Rhetorical Analysis Essay
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline

Crafting an Effective Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline - Free Samples!
10 min read

People also read
Rhetorical Analysis Essay - A Complete Guide With Examples
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics – 120+ Unique Ideas
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example - Free Samples
Ethos, Pathos, and Logos - Structure, Usage & Examples
Have you ever stared at a blank page, wondering how to begin your rhetorical analysis essay?
You're not alone. Many students find the first step, creating an outline, to be a challenge.
The truth is - tackling a rhetorical analysis without a well-structured outline can lead to confusion and disorganization. But fear not because there's a solution.
In this blog, we will show you how you can create a rhetorical analysis essay outline. By the end, you’ll have a thorough understanding of what your outline should look like.
So, keep reading to find out how you can beat the blank pages!
- 1. What Is Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
- 2. Why Create a Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline?
- 3. Components of a Rhetorical Analysis Outline
- 4. Steps to Create a Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline
- 5. Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline Examples
What Is Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
A rhetorical analysis essay is a type of analytical essay that examines how an author uses language and persuasion to get their message across.
It involves analyzing speeches or essays to understand how authors use strategies within the rhetorical triangle to influence their intended audience. These techniques usually involve logical appeal, moral argument, and vivid imagery that appeals to the listener.
Key Elements to Analyze
In a rhetorical analysis essay, you would be analyzing the text keeping these key rhetorical concepts in mind:
- Ethos: This concerns the credibility of the author or speaker.
- Logos: This focuses on the logical aspects of the argument.
- Pathos: Pathos explores the emotional appeal of the discourse.
- Style and Tone: This involves analyzing the author's writing style and the overall tone of the text.
These elements provide a structured approach to rhetorical analysis, revealing how effective communication is achieved.
Why Create a Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline?
Writing a rhetorical analysis essay requires a writer to draft a structured piece of writing. This essay type is one of the most challenging tasks students are assigned to do for their academics.
Apart from conducting a strong analysis, a rhetorical analysis essay depends on how perfectly the essay outline is drafted.
An outline organizes the raw information and makes it understandable for the readers. It serves as your compass, ensuring you stay on course throughout the rhetoric essay. It helps you structure your ideas and arguments, adding clarity to your essay writing process.
Moreover, an outline works as a checklist for your essay. It assures you that nothing important is missed in the content.
Components of a Rhetorical Analysis Outline
Now that we've explored why creating an essay outline is essential, it's important to explore the different components of a rhetorical analysis outline.
Here’s a detailed rhetorical analysis essay outline:
Each element plays a crucial role in crafting a well-structured and persuasive analysis, so let's explore them in detail:
Introduction
The introduction of your rhetorical analysis essay serves as the gateway to your analysis. It's where you captivate your reader's interest, provide essential background information, and present your thesis statement.
Here are the elements typically included in an introduction paragraph:
- Hook The " hook " is a sentence or two designed to grab the reader's attention. It could be a thought-provoking quote, a surprising fact, or a compelling question. The purpose is to make your reader interested in what you're about to discuss—how an author uses rhetorical devices.
- Background Information After the hook, provide some context. Here, you briefly introduce the text you're analyzing, the author or speaker, and the overall topic. It's like giving your reader a map to navigate through your analysis.
- Thesis Statement The thesis statement is the main argument, your "claim." This concise sentence outlines what you'll be analyzing and what your main points will be. Your thesis should tell the reader what to expect in your analysis.
The body of your essay is where you dissect the author's persuasive techniques and reveal their impact on the audience. It contains sections dedicated to each rhetorical strategy you're examining.
In these sections, you'll explain the strategies, provide evidence from the text, and offer your insightful analysis of their effectiveness.
Section for Each Rhetorical Strategy
In the body paragraphs, you'll have sections dedicated to each rhetorical strategy you're analyzing. These sections each will focus on a different aspect of the text. For each strategy, you'll do three things:
- Explanation of the Strategy Start by explaining what the rhetorical technique is. Define it clearly for your reader. This is like providing a dictionary definition.
- Examples from the Text Next, provide examples from the text you're analyzing. These are specific quotes or passages where the author or speaker uses the strategy you're discussing. It's like showing your reader the evidence.
- Analysis of the Effectiveness Finally, analyze how effective the strategy is. This is where you dive deep into the text and explain how and why the strategy persuades the audience.
The conclusion should leave your readers with a sense of closure and a clear understanding of your analysis.
You don't introduce new information or arguments in this section; instead, you tie everything together. Here are the three essential elements of an impactful essay conclusion:
- Restate Thesis Start by restating your thesis to remind readers of your main argument. Repeating your main argument clearly helps the reader tie in all they have read in your essay.
- Summarize Main Points Summarize the main points from each section of your analysis. This serves as a reminder of the highlights of your arguments made throughout the essay.
- Final Thoughts Conclude by sharing your thoughts on how the author's strategies affect the audience and the text's broader importance. Encourage readers to consider these strategies' impact and the text's relevance.
This structure in your rhetorical analysis outline ensures that your analysis is clear, well-organized, and persuasive. Each component plays a crucial role in guiding your reader through your analysis.
Steps to Create a Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline
Creating an essay outline is a crucial step in organizing your thoughts and effectively analyzing a piece of rhetoric. Here are the steps to craft an outline for a rhetorical analysis essay:
Step 1 - Choose the Text
Select the piece of rhetoric that you will be analyzing. It could be a speech, a written essay, an advertisement, a political campaign, or any other form of communication.
Step 2 - Identify Rhetorical Devices and Rhetorical Appeals
Look for rhetorical devices such as metaphor, simile, analogy, hyperbole, and alliteration. Analyze how these devices contribute to the message. Identify any repetition, parallelism, or rhetorical questions used in the text.
Moreover, look for common rhetorical appeals i,e., ethos, pathos, and logos.
Step 3 - Analyze Appeals and Strategies in Each Section
For each argument, dedicate a body paragraph that will analyze how the author/speaker uses ethos, pathos, and logos.
Note the specific rhetorical devices used in each section and their impact.
Step 4 - Consider the Effect on the Audience
While outlining the last body paragraph, add points that analyze how the appeals are intended to affect the audience.
Consider whether the author/speaker is trying to persuade, inform, entertain, or provoke a specific emotional response. Include specific examples and quotations from the text to support your analysis.
Step 5 - Filter Out Extra Information
It's important to know what parts of the arguments should be included and which should be filtered out.
After having a sketch of the introduction and body paragraphs, remove any information that might feel irrelevant.
Step 6 - Conclude and Summarize
For the ending, make sure to restate your thesis statement. Include points that directly support your arguments and sum up your analysis.
These steps help you plan your essay for a well-structured, clear, and cohesive essay.
Here's a sample rhetorical analysis essay outline template that analyzes ethos, pathos and logos :
Here’s a practice outline:
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline Fill In The Blanks
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline Examples
Here are some rhetorical analysis essay outline pdf that you can use as reference outlines:
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline Ethos Pathos Logos
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline Ap Lang
Visual Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline
Comparative Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Introduction Outline
Need more help getting started? Check out these expert rhetorical analysis essay examples to get inspired!
In conclusion, you've got the tools and examples you need to ace your rhetorical analysis essay. The steps we've gone through provide a strong starting point for your academic journey into analyzing persuasive writing.
But if you ever hit a wall or need help with tight deadlines, don't forget our experts are here to lend a helping hand. Our essay writing service for college has helped lots of students like you get top-notch essays.
So, why wait? Place your order now and set yourself up for academic success!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Nova Allison is a Digital Content Strategist with over eight years of experience. Nova has also worked as a technical and scientific writer. She is majorly involved in developing and reviewing online content plans that engage and resonate with audiences. Nova has a passion for writing that engages and informs her readers.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading

- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis Essay–Examples & Template
What is a Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
A rhetorical analysis essay is, as the name suggests, an analysis of someone else’s writing (or speech, or advert, or even cartoon) and how they use not only words but also rhetorical techniques to influence their audience in a certain way. A rhetorical analysis is less interested in what the author is saying and more in how they present it, what effect this has on their readers, whether they achieve their goals, and what approach they use to get there.
Its structure is similar to that of most essays: An Introduction presents your thesis, a Body analyzes the text you have chosen, breaks it down into sections and explains how arguments have been constructed and how each part persuades, informs, or entertains the reader, and a Conclusion section sums up your evaluation.
Note that your personal opinion on the matter is not relevant for your analysis and that you don’t state anywhere in your essay whether you agree or disagree with the stance the author takes.
In the following, we will define the key rhetorical concepts you need to write a good rhetorical analysis and give you some practical tips on where to start.
Key Rhetorical Concepts
Your goal when writing a rhetorical analysis is to think about and then carefully describe how the author has designed their text so that it has the intended effect on their audience. To do that, you need to consider a number of key rhetorical strategies: Rhetorical appeals (“Ethos”, “Logos”, and “Pathos”), context, as well as claims, supports, and warrants.
Ethos, Logos, and Pathos were introduced by Aristotle, way back in the 4th century BC, as the main ways in which language can be used to persuade an audience. They still represent the basis of any rhetorical analysis and are often referred to as the “rhetorical triangle”.
These and other rhetorical techniques can all be combined to create the intended effect, and your job as the one analyzing a text is to break the writer’s arguments down and identify the concepts they are based on.
Rhetorical Appeals
Rhetorical appeal #1: ethos.
Ethos refers to the reputation or authority of the writer regarding the topic of their essay or speech and to how they use this to appeal to their audience. Just like we are more likely to buy a product from a brand or vendor we have confidence in than one we don’t know or have reason to distrust, Ethos-driven texts or speeches rely on the reputation of the author to persuade the reader or listener. When you analyze an essay, you should therefore look at how the writer establishes Ethos through rhetorical devices.
Does the author present themselves as an authority on their subject? If so, how?
Do they highlight how impeccable their own behavior is to make a moral argument?
Do they present themselves as an expert by listing their qualifications or experience to convince the reader of their opinion on something?
Rhetorical appeal #2: Pathos
The purpose of Pathos-driven rhetoric is to appeal to the reader’s emotions. A common example of pathos as a rhetorical means is adverts by charities that try to make you donate money to a “good cause”. To evoke the intended emotions in the reader, an author may use passionate language, tell personal stories, and employ vivid imagery so that the reader can imagine themselves in a certain situation and feel empathy with or anger towards others.
Rhetorical appeal #3: Logos
Logos, the “logical” appeal, uses reason to persuade. Reason and logic, supported by data, evidence, clearly defined methodology, and well-constructed arguments, are what most academic writing is based on. Emotions, those of the researcher/writer as well as those of the reader, should stay out of such academic texts, as should anyone’s reputation, beliefs, or personal opinions.
Text and Context
To analyze a piece of writing, a speech, an advertisement, or even a satirical drawing, you need to look beyond the piece of communication and take the context in which it was created and/or published into account.
Who is the person who wrote the text/drew the cartoon/designed the ad..? What audience are they trying to reach? Where was the piece published and what was happening there around that time?
A political speech, for example, can be powerful even when read decades later, but the historical context surrounding it is an important aspect of the effect it was intended to have.
Claims, Supports, and Warrants
To make any kind of argument, a writer needs to put forward specific claims, support them with data or evidence or even a moral or emotional appeal, and connect the dots logically so that the reader can follow along and agree with the points made.
The connections between statements, so-called “warrants”, follow logical reasoning but are not always clearly stated—the author simply assumes the reader understands the underlying logic, whether they present it “explicitly” or “implicitly”. Implicit warrants are commonly used in advertisements where seemingly happy people use certain products, wear certain clothes, accessories, or perfumes, or live certain lifestyles – with the connotation that, first, the product/perfume/lifestyle is what makes that person happy and, second, the reader wants to be as happy as the person in the ad. Some warrants are never clearly stated, and your job when writing a rhetorical analysis essay is therefore to identify them and bring them to light, to evaluate their validity, their effect on the reader, and the use of such means by the writer/creator.

