
- Devices & Hardware


DD-WRT Configuration
Installing DD-WRT on a router in most cases is almost as simple as installing a program onto your computer. However, doing it incorrectly can leave you with a router that you have to throw away. In this guide, we will install DD-WRT firmware and configure Chillispot settings on the TP-Link router (TP-Link WR 841 ND in this example), but these instructions can be applied to other supported router models.
Warning! This section describes actions that might damage your device or firmware. Proceed with care!
It is required to have a DD-WRT-Compatible device programmed with a distribution of DD-WRT containing ChilliSpot.
Before you start, please check the DD-WRT router database first. For a list of devices working with DD-WRT, please see the wiki page DD-WRT Supported Devices.
If you have installed OpenWRT or some other firmware previously, please install default firmware for your router model before the start.
Use your cable connection to flash the device. NOT the wireless connection.
Connect your computer by network cable to the router LAN port . Go to the web browser and access to router configuration using default IP address e.g 192.168.0.1 . From System Tools find Firmware Upgrade .
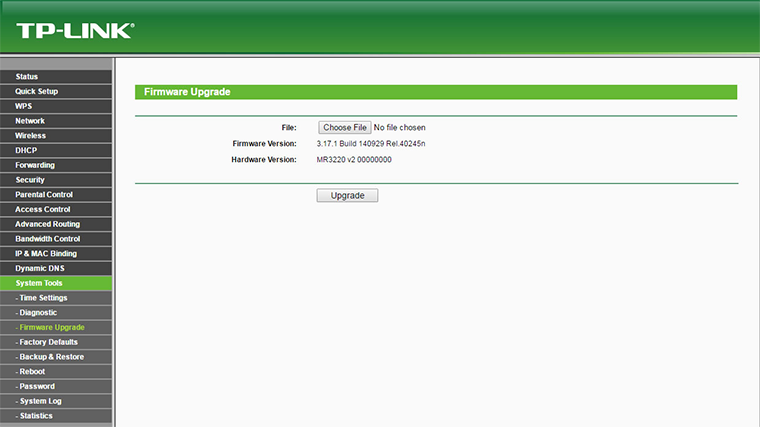
Click on Choose File . Navigate to the location where the DD-WRT firmware for your model is downloaded and press on Open . Press the Upgrade button.
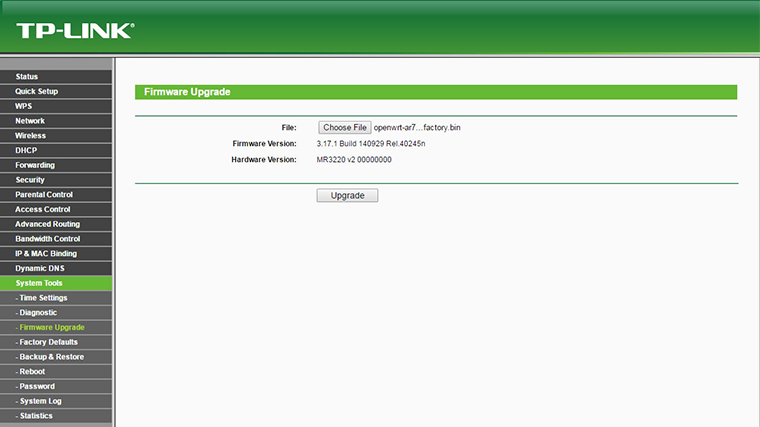
Do not power off the router during the firmware upgrade, as it can cause the device to crash or become unusable.
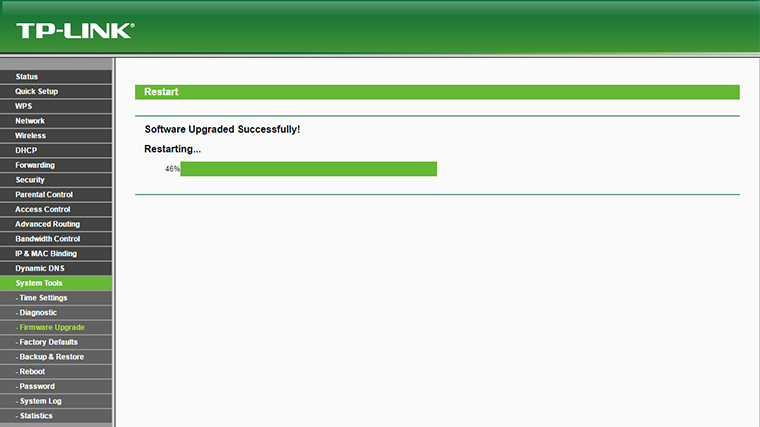
Reconnect LAN cable or Disable/Enable NIC card in order to get the new valid IP address in the IP range which is set in the router DHCP server (192.168.5.x in our case).
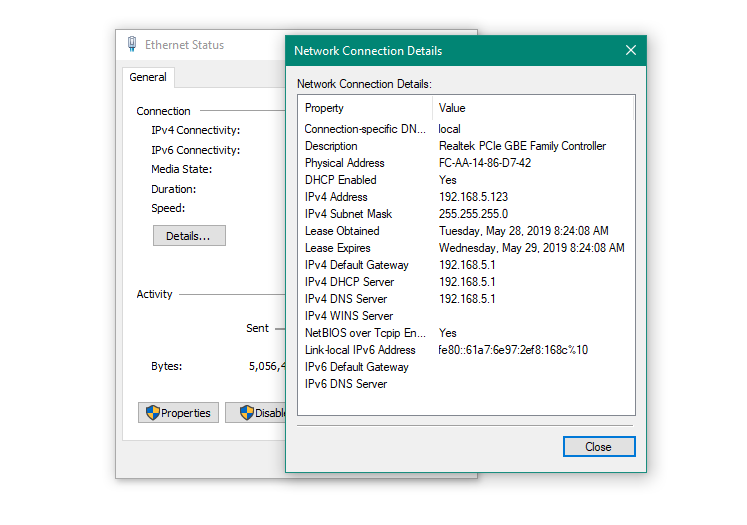
Configuring parameters
Start your browser and in URL field type https://192.168.1.1 Username : admin Password : admin
On the DD-WRT Control panel – Setup – Basic Setup page set Automatic Configuration – DHCP as Connection type . Set desired Router Name and Hostname , as Domain name type local .
In the Network Setup section set Local IP address and Subnet mask .
As DHCP type select DHCP server and enable it.
Click Save then Apply settings button.
