
How To Write A Presentation 101 | Step-by-Step Guides with Best Examples | 2024 Reveals
Jane Ng • 05 Apr 2024 • 8 min read
Is it difficult to start of presentation? You’re standing before a room full of eager listeners, ready to share your knowledge and captivate their attention. But where do you begin? How do you structure your ideas and convey them effectively?
Take a deep breath, and fear not! In this article, we’ll provide a road map on how to write a presentation covering everything from crafting a script to creating an engaging introduction.
So, let’s dive in!
Table of Contents
What is a presentation , what should be in a powerful presentation.
- How To Write A Presentation Script
- How to Write A Presentation Introduction
Key Takeaways
Tips for better presentation.
- How to start a presentation
- How to introduce yourself

Start in seconds.
Get free templates for your next interactive presentation. Sign up for free and take what you want from the template library!
Presentations are all about connecting with your audience.
Presenting is a fantastic way to share information, ideas, or arguments with your audience. Think of it as a structured approach to effectively convey your message. And you’ve got options such as slideshows, speeches, demos, videos, and even multimedia presentations!
The purpose of a presentation can vary depending on the situation and what the presenter wants to achieve.
- In the business world, presentations are commonly used to pitch proposals, share reports, or make sales pitches.
- In educational settings, presentations are a go-to for teaching or delivering engaging lectures.
- For conferences, seminars, and public events—presentations are perfect for dishing out information, inspiring folks, or even persuading the audience.
That sounds brilliant. But, how to write a presentation?

How To Write A Presentation? What should be in a powerful presentation? A great presentation encompasses several key elements to captivate your audience and effectively convey your message. Here’s what you should consider including in a winning presentation:
- Clear and Engaging Introduction: Start your presentation with a bang! Hook your audience’s attention right from the beginning by using a captivating story, a surprising fact, a thought-provoking question, or a powerful quote. Clearly state the purpose of your presentation and establish a connection with your listeners.
- Well-Structured Content: Organize your content logically and coherently. Divide your presentation into sections or main points and provide smooth transitions between them. Each section should flow seamlessly into the next, creating a cohesive narrative. Use clear headings and subheadings to guide your audience through the presentation.
- Compelling Visuals: Incorporate visual aids, such as images, graphs, or videos, to enhance your presentation. Make sure your visuals are visually appealing, relevant, and easy to understand. Use a clean and uncluttered design with legible fonts and appropriate color schemes.
- Engaging Delivery: Pay attention to your delivery style and body language. You should maintain eye contact with your audience, use gestures to emphasize key points, and vary your tone of voice to keep the presentation dynamic.
- Clear and Memorable Conclusion: Leave your audience with a lasting impression by providing a strong closing statement, a call to action, or a thought-provoking question. Make sure your conclusion ties back to your introduction and reinforces the core message of your presentation.

How To Write A Presentation Script (With Examples)
To successfully convey your message to your audience, you must carefully craft and organize your presentation script. Here are steps on how to write a presentation script:
1/ Understand Your Purpose and Audience
- Clarify the purpose of your presentation. Are you informing, persuading, or entertaining?
- Identify your target audience and their knowledge level, interests, and expectations.
- Define what presentation format you want to use
2/ Outline the Structure of Your Presentation
Strong opening.
Start with an engaging opening that grabs the audience’s attention and introduces your topic. Some types of openings you can use are:
- Start with a Thought-Provoking Question: “Have you ever…?”
- Begin with a Surprising Fact or Statistic: “Did you know that….?”
- Use a Powerful Quote: “As Maya Angelou once said,….”
- Tell a Compelling Story : “Picture this: You’re standing at….”
- Start with a Bold Statement: “In the fast-paced digital age….”
Main Points
Clearly state your main points or key ideas that you will discuss throughout the presentation.
- Clearly State the Purpose and Main Points: Example: “In this presentation, we will delve into three key areas. First,… Next,… Finally,…. we’ll discuss….”
- Provide Background and Context: Example: “Before we dive into the details, let’s understand the basics of…..”
- Present Supporting Information and Examples: Example: “To illustrate…., let’s look at an example. In,…..”
- Address Counterarguments or Potential Concerns: Example: “While…, we must also consider… .”
- Recap Key Points and Transition to the Next Section: Example: “To summarize, we’ve… Now, let’s shift our focus to…”
Remember to organize your content logically and coherently, ensuring smooth transitions between sections.
You can conclude with a strong closing statement summarizing your main points and leaving a lasting impression. Example: “As we conclude our presentation, it’s clear that… By…., we can….”
3/ Craft Clear and Concise Sentences
Once you’ve outlined your presentation, you need to edit your sentences. Use clear and straightforward language to ensure your message is easily understood.
Alternatively, you can break down complex ideas into simpler concepts and provide clear explanations or examples to aid comprehension.
4/ Use Visual Aids and Supporting Materials
Use supporting materials such as statistics, research findings, or real-life examples to back up your points and make them more compelling.
- Example: “As you can see from this graph,… This demonstrates….”
5/ Include Engagement Techniques
Incorporate interactive elements to engage your audience, such as Q&A sessions , conducting live polls, or encouraging participation. You can also spin more funs into group, by randomly dividing people into different groups to get more diverse feedbacks!
6/ Rehearse and Revise
- Practice delivering your presentation script to familiarize yourself with the content and improve your delivery.
- Revise and edit your script as needed, removing any unnecessary information or repetitions.
7/ Seek Feedback
You can share your script or deliver a practice presentation to a trusted friend, colleague, or mentor to gather feedback on your script and make adjustments accordingly.
More on Script Presentation

How to Write A Presentation Introduction with Examples
How to write presentations that are engaging and visually appealing? Looking for introduction ideas for the presentation? As mentioned earlier, once you have completed your script, it’s crucial to focus on editing and refining the most critical element—the opening of your presentation – the section that determines whether you can captivate and retain your audience’s attention right from the start.
Here is a guide on how to craft an opening that grabs your audience’s attention from the very first minute:
1/ Start with a Hook
To begin, you can choose from five different openings mentioned in the script based on your desired purpose and content. Alternatively, you can opt for the approach that resonates with you the most, and instills your confidence. Remember, the key is to choose a starting point that aligns with your objectives and allows you to deliver your message effectively.
2/ Establish Relevance and Context
Then you should establish the topic of your presentation and explain why it is important or relevant to your audience. Connect the topic to their interests, challenges, or aspirations to create a sense of relevance.
3/ State the Purpose
Clearly articulate the purpose or goal of your presentation. Let the audience know what they can expect to gain or achieve by listening to your presentation.
4/ Preview Your Main Points
Give a brief overview of the main points or sections you will cover in your presentation. It helps the audience understand the structure and flow of your presentation and creates anticipation.
5/ Establish Credibility
Share your expertise or credentials related to the topic to build trust with the audience, such as a brief personal story, relevant experience, or mentioning your professional background.
6/ Engage Emotionally
Connect emotional levels with your audience by appealing to their aspirations, fears, desires, or values. They help create a deeper connection and engagement from the very beginning.
Make sure your introduction is concise and to the point. Avoid unnecessary details or lengthy explanations. Aim for clarity and brevity to maintain the audience’s attention.
For example, Topic: Work-life balance
“Good morning, everyone! Can you imagine waking up each day feeling energized and ready to conquer both your personal and professional pursuits? Well, that’s exactly what we’ll explore today – the wonderful world of work-life balance. In a fast-paced society where work seems to consume every waking hour, it’s vital to find that spot where our careers and personal lives harmoniously coexist. Throughout this presentation, we’ll dive into practical strategies that help us achieve that coveted balance, boost productivity, and nurture our overall well-being.
But before we dive in, let me share a bit about my journey. As a working professional and a passionate advocate for work-life balance, I have spent years researching and implementing strategies that have transformed my own life. I am excited to share my knowledge and experiences with all of you today, with the hope of inspiring positive change and creating a more fulfilling work-life balance for everyone in this room. So, let’s get started!”
🎉 Check out: How to Start a Presentation?

Whether you’re a seasoned speaker or new to the stage, understanding how to write a presentation that conveys your message effectively is a valuable skill. By following the steps in this guide, you can become a captivating presenter and make your mark in every presentation you deliver.
Additionally, AhaSlides can significantly enhance your presentation’s impact. With AhaSlides, you can use live polls , quizzes , and word cloud to turn your presentation into an engaging and interactive experience. Let’s take a moment to explore our vast template library !
Frequently Asked Questions
How to write a presentation step by step .
You can refer to our step-by-step guide on How To Write A Presentation Script: Understand Your Purpose and Audience Outline the Structure of Your Presentation Craft Clear and Concise Sentences Use Visual Aids and Supporting Material Include Engagement Techniques Rehearse and Revise Seek Feedback
How do you start a presentation?
You can start with an engaging opening that grabs the audience’s attention and introduces your topic. Consider using one of the following approaches: Start with a Thought-Provoking Question: “Have you ever…?” Begin with a Surprising Fact or Statistic: “Did you know that….?” Use a Powerful Quote: “As Maya Angelou once said,….” Tell a Compelling Story : “Picture this: You’re standing at….” Start with a Bold Statement: “In the fast-paced digital age….”
What are the five parts of a presentation?
When it comes to presentation writing, a typical presentation consists of the following five parts: Introduction: Capturing the audience’s attention, introducing yourself, stating the purpose, and providing an overview. Main Body: Presenting main points, evidence, examples, and arguments. Visual Aids: Using visuals to enhance understanding and engage the audience. Conclusion: Summarizing main points, restating key message, and leaving a memorable takeaway or call to action. Q&A or Discussion: Optional part for addressing questions and encouraging audience participation.

A writer who wants to create practical and valuable content for the audience
More from AhaSlides


- PRESENTATION SKILLS
Writing Your Presentation
Search SkillsYouNeed:
Presentation Skills:
- A - Z List of Presentation Skills
- Top Tips for Effective Presentations
- General Presentation Skills
- What is a Presentation?
- Preparing for a Presentation
- Organising the Material
- Deciding the Presentation Method
- Managing your Presentation Notes
- Working with Visual Aids
- Presenting Data
- Managing the Event
- Coping with Presentation Nerves
- Dealing with Questions
- How to Build Presentations Like a Consultant
- 7 Qualities of Good Speakers That Can Help You Be More Successful
- Self-Presentation in Presentations
- Specific Presentation Events
- Remote Meetings and Presentations
- Giving a Speech
- Presentations in Interviews
- Presenting to Large Groups and Conferences
- Giving Lectures and Seminars
- Managing a Press Conference
- Attending Public Consultation Meetings
- Managing a Public Consultation Meeting
- Crisis Communications
- Elsewhere on Skills You Need:
- Communication Skills
- Facilitation Skills
- Teams, Groups and Meetings
- Effective Speaking
- Question Types
Subscribe to our FREE newsletter and start improving your life in just 5 minutes a day.
You'll get our 5 free 'One Minute Life Skills' and our weekly newsletter.
We'll never share your email address and you can unsubscribe at any time.
Few of us feel entirely comfortable writing a presentation. There is something very daunting for many people about the process of moving your thoughts from your head to paper (or a series of slides on the computer).
However, there are things that you can do to help yourself. These include knowing your material well and taking time to consider what you want to say.
This page provides advice on how to write a presentation. It discusses the initial writing, and then also explains how to review and edit your work. This will help to ensure that your presentation is as effective as possible.
Before you start...
Before you start to write your presentation, you need certain information: the objective, the subject, and details of the audience, for example. For more about this, see our page on Preparing Your Presentation .
Based on the information you have gathered, you should also have started to develop your ideas and select the main points to include. For more about this, see our page on Organising Your Material .
Some basic starting points
There are two really important things to remember when starting to write a presentation:
1. Give your presentation an introduction, a main message, and a conclusion.
Some people summarise this as ‘say what you’re going to say, say it, then say what you’ve said’ .
However, that is not the whole story. Your introduction needs to ‘set the scene’ a bit and give a broad outline of what you are going to cover in your presentation. If you are using presentation software such as PowerPoint, this should be a single slide. Your conclusion needs to sum up and present your main message to your audience, probably again in a single slide.
If you are taking questions after your presentation, and you are using PowerPoint, you will probably have a slide up on the screen during questions. You could, of course, have a final slide that says something like “Thank you for listening, any questions?”, or gives your contact details.
However, you could also leave up a final slide that highlights your conclusions.
This will help to ensure that your key messages remain in the minds of your audience.
2. Think about using stories to get your message across
We are hard-wired by thousands of years of evolution to listen to stories. Stories helped us survive by reminding us about important behaviours. We therefore tend to remember them much better than dry lists of facts or bullet points.
It is much easier to work with this than ignore it.
There are two aspects of this.
First, you should try to think about your presentation as telling a story to your audience. What is the point that you are trying to make, and how can you best get it across?
Second, it is helpful to use stories as part of your presentation . For example, if you start by telling a story or anecdote, it will act as a ‘hook’ to draw in your audience. You can also use stories to illustrate each point you want to make. Of course, your story has to link to your main message, because you can pretty much guarantee that your audience will remember the story much longer than the conclusion!
Structuring Your Presentation
The structure and content of your presentation will of course be unique to you.
Only you can decide on the best way to present your messages. However, you might like to consider some standard presentation structures for inspiration:
1. Harnessing the Power of Three
In public speaking and rhetorical debate, as well as in much communication, three is a magic number. The brain finds it relatively easy to grasp three points at a time.
People find three points, ideas or numbers, easier to understand and remember than four or more.
You could therefore structure your presentation using the magic number of three.
For example, your presentation should have three main elements: the introduction, middle and conclusions. Within the main body of your presentation, divide your key message into three elements and then expand each of these points into three sub-points. If you are using a visual aid such as PowerPoint, limit the number of bullet points to three on each slide and expand on each of these as you go along.
What should you do if you have more than three points to make?
Reduce them until you don’t have more than three points!
Your audience will probably only remember three of your five or six points anyway—but which three? Do the work for them, and identify the three most important points, and leave the others out.
2. What, Why, How?
An alternative structure uses the questions “What?”, “Why?” and “How?” to communicate your message to the audience. In a way, this also harnesses the power of three, but is a special case for driving action.
“What?” identifies the key message you wish to communicate. Think about the benefit of your message for your audience. What will they gain, what can they do with the information, and what will the benefit be?
“Why?” addresses the next obvious question that arises for the audience . Having been told “what”, the audience will naturally then start to think “why should I do that?”, “why should I think that?” or “why should that be the case?”. Directly addressing the “why?” question in the next stage of your presentation means that you are answering these questions and your talk is following a natural route through the material. This will ensure that you have the audience on your side immediately.
“How?” is the final question that naturally arises in the audience’s mind . They want to know how they are going to achieve what you have just suggested. Try not to be too prescriptive here. Instead of telling people exactly how they should act on your message, offer suggestions as to how they can act, perhaps using examples.
You should try to back up what you say with evidence. You can use case studies, personal examples or statistics here, but try to ensure that you use them in the form of stories.
There is more about this on our page Presenting Data .
Editing Your Content
Once you have a first draft of your presentation, it is important to review and edit this.
This will help to ensure that it really does get your message across in the most effective way.
When editing presentation content, you should consider:
The language . Make sure that what you are saying will be clear to your audience. Remove any jargon and try to use plain English instead. If necessary, explain terms when you first use them.
Sentence structure . Use short sentences and keep the structure simple. Remember that you will be talking through your ideas and that the audience will be listening rather than reading.
The flow . Make sure that your presentation structure leads your audience through your ideas and helps them to draw your conclusion for themselves.
Use metaphors and stories to aid understanding and retention.
‘Hooks’ to get and hold the audience’s attention . Ensure that you have included several ‘hooks’ at various points in the presentation. This will help you to get and then keep the audience’s attention. These might be stories, or audience participation, or some alternative visual aids , such as a short video.
Check, and double check, for spelling and grammar . Make sure that any presentation slides or illustrations, titles, captions, handouts or similar are free from spelling mistakes.
Ideally, you should take a break from the presentation before editing so that you can look at your writing with a fresh pair of eyes.
You might also want to ask a friend or colleague to have a look, particularly at the flow and the language. If possible, ask someone who is not familiar with the material .
A final thought
The actual writing of your presentation is really the final stage of your preparation.
If you have done your homework, you will already be clear about the reason why you are presenting, the subject matter, and the main points you want to make. Actually putting it down on paper should therefore be relatively straightforward.
Continue to: Deciding the Presentation Method Preparing for a Presentation
See also: Organising the Presentation Material Working with Visual Aids Coping with Presentation Nerves Dealing with Questions

- Presentation
What are the best introductions for a Presentation?
- January 12, 2023
Here we’re going to talk about the introduction for presentation and how to start a powerful presentation. Whether you’re an experienced public speaker or just starting, it’s always good to know what different audiences expect from your introduction. What should be the length of the intro? How should you start a presentation introduction?
I’m sure you’ve seen it happen plenty of times: after waiting for what feels like hours, the presenter finally comes on stage and starts his speech by walking from side to side as he speaks into his microphone. This is awkward and does not make a good impression.
It’s not just about making a memorable first impression, though! The intro of your Presentation design services is what attracts the audience and makes them feel comfortable enough to listen to you for the rest of the time.
Table of Contents
What’s a presentation introduction?
The presentation introduction is where you introduce yourself to your audience and tell them what you will be discussing. You may use visual aids such as charts and graphs to introduce your PowerPoint presentation. Or, you might just give a brief summary of yourself. Your introduction should show you are a competent professional and grab your audience’s attention to learn more about the topic.
What is the importance of knowing how to start a presentation introduction?
Starting a presentation is essential for capturing your audience’s interest and helping them focus on what you are going to share. Your introduction should introduce not only the purpose of your talk but also who will be speaking throughout it – introducing yourself as an expert in this field can help establish that connection between speaker/audience member When presenting before unfamiliar audiences (a new group with different needs), starting off by identifying those specific goals provides the necessary context so everyone feels connected even though there may not have been previous exposure or interaction beforehand.
Why is it difficult to start a presentation?
People are most scared of speaking in public around the time they start their presentations. This is because it’s very intimidating and we all tend to feel like our voice won’t be heard then, so what do you think? A lot more reading would help me out here- I’m guessing there was some kind of a phenomenon happening with regards to speech patterns or something along those lines that has been researched extensively over recent years.
To be successful at starting a presentation, you need to capture your audience’s attention and introduce them personally. It is important not just for the first few moments but throughout; otherwise, they will lose interest quickly because of how concisely we speak about our topics (or lack thereof).
What is the best introduction for presentation?
Depending on the event you are attending, a facilitator might introduce you to the crowd or you may need to introduce yourself.
Many people came to the event expecting a speaker, or maybe they even knew that you would be speaking. You should feel confident as the audience will be interested in your message.
Before you start your speech, wait until the audience is attentive.
Make sure you are welcoming the audience by introducing yourself. This should be followed by a brief biography that includes your experience. This will draw attention to your credibility (ethos) and help you to present your credentials to the audience.
Welcoming Your Audience. Tell them who you are
It’s polite to greet everyone and introduce yourself. Everyone will be interested in knowing who you are. Your name, job title or reason for being an expert in your field should be included in your introduction. Your audience will listen more if they trust you.
Share your presentation
Your audience should be able to understand what you are going to talk about in a concise and organized manner. Consider your content and identify three points that you want to explain in detail by the end.
Make an intriguing statement
You don’t need to tell a personal story, but you can share a thought-provoking fact about the relevance of your presentation.
Tell them why it’s important
Your audience must know what you are presenting. To help convey the importance of your message, you might consider bringing in statistics or data.
Tell a Story
Consider telling a brief, relevant story before you begin with the slide presentation. This will help you build rapport with your audience. You can tell a story that is humorous, inspirational, or thought-provoking. However, it should contain 30 seconds to one minute of information. Your story may benefit from a personal touch. You might have an experience that is relevant to the main points of your presentation. Share that with your audience.
Invite the audience to participate
Ask your audience to join you if you don’t intend to make bold statements or tell a story. Asking an open-ended question requires your audience to raise their hand or answer the question. Ask them to raise their hands if they are answering your question at a later time. This tactic is most effective in intimate or small-scale settings.
Stand up straight and have confident body language
When you are about to go on stage, take a few moments in front of your mirror and check yourself. Make sure that all aspects (including posture) match what we want them too!
Organize notes and other content
When speaking in front of an audience, it is crucial to ensure that you have everything organized beforehand. Before starting your presentation or speech for the day put all notes and other required content into order so there are no mistakes when delivering them with confidence!
9 Tips on Openings and How to Start Presentation Introduction
1-know your audience.
In every country across the world, people open their lectures with a different introductory routine. Secretary of State John Kerry always starts off by telling jokes and you can see this tradition appearing in various opening sequences everywhere today!
It is important to start your presentation with a joke, play their happy songs, and compliment them. This will make the student more interested in what you have got going on!
2-Have an exciting start with attracting attention
Start your speech with a strange device, an incredibly energetic start, or a unique movement to get people excited and wanting more! For example, you can play music while giving the introduction of who will be speaking so that it feels like someone is sitting on stage next door listening in.
3-Choose your opening sentences carefully
The opening sentences of a presentation are extremely important because they define the main theme and shape public opinion. We have said before that starting off with something interesting can make you seem more trustworthy to an audience, so be sure not only to start strong but also to continue in this manner throughout your speech!
4-Use visual aids
The image you choose for your presentation can have a huge impact on how much people learn and remember. Make sure it’s relevant, and interesting enough so they will want more information about what is being presented in real-time or later when looking back at their notes from the event (if any), and useful – this means providing context for everything we do every day by displaying symbols that represent ideas beyond just color schemes but also objects associated with tasks such as tools, numbers indicating days until deadlines, etc., aesthetically pleasing without having too many distracting elements which would take away attention span.
5-Compliment your audience
The audience is always more engaged when you start your speech with a compliment. You can make them feel good about themselves and their purchase decision by telling them how wonderful they are! “Everyone likes to be praised,” right? “Surely YOU are the one who loves receiving compliments from others.” That’s why starting off every presentation or meeting discussion on an uplifting note will have everyone paying attention better than ever before – because we’re seeking approval in this society today just as much (if not MORE) than physical sustenance at times…so let me tell ya: It works wonders!! When I perform talks/lectures where there’s.
6-Use an anecdote or a quick story
The human brain is naturally drawn to stories. And when you’re in a conversation, it can be hard not to make assumptions about what someone else knows or doesn’t know based on their story-telling abilities alone! But beware: even if the speaker has limited experience with certain topics (like my lack of knowledge when talking about football), I’m still trying to learn as much from them by asking questions and listening carefully – which also helps me better understand where this person fits into society overall.”
7-Ask for audience participation
At the beginning of the presentation ask for audience participation. you can ask an important question or a rhetorical question. If you do not answer at the beginning, it causes mental conflict in the audience. Since the only source of answers is this presentation, so everyone’s attention is focused on the speaker and his speeches.
8-Keep your introduction short
Introducing yourself to a crowd goes beyond just telling them who you are. It’s important that your presentation starts with an introduction, which should be between 90 seconds and two minutes long for small-scale audiences (or 29 seconds). This way people get acquainted before getting into the meat of things like content or topics so they know where exactly their attention needs lie from there on out!
The way to keep people waiting for your next word is by being silent. If you start talking before the others, they will all wait in suspense and see what’s coming out of their mouths next!
How to start with an Introduction?
Here are some tips to help you present yourself well in a presentation.
- A link-back memory formula is a good idea. You must connect with your audience to be able to deliver a powerful presentation. A simple story about who you are, your origins, and the reasons you are speaking is the best way to connect with your audience.
- A good story is a favorite of the human brain. This makes us more likely to retain and listen to it. We also feel more connected to the storyteller (or hero), and are more likely to listen to and retain the information.
- The Stereotype Formula is available for testing. This one is simple and efficient. You can introduce yourself by sharing a common stereotype about your profession. This will allow you to connect with your audience, make them laugh a little, and create a lighthearted mood for the speech.
What kind of opening you can use?
Ready to start a new chapter in your professional life? In this presentation, I will share with you some tips on how best practices for creating presentations that are engaging and informative. You can expect key points about what makes good content memorable as well strategies used by experts so even those who don’t have much experience remembering things remember them longer!
- I’m so happy to be here
- it’s great to be here
- you’ve all probably heard the rumors by now…
- thank you for inviting me today.
- can everyone hear me?
- hi there! how are you doing?
- good afternoon, everyone!
- hello guys! how are doing?
- it’s a pleasure to be here today.
- thank you for coming here today.
- good evening, everybody.
- ladies and gentlemen, boys and girls, children of all ages… I am so excited to see you all today.
What introduction for presentation is forbidden for an opening?
Here is a list of things that you should never do when you are opening a presentation:
- Do not apologize for anything during the presentation or opening. Some people start saying these things out of habit. By apologizing, you are telling your audience that you have not prepared something worthy for them. For example: “sorry to take your time.”
- Avoid complaining at the beginning of the presentation
- Never insult the audience
- Avoid jokes about your topic
- Do not mention any failures at all costs! Stick with positive emotions.
- Avoid long introductions. Introductions should be short And occupy less than 20% of the speech.
Introduction for presentation ideas
Engaging the audience is crucial right from the beginning. These are some ways to start a presentation.
Surprise the audience
There are many ways you can shock your audience. You could use a video or a prop to start talking to the audience, laugh at something, etc.
However, you need to make sure that the shock has the desired effect. You want your audience to be engaged because they enjoyed the surprise or found it interesting. They don’t need to feel upset so that they start looking for flaws in your argument. The shock must fit the purpose of your presentation and your audience.
Share personal stories
The audience loves hearing stories, and it’s even more enjoyable when it is about you, as the speaker. They get to see your human side.
If it is relevant to your presentation’s purpose, you might tell a story about a time when things weren’t going as well. This will be relatable as everyone has experienced failures and mistakes. Your audience will be more likely to stay engaged if they can relate to you.
If you feel comfortable, you can tell these stories in a humorous manner. There is also less risk of misinterpretation because you are not telling a joke.
Get the audience to “imagine” and “what if?”
Asking your audience to think about what if or imagine something will get them thinking creatively. This technique can be used to invoke certain emotions, which are often the same feelings that you feel over the same thing. Emotions can be a powerful way to ensure that people listen and are involved in your words.
Create your presentation in the future or past
Symbouleution/deliberative rhetoric is when the speaker tries to get the audience to take action by talking about a possible future. This technique is often used by politicians. Martin Luther’s speech “I have a Dream” is a good example.
Talking about the past can produce similar reactions from your audience. You can use lessons learned from successes and failures to help you create a similar response. You might, for example, remind the audience about times when the country was economically strong or when it made mistakes that led to economic chaos.
Refer to their problem or potential
Another way to get their attention is to put your finger on their pain points. This triggers an emotional response again. You might ask, “Have it been difficult to maintain a healthy diet?” Your audience will want to stay engaged as they are interested in the solution and the possibilities that you offer.
There is no better way to kill your presentation than by paying attention lessness. Whether you’re giving a presentation at work or school, it’s important to make sure that the audience is engaged from start to finish. This can be done by following some simple tips like making eye contact with them and speaking clearly so they know when their turn comes up for questions! If you pay attention to the points mentioned in this article and use these tips when starting a presentation, your speech will stay with audiences for many years.
What is a good start for a presentation?
Start your presentation by introducing yourself. Along with sharing your name, give your audience some information about your background. Choose details that are relevant to your presentation and help establish you as an expert in your chosen topic. Example: Good morning.
What do you say before starting a group presentation?
Before you begin your presentation, start by greeting your audience, welcoming them to the event and introducing yourself.

