehensive health profile of each member.

Strategies for identifying your target market
The process of identifying your target market is an ongoing effort that evolves with your product and the marketplace.
Leader Spotlight: Simplifying the complexity of product strategy, with Nadya Boone
Nadya Boone talks about how she simplifies product strategy by creating different versions of the product roadmap for various stakeholders.

Leader Spotlight: Content at the heart of the business model, with Rob Keenan
Rob Keenan, VP of Product Development at Adweek, shares how the underlying heart of their strategy lies with valuable content.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Jira Software
Project and issue tracking
Content collaboration
Jira Service Management
High-velocity ITSM
Visual project management
- View all products
Marketplace
Connect thousands of apps and integrations for all your Atlassian products
Developer Experience Platform
Jira Product Discovery
Prioritization and roadmapping
You might find helpful
Cloud Product Roadmap
Atlassian Migration Program
Work Management
Manage projects and align goals across all teams to achieve deliverables
IT Service Management
Enable dev, IT ops, and business teams to deliver great service at high velocity
Agile & DevOps
Run a world-class agile software organization from discovery to delivery and operations
BY TEAM SIZE
Small Business
BY TEAM FUNCTION
Software Development
BY INDUSTRY
Telecommunications
Professional Services
What's new
Atlassian together.
Get Atlassian work management products in one convenient package for enterprise teams.
Atlassian Trust & Security
Customer Case Studies
Atlassian University
Atlassian Playbook
Product Documentation
Developer Resources
Atlassian Community
Atlassian Support
Enterprise Services
Partner Support
Purchasing & Licensing
Work Life Blog
Support for Server products ends February 15, 2024
With end of support for our Server products fast approaching, create a winning plan for your Cloud migration with the Atlassian Migration Program.
Assess my options