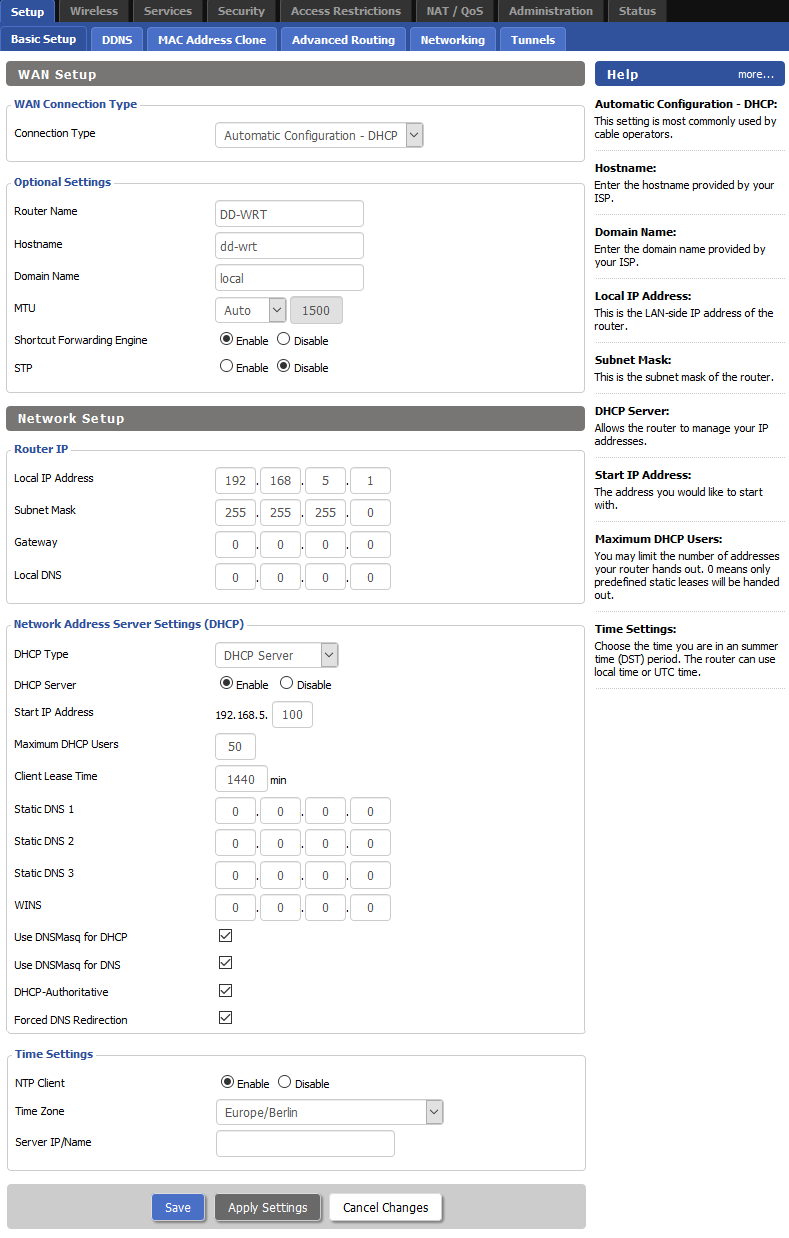
Under the Port Setup section, as WAN Port Assignment set eth0. Check router MAC address on the Status page and set it in the Network Configuration eth1 and Network Configuration ath0 MAC address field.
In the Port Setup – Network Configuration ath0 section, as Bridge assignment select Unbridged, Save changes and Apply settings.
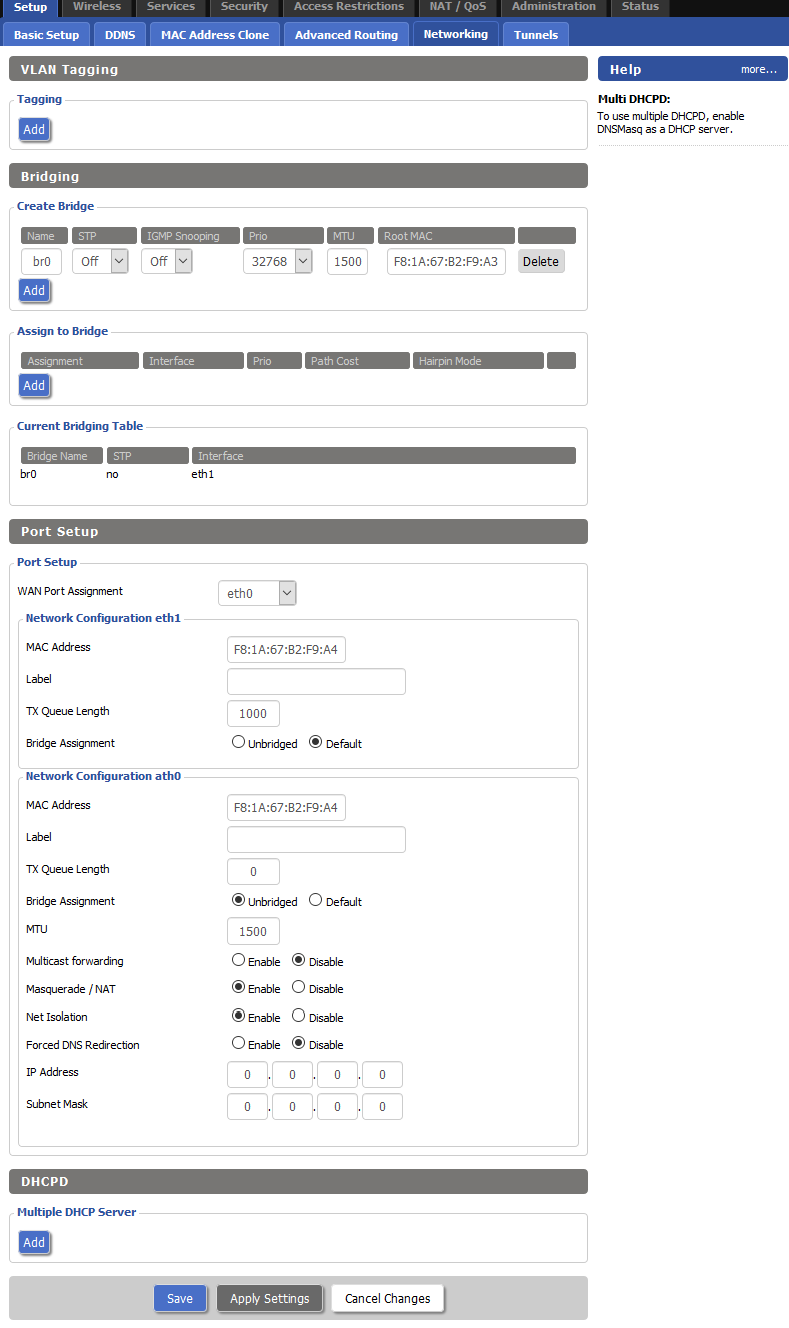
Under the DHCP Server section as Used Domain select LAN & WLAN .