What are the Five Rhetorical Situations?
A “rhetorical situation” refers to the circumstance behind a text or other piece of communication that arises from a given context. It explains why a rhetorical piece was created, what its purpose is, and how it was constructed to achieve its aims.
Rhetorical situations can be classified into the following five categories:
Asking such questions when you analyze a text will help you identify all the aspects that play a role in the effect it has on its audience, and will allow you to evaluate whether it achieved its aims or where it may have failed to do so.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline
Analyzing someone else’s work can seem like a big task, but as with every assignment or writing endeavor, you can break it down into smaller, well-defined steps that give you a practical structure to follow.
To give you an example of how the different parts of your text may look when it’s finished, we will provide you with some excerpts from this rhetorical analysis essay example (which even includes helpful comments) published on the Online Writing Lab website of Excelsior University in Albany, NY. The text that this essay analyzes is this article on why one should or shouldn’t buy an Ipad. If you want more examples so that you can build your own rhetorical analysis template, have a look at this essay on Nabokov’s Lolita and the one provided here about the “Shitty First Drafts” chapter of Anne Lamott’s writing instruction book “Bird by Bird”.
Analyzing the Text
When writing a rhetorical analysis, you don’t choose the concepts or key points you think are relevant or want to address. Rather, you carefully read the text several times asking yourself questions like those listed in the last section on rhetorical situations to identify how the text “works” and how it was written to achieve that effect.
Start with focusing on the author : What do you think was their purpose for writing the text? Do they make one principal claim and then elaborate on that? Or do they discuss different topics?
Then look at what audience they are talking to: Do they want to make a group of people take some action? Vote for someone? Donate money to a good cause? Who are these people? Is the text reaching this specific audience? Why or why not?
What tone is the author using to address their audience? Are they trying to evoke sympathy? Stir up anger? Are they writing from a personal perspective? Are they painting themselves as an authority on the topic? Are they using academic or informal language?
How does the author support their claims ? What kind of evidence are they presenting? Are they providing explicit or implicit warrants? Are these warrants valid or problematic? Is the provided evidence convincing?
Asking yourself such questions will help you identify what rhetorical devices a text uses and how well they are put together to achieve a certain aim. Remember, your own opinion and whether you agree with the author are not the point of a rhetorical analysis essay – your task is simply to take the text apart and evaluate it.
If you are still confused about how to write a rhetorical analysis essay, just follow the steps outlined below to write the different parts of your rhetorical analysis: As every other essay, it consists of an Introduction , a Body (the actual analysis), and a Conclusion .
Rhetorical Analysis Introduction
The Introduction section briefly presents the topic of the essay you are analyzing, the author, their main claims, a short summary of the work by you, and your thesis statement .
Tell the reader what the text you are going to analyze represents (e.g., historically) or why it is relevant (e.g., because it has become some kind of reference for how something is done). Describe what the author claims, asserts, or implies and what techniques they use to make their argument and persuade their audience. Finish off with your thesis statement that prepares the reader for what you are going to present in the next section – do you think that the author’s assumptions/claims/arguments were presented in a logical/appealing/powerful way and reached their audience as intended?
Have a look at an excerpt from the sample essay linked above to see what a rhetorical analysis introduction can look like. See how it introduces the author and article , the context in which it originally appeared , the main claims the author makes , and how this first paragraph ends in a clear thesis statement that the essay will then elaborate on in the following Body section:
Cory Doctorow ’s article on BoingBoing is an older review of the iPad , one of Apple’s most famous products. At the time of this article, however, the iPad was simply the latest Apple product to hit the market and was not yet so popular. Doctorow’s entire career has been entrenched in and around technology. He got his start as a CD-ROM programmer and is now a successful blogger and author. He is currently the co-editor of the BoingBoing blog on which this article was posted. One of his main points in this article comes from Doctorow’s passionate advocacy of free digital media sharing. He argues that the iPad is just another way for established technology companies to control our technological freedom and creativity . In “ Why I Won’t Buy an iPad (and Think You Shouldn’t, Either) ” published on Boing Boing in April of 2010, Cory Doctorow successfully uses his experience with technology, facts about the company Apple, and appeals to consumer needs to convince potential iPad buyers that Apple and its products, specifically the iPad, limit the digital rights of those who use them by controlling and mainstreaming the content that can be used and created on the device .
Doing the Rhetorical Analysis
The main part of your analysis is the Body , where you dissect the text in detail. Explain what methods the author uses to inform, entertain, and/or persuade the audience. Use Aristotle’s rhetorical triangle and the other key concepts we introduced above. Use quotations from the essay to demonstrate what you mean. Work out why the writer used a certain approach and evaluate (and again, demonstrate using the text itself) how successful they were. Evaluate the effect of each rhetorical technique you identify on the audience and judge whether the effect is in line with the author’s intentions.
To make it easy for the reader to follow your thought process, divide this part of your essay into paragraphs that each focus on one strategy or one concept , and make sure they are all necessary and contribute to the development of your argument(s).
One paragraph of this section of your essay could, for example, look like this:
One example of Doctorow’s position is his comparison of Apple’s iStore to Wal-Mart. This is an appeal to the consumer’s logic—or an appeal to logos. Doctorow wants the reader to take his comparison and consider how an all-powerful corporation like the iStore will affect them. An iPad will only allow for apps and programs purchased through the iStore to be run on it; therefore, a customer must not only purchase an iPad but also any programs he or she wishes to use. Customers cannot create their own programs or modify the hardware in any way.
As you can see, the author of this sample essay identifies and then explains to the reader how Doctorow uses the concept of Logos to appeal to his readers – not just by pointing out that he does it but by dissecting how it is done.
Rhetorical Analysis Conclusion
The conclusion section of your analysis should restate your main arguments and emphasize once more whether you think the author achieved their goal. Note that this is not the place to introduce new information—only rely on the points you have discussed in the body of your essay. End with a statement that sums up the impact the text has on its audience and maybe society as a whole:
Overall, Doctorow makes a good argument about why there are potentially many better things to drop a great deal of money on instead of the iPad. He gives some valuable information and facts that consumers should take into consideration before going out to purchase the new device. He clearly uses rhetorical tools to help make his case, and, overall, he is effective as a writer, even if, ultimately, he was ineffective in convincing the world not to buy an iPad .
Frequently Asked Questions about Rhetorical Analysis Essays
What is a rhetorical analysis essay.
A rhetorical analysis dissects a text or another piece of communication to work out and explain how it impacts its audience, how successfully it achieves its aims, and what rhetorical devices it uses to do that.
While argumentative essays usually take a stance on a certain topic and argue for it, a rhetorical analysis identifies how someone else constructs their arguments and supports their claims.
What is the correct rhetorical analysis essay format?
Like most other essays, a rhetorical analysis contains an Introduction that presents the thesis statement, a Body that analyzes the piece of communication, explains how arguments have been constructed, and illustrates how each part persuades, informs, or entertains the reader, and a Conclusion section that summarizes the results of the analysis.
What is the “rhetorical triangle”?
The rhetorical triangle was introduced by Aristotle as the main ways in which language can be used to persuade an audience: Logos appeals to the audience’s reason, Ethos to the writer’s status or authority, and Pathos to the reader’s emotions. Logos, Ethos, and Pathos can all be combined to create the intended effect, and your job as the one analyzing a text is to break the writer’s arguments down and identify what specific concepts each is based on.
Let Wordvice help you write a flawless rhetorical analysis essay!
Whether you have to write a rhetorical analysis essay as an assignment or whether it is part of an application, our professional proofreading services feature professional editors are trained subject experts that make sure your text is in line with the required format, as well as help you improve the flow and expression of your writing. Let them be your second pair of eyes so that after receiving paper editing services or essay editing services from Wordvice, you can submit your manuscript or apply to the school of your dreams with confidence.
And check out our editing services for writers (including blog editing , script editing , and book editing ) to correct your important personal or business-related work.
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
What Is a Rhetorical Analysis and How to Write a Great One

Helly Douglas

Do you have to write a rhetorical analysis essay? Fear not! We’re here to explain exactly what rhetorical analysis means, how you should structure your essay, and give you some essential “dos and don’ts.”
What is a Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
How do you write a rhetorical analysis, what are the three rhetorical strategies, what are the five rhetorical situations, how to plan a rhetorical analysis essay, creating a rhetorical analysis essay, examples of great rhetorical analysis essays, final thoughts.
A rhetorical analysis essay studies how writers and speakers have used words to influence their audience. Think less about the words the author has used and more about the techniques they employ, their goals, and the effect this has on the audience.

In your analysis essay, you break a piece of text (including cartoons, adverts, and speeches) into sections and explain how each part works to persuade, inform, or entertain. You’ll explore the effectiveness of the techniques used, how the argument has been constructed, and give examples from the text.
A strong rhetorical analysis evaluates a text rather than just describes the techniques used. You don’t include whether you personally agree or disagree with the argument.
Structure a rhetorical analysis in the same way as most other types of academic essays . You’ll have an introduction to present your thesis, a main body where you analyze the text, which then leads to a conclusion.
Think about how the writer (also known as a rhetor) considers the situation that frames their communication:
- Topic: the overall purpose of the rhetoric
- Audience: this includes primary, secondary, and tertiary audiences
- Purpose: there are often more than one to consider
- Context and culture: the wider situation within which the rhetoric is placed
Back in the 4th century BC, Aristotle was talking about how language can be used as a means of persuasion. He described three principal forms —Ethos, Logos, and Pathos—often referred to as the Rhetorical Triangle . These persuasive techniques are still used today.
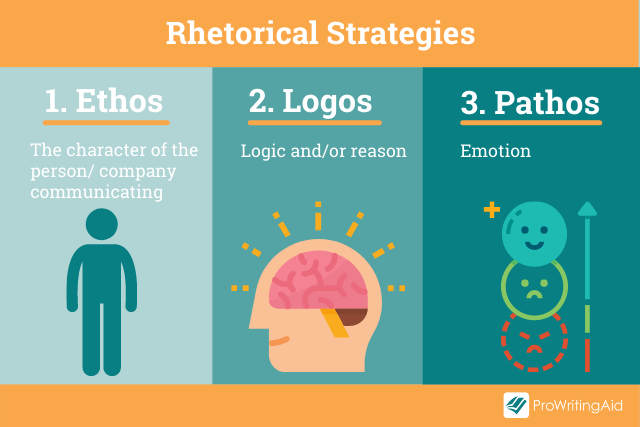
Rhetorical Strategy 1: Ethos
Are you more likely to buy a car from an established company that’s been an important part of your community for 50 years, or someone new who just started their business?
Reputation matters. Ethos explores how the character, disposition, and fundamental values of the author create appeal, along with their expertise and knowledge in the subject area.
Aristotle breaks ethos down into three further categories:
- Phronesis: skills and practical wisdom
- Arete: virtue
- Eunoia: goodwill towards the audience
Ethos-driven speeches and text rely on the reputation of the author. In your analysis, you can look at how the writer establishes ethos through both direct and indirect means.
Rhetorical Strategy 2: Pathos
Pathos-driven rhetoric hooks into our emotions. You’ll often see it used in advertisements, particularly by charities wanting you to donate money towards an appeal.
Common use of pathos includes:
- Vivid description so the reader can imagine themselves in the situation
- Personal stories to create feelings of empathy
- Emotional vocabulary that evokes a response
By using pathos to make the audience feel a particular emotion, the author can persuade them that the argument they’re making is compelling.
Rhetorical Strategy 3: Logos
Logos uses logic or reason. It’s commonly used in academic writing when arguments are created using evidence and reasoning rather than an emotional response. It’s constructed in a step-by-step approach that builds methodically to create a powerful effect upon the reader.
Rhetoric can use any one of these three techniques, but effective arguments often appeal to all three elements.
The rhetorical situation explains the circumstances behind and around a piece of rhetoric. It helps you think about why a text exists, its purpose, and how it’s carried out.
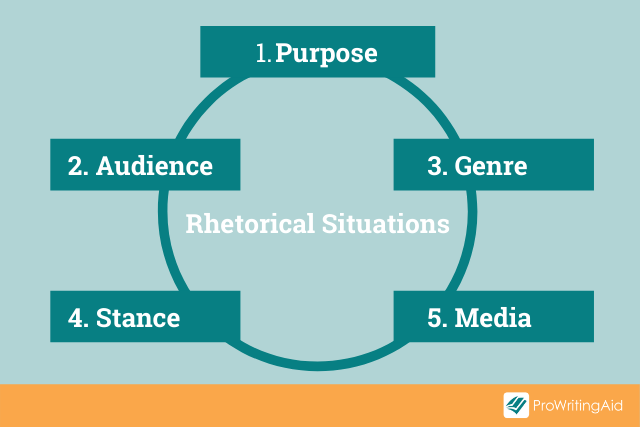
The rhetorical situations are:
- 1) Purpose: Why is this being written? (It could be trying to inform, persuade, instruct, or entertain.)
- 2) Audience: Which groups or individuals will read and take action (or have done so in the past)?
- 3) Genre: What type of writing is this?
- 4) Stance: What is the tone of the text? What position are they taking?
- 5) Media/Visuals: What means of communication are used?
Understanding and analyzing the rhetorical situation is essential for building a strong essay. Also think about any rhetoric restraints on the text, such as beliefs, attitudes, and traditions that could affect the author's decisions.
Before leaping into your essay, it’s worth taking time to explore the text at a deeper level and considering the rhetorical situations we looked at before. Throw away your assumptions and use these simple questions to help you unpick how and why the text is having an effect on the audience.

1: What is the Rhetorical Situation?
- Why is there a need or opportunity for persuasion?
- How do words and references help you identify the time and location?
- What are the rhetoric restraints?
- What historical occasions would lead to this text being created?
2: Who is the Author?
- How do they position themselves as an expert worth listening to?
- What is their ethos?
- Do they have a reputation that gives them authority?
- What is their intention?
- What values or customs do they have?
3: Who is it Written For?
- Who is the intended audience?
- How is this appealing to this particular audience?
- Who are the possible secondary and tertiary audiences?
4: What is the Central Idea?
- Can you summarize the key point of this rhetoric?
- What arguments are used?
- How has it developed a line of reasoning?
5: How is it Structured?
- What structure is used?
- How is the content arranged within the structure?
6: What Form is Used?
- Does this follow a specific literary genre?
- What type of style and tone is used, and why is this?
- Does the form used complement the content?
- What effect could this form have on the audience?
7: Is the Rhetoric Effective?
- Does the content fulfil the author’s intentions?
- Does the message effectively fit the audience, location, and time period?
Once you’ve fully explored the text, you’ll have a better understanding of the impact it’s having on the audience and feel more confident about writing your essay outline.
A great essay starts with an interesting topic. Choose carefully so you’re personally invested in the subject and familiar with it rather than just following trending topics. There are lots of great ideas on this blog post by My Perfect Words if you need some inspiration. Take some time to do background research to ensure your topic offers good analysis opportunities.

Remember to check the information given to you by your professor so you follow their preferred style guidelines. This outline example gives you a general idea of a format to follow, but there will likely be specific requests about layout and content in your course handbook. It’s always worth asking your institution if you’re unsure.
Make notes for each section of your essay before you write. This makes it easy for you to write a well-structured text that flows naturally to a conclusion. You will develop each note into a paragraph. Look at this example by College Essay for useful ideas about the structure.
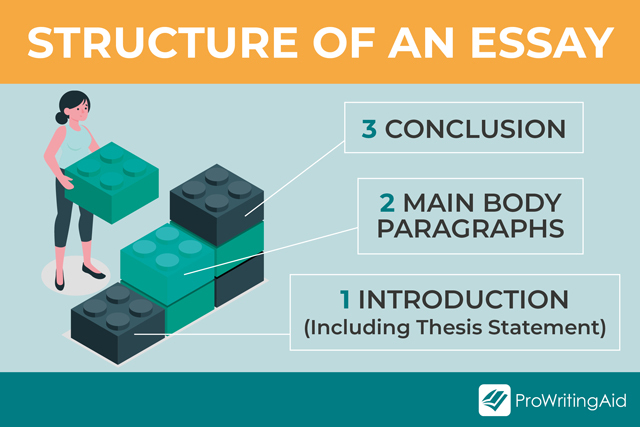
1: Introduction
This is a short, informative section that shows you understand the purpose of the text. It tempts the reader to find out more by mentioning what will come in the main body of your essay.
- Name the author of the text and the title of their work followed by the date in parentheses
- Use a verb to describe what the author does, e.g. “implies,” “asserts,” or “claims”
- Briefly summarize the text in your own words
- Mention the persuasive techniques used by the rhetor and its effect
Create a thesis statement to come at the end of your introduction.
After your introduction, move on to your critical analysis. This is the principal part of your essay.
- Explain the methods used by the author to inform, entertain, and/or persuade the audience using Aristotle's rhetorical triangle
- Use quotations to prove the statements you make
- Explain why the writer used this approach and how successful it is
- Consider how it makes the audience feel and react
Make each strategy a new paragraph rather than cramming them together, and always use proper citations. Check back to your course handbook if you’re unsure which citation style is preferred.
3: Conclusion
Your conclusion should summarize the points you’ve made in the main body of your essay. While you will draw the points together, this is not the place to introduce new information you’ve not previously mentioned.
Use your last sentence to share a powerful concluding statement that talks about the impact the text has on the audience(s) and wider society. How have its strategies helped to shape history?
Before You Submit
Poor spelling and grammatical errors ruin a great essay. Use ProWritingAid to check through your finished essay before you submit. It will pick up all the minor errors you’ve missed and help you give your essay a final polish. Look at this useful ProWritingAid webinar for further ideas to help you significantly improve your essays. Sign up for a free trial today and start editing your essays!
You’ll find countless examples of rhetorical analysis online, but they range widely in quality. Your institution may have example essays they can share with you to show you exactly what they’re looking for.
The following links should give you a good starting point if you’re looking for ideas:
Pearson Canada has a range of good examples. Look at how embedded quotations are used to prove the points being made. The end questions help you unpick how successful each essay is.
Excelsior College has an excellent sample essay complete with useful comments highlighting the techniques used.
Brighton Online has a selection of interesting essays to look at. In this specific example, consider how wider reading has deepened the exploration of the text.

