
140 Interesting Cybercrime Research Topics To Focus On
Table of Contents
Do you have to submit a cybercrime research paper? Are you looking for the best cybercrime research topics for your law assignments? Well, to help you out, here, we have compiled a list of interesting essays and research topic ideas on cybercrimes. Continue reading this blog post and gain unique ideas for writing a cybercrime research paper or an essay.
What is a Cybercrime?
Cybercrime is a criminal activity that is committed using a computer, a network, or a networked device. In recent times, the internet plays a vital role in the daily life of an individual. Particularly, a lot of financial transactions and data sharing are happening over the internet. So, considering that many cybercrimes are being carried out by cybercriminals for generating a profit. Basically, cybercrimes are of three categories.
- Crimes in which the computer is used as a weapon. E.g., launching a denial-of-service (DoS) attack, or malware attack.
- Crimes in which a computer or networked device is a target. E.g., gaining network access.
- Crimes in which a computer is used as an accessory to a crime. E.g., data theft, cyberstalking.
Under the above-mentioned categories, different types of cybercrimes are being carried out by cybercriminals. Cybercrimes include both monetary and non-monetary offenses. Mostly, cybercrimes result in damage to an individual, a device, or a government.
List of Cybercrimes
In the entire world, plenty of cybercrimes are happening. The masterminds behind all those dangerous crimes are the hackers with strong hacking and technical knowledge. Mainly, cybercrimes are carried out at locations where there is digital data.

Here is a list of some widely carried out cybercrimes across the world.
- Cyber Bullying
- Cyber Grooming
- Child Pornography
- Cyber Stalking
- Online Job Fraud
- Online Sextortion
- SIM Swap Scam
- Credit Card/Debit Card Fraud
- Impersonation/Identity Theft
- Viruses, Trojans, and Worms
- Online Drug Trafficking
- Data Breach
- Cryptojacking
- Cyber-Squatting
- Website Defacement
In order to prevent cybercrimes and reduce the risk of cyberattacks, cyber security is practiced. Also, to handle all the cybercrimes, each country has a separate cybercrime department and they follow strict cyber laws.
Cybercrime Research Topics and Ideas
Nowadays, a lot of questions are being raised about cybercrimes. To get answers for them all, conducting research is the only option. In case, you are asked to craft a cybercrime research paper on the topic of your preference, consider any topic related to common cybercrime cases such as personal data theft, financial theft, cyber-extortion, drug trafficking, and terrorism.

Are you a law student who has a keen interest to analyze and study cybercrimes? If yes, then the list of the best cybercrime research topics recommended below will be helpful to you. Without any hesitation, explore the full list and select any topic that is comfortable for you to analyze and write about.
Best Cybercrime Research Topics
- What is the role of America in protecting corporations from cybercrime?
- Have a close look at cybercrime, cyber forensics, and digital evidence.
- Is cybercrime the top IT threat?
- Write about the necessity of cyber security in preventing cybercrimes.
- Discuss the international laws and regulations related to cybercrime.
- Explain the effects of the UAE Cybercrime policy.
- What are the toolkits used in cybercrimes?
- Discuss the cybercrimes in Singapore.
- Write about UAE cybercrime laws.
- Explain the impact of cybercrime on the global criminal justice system.
- Have a detailed look at international cyberwar.
- Talk about Cybercrimes in the US.
- Discuss identity theft and cybercrime in contemporary society.
- Explain the significance of digital education and creating awareness of cybercrime.
- What are the effects of cybercrime on the world’s major countries?
- Explain UAE cybercrime laws.
- What is the need for cyber security in preventing cybercrimes?
- Discuss the role of America in protecting corporations from cybercrime.
- Importance of raising cybercrime awareness and digital education
- Analyze some recent cases of cybercrime in the banking industry and its consequences
- Discuss the impact of IP (intellectual property) rights, cyber piracy, and cybercrime on domestic and international business with the latest examples
- Critically analyze the degree and frequency of cybercrime in the United States
- Analyse the Cybercrime Legislation Amendment Act 2012(Cth) (CLAA)
- Compare and contrast the cybercrime prevention laws in India and the United Kingdom
- Analyze the Cybersecurity Laws and Regulations Report 2023 USA
- What are the key measures to undertake by a company to protect the cloud computing environment from cybersecurity issues?
- Identify and analyze the components of broadband industry structure and cybercrime
- Discuss the relationship between cybercrime, the economy, privacy, hacking, and terrorism

Good Cybercrime Essay Topics
- What are all the effects of cybercrime on the world’s major countries?
- Discuss the cybercrimes in the healthcare industry.
- Explain the developments in hacking.
- Discuss the trends of the future of good cybercrime.
- Write about Cybercrimes in Australia.
- What are the impacts of cybercrime on the banking industry?
- Is identity theft a cybercrime?
- Should capital punishment be given for cybercrime?
- Discuss the solutions for cybercrimes in Information Technology.
- Talk about cybercrime and social media.
- Explain the cybercrime challenges in public universities.
- Have a closer look at business fraud and cybercrime.
- Write about cybercrimes in India.
- Discuss terrorist cyberattacks with an example.
- Explain the impact of cybercrime on a government.
- Discuss the five biggest cyber security trends in 2022
- Remote working risks of cybersecurity
- Importance of Password-only Authentication in restricting cybercrime
- The Rise of Ransomware: Discuss
Unique Cybercrime Research Topics
- How to explain cybercrime using criminological theories ?
- How does crypto jacking work?
- Track the evolution of online scams.
- Analyze the implications of the Cyberpunk 2077 leak.
- How do cybercrimes afflict retail shops?
- What are man-in-the-middle attacks?
- What are the various phases of a DDoS attack?
- How to mitigate a denial-of-service attack?
- Analyze the success rate of email scams.
- Describe the working of WannaCry malware.
- Describe what happens during a Brute Force attack.
- How does ransomware work?
- How to protect children from cyberbullying?
- Have a closer look at big data and increased cybercrimes.
- Compare various types of fraud methods.
- What are identity theft and cybercrime in contemporary society
- Discuss the statistics on cybercrime as well as Fraud
Outstanding Cybercrime Essay Questions
- How to fight cybercrimes?
- Discuss the predictive models in cybercrime investigation.
- What are the major reasons for cybercrimes?
- What is hacking?
- How to avoid hacking?
- Whose responsibility is cybercrime?
- Discuss the cost of cybercrime and digital spying.
- How does cybercrime affect domestic and foreign business?
- How to investigate cybercrime?
- Discuss the link between fraud and invisible attackers.
Top-rated Cybercrime Research Topics
- Explain the difference between pharming and phishing.
- Explain the term “cyberwarfare.”
- Can hacking be ethical?
- How can online consumers protect themselves from fraud?
- Is jailbreaking a crime?
- How can parents monitor their children’s behavior on the web?
- How to prevent cyberbullying in the online learning environment?
- Would cyber communism decrease bullying?
- Discuss the connection between political protests and hacking.
- Talk about the mental health effects of internet bullying.
- Who is responsible for online misbehavior?
- Who are white hat and black hat hackers?
- Explain the effects and solutions of catfishing.
- Should schools teach online etiquette?
- Does internet anonymity bring out the worst in people?
- How to stay safe online?
- How does a firewall help to protect the network?
- Explain how cyberbullying differs from in-person harassment.
- How to cope with online harassment?
- Write about phishing and scam on the internet.
Also read: Best Cybersecurity Research Topics for Students to Consider
Excellent Research Topics on Cybercrime
- Write about the importance of cybercrime management.
- Explain the history of cybercrime.
- Discuss the effects of cybercrime on the Internet economy.
- Talk about the cyberattack on Sony Pictures in 2014.
- Explain how technology has influenced the evolution of cybercrime.
- Discuss the social effects of cyberbullying on children.
- What are the signs of phishing attempts?
- What emergency action should an individual take after being hacked?
- Research and explain the significant cyber threats to US national security.
- Different types of cybercriminals.
- How do private sectors battle cybercrimes?
- Discuss the impacts of mobile devices on cyber security.
- Take a closer look at cyberfeminism and social media.
- Compare the functions of various antivirus programs.
- Discuss the pros and cons of various InfoSec certificates.
Amazing Cybercrime Research Paper Topics
- Evaluate the issues related to botnets.
- What are the phases of a Trojan horse attack?
- Discuss the effective policy of cyberspace.
- Talk about cyber terrorism in the aviation sector.
- Explain the types of scams associated with cybercrime.
- Discuss the potential effects the cyber currencies have on South African Businesses.
- How the automotive software of smart cars can be protected from cyberattacks?
- Discuss the effects of cyberbullying on teen suicides.
- Have a closer look at the cyber policy and strategy of the United Kingdom.
- What are the dangers of public Wi-Fi networks?
High-quality Cybercrime Research Ideas
- Describe the technology of unlocking a phone through facial recognition and the fingerprint of the owner of the phone
- Select a company from the United States and discuss their efforts and strategies to ensure cyber security
- Discuss the reasons that make every individual aware when it comes to safeguarding and protecting personal data and information from hackers
- Face recognition vs. a simple security code vs. fingerprint: Which is the safest locking option for smart devices and why?
- The increasing use of the internet consecutively increases the likelihood of adolescents and young adults engaging in cybercrime-related activities (e.g., email and internet fraud, identify fraud)
- Compare and contrast the effects of Phishing Emails, DoS (Denial of Service) Attacks, and Social Engineering
- Describe the history of cybercrime and the way cybercriminals have introduced different strategies to commit such crimes over the past decades
- Discuss the similarities and differences between distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks and DoS (Denial of service) attacks
- Examination of the consequences a community or society would have to bear in case a hacker targeted the entire state
- Is purchasing from e-commerce sites such as eBay, Amazon, and Craigslist more ethical and safe compared to buying from other online marketplaces? Explain with reasons and the cyber security strategies of the aforementioned sites.
Impressive Cybercrime Research Topics
- Explain the importance of parental control mechanisms on children’s computers.
- What are effective strategies to cope with online harassment?
- Establish a link between feminism and the fight against cyberstalking.
- Analyze online gaming behavior from a psychological standpoint.
- How did industrial espionage evolve into hacking?
- Describe how an SQL injection attack unfolds.
- What are the safest ways to ensure data integrity?
- Discuss the pros and Cons of various cryptographic methods.
- How can a person reach maximum technological security?
- Explain the mechanics of password protection.
Final Words
From the list of ideas suggested above, choose any topic that matches your requirements and craft a detailed cybercrime research paper with proper citations and proofs to prove your thesis statement. In case, you need an expert to offer you help with cybercrime research paper topic selection and writing, get in touch with us immediately. We have numerous professional writers who are experts in the field of law and cybercrime to provide assignment help online according to your needs.
If you wish to make use of our cybercrime research paper writing service, just write your requirements in the order form and submit it. Based on the specifications you send us, our cybercrime research paper helpers will craft and dispatch a well-structured and plagiarism-free academic paper on time. Also, you can opt for endless paper revisions and round-the-clock customer support by availing of our assignment writing services.

Related Post

220 Amazing Religious Research Paper Topics and Ideas

Read and Understand How to Write a Research Proposal

100+ Controversial Research Topics and Ideas to Focus On
About author.
Jacob Smith
I am an Academic Writer and have affection to share my knowledge through posts’. I do not feel tiredness while research and analyzing the things. Sometime, I write down hundred of research topics as per the students requirements. I want to share solution oriented content to the students.
Comments are closed.
- Featured Posts
140 Unique Geology Research Topics to Focus On
200+ outstanding world history topics and ideas 2023, 190 excellent ap research topics and ideas, 150+ trending group discussion topics and ideas, 170 funny speech topics to blow the minds of audience, who invented exams learn the history of examination, how to focus on reading 15 effective tips for better concentration, what is a rhetorical analysis essay and how to write it, primary school teacher in australia- eligibility, job role, career options, and salary, 4 steps to build a flawless business letter format, get help instantly.
Raise Your Grades with Assignment Help Pro
116 CyberCrime Topics & Essay Samples
If you are writing a cybercrime essay, our team prepared this article just for you. Here, you will find 115 unique topics for any type of paper.
117 CyberCrime Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
Inside This Article
117 Cybercrime Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
In today's digitally interconnected world, cybercrime has become a significant concern for individuals, businesses, and governments alike. The ever-evolving nature of cyber threats poses challenges to law enforcement agencies and cybersecurity professionals. If you are tasked with writing an essay on cybercrime, but struggling to come up with a topic, fret not! Here, we present 117 cybercrime essay topic ideas and examples to help inspire your writing.
- The rise of ransomware attacks: Causes, consequences, and preventive measures.
- Cyberbullying: Analyzing its psychological impact on victims and strategies for prevention.
- Social engineering attacks: Understanding the methods and mitigating the risks.
- The role of international cooperation in combating cybercrime.
- The dark web: A haven for illegal activities.
- Cyber warfare: Assessing the implications and international norms.
- Online identity theft: Examining the financial and emotional consequences.
- The use of artificial intelligence in cybercrime prevention.
- Cyber espionage: Analyzing state-sponsored attacks and their impact on national security.
- The role of cryptocurrencies in facilitating cybercrime.
- Cyberstalking: Legal challenges and protective measures.
- The impact of cybercrime on small businesses.
- The ethics of hacking: White hat versus black hat.
- Cyberterrorism: Assessing the risks and counterterrorism strategies.
- The role of legislation in combating cybercrime.
- The psychological profile of cybercriminals: Identifying common characteristics.
- The influence of cybercrime on financial markets and economies.
- Cyber fraud: Analyzing different types and methods.
- The impact of cybercrime on critical infrastructure.
- Cybersecurity awareness: Strategies for educating individuals and organizations.
- The role of social media in facilitating cybercrime.
- Cyberbullying among teenagers: Causes, consequences, and preventive measures.
- The future of cybersecurity: Anticipating emerging threats.
- The impact of cybercrime on healthcare organizations.
- The role of machine learning in detecting and preventing cyber threats.
- Cyberattacks on the electoral process: Safeguarding democratic systems.
- The legal challenges of prosecuting cybercriminals.
- The role of international organizations in addressing cybercrime.
- Cyber insurance: Analyzing its effectiveness in mitigating financial losses.
- The impact of cybercrime on intellectual property theft.
- The vulnerabilities of IoT devices: Securing the interconnected world.
- The role of education in raising cybercrime awareness.
- The impact of cybercrime on national security.
- The role of cloud computing in enhancing cybersecurity.
- Cyberbullying in the workplace: Addressing its prevalence and impact.
- The psychology behind cybercriminals: Understanding their motivations.
- The impact of cybercrime on e-commerce and online transactions.
- Cybersecurity regulations: Balancing privacy and protection.
- The influence of state-sponsored hacking on international relations.
- The role of cybersecurity certifications in professional development.
- Cyberattacks on critical infrastructure: Analyzing vulnerabilities and protective measures.
- The impact of cybercrime on human rights and privacy.
- Cyber espionage: The blurred lines between nation-states and cybercriminals.
- The role of artificial intelligence in cyber defense.
- The psychology of phishing attacks: How do they manipulate human behavior?
- The impact of cybercrime on the banking sector.
- The role of information sharing in combating cyber threats.
- The rise of cybercrime during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- The legal challenges of extraditing cybercriminals across borders.
- The impact of cybercrime on children and adolescents.
- The role of cybersecurity in protecting personal data.
- Cyberattacks on the transportation industry: Analyzing risks and vulnerabilities.
- The impact of cybercrime on trust in digital systems.
- Cyber insurance: Its role in incentivizing cybersecurity investments.
- The ethical considerations of hacking for a cause: Hacktivism.
- The impact of cybercrime on national economies.
- Cybersecurity in the age of artificial intelligence: Challenges and opportunities.
- The role of open-source intelligence in investigating cybercrimes.
- Cyberattacks on critical infrastructure: Learning from historical incidents.
- The impact of cybercrime on the reputation of organizations.
- The psychology of online scams: Understanding victims' susceptibility.
- The vulnerabilities of smart cities: Securing the urban future.
- The impact of cybercrime on human trafficking and exploitation.
- The role of cybersecurity in protecting intellectual property.
- Cyber espionage: Analyzing the tactics and techniques of nation-state actors.
- The impact of cybercrime on the tourism industry.
- The role of cybersecurity in protecting elections and democratic processes.
- Cybersecurity in the era of quantum computing: Preparing for the future.
- The impact of cybercrime on the entertainment industry.
- The psychology of online radicalization: Analyzing the role of the internet.
- The vulnerabilities of supply chain networks: Safeguarding global trade.
- The impact of cybercrime on national healthcare systems.
- The role of cybersecurity in protecting critical research and development.
- Cyber insurance: Challenges and opportunities for insurance providers.
- The dark side of social media: Cyberbullying and harassment.
- The impact of cybercrime on the aviation industry.
- The role of cybersecurity in protecting autonomous vehicles.
- Cyber espionage: Analyzing the economic and political motivations behind attacks.
- The impact of cybercrime on the gaming industry.
- The vulnerabilities of smart home devices: Protecting personal privacy.
- The role of cybersecurity in protecting intellectual property in the pharmaceutical industry.
- Cyberattacks on the energy sector: Analyzing the risks and protective measures.
- The impact of cybercrime on the media and journalism.
- The psychology of online grooming: Protecting vulnerable individuals.
- The vulnerabilities of e-voting systems: Safeguarding democratic processes.
- The impact of cybercrime on the retail industry.
- The role of cybersecurity in protecting autonomous drones.
- Cyber espionage: Analyzing the impact on technological advancements.
- The impact of cybercrime on the music industry.
- The vulnerabilities of smart grid systems: Securing the future of energy.
- The role of cybersecurity in protecting intellectual property in the film industry.
- Cyberattacks on the water supply: Analyzing the risks and protective measures.
- The impact of cybercrime on the sports industry.
- The psychology of online addiction: Analyzing the impact on mental health.
- The vulnerabilities of smart transportation systems: Ensuring passenger safety.
- The impact of cybercrime on the fashion industry.
- The role of cybersecurity in protecting smart city infrastructure.
- Cyber espionage: Analyzing the impact on scientific advancements.
- The impact of cybercrime on the food and beverage industry.
- The vulnerabilities of wearable technology: Protecting personal health data.
- The role of cybersecurity in protecting intellectual property in the automotive industry.
- Cyberattacks on the telecommunications sector: Analyzing the risks and protective measures.
- The impact of cybercrime on the art and design industry.
- The psychology of online gaming addiction: Analyzing its effects on players.
- The vulnerabilities of smart healthcare systems: Protecting patient data.
- The impact of cybercrime on the hospitality industry.
- The role of cybersecurity in protecting smart home infrastructure.
- Cyber espionage: Analyzing the impact on military capabilities.
- The impact of cybercrime on the beauty and cosmetics industry.
- The vulnerabilities of augmented reality technology: Protecting user privacy.
- The role of cybersecurity in protecting intellectual property in the aerospace industry.
- Cyberattacks on the financial sector: Analyzing the risks and protective measures.
- The impact of cybercrime on the real estate industry.
- The psychology of online shopping addiction: Analyzing consumer behavior.
- The vulnerabilities of blockchain technology: Ensuring secure transactions.
- The impact of cybercrime on the agricultural industry.
- The role of cybersecurity in protecting smart grid infrastructure.
These 117 cybercrime essay topic ideas and examples should provide ample inspiration for your writing. Whether you choose to focus on the psychological aspects, the technical challenges, or the societal impacts of cybercrime, remember to approach the topic with a critical mindset and back your arguments with reliable sources. Good luck with your essay!
Want to create a presentation now?
Instantly Create A Deck
Let PitchGrade do this for me
Hassle Free
We will create your text and designs for you. Sit back and relax while we do the work.
Explore More Content
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
© 2023 Pitchgrade
A List of 181 Hot Cyber Security Topics for Research [2024]
Your computer stores your memories, contacts, and study-related materials. It’s probably one of your most valuable items. But how often do you think about its safety?
Our specialists will write a custom essay specially for you!
Cyber security is something that can help you with this. Simply put, it prevents digital attacks so that no one can access your data. Do you want to write a research paper related to the modern challenges of cyberspace? This article has all you need. In here, you’ll find:
- An overview of cyber security’s research areas.
- A selection of compelling cyber security research topics.
And don’t hesitate to contact our custom writing team in case you need any assistance!
- 🔝 Top 10 Topics
- ✅ Research Areas
- ⭐ Top 10 Cybersecurity Topics
- 🔒 Technology Security Topics
- 🖥️ Cybercrime Topics
- ⚖️ Cyber Law & Ethics Topics
🔍 References
🔝 top 10 cyber security topics.
- How does malware work?
- The principle of zero trust access
- 3 phases of application security
- Should removable media be encrypted?
- The importance of network security
- The importance of end-user education
- Cloud security posture management
- Do biometrics ensure security of IPhones?
- Can strong passwords protect information?
- Is security in critical infrastructure important?
✅ Cyber Security Topics & Research Areas
Cyber security is a vast, constantly evolving field. Its research takes place in many areas. Among them are:

- Safe quantum and space communications . Progress in quantum technologies and space travel calls for extra layers of protection.
- Data privacy. If someone’s personal information falls into the wrong hands, the consequences can be dire. That’s why research in this area focuses on encryption techniques.
- (Inter)national cyberethics, criminology, and law. This branch analyzes how international legal frameworks work online.
- AI and IoT security . We spend more and more of our daily lives online. Additionally, our reliance on AI increases. This scientific field strives to ensure a safe continuation of this path.
As you can see, cyber security extends in various exciting directions that you can explore. Naturally, every paper needs a cover page. We know that it’s one of the more annoying parts, so it’s not a bad thing to use a title page generator for your research paper . Now, let’s move on to our cyber topics list.
⭐ Top 10 Cybersecurity Topics 2024
- Is removable media a threat?
- Blockchain security vulnerabilities
- Why should you avoid public Wi-Fi?
- How to prevent phishing attacks
- Physical security measures in banks
- Security breaches of remote working
- How does two-factor authentication work?
- How to prevent social engineering attacks
- Cybersecurity standards for automotive
- Privacy settings of social media accounts
🔒 Computer Security Topics to Research
Safe computer and network usage is crucial. It concerns not only business but also individuals. Security programs and systems ensure this protection. Explore them with one of our topics:
Just in 1 hour! We will write you a plagiarism-free paper in hardly more than 1 hour
- How do companies avoid sending out confidential information ? Sending an email to the wrong person has happened to the best of us. But what happens if the message’s contents were classified? For your paper, you can find out what technologies can prevent such slip-ups.
- What are the best ways to detect malicious activity ? Any organization’s website gets plenty of daily traffic. People log in, browse, and interact with each other. Among all of them, it might be easy for an intruder to slip in.
- Internet censorship: classified information leaks . China takes internet censorship to the next level. Its comprehensive protection policies gave the system the nickname Great Firewall of China . Discuss this technology in your essay.
- Encrypted viruses as the plague of the century . Antivirus programs are installed on almost every computer. They prevent malicious code from tampering with your data. In your paper, you can conduct a comparison of several such programs.
- What are the pros and cons of various cryptographic methods? Data privacy is becoming more and more critical. That’s why leading messaging services frequently advertise with their encryption technologies .
- What makes blockchain secure ? This technique allows anonymity and decentralization when working with cryptocurrencies . How does it work? What risks are associated with it?
- What are the advantages of SIEM ? Security Incident and Event Management helps organizations detect and handle security threats. Your essay can focus on its relevance for businesses.
- What are the signs of phishing attempts?
- Discuss unified cyber security standards in healthcare .
- Compare and contrast various forms of data extraction techniques.
- What do computers need protocols for?
- Debate the significance of frequent system updates for data security .
- What methods does HTTPS use that make it more secure than HTTP?
- The role of prime numbers in cryptography .
- What are public key certificates , and why are they useful?
- What does a VPN do?
- Are wireless internet connections less secure than LAN ones? If so, why?
- How do authentication processes work?
- What can you do with IP addresses?
- Explain the technology of unlocking your phone via facial recognition vs. your fingerprint.
- How do you prevent intrusion attempts in networks ?
- What makes Telnet vulnerable?
- What are the phases of a Trojan horse attack?
- Compare the encryption technologies of various social networks.
- Asymmetric vs. symmetric algorithms.
- How can a person reach maximum security in the computer networking world ?
- Discuss autoencoders and reveal how they work.
💾 Information Security Topics to Research
Information security’s goal is to protect the transmission and storage of data. On top of that, network security topics are at the forefront of infosec research. If you’re looking for inspiration on the subject, check out these ideas.
- What are the mechanics of password protection ? Passwords are a simple tool to ensure confidentiality. What do users and developers need to keep in mind when handling passwords?
- What are the safest ways to ensure data integrity ? Everybody wants their data to be intact. Accidental or malicious modifications of data can have dire consequences for organizations and individuals. Explore ways to avoid it.
- How can one establish non-repudiation? Non-repudiation proves the validity of your data. It’s essential in legal cases and cyber security .
- How did the advent of these new technologies impact information security ? Mobile networks have changed the way we access information. On a smartphone , everything is permanently available at your fingertips. What adverse consequences did these technologies bring?
- How do big corporations ensure that their database environment stays conflict-free? We expect our computers to always run fast and without errors. For institutions such as hospitals, a smooth workflow is vital. Discuss how it can be achieved.
- Describe solid access control methods for organizations. In a company, employees need access to different things. This means that not everyone should have an admin account. How should we control access to information ?
- Medical device cyber security. For maximum safety, it’s best to employ several measures. Protection on the hard- and software side is just a part of it. What are some other means of security?
- Write an argumentative essay on why a career in information security doesn’t require a degree.
- Pros and cons of various infosec certificates.
- Cybersecurity in cruise ship industry
- The influence of remote work on a businesses’ infosec network .
- What should everyone be aware of when it comes to safeguarding private information?
- Select a company and calculate how much budget they should allocate on cyber security.
- What are the dangers of public Wi-Fi networks ?
- How secure are cloud services ?
- Apple vs. Microsoft : whose systems offer better security?
- Why is it important to remove a USB flash drive safely?
- Is it possible to create an unguessable password?
- Intranet security : best practices.
- Does the use of biometrics increase security?
- Face recognition vs. a simple code: what are the safest locking options for smartphones ?
- How do you recover data from a broken hard drive?
- Discuss the functions and risks of cookies and cache files.
- Online privacy regulations in the US and China.
- Physical components of infosec .
- Debate security concerns regarding electronic health records .
- What are unified user profiles, and what makes them potentially risky?
🖥️ Cybercrime Topics for a Research Paper
Knowledge is one of today’s most valuable assets. Because of this, cybercrimes usually target the extraction of information. This practice can have devastating effects. Do you want to learn more about the virtual world’s dark side? This section is for you.
- Give an overview of the various types of cybercrimes today . Cybercriminals are becoming more and more inventive. It’s not easy to keep up with the new threats appearing every day. What threats are currently the most prominent?
- How does cryptojacking work, and why is it problematic? Cryptocurrency’s value explosion has made people greedy. Countries such as Iceland have become a haven for datamining. Explore these issues in your essay.
- Analyze the success rate of email frauds . You’ve probably seen irrelevant ads in your spam folder before. They often sound so silly it’s hard to believe they work. Yet, unfortunately, many people become victims of such scams.
- How did the WannaCry malware work? WannaCry was ransomware that caused global trouble in 2017. It led to financial losses in the billions. What made it so dangerous and hard to stop?
- Give famous examples of cybercrimes that targeted people instead of money . Not all cybercrimes want to generate profit. Sometimes, the reasons are political or personal. Explore several instances of such crimes in your essay. How did they pan out?