As LAN Domain type local , Save changes and Apply settings .
Chillispot configuration
ChilliSpot is an open source captive portal or wireless LAN access point controller. It is used for authenticating users of a wireless LAN. It supports web based login which is today’s standard for public Hotspots. Authentication, authorization and accounting (AAA) is handled by your radius server.
To configure Chillispot go to the Services – Hotspot page. Under Chillispot section enable Chillispot, and as DHCP Interface select ath0 .
Chillispot Hotspot Network is by default set to 192.168.182.0/24 and our recommendation is to keep that setting.
Hotspot network: 192.168.182.0/24 Primary Radius server IP/DNS: 13.92.228.228 Backup Radius server IP/DNS: 13.90.247.200 DNS Server IP: 0.0.0.0 Redirect URL : https://wifihotspot.io/login Shared key: (contact our office) Radius NAS ID: set router MAC address
wifihotspot.io,cdn.wifihotspot.io,starthotspot.com, cdnhotspot.azureedge.net,cdn.starthotspot.com, static.cloudflareinsights.com, t-msedge.net,13.92.228.228,13.90.247.200,40.117.190.72,40.121.151.4
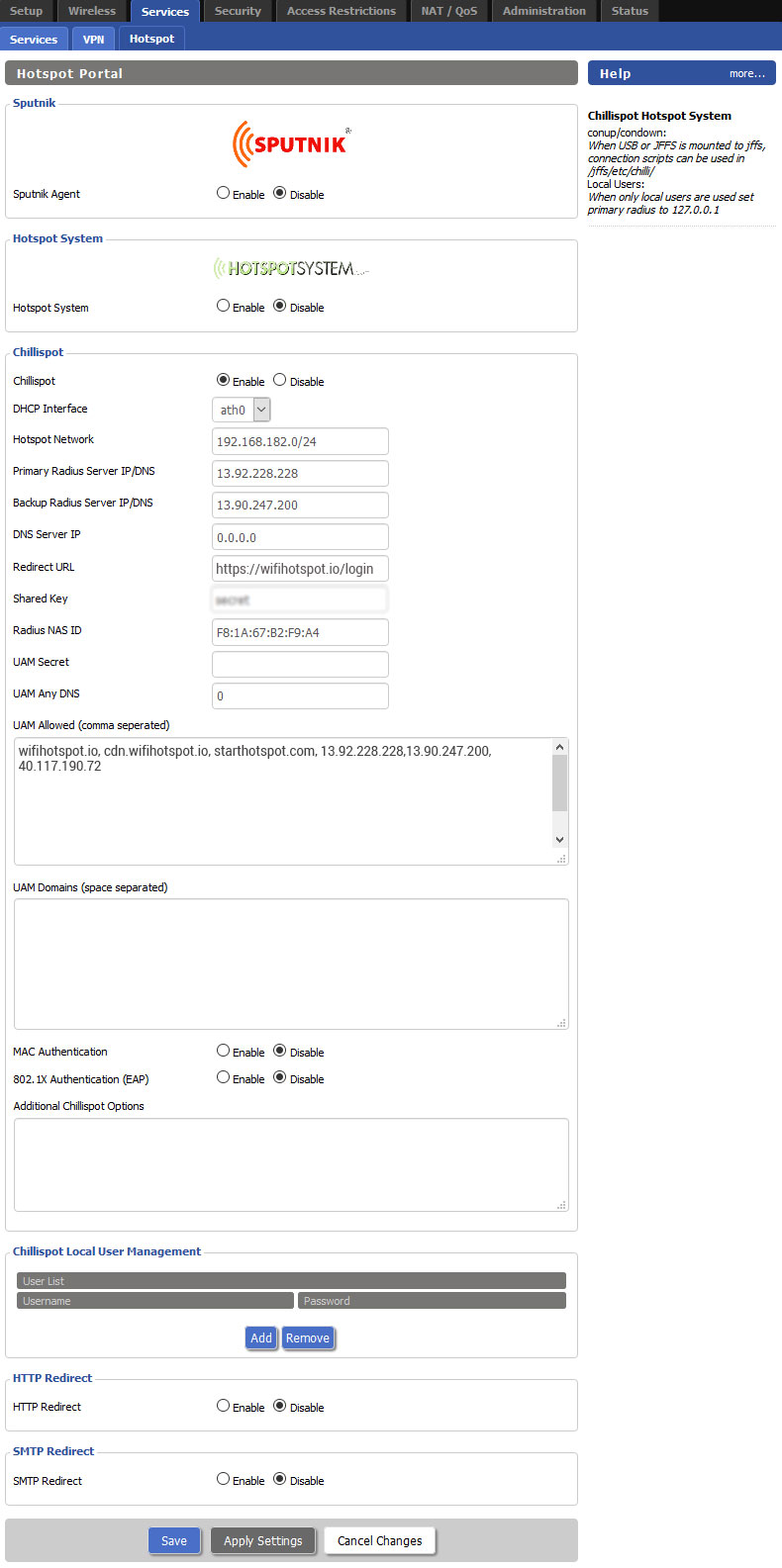
If you want to enable Social network login feature, add further domains and IP’s in the UAM Allowed (comma separated) field as per below for each network you plan to support.
Please note, these IP ranges are subject to change depending on the social network setup.
