
- 1-844-994-6376
- [email protected]


The Guide to Becoming a Medical Researcher
- February 1, 2023
Share Post:
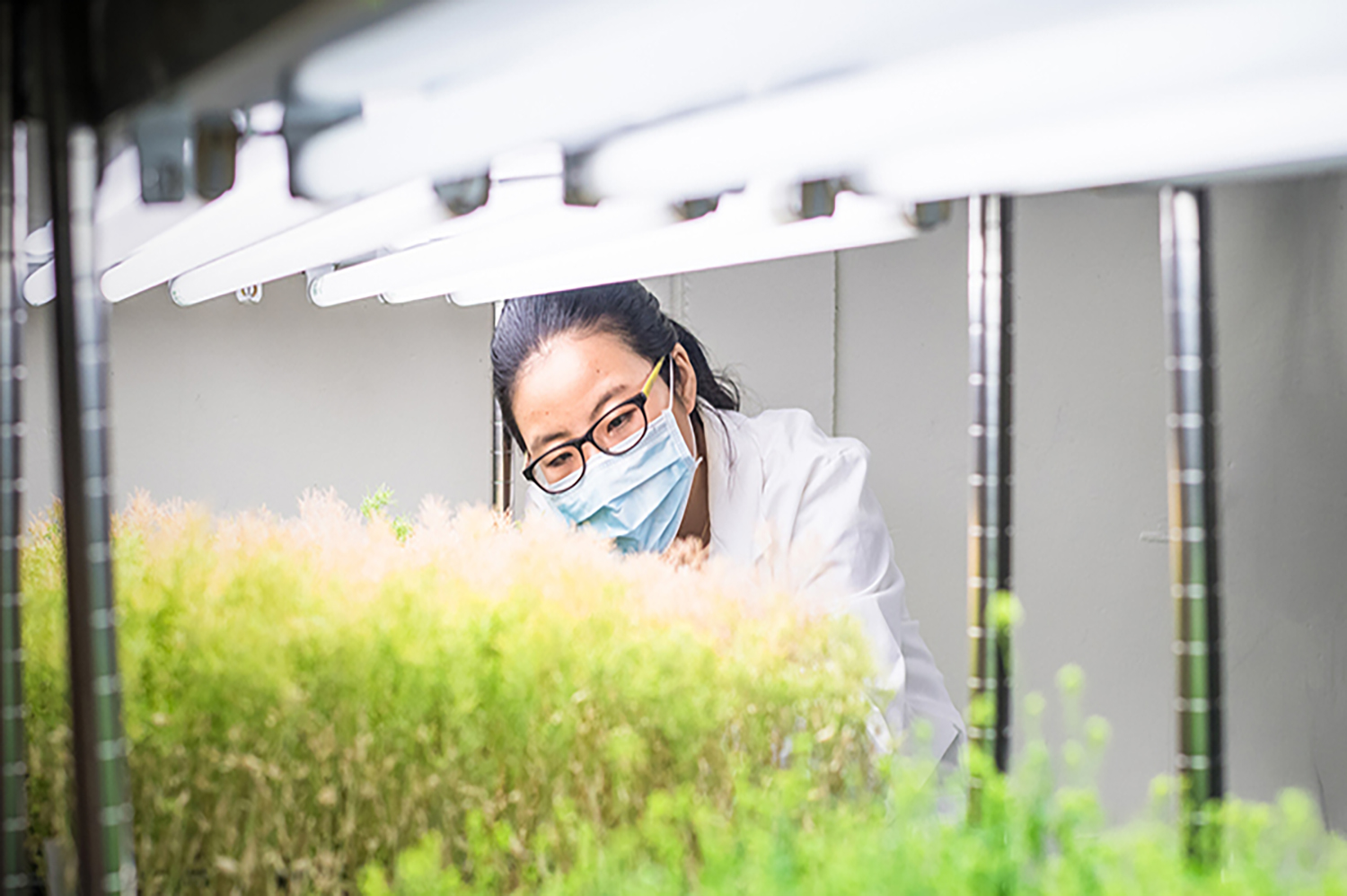
As a medical researcher, your job is to conduct research to improve the health status and longevity of the population. The career revolves around understanding the causes, treatments, and prevention of diseases and medical conditions through rigorous clinical investigations, epidemiological studies, and laboratory experiments. As a medical researcher, simply gaining formal education won’t suffice. You also need to hone your communication, critical thinking, decision-making, data collecting, data analyzing and observational skills. These skill sets will enable you to create a competitive edge in the research industry. On a typical day, a medical researcher would be collecting, interpreting, and analyzing data from clinical trials, working alongside engineering, regulatory, and quality assurance experts to evaluate the risk of medical devices, or maybe even preparing and examining medical samples for causes or treatments of toxicity, disease, or pathogens.
How To Become a Medical Research Doctor?
The roadmap to medical research is a bit tricky to navigate, because it is a profession that demands distinctive skills and expertise along with mandatory formal education. If you harbor an interest in scientific exploration and a desire to break new ground in medical knowledge, the first step is to earn a bachelor’s degree in a related field, such as biology, chemistry, or biochemistry. After completing your undergraduate education, you will need to earn a Medical Degree ( MD ) or a Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine (DO) degree, from a quality institution such as the Windsor university school of Medicine.
After that, the newly minted doctor of medicine (MD) may choose to complete a three-year residency program in a specialty related to medical research, such as internal medicine, pediatrics, or neurology, in addition to a doctor of philosophy (PhD) degree—the part that provides the research expertise. In some medical school programs, students may pursue a dual MD-PhD at the same time, which provides training in both medicine and research. They are specifically designed for those who want to become research physicians. Last but not the least, all physician-scientists must pass the first two steps of the United States Medical Learning Examination (USMLE).
Use your fellowship years to hone the research skills necessary to carry out independent research. You may also take courses in epidemiology, biostatistics, and other related fields. In order to publish your research in peer-reviewed journals to establish yourself as a medical researcher. To apply for a faculty position at a medical school, research institute, or hospital. To maintain your position as a medical research doctor, you must publish your research and make significant contributions to the field.
How Much Do Medical Researchers Make?
Having a clear idea of what to earn when you become a medical researcher can help you decide if this is a good career choice for you. The salaries of Medical Researchers in the US range from $26,980 to $155,180, with a median salary of $82,240. There is also room for career advancement and higher earning potential as you gain experience.
The Most Popular Careers in Medical Research
- Medical Scientists – conduct research and experiments to improve our understanding of diseases and to develop new treatments. They also develop new medical technologies and techniques.
- Biomedical engineers – design medical devices, such as pacemakers, prosthetics, and imaging machines. They also develop and improve existing medical technologies.
- Clinical Trial Coordinators – oversee and manage clinical trials, which test new drugs and treatments. They are responsible for recruiting participants, collecting and analyzing data, and ensuring the trial is conducted in compliance with ethical standards.
- Medical Laboratory Technicians – analyze bodily fluids and tissues to diagnose diseases and conditions. They perform tests using specialized equipment and techniques, and report results to physicians.
- Biostatisticians – collect statistics to analyze data and test hypotheses in medical research. They design and analyze clinical trials, and use statistical models to understand the causes and effects of diseases.
- Epidemiologists – study the causes, distribution, and control of diseases in populations. They collect and analyze data, and use their findings to develop strategies for preventing and controlling diseases.
- Pathologists – diagnose diseases by examining tissues and bodily fluids. They use microscopes and other diagnostic tools to identify and study the changes in tissues caused by disease.
- Genetic Counselors – help individuals understand and manage the risks associated with inherited genetic disorders. They educate patients about genetic tests and help families make informed decisions about their health.
- Health Services Researchers – study the delivery of healthcare and identify ways to improve it.
- Medical writers – write articles, reports, and other materials related to medical research.
- Microbiologists – study microorganisms, including bacteria and viruses, to understand their behavior and impact on human health.
- Neuroscientists – study the brain and nervous system to understand the underlying causes of neurological conditions.
- Toxicologists – study the effects of toxic substances on living organisms and the environment.
Skills You Need to Become a Medical Researcher?
To be a successful medical scientist, you need a range of soft and hard skills to excel in your work. First things first, medical researchers must be able to analyze data, identify patterns, and draw conclusions from their findings. They must be able to think critically, ask relevant questions, and design experiments to answer those questions. Additionally, you should also have the knack of articulating your findings clearly and effectively, be it writing research papers, grant proposals, or technical reports that are clear, concise, and free from errors.
Medical researchers must be proficient in using various computer programs and software to collect, manage, analyze and interpret research data. They must be able to use laboratory equipment and techniques, as well as statistical analysis software and other tools for data analysis. Since medical research involves precise and meticulous work, so you must also pay close attention to detail to ensure that your findings are accurate and reliable. Not to mention, medical researchers often work in teams, so it pays off if you are good at collaborating with others effectively, sharing ideas, and working together to solve complex problems.
Lastly, medical researchers must have a thorough understanding of regulations and ethical guidelines that govern research, such as obtaining informed consent from study participants, ensuring data confidentiality, and adhering to safety protocols.
Related posts

10 Surprising Traits Caribbean Medical Schools Look for in Applicants

Doctor in the Making? Questions Every Aspiring Physician Needs to Ask

Medical School Clerkships – What You Need to Know About?
Start online application.