- Analyze the implications of the Cyberpunk 2077 leak. The game’s bugs and issues made many people angry. Shortly after its flop, hackers released developer CD Projekt Red’s source codes. What far-reaching consequences could this have?
- Why do hackers commit identity theft? Social media has made it easy to steal identities . Many like to display their lives online. In your paper, research what happens to the victims of identity thefts.
- Should governments punish cybercrimes like real-life crimes?
- How does ransomware work?
- Describe the phases of a DDoS attack.
- What cybercrime cases led to changes in the legislature ?
- Track the evolution of online scams.
- Online grooming: how to protect children from predators.
- Are cybercrimes “gateway crimes” that lead to real-life misbehavior?
- What are man-in-the-middle attacks?
- Big data and the rise of internet crimes.
- Are cybercrimes more dangerous to society than they are to corporations?
- Is the internet increasing the likelihood of adolescents engaging in illegal activities?
- Do the downsides of cyberlife outweigh its positives?
- Is constantly checking your crush’s Facebook page cyberstalking?
- How do you recognize your online date is a scam?
- Describe what happens during a Brute Force attack.
- What’s the difference between pharming and phishing?
- The Lehman Bank cybercrimes
- Should the punishments for cybercriminals be harsher than they are now?
- Compare various types of fraud methods .
- How do you mitigate a denial-of-service attack?
🕵️ Topics for a Research Paper on Hacking
Blinking screens and flashing lines of code: the movie industry makes hacking look fascinating. But what actually happens when someone breaks into another person’s computer’s system? Write a paper about it and find out! The following prompts allow you to dive deeper into the subject.
- Is it vital to keep shutting down online movie streaming sites? Many websites offer free movie streaming. If one of their domains gets closed down, they just open another one. Are they a threat to the industry that must be stopped? Or should cyber law enforcement rather focus on more serious crimes?
- Explore the ethical side of whistleblowing. WikiLeaks is a platform for whistleblowers. Its founder, Julian Assange, has been under arrest for a long time. Should whistleblowing be a crime? Why or why not?
- How did Kevin Mitnick’s actions contribute to the American cyber legislature? Mitnick was one of the US’s first most notorious hackers. He claimed to have broken into NORAD’s system. What were the consequences?
- Examine how GhostNet operates. GhostNet is a large organization attacking governments. Its discovery in 2009 led to a major scandal.
- Describe how an SQL injection attack unfolds. Injection attacks target SQL databases and libraries. This way, hackers gain unauthorized access to data.
- What political consequences did the attack on The Interview imply? In 2014, hackers threatened to attack theaters that showed The Interview . As a result, Sony only showed the movie online and in limited releases.
- Write about cross-site request forgery attacks. Every website tells you that logging out is a crucial step. But what can happen if you don’t do it?
- What is “Anonymous,” and what do they do?
- Is it permissible to hack a system to raise awareness of its vulnerabilities?
- Investigate the origins of the hacking culture .
- How did industrial espionage evolve into hacking?
- Is piracy destroying the music and movie industries ?
- Explain the term “cyberwarfare.”
- Contrast different types of hacking .
- Connections between political protests and hacking.
- Is it possible to create an encryption that can’t be hacked?
- The role of hackers in modern warfare .
- Can hacking be ethical?
- Who or what are white hat hackers ?
- Discuss what various types of hackers do.
- Is jailbreaking a crime?
- How does hacking a phone differ from hacking a computer?
- Is hacking your personal home devices problematic?
- What is clickjacking?
- Why would hackers target newspapers ?
- Examine the consequences society would have to bear if a hacker targeted the state.
- Compare and analyze different hacking collectives.
⚖️ Topics on Cyber Law & Ethics to Look Into
Virtual life needs rules just like the real one does. The online world brings a different set of values and issues to the table. And, naturally, cyberlife has a legal framework. That’s where researching cyber law and ethics comes into play.
- Is it ethical that governments can always access their citizens’ data? In some countries, online platforms for personal information are standard. From medical exams to debts , everything is available with a click. The system is inarguably convenient. But what about its downsides?
- Is it still morally permissible to use Spotify ? Spotify has made listening to music more accessible than ever. However, artists only receive a tiny fraction of the company’s profits. Discuss the implications of this fact.
- Should internet forums require users to display their real names? Online harassment is a widespread problem. Nicknames hide the identities of ordinary users as well as perpetrators. Can the mandatory use of real names change the situation?
- Analyze online gaming behavior from a psychological standpoint. If one wants to play online games, one needs to have a thick skin. The community can be harsh. You can dedicate your paper to exploring these behaviors. Or you might want to ponder what game publishers can do to reduce hate speech.
- What type of restrictions should sellers implement to prevent domain speculation? Some people buy domains hoping that they will sell them later for more money. This practice makes registering a new website trickier.
- Does the internet need regulations to make adult content less visible? Every computer without parental control can access pornographic websites. Most of them don’t require registration . Their contents can be disturbing, and their ads can appear anywhere. What can be done about it?
- What are cyber laws still missing in America? The US has established many laws to regulate internet usage. Select the most significant ones and explain their relevance.
- Why should cyber ethics be different from real-world norms?
- Are there instances in which illegal downloading is justified?
- The rule of law in real life vs. in cyberspace.
- Does the internet need a government?
- What is cyber terrorism, and what makes it dangerous?
- Who is responsible for online misbehavior?
- How binding are netiquettes?
- What did the implementation of the GDPR change?
- Compare and contrast Indian vs. Venezuelan internet regulations.
- What does the CLOUD entail?
- How should law enforcement adapt to online technologies?
- AI applications : ethical limits and possibilities.
- Discuss trending topics in cyber law of the past ten years.
- Should schools teach online etiquette?
- Does internet anonymity bring out the worst in people?
- Is data privacy more important than convenience and centralization?
- Debate whether bitcoins could become the currency of the future.
- How can online consumers protect themselves from fraud ?
- Is buying from websites like eBay and Craigslist more ethical than buying from other online marketplaces?
- Present RSF’s Minecraft library and discuss its moral implications.
🖱️ Cyberbullying Topics for Essays and Papers
On the web, everyone can remain anonymous. With this added comfort, bullying rises to another level. It’s a serious issue that’s getting more and more problematic. Cyber security measures can alleviate the burden. Do you want to address the problem? Have a look at our cyberbullying topics below.
Receive a plagiarism-free paper tailored to your instructions. Cut 20% off your first order!
- Cyberbullying prevention in online learning environments . Online classes increase the possibility of cyberbullying. What can teachers do to watch out for their students?
- What makes online emotional abuse particularly difficult to bear? Bullying doesn’t necessarily have to be physical to hurt. Statistics show increased suicide rates among students who were harassed online. Explore the reasons behind this phenomenon.
- How can victims of identity theft reclaim their lives? Identity theft leads not only to mental distress. Thieves also have access to credit card information and other essential assets.
- What are the best methods to stay safe online? When surfing the internet, one always has to be on one’s toes. Avoiding harassment and bullying is a particularly challenging task.
- How can parents monitor their children’s behavior on the web? Children are particularly vulnerable online. They might enter dangerous online relationships with strangers if they feel lonely. They are also more susceptible to scams. What can parents do to protect them?
- Cyberbullying among university students. Online abuse in such websites is very common. Everyone can be a potential target, regardless of age or gender. Discuss whether the structure of social networks helps to spread cyberbullying.
- What societal factors contribute to online bullying? Not everyone who uses the internet becomes an abuser. It’s possible to establish several psychological characteristics of cyberbullies. Explore them in your paper.
- Define how cyberbullying differs from in-person harassment .
- Establish a link between feminism and the fight against cyberstalking .
- The emotional consequences of physical vs. verbal abuse.
- The effects of cyberbullying and academics.
- Short vs. long-term mental health effects of internet bullying .
- What are the most widespread means of cyberbullying ?
- Should people who want to play video games online get over the fact that the community is toxic?
- Is defending the freedom of speech more important than preventing the spread of hate speech?
- Reasons and consequences of Amanda Todd’s suicide.
- The dangers of pro-ana/-mia communities for adolescents.
- What are effective strategies to cope with online harassment ?
- Would cyber communism decrease bullying?
- How enhanced cyber security measures can help reduce abuse.
- The importance of parental control mechanisms on children’s computers.
- Traditional vs. cyberbullying in children.
- Do image-heavy websites such as Tumblr and Instagram affect one’s mental state similarly to active abuse?
- What kind of people does cyber abuse affect the most, and why?
- Analyze how the stalker uses the internet in Netflix’s series You .
- Catfishing: effects and solutions.
Thanks for reading through our article. If you found it helpful, consider sharing it with your friends. We wish you good luck with your project!
Further reading:
- 220 Best Science and Technology Essay Topics to Write About
- 204 Research Topics on Technology & Computer Science
- A List of 580 Interesting Research Topics [2024 Edition]
- A List of 179 Problem Solution Essay Topics & Questions
- 193 Interesting Proposal Essay Topics and Ideas
- 226 Research Topics on Criminal Justice & Criminology
- What Is Cybersecurity?: Cisco
- Cyber Security: Research Areas: The University of Queensland, Australia
- Cybersecurity: National Institute of Standards and Technology
- What Is Information Security?: CSO Online
- Articles on Cyber Ethics: The Conversation
- What Is Cybercrime?: Kaspersky
- Types of Cybercrime and How to Protect Yourself Against Them: Security Traits
- Hacking: Computing: Encyclopedia Britannica
- Hacking News: Science Daily
- Cyberbullying and Cybersecurity: How Are They Connected?: AT&T
- Cyberbullying: What Is It and How to Stop It: UNICEF
- Current Awareness: Cyberlaw Decoded: Florida State University
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

Have you ever wondered why everyone has a unique set of character traits? What is the connection between brain function and people’s behavior? How do we memorize things or make decisions? These are quite intriguing and puzzling questions, right? A science that will answer them is psychology. It’s a multi-faceted...
![cyber crime topics for research Student Exchange Program (Flex) Essay Topics [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/student-exchange-program-284x153.jpg)
Participating in a student exchange program is a perfect opportunity to visit different countries during your college years. You can discover more about other cultures and learn a new language or two. If you have a chance to take part in such a foreign exchange, don’t miss it. Keep in...

How can you define America? If you’ve ever asked yourself this question, studying US history will help you find the answer. This article will help you dive deeper into this versatile subject. Here, you will find: Early and modern US history topics to write about. We’ve also got topics for...
![cyber crime topics for research 380 Powerful Women’s Rights & Feminism Topics [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/Womens-Rights-284x153.jpg)
Are you looking for perfect feminist topics? Then you’ve come to the right place. With our help, you can be sure to craft a great essay. Here, you can find feminist topics for discussion, feminism research topics and other ideas and questions for students. Some people think all feminists hate...

If you have an assignment in politics, look no further—this article will help you ace your paper. Here, you will find a list of unique political topics to write about compiled by our custom writing team. But that’s not all of it! Keep reading if you want to: See how to tackle political essay topics in your paper; Choose a topic that will be interesting for you to research; Refresh your knowledge of essential political concepts. Now, without further ado, let’s get started! Below, you’ll find political topics and questions for your task. 🔝 Top 10...

It’s not a secret that our health largely depends on nutrition. A balanced and wholesome diet improves our immune system. It lowers the risk of getting sick and makes us more productive. But if we don’t eat right, our overall well-being and performance worsen. You see, nutrition topics are more...

A presentation is a speech in which you explain a topic to an audience. It usually includes visuals done in a program such as PowerPoint. Teachers in schools and in colleges love to assign presentations for various reasons: It requires students to put their knowledge into practice.It teaches them how...

In modern societies, people do everything to live peacefully. Still, tensions often arise. We call them social issues when they start negatively impacting a specific group of people. Poverty, discrimination, and addiction are examples of such problems. We need to confront them to ensure equal treatment for everyone.

There are many ways to define popular culture. Here’s one of them: pop culture includes mainstream preferences in society within a specific time frame. It covers fashion, music, language, and even food. Pop culture is always evolving, engaging in new trends, and leaving the old ones behind.
![cyber crime topics for research 500 Sociology Questions and Topics [Examples & Tips]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/Sociology-Questions-284x153.jpg)
Sociology is a study that focuses on people’s interactions. It looks at structures and changes in social life. Any situation involving people can become a topic of sociology. This article is designed to help high school and college students with sociology assignments. Whether you’re writing an essay, creating a presentation,...

Controversial issues are the ones that evoke a variety of opinions. They often cause heated debates. And, as you can guess, controversial research topics are not easy to handle. Luckily, we’ve got you covered. This article will: help you pick a controversial question for your essay;provide you a list of...

Plates break when you drop them. Glasses help you see better. Have you ever wondered why? Physics has the answer. It studies the observable as well as invisible aspects of nature. An essential part of this is examining the structure and interactions of matter.
105 Cybercrime Essay Topics
🏆 best essay topics on cybercrime, ✍️ cybercrime essay topics for college, 🎓 most interesting cybercrime research titles, 💡 simple cybercrime essay ideas, ❓ cybercrime research questions.
- The Hacking of Yahoo in 2013 and 2014
- Significance of Computer Forensics to Law Enforcement
- Cyber Security: The Nature and Scope of Cybercrime
- Cybercrime and Its Impact on Society
- Ethics of Hacking and Cracking
- Digital Forensic Examination of Counterfeit Documents
- Sexting and Related Cybercrime Legislation
- Computer Forensics Laboratory’ Legal Requirements Computer forensics scientists assess digital media to identify, preserve, recover, analyze, and present facts about the information under investigation.
- Cyber Crime : Issues and Threats Cyber crime involves the stealing or manipulation of information effectively distorting its values across global networks.
- Cybercrime From the Religious Viewpoint The paper focuses on identifying the points at which the religious worldview would be the most fitting for the cybercrime problem examination.
- Computer Forensics and Investigations A computer forensics examiner may be called to provide evidence and advice in a court of law. Before logs disappear, digital forensics investigators are required to capture them.
- Trends in Cybercrime and Society The internet has played a pivotal role in boosting science, business, and education. Nevertheless, the internet is an additional tool for committing many crimes.
- The Cybercrime Effect on Public Administration Cybercrime incidents occur in almost all government and public sectors and in the daily lives of individuals; such moments violate stability and the usual way of life.
- The Phone Hacking Scandal Among the major news event in the recent few days was the phone hacking scandal that was linked to the News of the World; a tabloid newspaper in the United Kingdom (UK).
- St. Louis County’s Cybercrime Task Force Plan The current paper presents a plan for the development of a cybercrime task force for St. Louis County to assign priorities for the task force.
- Digital Forensics in Law Enforcement The paper shows that digital forensics in law enforcement is useful in collecting extra proof after an occurrence to support charges against a suspect.
- Cybercrime and the Culture of Fear Sexual exploitation and other offenses against children remain tragic—in spite of their frequency—and those numbers have been diminishing since the advent of the internet.
- Computer Forensics Investigation Plan The US Constitution prohibits employers from conducting searches on employees. However, the protection does not apply to private organizations.
- The Justifiability of Hacking and the Government’s Role This paper discusses privacy in the age of technologies, government hacking, the human right to privacy, and the need for government surveillance.
- Network Security and Cyber Crime, Super-Highway Metaphor Some of the major practices that can be done in ensuring maximum data security and integrity is through making all the servers only accessible by the administrators of networks.
- IT Security: Hacking and Its Components The aim of this paper is to analyze hacking and its components, such as ethical hacking, and to manage cyber security, on the example of the University’s data break-in.
- Social Issues Surrounding Cybercrime Among many social problems that have already been discussed, the issue of rising cybercrime has been on my mind the most.
- Cybercrime and Ransomware: Literature Analysis Criminal justice and the processes that it involves is one of the most multi-layered, controversial, and ever topical areas of legal procedures in general.
- Researching of Cybersecurity and Cybercrime The paper will discuss the technology transfer processes followed by the funding sources for technologies in the cybersecurity field
- Cyber Law and Digital Forensic Science The advantage and disadvantage of external media at the same time is that information is easy to hide, steal, or destroy since it is located on a small object.
- Digital Forensics and Deoxyribonucleic Acid The practice of digital forensics involves analysis of data collected computing devices from a particular crime scene.
- Computer Forensics for Solving Cyber Crimes This paper presents research about the deployment of computer forensics in solving cybercrime. The paper brings out a number of cases concerning crimes in the cyberspace.
- Computer Forensics and Investigations: Basic Procedures In this paper, the author is going to show the basic procedures that ought to be undertaken while performing a digital forensic examination.
- Computer Forensics in the FCC vs. Jack Brown Case In the case of the FCC vs. Jack Brown, this will involve accessing the information that has been stored in different file formats.
- The Council of Europe Convention on Cybercrime of 2001 The Council of Europe Convention on Cybercrime was created to deal with what is well-thought-out to be a unique attribute of cybercrime.
- Cybercrime Legislation in the UAE, the US and the EU Cyber and computer crime definitions were developed after the enhancement of technology, and they improved after years of making proposals.
- Cybercrime Legislation in the UAE, US and India The paper will narrow down to present similarities and differences between the cybercrime laws in UAE and the United States, and between the cybercrime laws in the UAE and India.
- The Development of New Technologies: Wireless Hacking Techniques With the rapid development of new technologies, the safety of personal data is expected to increase. The purpose of this paper is to discuss some wireless hacking techniques.
- Cybercrime: Categories and Challenges This essay introduces the concept of cybercrime, informs the reader of its categories, and mentions several challenges that cybercrime presents.
- Gathering, Analyzing, and Presenting Digital Evidence: Computer Forensic Investigators This paper aims at accomplishing four tasks, which are to providing HCC Partners in Life with computer forensic services that would support a case in a court of law.
- Black Hat vs White Hat Hacking This paper explores hacking from the perspective of ethics. In this paper, white hat and black hat hackers are the ethical players and their actions will be tested for ethicality.
- The Greater Threat of Cybercrime Versus Cyberattack
- Cyber Bullying: Old Problem in New-Age Packaging – Cybercrime
- Capital Punishment for Cybercrime: The Case in Nigeria
- Bargaining Interpersonal Organization Accounts as a Form of Cybercrime
- Canada and China: Cybercrime and Cryptocurrency
- Corruption, Fraud, and Cybercrime as Dehumanizing Phenomena
- Cybercrime and Its Impact on International Business
- Explaining Cybercrime Using Criminological Theories
- Cybercrime: Fraud and Powerful Invisible Attacker
- Growth, Development, and Policing of Cybercrime in the 21st Century
- Cybercrime Has Become One of the Most Threatening Issues
- How Social Media Has Contributed to the Spread of Cybercrime
- Cybercrime: Identity Theft and New Criminal Opportunities
- The Crime Scene Characteristics for Cybercrime and the Process of Investigating It
- Cybercrime: Preventing the Horrific Crimes on the Internet
- The Protection From Cyberattacks and Cybercrime in Bangladesh
- Does the Pandemic Explain Recent Spikes in Cyber Crime?
- Cybercrime Prevention Measures: How to Avoid Hacking
- The Role of Digital Forensics in Solving Cybercrimes
- Cybercrime: The Latest Ways of Stealing Identity and Money
- Potential Impact of Cyber Crime on the Economy
- Cybercrime and Cyberpiracy Impact on Domestic and Foreign Business
- Cybercrime in the Banking Sector and Its Impact on the Banking Industry
- Development of the Prevention of Cyber Crime in Malaysia
- Good Cybercrime: Trends and Future
- The Solutions for Cybercrimes in Information Technology
- Cybercrimes, Their Types, and Measures That We Take to Keep Us Safe From the Happenings
- Peculiarities of Cybercrime and Security
- How Technology Has Influenced the Evolution of Cybercrime
- The Impact of Cybercrime on the Global Criminal Justice System
- Cybercrime and Society: Identity Theft
- Closing the Space Between Cybercrime and Cybersecurity
- A Fast-Growing Area of Cybercrime
- Cybercrimes: An Unprecedented Threat to Society
- Key Steps to Managing a Cybercrime Scene
- Rights to Anonymity in Cybercrime
- What Is the Role of America in Protecting Corporations From Cybercrime?
- Cybercrime and Its Effects on the World’s Major Countries
- Exploring Cybercrime: Realities and Challenges
- Cybercrime Trends: How to Protect Your Business
- The Rise of Cybercrime in the United States
- How the Russia-Ukraine Conflict Is Impacting Cybercrime
- Cybercrime: A Complete Guide to All Things Criminal on the Web
- Top 5 Cybercrimes and Prevention Tips
- How Does Cybercrime Impact Small Businesses?
- What Are the Different Types of Cybercrimes and Cybercriminals?
- Can We Tackle the Ever-Evolving Threat of Cybercrime?
- What Is the Difference Between Crime and Cybercrime?
- Is Cybercrime Civil or Criminal?
- Why Is Cybercrime Considered a Crime?
- When Did Cybercrime Become a Crime?
- How Can Cybercrimes Be Prevented?
- What Was the First Cybercrime?
- How Does Cybercrime Affect Human Rights?
- Who Is Responsible for Cybercrime?
- What Was the Biggest Cybercrime Ever?
- How Does Cybercrime Affect the Victim?
- What Are the Effects of Cybercrime on Society?
- Which Country Is Top in Cybercrime?
- Does Cybercrime Affect Social Media?
- Where Was the First Cybercrime?
- What Are the Major Categories of Cybercrimes?
- How Does Cybercrime Impact the Economy?
- Which City Is Famous for Cybercrime?
- Who Are the Victims of Cybercrime and Why?
- Are There Defining Characteristics of a Cybercrime?
- What Theory Best Explains Cybercrime?
- Is There a Difference Between Computer Crimes and Cybercrimes?
- What Is the Overlap Between Criminal Justice and Cybercrime?
Cite this post
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2022, June 5). 105 Cybercrime Essay Topics. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/cybercrime-essay-topics/
"105 Cybercrime Essay Topics." StudyCorgi , 5 June 2022, studycorgi.com/ideas/cybercrime-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . (2022) '105 Cybercrime Essay Topics'. 5 June.
1. StudyCorgi . "105 Cybercrime Essay Topics." June 5, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/cybercrime-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "105 Cybercrime Essay Topics." June 5, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/cybercrime-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . 2022. "105 Cybercrime Essay Topics." June 5, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/cybercrime-essay-topics/.
These essay examples and topics on Cybercrime were carefully selected by the StudyCorgi editorial team. They meet our highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, and fact accuracy. Please ensure you properly reference the materials if you’re using them to write your assignment.
This essay topic collection was updated on December 27, 2023 .
Research Topics & Ideas: Cybersecurity
50 Topic Ideas To Kickstart Your Research

If you’re just starting out exploring cybersecurity-related topics for your dissertation, thesis or research project, you’ve come to the right place. In this post, we’ll help kickstart your research by providing a hearty list of cybersecurity-related research topics and ideas , including examples from recent studies.
PS – This is just the start…
We know it’s exciting to run through a list of research topics, but please keep in mind that this list is just a starting point . These topic ideas provided here are intentionally broad and generic , so keep in mind that you will need to develop them further. Nevertheless, they should inspire some ideas for your project.
To develop a suitable research topic, you’ll need to identify a clear and convincing research gap , and a viable plan to fill that gap. If this sounds foreign to you, check out our free research topic webinar that explores how to find and refine a high-quality research topic, from scratch. Alternatively, consider our 1-on-1 coaching service .

Cybersecurity-Related Research Topics
- Developing machine learning algorithms for early detection of cybersecurity threats.
- The use of artificial intelligence in optimizing network traffic for telecommunication companies.
- Investigating the impact of quantum computing on existing encryption methods.
- The application of blockchain technology in securing Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
- Developing efficient data mining techniques for large-scale social media analytics.
- The role of virtual reality in enhancing online education platforms.
- Investigating the effectiveness of various algorithms in reducing energy consumption in data centers.
- The impact of edge computing on the performance of mobile applications in remote areas.
- The application of computer vision techniques in automated medical diagnostics.
- Developing natural language processing tools for sentiment analysis in customer service.
- The use of augmented reality for training in high-risk industries like oil and gas.
- Investigating the challenges of integrating AI into legacy enterprise systems.
- The role of IT in managing supply chain disruptions during global crises.
- Developing adaptive cybersecurity strategies for small and medium-sized enterprises.
- The impact of 5G technology on the development of smart city solutions.
- The application of machine learning in personalized e-commerce recommendations.
- Investigating the use of cloud computing in improving government service delivery.
- The role of IT in enhancing sustainability in the manufacturing sector.
- Developing advanced algorithms for autonomous vehicle navigation.
- The application of biometrics in enhancing banking security systems.
- Investigating the ethical implications of facial recognition technology.
- The role of data analytics in optimizing healthcare delivery systems.
- Developing IoT solutions for efficient energy management in smart homes.
- The impact of mobile computing on the evolution of e-health services.
- The application of IT in disaster response and management.

Cybersecurity Research Ideas (Continued)
- Assessing the security implications of quantum computing on modern encryption methods.
- The role of artificial intelligence in detecting and preventing phishing attacks.
- Blockchain technology in secure voting systems: opportunities and challenges.
- Cybersecurity strategies for protecting smart grids from targeted attacks.
- Developing a cyber incident response framework for small to medium-sized enterprises.
- The effectiveness of behavioural biometrics in preventing identity theft.
- Securing Internet of Things (IoT) devices in healthcare: risks and solutions.
- Analysis of cyber warfare tactics and their implications on national security.
- Exploring the ethical boundaries of offensive cybersecurity measures.
- Machine learning algorithms for predicting and mitigating DDoS attacks.
- Study of cryptocurrency-related cybercrimes: patterns and prevention strategies.
- Evaluating the impact of GDPR on data breach response strategies in the EU.
- Developing enhanced security protocols for mobile banking applications.
- An examination of cyber espionage tactics and countermeasures.
- The role of human error in cybersecurity breaches: a behavioural analysis.
- Investigating the use of deep fakes in cyber fraud: detection and prevention.
- Cloud computing security: managing risks in multi-tenant environments.
- Next-generation firewalls: evaluating performance and security features.
- The impact of 5G technology on cybersecurity strategies and policies.
- Secure coding practices: reducing vulnerabilities in software development.
- Assessing the role of cyber insurance in mitigating financial losses from cyber attacks.
- Implementing zero trust architecture in corporate networks: challenges and benefits.
- Ransomware attacks on critical infrastructure: case studies and defence strategies.
- Using big data analytics for proactive cyber threat intelligence.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of cybersecurity awareness training in organisations.
Recent Cybersecurity-Related Studies
While the ideas we’ve presented above are a decent starting point for finding a research topic, they are fairly generic and non-specific. So, it helps to look at actual studies in the cybersecurity space to see how this all comes together in practice.
Below, we’ve included a selection of recent studies to help refine your thinking. These are actual studies, so they can provide some useful insight as to what a research topic looks like in practice.
- Cyber Security Vulnerability Detection Using Natural Language Processing (Singh et al., 2022)
- Security for Cloud-Native Systems with an AI-Ops Engine (Ck et al., 2022)
- Overview of Cyber Security (Yadav, 2022)
- Exploring the Top Five Evolving Threats in Cybersecurity: An In-Depth Overview (Mijwil et al., 2023)
- Cyber Security: Strategy to Security Challenges A Review (Nistane & Sharma, 2022)
- A Review Paper on Cyber Security (K & Venkatesh, 2022)
- The Significance of Machine Learning and Deep Learning Techniques in Cybersecurity: A Comprehensive Review (Mijwil, 2023)
- Towards Artificial Intelligence-Based Cybersecurity: The Practices and ChatGPT Generated Ways to Combat Cybercrime (Mijwil et al., 2023)
- ESTABLISHING CYBERSECURITY AWARENESS OF TECHNICAL SECURITY MEASURES THROUGH A SERIOUS GAME (Harding et al., 2022)
- Efficiency Evaluation of Cyber Security Based on EBM-DEA Model (Nguyen et al., 2022)
- An Overview of the Present and Future of User Authentication (Al Kabir & Elmedany, 2022)
- Cybersecurity Enterprises Policies: A Comparative Study (Mishra et al., 2022)
- The Rise of Ransomware: A Review of Attacks, Detection Techniques, and Future Challenges (Kamil et al., 2022)
- On the scale of Cyberspace and Cybersecurity (Pathan, 2022)
- Analysis of techniques and attacking pattern in cyber security approach (Sharma et al., 2022)
- Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Information Security in Business (Alawadhi et al., 2022)
- Deployment of Artificial Intelligence with Bootstrapped Meta-Learning in Cyber Security (Sasikala & Sharma, 2022)
- Optimization of Secure Coding Practices in SDLC as Part of Cybersecurity Framework (Jakimoski et al., 2022)
- CySSS ’22: 1st International Workshop on Cybersecurity and Social Sciences (Chan-Tin & Kennison, 2022)
As you can see, these research topics are a lot more focused than the generic topic ideas we presented earlier. So, for you to develop a high-quality research topic, you’ll need to get specific and laser-focused on a specific context with specific variables of interest. In the video below, we explore some other important things you’ll need to consider when crafting your research topic.
Get 1-On-1 Help
If you’re still unsure about how to find a quality research topic, check out our Research Topic Kickstarter service, which is the perfect starting point for developing a unique, well-justified research topic.

You Might Also Like:

Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Articles on Cybercrime
Displaying 1 - 20 of 259 articles.