Writing a rhetorical analysis essay can seem daunting, but spending significant time deeply analyzing the text before you write will make it far more achievable and result in a better-quality essay overall.
It can take some time to write a good essay. Aim to complete it well before the deadline so you don’t feel rushed. Use ProWritingAid’s comprehensive checks to find any errors and make changes to improve readability. Then you’ll be ready to submit your finished essay, knowing it’s as good as you can possibly make it.
Try ProWritingAid's Editor for Yourself
Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
Helly Douglas is a UK writer and teacher, specialising in education, children, and parenting. She loves making the complex seem simple through blogs, articles, and curriculum content. You can check out her work at hellydouglas.com or connect on Twitter @hellydouglas. When she’s not writing, you will find her in a classroom, being a mum or battling against the wilderness of her garden—the garden is winning!
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to write a rhetorical analysis

What is a rhetorical analysis?
What are the key concepts of a rhetorical analysis, rhetorical situation, claims, supports, and warrants.
- Step 1: Plan and prepare
- Step 2: Write your introduction
- Step 3: Write the body
- Step 4: Write your conclusion
Frequently Asked Questions about rhetorical analysis
Related articles.
Rhetoric is the art of persuasion and aims to study writers’ or speakers' techniques to inform, persuade, or motivate their audience. Thus, a rhetorical analysis aims to explore the goals and motivations of an author, the techniques they’ve used to reach their audience, and how successful these techniques were.
This will generally involve analyzing a specific text and considering the following aspects to connect the rhetorical situation to the text:
- Does the author successfully support the thesis or claims made in the text? Here, you’ll analyze whether the author holds to their argument consistently throughout the text or whether they wander off-topic at some point.
- Does the author use evidence effectively considering the text’s intended audience? Here, you’ll consider the evidence used by the author to support their claims and whether the evidence resonates with the intended audience.
- What rhetorical strategies the author uses to achieve their goals. Here, you’ll consider the word choices by the author and whether these word choices align with their agenda for the text.
- The tone of the piece. Here, you’ll consider the tone used by the author in writing the piece by looking at specific words and aspects that set the tone.
- Whether the author is objective or trying to convince the audience of a particular viewpoint. When it comes to objectivity, you’ll consider whether the author is objective or holds a particular viewpoint they want to convince the audience of. If they are, you’ll also consider whether their persuasion interferes with how the text is read and understood.
- Does the author correctly identify the intended audience? It’s important to consider whether the author correctly writes the text for the intended audience and what assumptions the author makes about the audience.
- Does the text make sense? Here, you’ll consider whether the author effectively reasons, based on the evidence, to arrive at the text’s conclusion.
- Does the author try to appeal to the audience’s emotions? You’ll need to consider whether the author uses any words, ideas, or techniques to appeal to the audience’s emotions.
- Can the author be believed? Finally, you’ll consider whether the audience will accept the arguments and ideas of the author and why.
Summing up, unlike summaries that focus on what an author said, a rhetorical analysis focuses on how it’s said, and it doesn’t rely on an analysis of whether the author was right or wrong but rather how they made their case to arrive at their conclusions.
Although rhetorical analysis is most used by academics as part of scholarly work, it can be used to analyze any text including speeches, novels, television shows or films, advertisements, or cartoons.
Now that we’ve seen what rhetorical analysis is, let’s consider some of its key concepts .
Any rhetorical analysis starts with the rhetorical situation which identifies the relationships between the different elements of the text. These elements include the audience, author or writer, the author’s purpose, the delivery method or medium, and the content:
- Audience: The audience is simply the readers of a specific piece of text or content or printed material. For speeches or other mediums like film and video, the audience would be the listeners or viewers. Depending on the specific piece of text or the author’s perception, the audience might be real, imagined, or invoked. With a real audience, the author writes to the people actually reading or listening to the content while, for an imaginary audience, the author writes to an audience they imagine would read the content. Similarly, for an invoked audience, the author writes explicitly to a specific audience.
- Author or writer: The author or writer, also commonly referred to as the rhetor in the context of rhetorical analysis, is the person or the group of persons who authored the text or content.
- The author’s purpose: The author’s purpose is the author’s reason for communicating to the audience. In other words, the author’s purpose encompasses what the author expects or intends to achieve with the text or content.
- Alphabetic text includes essays, editorials, articles, speeches, and other written pieces.
- Imaging includes website and magazine advertisements, TV commercials, and the like.
- Audio includes speeches, website advertisements, radio or tv commercials, or podcasts.
- Context: The context of the text or content considers the time, place, and circumstances surrounding the delivery of the text to its audience. With respect to context, it might often also be helpful to analyze the text in a different context to determine its impact on a different audience and in different circumstances.
An author will use claims, supports, and warrants to build the case around their argument, irrespective of whether the argument is logical and clearly defined or needs to be inferred by the audience:
- Claim: The claim is the main idea or opinion of an argument that the author must prove to the intended audience. In other words, the claim is the fact or facts the author wants to convince the audience of. Claims are usually explicitly stated but can, depending on the specific piece of content or text, be implied from the content. Although these claims could be anything and an argument may be based on a single or several claims, the key is that these claims should be debatable.
- Support: The supports are used by the author to back up the claims they make in their argument. These supports can include anything from fact-based, objective evidence to subjective emotional appeals and personal experiences used by the author to convince the audience of a specific claim. Either way, the stronger and more reliable the supports, the more likely the audience will be to accept the claim.
- Warrant: The warrants are the logic and assumptions that connect the supports to the claims. In other words, they’re the assumptions that make the initial claim possible. The warrant is often unstated, and the author assumes that the audience will be able to understand the connection between the claims and supports. In turn, this is based on the author’s assumption that they share a set of values and beliefs with the audience that will make them understand the connection mentioned above. Conversely, if the audience doesn’t share these beliefs and values with the author, the argument will not be that effective.
Appeals are used by authors to convince their audience and, as such, are an integral part of the rhetoric and are often referred to as the rhetorical triangle. As a result, an author may combine all three appeals to convince their audience:
- Ethos: Ethos represents the authority or credibility of the author. To be successful, the author needs to convince the audience of their authority or credibility through the language and delivery techniques they use. This will, for example, be the case where an author writing on a technical subject positions themselves as an expert or authority by referring to their qualifications or experience.
- Logos: Logos refers to the reasoned argument the author uses to persuade their audience. In other words, it refers to the reasons or evidence the author proffers in substantiation of their claims and can include facts, statistics, and other forms of evidence. For this reason, logos is also the dominant approach in academic writing where authors present and build up arguments using reasoning and evidence.
- Pathos: Through pathos, also referred to as the pathetic appeal, the author attempts to evoke the audience’s emotions through the use of, for instance, passionate language, vivid imagery, anger, sympathy, or any other emotional response.
To write a rhetorical analysis, you need to follow the steps below:
With a rhetorical analysis, you don’t choose concepts in advance and apply them to a specific text or piece of content. Rather, you’ll have to analyze the text to identify the separate components and plan and prepare your analysis accordingly.
Here, it might be helpful to use the SOAPSTone technique to identify the components of the work. SOAPSTone is a common acronym in analysis and represents the:
- Speaker . Here, you’ll identify the author or the narrator delivering the content to the audience.
- Occasion . With the occasion, you’ll identify when and where the story takes place and what the surrounding context is.
- Audience . Here, you’ll identify who the audience or intended audience is.
- Purpose . With the purpose, you’ll need to identify the reason behind the text or what the author wants to achieve with their writing.
- Subject . You’ll also need to identify the subject matter or topic of the text.
- Tone . The tone identifies the author’s feelings towards the subject matter or topic.
Apart from gathering the information and analyzing the components mentioned above, you’ll also need to examine the appeals the author uses in writing the text and attempting to persuade the audience of their argument. Moreover, you’ll need to identify elements like word choice, word order, repetition, analogies, and imagery the writer uses to get a reaction from the audience.
Once you’ve gathered the information and examined the appeals and strategies used by the author as mentioned above, you’ll need to answer some questions relating to the information you’ve collected from the text. The answers to these questions will help you determine the reasons for the choices the author made and how well these choices support the overall argument.
Here, some of the questions you’ll ask include:
- What was the author’s intention?
- Who was the intended audience?
- What is the author’s argument?
- What strategies does the author use to build their argument and why do they use those strategies?
- What appeals the author uses to convince and persuade the audience?
- What effect the text has on the audience?
Keep in mind that these are just some of the questions you’ll ask, and depending on the specific text, there might be others.
Once you’ve done your preparation, you can start writing the rhetorical analysis. It will start off with an introduction which is a clear and concise paragraph that shows you understand the purpose of the text and gives more information about the author and the relevance of the text.
The introduction also summarizes the text and the main ideas you’ll discuss in your analysis. Most importantly, however, is your thesis statement . This statement should be one sentence at the end of the introduction that summarizes your argument and tempts your audience to read on and find out more about it.
After your introduction, you can proceed with the body of your analysis. Here, you’ll write at least three paragraphs that explain the strategies and techniques used by the author to convince and persuade the audience, the reasons why the writer used this approach, and why it’s either successful or unsuccessful.
You can structure the body of your analysis in several ways. For example, you can deal with every strategy the author uses in a new paragraph, but you can also structure the body around the specific appeals the author used or chronologically.
No matter how you structure the body and your paragraphs, it’s important to remember that you support each one of your arguments with facts, data, examples, or quotes and that, at the end of every paragraph, you tie the topic back to your original thesis.
Finally, you’ll write the conclusion of your rhetorical analysis. Here, you’ll repeat your thesis statement and summarize the points you’ve made in the body of your analysis. Ultimately, the goal of the conclusion is to pull the points of your analysis together so you should be careful to not raise any new issues in your conclusion.
After you’ve finished your conclusion, you’ll end your analysis with a powerful concluding statement of why your argument matters and an invitation to conduct more research if needed.
A rhetorical analysis aims to explore the goals and motivations of an author, the techniques they’ve used to reach their audience, and how successful these techniques were. Although rhetorical analysis is most used by academics as part of scholarly work, it can be used to analyze any text including speeches, novels, television shows or films, advertisements, or cartoons.
The steps to write a rhetorical analysis include:
Your rhetorical analysis introduction is a clear and concise paragraph that shows you understand the purpose of the text and gives more information about the author and the relevance of the text. The introduction also summarizes the text and the main ideas you’ll discuss in your analysis.
Ethos represents the authority or credibility of the author. To be successful, the author needs to convince the audience of their authority or credibility through the language and delivery techniques they use. This will, for example, be the case where an author writing on a technical subject positions themselves as an expert or authority by referring to their qualifications or experience.
Appeals are used by authors to convince their audience and, as such, are an integral part of the rhetoric and are often referred to as the rhetorical triangle. The 3 types of appeals are ethos, logos, and pathos.