- Graphic Design , UI-UX
How to Become a Motion Graphic Designer?

A Brief Overview of Lean UX

UX Strategy and Its Components
you'r more than welcome
7 days a week, 9:30 AM – 5:30 PM
contact info
[email protected] +351910923549
- LB07129, Jebel Ali Freezone, Dubai, UAE
Got a Project?
We’re a team of creatives who are excited about unique ideas and help companies to create amazing identity by offering wide range of digital services
© 2021 All rights reserved.
Be the first one who knows about updates!
enter your email address 📩
Welcome to the club 🎉.
From now on, Temis will inform you of its most valuable content and offers. You can also subscribe to this list at the moment. We will also protect your privacy

Starting a presentation: the decisive moment that captivates your audience
Have you ever wondered how to grab your audience's attention from the very first moment during presentations? The answer lies in a compelling and engaging introduction . In this article, we'll look at how you can create a captivating introduction for your presentation. And don't worry, we also have some fun ideas ready to make your audience laugh. So let's get started!
Why is the start of a presentation so important?
First impressions count, and that goes for presentations, too. Your introduction can make or break your audience's attention. It serves not only to introduce the topic of your presentation but also to establish a connection with your audience. An effective presentation start should grab your audience's interest, outline the main points of your topic, and provide a smooth transition to the main body of the presentation. Remember, first impressions are not repeatable, so make the most of them!
Starting a presentation - an example
It is useful to be clear about the message you want to convey before writing the introduction. Are you ready to see an example? Imagine you are giving a presentation on sustainable tourism. Your introduction might look like this: "Have you ever wondered what impact your vacation travel has on the environment? Today we're going to look at the concept of sustainable tourism and how we can enjoy our vacations without harming our planet." See how this example speaks directly to the audience and provides insight into the topic. You can also start your presentation introduction with a statistic, a personal story, or a question to pique your audience's interest.
Funny presentation introduction: humor as an icebreaker
Humor can be a great way to create a positive atmosphere and get your audience on your side. A funny start of a presentation can be especially useful if you are presenting a complex or dry topic. Let's say you're giving a presentation on tax law. Your introduction might go like this: "Who would have thought that one day we would voluntarily sit in a room and talk about taxes? But don't worry, I promise it won't be as bad as it sounds!" Remember that the humor in your introduction should fit your topic and audience. What may be funny in an informal setting may not be appropriate in a formal situation.
Formulating the introduction to a presentation: important tips
When it comes to formulating your presentation introduction, there are some important points to consider.
- Keep it short and to the point. Long and confusing introductions can lose your audience.
- Make it personal. Speak directly to your audience and try to make an emotional connection.
- Make sure your introduction clearly states the purpose of your presentation. Your audience should have a clear idea of what they can expect from the presentation after the introduction.
More important tips for presentation introductions
Use emotion.
The introduction is an ideal place to stir emotions in your presentation. This can be an exciting story, a surprising fact, or a shocking quote that will engage your audience emotionally and keep them interested in the rest of the presentation.
Integration of interactivity
Interactive elements in your introduction can help attract and hold the audience's attention. For example, you could conduct a short poll or quiz, ask a question to which the audience can respond, or ask them to share their experiences or opinions.
Reuse of the introduction at the end
To make your presentation coherent and rounded, you can use elements from your introduction at the conclusion of your presentation. This could be a quote, a statistic, or a question that you introduced at the beginning and that you pick up again at the end to close the circle and underline your central point.
Professional language and style
While it's important to speak in a language your audience understands and can relate to, you should also remember to maintain a professional tone and style. Avoid jargon unless necessary, and make sure your phrasing and word choice support and reinforce your message.
Step-by-step guide for a convincing presentation introduction
1.identify your audience.
Before you start writing your introduction, you should first identify and understand your audience. Will they already be familiar with the topic? What are their interests and needs? This information will help you tailor your introduction to them.
2.Define your main message
Determine what the main message or purpose of your presentation is. This will help you determine the focus of your introduction.
3.Arouse the interest of your audience
Start with a strong statement, an interesting statistic, a provocative question, or a short story to pique your audience's interest.
4.Make a connection to the topic
After piquing your audience's interest, make a clear connection to the topic of your presentation. Give an overview of what you are going to present.
5.Formulate your thesis or point of view
If relevant, state your thesis or point of view. This should be a clear and concise statement that summarizes the goal or purpose of your presentation.
6.Give a preview of the presentation
Conclude your introduction with a brief preview of the points or topics you will cover in your presentation. This gives your audience a guide to what they can expect. Make sure you use a good structure for your presentation. We've summarized tips for the best presentation structure for you here.
7. review and refine your introduction
Read through your introduction and make sure it is clear, concise, and interesting. Avoid giving too much detail - that will go into the body of the presentation. Your introduction should make your audience curious and want to hear more.
With this step-by-step guide, you will be well-prepared to create a powerful introduction for your presentation.
Adaptation of the introduction to different presentation formats
The way you craft your introduction can vary depending on the format of the presentation. A presentation at a conference or business setting will likely require a more formal approach than a presentation in an informal or social setting. It is important to adjust the tone, style, and content of your introduction accordingly.
Use of technology to improve the start of your presentation
Technology can help you make your introduction even more effective. For example, you could use a short video or animation to introduce your topic or include interactive elements like live polls or quizzes to encourage audience engagement. There are many online tools and platforms that can help you seamlessly incorporate these elements into your presentation.
Learn here step by step how to create Collaboard with online whiteboard.
The introduction in virtual presentations
With the rise of remote work and online meetings, introductions in virtual presentations also play an important role. Here, it is crucial to capture the audience's interest from the very beginning, as distractions are often greater in the online environment than in face-to-face meetings. A good approach could be to use interactive tools such as online polls or chat functions to engage the audience in the first few minutes.
The introduction as part of a storytelling approach
Storytelling is an effective way to convey complex topics in your presentation and engage your audience emotionally. Your introduction can begin with a story that runs through your entire presentation. It is important that this story is relevant to your topic and appeals to your audience. In the introduction, you can set the mood for your audience with a compelling yet insightful narrative. The introduction should present a clear and compelling premise or question that will be resolved or answered as your presentation progresses. By establishing this suspenseful starting point, you give your audience an emotional anchor to attach their interest. It is also critical that the story in your introduction relates to the rest of the content of your presentation and thus serves as a guide. This will help your audience understand and follow the connection between the introductory story and the overall topic. In addition, your narrative introduction paves the way for the other elements of your storytelling approach, such as detailed character portrayals, engaging conflict situations, or unexpected twists that will keep your audience's attention and help them understand your message.
Introduction Presentation: Summary and closing thoughts
An effective introduction is the key to a successful presentation. It captures the audience's attention, establishes a connection, and gives a clear overview of what's to follow. By identifying your audience and understanding their needs, you can create a customized introduction that will appeal to your audience. A strong opening, including an interesting statistic, a provocative question, or a personal story, can capture interest and encourage the audience to keep listening. Technology, including Collaboard and interactive elements, can help enhance your presentation and engage your audience. And by incorporating storytelling and awareness of cultural differences, you can create a deeper connection with your audience. Review and refine your introduction to ensure it is clear, concise, and interesting. A well-crafted introduction can make the difference between your presentation making a lasting impression or being forgotten. With these strategies and guidelines, you'll be well-prepared to create an impressive introduction for your next presentation. Now you're ready to engage your audience and deliver a compelling presentation. Good luck!
Introduction Presentation - Frequently Asked Questions & Answers
How long should the introduction of a presentation be.
The length of the introduction will depend on the overall length of your presentation, but a good rule of thumb is that it should take up about 10-15% of the total time.
What belongs in the introduction of a presentation?
In your introduction, you should introduce the topic, pique the audience's interest, briefly outline the main points you will cover, and present the benefit or goal of the presentation to the audience.
How can I capture the interest of my audience in the introduction?
There are many ways to capture the interest of your audience. You could start with an interesting statistic, a provocative question, a short story, or a surprising fact.
How important is the introduction in a presentation?
The introduction is very important because it sets the tone for the rest of the presentation. A well-designed introduction can capture your audience's attention, spark interest, and provide a clear context for what follows.
Can I use humor in my introduction?
Yes, humor can be an effective way to capture the interest of your audience and create a relaxed atmosphere. However, make sure that your humor is appropriate and respectful and that it fits your audience and the topic of your presentation.
How can I practice my presentation introduction?
You can practice your introduction in front of a mirror, with a friend or colleague, or even with a recording device. This way you can refine your choice of words, your tone of voice, and your body language and make sure your introduction is clear and convincing.
Do I always have to mention the topic directly in my introduction?
It is not always necessary to state the topic immediately. Sometimes it can be more effective to first pique your audience's interest or tell a story before revealing the exact topic of your presentation. However, the topic should always become clear in the first few minutes of the presentation.
Recent Posts from Blog
The 5-why method » the most important things at a glance.
In companies and in everyday life, we often face problems that at first glance appear to be solvable using simple methods....
Presentation structure » How to create the perfect structure!
A well-structured presentation is crucial to engaging your audience and getting your message across effectively. A clear...
Best questions in retrospective. These methods can help your team move forward
In many work and project environments, retrospective methods are among the key tools for improving processes. In a good...
On-Premises - When is it the right choice?
In this article, we would like to explain what on-premises means and what advantages it has for your company. We will also...
Stay up to date with the latest collaboration tips and news.
- Student Login:

How to Organize Your Introduction for a Presentation [+ FREE Presentation Checklist]
May 1, 2018 | Business Professional English , Free Resource , Public Speaking & Presentations

This lesson on how to organize your introduction for a presentation in English has been updated since its original posting in 2016 and a video has been added.
Getting ready to present in English? Here’s how to make sure your introduction for a presentation in English is successful.
But first… When you think about a presentation, I know you’re thinking about something like a TED video or a presentation at a conference. You’re thinking about a speech, with PowerPoint slides and a big audience.
But did you know we use the same skills when we share new information or ideas with our work colleagues? Or when we tell stories to our friends and family? The situation or speaking task may be different but we still use the same skills.
When presenting information or telling stories, we need to:
- Capture a listener’s attention
- Share information, ideas, or opinions
- Give the important details
- Make your information memorable
- Get your audience (family, friends, colleagues or strangers) to agree, to take action, to change their mind, etc.
So today you’re going to learn how to take the first big step in your English presentation: how to start with a great introduction.
The introduction is the most important part of your presentation. It is the first impression you’ll make on your audience. It’s your first opportunity to get their attention. You want them to trust you and listen to you right away.
However, that first moment when you start to speak is often the hardest. Knowing how to best prepare and knowing what to say will help you feel confident and ready to say that first word and start your presentation in English.
Be sure to include these 5 things in your inroduction.
Lesson by Annemarie
How to Organize Your Introduction for a Presentation in English and Key Phrases to Use
Organize Your Introduction Correctly
Okay, first let’s focus on what you need to include in your English introduction. Think of this as your formula for a good introduction. Using this general outline for your introduction will help you prepare. It will also help your audience know who you are, why you’re an expert, and what to expect from your presentation.
Use this general outline for your next presentation:
- Welcome your audience and introduce yourself
- Capture their attention
- Identify your number one goal or topic of presentation
- Give a quick outline of your presentation
- Provide instructions for how to ask questions (if appropriate for your situation)
Use Common Language to Make Your Introduction Easy to Understand
Great, now you have the general outline of an introduction for a speech or presentation in English. So let’s focus on some of the key expressions you can use for each step. This will help you think about what to say and how to say it so you can sound confident and prepared in your English presentation.
“The introduction is the most important part of your presentation. It is the first impression you’ll make on your audience. It’s your first opportunity to get their attention. You want them to trust you and listen to you right away.”
Welcome Your Audience & Introduction
It is polite to start with a warm welcome and to introduce yourself. Everyone in the audience will want to know who you are. Your introduction should include your name and job position or the reason you are an expert on your topic. The more the audience trusts you, the more they listen.
- Welcome to [name of company or event]. My name is [name] and I am the [job title or background information].
- Thank you for coming today. I’m [name] and I’m looking forward to talking with you today about [your topic].
- Good morning/afternoon ladies and gentlemen. I’d like to quickly introduce myself. I am [name] from [company or position]. (formal)
- On behalf of [name of company], I’d like to welcome you today. For those of you who don’t already know me, my name is [name] and I am [job title or background]. (formal)
- Hi everyone. I’m [name and background]. I’m glad to be here with you today. Now let’s get started. (informal)
Capture Their Attention
For more information about how to best capture your audience’s attention and why, please see the next session below. However, here are a few good phrases to get you started.
- Did you know that [insert an interesting fact or shocking statement]?
- Have you ever heard that [insert interesting fact or shocking statement]?
- Before I start, I’d like to share a quick story about [tell your story]…
- I remember [tell your story, experience or memory]…
- When I started preparing for this talk, I was reminded of [tell your story, share your quote or experience]…
Identify Your Goal or Topic of Presentation
At this stage, you want to be clear with your audience about your primary topic or goal. Do you want your audience to take action after your talk? Is it a topic everyone is curious about (or should be curious about)? This should be just one or two sentences and it should be very clear.
- This morning I’d like to present our new [product or service].
- Today I’d like to discuss…
- Today I’d like to share with you…
- What I want to share with you is…
- My goal today is to help you understand…
- During my talk this morning/afternoon, I’ll provide you with some background on [main topic] and why it is important to you.
- I will present my findings on…
- By the end of my presentation, I’d like for you to know…
- I aim to prove to you / change your mind about…
- I’d like to take this opportunity to talk about…
- As you know, this morning/afternoon I’ll be discussing…
Outline Your Presentation
You may have heard this about presentations in English before:
First, tell me what you’re going to tell me. Then tell me. And finally, tell me what you told me.
It sounds crazy and weird, but it’s true. This is how we structure presentations in English. So today we’re focusing on the “First, tell me what you’re going to tell me” for your introduction. This means you should outline the key points or highlights of your topic.
This prepares your listens and helps to get their attention. It will also help them follow your presentation and stay focused. Here are some great phrases to help you do that.
- First, I’m going to present… Then I’ll share with you… Finally, I’ll ask you to…
- The next thing I’ll share with you is…
- In the next section, I’ll show you…
- Today I will be covering these 3 (or 5) key points…
- In this presentation, we will discuss/evaluate…
- By the end of this presentation, you’ll be able to…
- My talk this morning is divided into [number] main sections… First, second, third… Finally…
On Asking Questions
You want to be sure to let you audience know when and how it is appropriate for them to ask you questions. For example, is the presentation informal and is it okay for someone to interrupt you with a question? Or do you prefer for everyone to wait until the end of the presentation to ask questions?
- If you have any questions, please don’t hesitate to interrupt me. I’m happy to answer any questions as we go along.
- Feel free to ask any questions, however, I do ask that you wait until the end of the presentation to ask.
- There will be plenty of time for questions at the end.
- Are there any questions at this point? If not, we’ll keep going.
- I would be happy to answer any questions you may have now.
Capture Your Audience’s Attention
Do you feel unsure about how to capture the attention of your audience? Don’t worry! Here are some common examples used in English-speaking culture for doing it perfectly!
Two of the most famous speakers in the English-speaking world are Steve Jobs and Oprah Winfrey. While Steve Jobs is no longer living, people still love to watch his speeches and presentations online. Oprah is so famous that no matter what she does, people are excited to see her and listen to her.
BUT, if you listen to a speech by Steve Jobs or Oprah Winfrey, they still work to get your attention!
The don’t start with a list of numbers or data. They don’t begin with a common fact or with the title of the presentation. No – they do much more.
From the moment they start their speech, they want you to listen. And they find interesting ways to get your attention. In his most famous speeches, Steve Jobs often started with a personal story. And Oprah often starts with an inspiring quote, a motivational part of a poem, or a personal story.
These are all great ways to help your audience to listen to you immediately – whether your presentation is 3 minutes or 20 minutes.
Here’s how you can do it.
Like Steve Jobs or Oprah Winfrey, start with a:
- Personal story or experience
- Motivational quote or line from a poem or book
- Joke (be careful with this – make sure it translates easily to everyone in the audience!)
- Shocking, bold statement (Think of Steve Jobs’ quote: “ Stay hungry. Stay Foolish .”)
- Rhetorical question ( =a question that you don’t want an answer to; the focus is to make someone think)
And finally, consider audience participation. Ask a question and get your audience to respond by raising hands.
Get the complete Presentations in English Series:
Part 1: How to Prepare for Your Presentation in English
Part 2: How to Start with a Great Introduction in Your Presentation
Part 3: How to Organize Your Presentation in English
Part 4: How to End Your Presentation Powerfully
As I mentioned in the video, I have two question for you today:
- What is the best introduction you’ve ever heard? Have you watched a TED Talk or a presentation on YouTube with a great introduction? Tell me about it. What do you think was great about the introduction?
- What frightens you the most about preparing your introduction in a presentation? Share your concerns with me so I can help you overcome any challenges you have.
Be sure to share in the comments below to get feedback from me and to learn from others in the Confident English Community.
Have a great week! ~ Annemarie
Get the Confidence to Say What You Want in English
Follow my 3-step solution to speak English with clarity, fluency, and freedom so you can say what you want with confidence.
You'll also get my Confident English lessons delivered by email every Wednesday and occasional information about available courses. You can unsubscribe any time.
More Like This

#309: How to Go Off Topic in English | English Conversation Skills
Learn how to gracefully go off topic in English without losing your audience. Whether you’re in a meeting or chatting with friends, in this lesson we dive deep into the art of smoothly navigating tangents while enhancing your English conversation skills.
![when should the introduction to your presentation be written #308: How to Use ‘Though’ in English [+ FREE Worksheet]](https://www.speakconfidentenglish.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/How-to-Use-Though-in-English-400x250.png)
#308: How to Use ‘Though’ in English [+ FREE Worksheet]
Learn and practice how to correctly use though, although, even though, and as thought in your English conversations.

#307: How to Use English Abbreviations in Emails, Texts, and Conversations
Follow this comprehensive guide to learn how to use English abbreviations for emails, texts, and conversations.

How to Describe Your Personality in English
Did you know it’s common in daily conversation & in job interviews to hear this question: “So, how would you describe yourself?” — How would you answer the question? Use this lesson to learn real-life English vocabulary for describing personalities in English.

#306: Friendly Ways to Invite Someone in English
Extend invitations in English with phrases that strike the perfect balance between formality, friendliness, and warmth to make your invitations feel genuine and welcoming.