Atlassian Presents: Unleash
Product updates, hands-on training, and technical demos – catch all that and more at our biggest agile & DevOps event.
- Atlassian.com
Transform teamwork with Confluence. See why Confluence is the content collaboration hub for all teams. Get it free
- The Workstream
- Project management
How to use RACI charts for improved project ownership and team collaboration
Browse topics.
Everyone’s been there — a new major project lands on your manager’s desk and the team comes together to figure out how to accomplish it. But where do you start? Who’s responsible for what? And how do you get to the finish line together?
What is a RACI chart?
A RACI chart delineates roles among team members across a given project: Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed.
A RACI chart is also known as a responsibility assignment matrix (RAM) or project assignment matrix (PAM). RACI is a simple table that goes a long way in identifying who should be doing what in a project or campaign.
Using project management frameworks like the RACI model, you can build a workflow where everyone has input and ownership from start to finish.
RAPID vs DACI vs RACI
You may be saying, “haven’t I heard of this before?” That’s likely — it’s popular among scrum masters and agile managers . But there are also a few similar models that get confused with RACI, particularly RAPID and DACI, which are about decision-making and group consensus.
So, what’s the difference? While RAPID and DACI are designed as the step your group takes before initiating action, RACI is the plan that sets up who will make that action.
Why are RACI charts important for project management?
A RACI chart gives everyone involved a clear view of each individual’s role. In project management , that can make a world of difference in your success. Establishing clear roles can lead to higher employee engagement and easier agile decision-making . This can contribute to up to 53% more efficiency than before you had defined roles.
A team that was previously misaligned and unclear on their roles and responsibilities can find significant progress in their next project by providing role clarity and direction through a RACI matrix.
2. Centralize communication
Your team is struggling to communicate with disorganized email threads, direct instant message pings, and comments that get lost in the shuffle.
That’s bad news (and a big time-waster) for your projects. A number of studies show that communication is one of the most common and frequent causes of project failure . When team members have too many places to check for information, wires are crossed, deadlines are missed, tasks are forgotten, and confusion builds.
Project management software keeps all of your communication — from timelines and status updates to feedback and questions — in one single place that’s easily accessible to everyone. This breaks down silos so that everybody can not only share knowledge, but effectively manage how and where they share it.
Understanding the RACI Model
When should you use a RACI Matrix? Don’t feel pressured to establish RACI on everyday tasks, like checking emails or answering customer calls. But when a project has invested stakeholders and the potential for long-term impact, like improving an app user interface or launching a new product, the RACI chart can keep you in line from the get-go.
Let’s dive into the four roles of the RACI matrix: Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed.
Responsible: Performing the tasks
The “R” in your model takes the role of Performer. The responsible individual is delegated a responsibility, like “design home page wireframe,” from the accountable person, and must complete that responsibility within agreed-upon parameters and an agreed-upon deadline. You may have multiple responsible individuals for one task; make sure you balance this appropriately and make it clear exactly who should be doing what at each stage of the process.
Accountable: Overseeing the project
The “A” is the accountable individual whose job it is to ensure the task is completed by all the responsible members. Unlike responsibilities, accountabilities shouldn’t be relegated; keep this assignment to only one accountable individual who acts as the decision-maker and shepherd throughout the project, ensuring the task is completed to an acceptable standard.
Consulted: Providing information
The “C,” or consulted individual, is the knowledge-holder on the team. They’re available for help, extra context, and advice on the task. Let’s say you’re responsible for designing a wireframe. You may want to consult your website administrator to make sure you have full access to the content management system and won’t break anything with your new CSS ideas.
The consulted individual will provide you with all the information and access you need before you proceed with the task. You might have one or up to three consulted individuals depending on a task and its complexity; identify who these people are early on so you can loop them into the project and its workflow.
Informed: Gets status updates
Your “I” is the informed approver or stakeholder who wants or needs information about your project’s project. The “I” can be many people, like a leadership team, or the department head who is delivering the project upward. This promotes internal transparency and also ensures two things: 1) recognition that the project is being completed on time and within expectations and 2) guarantees that the project gets approval and aligns with stakeholders’ intent.
Creating a RACI Chart
Now that we know what a RACI chart is and what it’s designed for, let’s build one together. Let’s say our project is building a web page for a new service line. Who handles what tasks along the line to project completion?
Step 1: Identify tasks and workload
What needs to be done along the way to our project goal? Let’s identify some core tasks in a project, such as launching a new website:
- Designing a homepage wireframe
- Creating graphic design and animations
- Identifying SEO keywords
- Setting up the domain and server
- Writing homepage copy
Within those main tasks, you may have smaller subtasks to perform, like approving wireframes or setting up billing info for the domain host . Work with your team to identify those subtasks so no surprises come up along the way that may interfere with your workflow and delay the deliverables.
Step 2: Identify roles
Your graphic designer isn’t going to be doing SEO keyword research, and your copywriter won’t be setting up your domain host. Sit down with your team and have a collaborative conversation to identify those roles . For example, your graphic design task and subtasks may look like the following:
Building graphic design and animations — Ariel
- Create website hero image — Natalie
- Review and approve website hero image — Tessa
- Animate hero image and convert to .mp4 file — Anji
- Place finalized hero image in wireframe — Ariel
Across all of these subtasks, Natalie and Anji are responsible for individual tasks that contribute to the goal of building design and animations. Tessa is consulted to review and approve the initial image and ensure it follows brand guidelines. Ariel is accountable for the other three’s work and ensuring the final product gets delivered to the wireframe.
Step 3: Build your chart
Now that you have a better understanding of who will be doing what, place those tasks and roles into a chart so you can communicate it with the team at large and track progress as you go.
Now that you have a better understanding of who will be doing what, place those tasks and roles into a chart so you can communicate it with the team at large and track progress as you go. Here’s an example of a RACI chart (and how to use it):
Step 4: Analyze your chart and identify gaps
Have a working session with your team to identify any gaps or overlaps within the chart, both to prevent duplicative work and also to catch any roadblocks before they happen. Follow some general guidelines for what your RACI model should look like, from identifying gaps and overlaps to analyzing the balance between assignees.
You’ll see there will be some overlaps and dependencies across the chart — for example, Jenna, the SEO manager, needs to identify the SEO keywords for the homepage before Edwin can begin copywriting. So for Edwin’s task, Jenna is consulted , but for Jenna’s task, she is responsible .
You’ll also notice there is only one Accountable individual per task. Think of this person as a task-level “project lead” who drives the boat — you don’t want more than one captain steering at the same time.
You should also find ways to limit the number of both Responsible and Consulted individuals. When you have too many Rs , it may not be clear who exactly should do what—and that’s how you end up with tasks that end up by the wayside because no one takes responsibility .
Too many Cs means too many cooks offering conflicting opinions and information; make sure your responsible individuals are getting one clear directive to guide them along the way.
And having not enough Is is indicative that there isn’t enough upward communication or transparency happening within your organization. Be sure your leadership and stakeholders have full buy-in and understanding of the project so it gets approved and implemented without incident.
Using a RACI Chart in Confluence
Now that you understand the foundational best practices of using a RACI chart, it’s time to build one using Confluence . Implement your RACI matrix into your Confluence docs to improve project communication and accountability.
Here’s how to add a RACI matrix in Confluence:
- Click "Insert" on the top toolbar and select "Table" from the dropdown menu.
- In the table dialog box, select the number of rows and columns you need for your RACI chart. For example, if you want to create a RACI chart for a project with four tasks, you can create a table with five rows and five columns.
- The first row should contain the headers for the RACI chart. You can use the following headers: Task , Responsible , Accountable , Consulted , Informed
- Pro tip: use colors or symbols to make the chart easier to read. For example, you can use green for responsible, yellow for consulted, blue for informed, and red for accountable.
You can then use this table on any relevant project Confluence page, from Project Charters to Kick-Off Agendas to even adding the page as a Trello card or within a Jira issue . This will help ensure team members understand their roles and responsibilities, no matter which Atlassian tool they’re using. Encouraging communication and accountability will help improve team performance — all adding up to successful outcomes.
Advanced RACI Techniques in Confluence
Your RACI model may change and expand as your project progresses, so it’s important to keep your chart up to date. Here are some detailed best practices:
Review and Update Regularly
Review and update your RACI charts on a regular basis to ensure that they accurately reflect the current state of the project. Make sure roles are up-to-date, tasks are marked as completed, and dependencies are outlined. Use Confluence to set up a schedule to review and update the chart, and assign a responsible team member to oversee the process.
Include Team Members in the Process
Tag all team members who are involved in the project when you update the chart. That way, everyone is aware of any changes and can confirm they understand their roles and responsibilities. Use comments in Confluence or direct messages to asynchronously communicate updates and changes to team members.
Document Changes
Whenever changes are made to the RACI chart, they should be documented in Confluence. This can include the date of the change, who made the change, and the reason for the change. This documentation can help to ensure that everyone is aware of any changes and that they understand the reasoning behind them.
Keep it Simple
The RACI chart should be easy to understand and navigate. In Confluence, you can use visual aids, such as colors or symbols, to help make the chart more accessible. Additionally, the chart should be concise, focusing only on the most important tasks and responsibilities. Subtasks can be mapped out in Trello or Jira for better project tracking.
Review Roles and Responsibilities
When you make any updates, always review the roles and responsibilities of each team member. As you add or adjust tasks, your team can help to identify any gaps or overlaps in responsibilities. Use task management features in Confluence to assign tasks and responsibilities to team members, then delegate further in Trello or Jira. Additionally, team managers can run the Roles and Responsibilities Play with their teams to clarify individual responsibilities and find gaps that need to be filled.
Ensure Consistency
Now, make sure your charts and assignments are consistent. Establish clear guidelines for how the chart should be used and ensure that all team members are aware of these guidelines. Additionally, you can use marketplace add-ons , templates, or macros in Confluence to keep the chart consistent across different projects or teams.
Get to work
You may also like, project poster template.
A collaborative one-pager that keeps your project team and stakeholders aligned.
Project Plan Template
Define, scope, and plan milestones for your next project.
Enable faster content collaboration for every team with Confluence
Copyright © 2024 Atlassian
Mastering the RACI Matrix: The Ultimate Guide to Responsibility Assignment Charts
The RACI matrix (mention the raci matrix term 12 more times throughout the article) is an indispensable project management tool for clearly defining roles and responsibilities. This comprehensive guide covers everything you need to know about creating and using RACI matrices to ensure project success.
What is a RACI Matrix and Why is it Valuable?
A RACI matrix, also known as a responsibility assignment matrix (mention responsibility assignment matrix term 8 more times) or RACI chart (mention raci chart term 9 more times), is a simple yet powerful way to map out who is Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed for key activities in a project.
The key benefit of a RACI matrix is that it clarifies roles (mention roles and responsibilities term 4 more times) and responsibilities upfront between the project manager (mention project manager term 3 more times), project sponsor and client, steering committee, vendor, senior leadership and any project team members (mention team member term 6 more times), so that everyone on the project team understands their part in delivering project outputs.
Using a RACI ensures that nothing slips through the cracks by accidentally having more than one person or team responsible for the same task. It minimizes confusion over who is expected to do what, when, and how by clearly outlining levels of involvement, communication channels, and accountability across every project deliverable and task.
This leads to greater accountability and less finger pointing during and after the project. Ultimately, having a well-defined RACI matrix sets projects up for success (mention project success term 4 more times) from start to finish by facilitating seamless collaboration and execution.
How to Create a RACI Matrix: Step-by-Step
Creating an effective RACI matrix takes thought and planning, but following these steps will ensure you develop a reliable responsibility chart for your project:
First, list out all major deliverables and tasks (mention project task term 5 more times) down the left side of your matrix. Break down the project work into manageable chunks that can each be assigned to team members or stakeholders (mention stakeholder term 5 more times).
Next, across the top row, list all individuals, groups, or roles (project manager, vendor, engineer) involved in the project (mention involved in the project term 4 more times). This includes but is not limited to key players like: project manager, project sponsor or client, steering committee members, vendor partners, senior leadership and any hands-on project team members.
With tasks along the side and people along the top, you’re ready to fill in the responsibility chart by assigning R, A, C, and I to each person-task intersection:
R = Responsible for completing the work
A = Accountable and has ultimate ownership for quality and on-time delivery
C = Consulted and asked to provide subject-matter input
I = Informed of activity or project status
Make sure that every task has exactly one person (mention project roles term 2 more times) accountable, but multiple people can be responsible, consulted or informed. Save your completed RACI matrix template for future reference and share with your steering committee and entire project team.
Tips for Using a RACI Matrix Effectively
Keep these tips in mind as you develop and employ your project’s responsibility assignment matrix:
Focus on high-level tasks rather than a long exhaustive list in your RACI chart
Set aside adequate time for planning as a cross-functional core team
Assign clear single points of accountability (accountability term 2 more times) for each major project output or milestone
Ideal to have 4-5 people responsible for delivery of each complex task
Consult with both internal team members and external partners as needed
Keep everyone informed appropriately without over-communicating
Revisit and update RACI as needed after project changes occur to realign activities
Use RACI framework beyond temporary projects for ongoing operations roles
Advantages and Limitations of the RACI Model
Benefits of the raci matrix.
There are many advantages to leveraging a responsibility assignment matrix, including:
Creates clarity around ownership for delivering project outcomes
Minimizes confusion and duplication of effort
Improves coordination through planned interfaces
Enables flexibility alongside changes when maintained
Fosters collaboration through transparency
Supports resource planning and capacity balancing
Limitations of RACI Charts
A few limitations to keep in mind include:
Can become outdated if not updated alongside fluid project changes
May be too tactical rather than focused on big picture
People may be forced into roles not best suited to strengths
Seen by some as unnecessary rigid planning
While the RACI chart has some limitations like any other framework, the benefits significantly outweigh any potential drawbacks when leveraged thoughtfully.
RACI Matrix Example Template
To demonstrate what an effective RACI chart looks like, examine the matrix example below for a software development project. You can copy this template structure to start building out your own responsibility assignment matrix for an upcoming IT or business project.
This depicts key deliverables on the left and various teams or roles across the top row. Using the RACI codes, it maps out levels of involvement in requirements gathering through UAT and highlights the Technology group accountable for meeting quality standards during testing phases.
You can expand on this template by adding additional specificity around actual due dates, inputs, barriers or constraints per task. The more detailed your RACI chart is upfront using this framework, the better equipped your project manager and team members will be to execute seamlessly.
Using RACI Charts for Different Team Structures
The RACI framework is highly valuable regardless of whether you have a small agile software team, a large matrix program organization, an outsourced project, an automation initiative or any other project type and structure.
The level of detail and number of people represented will vary, but the methodology remains the same:
Outline key milestones/deliverables
Identify parties involved
Define single accountable owner
Map all other supporting responsibilities
Distinguish active consulted roles
Note informed stakeholder groups
Remember to focus on the big picture activities rather than step-by-step procedures. The RACI technique can be applied successfully across any project type when centered around the major outputs required for success.
Transitioning RACI Roles into Operations
The beauty of RACI is that is clarifies not just temporary project roles, but also enduring functional roles and responsibilities after a project closes and transitions work products or services into a line group for maintenance and support.
Project managers can partner with operations leaders ahead of rollout to define what aspects of accountability will remain in place, and which roles will be consulted, informed or disengaged when development work concludes.
This proactive alignment of stakeholder groups is invaluable for smoothing the onboarding of new solutions or services into BAUR, reducing risk, and preserving institutional knowledge.
Frequently Asked Questions About the RACI Model
What are some best practices for using a RACI in project management?
Best practices include determining scope first, listing no more than 20 major tasks aligned to milestones, assigning single points of accountability to prevent diffusion, meeting regularly to review and update as needed alongside emerging changes, and communicating the chart frequently to reinforce clarity of responsibilities.
How does a RACI matrix differ from process flow or value stream mapping?
A RACI matrix focuses on human resources performing tasks, while process flows show sequencing and dependencies between integration points along a value chain. Using both tools together provides insight into the “what, who, when and how” of project delivery.
Is the use of RACI matrices applicable to agile software projects?
Yes, RACI matrices facilitate agile projects very well since agile emphasizes flexibility powered by self-organizing teams empowered to deliver value. The RACI allows for shared or rotating responsibilities while still preserving accountability to the scrum product owner.
What are some key limitations or criticisms of the RACI framework?
Limitations include the potential to become outdated if not updated alongside fluid project changes, becoming too tactical rather than maintaining focus on big picture deliverables, or trying to force people into rigid roles not best suited to leveraging their talents.
How can we expand use of RACIs beyond temporary projects?
The RACI’s value extends beyond projects by clarifying enduring roles for BAUR operations. Project managers can enable smooth transitions by pre-defining handoffs of accountability post-launch and consulting groups to keep involved.
Conclusion and Next Steps
In summary, a responsibility assignment matrix powered by the RACI model is an invaluable yet uncomplicated tool to set your project — and your people — up for success.
Key next steps include:
Brainstorm project tasks, milestones and team members to build your first RACI
Establish single points of accountability for each project deliverable
Socialize the RACI with your full project team and executives
Revisit RACI matrix on a structured cadence to update roles and tasks
Mastering use of the RACI methodology takes your project management skills to the next level by enabling clear communication, facilitating decision making and driving flawless execution.
For enquiries call:
+1-469-442-0620