How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis: Full Guide

Have you ever been completely fascinated by a speech or ad, wondering how it managed to convince you so effectively? From powerful political speeches to catchy commercials, persuasion is all around us, shaping our thoughts and choices every day.
In this guide, we'll explain all about a rhetorical analysis essay. We'll break down the clever tricks writers and speakers use to win over their audience, like how they choose their words carefully and play with our emotions. This article will give you the tools you need to understand and analyze texts more deeply. So, let’s jump right in and start by understanding the nature of this assignment first.
What is a Rhetorical Analysis Essay
A rhetorical analysis essay is a type of essay where you examine how authors or speakers use words, phrases, and other techniques to influence or persuade their audience. This type of essay focuses on analyzing the strategies used by the writer or speaker to achieve their purpose, whether it's to inform, persuade, entertain, or provoke.
You'll dissect the text or speech into its components, looking at how each part contributes to the overall message. This might involve examining the introduction, thesis statement, body paragraphs, evidence, and conclusion.
Once you've identified the strategies used, you'll assess their effectiveness in achieving the author's or speaker's purpose. This involves considering the intended audience, context, and the impact of the communication.
As per our essay writing service , some common topics for rhetorical analysis include analyzing speeches by influential leaders, dissecting political advertisements, or examining the rhetoric used in literary works.
Do You Want to Ease Your Academic Burden?
Order a rhetorical analysis essay from our expert writers today and experience the power of top-notch academic writing.
Rhetorical Analysis Topic Ideas
Now that we've grasped the essence of a rhetorical analysis essay let's explore some potential topics you might consider for your own analysis. Here are 15 specific ideas to get you started:
- The Use of Metaphors in Barack Obama's 'Yes We Can' Speech
- Visual Rhetoric in Dove's 'Real Beauty' Advertising Campaign
- The Role of Irony in Jonathan Swift's 'A Modest Proposal'
- The Manipulation of Emotions in Coca-Cola's 'Share a Coke' Campaign
- The Repetition Technique in Winston Churchill's 'We Shall Fight on the Beaches' Speech
- The Argument Structure in Michelle Obama's Speech on Education
- The Use of Imagery in Edgar Allan Poe's 'The Raven'
- Gender Stereotypes in Old Spice's 'The Man Your Man Could Smell Like' Ad
- Satirical Elements in George Orwell's 'Animal Farm'
- The Influence of Tone in Greta Thunberg's Climate Change Speeches
- Political Symbolism in Banksy's Street Art
- Humor as Persuasion in Ellen DeGeneres' Stand-Up Comedy
- The Power of Silence in Emma Watson's UN Speech on Gender Equality
- Ethical Appeals in ASPCA's Animal Rights Advertisements
- The Cultural References in Super Bowl Commercials: A Case Study
How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis
Understanding how to start a rhetorical analysis essay involves dissecting a piece of communication to learn how it works and what effect it aims to achieve. This analytical process typically includes five paragraphs and three main parts: an introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Below, our analytical essay writing service will explain each in more detail
.webp)
Major Rhetorical Elements
Before heading towards the analysis process, it's essential to grasp some key rhetorical concepts that will help guide your examination of the text or speech. These concepts provide a framework for understanding how authors and speakers use language to persuade and influence their audience.
Ethos, pathos logos in rhetorical analysis form the foundation of persuasive communication and are often intertwined in rhetorical strategies. Ethos refers to the credibility or authority of the speaker or author. Pathos involves appealing to the audience's emotions, while logos appeals to reason and logic.
There are also other rhetorical devices that are specific techniques or patterns of language used to convey meaning or evoke particular responses. Examples include metaphor, simile, imagery, irony, repetition, and hyperbole. Recognizing and analyzing these devices can provide insight into the author's intended message and its impact on the audience.
Tone and mood also play crucial roles in shaping the audience's perception and response to the communication. Tone refers to the author's attitude toward the subject matter, while mood describes the emotional atmosphere created by the text.
Whether you ask us - write my essay , or tackle the task yourself, familiarizing yourself with these concepts will help you analyze the text and persuade the audience more effectively.
Understanding Rhetorical Appeals
.webp)
First off, what is ethos in rhetorical analysis? Well, it revolves around establishing the credibility and authority of the speaker or author. This appeal seeks to convince the audience that the communicator is trustworthy, knowledgeable, and reliable. Ethos in rhetorical analysis can be built through various means, including:
- Professional Credentials : Demonstrating expertise in the subject matter through relevant qualifications or experience.
- Personal Character : Highlighting traits such as honesty, integrity, and sincerity to engender trust and respect.
- Association : Aligning oneself with respected individuals, institutions, or causes to enhance credibility by association.
For instance, in a health-related speech, a doctor might leverage their medical expertise and professional experience (credentials) to establish ethos. Similarly, a celebrity endorsing a product is using their fame and reputation (association) to persuade consumers.
Now, let's understand what is pathos in rhetorical analysis. Pathos involves appealing to the audience's emotions, aiming to evoke feelings such as empathy, sympathy, joy, anger, or fear. This emotional connection can be a powerful tool for persuasion, as it resonates with the audience on a personal level. Strategies for employing pathos in rhetorical analysis include:
- Vivid Imagery : Painting a vivid picture or narrative that elicits strong emotional responses from the audience.
- Anecdotes : Sharing personal stories or anecdotes that evoke empathy or sympathy and make the message more relatable.
- Language Choice : Using emotive language, sensory details, and rhetorical devices to evoke specific emotional reactions.
For example, in a charity advertisement for children in need, images of impoverished and suffering children coupled with heart-wrenching stories (anecdotes) are used to evoke feelings of compassion and a desire to help.
Lastly, what is logos in rhetorical analysis, you may ask. It appeals to reason and logic, aiming to persuade the audience through rational argumentation and evidence. This appeal relies on facts, statistics, logical reasoning, and sound arguments to convince the audience of the validity of the message. Strategies for employing logos in rhetorical analysis include:
- Factual Evidence : Providing empirical data, research findings, or expert opinions to support the argument.
- Logical Reasoning : Presenting a well-structured argument with clear premises and conclusions that logically follow one another.
- Counterarguments : Addressing potential counterarguments and refuting them with logical reasoning and evidence.
For instance, in a persuasive essay advocating for environmental conservation, the author might present scientific data on climate change (factual evidence) and use logical reasoning to explain the consequences of inaction.
Text and Context
Text analysis involves closely examining the language, structure, and rhetorical devices employed within the communication. This includes identifying key themes, rhetorical appeals, persuasive strategies, and stylistic elements used by the author or speaker to convey their message.
For example, in a political speech advocating for healthcare reform, text analysis might involve identifying the use of rhetorical appeals such as ethos (e.g., highlighting the speaker's experience in healthcare policy), pathos (e.g., sharing anecdotes of individuals struggling with medical costs), and logos (e.g., presenting statistics on healthcare affordability).
Contextual analysis involves considering the broader social, cultural, and historical factors that shape communication and influence its reception. This includes examining the audience demographics, the political and cultural climate, the historical events surrounding the communication, and any relevant societal norms or values.
For instance, when analyzing a historical speech advocating for civil rights, contextual research paper writers might involve considering the social and political context of the time, including prevailing attitudes towards race, ongoing civil rights movements, and recent legislative developments.
Claims, Supports, and Warrants
A claim is a statement or assertion that the author or speaker is advocating for or seeking to prove. Claims can take various forms, including factual claims (assertions of fact), value claims (judgments about what is good or bad), and policy claims (proposals for action). For example, in an argumentative essay about the importance of exercise, the claim might be that regular physical activity is essential for maintaining good health.
Supports are the evidence, reasoning, or examples provided to substantiate and strengthen the claims being made. Supports can take many forms, including empirical data, expert testimony, personal anecdotes, logical reasoning, and analogies. The quality and relevance of the supports provided play a critical role in the persuasiveness of the argument.
Continuing with the example of the argumentative essay about exercise, supports might include scientific studies demonstrating the health benefits of physical activity, testimonials from fitness experts, and personal stories of individuals who have experienced positive changes from incorporating exercise into their routine.
Warrants are the underlying assumptions or principles that connect the supports to the claims. They provide the reasoning or justification for why the supports are relevant and valid evidence for supporting the claims. Warrants are often implicit rather than explicit and require careful analysis to uncover. In the context of the essay on exercise, the warrant connecting the supports to the claim might be the assumption that actions that promote good health are inherently valuable and worthy of pursuit.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline
Whether you opt for the option to buy essay or start writing it yourself, it's important to use a clear plan to organize your thoughts well. This plan usually includes four main steps, each looking at different parts of your analysis.
Analyzing the Text
Before writing a rhetorical analysis, take the time to thoroughly analyze the text you'll be examining. This means more than just skimming through it; it requires a thorough understanding of its subtleties and complexities. Here are some questions to guide your analysis:
- How does the text try to sway its audience? What methods does it use to convince or influence them?
- Which rhetorical appeals—ethos (credibility), pathos (emotion), logos (logic)—does the author use, and how do they contribute to the overall argument?
- What specific rhetorical devices and strategies does the author employ to effectively convey their message? Are there any patterns or recurring motifs?
- How does the structure of the text contribute to its persuasive power or overall impact?
- Are there any cultural, historical, or contextual factors that influence how the text is perceived or understood?
By scrutinizing the text in this manner, you'll gain a deeper understanding of how it functions and the techniques employed by the author to achieve their desired effect.
Rhetorical Analysis Introduction
The introduction sets the stage for your analysis by providing essential context and framing the discussion. Start by introducing the text you're analyzing, including the author's name and the title of the work. Provide some background information to give context to your analysis. For example, if you're analyzing a speech, mention the occasion or event where it was delivered.
Next, summarize the main arguments or claims made by the author. Highlight the rhetorical techniques they use to persuade their audience. Are they appealing to logic, emotion, credibility, or a combination of these? Use specific examples from the text to illustrate these techniques discussed by our dissertation service .
For instance, if you're analyzing a speech on climate change, mention the speaker's expertise in environmental science to establish credibility. Summarize the key points they make about the consequences of inaction and the urgent need for change.
Finally, conclude your introduction with a clear thesis statement. This statement should encapsulate the main argument or purpose of your analysis.
Rhetorical Analysis Body Paragraph
The body paragraphs form the crux of your analysis, where you delve into the details of the text and dissect its rhetorical strategies. Each paragraph should focus on a specific aspect of the text, such as the use of ethos, pathos, logos, or specific rhetorical devices.
Utilize Aristotle's rhetorical triangle and other key concepts introduced earlier to guide your analysis. Provide quotations or examples from the text to illustrate your points and explain why the author chose certain approaches. Evaluate the effectiveness of these strategies in achieving the author's goals and persuading the audience.
For instance, if you're discussing the use of pathos in a marketing campaign, analyze the emotional appeal of the imagery or language used and consider how it resonates with the target audience.
Rhetorical Analysis Conclusion
In the conclusion, it's crucial to reinforce your main arguments and evaluate the author's effectiveness in achieving their goals, whether you're writing an MLA or APA essay format . Reflect on the overall impact of the text on both its immediate audience and society at large, underscoring the importance of your analysis.
Resist the temptation to introduce new ideas in the conclusion. Instead, draw upon the points you've already explored in the body of your essay to strengthen your analysis. Conclude with a poignant statement that resonates with your readers, encapsulating the essence of your interpretation and leaving a lasting impression. This final remark should tie together the threads of your analysis, leaving the reader with a deeper understanding of the text's rhetorical strategies and significance.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
In this section, you'll discover two essay samples that skillfully demonstrate the application of rhetorical analysis. These examples offer insightful insights into the effective use of rhetorical techniques in writing.
5 Rhetorical Analysis Essay Tips
Here are five focused tips that will help you lay a solid foundation for your examination.
- Dissect Rhetorical Strategies : Break down the text to identify specific rhetorical devices such as metaphor, simile, or parallelism.
- Evaluate Tone and Diction : Pay attention to the author's tone and word choice. Analyze how these elements contribute to the overall mood of the text.
- Probe Ethos, Pathos, Logos : Explore how the author establishes credibility (ethos), evokes emotions (pathos), and employs logic (logos) to sway the audience.
- Contextualize Historical Significance : Consider the historical, cultural, and social backdrop against which the text was written.
- Craft a Structured Analysis : Organize your essay with a clear introduction, body paragraphs focusing on specific rhetorical elements, and a conclusion that synthesizes your findings.
Final Words
As we near the end, it's important to analyze carefully whether you're examining a speech, an advertisement, or a story. Pay attention to the smart tactics that influence our thinking. It's all about revealing how we communicate and relate to one another. Ultimately, understanding rhetoric offers a fresh perspective on the world beyond just academic success.
Looking to Take Your Academic Performance to the Next Level?
Say goodbye to stress, endless research, and sleepless nights - and hello to a brighter academic future.
What is a Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
How to structure a rhetorical analysis essay, how to write a rhetorical analysis essay, related articles.
.webp)
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Guide
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline
Last updated on: Feb 9, 2023

Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline - Template & Writing Guide
By: Betty P.
Reviewed By: Melisa C.
Published on: Feb 11, 2020

Students often freak out when they hear the professor assigning a rhetorical analysis essay.
It is considered to be one of the most challenging tasks, and it sure is a little complicated, but definitely not impossible.
The first step for writing a rhetorical essay is to understand exactly what it is.
The reason why students find rhetorical essays to be a daunting task is the fact that writing such essays requires analysis of anything ranging from a literary work to a piece of art or even an advertisement.
The writer’s task is to analyze it and figure out the goal of the creator, author or painter, and the way he conveyed his views. The explanation also includes the extent to which he achieved his goal.
However, there is absolutely no need to be intimidated by it. Once you figure out the design to follow, writing a rhetorical analysis essay will be a piece of cake.

On this Page
How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline
The outline for any type of writing is just like a skeleton, keeping a human body erect and well-structured. After choosing a good rhetorical analysis essay topic, following the correct rhetorical analysis essay outline will make the writing process logical and ten times easier.
Before you jump straight to writing, take your time to read and understand the original text carefully and analyze the information side by side. Focus on the author, his intended audience, his purpose, the setting, and other details.
‘How do you write a rhetorical analysis essay outline?’
To learn how to write a rhetorical analysis essay, continue reading the section given below.
Introduction
The introduction section of your essay is the part where you inform your readers about the original text that you are going to analyze.
Consider the following elements of the text when doing the analysis:
- Target audience
- Background context
Keep this information clear and to the point by focusing on important aspects of the text only. Also, the introductory paragraph must specify whether or not the author was successful in achieving his goal.
Start your introduction with an interesting hook. Briefly describe the author and the work, followed by your judgment and purpose of choosing it.
Write a strong thesis statement at the end of the introduction and highlight the point that you are going to discuss in the essay. A thesis statement is the most important component of the essay as it provides a brief guide on what is going to be discussed in it.
Thesis Statement
A thesis is usually one to two sentences long, written at the end of the introductory paragraph to define the purpose of your essay.
The thesis statement should be clear and concise, with the sole purpose of informing the reader what to expect from your paper.
Point out the tools used by the author and how they supported his argument.
As mentioned above, the thesis statement must outline the tools that you are going to analyze in the essay.
Typically, the authors use the following kinds of tools in their work:
Simile - a direct comparison of two things by using "like" and "as."
Imagery – visually descriptive language.
Diction – the writer's choice of words and style of expression.
Body Paragraphs
The body of a rhetorical analysis essay should analyze the original text or work. Analyze how the tools used by the author helped fulfill the purpose of the text.
Start each paragraph in the body section with a topic sentence that should refer back to your thesis statement and fortify it further.
In addition to the topic sentence, it should also include a short quote from the original text that you will use to stress the idea and analyze it.
The body should be made up of the analysis, which should be three times more than the quoted text.
The persuasive methods, ethos, pathos, and logos, will be used in the body paragraphs to analyze the content. Also, respond to the questions that are mentioned in the previous step and describe the strategies used by the author.
You can also use quotes and findings to support your thesis.
Ethos, Pathos, Logos
Did the author use rhetorical appeals such as ethos, logos, pathos? When analyzing the text, notice how the author has used them to prove his point.
Ethos displays how the writer establishes reliability and integrity through tone or credentials, or both.
Pathos is the use of feelings as an appeal to the audience's emotions. The writer may add pathos by using emotional language or personal stories.
Logos indicates the logical use of the author's ideas and how he concludes things. Make sure you keep them in your mind while analyzing your text, and employ these tips in your paper.

Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
Rhetorical Strategies
Authors use different types of rhetorical techniques or strategies to examine and better analyze the paragraphs and the content of the entire essay. These strategies help the authors to express their point of view and persuade the audience by following a pattern.
The most common strategies leading to an engaging rhetorical analysis include:
1. Description
Defining strategy involves telling your reader about what something means. It explains what something is and something is not. Defining strategy makes sure your readers understand what you mean by a specific term.
2. Cause and Effect
It focuses on the causes to help readers understand why something happened. Cause concerns the future while effect looks back at the past. But you can use this strategy either way from the present to the past or from the present to the future.
3. Process Analysis
With the process strategy, the writer illustrates how something is done. It goes from everyday processes like writing an application letter to complex processes such as how to face death. This rhetorical strategy is mostly used in historical essays to show how something has been done in the past.
4. Exemplification
One of the most commonly used rhetorical analysis strategies is where the writer provides examples to illustrate a larger point in detail. To make a point, there should be a clear relationship between the examples and the point you make.
5. Compare and Contrast
This rhetorical strategy looks for similarities and differences. Compare and contrast strategy is widely used in writing reports, making an argument, or even giving a speech to convince your readers.
6. Narration
Another important and one of the fundamental rhetorical strategies. Narration is which we tell stories about our life experiences to make a point.
The concluding paragraph is where the reader leaves you; make sure you address your main argument to strengthen its effect.
Provide an overview of the positive and negative points of the text and state whether or not the text was effective.
This was the basic outline that needs to be followed when tackling a rhetorical analysis essay.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline Template
If this is your first time dealing with such essays, then this sample rhetorical analysis essay outline template will definitely come in handy. Just go through it once and fill out the sections one by one.
OUTLINE TEMPLATE FOR RHETORICAL ANALYSIS ESSAY (PDF)
AP RHETORICAL ANALYSIS ESSAY (PDF)
THOMAS PAINE RHETORICAL ANALYSIS ESSAY OUTLINE (PDF)
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
A great approach is to read some examples of rhetorical analysis essays to understand the concept of writing a great rhetorical piece of the paper better.
RHETORICAL ANALYSIS ESSAY EXAMPLE (PDF)
You can also explore a great rhetorical analysis essay example from our expert writers to understand what it takes to craft a brilliant piece of writing.
Great Rhetorical Analysis Essay Tips
When writing a detailed outline for your rhetorical analysis essay, make sure that you take care of the following things.
- Study an essay topic, book, painting, or any other piece of art, thoroughly before choosing a topic for your essay.
- Present the right information in each of the essay sections.
- Do not mention the main details in the introduction and thesis statement section.
- Do not add new information or ideas in the conclusion.
- Reread and recheck the entire outline and key points after you are done writing.
Hopefully, you have understood the basics of the rhetorical analysis essay outline by now, and you are confident and willing to give it a try. If you want to learn more about rhetorical analysis essays, here is a detailed guide that covers everything about writing a rhetorical analysis essay .
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Professional Writing Help
However, if you lack the time or writing skills and looking for a professional essay writing service . Then hand over your problems to 5staressays , and our expert essay writers will take care of the rest. Whether it is an AP rhetorical analysis essay outline or a research paper for a science class, we have got it all covered.
Reach out to us today and enjoy quality work!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of rhetorical analysis.
When writing a rhetorical analysis essay, the main purpose of the writer is to convey his message to the intended audience.
What is the difference between rhetorical analysis and critical analysis?
In a rhetorical analysis essay, different parts of a text or work are discussed as they work together to form meaning. In a critical essay, the different parts of the work are critically analyzed, and arguments are formed around them.