31.13.24.0/21 157.240.0.0/16 31.13.0.0/16 facebook.com www.facebook.com fbcdn.net facebook.net www.facebook.net connect.facebook.net maps.googleapis.com akamaihd.net staticxx.facebook.com static.xx.fbcdn.net pixel.facebook.com fbsbx.com – if it does not work, try adding: 45.64.40.0/22 66.220.144.0/20 69.63.176.0/20 69.171.224.0/19 74.119.76.0/22 103.4.96.0/22 129.134.0.0/16 173.252.64.0/18 179.60.192.0/22 185.60.216.0/22 204.15.20.0/22
twitter.com www.twitter.com abs.twitter.com abs.twitimg.com api.twitter.com pbs.twimg.com 199.16.156.0/22 199.59.148.0/22 199.96.56.0/21 192.133.76.0/22
91.225.248.0/23 linkedin.com www.linkedin.com platform.linkedin.com slicdn.com licdn.com static.licdn.com 184.51.0.0/16 108.174.0.0/16 – if it does not work, try adding: 103.20.94.0/23 108.174.0.0/22 108.174.4.0/24 108.174.8.0/22 108.174.12.0/23 144.2.0.0/22 144.2.192.0/24 216.52.16.0/23 216.52.18.0/24 216.52.20.0/23 216.52.22.0/24 65.156.227.0/24 8.39.53.0/24 185.63.144.0/24 185.63.147.0/24 199.101.161.0/24 64.152.25.0/24 8.22.161.0/24
google.com www.google.com clients1.google.com accounts.youtube.com accounts.google.com ssl.gstatic.com ssl.google-analytics.com googleusercontent.com youtube.com www.youtube.com doubleclick.net googlesyndication.com googlevideo.com ytimg.com
Facebook app setup instructions
Twitter app setup instructons
LinkedIn app setup instructons
Google app setup instructons
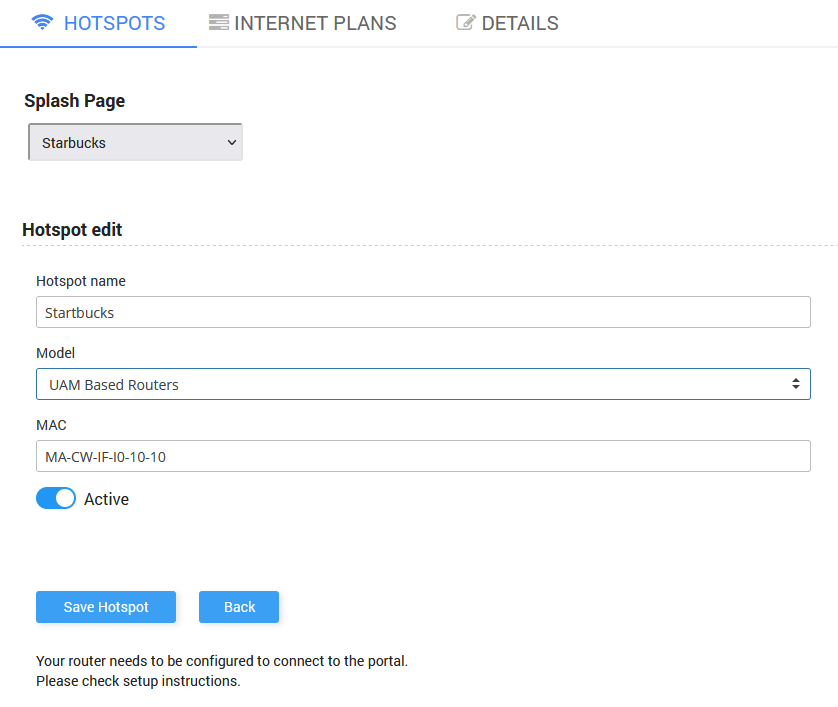
Login to your Start Hotspot portal account, go to the WiFi Locations page, select location, and from Hotspot section as Hotspot model select UAM Based Routers , add your router MAC address and Save changes.
If you need help with configuration, please go to starthotspot.com and contact our tech support. We’ll be glad to help you.
Was this article helpful?

- Preferences
- Forgot your password?
- Browse Source
- View Tickets
Context Navigation
- ← Previous Ticket
- Next Ticket →
Opened 12 years ago
Closed 11 years ago
#2312 closed ( fixed )
Assing wan port to internal switch does not work on ath9k builds for tp-link tl-wr1043nd, description (last modified by thiago maia de rezende ).
In AP, client, repeater and WDS modes, the button on the WebGUI for assinging WAN port to the internal switch has no effect. Devices connected to it do not join the network or communicate.
This is indeed for WAN disabled (is there another operation mode where the "assign WAN port to switch" button is displayed in the WebGUI? I don't think so)
If assigning WAN port to switch is not possible for Atheros builds, then the button should not be displayed.
Change History (11)
Comment:1 by thiago maia de rezende , 12 years ago, comment:2 by sash , 12 years ago.
in atheros this has no function! wan must be disabled
comment:3 by Thiago Maia de Rezende , 12 years ago
Comment:4 by thiago maia de rezende , 12 years ago.
The problem still occurs on build 18740
comment:5 by Thiago Maia de Rezende , 12 years ago
The problem still occurs on build 18777
comment:6 by Sash , 12 years ago
but anyway it makes no harm. problems should be fixed
comment:7 by Thiago Maia de Rezende , 12 years ago
The problem is not fixed in build 19327.
Devices plugged in WAN port still do not communicate.
comment:8 by Thiago Maia de Rezende , 12 years ago
Comment:9 by thiago maia de rezende , 12 years ago.
This problem is still an issue in build 19519.
comment:10 by Terje Rosenlund , 12 years ago
I have compared the default configuration for the Broadband based Linksys WRT54GL and the Atheros based Buffalo WZR-HP-G300NH2 in regards to this problem:
Recommended build for DD-WRT on the Broadband based Linksys WRT54GL 1.0/1.1 are build 13064 In the default configuration it has:
2 VLANs (vlan0 and vlan1) 1 bridge (br0)
all ports on eth0 + ath0 are assigned to vlan0 eth1 is assigned to vlan1
bridging table for br0: vlan0, eth1 (why is eth1 assigend to br0?) vlan1 is assigned to br0 when WAN is set to disable and 'Assign WAN-port to switch' is checked:
bridging table for br0: vlan0, eth1, vlan1 (eth1 is part of vlan1, not needed?)
Offered build for DD-WRT on the Atheros based Buffalo WZR-HP-G300NH2 are based on build 19154 In the default configuration it has:
2 VLANs (vlan1 and vlan2) (changed from vlan0 and vlan1, bug?) 1 bridge (br0)
all ports on eth0 and ath0 are assigned to vlan1 ?? eth1 is assigned to vlan2 ?? (?? Unknown because VLAN tab is missing from the WebGUI) bridging table for br0: vlan1, ath0 (ath0 is part of vlan1?, not needed?) vlan2 is not assigned to br0 when WAN is set to disable and 'Assign WAN-port to switch' is checked:
bridging table for br0: vlan1, ath0
Quoting from my post on http://forums.buffalotech.com/t5/Wireless/vlan-s-not-working-when-assigned-to-bridge-on-WZR-HP-G300NH2/td-p/106526 :
I'm using 3 x G300NH2 to build a gigabit LAN
All of them runs in 'Router' mode and wireless as 'AP'. All switches are connected to each other by cable. They are also connected to the lan-side of a NanoStation M5 acting as internet gateway. I can ping the gateway from all 3 routers when I connect true the wireless interfaces but not when connected by cable. In order to get this to work I had to manually assign eth0 to br0. I pressume ping true wireless works because ath0 is assigned to br0 as default while eth0 is indirectly assigned to br0 true vlan1 and does'nt work.