#305: Discover Effective Ways to Talk about Hope in English
Dive deep into the heart of English tenses—past, present, and future—highlighting how ‘hope’ evolves with each so you can talk about your hope in English.
© Copyright 2014-2024 Speak Confident English | Privacy Policy | Terms & Disclaimer | Online Class Policies
Thank you, Annemarie. thanks for the generosity of sharing useful and systemative information and content.
This is really a very informative message thank you.. And it’s help me a lot
hi thank you for this It was helpful. You used simple english that i understood well.
How to start with a great presentation on composition
Thankyou for the information . It was much helpful . I will definitely use this information in my presentation 🤗
Hi, I am Thang Sok Do you have a Sample presentation?
This was helpful but can you please tell me how to start a presentation in college because this is for work in a company. My presentation is on laboratory skills and all that
Its informative
Thank you for this video! I’ve learned quite a lot and will want to use all these knowledge in presenting my thesis proposal in 2 months. About your question no. 2, I’d just like to share that the mere fact of presenting in front of many respected professionals makes me already nervous and shaky even if i have studied everything about my presentation. What do you think should i do to deal with my concern?
Could you give me advise, how to start learning English for beginner.How to prepare presentation on any topic and how to make interesting..
Thank u so much for valuable advice. Definitely I will used this in my presentation!!
Thank you very much for these kind of useful advice. I hope my first presentation will be exciting for the audience.Your video is helping me again thanks a lot 😊
hi, i’m B.COM student and I have to prepare presentation about identifying business opportunities. How to start and an attractive attention to my audience.. Please Help me…
very nise and educative piece of information thank you nancy nairobi kenya
i am starting a video speech shooting in night about a famouse person how do i start my speech with a good intro.
Hi again how do you do a introduction goodbye
Hi i do not know what you are talking about
Hi Kate, I’m sorry to hear you’re not sure about the content. I recommend reviewing the video carefully if you haven’t already. Is there something specific you have a question about?
thanks a lot for guiding in such an easier way.
Your write-up on introduction helped a lot, thank you Annemarie. I work for cross-geography team and greetings get lengthy as timezones are different e.g. “Good evening to those joining from US office and good morning to colleagues from India office”. I replaced that with “Thank you everyone for joining”. Is it okay?
Hi Amit, I’m so glad it was helpful. As for your greeting, both of your options are perfectly appropriate and friendly.
How to introduce group members in online presentation?
Great question! I’d love to use that for a future Confident English lesson.
its amazing. i can’t explain in wording. this material helping me a lot. i am so happy after use this website . its make easy for me preparing my presentation more interesting. i am thankful too u.
thanks! i use your materials to teach my students(clinets) how to prepare a presentation. is it ok to use them on my materials?
Hi! I am a student from the USP from Tuvaluan and i take CEE45 so our assessment 2 is to prepared a group presentation and we presented in school. so need your help for how to start an attractive introduction to my teacher and my fellow students, they already kwow me.
Thank you.. very helpful
Very useful
It was very use Gul for or presentations
Hi. I am a 1st year BIT student and I have to prepare a presentation on 3D Printing. how to start an attractive introduction to my teachers, when they already know about me? Can you please help me out? Thank you.
I just took 1st place for my paper that I presented at an international students conference. I used a lot of your techniques to improve my speech and I have no words to say how grateful I am to you. Keep up the good work!
😲WOW!! That’s awesome, Andrew. 🙌Congratulations on your presentation. What a wonderful response to your hard work. I’d love to know what you presentation was about. And thank you for sharing your new here. I’m thrilled to know that my techniques were helpful to you.
The title of the presentation was “Handling burnout: A study regarding the the influence of job stressors over military and civilian personel”. I can sent you my paper through email if you would like to see it.
Hi Andrew, what a fascinating topic. And it’s interesting because I just had a newspaper reporter interview me about burnout as a small business owner. Must be a hot topic. 🙂 And sure, I’d love to see it.
🔥❤ too goodd
Hello Annemarie, Thank you so much for one of the best content on the English presentation, I’ve seen. I have a question: Is it impolite or informal to start the presentation without a greeting? I’m asking this question because I’ve seen a lot of TEDTalks and in only a few of them, they greet the audience and in most of it, they quickly go to the “CAPTURING the ATTENTION” with numbers and pictures. I would be so thankful if you could answer this question as soon as possible, my presentation is so close. Best regards, Helia
Hi Helia, What a great question. It has definitely become more common to skip the greeting and go straight to capturing the attention of the audience and you’re right that we often see this in TED talks. I would say it’s best to know your audience and what might be expected. For example, at more formal, traditional conferences or lecture, it might be more appropriate to start with a welcome. I prefer to welcome/thank my audience quickly at the start when I give presentations. A welcome can be very brief, just one sentence, and then you can quickly go into … Read more »
Hi Annemarie I would like to thank you for giving such types of presentation skills but I have a question can you give me some idea about vote of thinks.
I’m glad the lessons are helpful to you. Could you clarify what you mean by ‘vote of thinks?’ I’m not sure I understand that.
Please can you give me some idea about vote of thanks
Could you clarify what you’re asking for, Bello?
Thanks a lot
Glad it was helpful!
it is agood i learn alot from this english class
Hello.i would like to thank you for giving these beautiful tips to start a presentation.This article helped me a lot.
That’s great, Radha. Glad to hear it.
Thanks for your article. It’s simply for interpersonal skill development.
You’re welcome, Mithun. Glad to know it was helpful.
Hi Annemarie . Thank you so much for giving such helpful guildelines it’s really gonna help me
I’m glad it’s helpful, Swetha! 🙂
thank you for help me
You’re very welcome!
Hi Anne Marie, i ‘m from Catalonia and i came across with your site only by chance and i think it’gonna be so helpful for me to pass the next test for c1 level. Several weeks ago i did some rehersals with my presentation and i was so nervous and terrified about what was expected from me.
Some tips in your youtube channel are so cool !!! Thank you.
Hi Tom, I’m thrilled you’ve found this site in your preparations for your English exam and am glad to know it’s helpful! Best of luck as you continue to prepare.
Hi Annemarie Thanks it’s so useful to develop presentation skill. Fatima
You’re very welcome, Fatima! I’m glad it was helpful.
Awesome, especially this simple and clear motto: “First, tell me what you’re going to tell me. Then tell me. And finally, tell me what you told me.” This three sentences exactly explain the content you need to create a memorable presentation.
Hi Dzmitry,
Yes, I’ve always loved that simple motto on how to do a presentation. 🙂 It’s so easy to remember and tells you exactly what to do.
hello I need to introduce myself to language center. i am going to learn Danish Language and i want to introduce myself to them and i am little bit nervous because my grammar is not good at that level.so will you please guide me how to introduce myself to them with an example. i did go through your examples but that is for professionals and i am just a student (Graduate). I don’t have any experience . Please guide me how to do it.
I was in a confused state about starting a conversation and proceeding in it but when I read the guidelines you mentioned above I became confident. thank you for your innumerable ………….
Thank you so much…… it’s an excellent topic, and it helped me a lot
I’m so glad this was helpful to you! Thank you for sharing.
hi annemarie i have a few questions about a speech i have to make a englishi speech of what i want to become can you help me?
Hi Rebecca,
Thank you for the question. I have several lessons on the topic of presentations in English . However, for personal assistance with English or presentations, I only do that through my one-on-one classes .
thank you so much…… it’s really helpful for me….
You’re very welcome, Shalini.
Thanks its really nice to develop the presentation skills
Awesome. I’m glad it was helpful to you, Mohammed.
I have to give a demo on one of your programs next week. I would like you to check my self introduction – Good afternoon everyone and thank you for all of your presence. Before we get into the session I would like to quickly introduce myself. My name is Dinesh . I am working as a Pharmaceutical sale and promotion of the brands for Arrient Healthcare. I am in this filed for the past ten years. Before becoming trainer I worked as a medical representatives for different pharma company . I am highly interested in learning from people and … Read more »
Please ignore my previous comment. Yea the demo was a success. So hereafter I will say”I have been in this field for the past four years. Actually I worked for different consultancies so I didn’t include an article there.
I have to give a demo on one of your programs next week. I would like you to check my self introduction – Good afternoon everyone and thank you for all of your presence. Before we get into the session I would like to quickly introduce myself. My name is Monica. I am working as a Soft Skill Trainer at Synergy School of Business Skills. I am in this filed for the past four years. Before becoming trainer I worked as a Recruiter for different job consultancy. I am highly interested in learning from people and I think teaching/training is … Read more »
Thank you for sharing your example! One note: “I am in this field for the past four years.” –> Don’t forget, when we’re talking about something that started in the past and continues to now, we use the present perfect. How might you change this sentence to fix the grammar?
Also, we want to add an article to, “… I worked as a recruiter for [a] different job consultancy.”
I wish you much success in your demo this week! Best, Annemarie
Yea the demo was a success! So hereafter I will say”I have been for the past four years. Actually I worked for different consultancies.
I like it but I think capturing their attention is the most difficult part in preparing a presentation. From my little experience, I used to talk about something out of the scope of the presentation in order to grasp their attention. For example, I had a presentation about medical terminology and its parts (suffix, prefix —). So I provided example which is Ultra Violet then I talked about the ultraviolet in the sun and Vitamin D deficiency. They liked the talk because it is very important to them and by this topic I captured their attention more and more.
Hello Fadia, I’m sorry I’m so late in responding to your comment! I agree with you: capturing attention is very challenging to do. It requires understanding your audience, knowing what is important to them, and how to connect with them. In English-speaking culture, we often connect by telling a story or showing we understand a problem the audience has. I think you’re exactly right to talk about something that is maybe “off topic” or out of the scope of the presentation, as you said, to get their attention first. It sounds like you did a great job in your experience!! … Read more »
hi there it was great going through your enlightening presentation skills however i would be even more delighted if you put some quotes for various PPT’s which will give us an instant ideas during the adhoc PPT like myself…just a suggestion.
📣 The Confident Women Community in April The CWC is where women learn, practice, speak, and make progress. Coming in April we have speaking partner matching PLUS new study guides on travel. 🗺️
Pin It on Pinterest

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
14.1 Organizing a Visual Presentation
Learning objectives.
- Identify key ideas and details to create a concise, engaging presentation.
- Identify the steps involved in planning a comprehensive presentation.
Until now, you have interacted with your audience of readers indirectly, on the page. You have tried to anticipate their reactions and questions as all good writers do. Anticipating the audience’s needs can be tough, especially when you are sitting alone in front of your computer.
When you give a presentation, you connect directly with your audience. For most people, making a presentation is both exciting and stressful. The excitement comes from engaging in a two-way interaction about your ideas. The stress comes from the pressure of presenting your ideas without having a delete button to undo mistakes. Outside the classroom, you may be asked to give a presentation, often at the last minute, and the show must go on. Presentations can be stressful, but planning and preparation, when the time and opportunity are available, can make all the difference.
This chapter covers how to plan and deliver an effective, engaging presentation. By planning carefully, applying some time-honored presentation strategies, and practicing, you can make sure that your presentation comes across as confident, knowledgeable, and interesting—and that your audience actually learns from it. The specific tasks involved in creating a presentation may vary slightly depending on your purpose and your assignment. However, these are the general steps.
Follow these steps to create a presentation based on your ideas:
- Determine your purpose and identify the key ideas to present.
- Organize your ideas in an outline.
- Identify opportunities to incorporate visual or audio media, and create or locate these media aids.
- Rehearse your presentation in advance.
- Deliver your presentation to your audience.
Getting Started: Identifying and Organizing Key Ideas
To deliver a successful presentation, you need to develop content suitable for an effective presentation. Your ideas make up your presentation, but to deliver them effectively, you will need to identify key ideas and organize them carefully. Read the following considerations, which will help you first identify and then organize key ideas:
- Be concise. You will include the most important ideas and leave out others. Some concepts may need to be simplified.
- Employ more than one medium of expression. You should incorporate other media, such as charts, graphs, photographs, video or audio recordings, or websites.
- Prepare for a face-to-face presentation. If you must deliver a face-to-face presentation, it is important to project yourself as a serious and well-informed speaker. You will often speak extemporaneously, or in a rehearsed but not memorized manner, which allows for flexibility given the context or audience. You will need to know your points and keep your audience engaged.
Determine Your Purpose
As with a writing assignment, determining the purpose of your presentation early on is crucial. You want to inform your readers about the topic, but think about what else you hope to achieve.
Are you presenting information intended to move your audience to adopt certain beliefs or take action on a particular issue? If so, you are speaking not only to inform but also to persuade your listeners. Do you want your audience to come away from your presentation knowing how to do something they that they did not know before? In that case, you are not only informing them but also explaining or teaching a process.
Writing at Work
Schoolteachers are trained to structure lessons around one or more lesson objectives. Usually the objective, the mission or purpose, states what students should know or be able to do after they complete the lesson. For example, an objective might state, “Students will understand the specific freedoms guaranteed by the First Amendment” or “Students will be able to add two three-digit numbers correctly.”
As a manager, mentor, or supervisor, you may sometimes be required to teach or train other employees as part of your job. Determining the desired outcome of a training session will help you plan effectively. Identify your teaching objectives. What, specifically, do you want your audience to know (for instance, details of a new workplace policy) or be able to do (for instance, use a new software program)? Plan your teaching or training session to meet your objectives.
Identify Key Ideas
To plan your presentation, think in terms of three or four key points you want to get across. In a paper, you have the space to develop ideas at length and delve into complex details. In a presentation, however, you must convey your ideas more concisely.
One strategy you might try is to create an outline. What is your main idea? Would your main idea work well as key points for a brief presentation? How would you condense topics that might be too lengthy, or should you eliminate topics that may be too complicated to address in your presentation?
1. Revisit your presentation assignment, or think of a topic for your presentation. On your own sheet of notebook paper, write a list of at least three to five key ideas. Keep the following questions in mind when listing your key ideas:
- What is your purpose?
- Who is your audience?
- How will you engage your audience?
2. On the same paper, identify the steps you must complete before you begin creating your presentation.
Use an Outline to Organize Ideas
After you determine which ideas are most appropriate for your presentation, you will create an outline of those ideas. Your presentation, like a written assignment, should include an introduction, body, and conclusion. These components serve much the same purpose as they do in a written assignment.
- The introduction engages the audience’s attention, introduces the topic, and sets the tone for what is to come.
- The body develops your point of view with supporting ideas, details, and examples presented in a logical order.
- The conclusion restates your point of view, sums up your main points, and leaves your audience with something to think about.
Jorge, who wrote the research paper featured in Chapter 11 “Writing from Research: What Will I Learn?” , developed the following outline. Jorge relied heavily on this outline to plan his presentation, but he adjusted it to suit the new format.

Planning Your Introduction
In Chapter 12 “Writing a Research Paper” , you learned techniques for writing an interesting introduction, such as beginning with a surprising fact or statistic, a thought-provoking question or quotation, a brief anecdote that illustrates a larger concept or connects your topic to your audience’s experiences. You can use these techniques effectively in presentations as well. You might also consider actively engaging your audience by having members respond to questions or complete a brief activity related to your topic. For example, you may have your audience respond to a survey or tell about an experience related to your topic.
Incorporating media can also be an effective way to get your audience’s attention. Visual images such as a photograph or a cartoon can invoke an immediate emotional response. A graph or chart can highlight startling findings in research data or statistical information. Brief video or audio clips that clearly reinforce your message and do not distract or overwhelm your audience can provide a sense of immediacy when you plan to discuss an event or a current issue. A PowerPoint presentation allows you to integrate many of these different media sources into one presentation.
With the accessibility provided by the Internet, you can find interesting and appropriate audio and video with little difficulty. However, the clip alone will not sustain the presentation. To keep the audience interested and engaged, you must frame the beginning and end of the clip with your own words.
Jorge completed the introduction part of his outline by listing the key points he would use to open his presentation. He also planned to show various web links early on to illustrate the popularity of the low-carbohydrate diet trend.

Planning the Body of Your Presentation
The next step is to work with the key ideas you identified earlier. Determine the order in which you want to present these ideas, and flesh them out with important details. Chapter 10 “Rhetorical Modes” discusses several organizational structures you might work with, such as chronological order, comparison-and-contrast structure, or cause-and-effect structure.
How much detail you include will depend on the time allotted for your presentation. Your instructor will most likely give you a specific time limit or a specific slide limit, such as eight to ten slides. If the time limit is very brief (two to three minutes, for instance), you will need to focus on communicating your point of view, main supporting points, and only the most relevant details. Three minutes can feel like an eternity if you are speaking before a group, but the time will pass very quickly. It is important to use it well.
If you have more time to work with—ten minutes or half an hour—you will be able to discuss your topic in greater detail. More time also means you must devote more thought into how you will hold your audience’s interest. If your presentation is longer than five minutes, introduce some variety so the audience is not bored. Incorporate multimedia, invite the audience to complete an activity, or set aside time for a question-and-answer session.
Jorge was required to limit his presentation to five to seven minutes. In his outline, he made a note about where he would need to condense some complicated material to stay within his time limit. He also decided to focus only on cholesterol and heart disease in his discussion of long-term health outcomes. The research on other issues was inconclusive, so Jorge decided to omit this material. Jorge’s notes on his outline show the revisions he has made to his presentation.

You are responsible for using your presentation time effectively to inform your audience. You show respect for your audience by following the expected time limit. However, that does not mean you must fill all of that time with talk if you are giving a face-to-face presentation. Involving your audience can take some of the pressure off you while also keeping them engaged. Have them respond to a few brief questions to get them thinking. Display a relevant photograph, document, or object and ask your classmates to comment. In some presentations, if time allows, you may choose to have your classmates complete an individual or group activity.
Planning Your Conclusion
The conclusion should briefly sum up your main idea and leave your audience with something to think about. As in a written paper, you are essentially revisiting your thesis. Depending on your topic, you may also ask the audience to reconsider their thinking about an issue, to take action, or to think about a related issue. If you presented an attention-getting fact or anecdote in your introduction, consider revisiting it in your conclusion. Just as you have learned about an essay’s conclusion, do not add new content to the presentation’s conclusion.
No matter how you choose to structure your conclusion, make sure it is well planned so that you are not tempted to wrap up your presentation too quickly. Inexperienced speakers, in a face-to-face presentation, sometimes rush through the end of a presentation to avoid exceeding the allotted time or to end the stressful experience of presenting in public. Unfortunately, a hurried conclusion makes the presentation as a whole less memorable.
Time management is the key to delivering an effective presentation whether it is face-to-face or in PowerPoint. As you develop your outline, think about the amount of time you will devote to each section. For instance, in a five-minute face-to-face presentation, you might plan to spend one minute on the introduction, three minutes on the body, and one minute on the conclusion. Later, when you rehearse, you can time yourself to determine whether you need to adjust your content or delivery.
In a PowerPoint presentation, it is important that your presentation is visually stimulating, avoids information overload by limiting the text per slide, uses speaker notes effectively, and uses a font that is visible on the background (e.g., avoid white letters on a light background or black letters on a dark background).
Work with the list you created in Note 14.4 “Exercise 1” to develop a more complete outline for your presentation. Make sure your outline includes the following:
- An introduction that uses strategies to capture your audience’s attention
- A body section that summarizes your main points and supporting details
- A conclusion that will help you end on a memorable note
- Brief notes about how much time you plan to spend on each part of the presentation (you may adjust the timing later as needed)
Identifying Opportunities to Incorporate Visual and Audio Media
You may already have some ideas for how to incorporate visual and audio media in your presentation. If not, review your outline and begin thinking about where to include media. Presenting information in a variety of formats will help you keep your audience’s interest.
Use Presentation Software
Delivering your presentation as a slideshow is one way to use media to your advantage. As you speak, you use a computer and an attached projector to display a slideshow of text and graphics that complement the speech. Your audience will follow your ideas more easily, because you are communicating with them through more than one sense. The audience hears your words and also sees the corresponding visuals. A listener who momentarily loses track of what you are saying can rely on the slide to cue his or her memory.
To set up your presentation, you will need to work with the content of your outline to develop individual slides. Each slide should focus on just a few bullet points (or a similar amount of content presented in a graphic). Remember that your audience must be able to read the slides easily, whether the members sit in the front or the back of the room. Avoid overcrowding the slides with too much text.
Using presentation software, such as PowerPoint, allows you to incorporate graphics, sounds, and even web links directly into your slides. You can also work with available styles, color schemes, and fonts to give your presentation a polished, consistent appearance. Different slide templates make it easy to organize information to suit your purpose. Be sure your font is visible to you audience. Avoid using small font or colored font that is not visible against your background.
Use PowerPoint as a Visual Aid
PowerPoint and similar visual representation programs can be effective tools to help audiences remember your message, but they can also be an annoying distraction to your speech. How you prepare your slides and use the tool will determine your effectiveness.
PowerPoint is a slideware program that you have no doubt seen used in class, seen in a presentation at work, or perhaps used yourself to support a presentation. PowerPoint and similar slideware programs provide templates for creating electronic slides to present visual information to the audience, reinforcing the verbal message. You will be able to import or cut and paste words from text files, images, or video clips to create slides to represent your ideas. You can even incorporate web links. When using any software program, it is always a good idea to experiment with it long before you intend to use it; explore its many options and functions, and see how it can be an effective tool for you.
At first, you might be overwhelmed by the possibilities, and you might be tempted to use all the bells, whistles, and sound effects, not to mention the tumbling, flying, and animated graphics. If used wisely, a dissolve or key transition can be like a well-executed scene from a major motion picture and lead your audience to the next point. But if used indiscriminately, it can annoy the audience to the point where they cringe in anticipation of the sound effect at the start of each slide. This danger is inherent in the tool, but you are in charge of it and can make wise choices that enhance the understanding and retention of your information.
The first point to consider is which visual aid is the most important. The answer is you, the speaker. You will facilitate the discussion, give life to the information, and help the audience correlate the content to your goal or purpose. You do not want to be in a position where the PowerPoint presentation is the focus and you are on the side of the stage simply helping the audience follow along. Slides should support you in your presentation, rather than the other way around. Just as there is a number one rule for handouts (do not pass them out at the start of your presentation), there is also one for PowerPoint presentations: do not use PowerPoint slides as a read-aloud script for your speech. The PowerPoint slides should amplify and illustrate your main points, not reproduce everything you are going to say.
Your pictures are the second area of emphasis you will want to consider. The tool will allow you to show graphs, charts and illustrate relationships that words may only approach in terms of communication, but your verbal support of the visual images will make all the difference. Dense pictures or complicated graphics will confuse more than they clarify. Choose clear images that have an immediate connection to both your content and the audience, tailored to their specific needs. After the images, consider using only key words that can be easily read to accompany your pictures. The fewer words the better. Try to keep each slide to a total word count of less than ten words. Do not use full sentences. Using key words provides support for your verbal discussion, guiding you as well as your audience. The key words can serve as signposts or signal words related to key ideas.
A natural question at this point is, How do I communicate complex information simply? The answer comes with several options. The visual representation on the screen is for support and illustration. Should you need to communicate more technical, complex, or in-depth information in a visual way, consider preparing a handout to distribute at the conclusion of your speech. You may also consider using a printout of your slide show with a section for taking notes, but if you distribute it at the beginning of your speech, you run the risk of turning your presentation into a guided reading exercise and possibly distracting or losing members of the audience. Everyone reads at a different pace and takes notes in their own way. You do not want to be in the position of going back and forth between slides to help people follow along.
Another point to consider is how you want to use the tool to support your speech and how your audience will interpret its presentation. Most audiences wouldn’t want to read a page of text—as you might see in this book—on the big screen. They will be far more likely to glance at the screen and assess the information you present in relation to your discussion. Therefore, it is key to consider one main idea, relationship, or point per slide. The use of the tool should be guided with the idea that its presentation is for the audience’s benefit, not yours. People often understand pictures and images more quickly and easily than text, and you can use this to your advantage, using the knowledge that a picture is worth a thousand words.
Incorporate Visual Media
Even if you do not use a slideshow to complement your presentation, you can include visual media to support and enhance your content. Visual media are divided into two major categories: images and informational graphics.
Image-based media, such as photographs or videos, often have little or no accompanying text. Often these media are more powerful than words in getting a message across. Within the past decade, the images associated with major news stories, such as the Indian Ocean tsunami of 2004, the Abu Ghraib prison abuses from 2004 to 2006, and the 2010 earthquake in Haiti, have powerfully affected viewers’ emotions and drawn their attention to these news stories.
Figure 14.1
Even if your presentation addresses a less dramatic subject, you can still use images to draw in your audience. Consider how photographs, an illustration, or a video might help your audience connect with a particular person or place or bring a historical event to life. Use visual images to support descriptions of natural or man-made phenomena. What ideas lend themselves to being explained primarily through images?
In addition, consider how you might incorporate informational graphics in your presentation. Informational graphics include diagrams, tables, pie charts, bar and line graphs, and flow charts. Informational graphics usually include some text and often work well to present numerical information. Consider using them if you are presenting statistics, comparing facts or data about several different groups, describing changes over time, or presenting a process.
Incorporate Audio Media
Although audio media are not as versatile as visual media, you may wish to use them if they work well with your particular topic. If your presentation discusses trends in pop music or analyzes political speeches, playing an audio clip is an obvious and effective choice. Clips from historical speeches, radio talk shows, and interviews can also be used, but extended clips may be ineffective with modern audiences. Always assess your audience’s demographics and expectations before selecting and including audio media.
Review the outline you created in Note 14.11 “Exercise 2” . Complete the following steps:
- Identify at least two to three places in your presentation where you might incorporate visual or audio media. Brainstorm ideas for what media would be effective, and create a list of ideas. (In Chapter 14 “Creating Presentations: Sharing Your Ideas” , Section 14.2 “Incorporating Effective Visuals into a Presentation” , you will explore different media options in greater depth. For now, focus on coming up with a few general ideas.)
- Determine whether you will use presentation software to deliver your presentation as a slideshow. If you plan to do so, begin using your outline to draft your slides.
Figure 14.2
Source: http://www.agenciabrasil.gov.br/media/imagens/2010/01/14/14.01.10RP5978.jpg/view
Planning Ahead: Annotating Your Presentation
When you make a presentation, you are giving a performance of sorts. It may not be as dramatic as a play or a movie, but it requires smooth coordination of several elements—your words, your gestures, and any media you include. One way to ensure that the performance goes smoothly is to annotate your presentation ahead of time.
To annotate means to add comments or notes to a document. You can use this technique to plan how the different parts of your presentation will flow together. For instance, if you are working with slides, add notes to your outline indicating when you will show each slide. If you have other visual or audio media to include, make a note of that, too. Be as detailed as necessary. Jotting “Start video at 3:14” can spare you the awkwardness of searching for the right clip during your presentation.
In the workplace, employees are often asked to deliver presentations or conduct a meeting using standard office presentation software. If you are using presentation software, you can annotate your presentation easily as you create your slides. Use the notes feature at the bottom of the page to add notes for each slide. As you deliver your presentation, your notes will be visible to you on the computer screen but not to your audience on the projector screen.
In a face-to-face presentation, make sure your final annotated outline is easy to read. It will serve to cue you during your presentation, so it does not need to look polished, as long as it is clear to you. Double space the text. Use a larger-than-normal font size (14 or 16 points) if that will make it easier for you to read. Boldface or italics will set off text that should be emphasized or delivered with greater emotion. Write out main points, as well as your opening and closing remarks, in complete sentences, along with any material you want to quote verbatim. Use shorter phrases for supporting details. Using your speaker notes effectively will help you deliver an effective presentation. Highlighting, all capital letters, or different-colored font will help you easily distinguish notes from the text of your speech. Read Jorge’s annotated outline.

Some students prefer to write out the full text of their face-to-face presentation. This can be a useful strategy when you are practicing your delivery. However, keep in mind that reading your text aloud, word for word, will not help you capture and hold your audience’s attention. Write out and read your speech if that helps you rehearse. After a few practice sessions, when you are more comfortable with your material, switch to working from an outline. That will help you sound more natural when you speak to an audience.
In a PowerPoint presentation, remember to have your slides in logical sequential order. Annotating your presentation before submitting it to your audience or your instructor will help you check for order and logical transitions. Too much text or data may confuse your audience; strive for clarity and avoid unnecessary details. Let the pictures or graphics tell the story but do not overload your slideshow with visuals. Be sure your font is visible. Look for consistency in the time limit of your presentation to gauge your level of preparedness.
Begin to annotate your outline. (You will probably add more notes as you proceed, but including some annotations now will help you begin pulling your ideas together.) Mark your outline with the following information:
- Write notes in brackets to any sections where you definitely plan to incorporate visual or audio media.
- If you are presenting a slideshow, add notes in brackets indicating which slides go with each section of your outline.
- Identify and set off any text that should be emphasized.