Latest Post
Most viewed.
Embarking on the journey to become a medical professional is both exhilarating and challenging. Aspiring doctors not only face the rigorous academic demands of medical
Are you planning to become a physician? Choosing the right medical school is an important decision. It’s not just about the prestige or location; it’s
What are medical school clerkships? This is one of the most frequently asked questions WUSOM admission committee often hears from medical school applicants. To put
Follow us on Twitter

St. Kitts Campus Windsor University School of Medicine 1621 Brighton’s Estate, Cayon St. Kitts, West Indies Call: 1.844.994.6376 Email: [email protected]
U.S. Information Office Royal Medical & Technical Consultants Inc. Suite # 303 20646 Abbey Wood Ct. Frankfort, IL 60423 United States Call: 1 708 235 1940 Email: [email protected]
Copyrights © Windsor University School of Medicine 2024. All rights reserved.
- Job Search Advice
- Interviewing
- Login/Register
- Career Profiles and Employment Projections
- Medical Scientists: Jobs, Career, Salary and Education Information
Medical Scientists
Career, salary and education information.
What They Do : Medical scientists conduct research aimed at improving overall human health.
Work Environment : Medical scientists work in offices and laboratories. Most work full time.
How to Become One : Medical scientists typically have a Ph.D., usually in biology or a related life science. Some medical scientists get a medical degree instead of, or in addition to, a Ph.D.
Salary : The median annual wage for medical scientists is $95,310.
Job Outlook : Employment of medical scientists is projected to grow 17 percent over the next ten years, much faster than the average for all occupations.
Related Careers : Compare the job duties, education, job growth, and pay of medical scientists with similar occupations.
Following is everything you need to know about a career as a medical scientist with lots of details. As a first step, take a look at some of the following jobs, which are real jobs with real employers. You will be able to see the very real job career requirements for employers who are actively hiring. The link will open in a new tab so that you can come back to this page to continue reading about the career:
Top 3 Medical Scientist Jobs
Title: Medical Science Liaison, Northeast Region Location: Remote About Us: Vera Therapeutics (Nasdaq: VERA), is a late-stage biotechnology company focused on developing treatments for serious ...
The Position We are seeking an experienced cardiometabolic Medical Science Liaison (MSL) to join an exciting opportunity within our Medical Affairs (MA) team and work in a dynamic and collaborative ...
Following regulatory and corporate guidelines, they will facilitate and build scientific relationships and collaborations with the medical / scientific community. This position interacts with local ...
See all Medical Scientist jobs
What Medical Scientists Do [ About this section ] [ To Top ]
Medical scientists conduct research aimed at improving overall human health. They often use clinical trials and other investigative methods to reach their findings.
Duties of Medical Scientists
Medical scientists typically do the following:
- Design and conduct studies that investigate both human diseases and methods to prevent and treat them
- Prepare and analyze medical samples and data to investigate causes and treatment of toxicity, pathogens, or chronic diseases
- Standardize drug potency, doses, and methods to allow for the mass manufacturing and distribution of drugs and medicinal compounds
- Create and test medical devices
- Develop programs that improve health outcomes, in partnership with health departments, industry personnel, and physicians
- Write research grant proposals and apply for funding from government agencies and private funding sources
- Follow procedures to avoid contamination and maintain safety
Many medical scientists form hypotheses and develop experiments, with little supervision. They often lead teams of technicians and, sometimes, students, who perform support tasks. For example, a medical scientist working in a university laboratory may have undergraduate assistants take measurements and make observations for the scientist's research.
Medical scientists study the causes of diseases and other health problems. For example, a medical scientist who does cancer research might put together a combination of drugs that could slow the cancer's progress. A clinical trial may be done to test the drugs. A medical scientist may work with licensed physicians to test the new combination on patients who are willing to participate in the study.
In a clinical trial, patients agree to help determine if a particular drug, a combination of drugs, or some other medical intervention works. Without knowing which group they are in, patients in a drug-related clinical trial receive either the trial drug or a placebo—a pill or injection that looks like the trial drug but does not actually contain the drug.
Medical scientists analyze the data from all of the patients in the clinical trial, to see how the trial drug performed. They compare the results with those obtained from the control group that took the placebo, and they analyze the attributes of the participants. After they complete their analysis, medical scientists may write about and publish their findings.
Medical scientists do research both to develop new treatments and to try to prevent health problems. For example, they may study the link between smoking and lung cancer or between diet and diabetes.
Medical scientists who work in private industry usually have to research the topics that benefit their company the most, rather than investigate their own interests. Although they may not have the pressure of writing grant proposals to get money for their research, they may have to explain their research plans to nonscientist managers or executives.
Medical scientists usually specialize in an area of research within the broad area of understanding and improving human health. Medical scientists may engage in basic and translational research that seeks to improve the understanding of, or strategies for, improving health. They may also choose to engage in clinical research that studies specific experimental treatments.
Work Environment for Medical Scientists [ About this section ] [ To Top ]
Medical scientists hold about 119,200 jobs. The largest employers of medical scientists are as follows:
Medical scientists usually work in offices and laboratories. They spend most of their time studying data and reports. Medical scientists sometimes work with dangerous biological samples and chemicals, but they take precautions that ensure a safe environment.
Medical Scientist Work Schedules
Most medical scientists work full time.
How to Become a Medical Scientist [ About this section ] [ To Top ]
Get the education you need: Find schools for Medical Scientists near you!
Medical scientists typically have a Ph.D., usually in biology or a related life science. Some medical scientists get a medical degree instead of, or in addition to, a Ph.D.
Education for Medical Scientists
Students planning careers as medical scientists generally pursue a bachelor's degree in biology, chemistry, or a related field. Undergraduate students benefit from taking a broad range of classes, including life sciences, physical sciences, and math. Students also typically take courses that develop communication and writing skills, because they must learn to write grants effectively and publish their research findings.
After students have completed their undergraduate studies, they typically enter Ph.D. programs. Dual-degree programs are available that pair a Ph.D. with a range of specialized medical degrees. A few degree programs that are commonly paired with Ph.D. studies are Medical Doctor (M.D.), Doctor of Dental Surgery (D.D.S.), Doctor of Dental Medicine (D.M.D.), Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine (D.O.), and advanced nursing degrees. Whereas Ph.D. studies focus on research methods, such as project design and data interpretation, students in dual-degree programs learn both the clinical skills needed to be a physician and the research skills needed to be a scientist.
Graduate programs emphasize both laboratory work and original research. These programs offer prospective medical scientists the opportunity to develop their experiments and, sometimes, to supervise undergraduates. Ph.D. programs culminate in a dissertation that the candidate presents before a committee of professors. Students may specialize in a particular field, such as gerontology, neurology, or cancer.
Those who go to medical school spend most of the first 2 years in labs and classrooms, taking courses such as anatomy, biochemistry, physiology, pharmacology, psychology, microbiology, pathology, medical ethics, and medical law. They also learn how to record medical histories, examine patients, and diagnose illnesses. They may be required to participate in residency programs, meeting the same requirements that physicians and surgeons have to fulfill.
Medical scientists often continue their education with postdoctoral work. This provides additional and more independent lab experience, including experience in specific processes and techniques, such as gene splicing. Often, that experience is transferable to other research projects.
Licenses, Certifications, and Registrations for Medical Scientists
Medical scientists primarily conduct research and typically do not need licenses or certifications. However, those who administer drugs or gene therapy or who otherwise practice medicine on patients in clinical trials or a private practice need a license to practice as a physician.
Medical Scientist Training
Medical scientists often begin their careers in temporary postdoctoral research positions or in medical residency. During their postdoctoral appointments, they work with experienced scientists as they continue to learn about their specialties or develop a broader understanding of related areas of research. Graduates of M.D. or D.O. programs may enter a residency program in their specialty of interest. A residency usually takes place in a hospital and varies in duration, generally lasting from 3 to 7 years, depending on the specialty. Some fellowships exist that train medical practitioners in research skills. These may take place before or after residency.
Postdoctoral positions frequently offer the opportunity to publish research findings. A solid record of published research is essential to getting a permanent college or university faculty position.
Work Experience in a Related Occupation for Medical Scientists
Although it is not a requirement for entry, many medical scientists become interested in research after working as a physician or surgeon , or in another medical profession, such as dentist .
Important Qualities for Medical Scientists
Communication skills. Communication is critical, because medical scientists must be able to explain their conclusions. In addition, medical scientists write grant proposals, because grants often are required to fund their research.
Critical-thinking skills. Medical scientists must use their expertise to determine the best method for solving a specific research question.
Data-analysis skills. Medical scientists use statistical techniques, so that they can properly quantify and analyze health research questions.
Decisionmaking skills. Medical scientists must determine what research questions to ask, how best to investigate the questions, and what data will best answer the questions.
Observation skills. Medical scientists conduct experiments that require precise observation of samples and other health-related data. Any mistake could lead to inconclusive or misleading results.
Medical Scientist Salaries [ About this section ] [ More salary/earnings info ] [ To Top ]
The median annual wage for medical scientists is $95,310. The median wage is the wage at which half the workers in an occupation earned more than that amount and half earned less. The lowest 10 percent earned less than $50,100, and the highest 10 percent earned more than $166,980.
The median annual wages for medical scientists in the top industries in which they work are as follows:
Job Outlook for Medical Scientists [ About this section ] [ To Top ]
Employment of medical scientists is projected to grow 17 percent over the next ten years, much faster than the average for all occupations.
About 10,000 openings for medical scientists are projected each year, on average, over the decade. Many of those openings are expected to result from the need to replace workers who transfer to different occupations or exit the labor force, such as to retire.
Employment of Medical Scientists
Demand for medical scientists will stem from greater demand for a variety of healthcare services as the population continues to age and rates of chronic disease continue to increase. These scientists will be needed for research into treating diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease and cancer, and problems related to treatment, such as resistance to antibiotics. In addition, medical scientists will continue to be needed for medical research as a growing population travels globally and facilitates the spread of diseases.
The availability of federal funds for medical research grants also may affect opportunities for these scientists.
Careers Related to Medical Scientists [ About this section ] [ To Top ]
Agricultural and food scientists.
Agricultural and food scientists research ways to improve the efficiency and safety of agricultural establishments and products.
Biochemists and Biophysicists
Biochemists and biophysicists study the chemical and physical principles of living things and of biological processes, such as cell development, growth, heredity, and disease.
Epidemiologists
Epidemiologists are public health professionals who investigate patterns and causes of disease and injury in humans. They seek to reduce the risk and occurrence of negative health outcomes through research, community education, and health policy.
Health Educators and Community Health Workers
Health educators teach people about behaviors that promote wellness. They develop and implement strategies to improve the health of individuals and communities. Community health workers collect data and discuss health concerns with members of specific populations or communities.
Medical and Clinical Laboratory Technologists and Technicians
Medical laboratory technologists (commonly known as medical laboratory scientists) and medical laboratory technicians collect samples and perform tests to analyze body fluids, tissue, and other substances.
Microbiologists
Microbiologists study microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, algae, fungi, and some types of parasites. They try to understand how these organisms live, grow, and interact with their environments.
Physicians and Surgeons
Physicians and surgeons diagnose and treat injuries or illnesses. Physicians examine patients; take medical histories; prescribe medications; and order, perform, and interpret diagnostic tests. They counsel patients on diet, hygiene, and preventive healthcare. Surgeons operate on patients to treat injuries, such as broken bones; diseases, such as cancerous tumors; and deformities, such as cleft palates.
Postsecondary Teachers
Postsecondary teachers instruct students in a wide variety of academic and technical subjects beyond the high school level. They may also conduct research and publish scholarly papers and books.
Veterinarians
Veterinarians care for the health of animals and work to improve public health. They diagnose, treat, and research medical conditions and diseases of pets, livestock, and other animals.
More Medical Scientist Information [ About this section ] [ To Top ]
For more information about research specialties and opportunities within specialized fields for medical scientists, visit
American Association for Cancer Research
American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
The American Society for Clinical Laboratory Science
American Society for Clinical Pathology
American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics
The Gerontological Society of America
Infectious Diseases Society of America
National Institute of General Medical Sciences
Society for Neuroscience
Society of Toxicology
A portion of the information on this page is used by permission of the U.S. Department of Labor.
Explore more careers: View all Careers or the Top 30 Career Profiles
Search for jobs:.
How to Become a Medical Researcher
Home / Medical / How to Become a Medical Researcher
Trending Careers