To me it seems like this problem is caused by a bug in DD-WRT's VLAN implementation for Atheros-based routers
comment:11 by Thiago Maia de Rezende , 11 years ago
There is a workaround that was posted in this topic:
http://www.dd-wrt.com/phpBB2/viewtopic.php?t=149611
Basically, we have to save the following code as a start script:
swconfig dev rtl8366rb vlan 1 set ports '0 1 2 3 4 5t' stopservice lan startservice lan
After that the WAN port is added successfully to the internal switch.
A big thanks to Ptruman for the tip!
Download in other formats:
- Comma-delimited Text
- Tab-delimited Text
Powered by Trac 1.4 By Edgewall Software .
Experiences using a DD-WRT router with Hyper-V
I have been playing around with the idea of using a DD-WRT-V router on a Hyper-V VM to connect my local virtual machines to the Internet as discussed by Martin Hinshlewood in his blog post . I learned a few things that might be of use to others trying the same setup.
What I used to do
Prior to using the router I had been using three virtual switches on my Windows 8 Hyper-V setup with multiple network adaptors to connect both my VMs and host machine to the switches and networks
One internal virtual switch only accessible on my host machine and my VMs
Two external virtual switches
one linked to my physical Ethernet adaptor
the other linked to my physical WiFi adaptor
Arguably I could have had just one ‘public’ virtual switch and connected it to either my Ethernet or Wifi as needed. However, I found it easier to swap virtual switch in the VM settings rather than swap the network adaptor inside the virtual switch settings. I cannot really think of a compelling reason to pick one method over another, just person taste or habit I guess.
This setup had worked OK, if I needed to access a VM from my host PC I used the internal switch. This switch had no DHCP server on it, so I used the alternate configuration IP addresses assigned by Windows, managing machine IP addresses via a local hosts file. To allow the VMs to access the internet I added a second network adaptor to each VM which I bound to one of the externally connected switches, the choice being dependant which Internet connection I had at any given time.
However, all was not perfect, I have had problems with some Linux distributions running in Hyper-V with then not getting an IP address via DHCP over Wifi. There was also the complexity of having to add second network adaptors to each VM.
So would a virtual router help? I thought it worth a try, so I followed Martin’s process . But hit a few problems.
Setting up the DD-WRT router
As Martin said his post more work was needed to fully configure the router to allow external access. The problem I had for a long time was that as soon as I enabled the WAN port I seemed to lose connection. After much fiddling this was the process that worked for me
Install the router as detailed in Martin’s post
Link your internal Hyper-V switch to the first Ethernet (Eth0) port on the router VM. This seems a bit counter intuitive as the DD-WRT wiki says the first port is for the WAN – more on that later
Boot the router, your should be able to login on the address 192.168.1.1 as root with the password admin on both the console or via a web browser from your host PC
On the basic setup tab (the default page) enable the WAN by selecting ‘Automatic Configuration (DHCP)’ and save the change
It is at this point I kept getting disconnected. I then realised it was because the ports were being reassigned, at this point Eth0 had indeed become the WAN port and Eth1 the internal port
So in Hyper-V manager
Re-assign the first Ethernet port (eth0) to external hyper-v switch (in turn connected to your Internet connection)
Assign the second Ethernet port (Eth1) to the internal virtual switch
- You can now re-connect to 192.168.1.1 in a browser from your host machine to complete your configuration
So now all my VMs connected to the virtual switch could get a 192.168.1.x address via DHCP (using their single network adaptors) but they could not see the internet. However, on the plus side DHCP seems to work OK for all operating Systems, so my Linux issues seemed to be fixed
It is fair to say I now had a fairly complex network, so it was no unsurprising I had routing issues.
The issue seems to have been that the VMs were not being passed the correct default router and DNS entries by DHCP. I had expect this to be set by default by the router, but it was not the case. They seem to need to be set by hand as shown below.
Once these were set, the change saved on the router and the VMs renewed their DHCP settings they had Internet access
At one point I thought I had also lost Internet access from my host PC, or the Internet access was much slower. I though I had developed a routing loop with all traffic passing through the router whether it was needed or not. However, once the above router gateway IP settings were set these problem when away.
When I checked my Windows 8 host’s routing table using netstat –r it showed two default roots (0.0.0.0), my primary one (192.168.0.1) my home router and my Hyper-V router (192.168.1.1 ). The second one had a much higher metric, so should not be used unless sending packets to the 192.168.100.x network, all other traffic should go out the primary link it should be using.
It was at this time I noticed the problem of getting a DHCP based IP address from Wifi had not gone away completely. If I had my router’s WAN port connected to my WiFI virtual switch, depending on the model/setup of WiFI router DHCP worked sometimes and sometimes not. I think this was mostly down to an authentication issue; not a major issues as thus far the only place I have a problem is our office where our WiFi is secured via radius server based AD authentication. Here I just switched to using either our guest WiFi or our Ethernet which both worked.
So is this a workable solution?
It seems to be OK this far, but there were more IP address/routing issues during the setup than I would like, you need to know your IPV4.
There are many option on the DD-WRT console I am unfamiliar with. By default it is running just like a home one, in a Network Address Translation (NAT) mode. This has the advantage of hiding the internal switch, but I was thinking would it be easier to run the DD-WRT as simple router?
The problem with that mode of operation is I need to make sure my internal virtual LAN does not conflict with anything on networks I connect to, and with automated router protocols such as RIP could get interesting fast; making me a few enemies with IT managers who networks I connect too.
A niggle is that whenever I connect my PC to a new network I need to make sure I remember do a DHCP renew of my WAN port (Status > WAN > DHCP Renew), it does not automatically detect the change in connection.
Also I still need to manage my VMs IP addresses with a host file on the host Windows PC. As I don’t want to edit this file too often, it a good idea to increase the DHCP lease time on the router (Setup > Basic Setup) to a few days instead of a day.
As to how well this work we shall see, but it seems OK for now
- Log in / create account
- Privacy Policy
- Community portal
- Current events
- Recent changes
- Random page
Wireless access point
From dd-wrt wiki.