Key Takeaways
- An effective presentation presents ideas more concisely than a written document and uses media to explain ideas and hold the audience’s interest.
- Like an essay, a presentation should have a clear beginning, middle, and end.
- Good writers structure their presentations on the thesis, or point of view; main ideas; and key supporting details and create a presentation outline to organize their ideas.
- Annotating a presentation outline is a useful way to coordinate different parts of the presentation and manage time effectively.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
PowerPoint Tips Blog
Helping you with presenting, PowerPoint, and speaking
A good introduction/opener
February 10, 2011 by Ellen Finkelstein 263 Comments
You should start with an upbeat, positive mood. The first impression you make lasts. You want to quickly gain the attention, interest, and respect of your audience. Your first words should be lively, interesting, clear, and simple.
Start by expressing the fact that you’re glad to be there. A statement like, “I’m glad/excited/pleased/thrilled to be here” is almost obligatory. It invites the audience to be glad that they’re there, too. Your excitement is infectious and infuses the session with your energy.
Claudyne Wilder, in the July, 2007 issue of her newsletter, “Wilder’s Presentation Points,” said the following:
“A presenter who says, ‘I know you are busy people and have many things to do. Thank you for coming.’ only reminds everyone of all the things that they aren’t doing because they are sitting and listening. Distracting the audience before the presentation even begins is hardly a positive way to begin!”
Your introduction should answer the following
Who are you?
What is your topic, why is it important.
If you will be introduced, re-mention your name and re-affirm the most important fact about yourself that the audience will find meaningful, such as your experience with the topic. Otherwise, provide a slightly longer introduction, but just enough to let people know why they should listen to you.
Give a brief explanation of your topic, just a little longer than the title of your talk. Don’t give away the secret of your talk, but whet their appetite.
Finally, tell the audience why the topic is important to them. What will they have gained by the time the talk is finished? Don’t feel shy to promise that they’ll learn something useful; they really want to know that.
The entire opening should only take a minute or two. More than that, and it becomes boring because the audience will be impatient to hear the main content of your presentation.
Lori Giovannoni, in her e-book, So You Want to Be a Speaker , says, “Your intro should be well rehearsed, clear and filled with confidence. This is not the time to stammer and stutter and hope for the best. A poor intro will drop the energy in the room and you will spend the next half hour trying to recapture it.”
Here are some other ideas for openers:
- Ask your audience a question and ask them to raise hands in reply. For example, “How many of you regularly give presentations to small audiences of 1 to 10 people?”
- Begin with an interesting, relevant quote. Then use that quote to launch your talk. For example, “Author and columnist Earl Wilson said, ‘If you wouldn’t write it and sign it, don’t say it.’ This gives us a clue as to how you can gain believability from your audience.”
- Mention something another speaker said, or a current event, that is related to your presentation.
- Start with a short, relevant personal story or experience.
When you’ve written your introduction/opening, rewrite it and edit it until you like it. Then practice giving it out loud. Practice again. Time it. Record it and listen to it. Make adjustments and practice the new version. You should be able to speak it out without looking at your notes. When you’re done, you’ll have a great opener to your presentation!
Check out my other post on this topic, “How to start a presentation.”
Did you find this post helpful? Don’t miss out on new tips and get free video training here!
Please use the Share buttons below to share this with friends and colleagues, because they need to know how to start a presentation, too!
Learn easy principles and techniques that designers use. “ Slide Design for Non-Designers ” shows you, step-by-step, how to easily get the results you want. Plus bonus theme, template, sample slides, and 5 short video tutorials to make implementing the principles easy. Updated for PowerPoint 2016/365. Learn more at http://www.ellenfinkelstein.com/pptblog/slide-design-for-non-designers/
“101 Tips Every PowerPoint User Should Know” is for everyone who never took a course or read a book about PowerPoint! These tips will fill in the gaps, speed up your work, make presentations easier, and help you get better results. Now updated through PowerPoint 2016 and Office 365. Learn more at http://www.ellenfinkelstein.com/pptblog/101-tips/
Related posts:
- Create a looping introduction
- How to start a presentation
- Start your presentation BIG
- Use the 4 principles of meaningful communication
263 Leave a Reply
[…] This post was mentioned on Twitter by barbarashuck, Jen Juan. Jen Juan said: RT @EFinkelstein – a tip for PowerPoint: "A good introduction/opener" http://bit.ly/gWoTtC […]
I am 6th grade and I need to do the presentation about Bosnia and Herzegovina… And everyone knows my name because they all are my friends… I think it would be weird for me to introduce myself… What should I do to get people’s attention? Our teacher said that he is fairly disappointed about our introduction and conclusion… I would be thankful if you help me
Esther, You are right that you don’t need to introduce yourself in a classroom of your classmates. One way to get people’s attention would be to find some surprising fact about Bosnia and Herzegovina. Then you could start with, “Do you know that ….?” For example, you could ask your parents and parents of your friends where they are — show them a map. I bet that almost no one will be able to find them on the map. So you could start with, “Do you know that 90% of people don’t know where Bosnia and Herzegovina are?” Or you … Read more »
Hi,i am a 3rd year B.E student.I have to do the presentation about Global Wireless e-Voting.can you please help me, how to start my presentation and how to gain the attention of my audience?
hi i am a sophmore , and me and two other ppl r presenting a powerpoint on pandora (a godess) my teacher explained that “we should do an interesting introduction not just say,” my name is…this is a powerpoint on pandora” im not sure how my intro should be. help?
What is an interesting or surprising fact about Pandora? Start with that. For example, “Did you know that Pandora was the first mortal woman?”
“The first mortal women on earth, the releaser of disease,death and sorrow..pandora” sounds good? (:
and i do have stage fright, teachers have even deducted points off because i start out talking strong but i get real shacky and shy and my voice fades, ive been dealing with this for awhile, any recomdations? (thank you so much for your help)
Practice more. Videotape yourself and watch the videotape. Practice on your friends. Take a deep breath between sections–it’s good to pause! Don’t be too formal, be more conversational.
Yes, good start.
hye..i m a 9th standard student,and i want to give an introduction…on the topic lokpal bill.so would you please tell me..how to began my presentation…
Ishika, I don’t recognize that name, “lokpal bill.” Is it a person? If so, perhaps you can start with a surprising fact. Good luck!
Hi I am a 6th grader and I am doing a presentation on Justin Bieber and I dont know how to start it. Can you please help me?
Find some strange or funny fact about him and start, “Did you know that ….? That will get your audience interested. Maybe find a funny photo, too. Good luck!
Hello. I am an international researcher at a University and I am supposed to present my project in an international competition in from of a panel of internation judges. How do I introduce myself before I go to the main topic of my presentation? like who I am, where I am from, what do i do? Is it possible to provide me with a sentence? Thank you.
There won’t be any introduction for you at all? Not even your name? There won’t be a printed item with the list of presenters? If not, or even if there is, I would work it into the beginning of the presentation rather than a sentence before your topic. Is the competition based on the research — who did the best research? You could simply put your name and university on the title slide under the name of your presentation/research. You don’t need to say anything. Focus on the research. But, if you want to tell a story about how you … Read more »
Thank you. I will be starting with a story. I had an one on one coaching recently regarding this competition and I had my name and university on my slide just below my topic. After the presentation, one of the judge mentioned that I did not properly introduce myself, like my background, where I am from and so on. The reason was because I have a french accent, and the judge was wondering where I was from an so on.
Hi , I am doing a presentation about paper lantern and I don’t know how to start it. Can you please help me?
I’m not sure what you could say about paper lanterns, but perhaps start with a question to the audience, asking them what they use them for. Do something to engage the audience. Good luck!
i have to give a presentation on my internship.. how do i introduce & start my presentation to have a powerful impact on my examiner???
It’s hard to say, since I don’t know what your internship is about. Perhaps find a famous, philosophical quote and relate it to your internship to show you’ve thought deeply about its implications. Perhaps show a diagram placing the company where you worked in the context of the whole world, so they can see that you appreciate the larger impact of what they’re doing. Perhaps use a diagram showing the skills you learned and how they’ll apply to your professional life. Then go on and elaborate. Good luck!
Hi, I am a first year business student and me an my group need to do a presentation about the new venture we created. What would be a good introduction and how can we make our presentation interesting and engaging?
Rose, have you ever watched Shark Tank on TV? I’d recommend it, because the presentations are always engaging. They demo their product, wear costumes, etc. Aside from that, start by talking about the problem that your venture solves and relate it to the audience. “Have you ever experienced that….? Wasn’t it frustrating? How great would it be if….? Good luck!
Hi, i am doing a degree in early years and i have to do a 10 minute power point presentation on language and language theory in the early years. I am a little unsure how to start it because the group i am doing it in front of 5 people who already know my name and my job role?? also the presentation is all about how i promote language theory in my nursery setting so i am a little unsure about how to start it really.
thanks for reading
Tell a short story, ask a question, say a surprising fact, say something that’s different from usual. For example, you could start, “In this program, I’ve learned a lot of theory about language, but when I had an opportunity to use it in a nursery setting, I discovered some valuable approaches.”
hi, i am a student of pharmacy, and i have been given a topic of function of auxin(a phytohormone). can u please help me, that how would i start my topic and introduce myself in front of my classmates, as i’ll be the 3rd member in my group presentation of total 5 members. thanks,
Since I have NO idea what that is, it’s hard to give you an answer. Why is it important or interesting? Any stories about what happens when it doesn’t function properly?
Hi. I have to do a presentation over a lab that I did-oil spill cleanup. I’m not sure how to start. Could you give me some pointers, please? Thanks.
Hi , I am a student in the high school , I am going to give a presentation next week about positive thinking , I wonder how to start my presentation especially that I am with 3 friends in it !
Tell a horror story about an oil spill cleanup or just silently show some photos of birds covered with oil. Something striking.
I have to do a power point presentation in my class. How should I introduce my self – I am also doing business proposal
Unless your teacher expects you to introduce yourself, you don’t need to, since everyone in the class knows you, right? If it’s a huge class, that might be a different story. You could intertwine something about yourself into the business proposal — something about you that led you to decide that this proposal was the right thing.
Hello, Going through your previous replies, i must say you have done a wonderful job sharing your views and responding to each queries. I have one too 🙂 I am close to recruitment in a university as a lecturer, and before the official joining, the faculty head asked me to present a favorite topic of mine in front of the rest of the faculty members. I decided to present my Master’s thesis, but how would I introduce myself in front of my future co-workers? And what other details (apart from education details) would be relevant in the introduction slide?
Samir, Congratulations on your new job! I don’t think you want to put more than your education details on the first slide, but I think you want to say something verbally. You could introduce the topic of your Master’s thesis by saying something about how your background led you to this topic — so I’d add something personal because your future co-workers also want to get to know you as a person — but as a professional person. So don’t make it TOO personal.
i am a first year student and have been asked to make a presentation on myself, introducing myself to my new class mates and i have no clue where and how to start
Think of something unusual or especially interesting about you or your background or your goals and start with that. Then go on to the rest. Good luck!
i’m presenting a powerpoint presentation in front of my classmate together with my groupmates, I just like to have some tips on how to start my topic about recommendation report.?
Hi there, I am a grade 9 student and I have been assigned to do a presentation on the book ‘hatchet, by Gary Paulsen’. I am not too sure about what would be a good introduction to it, keeping everyone interested and involved. your help would be great, Please and Thank you
Since I know nothing about the book, it’s hard to say. Is there a surprising fact that you can find about the author if you do some research? Perhaps you can find a review of the book to find some background information. Did the book have an impact on you that your classmates wouldn’t expect? If the other students haven’t read it, is there a reason you think they should? How might it change their life? Good luck!
Im having a presentation about online shopping and I need help with my intruduction. Would you help me please? Thanks in advance!
Hai,this page is useful to us.I am doing my 3’rd year B.E.(EEE).i am going to present a paper on power electronics and drives.will u pls help me ? in wt way i have to introduce myself and impress my audience to my topic?
Hi Ellen. Judging by the number of comments and hits on this post, it’s a topic on many speakers’ minds! As you say, when speaking, your 1st impression lasts. I agree with many of your points, like the importance of whetting people’s appetites, and saying what they’ll gain. (To me though, saying “I’m glad to be here” seems a bit trite, and the audience doesn’t care (much) how you feel. They’re absorbed by their own needs and reason for attending, especially at the start.) As you say in your post’s last bullet, you can also use a short, relevant story. … Read more »
Hi, I recently join a company, and they told me to do a presentation on SDLC(Software Development Life Cycle. The problem is I don’t know how to introduce myself before the topic begin..
If everyone there knows you, you don’t have to introduce yourself. If they don’t, I suggest that you ask someone else to introduce you and say why you were chosen to do the presentation.
hello thank you for every thing you do. what i need to ask about is i’ll do a presentation of my self as a final test to get a job with the company(oil and gas company) what steps shoud i fallow to present my self as well.
Think about what the employer needs. Rather than talking about yourself, talk about how you can contribute to the success of the company. Do some research on the issues and future direction of the company and address that. Finally, be sure not to use slide after slide of bulleted text. Instead, make the presentation as visual as possible and practice giving it so you know what to say without reading the slides. Good luck!
I am doing a presentation on Emigration to Canada during the Famine. I am giving the talk in front of class mates and don’t want to introduce the presentation by saying ‘Hi my name is’. Can you give me any advice with regards to coming up with an interesting introduction. Much appreciated.
Nichola, I think your instincts are right. I’d just dive right in with a surprising or shocking fact or statistic about the emigration or the famine to bring home the emotional impact the situation had on the people involved. Are ask the audience a question. “What would you do if you had no food and your children were starving?” Good luck with the presentation!
Hi.. Good morning
I am doing a presentation on indian civilisation, can you please help with in how can i start my introduction and how to get the attention of the people listing ?
As I’ve mentioned in other comments, start with a surprising fact. Perhaps something like, “Did you know that Indian civilization ….?”
Hello, I have a presentation on American Conservative Union, and I don’t know how should I introduce the topic? What am I asking you is the introduction of this topic. Thank you
How to Write an Introduction in PowerPoint: A Step-by-Step Guide
Writing an introduction in PowerPoint is all about grabbing your audience’s attention and giving them a preview of what they are about to learn. It sets the tone for the rest of the presentation and can make or break your audience’s engagement. By following a few simple steps, you can craft an introduction that will captivate your audience and get your presentation off to a strong start.
After you complete your introduction, your audience should feel intrigued and eager to hear more. A well-crafted introduction can help establish your credibility and make your audience more receptive to your message.
Introduction
When it comes to presenting information, the introduction is your first impression, and as we all know, first impressions can be everything. Whether you’re presenting to a group of business professionals, teaching a class, or speaking at a conference, knowing how to write an engaging introduction in PowerPoint is essential. It’s not just about the content, but also about how you present it.
An introduction sets the stage for what’s to come, grabs your audience’s attention, and prepares them for the information they are about to receive. So, why is this topic important? Anyone who uses PowerPoint as a tool for presenting information can benefit from mastering the art of the introduction.
Step by Step Tutorial on Writing an Introduction in PowerPoint
Before diving into the step-by-step process, let’s first understand what these steps will help us achieve. By following the outlined steps, you will be able to craft a compelling introduction to your PowerPoint presentation that will engage your audience from the get-go.
Step 1: Open PowerPoint and Select a Theme
Choose a theme that aligns with the topic of your presentation.
Selecting a theme is the first step because it sets the visual tone for your presentation. The theme should be professional yet engaging, and it should complement, not distract from, your introduction.
Step 2: Add a Title Slide
Insert a new slide and choose the ‘Title Slide’ layout.
Your title slide is where you’ll introduce the topic of your presentation. Make sure the title is clear, concise, and reflective of the content to follow.
Step 3: Craft a Catchy Title
Write a title that is both informative and attention-grabbing.
Your title is the first text your audience will read, so it needs to make an impact. Use compelling language that piques curiosity and encourages your audience to want to learn more.
Step 4: Add a Subtitle (If Applicable)
Include a subtitle that provides additional context or a preview of the presentation’s focus.
Not all presentations will require a subtitle, but if yours covers a broad topic or has a specific angle, a subtitle can provide clarity.
Step 5: Create an Agenda or Overview Slide
Design a slide that outlines the main points you will be covering in your presentation.
An agenda or overview slide lets your audience know what to expect and helps them follow along more easily. Keep it brief and to the point.
Additional Information
Creating an engaging introduction in PowerPoint requires more than just following steps; it’s about understanding your audience and crafting a message that resonates with them. Remember, the introduction is your chance to make a lasting impression, so take the time to develop a hook that will capture the audience’s interest. Consider opening with a relevant quote, a surprising statistic, or a compelling question.
Use visuals effectively by incorporating images or short videos that complement your message. Pay attention to the design elements, such as font size, color, and layout, to ensure readability and visual appeal. Lastly, practice delivering your introduction to ensure a smooth and confident start to your presentation.
- Open PowerPoint and select a theme.
- Add a title slide.
- Craft a catchy title.
- Add a subtitle (if applicable).
- Create an agenda or overview slide.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long should a powerpoint introduction be.
An introduction should be brief, ideally less than two minutes, to set the stage without losing your audience’s attention.
Can I use humor in my presentation’s introduction?
Yes, humor can be an effective way to engage your audience, but make sure it’s appropriate for the setting and your audience.
Is it necessary to have an overview slide?
While not mandatory, an overview slide can be helpful for providing structure and helping your audience follow along.
How many slides should the introduction consist of?
Typically, one to three slides are sufficient for an introduction, depending on the complexity and length of your presentation.
Should my introduction include a personal introduction?
If it’s relevant and adds credibility, including a brief personal introduction can be beneficial.
Writing an introduction in PowerPoint is a critical skill for anyone looking to present information effectively. By following the steps outlined above and keeping in mind the pros and cons, you can create an introduction that not only captures your audience’s attention but also sets the stage for a successful presentation.
Remember, the introduction is your chance to make a lasting impression, so put in the effort to make it count. Good luck, and happy presenting!

Matthew Burleigh has been writing tech tutorials since 2008. His writing has appeared on dozens of different websites and been read over 50 million times.
After receiving his Bachelor’s and Master’s degrees in Computer Science he spent several years working in IT management for small businesses. However, he now works full time writing content online and creating websites.
His main writing topics include iPhones, Microsoft Office, Google Apps, Android, and Photoshop, but he has also written about many other tech topics as well.
Read his full bio here.
Share this:
Join our free newsletter.
Featured guides and deals
You may opt out at any time. Read our Privacy Policy
Related posts:
- How to Change Hyperlink Color in Powerpoint 2010 (An Easy 5 Step Guide)
- How to Set Time for Slides in Powerpoint
- How to Save Powerpoint as PDF with Notes
- How to Add Page Numbers in Powerpoint 2010
- How to Loop a Slideshow on Powerpoint 2013
- How to Delete a Slide in Powerpoint 2010
- How to End Powerpoint on Last Slide in Powerpoint 2010
- How to Unhide a Slide in Powerpoint 2013
- How to Rotate a Slide in PowerPoint: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Make a Powerpoint Slide Vertical in Powerpoint 2013
- How to: Effortlessly Create PowerPoint Looping Presentations
- How to Hide a Slide in Powerpoint 2010
- What Are Benefits of PowerPoint? A Comprehensive Guide
- How to Run Powerpoint in Kiosk Mode: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Change Line Spacing in Powerpoint for Every Slide at Once
- How to Duplicate a Slide in Powerpoint 2010
- How to Make GIFs as a Background on PowerPoint: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Embed a GIF in PowerPoint: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Can I Convert My Powerpoint to Google Slides?
- How to Insert Clipart in PowerPoint: A Step-by-Step Guide

Improve your practice.
Enhance your soft skills with a range of award-winning courses.
How to Structure your Presentation, with Examples
August 3, 2018 - Dom Barnard
For many people the thought of delivering a presentation is a daunting task and brings about a great deal of nerves . However, if you take some time to understand how effective presentations are structured and then apply this structure to your own presentation, you’ll appear much more confident and relaxed.
Here is our complete guide for structuring your presentation, with examples at the end of the article to demonstrate these points.
Why is structuring a presentation so important?
If you’ve ever sat through a great presentation, you’ll have left feeling either inspired or informed on a given topic. This isn’t because the speaker was the most knowledgeable or motivating person in the world. Instead, it’s because they know how to structure presentations – they have crafted their message in a logical and simple way that has allowed the audience can keep up with them and take away key messages.
Research has supported this, with studies showing that audiences retain structured information 40% more accurately than unstructured information.
In fact, not only is structuring a presentation important for the benefit of the audience’s understanding, it’s also important for you as the speaker. A good structure helps you remain calm, stay on topic, and avoid any awkward silences.
What will affect your presentation structure?
Generally speaking, there is a natural flow that any decent presentation will follow which we will go into shortly. However, you should be aware that all presentation structures will be different in their own unique way and this will be due to a number of factors, including:
- Whether you need to deliver any demonstrations
- How knowledgeable the audience already is on the given subject
- How much interaction you want from the audience
- Any time constraints there are for your talk
- What setting you are in
- Your ability to use any kinds of visual assistance
Before choosing the presentation’s structure answer these questions first:
- What is your presentation’s aim?
- Who are the audience?
- What are the main points your audience should remember afterwards?
When reading the points below, think critically about what things may cause your presentation structure to be slightly different. You can add in certain elements and add more focus to certain moments if that works better for your speech.

What is the typical presentation structure?
This is the usual flow of a presentation, which covers all the vital sections and is a good starting point for yours. It allows your audience to easily follow along and sets out a solid structure you can add your content to.
1. Greet the audience and introduce yourself
Before you start delivering your talk, introduce yourself to the audience and clarify who you are and your relevant expertise. This does not need to be long or incredibly detailed, but will help build an immediate relationship between you and the audience. It gives you the chance to briefly clarify your expertise and why you are worth listening to. This will help establish your ethos so the audience will trust you more and think you’re credible.
Read our tips on How to Start a Presentation Effectively
2. Introduction
In the introduction you need to explain the subject and purpose of your presentation whilst gaining the audience’s interest and confidence. It’s sometimes helpful to think of your introduction as funnel-shaped to help filter down your topic:
- Introduce your general topic
- Explain your topic area
- State the issues/challenges in this area you will be exploring
- State your presentation’s purpose – this is the basis of your presentation so ensure that you provide a statement explaining how the topic will be treated, for example, “I will argue that…” or maybe you will “compare”, “analyse”, “evaluate”, “describe” etc.
- Provide a statement of what you’re hoping the outcome of the presentation will be, for example, “I’m hoping this will be provide you with…”
- Show a preview of the organisation of your presentation
In this section also explain:
- The length of the talk.
- Signal whether you want audience interaction – some presenters prefer the audience to ask questions throughout whereas others allocate a specific section for this.
- If it applies, inform the audience whether to take notes or whether you will be providing handouts.
The way you structure your introduction can depend on the amount of time you have been given to present: a sales pitch may consist of a quick presentation so you may begin with your conclusion and then provide the evidence. Conversely, a speaker presenting their idea for change in the world would be better suited to start with the evidence and then conclude what this means for the audience.
Keep in mind that the main aim of the introduction is to grab the audience’s attention and connect with them.
3. The main body of your talk
The main body of your talk needs to meet the promises you made in the introduction. Depending on the nature of your presentation, clearly segment the different topics you will be discussing, and then work your way through them one at a time – it’s important for everything to be organised logically for the audience to fully understand. There are many different ways to organise your main points, such as, by priority, theme, chronologically etc.
- Main points should be addressed one by one with supporting evidence and examples.
- Before moving on to the next point you should provide a mini-summary.
- Links should be clearly stated between ideas and you must make it clear when you’re moving onto the next point.
- Allow time for people to take relevant notes and stick to the topics you have prepared beforehand rather than straying too far off topic.
When planning your presentation write a list of main points you want to make and ask yourself “What I am telling the audience? What should they understand from this?” refining your answers this way will help you produce clear messages.
4. Conclusion
In presentations the conclusion is frequently underdeveloped and lacks purpose which is a shame as it’s the best place to reinforce your messages. Typically, your presentation has a specific goal – that could be to convert a number of the audience members into customers, lead to a certain number of enquiries to make people knowledgeable on specific key points, or to motivate them towards a shared goal.
Regardless of what that goal is, be sure to summarise your main points and their implications. This clarifies the overall purpose of your talk and reinforces your reason for being there.
Follow these steps:
- Signal that it’s nearly the end of your presentation, for example, “As we wrap up/as we wind down the talk…”
- Restate the topic and purpose of your presentation – “In this speech I wanted to compare…”
- Summarise the main points, including their implications and conclusions
- Indicate what is next/a call to action/a thought-provoking takeaway
- Move on to the last section
5. Thank the audience and invite questions
Conclude your talk by thanking the audience for their time and invite them to ask any questions they may have. As mentioned earlier, personal circumstances will affect the structure of your presentation.
Many presenters prefer to make the Q&A session the key part of their talk and try to speed through the main body of the presentation. This is totally fine, but it is still best to focus on delivering some sort of initial presentation to set the tone and topics for discussion in the Q&A.