Speech, Literature
Betty is a freelance writer and researcher. She has a Masters in literature and enjoys providing writing services to her clients. Betty is an avid reader and loves learning new things. She has provided writing services to clients from all academic levels and related academic fields.
Was This Blog Helpful?
Keep reading.
- Rhetorical Analysis Essay - The Ultimate Guide

- Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example - Samples By Experts

- Top Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics for Students

People Also Read
- argumentative essay writing
- writing a book
- chicago style format
- types of autobiography
Burdened With Assignments?

Advertisement
- Homework Services: Essay Topics Generator
© 2024 - All rights reserved
My Speech Class
Public Speaking Tips & Speech Topics
How to Create a Compelling Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline

Jim Peterson has over 20 years experience on speech writing. He wrote over 300 free speech topic ideas and how-to guides for any kind of public speaking and speech writing assignments at My Speech Class.

Do you need to write a rhetorical analysis essay outline? Even the word is quite a mouthful, and it can seem far more intimidating than it really is, especially if you’re new to the style. That’s why we’ve put together this super helpful guide to the rhetorical essay format and everything you need to know to get the job done.
In this article:
What is a Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
How long should my rhetorical analysis essay be, rhetorical appeals, analysis and evaluation, thesis statement, prepare to write:, rhetorical analysis introduction, ethos, pathos, logos, rhetorical analysis essay strategies.
Before we look at the rhetorical analysis format, let’s answer a fundamental question – what is a rhetorical analysis essay, anyway? Rhetorical analysis essays take another person’s work of nonfiction (usually, sometimes fiction is allowed) and dig deep into how the message was presented and why. They can be about anything – from books to magazine articles, famous speeches, and even TV commercials and videos. It’s all about looking deeply into how the media created its message and whether it’s effective at delivering it.
Why learn how to write a rhetorical analysis essay? It’s essential to know how people deliver a message. Think of marketing. Successful marketers don’t just make things up and hope for the best! They review what their successful competition is doing and figure out how to leverage it for their brand. This includes creating the right effect with the message, using power words that will drive their campaign, and so on – all skills you will learn while creating the outline for your rhetorical analysis essay.
As you can see, it’s an important critical skill to develop, and your rhetorical analysis essay will help you learn a lot about how humans respond to what we consume as well.
There is no strict rule about how long a rhetorical analysis essay should be, unless you have been given a target word length by your school or professor. You will, however, need to include key parts in your rhetorical analysis-conclusion, opening paragraph, thesis statement, and enough body sections to adequately make your analysis and argument. Our rhetorical analysis thesis outline will assist with this.
How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
We will look at the rhetorical analysis essay outline in more detail below. First, however, it’s important to identify the steps you will take in writing your essay, to make sure it is insightful and clear to the reader. How do you analyze your source material?
Can We Write Your Speech?
Get your audience blown away with help from a professional speechwriter. Free proofreading and copy-editing included.
You will start by noting the overall rhetorical elements used. Here are four key elements:
- Purpose : Why did the speaker or author create this piece? What were they hoping to achieve or convince people of?
- Audience : Who was the piece directed at? What are their backgrounds and demographics? What unites them as an audience?
- Context : No piece is an island. What was/is happening around the work you are analyzing? What was the social climate, place, and time when it was written? What was happening around it?
- Medium : How is the message being delivered to us? Why would this be the best way to express the thought?
With that framework in mind, now move on to the rhetorical appeals and devices the author uses. This includes ethos, pathos, and logos, which we’ve looked at in detail in the next section. Also, consider how they are evoked – the imagery used, the tone taken, the syntax offered, and so on.
Of course, the point here is an analysis of the content you’ve chosen. So now it’s time to dig deep into how they used these methods and why they selected them. Were they successful or not? Why? Why not? If it wasn’t a successful attempt, what do you think the audience actually felt? At this point, you are building the ‘meat’ of your actual rhetorical analysis essay, so spend a lot of time with this. Remember, your evaluation is your main argument!
We revisit this a little later, but it’s worth adding here, too. Try to take these overall ideas and refine them into a straightforward thesis statement. This will help you build a strong foundation for your essay. This statement must demonstrate:
- The purpose the content creator had for the content
- The methods they used
- How effective they were
And contain the very core of your argument, which the rest of the essay develops further. It could look something like this:
In (content piece), the author compellingly demonstrates how removing access to some forms of public transport adversely affected vulnerable community members. They presented factual data, alongside personal experience and anecdotes that spoke to the problem’s root.
With that core element of your essay nailed down, you can begin to organize the thoughts, ideas, and evidence you’ve unearthed so far into your outline. Let’s take a closer look at it.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline
So, what goes into the outline of a rhetorical analysis essay? It’s worth spending some time creating a rhetorical analysis essay/thesis outline for your work, even if it seems like wasted time. With a streamlined, sensible process in place, and a solid framework to work within, it will be much easier to organize the flow of your thoughts. So it’s time to create your rhetorical analysis outline.
As you go, think about the work you’re analyzing. Focus on aspects like the creator, their intention and message, the setting, and other vital details. Not only will this help you easily create the rhetorical analysis outline, but it will also do a lot of the work.
How to start a rhetorical analysis is one of the most asked questions by students – and with good reason. The introduction needs to achieve many things. You will be telling the reader about what you’re analyzing, whether it achieved its goals, and hooking the reader to keep reading along with you. This means it has to be one of the strongest parts of your essay.
Open on something interesting to pull people into your writing, known as a hook . Then introduce the author and work you are examining. There is no need for deep detail as that’s for the body but enough to grasp the subject. Explain whether or not you think they were successful with their message and why you decided on that judgment.
Here at the end of the introduction is also where your thesis statement will reside. A strong thesis statement is critical to a rhetorical analysis essay. In many ways, it is the lynchpin of the whole essay. Think of it as a quick guide to the entire argument you will be making.
It should be one or two sentences long, very clear and concise, and carry the intent of informing what the reader will get from your paper. You will outline the tools you are using to analyze the source material. Three of these are most typical for rhetorical analysis essays:
- Diction : How the author uses words and styles
- Imagery : The visually descriptive language they use
- Simile : Direct ‘like’ and ‘as’ comparisons between items.
The Body of your rhetorical outline is the most changeable part of the rhetorical analysis essay template. You can make a convincing argument in as little as 500 words . Or you may need more space. Don’t confuse being wordy with being ‘smart’ or ‘effective’- try to use as few words as you need to be concise and clear.
Here is where you will do the bulk of your analysis. Look at how the author used their tools to drive the purpose of the text.
While you can use any number of paragraphs, we suggest at least 3. Each should open with a topic sentence that links it to your thesis statement, proving and fortifying it. Add a relevant quote from the original text that helps demonstrate your point. Then use the rest of the text for your analysis. This should be at least three times longer than the quoted text. Quotes and findings that support your point will be used throughout.
These are the three classic rhetorical appeals that you should use to help you analyze the text. Use them throughout the body.
- Ethos : How the author establishes themselves as reliable and trustworthy with their tone or credentials.
- Pathos : ‘Tugging on your feelings.’ This is how an appeal to the reader’s emotions is made through emotive language or touching stories.
- Logos : This is the root word for Logic, which should give you a hint. How does the author develop their ideas logically? Do they reach sensible conclusions?
Once you’ve established your argument and developed it through the body, you will round off with a paragraph as a conclusion. It’s the most forgotten part of the rhetorical analysis essay format, so keep it in mind! You need to reiterate your main argument to emphasize your point concisely. Give a quick overview of the pros and cons in the text, and restate whether you feel they were effective.
And there you have it! This is the basic rhetorical analysis template that can be adapted to a wide range of essays.
Now you have a rhetorical analysis essay outline/template to follow, but the hard work doesn’t stop there. Throughout your essay, you need to demonstrate strong use of rhetorical analysis strategies to examine the essay contents. This helps you persuade your audience and develop your argument. There are many different strategies, but these are the most commonly used:
- Description : This is the most straightforward strategy, merely telling your reader something through the direct description. What is it? What is it not? This helps them understand what a specific term means as you use it.
- Cause and effect : The key part of this strategy is the cause. The effect is what happened because of that cause. In this way, you join the present (effect) to the past (cause), or the present (cause) to future action (effect).
- Process Analysis : How was something achieved? This is a strategy that’s good for history-focused essays, as it shows how something was achieved in the past but can be used for any topic. For example, this article is a process analysis! You also find process analysis used to explore topics from simple descriptions of how to do tasks, to complex advice like processing grief.
- Exemplification : This is another commonly used strategy. You give examples to illustrate your overall point. Every time you analyze a quote, you’re using this. However, make sure that there is a transparent and explainable relationship between your quote and the point you’re making.
- Compare and Contrast : What is similar and different? This is a strong strategy used often in arguments, speeches, and reports, which is useful for rhetorical analysis.
- Narration : Narration takes the reader on a journey through storytelling, which is why it’s an essential rhetorical strategy. We use life experience and personal stories to make our points.
Analyzing rhetoric is how we evaluate and understand what other creators have made. We also arrive at better ways to make our arguments more efficient through such analysis. That’s why it’s worth exploring all of these rhetorical analysis strategies and how they can be applied to your topic even if you discard some for your practical purposes.
Don’t just mechanically approach your topic. That way, you just hear what they say. Instead, pay attention to how they say it, using these strategies. This will help you develop your critical thinking, one of the most important things you will ever do. This is your toolkit that will help you evaluate media critically, a skill that will help you throughout your life.
And there you have it! You have learned how to write a rhetorical analysis essay, from choosing your topics to developing a coherent argument in a logical outline. We’ve even looked at some key tips and strategies for your rhetorical analysis essay, too. With this outline and these tools in your kit, you will be able to take your conclusions and express them to the reader logically. Now it’s up to you to practice those skills!
How To Prepare & Write a Funeral Speech That’s Meaningful
50+ Hook Examples: The Opening Lines That Make Your Essay Successful
Leave a Comment
I accept the Privacy Policy
Reach out to us for sponsorship opportunities
Vivamus integer non suscipit taciti mus etiam at primis tempor sagittis euismod libero facilisi.
© 2024 My Speech Class
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline: Examples & Strategies
Rhetorical analysis is never a simple task. This essay type requires you to analyze rhetorical devices in a text and review them from different perspectives. Such an assignment can be a part of an AP Lang exam or a college home task. Either way, you will need a solid outline to succeed with your writing. And we can help you nail it.
Our specialists will write a custom essay specially for you!
In this article by our custom-writing team, you will find:
- the structure of a rhetorical analysis essay;
- a detailed guide and tips for writing a rhetorical essay outline;
- an example and a template for you to download.
- 📚 Rhetorical Analysis Structure
Introduction
- Body Paragraphs
- 📑 Example Outline & Template
🔍 References
📚 structure of a rhetorical analysis essay: pre-writing.
The first thing you need to know before you start working on your essay is that the analysis in your paper is strictly rhetorical. In other words, you don’t need to discuss what the author is saying. Instead, it’s a take on how the author says it.
And to understand “how,” you need to find rhetorical appeals. An appeal is a technique that the author uses to convince the reader. The main ones are logos, ethos, and pathos.
The whole analysis is structured around them and divided into 3 parts: appeals in the text’s introduction, in the body paragraphs, and in its conclusion.
Remember that it’s essential to structure your essay in chronological order. To put it simply, it’s better not to describe the appeals from the conclusion before the ones in the introduction. Follow the structure of the text you’re analyzing, and you’ll nail it.
Just in 1 hour! We will write you a plagiarism-free paper in hardly more than 1 hour
Rhetorical Analysis Triangle
We’ve already mentioned ethos, pathos, and logos. The rhetorical triangle is another name for these 3 main appeals. Let’s examine them in more detail:
In your essay, it’s best to mention all 3 appeals. It’s also necessary to measure their effectiveness and give examples. A good strategy is to find the appeals in the text, underline them, and analyze them before writing the outline.
Each appeal can be characterized by the following:
- Diction. Diction is the words that the author uses to describe the idea. When analyzing diction, you want to find words that stand out in the text.
- Syntax. Simply put, syntax is the order of words used by the author. You can also look at the sentence length as a part of the syntax.
- Punctuation. This characteristic is all about the usage of punctuation marks. Aside from commas, it’s good to pay attention to colons and dashes. Authors can use them to focus the audience’s attention on something or create a dramatic disjunction.
- Tone. It’s the author’s attitude towards the discussed idea. The tone is a combination of diction, syntax, and punctuation. For example, you can tell if the author is interested or not by evaluating the length of sentences.
Remember that all 3 appeals are artistic proofs, and you shouldn’t confuse them with factual evidence. The difference between them lies in the amount of effort:
- Citing factual evidence requires no skill. You create proof just by mentioning the fact.
- In the case of artistic proof , you must use your knowledge of rhetoric to create it.
SOAPS: Rhetorical Analysis
SOAPS is a helpful technique for conducting a rhetorical analysis. It’s fairly popular and is recommended for AP tests. SOAPS stands for:
Receive a plagiarism-free paper tailored to your instructions. Cut 15% off your first order!
Answering the questions above will make it easy for you to find the necessary appeals.
✍️ How to Write an Outline for a Rhetorical Analysis Essay
Now that you’ve found the appeals and analyzed them, it’s time to write the outline. We will explain it part by part, starting with the introduction.
How to Write an Introduction for a Rhetorical Analysis Essay
In a rhetorical analysis, the introduction is different from that of a regular essay. It covers all the necessary information about the author of the text:
- Name (or names, if there are several authors.)
- Genre and title of the reviewed work.
The author claims that cats are better pets than dogs.
- The target audience that the writer is aiming at.
- The context in which the text was produced, e.g. a specific event.
Aside from that, a rhetorical essay introduction should include a hook and a thesis statement. Want to know how to write them? Keep reading!
How to Write a Hook for a Rhetorical Analysis Essay
A hook is a sentence that grabs the reader’s attention. You can do it by presenting an interesting fact about the author. You may also use an inspiring or amusing quote. Make sure your hook is connected with the text you are writing about.
Get an originally-written paper according to your instructions!
For example, if you’re analyzing MLK’s I Have a Dream speech, you can hook the reader with the following sentence:
Martin Luther King is widely considered the most famous speaker in history.
Our article on hooks in writing can provide you with e great ideas.
Thesis Statement for Rhetorical Analysis Essay
In a rhetorical analysis essay, you don’t need to create a thesis statement in the usual sense. Instead, you describe the main point made by the author using a rhetorically accurate verb (such as “claims” or “asserts”) followed by a “that” clause.
For example, your thesis can focus on the techniques that the author uses to convince the audience. If we look at the I Have a Dream speech, we will notice several stylistic elements:
It’s not a complete list, but that’s enough to form a decent thesis.
We also need to mention the ideas behind the speech. The main idea is, obviously, equality. So, we’ll put it in our thesis as well. As a result, we have something like this:
Through the skillful usage of metaphor, repetition, and symbolism Martin Luther King effectively fills his audience’s hearts with the idea of unity and equality.
Rhetorical Analysis Body Paragraphs
If you are writing a generic 5-paragraph essay, you can divide your essay’s body into 3 parts:
- A paragraph about appeals in the text introduction.
- A section about rhetorical devices in the text’s body.
- A paragraph about rhetorical devices in the text’s conclusion.
Sometimes there is no distinct structure in a text. If that’s the case, just analyze the appeals in chronological order. You can also split the analysis based on the type of appeals. For example:
- A paragraph about emotional appeals.
- A section about logical appeals.
- A paragraph about ethical appeals.
Each of your essay’s body paragraphs should have 3 key elements:
- Topic sentence that shows what appeal you will discuss in the section.
- Examples that illustrate the rhetorical device you want to showcase.
- Your take on the effectiveness of the given device.
It’s good to remember that every appeal you talk about needs an example. If you can illustrate your claim about a strategy with more examples, then go for it. The more examples, the better.
Good Transition Words for Rhetorical Analysis Essay
Transition words allow you to follow up one idea with another. They also help build connections between paragraphs. Choosing correct transition words depends on the strategy you use. If you want to build a sequence of a cause and its effect, you will need words like “thus” or “hence.” If you’re going to clarify something, you should use a different set of words.
Here’s a list of helpful transition words suitable in different contexts:
Rhetorical Analysis Verbs to Use
A rhetorical analysis essay is a serious work that often touches on complex topics. Regular verbs like “tells us” or “shows” don’t always fit it. To make your paper more inclusive and precise, consider using strong verbs .
Strong verbs (or power verbs) are typically used when talking about the author. That includes their strategies, attitude, personality, or ideas.
For example, instead of “the author says,” you can use “suggests” or “clarifies,” depending on the context.
Some other rhetorically accurate verbs include:
- Sheds light
You don’t have to use strong verbs only. If you feel like “says” suits your point better than any strong verb, feel free to use it.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Conclusion
The conclusion is the ending of your paper. It sums your essay up and underlines the points you’ve made in the body paragraphs. A good conclusion should accomplish several things:
- Paraphrasing the thesis . You shouldn’t just rewrite the thesis from the introduction. The restatement is usually used to demonstrate a deeper understanding of your point.
- A summary of the body paragraphs . Again, simple repetition is not enough. We need to link the points to our thesis and underline the importance of our statements.
- Final thoughts . A powerful epilogue will leave a good impression about your work.
Make sure to avoid including any new ideas or statements. The conclusion is exclusively for summarizing. If you found yourself putting a new assertion in the ending, it’s probably a good idea to restructure your body paragraphs.
📑 Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example Outline & Template
To make the writing process even easier for you, we will show you what an outline for your essay can look like. As an example, we will outline a rhetorical analysis of MLK’s I Have a Dream speech. We are going to structure it according to the appeals.
Have a look:
- Hook . An interesting fact about the MLK or his quote. An emotional start about the importance and the lasting legacy of the speech will also work.
- The speaker’s name, occupation, and years of life.
- The context in which the subject of our essay was produced.
- The speech’s target audience.
- Thesis statement . Point out the appeals you are going to write about. Describe their impact on the author’s general argumentation.
Body paragraphs
- Underline the often use of metaphor. Set “lonely island of poverty” and “ocean of material prosperity” as examples.
- Talk about the usage of repetition. Use the constant repetition of “I have a dream…” as an illustration.
- Demonstrate the use of logos. Mention King citing President Lincoln as an authority for his argumentation.
- Showcase the ethos of the speech. Notice that MLK’s Civil Rights Movement logic correlates with social ethics at the time.
- Comparing segregation to a “bad check.”
- Referring to the Civil Rights Movement as “my people.”
- Comparing the acquisition of equality to “cashing a check.”
- Restate the thesis. Demonstrate a deeper understanding of the point made in the introduction.
- Summary of the body paragraphs. Connect them to the thesis statement. Give a final take on King’s rhetorical strategies and evaluate their effectiveness.
- Closing thought. Finish by stating the primary goal of your analysis.
Alternatively, you can structure your essay in chronological order. Below you’ll find a template you can use for this type of rhetorical analysis. Simply download the PDF file below and fill in the blanks.
Rhetorical Analysis Outline Template
(your essay’s title)
Introduction.
The speaker/author is (state the author’s name.) The purpose of the text is to (state the text’s purpose.) The text is intended for (describe the text’s intended audience.)
Check out the rhetorical analysis samples below to get some ideas for your paper.
- Greta Thunberg’s Speech: Rhetorical Analysis
- Rhetorical Analysis: “In Defense of the ‘Impractical’ English Major” by C. Gregoire and “Top 10 Reasons You’re Not Wasting Your Time as an English Major” by S. Reeves
- Steve Jobs’ Commencement Speech Rhetorical Analysis
- The Speech “Beyond Vietnam: A Time to Break Silence” by Martin Luther King, Jr: Rhetorical Analysis
- Rhetorical Analysis Through Lyrics: “The Times They Are A-Changing” and “The Wind of Change”
- Roiphe’s Confessions of a Female Chauvinist Sow: Rhetorical Analysis
- “Snack Attack”: Rhetorical Analysis
- Rhetorical Analysis of “Hidden Intellectualism” by Gerald Graff
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics
- Analyze rhetorical appeals of a Hallmark’s commercial
- Rhetorical devices and the atmosphere of Hamlet’s To Be or Not to Be monologue
- The author’s argument in Us film
- Compare pathos, ethos, and logos in two advertisements
- Google Analytics : rhetorical analysis
- The background and the audience of the Gillette commercial short film
- Rhetorical analysis of capitalism and socialism
- What makes John F. Kennedy’s inaugural address iconic?
- The significance of the historical parallel in Susan B. Anthony’s speech
- Sarcasm and skepticism in Shikha Dalmia’s article
- Rhetorical analysis of political debates between Biden, Harris, and Booker
- What makes Letter From Birmingham Jail powerful?
- Problems of the modern education in Moore’s Idiot Nation and Gatto’s Against School
- Rhetorical techniques in Learning to Read and Write by Frederick Douglass
- Compare and contrast Antigone and Creon
- The word framing of Michelle Obama’s TED speech
- James Q. Wilson’s arguments on gun ownership laws
- Analyze ethos, pathos, and logos in a video advertisement
- What makes the 2005 speech by Steve Jobs remarkable?
- How does Jenna Berko convince readers in her essay?
- Successful persuasion in the film Henry V
- Margaret Fuller and Frederick Douglass : a rhetorical comparison
- Characters, setting, and emotions in Of Mice and Men
- Web blogs rhetorical analysis
- Rhetorical devices in Barbara Holland’s collection of thoughts
- Conduct a rhetorical analysis of Louis C. K.’s Shameless
- What makes Claire Giordano’s essay convincing?
- Biblical allusions in Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglas
- Ali Siddiq’s ‘Prison Riot’ standup: a rhetorical analysis
- Presentation of interracial romance in Get Out movie
- Rhetoric Instruments in The Oxford Encyclopedia of Latinos and Latinas in the United States
- How does Barack Obama try to change reality with his speech?
- Target and purpose of L’Oreal EverCrème advertisement
- Perform a rhetorical analysis of Pop Can: Popular Culture in Canada
- The Myth of the Charioteer by Plato : rhetorical devices
- Rhetorical goals of the authors of African-American history articles
- The effectiveness of the Michelin advertising campaign
- Rhetorical analysis of the Double Cola Company’s image
- Compare the use of argument in Lincoln’s and Dickinson’s works
- Rhetoric analysis of anti-communist and anti-Islam promotion
We hope this article helped you with your assignment. Make sure to tell us what part helped you the most in the comments. And good luck with your studies!
Further reading:
- How to Write a Reflection Paper: Example & Tips
- How to Write a Narrative Essay Outline: Template & Examples
- What Is a Discourse Analysis Essay: Example & Guide
- How to Write a Critical Thinking Essay: Examples & Outline
- How to Write a Precis: Definition, Guide, & Examples
- How to Write a Process Analysis Essay: Examples & Outline
🤔 Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline FAQs
According to SOAPS, the main 5 elements of a rhetorical analysis are:
1. Subject, or the author’s ideas. 2. Occasion, or the text’s background. 3. Audience, or the people who would find the text interesting. 4. Purpose, or the reasoning behind the writing. 5. Speaker’s characteristics, or the author’s personal beliefs.
1. Logos— the appeal to logic. It includes argumentation, statistics, and facts. 2. Ethos— the ethical appeal. Ethos appeal to the morality and ethical norms of the target audience. 3. Pathos —the appeal to the reader’s emotions. 4. Kairos— the time of the argument.
Every rhetorical analysis ends with a conclusion. A good conclusion should:
1. Restate the thesis. 2. Summarize the points and strategies described in the body paragraphs. 3. End with concluding thoughts on the analysis.
A thesis for a rhetorical analysis is a bit different from the usual one. It needs to include the author’s appeals and the main point the author is trying to make. Like any other thesis, it must structure the further analysis and be connected to every paragraph.
Kairos is the timeliness of the argument. It is the appeal of the right time. The usage of kairos usually means that the author’s text is relevant for a certain period of time only.
- Rhetorical Analysis: Miami University
- Rhetorical Analysis Essay: Formatting: California State University, East Bay
- The Rhetorical Triangle: Understanding and Using Logos, Ethos, and Pathos: Louisiana State University
- The Rhetorical Triangle: The University of North Carolina at Charlotte
- General Notes on Rhetorical Analysis: Deer Valley Unified School District
- SOAPS: Rhetorical Analysis of a Reading Source: Kent Campus
- How To Write a Rhetorical Analysis in 8 Simple Steps: Indeed
- Rhetorical Analysis: Texas A&M University
- Rhetorical Analysis Thesis Statements: Virginia Wesleyan University
- What Are Logos, Ethos, Pathos, and Kairos?: University of Louisville
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

