Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples

What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples
Published on September 14, 2022 by Tegan George . Revised on November 21, 2023.
A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a master’s program or a capstone to a bachelor’s degree.
Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation , it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete. It relies on your ability to conduct research from start to finish: choosing a relevant topic , crafting a proposal , designing your research , collecting data , developing a robust analysis, drawing strong conclusions , and writing concisely .
Thesis template
You can also download our full thesis template in the format of your choice below. Our template includes a ready-made table of contents , as well as guidance for what each chapter should include. It’s easy to make it your own, and can help you get started.
Download Word template Download Google Docs template
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Thesis vs. thesis statement, how to structure a thesis, acknowledgements or preface, list of figures and tables, list of abbreviations, introduction, literature review, methodology, reference list, proofreading and editing, defending your thesis, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about theses.
You may have heard the word thesis as a standalone term or as a component of academic writing called a thesis statement . Keep in mind that these are two very different things.
- A thesis statement is a very common component of an essay, particularly in the humanities. It usually comprises 1 or 2 sentences in the introduction of your essay , and should clearly and concisely summarize the central points of your academic essay .
- A thesis is a long-form piece of academic writing, often taking more than a full semester to complete. It is generally a degree requirement for Master’s programs, and is also sometimes required to complete a bachelor’s degree in liberal arts colleges.
- In the US, a dissertation is generally written as a final step toward obtaining a PhD.
- In other countries (particularly the UK), a dissertation is generally written at the bachelor’s or master’s level.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

The final structure of your thesis depends on a variety of components, such as:
- Your discipline
- Your theoretical approach
Humanities theses are often structured more like a longer-form essay . Just like in an essay, you build an argument to support a central thesis.
In both hard and social sciences, theses typically include an introduction , literature review , methodology section , results section , discussion section , and conclusion section . These are each presented in their own dedicated section or chapter. In some cases, you might want to add an appendix .
Thesis examples
We’ve compiled a short list of thesis examples to help you get started.
- Example thesis #1: “Abolition, Africans, and Abstraction: the Influence of the ‘Noble Savage’ on British and French Antislavery Thought, 1787-1807” by Suchait Kahlon.
- Example thesis #2: “’A Starving Man Helping Another Starving Man’: UNRRA, India, and the Genesis of Global Relief, 1943-1947″ by Julian Saint Reiman.
The very first page of your thesis contains all necessary identifying information, including:
- Your full title
- Your full name
- Your department
- Your institution and degree program
- Your submission date.
Sometimes the title page also includes your student ID, the name of your supervisor, or the university’s logo. Check out your university’s guidelines if you’re not sure.
Read more about title pages
The acknowledgements section is usually optional. Its main point is to allow you to thank everyone who helped you in your thesis journey, such as supervisors, friends, or family. You can also choose to write a preface , but it’s typically one or the other, not both.
Read more about acknowledgements Read more about prefaces
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
An abstract is a short summary of your thesis. Usually a maximum of 300 words long, it’s should include brief descriptions of your research objectives , methods, results, and conclusions. Though it may seem short, it introduces your work to your audience, serving as a first impression of your thesis.
Read more about abstracts
A table of contents lists all of your sections, plus their corresponding page numbers and subheadings if you have them. This helps your reader seamlessly navigate your document.
Your table of contents should include all the major parts of your thesis. In particular, don’t forget the the appendices. If you used heading styles, it’s easy to generate an automatic table Microsoft Word.
Read more about tables of contents
While not mandatory, if you used a lot of tables and/or figures, it’s nice to include a list of them to help guide your reader. It’s also easy to generate one of these in Word: just use the “Insert Caption” feature.
Read more about lists of figures and tables
If you have used a lot of industry- or field-specific abbreviations in your thesis, you should include them in an alphabetized list of abbreviations . This way, your readers can easily look up any meanings they aren’t familiar with.
Read more about lists of abbreviations
Relatedly, if you find yourself using a lot of very specialized or field-specific terms that may not be familiar to your reader, consider including a glossary . Alphabetize the terms you want to include with a brief definition.
Read more about glossaries
An introduction sets up the topic, purpose, and relevance of your thesis, as well as expectations for your reader. This should:
- Ground your research topic , sharing any background information your reader may need
- Define the scope of your work
- Introduce any existing research on your topic, situating your work within a broader problem or debate
- State your research question(s)
- Outline (briefly) how the remainder of your work will proceed
In other words, your introduction should clearly and concisely show your reader the “what, why, and how” of your research.
Read more about introductions
A literature review helps you gain a robust understanding of any extant academic work on your topic, encompassing:
- Selecting relevant sources
- Determining the credibility of your sources
- Critically evaluating each of your sources
- Drawing connections between sources, including any themes, patterns, conflicts, or gaps
A literature review is not merely a summary of existing work. Rather, your literature review should ultimately lead to a clear justification for your own research, perhaps via:
- Addressing a gap in the literature
- Building on existing knowledge to draw new conclusions
- Exploring a new theoretical or methodological approach
- Introducing a new solution to an unresolved problem
- Definitively advocating for one side of a theoretical debate
Read more about literature reviews
Theoretical framework
Your literature review can often form the basis for your theoretical framework, but these are not the same thing. A theoretical framework defines and analyzes the concepts and theories that your research hinges on.
Read more about theoretical frameworks
Your methodology chapter shows your reader how you conducted your research. It should be written clearly and methodically, easily allowing your reader to critically assess the credibility of your argument. Furthermore, your methods section should convince your reader that your method was the best way to answer your research question.
A methodology section should generally include:
- Your overall approach ( quantitative vs. qualitative )
- Your research methods (e.g., a longitudinal study )
- Your data collection methods (e.g., interviews or a controlled experiment
- Any tools or materials you used (e.g., computer software)
- The data analysis methods you chose (e.g., statistical analysis , discourse analysis )
- A strong, but not defensive justification of your methods
Read more about methodology sections
Your results section should highlight what your methodology discovered. These two sections work in tandem, but shouldn’t repeat each other. While your results section can include hypotheses or themes, don’t include any speculation or new arguments here.
Your results section should:
- State each (relevant) result with any (relevant) descriptive statistics (e.g., mean , standard deviation ) and inferential statistics (e.g., test statistics , p values )
- Explain how each result relates to the research question
- Determine whether the hypothesis was supported
Additional data (like raw numbers or interview transcripts ) can be included as an appendix . You can include tables and figures, but only if they help the reader better understand your results.
Read more about results sections
Your discussion section is where you can interpret your results in detail. Did they meet your expectations? How well do they fit within the framework that you built? You can refer back to any relevant source material to situate your results within your field, but leave most of that analysis in your literature review.
For any unexpected results, offer explanations or alternative interpretations of your data.
Read more about discussion sections
Your thesis conclusion should concisely answer your main research question. It should leave your reader with an ultra-clear understanding of your central argument, and emphasize what your research specifically has contributed to your field.
Why does your research matter? What recommendations for future research do you have? Lastly, wrap up your work with any concluding remarks.
Read more about conclusions
In order to avoid plagiarism , don’t forget to include a full reference list at the end of your thesis, citing the sources that you used. Choose one citation style and follow it consistently throughout your thesis, taking note of the formatting requirements of each style.
Which style you choose is often set by your department or your field, but common styles include MLA , Chicago , and APA.
Create APA citations Create MLA citations
In order to stay clear and concise, your thesis should include the most essential information needed to answer your research question. However, chances are you have many contributing documents, like interview transcripts or survey questions . These can be added as appendices , to save space in the main body.
Read more about appendices
Once you’re done writing, the next part of your editing process begins. Leave plenty of time for proofreading and editing prior to submission. Nothing looks worse than grammar mistakes or sloppy spelling errors!
Consider using a professional thesis editing service or grammar checker to make sure your final project is perfect.
Once you’ve submitted your final product, it’s common practice to have a thesis defense, an oral component of your finished work. This is scheduled by your advisor or committee, and usually entails a presentation and Q&A session.
After your defense , your committee will meet to determine if you deserve any departmental honors or accolades. However, keep in mind that defenses are usually just a formality. If there are any serious issues with your work, these should be resolved with your advisor way before a defense.
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Survivorship bias
- Self-serving bias
- Availability heuristic
- Halo effect
- Hindsight bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
The conclusion of your thesis or dissertation shouldn’t take up more than 5–7% of your overall word count.
If you only used a few abbreviations in your thesis or dissertation , you don’t necessarily need to include a list of abbreviations .
If your abbreviations are numerous, or if you think they won’t be known to your audience, it’s never a bad idea to add one. They can also improve readability, minimizing confusion about abbreviations unfamiliar to your reader.
When you mention different chapters within your text, it’s considered best to use Roman numerals for most citation styles. However, the most important thing here is to remain consistent whenever using numbers in your dissertation .
A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical first steps in your writing process. It helps you to lay out and organize your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding what kind of research you’d like to undertake.
Generally, an outline contains information on the different sections included in your thesis or dissertation , such as:
- Your anticipated title
- Your abstract
- Your chapters (sometimes subdivided into further topics like literature review , research methods , avenues for future research, etc.)
A thesis is typically written by students finishing up a bachelor’s or Master’s degree. Some educational institutions, particularly in the liberal arts, have mandatory theses, but they are often not mandatory to graduate from bachelor’s degrees. It is more common for a thesis to be a graduation requirement from a Master’s degree.
Even if not mandatory, you may want to consider writing a thesis if you:
- Plan to attend graduate school soon
- Have a particular topic you’d like to study more in-depth
- Are considering a career in research
- Would like a capstone experience to tie up your academic experience
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. (2023, November 21). What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved March 25, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/thesis/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, dissertation & thesis outline | example & free templates, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, 10 research question examples to guide your research project, what is your plagiarism score.