AI is making smart devices – watches, speakers, doorbells – easier to hack. Here’s how to stay safe
Chao Chen , RMIT University ; Kok-Leong Ong , RMIT University , and Lin Li , RMIT University

The government wants to criminalise doxing. It may not work to stamp out bad behaviour online
Jennifer Beckett , The University of Melbourne

What is doxing, and how can you protect yourself?
Rob Cover , RMIT University

Cybercriminals are creating their own AI chatbots to support hacking and scam users
Oli Buckley , University of East Anglia and Jason R.C. Nurse , University of Kent

What is credential stuffing and how can I protect myself? A cybersecurity researcher explains
David Tuffley , Griffith University

Phishing scams: 7 safety tips from a cybersecurity expert
Thembekile Olivia Mayayise , University of the Witwatersrand

How to protect yourself from cyber-scammers over the festive period
Rachael Medhurst , University of South Wales

Forgiveness or punishment? The government’s proposed ‘safe harbour’ laws send mixed messages on cyber security
Greg Austin , University of Technology Sydney

What is LockBit, the cybercrime gang hacking some of the world’s largest organisations?
Jennifer Medbury , Edith Cowan University and Paul Haskell-Dowland , Edith Cowan University

Can you spot the AI impostors? We found AI faces can look more real than actual humans
Amy Dawel , Australian National University ; Ben Albert Steward , Australian National University ; Clare Sutherland , University of Aberdeen ; Eva Krumhuber , UCL , and Zachary Witkower , University of Amsterdam

Major cyberattack on Australian ports suggests sabotage by a ‘foreign state actor’

Internet shutdowns: here’s how governments do it
Lisa Garbe , WZB Berlin Social Science Center.

AI might eventually be an extinction threat, but it poses more pressing risks
Amin Al-Habaibeh , Nottingham Trent University

Four ways criminals could use AI to target more victims
Daniel Prince , Lancaster University

Heists Worth Billions: An investigation found criminal gangs using sham bank accounts and secret online marketplaces to steal from almost anyone – and little being done to combat the fraud
David Maimon , Georgia State University and Kurt Eichenwald , The Conversation

How to protect yourself from drop account fraud – tips from our investigative unit
Kurt Eichenwald , The Conversation

The highly secretive Five Eyes alliance has disrupted a China-backed hacker group – in an unusually public manner
Dennis B. Desmond , University of the Sunshine Coast

It’s being called Russia’s most sophisticated cyber espionage tool. What is Snake, and why is it so dangerous?
Greg Skulmoski , Bond University

Protecting children from exploitation means rethinking how we approach online behaviour
Jan Kietzmann , University of Victoria and Dionysios Demetis , University of Hull

Scammers can slip fake texts into legitimate SMS threads. Will a government crackdown stop them?
Suranga Seneviratne , University of Sydney and Carol Hsu , University of Sydney
Related Topics
- Cyberattacks
- Cybersecurity
- Data breaches
- Digital economy
- Online security
Top contributors
Senior Lecturer in Networking, The Open University
Professor of Cyber Security Practice, Edith Cowan University
Professor of Criminology, University of Leeds
Director of UWA Centre for Software Practice, The University of Western Australia
Professor of Cyber Security, Lancaster University
Senior Lecturer of Computing and Security, Edith Cowan University
Associate Dean (Learning & Teaching) Faculty of Creative Industries, Education and Social Justice, Queensland University of Technology
Head, The Cyber Academy, Edinburgh Napier University
Director, Centre for Internet Safety, University of Canberra
Professor of Cybersecurity, School of Computer Science and Informatics, De Montfort University
Lecturer in Computer Security, University of Kent
Professor of Criminal Justice and Criminology, Georgia State University
Lecturer in Software Engineering, Monash University
Professor, Department of Computer Science, University of Surrey
Lawyer, Curtin University
- X (Twitter)
- Unfollow topic Follow topic
- University of Wisconsin–Madison
- University of Wisconsin-Madison
- Research Guides
- College Undergraduate Research Group
- Internet and Online Culture: An Undergraduate Research Guide
Internet and Online Culture: An Undergraduate Research Guide : Cybercrime
- Writing, Citing, & Research Help
- Artificial Intelligence
- Copyright/Intellectual Property
- Cyberbullying
- Net Neutrality
- Online Privacy
- Social Media
- Surveillance
- Video Games
- Newspaper Source Plus Newspaper Source Plus includes 1,520 full-text newspapers, providing more than 28 million full-text articles.
- CQ Researcher Contains weekly in-depth reports that cover the most current and controversial issues of the day with complete summaries, insight into all sides of the issues, bibliographies and more.
- Newspaper Research Guide This guide describes sources for current and historical newspapers available in print, electronically, and on microfilm through the UW-Madison Libraries. These sources are categorized by pages: Current, Historical, Local/Madison, Wisconsin, US, Alternative/Ethnic, and International.
Organizations
- National Fraud Information Center "The NFIC was originally established in 1992 by the National Consumers League, the oldest nonprofit consumer organization in the United States, to fight the growing menace of telemarketing fraud by improving prevention and enforcement."
- National Crime Prevention Council NCPC is a national non-profit dedicated to the prevention of crime. There is specific information on cybercrime as well.
- Computer Crime Research Center Founded in 2001, the Computer Crime Research Center (CCRC) is an independent institute dedicated to the research of cyber crime, cyber terrorism and other issues of computer crimes and internet fraud phenomena.
- The International Association of Computer Investigative Specialists IACIS is an international volunteer non-profit corporation composed of law enforcement professionals dedicated to education in the field of forensic computer science.
- Electronic Frontier Foundation The Electronic Frontier Foundation is the leading nonprofit organization defending civil liberties in the digital world. Founded in 1990, EFF champions user privacy, free expression, and innovation through impact litigation, policy analysis, grassroots activism, and technology development.
- Centre for International Governance Innovation The Global Commission on Internet Governance’s One Internet report makes practical recommendations for the international community to ensure that the future of the Internet remains open, secure, trustworthy and inclusive. The recommendations continue to gain traction on cybersecurity, multi-stakeholder governance and accessibility.
About Cybercrime
This guide focuses on cybercrime, a term used to describe electronic or computer crimes. This broad term covers issues such as hacking, identity theft, doxxing, cracking, spam, computer security, privacy invasion, viruses, and piracy.
Try searching these terms using the resources linked on this page: computer software piracy, computer crime, computer viruses, Internet crimes, identity theft, cracker* and computer*, internet terroris*, phreaker*, doxxing, computer hacker*, cybercriminal*, cybercrime*
Overview Resources - Background Information
- U.S. Department of Justice - Computer Crime and Intellectual Property This is the homepage of the Computer Crime and Intellectual Property Section of the Criminal Division of the U.S. Department of Justice.
- Opposing Viewpoints Resource Center Opposing Viewpoints Resource Center (OVRC) provides viewpoint articles, topic overviews, statistics, primary documents, links to websites, and full-text magazine and newspaper articles related to controversial social issues.
- Department of Homeland Security - Cybersecurity The Department of Homeland Security's overview page about topics related to cybersecurity and cybercrime.
Articles - Scholarly and Popular
- Academic Search Complete A general/multi-disciplinary database with articles on many topics.
- INSPEC (via Web of Knowledge) Includes articles on computer and cyber-related topics.
- Sourcebook of Criminal Justice Statistics Online A collaboration between the Hindelang Criminal Justice Research Center and the U.S. Department of Justice, Bureau of Justice Statistics that has presented over 10,000 tables displaying statistical data from over 2,500 public and private agencies, academic institutions, research organizations, public opinion polling firms, and other groups.
- << Previous: Copyright/Intellectual Property
- Next: Cyberbullying >>
- Last Updated: Jan 11, 2024 1:22 PM
- URL: https://researchguides.library.wisc.edu/internetandonlinecultureURG
For enquiries call:
+1-469-442-0620

60+ Latest Cyber Security Research Topics for 2024
Home Blog Security 60+ Latest Cyber Security Research Topics for 2024
The concept of cybersecurity refers to cracking the security mechanisms that break in dynamic environments. Implementing Cyber Security Project topics and cyber security thesis topics /ideas helps overcome attacks and take mitigation approaches to security risks and threats in real-time. Undoubtedly, it focuses on events injected into the system, data, and the whole network to attack/disturb it.
The network can be attacked in various ways, including Distributed DoS, Knowledge Disruptions, Computer Viruses / Worms, and many more. Cyber-attacks are still rising, and more are waiting to harm their targeted systems and networks. Detecting Intrusions in cybersecurity has become challenging due to their Intelligence Performance. Therefore, it may negatively affect data integrity, privacy, availability, and security.
This article aims to demonstrate the most current Cyber Security Topics for Projects and areas of research currently lacking. We will talk about cyber security research questions, cyber security research questions, cyber security topics for the project, best cyber security research topics, research titles about cyber security and web security research topics.
.jpg&w=3840&q=75)
List of Trending Cyber Security Research Topics for 2024
Digital technology has revolutionized how all businesses, large or small, work, and even governments manage their day-to-day activities, requiring organizations, corporations, and government agencies to utilize computerized systems. To protect data against online attacks or unauthorized access, cybersecurity is a priority. There are many Cyber Security Courses online where you can learn about these topics. With the rapid development of technology comes an equally rapid shift in Cyber Security Research Topics and cybersecurity trends, as data breaches, ransomware, and hacks become almost routine news items. In 2024, these will be the top cybersecurity trends.
A) Exciting Mobile Cyber Security Research Paper Topics
- The significance of continuous user authentication on mobile gadgets.
- The efficacy of different mobile security approaches.
- Detecting mobile phone hacking.
- Assessing the threat of using portable devices to access banking services.
- Cybersecurity and mobile applications.
- The vulnerabilities in wireless mobile data exchange.
- The rise of mobile malware.
- The evolution of Android malware.
- How to know you’ve been hacked on mobile.
- The impact of mobile gadgets on cybersecurity.
B) Top Computer and Software Security Topics to Research
- Learn algorithms for data encryption
- Concept of risk management security
- How to develop the best Internet security software
- What are Encrypting Viruses- How does it work?
- How does a Ransomware attack work?
- Scanning of malware on your PC
- Infiltrating a Mac OS X operating system
- What are the effects of RSA on network security ?
- How do encrypting viruses work?
- DDoS attacks on IoT devices
C) Trending Information Security Research Topics
- Why should people avoid sharing their details on Facebook?
- What is the importance of unified user profiles?
- Discuss Cookies and Privacy
- White hat and black hat hackers
- What are the most secure methods for ensuring data integrity?
- Talk about the implications of Wi-Fi hacking apps on mobile phones
- Analyze the data breaches in 2024
- Discuss digital piracy in 2024
- critical cyber-attack concepts
- Social engineering and its importance
D) Current Network Security Research Topics
- Data storage centralization
- Identify Malicious activity on a computer system.
- Firewall
- Importance of keeping updated Software
- wireless sensor network
- What are the effects of ad-hoc networks
- How can a company network be safe?
- What are Network segmentation and its applications?
- Discuss Data Loss Prevention systems
- Discuss various methods for establishing secure algorithms in a network.
- Talk about two-factor authentication
E) Best Data Security Research Topics
- Importance of backup and recovery
- Benefits of logging for applications
- Understand physical data security
- Importance of Cloud Security
- In computing, the relationship between privacy and data security
- Talk about data leaks in mobile apps
- Discuss the effects of a black hole on a network system.
F) Important Application Security Research Topics
- Detect Malicious Activity on Google Play Apps
- Dangers of XSS attacks on apps
- Discuss SQL injection attacks.
- Insecure Deserialization Effect
- Check Security protocols
G) Cybersecurity Law & Ethics Research Topics
- Strict cybersecurity laws in China
- Importance of the Cybersecurity Information Sharing Act.
- USA, UK, and other countries' cybersecurity laws
- Discuss The Pipeline Security Act in the United States
H) Recent Cyberbullying Topics
- Protecting your Online Identity and Reputation
- Online Safety
- Sexual Harassment and Sexual Bullying
- Dealing with Bullying
- Stress Center for Teens
I) Operational Security Topics
- Identify sensitive data
- Identify possible threats
- Analyze security threats and vulnerabilities
- Appraise the threat level and vulnerability risk
- Devise a plan to mitigate the threats
J) Cybercrime Topics for a Research Paper
- Crime Prevention.
- Criminal Specialization.
- Drug Courts.
- Criminal Courts.
- Criminal Justice Ethics.
- Capital Punishment.
- Community Corrections.
- Criminal Law.
Research Area in Cyber Security
The field of cyber security is extensive and constantly evolving. Its research covers a wide range of subjects, including:
- Quantum & Space
- Data Privacy
- Criminology & Law
- AI & IoT Security
How to Choose the Best Research Topics in Cyber Security
A good cybersecurity assignment heading is a skill that not everyone has, and unfortunately, not everyone has one. You might have your teacher provide you with the topics, or you might be asked to come up with your own. If you want more research topics, you can take references from Certified Ethical Hacker Certification, where you will get more hints on new topics. If you don't know where to start, here are some tips. Follow them to create compelling cybersecurity assignment topics.
1. Brainstorm
In order to select the most appropriate heading for your cybersecurity assignment, you first need to brainstorm ideas. What specific matter do you wish to explore? In this case, come up with relevant topics about the subject and select those relevant to your issue when you use our list of topics. You can also go to cyber security-oriented websites to get some ideas. Using any blog post on the internet can prove helpful if you intend to write a research paper on security threats in 2024. Creating a brainstorming list with all the keywords and cybersecurity concepts you wish to discuss is another great way to start. Once that's done, pick the topics you feel most comfortable handling. Keep in mind to stay away from common topics as much as possible.
2. Understanding the Background
In order to write a cybersecurity assignment, you need to identify two or three research paper topics. Obtain the necessary resources and review them to gain background information on your heading. This will also allow you to learn new terminologies that can be used in your title to enhance it.
3. Write a Single Topic
Make sure the subject of your cybersecurity research paper doesn't fall into either extreme. Make sure the title is neither too narrow nor too broad. Topics on either extreme will be challenging to research and write about.
4. Be Flexible
There is no rule to say that the title you choose is permanent. It is perfectly okay to change your research paper topic along the way. For example, if you find another topic on this list to better suit your research paper, consider swapping it out.
The Layout of Cybersecurity Research Guidance
It is undeniable that usability is one of cybersecurity's most important social issues today. Increasingly, security features have become standard components of our digital environment, which pervade our lives and require both novices and experts to use them. Supported by confidentiality, integrity, and availability concerns, security features have become essential components of our digital environment.
In order to make security features easily accessible to a wider population, these functions need to be highly usable. This is especially true in this context because poor usability typically translates into the inadequate application of cybersecurity tools and functionality, resulting in their limited effectiveness.
Writing Tips from Expert
Additionally, a well-planned action plan and a set of useful tools are essential for delving into Cyber Security Research Topics. Not only do these topics present a vast realm of knowledge and potential innovation, but they also have paramount importance in today's digital age. Addressing the challenges and nuances of these research areas will contribute significantly to the global cybersecurity landscape, ensuring safer digital environments for all. It's crucial to approach these topics with diligence and an open mind to uncover groundbreaking insights.
- Before you begin writing your research paper, make sure you understand the assignment.
- Your Research Paper Should Have an Engaging Topic
- Find reputable sources by doing a little research
- Precisely state your thesis on cybersecurity
- A rough outline should be developed
- Finish your paper by writing a draft
- Make sure that your bibliography is formatted correctly and cites your sources.
Discover the Power of ITIL 4 Foundation - Unleash the Potential of Your Business with this Cost-Effective Solution. Boost Efficiency, Streamline Processes, and Stay Ahead of the Competition. Learn More!
Studies in the literature have identified and recommended guidelines and recommendations for addressing security usability problems to provide highly usable security. The purpose of such papers is to consolidate existing design guidelines and define an initial core list that can be used for future reference in the field of Cyber Security Research Topics.
The researcher takes advantage of the opportunity to provide an up-to-date analysis of cybersecurity usability issues and evaluation techniques applied so far. As a result of this research paper, researchers and practitioners interested in cybersecurity systems who value human and social design elements are likely to find it useful. You can find KnowledgeHut’s Cyber Security courses online and take maximum advantage of them.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Businesses and individuals are changing how they handle cybersecurity as technology changes rapidly - from cloud-based services to new IoT devices.
Ideally, you should have read many papers and know their structure, what information they contain, and so on if you want to write something of interest to others.
The field of cyber security is extensive and constantly evolving. Its research covers various subjects, including Quantum & Space, Data Privacy, Criminology & Law, and AI & IoT Security.
Inmates having the right to work, transportation of concealed weapons, rape and violence in prison, verdicts on plea agreements, rehab versus reform, and how reliable are eyewitnesses?

Mrinal Prakash
I am a B.Tech Student who blogs about various topics on cyber security and is specialized in web application security
Avail your free 1:1 mentorship session.
Something went wrong
Upcoming Cyber Security Batches & Dates
- How it works
Useful Links
How much will your dissertation cost?
Have an expert academic write your dissertation paper!
Dissertation Services

Get unlimited topic ideas and a dissertation plan for just £45.00
Order topics and plan

Get 1 free topic in your area of study with aim and justification
Yes I want the free topic

5 Dissertation Topics on Cyber Crime
Published by Owen Ingram at January 9th, 2023 , Revised On August 15, 2023
Introduction
Any crime that is conducted using a computer and a network is known as cybercrime. Cybercrimes can target individuals in their personal capacity by targeting their property, the person himself, harming their mental health, and can even cause damage to governments.
Everyone using a computer and the internet can fall victim to cybercrime; however, understanding these crimes’ nature and how these are conducted can help people keep themselves safe and avoid falling victim.
Networks have weak spots, thus identifying those that can help you in determining possible attack points. This will eventually enable you to keep yourself safe from cybercrimes. Keeping your personal information safe at all times is critically important.
Never give out your passwords or any other personal information openly on any forum. This is one of the most effective ways of avoiding falling victim to cybercrime.
Being a pressing issue, cybercrime is continuously explored as to how it is conducted, what its types are, how it can be detected, how people can stay safe, etc. Here are five dissertation topics on cybercrime that will help gain an in-depth understanding of the issue.
These topics have been developed by PhD-qualified writers of our team , so you can trust to use these topics for drafting your dissertation.
You may also want to start your dissertation by requesting a brief research proposal from our writers on any of these topics, which includes an introduction to the topic, research question , aim and objectives , literature review along with the proposed methodology of research to be conducted. Let us know if you need any help in getting started.
Check our dissertation examples to get an idea of how to structure your dissertation .
Review the full list of dissertation topics for 2022 here.
5 Dissertation Topics on Cyber Crime 2022
Topic 1: is cybercrime a threat to banking sector in developing countries a case study of banking sector in pakistan.
Research Aim: This study aims to analyze the impact of cybercrime on the banking sector in developing countries. It will identify the possible threats faced by the banking sector due to increasing cybercrimes. These threats are related to the information security of the banks in developing countries. This research will be using Pakistan as a case study to find the threats posed by cybercrime to fragile banking. And after identifying the threats, the study will try to recommend possible solutions to ensure information security.
Topic 2: Impact of Cybercrime on E-Governance. Is cybercrime affecting the Confidentiality of Government Data?
Research Aim: This research aims to find the impact of cybercrime on modern-day governance systems or e-governance. It will identify the possible hindrances caused by cybercrime in implementing effective e-governance. This research will also investigate the impact of cybercrime on the confidentiality of government data. And after investigating the impact of cybercrime on the confidentiality of government data, this research will recommend the modern-day practices used to maintain the security of the information.
Topic 3: Is Information Safe Today? A survey to find the impact of cybercrime on the information security of the businesses
Research Aim: This study aims to find the impact of cybercrime on the information security of modern-day businesses. It will be a survey-based study to find out the problems faced by modern-day businesses due to cybercrime. These problems include confidential information leakage, which can benefit the competitors in the market. And another major problem is data stealing. This study will identify all these problems. And it will also recommend modern-day solutions to increase the security of the information.
Topic 4: A Socio-Technological Examination of Cybercrime and Information Security in Nigeria
Research Aim: This current research intends to determine Nigerian society’s vulnerabilities to cybercrime and exploitation and the global information infrastructure in general. It also aims to determine the informal, social, and technical drivers of Nigerian cybercrime and cybersecurity. To examine Nigerian law enforcement agencies and cybersecurity stakeholders’ efforts to combat cybercrime and guarantee cybersecurity. This analysis provides an opportunity for legislators, policymakers, and law enforcement agencies can utilize the law to establish legally valid definitions of cybercrime and information security from sociological and technological points of view
Topic 5: Impact of Cyber laws on Information Security. A Cross-Country Analysis
Research Aim: This study aims to analyse the impact of cyber laws on information security. This study is a cross-country analysis that will find the effectiveness of cyber laws across countries. It will see how over time, the introduction of cyber laws has affected information security after the find out the relationship between cyber laws and information security. This research will identify the most effective cyber laws in the countries under study. And after identifying the best laws among the countries under study. This study will recommend the best laws from individual countries or a set of laws from different countries.
Covid-19 Cyber Crime Research Topics
Topic 1: cybercrimes and coronavirus pandemic.
Research Aim: This study will focus on the increased cybercrimes during the coronavirus pandemic and the effective ways to overcome them.
Topic 2: Cybersecurity and COVID-19
Research Aim: This study will focus on the role of cybersecurity in minimizing cybercrimes during the crisis of the pandemic.
Topic 3: Cyber threats can harm industries
Research Aim: This study will address the growing cyber threats during COVID-19, where remote work has been adopted to combat the pandemic. It’ll highlight the threats, their harmful effect, and their solution.
Cyber Crime Research Topics 2021
Topic 1: importance of password security.
Research Aim: This research aims to identify the importance of Password security in safe computing.
Topic 2: Phishing scams
Research Aim: This research aims to highlight phishing scams issues and suggest various tips to avoid such scams.
Topic 3: Mobile protection
Research Aim: This research aims to highlight mobile security threats and suggest possible ways to protect mobile phones from hackers.
Topic 4: How to ensure safe computing?
Research Aim: This research will focus on types of hackings, scams and suggests possible ways to ensure safe computing
Topic 5: Cybercrime Dissertation Topics – The Evolution of Cyber Crime and the Attacks that Led to the Formation of Cyber Crime Policies
Research Aim: This dissertation will focus on the history of how this crime came into existence. The thesis’s main focus will be on understanding cybercrime, how it is being conducted worldwide, and what has led to an increase in these types of attacks.
The thesis will also discuss the initial attacks due to which cybercrime policies came into place. All policies will be discussed as to how they help curb cybercrimes and the extent to which they have been successful in reducing them.
Finally, the thesis will suggest if any new policies must be developed. What aspects need to be focused on, are there any new areas that need attention, or do the existing policies need to be revised?
Topic 6: Cybercrime Dissertation Topics – Cyber Crime: How it Impacts Young Adults
Research Aim: Cybercrime can have a great impact on the younger generation. Young adults use the internet more than any other age group, which is why they are the first victims of cybercrime. This dissertation will explore how cybercrime affects the younger generation and how it causes problems for them.
Issues such as health, specifically mental health, will be discussed to understand the many problems caused by cybercrime. Many individuals from the younger generation have attempted suicide after falling victim to cybercrime.
This research study will discuss all such effects of cybercrime, including cyberbullying (a form of cybercrime). The study will also present ways as to how they can avoid falling victim to cybercrime.
How Can ResearchProspect Help?
ResearchProspect writers can send several custom topic ideas to your email address. Once you have chosen a topic that suits your needs and interests, you can order for our dissertation outline service which will include a brief introduction to the topic, research questions , literature review , methodology , expected results , and conclusion . The dissertation outline will enable you to review the quality of our work before placing the order for our full dissertation writing service !
Topic 7: Cybercrime Dissertation Topics – Investigating Various Approaches and Ways to Detect Cyber Crime
Research Aim: Cybercrime, one of the most secret crimes, is spread all over the world. The number of cybercrimes worldwide is on the rise. Thus, every individual using a computer and connected to a network must be aware of the different types of cybercrimes.
Before discussing the different ways to detect cybercrime, this dissertation study will briefly discuss the many cybercrime types. Essentially, the research will focus on various ways through which each form of cybercrime can be detected.
Different forms of cybercrimes can be detected differently. For instance, data theft can be determined by asking for a password or other sensitive information through a call or an email. The research will then conclude how people can identify different forms of cybercrime and not fall victim to any of them.
Topic 8: Cybercrime Dissertation Topics – Evaluating Existing Cyber Crime Policies: Do They Suffice in Today’s World?
Research Aim: Cybercrime, being a major cause of concern throughout the world, is controlled and curbed by different policies in place. These policies are designed to make sure that cybercrime is reduced and gradually eliminated from society. However, with the increased numbers, the need for a policy change or amendment seems inevitable.
This means that the existing policies need to be reworked or revised, or abandoned completely, and new policies should be formed. This dissertation will investigate both these options and emphasize whether policies should be revised or new policies should be formed.
If new policies should be formed, the research will explain how these should be shaped, and if they need to be revised, then which aspects need to be considered for amendments will be the main focus of the dissertation. A detailed analysis will be presented to make an informed decision.
Topic 9: Cybercrime Dissertation Topics – Understanding the Different Types of Cyber Crime
Research Aim: Cybercrime, undoubtedly, is one of the most deadly forms of crime. Without causing physical harm, the crime causes the victim to attempt suicide or suffer from mental diseases such as anxiety, depression, etc.
This research will focus on the different types of cybercrimes that impact people in today’s world. This research will highlight almost all cybercrime forms while emphasising the most common forms such as cyberbullying, hacking, data theft, child pornography, etc.
In-depth research will be conducted through surveys and by using numbers and percentages of cybercrime from credible resources such as government websites, etc.
This will help understand the various forms of cybercrime, how widespread the crime is, and how many people are impacted by cybercrime throughout the world.
Important Notes:
As a cybercrime student looking to get good grades, it is essential to develop new ideas and experiment with existing cybercrime theories – i.e., to add value and interest to your research topic.
The field of cybercrime is vast and interrelated to so many other academic disciplines like Facebook , Instagram , Cryptocurrency , Twitter , civil engineering , facial recognition , construction , project management , engineering management , healthcare , finance and accounting , artificial intelligence , tourism , physiotherapy , sociology , management , and project management , graphic design , and nursing . That is why it is imperative to create a project management dissertation topic that is articular, sound, and actually solves a practical problem that may be rampant in the field.
We can’t stress how important it is to develop a logical research topic based on your entire research. There are several significant downfalls to getting your topic wrong; your supervisor may not be interested in working on it, the topic has no academic creditability, the research may not make logical sense, and there is a possibility that the study is not viable.
This impacts your time and efforts in writing your dissertation as you may end up in the cycle of rejection at the initial stage of the dissertation. That is why we recommend reviewing existing research to develop a topic, taking advice from your supervisor, and even asking for help in this particular stage of your dissertation.
Keeping our advice in mind while developing a research topic will allow you to pick one of the best cyber crime dissertation topics that fulfil your requirement of writing a research paper and add to the body of knowledge.
Therefore, it is recommended that when finalizing your dissertation topic, you read recently published literature to identify gaps in the research that you may help fill.
Remember- dissertation topics need to be unique, solve an identified problem, be logical, and be practically implemented. Please look at some of our sample cybercrime dissertation topics to get an idea for your own dissertation.
How to Structure your Cyber Crime Dissertation
A well-structured dissertation can help students to achieve a high overall academic grade.
- A Title Page
- Acknowledgements
- Declaration
- Abstract: A summary of the research completed
- Table of Contents
- Introduction : This chapter includes the project rationale, research background, key research aims and objectives, and the research problems. An outline of the structure of a dissertation can also be added to this chapter.
- Literature Review : This chapter presents relevant theories and frameworks by analysing published and unpublished literature available on the chosen research topic to address research questions . The purpose is to highlight and discuss the selected research area’s relative weaknesses and strengths whilst identifying any research gaps. Break down the topic, and key terms that can positively impact your dissertation and your tutor.
- Methodology : The data collection and analysis methods and techniques employed by the researcher are presented in the Methodology chapter which usually includes research design , research philosophy, research limitations, code of conduct, ethical consideration, data collection methods, and data analysis strategy .
- Findings and Analysis : Findings of the research are analysed in detail under the Findings and Analysis chapter. All key findings/results are outlined in this chapter without interpreting the data or drawing any conclusions. It can be useful to include graphs, charts, and tables in this chapter to identify meaningful trends and relationships.
- Discussion and Conclusion : The researcher presents his interpretation of the results in this chapter, and states whether the research hypothesis has been verified or not. An essential aspect of this section of the paper is to draw a linkage between the results and evidence from the literature. Recommendations with regards to implications of the findings and directions for the future may also be provided. Finally, a summary of the overall research, along with final judgments, opinions, and comments, must be included in the form of suggestions for improvement.
- References : This should be completed following your University’s requirements
- Bibliography
- Appendices : Any additional information, diagrams, and graphs used to complete the dissertation but not part of the dissertation should be included in the Appendices chapter. Essentially, the purpose is to expand the information/data.
About ResearchProspect Ltd
ResearchProspect is the world’s best academic writing service that provides help with Dissertation Proposal Writing , PhD Proposal Writing , Dissertation Writing , Dissertation Editing, and Improvement .
Our team of writers is highly qualified. They are experts in their respective fields. They have been working in the industry for a long, thus are aware of the issues and the trends of the industry they are working in.
Free Dissertation Topic
Phone Number
Academic Level Select Academic Level Undergraduate Graduate PHD
Academic Subject
Area of Research
Frequently Asked Questions
How to find dissertation topics on cyber crime.
To find dissertation topics on cybercrime:
- Study recent cyber threats and attacks.
- Analyze legal and ethical aspects.
- Explore technological advancements.
- Investigate prevention measures.
- Consider international perspectives.
- Select a focused area of interest for in-depth research.
You May Also Like
Need interesting and manageable Brexit dissertation topics? Here are the trending Brexit dissertation titles so you can choose the most suitable one.
Do you have a dissertation topic in the field of information technology? If not, our competent dissertation writers are at your disposal. The importance of technology research cannot be overstated.
Here is a list of sports dissertation topics to help you choose the one studies any one as per your requirements.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
Click through the PLOS taxonomy to find articles in your field.
For more information about PLOS Subject Areas, click here .
Loading metrics
Open Access
Peer-reviewed
Research Article
Mapping the global geography of cybercrime with the World Cybercrime Index
Roles Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – original draft
* E-mail: [email protected]
Affiliations Department of Sociology, University of Oxford, Oxford, United Kingdom, Canberra School of Professional Studies, University of New South Wales, Canberra, Australia
Roles Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft
Affiliations Department of Sociology, University of Oxford, Oxford, United Kingdom, Oxford School of Global and Area Studies, University of Oxford, Oxford, United Kingdom
Roles Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – review & editing
Affiliations Department of Sociology, University of Oxford, Oxford, United Kingdom, Leverhulme Centre for Demographic Science, University of Oxford, Oxford, United Kingdom
Roles Funding acquisition, Methodology, Writing – review & editing
Affiliation Department of Software Systems and Cybersecurity, Faculty of IT, Monash University, Victoria, Australia
Roles Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Writing – review & editing
Affiliation Centre d’études européennes et de politique comparée, Sciences Po, Paris, France
- Miranda Bruce,
- Jonathan Lusthaus,
- Ridhi Kashyap,
- Nigel Phair,
- Federico Varese