Other common presentation structures
The above was a description of a basic presentation, here are some more specific presentation layouts:
Demonstration
Use the demonstration structure when you have something useful to show. This is usually used when you want to show how a product works. Steve Jobs frequently used this technique in his presentations.
- Explain why the product is valuable.
- Describe why the product is necessary.
- Explain what problems it can solve for the audience.
- Demonstrate the product to support what you’ve been saying.
- Make suggestions of other things it can do to make the audience curious.
Problem-solution
This structure is particularly useful in persuading the audience.
- Briefly frame the issue.
- Go into the issue in detail showing why it ‘s such a problem. Use logos and pathos for this – the logical and emotional appeals.
- Provide the solution and explain why this would also help the audience.
- Call to action – something you want the audience to do which is straightforward and pertinent to the solution.
Storytelling
As well as incorporating stories in your presentation , you can organise your whole presentation as a story. There are lots of different type of story structures you can use – a popular choice is the monomyth – the hero’s journey. In a monomyth, a hero goes on a difficult journey or takes on a challenge – they move from the familiar into the unknown. After facing obstacles and ultimately succeeding the hero returns home, transformed and with newfound wisdom.
Storytelling for Business Success webinar , where well-know storyteller Javier Bernad shares strategies for crafting compelling narratives.
Another popular choice for using a story to structure your presentation is in media ras (in the middle of thing). In this type of story you launch right into the action by providing a snippet/teaser of what’s happening and then you start explaining the events that led to that event. This is engaging because you’re starting your story at the most exciting part which will make the audience curious – they’ll want to know how you got there.
- Great storytelling: Examples from Alibaba Founder, Jack Ma
Remaining method
The remaining method structure is good for situations where you’re presenting your perspective on a controversial topic which has split people’s opinions.
- Go into the issue in detail showing why it’s such a problem – use logos and pathos.
- Rebut your opponents’ solutions – explain why their solutions could be useful because the audience will see this as fair and will therefore think you’re trustworthy, and then explain why you think these solutions are not valid.
- After you’ve presented all the alternatives provide your solution, the remaining solution. This is very persuasive because it looks like the winning idea, especially with the audience believing that you’re fair and trustworthy.
Transitions
When delivering presentations it’s important for your words and ideas to flow so your audience can understand how everything links together and why it’s all relevant. This can be done using speech transitions which are words and phrases that allow you to smoothly move from one point to another so that your speech flows and your presentation is unified.
Transitions can be one word, a phrase or a full sentence – there are many different forms, here are some examples:
Moving from the introduction to the first point
Signify to the audience that you will now begin discussing the first main point:
- Now that you’re aware of the overview, let’s begin with…
- First, let’s begin with…
- I will first cover…
- My first point covers…
- To get started, let’s look at…
Shifting between similar points
Move from one point to a similar one:
- In the same way…
- Likewise…
- Equally…
- This is similar to…
- Similarly…
Internal summaries
Internal summarising consists of summarising before moving on to the next point. You must inform the audience:
- What part of the presentation you covered – “In the first part of this speech we’ve covered…”
- What the key points were – “Precisely how…”
- How this links in with the overall presentation – “So that’s the context…”
- What you’re moving on to – “Now I’d like to move on to the second part of presentation which looks at…”
Physical movement
You can move your body and your standing location when you transition to another point. The audience find it easier to follow your presentation and movement will increase their interest.
A common technique for incorporating movement into your presentation is to:
- Start your introduction by standing in the centre of the stage.
- For your first point you stand on the left side of the stage.
- You discuss your second point from the centre again.
- You stand on the right side of the stage for your third point.
- The conclusion occurs in the centre.
Key slides for your presentation
Slides are a useful tool for most presentations: they can greatly assist in the delivery of your message and help the audience follow along with what you are saying. Key slides include:
- An intro slide outlining your ideas
- A summary slide with core points to remember
- High quality image slides to supplement what you are saying
There are some presenters who choose not to use slides at all, though this is more of a rarity. Slides can be a powerful tool if used properly, but the problem is that many fail to do just that. Here are some golden rules to follow when using slides in a presentation:
- Don’t over fill them – your slides are there to assist your speech, rather than be the focal point. They should have as little information as possible, to avoid distracting people from your talk.
- A picture says a thousand words – instead of filling a slide with text, instead, focus on one or two images or diagrams to help support and explain the point you are discussing at that time.
- Make them readable – depending on the size of your audience, some may not be able to see small text or images, so make everything large enough to fill the space.
- Don’t rush through slides – give the audience enough time to digest each slide.
Guy Kawasaki, an entrepreneur and author, suggests that slideshows should follow a 10-20-30 rule :
- There should be a maximum of 10 slides – people rarely remember more than one concept afterwards so there’s no point overwhelming them with unnecessary information.
- The presentation should last no longer than 20 minutes as this will leave time for questions and discussion.
- The font size should be a minimum of 30pt because the audience reads faster than you talk so less information on the slides means that there is less chance of the audience being distracted.
Here are some additional resources for slide design:
- 7 design tips for effective, beautiful PowerPoint presentations
- 11 design tips for beautiful presentations
- 10 tips on how to make slides that communicate your idea
Group Presentations
Group presentations are structured in the same way as presentations with one speaker but usually require more rehearsal and practices. Clean transitioning between speakers is very important in producing a presentation that flows well. One way of doing this consists of:
- Briefly recap on what you covered in your section: “So that was a brief introduction on what health anxiety is and how it can affect somebody”
- Introduce the next speaker in the team and explain what they will discuss: “Now Elnaz will talk about the prevalence of health anxiety.”
- Then end by looking at the next speaker, gesturing towards them and saying their name: “Elnaz”.
- The next speaker should acknowledge this with a quick: “Thank you Joe.”
From this example you can see how the different sections of the presentations link which makes it easier for the audience to follow and remain engaged.
Example of great presentation structure and delivery
Having examples of great presentations will help inspire your own structures, here are a few such examples, each unique and inspiring in their own way.
How Google Works – by Eric Schmidt
This presentation by ex-Google CEO Eric Schmidt demonstrates some of the most important lessons he and his team have learnt with regards to working with some of the most talented individuals they hired. The simplistic yet cohesive style of all of the slides is something to be appreciated. They are relatively straightforward, yet add power and clarity to the narrative of the presentation.

Start with why – by Simon Sinek
Since being released in 2009, this presentation has been viewed almost four million times all around the world. The message itself is very powerful, however, it’s not an idea that hasn’t been heard before. What makes this presentation so powerful is the simple message he is getting across, and the straightforward and understandable manner in which he delivers it. Also note that he doesn’t use any slides, just a whiteboard where he creates a simple diagram of his opinion.
The Wisdom of a Third Grade Dropout – by Rick Rigsby
Here’s an example of a presentation given by a relatively unknown individual looking to inspire the next generation of graduates. Rick’s presentation is unique in many ways compared to the two above. Notably, he uses no visual prompts and includes a great deal of humour.
However, what is similar is the structure he uses. He first introduces his message that the wisest man he knew was a third-grade dropout. He then proceeds to deliver his main body of argument, and in the end, concludes with his message. This powerful speech keeps the viewer engaged throughout, through a mixture of heart-warming sentiment, powerful life advice and engaging humour.
As you can see from the examples above, and as it has been expressed throughout, a great presentation structure means analysing the core message of your presentation. Decide on a key message you want to impart the audience with, and then craft an engaging way of delivering it.
By preparing a solid structure, and practising your talk beforehand, you can walk into the presentation with confidence and deliver a meaningful message to an interested audience.
It’s important for a presentation to be well-structured so it can have the most impact on your audience. An unstructured presentation can be difficult to follow and even frustrating to listen to. The heart of your speech are your main points supported by evidence and your transitions should assist the movement between points and clarify how everything is linked.
Research suggests that the audience remember the first and last things you say so your introduction and conclusion are vital for reinforcing your points. Essentially, ensure you spend the time structuring your presentation and addressing all of the sections.
Blog > How to structure a good PowerPoint Presentation
How to structure a good PowerPoint Presentation
08.09.21 • #powerpoint #tips.
When creating presentations, it is particularly important that they are well organized and have a consistent structure.
A logical structure helps the audience to follow you and to remember the core information as best as possible. It is also important for the presenter, as a good presentation structure helps to keep calm, to stay on the topic and to avoid awkward pauses.
But what does such a structure actually look like? Here we show you how to best organize your presentation and what a good structure looks like.
Plan your presentation
Before you start creating your presentation, you should always brainstorm. Think about the topic and write all your ideas down. Then think about the message you want to communicate, what your goal is and what you want your audience to remember at the end.
Think about who your audience is so that you can address them in the best possible way. One possibility is to start your presentation with a few polls to get to know your audience better. Based on the results, you can then adapt your presentation a little. Use the poll function of SlideLizard and have all the answers at a glance. SlideLizard makes it possible to integrate the polls directly into your PowerPoint presentation which helps you to avoid annoying switching between presentation and interaction tool. You can keep an eye on the results while the votes come in and then decide whether you want to share them or not.
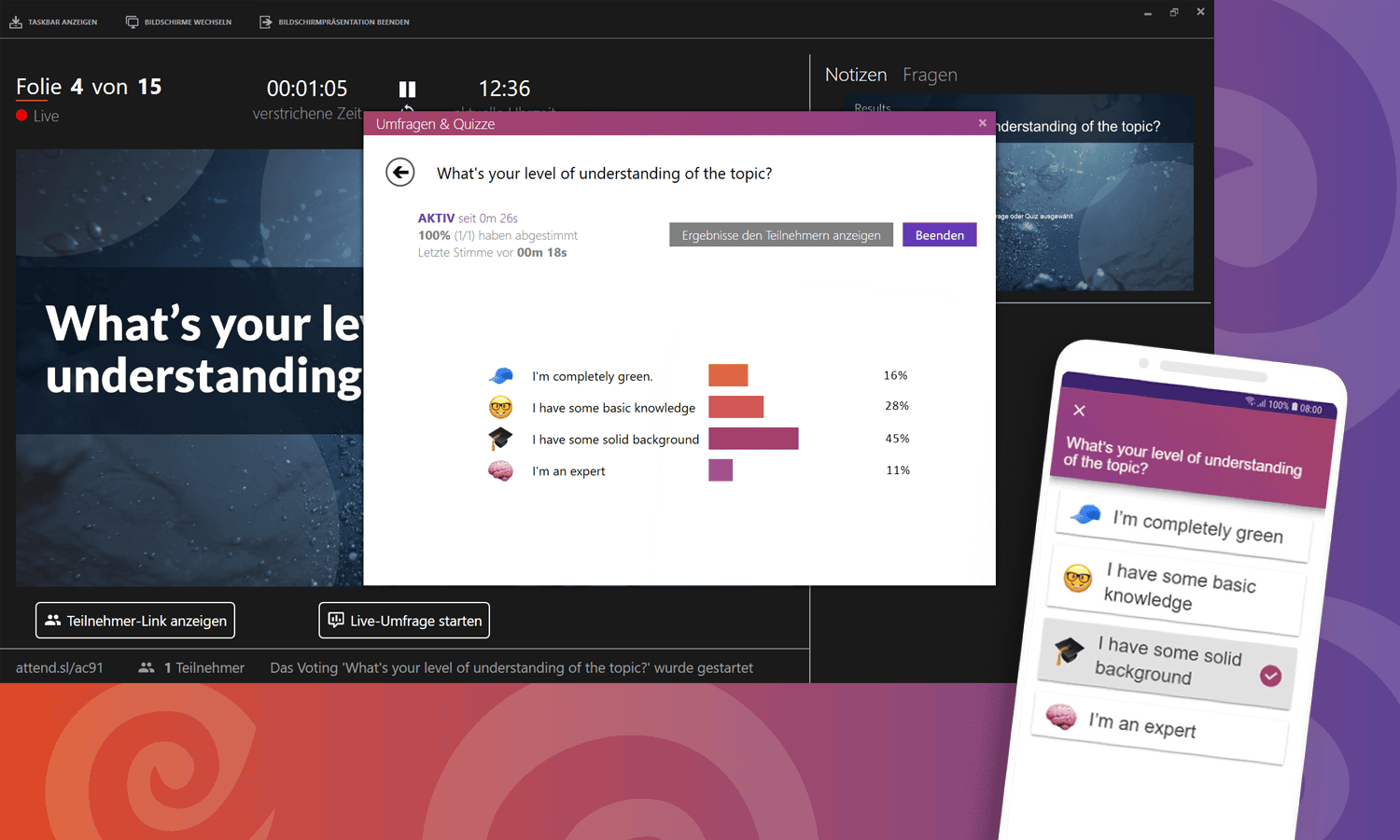
- an informative
- an entertaining
- an inspiring
- or a persuasive presentation?
Typical Presentation Structure
The basic structure of a presentation is actually always the same and should consist of:
Introduction
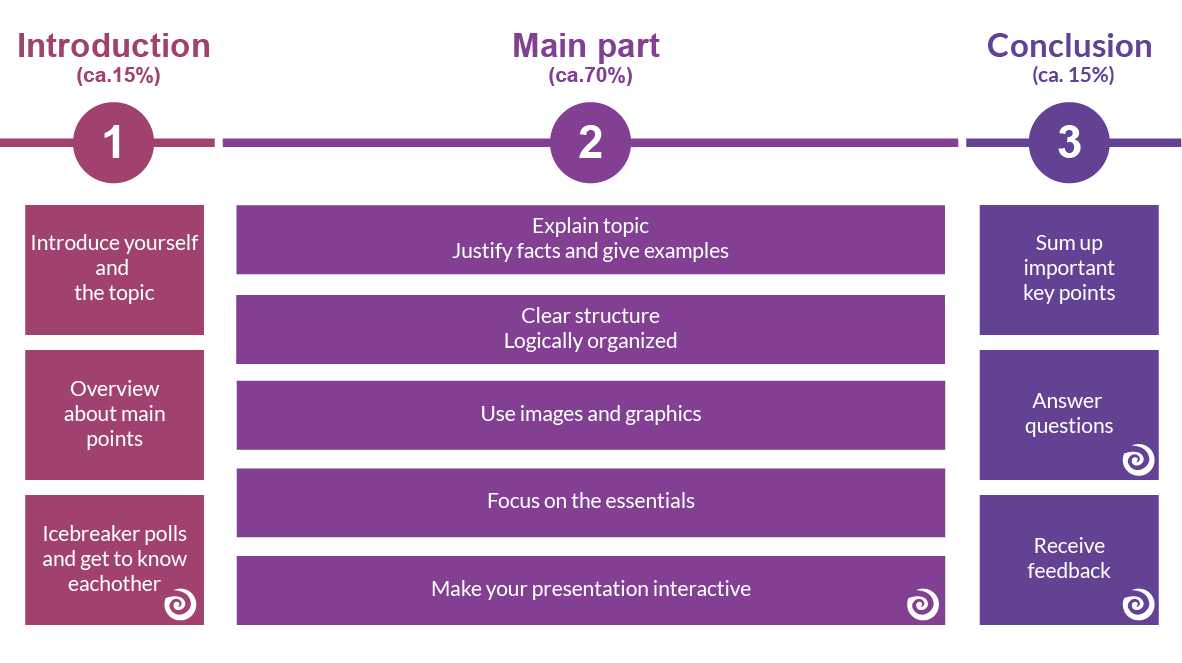
Make sure that the structure of your presentation is not too complicated. The simpler it is, the better the audience can follow.
Personal Introduction
It is best to start your presentation by briefly introducing yourself which helps to build a connection with your audience right away.
Introduce the topic
Then introduce the topic, state the purpose of the presentation and provide a brief outline of the main points you will be addressing.
Mention the length
In the introduction, mention the approximate length of the talk and then also make sure you stick to it.
The introduction should be no longer than two slides and provide a good overview of the topic.
Icebreaker Polls
According to studies, people in the audience only have an average attention span of 10 minutes, which is why it is important to increase their attention right at the beginning and to arouse the audience's interest. You could make a good start with a few icebreaker polls for example. They lighten the mood right at the beginning and you can secure your audience's attention from the start.
For example, you could use SlideLizard to have all the answers at a glance and share them with your audience. In addition, the audience can try out how the polls work and already know how it works if you include more polls in the main part.
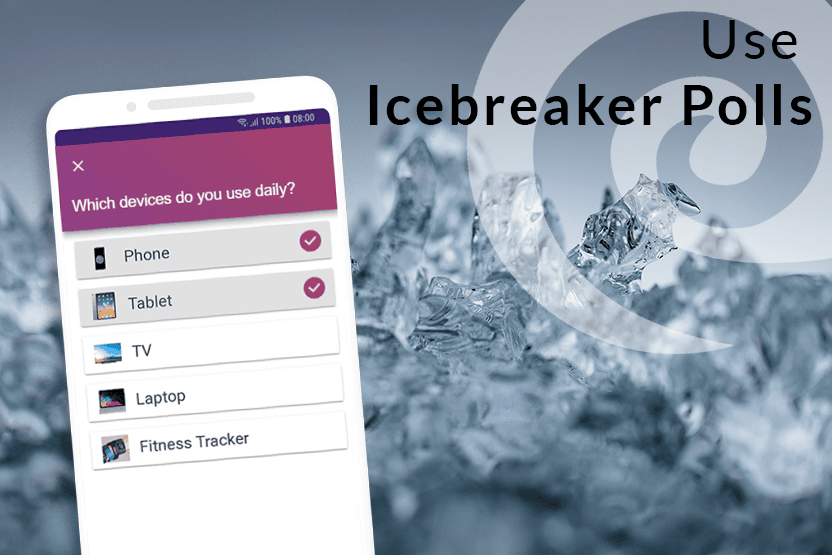
Get to know your audience
As mentioned earlier, it is always useful to think about who your audience actually is. Ask them questions at the beginning about how well they already know the topic of your presentation. Use SlideLizard for this so that you have a clear overview about the answers. You can use both single- and multiple-choice questions or also open questions and display their results as a WordCloud in your presentation, for example.
Include a quote
To make the beginning (or the end) of your presentation more exciting, it is always a good idea to include a quote. We have selected some powerful quotes for PowerPoint presentations for you.
Present your topic
The main part of a presentation should explain the topic well, state facts, justify them and give examples. Keep all the promises you made earlier in the introduction.
Length and Structure
The main part should make up about 70% of the presentation and also include a clear structure. Explain your ideas in detail and build them up logically. It should be organized chronologically, by priority or by topic. There should be a smooth transition between the individual issues. However, it is also important to use phrases that make it clear that a new topic is starting. We have listed some useful phrases for presentations here.
Visualize data and statistics and show pictures to underline facts. If you are still looking for good images, we have selected 5 sources of free images for you here.
Focus on the essentials
Focus on what is most important and summarize a bit. You don't have to say everything about a topic because your audience won’t remember everything either. Avoid complicated sentence structure, because if the audience does not understand something, they will not be able to read it again.
Make your presentation interactive
Make your presentation interactive to keep the attention of your audience. Use SlideLizard to include polls in your presentation, where your audience can vote directly from their smartphone and discuss the answers as soon as you received all votes. Here you can also find more tips for increasing audience engagement.
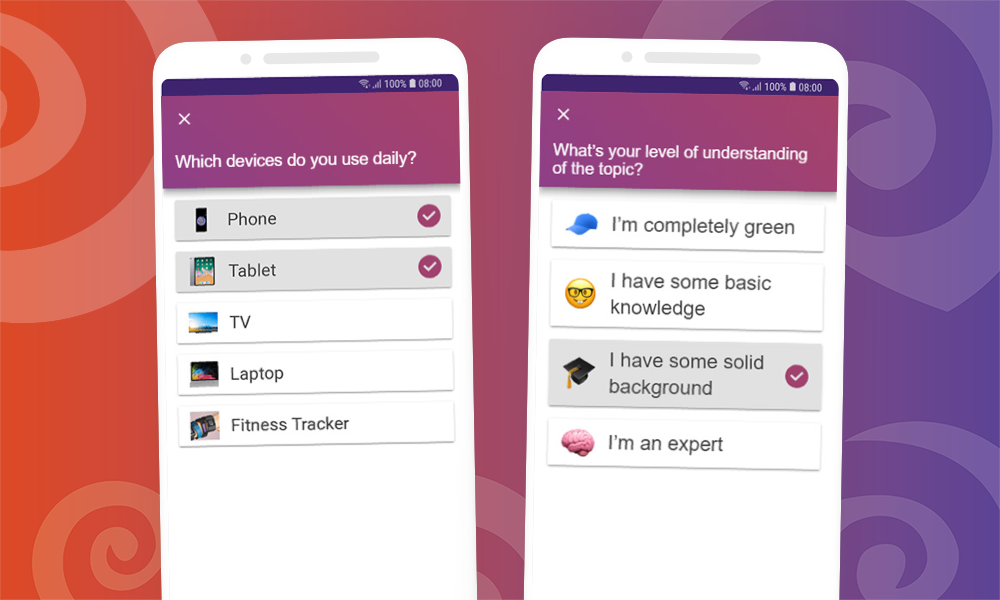
Repeat the main points
The conclusion should contain a summary of the most important key points. Repeat the main points you have made, summarize what the audience should have learned and explain how the new information can help in the future.
Include a Q&A part
Include a Q&A part at the end to make sure you don't leave any questions open. It's a good idea to use tools like SlideLizard for it. Your audience can ask anonymous questions and if there is not enough time, you can give them the answers afterwards. You can read more about the right way to do a question slide in PowerPoint here.
Get Feedback
It is also important to get feedback on your presentation at the end to keep improving. With SlideLizard you can ask your audience for anonymous feedback through star ratings, number ratings or open texts directly after your presentation. You can then export the responses and analyse them later in Excel.
Presentation style
Depending on the type of presentation you give, the structure will always be slightly different. We have selected a few different presentation styles and their structure for you.
Short Presentation

If you are one of many presenters on the day, you will only have a very limited time to present your idea and to convince your audience. It is very important to stand out with your presentation.
So you need to summarize your ideas as briefly as possible and probably should not need more than 3-5 slides.
Problem Solving Presentation
Start your presentation by explaining a problem and giving a short overview of it.
Then go into the problem a little more, providing both intellectual and emotional arguments for the seriousness of the problem. You should spend about the first 25% of your presentation on the problem.
After that, you should spend about 50% of your presentation proposing a solution and explaining it in detail.
In the last 25%, describe what benefits this solution will bring to your audience and ask them to take a simple but relevant action that relates to the problem being discussed.
Tell a Story

A great way to build an emotional connection with the audience is to structure a presentation like a story.
In the introduction, introduce a character who has to deal with a conflict. In the main part, tell how he tries to solve his problem but fails again and again. In the end, he manages to find a solution and wins.
Stories have the power to win customers, align colleagues and motivate employees. They’re the most compelling platform we have for managing imaginations. - Nancy Duarte / HBR Guide to Persuasive Presentations
Make a demonstration

Use the demonstration structure to show how a product works. First talk about a need or a problem that has to be solved.
Then explain how the product will help solve the problem and try to convince your audience of the need for your product.
Spend the end clarifying where and when the product can be purchased.
Chronological structure

When you have something historical to tell, it is always good to use a chronological structure. You always have to ask yourself what happens next.
To make it more interesting and exciting, it is a good idea to start by telling the end of something and after that you explain how you got there. This way you make the audience curious and you can gain their attention faster.
Nancy Duarte TED Talk
Nancy Duarte is a speaker and presentation design expert. She gives speeches all over the world, trying to improve the power of public presentations.
In her famous TED Talk "The Secret Structure of Great Talks" she dissects famous speeches such as Steve Jobs' iPhone launch speech and Martin Luther King's "I have a dream" speech. In doing so, she found out that each presentation is made up of 4 parts:
- What could be
- A moment to remember
- Promise of “New Bliss”
Related articles
About the author.