- Langson Library
- Science Library
- Grunigen Medical Library
- Law Library
- Connect From Off-Campus
- Accessibility
- Gateway Study Center

Email this link
Thesis / dissertation formatting manual (2024).
- Filing Fees and Student Status
- Submission Process Overview
- Electronic Thesis Submission
- Paper Thesis Submission
- Formatting Overview
- Fonts/Typeface
- Pagination, Margins, Spacing
- Paper Thesis Formatting
- Preliminary Pages Overview
- Copyright Page
- Dedication Page
Table of Contents
- List of Figures (etc.)
- Acknowledgements
- Text and References Overview
- Figures and Illustrations
- Using Your Own Previously Published Materials
- Using Copyrighted Materials by Another Author
- Open Access and Embargoes
- Copyright and Creative Commons
- Ordering Print (Bound) Copies
- Tutorials and Assistance
- FAQ This link opens in a new window
The Table of Contents should follow these guidelines:
- All sections of the manuscript are listed in the Table of Contents except the Title Page, the Copyright Page, the Dedication Page, and the Table of Contents.
- You may list subsections within chapters
- Creative works are not exempt from the requirement to include a Table of Contents
Table of Contents Example
Here is an example of a Table of Contents page from the Template. Please note that your table of contents may be longer than one page.

- << Previous: Dedication Page
- Next: List of Figures (etc.) >>
- Last Updated: Feb 20, 2024 2:09 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uci.edu/gradmanual
Off-campus? Please use the Software VPN and choose the group UCIFull to access licensed content. For more information, please Click here
Software VPN is not available for guests, so they may not have access to some content when connecting from off-campus.
How to Write a Master's Thesis: A Guide to Planning Your Thesis, Pursuing It, and Avoiding Pitfalls
#scribendiinc
Part 1: Initial Considerations
Who needs to write a master’s thesis.
Thesis writing is one of the more daunting challenges of higher education. That being said, not all master's students have to write a thesis. For example, fields that place a stronger emphasis on applied knowledge, such as nursing, business, and education, tend to have projects and exams to test students on the skills and abilities associated with those fields. Conversely, in disciplines that require in-depth research or highly polished creative abilities, students are usually expected to prove their understanding and independence with a thesis.
What's Your Goal?
Do you want to write a thesis? The process is a long one, often spanning years. It's best to know exactly what you want before you begin. Many people are motivated by career goals. For example, hiring managers may see a master's degree as proof that the candidate is an expert within their field and can lead, motivate, and demonstrate initiative for themselves and others. Others dream of earning their doctorate, and they see a master's degree as a stepping stone toward their Ph.D .

No matter what your desired goal is, you should have one before you start your thesis. With your goal in mind, your work will have a purpose, which will allow you to measure your progress more easily.
Major Types of Theses
Once you've carefully researched or even enrolled in a master's program—a feat that involves its own planning and resources —you should know if you are expected to produce a quantitative (which occurs in many math and science programs), qualitative (which occurs in many humanities programs), or creative (which occurs in many creative writing, music, or fine arts programs) thesis.
Time and Energy Considerations
Advanced degrees are notoriously time and energy consuming. If you have a job, thesis writing will become your second job. If you have a family, they will need to know that your thesis will take a great deal of your attention, energy, and focus.

Your studies should not consume you, but they also should not take a back seat to everything else. You will be expected to attend classes, conduct research, source relevant literature, and schedule meetings with various people as you pursue your master's, so it's important to let those you care about know what's going on.
As a general note, most master's programs expect students to finish within a two-year period but are willing to grant extra time if requested, especially if that time is needed to deal with unexpected life events (more on those later).
Part 2: Form an Initial Thesis Question, and Find a Supervisor
When to begin forming your initial thesis question.
Some fields, such as history, may require you to have already formed your thesis question and to have used it to create a statement of intent (outlining the nature of your research) prior to applying to a master’s program. Others may require this information only after you've been accepted. Most of the time, you will be expected to come up with your topic yourself. However, in some disciplines, your supervisor may assign a general research topic to you.
Overall, requirements vary immensely from program to program, so it's best to confirm the exact requirements of your specific program.
What to Say to Your Supervisor
You will have a supervisor during your master's studies. Have you identified who that person will be? If yes, have you introduced yourself via email or phone and obtained information on the processes and procedures that are in place for your master's program? Once you've established contact, request an in-person meeting with him or her, and take a page of questions along with you. Your questions might include:
- Is there a research subject you can recommend in my field?
- I would like to pursue [target research subject] for my thesis. Can you help me narrow my focus?
- Can you give me an example of a properly formatted thesis proposal for my program?
Don't Be Afraid to Ask for Help (to a Degree)
Procedures and expectations vary from program to program, and your supervisor is there to help remove doubt and provide encouragement so you can follow the right path when you embark on writing your thesis. Since your supervisor has almost certainly worked with other graduate students (and was one at some point), take advantage of their experience, and ask questions to put your mind at ease about how to write a master’s thesis.
That being said, do not rely too heavily on your supervisor. As a graduate student, you are also expected to be able to work independently. Proving your independent initiative and capacity is part of what will earn you your master's degree.
Part 3: Revise Your Thesis
Read everything you can get your hands on.
Whether you have a question or need to create one, your next step is simple and applies to all kinds of theses: read.

Seek Out Knowledge or Research Gaps
Read everything you can that relates to the question or the field you are studying. The only way you will be able to determine where you can go is to see where everyone else has been. After you have read some published material, you will start to spot gaps in current research or notice things that could be developed further with an alternative approach. Things that are known but not understood or understood but not explained clearly or consistently are great potential thesis subjects. Addressing something already known from a new perspective or with a different style could also be a potentially valuable project. Whichever way you choose to do it, keep in mind that your project should make a valuable contribution to your field.

Talk with Experts in Your Field (and Don't Be Afraid to Revise Your Thesis)
To help narrow down your thesis topic, talk to your supervisor. Your supervisor will have an idea of what is current in your field and what can be left alone because others are already working on it. Additionally, the school you are attending will have programs and faculty with particular areas of interest within your chosen field.
On a similar note, don't be surprised if your thesis question changes as you study. Other students and researchers are out there, and as they publish, what you are working on can change. You might also discover that your question is too vague, not substantial enough, or even no longer relevant. Do not lose heart! Take what you know and adjust the question to address these concerns as they arise. The freedom to adapt is part of the power you hold as a graduate student.
Part 4: Select a Proposal Committee
What proposal committees are and why they're useful.
When you have a solid question or set of questions, draft a proposal.

You'll need an original stance and a clear justification for asking, and answering, your thesis question. To ensure this, a committee will review your thesis proposal. Thankfully, that committee will consist of people assigned by your supervisor or department head or handpicked by you. These people will be experts who understand your field of study and will do everything in their power to ensure that you are pursuing something worthwhile. And yes, it is okay to put your supervisor on your committee. Some programs even require that your supervisor be on your committee.
Just remember that the committee will expect you to schedule meetings with them, present your proposal, respond to any questions they might have for you, and ultimately present your findings and thesis when all the work is done. Choose those who are willing to support you, give constructive feedback, and help address issues with your proposal. And don't forget to give your proposal a good, thorough edit and proofread before you present it.
How to Prepare for Committee Meetings
Be ready for committee meetings with synopses of your material for committee members, answers for expected questions, and a calm attitude. To prepare for those meetings, sit in on proposal and thesis defenses so you can watch how other graduate students handle them and see what your committee might ask of you. You can even hold rehearsals with friends and fellow students acting as your committee to help you build confidence for your presentation.

Part 5: Write Your Thesis
What to do once your proposal is approved.
After you have written your thesis proposal and received feedback from your committee, the fun part starts: doing the work. This is where you will take your proposal and carry it out. If you drafted a qualitative or quantitative proposal, your experimentation or will begin here. If you wrote a creative proposal, you will now start working on your material. Your proposal should be strong enough to give you direction when you perform your experiments, conduct interviews, or craft your work. Take note that you will have to check in with your supervisor from time to time to give progress updates.

Thesis Writing: It's Important to Pace Yourself and Take Breaks
Do not expect the work to go quickly. You will need to pace yourself and make sure you record your progress meticulously. You can always discard information you don't need, but you cannot go back and grab a crucial fact that you can't quite remember. When in doubt, write it down. When drawing from a source, always create a citation for the information to save your future self time and stress. In the same sense, you may also find journaling to be a helpful process.
Additionally, take breaks and allow yourself to step away from your thesis, even if you're having fun (and especially if you're not). Ideally, your proposal should have milestones in it— points where you can stop and assess what you've already completed and what's left to do. When you reach a milestone, celebrate. Take a day off and relax. Better yet, give yourself a week's vacation! The rest will help you regain your focus and ensure that you function at your best.
How to Become More Comfortable with Presenting Your Work
Once you start reaching your milestones, you should be able to start sharing what you have. Just about everyone in a graduate program has experience giving a presentation at the front of the class, attending a seminar, or watching an interview. If you haven't (or even if you have), look for conferences and clubs that will give you the opportunity to learn about presenting your work and become comfortable with the idea of public speaking. The more you practice talking about what you are studying, the more comfortable you'll be with the information, which will make your committee defenses and other official meetings easier.
Published authors can be called upon to present at conferences, and if your thesis is strong, you may receive an email or a phone call asking if you would share your findings onstage.
Presenting at conferences is also a great way to boost your CV and network within your field. Make presenting part of your education, and it will become something you look forward to instead of fear.
What to Do If Your Relationship with Your Supervisor Sours
A small aside: If it isn't already obvious, you will be communicating extensively with others as you pursue your thesis. That also means that others will need to communicate with you, and if you've been noticing things getting quiet, you will need to be the one to speak up. Your supervisor should speak to you at least once a term and preferably once a week in the more active parts of your research and writing. If you give written work to your supervisor, you should have feedback within three weeks.
If your supervisor does not provide feedback, frequently misses appointments, or is consistently discouraging of your work, contact your graduate program advisor and ask for a new supervisor. The relationship with your supervisor is crucial to your success, especially if she or he is on your committee, and while your supervisor does not have to be friendly, there should at least be professional respect between you.
What to Do If a Crisis Strikes
If something happens in your life that disrupts everything (e.g., emotional strain, the birth of a child, or the death of a family member), ask for help. You are a human being, and personal lives can and do change without warning. Do not wait until you are falling apart before asking for help, either. Learn what resources exist for crises before you have one, so you can head off trauma before it hits. That being said, if you get blindsided, don't refuse help. Seek it out, and take the time you need to recover. Your degree is supposed to help you become a stronger and smarter person, not break you.
Part 6: Polish and Defend Your Master's Thesis
How to write a master’s thesis: the final stages.
After your work is done and everything is written down, you will have to give your thesis a good, thorough polishing. This is where you will have to organize the information, draft it into a paper format with an abstract, and abbreviate things to help meet your word-count limit. This is also where your final editing and proofreading passes will occur, after which you will face your final hurdle: presenting your thesis defense to your committee. If they approve your thesis, then congratulations! You are now a master of your chosen field.
Conclusion and Parting Thoughts
Remember that you do not (and should not) have to learn how to write a master’s thesis on your own. Thesis writing is collaborative, as is practically any kind of research.