- Published: April 10, 2024
- https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0297312
- Peer Review
- Reader Comments
Cybercrime is a major challenge facing the world, with estimated costs ranging from the hundreds of millions to the trillions. Despite the threat it poses, cybercrime is somewhat an invisible phenomenon. In carrying out their virtual attacks, offenders often mask their physical locations by hiding behind online nicknames and technical protections. This means technical data are not well suited to establishing the true location of offenders and scholarly knowledge of cybercrime geography is limited. This paper proposes a solution: an expert survey. From March to October 2021 we invited leading experts in cybercrime intelligence/investigations from across the world to participate in an anonymized online survey on the geographical location of cybercrime offenders. The survey asked participants to consider five major categories of cybercrime, nominate the countries that they consider to be the most significant sources of each of these types of cybercrimes, and then rank each nominated country according to the impact, professionalism, and technical skill of its offenders. The outcome of the survey is the World Cybercrime Index, a global metric of cybercriminality organised around five types of cybercrime. The results indicate that a relatively small number of countries house the greatest cybercriminal threats. These findings partially remove the veil of anonymity around cybercriminal offenders, may aid law enforcement and policymakers in fighting this threat, and contribute to the study of cybercrime as a local phenomenon.
Citation: Bruce M, Lusthaus J, Kashyap R, Phair N, Varese F (2024) Mapping the global geography of cybercrime with the World Cybercrime Index. PLoS ONE 19(4): e0297312. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0297312
Editor: Naeem Jan, Korea National University of Transportation, REPUBLIC OF KOREA
Received: October 11, 2023; Accepted: January 3, 2024; Published: April 10, 2024
Copyright: © 2024 Bruce et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Data Availability: The dataset and relevant documents have been uploaded to the Open Science Framework. Data can be accessed via the following URL: https://osf.io/5s72x/?view_only=ea7ee238f3084054a6433fbab43dc9fb .
Funding: This project has received funding from the European Research Council (ERC) under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program (Grant agreement No. 101020598 – CRIMGOV, Federico Varese PI). FV received the award and is the Primary Investigator. The ERC did not play any role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. Funder website: https://erc.europa.eu/faq-programme/h2020 .
Competing interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Introduction
Although the geography of cybercrime attacks has been documented, the geography of cybercrime offenders–and the corresponding level of “cybercriminality” present within each country–is largely unknown. A number of scholars have noted that valid and reliable data on offender geography are sparse [ 1 – 4 ], and there are several significant obstacles to establishing a robust metric of cybercriminality by country. First, there are the general challenges associated with the study of any hidden population, for whom no sampling frame exists [ 5 , 6 ]. If cybercriminals themselves cannot be easily accessed or reliably surveyed, then cybercriminality must be measured through a proxy. This is the second major obstacle: deciding what kind of proxy data would produce the most valid measure of cybercriminality. While there is much technical data on cybercrime attacks, this data captures artefacts of the digital infrastructure or proxy (obfuscation) services used by cybercriminals, rather than their true physical location. Non-technical data, such as legal cases, can provide geographical attribution for a small number of cases, but the data are not representative of global cybercrime. In short, the question of how best to measure the geography of cybercriminal offenders is complex and unresolved.
There is tremendous value in developing a metric for cybercrime. Cybercrime is a major challenge facing the world, with the most sober cost estimates in the hundreds of millions [ 7 , 8 ], but with high-end estimates in the trillions [ 9 ]. By accurately identifying which countries are cybercrime hotspots, the public and private sectors could concentrate their resources on these hotspots and spend less time and funds on cybercrime countermeasures in countries where the problem is limited. Whichever strategies are deployed in the fight against cybercrime (see for example [ 10 – 12 ]), they should be targeted at countries that produce the largest cybercriminal threat [ 3 ]. A measure of cybercriminality would also enable other lines of scholarly inquiry. For instance, an index of cybercriminality by country would allow for a genuine dependent variable to be deployed in studies attempting to assess which national characteristics–such as educational attainment, Internet penetration, or GDP–are associated with cybercrime [ 4 , 13 ]. These associations could also be used to identify future cybercrime hubs so that early interventions could be made in at-risk countries before a serious cybercrime problem develops. Finally, this metric would speak directly to theoretical debates on the locality of cybercrime, and organized crime more generally [ 11 – 14 ]. The challenge we have accepted is to develop a metric that is both global and robust. The following sections respectively outline the background elements of this study, the methods, the results, and then discussion and limitations.
Profit-driven cybercrime, which is the focus of this paper/research, has been studied by both social scientists and computer scientists. It has been characterised by empirical contributions that have sought to illuminate the nature and organisation of cybercrime both online and offline [ 15 – 20 ]. But, as noted above, the geography of cybercrime has only been addressed by a handful of scholars, and they have identified a number of challenges connected to existing data. In a review of existing work in this area, Lusthaus et al. [ 2 ] identify two flaws in existing cybercrime metrics: 1) their ability to correctly attribute the location of cybercrime offenders; 2) beyond a handful of examples, their ability to compare the severity and scale of cybercrime between countries.
Building attribution into a cybercrime index is challenging. Often using technical data, cybersecurity firms, law enforcement agencies and international organisations regularly publish reports that identify the major sources of cyber attacks (see for example [ 21 – 24 ]). Some of these sources have been aggregated by scholars (see [ 20 , 25 – 29 ]). But the kind of technical data contained in these reports cannot accurately measure offender location. Kigerl [ 1 ] provides some illustrative remarks:
Where the cybercriminals live is not necessarily where the cyberattacks are coming from. An offender from Romania can control zombies in a botnet, mostly located in the United States, from which to send spam to countries all over the world, with links contained in them to phishing sites located in China. The cybercriminal’s reach is not limited by national borders (p. 473).
As cybercriminals often employ proxy services to hide their IP addresses, carry out attacks across national boundaries, collaborate with partners around the world, and can draw on infrastructure based in different countries, superficial measures do not capture the true geographical distribution of these offenders. Lusthaus et al. [ 2 ] conclude that attempts to produce an index of cybercrime by country using technical data suffer from a problem of validity. “If they are a measure of anything”, they argue, “they are a measure of cyber-attack geography”, not of the geography of offenders themselves (p. 452).
Non-technical data are far better suited to incorporating attribution. Court records, indictments and other investigatory materials speak more directly to the identification of offenders and provide more granular detail on their location. But while this type of data is well matched to micro-level analysis and case studies, there are fundamental questions about the representativeness of these small samples, even if collated. First, any sample would capture cases only where cybercriminals had been prosecuted, and would not include offenders that remain at large. Second, if the aim was to count the number of cybercrime prosecutions by country, this may reflect the seriousness with which various countries take cybercrime law enforcement or the resources they have to pursue it, rather than the actual level of cybercrime within each country (for a discussion see [ 30 , 31 ]). Given such concerns, legal data is also not an appropriate approach for such a research program.
Furthermore, to carry out serious study on this topic, a cybercrime metric should aim to include as many countries as possible, and the sample must allow for variation so that high and low cybercrime countries can be compared. If only a handful of widely known cybercrime hubs are studied, this will result in selection on the dependent variable. The obvious challenge in providing such a comparative scale is the lack of good quality data to devise it. As an illustration, in their literature review Hall et al. [ 10 ] identify the “dearth of robust data” on the geographical location of cybercriminals, which means they are only able to include six countries in their final analysis (p. 285. See also [ 4 , 32 , 33 ]).
Considering the weaknesses within both existing technical and legal data discussed above, Lusthaus et al. [ 2 ] argue for the use of an expert survey to establish a global metric of cybercriminality. Expert survey data “can be extrapolated and operationalised”, and “attribution can remain a key part of the survey, as long as the participants in the sample have an extensive knowledge of cybercriminals and their operations” (p. 453). Up to this point, no such study has been produced. Such a survey would need to be very carefully designed for the resulting data to be both reliable and valid. One criticism of past cybercrime research is that surveys were used whenever other data was not immediately available, and that they were not always designed with care (for a discussion see [ 34 ]).
In response to the preceding considerations, we designed an expert survey in 2020, refined it through focus groups, and deployed it throughout 2021. The survey asked participants to consider five major types of cybercrime– Technical products/services ; Attacks and extortion ; Data/identity theft ; Scams ; and Cashing out/money laundering –and nominate the countries that they consider to be the most significant sources of each of these cybercrime types. Participants then rated each nominated country according to the impact of the offenses produced there, and the professionalism and technical skill of the offenders based there. Using the expert responses, we generated scores for each type of cybercrime, which we then combined into an overall metric of cybercriminality by country: the World Cybercrime Index (WCI). The WCI achieves our initial goal to devise a valid measure of cybercrime hub location and significance, and is the first step in our broader aim to understand the local dimensions of cybercrime production across the world.
Participants
Identifying and recruiting cybercrime experts is challenging. Much like the hidden population of cybercriminals we were trying to study, cybercrime experts themselves are also something of a hidden population. Due to the nature of their work, professionals working in the field of cybercrime tend to be particularly wary of unsolicited communication. There is also the problem of determining who is a true cybercrime expert, and who is simply presenting themselves as one. We designed a multi-layered sampling method to address such challenges.
The heart of our strategy involved purposive sampling. For an index based entirely on expert opinion, ensuring the quality of these experts (and thereby the quality of our survey results) was of the utmost importance. We defined “expertise” as adult professionals who have been engaged in cybercrime intelligence, investigation, and/or attribution for a minimum of five years and had a reputation for excellence amongst their peers. Only currently- or recently-practicing intelligence officers and investigators were included in the participant pool. While participants could be from either the public or private sectors, we explicitly excluded professionals working in the field of cybercrime research who are not actively involved in tracking offenders, which includes writers and academics. In short, only experts with first-hand knowledge of cybercriminals are included in our sample. To ensure we had the leading experts from a wide range of backgrounds and geographical areas, we adopted two approaches for recruitment. We searched extensively through a range of online sources including social media (e.g. LinkedIn), corporate sites, news articles and cybercrime conference programs to identify individuals who met our inclusion criteria. We then faced a second challenge of having to find or discern contact information for these individuals.
Complementing this strategy, the authors also used their existing relationships with recognised cybercrime experts to recruit participants using the “snowball” method [ 35 ]. This both enhanced access and provided a mechanism for those we knew were bona fide experts to recommend other bona fide experts. The majority of our participants were recruited in this manner, either directly through our initial contacts or through a series of referrals that followed. But it is important to note that this snowball sampling fell under our broader purposive sampling strategy. That is, all the original “seeds” had to meet our inclusion criteria of being a top expert in the first instance. Any connections we were offered also had to meet our criteria or we would not invite them to participate. Another important aspect of this sampling strategy is that we did not rely on only one gatekeeper, but numerous, often unrelated, individuals who helped us with introductions. This approach reduced bias in the sample. It was particularly important to deploy a number of different “snowballs” to ensure that we included experts from each region of the world (Africa, Asia Pacific, Europe, North America and South America) and from a range of relevant professional backgrounds. We limited our sampling strategy to English speakers. The survey itself was likewise written in English. The use of English was partly driven by the resources available for this study, but the population of cybercrime experts is itself very global, with many attending international conferences and cooperating with colleagues from across the world. English is widely spoken within this community. While we expect the gains to be limited, future surveys will be translated into some additional languages (e.g. Spanish and Chinese) to accommodate any non-English speaking experts that we may not otherwise be able to reach.
Our survey design, detailed below, received ethics approval from the Human Research Advisory Panel (HREAP A) at the University of New South Wales in Australia, approval number HC200488, and the Research Ethics Committee of the Department of Sociology (DREC) at the University of Oxford in the United Kingdom, approval number SOC_R2_001_C1A_20_23. Participants were recruited in waves between 1 August 2020 and 30 September 2021. All participants provided consent to participate in the focus groups, pilot survey, and final survey.
Survey design
The survey comprised three stages. First, we conducted three focus groups with seven experts in cybercrime intelligence/investigations to evaluate our initial assumptions, concepts, and framework. These experts were recruited because they had reputations as some of the very top experts in the field; they represented a range of backgrounds in terms of their own geographical locations and expertise across different types of cybercrime; and they spanned both the public and private sectors. In short, they offered a cross-section of the survey sample we aimed to recruit. These focus groups informed several refinements to the survey design and specific terms to make them better comprehensible to participants. Some of the key terms, such as “professionalism” and “impact”, were a direct result of this process. Second, some participants from the focus groups then completed a pilot version of the survey, alongside others who had not taken part in these focus groups, who could offer a fresh perspective. This allowed us to test technical components, survey questions, and user experience. The pilot participants provided useful feedback and prompted a further refinement of our approach. The final survey was released online in March 2021 and closed in October 2021. We implemented several elements to ensure data quality, including a series of preceding statements about time expectations, attention checks, and visual cues throughout the survey. These elements significantly increased the likelihood that our participants were both suitable and would provide full and thoughtful responses.
The introduction to the survey outlined the survey’s two main purposes: to identify which countries are the most significant sources of profit-driven cybercrime, and to determine how impactful the cybercrime is in these locations. Participants were reminded that state-based actors and offenders driven primarily by personal interests (for instance, cyberbullying or harassment) should be excluded from their consideration. We defined the “source” of cybercrime as the country where offenders are primarily based, rather than their nationality. To maintain a level of consistency, we made the decision to only include countries formally recognised by the United Nations. We initially developed seven categories of cybercrime to be included in the survey, based on existing research. But during the focus groups and pilot survey, our experts converged on five categories as the most significant cybercrime threats on a global scale:
- Technical products/services (e.g. malware coding, botnet access, access to compromised systems, tool production).
- Attacks and extortion (e.g. DDoS attacks, ransomware).
- Data/identity theft (e.g. hacking, phishing, account compromises, credit card comprises).
- Scams (e.g. advance fee fraud, business email compromise, online auction fraud).
- Cashing out/money laundering (e.g. credit card fraud, money mules, illicit virtual currency platforms).
After being prompted with these descriptions and a series of images of world maps to ensure participants considered a wide range of regions/countries, participants were asked to nominate up to five countries that they believed were the most significant sources of each of these types of cybercrime. Countries could be listed in any order; participants were not instructed to rank them. Nominating countries was optional and participants were free to skip entire categories if they wished. Participants were then asked to rate each of the countries they nominated against three measures: how impactful the cybercrime is, how professional the cybercrime offenders are, and how technically skilled the cybercrime offenders are. Across each of these three measures, participants were asked to assign scores on a Likert-type scale between 1 (e.g. least professional) to 10 (e.g. most professional). Nominating and then rating countries was repeated for all five cybercrime categories.
This process, of nominating and then rating countries across each category, introduces a potential limitation in the survey design: the possibility of survey response fatigue. If a participant nominated the maximum number of countries across each cybercrime category– 25 countries–by the end of the survey they would have completed 75 Likert-type scales. The repetition of this task, paired with the consideration that it requires, has the potential to introduce respondent fatigue as the survey progresses, in the form of response attrition, an increase in careless responses, and/or increased likelihood of significantly higher/lower scores given. This is a common phenomenon in long-form surveys [ 36 ], and especially online surveys [ 37 , 38 ]. Jeong et al [ 39 ], for instance, found that questions asked near the end of a 2.5 hour survey were 10–64% more likely to be skipped than those at the beginning. We designed the survey carefully, refined with the aid of focus groups and a pilot, to ensure that only the most essential questions were asked. As such, the survey was not overly long (estimated to take 30 minutes). To accommodate any cognitive load, participants were allowed to complete the survey anytime within a two-week window. Their progress was saved after each session, which enabled participants to take breaks between completing each section (a suggestion made by Jeong et al [ 39 ]). Crucially, throughout survey recruitment, participants were informed that the survey is time-intensive and required significant attention. At the beginning of the survey, participants were instructed not to undertake the survey unless they could allocate 30 minutes to it. This approach pre-empted survey fatigue by discouraging those likely to lose interest from participating. This compounds the fact that only experts with a specific/strong interest in the subject matter of the survey were invited to participate. Survey fatigue is addressed further in the Discussion section, where we provide an analysis suggesting little evidence of participant fatigue.
In sum, we designed the survey to protect against various sources of bias and error, and there are encouraging signs that the effects of these issues in the data are limited (see Discussion ). Yet expert surveys are inherently prone to some types of bias and response issues; in the WCI, the issue of selection and self-selection within our pool of experts, as well as geo-political biases that may lead to systematic over- or under-scoring of certain countries, is something we considered closely. We discuss these issues in detail in the subsection on Limitations below.
This “type” score is then multiplied by the proportion of experts who nominated that country. Within each cybercrime type, a country could be nominated a possible total of 92 times–once per participant. We then multiply this weighted score by ten to produce a continuous scale out of 100 (see Eq (2) ). This process prevents countries that received high scores, but a low number of nominations, from receiving artificially high rankings.
The analyses for this paper were performed in R. All data and code have been made publicly available so that our analysis can be reproduced and extended.
We contacted 245 individuals to participate in the survey, of which 147 agreed and were sent invitation links to participate. Out of these 147, a total of 92 people completed the survey, giving us an overall response rate of 37.5%. Given the expert nature of the sample, this is a high response rate (for a detailed discussion see [ 40 ]), and one just below what Wu, Zhao, and Fils-Aime estimate of response rates for general online surveys in social science: 44% [ 41 ]. The survey collected information on the participants’ primary nationality and their current country of residence. Four participants chose not to identify their nationality. Overall, participants represented all five major geopolitical regions (Africa, the Asia-Pacific, Europe, North America and South America), both in nationality and residence, though the distribution was uneven and concentrated in particular regions/countries. There were 8 participants from Africa, 11 participants from the Asia Pacific, 27 from North America, and 39 from Europe. South America was the least represented region with only 3 participants. A full breakdown of participants’ nationality, residence, and areas of expertise is included in the Supporting Information document (see S1 Appendix ).
Table 1 shows the scores for the top fifteen countries of the WCI overall index. Each entry shows the country, along with the mean score (out of 10) averaged across the participants who nominated this country, for three categories: impact, professionalism, and technical skill. This is followed by each country’s WCI overall and WCI type scores. Countries are ordered by their WCI overall score. Each country’s highest WCI type scores are highlighted. Full indices that include all 197 UN-recognised countries can be found in S1 Indices .
- PPT PowerPoint slide
- PNG larger image
- TIFF original image
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0297312.t001
Some initial patterns can be observed from this table, as well as the full indices in the supplementary document (see S1 Indices ). First, a small number of countries hold consistently high ranks for cybercrime. Six countries–China, Russia, Ukraine, the US, Romania, and Nigeria–appear in the top 10 of every WCI type index, including the WCI overall index. Aside from Romania, all appear in the top three at least once. While appearing in a different order, the first ten countries in the Technical products/services and Attacks and extortion indices are the same. Second, despite this small list of countries regularly appearing as cybercrime hubs, the survey results capture a broad geographical diversity. All five geopolitical regions are represented across each type. Overall, 97 distinct countries were nominated by at least one expert. This can be broken down into the cybercrime categories. Technical products/services includes 41 different countries; Attacks and extortion 43; Data/identity theft 51; Scams 49; and Cashing out/money laundering 63.
Some key findings emerge from these results, which are further illustrated by the following Figs 1 and 2 . First, cybercrime is not universally distributed. Certain countries are cybercrime hubs, while many others are not associated with cybercriminality in a serious way. Second, countries that are cybercrime hubs specialise in particular types of cybercrime. That is, despite a small number of countries being leading producers of cybercrime, there is meaningful variation between them both across categories, and in relation to scores for impact, professionalism and technical skill. Third, the results show a longer list of cybercrime-producing countries than are usually included in publications on the geography of cybercrime. As the survey captures leading producers of cybercrime, rather than just any country where cybercrime is present, this suggests that, even if a small number of countries are of serious concern, and close to 100 are of little concern at all, the remaining half are of at least moderate concern.
Base map and data from OpenStreetMap and OpenStreetMap Foundation.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0297312.g001
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0297312.g002
To examine further the second finding concerning hub specialisation, we calculated an overall “Technicality score”–or “T-score”–for the top 15 countries of the WCI overall index. We assigned a value from 2 to -2 to each type of cybercrime to designate the level of technical complexity involved. Technical products/services is the most technically complex type (2), followed by Attacks and extortion (1), Data/identity theft (0), Scams (-1), and finally Cashing out and money laundering (-2), which has very low technical complexity. We then multiplied each country’s WCI score for each cybercrime type by its assigned value–for instance, a Scams WCI score of 5 would be multiplied by -1, with a final modified score of -5. As a final step, for each country, we added all of their modified WCI scores across all five categories together to generate the T-score. Fig 3 plots the top 15 WCI overall countries’ T-scores, ordering them by score. Countries with negative T-scores are highlighted in red, and countries with positive scores are in black.
Negative values correspond to lower technicality, positive values to higher technicality.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0297312.g003
The T-score is best suited to characterising a given hub’s specialisation. For instance, as the line graph makes clear, Russia and Ukraine are highly technical cybercrime hubs, whereas Nigerian cybercriminals are engaged in less technical forms of cybercrime. But for countries that lie close to the centre (0), the story is more complex. Some may specialise in cybercrime types with middling technical complexity (e.g. Data/identity theft ). Others may specialise in both high- and low-tech crimes. In this sample of countries, India (-6.02) somewhat specialises in Scams but is otherwise a balanced hub, whereas Romania (10.41) and the USA (-2.62) specialise in both technical and non-technical crimes, balancing their scores towards zero. In short, each country has a distinct profile, indicating a unique local dimension.
This paper introduces a global and robust metric of cybercriminality–the World Cybercrime Index. The WCI moves past previous technical measures of cyber attack geography to establish a more focused measure of the geography of cybercrime offenders. Elicited through an expert survey, the WCI shows that cybercrime is not universally distributed. The key theoretical contribution of this index is to illustrate that cybercrime, often seen as a fluid and global type of organized crime, actually has a strong local dimension (in keeping with broader arguments by some scholars, such as [ 14 , 42 ]).
While we took a number of steps to ensure our sample of experts was geographically representative, the sample is skewed towards some regions (such as Europe) and some countries (such as the US). This may simply reflect the high concentration of leading cybercrime experts in these locations. But it is also possible this distribution reflects other factors, including the authors’ own social networks; the concentration of cybercrime taskforces and organisations in particular countries; the visibility of different nations on networking platforms like LinkedIn; and also perhaps norms of enthusiasm or suspicion towards foreign research projects, both inside particular organisations and between nations.
To better understand what biases might have influenced the survey data, we analysed participant rating behaviours with a series of linear regressions. Numerical ratings were the response and different participant characteristics–country of nationality; country of residence; crime type expertise; and regional expertise–were the predictors. Our analysis found evidence (p < 0.05) that participants assigned higher ratings to the countr(ies) they either reside in or are citizens of, though this was not a strong or consistent result. For instance, regional experts did not consistently rate their region of expertise more highly than other regions. European and North American experts, for example, rated countries from these regions lower than countries from other regions. Our analysis of cybercrime type expertise showed even less systematic rating behaviour, with no regression yielding a statistically significant (p < 0.05) result. Small sample sizes across other known participant characteristics meant that further analyses of rating behaviour could not be performed. This applied to, for instance, whether residents and citizens of the top ten countries in the WCI nominated their own countries more or less often than other experts. On this point: 46% of participants nominated their own country at some point in the survey, but the majority (83%) of nominations were for a country different to the participant’s own country of residence or nationality. This suggested limited bias towards nominating one’s own country. Overall, these analyses point to an encouraging observation: while there is a slight home-country bias, this does not systematically result in higher rating behaviour. Longitudinal data from future surveys, as well as a larger participant pool, will better clarify what other biases may affect rating behaviour.
There is little evidence to suggest that survey fatigue affected our data. As the survey progressed, the heterogeneity of nominated countries across all experts increased, from 41 different countries nominated in the first category to 63 different countries nominated in the final category. If fatigue played a significant role in the results then we would expect this number to decrease, as participants were not required to nominate countries within a category and would have been motivated to nominate fewer countries to avoid extending their survey time. We further investigated the data for evidence of survey fatigue in two additional ways: by performing a Mann-Kendall/Sen’s slope trend test (MK/S) to determine whether scores skewed significantly upwards or downwards towards the end of the survey; and by compiling an intra-individual response variability (IRV) index to search for long strings of repeated scores at the end of the survey [ 43 ]. The MK/S test was marginally statistically significant (p<0.048), but the results indicated that scores trended downwards only minimally (-0.002 slope coefficient). Likewise, while the IRV index uncovered a small group of participants (n = 5) who repeatedly inserted the same score, this behaviour was not more likely to happen at the end of the survey (see S7 and S8 Tables in S1 Appendix ).
It is encouraging that there is at least some external validation for the WCI’s highest ranked countries. Steenbergen and Marks [ 44 ] recommend that data produced from expert judgements should “demonstrate convergent validity with other measures of [the topic]–that is, the experts should provide evaluations of the same […] phenomenon that other measurement instruments pick up.” (p. 359) Most studies of the global cybercrime geography are, as noted in the introduction, based on technical measures that cannot accurately establish the true physical location of offenders (for example [ 1 , 4 , 28 , 33 , 45 ]). Comparing our results to these studies would therefore be of little value, as the phenomena being measured differs: they are measuring attack infrastructure, whereas the WCI measures offender location. Instead, looking at in-depth qualitative cybercrime case studies would provide a better comparison, at least for the small number of higher ranked countries. Though few such studies into profit-driven cybercrime exist, and the number of countries included are limited, we can see that the top ranked countries in the WCI match the key cybercrime producing countries discussed in the qualitative literature (see for example [ 3 , 10 , 32 , 46 – 50 ]). Beyond this qualitative support, our sampling strategy–discussed in the Methods section above–is our most robust control for ensuring the validity of our data.
Along with contributing to theoretical debates on the (local) nature of organized crime [ 1 , 14 ], this index can also contribute to policy discussions. For instance, there is an ongoing debate as to the best approaches to take in cybercrime reduction, whether this involves improving cyber-law enforcement capacity [ 3 , 51 ], increasing legitimate job opportunities and access to youth programs for potential offenders [ 52 , 53 ], strengthening international agreements and law harmonization [ 54 – 56 ], developing more sophisticated and culturally-specific social engineering countermeasures [ 57 ], or reducing corruption [ 3 , 58 ]. As demonstrated by the geographical, economic, and political diversity of the top 15 countries (see Table 1 ), the likelihood that a single strategy will work in all cases is low. If cybercrime is driven by local factors, then mitigating it may require a localised approach that considers the different features of cybercrime in these contexts. But no matter what strategies are applied in the fight against cybercrime, they should be targeted at the countries that produce the most cybercrime, or at least produce the most impactful forms of it [ 3 ]. An index is a valuable resource for determining these countries and directing resources appropriately. Future research that explains what is driving cybercrime in these locations might also suggest more appropriate means for tackling the problem. Such an analysis could examine relevant correlates, such as corruption, law enforcement capacity, internet penetration, education levels and so on to inform/test a theoretically-driven model of what drives cybercrime production in some locations, but not others. It also might be possible to make a kind of prediction: to identify those nations that have not yet emerged as cybercrime hubs but may in the future. This would allow an early warning system of sorts for policymakers seeking to prevent cybercrime around the world.
Limitations
In addition to the points discussed above, the findings of the WCI should be considered in light of some remaining limitations. Firstly, as noted in the methods, our pool of experts was not as large or as globally representative as we had hoped. Achieving a significant response rate is a common issue across all surveys, and is especially difficult in those that employ the snowball technique [ 59 ] and also attempt to recruit experts [ 60 ]. However, ensuring that our survey data captures the most accurate picture of cybercrime activity is an essential aspect of the project, and the under-representation of experts from Africa and South America is noteworthy. More generally, our sample size (n = 92) is relatively small. Future iterations of the WCI survey should focus on recruiting a larger pool of experts, especially those from under-represented regions. However, this is a small and hard-to-reach population, which likely means the sample size will not grow significantly. While this limits statistical power, it is also a strength of the survey: by ensuring that we only recruit the top cybercrime experts in the world, the weight and validity of our data increases.
Secondly, though we developed our cybercrime types and measures with expert focus groups, the definitions used in the WCI will always be contestable. For instance, a small number of comments left at the end of the survey indicated that the Cashing out/money laundering category was unclear to some participants, who were unsure whether they should nominate the country in which these schemes are organised or the countries in which the actual cash out occurs. A small number of participants also commented that they were not sure whether the ‘impact’ of a country’s cybercrime output should be measured in terms of cost, social change, or some other metric. We limited any such uncertainties by running a series of focus groups to check that our categories were accurate to the cybercrime reality and comprehensible to practitioners in this area. We also ran a pilot version of the survey. The beginning of the survey described the WCI’s purpose and terms of reference, and participants were able to download a document that described the project’s methodology in further detail. Each time a participant was prompted to nominate countries as a significant source of a type of cybercrime, the type was re-defined and examples of offences under that type were provided. However, the examples were not exhaustive and the definitions were brief. This was done partly to avoid significantly lengthening the survey with detailed definitions and clarifications. We also wanted to avoid over-defining the cybercrime types so that any new techniques or attack types that emerged while the survey ran would be included in the data. Nonetheless, there will always remain some elasticity around participant interpretations of the survey.
Finally, although we restricted the WCI to profit-driven activity, the distinction between cybercrime that is financially-motivated, and cybercrime that is motivated by other interests, is sometimes blurred. Offenders who typically commit profit-driven offences may also engage in state-sponsored activities. Some of the countries with high rankings within the WCI may shelter profit-driven cybercriminals who are protected by corrupt state actors of various kinds, or who have other kinds of relationships with the state. Actors in these countries may operate under the (implicit or explicit) sanctioning of local police or government officials to engage in cybercrime. Thus while the WCI excludes state-based attacks, it may include profit-driven cybercriminals who are protected by states. Investigating the intersection between profit-driven cybercrime and the state is a strong focus in our ongoing and future research. If we continue to see evidence that these activities can overlap (see for example [ 32 , 61 – 63 ]), then any models explaining the drivers of cybercrime will need to address this increasingly important aspect of local cybercrime hubs.
This study makes use of an expert survey to better measure the geography of profit-driven cybercrime and presents the output of this effort: the World Cybercrime Index. This index, organised around five major categories of cybercrime, sheds light on the geographical concentrations of financially-motivated cybercrime offenders. The findings reveal that a select few countries pose the most significant cybercriminal threat. By illustrating that hubs often specialise in particular forms of cybercrime, the WCI also offers valuable insights into the local dimension of cybercrime. This study provides a foundation for devising a theoretically-driven model to explain why some countries produce more cybercrime than others. By contributing to a deeper understanding of cybercrime as a localised phenomenon, the WCI may help lift the veil of anonymity that protects cybercriminals and thereby enhance global efforts to combat this evolving threat.
Supporting information
S1 indices. wci indices..
Full indices for the WCI Overall and each WCI Type.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0297312.s001

