
A Beginner’s Guide to Salesforce Territory Management
Many companies organize their salespeople into territories. A territory might be defined by geography, demographics, or some other criteria.
Territory management lets you easily see which reps are assigned to which accounts, regions, and opportunities. You can then track your reps’ performance by territory and determine how best to marshal your resources going forward.
If you use Salesforce CRM, you can take advantage of Salesforce’s Territory Management feature. It’s a powerful set of tools that let you assign accounts and territories to your reps, track sales opportunities, generate detailed reports, and more.
Why Do You Need Territory Management?
Gartner defines territory management as the process that selling organizations use to prioritize and manage groups of current and prospective customers. These customers are typically organized by segment, such as geographic location, industry, type of product, and the like. The segments are commonly called “territories.”
Organizations of all types and sizes can benefit from effective territory management. To make the best use of company resources, it’s beneficial to align sales teams and individual reps to specific territories – whether those territories are defined geographically, by industry, by customer type, or by type of product. Territory management can also help you also avoid overservicing certain territories, which can reduce the efficiency of your sales force and increase costs. (A report by the Society of Digital Agencies reveals that overservicing results in an average profit loss of 11%.)
By ensuring that all territories and market segments are adequately served, you can increase your company’s overall revenues. The Harvard Business Review reports that businesses can increase sales by 2% to 7% by optimizing the design of their territories.
What is Salesforce Territory Management?
Salesforce Territory Management is a tool that helps organizations like yours manage accounts and opportunities by territory. It lets you organize your accounts by any field and create hierarchies of accounts. For example, you can create a hierarchy with c-suite VPs at the top, regional managers in the middle, and sales reps on the bottom. Or you could create a hierarchy based on global regions, countries, states, cities, and even neighborhoods within major cities.
SOURCE: Trailhead.Salesforce.com
Access to different data and accounts can be assigned to specific levels. You can also grant access and generate reports based on account characteristics such as industry, revenue, ZIP code, or your own custom fields.
In essence, Salesforce Territory Management lets you structure your Salesforce users, accounts, and data the same way you structure your sales territories in the real world. By structuring Salesforce data in this manner, your reporting and analysis becomes more relevant and useful.
How Do You Activate Territory Management in Salesforce?
Territory Management is not activated by default in Salesforce. To enable the Territory Management feature, follow these steps:
- Go to Setup.
- In the Quick Find box, enter territories then select Territory Settings.
- Click Enable Enterprise Territory Management.
- To start out, select the most restrictive access levels, then click Save.
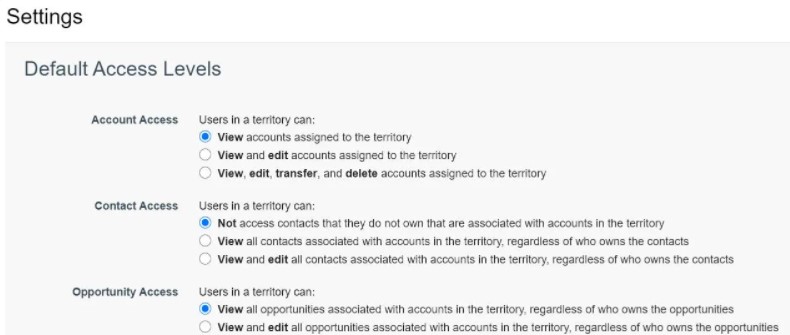
You can then change the default user access levels for accounts, contacts, and opportunities. You can also configure how opportunity territory assignments work.
How Do You Use Salesforce Territory Management?
Salesforce Territory Management is a powerful solution for managing sales reps, accounts, and territories. Sales managers and territory managers can use Territory Management to more closely track the performance of individual reps and territories, as well as maximize new sales opportunities.
Managing Roles, Accounts and Territories
The most obvious way to utilize this feature is for managing accounts and sales territories – as well as the roles assigned to sales reps and other management and staff.
Managing sales roles is important because every position has its own defined responsibilities. Not every role should have access to all data – only the information that helps them carry out their assigned duties. Salesforce Territory Management lets you create a role hierarchy and enable access to specific information based on position within that hierarchy.
Managing accounts is made easier by assigning specific accounts to the sales reps best prepared to handle them. Accounts can be assigned based on set rules regarding information entered for that account, or simply by name or number. For example, you might assign accounts starting with the letters A through E to a specific sales rep unless that account is flagged as a high-priority account, in which case a rule kicks in that assigns the account to a specific high-performance individual.
Managing territories is focused on producing accurate sales and revenue forecasts. Forecasts for territories ranked lower in the overall hierarchy are rolled up to create higher-level forecasts.
Managing Assignment Rules
Salesforce uses a variety of rules to help assign accounts to specific sales reps. When you create a new level in your sales hierarchy, you can assign accounts manually, or use inherited account assignment rules to assign those accounts automatically. Using inherited rules saves a lot of time. For example, if you add a new territory in an existing state, the rules from that parent state will be inherited by the new child region.
You can also create your own customized assignment rules. If you do so, you need to perform adequate testing to ensure that the rules work as intended. This is sometimes an issue, especially if you move reps or accounts from one territory (with its own rules) to another territory (with different custom rules).
Managing Leads and Opportunities
Lead assignment rules determine how new leads are assigned to specific sales reps. Sales leads can be assigned to reps using Salesforce’s standard lead assignment rules, or via custom rules that you create.
Salesforce Territory Management also facilitates lead sharing for emerging opportunities. You can give sales reps access to new opportunities based on their assigned territories or via sharing rules.
Managing Integrations
Your business doesn’t have to rely solely on Salesforce Territory Management. Salesforce can integrate with other applications to enable you to get even more value out of the Territory Management system. Ask your Salesforce consultant which third-party apps and solutions will best enhance your Salesforce Territory Management.
Let Rainmaker Help You with Salesforce Territory Management
The certified Salesforce experts at Rainmaker can help you deploy Salesforce Territory Management in your business. We can provide all manner of Salesforce Managed Services, from initial implementation to administration. Find out how you can improve your company’s territory management with Salesforce Territory Management – and Rainmaker.
Contact Rainmaker today to learn more about Salesforce Territory Management!
Related resources.

Streamlining Order Operations: Orders & AssetsAI Revolution

Navigating Vendor Complexity with Ease: How ResellerOS Makes Multivendor Management a Breeze

4 Things to Do with Your Salesforce Customer Data

4 Trends that Predict the Future of CRM

How to Determine the Value of Your Ad Inventory

The Complete Guide to Salesforce App Building
Share this story, choose your platform.
- Product Overview
- Select Accounts
- Assign Accounts
- Optimize Coverage
- Dynamic Books
- RevOps Resources
- Documentation

4.5 ways to do round robin assignment in Salesforce
Fairly assigning leads, accounts or opportunities to sales reps is core to how sales teams manage ownership. In most cases that means round robin assignment in Salesforce. This post outlines the (many) ways you can use Salesforce's tools to get this done.
Before you implement round robin assignment in Salesforce, think about what you're trying to achieve. Some of the options below (e.g. Lead Assignment Rules) only apply to Leads and won't work for Accounts , Opportunities , Tasks, etc. For example, if you're assigning qualified opportunities to account executives (AEs) you'll need to make sure you pick the right option.
As a refresher, using round robin to assign something in Salesforce is a lot like a dealer dealing cards. Here's how we described it in our advanced round robin post:
The dealer starts with one player, gives that player a card and then goes around the table, handing each player a card until some number of cards have been given out. This is a good way to evenly divide a large number of things (cards) among a small number of people (players). That's basic round-robin.
You should consider whether you want to do the basics or if your round robin needs weighting, capping, load balancing or availability management . Just be aware that the methods below will focus on the most basic form of round robin.
The rest of this post will cover the following methods for doing round robin assignment in Salesforce:
- Lead Assignment Rules
- Process Builder [Deprecated]
- Using sales engagement software
- Bonus method using Gradient Works
But first, some math and an example involving a deli...
Round robin, modulo and... deli tickets?
Most of the examples below use the MOD Salesforce formula operator in some way. Mod is short for the " modulo operation " which sounds complicated but is actually pretty simple: it just gives you the remainder left over after you divide two numbers. For example:
- MOD(5,3) is 2 because 5 divided by 3 has a remainder of 2
- MOD(9,3) is 0 because 9 divided by 3 has no remainder (3 goes evenly into 9)
- MOD(2731,3) is 1 because 2731 divided by 3 has a remainder of 1 (3 goes into 2731 910 times if you're curious)
The neat part about the mod operation is that it's always a number between 0 and 1 less than the number you're dividing by. So if you take any number mod 3, the result will always be either 0, 1 or 2. Ok, maybe that could be useful... but how? Glad you asked! Let's see how we can use MOD to evenly assign something.
Imagine you run a deli and you've got 3 sandwich artists. The artists get paid $0.50 per sandwich so you want to make sure each gets an equal number of customers throughout the day or else somebody will make less money and be upset.
The good news is that every customer that walks in takes a number from the little ticket dispenser by the door. Each new customer's number is 1 more than the previous customer's number. Cool so how do you turn this system into a way of allocating customers? Glad you asked that too! Here's a little algorithm:
- Write the names of each sandwich artist on a board and give them each a number between 1 and 3.
- Take each new customer's ticket number and MOD it by 3 (the number of sandwich artists). This gives you a remainder between 0 and 2.
- Add 1 to the remainder so you have a tidy result between 1 and 3.
- Use the resulting number between 1 and 3 to pick that customer's sandwich artist from the board.
Putting it all together, let's say your new customer takes a ticket with the number 8. You do 8 mod 3 and get 2. Add 1 and you get 3. Pick sandwich artist number 3 and send them this new customer. The next customer pulls a 9. 9 mod 3 is 0. Add 1 and you've got, well, 1. Send them on to sandwich artist one. Repeat.
I don't know about you but those customers sound suspiciously like Leads (or really anything else you'd want to assign) to me. It turns out that most of the solutions below use a variation on this where the ticket dispenser machine is replaced by an auto number field .
Now if you're not too hungry for a pastrami on rye , let's actually look at our options.