While you will be expected to develop your thesis using your own initiative, pursue it with your own ambition, and complete it with your own abilities, you will also be expected to use all available resources to do so. The purpose of a master's thesis is to help you develop your own independent abilities, ensuring that you can drive your own career forward without constantly looking to others to provide direction. Leaders get master's degrees. That's why many business professionals in leadership roles have graduate degree initials after their last names. If you already have the skills necessary to motivate yourself, lead others, and drive change, you may only need your master's as an acknowledgement of your abilities. If you do not, but you apply yourself carefully and thoroughly to the pursuit of your thesis, you should come away from your studies with those skills in place.
A final thought regarding collaboration: all theses have a section for acknowledgements. Be sure to say thank you to those who helped you become a master. One day, someone might be doing the same for you.
Image source: Falkenpost/Pixabay.com
We’re Masters at Master’s Theses! Make Yours Shine.
Let our expert academic editors perfect your writing, or get a free sample, about the author.

A Scribendi in-house editor, Anthony is happily putting his BA in English from Western University to good use with thoughtful feedback and incisive editing. An avid reader and gamer, he can be found during his off hours enjoying narrative-driven games and obscure and amusing texts, as well as cooking for his family.
Have You Read?
"The Complete Beginner's Guide to Academic Writing"
Related Posts

How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation

Selecting a Thesis Committee

Thesis/Dissertation Writing Series: How to Write a Literature Review
Upload your file(s) so we can calculate your word count, or enter your word count manually.
We will also recommend a service based on the file(s) you upload.
English is not my first language. I need English editing and proofreading so that I sound like a native speaker.
I need to have my journal article, dissertation, or term paper edited and proofread, or I need help with an admissions essay or proposal.
I have a novel, manuscript, play, or ebook. I need editing, copy editing, proofreading, a critique of my work, or a query package.
I need editing and proofreading for my white papers, reports, manuals, press releases, marketing materials, and other business documents.
I need to have my essay, project, assignment, or term paper edited and proofread.
I want to sound professional and to get hired. I have a resume, letter, email, or personal document that I need to have edited and proofread.
Prices include your personal % discount.
Prices include % sales tax ( ).

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- Dissertation Table of Contents in Word | Instructions & Examples
Dissertation Table of Contents in Word | Instructions & Examples
Published on 15 May 2022 by Tegan George .
The table of contents is where you list the chapters and major sections of your thesis, dissertation, or research paper, alongside their page numbers. A clear and well-formatted table of contents is essential, as it demonstrates to your reader that a quality paper will follow.
The table of contents (TOC) should be placed between the abstract and the introduction. The maximum length should be two pages. Depending on the nature of your thesis, dissertation, or paper, there are a few formatting options you can choose from.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
What to include in your table of contents, what not to include in your table of contents, creating a table of contents in microsoft word, table of contents examples, updating a table of contents in microsoft word, other lists in your thesis, dissertation, or research paper, frequently asked questions about the table of contents.
Depending on the length of your document, you can choose between a single-level, subdivided, or multi-level table of contents.
- A single-level table of contents only includes ‘level 1’ headings, or chapters. This is the simplest option, but it may be too broad for a long document like a dissertation.
- A subdivided table of contents includes chapters as well as ‘level 2’ headings, or sections. These show your reader what each chapter contains.
- A multi-level table of contents also further divides sections into ‘level 3’ headings. This option can get messy quickly, so proceed with caution. Remember your table of contents should not be longer than 2 pages. A multi-level table is often a good choice for a shorter document like a research paper.
Examples of level 1 headings are Introduction, Literature Review, Methodology, and Bibliography. Subsections of each of these would be level 2 headings, further describing the contents of each chapter or large section. Any further subsections would be level 3.
In these introductory sections, less is often more. As you decide which sections to include, narrow it down to only the most essential.
Including appendices and tables
You should include all appendices in your table of contents. Whether or not you include tables and figures depends largely on how many there are in your document.
If there are more than three figures and tables, you might consider listing them on a separate page. Otherwise, you can include each one in the table of contents.
- Theses and dissertations often have a separate list of figures and tables.
- Research papers generally don’t have a separate list of figures and tables.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
All level 1 and level 2 headings should be included in your table of contents, with level 3 headings used very sparingly.
The following things should never be included in a table of contents:
- Your acknowledgements page
- Your abstract
- The table of contents itself
The acknowledgements and abstract always precede the table of contents, so there’s no need to include them. This goes for any sections that precede the table of contents.
To automatically insert a table of contents in Microsoft Word, be sure to first apply the correct heading styles throughout the document, as shown below.
- Choose which headings are heading 1 and which are heading 2 (or 3!
- For example, if all level 1 headings should be Times New Roman, 12-point font, and bold, add this formatting to the first level 1 heading.
- Highlight the level 1 heading.
- Right-click the style that says ‘Heading 1’.
- Select ‘Update Heading 1 to Match Selection’.
- Allocate the formatting for each heading throughout your document by highlighting the heading in question and clicking the style you wish to apply.
Once that’s all set, follow these steps:
- Add a title to your table of contents. Be sure to check if your citation style or university has guidelines for this.
- Place your cursor where you would like your table of contents to go.
- In the ‘References’ section at the top, locate the Table of Contents group.
- Here, you can select which levels of headings you would like to include. You can also make manual adjustments to each level by clicking the Modify button.
- When you are ready to insert the table of contents, click ‘OK’ and it will be automatically generated, as shown below.
The key features of a table of contents are:
- Clear headings and subheadings
- Corresponding page numbers
Check with your educational institution to see if they have any specific formatting or design requirements.
Write yourself a reminder to update your table of contents as one of your final tasks before submitting your dissertation or paper. It’s normal for your text to shift a bit as you input your final edits, and it’s crucial that your page numbers correspond correctly.
It’s easy to update your page numbers automatically in Microsoft Word. Simply right-click the table of contents and select ‘Update Field’. You can choose either to update page numbers only or to update all information in your table of contents.
In addition to a table of contents, you might also want to include a list of figures and tables, a list of abbreviations and a glossary in your thesis or dissertation. You can use the following guides to do so:
- List of figures and tables
- List of abbreviations
It is less common to include these lists in a research paper.
All level 1 and 2 headings should be included in your table of contents . That means the titles of your chapters and the main sections within them.
The contents should also include all appendices and the lists of tables and figures, if applicable, as well as your reference list .
Do not include the acknowledgements or abstract in the table of contents.
To automatically insert a table of contents in Microsoft Word, follow these steps:
- Apply heading styles throughout the document.
- In the references section in the ribbon, locate the Table of Contents group.
- Click the arrow next to the Table of Contents icon and select Custom Table of Contents.
- Select which levels of headings you would like to include in the table of contents.
Make sure to update your table of contents if you move text or change headings. To update, simply right click and select Update Field.
The table of contents in a thesis or dissertation always goes between your abstract and your introduction.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
George, T. (2022, May 15). Dissertation Table of Contents in Word | Instructions & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 25 March 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/contents-page/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, dissertation title page, how to write an abstract | steps & examples, thesis & dissertation acknowledgements | tips & examples.
Google Custom Search
Wir verwenden Google für unsere Suche. Mit Klick auf „Suche aktivieren“ aktivieren Sie das Suchfeld und akzeptieren die Nutzungsbedingungen.
Hinweise zum Einsatz der Google Suche
- Associate Professorship of Travel Behavior
- TUM School of Engineering and Design
- Technical University of Munich
Typical Structure of a Bachelor's or Master's Thesis
Most thesis are structured as shown below. Each part may be split into several chapter. For example, the part introduction may have two separate chapters for a the general introduction to the topic and the research question. But the parts commonly appear in the following order:
- Acknowledgement (Optional)
Table of Contents
1. introduction, 2. literature review, 3. data collection, 4. analysis, 5. conclusions, list of references, statement of independent work.
- Appendix (Optional)
TUM provides a template for theses that is recommended to use. You can download this template in Word or LaTeX format (login with your TUM account required to access).
There is no mandatory length of a thesis. Most well-written master's theses have between 50 and 80 pages, Bachelor's theses typically have between 40 and 60 pages. However, depending on your topic and your writing style, more or fewer pages may be appropriate. Be aware that your thesis will only be evaluated based on the written document and the defense. If you did some nice work (that you might have shown to your adviser at some point) and forget to add it to your written document, it cannot be evaluated.