Helena Reitinger
Helena supports the SlideLizard team in marketing and design. She loves to express her creativity in texts and graphics.
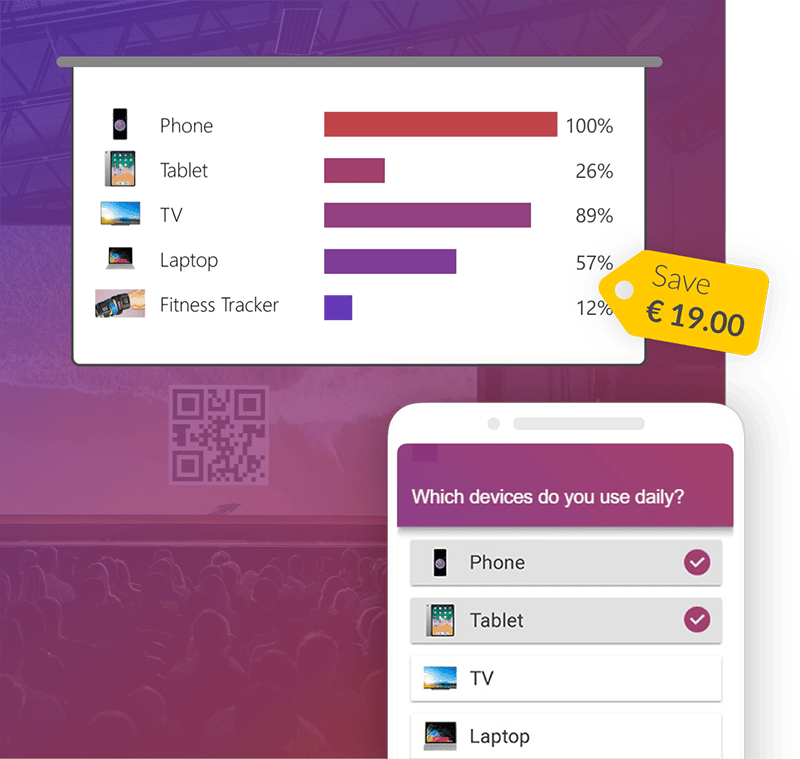
Get 1 Month for free!
Do you want to make your presentations more interactive.
With SlideLizard you can engage your audience with live polls, questions and feedback . Directly within your PowerPoint Presentation. Learn more

Top blog articles More posts

6 Tips to turn your boring slides into stunning presentations

The History and Evolution of PowerPoint
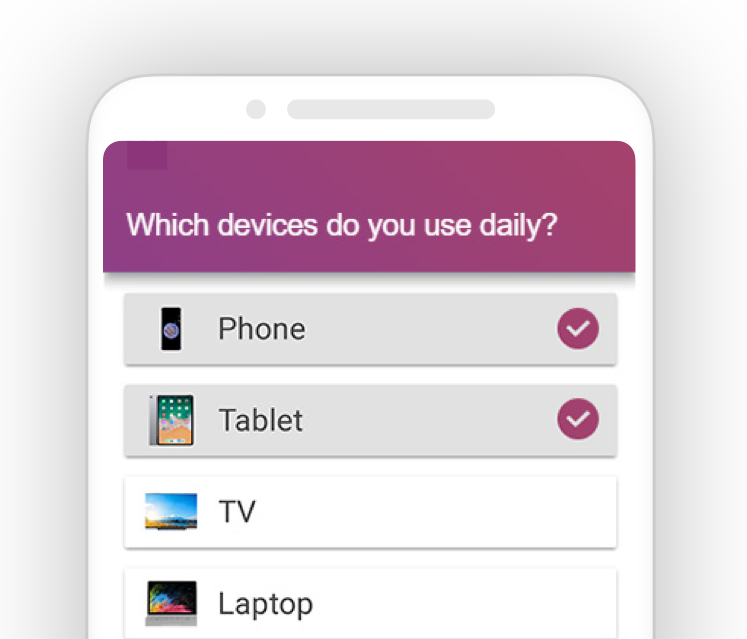
Get started with Live Polls, Q&A and slides
for your PowerPoint Presentations
The big SlideLizard presentation glossary
Process questions.
Process questions are similar to recall questions but they need some deeper thoughts and maybe also analysis.
An e-lecture is a lecture that is held online. Many schools and universities offer e-lectures as technical opportunities improve.
Internal Communication
Internal communication is particularly important for corporate communication. It communicates important information from leadership to staff so that they can do their jobs in the best possible way and work processes run well.
Glossophobia
Glossophobia means the strong fear of public speaking.
Be the first to know!
The latest SlideLizard news, articles, and resources, sent straight to your inbox.
- or follow us on -
We use cookies to personalize content and analyze traffic to our website. You can choose to accept only cookies that are necessary for the website to function or to also allow tracking cookies. For more information, please see our privacy policy .
Cookie Settings
Necessary cookies are required for the proper functioning of the website. These cookies ensure basic functionalities and security features of the website.
Analytical cookies are used to understand how visitors interact with the website. These cookies help provide information about the number of visitors, etc.

- High-impact business writing
- Effective email writing
- Bid, tender and sales-proposal writing
- Technical writing
- Writing for customer service

- Customer-service writing
- Effective report writing

Business writing essentials
How to write a presentation (and deliver it, even via Zoom)
Jack elliott.
31 minute read

You’ve been asked to give a presentation. Chances are, your response will be roughly one of the following:
1. It’s a subject you’re passionate about and you’re a confident speaker. You’re pleased to have the opportunity.
2. You secretly worry that your style is flat and unengaging. You’re not looking forward to it.
3. At best, the prospect makes you nervous; at worst, terrified. You’d rather have root canal surgery.
If you belong in one of the last two categories, you probably know you’re not alone. You may have heard the statistic that public speaking is more widely feared even than death .

However you feel about the prospect of presenting, this comprehensive guide will take you step by step through the process of planning, writing and delivering a presentation you can be proud of (even via Zoom).
Use the contents links below to jump to the section you need most, make your way through methodically from start to finish, or bookmark this page for next time you need it.
What is a presentation?
Essentially, it’s a story. And its origins go back thousands of years – to when our ancestors gathered around the campfire to listen to the wise elders of the tribe. Without PowerPoint!
These days, presentations encompass the glitz and scale of the Oscars or the new iPhone launch through to business briefings to smaller audiences, in person or – increasingly – online. We’re focusing on the business side.
Whatever the occasion, there’s always an element of drama involved. A presentation is not a report you can read at your leisure, it’s an event – speakers are putting themselves on the spot to explain, persuade or inspire you. Good presentations use this dynamic to support their story.
Always remember: everyone wants you to do well
If you are nervous, always remember: no one sets out to write a poor presentation and no one wants to go to one either. There may be private agendas in the room, but for the most part audiences approach presentations positively. They want to be engaged and to learn. They want you to do well.
First things first: the date’s in the diary and you need to prepare. Let’s break it down.

1. Preparing your presentation
Imagine you’re a designer in the automotive industry and your boss has asked you to give a presentation. The subject: the future of the car and how it will fit with all the other modes of transport.
Where to start? How to approach it? First you need an angle, a key idea.
We talk about ‘giving’ a presentation – and of course it’s the audience who will be receiving it. So, instead of beginning with cars (in this case), let’s think about people. That way we can root the talk in the everyday experience we all share.
Maybe you remember a time you were stuck in traffic on a motorway. Morning rush hour. No one moving. Up ahead children were crossing a footbridge on their way to school, laughing at the cars going nowhere. And you thought, ‘Enjoy it while you can! This will be you one day.’ But maybe not. Surely we can do better for future generations!
There’s your opening – the whole issue captured in a single image, and you’ve immediately engaged your audience with a simple story.
The who, the why and the what
Always begin with the people you’ll be addressing in mind. Before you start writing, answer three fundamental questions: who is your audience, why are you talking to them and what do you want to say?
The answers will provide the strong foundations you need and start the ideas flowing. Ignore them and you risk being vague and unfocused. Clear writing is the result of clear thinking and thinking takes time, but it’s time well spent.
Got a presentation to write? Before you do anything else, answer three fundamental questions: who is your audience, why are you talking to them and what do you want to say? @EmphasisWriting Click To Tweet
Start with the audience
Are you a senior car designer talking to your team? If the answer’s yes, you can assume high-level, shared knowledge.
But if you’re talking to the sales or marketing departments, you can’t make the same assumptions – there are issues you might have to explain and justify. And if it’s a press briefing, it’s about getting the message out to the general public – a different story again.
Knowing your audience will also dictate your tone. Your presentation to the board is likely to be quite formal, whereas a talk for your team can be more relaxed.
And what’s the audience’s mood? On another occasion you might have bad news to deliver – perhaps the national economy and the company’s finances are threatening people’s jobs. Then you must empathise – put yourself in their position and adapt your tone accordingly.
I want to …
You also need a clear objective (the why ). For our car designer, the overriding objective should be to plant a key idea in the audience’s mind. Starting with that image of the schoolchildren, it’s to convince the audience that the company has a radical and distinctive design future.
That’s the takeaway. How should they do that? Should they explain, persuade or inspire – the three key strategies for any presentation? You may need to use several of them to achieve your goal.
Objectives should always complete the statement ‘I want to …’. What do you want to do ?
It’s about …
The what is the substance of your presentation – the building blocks, all the facts and figures that tell the audience ‘It’s about …’.
Back to our designer. The move away from petrol and diesel will allow a complete rethink of car design. The electric power unit and battery can lie under the car’s floor, freeing up all the space taken up by the conventional engine. And then there are all the issues around emission-free, autonomous vehicles in the ‘smart’ cities of the future.
When you’re planning, it can be helpful to get all the information out of your head and onto the page, using a mind map , like the example below (for a talk on UK transport policy).
This is an effective way of unlocking everything you know (or still need to do more research on). Start with your main topic, then keep asking yourself questions (like who, what, when, where, how and why) to dig into all the aspects.
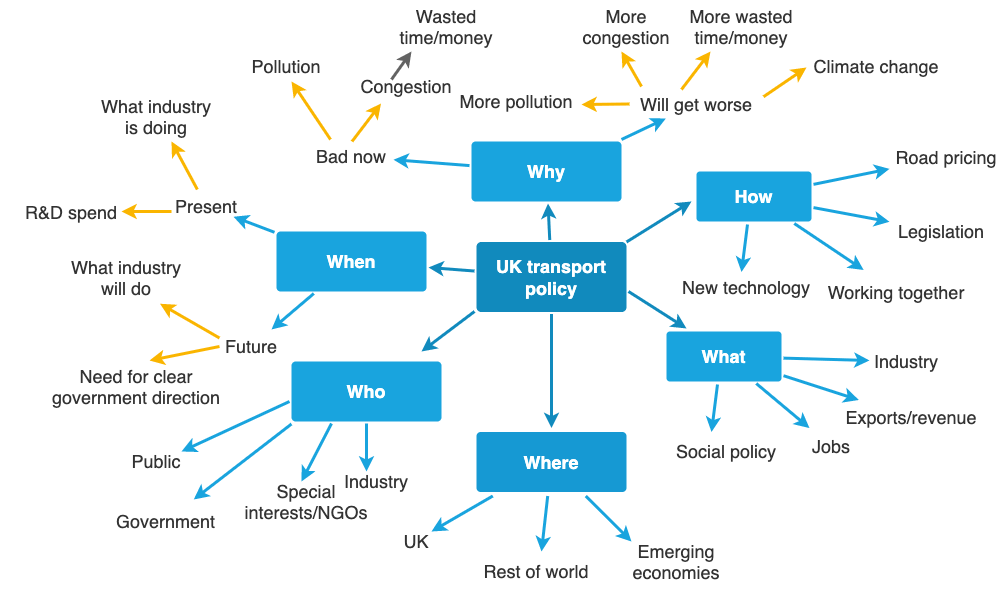
Mind map with the topic of ‘UK transport policy at the centre. Arrows point out to six bubbles with the labels ‘Who’, ‘When’, ‘Why’, ‘How’, ‘What’ and ‘Where’. More arrows point out from each of these bubbles to explore related points in each area, and still more arrows from some of those points to expand further. The information reads:
- Special interests / NGOs
- Need for clear government direction
- What industry will do
- R&D spend
- What industry is doing
- Congestion [this leads to the sub-point ‘Wasted time and money’]
- More pollution
- More congestion
- More wasted time and money
- Climate change
- Road pricing
- Legislation
- Working together
- New technology
- Exports/revenue
- Social policy
- Rest of world
- Emerging economies
Once you’ve got it all out on the page, you can identify which parts actually belong in your presentation. Don’t try to include every last detail: audiences don’t want to process piles of information. They are more interested in your ideas and conclusions.
Now let’s put all this research and planning into a structure.
2. How to structure your presentation
On 28 August 1963, Dr Martin Luther King Jr stood on the steps of the Lincoln Memorial in Washington DC and delivered one of the most powerful speeches in history: ‘I have a dream’.
He was the leader of the civil rights movement in the US and his audience that day numbered in the hundreds of thousands. His goal was to inspire them to continue the struggle.
Presentations usually aim to either explain, persuade or inspire – sometimes with elements of all three. Your aim will determine your structure. This will be the backbone of your presentation, giving it strength and direction.
Explain in a logical sequence
When you explain, you add to people’s knowledge to build the key idea. But ask yourself, what does this audience already know?
If you’re an astrophysicist talking to an audience of your peers, you can use terms and concepts you know they’ll be familiar with. If you’re explaining black holes to Joe Public, you can’t do that. Typically, you’ll have to use simple analogies to keep the audience with you (‘Imagine you’re in a huge dark room …’).
Whether it’s black holes or new software, good explanations start with what we know and then build on that understanding, step by step, layer by layer. The audience will stay with you if they can follow your logic and you can help this with linking comments – ‘Building on that … ‘, ‘This means …’, ‘To illustrate that, I’ve always found …’.
Presentations usually aim to either explain, persuade or inspire – sometimes with elements of all three. Your aim will determine your presentation's structure. @EmphasisWriting Click To Tweet
We need to change
If you’re writing a persuasive presentation, you also need to follow a particular sequence.
Whether you’re writing a pitch for a prospective customer or making research-based recommendations to a client, you follow the same structure. That structure is the Four Ps . It’s a powerful way of leading your audience’s thinking.
Start with the current situation – where you are now ( position ). Explain why you can’t stay there, so the audience agrees things have to change ( problem ). Suggest up to three credible ways you can address the issue ( possibilities ). Then decide which one is the optimum solution ( proposal ).
Three is a magic number for writers – not too many, not too few. But there may be one standout possibility, in which case you go straight to it ( position, problem, proposal ).
Think about how the pandemic has profoundly changed our working lives. Towns and cities are full of offices that people used to commute to. But to maintain social distancing, we’ve been encouraged to work from home where possible and to stay away from public transport.
At some point, decision-makers within organisations will have to make a call – or share a recommendation – about what to do long term. Should we go back to the office, stay at home or combine the two?
If we had to present on this choice using the Four Ps structure, we could outline the pros and cons of each possibility and then make a push for the one we recommend above the others. Or we could join the likes of Google and Twitter and simply propose purely remote working well into the future.
I have a dream
A presentation that inspires is about the future – about what could be. Scientists inspire children to follow careers in astronomy or physics with their passion and stunning visuals. Designers re-energise companies with their radical, exciting visions. Business leaders convince their staff that they really can turn things around.

An audience watching an inspirational presentation is not going to take away lots of facts and figures. What’s important is their emotional and intellectual engagement with the speaker, their shared sense of purpose. One way to build that engagement is with your structure.
From dark to light
The most inspiring presentations are so often born of shared struggle. On 13 May 1940, Winston Churchill addressed the British parliament – and the British people listening on their radios – in the darkest days of the Second World War.
He was brutally realistic in his assessment of the current position: ‘We have before us many, many long months of struggle and of suffering.’ He then set out his policy: ‘To wage war by sea, land and air, with all our might … against a monstrous tyranny’, and the prize: ‘Victory, however long and hard the road may be.’
In difficult situations, audiences immediately see through false hope and empty rhetoric. They want honest acknowledgement, and the determination and clear strategy to lead them to the future.
We can imagine how the same structure could show up in a more business-related context:
‘I’m not going to sugar-coat the figures. We have to change to save jobs and secure our future. There will be dark days and sacrifices along the way, but what’s the hardest part of any turnaround? It’s getting started. To do that, we all need to keep asking two fundamental questions: where can we improve, how can we improve? And if we push hard enough and if we’re utterly relentless, change will come and our momentum will build.’

Are you going to appeal to your audience’s
- habits of thought (current beliefs)?
If your recommendations run counter to their current beliefs, try appealing to their emotions.
3. Writing your presentation script
You don’t have to write a script. Some people put a few PowerPoint slides together and wing it; others make do with bullets on a smartphone, laptop or cue cards. It depends on the event and the presenter.
Writing a full script takes time, but if it’s a very important presentation and you might use it again – perhaps to appeal for investment – it will be worth it.
Some people will write a full script because the company or organisation that’s commissioned a presentation will want to see a copy well ahead of the event (often for legal reasons). Others will write the script, edit it down to the required time and then edit it down again to bullets or notes.
If the presentation is to a small audience, your notes or bullets will suit a more conversational approach. There are no rules here – see what works best for you. But what you must do is know your subject inside out.
To write clearly, you must think clearly and a full script will expose the areas that aren’t clear – where an explanation needs strengthening, for example, or where you should work on a transition.
Timing is everything
A full script also helps with working out timing, and timing is crucial. TED talks, for example, have a strict 18-minute limit, whether in front of an audience or online. That’s short enough to hold attention, but long enough to communicate a key idea. (The ‘I have a dream’ speech lasted 17 minutes 40 seconds and it changed the world.)
It takes a very skilled presenter to go much over 30 minutes. If you are taking questions during or after your presentation , however, it’s fine to build in extra time.
Imagine you’re writing your presentation in full and your slot is 20 minutes. On an A4 page with a 14-point Calibri font and 1.5 line spacing, that will equate to about 10 pages.
You can also divide the page in two, with slides on the left and text on the right (or vice versa). Then you can plan your words and visuals in parallel – and that will be roughly 20 pages.
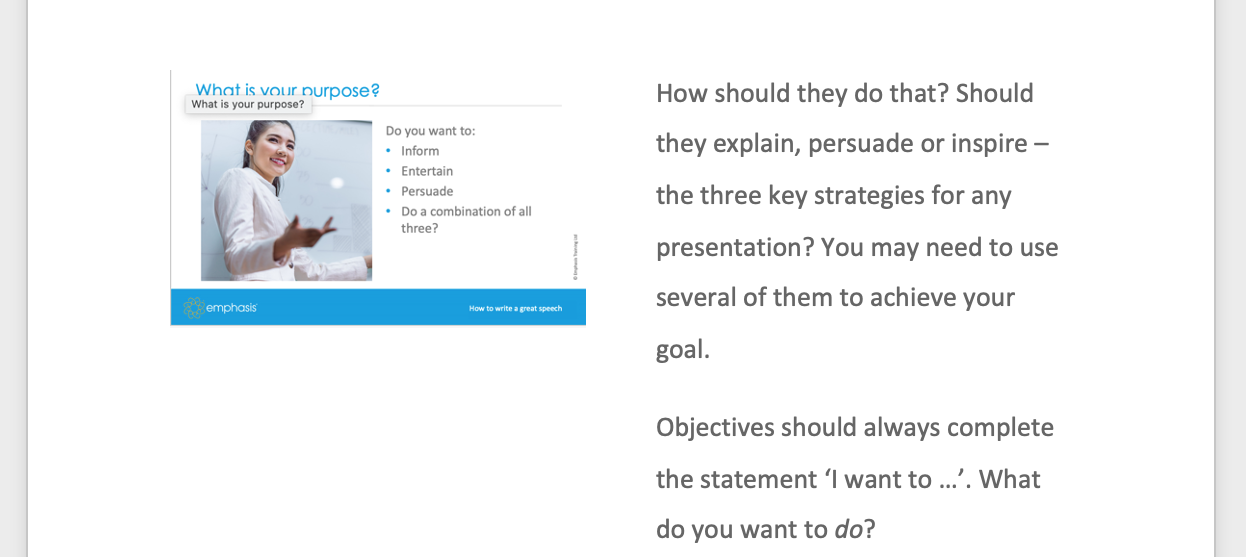
Script page with a slide on the left-hand side and text on the right. The slide has the heading ‘What is your purpose?’ and has a photo of a smiling person at a whiteboard mid-presentation. The text on the slide reads:
Do you want to:
- do a combination of all three?
The notes next to the slide read:
How should they do that? Should they explain, persuade or inspire – the three key strategies for any presentation? You may need to use several of them to achieve your goal.
The most powerful key on your keyboard – Delete
Use these numbers as your goal, but your first draft will probably be longer. That’s when you start deleting.
Be ruthless. Anything not adding to the story must go, including those anecdotes you’ve been telling for years ( especially those anecdotes). It’s not about what you want to tell the audience, it’s about what they need to hear.
Don’t feel you have to include every single issue either. Dealing with two or three examples in some detail is far better than saying a little bit about many more.
And interpret visual material you’re displaying rather than describing it, just as you wouldn’t repeat the text that’s on the screen. The audience can see it already.
It’s a conversation
Be yourself – don’t write a script that’s not in your style. We want the real you, not a supercharged version.
Some people are naturals when it comes to presenting – which can mean they’ve learned how to draw on their authentic strengths.
Sir David Attenborough is a great example. He has a wide-ranging knowledge of the natural world. He has an infectious passion and enthusiasm for his subject. And most importantly, he doesn’t lecture the camera: he talks naturally to his audience (and he’s now using Instagram to inspire new generations).
You can take a cue from Sir David and make your presentation style your own. Knowing your own strengths and really understanding your why will help you speak with purpose and passion.
And aim to speak naturally. Use conversational, inclusive language. That means lots of personal pronouns ( I believe, we can) and contractions ( Don’t you wonder …, you’re probably thinking …).
Sir David Attenborough introduces his new series, Our Planet at its premiere. He builds up our awareness by layering information alongside arresting statistics. These are framed simply, in relatable terms (‘96% of mass on the planet is us …’), so we easily grasp their shocking significance. He also uses ‘we’ and ‘us’ a lot to underline how this environmental emergency affects us all on ‘the planet we all call home’.
Finding the right words
Imagine you’re talking to someone as you write. And try saying the words out loud – it’s a good way to catch those complex, overlong sentences or particular words that will be difficult to say.
Presentations are not reports that can be reread – the audience has to understand what you are saying in the moment . Don’t leave them wondering what on earth you’re talking about, as they will only fall behind.
So avoid using long or complex words, or words you wouldn’t hear in everyday conversation (if your everyday conversation includes ‘quarks’ and ‘vectors’, that’s fine). And beware of jargon – it can exclude the audience and it quickly becomes clichéd and outdated.
Here are some more hints and tips on how to write effectively for speaking:
Syntax (word order): Disentangle your thoughts and arrange the words in your sentences to be simple and logical. Often, complex syntax shows up when the main point is getting lost inside excess information (or that the speaker is unsure what their main point is).
Pace, rhythm and tone: Varying the pace, rhythm and tone of sentences makes both the speaking and listening experience far more enjoyable.
Make sure the stress falls on the most important words. For example, ‘To be or not to be ‘ (where the stress rises and falls on alternate words) or ‘I have a dream ‘ (where the stress falls on the final word).
Vary the length of sentences and experiment with using very short sentences to emphasise a point.
Play with rhythm by arranging words in pairs and trios. Saying things in threes gives a sense of movement, progression and resolution: Going, going … gone . Saying words in pairs gives a more balanced tone (‘courage and commitment’, ‘energy and effort’) or a sense of tension between the words (‘war and peace’, ‘imports and exports’).
Analogies: Good analogies can work well in presentations because they paint vivid pictures for the audience. The best way to do it is to use either a simile (‘It wasn’t so much a dinner party, more like feeding time at the zoo’) or a metaphor (‘He was the fox and the company was the henhouse’).
Alliteration: This means using two or more words that start with the same sound, like ‘big and bold’, ‘sleek and shiny’ or ‘key components’. On the page alliteration may look contrived, but it can effectively highlight important phrases in a presentation.
Words to avoid: Be careful about using clichés like ‘pushing the envelope’, ‘playing hardball’ and ‘thinking outside the box’. And think carefully about using any word that ends with -ism, -ise, -based, -gate, -focused and -driven.
Be careful with humour too: don’t write jokes unless you can naturally tell them well. Keep the tone light if it fits the occasion, but a badly told joke can be excruciating.
4. How to start your presentation
People tend to remember beginnings and endings the most, so make sure your opening and conclusion are both strong.
You have about a minute to engage an audience. You want them to be intrigued, to want to know more, to come slightly forward in their seats. If you only learn one part of your presentation by heart, make it that minute.
A quick ‘thank you’ is fine if someone has introduced you. A quick ‘good morning’ to the audience is fine too. But don’t start thanking them for coming and hoping they’ll enjoy what you have to say – you’re not accepting an Oscar, and they can tell you what they thought when it’s over. Get straight down to business.
There are four basic types of introduction which will draw your audience in:
- News – ‘Positive Covid-19 tests worldwide have now reached …’
- Anecdotal – ‘About ten years ago, I was walking to work and I saw …’
- Surprise – ‘Every five minutes, an American will die because of the food they eat.’
- Historical – ‘In 1800, the world’s population was one billion. It’s now 7.8 billion.’
You can interpret these beginnings in any number of ways. If you were to say, ‘I have an admission to make …’, we will expect a personal anecdote relating to your main theme. And because you’re alone in front of us, it’s playing on your vulnerability. We’re intrigued straight away, and you’ve established a good platform for the rest of the presentation.
You can also combine these techniques. The historical beginning creates a sense of movement – that was then and this is now – as well as a surprising fact. It may prompt a thought like, ‘Wow, where’s this going?’ And you can trade on this with your own rhetorical question: ‘What does this mean for everyone in this room? It’s not what you think …’.
As well as setting up your story, you need to quickly reassure the audience they’re in safe hands. One way to do that is to give them a map – to tell them where you’re going to take them and what they’re going to see along the way.
Then you’re starting the journey together.
5. How to end your presentation
Your ending is what you want the audience to take away: your call to action, your vision of the future and how they can contribute.
If your presentation is online or to a small group in a small room, your ending is not going to be a battle cry, a call to man the barricades – that would be totally inappropriate. But equally don’t waste it with something flat and uninspiring.
Here are four effective ways to end your talk (like the intros, you can combine them or come up with your own):
- Predict the future – ‘So what can we expect in the next ten years? …’
- Quotation – ‘As our chief exec said at the meeting yesterday, …’
- Repeat a major issue – ‘We can’t carry on with the same old same old.’
- Summarise – ‘Continuous improvement isn’t our goal. It’s our culture.’
Predicting the future fits well with a historical beginning – it completes the arc of your presentation.
If you end with a quotation, make sure it’s relevant and credible – it has to be an authoritative stamp.
Repeating a major issue means pulling out and highlighting a major strand of your presentation, while summarising is about encapsulating your argument in a couple of sentences.
Your ending can also be a change of tone, perhaps signalled by the single word ‘Finally …’. It’s the audience’s cue to come slightly forward again and pay close attention.
As with your opening, it will have more impact if you’ve learned your ending – put down your notes, take a couple of steps towards the audience and address them directly, before a simple ‘Thank you.’
6. Creating your PowerPoint slides
We’ve all been there – watching a seemingly endless, poorly designed slide deck that’s simply restating what the presenter is saying. So common is this tortuous experience that there’s a name for it: Death by PowerPoint. But it doesn’t have to be like this.
Do you need slides at all?
As with your script, the first thing you should ask is ‘Do I actually need this?’ In 2019, Sir Tim Berners-Lee gave the Richard Dimbleby lecture for the BBC. He spoke for about 40 minutes with no autocue (he’d memorised his script) – and no speaker support.
This is a uniquely powerful form of presentation because the audience’s attention is totally focused on that one person. The call to action at the end of a presentation and delivering bad news are also best done without visuals.
Visual support
But if they’re well-judged and relevant, slides or other visuals can add enormously to a presentation – whether it’s photography, video or the ubiquitous PowerPoint. There are, however, two things everyone should know about PowerPoint in particular:
- It’s incredibly versatile and convenient.
- In the wrong hands, it can be unbearably tedious.
Your PowerPoint slides should not essentially be your cue cards projected onto a screen. They shouldn’t be packed margin to margin with text or full of complex diagrams.
If the presentation is live, the audience has come to watch you, not your slide deck. Online, the deck may have to work harder to sustain visual interest.
As with the script, keep your finger poised over that Delete key when you’re putting the deck together.
How many slides?
There’s no hard-and-fast rule about how many slides you should use, but think in terms of no more than one or two a minute on average. And don’t use more than a couple of short video inserts in a 20-minute presentation.
You might have a section where you show a few slides in a sequence or hold a single slide for a couple of minutes, which is fine. Varying the pacing helps to keep a presentation moving.
Optimise for psychology
As self-professed presentation aficionado David JP Phillips notes in his TEDx talk , people – and that includes your audience – have terrible working memories. If you don’t account for this fact in your slides, your talk will not have a lasting impact. In fact, most of it will be forgotten within around 30 seconds.
To counter this effect, David identifies five key strategies to use when designing your PowerPoint:
- Only have one message per slide: more than that and you’re splitting your audience’s attention.
- Don’t use full sentences on slides, and certainly don’t imagine you can talk over them if you do. People trying to read and listen at the same time will fail at both and absorb nothing. Move your running text into the documentation section instead, and keep the slide content short and sweet.
- People’s focus will be drawn to the biggest thing on the slide. If your headline is less important than the content below it, make the headline text the smaller of the two.
- You can also direct people’s attention using contrast. This can be as simple as guiding their point of focus by using white text (on a dark background) for the words you want to highlight, while the surrounding text is greyed out.
- Including too many objects per slide will sap your audience’s cognitive resources. (Your headline, every bullet, any references, even a page number each count as an object.) Include a maximum of six objects per slide and viewers will give a mental sigh of relief. This will probably mean creating more slides overall – and that’s fine.
More Powerpoint and visual aid tips
Here are a few more guidelines for creating your visual aids:
- Never dive into PowerPoint as job one in creating your presentation. Work out your talk’s structure (at least) before designing your slide deck. Making a genuinely effective PowerPoint requires that you know your subject inside out.
- List any visuals you’ll need as you prepare your script. That terrific photo you saw recently could be difficult to track down, and you might need permission and to pay to use it.
- It bears repeating: keep each slide to one key idea.
- Use the build effect of adding one bullet at a time (or use the contrast trick above) and try not to use more than three bullets per frame (or six objects overall).
- Strip each bullet to the bare minimum – no articles (‘a’, ‘an’ and ‘the’), no prepositions (‘in’, ‘at’, ‘to’ etc) and cut right back on punctuation.
- Every word that’s not there for a reason has to go. Delete, delete, delete.
‘Extra’ slides
- Use a ‘walk-in’ slide. Rather than have the audience arrive to a blank screen, this tells them who you are and your presentation’s title.
- Use occasional holding slides in between those with more content – perhaps an image but no text. They give the audience a visual rest and put the focus back on you.
- A plain white background might look fine on a computer monitor, but it will be glaring on a big screen. Invert the norm with a dark background, or use shading or ‘ghosted’ images to break up backgrounds and add visual interest.
- Some colours work better than others on-screen. Blues and greys are soft and easy on the eye. Red is a no-no, whether for backgrounds or text. And if you stick with a light background, favour a more subtle dark grey over black for the text.
- Use sans serif fonts (like Arial, Helvetica or Calibri) and think about point size – make sure it’s easily legible.
- Only use upper case where absolutely necessary.
Images and data
- Photos work well full screen, but they also really stand out well on a black background.
- Make sure your charts and graphics aren’t too complex. The dense information that’s fine on the page will not work on-screen – it’s too much to take in. Graphs behind a TV newsreader are often reduced to a single line going dramatically up or down.
- Don’t present data or graphs and expect them to speak for themselves. You need to find the story and significance in the data and present that .
And finally
- Proofread, proofread, proofread – or risk standing in front of an embarrassing spelling mistake.
Technical check
- Check what laptop they’re using at your venue. If you’ve written your deck on a PC, run it on a PC (and, of course, the same rule applies if you’ve used a Mac).
- If you’ve emailed your presentation to the venue, take a USB copy along as back-up.
- If you’re presenting online, check which platform you’ll be using and get comfortable with it. If someone else will be hosting the event, make sure you arrange a time for a rehearsal, especially if there will be a producer.
7. Delivering your presentation
You’ve put a lot of time and effort into preparing your presentation and now you’ve come to the sharp end – it’s time to stand and deliver.
Run it through
You don’t have to rehearse, but most presenters do and for good reason – it catches weak points and awkward transitions. And, crucially, it bolsters confidence.
Read your script or go through your bullets aloud – it will help to settle your nerves. If you use colleagues as a dummy audience, you can do a sense check too: ‘Does that bit work?’ ‘Have I explained it clearly?’ ‘Do you get the big picture?’ And rehearsing out loud will catch those words and sentences you thought you could say but can’t.
The more you rehearse, the more familiar and natural the presentation will become. Rehearse the technical side too – where the video is going to come in, how you’re going to vary your pace and tone to maintain interest.
Try speaking slightly more slowly than you would normally so the audience catches every word, and don’t be afraid to pause now and again. It gives a breathing space for you and the audience.