The medical industry heavily relies on the specialized work provided by Medical Researchers.
These professionals are at the forefront of medical advancements to develop treatments, medicines and possible cures for a variety of medical diseases and disorders.
Some common medical maladies and diseases Medical Researchers may study and investigate include: cancer, diabetes, Alzheimer’s and the medicines and treatments being developed for these disorders.
Individuals who want to become a Medical Researcher will need an extensive medical background, postsecondary degree and skills in data analysis in order to succeed in this profession.
Table of Contents
Education Requirements to Become a Medical Researcher
Medical researcher job description, national average salary, average salary by state.
These are the top 5 earning states in the field:
What does a medical researcher do?
How much does a medical researcher make, how much does it cost to become a medical researcher, what is the demand for medical researchers, how long does it take to become a medical researcher.
Individuals who want to become a Medical Researcher will need a strong background in medicine and complete required postsecondary degrees in order to enter this profession.
Medical Researchers will also have to attend medical school to attain a PhD in Biomedical Sciences or a Medical Degree (MD).
A medical license is a requirement for individuals who want to do medical research and treat patients.
As undergraduates, individuals who want to become a Medical Researcher will need pursue a degree in a science related field.
Some typical degrees individuals can seek include biology, chemistry and microbiology.
It is also highly recommended that undergraduates take classes in writing and English in order to develop skills useful in research and grant writing.
Other helpful courses include: mathematics, physical science and life sciences.
As graduate students, individuals who want to become a Medical Researcher have the option to pursue a PhD program or a dual program that combines a PhD and a medical degree.
Medical degree/PhD programs provide training in both research and medicine.
Under these dual programs, individuals can combine a PhD with the following degrees: Medical Doctor (M.D.), Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine (D.O.) or Doctor of Dental Medicine (DMD).
Traditional PhD programs are approximately 4 years in length and focus more on laboratory work and an individual’s own research.
During this phase, students will have the opportunity to focus on a specialization such as: cancers, neurology or gerontology.
Individuals will also be given the opportunity to supervise undergraduate students.
Students will also work in depth on their original research and prepare for a thesis reporting on their findings.
A thesis is a written hypothesis focusing on a student’s research that needs to be presented to a committee of professors.
Medical Researchers are highly educated professionals who work in the medical field providing research that help improve human health.
These professionals will spend their time researching medical problems, writing grants to keep their projects funded and write reports on their findings.
Some laboratory work includes developing and managing studies that help understand a variety of human ailments.
They will also investigate preventative care and treatment for the diseases they research.
They will work with medical samples and information to determine the causes and treatments.
Medical Researchers also work in conjunction with a variety of professionals such as industry experts, doctors and health departments to create programs that improve a population’s health.
Medical Researcher Salary and Career Path
In 2012, the median salary for Medical Researchers and Scientists was approximately $76,980 per year.
Exact wages will depend on a variety of factors including industry, level of experience and company size.
For example, Medical Researchers who work for state colleges, universities or professional schools earn an annual median salary of approximately $53,740 while individuals who work for pharmaceutical and medicine production companies earn a median income of approximately $92,940 per year.
The job outlook for Medical Researchers is expected to grow by 13 percent through the year 2022.
This job growth is expected to grow as fast as average when compared to other professions and is attributed to the increased demand for research into illnesses such as cancer, AIDS and Alzheimer’s.
In addition, Medical Researchers are also needed to study treatments and medicines such as resistance to antibiotics.
Clearly, this profession is one that many people depend on to help solve medical problems.
A career in Medical Research may be a great path for individuals who would like to work in medicine, but not directly treat patients.
This career gives individuals the opportunity to help make advancements in medicine, work in a challenging environment and work in one of the fastest growing industries.
The top earning state in the field is Massachusetts, where the average salary is $118,880.
The top earning state in the field is Massachusetts, where the average salary is $9,833.
The top earning state in the field is Massachusetts, where the average salary is $57.15.
Frequently Asked Questions
Medical researchers study diseases and try to find new treatments and ways of preventing illness in order to help improve human health.
They usually work in offices and laboratories and spend most of their time studying data and writing reports.
Medical researchers sometimes work with dangerous samples and chemicals and this is why they have to follow strict safety and sanitation procedures.
The exact job requirements vary depending on the field of employment.
Some medical researchers design and conduct studies to investigate a particular disease while others create and test medical devices.
As a medical researcher, you may also have to apply for funding for a particular research project.
To become a medical researcher you need not only a strong scientific background but also several important skills, such as dexterity, attention to detail, research, writing and communication skills.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual wage for medical scientists, in general, was $84,810 as of May 2018.
However, salaries in this field vary widely depending on the field of employment.
For example, those who work from the pharmaceutical and manufacturing field earned a median wage of $115,450 a year, while those who work in hospitals earned a median wage of $87,060 a year as of May 2018.
In order to become a medical researcher, you will usually need a bachelor’s degree in biology, chemistry, biotechnology or a related field and a Ph.D. in the field in which you want to specialize.
A four-year bachelor’s degree program can cost you anywhere between $5,000 and more than $30,000 a year.
Ph.D. programs usually focus on teaching students how to interpret data and how to design a research project, skills that are very important for medical scientists.
Some schools also offer dual programs that teach both the clinical skills needed to become a physician and the research skills needed if you decide to work in a lab.
Research-based Ph.D. programs cost, on average, around $35,000-$40,000 a year but tuition costs vary widely depending on the school you choose.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, employment of medical scientists is expected to grow 8 percent from 2018 to 2028, faster than the average for all occupations.
This growth is explained in part by the fact that more people are diagnosed with chronic conditions and rely on medical treatment to help control their illnesses.
Job prospects should be especially good for researchers who specialize in studying diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease, AIDS or cancer.
Medical researchers usually hold a bachelor’s degree in science and a Ph.D. in the field in their specialty.
While a bachelor’s degree can be earned after 4 years of post-secondary study, Ph.D. programs typically take 5-6 years.
This means that medical researchers may need up to 10 years of training beyond high school.
Related Careers

Clinical researchers plan and monitor trials to test how effective and safe new medical inventions are.

A cancer researcher conducts studies designed to answer specific questions about cancer.

Medical Assistant is responsible for a variety of patient care, technical, and clerical related functions.
Medical technicians, work closely with nurses to provide quality care for patients.
One thought on “ How to Become a Medical Researcher ”
I’m just from graduating from college and I’m looking for an university which offers medical research courses with full scholarship.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Careers in Biomedical Research
New section.
Learn more about careers in medical research.

If you have an interest in scientific exploration and a desire to break new ground in medical knowledge, a career in medical research might be for you.
MD-PhD programs provide training in both medicine and research. They are specifically designed for those who want to become research physicians.
The AAMC MD-PhD section is committed to recruiting and training a diverse Physician-Scientist workforce and an inclusive learning and working environment.

Biomedical scientists bridge the gap between the basic sciences and medicine. The PhD degree is the gateway to a career in biomedical research.

Starting a career in medical research
If you have the intellectual and emotional resilience, also if you wish to contribute to the body of knowledge in medical sciences then you are a right candidate for a career in Medical Research. Devising and conducting experiments, investigating the epidemiological basis of a disease, working in collaboration with a team, ability to question intricate complexities of genome and proteome and effective written and oral communication skills are the chief qualities of an inborn medical researcher. If the following description sounds like you, then you are probably well suited for a career as a medical researcher.
Qualifications to become a medial researcher
The roadmap to medical researcher is complex because it’s a profession that demands distinctive skills and expertise along with mandatory formal education. The simplest formal degree requirement is minimum Masters or a Ph.D. For an outstanding career as a medical researcher, a Ph.D. will help you to go the distance in an academic career. There is right now an extraordinarily extensive overabundance of post-doctoral partnerships battling for an exceptional set number of lasting scholarly positions. Having said that, accomplishing a PhD in a science subject will stand you in great stead for various research positions. You can pursue a career in medical research by obtaining a formal education in either biological sciences or medicine however; medicine can broaden your options. Furthermore, after earning a formal education in either biology or medicine, the next milestone towards the development of a career in medical research is participating in a research-based internship. In most graduate schools, participating in a research internship and undertaking a research project is the part of the exclusively designed curriculum. This opportunity will allow you to get a chance to be mentored by a physician or research scientist where you can work in collaboration with the team on the ongoing research project.
In order to escalate to the position of the medical researcher, it is integral to complete an advanced degree program in either science or medicine. According to the US Bureau Labor Statistics (BLS), postgraduates and graduates with dual undergraduate degrees become successful candidates for the job positions.
After completing your advanced education, as a medical researcher you can start your aspiring and a challenging career with entry-level positions of medical research associate. As an associate, you are required to assist a scientist in devising, planning and conducting research trials. You can add something extraordinary to your resume by earning credentials offered to research professionals by regulatory bodies. Credential based certifications are not only going to prepare you for some verifiable skills needed in the career but will also aid you in advancing your career path to medical research.
The job role
As a medical researcher, it is your utmost responsibility to conduct research to improve the health status and longevity of the population. The career revolves around clinical investigations to understand human diseases and rigorous lab work. As a medical researcher, formal education will not suffice. As a developing medical researcher, you need to have effective communication, critical thinking, decision-making, data collecting, data analysing and observational skills. These skill sets will enable you to create a competitive edge in the research industry.
Your interest in scientific exploration and a desire to provide a breakthrough in medical knowledge will help you to explore and solve some unknown mysteries associated with complex diseases.
Share this article
Related articles