A synthesis essay requires you to work with multiple sources. You combine the information gathered from them to present a well-rounded argument on a topic. Are you looking for the ultimate guide on synthesis essay writing? You’ve come to the right place! In this guide by our custom writing team,...

A critical analysis essay is an academic paper that requires a thorough examination of theoretical concepts and ideas. It includes a comparison of facts, differentiation between evidence and argument, and identification of biases. Crafting a good paper can be a daunting experience, but it will be much easier if you...

A visual analysis essay is an academic paper type that history and art students often deal with. It consists of a detailed description of an image or object. It can also include an interpretation or an argument that is supported by visual evidence. In this article, our custom writing experts...

A character analysis is an examination of the personalities and actions of protagonists and antagonists that make up a story. It discusses their role in the story, evaluates their traits, and looks at their conflicts and experiences. You might need to write this assignment in school or college. Like any...
![rhetorical analysis essay outline Critical Writing: Examples & Brilliant Tips [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/fingers-note-report-journalist-filling-284x153.jpg)
Any critique is nothing more than critical analysis, and the word “analysis” does not have a negative meaning. Critical writing relies on objective evaluations of or a response to an author’s creation. As such, they can be either positive or negative, as the work deserves. To write a critique, you...

If you are assigned to write a rhetorical analysis essay, you have one significant advantage. You can choose a text from an almost infinite number of resources. The most important thing is that you analyze the statement addressed to an audience. The task of a rhetorical analysis essay is to...

Any literary analysis is a challenging task since literature includes many elements that can be interpreted differently. However, a stylistic analysis of all the figurative language the poets use may seem even harder. You may never realize what the author actually meant and how to comment on it! While analyzing...

As a student, you may be asked to write a book review. Unlike an argumentative essay, a book review is an opportunity to convey the central theme of a story while offering a new perspective on the author’s ideas. Knowing how to create a well-organized and coherent review, however, is...

The difference between an argumentative and persuasive essay isn’t always clear. If you’re struggling with either style for your next assignment, don’t worry. The following will clarify everything you need to know so you can write with confidence. First, we define the primary objectives of argumentative vs. persuasive writing. We...