The title page should include the following information:
- Technical University of Munich Logo
- Title of the thesis
- Subtitle of the thesis (optional)
- Full author name
- Name of advisers
It is also nice (but optional) to add a pretty graphic from your research to the title page.
Acknowledgement
In this part, you acknowledge any support you may have gotten while preparing your thesis. For example, if an agency provided you with data, you definitely should thank them here. It is also not uncommon to offer personal thank to friends and/or family who supported the thesis. You may also mention your adviser if (s)he was helpful, but that is optional of course.
If you received a scholarship that supported you during the time you wrote your thesis, you definitely should acknowledge that support here as well.
The summary is a key part of your thesis and part of what is evaluated by your thesis committee. Make sure to reserve sufficient time at the very end to write a very good summary. The summary should be about one page long and include your research question, describe the data you used, briefly describe the methodology applied and (very important) also summarize the results you found.
The table of contents lists all chapters and subchapters of your thesis and provides the page number where each chapter starts. Word and LaTeX offer automated functions to create a table of contents if you defined headers properly. Make sure to update the table of contents before you print to ensure that all page numbers are correct.
Following the table of contents, you also need to provide a list of figures and a list of tables. Likewise, these lists also provide the page number where the figures and tables can be found. Again, word and LaTeX provide automated functions for creating such lists.
The introduction shall provide the reader with an entryway to your topic. Commonly, the introduction is not too technical and provides the reader with a very general introduction why the topic of the thesis is relevant. Empirical examples are particular popular in introductions (make sure to provide citations), such as:
Thesis Topic: Managing Freight Flows to Reduce Highway Maintenance Costs
The first sentence of introduction could be: Freight flows largely define the costs for maintaining infrastructure, as the rear axles of a typical 13 ton van cause 1,000-times the structural damage of a car (Small, Winston, and Evans 1989: 11).
The introduction should also provide at least one research question that you try to answer. Last but not least, the introduction should also introduce the structure of the thesis (i.e., which chapters the reader should expect) in one paragraph.
The literature review is a core element of your thesis and shows that you are capable of working scientifically. As you explain what other researchers have found on your topic, the reader will realize that you know this topic extremely well. This will build trust that you can provide a piece of work yourself that is scientifically relevant.
Equally important, you will need to identify a gap in the literature that you intent to fill. This is how you justify your thesis, and it helps the reader to assess the importance of your work. This gap may be methodological ("I will develop a new method that is able to answer my research question, which previously applied methods cannot as well."), use new data ("Other researchers used database X, but I will use data retrieved by Y."), or a new application ("This method has never been applied to the city of Munich.").
Describe in detail which data you use and how you collect these data. This may include qualitative data ("I analyze these in-depth travel behavior surveys."), or statistics you use, or data you collect yourself. The description should be as detailed that a very good fellow student in your field would be able to more or less reproduce your work.
If you conduct a case study, the study area needs to be introduced here.
Obviously, here you describe in great detail the actual analysis you conducted. The level of detail should be sufficient to allow a very smart fellow student in your field to reproduce more or less your research.
The most important at the beginning: The chapter Conclusions does not contain a summary of your thesis! The summary is provided in the abstract of the beginning of your thesis, but not here.
Instead, the conclusions shall do what the title suggests: Synthesize your findings and conclude what we learn from that. It will be useful to refer to your research question(s) and discuss if those were confirmed or rejected by your research. You may also refer back to you literature review and compare your findings with the findings that others have published.
This is also a good place to talk about limitations of your research. By clearly stating what your research is not able to do well, your thesis becomes stronger. If you show that you understand what your methodology misses, you show the reader that you understand very well what you research has accomplished, and what may need further research.
Which brings us to another topic you should touch on in your conclusions: What are future research needs? If a fellow student of you wanted to build on your research, what would be the next logical step that (s)he should try to address?
Last but not least, you may also assess if your findings have practical implications. Examples: Should waste water engineers use an additional test to assess water quality? Should transportation planners use different data to assess the level of service?
Here you list all references that were cited in your work, and only those references. References you read but did not cite do not appear here. After all, they were not relevant enough for this thesis to be cited, so they do not belong in your list of references.
If you use a reference management system (highly recommended), the list of references is created automatically. LaTeX also nicely integrated with Bibtex to automatically create a list of references. TUM offers Citavi and Endnote for free to students (access here , log in required), and there are a number of other systems that also may work well for you (see this list on wikipedia).
Finally, you need to provide a statement that reads as follows:
In German: Ich versichere hiermit, dass ich die von mir eingereichte Abschlussarbeit selbstständig verfasst und keine anderen als die angegebenen Quellen und Hilfsmittel benutzt habe.
Or in English: I hereby confirm that this thesis was written independently by myself without the use of any sources beyond those cited, and all passages and ideas taken from other sources are cited accordingly.
Appendix (or Appendices)
You may provide additional information in appendices. Some researchers are of the opinion that if something is important it should go into the main body of the thesis; and if it doesn't deserve being in the main body of the thesis, it should not be provided at all. Others say that is may be useful to provide extensive tables, mathematical proofs or series of graphics in the appendix if they are not required to understand the main text but useful for the interested reader.
It is very uncommon to provide a single graphic or a single table in the appendix. Those usually work better in the main body of the text. Commonly, only material that covers several pages would go into the appendix, it it distracts the reader if all those materials were shown in the main body of the thesis.
Extensive appendices may be left out in the printed version and only be provided on a CD or a thumb drive. Note, however, that some advisers refuse to open any files stored on a CD or a thumb drive while evaluating your thesis. As a rule of thumb, your thesis needs to be understandable without reading any appendices.
Thesis and Dissertation Guide
- « Thesis & Dissertation Resources
- The Graduate School Home
- Introduction
Copyright Page
Dedication, acknowledgements, preface (optional), table of contents.
- List of Tables, Figures, and Illustrations
List of Abbreviations
List of symbols.
- Non-Traditional Formats
- Font Type and Size
- Spacing and Indentation
- Tables, Figures, and Illustrations
- Formatting Previously Published Work
- Internet Distribution
- Open Access
- Registering Copyright
- Using Copyrighted Materials
- Use of Your Own Previously Published Materials
- Submission Steps
- Submission Checklist
- Sample Pages

I. Order and Components
Please see the sample thesis or dissertation pages throughout and at the end of this document for illustrations. The following order is required for components of your thesis or dissertation:
- Dedication, Acknowledgements, and Preface (each optional)
- Table of Contents, with page numbers
- List of Tables, List of Figures, or List of Illustrations, with titles and page numbers (if applicable)
- List of Abbreviations (if applicable)
- List of Symbols (if applicable)
- Introduction, if any
- Main body, with consistent subheadings as appropriate
- Appendices (if applicable)
- Endnotes (if applicable)
- References (see section on References for options)
Many of the components following the title and copyright pages have required headings and formatting guidelines, which are described in the following sections.
Please consult the Sample Pages to compare your document to the requirements. A Checklist is provided to assist you in ensuring your thesis or dissertation meets all formatting guidelines.
The title page of a thesis or dissertation must include the following information:

- The title of the thesis or dissertation in all capital letters and centered 2″ below the top of the page.
- Your name, centered 1″ below the title. Do not include titles, degrees, or identifiers. The name you use here does not need to exactly match the name on your university records, but we recommend considering how you will want your name to appear in professional publications in the future.
Notes on this statement:
- When indicating your degree in the second bracketed space, use the full degree name (i.e., Doctor of Philosophy, not Ph.D. or PHD; Master of Public Health, not M.P.H. or MPH; Master of Social Work, not M.S.W. or MSW).
- List your department, school, or curriculum rather than your subject area or specialty discipline in the third bracketed space. You may include your subject area or specialty discipline in parentheses (i.e., Department of Romance Languages (French); School of Pharmacy (Molecular Pharmaceutics); School of Education (School Psychology); or similar official area).
- If you wish to include both your department and school names, list the school at the end of the statement (i.e., Department of Pharmacology in the School of Medicine).
- A dissertation submitted to the faculty at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in the Department of Public Policy.
- A thesis submitted to the faculty at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in the School of Dentistry (Endodontics).
- A thesis submitted to the faculty at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in the Department of Nutrition in the Gillings School of Global Public Health.
- A dissertation submitted to the faculty at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in the School of Education (Cultural Studies and Literacies).
- The words “Chapel Hill” must be centered 1″ below the statement.
- One single-spaced line below that, center the year in which your committee approves the completed thesis or dissertation. This need not be the year you graduate.
- Approximately 2/3 of the way across the page on the right-hand side of the page, 1″ below the year, include the phrase “Approved by:” (with colon) followed by each faculty member's name on subsequent double-spaced lines. Do not include titles such as Professor, Doctor, Dr., PhD, or any identifiers such as “chair” or “advisor” before or after any names. Line up the first letter of each name on the left under the “A” in the “Approved by:” line. If a name is too long to fit on one line, move this entire section of text slightly to the left so that formatting can be maintained.
- No signatures, signature lines, or page numbers should be included on the title page.
Include a copyright page with the following information single-spaced and centered 2″ above the bottom of the page:

© Year Author's Full Name (as it appears on the title page) ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
This page immediately follows the title page. It should be numbered with the lower case Roman numeral ii centered with a 1/2″ margin from the bottom edge.
Inclusion of this page offers you, as the author, additional protection against copyright infringement as it eliminates any question of authorship and copyright ownership. You do not need to file for copyright in order to include this statement in your thesis or dissertation. However, filing for copyright can offer other protections.
See Section IV for more information on copyrighting your thesis or dissertation.
Include an abstract page following these guidelines:

- Include the heading “ABSTRACT” in all capital letters, and center it 2″ below the top of the page.
- One double-spaced line below “ABSTRACT”, center your name, followed by a colon and the title of the thesis or dissertation. Use as many lines as necessary. Be sure that your name and the title exactly match the name and title used on the Title page.
- One single-spaced line below the title, center the phrase “(Under the direction of [advisor's name])”. Include the phrase in parentheses. Include the first and last name(s) of your advisor or formal co-advisors. Do not include the name of other committee members. Use the advisor's name only; do not include any professional titles such as PhD, Professor, or Dr. or any identifiers such as “chair” or “advisor”.
- Skip one double-spaced line and begin the abstract. The text of your abstract must be double-spaced and aligned with the document's left margin with the exception of indenting new paragraphs. Do not center or right-justify the abstract.
- Abstracts cannot exceed 150 words for a thesis or 350 words for a dissertation.
- Number the abstract page with the lower case Roman numeral iii (and iv, if more than one page) centered with a 1/2″ margin from the bottom edge.
Please write and proofread your abstract carefully. When possible, avoid including symbols or foreign words in your abstract, as they cannot be indexed or searched. Avoid mathematical formulas, diagrams, and other illustrative materials in the abstract. Offer a brief description of your thesis or dissertation and a concise summary of its conclusions. Be sure to describe the subject and focus of your work with clear details and avoid including lengthy explanations or opinions.
Your title and abstract will be used by search engines to help potential audiences locate your work, so clarity will help to draw the attention of your targeted readers.
You have an option to include a dedication, acknowledgements, or preface. If you choose to include any or all of these elements, give each its own page(s).