Best universities for biomedical science in the UK - A New Scientist Careers Guide

How to become a Clinical Scientist - A New Scientist Careers Guide

How to become an oncologist - A New Scientist Careers Guide
Latest articles.
- Programs and Courses
- Explore Programs
- Find Courses
- Careers and Relevant NC State Programs
- How to Apply
- Graduate Students
- Non-Degree Studies
- International Students
- Military and Veterans
- Affordability
- Tuition and Fees
- Financial Aid
- Student Resources
- State Authorization
- Professional Licensure
- Student Complaint and Grievance Process
- Faculty and Staff
- Frequently Asked Questions

Science and Research
- Health Physics Graduate Certificates
- Microbiology Undergraduate Certificates
Medical Research Scientist
What does a professional in this career do.
A Medical Research Scientist conducts research with the goal of understanding diseases and improving human health. May study biology and causes of health problems, assess effectiveness of treatments or develop new pharmaceutical products. May direct clinical trials to gather data..
Job Outlook
There were 186 Medical Research Scientist job postings in North Carolina in the past year and 8563 in the United States.
In combination with other careers in the Medical Scientist industry, which includes the Medical Research Scientist career, the following graph shows the number of people employed for each year since 2015:
Many new Medical Research Scientist jobs have salaries estimated to be in the following ranges, based on the requirements and responsibilities listed in job postings from the past year.
The average estimated salary in the United States for this career, based on job postings in the past year, is $141,677.
The average estimated salary in North Carolina for this career, based on job postings in the past year, is $142,784.
Percentiles represent the percentage that is lower than the value. For example, 25% of estimated salaries for Medical Research Scientist postings in the United States in the past year were lower than $63,416.
Education and Experience
Posted Medical Research Scientist jobs typically require the following level of education. The numbers below are based on job postings in the United States from the past year. Not all job postings list education requirements.
Posted Medical Research Scientist jobs typically require the following number of years of experience. The numbers below are based on job postings in the United States from the past year. Not all job postings list experience requirements.
Below are listings of the most common general and specialized skills Medical Research Scientist positions expect applicants to have as well as the most common skills that distinguish individuals from their peers. The percentage of job postings that specifically mention each skill is also listed.
Baseline Skills
A skill that is required across a broad range of occupations, including this one.
- Research (27.07%)
- Communication (14.66%)
- Teaching (9.95%)
- Management (9.12%)
- Leadership (8.48%)
- Writing (6.64%)
- Presentations (5.92%)
- Operations (5.62%)
- Innovation (5.58%)
- Planning (5.27%)
Defining Skills
A core skill for this occupation, it occurs frequently in job postings.
- Endocrinology (79.78%)
Necessary Skills
A skill that is requested frequently in this occupation but isn’t specific to it.
- Biology (8.48%)
- Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent (ELISA) Assay (3.33%)
- Diabetes Mellitus (21.47%)
- Biochemical Assays (6.41%)
- Metabolism (6.43%)
- Cell Cultures (4.86%)
- Biomarkers (2.82%)
- Drug Discovery (2.6%)
- Pharmaceuticals (3.89%)
- Marketing (1.59%)
- Oncology (10.45%)
- Clinical Trials (6.39%)
- Pediatrics (10.14%)
- Cell Biology (5.26%)
- Nursing (5.77%)
- Molecular Biology (5.7%)
- Immunology (5.75%)
- Good Clinical Practices (GCP) (1.49%)
- Workflow Management (1.73%)
- Clinical Research (8.5%)
- Internal Medicine (6.77%)
- Project Management (2.67%)
- Data Analysis (4.65%)
- Flow Cytometry (4.42%)
Distinguishing Skills
A skill that may distinguish a subset of the occupation.
- Thyroid (6.14%)
Salary Boosting Skills
A professional who wishes to excel in this career path may consider developing the following highly valued skills. The percentage of job postings that specifically mention each skill is listed.
- Thyroid (7.69%)
- Endocrinology (99.95%)
Alternative Job Titles
Sometimes employers post jobs with Medical Research Scientist skills but a different job title. Some common alternative job titles include:
- Endocrinology Physician
- Endocrinologist
- Endocrinology Registered Nurse
- Pediatric Endocrinologist
- Oncology Research Scientist
- Endocrinology Medical Assistant
- Reproductive Endocrinologist
- Endocrinology Diabetes Care Specialist
- Associate Scientist
Similar Occupations
If you are interested in exploring occupations with similar skills, you may want to research the following job titles. Note that we only list occupations that have at least one corresponding NC State Online and Distance Education program.
- Biomedical Scientist
Common Employers
Here are the employers that have posted the most Medical Research Scientist jobs in the past year along with how many they have posted.
United States
- Archway Physician Recruitment (257)
- Britt Medical Search (203)
- Enterprise Medical Recruiting (158)
- CompHealth (154)
- Cedars-Sinai (119)
- AMN Healthcare (118)
- AstraZeneca (101)
- The Curare Group (98)
- Summit Recruiting Services, LLC. (93)
- Pacific Companies (82)
North Carolina
- Atrium Health (17)
- Atrium Health Floyd (14)
- AMN Healthcare (13)
- Archway Physician Recruitment (13)
- Wake Forest Baptist Health (8)
- University of North Carolina (7)
- HCA Healthcare (7)
- UNC Health (7)
- Novant Health (6)
- Duke University (6)
NC State Programs Relevant to this Career
If you are interested in preparing for a career in this field, the following NC State Online and Distance Education programs offer a great place to start!
All wages, job posting statistics, employment trend projections, and information about skill desirability on this page represents historical data and does not guarantee future conditions. Data is provided by and downloaded regularly from Lightcast. For more information about how Lightcast gathers data and what it represents, see Lightcast Data: Basic Overview on Lightcast's Knowledge Base website.
Medical Research Scientist Education Requirements
The educational requirements for a medical research scientist typically include a doctorate degree. According to Professor of Biology, David Cool Ph.D. from Wright State University, "Every medical student has to do research, and most large teaching hospitals have a research coordinator that will work to generate grants in the department. This means that lab personnel is required for these positions and valuable to the clinical research team." The majority of medical research scientists hold a doctorate degree, with over 60% having this level of education. However, there are still opportunities for those with a bachelor's or master's degree, with around 30% of medical research scientists holding a master's degree and less than 10% having a bachelor's degree.
What education do you need to become a medical research scientist?
What degree do you need to be a medical research scientist.
The most common degree for medical research scientists is bachelor's degree, with 51% of medical research scientists earning that degree. The second and third most common degree levels are doctoral degree degree at 22% and doctoral degree degree at 18%.
- Bachelor's , 51%
- Doctorate , 22%
- Master's , 18%
- Associate , 8%
What should I major in to become a medical research scientist?
According to the education requirements, medical scientists typically need a Ph.D. or medical degree, with candidates sometimes qualifying for positions with a master's degree and experience. Applicants to these programs typically have a bachelor's degree in biology or a related physical science field. As per the data, the most popular majors for medical research scientists include biology, biochemistry, molecular biology, medicine, chemistry, psychology, public health, microbiology, pharmacy, and genetics.
- Biology , 20%
- Biochemistry, Biophysics, Molecular Biology , 17%
- Medicine , 7%
- Chemistry , 7%
- Other Majors , 49%
Most common colleges for medical research scientists
Medical research scientists often get their degrees at Boston University, Rice University, and University of Connecticut. Here are the most common colleges for medical research scientists in the US based on their resumes.
Best majors for medical research scientists
Best colleges for medical research scientists.
To excel in their field, medical research scientists often pursue advanced education. Top colleges such as University of Southern California, Duke University, and University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill offer robust programs. These institutions stand out due to factors like admissions rate, retention rate, and mean earnings of graduates. Moreover, they consider the ratio of working to non-working alumni ten years after admission, cost of attendance, and median debt for medical research scientist graduates. This ensures a well-rounded education that prepares students for the field's demands.