1) Round robin with Lead Assignment Rules (LARs)
We've done a deep dive on Salesforce Lead Assignment Rules in another post so we won't repeat everything here. However, if you've done any googling at all for "automated round robin lead assignment in Salesforce" you've probably encountered this Salesforce Help doc about creating round robin lead assignment rules .
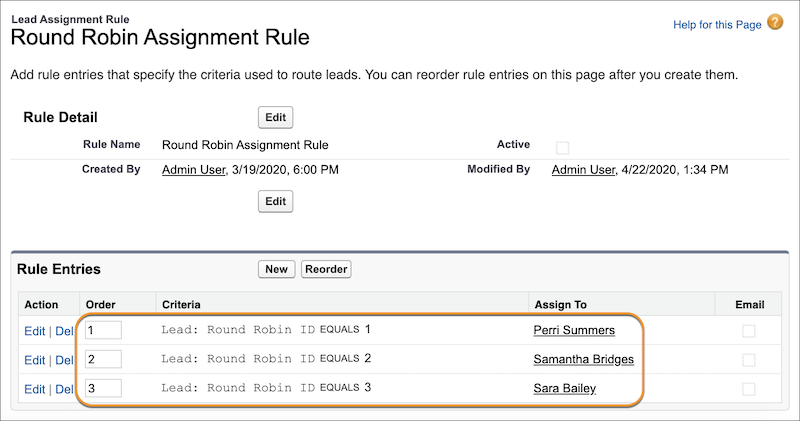
The basic idea in the Salesforce Help doc is precisely the deli counter example above:
- Add an auto-number field to Lead that counts up every time there's a new lead
- Add a formula field on Lead to calculate the "Round Robin Id" by MODing the Lead number by the number of sales reps and adding 1
- Hard-code Lead Assignment Rule Entries matching "Round Robin Id" to a rep
Step 3 looks like this:
Let's break down the good, the bad and the ugly of this approach.
- It's pretty simple with no complicated automation
- It's built-in so it comes with no strings attached (besides that Salesforce license $$$)
- Leads only - Lead Assignment Rules only work for - you guessed it - leads
- Hard to manage - Whenever reps get added, leave the company or just go on PTO, you have to update both the Round Robin Id formula to change the number of reps and update out the rule entries to assign Round Robin Ids to different reps
- No audit trail - However, you can help by tracking field history for the owner field.
- The minute you have any additional routing rules where some leads are created but aren't assigned to this group, your assignment gets skewed. Here's an example. Let's say 4 leads are created and given numbers 1, 2, 3, and 4. Let's say 2 and 3 aren't assigned because they used a Gmail address. What happens when Leads 1 and 4 get assigned? They'll both get assigned to the rep in slot 2 (MOD(1,3)+1 = 2, MOD(4,3)+1 = 2). Reps 1 and 3 aren't going to be happy about that.
2) Round robin with Process Builder
[Ed. Note: Please don't use this method since Salesforce is retiring process builder .]
Emily Douglas from Formstack discussed how to use Process Builder for round robin lead assignment at Dreamforce 2018. This solution is nice and flexible because it can be applied to any object. In fact, her example uses Contacts . Here's her overview slide:
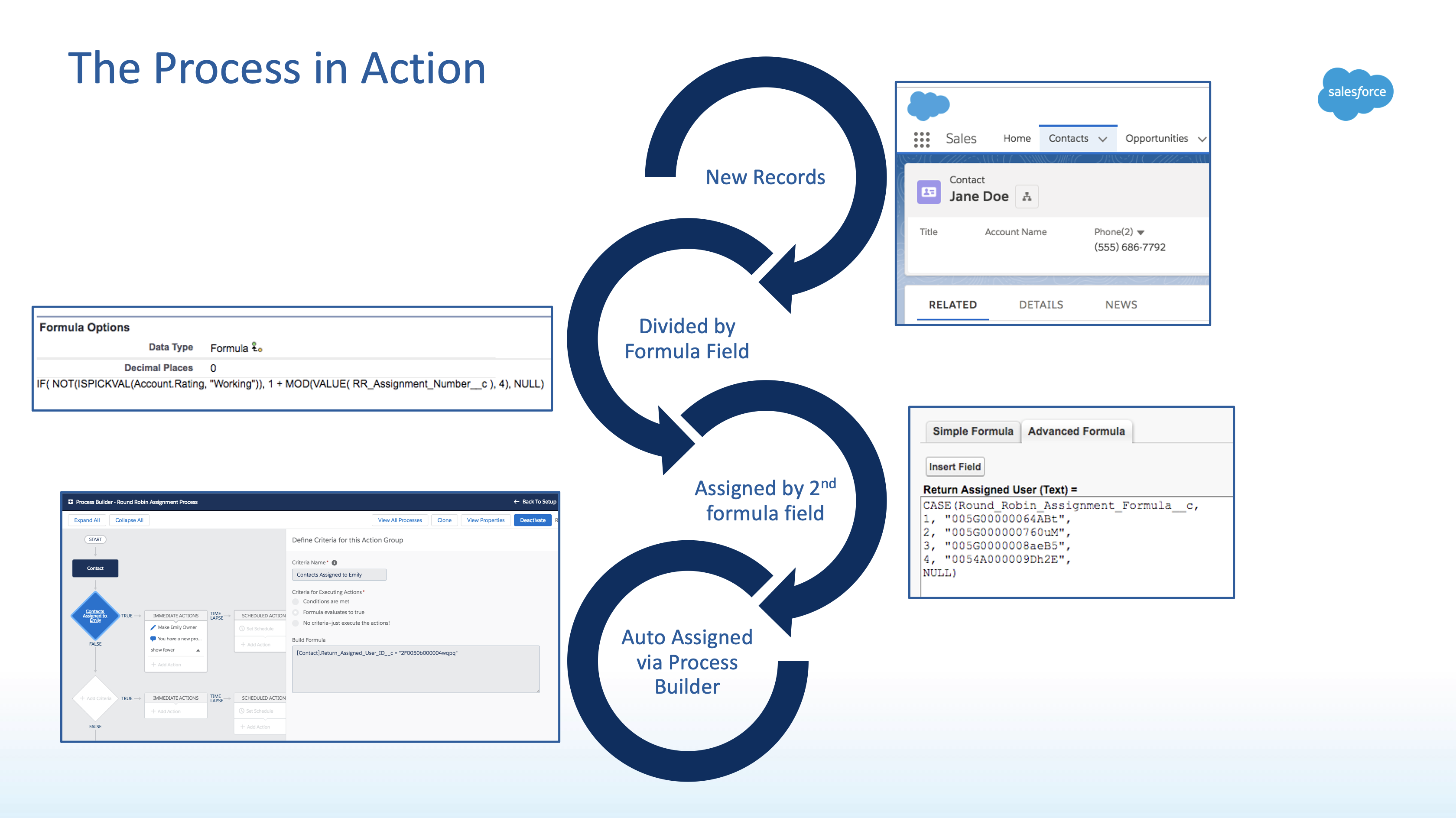
This means that the good, bad, and ugly of this approach are pretty similar to the earlier approach.
- Built-in - You don't need anything besides Salesforce
- Any object - The pattern can work for any object, not just Leads. All you have to do is set up the custom fields on the object and set up a process builder to operate on objects of that type
- Versioning - Process builder maintains versions as you make changes so at least you can refer back to the way things used to be if you make a tweak. Just note that this doesn't apply to the formula fields, only the logic in process builder
- Duplication - This approach describes a pattern you can use for any given object with some custom fields and a process builder. You'll need to try to keep that pattern consistent across every object you build this for.
- Hard to manage - As with the LAR approach, you've got to manually edit a formula field to change the list of reps
- More workflow effort - Unlike the LAR approach, you have to explicitly build in logic in process builder to do the assignments
- Process Builder is on its way out - Salesforce has publicly stated that Flow is the future of workflow automation on the platform, not Process Builder. It's not going anywhere soon but it's not being improved.
- Skewed assignments - Just like the LAR approach, this relies on a single deli-counter style auto number field. This will skew in the exact same way if you start implementing more complex routing rules. It is possible to eliminate some of these issues in process builder, but at the expense of a lot more complexity.
3) Round robin with Apex
As you probably know, developers can build entirely custom logic on the Salesforce platform using the Apex programming language . A typical Apex solution for round robin assignment usually takes the form of one of these two approaches:
- A variation on the deli-counter approach we've discussed so far, using a combination of formula fields to compute an auto-number value, the Apex version of the modulo operation ( Math.mod ) and triggers to kick off the code. This approach has all the drawbacks of the LAR and Process Builder approach.