A dedication is a message from the author prefixed to a work in tribute to a person, group, or cause. Most dedications are short statements of tribute beginning with “To…” such as “To my family”.
Acknowledgements are the author's statement of gratitude to and recognition of the people and institutions that helped the author's research and writing.
A preface is a statement of the author's reasons for undertaking the work and other personal comments that are not directly germane to the materials presented in other sections of the thesis or dissertation. These reasons tend to be of a personal nature.
Any of the pages must be prepared following these guidelines:
- Do not place a heading on the dedication page.
- The text of short dedications must be centered and begin 2″ from the top of the page.
- Headings are required for the “ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS” and “PREFACE” pages. Headings must be in all capital letters and centered 2″ below the top of the page.
- The text of the acknowledgements and preface pages must begin one double-spaced line below the heading, be double-spaced, and be aligned with the document's left margin with the exception of indenting new paragraphs.
- Subsequent pages of text return to the 1″ top margin.
- The page(s) must be numbered with consecutive lower case Roman numerals (starting with the page number after the abstract) centered with a 1/2″ margin from the bottom edge.
Include a table of contents following these guidelines:

- Include the heading “TABLE OF CONTENTS” in all capital letters, and center it 2″ below the top of the page.
- Include one double-spaced line between the heading and the first entry.
- The table of contents should not contain listings for the pages that precede it, but it must list all parts of the thesis or dissertation that follow it.
- If relevant, be sure to list all appendices and a references section in your table of contents. Include page numbers for these items but do not assign separate chapter numbers.
- Entries must align with the document's left margin or be indented to the right of the left page margin using consistent tabs.
- Major subheadings within chapters must be included in the table of contents. The subheading(s) should be indented to the right of the left page margin using consistent tabs.
- If an entry takes up more than one line, break up the entry about three-fourths of the way across the page and place the rest of the text on a second line, single-spacing the two lines.
- Include one double-spaced line between each entry.
- Page numbers listed in the table of contents must be located just inside the right page margin with leaders (lines of periods) filling out the space between the end of the entry and the page number. The last digit of each number must line up on the right margin.
- Information included in the table of contents must match the headings, major subheadings, and numbering used in the body of the thesis or dissertation.
- The Table of Contents page(s) must be numbered with consecutive lower case Roman numerals centered with a 1/2″ margin from the bottom edge.
Lists of Tables, Figures, and Illustrations
If applicable, include a list of tables, list of figures, and/or list of illustrations following these guidelines:

- Include the heading(s) in all capital letters, centered 1″ below the top of the page.
- Each entry must include a number, title, and page number.
- Assign each table, figure, or illustration in your thesis or dissertation an Arabic numeral. You may number consecutively throughout the entire work (e.g., Figure 1, Figure 2, etc.), or you may assign a two-part Arabic numeral with the first number designating the chapter in which it appears, separated by a period, followed by a second number to indicate its consecutive placement in the chapter (e.g., Table 3.2 is the second table in Chapter Three).
- Numerals and titles must align with the document's left margin or be indented to the right of the left page margin using consistent tabs.
- Page numbers must be located just inside the right page margin with leaders (lines of periods) filling out the space between the end of the entry and the page number. The last digit of each number must line up on the right margin.
- Numbers, titles, and page numbers must each match the corresponding numbers, titles, and page numbers appearing in the thesis or dissertation.
- All Lists of Tables, Figures, and Illustrations page(s) must be numbered with consecutive lower case Roman numerals centered with a 1/2″ margin from the bottom edge.
If you use abbreviations extensively in your thesis or dissertation, you must include a list of abbreviations and their corresponding definitions following these guidelines:

- Include the heading “LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS” in all capital letters, and center it 1″ below the top of the page.
- Arrange your abbreviations alphabetically.
- Abbreviations must align with the document's left margin or be indented to the right of the left page margin using consistent tabs.
- If an entry takes up more than one line, single-space between the two lines.
- The List of Abbreviations page(s) must be numbered with consecutive lower case Roman numerals centered with a 1/2″ margin from the bottom edge.
If you use symbols in your thesis or dissertation, you may combine them with your abbreviations, titling the section “LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS AND SYMBOLS”, or you may set up a separate list of symbols and their definitions by following the formatting instructions above for abbreviations. The heading you choose must be in all capital letters and centered 1″ below the top of the page.
Previous: Introduction
Next: Format

Creating an Outline for Your Master’s Thesis
1. introduction.
Your master’s thesis serves to explain the research that you have done during your time as a masters student. For many students, the master’s thesis is the longest document that they’ve ever written, and the length of the document can feel intimidating. The purpose of this CommKit is to cover a key element of writing your thesis: the outline.
2. Criteria for Success
The most important criterion for success is that you’ve shown an outline with your chapter breakdown to your advisor. Your advisor is the one that formally signs off on your thesis as completed, so their feedback is the most important.
Every master’s thesis will have the following elements.
- Introduction – Familiarize the reader with the topic and what gap exists in the field.
- Literature Review – Provide a detailed analysis of similar work in the field and how your work is unique. Master’s thesis literature reviews typically have at least 60 citations throughout the entire document
- Methods – Explain how you produced your results
- Results – Show your results and comment on their significance and implications.
- Conclusion – Summarize the methodology you used to generate results, your key findings, and any future areas of work.
Having an outline for your master’s thesis will help you explain the motivation behind your work, and also connect the different experiments or results that you completed. Furthermore, an outline for your master’s thesis can help break down the larger task of writing the entire thesis into smaller, more manageable chapter-sized subtasks.
4. Analyze Your Audience
The most important audience member for your master’s thesis is your advisor, as they are ultimately the person that signs off on whether or not your thesis is sufficient enough to graduate. The needs of any other audience members are secondary.
Ideally, a good master’s thesis is accessible to people that work in your field. In some cases, master’s theses are passed on to newer students so that that research can continue. In these cases, the thesis is used as a guide to introduce newer students to the research area. If you intend for your thesis to be used as a guide for new students, you may spend more time explaining the state of the field in your introduction and literature review. Additionally, your thesis will be posted publicly on DSpace , MIT’s digital repository for all theses.

5. Best Practices
5.1. identify your claims.
A key element to figuring out the unique structure to your master’s thesis is identifying the claims of your work. A claim is an answer to a research question or gap. Your thesis can have both a higher level claim and also lower level claims that motivate the research projects that you worked on. Identifying your claims will help you spot the key objectives which you want to highlight in the thesis. This will keep your writing on topic.
Some examples are shown below:
Gap/Question : There are no field-portable microplastic sensing technologies to measure their distribution in the environment.
→ Claim : Impedance spectroscopy can be used in a microfluidic device to rapidly distinguish organic matter from polymers.
Gap/Question: How effective are convolutional neural networks for pose estimation during in-space assembly?
→ Claim : Convolutional neural networks can be used to estimate the pose of satellites, but struggle with oversaturated images and images with multiple satellites.
5.2. Support Your Claims
Once you have identified your claim, the next step is to identify evidence that will support it. The structure of your paper will be very dependent on the claim that you make. Figure 1 and 2 demonstrate two different structures to support a claim. In one outline, the claim is best supported by a linear structure that describes the building, testing, and validation of a model. In another outline, the claim is best supported by a trifold structure, where three independent methods are discussed. Depending on the extent of the evidence, you could break this trifold structure into 3 separate chapters, or they could all be discussed in a singular chapter. The value of identifying claims and evidence is that it helps you organize your paper coherently at a high level. The number of chapters that are output as a result of your claim identification is up to you and what you think would be sufficient discussion for a chapter within your thesis.
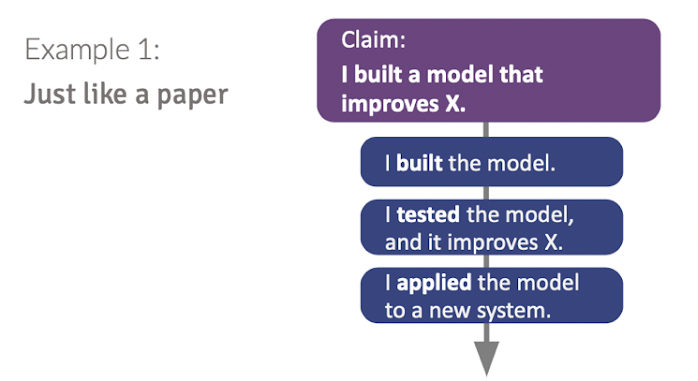
5.3. Connect the Evidence to Your Claims with Reasoning
One common mistake that students make when writing their thesis is treating each chapter as an isolated piece of writing. While it is helpful to break down the actual task of thesis writing into chapter-size pieces, these chapters should have some connection to one another. For your outline, it is ideal to identify what these connections were. Perhaps what made you start on one project was that you realized the weaknesses in your prior work and you wanted to make improvements. For readers who were not doing the research with you, describing the connections between your work in different chapters can help them understand the motivation and value of why you pursued each component.
5.4. Combine Your Claims, Evidence, and Reasoning to Produce Your Outline
Once you have identified your claims, the evidence you have surrounding each claim, and the reasoning that connects each piece of your work, you can now create your full outline, putting the pieces together like a jigsaw puzzle. An example outline is provided as an annotated example.
There are no requirements for minimum or maximum number of chapters that your master’s thesis can have. Therefore, when translating your outline to a literal chapter breakdown, you should feel free to use as many chapters as needed. If your methods section for a claim is extremely long, it may make more sense to have it be a standalone chapter, as shown in the attached annotated pdf.
6. Additional Resources
Every IAP, the Comm Lab hosts a workshop on how to write your master’s thesis. This workshop provides tips for writing each of these sections, and steps you through the process of creating an outline.
Resources and Annotated Examples
Example 1. structure diagram and table of contents, example 2. table of contents.