1. University of Southern California
Los Angeles, CA • Private
In-State Tuition

2. Duke University
Durham, NC • Private

3. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Chapel Hill, NC • Private

4. Harvard University
Cambridge, MA • Private

5. University of Michigan - Ann Arbor
Ann Arbor, MI • Private

6. Columbia University in the City of New York
New York, NY • Private

7. University of California - Los Angeles

8. University of Pennsylvania
Philadelphia, PA • Private

9. Stanford University
Stanford, CA • Private

10. Yale University
New Haven, CT • Private
20 best online courses for medical research scientists
1. Medical Terminology II
This is the second course of the Medical Terminology specialization. It builds on the basic concepts of medical terminology with the introduction of new roots, terms, and abbreviations specific to the endocrine system (hormones). The body's transportation and defense systems (cardiovascular, blood, and lymphatic) will also be covered as well as the respiratory system (lungs)...
2. Medical Terminology and the Human Body Fundamentals
In this Introduction to Medical Terminology and the Human Body course, you will learn about the medical language that is used to describe the human body. Throughout each Lesson, the roots of terms are explained to help students understand how medical terminology works in healthcare and to increase their knowledge and understanding of the material discussed. This course will provide you with a better understanding and working knowledge of medicine that is required for understanding of medical...
3. Practical Regulatory Affairs 2020 - US FDA Medical Devices
A practical course discussing the US FDA Medical Device regulations for real-world situations...
4. Medical Terminology
Introduction to the meaning of various roots, terms and combining forms that are components of medical words...
5. ICD 10 & 11 Medical Coding and Billing
Preparation for Medical Coding Certification Exam...
6. A Specialty Approach to Learning Medical Billing and Coding
Volume One: Medical Hematology...
7. Introduction to Medical Imaging
Your guide to the history, science, math, and economics of medical imaging systems (e.g., X-ray, CT, MRI, Ultrasound)...
8. AMCI Introduction to Medical Coding (I2MC) Course
Introduction to Medical Coding (I2MC) Course...
9. Medical Terminology 101
For those in healthcare, billing, and more. Boost earning ability and marketable skills by learning to speak medicine...
10. EU Medical Device Regulatory Affairs explained Simply
How to get approval to sell Medical Devices within the European Union. Understand regulatory affairs & ISO 13485 2016...
11. Medical Writing for Healthcare Professionals
Launch your scientific and medical writing career today. Learn from an experienced medical writer!...
12. Medical Device Regulation (MDR): Intro for Device Designers
An introduction to the EU's Medical Device Regulation (MDR) for those involved in developing medical devices...
13. Medical Device Regulation 2017/745 EU regulatory affairs.
Understand regulations for medical devices in simple terms to gain market approval of a medical device in the EU...
14. Practical Regulatory Affairs 2020 - European Medical Devices
A practical course discussing the EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR) in real-world situations...
15. Medical Coding: ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code Training
Learn medical coding and prepare yourself for today's healthcare workplace...
16. ISO 13485 - IQOQPQ - Process Validation for Medical Devices
Installation Qualification (IQ), Operational Qualification (OQ) & Performance Qualification (PQ) Medical Devices...
17. ISO 13485 Demystified - Medical Devices' QMS 360° Insights
Deep dive into the world of ISO 13485 international standard for medical devices' QMS, basic concepts & requirements...
18. Internal audit on Medical Device QMS - ISO 13485:2016
Successfully conduct an internal audit based on requirements of ISO 13485:2016 for Medical Device Development and QMS...
19. Medical Devices Quality Management System - ISO 13485:2016
Awareness and Application for the requirements of ISO 13485:2016 for Medical Device Development and QMS...
20. ISO 13485:2016 - Design and Development of Medical Devices
Design and Development of Medical Devices in the perspective of ISO 13485:2016 and Medical Devices Industry...

Top 10 most affordable universities for medical research scientists
The most affordable schools for medical research scientists are University of Florida, hunter college of the city university of new york, and california state university - long beach.
If the best universities for medical research scientists are out of your price range, check out these affordable schools. After factoring in in-state tuition and fees, the average cost of attendance, admissions rate, average net price, and mean earnings after six years, we found that these are the most affordable schools for medical research scientists.

1. University of Florida
Gainesville, FL • Private
Cost of Attendance

2. Hunter College of the City University of New York

3. California State University - Long Beach
Long Beach, CA • Private

4. California State University - Los Angeles

5. Brigham Young University
Provo, UT • Private

6. University of South Florida
Tampa, FL • Private

7. California State University - Fullerton
Fullerton, CA • Private

8. Brooklyn College of the City University of New York
Brooklyn, NY • Private

9. Florida State University
Tallahassee, FL • Private

10. California State University - Bakersfield
Bakersfield, CA • Private
Top 10 hardest universities to get into for medical research scientists
The hardest universities for medical research scientists to get into are Harvard University, Duke University, and Columbia University in the City of New York.
Some great schools for medical research scientists are hard to get into, but they also set your career up for greater success. The list below shows the most challenging universities to get into for medical research scientists based on an institution's admissions rates, average SAT scores accepted, median ACT scores accepted, and mean earnings of students six years after admission.
1. Harvard University
Admissions Rate
SAT Average
3. Columbia University in the City of New York
4. stanford university, 5. university of pennsylvania.

6. Johns Hopkins University
Baltimore, MD • Private
7. Yale University

8. University of Chicago
Chicago, IL • Private

9. Northwestern University
Evanston, IL • Private

10. Vanderbilt University
Nashville, TN • Private
Top 10 easy-to-apply-to universities for medical research scientists
The easiest schools for medical research scientists to get into are Mount Saint Mary's University, d'youville college, and barry university.
Some schools are much easier to get into. If you want to start your career as a medical research scientist without much hassle, check out the list of schools where you will be accepted in no time. We compiled admissions rates, average SAT scores, average ACT scores, and average salary of students six years after graduation to uncover which were the easiest schools to get into for medical research scientists.