- A more flexible (and powerful) approach that uses a set of custom objects, each of which define "slots" in multiple round-robin queues. At the expense of a lot more complexity, this approach allows you to distribute the same type of object fairly to different groups based on any routing logic you can imagine.
A full Apex implementation is too complex to discuss here so let's just look at the good, the bad and the ugly of using Apex to do round-robin:
- Nearly-infinite flexibility - If you can describe it, you can most likely do it with Apex. Assigning any object, with any logic is entirely possible.
- Round-robin can coexist with other routing rules - It's entirely possible to build complex routing rules to different groups of users without skewing your round robin
- Version control - Modern development approaches mean you can keep track of and independently test different versions of the code.
- Developers, developers, developers - It's code. You'll need a developer to write it in the first place and you'll need a developer to maintain it, debug it and change it.
- Maintenance and change will be difficult. In my experience, most code solutions in Salesforce become very hard to maintain over time, especially when the original author leaves. Even if you do have developers to support the custom solution, they're often very busy with other priorities and can't make changes on a time schedule that the business leads.
4) Round robin with Flow
We've talked a lot about Salesforce Flow around these parts because it's the future of Salesforce automation. The important thing to know about Flow is that it provides nearly all the flexibility of Apex with the low-code approachability of Process Builder. That makes it an ideal way to build solutions like round robin assignment.
There are several good examples of using Flow for this. You can find one in the book Lightning Sales Ops by Matt Bertuzzi but I'm going to specifically focus on this one by the sales operations consultants Kicksaw .
Here's a screenshot of Kicksaw's Flow in action:
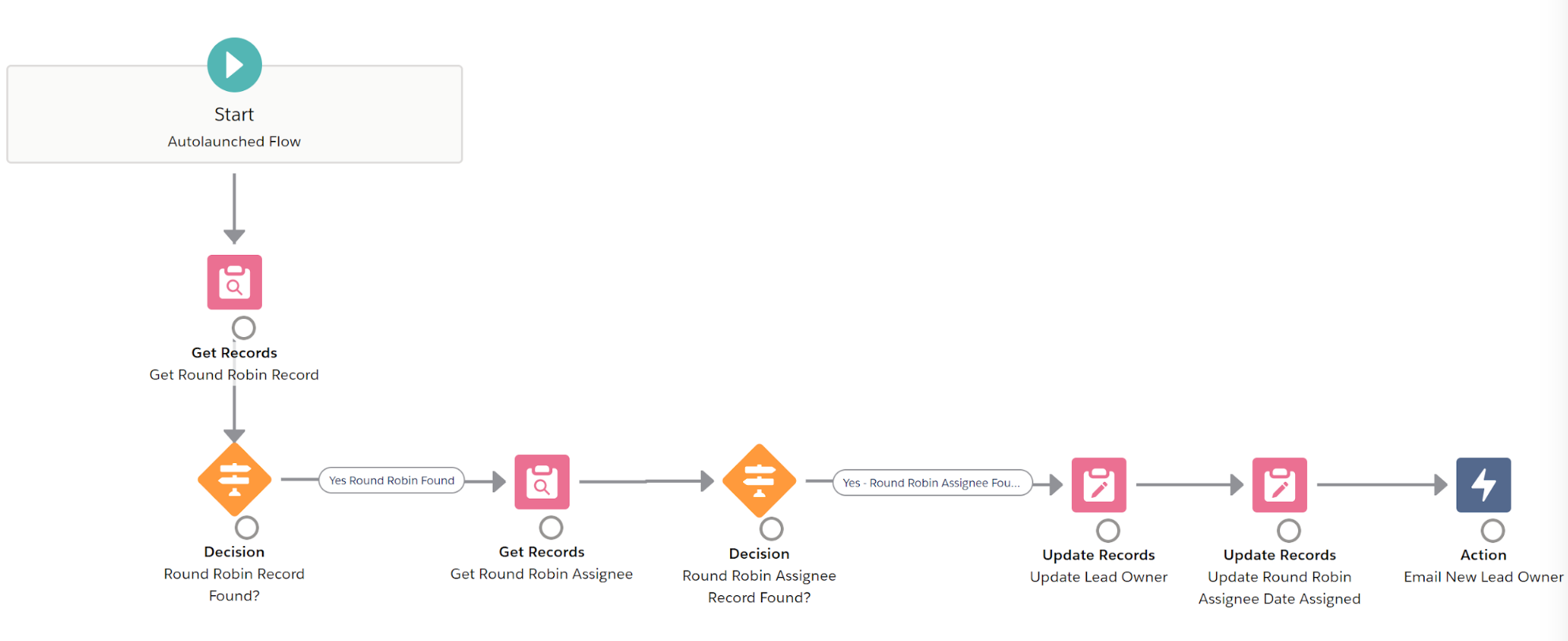
My main issue with the Kicksaw solution is that it introduces an unnecessary process builder component to trigger the execution of the Flow. That's easily done with record-triggered Flows.
- Flexibility - Flow gives you the flexibility to do most things you can do in Apex
- Maintainability - Admins can update the Flow logic and change the various user lists without needing any developer help
- Routing rules without skew - Support multiple territories and routing logic without worrying that it will skew your assignment process
- Future proof(ish) - Flow is the (current) future of automation on Salesforce
- More logic to deal with - Flow can require sorting out some tricky logic similar to programming; not all admins are comfortable with that
- A lot to configure - The full Kicksaw solution requires some custom objects, a queue and even some Lead Assignment Rules in addition to Flow. That can be a lot.
- It's all on you - In the end, this solution is custom to your Salesforce and relies on you and your team to maintain it.
4.5) Round robin with Sales Engagement software
I'm throwing in a "4.5" here because these recommendations aren't strictly Salesforce but instead might give you the ability to do basic round robin assignment with tools you already have. Sales engagement tools like Outreach and Salesloft have some basic round robin capabilities backed in so you may be able to get away with using them.
- You're already paying for it
- Functionality is super limited and generally only applies to a few use cases
- If you get rid of your sales engagement product, you'll also lose any round robin functionality you're using
Bonus! Round robin with Gradient Works
You didn't think I was going to let you get out of here without talking about how Gradient Works makes round robin assignment in Salesforce easy , did you?
If you're looking for a no-code round robin assignment solution that's flexible enough to handle whatever routing rules you throw at and advanced enough to optimize any of the assignments in your customer lifecycle, check us out .
Happy assigning!
By the way, round robin is such an important part of how sales teams manage assignments and handoffs, that we put together a whole round robin assignment knowledge base for sales teams . Go check it out.