Connect with your audience
When you deliver your presentation for real, establish eye contact with the audience, just as you would in a conversation. In a small room with a small audience, talk to individuals. In a larger space, don’t talk to the first couple of rows and ignore the rest – include everyone.
And if you stumble over your words here or there, carry on and don’t dwell on it – you’ll lose your concentration. Audiences are generally forgiving and they might not even notice.
Each audience is unique: they react differently in different places. And although tomorrow might be the tenth time you’ve done the same presentation, it will be the first time this audience sees it. Your duty is to keep it fresh for them.
A final point
This is your presentation – you’re in control and the audience needs to feel they’re in safe hands.
It’s perfectly natural to feel nervous , but it’s the thought of doing it that’s the worst bit. Once you get going – and especially when you sense the audience is with you – the nerves will start to disappear. Try to enjoy it. If you enjoy it, it’s far more likely the audience will too.
And remember: everyone wants you to do well.

8. How to present online
Taking to Zoom or another online platform to present was once the exception. These days, online presenting is as essential a skill as presenting in person.
The switch to online can be nerve-wracking and cause even usually skilled presenters to falter. But there’s no need for that to happen.
Indeed, all of the advice we’ve talked about on preparing, structuring and writing for in-person presenting is equally relevant for your online delivery. You just need to be ready for the unique challenges that remote presentations pose.
An obvious one is that while you still have an audience, it will probably be muted and possibly even unseen (if webcams are switched off). This makes it far more difficult to gauge audience reaction, and if the event is pre-recorded, there might not be any at all – at least not immediately. Clapping and laughing emojis are not quite like the real thing.
Keep eye contact
But although your audience may be many miles away, there are still ways you can – and should – create a sense of connection with them. Your presentation will have much more impact if you do.
Whether the event is live or recorded, at least start with your webcam on (unless you really can only use slides). If it’s an option and feels appropriate, consider keeping your camera on throughout – remember, you are the presentation as much as any visuals.
If you will be on display, make sure you know where your webcam’s lens is and at key moments of your talk look directly into it – and out at your audience – to punctuate those points.
And don’t look at a second screen to cue up your PowerPoint – viewers will think your attention is wandering.
Engage your online audience
Being an engaging speaker is always important, but remember that the online world is already a place we associate with distraction. It’s also easier for a viewer behind their laptop to disguise their wandering attention than it would be for one in an auditorium or boardroom.
This isn’t to say your audience don’t want to give you their attention. But it is more important than ever to keep your presentation sharp and concise. Revisit your structure, your script or cue cards and your slides. Take a really critical eye to it and (as always) delete, delete, delete anything that’s not directly relevant.
If it works for your format, you can look at making your presentation interactive. You can then break the content into short segments, interspersed with comment, polls, questions and discussion. The variety will be a welcome change for your viewers.
Your visuals are part of what will keep people with you – along with the interplay you create between you and them. This means following the best-practice guidance we covered earlier is even more important.
Using Zoom for your presentation? Master the art of online delivery through this simple mix of set-up, delivery and technical tricks @EmphasisWriting Click To Tweet
Modulate your voice
Your tone of voice is extremely important here because presenting online is like radio with pictures. When people say ‘You have a great voice for radio’ what they mean is that it’s easy to listen to, often because you’re using quite a low-pitched, warm and relaxed register.
Listen to voices on the radio and voiceovers and identify the ones you particularly enjoy. What do you like about them? Why do you enjoy some voices and not others?
A flat, unmodulated voice, for instance, is difficult to listen to for long periods (and isn’t likely to inspire anyone).
Experiment with intentionally adding energy to your voice, as internet audio can have a dulling effect. As our trainer Gary Woodward puts it: ‘Turn up the enthusiasm dial even higher than you think, to make sure it comes through.’ And always vary your pace and tone as you would in a normal conversation.
And if it suits the tone of your talk, smile now and again. Smiling is contagious, and people will hear it in your voice even if they can’t see you.
Perfect your transitions
One of the other key challenges of remote presentations is that you have another layer of technology to wrestle with: sharing your PowerPoint online.
This means that many presentations begin with the popular catchphrase ‘Can you see my screen?’
This can also cause many presenters to stumble through their transitions, making the links between their slides clunky. And while remote audiences may be forgiving, for a slick presentation it’s best to prevent these sort of fumbles.
Naturally, practice plays a part here. But you can also give yourself the advantage with your set-up.
Dave Paradi from Think Outside the Slide explains one great way of setting up Zoom so you can smoothly cue up and run your slide deck – and be certain what’s being displayed.
You’ll even be able to see the rest of your screen (but the audience won’t). As you’ll be able to see what’s coming up, your transitions can also be seamless.
The trick is to use one of Zoom’s advanced settings after you hit ‘Share screen’, to share only a portion of your screen:
Advanced screensharing options pop-up box in Zoom, with the options ‘Portion of Screen’, ‘Music or Computer Sound Only’ and ‘Content from 2nd Camera’. The ‘Portion of Screen’ option is highlighted in blue.
This will give you a frame you can move to the part of the screen you want the audience to see.
Put your PowerPoint slides into ‘presenter view’ before launching the screenshare. Then you’ll be able to see the upcoming slides and your notes throughout, and your animations (like build slides) will work as normal.
Zoom’s ‘portion of screen’ setting in action
Presenter view in PowerPoint, with the current displayed slide on the left and the upcoming slide displaying smaller on the right, with notes below it. There is a notification saying ‘You are screen sharing’ at the top and a sharing frame positioned around the current slide.
The other part of the trick? Set it up in advance shortly before you’re due to speak. Once you’re happy with the set up, you can stop sharing until it’s time to kick off your talk. When you return to ‘Share screen’ again, it will reopen the frame in the same place.
Dave shows you the process in this video:
Five practical tips for a truly professional online presentation
You’re happy with the content of your talk, you’ve ruthlessly streamlined your slides and mastered your radio voice. Now just make sure you cover these crucial practicalities for a polished presentation:
1. Create a good space Make sure you have your environment well set up:
- Keep the background on display as tidy and minimalist as possible – a plain wall or backdrop is great, if you can.
- Manage and minimise background noise (shut the window, ensure your phone’s on silent, put the cat out, make sure someone’s watching the kids in another room – whatever it takes).
- Check your lighting: have your light source in front of you, not behind you (or you’ll be in shadow).
- Set up your computer or device at eye level so that you are well-framed and facing it straight on – avoid looming above it while providing a lovely view into your nostrils.
2. Think about your appearance Dress in the same way you would if the presentation were in person, and judge your choice of attire based on the formality of the event and your audience.
3. Practise! Run through the presentation and rehearse the technical side. Practise your transitions, including the initial cueing up of your slides (perhaps using the Zoom tip above), so that you can be confident in doing it all smoothly.
4. Be primed and ready Log in early on the day of your talk. Check all your tech is working, get your headset on and ensure everything is set up well ahead of time. This will save any last-minute issues (and stress) and means you can hit the ground running.
5. Stand and deliver Even online, consider giving your presentation standing up, if you can do so comfortably (adjusting your device or webcam accordingly). This may put you more into a presenting frame of mind and will differentiate you from most remote presenters.
Are you still there?
Live audiences have a group dynamic – as soon as a few people start laughing it becomes infectious and the others join in. It’s naturally different online. But that doesn’t have to throw you.
You might not get that immediate feedback, but don’t overcompensate and feel you have to win them back.
Yes, it’s often more difficult to gauge an audience’s reaction online – especially if their audio is muted and their webcams off. Yes, this can be daunting. But they are still out there listening. You may or may not hear (or see) laughter, but they could still be smiling and very interested in what you have to say. Have faith in your own content. Whatever form your delivery will take, keep coming back to your purpose and message for giving this talk – and keep considering the people you’ll be talking to. Whether the address will be online or in person, it is keeping this focus which is the key to every powerful presentation.
Ready to learn even more? Work one-to-one on your presentation-writing skills with one of our expert trainers or join our scheduled presentation-writing courses . If your team are looking to upskill, we also offer tailored in-house training . And if fear of presenting is holding your team back, check out our in-house course The reluctant presenter .
Image credit: lightpoet / Shutterstock

Your go-to guide to better writing
Get your own PDF copy of The Write Stuff , the definitive guide for everyone who writes at work.

These days he's one of Emphasis' top business-writing trainers, but in previous career lives Jack has written for many public and private sector organisations. He has an in-depth knowledge of the engineering and manufacturing sectors, particularly the UK automotive industry. As the lead scriptwriter for chairmen and CEOs, he has been responsible for proposals, pitches and reports as well as high-profile speeches and global product launches.
Was this article helpful?
This helps us make better content for you

You might also like

The readability techniques you need for clear business writing

Writing to the board
Writing a report for the board? Here’s what you need to know

Writing for marketing
How to write a winning marketing proposal [with presentation template]

Bids and proposals
Is your bid presentation pushing prospects into the cold?
Get expert advice, how-tos and resources for good writing (and great work).

- Learn English
- Open Your World
Different Techniques in Writing the Introduction of your Presentation
The first requirement when giving a presentation is to grasp the audience’s attention. Normally by wanting to introduce ourselves and complete the formalities as immediately as possible, we begin with an awkward greeting, thank everyone for coming, give a little self-introduction then begin to mumble about the subject such as “Good morning, thank you for coming today, my name is… Today, I’m going to talk about….” But have you ever thought if this kind of opening performance is effective? You may be able to deliver the points you want to share in your introduction but you started without creating any interest for the audience to want to listen .
In order to catch the attention and keep your audience’s interest throughout your presentation, you must carefully plan on how you would deliver your introduction. It is best to write it to make sure that it is well structured and at the same time , you have a reference when you are reviewing your talk. In crafting your introduction, you may use different techniques to put some spice on it and make it more appealing to your audience. Depending on your preference and purpose, you may choose among the following techniques below to make your introduction impactful.
A. Common Introduction Techniques
1. start with personal reference.
This is one of the simplest strategies to begin your presentation where you will discuss your relationship to the topic or audience in your introduction. This kind of beginning can be effective when you have established yourself in a certain field and have already positioned yourself to be a credible authoritative resource on the subject. You may also use this if the audience recognizes you and have high regard for you. However, make sure that you use this appropriately otherwise, your audience may set off defense mechanisms even at the onset of your presentation.
2. State your Begin with a Reference to the Subject
In this strategy, you show your listeners how important the topic is to them . You emphasize the applicability of the subject in their life. This technique can be effective when arousing the curiosity of your audience because people would normally listen and are interested in something that they find useful and beneficial for them to know.
3. State your Main Point
When considering time constraints you may state your central idea at the very beginning of your presentation . You need not make your audience think first then realize the gist of your presentation eventually. This is apt to the kind of audience that is busy and prefers directness.
4. Open with a Reference to the Event
In some instances, you may be requested to talk about an eventful situation . In this case, you may start your speech with a brief reference to the event, state the relevance of your topic and why it is timely to discuss it.
5. Provide the Definition
If you want your audience to remember a certain word or concept, then you may elaborate it by giving its definition. This way, they will be able to analyze and absorb it even at the start of your presentation. Also, this will help them to be able to connect your main points to the defined concept. However just make sure that you don’t overly elaborate it, as others who have been so familiar with the word might feel that you are just stating the obvious.
B. Introduction Techniques that Appeal and Invoke Certain Emotions
Whether its curiosity, amusement, surprise, or fear, introduction techniques that appeal to certain emotions will engage the hearts and minds of the people you are presenting to. The introduction techniques below will help you to invoke the emotions of your audience.
1. Tell a short story
Since everybody enjoys hearing good stories, storytelling is one of the best ways to connect with your audience . With a relatable character, your audience is more inclined to listen to your presentation and in the process, they can also identify with the character’s emotions. If you are sharing a personal experience that they can relate to, this would create a bond between you and them that would encourage them to be more collaborative. To be able to make this technique effective, your story should c ontain a message that you can connect to the points that will follow. Just make sure that the story won’t consume time as much as it should and won’t bore the audience.
2. Quote someone else.
A brief and relevant quotation can be a strong opening that will catch the attention of your audience. This can be from a statement made by a notable person through printed material or oral testimony. Quotations provide an initial thought to your audience that helps in setting up what you’re going to talk about next. Just be mindful to avoid choosing quotes that sound cliché.
3. Tell a joke.
A touch of humor can be effective in starting any presentation as it breaks the ice and helps your audience to relax. Your listeners will be instantly engaged if you make them laugh and you can easily establish a connection with them. For this to work well, you must choose a joke that is relevant to your presentation and be careful not to overdo it to the point that it would steer people away from your main purpose. Choose a fresh, amusing and appropriate joke, to avoid turning the audience off. Be careful also in your humor choice as some jokes are easily misinterpreted and may offend your audience. Only use jokes that you are confident in delivering and only use this technique if you are comfortable with it. If not, then it’s more advisable to use other techniques.
4. Begin with Stimulating Statements
Using thought-provoking statement in your introduction is helpful when your listeners are apathetic. B y sharing something that your audience doesn’t expect to hear , it catches and holds their attention . People tend to ignore something that they are familiar with , but pay attention to something that they are uncertain on what would happen next. Striking statements and u npredictable twists create an instant jolt that makes your audience intrigued on what you’re going to say next.
5. Ask a rhetorical question.
Another clever way to kick off a presentation is to ask a rhetorical question to your audience. It is intended to make them think but does not really require them to answer out loud. You only hope that they will consider the question and answer it in their minds. To employ this technique, you can ask the questions like ‘Have you ever thought of’… ‘Do you wonder why’… ‘What would you do’. Since your question arouses the curiosity of your audience, it motivates them to remain attentive and find out more in your presentation. When using this strategy, use a rhetorical question that is relevant to your topic and your audience profile, or else it will confuse them why you asked it.
6. Present a Surprising Statistic
With this type of introduction, you begin by sharing a surprising statistic that would stimulate the interest of your audience . Since we are living in an information age, this technique creates a strong impact when the facts you presented are not common knowledge yet are relevant. This may either help you to startle, create an empathy, call to action or spark curiosity among your audience. Just be sure that you don’t go overboard when using this strategy. It is better to keep your statement brief and avoid very complicated data. Focusing on numbers too much may overwhelm your listeners and you may lose them by having too many easy-to-forget details.
7. Start Presentation In Future Or Past
You may start a presentation by telling a scene in the far past or in the future and then connect it back to the main topic. To encourage your audience to take action, you can talk about the possible future on how things could be if something is done in a certain way. You can also talk about the past and use the lessons learned from the things that were done well and the things that didn’t work out for a similar purpose. This technique enables your audience to realize what could have been done or must be done to make something better.
8. Point to a problem or opportunity
Another strategic way of beginning your presentation is by talking about your audience’s pain point. This catches their attention and interests them as it triggers an emotional reaction on them. Their curiosity on how t o deal properly with their pain points enables them to be more engaged in your talk and wonder about the solution and opportunities you might suggest in your presentation.
9. Begin with a Descriptive Scene and Use The Power Of “What If”
Another way of gaining the attention of your audience is to get them to imagine something. You may do this by using words like “imagine”, “think of”, “close your eyes”, “picture this” and utilize descriptive words in order for them to be able to visualize effectively. You may also ask them the question ‘what if’ to encourage them to envisage something. This enables them to think of how things can be if the situation is really what it is according to how you described it in your message. As a result of sharing the same vision with you, it encourages them to follow your lead. When using this strategy, make sure that you have described everything down to the last detail in your introduction and not just abruptly cut it.
10. Use a Combination of Techniques
To ensure that you give an impactful introduction, you may start your presentation by combining the above-listed techniques. Just be creative on how you can smoothly tie your chosen techniques together to make it more appealing to your audience.
The key to having a cogent introduction is by carefully planning it. Write down all your ideas and considerations, then identify which introduction technique is the most fitting to use in your presentation, If uncertain what works well, you may try different strategies until you come up with the most appropriate one. Also, If you are not comfortable in one technique then you may use the other. What matters is that you are able to craft a rousing introduction because the first few minutes of your presentation will be the determining factor whether you will be able to grasp or lose the attention of your audience
Pro Tip: The techniques cited above don’t only apply for introductions as they can also be used throughout your presentation. Some of these may be used in the closing or body of your speech so it would be advisable to get yourself familiar with them. To easily craft and use these techniques, you may read English materials and watch videos of presenters to further increase your ideas and get some inspiration.
- Business English
- presentation
Related Articles
Career English
11 Essential Vocabulary to Know for When You’re Working in a Project
8 business documents that everyone should know about, 8 traits to look for in a good boss, how to write a resignation letter, start learning english online at affordable prices..
Try two classes for free, no credit card is required.
Home Blog Presentation Ideas How to Start a Presentation: 5 Strong Opening Slides and 12 Tricks To Test
How to Start a Presentation: 5 Strong Opening Slides and 12 Tricks To Test