1. Mount Saint Mary's University

2. D'Youville College
Buffalo, NY • Private

3. Barry University
Miami, FL • Private

4. Notre Dame de Namur University
Belmont, CA • Private

5. Curry College
Milton, MA • Private

6. University of the Incarnate Word
San Antonio, TX • Private

7. Gwynedd Mercy University
Gwynedd Valley, PA • Private

8. The University of Texas at El Paso
El Paso, TX • Private

9. San Francisco State University
San Francisco, CA • Private

10. Marymount University
Arlington, VA • Private
Average medical research scientist salary by education level
According to our data, medical research scientists with a Doctorate degree earn the highest average salary, at $80,196 annually. Medical research scientists with a Master's degree earn an average annual salary of $74,822.
Medical Research Scientist Education FAQs
What is the best college for medical research scientists, search for medical research scientist jobs.
Updated April 5, 2024
Editorial Staff
The Zippia Research Team has spent countless hours reviewing resumes, job postings, and government data to determine what goes into getting a job in each phase of life. Professional writers and data scientists comprise the Zippia Research Team.
- Assistant Research Scientist Education Requirements
- Associate Scientist Education Requirements
- Doctoral Fellow Education Requirements
- Fellow Education Requirements
- Laboratory Researcher Education Requirements
- Medical Science Liaison Education Requirements
- PHD Researcher Education Requirements
- Postdoctoral Associate Education Requirements
- Postdoctoral Research Associate Education Requirements
- Postdoctoral Scholar Education Requirements
- Principal Scientist Education Requirements
- Research And Development Scientist Education Requirements
- Research Fellow Education Requirements
- Research Laboratory Manager Education Requirements
- Research Scientist Education Requirements
- Assistant Research Scientist
- Associate Scientist
- Doctoral Fellow
- Laboratory Researcher
- Medical Science Liaison
- PHD Researcher
- Postdoctoral Associate
- Postdoctoral Research Associate
- Postdoctoral Scholar
- Principal Scientist
- Research And Development Scientist
- Research Fellow
- Research Laboratory Manager
- Research Scientist
- What an Assistant Research Scientist Does
- What an Associate Scientist Does
- What a Doctoral Fellow Does
- What a Fellow Does
- What a Laboratory Researcher Does
- What a Medical Science Liaison Does
- What an PHD Researcher Does
- What a Postdoctoral Associate Does
- What a Postdoctoral Research Associate Does
- What a Postdoctoral Scholar Does
- What a Principal Scientist Does
- What a Research And Development Scientist Does
- What a Research Fellow Does
- What a Research Laboratory Manager Does
- What a Research Scientist Does
- Zippia Careers
- Life, Physical, and Social Science Industry
- Medical Research Scientist
- Medical Research Scientist Education
Browse life, physical, and social science jobs
Medical Education Research Certificate (MERC) Program
The Medical Education Research Certificate (MERC) program is intended to provide the knowledge necessary to understand the purposes and processes of medical education research, to become informed consumers of the medical education research literature, and to be effective collaborators in medical education research. Alone, MERC is not intended to produce independent medical education researchers.
The program is open to all who are interested in improving their educational research skills and is targeted for those with a background in medical education but relatively less experience in conducting educational research. The courses are targeted for clinicians and other educators who desire to learn research skills that will enable collaborative participation in medical education research projects.
Each three-hour workshop focuses on a key skill or area in educational research, emphasizes opportunities for hands-on activities and active participation so as to maximize the applicability of the workshop principles. Six workshops of the participant's choosing must be completed to qualify for the certificate. These can be taken in any order. Read the workshop descriptions .
Register for an upcoming virtual workshop.
Certificate Registration
Those interested in receiving a MERC Certificate must complete six (6) workshops. In order to receive a MERC Certificate, you must first complete six (6) workshops. Upon completion, you may request your certificate . Certificates are sent via email at the end of each month. There is no fee associated with the certificates at this time.
Cancellation Policy
If there are fewer than 8 people registered for the MERC workshop by the deadline, the workshop will be canceled. You will be notified and your money refunded.
Resources & Additional Information
- FAQ for Hosting MERC Workshops
- MERC Virtual Workshop Registration and Fees
Workshop Descriptions
MERC Steering Committee
Current MERC Faculty
MERC Contacts
Jean Bailey, PhD Associate Dean for Faculty Development Virginia Commonwealth University, School of Medicine [email protected]
- Medical Education
- MTS Health Sciences How to Become a Clinical Research Associate
- Anesthesia Technician
- Audiologist & SLP
- Cardiovascular Technologist
- Dental Assistant
- Dental Hygienist
- Diagnostic Medical Sonographer
- Dialysis Technician
- EKG Technician
- EMT & Paramedic
- Kinesiologist
- Mammography Technologist
- Medical Assistant
- MRI Technologist
- Neurodiagnostic Technologist
- Nuclear Medicine Technologist
- Ophthalmic Technician
- Pharmacy Technician
- Phlebotomist
- Physical Therapist Assistant & Aide
- Psychiatric & Mental Health Technician
- Radiation Therapist
- Radiologic Technologist
- Respiratory Therapist
- Surgical Technologist
- Cytologist (Cytotechnologist)
- Dental Lab Technician
- Histotechnologist
- Medical Lab Assistant
- Medical Lab Technician
- Biological Sciences
- Biomedical Science
- Biotechnology
- Health Sciences
- Medical Laboratory Scientist
- Nutritionist & Dietitian
- Pathologists' Assistant (PathA)
- Pre-Vet (Veterinarian)
- Biomedical Equipment Technician
- Biomedical Informatics
- Health Informatics
- Health Information Management
- Health Information Technology
- Healthcare Administration
- Medical Billing & Coding
- Nursing Informatics
- Sterile Processing Technician
- Patient-Facing Technology Programs
- Laboratory Technology programs
- Natural & Clinical Lab Science
- Medical IT & Administrative
Certification Guides
Career guides, interviews & features, how to become a clinical research associate (cra), search for schools.
When you click on a sponsoring school or program advertised on our site, or fill out a form to request information from a sponsoring school, we may earn a commission. View our advertising disclosure for more details.
Scientists, researchers, and doctors make discoveries about drugs, surgical procedures, behavioral therapies, or medical devices through their work in laboratories and healthcare settings. This is only the beginning of the journey for pharmaceuticals, therapies, and devices, as bringing the findings from the lab to the street requires a vigorous scientific process known as a clinical trial. Clinical research associates (CRAs) are the professionals responsible for ensuring that clinical trials move forward following established guidelines and regulations for ethics, safety, and reporting.
Clinical research associates, also known as “monitors,” work on behalf of sponsors funding clinical trials for the new or existing drug, device, surgery, or behavioral intervention. Working directly for the sponsor or through a contract research organization, the main task of a CRA is to monitor the progress of an ongoing clinical trial.
Through in-person site visits or remote monitoring systems, a CRA serves as the central point of contact between a sponsor and testing sites; ensures that the trial is being administered per approved protocols; verifies that the clinical trial is being conducted ethically at all sites; and confirms the validity and accuracy of all data being collected and reported at test sites.
In addition to reading, interpreting, and understanding medical technology, clinical research associates must have excellent interpersonal and communication skills. The ability to understand best clinical practices, design protocols, and data standards requires CRAs to have outstanding attention to detail, analytical skills, and the capacity to deliver constructive feedback to participating research sites on their performance.
Although not a requirement, many CRAs travel between multiple research sites for study oversight, which may require a valid driver’s license, the physical capacity to travel, and/or willingness to fly or drive regularly.
This detailed guide explores the education and credentials required to become a clinical research associate (CRA).
Arizona State University
Johns hopkins university (aap), university of west florida, steps to become a clinical research associate (cra).
The pathways to becoming a clinical research associate are numerous and available to anyone with a high school diploma or higher. While formal education is not technically required to enter the field, having a bachelor’s degree or higher can make potential candidates much more competitive.
Certification in the field is also not required, but obtaining certification from the Society of Clinical Research Associates (SOCRA) or the Association of Clinical Research Professionals (ACRP) can result in more opportunities and even more competitive salaries.
Finally, all aspiring CRAs are advised to check out the International Conference on Harmonisation’s (ICH) guidelines for Good Clinical Practice (GCP) to get a feel for the professional expectations and responsibilities.
Here is how to become a CRA depending on one’s level of education. Please note that in the United States, there are two major certification bodies for CRAs: the Society of Clinical Research Associates (SOCRA) and the Association of Clinical Research Professionals (ACRP). Each pathway includes the eligibility requirements to pursue credentialing through either of these entities.
PATH 1: Earn a High School Diploma and Gain Experience
Perhaps the most strenuous route to this career is becoming a certified CRA with a high school diploma and between 3,000 and 3,500 hours of qualifying work experience (depending on the certification entity).
These candidates often start out in support positions assisting a more experienced or certified CRA with mundane tasks. An entry-level worker can earn increased responsibilities through a demonstrated capacity to learn the regulations, protocols, and ethical considerations. To qualify for the following CRA certification exams, high school graduates must:
SOCRA Category 1
- Complete two full-time years of CRA work within five years, or 3,500 hours of part-time work
ACRP CCRA (Certified Clinical Research Associate)
- Complete 3,000 hours performing essential duties
- Submit a resume documenting and demonstrating job performance
Please note that in some cases, additional education can be used to substitute for work experience hours. Please see credentialing websites for details.
PATH 2: Earn an Associate Degree and Gain Experience
Depending on the program, an associate’s degree of applied science (AAS) in clinical research can be a standalone degree or a stepping-stone to a bachelor’s or master’s. Licensed vocational or practical nurse (LVN or LPN) programs are designed specifically for practical, job-ready skills and may qualify aspiring CRAs for the ACRP certification.
Similar to the path taken by those with a high school diploma, having an associate degree, LPN, or LVN can open the door to some entry-level jobs in the industry. At this level, some prospective CRAs assist more experienced CRAs or some engage independently in entry-level tasks related to study monitoring. Those working as CRAs with an associate’s degree, LPN, or LVN can qualify for certification after working a certain number of hours in the field.
To qualify for the following CRA certification exams, associate degree graduates must:
SOCRA Category 2
- Hold a “clinical research” degree
- Complete one full-time year as a CRA or 1,750 hours part-time
ACRP Option 2 (Also for LVN, LPN)
- Hold a “clinical research degree” or complete 1,500 hours performing essential duties
PATH 3: Earn a Bachelor’s Degree and Gain Experience
Most entry-level clinical research associate positions require candidates to have a bachelor’s of science (BS) in a health-related field from an accredited four-year university. In some cases, programs are designed to add practical hours needed to qualify for certification tests.
Those interested in becoming a CRA can study nursing, health sciences, biological sciences, clinical research, clinical research administration, clinical research management, medical technology, or life sciences, among many other subjects. Because many entry-level positions are looking for those with previous work in the field, those earning a BS should seek internships, part-time work, and/or fellowships involving participation in research, if possible.
To qualify for the following CRA certification exams, bachelor’s degree graduates must:
SOCRA Category 3
- Hold a “clinical research” undergraduate degree
ACRP Options 1 & 2
- Complete 3,000 hours performing essential job duties or 1,500 hours of equivalent work experience requirements through ACRP certifications or approved clinical research degree programs accredited by the Council for Higher Education
PATH 4: Earn a Master’s Degree for Opportunities in Management
A master’s program in clinical research is generally designed for those already working as CRAs to expand their skills or to advance into management or supervisory roles within the field. However, for those with non-health science bachelor’s degrees who want to become CRAs, seeking a master’s of science in clinical research or a master’s of science in clinical research management could be a pathway to breaking into the field.
Because many of these programs are offered online, earning a degree is possible for even those students who need full flexibility of schedule to complete the degree. Although requirements for admission into master’s programs vary, those looking to gain admission into a master’s of science for clinical research commonly need the following:
- A bachelor’s degree
- Official transcripts demonstrating specific coursework in science
- A statement of purpose
- Letters of Recommendation or Reference
- A resume or CV
- An application fee
- TOEFL or IELTS scores (international students only)
Clinical Research Associate (CRA) Degree Programs
There is a range of formalized training programs that prepare professionals for this key role in ensuring the safe, and ethical development of medical technologies. Below you will find examples of programs at a range of educational levels available to those interested in a career as a CRA.
Durham Tech – AAS Program
Durham tech, located in Durham, North Carolina, offers a 71-credit hybrid on-campus and online clinical trials research associate (CTRA) associate of applied science (AAS) program. Durham’s CTRA AAS prepares graduates to work on any side of clinical research in an assistant’s role.
While most programs require the student to attend on-campus courses, there are several courses that are offered completely online. The program takes 20 to 21 months and includes coursework in research site management; clinical research management; research protocol design; an introduction to ethics; anatomy and physiology; an introduction to clinical data; pathophysiology; and clinical research terminology.
Graduates of the program may be eligible to sit for national certification examinations and will be prepared for opportunities at medical centers, pharmaceutical industries, hospitals, research facilities, clinics, physicians’ offices, and device companies.
- Location: Durham, NC
- Accreditation: Southern Association of Colleges and Schools Commission on Colleges (SACSCOC); Commission on Accreditation of Allied Health Education Programs (CAAHEP)
- Expected Time to Completion: 20 to 21 months
- Estimated Tuition: $5,396
Washington University in St.Louis University College – BS, MS, Certificates
Washington University in St. Louis, Missouri, has various degree options for CRAs at all stages of their career to work as monitors. Students can enhance their current skills and knowledge in clinical research management, as well as gain a deep mastery regarding how to best move clinical research forward in an ethical, compliant, and safe way.
Those with at least six units of transferable coursework qualify to apply to the 120-credit-hour bachelor of science in clinical research management to start their careers. Anyone with any educational background can pursue University College’s 21-credit undergraduate certificate in clinical research management to enhance career skills or make a resume more competitive.
Students who already have a BA or BS also have options at Washington University. Experienced professionals in the clinical research field who wish to seek formalized training can earn a 21-credit advanced certificate in clinical research management or a 30-credit master of science (MS) in clinical research management. Those with a non-healthcare bachelor’s degree who wish to become high-level CRAs can up their skills and knowledge by choosing the combined bachelor’s and master’s degree options.
Although the coursework in each program varies to suit the level of education, themes across all the programs include the fundamentals of clinical research management; research ethics and regulatory affairs; compliance, legal and regulatory issues; and data and information management in health sciences.
- Location: St. Louis, MO
- Accreditation: Higher Learning Commission (HLC)
- Expected Time to Completion: BS (up to 48 months); certificate (12 months); MS (24 months)
- Estimated Tuition: Undergraduate courses ($695 to 895 per credit); Graduate courses ($665 to 995 per credit)
Barnett International – Online Seminar
Designed for CRAs with two years of experience or less, this online clinical research associate onboarding program by Barnett International prepares entry-level employees to monitor clinical trials at high levels appropriate to industry standards.
Over ten weeks of synchronous online coursework lasting three hours per week, participants will learn topics including informed consent, investigational product accountability, safety definitions and reporting requirements, and regulatory compliance and quality assurance: audits and inspections. Participants receive 30 hours (3.0 CEUs) of continuing education credits.
- Location: Needham, MA
- Accreditation: Accreditation Council for Pharmacy Education
- Expected Time to Completion: Ten weeks
- Estimated Tuition: By Early Bird Deadline ($1,795); After Early Bird Deadline ($1,995); June 10 is the early bird deadline
Continuing Education for Clinical Research Associates (CRAs)
Both CRA certification bodies require continuing education to maintain active certification status.
SOCRA requires recertification every three years. It calls for 45 hours of CE to be completed over the course of the first three years beyond passing the initial test. Twenty-two CE units must be related to clinical research; the remainder can be in the professional or therapeutic area in which one works or specializes. In addition, those looking to maintain or renew certification must complete a “recertification continuing competence learning module.”
The ACRP expects certified CRAs to engage in continuing education (CE) and continuing involvement (CI) to maintain certifications. Continuing education should include coursework in research and healthcare, and continuing involvement requires candidates to engage in activities such as authorship, participating in investigator meetings, or working as a peer reviewer, among other opportunities. Notably, ACRP utilizes an ongoing point system for professionals to maintain their certifications.
CRA Career and Salary
Clinical trials and the objectivity they bring to advances in treatment are extremely important. In an increasingly globalized society, diseases spread across borders, and in an age of increased antibiotic resistance, new ways to fight bacteria will be needed. Furthermore, with an aging U.S. population comes increased rates of chronic conditions and the subsequent reliance on pharmaceuticals to improve people’s quality of life.
It’s not surprising that the Bureau of Labor Statistics (2022) predicted a 7 percent increase in openings for medical and clinical laboratory technicians between 2021 and 2031, much more than the average growth anticipated across all U.S. occupations during that same decade (5 percent). As far as the salaries are concerned, here are the salary percentiles for clinical laboratory technologists and technicians in the US ( BLS May 2022):
Lastly, while the BLS doesn’t track salaries for CRAs, PayScale.com (June 2023)—a site that relies on self-reported data—found that the median annual salary for a CRA was $72,393. Among the 1,391 CRAs reporting their annual salaries, Payscale found these percentiles:
- 10th percentile: $48,000
- 50th percentile (median): $72,393
- 90th percentile: $101,000
Specialized skills in CRA that increased salaries included medical devices (37 percent pay increase over average), team leadership (35 percent), and writing procedures & documentation (20 percent).
Years of experience, predictably, also have an impact on salary. Entry-level CRAs earn 15 percent below the average, while experienced CRAs (ten to 19 years) earn 16 percent above the average and late-career CRAs (20+ years) earn 25 percent above the average.
It is important to note that these figures also vary based on the data source. For illustration, Indeed.com (June 2023) found an average annual salary of $80,957 among United States clinical research associates.