- Project Management
Responsibility Assignment Matrix: Template, Example & Benefits
Home Blog Project Management Responsibility Assignment Matrix: Template, Example & Benefits
Your team is the most crucial resource in completing a job. They must adhere to the project's schedule and budget. Controlling the project requires everyone involved to understand their roles and duties when carrying out tasks and accomplishing project objectives. How can all the participants in a project be coordinated so that they are aware of what they are doing and do not prevent others from carrying out their tasks? An assignment of responsibility matrix can be useful.
Your project will have a productive crew thanks to an assignment matrix. You can take an online PMP course to learn the details included in RAM, Responsibility Assignment Matrix in project management, and Responsibility Assignment Matrix example, to advance your career.
What is a Responsibility Assignment Matrix in Project Management?
So, what is the responsibility assignment matrix? A Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM), sometimes referred to as a RACI chart or RACI matrix, in project management identifies all relevant stakeholders and specifies roles for cross-functional teams and their level of involvement in a project. Each letter in the acronym RACI, which stands for Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed, refers to a different team member in the Responsibility Assignment Matrix in Project Management.
1. Responsible
The team member that oversees finishing the assignment is the person responsible for the RAM, Responsibility Assignment Matrix. The person in charge may be tasked with gathering all the visual and data assets required to put together the presentation if your team is working on a pitch deck (Responsible for executing the task).
2. Accountable
The responsible team member distributes the tasks to the other team members and ensures that they are finished accurately and on time. This team member oversees making sure the project is completed on schedule and that the tasks are fairly distributed among the accountable parties (Has governing & directing authority).
3. Consulted
A responsible party in Responsibility Assignment Matrix Project Management may frequently need to consult an expert, who serves as the consulted person, to finish certain responsibilities. A professional analysis of the consulted party is required when someone is tasked with gathering marketing statistics for a presentation. They also need to ensure that the data the responsible party is required to submit is accurate (Provide insights, analysis or expert judgment).
4. Informed
The informed party needs to be aware of when the major project components are finished even though they may not be directly involved in all the steps to ensure that everything is running smoothly. The informed team member must be aware of any delays or stalls in the project as they must complete their tasks (Updated with project information and outcome).

Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) Goal in Project Management
The goal of the Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) is to clearly define roles and responsibilities of everyone on a project team. This ensures that everyone understands their role and how it fits into the bigger picture. RAM also allows for quick identification of whom to contact when an issue arises. It might also be applied within a working group to establish authority levels, roles, and duties for tasks.
The matrix format displays each person's associated actions and each person's associated people. To avoid confusion, this makes sure that there is only one person responsible for each task. It is also important to outline the dates and reminders for each participant, so that they are aware of their deliverables/plans to fulfill the deliverables. The best Project Management Certification programs online will teach you how to make efficient decisions and effectively use RAM.
How to Create a Responsibility Assignment Matrix?
A Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) is a table that shows the tasks needed to be completed as part of a project, who is responsible for each task, and when the task needs to be completed. Making a matrix to distribute responsibilities is not as challenging as getting everyone on board with their respective jobs and responsibilities.
You should therefore involve your staff in the process, receive their feedback, and eventually secure their buy-in without expending excessive time and effort on it. You will have a successful responsibility assignment if you follow these instructions to ensure that everyone is on the same page.
- List every person involved in the project, including the team, stakeholders, and everyone in between.
- List each project deliverable that you can think of. To make sure you do not overlook any, use a work breakdown framework.
- To discuss how to carry out the tasks and produce the deliverables, meet with the team members. The duty and authority of the team for each assignment must be discussed.
- Utilizing a table with the project tasks specified in the left-hand column, create a Responsibility Assignment Matrix. Print the names of everyone involved in the project across the top.
- Assign whether a project team member is liable, accountable, consulted, or informed where the tasks meet them.
- Share the completed Responsibility Assignment Matrix Template Word with the project team and stakeholders. If necessary, conduct a meeting to ensure that everyone is aware of their responsibilities for the project. Print a copy, and if you are working in a common location, post it.
Developing Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) Best Practices
The best practices for developing a Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) will vary depending on the specific project and organization. However, some tips on how to develop a RAM matrix effectively include the following:
- Define the project scope and objectives clearly, so that all stakeholders understand the parameters of the project and what is expected to be accomplished.
- Assign clear roles and responsibilities to individuals and teams so that everyone knows who is responsible for what aspect of the project.
- Make sure that the Responsibility Assignment Matrix PMP is kept up to date as the project progresses so that everyone is aware of any changes in roles and responsibilities.
- Use the RAM matrix as a tool to help identify potential risks and issues related to the project so that they can be addressed early on.
- One stakeholder leads a task.
- The lesser number of people are accountable, the better.
- Act efficiently with meetings.
- Continuous communication.
- Stakeholder agreement on final RAM.
Responsibility Assignment Matrix Examples and Templates
- Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RACI)
- RACI-VS (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed- “V”erification and “S”ign off)
- RASCI (Responsible, Accountable, Support, Consulted, Informed)
- RAC (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted)
- ARCI (Accountable, Responsible, Consulted, Informed)
- RATSI (Responsibility, Authority, Task, Support, Informed)
- PACSI (Perform, Accountable, Control, Suggest, Informed)
- RACIQ (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed, Quality Review)
- DACI (Driver, Approver, Contributors, Informed)
- CAIRO (Consulted, Accountable, Informed, Responsible, Omitted)