You don’t need to be a nerd to understand the general idea behind cause and effect essays. Let’s see! If you skip a meal, you get hungry. And if you write an essay about it, your goal is achieved! However, following multiple rules of academic writing can be a tough...
![rhetorical analysis essay outline How to Write an Argumentative Essay: 101 Guide [+ Examples]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/young-writer-taking-notes-284x153.jpg)
An argumentative essay is a genre of academic writing that investigates different sides of a particular issue. Its central purpose is to inform the readers rather than expressively persuade them. Thus, it is crucial to differentiate between argumentative and persuasive essays. While composing an argumentative essay, the students have to...
![rhetorical analysis essay outline How to Title an Essay: Guide with Creative Examples [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/close-up-woman-making-greeting-card-new-year-christmas-2021-friends-family-scrap-booking-diy-writing-letter-with-best-wishes-design-her-homemade-card-holidays-celebration-284x153.jpg)
It’s not a secret that the reader notices an essay title first. No catchy hook or colorful examples attract more attention from a quick glance. Composing a creative title for your essay is essential if you strive to succeed, as it: Thus, how you name your paper is of the...
Extremely helpful. Gave me wonderful definitions of Pathos,Lagos and Ethos.Broke down how to use these points to write my analysis. Thank you
Rhetorical Analyses
A rhetorical analysis considers all elements of the rhetorical situation--the audience, purpose, medium, and context--within which a communication was generated and delivered in order to make an argument about that communication. A strong rhetorical analysis will not only describe and analyze the text, but will also evaluate it; that evaluation represents your argument.
- Description: What does this text look like? Where did you find the text? Who sponsored it? What are the rhetorical appeals? (i.e. calm music in the background of a commercial establishes pathos) When was it written?
- Analysis: Why does the author incorporate these rhetorical appeals? (For example, why does the author incorporate calm music? What is the point of the pathos?) How would the reception of this text change if it were written today, as opposed to twenty years ago? What is left out of this text and why? Should there be more logos in the ad? Why?
- Evaluation: Is the text effective? Is the text ethical? What might you change about this text to make it more persuasive?
Rhetoric Defined
- Classically, "the art of persuasion".
- "About using language purposefully, in order to get something done in the world" ("What is Rhetoric").
- "Something that allows you to formulate ethical reading strategies [...] but also to invent your own responses to the world" ("What is Rhetoric").
Keywords and Concepts
Following are some basic terms and concepts (far from inclusive) that you should consider and use in a rhetorical analysis.
Rhetorical Situation
The rhetorical situation identifies the relationship among the elements of any communication--audience, author (rhetor), purpose, medium, context, and content.
Spectator, listeners, and/or readers of a performance, a speech, a reading, or printed material. Depending on the author's/writer's perception, an audience may be real (actually listening or reading), invoked (those to whom the writer explicitly writes) or imagined(those who the writer believes will read/hear her work) (Dept. of English)
Author/Rhetor/Speaker/Writer
The person or group of people who composed the text.
Purpose of the Author
The reason for communicating; the expected or intended outcome.
The delivery method, which varies by type of text:
- Alphabetic Text (for example, written speech, newspaper editorial, essay, passage out of a novel, poetry)
- Images (for example, TV commercials, advertisements in magazines or on websites)
- Sound (for example, radio or TV commercials, a website advertisement, speeches)
- Multimodal texts (YouTube videos, performances, digital stories)
The time, place, public conversations surrounding the text during its original generation and delivery; the text may also be analyzed within a different context such as how an historical text would be received by its audience today.
The main idea, thesis, opinion, or belief of an argument that the author must prove. The claim should be debatable and answer the question, "What's the point?"
The statements given to back up the claim. These can take the form of facts, data, personal experience, expert opinion, evidence from other texts or sources, emotional appeals, or other means. The more reliable and comprehensive the support, the more likely the audience is to accept the claim.
The connection, often unstated and assumed, between the claim and the supporting reason(s), or support. The warrant is the assumption that makes the claim seem plausible. More specifically, warrants are the beliefs, values, inferences and/or experiences that the writers/speakers assume they share with the audience. If the audience doesn't share the writers'/speakers' assumptions within the text, the argument will not be effective.
Rhetorical Triangle
The elements of the rhetorical situation interact with and influence one another. In learning to write an analysis, it is thus helpful to think about the relationship among these elements within the rhetorical triangle. By doing this, writers will be able to better understand how the elements of each text come together (often overlap) to make an argument or persuade an audience.
The authority or credibility of the author. Can refer to any of the following: the actual character of the speaker/writer, the character of the writer as it is presented in a text, or as a series of ground rules/customs, which are negotiated between speaker, audience, and specific traditions or locations. The speaker must convince the audience of their credibility through the language they use and through the delivery, or embodied performance, of their speech.
Did you analyze ethos enough in your essay?
- Have you looked at what experiences or claims to authority qualify this author to speak or write?
- Have you considered the credibility and moral character of the writer/speaker?
- Have you considered the design or appearance of the text you are analyzing? Does it look professional? What can you say about the author based on the appearance of the text alone?
Emotional appeals to the audience to evoke feelings of pity, sympathy, tenderness, or sorrow. The speaker may also want the audience to feel anger, fear, courage, love, happiness, sadness, etc.
Have you analyzed pathos enough in your essay?
- Have you considered how the author appeals to the emotions of the reader/viewer?
- How does the author establish a bond with his audience?
- How might the author change his strategy if he was trying to establish a bond with a different audience?
- Have you considered your own personal reaction to the background music of this advertisement?
- What kinds of feelings do the colors that the author uses provoke?
- What other images in the text provoke an emotional response? Why would the author include these images?
In classical rhetoric, logos is the means of persuasion by demonstration of the truth, real or apparent, the reasons or supporting information used to support a claim, the use of logic or reason to make an argument. Logos can include citing facts and statistics, historical events, and other forms of fact based evidence.
Do you analyze logos enough in your essay?
- How does the author back up his argument in this text? Does he incorporate facts, statistics, or numbers?
- Have you considered how logical the author's argument is?
- Are the claims this author is making realistic?
- Does the author consider alternative arguments?
The right time to speak or write; advantageous, exact, or critical time; a window of time during which action is most effective. (Ex. Martin Luther King Jr.'s "I Have a dream speech was delivered at the right moment in history—in the heat of civil rights debates.)
Literally, stasis is "a stand" or a "resting place" in an argument where opponents agree on what the issue is but disagree on what to do about it. The skilled rhetor is able to move the argument away from stasis. (Ex. Rhetor A asserts that abortion is murder. Rhetor B asserts that abortion is not murder. This is the point of stasis. The argument cannot rest here indefinitely. One of these rhetors must get the argument beyond the issue of murder.)
501 E. High Street Oxford, OH 45056
- Online: Miami Online
- Main Operator 513-529-1809
- Office of Admission 513-529-2531
- Vine Hotline 513-529-6400
- Emergency Info https://miamioh.edu/emergency
1601 University Blvd. Hamilton, OH 45011
- Online: E-Campus
- Main Operator 513-785-3000
- Office of Admission 513-785-3111
- Campus Status Line 513-785-3077
- Emergency Info https://miamioh.edu/regionals/emergency
4200 N. University Blvd. Middletown, OH 45042
- Main Operator 513-727-3200
- Office of Admission 513-727-3216
- Campus Status 513-727-3477
7847 VOA Park Dr. (Corner of VOA Park Dr. and Cox Rd.) West Chester, OH 45069
- Main Operator 513-895-8862
- From Middletown 513-217-8862
Chateau de Differdange 1, Impasse du Chateau, L-4524 Differdange Grand Duchy of Luxembourg
- Main Operator 011-352-582222-1
- Email [email protected]
- Website https://miamioh.edu/luxembourg
217-222 MacMillan Hall 501 E. Spring St. Oxford, OH 45056, USA
- Main Operator 513-529-8600
Initiatives
- Miami THRIVE Strategic Plan
- Miami Rise Strategic Plan
- Boldly Creative
- Annual Report
- Moon Shot for Equity
- Miami and Ohio
- Majors, Minors, and Programs
- Inclusive Excellence
- Employment Opportunities
- University Safety and Security
- Parking, Directions, and Maps
- Equal Opportunity
- Consumer Information
- Land Acknowledgement
- Privacy Statement
- Title IX Statement
- Report an Accessibility Issue
- Annual Security and Fire Safety Report
- Report a Problem with this Website
- Policy Library
Rhetorical Analysis Essay

How To Write A Rhetorical Analysis Essay That Stands Out
17 min read
Published on: Jul 17, 2020
Last updated on: Jan 29, 2024

People also read
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics & Ideas for Students
Top 15+ Rhetorical Analysis Essay Examples for Students
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline - Tips & Examples
Understanding Ethos, Pathos, Logos - The Three Rhetorical Appeals
Share this article
Are you struggling to write a compelling rhetorical analysis essay that captures your readers' attention?
Don't worry, you're not alone!
Crafting an effective analysis requires a deep understanding of rhetorical devices and techniques.
In this comprehensive guide, we will equip you with the essential knowledge of writing impactful rhetorical analysis essays.
By following our step-by-step approach you'll gain the skills needed to analyse texts, engage your audience, and leave a lasting impression.
Let's dive into the world of rhetorical analysis essays and embark on a transformative writing journey!
On This Page On This Page -->
What is a Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
Rhetorical analysis is a type of college essay in which the writer conducts a deep analysis of an object.
In this type of analysis, the object of analysis is mostly some kind of book, a movie, or any other type of creative work.
When it comes to rhetorical analysis, a writer picks a particular subject and analyzes its effects on the surroundings and the target audience.
It is important to mention that rhetorical analysis can be done on nearly anything that comes to your mind. Be it a billboard, a logo, a motto, or anything else you can think of.
What are the Five Rhetorical Situations?
The concept of the rhetorical situation is an essential aspect of rhetorical analysis. The following are the five rhetorical situations that you need to consider when analyzing a text:
- Audience : The audience refers to the individuals who receive the message. Understanding the audience's characteristics, values, and expectations is crucial in crafting persuasive communication that resonates with them.
- Purpose : The purpose is the reason why the communication is created. It could be to inform, entertain, persuade, or educate the audience.
- Speaker : The speaker is the person who creates or delivers the communication. The speaker's characteristics, such as their credibility, expertise, and reputation, play a significant role in how the audience perceives and responds to the message.
- Occasion : The occasion is the event or situation that prompts the creation of the communication. The occasion may affect the tone, language, and overall message of the communication.
- Context : The context is the broader environment that shapes the communication, including the cultural, social, political, and historical factors. Understanding the context helps you analyze how the message relates to larger societal issues and trends.
What are the Three Rhetorical Analysis Strategies?
There are three main methods of persuasion: ethos, pathos, and logos. To be successful in persuading someone, you need to understand how to use each of these methods.
- Ethos (Credibility)
Ethos focuses on the credibility and authority of the speaker or author. It involves evaluating their expertise, knowledge, experience, and reputation. By examining the speaker's ethos, you can assess how their credibility influences the audience's perception of the message.
Look for elements such as professional qualifications, personal anecdotes, or references to establish ethos.
- Pathos (Emotional Appeal)
Pathos involves appealing to the emotions and values of the audience. This strategy aims to evoke specific emotions, such as empathy, fear, joy, or anger, to create a connection with the audience. Analyze the use of vivid language, storytelling, imagery, personal anecdotes, or appeals to shared values and beliefs.
Consider how these emotional appeals impact the audience's engagement and response.
- Logos (Logical Reasoning)
Logos centers on logical reasoning and appeals to the audience's rationality and critical thinking. It involves analyzing the use of evidence, statistics, logical arguments, facts, and logical structures within the text.
Assess how the author or speaker supports their claims, presents a logical progression of ideas, and uses reasoning to persuade the audience.
Check out this blog on ethos, pathos, logos for dig deeper into these rhetorical strategies!
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Structure
Below is a rhetorical analysis essay structure for your help.
How To Write a Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
Writing a rhetorical analysis essay may seem challenging at first, but with a systematic approach, you can effectively analyze and interpret a piece of rhetoric.
Here is a step-by-step guide to help you craft a successful rhetorical analysis essay.
Analyzing The Text
Before you directly hop on to write your rhetorical analysis essay, make sure that you follow some prewriting steps. These steps will make essay writing easy and less time-consuming.
Some simple pre-writing steps of such an essay are as follows:
- Identify your Target Audience
Identifying the audience is the most important factor for an essay. Identifying the audience allows the writer to write the essay according to the intellectual level of the intended audience.
If a writer writes the essay without knowing the audience, all the effort will go in vain as the audience will not understand the essay's purpose.
- The Subject of the Essay
Another important thing about a rhetorical analysis essay is identifying and analyzing the chosen subjectâs underlying meaning. A writer of this essay type should understand that message and explain it in a few words.
- Define Purpose
Defining the purpose of the rhetorical analysis essay provides logic to the reader for the essay. The writer explains the reason behind the composition and what made them choose a particular topic for an essay.
- Mention the Occasion
The occasion refers to the work and its setting. When analyzing the occasion, two approaches are used, i.e., micro view and macro view. Both these views are used to explain where the occasion took place.
- Identify the SOAPSTone
The SOAPSTone of a text includes its Speaker, Occasion, Audience, Purpose, Subject, and Tone. Further elaboration of SOAPSTone is as follows:
- Speaker: The speaker basically refers to the first and last name of the writer.
- Occasion: The occasion mostly refers to the type of text and the context under which the text was written.
- Audience: The audience is who the text was written for.
- Purpose: The purpose refers to what the writer wants to accomplish in the text.
- Subject: The subject is simply the topic the writer discusses in the text.
These were some basic pre-writing steps for a rhetorical analysis essay. Letâs move forward and see what steps we need to follow to write a good rhetorical analysis essay.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline
An outline is an essential part of essay writing. It serves as a guide for the reader throughout the essay.
All the information you have gathered so far needs to be organized. A rhetorical analysis outline can help you in this regard.
A rhetorical analysis essay uses the typical 5-paragraph outline. It has the following elements:
- Introduction
- Body Paragraphs
- Conclusion
Let us see what elements are added in these five parts of a rhetorical analysis essay.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Introduction
The introduction is the first part of an essay. This part of the essay must be made as attractive as possible.
The reader can perceive the whole idea of the essay by just reading the introduction. This is why this part should be interesting, as well as expressive.
Essay introduction usually starts with a hook sentence. The hook sentence is an attention-grabbing sentence that can be a quotation, fact, or even a question.
The most important part of the essay, the thesis statement, is stated in this part. It is stated somewhere before the last sentence of the introduction.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Body Paragraphs
Body paragraphs are the scene element in an outline and come after the introductory paragraph.
In these paragraphs, the writer elaborates on the key elements in detail. Usually, there are three body paragraphs in this type of academic essay.
Each body paragraph is written to explain a key element. All the facts and evidence the writer has collected for that point are also mentioned in that paragraph.
Keep in mind a topic sentence is used to start a paragraph. This sentence is just like a short introduction to the body paragraph. It gives the reader an idea about the element that will be discussed in the following paragraph.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Conclusion
After all the information is mentioned in the body paragraphs, the reader expects to see how you represent your final analysis. The writer is supposed to give the final verdict in the last part, which is the conclusion.
The conclusion is the shortest but the most technical part of an essay. In this part, the entire essay is summarized in such a way that all the key elements are once again revised.
Also, the thesis statement is reiterated but uses more convincing words.
In a rhetorical analysis essay conclusion, it should be mentioned how the main argument is proved right. The writer also presents the impact of the authorâs work on the audience in the past paragraph.
Make sure to look at the example below for more information.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Sample (PDF)
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Examples
To gain a better understanding of how to write a rhetorical analysis essay, it can be helpful to examine some examples. Here are a few notable examples that showcase the application of rhetorical analysis techniques:
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example (PDF)
A visual rhetorical analysis essay document communicates primarily through images or the interaction of image and text.
Here is an example of such an essay.
Visual Rhetorical Essay Example (PDF)
H3- Rh etorical Analysis Essay Example: AP Language
Rhetorical analysis done in AP Language and Composition is one of the biggest tasks a student can ever get. There are some specific tips that you need to follow for this purpose. Those major tips are mentioned below:
- Understand the Prompt
It is a must for this type of essay to understand the prompt to know what the task demands from you.
- Stick to the Format
The content for the rhetorical analysis should be properly organized and structured. The rhetorical analysis essay outline divides all the information into different sections such as introduction, body, and conclusion.
Look at the example given below and see how a well-written rhetorical analysis essay is written for AP language.
AP Rhetorical Analysis Essay (PDF)
Letter from Birmingham Jail Rhetorical Analysis Essay (PDF)
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Rubric (PDF)
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Format (PDF)
Comparative Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example (PDF)
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example High School (PDF)
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics
Writing an essay is easy, but finding a good topic to compose an essay on is the real deal. Similarly, writing a rhetorical analysis essay becomes very easy when a writer has a good topic in hand.
Here we have summed up some very good rhetorical analysis essay topics. One of them might help you to compose an impressive rhetorical analysis essay.
Easy Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics
- âI Am Prepared to Dieâ by Nelson Mandela
- Nobel Peace Prize Speech by Malala Yousafzai
- The Gettysburg Address by Abraham Lincoln
- âFull Power of Womenâ by Priyanka Chopra
- Emma Watsonâs speech on the Power of Women
- âIntegrityâ speech by Warren Buffet
- Freedom Speech from Braveheart
- Ending Scene from The Breakfast Club
- Maximusâ Speech to Commodus from Gladiator
- Oprahâs 2018 Golden Globes speech
High School Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics
- Rhetorical Analysis of âThe Olympic Gamesâ
- âNFL And the Concussion Rulesâ
- BCS or Playoffs
- AAU or NBA; which team has more fan following?
- Rhetorical Analysis of âFootball World Cupâ
- Kobe Bryant or LeBron
- Rhetorical Analysis of Presidential Sports Encomia
- Rhetorical Analysis of Symbolic Power of Sports
- The communication between the players and a coach.
- Rhetorical Analysis of the use of steroids
College Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics
- Importance of theme of hope in literature
- The fact does not support the rhetorical questions.
- A streetcar named desire.
- Conduct a rhetorical analysis of the Bible
- The key allegories are used in Daddy by Sylvia Plath.
- The absurdity of the Afterlife
- Do we laugh when someone tickles us?
- The year of magical thinking
- Rhetorical analysis of James Joyceâs Ulysses
- Analyze a piece of work from the Parks library
Tips to Write an Effective Rhetorical Analysis Essay
Writing a strong rhetorical analysis essay requires careful analysis, persuasive writing skills, and attention to detail.
Here are five tips to help you write an effective essay:
- Analyze the Rhetorical Situation
Before diving into the analysis, thoroughly understand the rhetorical situation. Consider the author, audience, purpose, and context of the text. This understanding will shape your analysis and help you identify the most relevant rhetorical devices.
- Focus on Key Rhetorical Devices
Identify and analyze the key rhetorical devices used in the text. Look for devices such as ethos, logos, pathos, rhetorical questions, metaphors, and analogies. Discuss how these devices contribute to the author's persuasive techniques and the overall effectiveness of the text.
- Provide Strong Evidence
Back up your analysis with strong evidence from the text. Quote specific passages, examples, or statistics to support your claims. Ensure that your evidence directly relates to the rhetorical devices and strategies you are discussing.
- Consider the Impact on the Audience
Evaluate how the rhetorical devices and strategies used in the text affect the target audience. Discuss the emotional, logical, and ethical appeals created by these devices and their potential influence on the readers or listeners.
- Structure and Coherence
Organize your essay in a logical and coherent manner. Use a clear introduction that provides context and presents your thesis statement. Develop body paragraphs that focus on specific rhetorical devices, supporting your analysis with evidence.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid While Writing a Rhetorical Analysis Essay
Writing a rhetorical analysis essay requires careful attention to detail and critical thinking. To ensure a successful essay, be mindful of these common pitfalls and avoid them:
- Summarizing Instead of Analyzing
One of the main pitfalls is falling into the trap of summarizing the text instead of analyzing it. Remember that your task is to dissect the rhetorical devices and strategies used by the author, not simply summarize the content of the text.
- Neglecting the Rhetorical Context
Failing to consider the rhetorical context of the text can weaken your analysis. Always take into account the author's purpose, intended audience, and the social, historical, or cultural context in which the text was produced.
- Lack of Focus
Stay focused on the main argument or thesis of your essay. Avoid going off on tangents or including irrelevant information. Every point you make should directly support your thesis and contribute to the overall analysis.
- Insufficient Evidence and Examples
To strengthen your analysis, provide ample evidence and examples from the text. Merely stating your interpretation is not enough; you need to back it up with specific quotes, examples, or references.
Overgeneralizing or Oversimplifying
Be cautious of overgeneralizing or oversimplifying the author's intent or the impact of rhetorical devices. Avoid making broad statements without proper evidence or disregarding the complexity of the text.
- Lack of Structure and Coherence
A poorly structured essay can undermine the effectiveness of your analysis. Ensure that your essay has a clear introduction, well-developed body paragraphs, and a concise conclusion.
- Neglecting Revision and Proofreading
Failing to revise and proofread your essay can lead to errors and inconsistencies. Take the time to review your essay, checking for grammar, spelling, and punctuation mistakes.
In conclusion, mastering the art of writing a rhetorical analysis essay can open doors to a deeper understanding of persuasive communication.
By following the outlined structure and incorporating the provided tips, you can confidently navigate the process and produce a compelling essay.
Now that you have a solid understanding of rhetorical analysis, it's time to put your knowledge into practice.
If you need assistance with your college essays or any other academic writing, consider trying our AI writing tool .
Our writing service consists of experienced writers who can provide professional essay help .
Visit our rhetorical analysis essay writing service today and take the first step towards academic success.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the elements of a rhetorical analysis.
The main elements of a rhetorical analysis essay are:
- Situation
- Audience
- Purpose
- Medium
- Context
How do you end a rhetorical analysis essay?
Here are some ways that help you to end the rhetorical analysis essay.
- Summarize the entire essay.
- Restate the thesis statement.
- Focus on the main ideas.
Cathy A. (Literature, Marketing)
For more than five years now, Cathy has been one of our most hardworking authors on the platform. With a Masters degree in mass communication, she knows the ins and outs of professional writing. Clients often leave her glowing reviews for being an amazing writer who takes her work very seriously.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Keep reading