Becca Brewer is building a better future on a thriving earth by healing herself into wholeness, divesting from separation, and walking the path of the loving heart. Previously to her journey as an adventurer for a just, meaningful, and regenerative world, Becca was a formally trained sexuality educator with a master of education.
Related Articles
- Upskilling in the Allied Health Professions
- Single-use Plastics in Medicine Raise Concerns About Sustainability
- Clinical Research Certification - CCRA, CCRC, CPI
- Online Master’s in Clinical and Translational Research Programs
- Online Bachelor’s in Health Science Programs (BSHS Degree)
- Online Master's Programs in Clinical Management and Leadership
- Clinical Lab Science vs. Clinical Research
- BSHS (Health Sciences) vs BSHA (Health Administration) Programs
- Clinical vs Translational Research
- Guide to Health Science Careers
Related Programs
Reasons for Completing Medical School in Five Years
Some students are taking an extra year when earning their M.D. Here's why.
Completing Medical School in Five Years

Getty Images
Students might want to add an extra year of medical school for personal exploration or to gain a competitive edge for residency after they graduate.
For someone considering becoming a doctor, the road ahead may look long. After finishing an undergraduate degree, there’s four years of medical school and then three to seven years to complete a residency. Aspiring subspecialists might follow that up with a fellowship.
It can all add up to a decade or more of advanced study before a new physician even interviews for their first job.
But for various reasons, many medical school students are opting to take another year – or even two – to complete their education, administrators say.
Dr. Michael Kim, an assistant professor of medicine and pediatrics at the University of Minnesota Medical School , recommends that students use early meetings with their academic adviser to explore their goals and passions. What sort of medicine do they want to practice? Do they have interests outside of medicine that they want to pursue? At this early stage, the idea of using an extra year to add outside experiences might come up.
Traditionally, med school entails two years of full-time coursework followed by two years of clinical clerkship, or rotation, in a university hospital. Since the first two years are spent in class, Kim and other experts say the best time to add an extra year isn’t at the end, but in the middle after the second year. This way, coursework is finished but the intense schedule of clinical rotation hasn't begun.
Students considering taking a longer track should think carefully before making that decision, experts say, but here are some of the reasons it may be worth it.
Pursue Other Interests or Earn a Dual Degree
Some students take extra time to pursue career-enhancing experiences outside medical school or work toward a dual degree . The University of Minnesota offers a flexible M.D. program for students interested in this approach. They can take a pause from med school to pursue other interests or take courses toward a dual degree.
Students interested in global health , for example, can work on research in one of eleven rotation sites that the university partners with, Kim says. Students can also earn graduate degrees in other subjects, like business or law. These programs typically are modified to be shorter than they would be for students who are not in medical school, so they can be completed in one year, Kim says.
Whichever path students choose, he says, the university wants to encourage them to broaden their experience and skills. “There is a lot that a physician can do to improve health that isn’t direct patient care. If they come in with medical legal expertise or have done other research to expand medical knowledge, they can contribute to public health and communities.”
Dr. Vineet Arora, dean for medical education at the University of Chicago Pritzker School of Medicine , received her master’s in health policy while doing her residency at the university. Having clinical experience added to what she could bring to health policy classes, and vice versa.
“I was in class with students who didn’t have med expertise,” she says. “I got a lot out of that experience because I could apply what I was learning directly to patients.”
Gain a Competitive Edge for Residency
Arora says she is seeing “an explosion” of interest in adding an extra year to medical school. For many students, she says, the decision is a strategic move to improve their chances during “the match,” when medical school graduates find out where they’ll be doing their residencies .
Medical residencies, required after medical school, are more competitive than ever, Arora says. And many are asking applicants whether they have published research papers.
“Some students think about taking an extra year to do research for a competitive edge during the match,” but that's a gamble, she says. “My personal belief is that you’re unlikely to get a publication off of just one year of research.”
So, it’s crucial to work closely with a career adviser to make sure it’s the right move, she says. An adviser — usually on the student affairs team, a dean or a faculty member — can direct you toward research opportunities with stipends. Recent graduates can also be a great source of advice about research opportunities.
“ But there is a risk if you’re not able to present why you did it or show much for it,” Arora says.
Personal Exploration
Another reason med students might add an extra year is for personal exploration. Some students decide that before they head into the intensity of clinical rotation and residencies, they want to have that adventure they’ve been dreaming about. Other students might want to delay their graduation so that it aligns with their romantic partner’s education timeline.
A little-known side benefit of taking five years or more to finish medical school is that you are more likely to finish and graduate. Graduation rates for med students who take five years are significantly higher than those who take just four, according to a 2023 report by the Association of American Medical Colleges.
The only big drawback to spending an extra year in medical school is financial , Kim says. Adding more time in school may mean more student loans and more accrued interest on them. The average debt for medical school graduates is more than $200,000, according to the Education Data Initiative, so it’s important to think about the financial impact of adding a year.
A related downside is that you lose a year of earning a practicing physician's salary.
But it's a personal decision, Arora says.
“There’s no one right way to finish medical school. Everyone has a different set of things they’re balancing in the back of their minds.”
Where Famous Docs Earned Medical Degrees

Tags: medical school , graduate schools , education , students
Popular Stories
Best Colleges

Best Global Universities

Medical School Admissions Doctor

Best Graduate Schools

Top Medical Schools

You May Also Like
Premeds take 5 public health courses.
Rachel Rizal May 7, 2024
Fortune 500 CEOs With a Law Degree
Cole Claybourn May 7, 2024
Why It's Hard to Get Into Med School
A.R. Cabral May 6, 2024
Pros, Cons of Unaccredited Law Schools
Gabriel Kuris May 6, 2024