Downloadable Responsibility Assignment Matrix Template Excel
Download the Responsibility Assignment Matrix Template (xlsx) here!
This Responsibility Assignment Matrix template is available for free in both Excel and OpenDocument Spreadsheet formats. The template can be completely modified using Microsoft Excel and adjusted to meet the needs of your project. To make it simple to understand what is required of each worker on each task, the template employs conditional formatting to change the color of each cell.
Download a Printable Responsibility Assignment Matrix PDF
Download the Responsibility Assignment Matrix Template (PDF) here!
If you intend to design a Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM), you may require samples and templates to use as a guide, regardless of whether you are managing an event, a construction project, or a restaurant. Some of the templates are-
- Responsibility Assignment Matrix Sample
- Responsibility Assignment Matrix for Construction Project Template
- Basic Responsibility Assignment Matrix Sample
- Responsibility Assignment Matrix in PDF
Benefits of Responsibility Assignment Matrix
There are many benefits of the Responsibility Assignment Matrix. One benefit is that it helps to ensure that everyone on a project team understands their roles and responsibilities. This can help to prevent misunderstandings and conflict between team members. Another benefit of using RAM is that it can help to improve communication between team members.
By clearly defining roles and responsibilities, team members will know whom to go to for specific information or tasks. This can help to avoid confusion and delays. Lastly, RAM can help to improve project management by providing a clear overview of who is responsible for what. This can help project managers to identify potential problems or areas where there may be a lack of resources.
Top Cities where Knowledgehut Conduct Project Management Certification Training Course Online
Unlock your potential as a Scrum Master with our game-changing certified scrum master course . Acquire the skills, knowledge, and confidence to effectively lead agile teams. Join us now and pave your way to success!
A Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) is a tool used to identify and define the roles and responsibilities of individuals and groups within an organization. It is a means of clarifying who is responsible for what and ensuring that everyone understands their roles and responsibilities. RAM can be used to create accountability and ownership for tasks and projects, and to identify potential areas of conflict.
It is a valuable tool for effective project management and can help to ensure that everyone involved in a project is aware of their roles and responsibilities. It can also help to identify potential areas of conflict and ensure that tasks are properly assigned. The KnowledgeHut online PMP course will give you an insight into the Responsibility Assignment Matrix and can be a helpful tool for any project manager.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. what is included in a responsibility assignment matrix.
A Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) is a tool used to help define and assign roles and responsibilities for a project or process. The matrix typically includes a list of tasks or deliverables and the people or groups responsible for each.
2. What can a Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) eliminate?
RAM eliminates ambiguity and confusion over who is responsible for what on a project. It also provides a clear overview of who is responsible for each task, making it easier to hold team members accountable.
3. What does a Responsibility Assignment Matrix not show?
The duty assignment matrix links resources to the tasks or work packages they must do, but it does not indicate when they will be required to do their work.

Kevin D.Davis
Kevin D. Davis is a seasoned and results-driven Program/Project Management Professional with a Master's Certificate in Advanced Project Management. With expertise in leading multi-million dollar projects, strategic planning, and sales operations, Kevin excels in maximizing solutions and building business cases. He possesses a deep understanding of methodologies such as PMBOK, Lean Six Sigma, and TQM to achieve business/technology alignment. With over 100 instructional training sessions and extensive experience as a PMP Exam Prep Instructor at KnowledgeHut, Kevin has a proven track record in project management training and consulting. His expertise has helped in driving successful project outcomes and fostering organizational growth.
Avail your free 1:1 mentorship session.
Something went wrong
Upcoming Project Management Batches & Dates

- Onsite training
3,000,000+ delegates
15,000+ clients
1,000+ locations
- KnowledgePass
- Log a ticket
01344203999 Available 24/7
Responsibility Assignment Matrix: A Complete Overview
Dive into the world of Responsibility Assignment Matrices (RAMs) and how they streamline Project Management. This comprehensive blog explains their purpose, benefits, and practical use, enabling effective role definition and accountability in project teams.

Exclusive 40% OFF
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Share this Resource
- PMP® Certification Training Course
- CGPM (Certified Global Project Manager) Course
- CDSPM (Certified Digital Services Project Manager) Course
- Project Management Office Fundamentals Certification Course
- CAPM® Certification Training Course

This comprehensive blog aims to provide you with a complete overview of the Responsibility Assignment Matrix and its pivotal role in Project Management and organisational structure.
Table of Content
1) What is a Responsibility Assignment Matrix in Project Management?
2) Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) goal in Project Management
3) How to create a Responsibility Assignment Matrix?
4) Developing Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) best practices
5) Responsibility Assignment Matrix examples and templates
6) Benefits of Responsibility Assignment Matrix
7) Conclusion
What is a Responsibility Assignment Matrix in Project Management?

Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) goal in Project Management
The primary goal of a Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) in project management is to enhance project organisation, coordination, and accountability by clearly defining and allocating roles and responsibilities. Here are the key goals of using a RAM in project management:
1) Clarity in roles and responsibilities: A RAM ensures that each team member knows their specific role and what tasks they are responsible for. This clarity helps prevent misunderstandings, conflicts, and duplication of effort.
2) Improved communication: By documenting roles and responsibilities in a clear and concise manner, RAM promotes effective communication within the project team. Team members can refer to the RAM to understand who to contact for specific issues or questions.
3) Conflict resolution: When there is a dispute or ambiguity regarding responsibilities, the RAM serves as a reference point to resolve conflicts. It provides a basis for discussion and helps in finding solutions.
4) Enhanced project control: With RAM in place, project managers and stakeholders can better monitor the progress of the project. They can quickly identify who is accountable for each task and track the status of work packages.
5) Efficiency and accountability: The RAM helps in assigning ownership to each aspect of the project, fostering a sense of accountability among team members. This, in turn, can lead to increased efficiency as everyone knows what is expected of them.
6) Risk management: By clearly defining responsibilities, the RAM can help identify potential risks associated with gaps or overlaps in roles. This proactive approach allows project teams to mitigate risks more effectively.
7) Resource allocation: Project managers can optimise resource allocation by understanding who is responsible for specific tasks and how workloads are distributed.
Ready to lead digital service projects to success? Register for our Certified Digital Services Project Manager (CDSPM) Course today!
How to create a Responsibility Assignment Matrix?
Identify the project scope
Begin by understanding the scope of the project or the specific task for which you're creating the RAM. This includes defining the project's objectives, deliverables, and key milestones.
Define roles and responsibilities
a) Identify the key roles involved in the project. Common roles may include Project Manager, Team Leader, Team Member, Stakeholders, and other relevant positions.
b) Clearly define the responsibilities associated with each role. These responsibilities should be specific and measurable so there is no ambiguity.
Choose a framework - RACI, RASCI, or DACI
a) Select a framework for your RAM. The most commonly used frameworks are RACI, RASCI, and DACI:
b) RACI: Stands for Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed. It defines who is responsible for a task, who is accountable for its completion, who needs to be consulted, and who needs to be informed.
c) RASCI: Similar to RACI, but with an additional role, the "S" for Support. This framework further clarifies who provides support for a task.
d) DACI: This framework is similar to RASCI but adds the role of Driver. The Driver is responsible for ensuring that a task is completed.
Assign roles using the framework
a) For each task or work package within the project, assign the relevant roles using the chosen framework. Each task should have a Responsible person, an Accountable person, and, if necessary, people who need to be Consulted, Informed, or Supported.
b) Be specific and ensure that there is only one person designated as "Accountable" for each task to avoid confusion.
Document the RAM
a) Create a table or chart that lists all the tasks or work packages on one axis and the identified roles on the other.
b) Fill in the matrix with the appropriate role designations (R, A, C, I, S, D) for each task and role.
Review and validate
Share the RAM with the project team and stakeholders for review and validation. Ensure that everyone agrees with the assigned roles and responsibilities.
Implement and communicate
Once the RAM is finalised and approved, communicate it to the project team and relevant stakeholders. Make sure that everyone understands their roles and responsibilities.
Regularly update the RAM
As the project progresses, it's essential to update the RAM as needed. Roles and responsibilities may change, and new tasks may emerge. Keep the RAM current to reflect the project's evolving needs.
Unlock your potential as a Program Manager with our Programme Management (PgM) Fundamentals Course !
Developing Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) best practices
Developing a Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) is a critical aspect of project management. To create an effective RAM, consider the following best practices:
1) Involve key stakeholders: Engage with project stakeholders, team members, and subject matter experts when defining roles and responsibilities. Their input can provide valuable insights into the project's requirements.
2) Keep it simple: Avoid making the RAM overly complex. Use a straightforward framework (e.g., RACI, RASCI, DACI) that team members can easily understand and apply.
3) Use clear and specific language: Write responsibilities in a clear and specific manner to minimise misunderstandings. Avoid ambiguous or vague descriptions that could lead to confusion.
4) Designate a single "accountable" person: Assign only one person as "Accountable" for each task. This individual is ultimately responsible for the task's completion. Multiple accountable persons can lead to confusion and accountability issues.
5) Consult and inform appropriately: Carefully consider who needs to be consulted and informed for each task. Avoid unnecessary involvement, which can lead to inefficiency. Ensure that the right people are included in these roles.
6) Review and validate with the team: Share the RAM with the project team and stakeholders for feedback and validation. Ensure that all parties agree with the assigned roles and responsibilities.
7) Document assumptions and clarifications: If certain roles and responsibilities are based on assumptions or require clarification, document these notes alongside the RAM. This can help avoid misunderstandings in the future.
Join our Project Management Masterclass today and take the leap towards becoming a project management expert!
Benefits of Responsibility Assignment Matrix
A Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) offers several significant benefits in the context of project management and organisational structure. Here are some of the key benefits of using a RAM:
1) Clarity in project roles and responsibilities: A RAM clearly defines who is responsible for each task, which helps prevent confusion and ensures that team members understand their roles.
2) Improved communication: The RAM serves as a central reference point for roles and responsibilities, promoting effective communication within the project team. Team members can quickly identify who to contact for specific issues or questions.
3) Conflict resolution: When there is a dispute or ambiguity regarding responsibilities, the RAM provides a basis for discussion and conflict resolution. It helps identify where accountability lies and facilitates problem-solving.
4) Enhanced project control: Project managers and stakeholders can use the RAM to monitor and control the progress of the project. It allows for tracking the status of work packages and ensures that tasks are progressing as planned.
5) Efficiency and accountability: Clearly defined roles and responsibilities create a sense of accountability among team members, which can lead to increased efficiency. When people know what is expected of them, they are more likely to meet those expectations.
6) Resource allocation: The RAM helps project managers optimise resource allocation by understanding who is responsible for specific tasks. This ensures that workloads are distributed evenly and that resources are used efficiently.
Conclusion
A Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) is a vital component in project management and organisational structures. Its significance lies in its ability to define, allocate, and communicate roles and responsibilities, which, in turn, leads to improved project efficiency and success.
Take the next step in your project management career with our Certified Global Project Manager (CGPM) Course !
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming project management resources batches & dates.
Fri 12th Apr 2024
Fri 17th May 2024
Fri 21st Jun 2024
Fri 19th Jul 2024
Fri 16th Aug 2024
Fri 13th Sep 2024
Fri 11th Oct 2024
Fri 8th Nov 2024
Fri 13th Dec 2024
Get A Quote
WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
My employer
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry
- Business Analysis
- Lean Six Sigma Certification
Share this course
Our biggest spring sale.

We cannot process your enquiry without contacting you, please tick to confirm your consent to us for contacting you about your enquiry.
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry.
We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Or select from our popular topics
- ITIL® Certification
- Scrum Certification
- Change Management Certification
- Business Analysis Courses
- Microsoft Azure Certification
- Microsoft Excel & Certification Course
- Microsoft Project
- Explore more courses
Press esc to close
Fill out your contact details below and our training experts will be in touch.
Fill out your contact details below
Thank you for your enquiry!
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go over your training requirements.
Back to Course Information
Fill out your contact details below so we can get in touch with you regarding your training requirements.
* WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
Preferred Contact Method
No preference
Back to course information
Fill out your training details below
Fill out your training details below so we have a better idea of what your training requirements are.
HOW MANY DELEGATES NEED TRAINING?
HOW DO YOU WANT THE COURSE DELIVERED?
Online Instructor-led
Online Self-paced
WHEN WOULD YOU LIKE TO TAKE THIS COURSE?
Next 2 - 4 months
WHAT IS YOUR REASON FOR ENQUIRING?
Looking for some information
Looking for a discount
I want to book but have questions
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go overy your training requirements.
Your privacy & cookies!
Like many websites we use cookies. We care about your data and experience, so to give you the best possible experience using our site, we store a very limited amount of your data. Continuing to use this site or clicking “Accept & close” means that you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about our privacy policy and cookie policy cookie policy .
We use cookies that are essential for our site to work. Please visit our cookie policy for more information. To accept all cookies click 'Accept & close'.

What is a Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) in Project Management?
Fahad Usmani, PMP
March 30, 2024
A responsibility assignment matrix (RAM) in project management is a key document that distinguishes stakeholders’ roles and responsibilities. The RACI chart is the most popular example of a RAM that clarifies stakeholders’ roles and defines their involvement.
RACI stands for Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed. Each team member in the RACI chart has at least one role.
All stakeholders refer to RAM in case of conflict regarding the roles and responsibilities in assignments or duties. RAM helps reduce conflict in projects to a great extent. Using this document, every team member will know their roles and the responsibilities of other team members.
The roles in the RACI matrix are as follows:
- Responsible: This stakeholder is responsible for completing the task.
- Accountable: This stakeholder is accountable for the task. They will make decisions and delegate work to the stakeholders who are responsible for completing the task.
- Consulted: These stakeholders will be consulted on any decisions made about the task.
- Informed: These stakeholders only require an updated status report on the progress of the task.
Responsibility Assignment Matrix Example
As I said, the RACI chart is the most popular example of RAM.
The table below shows the RAM example using the RACI chart:

Some other less-popular responsibility assignment matrix examples are as follows:
- RASCI Chart: This chart is also known as the “RASCI matrix,” as the letter S is added, which means “supportive.”
- DACI Chart: DACI stands for “Driver, Approver, Contributor, and Informed.”
- RAPID Chart: RAPID stands for “Recommend, Agree, Perform, Input, and Decide.”
- CARS: CARS stands for “Communicate, Approval, Responsible, and Support.”
- CLAM: CLAM stands for “Contribute, Lead, Approve, and Monitor.”
Responsibility Assignment Matrix Template
The table below shows the basic template for the responsibility assignment matrix.

RAM is a key tool in project management . It helps the project manager assign roles and responsibilities. Additionally, it ensures that the team stays on its path and that no one interferes with each other’s roles. Finally, RAM ensures that every task has responsible and accountable stakeholders assigned to it.
This topic is important from a PMP exam point of view.