Hayes Davis
Hayes Davis is co-founder of Gradient Works. Previously, Hayes was SVP of Revenue Operations at Cision, where he ran a global team of 50 supporting nearly 600 sellers. He was also co-founder and CEO of Union Metrics until its successful acquisition by TrendKite in 2018. Hayes has a background in computer science.
CONNECT WITH ME
Related posts.



Salesforce is closed for new business in your area.
Product Area
Feature impact.
- Learn About, Implement, and Optimize Sales Cloud Features
- See an Overview of Metrics, Goals, Suggestions, Tasks, and...
- Tour the Campaigns Object
- How Campaigns Can Help
- Use Campaigns with Other Clouds
- Understand Campaign Hierarchy
- Getting Started Worksheet
- Campaign Fields
- Considerations for Using Campaigns
- Can I use list email or mass email for my email campaigns?
- How do I add contacts and leads to campaigns?
- How can I calculate the ROI for my campaigns?
- How can I track which opportunities resulted from campaigns?
- How is Campaign influence different from ROI reports?
- Who has access to Campaigns?
- Customize Campaign Types in Lightning Experience
- Customize Campaign Types in Salesforce Classic
- Campaign Member Statuses
- Allow Users to Create Campaign Hierarchies
- Create or Edit a Campaign
- Field Handling for Cloning Campaigns with Related Records
- Allocations for Cloning Campaigns with Related Records
- Create a Campaign Hierarchy
- Share Campaigns
- Track Campaign Field History
- Campaign Member Fields
- Add Individual Leads, Contacts, or Person Accounts to Campaigns
- Add Campaign Members with Manage Members
- Add Members by Account from a Campaign Page
- Add Campaign Members from an Account Page
- Add Multiple Contacts and Leads to Campaigns
- Add Multiple Members to a Campaign from a List View
- Add Campaign Members from Standard and Custom Reports
- Import Campaign Members
- Add Existing Contacts to a Campaign with the Data Import Wizard
- Add Existing Leads to a Campaign with the Data Import Wizard
- Add Existing Person Accounts to a Campaign with the Data Import Wizard
- Create Contacts and Add Them to a Campaign with the Data Import Wizard
- Create Leads and Add Them to a Campaign with the Data Import Wizard
- Considerations for Using Accounts as Campaign Members
- Enable Accounts as Campaign Members
- Adding Accounts as Campaign Members
- Displaying and Editing a Campaign Member
- Campaign Member Task Overview
- Manage Members with the Campaign Members Related List
- Editing Multiple Campaign Members
- Add or Update Campaign Members with the Data Import Wizard
- Delete Individual Members from Campaigns
- Delete Multiple Contacts and Leads from Campaigns
- How Customizable Campaign Influence Works
- Switching to Customizable Campaign Influence
- Enable Customizable Campaign Influence
- Add Customizable Campaign Influence Related Lists
- Create a Custom Campaign Influence Model
- Add Influential Campaigns to an Opportunity
- Find Campaign Influence Results
- Configure Campaign Influence
- Add Campaign Influence Manually
- Get Started with Connected Campaigns
- Considerations for Connecting Campaigns
- Enable Connected Campaigns
- Connect Individual Campaigns
- Connect Multiple Campaigns at Once
- Connect Existing Campaigns with Salesforce Data Loader
- Considerations for Member Sync
- Sync Campaign Members
- Engagement History for Campaigns
- Configure Lead Management
- Define Default Settings for Lead Creation
- Leads Created from Your Company’s Website
- Generate Leads from Your Website for Your Sales Teams
- Generate Leads with Buyer Assistant
- Generate Leads from LinkedIn Lead Gen Ads
- Let Users View and Edit Converted Leads
- Map Custom Lead Fields for Lead Conversion
- Enable Lead Conversion in the Salesforce Mobile App
- Lead Intelligence View
- Leads List View Home
- Display and Edit Leads
- Convert Qualified Leads
- Troubleshoot Lead Conversion
- Things to Know About Merging Duplicate Leads
- Merge Duplicate Leads in Lightning Experience
- Merge Duplicate Leads in Salesforce Classic
- Update Leads with Third-Party Data
- Reassign Leads from a Queue
- Lead Sharing in Salesforce Classic
- Guidelines for Creating Leads
- Considerations for Converting Leads
- Considerations for Deleting Leads
- Lead Fields
- Lead Conversion Field Mapping
- Guidelines for Mapping Custom Lead Fields for Lead Conversion
- Guidelines for Setting Up Web-to-Lead
- Leads: What’s Different or Not Available in the Salesforce Mobile App
- What Is a Lead?
- What are the advantages of using leads?
- Can I automatically email leads that come from my website?
- Can I capture leads from multiple web pages?
- Can I convert existing accounts or contacts into leads?
- How are lead fields mapped to other fields during conversion?
- How can I be sure that leads aren’t lost?
- How can I tell which of my leads are new?
- How can our webmaster test the Web-to-Lead page?
- How many leads can we capture from our website?
- What happens when I convert leads?
- What if my company reaches the limit for web-generated leads?
- What status is assigned to web-generated leads?
- Who owns new web-generated leads?
- Activate and Deactivate Product Prices with Their Products...
- Organize Products with Product Families
- Products Concepts
- Guidelines for Creating Products
- Considerations for Cloning Products
- Set and Edit Product Prices in Salesforce Classic
- Set Product Prices in Lightning Experience
- Considerations for Setting Prices
- Enable Product Schedules
- Considerations for Using Product Schedules
- Add and Edit Product Schedules
- Establish Schedules for Products on Opportunities
- Create Custom Price Books
- Considerations for Creating and Maintaining Price Books
- Guidelines for Sharing Price Books
- Considerations for Removing Price Books
- Considerations for Removing a Product from a Price Book
- Product, Price Book, Price Book Entry, and Product Schedule Fields
- Considerations for Removing Products and Price Books
- Set a Default Product Quantity of 1 on Opportunities
- Automatically Enter the List Price as the Sales Price on Opportunities
- Enable Opportunity Update Reminders
- Set Up Big Deal Alerts for Opportunities
- Enable and Configure Similar Opportunities
- Manage Settings to Show Changed Deals
- Considerations for Creating and Updating Opportunities
- Considerations for Cloning Opportunities
- Things to Know About Sharing Opportunities
- Move an Opportunity to the Next Stage in Lightning Experience
- Move an Opportunity to the Next Stage in Salesforce Classic
- Opportunity History
- Things to Know About Deleting Opportunities
- Schedule Reminders to Update Opportunities
- Considerations for Scheduling Opportunity Update Reminders
- Guidelines for Finding Similar Opportunities
- Add Products to Opportunities
- Things to Know About Adding Products to Opportunities
- Define Competitors
- Competitor Fields
- Opportunity Fields
- Opportunity Product Fields
- Opportunities: What’s Different or Not Available in the Salesforce...
- Set Up Quotes
- Enable Quote Creation Without a Related Opportunity
- Create, Preview, and Activate Quote Templates
- Add Rich Text to a Quote Template
- Add a List to a Quote Template
- Add an Image to a Quote Template
- Add a Totals Section to a Quote Template
- Add a Signature Block to a Quote Template
- Create and Manage Quotes
- How Quote Syncing Works
- Sync Quotes and Opportunities
- Create a Quote PDF from the Standard Template
- Create a Quote PDF by Selecting a Template
- Email Quote PDFs
- Considerations for Creating Quote Templates
- Guidelines for Using the Quote Templates Editor
- Considerations for Adding Images to Quote Templates
- Quote Template Fields
- Quote Template and PDF Limitations
- Considerations for Deleting Quotes
- Considerations for Creating and Managing Quotes and Quote Line Items
- Considerations for Creating Quote PDFs
- Quotes Fields
- Troubleshooting Quote Syncing
- Quotes: What’s Different or Not Available in the Salesforce Mobile App
- Set Up Contracts
- Activate Contracts
- Contract History
- Delete Contracts
- Contract Fields
- Enable Orders
- Enable Negative Quantities for Order Products
- Enable Reduction Orders
- Enable Zero Quantity Orders
- Enable Orders Without Price Books
- Share Orders
- Order History
- Order Products
- Add Products to an Order
- Reduction Orders
- Reduce Orders
- Add Products to a Reduction Order
- Guidelines for Creating Orders
- Editing and Deletion Limitations for Orders and Reduction Orders
- Considerations for Activation Limitations
- Salesforce CPQ Reduction Orders Limitations
- Editing and Deletion Limitations for Order Products
- Order Fields
- Order Product Fields
- Enable New Order Save Behavior
- Account Intelligence View
- Considerations for the Account Intelligence View
- Guidelines for the Account Intelligence View
- Turn On the Account Intelligence View
- Share Accounts
- Guidelines for Merging Duplicate Accounts
- Things to Know About Merging Duplicate Accounts Associated with...
- Merge Duplicate Accounts in Lightning Experience
- Merge Duplicate Accounts in Salesforce Classic
- Update Accounts with Third-Party Data
- View and Convert Leads on an Account
- Account History
- Set Up Account Hierarchy in Salesforce Classic
- Set Up Account Hierarchy in Lightning Experience
- Enable Automated Account Fields
- Enable Account Logos
- Business Contact Sharing for Orgs That Use Person Accounts
- Considerations for Using Person Accounts
- Considerations for Using Merge Fields for Person Accounts
- Considerations for Using Merge Fields in Validation Rules for Person...
- Enable Person Accounts
- Add Teams to Your Accounts
- Set Up a Default Account Team
- Use Reports to Maintain Account Teams
- Considerations for Account Access via Teams
- Facilitate Collaboration by Enabling Account Teams
- Customize Account Team Roles
- Maintain Your Users’ Account Teams
- Disable Account Teams
- Considerations for Customizing Account Teams
- Account Team Fields
- Guidelines for Creating Accounts
- Guidelines for Deleting Accounts
- Considerations for Using Account Hierarchy in Lightning Experience
- Considerations for Using Account Hierarchy in Salesforce Classic
Account Fields
- Considerations for Creating Contacts
- Guidelines for Viewing and Managing Contacts
- Contact Intelligence View
- Considerations for Deleting Contacts
- Merge Duplicate Contacts in Lightning Experience
- Merge Duplicate Contacts in Salesforce Classic
- Retain Recently Updated Data Privacy Records for Merged Leads and...
- Considerations for Merging Duplicate Contacts
- Considerations for Merging Contacts Associated with Portal Users
- Update Contacts with Third-Party Data
- Considerations for Sharing and Accessing Contacts
- Considerations for Importing Contacts from a Mobile Device
- Turn On Contact Intelligence View
- Enable Self-Service for Contacts and Person Accounts
- Set Up Contact Hierarchy in Lightning Experience
- Display Contacts in an Org Chart in Salesforce Classic
- Allow Users to Create Private Contacts
- Comparing Contacts to Multiple Accounts to Other Options