An MBA and Management Consulting
Sammy Allen May 2, 2024

Med School Access for Minority Students
Cole Claybourn May 2, 2024

Different jobs with med degree
Jarek Rutz April 30, 2024

Dealing With Medical School Rejection
Kathleen Franco, M.D., M.S. April 30, 2024

Should I Get a Master's Before a Ph.D?
Andrew Warner April 29, 2024

Should You Take the LSAT More Than Once?
Gabriel Kuris April 29, 2024

How to Become a Research Nurse
What is a research nurse.
- Career Outlook

Research Nurses, also referred to as Clinical Nurse Researchers or Nurse Researchers, develop and implement studies to investigate and provide information on new medications, vaccinations, and medical procedures. They assist in providing evidence-based research that is essential to safe and quality nursing care. This guide will explain what a Research Nurse does, how much they make, how to become one, and more!
Research nurses play a pivotal role in developing new and potentially life-saving medical treatments. Typically, clinical research nurses have advanced degrees, assist in the development of studies regarding medications, vaccines, and medical procedures, and also the care of research participants.
Nurses that know they want to be a clinical research nurse will often work as a research assistant, a clinical data collector, and/or clinical research monitor. It is essential to gain some bedside experience, but not as important as other nursing specialties.
Clinical research nurses have advanced degrees such as an MSN or Ph.D. This is vital to those that want to conduct independent research. For that reason, most clinical research nurses do not work in this field until they are in their 40s-50s.
Find Nursing Programs
What does a research nurse do.
Research Nurses primarily conduct evidence-based research through these two types of research methods:
- Quantitative: Meaning it’s researched that can be measured via statistical, mathematical, or computational techniques.
- Phenomenology
- Grounded Theory
- Ethnography
- Narrative Inquiry
Clinical research nurses perform a variety of tasks, all centered around research. These specific job responsibilities include:
- Collaborating with industry sponsors and other investigators from multi-institutional studies
- Educating and training of new research staff
- Overseeing the running of clinical trials
- Administering questionnaires to clinical trial participants
- Writing articles and research reports in nursing or medical professional journals or other publications
- Monitoring research participants to ensure adherence to study rules
- Adhering to research regulatory standards
- Writing grant applications to secure funding for studies
- Reporting findings of research, which may include presenting findings at industry conferences, meetings and other speaking engagements
- Adhering to ethical standards
- Maintaining detailed records of studies as per FDA guidelines, including things such as drug dispensation
- Participating in subject recruitment efforts
- Ensuring the necessary supplies and equipment for a study are in stock and in working order
- Engaging with subjects and understanding their concerns
- Providing patients with thorough explanation of trial prior to obtaining Informed Consent, in collaboration with treating physician and provides patient education on an ongoing basis throughout the patient’s course of trial.
>> Show Me Online MSN Programs
Research Nurse Salary
Glassdoor.com states an annual median salary of $95,396 for Research Nurses and Payscale reports that Clinical Research Nurses earn an average annual salary of $75,217 or $36.86/hr .
Research Nurse Salary by Years of Experience
Research Nurses can earn a higher annual salary with increased years of experience.
- Less than 1 year of experience earn an average salary of $68,000
- 1-4 years of experience earn an average salary of $73,000
- 5-9 years of experience earns an average salary of $73,000
- 10-19 years of experience earns an average salary of $80,000
- 20 years or more of experience earns an average salary of $78,000
Via Payscale
To become a Research Nurse, you’ll need to complete the following steps:
Step 1: Attend Nursing School
You’ll need to earn either an ADN or a BSN from an accredited nursing program in order to take the first steps to become a registered nurse.
Step 2: Pass the NCLEX-RN
Become a Registered Nurse by passing the NCLEX examination.
Step 3: Gain Experience at the Bedside
Though not as important as in some other nursing careers, gaining experience is still a vital step for those wanting to become Nurse Researchers.
Step 4: Earn an MSN and/or Ph.D
Research Nurses typically need an advanced degree, so ADN-prepared nurses will need to complete an additional step of either completing their BSN degree or entering into an accelerated RN to MSN program which will let them earn their BSN and MSN at the same time.
Step 5: Earn Your Certification
There are currently two certifications available for Clinical Research Nurses. They are both offered by the Association of Clinical Research Professionals.
- Clinical Research Association (CCRA)
- Clinical Research Coordinator (CCRC)
These certifications are not specific to nurses but rather those that work in the research field.
CCRA Certification
In order to be deemed eligible for the CCRA Certification exam, applicants must attest to having earned 3,000 hours of professional experience performing the knowledge and tasks located in the six content areas of the CRA Detailed Content Outline. Any experience older than ten years will not be considered.
What’s on the Exam?
- Scientific Concepts and Research Design
- Ethical and Participant Safety Considerations
- Product Development and Regulation
- Clinical Trial Operations (GCPs)
- Study and Site Management
- Data Management and Informatics
Exam Information
- Exam Fee: $435 Member; $485 Nonmember
- Exam Fee: $460 Member; $600 Nonmember
- Multiple choice examination with 125 questions (25 pretest non-graded questions)
CCRC Certification
In order to be deemed eligible for the CCRC Certification exam, applicants must attest to having earned 3,000 hours of professional experience performing the knowledge and tasks located in the six content areas of the CCRC Detailed Content Outline. Any experience older than ten years will not be considered.
Where Do Research Nurses Work?
Clinical Research nurses can work in a variety of locations, including:
- Government Agencies
- Teaching Hospitals
- Medical Clinics
- International Review Board
- Medicine manufacturing
- Pharmaceutical companies
- Medical research organizations
- Research Organizations
- International Health Organizations
- Private practice
- Private and public foundations
What is the Career Outlook for a Research Nurse?
According to the BLS , from 2022 to 2032, there is an expected growth of 6% for registered nurses. With the aging population and nursing shortage, this number is expected to be even higher.
The BLS does identify medical scientists, which includes clinical research nurses, as having a growth potential of 10% between 2022-2032.
What are the Continuing Education Requirements for a Research Nurse?
Generally, in order for an individual to renew their RN license, they will need to fill out an application, complete a specific number of CEU hours, and pay a nominal fee. Each state has specific requirements and it is important to check with the board of nursing prior to applying for license renewal.
If the RN license is part of a compact nursing license, the CEU requirement will be for the state of permanent residence. Furthermore, some states require CEUs related to child abuse, narcotics, and/or pain management.
A detailed look at Continuing Nurse Education hours can be found here .
Where Can I Learn More About Becoming a Research Nurse?
- American Nurses Association (ANA)
- Nurse Researcher Magazine
- National Institute of Nursing Research
- International Association of Clinical Research Nurses
- Association of Clinical Research Professionals
- Society of Clinical Research Associates
- American Association of Colleges of Nursing
Research Nurse FAQs
What is the role of a research nurse.
- Research nursing is a nursing practice with a specialty focus on the care of research participants.
What makes a good Research Nurse?
- Research Nurses should be excellent communicators, have strong attention to detail, be self-assured, have strong clinical abilities, be flexible, autonomous, organized, and eager to learn new information.
How much does a Research Nurse make?
- Research nurses earn an average salary of $95,396 according to Glassdoor.com.
What is it like being a Research Nurse?
- Research Nurses provide and coordinate clinical care. Research Nurses have a central role in ensuring participant safety, maintaining informed consent, the integrity of protocol implementation, and the accuracy of data collection and data recording.

Kathleen Gaines (nee Colduvell) is a nationally published writer turned Pediatric ICU nurse from Philadelphia with over 13 years of ICU experience. She has an extensive ICU background having formerly worked in the CICU and NICU at several major hospitals in the Philadelphia region. After earning her MSN in Education from Loyola University of New Orleans, she currently also teaches for several prominent Universities making sure the next generation is ready for the bedside. As a certified breastfeeding counselor and trauma certified nurse, she is always ready for the next nursing challenge.

Plus, get exclusive access to discounts for nurses, stay informed on the latest nurse news, and learn how to take the next steps in your career.
By clicking “Join Now”, you agree to receive email newsletters and special offers from Nurse.org. We will not sell or distribute your email address to any third party, and you may unsubscribe at any time by using the unsubscribe link, found at the bottom of every email.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Related: 10 Careers You Can Pursue in Medical Research 2. Continue your education After earning a bachelor's degree from an accredited college or university, most prospective medical scientists decide to continue pursuing advanced degrees. ... which allows you to tailor your documents to a specific position's requirements. For example, if a job ...
As a medical researcher, you may start your day with an 8am lecture, followed by a day of lab work. Or, you may be working on a report to present at a board meeting for your company. Or you might be working with a specific group of patients as you search for a new medical treatment that will help afflicted people.
Step 1a: Earn a Bachelor's Degree (Four Years) After graduating from high school, an aspiring biomedical scientist needs to earn a bachelor's degree. At this stage, practically any major related to the life sciences is suitable: biology, chemistry, or biomedical engineering are all possibilities. Admissions requirements for undergraduate ...
The roadmap to medical research is a bit tricky to navigate, because it is a profession that demands distinctive skills and expertise along with mandatory formal education. If you harbor an interest in scientific exploration and a desire to break new ground in medical knowledge, the first step is to earn a bachelor's degree in a related field ...
Applying to Biomedical Research Programs. Learn about the process of applying to medical research programs. Applying to PhD Programs. A diligent, well-organized approach to applying to graduate school can help you gain admission to a program that best matches your professional goals. Applying to MD-PhD Programs.
The lowest 10 percent earned less than $50,100, and the highest 10 percent earned more than $166,980. The median annual wages for medical scientists in the top industries in which they work are as follows: Research and development in the physical, engineering, and life sciences. $102,210.
To enroll in the at Brookline College, you'll need a high school diploma or GED and a passing grade on a Scholastic Level Exam. 2. Earn Your Bachelor's Degree in Medical Laboratory Science. Every bachelor's degree program will have general education requirements like math, communications, and social and behavioral sciences.
Avg. Pay / hour. $31.17. Education. 4+ Years. Job Outlook. 8%. The medical industry heavily relies on the specialized work provided by Medical Researchers. These professionals are at the forefront of medical advancements to develop treatments, medicines and possible cures for a variety of medical diseases and disorders.
Here are four steps you can take to become a researcher: 1. Take relevant classes. Clinical researchers typically pursue an undergraduate degree in biology, chemistry, medicine, psychology or a related field. Many also earn a master's, especially if they hope to work at a university or pharmaceutical company.
MD-PhD Dual Degree Training. MD-PhD programs provide training in both medicine and research. They are specifically designed for those who want to become research physicians. The AAMC MD-PhD section is committed to recruiting and training a diverse Physician-Scientist workforce and an inclusive learning and working environment.
The career revolves around clinical investigations to understand human diseases and rigorous lab work. As a medical researcher, formal education will not suffice. As a developing medical ...
Research Training. Academic medical centers play a leading role in training the next generation of scientists. These researchers are trained across the continuum of research disciplines- to ensure future breakthroughs to improve health and transform health care. There are multiple training pathways for pursuing a career in medical research ...
4. Consider pursuing a medical degree If you want to pursue clinical work, earn a medical degree. In order to practice medicine, you also need to complete an internship, a residency and your license. Keep in mind that if you only want to work in research instead of clinical studies, you don't need a medical degree to become a biomedical scientist.
What level of education is required for Medical Researchers? 56% of Medical Researchers have a bachelor's degree, 22% major in biology. Learn all about Medical Researcher educational requirements, degrees, majors, certifications, online courses, and top colleges that will help you advance in a Medical Researcher career.
To earn this certification, you must have one of the following: At least two years of clinical research experience or 3,500 hours of part-time experience in the past five years. A degree in clinical research and at least one year of full-time experience. A certificate in clinical research, a bachelor's or associate degree in health science ...
A Medical Research Scientist conducts research with the goal of understanding diseases and improving human health. May study biology and causes of health problems, assess effectiveness of treatments or develop new pharmaceutical products. ... Not all job postings list education requirements. Education Level Percentage; Associate's Degree: 4.13% ...
The educational requirements for a medical research scientist typically include a doctorate degree. According to Professor of Biology, David Cool Ph.D. from Wright State University, "Every medical student has to do research, and most large teaching hospitals have a research coordinator that will work to generate grants in the department. This means that lab personnel is required for these ...
The Medical Education Research Certificate (MERC) program is intended to provide the knowledge necessary to understand the purposes and processes of medical education research, to become informed consumers of the medical education research literature, and to be effective collaborators in medical education research.
Hold a "clinical research degree" or complete 1,500 hours performing essential duties. Submit a resume documenting and demonstrating job performance. Please note that in some cases, additional education can be used to substitute for work experience hours. Please see credentialing websites for details.
Medical residencies, required after medical school, are more competitive than ever, Arora says. And many are asking applicants whether they have published research papers.
Research Nurses can earn a higher annual salary with increased years of experience. Less than 1 year of experience earn an average salary of $68,000. 1-4 years of experience earn an average salary of $73,000. 5-9 years of experience earns an average salary of $73,000. 10-19 years of experience earns an average salary of $80,000.
The UT Tyler Health Science Center facility offers an array of crucial medical and healthcare education resources, fostering an environment dedicated to excellence in education. From cutting-edge simulation labs to dedicated research spaces, every aspect of the UT Tyler Health Science Center is designed to enhance the educational experience.
Developing and managing VHA's research regulatory policies. Coordinating, prioritizing, and evaluating research education and training. Developing, coordinating and managing the enterprise-wide access to central research repositories and digital research systems (e.g., IT, data, and repository resources).
Research also reflects, in a quantifiable way, an applicant's interest in a field. Residency program directors began valuing research more after the U.S. Medical Licensing Exam (USMLE) Step 1 ...