Wiki Path : DD-WRT Wiki Main / Tutorials / Linking Routers / Wireless Access Point

[ edit ] Introduction

For a large network where the DD-WRT router does not provide suitable network core, Wireless Access Point (WAP or just 'AP') allows wireless clients to be a part of the larger network. In this case, clients normally get DHCP configuration from the gateway or some other DHCP server, and could be accessed by other clients on the network (if allowed).
Linking routers by Ethernet cables does not require DD-WRT on any router. However, some more advanced settings are available in DD-WRT. As an example, some colleges still allow students to have their own WAP. They require that the WAPs not lease private IP addresses (like a gateway configuration with DHCP/NAT) because it makes it difficult to track down which client is causing problems (e.g. virus infections, trojans, worms, etc.)
Vendors such as Linksys typically charge more for devices which work as standalone WAPs because routers are typically used by home users and WAPs are more popular for businesses. With DD-WRT you can buy a device marketed as a router and use it as a WAP.
[ edit ] Secondary Router on a Separate Subnet
- This is simply a gateway router that is downstream of a primary gateway router.
If you want a secondary router to be on a separate subnet from the primary, just hard reset the router and set the router's IP to, e.g., 192.168.5.1 on the basic setup page. Then set security and SSID on the Wireless tab, hit Save then Apply, and finally plug the LAN cable from your primary to the WAN of the second router.
If you wish to be able to access your secondary router from devices on your primary LAN, enable Web GUI management in the Remote Access section of the Administration/Management page. You should then be able to access the secondary router by typing in its WAN IP. Setting up a static lease for the second router's WAN interface in Services on the first router will allow you to always know where the second one is to access it. This is the usual router/gateway mode, which is NOT the main goal of this Wiki.
[ edit ] Access Point (AP) instructions
A secondary router on the same subnet, so all wireless and wired network devices can access each other.
[ edit ] Simple Version (Same Subnet)
On the secondary access point router:
- Do a hard reset
- Disable DHCP and set the wireless channel different from the other router(s)
- Set the IP address to 192.168.1.2 (or any IP outside the gateway DHCP range that does not collide with the gateway nor any other static devices)
- Connect a LAN port from the Access Point to a LAN port on the primary router
[ edit ] Normal Version (Same Subnet)
Side note-If you want to have clients on one router isolated from those on the main router, you need to use iptables rules to do this fully. However, following the above "Separate Subnet" instructions will achieve this.
Now, the main how to: Pay special attention to the Review section of this article, especially if you are using an older version.
- Hard reset the router to DD-WRT default settings
- Note: If this router is wired to another router, there may be conflicts (both routers could have the same IP address). For the time being, disconnect this router from the main one.
- WAN Connection Type: Disabled
- Local IP Address: e.g. 192.168.1.2 (same subnet as primary router but outside the DHCP range)
- Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0 (unless you know what you're doing)
- DHCP Server: Disable (do not use DHCP Forwarder ), also uncheck DNSmasq options
- Gateway: IP address of primary router
- (Optional) Local DNS: IP address of primary router / local DNS server
- NOTE: Builds 46788 and later do not have this feature; there are mixed reports on whether or not the WAN port is usable.
- This allows connection to the router's default address after a reset, to avoid colliding with the LAN
- (Recommended) NTP Client: Enable Help
- (Recommended) Change operating mode to: Router, then Save
- Set the Wireless Network Name (SSID) as desired
- (Optional) Sensitivity Range: The max distance (in meters) to clients * 2 (or 0 to disable), then Save
- Note: Security is optional, but recommended! Clients must support whatever mode you select here.
- (Recommended) Security Mode: WPA2
- (Recommended) WPA Algorithm: AES
- (Recommended) WPA Shared Key: =>8 characters, then Save
- (Recommended) DNSMasq: Disable (enable if you use additional DNSMasq settings)
- (Recommended) ttraff Daemon: Disable, then Save
- Disable SPI firewall, then Save
- Check "Filter Multicast", then Save
- (Recommended) Info Site Password Protection: Enable
- Save then Apply Settings and connect Ethernet cable to main router LAN port
- If not working, reboot the router to be sure all settings have been applied.
- You may have to reboot the PC or "ipconfig /release" then "ipconfig /renew" in Windows
[ edit ] Review
There were three basic configuration changes you made to set up your router as a wireless access point.
[ edit ] Turn Off DHCP
If you did not turn off DHCP, when you plug your router into the network (after configuration), your WAP may provide IP addresses to clients on the wired network, and this may be inappropriate. Tracking down problems caused by multiple DHCP servers can be time-consuming and difficult.
Because it's so important, it is worth repeating: Turn off DHCP before you continue!
[ edit ] Set the IP address of the LAN Interface
Immediately after turning off DHCP, while your PC still has the IP address the WAP gave you, set the LAN interface of the WAP to the IP address you want it to use, e.g., if the host router is 192.168.1.1, give the WAP an IP of 192.168.1.2. Alternatively, you can use the instructions below to set the WAP's IP address via DHCP.
If you cannot connect to the WAP in order to set the LAN interface's IP address, it is probably because your computer no longer has an IP address on the same subnet. To get past this issue, simply set your computer's IP address and subnet to 192.168.1.8 and 255.255.255.0 respectively. (This assumes you are still using the default settings. If not, change the IP address and subnet as appropriate) You should now be able to point your browser at 192.168.1.1 (again assuming default settings).
[ edit ] LAN Uplink
There are two ways to connect your WAP to the LAN. You can either Uplink through one of the router's LAN ports, or use the WAN port that is normally connected to the cable/DSL modem.
[ edit ] LAN Uplink Through LAN Port
To complete the link between the two routers, connect a LAN port on the central router, to a LAN port on Linksys router (to be used as your WAP). You may need a crossover cable to do this, although many modern routers have automatic polarity sensing. To test this, connect a standard Ethernet cable between the two routers. If the LAN light comes on, the router has automatically switched the polarity and a crossover cable is not required.
[ edit ] LAN Uplink Through WAN Port
If you use your DD-WRT router as a WAP only, you may use your DD-WRT router's WAN port to connect it to your existing LAN. To do this, you need to disable the Internet Connection and "Assign WAN Port to Switch".
Normally, the router does Layer 3 IP routing. but by "Assigning WAN Port to Switch," your DD-WRT router will bypass that functionality and just pass on the Layer 2 ethernet packets from your wired network to the wireless network and vice versa.
Alternatively, if you have a router that supports assigning the WAN port to the switch: Setup -> Basic Setup -> Internet Connection Type -> Connection Type = Disabled Setup -> Basic Setup -> Network Setup -> WAN Port -> Assign WAN Port to Switch you can connect the WAN port as your uplink to your main router. All this really buys you is an extra port (4 available instead of 3), but why not?