- Set Up Contacts to Multiple Accounts
- Account Contact Relationship Fields
- Create Custom Report Types for Account Contact Relationships
- Validation Rules for Account Contact Relationships
- Create and Edit Relationships Between Contacts and Accounts
- Considerations for Relating a Contact to Multiple Accounts
- Set Up Contact Roles
- Add and Manage Contact Roles in Lightning Experience
- Add and Manage Contact Roles in Salesforce Classic
- Considerations for Using Contact Roles
- Contact Role Fields
- Set Up and Customize Opportunity Contact Roles in Lightning Experience
- Considerations for Customizing Opportunity Contact Roles
- Set Up Opportunity Contact Roles in Salesforce Classic
- Add and Manage Opportunity Contact Roles
- Guidelines for Using Opportunity Contact Roles
- Opportunity Contact Role Fields
- Considerations for Changing the Account for Contacts
- Considerations for Using Contact Hierarchy in Lightning Experience
- Contacts: What’s Different or Not Available in the Salesforce Mobile...
- Contact Fields
- Before You Turn On Salesforce Maps Lite
- Visualize Customers and Prospects on a Map
- Resolve Latitude and Longitude Discrepancies
- Considerations for Setting up Revenue Insights
- Revenue Insights Assets
- Enable and Configure Revenue Insights
- Revenue Insights Post Installation Steps
- Monitor, Update, and Delete Revenue Intelligence Apps
- Troubleshoot Revenue Insights Enablement
- Select Who Can Use Revenue Intelligence
- Enable More Features for Revenue Intelligence
- Revenue Insights Team Tab
- Revenue Insights Sales Performance Tab
- Revenue Insights Forecast Historical Trend Tab
- Sales Rep Command Center Dashboard
- Sales Stage Analysis Progression
- Sales Stage Analysis Conversion
- Forecast Insights Dashboard
- Commit Calculator Dashboard
- Product Insights Dashboard
- Considerations for Einstein Account Management
- Set Up Einstein Account Management
- Use Einstein Account Management
- Considerations for Setting Up Pipeline Inspection
- Turn On Pipeline Inspection
- Select Who Can Use Pipeline Inspection
- Select Summary Fields For Pipeline Inspection Metrics
- Manage Pipeline Inspection Metrics
- Select a Forecast Rollups Method in Pipeline Inspection
- Configure Deal Insights in Pipeline Inspection
- Show Opportunity Scores in Pipeline Inspection
- Enable the Flow Chart in Pipeline Inspection
- Enable More Features for Pipeline Inspection
- Managing Pipelines with Pipeline Inspection
- Set or Change the Summary Field for Pipeline Inspection Metrics
- Pipeline Inspection Charts
- Einstein Deal Insights
- Tiered Einstein Opportunity Scores
- Guidelines and Limits for Pipeline Inspection
- Pipeline Inspection Metrics and Fields
- Collaborative Forecasts Concepts
- Turn On Collaborative Forecasts and Define Forecasts Settings
- Forecast Types
- Group Sales Forecasts to Match Your Business
- Create and Activate Forecast Types
- Schedule and Product Date Forecasts
- Territory Forecasts
- Guidelines for Showing Opportunity Fields in Forecasts Pages
- Forecast Rollup Methods
- Select a Forecast Rollup Method
- Give Users Access to Collaborative Forecasts
- Set Up Your Forecast Hierarchy
- Enable Partner Portal Users to Add Opportunities in Collaborative...
- Activate and Assign Custom Forecasts Pages
- Considerations and Guidelines for Custom Forecasts Pages
- Define Your Company’s Forecast Date Range
- Customizing Forecasts Categories
- Show, Hide, and Reorder Forecast Columns
- Allow Forecast Adjustments and Manager Judgments
- Show Quota Information in Collaborative Forecasts
- Manage Quota Data in Setup
- Managing Quota Data from External Sources
- Select a Forecast Currency in Collaborative Forecasts
- Guidelines for Using Multiple Currencies in Collaborative Forecasts
- Add Custom Calculated Columns
- Considerations for Using Custom Calculated Columns
- Managing External Data to Include in Collaborative Forecasts
- Add Custom Columns That Include External Data
- Set Up Historical Data for Forecast Charts
- Manage Opportunity-State-to_Forecast-Category Mappings
- Considerations for Disabling Collaborative Forecasts Features
- Guidelines for Using Collaborative Forecasts
- Revenue and Quantity Forecasts
- Custom Measure Forecasts
- Overlay Splits Forecasts
- Considerations for Managing Territory Forecasts
- Showing or Hiding Quota Information
- Considerations for Using Quotas
- Forecasts Hierarchy
- View Different Forecast Types
- See Recent Changes in Forecast Value Changes
- Reviewing Week-to-Week Forecast Changes
- Finding Trends Across Forecast Periods
- Monthly and Quarterly Forecasts
- Change Your Forecast Date Range
- Partner Portal User Opportunities in Collaborative Forecasts
- Guidelines for Viewing Opportunity Details in Collaborative Forecasts
- Guidelines for Refreshing Forecasts in Collaborative Forecasts
- Manager Judgments
- Apply Manager Judgment
- Forecast Adjustments
- Adjust Forecast Values
- Who Can Apply Manager Judgments and Adjust Forecasts
- Manager Judgment and Forecast Adjustment Deletions
- Share Forecasts with Stakeholders
- Preparing Sales Leaders to Report on Forecasts
- Guidelines for Using Collaborative Forecasts Reports
- What's Different or Not Available in the Salesforce Mobile App
- Bird’s-Eye View of Planning and Managing Territories
- Designing Territory Models
- Managing Territories
- Optimizing Your Territory Model Continuously
- Territory Type
- Territory Type Priority
- Territory Model
- Territory Hierarchy
- Territory Model State
- How Do Permissions for Territories Affect Feature and Data Access?
- Territory Management 2.0 Data Model
- Enable Enterprise Territory Management
- Define Default User Access for Territory Records
- Enable Filter-Based Opportunity Territory Assignment
- Collaborate on Territory Models
- Create Territory Types
- Create a Territory Model Record
- Create Territories
- Assign Forecast Managers to Territories
- Customize Territory Labels
- Assign Users to Territories
- Define a Picklist for Territory User Roles
- Assign Territory Roles to Users
- Identify Users in Territories Assigned to Accounts
- Identify Territory Users by Territory Role
- Show Your Reps Other Users Assigned to Their Leads’ Territories
- Track Historical User Assignments in Territories
- Create Rules to Assign Accounts to Territories
- Assign Accounts Directly to Territory Records
- Preview Territory Assignments for Accounts
- Assign Accounts and Leads to Territories Manually
- Add Assignment Rules to Territories
- Requirements for Assigning Opportunities to Territories Manually
- Assign Opportunities to Territories Manually
- Run the Opportunity Territory Assignment Filter
- Clone Territory Models
- Activate a Territory Model
- Configure Territory Permissions and Access for Salesforce Admins and...
- Run Assignment Rules for a Territory
- Find Out Which Territories an Assignment Rule Applies To
- View and Manage Assignment Rules at the Territory Model Level
- Activating Assignment Rules and Applying Them to Descendant...
- Preparing Sales Management for Territory Reporting
- Report on Accounts Assigned to Territories
- Report on Territories Without Assigned Accounts
- Report on Users Not Assigned to Territories
- Report on Territories with Assigned Users
- Report on Summarizable Account Fields by Territory
- Archive a Territory Model
- Delete a Territory Model
- Disable Enterprise Territory Management
- Explore Your Company’s Territory Model
- Identify an Account’s Sales Territories
- View a List of the Accounts or Opportunities in Your Territories
- Report on the Accounts and Opportunities in Your Territories
- Enterprise Territory Management Allocations
- Enterprise Territory Management: What’s Different or Not Available...
- How Account Assignment Rules Work
- Add Teams to Your Opportunities
- Set Up a Default Opportunity Team
- Use Reports to Track Teams
- Considerations and Guidelines for Using Teams
- Guidelines and Considerations for Using Opportunity Splits and...
- Enable Opportunity Teams
- Customize Team Roles
- Maintain Users’ Opportunity Teams
- Disable Opportunity Teams
- Considerations for Customizing Teams
- Opportunity Teams Fields
- Get Ready to Enable Splits
- Enable Opportunity Splits
- Edit Splits Layouts
- Customize Split Types
- Add Opportunity Product Splits
- Deactivate or Delete Opportunity Split Types
- Disable Opportunity Splits and Opportunity Product Splits
- Set Up Audit History for Splits and Opportunity Teams
- Considerations for Managing Audit History
- Enable Multiple Currencies
- Considerations for Enabling Multiple Currencies
- Activate and Deactivate Currencies
- Enable or Disable Advanced Currency Management
- Edit Dated Exchange Rates
- Enable Path
- Create a Path
- Configure the Last Path Step
- Considerations and Guidelines for Creating Paths
- Considerations for Setting Up WDC
- Assign a WDC Administrator
- Recommended WDC Permission Sets
- Recommended WDC Profiles
- Assign WDC Only User Licenses
- Assign WDC User Feature Licenses
- Configure Thanks in the Chatter Publisher and Salesforce Mobile App...
- Assign Publisher Layout to Profiles
- WDC Editions and Permissions
- Enable or Disable WDC Settings
- Create a Support Case
- Skills Customization
- Skills Limitations
- Create a Badge
- Configure Access to Thanks Badges
- Add a Skill Via Record Detail Pages
- Remove a Skill Via Record Detail Pages
- Endorse a Skill Via Record Detail Pages
- Einstein Features in Sales Cloud
- Set Up Einstein Opportunity Scoring for Sales Cloud Users
- Manage Sales Cloud Users’ Access to Einstein Features
- Set Up Sales Summaries for Einstein Copilot
- Digital Engagement for Sales Cloud
- Sharing Information with Partners
- Add Partner Relationships
- Partner Fields
- Deleting Partners
- Create a Partner Portal
- Add LinkedIn Sales Navigator Components to Lead, Contact, and...
- Add LinkedIn Sales Navigator Lightning Actions to Lead, Contact, and...
- Send LinkedIn InMail and Connection Requests from Salesforce
- Resources for the Sales Professional
Accounts have business account fields and person account fields.
Required Editions
Business account fields.
A business account has the following fields, listed in alphabetical order. Depending on your page layout and field-level security settings, some fields may not be visible or editable.
If the account record was added from Data.com, certain fields, as identified here, are populated with the Data.com or Dun & Bradstreet (D&B) value, if available. Some Data.com fields are available only in orgs licensed to use a specific Data.com product. Those fields are identified in their descriptions.
Person Account Fields
A person account has the following standard fields, listed in alphabetical order. Depending on your page layout and field-level security settings, some fields may not be visible or editable. Fields with a prefix “Person” or suffix “_pc” are contact fields that are supported for person accounts but not business accounts.
This list doesn’t include custom fields that your Salesforce admin has created. Both account and contact custom fields are available for person accounts.