S1 Appendix. Supporting information.
Details of respondent characteristics and analysis of rating behaviour.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0297312.s002
Acknowledgments
The data collection for this project was carried out as part of a partnership between the Department of Sociology, University of Oxford and UNSW Canberra Cyber. The analysis and writing phases received support from CRIMGOV. Fig 1 was generated using information from OpenStreetMap and OpenStreetMap Foundation, which is made available under the Open Database License.
- View Article
- Google Scholar
- 2. Lusthaus J, Bruce M, Phair N. Mapping the geography of cybercrime: A review of indices of digital offending by country. 2020.
- 4. McCombie S, Pieprzyk J, Watters P. Cybercrime Attribution: An Eastern European Case Study. Proceedings of the 7th Australian Digital Forensics Conference. Perth, Australia: secAU—Security Research Centre, Edith Cowan University; 2009. pp. 41–51. https://researchers.mq.edu.au/en/publications/cybercrime-attribution-an-eastern-european-case-study
- 7. Anderson R, Barton C, Bohme R, Clayton R, van Eeten M, Levi M, et al. Measuring the cost of cybercrime. The Economics of Information Security and Privacy. Springer; 2013. pp. 265–300. https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-642-39498-0_12
- 8. Anderson R, Barton C, Bohme R, Clayton R, Ganan C, Grasso T, et al. Measuring the Changing Cost of Cybercrime. California, USA; 2017.
- 9. Morgan S. 2022 Official Cybercrime Report. Cybersecurity Ventures; 2022. https://s3.ca-central-1.amazonaws.com/esentire-dot-com-assets/assets/resourcefiles/2022-Official-Cybercrime-Report.pdf
- 12. Wall D. Cybercrime: The Transformation of Crime in the Information Age. Polity Press; 2007.
- 14. Varese F. Mafias on the move: how organized crime conquers new territories. Princeton University Press; 2011.
- 15. Dupont B. Skills and Trust: A Tour Inside the Hard Drives of Computer Hackers. Crime and networks. Routledge; 2013.
- 16. Franklin J, Paxson V, Savage S. An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Internet Miscreants. Proceedings of the 2007 ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security. Alexandria, Virginia, USA; 2007.
- 17. Hutchings A, Clayton R. Configuring Zeus: A case study of online crime target selection and knowledge transmission. Scottsdale, AZ, USA: IEEE; 2017.
- 20. Levesque F, Fernandez J, Somayaji A, Batchelder. National-level risk assessment: A multi-country study of malware infections. 2016. https://homeostasis.scs.carleton.ca/~soma/pubs/levesque-weis2016.pdf
- 21. Crowdstrike. 2022 Global Threat Report. Crowdstrike; 2022. https://go.crowdstrike.com/crowdstrike/gtr
- 22. EC3. Internet Organised Crime Threat Assessment (IOCTA) 2021. EC3; 2021. https://www.europol.europa.eu/publications-events/main-reports/internet-organised-crime-threat-assessment-iocta-2021
- 23. ENISA. ENISA threat Landscape 2021. ENISA; 2021. https://www.enisa.europa.eu/publications/enisa-threat-landscape-2021
- 24. Sophos. Sophos 2022 Threat Report. Sophos; 2022. https://www.sophos.com/ en-us/labs/security-threat-report
- 25. van Eeten M, Bauer J, Asghari H, Tabatabaie S, Rand D. The Role of Internet Service Providers in Botnet Mitigation. An Empirical Analysis Based on Spam Data WEIS. 2010. van Eeten, Michel and Bauer, Johannes M. and Asghari, Hadi and Tabatabaie, Shirin and Rand, David, The Role of Internet Service Providers in Botnet Mitigation an Empirical Analysis Based on Spam Data (August 15, 2010). TPRC 2010, SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=1989198
- 26. He S, Lee GM, Quarterman JS, Whinston A. Cybersecurity Policies Design and Evaluation: Evidence from a Large-Scale Randomized Field Experiment. 2015. https://econinfosec.org/archive/weis2015/papers/WEIS_2015_he.pdf
- 27. Snyder P, Kanich C. No Please, After You: Detecting Fraud in Affiliate Marketing Networks. 2015. https://econinfosec.org/archive/weis2015/papers/WEIS_2015_snyder.pdf
- 29. Wang Q-H, Kim S-H. Cyber Attacks: Cross-Country Interdependence and Enforcement. 2009. http://weis09.infosecon.net/files/153/paper153.pdf
- 32. Lusthaus J. Industry of Anonymity: Inside the Business of Cybercrime. Harvard University Press; 2018.
- 33. Kshetri N. The Global Cybercrime Industry: Economic, Institutional and Strategic Perspectives. Berlin: Springer; 2010.
- 36. Backor K, Golde S, Nie N. Estimating Survey Fatigue in Time Use Study. Washington, DC.; 2007. https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/document?repid=rep1&type=pdf&doi=401f97f2d7c684b295486636d8a84c627eb33446
- 42. Reuter P. Disorganized Crime: Illegal Markets and the Mafia. MIT Press; 1985.
- PubMed/NCBI
- 47. Sotande E. Transnational Organised Crime and Illicit Financial Flows: Nigeria, West Africa and the Global North. University of Leeds, School of Law. 2016. https://etheses.whiterose.ac.uk/15473/1/Emmanuel%20Sotande%20Thessis%20at%20the%20University%20of%20Leeds.%20viva%20corrected%20version%20%281%29.pdf
- 48. Lusthaus J. Modelling cybercrime development: the case of Vietnam. The Human Factor of Cybercrime. Routledge; 2020. pp. 240–257.
- 51. Lusthaus J. Electronic Ghosts. In: Democracy: A Journal of Ideas [Internet]. 2014. https://democracyjournal.org/author/jlusthaus/
- 52. Brewer R, de Vel-Palumbo M, Hutchings A, Maimon D. Positive Diversions. Cybercrime Prevention. 2019. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/337297392_Positive_Diversions
- 53. National Cyber Crime Unit / Prevent Team. Pathways Into Cyber Crime. National Crime Agency; 2017. https://www.nationalcrimeagency.gov.uk/who-we-are/publications/6-pathways-into-cyber-crime-1/file
- 60. Christopoulos D. Peer Esteem Snowballing: A methodology for expert surveys. 2009. https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/document?repid=rep1&type=pdf&doi=63ac9f6db0a2fa2e0ca08cd28961385f98ec21ec
Custom Essay, Term Paper & Research paper writing services
- testimonials
Toll Free: +1 (888) 354-4744
Email: [email protected]
Writing custom essays & research papers since 2008
154 exceptional cybersecurity research topics for you.

If you are studying computer science or IT-related course, you will encounter such a task. It is one of the most technical assignments, primarily in the era of advanced digital technologies. Students may not have the muscles to complete such papers on their own. That is why we provide expert help and ideas to make the process easier.
Do you want to excel in your cybersecurity paper? Here is your number one arsenal!
What You Need To Know About Cyber Security Research Topics
A cybersecurity paper deals with the practices of protecting servers, electronic systems, computers, and networks from malicious attacks. Although most students think this only applies to computers, it also applies to mobile computing and other business models.
There are various categories in cybersecurity, including:
Network security Application security Information security Operational security Disaster recovery and business continuity
Therefore, your cybersecurity topics for research should:
Examine the common security breaches in systems and networks Offer practical ways of protecting computers from such attacks Highlight the legal and ethical implications of hacking and other related practices Point out the challenges encountered in combating cybercrime
Since this is a technical paper, you should endeavor to do your research extensively to prevent rumors and unverified facts. The topics should also inform and educate people who are not conversant with cybersecurity in simple terms. Avoid using jargon at all costs, as this will make the paper difficult to read and understand.
Are you worried about where you can get professional cybersecurity topics and ideas? Well, here are a few of the most reliable sources that can furnish you with top-rated issues.
- Government legislation on cybersecurity (Acts of Parliament)
- The UN Office of Counter-Terrorism (Cybersecurity initiatives)
- The CISCO magazine
- Forbes also has excellent coverage on cybersecurity
You can find impressive topic ideas from these sources and more. Furthermore, news headlines and stories on cybersecurity can also help you gather many writing ideas. If all these prove futile, use our tip-top writing prompts below:
Quality Cyber Security Thesis Topics
- Impacts of coronavirus lockdowns on cybersecurity threats in the US
- Why ethical hacking is contributing to more harm than good
- The role of computer specialists in combating cyber threats before they occur
- Technological trends that are making it difficult to manage systems
- Are passwords reliable when protecting computer systems?
- Effects of having more than one systems administrator in a company
- Can the government shut down the dark web once and for all?
- Why should you bother about the security of your mobile device?
- Evaluate reasons why using public WIFI can be harmful to your security
- The role of cybersecurity seminars and conferences
- How universities can produce ethical computer hackers who can help the society
- How to counter-terrorism with advanced cybersecurity measures
- Impacts of teaching children how to use computers at a tender age
- Latest innovations that are a threat to cybersecurity
- The role of monitoring in combating frequent cyber attacks
- How social media is contributing to cyber attacks
- Discuss the relationship between cyberbullying and cybersecurity
- Why fingerprints may be the best method of protecting devices
- The role of YouTube in contributing to the rising number of hackers
Top Research Topics For Cyber Security For Master Thesis
- Impact of cyber threats on attaining the sustainable development goals
- Why websites are becoming easy to hack in the 21 st century
- Effects of not having an SSL certificate for a website
- Discuss the security threats associated with WordPress websites
- Impacts of frequent maintenance while the website is still running
- How computer colleges can contribute to a safe cyberspace
- Latest cyber threats to business and financial websites
- Discuss the implications of cyber threats on privacy
- The role of Facebook in advancing cyberbullying and hacking
- Is hacking becoming a global epidemic in the digital world?
- Why using Cyber Cafes may be detrimental to your digital security
- The role of systems analysts in responding to data breaches
- How cybersecurity movies are contributing to cyber threats
- Should hackers face lifetime jail imprisonment when found guilty?
- Loopholes in cyber laws that make the practice challenging to curtail
Good Thesis Topics For Cyber Security
- The relationship between privacy and data security in computing
- Why cloud computing offers a haven for computer hackers
- The role of character and human-based behavior in cybersecurity
- How to determine safe organizational security management and policy
- How the Internet of Things is promoting cyber attacks
- Effects of using cracked computer software
- Are biometrics in cybersecurity able to put off hackers?
- The role of studying mobile platform security
- Why companies should frequently monitor their firewalls
- The role of antimalware in curbing cyber attacks
- Why is Ransomware a headache to most companies handling big data?
- How does antivirus software improve the security of your computer?
- Compare and contrast between the security of UNIX and Ubuntu
- The role of data encryption technologies in ensuring system security
- Is the process of encrypting viruses safe?
Top-Grade Thesis Topics For Cyber Security
- Describe the effectiveness of cybersecurity audits on company systems
- Is it proper to conduct device synchronization?
- Why is it difficult to manage the security of an intranet?
- Discuss the effects of logging in to many devices at the same time
- Evaluate the significance of computer forensics
- How are hackers inventing new ways of breaching the systems of companies?
- Why it is necessary to review the data protection laws
- Practices that increase the vulnerability of a system to cyber attacks
- Can organizations implement impenetrable network systems?
- Why administrators should check the background of users before giving them rights and privileges
- The role of risk management cybersecurity
- Discuss the impact of reverse engineering on computing systems
- Effects of a cyber-attack on a company’s economic performance
- What legal frameworks work best for a computer company?
- The role of social engineering in cybersecurity
Information Security Research Topics
- The implication of the proliferation of the internet globally
- Innovative technologies used in keeping off hackers
- The role of information communication technologies in maintaining the security
- Are online courses on informative security practical?
- Why should people avoid sharing their details on Facebook?
- Effects of using your image on social media
- The role of pseudo names and nicknames on social media
- Discuss the implications of Wi-Fi hacking apps on mobile phones
- How to detect malicious activity on a system
- Evaluate the potential threats of conduct self-hacking on a system
- The impact of sharing personal details with hiring agencies
- How con artists lure unsuspecting applicants into giving out their details
- Effects of frequent maintenance on systems
- How to strengthen the firewall of an information system
- The role of the media in propagating security breaches to information systems
Latest Computer Security Research Topics
- Tricks that black hat hackers use to infiltrate company systems
- How children learn about cybersecurity from their parents
- The impact of watching hacking movies and TV series
- How various companies are protecting themselves from cyber attacks
- Why every company should have a systems security consultant
- Discuss the implication of digital piracy
- Threats that biometrics are bringing to digital systems
- How to block a network intrusion before it causes any effect
- Why MacOS is challenging to infiltrate, unlike Windows
- Results of two-step authentication security measures for login systems
- The role of updating computer systems during working days
- Evaluate times of the year when hackers infiltrate systems the most
- Why it isn’t easy to manage big data on the cloud
- What happens during a system breakdown and maintenance?
- Discuss the role of data synchronization in creating a backup
Network Security Research Paper Topics
- The impact of having self-configuring and decentralized network systems
- Effects of ad-hoc networks for large companies
- Discuss the role of wireless sensor networks in contributing to security breaches
- How malicious nodes join a network
- Why it is difficult to detect a passive network attack
- How active network attacks reduce a network’s performance
- Evaluate the various parameters used in network security
- Analyze how a black hole affects a network system
- Describe techniques used in detecting malicious nodes on networks
- How to improve the safety of a company network
- The role of data encryption in maintaining the security of a network
- Describe the various channels of establishing secure algorithms in a network
- How does RSA increase the safety of a particular network?
- Effective policies and procedures for maintaining network security
- The role of a unique ID and Password in securing a website
Computer Security Research Topics
- Why it is challenging to maintain endpoint security
- The role of a critical infrastructure cybersecurity
- How to create secure passwords for your computer network
- The part of scanning for malware often on your PC
- How to detect apps that invade your privacy unknowingly
- Why ordering software from the black market is a threat to security
- Safe computing techniques for first-time computer users
- The role of digital literacy in preventing hacking
- Why most online users fall to online scams
- The role of smartphones in enhancing cybersecurity threats
- Evaluate the mobile landscape concerning data security
- The implication of private email accounts in data breaches
- Sites that contain a barrel of internet criminals
- How to develop comprehensive internet security software
- How children can navigate the internet safely
Impressive Cyber Crime Research Topics
- Why cyber currencies are a threat to online security
- Why cyberbullying is rampant in the 21 st century unlike in any other time
- The impact of online persuasion campaigns on cybersecurity
- Why teenagers are victims of cyberbullying than adults
- Discuss the effects of technology evolution on cybercrime
- How online hackers collect information without the knowledge of the victim
- Traits of a robust cybersecurity system
- Practices that can help reduce cybercrime in institutions of higher learning.
- Effects of global coordinated cyber attacks
- The penalties of cyber-attack in the First Amendment
- Why the world is experiencing increased cyber attacks
- Critical concepts of cyber attacks
- Cybercriminals and enterprises
- Role of NGOs in combating cyber terrorism
- Cyberbullying in campus
World-Class Cyber Security Thesis Ideas
- Effects of the cyber-attack on Sony in 2014
- The role of globalization in enhancing cybersecurity
- How to prevent automotive software from malicious cyber attacks
- The role of cyber technology in changing the world since the 1990s
- How the private sector is essential in combating cyber threats
- Computer infrastructure protection against cyber attacks
- Impact of social networking sites on cybersecurity
- Threats that cyber-attacks pose the national security of a country
- How cyber monitoring affects ethical and legal considerations
- Factors leading to the global nature of cyber attacks
- Analyze law enforcement agencies that deal with cyber attacks
- Evaluate cyber-crime court cases
- Evolution of the cybersecurity industry
- Cyber terrorism in the US
- Implementing adequate data protection strategies
We offer paper writing help on any cybersecurity topic. Try us now!

Home — Essay Samples — Law, Crime & Punishment — Crime — Cyber Crimes
Essays on Cyber Crimes
When it comes to writing an essay on cyber crimes, choosing the right topic is crucial. With the increasing prevalence of cyber crimes in today’s digital age, it is important to shed light on various aspects of this issue through well-researched and thought-provoking essays. By selecting the right topic, you can ensure that your essay captures the attention of your readers and provides valuable insights into the world of cyber crimes.
Choosing the right cyber crimes essay topic is important for several reasons. Firstly, it allows you to delve into a specific aspect of cyber crimes, providing in-depth analysis and understanding. Secondly, a well-chosen topic can help you demonstrate your knowledge and expertise in the field of cyber crimes. Lastly, by selecting an engaging and relevant topic, you can capture the interest of your readers and make a meaningful impact with your essay.
When it comes to choosing a cyber crimes essay topic, it is important to consider your interests, the relevance of the topic, and the availability of credible sources for research. Consider topics that are current and have a significant impact on society. Additionally, ensure that the topic is specific enough to allow for in-depth analysis, yet broad enough to provide various angles for exploration.
Recommended Cyber Crimes Essay Topics
If you are looking for essay topics related to cyber crimes, you have come to the right place. Below is a list of recommended cyber crimes essay topics, categorized for ease of selection. These topics cover a wide range of issues related to cyber crimes and provide ample opportunities for in-depth research and analysis.
Privacy and Data Protection
- The impact of data breaches on consumer privacy
- Legal and ethical considerations in data privacy
- The role of social media in compromising personal privacy
Cybersecurity and Hacking
- The evolution of hacking techniques and their impact on cybersecurity
- The role of artificial intelligence in cyber warfare
- The implications of ransomware attacks on businesses and individuals
Cyberbullying and Online Harassment
- The psychological impact of cyberbullying on adolescents
- Legal measures to combat online harassment and cyberbullying
- The role of social media platforms in addressing cyberbullying
Financial Fraud and Identity Theft
- The impact of identity theft on individuals and businesses
- The role of cryptocurrency in facilitating financial fraud
- Preventive measures for combating credit card fraud in the digital age
Cyber Warfare and State-Sponsored Attacks
- The implications of state-sponsored cyber attacks on international relations
- The role of cyber warfare in modern warfare strategies
- The legal and ethical considerations of cyber warfare
With these recommended essay topics, you can explore various aspects of cyber crimes and make a meaningful contribution to the discourse on this important issue. By selecting a topic that resonates with your interests and allows for in-depth research, you can create an impactful essay that sheds light on the complexities of cyber crimes in today’s digital landscape.
Cyber Crimes
The problem of cyber crimes, made-to-order essay as fast as you need it.
Each essay is customized to cater to your unique preferences
+ experts online
Cyber Terrorism as a Major Security Challenge
Cyber crimes and cyber security in modern world, cybercrime: theories and managing, the information age and cyber crimes, let us write you an essay from scratch.
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Online Threats: Geotagging, Email and Phishing
The cydercrime: hacking and cyberstalking, cyber crime: the meaning, types, and ways to avoid, review of types and categories of cyber crimes, get a personalized essay in under 3 hours.
Expert-written essays crafted with your exact needs in mind
Cybercrime in Banking Industry and Its Impacts on Banking Industry
Phishing attacks in social media, cybercrimes & ways to prevent them, privacy and cyber harassment, effects of cyber crime on social media, churchill and cyber attacks in russia, the role of digital forensic in solving cyber-crimes, cybercrime and society: identity theft, the potential impact of cyber crime on the economy, the detailing of cyberstalking, cyber warfare and espionage: country stance and solutions, cyber crime and internet privacy, what kind of ethical issues related to it we are facing today, overview of the common internet threats, the most damaging hackers' attacks in history, international cybercrime law: past, present, future perspectives, the differences and similarities between the real world and cyber space criminology, the reasons why we need cyber law, lack of protection as the main factor of identity theft, human rights on the digital era, relevant topics.
- Serial Killer
- Drunk Driving
- Child Abuse
- Animal Cruelty
- Domestic Violence
- Identity Theft
- Broken Windows Theory
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Bibliography
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

World-first “Cybercrime Index” ranks countries by cybercrime threat level
Following three years of intensive research, an international team of researchers have compiled the first ever ‘World Cybercrime Index’, which identifies the globe’s key cybercrime hotspots by ranking the most significant sources of cybercrime at a national level.
The Index, published today in the journal PLOS ONE , shows that a relatively small number of countries house the greatest cybercriminal threat. Russia tops the list, followed by Ukraine, China, the USA, Nigeria, and Romania. The UK comes in at number eight.

‘The research that underpins the Index will help remove the veil of anonymity around cybercriminal offenders, and we hope that it will aid the fight against the growing threat of profit-driven cybercrime,’ Dr Bruce said.
‘We now have a deeper understanding of the geography of cybercrime, and how different countries specialise in different types of cybercrime.’
‘By continuing to collect this data, we’ll be able to monitor the emergence of any new hotspots and it is possible early interventions could be made in at-risk countries before a serious cybercrime problem even develops.’
The data that underpins the Index was gathered through a survey of 92 leading cybercrime experts from around the world who are involved in cybercrime intelligence gathering and investigations. The survey asked the experts to consider five major categories of cybercrime*, nominate the countries that they consider to be the most significant sources of each of these types of cybercrime, and then rank each country according to the impact, professionalism, and technical skill of its cybercriminals.