[ edit ] Roaming access
If you are installing additional Access Points to cover a broader area with Wi-Fi access, it is possible to allow clients to roam freely between them. The common method is to use the same SSID and Security settings on each access point. The clients control when to switch in between APs. Most clients will switch when they see a more powerful AP available but some client radios are not able to listen for a new AP when connected to an existing AP and as a result those clients will not roam to the new AP until they completely lose signal from the old one. A typical roaming transition from one AP to the other takes about 50ms if using simple authentication (open or WPA2 PSK AES)
Use a different channel on each AP . e.g. if you are in the US and installed two access points, use channels #1 and #11. Or if three access points, then use channels #1, #6, and #11 (setting the channels at least 5 apart should help keep interference between APs to a minimum). If you have a residential gateway with wireless turned on, and just one AP, then the same applies: each gets a different channel. If you are in Europe, use channels 1, 5, 9 & 13.
When using multiple Access Points, each one should be connected by LAN to LAN uplink as described above. They can even be attached to different switches within the same organization.
Access Point placements need to be carefully done. If the APs are too far away then there will be holes in the coverage and the clients will drop off when going from one AP to the other. If the APs are too close then clients will "stick" to one AP while moving out of its region and into another's. If the APs are too close and moving them farther apart is not practical then the transmit power on each AP can be reduced.
You can also try setting the APs to use the same channel. This will halve bandwidth when both APs are talking to clients but it may help clients that have problems sticking to one AP.
It can also be helpful to disable the slower 802.11 transfer rates with the Wl_command#rateset command for example:
This sets the minimum access to 18Mbit and clients will drop off as the signal level falls below what's needed to support this.
There are additional considerations with roaming using wireless VoIP gear, and WPA Enterprise modes. These environments require additional authentication from the client that could exceed the TCP/IP TTL and cause a disconnection of a higher level application such as the VoIP client. Because of that, the IEEE 802.11r-2008 protocol, a.k.a. Fast Transition (FT), was developed. DD-WRT does not currently support 802.11r FT but there is support for it in OpenWRT. The wireless client must also support Fast Roaming for this protocol for it to work; typically it will be cell phones that support it.
[ edit ] How To Use DHCP to Set the WAP's IP Address
Note: This step is optional. Having the WAP's IP address set by a DHCP server is not required. It can be made static, as shown above.
Note also that the steps below assume a DHCP server is running outside this DD-WRT WAP box on the LAN (e.g., in the FAI DSL box/gateway), so, keep this internal DD-WRT WAP DHCP server disabled as stated above, as well as all other settings.
It is not possible to set the LAN interface to get its IP address via DHCP using the web configuration interface. You can, however, set your startup script to obtain an IP address.
Simply set your IP address to (starting DHCP client):
Only the two first lines are required if you don't want your WAP to set its name based on the IP address it gets. However, if you want to save a configuration file which will apply to several WAPs, that can be a handy feature.
EDIT 2013/09/19: If you leave the "Local DNS" GUI field to 0.0.0.0, then the WAP will use the DNS supplied by DHCP. To be functional, this requires the "Gateway" is set too. So, you also wish the gateway to be assigned by DHCP too. You do it appending
after the udhcpc command in the script. You will leave the unused Basic/Network Setup/"Gateway" GUI field to 0.0.0.0, or, to get a GUI feedback of the currently assigned wan_gateway nvram value, have this field filled by the value of the nvram lan_gateway value by setting this last the same way as the one below for wds_watchdog_ips .
Then you may want the optional WDS/Connection Watchdog to ping the gateway it just got from DHCP: just enable the watchdog in the GUI, set the wanted delay to have the WAP monitor the connection to the gateway, leave the IP's field blank, append the following 4 lines after the route add ... command above, so that they will fill it in for you and the watchdog will help your WAP to follow any change of the gateway IP address (as long as the previous gateway IP is no longer used. You can work around the case when the previous IP is reused for another purpose with a reboot on URL ping failure custom script plus the cron job that triggers it in the GUI Management tab, but if the gateway loses its WAN connection, the WAP's wireless clients may lose their wireless connection at the same rhythm the WAP reboots. To prevent this, think to ping both external(s) URL(s) and internal IP(s) and make the custom script to reboot the WAP when all pings fail - this will preserve internal connections in the case the Internet is lost at the gateway WAN side).
The if tests below are just here to preserve the nvram service life with no rewrite when not needed on boot. Even the WAP's ip will survive over reboots thanks to a static lease - this applies to other scripts.
Once you have manually set the router & hostname name fields, you should set the DHCP startup script this way:
The whole ip/mask/gateway will show correctly in the Settings web GUI page.
[ edit ] Related wiki links
Secure remote management for a WAP
Categories : Wlan | Basic tutorials | Linking Routers
- Discussion |
- What links here |
- Related changes |
- Upload file |
- Special pages
- | Permanent link
- Print as PDF
- About DD-WRT Wiki |
- Disclaimers |
- Powered by MediaWiki |
- Design by Paul Gu
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
WAN port security assessment (DD-WRT)
I am running an Ethernet cable around my house to connect a cable modem in one room with the WAN port of the Netgear 6700 router (ddwrt) in another room.
I am wondering if this poses a security risk. Especially if an intruder could gain access to my LAN via that Ethernet cable that’s connected to the WAN port.
Is it possible to gain access to the LAN machines via the WAN port? If yes, is there a way to prevent that?
Thanks for your help in advance.
Law 3 of the Immutable laws of security states:
If a bad guy has unrestricted physical access to your computer, it's not your computer anymore
So if someone has enough access to your system that they can replace your modem or put their own hardware in, you are in much more trouble than simply being able to see your network.
That being said, it is a common thing to link a modem to a router via a WAN port. You could look at locking down MAC addresses maybe to restrict which devices can get on your network, or you could run some software on a server on your system to look at any changes of hardware/gateways etc on your network.
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged router security routing port wan ..
- The Overflow Blog
- Are long context windows the end of RAG?
- Developers with AI assistants need to follow the pair programming model
- Featured on Meta
- New Focus Styles & Updated Styling for Button Groups
- Upcoming initiatives on Stack Overflow and across the Stack Exchange network
- Google Cloud will be Sponsoring Super User SE
Hot Network Questions
- Why ", removing ..." is better than ", which removes ..." in this case?
- Open loop gain of Op Amp 20 dB lower
- What do the inhabitants of Mongo name themselves?
- Traffic is too loud to hear you
- Does the "gradual brain replacement" thought experiment prove consciousness is independent of substrate?