Cookie Consent Manager
General information, required cookies, functional cookies, advertising cookies.
We use three kinds of cookies on our websites: required, functional, and advertising. You can choose whether functional and advertising cookies apply. Click on the different cookie categories to find out more about each category and to change the default settings. Privacy Statement
Required cookies are necessary for basic website functionality. Some examples include: session cookies needed to transmit the website, authentication cookies, and security cookies.
Functional cookies enhance functions, performance, and services on the website. Some examples include: cookies used to analyze site traffic, cookies used for market research, and cookies used to display advertising that is not directed to a particular individual.
Advertising cookies track activity across websites in order to understand a viewer’s interests, and direct them specific marketing. Some examples include: cookies used for remarketing, or interest-based advertising.
Cookie List
- Support Portals
- PRM Portals
- Member Portals
- Online Communities
- User Experience
- Accelerators
- AC Knowledge Management Enterprise
- AC Events Enterprise
- AC Ideas Ultimate
- AC Partner Marketplace
- AC Partner Co-Branding
- AC eCommerce for Nonprofits
- AC Job Board
- AC B2B Commerce Recurring Orders
- AC MemberSmart
- AC Fundraising
- AC B2B Commerce OrderPad
- Higher Education
- Member Organizations
- Manufacturing
- IT\High-Tech
- Video library
- Success stories
- SI Partners
Book a demo
If you'd like to book a demo with us and see how our products work, please complete the form and we'll arrange a demo with you as soon as we can.
I agree to the Privacy Policy and Terms and Conditions
By submitting this form, you agree to occasionally receive guides, tips, and tricks from AC. You can unsubscribe at any time.
How to Create Assignment Rules in Salesforce
Assignment rules are a great instrument to better organize your sales and support teams’ work.
Using assignment rules you can automate the process of assigning owners to Leads and Cases.
Assignment rules description
There are two types of assignment rules in Salesforce: Lead Assignment Rules and Case Assignment Rules.
To better understand Salesforce terminology we’ll give you a short definition of what is a Lead and what is a Case in Salesforce.
Lead – prospect, someone interested in your product or service, but not yet ready to buy.
Case – customer’s question, complaint, or suggestion about your product or service.
Assignment rules can help you to automatically deliver specific Cases to the right people in the team who are specialized in a certain area so that the customers receive timely and qualified responses.
It also enables you to sort cases by priority according to the customer’s support package (Platinum, Silver, etc.).
The same thing applies with lead assignment rules Salesforce – you can define which users will be assigned leads that come from your website and which users will be assigned leads that come from social media.
Assignment rules and Queue creation
Now you know what assignment rules are for, we’ll show you how to set them up.
As an example, we’ll use Case Queue and Case Assignment Rules creation in Salesforce.
To create a Case queue in Salesforce, do the following:
- Setup -> type Queue in the Quick Find box -> enter the Name and Label.
- Leave the Queue Email field empty if you want the support employees included in the queue to receive emails when new cases are created or type the email addresses of the people who will receive this kind of notification.
- Choose Case and add it to the Selected Objects column.
- Choose members and add them to the Selected Members column -> click Save.
To create a Case assignment rule do the following:
- Go to Setup -> type Assignment Rules in the Quick Find box -> choose Case Assignment Rules -> click New -> enter the Rule Name and click Save.
- Click on the rule you just created -> click New in the Rule Entries section.
- Sort Order – defines the order in which entries will be processed (entering “1” means that this entry will be processed first).
- Select the criteria for this rule entry.
- Choose the User to whom this rule entry will be assigned.
- Choose the Email Template this user will receive when the new case will be assigned to him -> click Save.
- Click Edit in the Rule Detail section -> mark this rule as Active ->click Save.
Don’t miss the benefits you can get from using assignment rules – give them a try on your organisation!
We hope that this post was informative for you.
Check our AC Events Enterprise tool that will help you with events management and AC Knowledge Management Enterprise for comprehensive and effective data management.
Follow us on Facebook and Youtube for even more useful content about Salesforce and Experience Cloud.
Rate the article
3.1 / 5. 12