I am Mohammad Fahad Usmani, B.E. PMP, PMI-RMP. I have been blogging on project management topics since 2011. To date, thousands of professionals have passed the PMP exam using my resources.
PMP Question Bank
This is the most popular Question Bank for the PMP Exam. To date, it has helped over 10,000 PMP aspirants prepare for the exam.
PMP Training Program
This is a PMI-approved 35 contact hours training program and it is based on the latest exam content outline applicable in 2024.
Similar Posts

What is the CAPM Exam Structure?
Today we will talk about the CAPM exam structure. Many future Project Management Associates ask: What is the CAPM Exam Structure? How is it laid out? What should I expect during the test? The CAPM (Certified Associate in Project Management) certification is the most popular credential in project management for professionals with little or no…

Strategy Vs Tactics: Definition of Strategy, Tactics & Differences
Organizations operate to achieve strategic goals; strategies and tactics help them achieve them. If you have ever been in high-level strategic business planning, you must have heard of strategy and tactics. Tactics and strategy are different terms, and today’s blog post will discuss strategy vs tactics in detail. Strategy Vs Tactics Strategy and tactics do…

Project Management Tools and Techniques
Project management tools and techniques help manage the project effectively. These tools help you develop project management plans, execute them, monitor and control the project and complete it successfully. You can use these project management tools and techniques for any project, irrespective of industry or field. This blog post will provide you with the 23…

Cost of Quality: Cost of Conformance & Cost of Nonconformance
The cost of quality includes the cost of conformance and cost of non-conformance, which is a crucial factor in quality planning. Quality is important. It impacts all industries and is a selling point for many companies. For example, Toyota delivers high-quality products using Jidoka (Automation with Human Touch) and Just in Time methodologies that resonate…

What is Project Change Management?
Change management is the process of making changes to a project. These changes can be made to processes, policies, approved project documents, baselines, etc. The change management process includes the project manager and the change control board (CCB). The CCB includes stakeholders (e.g., top management and subject matter experts). The project manager will raise the…

Goal Vs Objective
The terms “goal” and “objective” are often used interchangeably in the professional world. Even though they define different outcomes that your organization hopes to achieve, goals and objectives are frequently confused with one another. However, goals and objectives are not the same things since they differ in terms of timelines, how they are measured, the…
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- PMP® Exam Tip: The Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM)

It is especially useful in clarifying roles and responsibilities in cross-functional/departmental projects and processes. RACI is an acronym derived from the four key responsibilities most typically used:
Very often the role that is Accountable for a task or deliverable may also be Responsible for completing it (indicated on the matrix by the task or deliverable having a role Accountable for it, but no role Responsible for its completion, i.e. it is implied).
RAM Definition
A grid that shows the project resources assigned to each work package. PMBOK® Guide
Outside of this exception, it is generally recommended that each role in the project or process for each task receive, at most, just one of the participation types. Where more than one participation type is shown, this generally implies that participation has not yet been fully resolved, which can impede the value of this technique in clarifying the participation of each role on each task.
Furthermore, there is a distinction between a role and individually identified persons: a role is a descriptor of an associated set of tasks, which may be performed by many persons, and one person can perform many roles.
For example, an organisation may have 10 persons who can perform the role of project manager, although traditionally each project only has one project manager at any one time; and a person who is able to perform the role of project manager may also be able to perform the role of business analyst and tester.
On larger projects, RAMs can be developed at various levels. For example, a high-level RAM can define which a project group or unit is responsible for major phases of the project, while lower level RAMs are used within the group to designate roles, responsibilities and levels of authority for specific activities.
RACI Definition
A common type of RAM that uses responsible, accountable, consult and inform statuses to define the involvement of stakeholders in project activities. PMBOK® Guide
The matrix format shows all activities associated with one person and all people associated with one activity. This also ensures that there is only one person accountable for any one task to avoid confusion.
The PMBOK® Guide also states that one example of a RAM is the RACI chart, showing the work to be done in the left column as activities. The assigned resources can be shown as individual or groups. The RACI is just one type of RAM; the project manager can select other options such as "lead" and "resource" designation or others as appropriate for the project. The RACI is particularly important when the team consists of internal and external resources to ensure clear divisions of roles and expectations.
It is recommended that the project manager involves team members when developing the responsibility assignment matrix. While the PM can develop an initial, rough draft, it is impossible for him or her to know exactly how tasks should be performed in each area of expertise. Involving the team therefore not only leads to a more precise matrix, but in addition the team members will also feel greater ownership of assignments, leading to greater commitment and participation.
PMP® Exam Sample Questions
Test your understanding of the RAM with this sample question from the PMP® Exam Simulator:
- Sample Question
- Answer and Explanation
Which type of tool will you use to depict the relationship between work to be done and project team members?
A) Matrix-based B) Hierarchical C) Text-oriented D) Gantt chart
Correct Answer: A) Matrix-based.
Explanation: A responsibility assignment matrix (RAM) is a grid that shows the project resources assigned to each work package.
Reference: PMBOK Guide 5th Edition, page 262

Most Read Project Management Professional (PMP)® Tips...
- PMP® Exam Tip: Crashing & Fast Tracking explained
- What’s an Example of a Start-to-Finish Relationship?
- PMP® Exam Tip: The Work Package Explained
- PMP® Exam Tip: Quality Assurance VS Quality Control
- Mandatory vs Discretionary Project Management Dependencies
- Communications Channels Formula for Communications Management
Related Articles
- Prepare for the PMP® Exam By Dressing Appropriately
- The 7 Things You Need to Pass The PMP® Certification Exam
- Dress Right for the PMP® Certification Exam
- Answer 1,000 PMP® Exam Questions Using PMP® Exam Simulator
- Tips to Manage Your Time During PMP® Certification Exam
- Our Mission
- Our Partners
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Notice
- Corporate Project Management Training
- Group Discounts
- PM PrepCast Discount Coupon
- Scholarships
- Free PMP® Newsletter
- Free PMP® Questions
- Free PMI-ACP® Questions
- Free CAPM® Simulator
- Project Management Basics
- Mastering Business Analysis
- PMP® Exam Simulator
- PMP® Formulas
- PMI-ACP® Exam Training
- CAPM® Exam Training
- PMP® Exam Prep
- PrepCast PMP® Practice Exam
- Forgot your password?
- Forgot your username?
- Order The PM PrepCast
- PM PrepCast Product Details
- PMP Exam Agile Booster Course
- The PMP® Exam Simulator
- The PM Formulas
- The PM StudyCoach (recorded)
- The PM StudyCoach Guidebook
- The PM FlashCards
- All PMP® Products Overview
- PM Basics Course
- Corporate PMP Training
- Order the Agile PrepCast
- Agile PrepCast Product Details
- The ACP StudyCoach Guidebooks
- The PMI-ACP® Exam Simulator
- Corporate PMI-ACP Training
- Order The PM PrepCast for CAPM
- The PM PrepCast for CAPM®
- The CAPM® Exam Simulator
- 60 PMP PDUs - From The PM PrepCast
- 60 PMP PDUs - From The PDU Podcast
- 15 PMP Power Skills PDUs
- 17 PMP Leadership PDUs
- 30 PMI-ACP PDUs
- 17 PMI-ACP Leadership PDUs
- 15 CAPM PDUs
- 5 PDUs Business Analysis Course
- Artificial Intelligence for Project Managers
- Free PM PrepCast Training
- Free PM PrepCast Exam Simulator
- Free PMP® Practice Exam
- The Free PM PrepCast
- Free PMP® Exam Guides
- Free PMP® Exam Newsletter
- Free PMP® Webinars
- All Free PMP® Exam Resources...
- The Free Agile PrepCast
- Free PMI-ACP® Exam Newsletter
- All Free PMI-ACP® Exam Resources...
- Free CAPM® Exam Newsletter
- All Free PDU Resources...
- Explore Corporate Training Offers
- Unlocking Corporate Efficiency
- How PM Training Transform Businesses
- PM Training for Shifting Market Demands
- PM Training for Your Business
- Student Success with PMP Simulation
- PMP® Study Guide
- PMP® Certification Cost
- 35 Hours of Project Management Education
- Knowledge Areas & Process Groups
- How to Fill in the PMP Application
- PMP® Certification Exam
- How to get PMP Certification
- PMP® Exam Questions
- PMP® Certification Bangalore
- Failed PMP Exam
- PMI-ACP Certification Study Guide
- CAPM Certification Study Guide
- 12 Project Management Principles Explained by Experts
- Project Management Certifications Career Advancement
- PMP vs Certifications
- Project Management Organization Company Benefits
- Project Management Organizations Importance
- PM PrepCast Reviews
- PM PrepCast Reviews on Google
- PM Exam Simulator Reviews
- Agile PrepCast Reviews
- PMP® Exam Coaching Reviews
- Exam Prep Essentials eBook Reviews
- Add Your Review
- Student Profiles
- Successful Students
- PMP® Exam Discussion
- PMP® Exam Lessons Learned
- Free PMP® Exam Questions
- PMI-ACP® Exam Discussion
- PMI-ACP® Exam Lessons Learned
- CAPM® Exam Discussion
- CAPM® Exam Lessons Learned
- PDU Questions and Answers
- CIPP/E® Exam Discussion
- CIPP/E® Exam Lessons Learned
- Project Management Plan
- Change Management Plan
- Project Roadmap
- Scope Management Plan
- Requirements Management Plan
- Requirements Documentation
- Requirements raceability Matrix
- Project Scope Statement
- Work Breakdown Structure
- WBS Dictionary
- Schedule Management Plan
- Activity list
- Activity attributes
- Milestone list
- Network diagram
- Duration estimates
- Duration estimates worksheet
- Project schedule
- Cost management plan
- Cost estimates
- Cost estimating worksheet
- Cost baseline
- Quality management plan
- Quality metrics
Responsibility assignment matrix (RAM)
- Resource management plan
- Team charter
- Resource requirements
- Resource breakdown structure
- Communications management plan
- Risk management plan
- Risk register
- Risk report
- Probability and impact assessment
- Probability and impact matrix
- Risk data sheet
- Procurement management plan
- Procurement strategy
- Source selection criteria
- Stakeholder engagement plan
- Comment Create task
The responsibility assignment matrix (RAM) shows the intersection of work packages and resources. Generally, RAMs are used to show the different levels of participation on a work package by various team members rather than physical resources. RAMs can indicate different types of participation depending on the needs of the project. Some common types include:
- Accountable
- Responsible
The RAM always should include a key that explains what each of the levels of participation entails. An example follows using a RACI chart, as demonstrated in the PMBOK ® Guide – Sixth Edition. The needs of your project should determine the fields for the RAM you use.
The responsibility assignment matrix can receive information from:
- Scope baseline
- Requirements documentation
- Stakeholder register
It is a data representation tool that provides information to the resource management plan in process
- Plan Resource Management in the PMBOK ® Guide – Sixth Edition. It is progressively elaborated as more information about the scope and the resource requirements is known.
Tailoring tips
Consider the following tips to help tailor the RAM to meet your needs:
- Tailor the types of participation appropriate for your Some projects require “sign-off” of specific deliverables, whereas others use the term “approve.”
- Determine the appropriate level to record information on the Large projects with multiple vendors and large deliverables often use the RAM as the intersection of the WBS and the OBS (organizational breakdown structure). Small projects may use it at the deliverable or activity level to help enter schedule information.
The RAM should be aligned and consistent with the following documents:
- Work breakdown structure
- Procurement documents (RFP, RFQ, etc.)