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Organizing Your Analysis

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
There is no one perfect way to organize a rhetorical analysis essay. In fact, writers should always be a bit leery of plug-in formulas that offer a perfect essay format. Remember, organization itself is not the enemy, only organization without considering the specific demands of your particular writing task. That said, here are some general tips for plotting out the overall form of your essay.
Introduction
Like any rhetorical analysis essay, an essay analyzing a visual document should quickly set the stage for what you’re doing. Try to cover the following concerns in the initial paragraphs:
- Make sure to let the reader know you’re performing a rhetorical analysis. Otherwise, they may expect you to take positions or make an evaluative argument that may not be coming.
- Clearly state what the document under consideration is and possibly give some pertinent background information about its history or development. The intro can be a good place for a quick, narrative summary of the document. The key word here is “quick, for you may be dealing with something large (for example, an entire episode of a cartoon like the Simpsons). Save more in-depth descriptions for your body paragraph analysis.
- If you’re dealing with a smaller document (like a photograph or an advertisement), and copyright allows, the introduction or first page is a good place to integrate it into your page.
- Give a basic run down of the rhetorical situation surrounding the document: the author, the audience, the purpose, the context, etc.
Thesis Statements and Focus
Many authors struggle with thesis statements or controlling ideas in regards to rhetorical analysis essays. There may be a temptation to think that merely announcing the text as a rhetorical analysis is purpose enough. However, especially depending on your essay’s length, your reader may need a more direct and clear statement of your intentions. Below are a few examples.
1. Clearly narrow the focus of what your essay will cover. Ask yourself if one or two design aspects of the document is interesting and complex enough to warrant a full analytical treatment.
The website for Amazon.com provides an excellent example of alignment and proximity to assist its visitors in navigating a potentially large and confusing amount of information.
2. Since visual documents often seek to move people towards a certain action (buying a product, attending an event, expressing a sentiment), an essay may analyze the rhetorical techniques used to accomplish this purpose. The thesis statement should reflect this goal.
The call-out flyer for the Purdue Rowing Team uses a mixture of dynamic imagery and tantalizing promises to create interest in potential, new members.
3. Rhetorical analysis can also easily lead to making original arguments. Performing the analysis may lead you to an argument; or vice versa, you may start with an argument and search for proof that supports it.
A close analysis of the female body images in the July 2007 issue of Cosmopolitan magazine reveals contradictions between the articles’ calls for self-esteem and the advertisements’ unrealistic, beauty demands.
These are merely suggestions. The best measure for what your focus and thesis statement should be the document itself and the demands of your writing situation. Remember that the main thrust of your thesis statement should be on how the document creates meaning and accomplishes its purposes. The OWl has additional information on writing thesis statements.
Analysis Order (Body Paragraphs)
Depending on the genre and size of the document under analysis, there are a number of logical ways to organize your body paragraphs. Below are a few possible options. Which ever you choose, the goal of your body paragraphs is to present parts of the document, give an extended analysis of how that part functions, and suggest how the part ties into a larger point (your thesis statement or goal).
Chronological
This is the most straight-forward approach, but it can also be effective if done for a reason (as opposed to not being able to think of another way). For example, if you are analyzing a photo essay on the web or in a booklet, a chronological treatment allows you to present your insights in the same order that a viewer of the document experiences those images. It is likely that the images have been put in that order and juxtaposed for a reason, so this line of analysis can be easily integrated into the essay.
Be careful using chronological ordering when dealing with a document that contains a narrative (i.e. a television show or music video). Focusing on the chronological could easily lead you to plot summary which is not the point of a rhetorical analysis.
A spatial ordering covers the parts of a document in the order the eye is likely to scan them. This is different than chronological order, for that is dictated by pages or screens where spatial order concerns order amongst a single page or plane. There are no unwavering guidelines for this, but you can use the following general guidelines.
- Left to right and top to down is still the normal reading and scanning pattern for English-speaking countries.
- The eye will naturally look for centers. This may be the technical center of the page or the center of the largest item on the page.
- Lines are often used to provide directions and paths for the eye to follow.
- Research has shown that on web pages, the eye tends to linger in the top left quadrant before moving left to right. Only after spending a considerable amount of time on the top, visible portion of the page will they then scroll down.
Persuasive Appeals
The classic, rhetorical appeals are logos, pathos, and ethos. These concepts roughly correspond to the logic, emotion, and character of the document’s attempt to persuade. You can find more information on these concepts elsewhere on the OWL. Once you understand these devices, you could potentially order your essay by analyzing the document’s use of logos, ethos, and pathos in different sections.
The conclusion of a rhetorical analysis essay may not operate too differently from the conclusion of any other kind of essay. Still, many writers struggle with what a conclusion should or should not do. You can find tips elsewhere on the OWL on writing conclusions. In short, however, you should restate your main ideas and explain why they are important; restate your thesis; and outline further research or work you believe should be completed to further your efforts.
Free Rhetorical Analysis Generator
- 🌟 Intro to Rhetorical Analysis Generator
🤔 What Is Rhetorical Analysis?
- ✒️ Components of Rhetorical Analysis
- 💎 SOAPSTone Template
- 📝 Essay Outline
🔗 References
🌟 intro to our free rhetorical analysis generator.
Rhetoric refers to the use of language that helps motivate, persuade, or get the point across to a particular audience. Rhetorical analysis involves studying and evaluating strategies authors and speakers use to achieve this goal. Here, you’ll learn how to use our generator, the fundamentals of rhetorical analysis, and the components of making a great essay.
Rhetorical Analysis Generator & Reasons to Try
It’s not always easy to conduct a good rhetorical analysis. Many students struggle with it and may even fail to submit their work on time. Our rhetorical analysis generator is here to help! It has many benefits that help you finish your work faster:
A rhetorical analysis evaluates a piece of work and the effectiveness with which the author communicated their ideas. It can be anything from a novel to a movie, as long as the work wants to persuade an audience. In other words, instead of discussing the events of The Count of Monte Cristo, you explore what Alexander Dumas wanted to tell his readers, which techniques were used to convey the message, and whether it was successful.
11 Common Rhetorical Analysis Devices
Look at some of the most popular rhetorical devices you can encounter in written and spoken works. They will help you better identify and include them in your upcoming papers.
✒️ Rhetorical Analysis Components & Their Meaning
You can come across several rhetorical analysis methods in your professional and academic work. The rhetorical triangle is the most popular type but has several lesser-known subtypes.
Its components are:
- Ethos . This notion appeals to the author or speaker’s credibility. It evaluates a person’s authority on a subject and tells the audience if they should trust them.
- Pathos . Pathos deals with emotions. It’s the most effective rhetorical device as it’s used to connect the speaker and the audience. For example, an emotional appeal over the use of facts is a tell-tale sign of propaganda.
- Logos . This element backs up a claim with logical and reasonable substance. Through it, the author provides factual evidence that supports their claims.
- Kairos . When a writer or a speaker addresses a particular time and place, they use kairos to provide specific context. To illustrate, an address concerning the First Amendment is most effective during a political debate.
- Stasis . The final segment of the rhetorical analysis lets people view arguments from different perspectives. This adds an impact and makes the audience more likely to side with the writer or speaker.
💎 Rhetorical Analysis: SOAPSTone Template
Like any analysis, evaluating a person’s rhetorical capabilities requires structure. Without it, you may fail to address some aspects of the work, making your paper incomplete. You can make this process easier with the SOAPSTone template and its components:
📝 Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline
Writing any type of essay requires structure and cohesion. While you may have encountered this structure before, it’s worth to remember the basics. A rhetorical analysis paper outline requires the following elements:
- Introduction . This paragraph introduces the text and its author. Some experts recommend including a summary of the work and elements of the SOAPStone analysis you uncovered. Explain why you’re conducting the research and give a clear thesis statement.
- Body . The section where you present arguments about work and what makes it persuasive. Here you discuss the methods, strategies, and rhetorical and literary devices the author used to convey their message.
- Conclusion . The conclusive paragraph ties your analysis together by driving home the main arguments provided in its body. It can also explain how the work impacted society or its target audience.
3 Good Rhetorical Analysis Essay Examples
Here we have picked up some samples with rhetorical analysis of different types of works that can inspire you to create own impressive essay.
- Rhetorical Analysis of Paypal’s Online Payments Commercial Essay . PayPal's online payments commercial employs a potent blend of rhetorical techniques to convey its message effectively. The ad emotionally connects with the audience through vibrant visuals, stirring music, and relatable scenarios. Using real-life situations highlights the convenience and security of PayPal's services, appealing to the ethos and building trust. Additionally, persuasive language and a call to action stimulate a sense of urgency, prompting viewers to adopt PayPal as their preferred online payment platform. By artfully combining pathos, ethos, and logos, the commercial convinces viewers that PayPal is a trustworthy and convenient decision for their online payment requirements.
- “The Myth of Multitasking” by Rosen: Rhetorical Analysis Essay . The author adeptly employs rhetorical strategies to debunk the notion of multitasking. Christine Rosen dismantles the prevalent belief in multitasking efficiency through persuasive arguments and compelling evidence, revealing its detrimental effects on productivity and cognitive abilities. Her skillful use of logic and reasoning challenges readers to question their habits and consider a more focused approach to tasks. By strategically dismantling this cultural trend, Rosen urges her audience to reassess their attitudes toward multitasking, prompting a profound reevaluation of its impact on daily life and productivity.
- A Rhetorical Analysis: “Chevy Commercial 2014” Essay . Chevy Commercial from 2014 is a captivating piece of rhetoric that skillfully employs various persuasive techniques to resonate with its audience. The ad establishes an immediate connection with viewers through emotional storytelling. The commercial artfully weaves heartwarming scenes of people's lives, accompanied by an inspiring soundtrack, evoking a sense of nostalgia and relatability. Ethos is reinforced by showcasing real people in everyday situations, enhancing the credibility of Chevy's brand positioning as an integral part of consumers' lives. Furthermore, logos strategically highlights the car's innovative features and performance. By aligning Chevy with moments of happiness and adventure, the ad compels viewers to consider Chevy as the vehicle that can accompany them on their life journeys.
We hope our tool will facilitate your rhetorical analysis of books, commercials, or speeches, so you'll create a unique essay! Besides, you may try our hook generator to engage the audience to read your paper from the beginning.
📌 Rhetorical Analysis Generator – FAQ
Updated: Oct 25th, 2023
- Rhetorical Analysis – Jessica Allee, University of Arkansas
- How To Write a Rhetorical Analysis in 8 Simple Steps – Jennifer Herrity, Indeed
- Rhetorical Analysis – Blinn College District
- What Is a Rhetorical Device? Definition, List, Examples – Jeffrey Somers, ThoughtCo
- Rhetorical Analysis Essay: Formatting – Brandon Everett, California State University, East Bay
- What is Rhetorical Analysis? – Melanie Gagich & Emilie Zickel, PressBooks
- SOAPStone Graphic Organizer for Rhetorical Analysis – Sacramento City Unified School District
- Free Essays
- Writing Tools
- Lit. Guides
- Donate a Paper
- Referencing Guides
- Free Textbooks
- Tongue Twisters
- Job Openings
- Expert Application
- Video Contest
- Writing Scholarship
- Discount Codes
- IvyPanda Shop
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Copyright Principles
- DMCA Request
- Service Notice
This page contains a free tool for conducting rhetorical analysis. It is user-friendly, accurate, and fast. You can customize the analysis according to your text type and context. Also, we have prepared a guide where you can find out about literary devices, components of rhetorical analysis, and the structure of your future essay.

IMAGES
VIDEO