How to Improve Your Community’s Success and Better Engage With Your Customers
In this article I wanted to share my thoughts on the most important factors that every community manager should consider when creating a successful community.

Everything You Wanted to Know About Spring ’16 Release But Were Afraid to Ask
t’s only January, but Salesforce has already published its Spring ’16 Release Notes. In order to provide better business capabilities, Salesforce has improved various features.

CMS for Community Cloud becomes Salesforce CMS: top five benefits
Learn more about new Salesforce CMS app.
To go to your company's login page, enter the custom domain name.
Not a customer?
About 15 mins
Create Case Queues
Create a case assignment rule, test the case assignment rule.
- Challenge +100 points
Create Case Queues and Assignment Rules
Now that you have your basic support processes and layouts configured for cases, create case queues and assignment rules to route your cases to the correct support teams at Ursa Major Solar.
Create Product Support Tier 1 and Product Support Tier 2 queues so product support cases can be routed to one of these queues based on case criteria and how long the case has been open.

- From Service Setup, enter Queues in the Quick Find box and select Queues .
- Click New and complete the queue details.
- Label: Product Support Tier 1
- Queue email: [email protected]
- Supported Objects: select Case and click Add .
- Queue Members: Click User: (Your Name) in the Available Members list, and click Add to add yourself to the Selected Members list.
- Click Save .
- From the Queue page, click New and complete the queue details.
- Label: Product Support Tier 2
- Queue email: [email protected]

Now, create the Inquiry queue for inquiry cases.
- From the Queues page, click New .
- Enter the queue details.
- Label: Inquiry
- Queue Email: [email protected]
- Queue Members: Click User: Ada Balewa in the Available Members list, and click Add to add her to the Selected Members list.
So, now you have case queues set up and ready to handle different types of cases as they’re created. Next, create and activate a standard case assignment rule to assign cases to the correct team members. This is how cases get sent to specific case queues, like the ones you just created.
- From Service Setup, enter Case Assignment Rules in the Quick Find box and select Case Assignment Rules .
- Click New and enter the rule details.
- Rule Name: Standard Case Assignment
- Select the Active checkbox to make this the active case assignment rule.
Add a rule entry that assigns Product Support cases to the Product Support Tier 1 queue.
- Click the Standard Case Assignment link.
- Under the Rule Entries, click New and enter the details.

- Click Save & New .
Next, add a rule entry that assigns inquiry cases to the Inquiry queue.
- Enter the details.
Now rename the Automated Case User to System. Every time there’s an automated case change from an assignment rule, for example, the automated case user name will show up in the case history. It will now show an automated “system” change, rather than showing your name as the admin, whenever an automated case change occurs.
- Enter Support Settings in the Quick Find box and select Support Settings .
- Click Edit .

You want to make sure the assignment rules work for Ursa Major Solar by creating a case.

- Click the Contacts tab.
- Select Recently Viewed from the dropdown, and click the Pat Stumuller link.
- In the Cases related list, click New .
- Select a record type: Product Support .
- Click Next and enter the case information.
- Click the Case Number for the case you just created. Ensure that the Case Owner is Product Support Tier 1.
By setting up case queues and assignment rules, cases are now automatically routed to the correct teams. Next, escalate higher priority cases to the Product Support Tier 2 team by creating an Escalation Rule.
- Salesforce Help: Rules
- Salesforce Help: Create Queues
- Salesforce Help: Set Up Assignment Rules
- Get personalized recommendations for your career goals
- Practice your skills with hands-on challenges and quizzes
- Track and share your progress with employers
- Connect to mentorship and career opportunities
Using apex:repeat in Visualforce Page
System.NullPointerException: Attempt to de-reference a null object
Assignment rules in Salesforce
- By Ankush Dureja in salesforce
December 6, 2018
Page Contents
What are assignment rules in salesforce ?
Assignment rules in salesforce are used to automatically assign lead or Case to owner( User Or Queue ). Assignment rule is used to automate owner assignment on Case and Lead based on conditions on Case or Lead. For example, there could on lead assignment rule for web-generated leads and one case assignment rule for the holiday use.
Types of assignment rules
There are two type of assignment rules
Lead Assignment Rules
Case assignment rules.
Specify how leads are assigned to users or queues as they are created manually, captured from the web, or imported via the Data Import Wizard.
Determine how cases are assigned to users or put into queues as they are created manually, using Web-to-Case, Email-to-Case, On-Demand Email-to-Case, the Self-Service portal, the Customer Portal, Outlook, or Lotus Notes.
Create or Setup assignment rules
- From Setup, enter Assignment Rules in the Quick Find box, then select either Lead Assignment Rules or Case Assignment Rules .
- Choose New , and then give the rule a name. Specify whether you want this to be the active rule for leads or cases created manually and via the web and email. Then click Save .
- To create the rule entries, click New . For each entry, you can specify:
- Order : Sets the order in which the entry will be processed in the rule, for example, 1, 2, 3. Salesforce evaluates each entry in order and tries to match the criteria of the entry. As soon as a match is found, Salesforce processes the item and stops evaluating the rule entries for that item. If no match is found, the item is reassigned to either the default Web-to-Lead owner, the administrator doing a lead import, or the default case owner.
- Choose criteria are met and select the filter criteria that a record must meet to trigger the rule.For example, set a case filter to Priority equals High if you want case records with the Priority field marked High to trigger the rule. If your organization uses multiple languages, enter filter values in your organization’s default language. You can add up to 25 filter criteria, of up to 255 characters each. When you use picklists to specify filter criteria, the selected values are stored in the organization’s default language. If you edit or clone existing filter criteria, first set the Default Language on the Company Information page to the same language that was used to set the original filter criteria. Otherwise, the filter criteria may not be evaluated as expected.
- Choose formula evaluates to true and enter a formula that returns a value of “True” or “False.” Salesforce triggers the rule if the formula returns “True.” For example, the formula AND(ISCHANGED( Priority ), ISPICKVAL (Priority, “High”) ) triggers a rule that changes the owner of a case when the Priority field is changed to High. If your condition uses a custom field, the rule entry will be deleted automatically if the custom field is deleted.
- User : Specifies the user or queue to which the lead or case will be assigned if it matches the condition. Users specified here cannot be marked “inactive” and they must have “Read” permission on leads or cases.
- Do Not Reassign Owner : Specifies that the current owner on a lead or case will not be reassigned to the lead or case when it is updated.
- Email Template : We can specifies the template to use for the email that is automatically sent to the new owner. If no template is specified, no email will be sent. When assigning a lead or case to a queue, the notification goes to the Queue Email address specified for the queue and all queue members.
- Predefined Case Teams : Specifies the predefined case team(s) to add to a case when it matches the condition. A case team is a group of people that work together to solve cases.
- Replace any existing predefined case teams on the case : Specifies that any existing predefined case teams on the case are replaced with the predefined case teams on the condition, when a case matches the condition.
After creating the entry, click Save , or Save & New to save the entry and create more entries.
Assignment Rule Example
Following is sample Case assignment rule which assigns case to different queues based on Billing Country, Account SLA and customer type:
For more details about assignment rules please refer to assignment rules official link.
Assignment rules in Salesforce trailhead
Good luck for creating Assignment rules in Salesforce 🙂
- Assignment rules , Assignment rules Salesforce , Case Assignment rules , Lead Assignment Rules , salesforce , sfdc
Ankush Dureja
Permanent link to this article: https://www.sfdcpoint.com/salesforce/assignment-rules-in-salesforce/
Skip to comment form
- Stremove.com on August 2, 2020 at 9:10 am
Case Assignment Rules Determine how cases are assigned to users or put into queues as they are created manually, using Web-to-Case, Email-to-Case, On-Demand Email-to-Case, the Self-Service portal, the Customer Portal, Outlook, or Lotus Notes.
- Dayene on August 25, 2020 at 7:01 pm
Hi! What about when I want my assignment to change when the Lead status is changed? I’ve created two criterias. First when the status is new and second when the status has other values. But when the Lead is updated and the status changes the assignment doesn´t follow this change and it does not assignment the Lead Owner correctly. Thanks.
- Vrushabh LEngade on October 27, 2020 at 3:51 pm
Use Escalation Rules and escalate the case to another user or queue
- subhasini on December 23, 2021 at 6:19 pm
Hi Ankush Dureja, there is a interview question on assignment and the question is : What will happen if the user becomes inactive(or user is deactivated) on whom the rule is assigned. Please reply me ASAP
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
Popular Posts
- Navigation Service in LWC(Lightning Web Components) 16 comments
- Modal/Popup Lightning Web Component(LWC) 6 comments
- Batch Apex Example In Salesforce 17 comments
- Wrapper Class in Apex Salesforce 20 comments
- for:each template directives in LWC 1 comment
- Get Record Id in Lightning Web Component 9 comments
- Lightning Web Components(LWC)Tutorial 4 comments
- template if:true Conditional Rendering LWC 8 comments
- Triggers in Salesforce 5 comments
- Lightning Web Component(LWC) Toast Messages 13 comments
- May 2023 (1)
- March 2023 (1)
- January 2023 (1)
- November 2022 (1)
- October 2022 (1)
- September 2022 (2)
- August 2022 (2)
- June 2022 (1)
- February 2022 (1)
- January 2022 (1)
- September 2021 (2)
- August 2021 (1)
- June 2021 (2)
- May 2021 (2)
- April 2021 (2)
- January 2021 (2)
- December 2020 (1)
- October 2020 (1)
- September 2020 (1)
- August 2020 (2)
- June 2020 (2)
- May 2020 (20)
- April 2020 (10)
- March 2020 (6)
- February 2020 (6)
- January 2020 (2)
- December 2019 (6)
- November 2019 (3)
- March 2019 (1)
- February 2019 (1)
- January 2019 (2)
- December 2018 (7)
- November 2018 (4)
- October 2018 (2)
- June 2018 (1)
- April 2018 (1)
- March 2018 (1)
- January 2018 (1)
- December 2017 (2)
- November 2017 (1)
- October 2017 (2)
- September 2017 (2)
- August 2017 (1)
- July 2017 (1)
- May 2017 (2)
- April 2017 (8)
- October 2016 (1)
- June 2015 (1)
- February 2015 (1)
- October 2014 (1)
- August 2014 (1)
- June 2014 (4)
- May 2014 (1)
- April 2014 (2)
- March 2014 (4)
- February 2014 (22)
Recent Posts
- How Salesforce Einstein GPT is changing the Game for Small-Medium Enterprises
- What are the benefits of Salesforce health cloud?
- salesforce customer 360 overview and features
- Difference Between Workflow Process Builder and Flow
- Salesforce Integration Interview Questions And Answers
- Salesforce developer interview questions
- Salesforce Admin Interview questions
- Salesforce Lightning Interview Questions
- Salesforce Field Service Implementation
- Salesforce Course Details | Eligibility, Fees, Duration
Recent Comments
- luqmaan s on Pagination using StandardSetController with wrapper class
- Santosh on Get Record Id in Lightning Web Component
- Micky on custom label in visualforce page
- Syed Wassim on salesforce order of execution
- NoviceDev on Avoid recursive trigger in salesforce
TOTAL PAGEVIEWS
- SFDC Share Point
Our Facebook page
https://www.facebook.com/sfdcpoint
© 2024 Salesforce Blog.
Made with by Graphene Themes .
Privacy Overview