Co-author Associate Professor Jonathan Lusthaus , from the University of Oxford’s Department of Sociology and Oxford School of Global and Area Studies, said cybercrime has largely been an invisible phenomenon because offenders often mask their physical locations by hiding behind fake profiles and technical protections.
'Due to the illicit and anonymous nature of their activities, cybercriminals cannot be easily accessed or reliably surveyed. They are actively hiding. If you try to use technical data to map their location, you will also fail, as cybercriminals bounce their attacks around internet infrastructure across the world. The best means we have to draw a picture of where these offenders are actually located is to survey those whose job it is to track these people,' Dr Lusthaus said.
Figuring out why some countries are cybercrime hotspots, and others aren't, is the next stage of the research. There are existing theories about why some countries have become hubs of cybercriminal activity - for example, that a technically skilled workforce with few employment opportunities may turn to illicit activity to make ends meet - which we'll be able to test against our global data set. Dr Miranda Bruce Department of Sociology, University of Oxford and UNSW Canberra
Co-author of the study, Professor Federico Varese from Sciences Po in France, said the World Cybercrime Index is the first step in a broader aim to understand the local dimensions of cybercrime production across the world.
‘We are hoping to expand the study so that we can determine whether national characteristics like educational attainment, internet penetration, GDP, or levels of corruption are associated with cybercrime. Many people think that cybercrime is global and fluid, but this study supports the view that, much like forms of organised crime, it is embedded within particular contexts,’ Professor Varese said.
The World Cybercrime Index has been developed as a joint partnership between the University of Oxford and UNSW and has also been funded by CRIMGOV , a European Union-supported project based at the University of Oxford and Sciences Po. The other co-authors of the study include Professor Ridhi Kashyap from the University of Oxford and Professor Nigel Phair from Monash University.
The study ‘Mapping the global geography of cybercrime with the World Cybercrime Index’ has been published in the journal PLOS ONE .
*The five major categories of cybercrime assessed by the study were:
1. Technical products/services (e.g. malware coding, botnet access, access to compromised systems, tool production).
2. Attacks and extortion (e.g. denial-of-service attacks, ransomware).
3. Data/identity theft (e.g. hacking, phishing, account compromises, credit card comprises).
4. Scams (e.g. advance fee fraud, business email compromise, online auction fraud).
5. Cashing out/money laundering (e.g. credit card fraud, money mules, illicit virtual currency platforms).
DISCOVER MORE
- Support Oxford's research
- Partner with Oxford on research
- Study at Oxford
- Research jobs at Oxford
You can view all news or browse by category
share this!
April 10, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
Most cybercriminal threats are concentrated in just a few countries, new index shows
by Public Library of Science
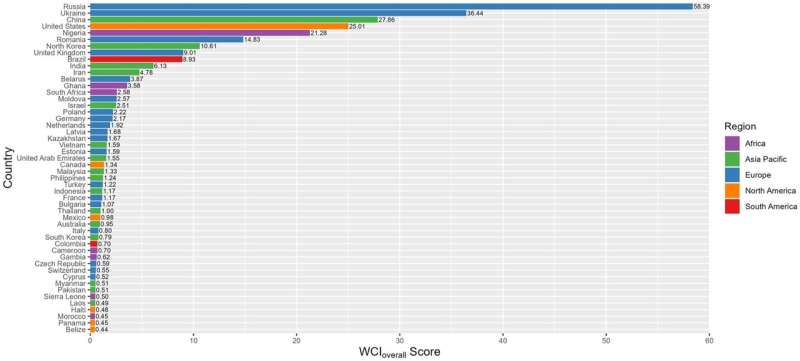
A newly developed World Cybercrime Index shows that most cybercriminal threats are concentrated in several countries, with different countries associated with distinct cybercrime types. Miranda Bruce (University of Oxford/University of New South Wales), Jonathan Lusthaus (University of Oxford), Ridhi Kashyap (University of Oxford), Nigel Phair (Monash University), and Federico Varese (Sciences Po) present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE .
Worldwide, cybercrimes are estimated to cost hundreds of millions to perhaps trillions. However, locating where offenders tend to operate poses challenges because they often use strategies to mask their locations, and legal documents capture a limited number of cases that may not be globally representative.
To help clarify, the authors surveyed leading cybercrime experts on the geographical distribution of cybercriminal threats. They developed and refined the survey through expert focus groups and pilot surveys before distributing it widely in 2021.
A total of 92 top cybercrime experts from around the world completed the survey, in which they named the countries they believed to be the biggest hubs for five cybercrime categories—technical products or services, attacks and extortion, data or identity theft, scams, and cashing out or money laundering.
The researchers used the survey results to construct the novel World Cybercrime Index, enabling comparison between countries. It suggests that cybercriminal threats are primarily concentrated in a small number of countries, with China, Russia, Ukraine, the US, Romania, and Nigeria ranking in the top 10 for each of the five categories. However, 97 countries were named by at least one expert as being a hub for a particular category.
Different countries were associated more often with distinct categories. For instance, cybercrimes related to technical products or services were the top category in China, data or identity theft in the US, and attacks and extortion in Iran.
The World Cybercrime Index could aid future cybercrime research, and it could help target preventive efforts tailored to specific hubs. However, the authors also note the need to address their study's limitations, such as by including a larger, more globally representative pool of experts, reducing variation in participants' interpretations of survey questions, and addressing the sometimes blurred lines between profit-driven cybercrime and state-protected actions.
The authors add, "Profit-driven cybercrime, often seen as a fluid and global type of organized crime, actually has a strong local dimension. The World Cybercrime Index shows that 97 countries are significant cybercrime hubs, but most cybercrime is produced in just six of them."
Journal information: PLoS ONE
Provided by Public Library of Science
Explore further
Feedback to editors
Researchers create nanomembrane to increase reaction rate in chemical production
7 minutes ago
Researchers reveal a hidden trait in Mycobacterium genomes governing stress adaptation
9 minutes ago
Scientists experimentally observe current-driven antiskyrmion sliding
34 minutes ago
Amazonia's fire crises: Emergency fire bans insufficient, strategic action needed before next burning season
36 minutes ago
Researchers realize hydrogen formation by contact electrification of water microdroplets and its regulation

Scientists construct organo-phosphatic shells of brachiopods
38 minutes ago

Instinct for 'fight or flight' may be much older than we thought
40 minutes ago
Capturing DNA origami folding with a new dynamic model
44 minutes ago

Researchers investigate three star-forming regions, identify hundreds young stellar objects
55 minutes ago

New device harnesses sweat power for fitness trackers
Relevant physicsforums posts, cover songs versus the original track, which ones are better.
6 hours ago
Interesting anecdotes in the history of physics?
21 hours ago
Biographies, history, personal accounts
Apr 16, 2024
Who is your favorite Jazz musician and what is your favorite song?
Esoteric music recommendations, for ww2 buffs.
Apr 15, 2024
More from Art, Music, History, and Linguistics
Related Stories

World-first 'Cybercrime Index' ranks countries by cybercrime threat level
Apr 10, 2024

Global cost of cybercrime topped $6 trillion in 2021: defence firm
May 10, 2022

Warning on rising cybercrime during the pandemic
Jul 21, 2021

Evidence suggests that the U.S. loses hundreds of billions to cybercrime, possibly as much as 1% to 4% of GDP annually
May 28, 2020

Researchers reveal hidden fortunes and surprising underestimations in cybercrime revenue
Dec 16, 2023

World cybercrime shifts to state-backed hackers: Russian group
Oct 9, 2018
Recommended for you

Researchers find lower grades given to students with surnames that come later in alphabetical order
18 hours ago

Study finds world economy already committed to income reduction of 19% due to climate change
23 hours ago

Study reveals how humanity could unite to address global challenges

Building footprints could help identify neighborhood sociodemographic traits

Are the world's cultures growing apart?
First languages of North America traced back to two very different language groups from Siberia
Apr 9, 2024
Let us know if there is a problem with our content
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
Advertisement
Research trends in cybercrime victimization during 2010–2020: a bibliometric analysis
- Review Paper
- Published: 06 January 2022
- Volume 2 , article number 4 , ( 2022 )
Cite this article
- Huong Thi Ngoc Ho 1 &
- Hai Thanh Luong ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2421-9149 2
10k Accesses
10 Citations
1 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Research on cybercrime victimization is relatively diversified; however, no bibliometric study has been found to introduce the panorama of this subject. The current study aims to address this research gap by performing a bibliometric analysis of 387 Social Science Citation Index articles relevant to cybercrime victimization from Web of Science database during the period of 2010–2020. The purpose of the article is to examine the research trend and distribution of publications by five main fields, including time, productive authors, prominent sources, active institutions, and leading countries/regions. Furthermore, this study aims to determine the global collaborations and current gaps in research of cybercrime victimization. Findings indicated the decidedly upward trend of publications in the given period. The USA and its authors and institutions were likely to connect widely and took a crucial position in research of cybercrime victimization. Cyberbullying was identified as the most concerned issue over the years and cyber interpersonal crimes had the large number of research comparing to cyber-dependent crimes. Future research is suggested to concern more about sample of the elder and collect data in different countries which are not only European countries or the USA. Cross-nation research in less popular continents in research map was recommended to be conducted more. This paper contributed an overview of scholarly status of cybercrime victimization through statistical evidence and visual findings; assisted researchers to optimize their own research direction; and supported authors and institutions to build strategies for research collaboration.
Similar content being viewed by others

Research synthesis of cybercrime laws and COVID-19 in Indonesia: lessons for developed and developing countries
Agus Nugroho & An An Chandrawulan

The Nuts and Bolts of the India-Abusive Fake Government of Telangana: Cyberpolicing Against Online Sedition