Get Abroad Education Loan At Affordable Interest Rates

800 Cr. + Disbursed
15+ Lending Partners

30K+ Students Counselled
Master’s thesis examples: tips and ideas for your next academic paper.
- January 1, 2023
- Last Updated: July 21, 2023

Table of Contents
A master’s thesis is extremely important, it represents how you ideate and your interest. Additionally, a master’s thesis also tells your employer a lot about you and what you can bring to the table. It might surprise you, but in most cases, a good master’s thesis can typically help you get the job of your dreams. However, picking a good thesis topic can be a total nightmare. So, We have compiled some tips and curated a few master’s thesis examples in this blog to make your writing process easier and more interesting.
Before we dive into master’s dissertation examples, let’s understand what a master’s thesis is and how to write a good master’s thesis proposal.
What Exactly Is A Master’s Thesis?
The master’s thesis is a unique piece of academic writing that enables students to delve deeply into a subject and develop an extensive report that illustrates how one‘s understanding has increased over the course of the master’s degree programme. To support the underlying argument in the thesis paper, there is a requirement for exhaustive primary and secondary research. In-depth research also helps college students gain knowledge significantly and it improves their learning skills.
What Makes A Good Thesis Paper?
The steps to writing a good master’s thesis are as follows:
Choose a relevant and a good topic
There is no secret recipe for selecting the perfect thesis topic. Students can explore topics of their interest and then widely read up on that subject. Talking to other scholars who are invested in that field also significantly helps. They should start looking for unexplored angles which will help them shed new light on the selected topic. A good topic leads to a good thesis argument and a good argument will result in an excellent thesis paper.
Choose An Accurate Thesis Question
Make certain that your thesis questions are carefully crafted because these questions generate valuable research. It’s important to choose a unique question as your answer will add new substance to the existing body of research. A well-chosen question will also help to keep the research focused, organised, and interesting.
Conduct Extensive Research
As a next step, you must conduct the required research to find the answer to the main question of your Master’s thesis. Do whatever it takes to accurately answer the thesis question which includes reading other research papers that already exist and carrying out surveys and interviews.
It is not enough to just conduct research; one must also know how to format the thesis paper. The manner in which you present your report is also critical.
Here Are The Steps To Follow While Writing A Master’s Thesis

Although formatting varies by university, there are some general steps that must be followed when writing a thesis paper. The following are some basic guidelines:
- Introduction
Draft a coherent introduction. The introductory section is important, as it is the first section a reader comes across and the writer must clearly establish their goal. The objectives of the dissertation and the broader hypothesis must be stated clearly in the introduction. The introduction must be drafted in an accessible tone that allows people who aren’t experts in the field to understand the context.
- Literature review
This segment enables students to show their extensive understanding of the subject by contextualising existing texts in their specialised area. Students go over the main pieces of work, outlining any problems they find. The review of literature is basically an overview of all the previous research on your selected topic.
- Contextualise
After the literature review, contextualise your report. It simply means you should describe how your primary and secondary research adds to the existing body of knowledge after reviewing it. In other words, you should describe how your work advances the field. In this section, you can describe how you found information on the subject. This segment’s purpose is to show the cognitive processes that contributed to your research results.
- Write Your Results
This section gives students the chance to objectively demonstrate what they discovered while conducting their research. Students could perhaps simply list the data they collected using a particular framework or research methods and arrange their findings in a comprehensible way without providing any analysis.
- Conclusion
Your conclusion should explain the significance of this Master’s thesis and possibly offer a route for future researchers to take in order to continue gathering pertinent data. Additionally, after giving readers all the information they need, this portion is where students can decipher the raw data and illustrate how their research has changed their understanding of the subject or given the readers a new perspective.
The following are some master’s thesis examples from a variety of disciplines, ranging from science to architecture. However, these are just a few master’s dissertation examples, and students should conduct their own research to find out relevant topics for themselves.
Here’s The List Of Master’s Thesis Examples :
- An explanation based on the science of COVID-19 and its effects on individuals
- How important is the legalisation of same-sex marriage?
- Pros and cons of the rise of artificial intelligence. Will it soon take over humanity?
- How will the economic downturn affect job opportunities for new graduates?
- What are the workplace sexual harassment issues for all genders
- What is the housing model of the 21st century?
- The significance of recycled materials in environmentally friendly real design
- What are digital marketing trends to expect and how they will affect businesses?
- What is the online advertising impact on consumer behaviour?
- Climate change and its implications in 2023
Master’s Thesis Examples: FAQs
1. Why is a master’s thesis important?
A thesis provides you with an excellent opportunity to dive deep into interesting research in order to acquire a deeper understanding of your field of work.
2. Who should take up a thesis for their final project in their master’s degree?
Students who want to work in academia or do their PhD should always pursue a thesis. They should also take this route if they want to pursue a doctorate.
3. What is the most important factor to consider when deciding on a thesis topic?
Choose a topic that excites you the most. Your topic of interest will make the writing process much easier.
4. Can I co-author my master’s thesis with a faculty member?
If your degree allows that, then absolutely. In many cases, your thesis guide is your co-author.
Thank you for reading this blog on ‘Master’s Thesis Examples: Tips and Ideas For Your Next Academic Paper’ . If you’d like to read more blogs, here are some recommendations that may be of interest to you –
- All About Travel Cards For Students Studying Abroad
- A Beginners Guide On SOP For The UK
- Education Loan In The UAE – A Complete Guide
Looking for student Education Loans?
Your enquiry has been successfully received. We’ll get in touch within 24 hours via email/phone.
Don’t let your friends miss out on all the fun! Simply refer your friend to take loan and get Rs. 5000 .
Error! Please check all the values and try again
Related Categories
- PR and Visa
- Student Loan
- Study Abroad
- EMI Calculator
- Check Eligibility
- Repayment Calculator
- Interest Calculator

Recent Posts

University Of Chicago Scholarships List For 2024
- by Namrata Sukhtankar
- Mar 22, 2024
- Scholarship
- Earning a degree from the prestigious University of Chicago can be a passport to a world of...

University Of Huddersfield Scholarships List For 2024!
- Do you dream of studying at the renowned University of Huddersfield) but worried about the financial burden?...

ITR Requirements For Education Loan Explained!
- Mar 16, 2024
- For students aspiring to study abroad, understanding the significance of Income Tax Return (ITR) submissions is crucial...

Avanse Vs. Leap Finance Education Loan: Key Differences!
- Mar 15, 2024
- When considering financing options for education, Avanse and Leap Finance stand out as prominent choices for students...

ICICI Vs. Bank Of Baroda Education Loan: Key Comparisons!
- Getting a higher education degree is expensive these days. Many students rely on education loans from banks...

Public Vs Private Banks: Comparing Two Major Types In India!
- by Shrishaila Bhandary
- Mar 11, 2024
- The amount of money students spend studying abroad is expected to increase due to rising education costs....
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Share this blog

🚀 Over 5K Students Secured Abroad Education Loan With UniCreds!
- Check your Loan Eligibility

The Plagiarism Checker Online For Your Academic Work
Start Plagiarism Check
Editing & Proofreading for Your Research Paper
Get it proofread now
Online Printing & Binding with Free Express Delivery
Configure binding now
- Academic essay overview
- The writing process
- Structuring academic essays
- Types of academic essays
- Academic writing overview
- Sentence structure
- Academic writing process
- Improving your academic writing
- Titles and headings
- APA style overview
- APA citation & referencing
- APA structure & sections
- Citation & referencing
- Structure and sections
- APA examples overview
- Commonly used citations
- Other examples
- British English vs. American English
- Chicago style overview
- Chicago citation & referencing
- Chicago structure & sections
- Chicago style examples
- Citing sources overview
- Citation format
- Citation examples
- College essay overview
- Application
- How to write a college essay
- Types of college essays
- Commonly confused words
- Definitions
- Dissertation overview
- Dissertation structure & sections
- Dissertation writing process
- Graduate school overview
- Application & admission
- Study abroad
- Master degree
- Harvard referencing overview
- Language rules overview
- Grammatical rules & structures
- Parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Methodology overview
- Analyzing data
- Experiments
- Observations
- Inductive vs. Deductive
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Types of validity
- Types of reliability
- Sampling methods
- Theories & Concepts
- Types of research studies
- Types of variables
- MLA style overview
- MLA examples
- MLA citation & referencing
- MLA structure & sections
- Plagiarism overview
- Plagiarism checker
- Types of plagiarism
- Printing production overview
- Research bias overview
- Types of research bias
- Example sections
- Types of research papers
- Research process overview
- Problem statement
- Research proposal
- Research topic
- Statistics overview
- Levels of measurment
- Frequency distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability
- Hypothesis testing
- Parameters & test statistics
- Types of distributions
- Correlation
- Effect size
- Hypothesis testing assumptions
- Types of ANOVAs
- Types of chi-square
- Statistical data
- Statistical models
- Spelling mistakes
- Tips overview
- Academic writing tips
- Dissertation tips
- Sources tips
- Working with sources overview
- Evaluating sources
- Finding sources
- Including sources
- Types of sources
Your Step to Success
Plagiarism Check within 10min
Printing & Binding with 3D Live Preview
Example for Table of Contents
How do you like this article cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 Definition
- 3 Examples for Your Thesis
- 4 Master’s Thesis Examples
- 5 Microsoft Word Tutorial
- 6 In a Nutshell
Definition
A table of contents example will help structure a long academic manuscript and a table of contents page is necessary for academic submission. The table of contents contains an organised listing of your manuscript’s chapters and sections with clearly marked (and accurate) page numbers. The aim of the table of contents is to allow the reader to flip easily to the section they require and to get a feel of your argument’s structure.
What comes first, table of contents or abstract?
If you are writing an academic paper, you have to take the order of your paper into account. Usually, the first sections of your thesis are the title page, cover page, acknowledgements and the abstract . After these pages, you place the table of contents. Be sure to check that all of the page numbers in your table of contents are correct.
What variations of table of content examples exist?
The table of contents can be displayed in the following formats:
- Single level table of contents
- Subdivided table of contents
- Multi-level table of contents
- Academic table of contents
You will find further details about what needs to be included inside of the table of contents on our blog.
Are references included in table of contents?
Yes. The references are included in the table of contents. You add them in as you would any other section of your thesis. Simply write the section in the table of contents with the corresponding page number. However, the acknowledgement for thesis and the abstract are usually not included in the table of contents. However, check with your institution as this could be dependent upon the formatting that you’re required to follow.
How can I make a table of contents in Microsoft Word?
On Microsoft Word, you will find the function to create a table of contents under the ‘references’ tab. Click on the tab and select ‘table of contents’. You can use one that has been designed by Microsoft Word, or you can create a custom one by yourself. Scroll down for a full tutorial on Microsoft Word and creating a table of contents.
Examples for Your Thesis
Below, you will find different examples for table of contents, including a
- Single level table of contents example
- Subdivided table of contents example
- Multi-level table of contents example
We will also show you with an example how the table of contents for a bachelor’s thesis could look like, as well as for a master’s thesis.
Advice for creating a good table of contents: A good table of contents must be easy to read and formatted accurately, containing quick reference pages for all figures and illustrations. A table of contents example will help you structure your own thesis, but remember to make it relevant to your discipline. Table of contents example structures can be created for different disciplines, such as social sciences, humanities and engineering.
The type and length of a table of contents example will depend on the manuscript. Some thesis’ are short, containing just several chapters, whilst others (like a PhD thesis) are as lengthy as a book. This length will dictate the amount of detail that goes into forming a table of contents example page and the amount of “levels” (or subdivisions) in each chapter.
Single Level Table of Contents Example
For shorter documents, a single level table of contents example can be used. This is a short and succinct table of contents example which utilises only single-level entries on sections or chapters. Remember, you’ll need to include properly formatted dots to lead the reader’s eye to the page number on the far right. The following table of contents example explores this basic structure:
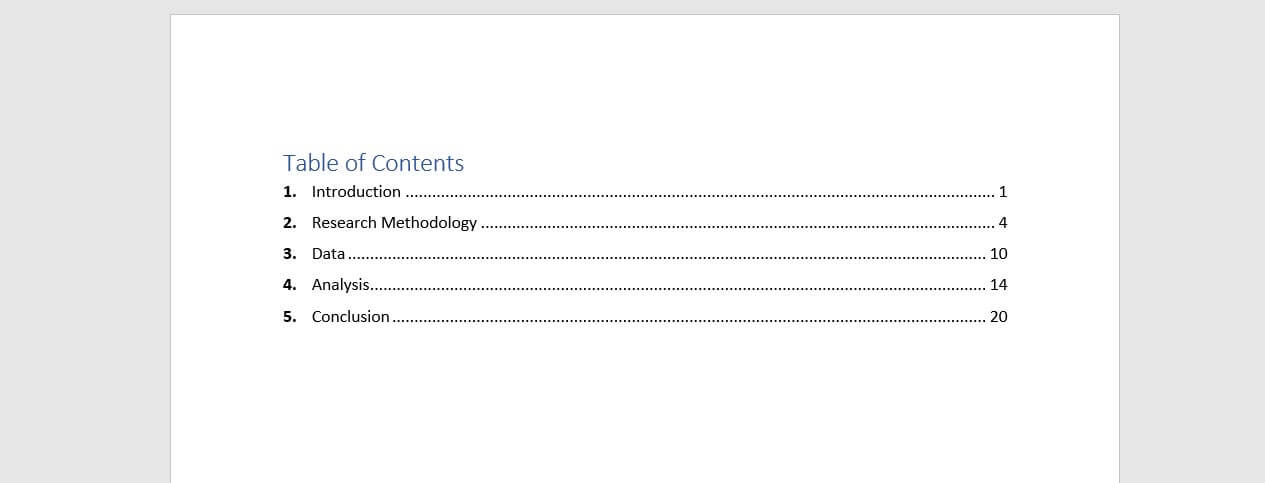
Subdivided Table of Contents E xample
A subdivided table of contents example is required for more lengthy papers, offering a subdivision of chapters and sections within chapters. These are more detailed and are recommended for higher-level dissertations like masters or PhD thesis’ (as well as some more detailed bachelor’s dissertations).
When formating subdivided table of contents example, ensure that chapters are listed in bold font and that subsections are not. It’s common (though not necessary) to denote each subsection by a number (1.1, etc.). You’ll also want to indent the subsections so that they can be read easily. The following table of contents example explores this structure:

Multi-level Table of Contents E xample
Adding additional levels to your table of contents is known as a multi-level table of contents example. These would be numbered onwards at 1.1.1, etc. Be aware that although you want to guide your reader through your manuscript, you should only highlight important areas of your manuscript, like sections and sub-sections, rather than random areas or thoughts in your manuscript. Creating too many levels will make your table of contents unnecessarily busy and too complex.

Academic Table of Contents
All of the above can be used as an academic table of contents example. Often, each separate heading in an academic work needs to be both numbered and labelled in accordance with your preferred reference style (consult your department). The following table of contents example sections will illustrate a table of contents example for a bachelor thesis and a table of contents example for a master thesis.
Table of Contents Example: Bachelor’s Thesis
A bachelor’s degree thesis has no set word or page limit nationwide and will depend entirely on your university or department’s guidelines. However, you can expect a thesis under 60 pages of length at between 10,000 – 15,000 words. As such, you won’t be expected to produce a long and detailed table of contents example with multiple levels and subsections. This is because your main body is more limited in terms of word count. At most, you may find yourself using a subdivided table of contents similar to the table of contents example above.
A bachelor’s thesis table of contents example may be structured like so:

This table of contents example may change depending on your discipline and thesis structure, but note that a single-level structure will often suffice. Subdivided structures like the table of contents example listed earlier will only be necessary when writing several chapters, like in a Master’s thesis.

Master’s Thesis Examples
A master’s table of contents example is more complex than a bachelor’s thesis. This is because they average at about 80 pages with up to 40,000 words. Because this work is produced at a higher academic level, it normally includes a subdivision of chapters and subheadings, with a separate introduction and conclusion, as well as an abstract.
A table of contents example for a master’s thesis may then look something like this:

Microsoft Word Tutorial
Creating a table of contents page with Microsoft Word is simple.
In a Nutshell
- All theses are different. Various departments and disciplines follow different structures and rules. The table of contents example pages here will help you in general to format your document, but remember to consult your university guidelines
- Consistency and accuracy are the most important things to remember. You need the correct page number and the same layout for each chapter. It’s no good combining single-level table of contents with a multi-level table of contents
- Simply put, bachelor’s thesis’ generally follow a single-level table of contents example unless otherwise specified
- Postgraduate thesis’ like master and PhD-level work generally require a more detailed subdivision table of contents example. This is because they deal with both more complex arguments and more words
- Remember to include all aspects of your thesis within the table of contents. Pre-thesis material needs to be listed in Roman numerals and you need to include all back-matter as well, such as References and Bibliography
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
Privacy Policy Imprint
3 inspiring master’s thesis acknowledgement examples
Writing a thesis acknowledgment is a meaningful milestone, marking the completion of a master’s thesis and the end of a master’s education. Questions about its length, tone, and acceptability commonly arise for many students. To provide inspiration, here are three concise master’s thesis acknowledgment examples for you to consider as you compose your own.
What to consider when writing a master’s thesis acknowledgement
Master’s thesis acknowledgement example 1: formal and polite, master’s thesis acknowledgement example 2: emotional and personal, master’s thesis acknowledgement example 3: humorous and grateful.
It is very rare not to have an acknowledgment for your thesis, so almost all master’s students will face the challenge of writing one sooner or later if they are working on a thesis. Master thesis acknowledgments typically range between 100-350 words.
While there are usually no fixed rules on how to write it, remember that the acknowledgment is one of the first things that the reader (including potential assessors!) will see, as it is usually placed before the thesis introduction . Thus, you want to make a good impression. While making an acknowledgment personal, keep it somewhat formal.
Furthermore, it is good to thank your supervisor, even if you did not have the best relationship, out of courtesy. You can also express gratitude to family, friends, or even pets, but keep in mind that many theses are publicly available, so do not share anything that you would not want the world to know. Again, maintaining a somewhat formal tone will help with this.
If you want more information, check out this post on general tips that I wrote on how to create a distinct and meaningful acknowledgment section that reflects your gratitude and appreciation.
You may also like: 5 inspiring PhD thesis acknowledgement examples
While some individuals are naturally expressive, openly sharing their private lives even in public, others may not feel as comfortable with such openness—and that’s perfectly acceptable.
Crafting a brief, formal, and polite thesis acknowledgement is a universal practice, ensuring that you convey appreciation without overstepping personal boundaries.
If you are more emotional and personal, and want to include that in your thesis acknowledgement, this is also perfectly fine. Remember, do you, as long as you keep it to an acceptable level of formality.
While maintaining a degree of formality in a thesis acknowledgement, there’s room for a touch of humor to let your personality shine through. Embracing a lighthearted tone doesn’t diminish the significance of the acknowledgment; rather, it can add a personal and engaging touch.
Get new content delivered directly to your inbox!
Subscribe and receive Master Academia's quarterly newsletter.
10 common challenges of first-year students (+ practical solutions)
The best ai tools for academic paraphrasing: tested and ranked, related articles.

How to write a unique thesis acknowledgement (+ FAQs)

Dealing with conflicting feedback from different supervisors

Theoretical vs. conceptual frameworks: Simple definitions and an overview of key differences

75 linking words for academic writing (+examples)
Master of Design in Design for Interactions
Our mdes program supports those with design backgrounds who seek to transform their practice..
The School of Design welcomes students who hold undergraduate degrees in a design-based field and at least one year of professional experience to enroll in our MDes program. If you’re looking to build onto your strong foundation in design by studying the “big picture” aspect of designing for interactions—people, organizations, cultures, contexts, and systems—our MDes program can help you. Throughout the program, you will work with some of the brightest thinkers and most talented practitioners in the field, gaining exposure to approaches, ideas, and methods at the forefront of design. Studies rooted in communication, systems thinking, futuring, speculative design, design technology, ethics, and design research form the basis of the MDes. The curriculum enables us to teach you a rigorous process for documenting, analyzing, and understanding the past and present so that you are well-positioned to propose more desirable systems and interactions for the future.
The diversity of our MDes cohort creates an incredible group of people with whom to learn.
In addition to bringing rich cultural experiences from around the world, our MDes students hold a wide range of professional and academic expertise. Holding undergraduate degrees in design-based disciplines such as communication design, product design, user experience design, architecture, and service design, our MDes students bring their unique perspectives to design coursework, which enriches everyone’s learning. Our requirement for MDes students to have at least one year of professional experience also bolsters our program as students bring valuable lessons learned in practice, such as effective collaboration, to their academic studies.