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
If you use rules to assign accounts to territories, it can be helpful to find out which territories a single rule applies to. View and Manage Assignment Rules at the Territory Model Level View and manage account assignment rules at a high level. Start from the territory model record to create, edit, or view rules for the model's territories.
Take care of data cleanup separately from territory assignment to keep your territory rule structure lean. We recommend using: Built-in duplicate management features to manage and merge duplicate records. Lightning Data to keep your records current and to find new accounts similar to your best customers.
Managing Assignment Rules. Salesforce uses a variety of rules to help assign accounts to specific sales reps. When you create a new level in your sales hierarchy, you can assign accounts manually, or use inherited account assignment rules to assign those accounts automatically. Using inherited rules saves a lot of time.
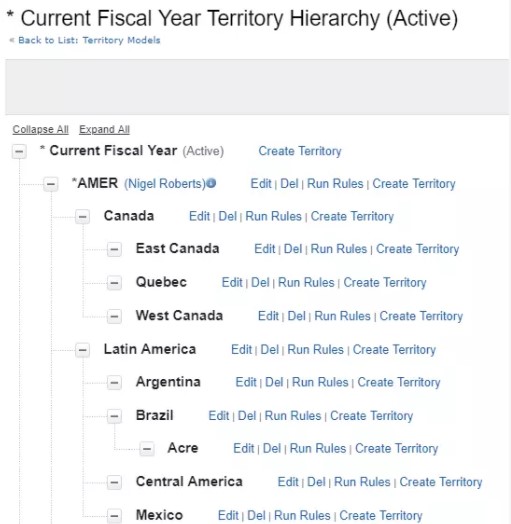
The name and state of the territory model appear at the top node of the hierarchy (1). Parent and child territories are nested beneath the model name. If a territory has a forecast manager assigned, the manager's name appears here (2). Create or edit child territories, or run their assignment rules (3).
The basic idea in the Salesforce Help doc is precisely the deli counter example above: Add an auto-number field to Lead that counts up every time there's a new lead. Add a formula field on Lead to calculate the "Round Robin Id" by MODing the Lead number by the number of sales reps and adding 1. Hard-code Lead Assignment Rule Entries matching ...
To set it up on the account edit page, select Evaluate this account against territory rules on save. To set it up using the API, set the appropriate header parameter in the SOAP API or REST API update call. But because Salesforce runs the assignment rules for all your accounts even when just one was updated, performance can take a hit.
Marketing Cloud Account Engagement Knowledge Base: Market to Your Customers with Marketing Cloud Account Engagement. Explore multiple ways to assign prospects within Marketing Cloud Account Engagement and Salesforce, including manual assignment and using automation rules or completion actions to assign prospects to a user or group based on their activity or information.
The parent account must be an existing account in Salesforce. You can enter the account name, or select (or optionally, create) the account using the lookup icon. Partner Account: Read-only field that indicates whether an account is a partner account. ... When checked, causes account assignment rules to run when the account is edited and saved ...
Assignment Rules are supported on the Lead and Case objects. Assignment rules automate your organization's lead generation and support processes. Use lead assignment rules to specify how leads are assigned to users or queues. Use case assignment rules to determine how cases are assigned to users or put into queues.
Go to Setup -> type Assignment Rules in the Quick Find box -> choose Case Assignment Rules -> click New -> enter the Rule Name and click Save. Click on the rule you just created -> click New in the Rule Entries section. Sort Order - defines the order in which entries will be processed (entering "1" means that this entry will be processed ...
Salesforce Customer Secure Login Page. Login to your Salesforce Customer Account.
Salesforce Lead Assignment Rules are a numbered set of distribution rules that determine which owner a Lead record should be assigned (either a specific user or to a Salesforce Queue).They are generally used at the point in time when a Lead is created (typically by Web-to-lead or an integrated marketing automation platform like Pardot, Marketo, HubSpot).
From Service Setup, enter Queues in the Quick Find box and select Queues . Click New and complete the queue details. Supported Objects: select Case and click Add . Queue Members: Click User: (Your Name) in the Available Members list, and click Add to add yourself to the Selected Members list. Click Save .
Assignment Rules in Salesforce: Imagine this: You're a lone wolf in the Salesforce jungle, battling a relentless tide of leads and cases. Hours melt away as you manually assign each one, feeling ...
Create or Setup assignment rules. From Setup, enter Assignment Rules in the Quick Find box, then select either Lead Assignment Rules or Case Assignment Rules. Choose New, and then give the rule a name. Specify whether you want this to be the active rule for leads or cases created manually and via the web and email. Then click Save.
When you set up Email-to-case, you can take those emails and turn them automatically to Case records in Salesforce, send auto-replies, distribute them to your support team, and take other automated actions. These will save support teams a lot of energy creating Case records and managing them appropriately. Instead, you have the chance to free ...
An assignment rule dictates to whom a lead or case is assigned based on criteria that is specified within Salesforce. Typically, your organization will have ...