Cybercrime in the Russian Federation: Criminological and Criminal Law Analysis
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
To date, the debate of cybercrime definition has been controversial which is considered as one of the five areas of cyber criminology (Ngo and Jaishankar 2017 ; Drew 2020 ). Footnote 1 Several terms are used to illustrate ‘cybercrime’, such as ‘high-tech crime’ (Insa 2007 ), ‘computer crime’ (Choi 2008 ; Skinner and Fream 1997 ), ‘digital crime’ (Gogolin 2010 ), or ‘virtual crime’ (Brenner 2001 ). ‘Cybercrime’, however, has been the most popular in the public parlance (Wall 2004 ). A propensity considers crime directly against computer as cybercrime, while other tendency asserts that any crime committed via internet or related to a computer is cybercrime (Marsh and Melville 2008 ; Wall 2004 ). Hence, there is a distinction between ‘true cybercrime’ or ‘high-tech’ cybercrime and ‘low-tech’ cybercrime (Wagen and Pieters 2020 ). Council of Europe defines ‘any criminal offense committed against or with the help of a computer network’ as cybercrime (Abdullah and Jahan 2020 , p. 90). Despite different approaches, cybercrime generally includes not only new types of crimes which have just occurred after the invention of computer and internet (Holt and Bossler 2014 ; Drew 2020 ) but also traditional types of crimes which took the advantages of information communication technology (ICT) as vehicle for illegal behaviors (Luong 2021 ; Nguyen and Luong 2020 ; Luong et al. 2019 ). Two main cybercrime categories identified, respectively, are cyber-dependent crime (hacking, malware, denial of service attacks) and cyber-enable crime (phishing, identity theft, cyber romance scam, online shopping fraud). Nevertheless, there are several different classifications of cybercrime such as cybercrime against certain individuals, groups of individuals, computer networks, computer users, critical infrastructures, virtual entities (Wagen and Pieters 2020 ); cyber-trespass, cyber-deceptions, cyber-pornography, and cyber-violence (Wall 2001 ).
Due to the common prevalence of cybercrime, the increasing threats of cybercrime victimization are obviously serious. Cybercrime victimization has become a crucial research subfield in recent years (Wagen and Pieters 2020 ). It is difficult to differ “forms of online victimization” and “acts that actually constitute a crime”, then it is usual for researchers to focus less on perspective of criminal law and consider any negative experiences online as cybercrime (Näsi et al. 2015 , p. 2). It was likely to lead to practical gaps between theory and practice in terms of investigating the nexus of offender and victims on cyberspace. In the light of literature review, numerous specific aspects of cybercrime victimization were investigated by questionnaire surveys or interview survey such as the prevalence of cybercrime victimization (Näsi et al. 2015 ; Whitty and Buchanan 2012 ); causes and predictors of cybercrime victimization (Abdullah and Jahan 2020 ; Algarni et al. 2017 ; Ilievski 2016 ; Jahankhani 2013 ; Kirwan et al. 2018 ; Näsi et al. 2015 ; Reyns et al. 2019 ; Saad et al. 2018 ); and the relationship between social networking sites (SNS) and cybercrime victimization (Das and Sahoo 2011 ; Algarni et al. 2017 ; Benson et al. 2015 ; Seng et al. 2018 ). To some extent, therefore, the current study examines cybercrime victimization in the large scale, referring to any negative experiences on cyberspace or computer systems. Nevertheless, no bibliometric analysis was found to show the research trend and general landscape of this domain.
Bibliometric is a kind of statistical analysis which uses information in a database to provide the depth insight into the development of a specified area (Leung et al. 2017 ). The present study aims to address this research gap by providing a bibliometric review of the relevant SSCI articles in WoS database during the period of 2010–2020. The pattern of publications, the productivity of main elements (authors, journals, institutions, and countries/regions), statistic of citations, classification of key terms, research gaps, and other collaborations will be presented and discussed in section four and five after reviewing literatures and presenting our methods conducted. This article contributes an overview of research achievements pertaining to cybercrime victimization in the given period through statistical evidence and visual findings; assists researchers to perceive clearly about the key positions in research maps of this field, and obtain more suggestions to develop their own research direction.
Literature review
- Cybercrime victimization
Cybercrime victimization may exist in two levels including institutional and individual level (Näsi et al. 2015 ). For the former, victim is governments, institutions, or corporations, whereas for the latter, victim is a specific individual (Näsi et al. 2015 ). A wide range of previous studies concerned about individual level of victim and applied Lifestyle Exposure Theory (LET), Routine Activity Theory (RAT) and General Theory of Crime to explain cybercrime victimization (Choi 2008 ; Holt and Bossler 2009 ; Ngo and Paternoster 2011 ). Basing on these theories, situational and individual factors were supposed to play an important role in understanding cybercrime victimization (Choi 2008 ; Van Wilsem 2013 ). However, there was another argument that situational and individual factors did not predict cybercrime victimization (Ngo and Paternoster 2011 ; Wagen and Pieters 2020 ). Overall, most of those studies just focused only one distinctive kind of cybercrime such as computer viruses, malware infection, phishing, cyberbullying, online harassment, online defamation, identity theft, cyberstalking, online sexual solicitation, cyber romance scams or online consumer fraud. Referring to results of the prior research, some supported for the applicability of mentioned theories but other did not share the same viewpoint (Leukfeldt and Yar 2016 ). It was hard to evaluate the effect of LET or RAT for explanation of cybercrime victimization because the nature of examined cybercrime were different (Leukfeldt and Holt 2020 ; Leukfeldt and Yar 2016 ).
Previous research determined that cybercrime victimization was more common in younger group compared to older group because the young is the most active online user (Näsi et al. 2015 ; Oksanen and Keipi 2013 ) and males tended to become victims of cybercrime more than females in general (Näsi et al. 2015 ). However, findings might be different in research which concerned specific types of cybercrime. Women were more likely to be victims of the online romance scam (Whitty and Buchanan 2012 ) and sexual harassment (Näsi et al. 2015 ), while men recorded higher rate of victimization of cyber-violence and defamation. Other demographic factors were also examined such as living areas (Näsi et al. 2015 ), education (Oksanen and Keipi 2013 ; Saad et al. 2018 ) and economic status (Oksanen and Keipi 2013 ; Saad et al. 2018 ). Furthermore, several prior studies focus on the association of psychological factors and cybercrime victimization, including awareness and perception (Ariola et al. 2018 ; Saridakis et al. 2016 ), personality (Kirwan et al. 2018 ; Orchard et al. 2014 ; Parrish et al. 2009 ), self-control (Ilievski 2016 ; Ngo and Paternoster 2011 ; Reyns et al. 2019 ), fear of cybercrime (Lee et al. 2019 ), online behaviors (Al-Nemrat and Benzaïd 2015 ; Saridakis et al. 2016 ). Psychological factors were assumed to have effects on cybercrime victimization at distinctive levels.
Another perspective which was much concerned by researchers was the relationship between cybercrime victimization and SNS. SNS has been a fertile land for cybercriminals due to the plenty of personal information shared, lack of guard, the availability of communication channels (Seng et al. 2018 ), and the networked nature of social media (Vishwanath 2015 ). When users disclosed their personal information, they turned themselves into prey for predators in cyberspace. Seng et al. ( 2018 ) did research to understand impact factors on user’s decision to react and click on suspicious posts or links on Facebook. The findings indicated that participants’ interactions with shared contents on SNS were affected by their relationship with author of those contents; they often ignored the location of shared posts; several warning signals of suspicious posts were not concerned. Additionally, Vishwanath ( 2015 ) indicated factors that led users to fall victims on the SNS; Algarni et al. ( 2017 ) investigated users’ susceptibility to social engineering victimization on Facebook; and Kirwan et al. ( 2018 ) determined risk factors resulting in falling victims of SNS scam.
Bibliometric of cybercrime victimization
“Bibliometric” is a term which was coined by Pritchard in 1969 and a useful method which structures, quantifies bibliometric information to indicate the factors constituting the scientific research within a specific field (Serafin et al. 2019 ). Bibliometric method relies on some basic types of analysis, namely co-authorship, co-occurrence, citation, co-citation, and bibliographic coupling. This method was employed to various research domains such as criminology (Alalehto and Persson 2013 ), criminal law (Jamshed et al. 2020 ), marketing communication (Kim et al. 2019 ), social media (Chen et al. 2019 ; Gan and Wang 2014 ; Leung et al. 2017 ; Li et al. 2017 ; You et al. 2014 ; Zyoud et al. 2018 ), communication (Feeley 2008 ), advertising (Pasadeos 1985 ), education (Martí-Parreño et al. 2016 ).
Also, there are more and more scholars preferring to use bibliometric analysis on cyberspace-related subject such as: cyber behaviors (Serafin et al. 2019 ), cybersecurity (Cojocaru and Cojocaru 2019 ), cyber parental control (Altarturi et al. 2020 ). Serafin et al. ( 2019 ) accessed the Scopus database to perform a bibliometric analysis of cyber behavior. All documents were published by four journals: Cyberpsychology, Behavior and Social Networking (ISSN: 21522723), Cyberpsychology and Behavior (ISSN: 10949313) , Computers in Human Behavior (ISSN: 07475632) and Human–Computer Interaction (ISSN: 07370024), in duration of 2000–2018. Findings indicated the use of Facebook and other social media was the most common in research during this period, while psychological matters were less concerned (Serafin et al. 2019 ). Cojocaru and Cojocaru ( 2019 ) examined the research status of cybersecurity in the Republic of Moldavo, then made a comparison with the Eastern Europe countries’ status. This study employed bibliometric analysis of publications from three data sources: National Bibliometric Instrument (database from Republic of Moldavo), Scopus Elsevier and WoS. The Republic of Moldavo had the moderate number of scientific publications on cybersecurity; Russian Federation, Poland, Romania, Czech Republic, and Ukraine were the leading countries in Eastern Europe area (Cojocaru and Cojocaru 2019 ). Altarturi et al. ( 2020 ) was interested in bibliometric analysis of cyber parental control, basing on publications between 2000 and 2019 in Scopus and WoS. This research identified some most used keywords including ‘cyberbullying’, ‘bullying’, ‘adolescents’ and ‘adolescence’, showing their crucial position in the domain of cyber parental control (Altarturi et al. 2020 ). ‘Cyber victimization’ and ‘victimization’ were also mentioned as the common keywords by Altarturi et al. ( 2020 ). Prior research much focus on how to protect children from cyberbullying. Besides, four online threats for children were determined: content, contact, conduct and commercial threats (Altarturi et al. 2020 ).
Generally, it has been recorded several published bibliometric analyses of cyber-related issues but remained a lack of bibliometric research targeting cybercrime victimization. Thus, the present study attempts to fill this gap, reviewing the achievements of existed publications as well as updating the research trend in this field.
In detail, our current study aims to address four research questions (RQs):
What is overall distribution of publication based on year, institutions and countries, sources, and authors in cybercrime victimization?
Which are the topmost cited publications in terms of cybercrime victimization?
Who are the top co-authorships among authors, institutions, and countries in research cybercrime victimization?
What are top keywords, co-occurrences and research gaps in the field of cybercrime victimization?
Data collection procedure
Currently, among specific approaches in cybercrime’s fileds, WoS is “one of the largest and comprehensive bibliographic data covering multidisciplinary areas” (Zyoud et al. 2018 , p. 2). This paper retrieved data from the SSCI by searching publications of cybercrime victimization on WoS database to examine the growth of publication; top keywords; popular topics; research gaps; and top influential authors, institutions, countries, and journals in the academic community.
This paper employed Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) for data collection procedure. For timeline, we preferred to search between 2010 and 2020 on the WoS system with two main reasons. First, when the official update of the 2009 PRISMA Statement had ready upgraded with the specific guidelines and stable techniques, we consider beginning since 2010 that is timely to test. Secondly, although there are several publications from the early of 2021 to collect by the WoS, its updated articles will be continued until the end of the year. Therefore, we only searched until the end of 2020 to ensure the full updates.
To identify publications on cybercrime victimization, the study accessed WoS and used two keywords for searching: ‘cybercrime victimization’ or ‘cyber victimization’ after testing and looking for some terminology-related topics. Accordingly, the paper applied a combination of many other searching terms besides two selected words such as “online victimization”, “victim of cybercrime”, “phishing victimization”, “online romance victimization”, “cyberstalking victim”, “interpersonal cybercrime victimization”, or “sexting victimization”, the results, however, were not really appropriate. A lot of papers did not contain search keywords in their titles, abstracts, keywords and were not relavant to study topic. After searching with many different terms and comparing the results, the current study selected the two search terms for the most appropriate articles. The query result consisted of 962 documents. Basing on the result from preliminary searching, retrieved publications were refined automatically on WoS by criteria of timespan, document types, language, research areas, and WoS Index as presented in Table 1 . Accordingly, the criteria for automatic filter process were basic information of an articles and classified clearly in WoS system so the results reached high accuracy. The refined results are 473 articles.
After automatic filters, file of data was converted to Microsoft Excel 2016 for screening. The present study examined titles and abstracts of 473 articles to assess the eligibility of each publication according to the relevance with given topic. There are 387 articles are eligible,while 86 irrelevant publications were excluded.
Data analysis
Prior to data analysis, the raw data were cleaned in Microsoft Excel 2016. Different forms of the same author’s name were corrected for consistency, for example “Zhou, Zong-Kui” and “Zhou Zongkui”, “Van Cleemput, Katrien” and “Van Cleemput, K.”, “Williams, Matthew L.” and “Williams, Matthew”. Similarly, different keywords (single/plural or synonyms) used for the same concept were identified and standardized such as “victimization” and “victimisation”; “adolescent” and “adolescents”; “cyber bullying”, “cyber-bullying” and “cyberbullying”; “routine activity theory” and “routine activities theory”.
The data were processed by Microsoft Excel 2016 and VOS Viewer version 1.6.16; then it was analyzed according to three main aspects. First, descriptive statistic provided evidence for yearly distribution and growth trend of publications, frequency counts of citations, the influential authors, the predominant journals, the top institutions and countries/territories, most-cited publications. Second, co-authorship and co-occurrence analysis were constructed and visualized by VOS Viewer version 1.6.16 to explore the network collaborations. Finally, the current study also investigated research topics through content analysis of keywords. The authors’ keywords were classified into 15 themes, including: #1 cybercrime; #2 sample and demographic factors; #3 location; #4 theory; #5 methodology; #6 technology, platforms and related others; #7 psychology and mental health; #8 physical health; #9 family; #10 school; #11 society; #12 crimes and deviant behaviors; #13 victim; #14 prevention and intervention; and #15 others. Besides, the study also added other keywords from titles and abstracts basing on these themes, then indicated aspects examined in previous research.
In this section, all findings corresponding with four research questions identified at the ouset of this study would be illustrated (Fig. 1 ).
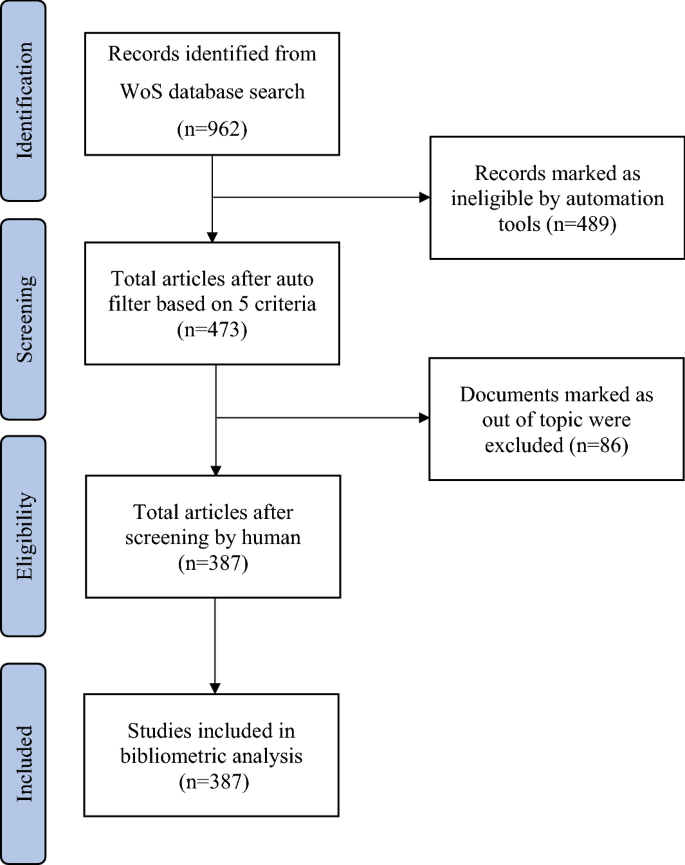
PRISMA diagram depicts data collection from WoS database
Distribution of publication
Distribution by year, institutions and countries.
Basing on retrieved data, it was witnessed an increasing trend of articles relevant to cybercrime victimization in SSCI list during the time of 2010–2020 but it had slight fluctuations in each year as shown in Fig. 2 . The total number of articles over this time was 387 items, which were broken into two sub-periods: 2010–2014 and 2015–2020. It is evident that the latter period demonstrated the superiority of the rate of articles (79.33%) compared to the previous period (20.67%). The yearly quantity of publications in this research subject was fewer than forty before 2015. Research of cybercrime victimization reached a noticeable development in 2016 with over fifty publications, remained the large number of publications in the following years and peaked at 60 items in 2018.
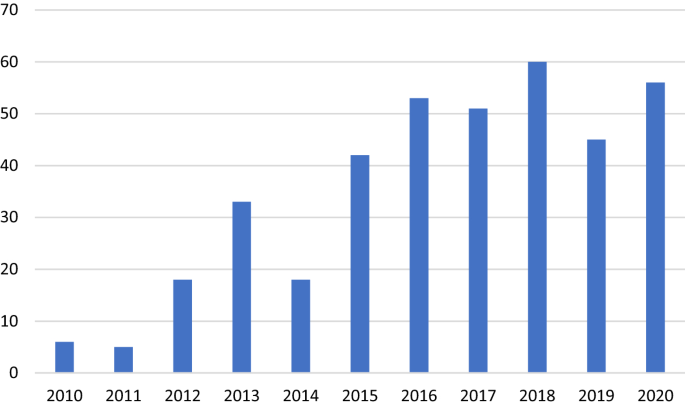
Annual distribution of publications
Distribution by institutions and countries
Table 2 shows the top contributing institutions according to the quantity of publications related to cybercrime victimization. Of the top institutions, four universities were from the USA, two ones were from Spain, two institutions were from Australia and the rest ones were from Czech Republic, Belgium, Greece, and Austria. Specifically, Masaryk University (17 documents) became the most productive publishing institution, closely followed by Michigan State University (16 documents). The third and fourth places were University of Antwerp (13 documents) and Weber State University (10 documents). Accordingly, the institutions from The USA and Europe occupied the vast majority.
In Table 2 , University of Seville (total citations: 495, average citations: 70.71) ranked first and University of Cordoba (total citations: 484, average citations: 60.50) stayed at the second place in both total citations and average citations.
Referring to distribution of publications by countries, there were 45 countries in database contributing to the literature of cybercrime victimization. The USA recorded the highest quantity of papers, creating an overwhelming difference from other countries (159 documents) as illustrated in Fig. 3 . Of the top productive countries, eight European countries which achieved total of 173 publications were England (39 documents), Spain (34 documents), Germany (22 documents), Netherlands (18 documents), Italy (17 documents) and Czech Republic (17 documents), Belgium (14 documents), Greece (12 documents). Australia ranked the fourth point (32 documents), followed by Canada (30 documents). One Asian country which came out seventh place, at the same position with Netherlands was China (18 documents).
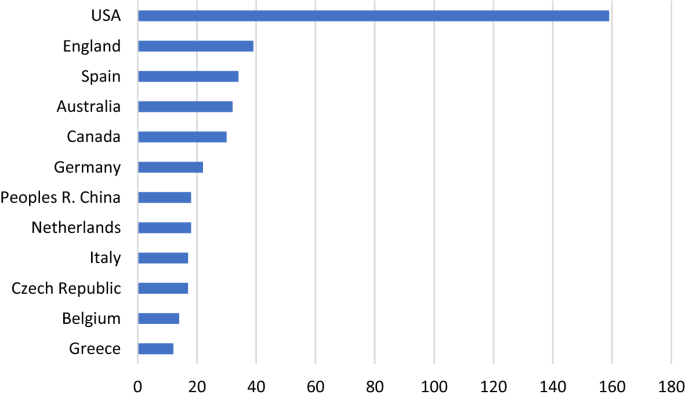
Top productive countries based on the number of publications
Distribution by sources
Table 3 enumerates the top leading journals in the number of publications relevant to cybercrime victimization. The total publications of the first ranking journal— Computers in Human Behavior were 56, over twice as higher as the second raking journal— Cyberpsychology, Behavior and Social Networking (24 articles). Most of these journals have had long publishing history, starting their publications before 2000. Only three journals launched after 2000, consisting of Journal of School Violence (2002), Cyberpsychology: Journal of Psychosocial Research on Cyberspace (2007) and Frontiers in Psychology (2010). Besides, it is remarked that one third of the top journals focuses on youth related issues: Journal of Youth and Adolescence , Journal of Adolescence, School Psychology International and Journal of School Violence .
In Table 3 , relating to total citations, Computers in Human Behavior remained the first position with 2055 citations. Journal of Youth and Adolescence had total 1285 citations, ranked second and followed by Aggressive Behavior with 661 citations. In terms of average citations per documents, an article of Journal of Youth and Adolescence was cited 67.63 times in average, much higher than average citations of one in Computers in Human Behavior (36.70 times). The other journals which achieved the high number of average citations per document were School Psychology International (59.00 times), Journal of Adolescence (44.83 times) and Aggressive Behavior (44.07 times).
Distribution by authors
Table 4 displays ten productive authors based on article count; total citations of each author and their average citations per document are also included. Michelle F. Wright from Pennsylvania State University ranked first with twenty publications, twice as higher as the second positions, Thomas J. Holt (10 articles) from Michigan State University and Bradford W. Reyns (10 articles) from Weber State University. Rosario Ortega-Ruiz from University of Cordoba stayed at the third place in terms of total publications but the first place in aspect of total citations (483 citations) and the average citations (60.38 times).
Of the most productive authors based on total publications, there were three authors from universities in the USA; one from the university in Canada (Brett Holfeld); the others were from institutions in Euro, including Spain (Rosario Ortega-Ruiz), Greece (Constantinos M. Kokkinos) and Belgium (Heidi Vandebosch), Netherlands (Rutger Leukfeldt) and Austria (Takuya Yanagida and Christiane Spiel).
Most-cited publications
The most-cited literature items are displayed in Table 5 . The article which recorded the highest number of citations was ‘Psychological, Physical, and Academic Correlates of Cyberbullying and Traditional Bullying’ (442 citations) by Robin M. Kowalski et al. published in Journal of Adolescent Health , 2013. Seven of ten most-cited articles were about cyberbullying; focused on youth population; made comparisons between cyberbullying and traditional bullying; analyzed the impact of several factors such as psychological, physical, academic factors or use of Internet; discussed on preventing strategies. The other publications studied victimization of cyberstalking and cyber dating abuse. All most-cited articles were from 2015 and earlier.
Of the top productive authors, only Bradford W. Reyns had an article appeared in the group of most-cited publications. His article ‘Being Pursued Online: Applying Cyberlifestyle-Routine Activities Theory to Cyberstalking Victimization’ (2011) was cited 172 times.
- Co-authorship analysis
“Scientific collaboration is a complex social phenomenon in research” (Glänzel and Schubert 2006 , p. 257) and becomes the increasing trend in individual, institutional and national levels. In bibliometric analysis, it is common to assess the productivity and international collaboration of research; identify key leading researchers, institutions, or countries (E Fonseca et al. 2016 ) as well as potential collaborators in a specific scientific area (Romero and Portillo-Salido 2019 ) by co-authorship analysis which constructs networks of authors and countries (Eck and Waltman 2020 ).
This section analyses international collaboration relevant to research of cybercrime victimization among authors, institutions, and countries during 2010–2020 through visualization of VOS Viewer software.
Collaboration between authors
Referring to the threshold of choose in this analysis, minimum number of documents of author is three and there were 80 authors for final results. Figure 4 illustrates the relationships between 80 scientists who study in subject of cybercrime victimization during 2010–2020. It shows several big groups of researchers (Wright’s group, Vandebosch’s group, or Holt’s group), while numerous authors had limited or no connections to others (Sheri Bauman, Michelle K. Demaray or Jennifer D. Shapka).
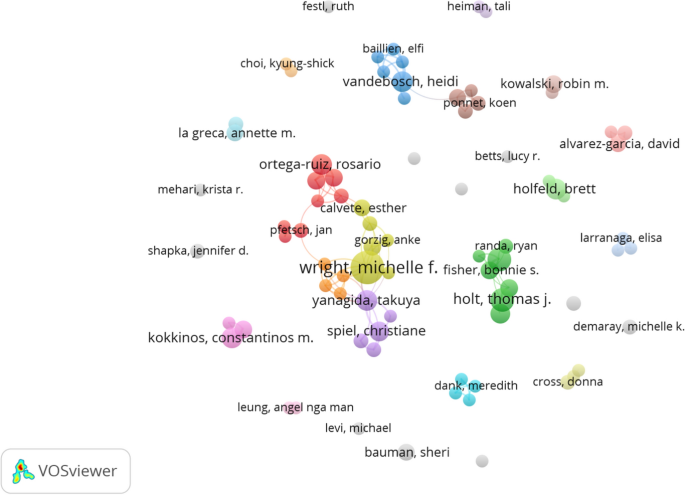
Collaboration among authors via network visualization (threshold three articles for an author, displayed 80 authors)
Figure 5 displayed a significant network containing 23 authors who were active in collaboration in detail. The displayed items in Fig. 5 are divided into five clusters coded with distinctive colors, including red, green, blue, yellow, and purple. Each author item was represented by their label and a circle; the size of label and circle are depended on the weight of the item, measured by the total publications (Eck and Waltman 2020 ). The thickness of lines depends on the strength of collaboration (Eck and Waltman 2020 ).
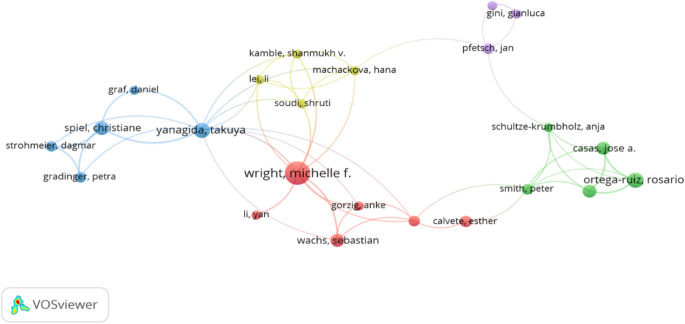
Collaboration among authors via network visualization (threshold three articles for an author, displayed 23 authors)
The most significant cluster was red one which is comprised of six researchers: Michelle F. Wright, Sebastian Wachs, Yan Li, Anke Gorzig, Manuel Gamez-Guadix and Esther Calvete. The remarked author for the red cluster was Michelle F. Wright whose value of total link strength is 24. She had the strongest links with Sebastian Wachs; closely link with Yan Li, Anke Gorzig, Manuel Gamez-Guadix and collaborated with authors of yellow cluster, including Shanmukh V. Kamble, Li Lei, Hana Machackova, Shruti Soudi as well as Takuya Yanagida of blue cluster. Michelle F. Wright who obtained the largest number of published articles based on criteria of this study made various connections with other scholars who were from many different institutions in the world. This is also an effective way to achieve more publications.
Takuya Yanagida was the biggest node for the blue cluster including Petra Gradinger, Daniel Graf, Christiane Spiel, Dagmar Strohmeier. Total link strength for Takuya Yanagida was 28; twelve connections. It is observed that Takuya Yanagida’ s research collaboration is definitely active. Besides, other research groups showed limited collaborations comparing with the red and blue ones.
Collaboration between institutions
The connections among 156 institutions which published at least two documents per one are shown in Fig. 6 . Interestingly, there is obvious connections among several distinctive clusters which were coded in color of light steel blue, orange, purple, steel blue, green, red, yellow, light red, dark turquoise, light blue, brown and light green. These clusters created a big chain of connected institutions and were in the center of the figure, while other smaller clusters or unlinked bubbles (gray color) were distributed in two sides. The biggest chain consisted of most of productive institutions such as Masaryk University, Michigan State University, University of Antwerp, Weber State University, University of Cordoba, Edith Cowan University, University of Cincinnati, University of Victoria, University of Vienna, and University of Seville.
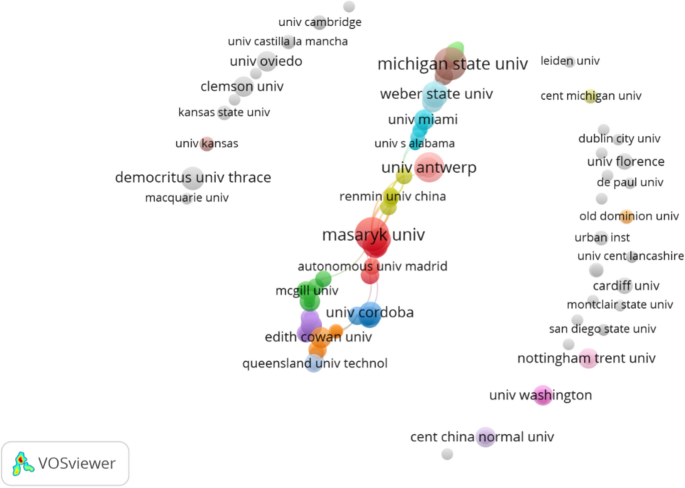
Collaboration among institutions via network visualization (threshold two articles for an institution, 156 institutions were displayed)
Light steel blue and orange clusters presented connections among organizations from Australia. Light green included institutions from Netherland, while turquoise and light blue consisted of institutions from the USA. Yellow cluster was remarked by the various collaborations among institutions from China and Hong Kong Special Administrative Region (Renmin University of China and South China Normal University, University of Hong Kong, the Hong Kong Polytechnic University and the Chinese University of Hong Kong), the USA (University of Virginia), Cyprus (Eastern Mediterranean University), Japan (Shizuoka University), India (Karnataka University) and Austria (University Applied Sciences Upper Austria). Central China Normal University is another Chinese institution which appeared in Fig. 5 , linking with Ministry of Education of the People’s Republic of China, Suny Stony Brook and University of Memphis from the USA.
Masaryk University and Michigan State University demonstrated their productivity in both the quantity of publications and the collaboration network. They were active in research collaboration, reaching twelve and eleven links, respectively, with different institutions, but focused much on networking with institutions in the USA and Europe.
Collaboration between countries
The collaboration among 45 countries which published at least one SSCI documents of cybercrime victimization during the given period was examined in VOS Viewer but just 42 items were displayed via overlay visualization. Figure 7 depicts the international collaborations among significant countries. The USA is the biggest bubble due to its biggest number of documents and shows connections with 26 countries/regions in Euro, Asia, Australia, Middle East. Excepting European countries, England collaborate with the USA, Australia, South Korea, Japan, Thailand, Singapore, Sri Lanka, and Colombia. Spain and Germany almost focus on research network within Euro. China has the strongest tie with the USA, link with Australia, Germany, Czech Republic, Austria, Cyprus and Turkey, Japan, Indian, Vietnam.
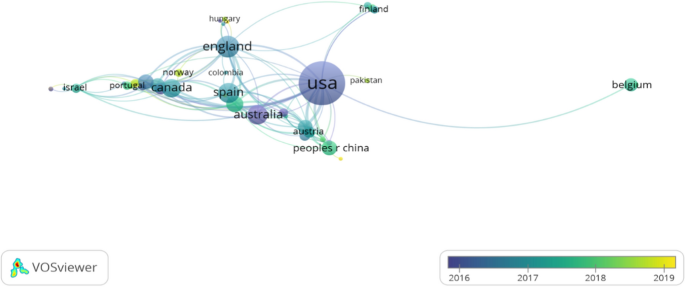
Collaboration among countries via overlay visualization
Color bar in Fig. 7 is determined by the average publication year of each country and the color of circles based on it. It is unsurprised that the USA, Australia, England, or Spain shows much research experience in this field and maintain the large number of publications steadily. Interestingly, although the average publication year of South Korea or Cyprus was earlier than other countries (purple color), their quantities of documents were moderate. The new nodes (yellow circles) in the map included Vietnam, Norway, Pakistan, Ireland, Scotland, Switzerland.
Keywords and co-occurrence
The present paper examined the related themes and contents in research of cybercrime victimization during 2010–2020 through collecting author keywords, adding several keywords from tiles and abstracts. Besides, this study also conducted co-occurrence analysis of author keywords to show the relationships among these keywords.
The keywords were collected and categorized into 15 themes in Table 6 , including cybercrime; sample and demographic factors; location; theory; methodology; technology, platform, and related others; psychology and mental health; physical health; family; school; society; crimes and other deviant behaviors; victim; prevention and intervention; and others.
In the theme of cybercrime, there were numerous types of cybercrimes such as cyberbullying, cyber aggression, cyberstalking, cyber harassment, sextortion and other cyber dating crimes, cyber fraud, identity theft, phishing, hacking, malware, or ransomware. Generally, the frequency of interpersonal cybercrimes or cyber-enable crimes was much higher than cyber-dependent crimes. Cyberbullying was the most common cybercrime in research.
Relating to sample and demographic factors, there were sample of children, adolescent, adults, and the elder who were divided into more detail levels in each research; however, adolescent was the most significant sample. Besides, demographic factor of gender received a remarked concern from scholars.
It is usual that most of the research were carried out in one country, in popular it was the USA, Spain, Germany, England, Australia, Canada or Netherland but sometimes the new ones were published such as Chile, Vietnam, Thailand or Singapore. It was witnessed that some studies showed data collected from a group of countries such as two countries (Canada and the United State), three countries (Israel, Litva, Luxembourg), four countries (the USA, the UK, Germany, and Finland), or six Europe countries (Spain, Germany, Italy, Poland, the United Kingdom and Greece).
A wide range of theories were applied in this research focusing on criminological and psychological theories such as Routine Activities Theory, Lifestyle—Routine Activities Theory, General Strain Theory, the Theory of Reasoned Action or Self-control Theory.
Table 6 indicated a lot of different research methods covering various perspective of cybercrime victimization: systematic review, questionnaire survey, interview, experiment, mix method, longitudinal study, or cross-national research; many kinds of analysis such as meta-analysis, social network analysis, latent class analysis, confirmatory factor analysis; and a wide range of measurement scales which were appropriate for each variable.
Topic of cybercrime victimization had connections with some main aspects of technology (information and communication technologies, internet, social media or technology related activities), psychology (self-esteem, fear, attitude, personality, psychological problems, empathy, perceptions or emotion), physical health, family (parents), school (peers, school climate), society (norms, culture, social bonds), victim, other crimes (violence, substance use), prevention and intervention.
Co-occurrence analysis was performed with keywords suggested by authors and the minimum number of occurrences per word is seven. The result showed 36 frequent keywords which clustered into five clusters as illustrated in Fig. 8 .
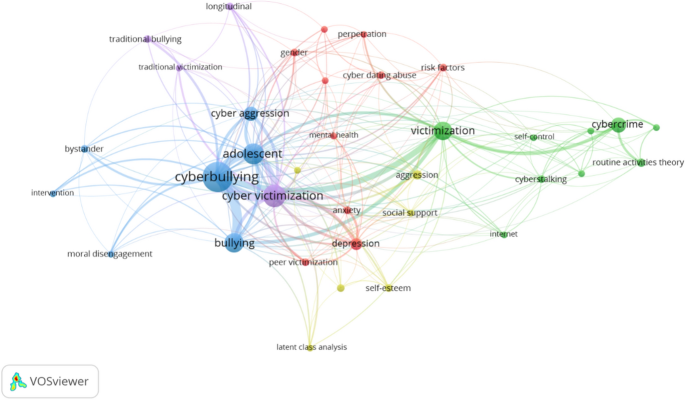
Co-occurrence between author keywords via network visualization (the minimum number of occurrences per word is seven, 36 keywords were displayed)
Figure 8 illustrates some main issues which were concerned in subject of cybercrime victimization, as well as the relationship among them. Fifteen most frequent keywords were presented by big bubbles, including: ‘cyberbullying’ (174 times), ‘cyber victimization’ (90 times), ‘adolescent’ (79 times), ‘bullying’ (66 times), ‘victimization’ (56 times), ‘cybercrime’ (40 times), ‘cyber aggression’ (37 times), ‘depression’ (23 times), ‘aggression’ (14 times), ‘routine activities theory’ (13 times), ‘cyberstalking’ (11 times), ‘gender’ (11 times), ‘longitudinal’ (10 times), ‘peer victimization’ (10 times) and ‘self-esteem’ (10 times).
‘Cyberbullying’ linked with many other keywords, demonstrating the various perspectives in research of this topic. The thick lines which linked ‘cyberbullying’ and ‘bullying’, ‘adolescent’, ‘cyber victimization’, ‘victimization’ showed the strong connections between them; there were close relationship between ‘cyber aggression’, ‘bystander”, ‘self-esteem’ or ‘moral disengagement’ and ‘cyberbullying’.
‘Cybercrime’ had strong links with ‘victimization’, ‘routine activities theory’. In Fig. 8 , the types of cybercrime which occurred at least seven times were: cyberbullying, cyber aggression, hacking, cyberstalking, and cyber dating abuse.
The increasing trend over the years reveals the increasing concern of scholarly community on this field, especially in the boom of information technology and other communication devices and the upward trend in research of cyberspace-related issues (Altarturi et al. 2020 ; Leung et al. 2017 ; Serafin et al. 2019 ). It predicts the growth of cybercrime victimization research in future.
Psychology was the more popular research areas in database, defeating criminology penology. As part of the ‘human factors of cybercrime’, human decision-making based on their psychological perspectives plays as a hot topic in cyber criminology (Leukfeldt and Holt 2020 ). Then, it is observed that journals in psychology field was more prevalent in top of productive sources. Besides, journal Computers in Human Behavior ranked first in total publications, but Journal of Youth and Adolescence ranked higher place in the average citations per document. Generally, top ten journals having highest number of publications on cybercrime victimization are highly qualified ones and at least 10 years in publishing industry.
The USA demonstrated its leading position in the studied domain in terms of total publications as well as the various collaborations with other countries. The publications of the USA occupied much higher than the second and third countries: England and Spain. It is not difficult to explain for this fact due to the impressive productivity of institutions and authors from the USA. A third of top twelve productive institutions were from the USA. Three leading positions of top ten productive authors based on document count were from institutions of the USA, number one was Michelle F. Wright; others were Thomas J. Holt and Bradford W. Reyns.
Furthermore, these authors also participated in significant research groups and become the important nodes in those clusters. The most noticeable authors in co-authors network were Michelle F. Wright. The US institutions also had strong links in research network. The USA was likely to be open in collaboration with numerous countries from different continents in the world. It was assessed to be a crucial partner for others in the international co-publication network (Glänzel and Schubert 2006 ).
As opposed to the USA, most of European countries prefer developing research network within Europe and had a limited collaboration with other areas. Australia, the USA, or Japan was in a small group of countries which had connections with European ones. Nevertheless, European countries still showed great contributions for research of cybercrime victimization and remained stable links in international collaboration. The prominent authors from Euro are Rosario Ortega-Ruiz, Constantinos M. Kokkinos or Rutger Leukfeldt.
It is obvious that the limited number of publications from Asia, Middle East, Africa, or other areas resulted in the uncomprehensive picture of studied subject. For example, in the Southeast Asia, Malaysia and Vietnam lacked the leading authors with their empirical studies to review and examine the nature of cybercrimes, though they are facing to practical challenges and potential threats in the cyberspace (Lusthaus 2020a , b ). The present study indicated that Vietnam, Ireland, or Norway was the new nodes and links in research network.
Several nations which had a small number of publications such as Vietnam, Thailand, Sri Lanka, or Chile started their journey of international publications. It is undeniable that globalization and the context of global village (McLuhan 1992 ) requires more understanding about the whole nations and areas. Conversely, each country or area also desires to engage in international publications. Therefore, new nodes and clusters are expected to increase and expand.
The findings indicated that cyberbullying was the most popular topic on research of cybercrime victimization over the given period. Over a half of most-cited publications was focus on cyberbullying. Additionally, ‘cyberbullying’ was the most frequent author keyword which co-occurred widely with distinctive keywords such as ‘victimization’, ‘adolescents’, ‘bullying’, ‘social media’, ‘internet’, ‘peer victimization’ or ‘anxiety’.
By reviewing keywords, several research gaps were indicated. Research samples were lack of population of the children and elders, while adolescent and youth were frequent samples of numerous studies. Although young people are most active in cyberspace, it is still necessary to understand other populations. Meanwhile, the elderly was assumed to use information and communication technologies to improve their quality of life (Tsai et al. 2015 ), their vulnerability to the risk of cybercrime victimization did not reduce. Those older women were most vulnerable to phishing attacks (Lin et al. 2019 ; Oliveira et al. 2017 ). Similarly, the population of children with distinctive attributes has become a suitable target for cybercriminals, particularly given the context of increasing online learning due to Covid-19 pandemic impacts. These practical gaps should be prioritized to focus on research for looking the suitable solutions in the future. Besides, a vast majority of research were conducted in the scope of one country; some studies collected cross-national data, but the number of these studies were moderate and focused much on developed countries. There are rooms for studies to cover several countries in Southeast Asia or South Africa.
Furthermore, although victims may be both individuals and organizations, most of research concentrated much more on individuals rather than organizations or companies. Wagen and Pieters ( 2020 ) indicated that victims include both human and non-human. They conducted research covering cases of ransomware victimization, Bonet victimization and high-tech virtual theft victimization and applying Actor-Network Theory to provide new aspect which did not aim to individual victims. The number of this kind of research, however, was very limited. Additionally, excepting cyberbullying and cyber aggression were occupied the outstanding quantity of research, other types of cybercrime, especially, e-whoring, or social media-related cybercrime should still be studied more in the future.
Another interesting topic is the impact of family on cybercrime victimization. By reviewing keyword, it is clear that the previous studies aimed to sample of adolescent, hence, there are many keywords linking with parents such as ‘parent-adolescent communication’, ‘parent-adolescent information sharing’, ‘parental mediation’, ‘parental monitoring of cyber behavior’, ‘parental style’. As mentioned above, it is necessary to research more on sample of the elder, then, it is also essential to find out how family members affect the elder’s cybercrime victimization.
It is a big challenge to deal with problems of cybercrime victimization because cybercrime forms become different daily (Näsi et al. 2015 ). Numerous researchers engage in understanding this phenomenon from various angles. The current bibliometric study assessed the scholarly status on cybercrime victimization during 2010–2020 by retrieving SSCI articles from WoS database. There is no study that applied bibliometric method to research on the examined subject. Hence, this paper firstly contributed statistical evidence and visualized findings to literature of cybercrime victimization.
Statistical description was applied to measure the productive authors, institutions, countries/regions, sources, and most-cited documents, mainly based on publication and citation count. The international collaborations among authors, institutions, and countries were assessed by co-authors, while the network of author keywords was created by co-occurrence analysis. The overall scholarly status of cybercrime victimization research was drawn clearly and objectively. The research trend, popular issues and current gaps were reviewed, providing numerous suggestions for policymakers, scholars, and practitioners about cyber-related victimization (Pickering and Byrne 2014 ). Accordingly, the paper indicated the most prevalent authors, most-cited papers but also made summary of contributions of previous research as well as identified research gaps. First, this article supports for PhD candidates or early-career researchers concerning about cybercrime victimization. Identifying the leading authors, remarked journals, or influencing articles, gaps related to a specific research topic is important and useful task for new researchers to start their academic journey. Although this information is relatively simple, it takes time and is not easy for newcomers to find out, especially for ones in poor or developing areas which have limited conditions and opportunities to access international academic sources. Thus, the findings in the current paper provided for them basic but necessary answers to conduct the first step in research. Secondly, by indicating research gaps in relevance to sample, narrow topics or scope of country, the paper suggests future study fulfilling them to complete the field of cybercrime victimization, especial calling for publications from countries which has had a modest position in global research map. Science requires the balance and diversity, not just focusing on a few developed countries or areas. Finally, the present study assists researchers and institutions to determined strategy and potential partners for their development of research collaborations. It not only improve productivity of publication but also create an open and dynamic environment for the development of academic field.
Despite mentioned contributions, this study still has unavoidable limitations. The present paper just focused on SSCI articles from WoS database during 2010–2020. It did not cover other sources of databases that are known such as Scopus, ScienceDirect, or Springer; other types of documents; the whole time; or articles in other languages excepting English. Hence it may not cover all data of examined subject in fact. Moreover, this bibliometric study just performed co-authorship and co-occurrence analysis. The rest of analysis such as citation, co-citation and bibliographic coupling have not been conducted. Research in the future is recommended to perform these kinds of assessment to fill this gap. To visualize the collaboration among authors, institutions, countries, or network of keywords, this study used VOS Viewer software and saved the screenshots as illustrations. Therefore, not all items were displayed in the screenshot figures.
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
In the ‘commemorating a decade in existence of the International Journal of Cyber Criminoogy’, Ngo and Jaishankar ( 2017 ) called for further research with focusing on five main areas in the Cyber Criminiology, including (1) defining and classifying cybercrime, (2) assessing the prevalence, nature, and trends of cybercrime, (3) advancing the field of cyber criminology, (4) documenting best practices in combating and preventing cybercrime, and (5) cybercrime and privacy issues.
Abdullah ATM, Jahan I (2020) Causes of cybercrime victimization: a systematic literature review. Int J Res Rev 7(5):89–98
Google Scholar
Al-Nemrat A, Benzaïd C (2015) Cybercrime profiling: Decision-tree induction, examining perceptions of internet risk and cybercrime victimisation. In: Proceedings—14th IEEE International Conference on Trust, Security and Privacy in Computing and Communications, TrustCom 2015, vol 1, pp 1380–1385. https://doi.org/10.1109/Trustcom.2015.534
Alalehto TI, Persson O (2013) The Sutherland tradition in criminology: a bibliometric story. Crim Justice Stud 26(1):1–18
Article Google Scholar
Algarni A, Xu Y, Chan T (2017) An empirical study on the susceptibility to social engineering in social networking sites: the case of Facebook. Eur J Inf Syst 26(6):661–687
Altarturi HHM, Saadoon M, Anuar NB (2020) Cyber parental control: a bibliometric study. Child Youth Serv Rev. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2020.105134
Ariola B, Laure ERF, Perol ML, Talines PJ (2018) Cybercrime awareness and perception among Students of Saint Michael College of Caraga. SMCC Higher Educ Res J 1(1):1. https://doi.org/10.18868/cje.01.060119.03
Benson V, Saridakis G, Tennakoon H (2015) Purpose of social networking use and victimisation: are there any differences between university students and those not in HE? Comput Hum Behav 51:867–872
Brenner SW (2001) Is there such a thing as “rough”? Calif Crim Law Rev 4(1):348–349. https://doi.org/10.3109/09637487909143344
Chen X, Wang S, Tang Y, Hao T (2019) A bibliometric analysis of event detection in social media. Online Inf Rev 43(1):29–52. https://doi.org/10.1108/OIR-03-2018-0068
Choi K (2008) Computer Crime Victimization and Integrated Theory: an empirical assessment. Int J Cyber Criminol 2(1):308–333
Cojocaru I, Cojocaru I (2019) A bibliomentric analysis of cybersecurity research papers in Eastern Europe: case study from the Republic of Moldova. In: Central and Eastern European E|Dem and E|Gov Days, pp 151–161
Das B, Sahoo JS (2011) Social networking sites—a critical analysis of its impact on personal and social life. Int J Bus Soc Sci 2(14):222–228
Drew JM (2020) A study of cybercrime victimisation and prevention: exploring the use of online crime prevention behaviours and strategies. J Criminol Res Policy Pract 6(1):17–33. https://doi.org/10.1108/JCRPP-12-2019-0070
E Fonseca B, Sampaio, de Araújo Fonseca MV, Zicker F (2016). Co-authorship network analysis in health research: method and potential use. Health Res Policy Syst 14(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12961-016-0104-5
Feeley TH (2008) A bibliometric analysis of communication journals from 2002 to 2005. Hum Commun Res 34:505–520
Gan C, Wang W (2014) A bibliometric analysis of social media research from the perspective of library and information science. IFIP Adv Inf Commun Technol 445:23–32. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-45526-5_3
Glänzel W, Schubert A (2006) Analysing scientific networks through co-authorship. Handb Quant Sci Technol Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/1-4020-2755-9_12
Gogolin G (2010) The digital crime tsunami. Digit Investig 7(1–2):3–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diin.2010.07.001
Holt TJ, Bossler AM (2009) Examining the applicability of lifestyle-routine activities theory for cybercrime victimization. Deviant Behav 30(1):1–25. https://doi.org/10.1080/01639620701876577
Holt TJ, Bossler AM (2014) An assessment of the current state of cybercrime scholarship. Deviant Behav 35(1):20–40. https://doi.org/10.1080/01639625.2013.822209
Ilievski A (2016) An explanation of the cybercrime victimisation: self-control and lifestile/routine activity theory. Innov Issues Approaches Soc Sci 9(1):30–47. https://doi.org/10.12959/issn.1855-0541.iiass-2016-no1-art02
Insa F (2007) The Admissibility of Electronic Evidence in Court (A.E.E.C.): Fighting against high-tech crime—results of a European study. J Digital Forensic Pract 1(4):285–289. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567280701418049
Jahankhani H (2013) Developing a model to reduce and/or prevent cybercrime victimization among the user individuals. Strategic Intell Manag. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-407191-9.00021-1
Jamshed J, Naeem S, Ahmad K (2020) Analysis of Criminal Law Literature: a bibliometric study from 2010–2019. Library Philos Pract
Kim J, Kang S, Lee KH (2019) Evolution of digital marketing communication: Bibliometric analysis and networs visualization from key articles. J Bus Res
Kirwan GH, Fullwood C, Rooney B (2018) Risk factors for social networking site scam victimization among Malaysian students. Cyberpsychol Behav Soc Netw 21(2):123–128. https://doi.org/10.1089/cyber.2016.0714
Lee S-S, Choi KS, Choi S, Englander E (2019) A test of structural model for fear of crime in social networking sites A test of structural model for fear of crime in social networking sites. Int J Cybersecur Intell Cybercrime 2(2):5–22
Leukfeldt R, Holt T (eds) (2020) The human factor of cybercrime. Routledge, New York
Leukfeldt ER, Yar M (2016) Applying routine activity theory to cybercrime: a theoretical and empirical analysis. Deviant Behav 37(3):263–280. https://doi.org/10.1080/01639625.2015.1012409
Leung XY, Sun J, Bai B (2017) Bibliometrics of social media research: a co-citation and co-word analysis. Int J Hosp Manag 66:35–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhm.2017.06.012
Li Q, Wei W, Xiong N, Feng D, Ye X, Jiang Y (2017) Social media research, human behavior, and sustainable society. Sustainability 9(3):384. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9030384
Lin T, Capecci DE, Ellis DM, Rocha HA, Dommaraju S, Oliveira DS, Ebner NC (2019) Susceptibility to spear-phishing emails: effects of internet user demographics and email content. ACM Trans Comput-Hum Interact 26(5):1–28. https://doi.org/10.1145/3336141
Luong TH (2021) Prevent and combat sexual assault and exploitation of children on cyberspace in Vietnam: situations, challenges, and responses. In: Elshenraki H (ed) Combating the exploitation of children in cyberspace: emerging research and opportunities. IGI Global, Hershey, pp 68–94
Chapter Google Scholar
Luong HT, Phan HD, Van Chu D, Nguyen VQ, Le KT, Hoang LT (2019) Understanding cybercrimes in Vietnam: from leading-point provisions to legislative system and law enforcement. Int J Cyber Criminol 13(2):290–308. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3700724
Lusthaus J (2020a) Cybercrime in Southeast Asia: Combating a Global Threat Locally. Retrieved from Canberra, Australia: https://s3-ap-southeast-2.amazonaws.com/ad-aspi/202005/Cybercrime%20in%20Southeast%20Asia.pdf?naTsKQp2jtSPYsWpSo4YmE1sVBNv_exJ
Lusthaus J (2020b) Modelling cybercrime development: the case of Vietnam. In: Leukfeldt R, Holt T (eds) The human factor of cybercrime. Routledge, New York, pp 240–257
Marsh I, Melville G (2008) Crime justice and the media. Crime Justice Med. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203894781
Martí-Parreño J, Méndez-Ibáñezt E, Alonso-Arroyo A (2016) The use of gamification in education: a bibliometric and text mining analysis. J Comput Assist Learn
McLuhan M (1992) The Global Village: Transformations in World Life and Media in the 21st Century (Communication and Society). Oxford University Press, Oxford
Näsi M, Oksanen A, Keipi T, Räsänen P (2015) Cybercrime victimization among young people: a multi-nation study. J Scand Stud Criminol Crime Prev. https://doi.org/10.1080/14043858.2015.1046640
Ngo F, Jaishankar K (2017) Commemorating a decade in existence of the international journal of cyber criminology: a research agenda to advance the scholarship on cyber crime. Int J Cyber Criminol 11(1):1–9
Ngo F, Paternoster R (2011) Cybercrime victimization: an examination of individual and situational level factors. Int J Cyber Criminol 5(1):773
Nguyen VT, Luong TH (2020) The structure of cybercrime networks: transnational computer fraud in Vietnam. J Crime Justice. https://doi.org/10.1080/0735648X.2020.1818605
Oksanen A, Keipi T (2013) Young people as victims of crime on the internet: a population-based study in Finland. Vulnerable Child Youth Stud 8(4):298–309
Oliveira D, Rocha H, Yang H, Ellis D, Dommaraju S, Muradoglu M, Weir D, Soliman A, Lin T, Ebner N (2017) Dissecting spear phishing emails for older vs young adults: on the interplay of weapons of influence and life domains in predicting susceptibility to phishing. In: Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems—Proceedings, 2017-May, 6412–6424. https://doi.org/10.1145/3025453.3025831
Orchard LJ, Fullwood C, Galbraith N, Morris N (2014) Individual differences as predictors of social networking. J Comput-Mediat Commun 19(3):388–402. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcc4.12068
Parrish JL Jr, Bailey JL, Courtney JF (2009) A personality based model for determining susceptibility to phishing attacks. University of Arkansas, Little Rock, pp 285–296
Pasadeos Y (1985) A bibliometric study of advertising citations. J Advert 14(4):52–59
Pickering C, Byrne J (2014) The benefits of publishing systematic quantitative literature reviews for PhD candidates and other early-career researchers. Higher Educ Res Devel ISSN 33(3):534–548
Reyns BW, Fisher BS, Bossler AM, Holt TJ (2019) Opportunity and Self-control: do they predict multiple forms of online victimization? Am J Crim Justice 44(1):63–82. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12103-018-9447-5
Romero L, Portillo-Salido E (2019) Trends in sigma-1 receptor research: a 25-year bibliometric analysis. Front Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.00564
Saad ME, Huda Sheikh Abdullah SN, Murah MZ (2018) Cyber romance scam victimization analysis using Routine Activity Theory versus apriori algorithm. Int J Adv Comput Sci Appl 9(12):479–485. https://doi.org/10.14569/IJACSA.2018.091267
Saridakis G, Benson V, Ezingeard JN, Tennakoon H (2016) Individual information security, user behaviour and cyber victimisation: an empirical study of social networking users. Technol Forecast Soc Change 102:320–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2015.08.012
Seng S, Wright M, Al-Ameen MN (2018) Understanding users’ decision of clicking on posts in facebook with implications for phishing. Workshop on Technology and Consumer Protection (ConPro 18), May, 1–6
Serafin MJ, Garcia-Vargas GR, García-Chivita MDP, Caicedo MI, Correra JC (2019) Cyberbehavior: a bibliometric analysis. Annu Rev Cyber Ther Telemed 17:17–24. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/prfcw
Skinner WF, Fream AM (1997) A social learning theory analysis of computer crime among college students. J Res Crime Delinq 34(4):495–518. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022427897034004005
Tsai H, Yi S, Shillair R, Cotten SR, Winstead V, Yost E (2015) Getting grandma online: are tablets the answer for increasing digital inclusion for older adults in the US? Educ Gerontol 41(10):695–709. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601277.2015.1048165
van Eck NJ, Waltman L (2020) Manual for VOSviewer version 1.6.16
Van Wilsem J (2013) “Bought it, but never got it” assessing risk factors for online consumer fraud victimization. Eur Sociol Rev 29(2):168–178. https://doi.org/10.1093/esr/jcr053
van der Wagen W, Pieters W (2020) The hybrid victim: re-conceptualizing high-tech cyber victimization through actor-network theory. Eur J Criminol 17(4):480–497. https://doi.org/10.1177/1477370818812016
Vishwanath A (2015) Habitual Facebook use and its impact on getting deceived on social media. J Comput-Mediat Commun 20(1):83–98. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcc4.12100
Wall D (2001) Crime and the Internet: Cybercrime and cyberfears, 1st edn. Routledge, London
Wall D (2004) What are cybercrimes? Crim Justice Matters 58(1):20–21
Whitty MT, Buchanan T (2012) The online romance scam: a serious cybercrime. Cyberpsychol Behav Soc Netw 15(3):181–183. https://doi.org/10.1089/cyber.2011.0352
You GR, Sun X, Sun M, Wang JM, Chen YW (2014) Bibliometric and social network analysis of the SoS field. In: Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on System of Systems Engineering: The Socio-Technical Perspective, SoSE 2014, 13–18. https://doi.org/10.1109/SYSOSE.2014.6892456
Zyoud SH, Sweileh WM, Awang R, Al-Jabi SW (2018) Global trends in research related to social media in psychology: Mapping and bibliometric analysis. Int J Ment Health Syst 12(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13033-018-0182-6
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Journalism and Communication, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China
Huong Thi Ngoc Ho
School of Global, Urban and Social Studies, RMIT University, Melbourne, Australia
Hai Thanh Luong
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Hai Thanh Luong .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Ho, H.T.N., Luong, H.T. Research trends in cybercrime victimization during 2010–2020: a bibliometric analysis. SN Soc Sci 2 , 4 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43545-021-00305-4
Download citation
Received : 13 September 2021
Accepted : 15 December 2021
Published : 06 January 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s43545-021-00305-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Bibliometric analysis
- Web of science
- Co-occurrence analysis
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
share this!
April 10, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
World-first 'Cybercrime Index' ranks countries by cybercrime threat level
by University of Oxford