Our rigorous curriculum balances structure and autonomy.
Spanning four semesters over the course of two years, the MDes program will challenge your thinking of the roles design can and should play in aiding various forms of interactions throughout society. Through individual and team-based projects that focus on the design of services or social innovation concepts, you will learn design principles, approaches, theories, and tools that are essential to designing for interactions. Each semester is comprised of thoughtfully-aligned seminars, studios, and labs that equip you with important knowledge and skills that aid your development as a design leader. Despite designers typically working in service of others and responding to specific prompts, our MDes courses provide you with ample autonomy in directing your individual work. We take this approach because we recognize the importance of your individual interests and strive to support you as you chart your personal path that builds on your unique design background and voice. Given that CMU is a liberal arts research university, students may also appreciate pursuing research opportunities with faculty and taking courses across campus to broaden and deepen their education.
The MDes thesis provides an opportunity for you to conduct rigorous design research.
A unique feature of the MDes program is the design thesis, which is characterized as an independent research and design project that you will conduct under the mentorship of a faculty advisor. The thesis is complemented by a required second-year seminar, elective coursework in the School of Design, and other departments across the Carnegie Mellon campus. In the first year, you'll identify possible thesis topics relative to School of Design faculty expertise, investigate ways of conducting a thesis, construct a researchable question that will frame your project, secure a thesis advisor, and write a proposal for your second year of study. In the second year, you'll conduct intensive research that aligns with an appropriate design process and culminates in a robust design project that addresses your research question. You will also write a document that describes your steps and discoveries. Throughout the process you will participate in public sharing sessions of thesis work, where you will give and receive feedback to further your inquiry and understanding. You can peruse masters theses from students in the School of Design online at KiltHub .
- Beyond Big Beef: Transitions to Food Citizenship Through Community, Ema Karavdic
- Affordances for Multi-device Gestural Interactions in Augmented Reality, Shengzhi Wi
- Amplifying ASL: Designing with Futuring and Inclusion, Mackenzie Cherban
- tac.tic: Tactile design language for indoor-outdoor pedestrian navigation, Chirag Murthy
- Designing for Trust, Meric Dagli
- Building Long-Term Relationships between People and Products through Customization, Ashlesha Dhotey
- Designing for Learning Growth: Encouraging Metacognitive Practice to Support Growth Mindsets in Students, Chen Ni
- Project Care: Empowering Elderly Chronic Disease Patients to Better Understand and Manage Their Treatment Plans Through Enhanced Patient-Centric Services and Systems, Suzanne Choi & Laura Rodriguez-eng
Our MDes equips you with important design skills and knowledge that enable you to realize a lifelong career in design.
The MDes is regarded as a terminal degree in design. As a result, graduates are poised to take on leading design roles in professional practice worldwide. Alumni are also well-positioned to acquire entry-level teaching and research positions at universities. As a graduate, you may also seek to deepen your studies through a design-focused PhD program like ours, or continue your education in areas such as business, human-computer interaction, or public policy. However you chart your path, we are confident that our MDes will provide you with a strong design education that builds on your background and strengthens the positive trajectory for achieving your professional goals.
Master of Design in Design for Interactions (MDes) Curriculum
Fall semester, year 1.
Explore design for interactions, design for services, and design for social innovation and study their potential impact in business and policy. Expand your skills in communication and interaction design.
Investigate the history, current state, and future of interaction design practice and research.
Envision and prototype preferred futures by giving form to the behaviors and interactions of products, services, and systems.
Use design strategies to decode complex information and communicate messages clearly.
Learn to use design tools for physical and digital environments to support your studio projects.
Investigate your personal interests, probe existing theses, and study various ways of conducting a thesis.
Learn about faculty research.
Spring Semester, Year 1
Investigate business and policy opportunities in design for services and social innovation through research-based team project work in your studio course. Work with advisors to prepare your thesis proposal.
Choose to study either Transition Design, Social Innovation or Design for Service.
Tackle a client-sponsored team project using an integrated research and design process.
Learn and apply a range of participatory methods for exploratory, generative, and evaluative research and design.
Construct a researchable question to frame your project, secure an advisor, and plan and propose the research and design approach you'll conduct in your second year of study.
Take a design elective or a course outside of design to complement your skills and knowledge. We recommend courses in policy, business, service or social innovation, interaction or communication design, or professional writing.
Fall Semester, Year 2
Through thesis project work and your choice of electives, craft a generalist degree in design for interaction, or develop a concentration in design for services or social innovation.
Build on the foundation of coursework and studios through thesis research with your advisor. Conduct research and develop creative concepts to investigate a significant challenge, engage with stakeholders in the real world to inspire and evaluate your ideas, and review your progress and evolving body of work with peers and your advisor to inform your subsequent steps.
Survey new models and approaches to interaction design and design for service in professional practice.
Learn research strategies and tools to assist you in your literature and artifact reviews, investigate making as a means of exploring and understanding your topic, and explore ways of visualizing your discoveries to aid your learning and share your findings with others.
Spring Semester, Year 2
Bring your thesis project to fruition by synthesizing your discoveries and disseminating valuable insights that have the potential to benefit others. Take advantage of electives to cultivate your expertise in design for interaction, and design for services or social innovation.
Model, test, and refine, your design concepts that have emerged from your year of deep research and design exploration to deepen your understanding of your topic, synthesize your findings and apply what you learned to your project, document, present, and publicly defend your thesis, and showcase your project as a unique feature of your design portfolio to demonstrate your ability to take on a significant research and design project.
Explore ways of encapsulating your study, synthesizing and structuring your discoveries, and writing and designing your thesis for dissemination.
We invite you to connect with us and learn more about the School of Design and our MDes program.
Check out examples of students’ work . Join us for an online visitors session . Review other areas of our site such as Frequently Asked Questions and Application Process . Plan a visit to Carnegie Mellon and coordinate a tour of the School of Design while you’re here. Contact us to schedule a call with our academic advisor to discuss any outstanding questions that arise. We look forward to meeting you!

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a master's program or a capstone to a bachelor's degree. Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation, it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete.
Sample Thesis/Dissertation Approval (TDA) Form Master's Students . Number of signatures required for . master's students = student's adviser (at least one signature in the adviser approval section or additional approval section must be that of a graduate faculty member) + department head . Title must ma tch title found on title page ...
Thesis / Dissertation Formatting Manual (2024) Email this link: Home; Filing Fees and Student Status; Submitting ... Table of Contents Example. Here is an example of a Table of Contents page from the Template. Please note that your table of contents may be longer than one page. << Previous: Dedication Page;
Tip #2: Begin Work on the Thesis Statement and Break Up the Thesis into Manageable Sections. After selecting an appropriate topic and developing a central research question for the thesis statement, it is then necessary to apply the research and writing skills you have learned throughout your degree program.
Examples of Tables of Contents . The Table of Contents must include the major sections headings for Text and Bibliography and their respective page numbers. All chapter titles and subheadings listed on the Table of Contents must exactly match the headings as presented in the text. For example, a chapter labeled "Chapter 3" in the Table of
That being said, not all master's students have to write a thesis. For example, fields that place a stronger emphasis on applied knowledge, such as nursing, business, and education, tend to have projects and exams to test students on the skills and abilities associated with those fields. ... How to Write a Master's Thesis: The Final Stages.
Writing a Master's thesis is a challenging mission in higher education. This work requires in-depth research executed by motivated students. ... Example presenting the table of contents from the ...
Click the arrow next to the Table of Contents icon and select Custom Table of Contents. Select which levels of headings you would like to include in the table of contents. Click OK. Make sure to update your table of contents if you move text or change headings. To update, simply right click and select Update Field.
The steps to writing a thesis. The process of writing a thesis is generally characterized by the following. main steps: Choose a topic of your interest and a possible supervisor. Collect, gather, study, analyze and synthesize the relevant academic. literature regarding the topic, to delineate the state-of-the-art and.
have "mastered" the necessary content. Thus, before you proceed in your studies, it is best to find out the requirements for the master's degree within your own discipline, field, and institution of higher education. For the pur - poses of this book, I will only address the master's thesis option. OverviewoftheMaster'sDegreeandThesis ...
1.1) Develop and formulate a research question. Place it in current scholarly and public debate. Highlight the relevance of this topic for sociology. Identify a gap in the literature or a current problem. Formulate the general aim and research question. Optional: narrow down the topic and specify the research question (alternatively in 2.)
Typical Structure of a Bachelor's or Master's Thesis Most thesis are structured as shown below. Each part may be split into several chapter. For example, the part introduction may have two separate chapters for a the general introduction to the topic and the research question. But the parts commonly appear in the following order: Title page
The title page of a thesis or dissertation must include the following information: The title of the thesis or dissertation in all capital letters and centered 2″ below the top of the page. Your name, centered 1″ below the title. Do not include titles, degrees, or identifiers. The name you use here does not need to exactly match the name on ...
Results - Show your results and comment on their significance and implications. Conclusion - Summarize the methodology you used to generate results, your key findings, and any future areas of work. 3. Purpose. Having an outline for your master's thesis will help you explain the motivation behind your work, and also connect the different ...
The thesis introduction, usually chapter 1, is one of the most important chapters of a thesis. It sets the scene. It previews key arguments and findings. And it helps the reader to understand the structure of the thesis. In short, a lot is riding on this first chapter. With the following tips, you can write
A master's thesis is extremely important, it represents how you ideate and your interest. Additionally, a master's thesis also tells your employer a lot about you and what you can bring to the table. It might surprise you, but in most cases, a good master's thesis can typically help you get the job of your dreams.
A master's table of contents example is more complex than a bachelor's thesis. This is because they average at about 80 pages with up to 40,000 words. Because this work is produced at a higher academic level, it normally includes a subdivision of chapters and subheadings, with a separate introduction and conclusion, as well as an abstract.
Writing a thesis acknowledgment is a meaningful milestone, marking the completion of a master's thesis and the end of a master's education. Questions about its length, tone, and acceptability commonly arise for many students. To provide inspiration, here are three concise master's thesis acknowledgment examples for you to consider as you compose your own. Contents
The thesis is complemented by a required second-year seminar, elective coursework in the School of Design, and other departments across the Carnegie Mellon campus. ... where you will give and receive feedback to further your inquiry and understanding. You can peruse masters theses from students in the School of Design online at KiltHub ...
The Francis College of Engineering, Department of Plastics Engineering, invites you to attend a Master's Thesis defense by Rohit Suryakant Jagtap on: Plant-based Protein Fiber Spinning and Whole Cut Meat Composite Assembly Candidate Name: Rohit Suryakant Jagtap Degree: Master's Defense: Tuesday, April 9, 2024 Time: 11:30 a.m. - 1:30 p.m.