- Gravitational forces
- Expired passport and flight tomorrow
- Does it matters who your thesis examiner is?
- What was this television history series?
- Is multiplication of two complex numbers that are inside a complex regular polygon still in this polygon?
- How can I fit a protagonist and his character arc to an existing world and plot?
- Scene from The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy where Arthur fails to explain how Earth technology works
- Hilbert's and Gödel's expanded definition of "Recursive Function"
- Expressiveness in arithmetic
- What is "trickle-down economics"?
- Express Integer as Product Complex Number
- How would I pull off FTL travel in a universe where inter-universal travel is also widely used?
- Function that returns activation function, as well as its derivative
- Circles crossing every cell of an 8x8 grid
- Staying out of the blind spot of a truck that doesn't have mirrors?
- An unusual scotch sequence -- why not take a free pawn?
- Is elision applicable to acronyms? For instance, is it "LE xml" or "L'xml" ?
- A single piece of jargon
- Break a hline between two slide
- ACTIVATION CENTER
- Professional
- Privacy Policy
TP-Link TL-WR710N support
Quick Links

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
DD-WRT Novice. Joined: 23 Nov 2008. Posts: 4. Posted: Sun Nov 23, 2008 16:07 Post subject: WAN Port Assignment. Under Setup - Networking - Port Setup there is a drop-down list for selecting the WAN port. It is currently set to vlan1. Other options are eth0, eth1 and vlan0. The bridge table is. Code:
Firmware: DD-WRT v3.0-r47608 std (10/28/21) I'm going to set up my router as an AP (access point). I'm following the Wireless Access Point article from the Wiki ( ... Should I keep this "WAN Port Assignment" set to "eth0" or what? Or else, should there be a "switch" option in this selection box? thanks! _____ Linksys WRT3200ACM ...
The 10Gbit SFP port is not connected to the switch at all, so it has nothing to do with any VLAN stuff. You just have to select the correct interface in the "networking" tab under "WAN port assignment". That should be eth0 - but I'm not quite sure about that. That worked. Changing the WAN port assignment to eth0.
how to undisable assign wan port to eth0 DD-WRT Forum Index-> General Questions: View previous topic:: ... Soleous75 DD-WRT Novice Joined: 21 May 2014 Posts: 1: Posted: Wed May 21, 2014 14:22 ...
Installing DD-WRT on a router in most cases is almost as simple as installing a program onto your computer. However, doing it incorrectly can leave you with a router that you have to throw away. ... Under the Port Setup section, as WAN Port Assignment set eth0. Check router MAC address on the Status page and set it in the Network Configuration ...
The 2mb of flash and 8mb of ram is very limiting. In a network (LAN side interconnected with wired or wireless links) DHCP broadcasts will be answered by all DHCP servers on the LAN with the client picking the one that responded first. If you do want to use it as a router makes sure: Setup -> Networking: Port Setup: Wan Port Assignment: eth0 ...
1) Setup->Networking->VLAN Tagging, Add a VLAN interface for the WAN port with Tag Number 201. On my router 'eth0' is the WAN port and applying this configuration creates an 'eth0.201' port. 2) Setup->Networking->Port Setup, Select 'eth0.201' for the WAN Port Assignment. You may need to refresh the page until the 'eth0.201' port shows up.
I noticed that on my Negear R6700v3, the option on the "Basic Setup" to "Assign WAN port to Switch" has been removed from version r47142. However, the WAN port *seems* to be working OK as a LAN switch even without changing anything on the "Switch Cfg" page. i.e. I can ping both directions between devices connect to the "WAN port" and to any of ...
If the WAN IP begins with 192.168.x.x, 172.[16-31].x.x, or 10.x.x.x then the router is behind another router that is also doing NAT. You must configure that router to either DMZ or port forward to the DD-WRT router. Any other WAN IP is likely a public (routable) address that just needs a properly configured port forward on the router.
ifconfig eth0:1 [NEW SUBNET ROUTER IP] netmask [NETMASK] broadcast [BROADCAST] Baseline Reference Example. Now let's say you have three routers connected together. Router1's WAN port is connected to the internet which makes it the gateway of your entire LAN, and Router2 and Router3 have their WAN ports connected to Router1's LAN ports.
Put your guest router in bridge mode and then connect one of its switch ports to a port set to VLAN 20 untagged on your managed switch. Then add the VLAN 10 interface on eth1 to the bridge with eth0, ath0, and ath1. Configure the other ports on your managed switch to access VLAN 10 or 20 as desired. This all should be within the capabilities of ...
Assuming you have also ebtables (or ebtables-nft) in addition to iptables on the router, and that all the (W)LAN interfaces are bridge slaves to the same master (say named bridge0):. ebtables -I INPUT -i ath0 -j mark --set-mark 0xabcd iptables -I FORWARD -i bridge0 -m mark --mark 0xabcd -j DROP (Note that the mark value 0xabcd is arbitrary.). This causes all traffics that comes into the router ...
In order to get this to work I had to manually assign eth0 to br0. I pressume ping true wireless works because ath0 is assigned to br0 as default while eth0 is indirectly assigned to br0 true vlan1 and does'nt work. To me it seems like this problem is caused by a bug in DD-WRT's VLAN implementation for Atheros-based routers
There is two modes with eth0. One is master mode and the other one is client mode.If you use option ifname 'eth0' in wan interface (/etc/config/network) your ethernet will be in client mode. If you use that in lan, then ethernet will be in master mode.Also if you want wifi connection be sure to have wifi drivers in your compiled kernel/firmware of openWRT.
Link your internal Hyper-V switch to the first Ethernet (Eth0) port on the router VM. This seems a bit counter intuitive as the DD-WRT wiki says the first port is for the WAN - more on that later. image. Boot the router, your should be able to login on the address 192.168.1.1 as root with the password admin on both the console or via a web ...
To do this, you need to disable the Internet Connection and "Assign WAN Port to Switch". Normally, the router does Layer 3 IP routing. but by "Assigning WAN Port to Switch," your DD-WRT router will bypass that functionality and just pass on the Layer 2 ethernet packets from your wired network to the wireless network and vice versa.
WAN port security assessment (DD-WRT) I am running an Ethernet cable around my house to connect a cable modem in one room with the WAN port of the Netgear 6700 router (ddwrt) in another room. I am wondering if this poses a security risk. Especially if an intruder could gain access to my LAN via that Ethernet cable that's connected to the WAN ...
TP-Link TL-WR710N support DD-WRT Forum Index-> Atheros WiSOC based Hardware: Goto page Previous 1, 2, Previous 1, 2,