Following three years of intensive research, an international team of researchers have compiled the first ever "World Cybercrime Index," which identifies the globe's key cybercrime hotspots by ranking the most significant sources of cybercrime at a national level.
The Index, published in the journal PLOS ONE , shows that a relatively small number of countries house the greatest cybercriminal threat. Russia tops the list, followed by Ukraine, China, the U.S., Nigeria, and Romania. The UK comes in at number eight.
Co-author of the study, Dr. Miranda Bruce from the University of Oxford and UNSW Canberra said the study will enable the public and private sectors to focus their resources on key cybercrime hubs and spend less time and funds on cybercrime countermeasures in countries where the problem is not as significant.
"The research that underpins the Index will help remove the veil of anonymity around cybercriminal offenders, and we hope that it will aid the fight against the growing threat of profit-driven cybercrime," Dr. Bruce said.
"We now have a deeper understanding of the geography of cybercrime, and how different countries specialize in different types of cybercrime."
"By continuing to collect this data, we'll be able to monitor the emergence of any new hotspots and it is possible early interventions could be made in at-risk countries before a serious cybercrime problem even develops."

The data that underpins the Index was gathered through a survey of 92 leading cybercrime experts from around the world who are involved in cybercrime intelligence gathering and investigations. The survey asked the experts to consider five major categories of cybercrime, nominate the countries that they consider to be the most significant sources of each of these types of cybercrime, and then rank each country according to the impact, professionalism, and technical skill of its cybercriminals.
Co-author Associate Professor Jonathan Lusthaus, from the University of Oxford's Department of Sociology and Oxford School of Global and Area Studies, said cybercrime has largely been an invisible phenomenon because offenders often mask their physical locations by hiding behind fake profiles and technical protections.
"Due to the illicit and anonymous nature of their activities, cybercriminals cannot be easily accessed or reliably surveyed. They are actively hiding. If you try to use technical data to map their location, you will also fail, as cybercriminals bounce their attacks around internet infrastructure across the world. The best means we have to draw a picture of where these offenders are actually located is to survey those whose job it is to track these people," Dr. Lusthaus said.
Co-author of the study, Professor Federico Varese from Sciences Po in France, said the World Cybercrime Index is the first step in a broader aim to understand the local dimensions of cybercrime production across the world.
"We are hoping to expand the study so that we can determine whether national characteristics like educational attainment , internet penetration, GDP or levels of corruption are associated with cybercrime. Many people think that cybercrime is global and fluid, but this study supports the view that, much like forms of organized crime, it is embedded within particular contexts," Professor Varese said.
The World Cybercrime Index has been developed as a joint partnership between the University of Oxford and UNSW.
Explore further
Feedback to editors

Octopus inspires new suction mechanism for robots
42 minutes ago

Proof-of-concept nanogenerator turns CO₂ into sustainable power

Using sim-to-real reinforcement learning to train robots to do simple tasks in broad environments

Engineers design spider-like robot that may be used to explore caves on Mars

How 3D printers can give robots a soft touch
17 hours ago

Clearing the air: Wind farms more land efficient than previously thought

National roaming can increase resilience of Dutch mobile networks
19 hours ago

Researchers use machine learning to create a fabric-based touch sensor

Retro-reflectors could help future cities keep their cool
22 hours ago

New material for hydrogen storage confines this clean yet troublesome fuel
Related stories, latest research suggests cybercriminals are not as anonymous as we think.
Aug 7, 2017
Cybercrime money-launders busted by European police, FBI
Oct 15, 2020

Researchers reveal hidden fortunes and surprising underestimations in cybercrime revenue
Dec 16, 2023

EU police agency calls for better action against cybercrime
Sep 27, 2017

Evidence suggests that the U.S. loses hundreds of billions to cybercrime, possibly as much as 1% to 4% of GDP annually
May 28, 2020

Global cost of cybercrime topped $6 trillion in 2021: defence firm
May 10, 2022
Recommended for you
Researchers find a faster, better way to prevent an AI chatbot from giving toxic responses
Apr 10, 2024

Protecting art and passwords with biochemistry
Apr 8, 2024

New privacy-preserving robotic cameras obscure images beyond human recognition
Apr 4, 2024

Keeping your data from Apple is harder than expected, finds study
Apr 3, 2024
Vulnerability in virtual reality systems identified
Mar 25, 2024

Researchers' approach may protect quantum computers from attacks
Mar 7, 2024
Let us know if there is a problem with our content
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Tech Xplore in any form.
Your Privacy
This site uses cookies to assist with navigation, analyse your use of our services, collect data for ads personalisation and provide content from third parties. By using our site, you acknowledge that you have read and understand our Privacy Policy and Terms of Use .
E-mail newsletter
New research reveals the globe's cybercrime hotspots

A new study from researchers in Australia and the UK has mapped out the sources of cybercrime around the world.
Researchers measured a country's scale of cyberattacks based on categories including impact, professionalism, technical skill, money laundering, and identity theft to deliver a score out of 100.
Australia, a comparative minnow in the world of big-time hacking, only came in at 34th with a score of 0.95.
Here are the top 10 on the groundbreaking new World Cybercrime Index.
- Cyber Security
- Cyber Attack

India was 10th with a score of 6.13.
Co-author of the study, Dr Miranda Bruce from UNSW Canberra and the University of Oxford, said the study will enable the public and private sectors to focus their resources on key cybercrime hubs and spend less time and funds on cybercrime countermeasures in countries where the problem is not as significant.

Brazil's score of 8.93 saw it come in ninth.
The data for the Index was gathered through a survey of 92 leading cybercrime experts from around the world who are involved in cybercrime intelligence gathering and investigations.

8. United Kingdom
The UK was eighth with a score of 9.01.
The survey asked the experts to consider five major categories of cybercrime, nominate the countries that they consider to be the most significant sources of each of these types of cybercrime, and then rank each country according to the impact, professionalism, and technical skill of its cybercriminals.

7. North Korea
North Korea made the list at seventh, with a score of 10.61.
Another co-author of the study, Associate Professor Jonathan Lusthaus from the University of Oxford in the UK, said cybercrime has largely been an invisible phenomenon because offenders often mask their physical locations by hiding behind fake profiles and highly technical protections.

Romania was sixth with a score of 14.83.
"The best means we have to draw a picture of where these offenders are actually located is to survey those whose job it is to track these people," Lusthaus said.

Nigeria, with a score of 21.28, was the only African country inside the top 10 at fifth spot.

The US scored 25.01 to come in fourth.

China, with 27.86 per cent, made the top three.

War-torn Ukraine was the second most prolific nation for cybercrime with a score of 36.44.

And their invaders, Russia, outstripped the lot.
Russia scored 58.39 on the Index, well ahead of all others.
The data has been published in the journal PLOS One .
Russia and Ukraine Top Inaugural World Cybercrime Index

Kevin Poireault
Reporter , Infosecurity Magazine
- Follow @Kpoireault
- Connect on LinkedIn
Russia, Ukraine and China harbor the greatest cybercriminal threat, according to the first World Cybercrime Index (WCI).
This world-first cybercrime ranking is the result of work by an international team of academic researchers who surveyed 92 leading cybercrime experts and analyzed the results following a scientific methodology.
The research project for the World Cybercrime Index took four years to complete.
The scientific paper backing the Index, titled Mapping the Global Geography of Cybercrime with the World Cybercrime Index , was in the PLOS ONE journal published on April 10, 2024.
Five Types of Cybercrime
The survey asked the 92 experts to consider five types of financially driven cybercrime, name the countries they consider each of these types of cybercrime to originate from and then rank them according to the impact, professionalism, and technical skill of its cybercriminals.
The five categories of cybercrime are:
- Technical products/services (e.g. malware coding, botnet access, access to compromised systems, tool production)
- Attacks and extortion (e.g. DDoS attacks, ransomware)
- Data/identity theft (e.g. hacking, phishing, account compromises, credit card comprises)
- Scams (e.g. advance fee fraud, business email compromise, online auction fraud)
- Cashing out/money laundering (e.g. credit card fraud, money mules, illicit virtual currency platforms)
The researchers attributed a score to every nominated country in each category and then calculated an overall score, called the WCI score, that was used to make the general ranking. A description of the calculations used can be found in the scientific paper.
Top 20 Countries with the Highest Cybercrime Threat Levels
Russia comes as the country where most cybercrime originates, with a WCI score of 58.39, followed by Ukraine (36.44) and China (27.84).
The US (25.01) and Nigeria (21.28) also make the top five. The UK, India, North Korea and Brazil all make the top ten.

WCI Updates and Upgrades Are “Likely”
The World Cybercrime Index was developed as a joint partnership between the University of Oxford and the University of New South Wales in Australia and funded by CRIMGOV, an EU-supported project based at the University of Oxford and Sciences Po Paris.
Jonathan Lusthaus, associate professor at the University of Oxford’s Department of Sociology and Oxford School of Global and Area Studies, is one of the study's five co-authors.
During a press conference, Lusthaus highlighted the need to unveil where cybercrime originates, which has largely been an invisible phenomenon because offenders often mask their physical locations by hiding behind fake profiles and technical protections.
“If you try to use technical data to map their location, you will also fail, as cybercriminals bounce their attacks around internet infrastructure across the world. The best means we have to draw a picture of where these offenders are actually located is to survey those whose job it is to track these people,” he said.
According to another co-author, Federico Varese, a professor at Sciences Po in Paris, the World Cybercrime Index will likely be updated and upgraded in the future.
He said the researchers are hoping to expand the study in order to determine whether national characteristics like educational attainment, internet penetration, GDP, or levels of corruption are associated with cybercrime.
“Many people think that cybercrime is global and fluid, but this study supports the view that, much like forms of organized crime, it is embedded within particular contexts,” Varese said.
One specific metric the index used, the Technicality score (T-score), characterized how skilled cybercriminals based the top 15 countries those countries are.
“For instance, Russia and Ukraine are highly technical cybercrime hubs, whereas Nigerian cybercriminals are engaged in less technical forms of cybercrime,” read the paper.
“But for countries that lie close to the centre (0), the story is more complex. Some may specialize in cybercrime types with middling technical complexity (e.g., Data/identity theft). Others may specialize in both high- and low-tech crimes,” it continued.
You may also like
Operation cronos: who are the lockbit admins, us intelligence predicts upcoming cyber threats for 2024, interview: microsoft shares its experience of migrating data in times of cyber warfare, russian it “brain drain” decentralizes cybercrime, ncsc: uk organizations can learn from ukraine's impressive cyber defenses, what’s hot on infosecurity magazine.
- Editor's Choice
Insider Threats Surge 14% Annually as Cost-of-Living Crisis Bites
Cybersecurity pros urge us congress to help nist restore nvd operation, fbi warns of massive toll services smishing scam, how to backup and restore database in sql server, how to open and view ost files without outlook, banning ransomware payments will do more harm than good, palo alto networks warns about critical zero-day in pan-os, women experience exclusion twice as often as men in cybersecurity, cisa urges immediate credential reset after sisense breach, windows: new 'batbadbut' rust vulnerability given highest severity score, is mfa enough strategies for next-level identity security in 2024, beyond passwords: securing the digital age with mfa, 2fa, and passwordless authentication, disinformation defense: protecting businesses from the new wave of ai-powered cyber threats, adapting to tomorrow's threat landscape: ai's role in cybersecurity and security operations in 2024, untangling the web: navigating third-party risk in a hyperconnected world, bouncing back: building organizational resilience in the face of cyber-attack, infosecurity magazine spring online summit 2024: day one, infosecurity magazine spring online summit 2024: day two, russia’s midnight blizzard accesses microsoft source code, i-soon github leak: what cyber experts learned about chinese cyber espionage, lockbit takedown: what you need to know about operation cronos, women in cybersecurity at infosecurity europe 2024.
Cybercrime Classification and Measurement Meeting 3
The open sessions will include presentations by the FBI.
Is it a Closed Session event?
Some sessions are open and some sessions are closed
Anthony Mann
(202) 334-3266
Responsible Staff Officers
- Melissa Chiu
- Daniel Cork
Additional Project Staff

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Excellent Research Topics on Cybercrime. Write about the importance of cybercrime management. Explain the history of cybercrime. Discuss the effects of cybercrime on the Internet economy. Talk about the cyberattack on Sony Pictures in 2014. Explain how technology has influenced the evolution of cybercrime.
116 CyberCrime Topics & Essay Samples. Updated: Mar 2nd, 2024. 9 min. If you are writing a cybercrime essay, our team prepared this article just for you. Here, you will find 115 unique topics for any type of paper. We will write. a custom essay specifically for you by our professional experts. 809 writers online.
Here, we present 117 cybercrime essay topic ideas and examples to help inspire your writing. The rise of ransomware attacks: Causes, consequences, and preventive measures. Cyberbullying: Analyzing its psychological impact on victims and strategies for prevention. Social engineering attacks: Understanding the methods and mitigating the risks.
204 Research Topics on Technology & Computer Science. A List of 580 Interesting Research Topics [2024 Edition] A List of 179 Problem Solution Essay Topics & Questions. 193 Interesting Proposal Essay Topics and Ideas. 226 Research Topics on Criminal Justice & Criminology.
These essay examples and topics on Cybercrime were carefully selected by the StudyCorgi editorial team. They meet our highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, and fact accuracy. Please ensure you properly reference the materials if you're using them to write your assignment. This essay topic collection was updated on ...
Introduction. To date, the debate of cybercrime definition has been controversial which is considered as one of the five areas of cyber criminology (Ngo and Jaishankar 2017; Drew 2020). 1 Several terms are used to illustrate 'cybercrime', such as 'high-tech crime' (Insa 2007), 'computer crime' (Choi 2008; Skinner and Fream 1997), 'digital crime' (Gogolin 2010), or 'virtual ...
Dr. Tamar Berenblum is the research director of the The Federmann Cyber Security Center - Cyber Law Program, Faculty of Law, the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel, and the co-chair of the European Society of Criminology (ESC) Working Group on Cybercrime. Tamar is also a Post-Doc Research Fellow at the Netherlands Institute for the Study of Crime and Law Enforcement (NSCR), Netherlands ...
Cybersecurity-Related Research Topics. Developing machine learning algorithms for early detection of cybersecurity threats. The use of artificial intelligence in optimizing network traffic for telecommunication companies. Investigating the impact of quantum computing on existing encryption methods.
Cybercrime, or the use of computer technology or online networks to commit crimes, ranges from fraud and identity theft to threats and intimidation. Cybercrime and its many manifestations has clearly increased over the past 20 years. For example, cybercrime costs increased from approximately $3 trillion in 2015 to more than $6 trillion in 2021 ...
Reviews. "In Researching Cybercrimes: Methodologies, Ethics, and Critical Approaches Lavorgna and Holt bring together a wealth of expertise addressing the challenges and opportunities for conducting criminological research in a digital society. This collection is an invaluable resource for both early and established scholars of cybercrime, or ...
Cybercriminals are creating their own AI chatbots to support hacking and scam users. Oli Buckley, University of East Anglia and Jason R.C. Nurse, University of Kent. Like many technologies, AI can ...
Cybercrime is estimated to have cost the global economy just under USD 1 trillion in 2020, indicating an increase of more than 50% since 2018. With the average cyber insurance claim rising from USD 145,000 in 2019 to USD 359,000 in 2020, there is a growing necessity for better cyber information sources, standardised databases, mandatory reporting and public awareness. This research analyses ...
A wide range of computer security threats exists—including faulty software, password trafficking and fraud, and hostile groups intending to inflict damage—and awareness of these threats varies. RAND has conducted research to measure and increase understanding of the impact of cybercrime on businesses and governments and has addressed such issues as the pros and cons of counterattack, the ...
As technology has become pivotal a part of life, it has also become a part of criminal life. Criminals use new technology developments to commit crimes, and investigators must adapt to these changes. Many people have, and will become, victims of cybercrime, making it even more important for investigators to understand current methods used in cyber investigations. The two general categories of ...
"zoom out" approach and outward thinking can facilitate future research in cybercrime and cybersecurity. This is because research is needed to understand how the larger criminal justice system responds to cyber-crime at all levels (Holt & Bossler, 2014). More importantly, true interdisciplinary research in cybercrime
Founded in 2001, the Computer Crime Research Center (CCRC) is an independent institute dedicated to the research of cyber crime, cyber terrorism and other issues of computer crimes and internet fraud phenomena. ... Opposing Viewpoints Resource Center (OVRC) provides viewpoint articles, topic overviews, statistics, primary documents, links to ...
In 2024, these will be the top cybersecurity trends. A) Exciting Mobile Cyber Security Research Paper Topics. The significance of continuous user authentication on mobile gadgets. The efficacy of different mobile security approaches. Detecting mobile phone hacking.
Topic 9: Cybercrime Dissertation Topics - Understanding the Different Types of Cyber Crime. Research Aim: Cybercrime, undoubtedly, is one of the most deadly forms of crime. Without causing physical harm, the crime causes the victim to attempt suicide or suffer from mental diseases such as anxiety, depression, etc.
One criticism of past cybercrime research is that surveys were used whenever other data was not immediately available, ... [the topic]-that is, the experts should provide evaluations of the same ... National Cyber Crime Unit / Prevent Team. Pathways Into Cyber Crime. National Crime Agency; 2017.
Impressive Cyber Crime Research Topics. Why cyber currencies are a threat to online security; Why cyberbullying is rampant in the 21 st century unlike in any other time; The impact of online persuasion campaigns on cybersecurity; Why teenagers are victims of cyberbullying than adults; Discuss the effects of technology evolution on cybercrime
When it comes to choosing a cyber crimes essay topic, it is important to consider your interests, the relevance of the topic, and the availability of credible sources for research. Consider topics that are current and have a significant impact on society. Additionally, ensure that the topic is specific enough to allow for in-depth analysis, yet ...
Co-author of the study, Dr Miranda Bruce from the University of Oxford and UNSW Canberra said the study will enable the public and private sectors to focus their resources on key cybercrime hubs and spend less time and funds on cybercrime countermeasures in countries where the problem is not as significant. 'The research that underpins the Index will help remove the veil of anonymity around ...
The articles included in this issue reflect three broad areas of cybercrime research: cybercrime victimization, cybercrime perpetration, and techniques and facilitators of cybercrime. While there is some overlap, the issue includes three papers focused on each of these three areas. The first area covered in the special issue focuses on ...
The researchers used the survey results to construct the novel World Cybercrime Index, enabling comparison between countries. It suggests that cybercriminal threats are primarily concentrated in a ...
Research on cybercrime victimization is relatively diversified; however, no bibliometric study has been found to introduce the panorama of this subject. The current study aims to address this research gap by performing a bibliometric analysis of 387 Social Science Citation Index articles relevant to cybercrime victimization from Web of Science database during the period of 2010-2020. The ...
The Index, published in the journal PLOS ONE, shows that a relatively small number of countries house the greatest cybercriminal threat.Russia tops the list, followed by Ukraine, China, the U.S., Nigeria, and Romania. The UK comes in at number eight. Co-author of the study, Dr. Miranda Bruce from the University of Oxford and UNSW Canberra said the study will enable the public and private ...
By 9News Staff April 10, 2024 - 1:37PM. A new study from researchers in Australia and the UK has mapped out the sources of cybercrime around the world. Researchers measured a country's scale of ...
An academic research project to gain insight into which nations produce the most cybercrime has ranked the usual suspects of Russia, Ukraine, China, and the United States at the very top but also ...
Top 20 Countries with the Highest Cybercrime Threat Levels. Russia comes as the country where most cybercrime originates, with a WCI score of 58.39, followed by Ukraine (36.44) and China (27.84). The US (25.01) and Nigeria (21.28) also make the top five. The UK, India, North Korea and Brazil all make the top ten.
Access Transportation Research Board Publications Our peer-reviewed reports present the evidence-based consensus of committees of experts. Published proceedings record the presentations and discussions that take place at hundreds of conferences, workshops, symposia, forums, roundtables, and other gatherings every year.