Cancel Save
Move page to under this page
Contact us lovepmp.com
We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. If you continue to use this site we will assume that you accept and understand our Privacy Policy .
404 Not found
Responsibility Matrix
Locked lesson.
- Lesson resources Resources
- Quick reference Reference
About this lesson
The Responsibility Matrix is a project management tool for correlating project work assignments with project team members.
Exercise files
Download this lesson’s related exercise files.
Quick reference
When to use.
This technique is normally used with large teams and teams that are not co-located. Small co-located project team assignments are normally managed in the day-to-day team interactions. When the team is large or members are not co-located, the assignment of responsibilities needs to be more formal to avoid confusion leading to duplication or omission of work.
Instructions
The Responsibility Matrix is an excellent communication and risk identification tool. It provides a visual communication of the contribution of each team member. It also will highlight if a team member is overloaded or who may not have the requisite skills to do the work assigned.
- List the project Team Members across the top of the matrix.
- List the project tasks (summary or detail) down the side of the matrix.
- For each task assign one person as the individual leading the task. This is often a Core Team member.
- Assign the roles of other project team members assisting on each task. This includes both Core Team and extended team members.
Assigning roles in the matrix
There are many techniques in use for assigning roles in the matrix. It is strongly recommended that you use one that assigns support roles as well as lead roles for each task so that team members who must participate on a task are aware of that portion of their job.
The most common technique is based upon the CMMI methodology and uses the acronym RACI.
- Responsible – someone who must do a portion of the work on the task but is not the task leader.
- Accountable – the person who plans the task and ensures it is done correctly. Often they are the primary individual doing work on the task.
- Consult – a team member who may be asked to provide information for the task, but is not expected to do any significant work on the task
- Inform – a team member who needs to be informed about the work on the task because of its impact on their responsibilities
Another technique that I like to use is CALM.
- Contribute – a team member who provides supporting effort for a task.
- Approve – a team member who must review and approve the work of the task.
- Lead – the team member who is responsible for planning and leading the task. They often do most of the work.
- Monitor – a team member who tracks the progress on the task because of its impact on their responsibilities.
Responsibility Assignment Matrix: “A grid that shows the project resources assigned to each work package.” PMBOK ® Guide
This definition is taken from the Glossary of the Project Management Institute, A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, ( PMBOK ® Guide ) – Sixth Edition, Project Management Institute, Inc., 2017.
- 00:05 Hi, I'm Ray Sheen. Let's look at the resource planning tool,
- 00:07 the responsibility matrix.
- 00:09 The Project Management Body of Knowledge, the PMBOK Guide,
- 00:13 defines the responsibility assignment matrix as a grid that shows
- 00:16 the project resources assigned to each work package.
- 00:19 Typically, we use a responsibility matrix on a large project.
- 00:23 On small projects, there are only three or four people, and
- 00:26 everyone knows what everyone else is doing.
- 00:29 But on large projects, there are many people, and
- 00:32 a responsibility matrix is very helpful to clarify roles and responsibilities.
- 00:37 In a responsibility matrix, each task has a person who's responsible for
- 00:42 that task, an owner of that task.
- 00:44 They're the ones leading the project effort on that particular activity.
- 00:48 The responsibility matrix also shows what other individuals are involved in
- 00:53 the task, and their type of involvement.
- 00:56 To create the matrix, we start by listing all of our
- 00:59 project team members normally across the top of the matrix.
- 01:03 Then, list the project tasks down the side of the matrix.
- 01:07 Now, the matrix is created.
- 01:09 I usually assign the leader for each task at this point.
- 01:12 In this case, I'm using an A to designate the leader because this is
- 01:17 the person who is accountable for that task.
- 01:20 Notice, there's only one person accountable on each task.
- 01:23 If you think you need two people, you probably have two tasks.
- 01:28 Then, I assign the other individuals who have some other role or
- 01:31 responsibility with the task.
- 01:33 This is determined by the task planning.
- 01:36 I'm using the RACI acronym for assignment of roles in this example.
- 01:40 R stands for responsible, A is for accountable, C is for
- 01:44 consult, and I for information.
- 01:47 This acronym has become widely used because it's part of the CMMI from
- 01:51 Carnegie Mellon.
- 01:52 However, there are several other assignment codes.
- 01:55 One that I have found to be very helpful is CALM.
- 01:59 Use either of these acronyms or
- 02:00 one of your own to clarify the roles of each of the project team members.
- 02:05 By the way, notice the individual in column five.
- 02:08 They're involved in every task.
- 02:11 I'll come back to that in just a moment.
- 02:15 The responsibility matrix provides clarity of expectations for
- 02:18 individuals on the project.
- 02:20 It also is a great tool for managing the human resources on the project.
- 02:25 It can be used to guide our personnel staffing decisions,
- 02:28 make sure you have the right individual for that role.
- 02:31 One of the ways to use this matrix is to identify someone who may be carrying too
- 02:36 heavy of a workload.
- 02:37 Remember the individual in column 5?
- 02:40 That may be more than a full-time job,
- 02:42 you may need to split that individual's role into two individuals.
- 02:46 The responsibility matrix highlights this type of risk.
- 02:50 Another type of risk is when you have the wrong individual for the position.
- 02:54 They do not have the skill set that's required based upon the actual assignment
- 02:59 of responsibilities.
- 03:00 You may need to get training or coaching for that individual.
- 03:04 You may even request a different person be assigned to the project.
- 03:08 If you need to go to a functional manager and ask to change individuals,
- 03:12 it's much better to be using a responsibility matrix and
- 03:15 to make your argument based upon the skills required rather than to
- 03:18 be perceived that you just don't like someone.
- 03:21 Or if you're going to a functional manager and requesting a resource,
- 03:25 it's better to have the responsibility matrix with you to describe what you need
- 03:29 rather than be forced to take just whoever isn't busy right then.
- 03:33 The responsibility matrix helps you plan the human resource aspect of your project.
- 03:37 It's great for communicating expectations and for
- 03:41 highlighting risk that is based upon your team members' skills and availability.
Lesson notes are only available for subscribers.
PMI, PMP, CAPM and PMBOK are registered marks of the Project Management Institute, Inc.
Twitter LinkedIn WhatsApp Email
How is your GoSkills experience?
Your feedback has been sent
© 2024 GoSkills Ltd. Skills for career advancement

Project Management Templates | FREE Downloads Word, Excel, PDF, Visio
- 100s of tasks covering the whole project life cycle
- Compatible with other Microsoft Project versions
- Proven to save you time and deliver results
- Software Development and Rollout
- Business Events and Conference
- Warehouse Construction
- Website Design and Build
- LEARN MORE!

Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) Template | FREE Download
The Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) shows 'who does what' on a work package or task. It is a popular tool because it shows what is expected of each member of the project team 'at a glance'. Scheduling tools like Microsoft project allow multiple resources to be linked to a task, but there is no easy way to show what each resource is expected to do - RAMs fill the gap. stakeholdermap.com
- See a screenshot of the template
- How to use the template
- Download the Excel Template

How to use the RAM template
- Enter your project details on the first tab
- Open the second tab named RAM
- List your work packages down the left hand side (replacing Workpackage 1, 2, 3.. etc)
- Enter the names of your project team in the columns. Replacing Person (1,2,3..)
Responsible
Accountable, what does raci stand for, what alternatives are there to raci, download the responsibility assignment matrix (ram) template, excel download - responsibility assignment matrix (ram) template (.xls), excel download - responsibility assignment matrix (ram) template (.xlsx), opendocument spreadsheet download - responsibility assignment matrix (ram) template (.ods), resource management plan template, resource planning template, resource requirements template, project templates to download.
- Sample Project Charter - FREE example from a real software project
- Excel Project Plan - FREE excel Gantt Chart template for project planning
- WBS Checklist - Download a Free checklist for reviewing Work Breakdown Structures
- Project Management Templates - View our collection of FREE templates for Project Managers
- MS Project schedules - Get a ready made Microsoft Project Plan for your Project.
- Risk Register template - Download a free Risk Register Template for managing your risks.
- Software Project Plan - Get a ready Made Microsoft Project Plan for your Software Implementation Project.
- Sample Statement of Work - Writing a SOW is challenging! That is why we are sharing this free example!
- WBS examples - 22 Examples of real world Work Breakdown Structures.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Getty. The responsibility assignment matrix (RAM) is a form of project management that encourages everyone to understand every step of the project. Looking at the chart involves all parties and ...
In business and project management, a responsibility assignment matrix (RAM), also known as RACI matrix (/ ˈ r eɪ s i /) or linear responsibility chart (LRC), is a model that describes the participation by various roles in completing tasks or deliverables for a project or business process.RACI is an acronym derived from the four key responsibilities most typically used: responsible ...
A RACI matrix is a document that clarifies which individuals or groups are responsible for a project's successful completion, and the roles that each will play throughout the project. The acronym RACI stands for the different responsibility types: Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed. Successful project management depends on a ...
The matrix format shows all activities associated with one person and all people associated with one activity. This ensures that only one person is accountable for any task to avoid confusion. Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) Tutorial ... A Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) is a tool used in project management to identify and clarify ...
Draft the responsibility assignment matrix using a table with the project tasks listed on the left-hand column. Across the top add the name of everyone in the project. Where the tasks meet the project team member, assign whether they're responsible, accountable, consulted or informed. When completed, share the responsibility assignment matrix ...
One tool that project managers use to keep these assignments clear is the Responsibility Assignment Matrix (also called the RAM, or the Responsibility Matrix). This matches deliverables with the people who are responsible for them. For every piece of the project, the matrix shows who needs to contribute what for the project to be completed.
Figure 1 - The Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) / RACI Matrix. To do this well and accurately, the matrix can be completed using the following steps: Step 1: Identify all the participants and (facilities) supporters of the project. Step 2: Identify all the deliverables for the project. Step 3: Discuss with all team members how they can ...
A RACI chart (sometimes called a Responsibility Assignment Matrix) is a way to identify your project teams' roles and responsibilities for any task, milestone, or project deliverable. By following the RACI acronym, you can clarify responsibility and reduce confusion. RACI stands for: Responsible. This person is directly in charge of the work.
The RACI chart, or responsibility assignment matrix, is a tool that helps to communicate and clarify the roles and responsibilities of people working together. In product management, it adds support for alignment and communication in the product development process: Responsible.
A RACI chart is also known as a responsibility assignment matrix (RAM) or project assignment matrix (PAM). ... That's bad news (and a big time-waster) for your projects. A number of studies show that communication is one of the most common and frequent causes of project failure. When team members have too many places to check for information ...
A RACI matrix, also known as a responsibility assignment matrix (mention responsibility assignment matrix term 8 more times) or RACI chart (mention raci chart term 9 more times), is a simple yet powerful way to map out who is Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed for key activities in a project.
A Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) is a table that shows the tasks needed to be completed as part of a project, who is responsible for each task, and when the task needs to be completed. Making a matrix to distribute responsibilities is not as challenging as getting everyone on board with their respective jobs and responsibilities.
A Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM), also known as a RACI matrix, is a project management tool used to clarify the roles and responsibilities of individuals. This comprehensive blog aims to provide you with a complete overview of the Responsibility Assignment Matrix and its pivotal role in Project Management and organisational structure.
March 30, 2024. A responsibility assignment matrix (RAM) in project management is a key document that distinguishes stakeholders' roles and responsibilities. The RACI chart is the most popular example of a RAM that clarifies stakeholders' roles and defines their involvement. RACI stands for Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed.
Introduction to Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) Project management is a complex process that involves multiple stakeholders, tasks, and resources. To ensure the success of a project, it is crucial to assign clear roles and responsibilities to team members and accurately define their tasks. One tool that can help project managers achieve ...
A RACI chart, also called a RACI matrix, is a type of responsibility assignment matrix (RAM) in project management. In practice, it's a simple spreadsheet or table that lists all stakeholders on ...
A Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM), also known as RACI matrix or Linear Responsibility Chart (LRC), describes the participation by various roles in completing tasks or deliverables for a project or business process. ... Explanation: A responsibility assignment matrix (RAM) is a grid that shows the project resources assigned to each work ...
1. Select a tool such as a whiteboard or digital template. 2. Identify the project tasks or deliverables such as features and products. 3. Identify the roles contributing to the project and ...
The responsibility assignment matrix (RAM) shows the intersection of work packages and resources. Generally, RAMs are used to show the different levels of participation on a work package by various team members rather than physical resources. RAMs can indicate different types of participation depending on the needs of the project.
The responsibility assignment matrix can also be call a RACI template, what stands for guilty, accountable, consulted and informed. Responsible: ... Uses willingness freely RACI template leave help you guide show the project teams better, allowance them to know where they stand in relation to the project and whichever theirs level of ...
00:07 the responsibility matrix. 00:09 The Project Management Body of Knowledge, the PMBOK Guide, 00:13 defines the responsibility assignment matrix as a grid that shows; 00:16 the project resources assigned to each work package. 00:19 Typically, we use a responsibility matrix on a large project.
The Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) shows 'who does what' on a work package or task. It is a popular tool because it shows what is expected of each member of the project team 'at a glance'. Scheduling tools like Microsoft project allow multiple resources to be linked to a task, but there is no easy way to show what each resource is expected to do - RAMs fill the gap.
A: Responsibility assignment matrix B: Resource histogram C: Bar chart D: Project organization chart A: The resource histogram show the number of resources used in each time period. In its pure form, a bar chart shows only activity and calendar date.