Knowing how to start a presentation is crucial: if you fail to capture the audience’s attention right off the bat, your entire presentation will flop. Few listeners will stick with you to the end and retain what you have told.
That is mildly unpleasant when you are doing an in-house presentation in front of your colleagues. But it can become utterly embarrassing when you present in front of larger audiences (e.g., at a conference) or worse – delivering a sales presentation to prospective customers.
Here is how most of us begin a presentation: give an awkward greeting, thank everyone for coming, clear our throats, tap the mic, and humbly start to mumble about our subject. The problem with such an opening performance? It effectively kills and buries even the best messages.
Table of Contents
- The Classic Trick: Open a Presentation with an Introduction
- Open a Presentation with a Hook
- Begin with a Captivating Visual
- Ask a “What if…” Question
- Use the Word “Imagine”
- Leverage The Curiosity Gap
- The Power of Silence
- Facts as Weapons of Communication
- Fact vs. Myths
- The Power of Music
- Physical Activity
- Acknowledging a Person
How to Start a PowerPoint Presentation The Right Way
Let’s say you have all of your presentation slides polished up (in case you don’t, check our quick & effective PowerPoint presentation design tips first). Your presentation has a clear storyline and agenda. Main ideas are broken into bite-sized statements for your slides and complemented with visuals. All you have left is to figure out how you begin presenting.
The best way is to appeal to and invoke certain emotions in your audience – curiosity, surprise, fear, or good old amusements. Also, it is recommended to present your main idea in the first 30 seconds of the presentation. And here’s how it’s done.
1. The Classic Trick: Open a Presentation with an Introduction

When you don’t feel like reinventing the wheel, use a classic trick from the book – start with a quick personal introduction. Don’t want to sound as boring as everyone else with your humble “Hi, I’m John, the head of the Customer Support Department”? Great, because we are all about promoting effective presentation techniques (hint: using a dull welcome slide isn’t one of them).
Here’s how to introduce yourself in a presentation the right way.
a. Use a link-back memory formula
To ace a presentation, you need to connect with your audience. The best way to do so is by throwing in a simple story showing who you are, where you came from, and why your words matter.
The human brain loves a good story, and we are more inclined to listen and retain the information told this way. Besides, when we can relate to the narrator (or story hero), we create an emotional bond with them, and, again – become more receptive, and less skeptical of the information that is about to be delivered.
So here are your presentation introduction lines:
My name is Joanne, and I’m the Head of Marketing at company XYZ. Five years ago I was working as a waitress, earning $10/hour and collecting rejection letters from editors. About ten letters every week landed to my mailbox. You see, I love words, but decent publisher thought mine were good enough. Except for the restaurant owner. I was very good at up-selling and recommending dishes to the customers. My boss even bumped my salary to $15/hour as a token of appreciation for my skill. And this made me realize: I should ditch creative writing and focus on copywriting instead. After loads of trial and error back in the day, I learned how to write persuasive copy. I was no longer getting rejection letters. I was receiving thousands of emails saying that someone just bought another product from our company. My sales copy pages generated over $1,500,000 in revenue over last year. And I want to teach you how to do the same”
b. Test the Stereotype Formula
This one’s simple and effective as well. Introduce yourself by sharing an obvious stereotype about your profession. This cue will help you connect with your audience better, make them chuckle a bit, and set a lighter mood for the speech to follow.
Here’s how you can frame your intro:
“My name is ___, and I am a lead software engineer at our platform [Your Job Title]. And yes, I’m that nerdy type who never liked presenting in front of large groups of people. I would rather stay in my den and write code all day long. [Stereotype]. But hey, since I have mustered enough courage…let’s talk today about the new product features my team is about to release….”
After sharing a quick, self-deprecating line, you transition back to your topic, reinforcing the audience’s attention . Both of these formulas help you set the “mood” for your further presentation, so try using them interchangeably on different occasions.
2. Open a Presentation with a Hook
Wow your audience straight off the bat by sharing something they would not expect to hear. This may be one of the popular first-time presentation tips but don’t rush to discard it.
Because here’s the thing: psychologically , we are more inclined to pay attention whenever presented with an unexpected cue. When we know what will happen next – someone flips the switch, and lights turn on – we don’t really pay much attention to that action.
But when we don’t know what to expect next – e.g., someone flips the switch and a bell starts ringing – we are likely to pay more attention to what will happen next. The same goes for words: everyone loves stories with unpredictable twists. So begin your presentation with a PowerPoint introduction slide or a line that no one expects to hear.
Here are a few hook examples you can swipe:
a. Open with a provocative statement
It creates an instant jolt and makes the audience intrigued to hear what you are about to say next – pedal back, continue with the provocation, or do something else that they will not expect.

“You will live seven and a half minutes longer than you would have otherwise, just because you watched this talk.”
That’s how Jane McGonigal opens one of her TED talks . Shocking and intriguing, right?
b. Ask a rhetorical, thought-provoking question
Seasoned presenters know that one good practice is to ask a question at the beginning of a presentation to increase audience engagement. Rhetorical questions have a great persuasive effect – instead of answering aloud, your audience will silently start musing over it during your presentation. They aroused curiosity and motivated the audience to remain attentive, as they did want to learn your answer to this question.
To reinforce your message throughout the presentation, you can further use the Rhetorical Triangle Concept – a rhetorical approach to building a persuasive argument based on Aristotle’s teachings.
c. Use a bold number, factor stat
A clean slide with some mind-boggling stat makes an undeniably strong impact. Here are a few opening statement examples you can use along with your slide:
- Shock them: “We are effectively wasting over $1.2 billion per year on producing clothes no one will ever purchase”
- Create empathy: “Are you among the 20% of people with undiagnosed ADHD?”
- Call to arms: “58% of marketing budgets are wasted due to poor landing page design. Let’s change this!”
- Spark curiosity: “Did you know that companies who invested in speech recognition have seen a 13% increase in ROI within just 3 years?”
3. Begin with a Captivating Visual
Compelling visuals are the ABC of presentation design – use them strategically to make an interesting statement at the beginning and throughout your presentation. Your first presentation slide can be text-free. Communicate your idea with a visual instead – a photo, a chart, an infographic, or another graphics asset.
Visuals are a powerful medium for communication as our brain needs just 13 milliseconds to render what our eyes see, whereas text comprehension requires more cognitive effort.
Relevant images add additional aesthetic appeal to your deck, bolster the audience’s imagination, and make your key message instantly more memorable.
Here’s an intro slide example. You want to make a strong presentation introduction to global pollution. Use the following slide to reinforce the statement you share:

“Seven of nine snow samples taken on land in Antarctica found chemicals known as PFAs, which are used in industrial products and can harm wildlife”
Source: Reuters
4. Ask a “What if…” Question
The “what if” combo carries massive power. It gives your audience a sense of what will happen if they choose to listen to you and follow your advice. Here are a few presentations with starting sentences + slides to illustrate this option:

Alternatively, you can work your way to this point using different questions:
- Ask the audience about their “Why.” Why are they attending this event, or why do they find this topic relevant?
- Use “How” as your question hook if you plan to introduce a potential solution to a problem.
- If your presentation has a persuasion factor associated, use “When” as a question to trigger the interest of the audience on, for example, when they are planning to take action regarding the topic being presented (if we talk about an inspirational presentation).

5. Use the Word “Imagine”
“Imagine,” “Picture This,” and “Think of” are better word choices for when you plan to begin your presentation with a quick story.
Our brain loves interacting with stories. In fact, a captivating story makes us more collaborative. Scientists have discovered that stories with tension during narrative make us:
- Pay more attention,
- Share emotions with the characters and even mimic the feelings and behaviors of those characters afterward.
That’s why good action movies often feel empowering and make us want to change the world too. By incorporating a good, persuasive story with a relatable hero, you can also create that “bond” with your audience and make them more perceptive to your pitch – donate money to support the cause; explore the solution you are offering, and so on.
6. Leverage The Curiosity Gap
The curiosity gap is another psychological trick frequently used by marketers to solicit more clicks, reads, and other interactions from the audience. In essence, it’s the trick you see behind all those clickbait, Buzzfeed-style headlines:

Not everyone is a fan of such titles. But the truth is – they do the trick and instantly capture attention. The curiosity gap sparks our desire to dig deeper into the matter. We are explicitly told that we don’t know something important, and now we crave to change that. Curiosity is an incredibly strong driving force for action – think Eve, think Pandora’s Box.
So consider incorporating these attention grabbers for your presentation speech to shock the audience. You can open with one, or strategically weave them in the middle of your presentation when you feel like your audience is getting tired and may lose their focus.
Here’s how you can use the curiosity gap during your presentation:
- Start telling a story, pause in the middle, and delay the conclusion of it.
- Withhold the key information (e.g., the best solution to the problem you have described) for a bit – but not for too long, as this can reduce the initial curiosity.
- Introduce an idea or concept and link it with an unexpected outcome or subject – this is the best opening for a presentation tip.
7. The Power of Silence
What would you do if you attended a presentation in which the speaker remains silent for 30 seconds after the presentation starts? Just the presenter, standing in front of the audience, in absolute silence.
Most likely, your mind starts racing with thoughts, expecting something of vital importance to be disclosed. The surprise factor with this effect is for us to acknowledge things we tend to take for granted.
It is a powerful resource to introduce a product or to start an inspirational presentation if followed by a fact.
8. Facts as Weapons of Communication
In some niches, using statistics as the icebreaker is the best method to retain the audience’s interest.
Say your presentation is about climate change. Why not introduce a not-so-common fact, such as the amount of wool that can be produced out of oceanic plastic waste per month? And since you have to base your introduction on facts, research manufacturers that work with Oceanic fabrics from recycled plastic bottles .
Using facts helps to build a better narrative, and also gives leverage to your presentation as you are speaking not just from emotional elements but from actually recorded data backed up by research.
9. Fact vs. Myths
Related to our previous point, we make quite an interesting speech if we contrast a fact vs. a myth in a non-conventional way: using a myth to question a well-accepted fact, then introducing a new point of view or theory, backed on sufficient research, that proves the fact wrong. This technique, when used in niches related to academia, can significantly increase the audience’s interest, and it will highlight your presentation as innovative.
Another approach is to debunk a myth using a fact. This contrast immediately piques interest because it promises to overturn commonly held beliefs, and people naturally find it compelling when their existing knowledge is put to the test. An example of this is when a nutritionist wishes to speak about how to lose weight via diet, and debunks the myth that all carbohydrates are “bad”.
10. The Power of Music
Think about a presentation that discusses the benefits of using alternative therapies to treat anxiety, reducing the need to rely on benzodiazepines. Rather than going technical and introducing facts, the presenter can play a soothing tune and invite the audience to follow an exercise that teaches how to practice breathing meditation . Perhaps, in less than 2 minutes, the presenter can accomplish the goal of exposing the advantages of this practice with a live case study fueled by the proper ambiance (due to the music played in the beginning).
11. Physical Activity
Let’s picture ourselves in an in-company presentation about workspace wellness. For this company, the sedentary lifestyle their employees engage in is a worrying factor, so they brought a personal trainer to coach the employees on a basic flexibility routine they can practice in 5 minutes after a couple of hours of desk time.
“Before we dive in, let’s all stand up for a moment.” This simple instruction breaks the ice and creates a moment of shared experience among the attendees. You could then lead them through a brief stretching routine, saying something like, “Let’s reach up high, and stretch out those muscles that get so tight sitting at our desks all day.” With this action, you’re not just talking about workplace wellness, you’re giving them a direct, personal experience of it.
This approach has several advantages. Firstly, it infuses energy into the room and increases the oxygen flow to the brain, potentially boosting the audience’s concentration and retention. Secondly, it sets a precedent that your presentation is not going to be a standard lecture, but rather an interactive experience. This can raise the level of anticipation for what’s to come, and make the presentation a topic for future conversation between coworkers.
12. Acknowledging a Person
How many times have you heard the phrase: “Before we begin, I’d like to dedicate a few words to …” . The speaker could be referring to a mentor figure, a prominent person in the local community, or a group of people who performed charity work or obtained a prize for their hard work and dedication. Whichever is the reason behind this, acknowledgment is a powerful force to use as a method of starting a presentation. It builds a connection with the audience, it speaks about your values and who you admire, and it can transmit what the conversation is going to be about based on who the acknowledged person is.
Closing Thoughts
Now you know how to start your presentation – you have the opening lines, you have the slides to use, and you can browse even more attractive PowerPoint presentation slides and templates on our website. Also, we recommend you visit our article on how to make a PowerPoint Presentation to get familiarized with the best tactics for professional presentation design and delivery, or if you need to save time preparing your presentation, we highly recommend you check our AI Presentation Maker to pair these concepts with cutting-edge slide design powered by AI.

Like this article? Please share
Curiosity Gap, Opening, Public Speaking, Rhetorical Triangle, Speech, What If Filed under Presentation Ideas
Related Articles

Filed under Presentation Ideas • September 5th, 2023
Persuasive Speech: Actionable Writing Tips and Sample Topics
Business professionals, students, and others can all benefit from learning the principles of persuasive speech. After all, the art of persuasion can be applied to any area of life where getting people to agree with you is important. In this article, we get into the basics of persuasive speaking, persuasive speech writing, and lastly persuasive speech topics.

Filed under Presentation Ideas • August 5th, 2023
How Parkinson’s Law Can Make Your Presentations Better
Sometimes even the best presenters procrastinate their work until the very last moment. And then, suddenly, they get a flow of ideas to complete their slide deck and present like they have been preparing for it for ages. However, doing so has drawbacks, as even professional presenters cannot always elude the side effects of […]

Filed under Presentation Ideas • April 29th, 2022
How to Become Great in Public Speaking: Presenting Best Practices
Public Speaking takes a lot of practice and grit, however, it also requires a method that can help you through your presentation. Explore more about this subject in this blog post.
5 Responses to “How to Start a Presentation: 5 Strong Opening Slides and 12 Tricks To Test”
I love to follow the ideas, it’s good for a freshman
Leave a Reply
Presentation Introduction: Useful Phrases and Tips
- By Garry Evans
- Published November 7, 2023
- Updated November 7, 2023
- 7 mins read
Crafting an effective introduction for presentations is crucial to engage your audience and set the tone for your speech. A well-structured introduction can capture the audience’s attention, introduce the topic, and establish your credibility as a speaker. Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to start a presentation, along with more than 30 examples of introductory phrases categorized for various situations.
How to Start a Presentation:
**1. grab the audience’s attention:.
Use a surprising fact or statistic: “Did you know that over a million plastic bottles are sold every minute worldwide?” Begin with a relevant quote: “As Albert Einstein once said, ‘Imagination is more important than knowledge.'” Share a personal anecdote: “A few years ago, I found myself lost in the wilderness, miles away from civilization.”
**2. Pose a Rhetorical Question:
“Have you ever wondered what it takes to create a successful business from scratch?” “Do you know the impact of climate change on our future generations?” “Have you ever asked yourself what motivates us to achieve our goals?”
**3. State a Bold Statement or Hypothetical Scenario:
“Imagine a world where poverty is eradicated, and every child has access to quality education.” “In a society where technology reigns supreme, human connection remains the key to happiness and success.” “We stand on the verge of a groundbreaking scientific discovery that could revolutionize medicine.”
**4. Use a Story or Narrative:
Share a success story: “Let me tell you about John, who went from living in a homeless shelter to becoming a successful entrepreneur.” Narrate an inspiring journey: “In the early 1900s, a group of pioneers set out to conquer the world’s highest mountain, Mount Everest.”
**5. Refer to the Current Situation or Problem:
“In our fast-paced world, stress has become an epidemic that affects millions of lives.” “Today, we face an unprecedented challenge in combating climate change and preserving our planet for future generations.”
**6. Connect to the Audience’s Emotions:
“Think about the joy you feel when you make a child smile. Now, imagine spreading that joy to those who need it most.” “We all share a common fear – the fear of missed opportunities. Today, we’ll explore how to conquer that fear.”
Introductory Phrases for Presentations – Categorized:
To introduce the topic:.
“Today, I’ll be discussing…” “The focus of our presentation is…” “Our topic for today is…” “Let’s dive into the subject of…”
To Establish Credibility: 5. “As someone who has spent years in this field…”
“My extensive research in this area has revealed…” “Having worked on countless projects related to this topic…” “I am honored to share my expertise in…”
To Connect with the Audience: 9. “Just like many of you, I have experienced…”
“We all share a common interest in…” “I believe we can all relate to the idea that…”
To Set the Tone: 12. “Our goal today is to inform, inspire, and…”
“I invite you to join me on a journey of…” “By the end of this presentation, you’ll be equipped to…”
To Highlight the Importance: 15. “This topic is not just relevant; it’s critical to our…”
“Understanding this concept is key to addressing…” “The implications of this subject stretch far beyond…” “It is our responsibility to tackle this issue, and here’s how…”
To Signal Structure: 19. “We will explore this topic in three main parts:…”
“Our presentation is divided into five sections:…” “I’ve organized our discussion into the following segments:…”
To Generate Curiosity: 22. “I bet you’ve never thought about it this way…”
“In the next few minutes, you’ll discover a surprising twist on this idea…” “Stay tuned, as we unveil an unexpected connection between…”
Glossary: Credibility: The quality of being trusted and believed in, often established through expertise and experience. Anecdote: A short and engaging story or narrative that adds a personal touch to your presentation. Rhetorical Question: A question that doesn’t require an answer but is posed to provoke thought and engage the audience. Narrative: A story or account of events, often used to convey information or entertain. Emotions: Feelings or states of mind that can be used to connect with your audience on a personal level. Cliché: Overused phrases or expressions that can make your presentation less engaging. Relevance: The quality of being closely connected or appropriate to the topic at hand. In summary, a well-crafted introduction is a critical component of a successful presentation. It sets the stage for what your audience can expect, captures their interest, and establishes your credibility as a speaker. By using the right introductory phrases and techniques, you can create an engaging and memorable opening that piques your audience’s curiosity and prepares them for the rest of your presentation.
At English Al Fresco we can help you learn how to create an introduction for a presentation and how to start a presentation speech. It’s important to know which introductory phrases to use and how to use them. Find out more about our courses and how we can help you by sending us a quick message: https://speakenglishalfresco.com/contact-us/
Improving your English skills to start writing presentations is a valuable goal, and it’s definitely achievable with consistent effort and practice. Here are some steps to help non-native speakers enhance their English for presentation writing:
English Language Courses:
Consider enrolling in an English language course, either in person or online. Courses can provide structured lessons and opportunities for speaking, writing, and listening practice.
Self-Study with Language Apps:
Language learning apps like Duolingo, Babbel, and Rosetta Stone offer interactive exercises and lessons to help improve your language skills at your own pace. Read Regularly:
Reading English-language books, newspapers, websites, and magazines can help you become more familiar with the language’s structure, vocabulary, and idiomatic expressions. Choose materials related to the topics you plan to present. Watch English Media:
Watching movies, TV shows, and YouTube channels in English can help you become accustomed to spoken English, improve your listening skills, and expose you to different accents. Practice Writing:
Start a journal in English to practice writing regularly. Describe your daily activities, thoughts, and experiences. This will help you gain confidence in expressing yourself in writing.
Vocabulary Building:
Learn new words and phrases daily. You can use flashcards or language learning apps to help build your vocabulary. Focus on words and phrases relevant to the topics you intend to present.
Study English grammar and sentence structure. Online resources, textbooks, and grammar checkers can be helpful. Practice constructing sentences and paragraphs correctly.
Engage in Conversations:
Speak with native speakers or fellow English learners. Engaging in conversations allows you to practice speaking, improve your pronunciation, and gain confidence. Use Language Learning Websites:
Websites like BBC Learning English, Duolingo, and Cambridge English offer resources, lessons, and exercises to improve your language skills.
Record Yourself:
Record your spoken English and presentations. Listen to the recordings to identify areas where you can improve your pronunciation and fluency.
Take Online Courses:
Platforms like Coursera and edX offer English language courses specifically designed for non-native speakers.
Find a Language Exchange Partner:
Connect with native English speakers who want to learn your language. Language exchange partners can help you practice speaking and receive valuable feedback.
Join English Writing Groups:
Join online writing groups or forums to share your writing and get feedback from native speakers. This can improve your writing skills and confidence.
Use Presentation Templates:
Utilise presentation templates and tools, like PowerPoint or Google Slides, which can help you structure your content effectively and visually enhance your presentations.
Practice, Practice, Practice:
Consistency is key. Set aside time each day to practice your English skills, whether through reading, writing, speaking, or listening.
Seek Professional Feedback:
Consider working with a language tutor or language coach who can provide personalized guidance and feedback on your language skills and presentations.
Prepare Speeches and Presentations:
As you become more comfortable with the language, start preparing speeches and presentations on topics that interest you. Practice delivering them to friends, family, or colleagues to receive feedback and improve your public speaking skills. Improving your English language skills for presentations is a gradual process that requires patience and persistence. With regular practice and a variety of learning methods, you can gain the confidence and proficiency needed to write and deliver effective presentations in English.
Join us at English Al Fresco on our 5-day courses for full immersion in British culture and let us help you improve your English in whatever way you need.
Get in touch!
- [email protected]
- +447452960440
Copyright 2023 – English Al Fresco Website

- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
How to Make a “Good” Presentation “Great”
- Guy Kawasaki

Remember: Less is more.
A strong presentation is so much more than information pasted onto a series of slides with fancy backgrounds. Whether you’re pitching an idea, reporting market research, or sharing something else, a great presentation can give you a competitive advantage, and be a powerful tool when aiming to persuade, educate, or inspire others. Here are some unique elements that make a presentation stand out.
- Fonts: Sans Serif fonts such as Helvetica or Arial are preferred for their clean lines, which make them easy to digest at various sizes and distances. Limit the number of font styles to two: one for headings and another for body text, to avoid visual confusion or distractions.
- Colors: Colors can evoke emotions and highlight critical points, but their overuse can lead to a cluttered and confusing presentation. A limited palette of two to three main colors, complemented by a simple background, can help you draw attention to key elements without overwhelming the audience.
- Pictures: Pictures can communicate complex ideas quickly and memorably but choosing the right images is key. Images or pictures should be big (perhaps 20-25% of the page), bold, and have a clear purpose that complements the slide’s text.
- Layout: Don’t overcrowd your slides with too much information. When in doubt, adhere to the principle of simplicity, and aim for a clean and uncluttered layout with plenty of white space around text and images. Think phrases and bullets, not sentences.
As an intern or early career professional, chances are that you’ll be tasked with making or giving a presentation in the near future. Whether you’re pitching an idea, reporting market research, or sharing something else, a great presentation can give you a competitive advantage, and be a powerful tool when aiming to persuade, educate, or inspire others.
- Guy Kawasaki is the chief evangelist at Canva and was the former chief evangelist at Apple. Guy is the author of 16 books including Think Remarkable : 9 Paths to Transform Your Life and Make a Difference.
Partner Center
PHILADELPHIA, MAY 9-10 PUBLIC SPEAKING CLASS IS ALMOST FULL! RESERVE YOUR SPOT NOW

- Public Speaking Classes
- Corporate Presentation Training
- Online Public Speaking Course
- Northeast Region
- Midwest Region
- Southeast Region
- Central Region
- Western Region
- Presentation Skills
- 101 Public Speaking Tips
- Fear of Public Speaking
How to Introduce Yourself in a Presentation [with Examples]

In this post, we are going to cover the best way, a very simple three-step process that will help you introduce yourself in a presentation. A summary of the steps is below.
- Start with your name and company (or organization or school).
- Tell your audience what problem you can solve for them.
- Share some type of proof (social proof works best) that you can solve this problem.
I will break down each step into a simple-to-follow process. But first… a little background.
First, Identify What Your Audience Wants from Your Presentation

So, before you design your introduction, think about what your audience wants from your presentation. Why do they want to spend their valuable time listening to you? Are going to waste their time? Or, are you going to provide them with something valuable?
For instance, I have expertise in a number of different areas. I’m a public speaking coach, a keynote speaker, a best-selling author, a search engine optimization specialist, and a popular podcaster. However, if I delivered that sentence to any audience, the most likely reaction would be, “So what?” That sentence doesn’t answer any of the above questions. The statement is also really “me-focused” not “audience-focused.”
So, when I start to design my self-introduction, I want to focus just on the area of expertise related to my topic. I’m then going to answer the questions above about that particular topic. Once you have these answers, set them aside for a second. They will be important later.
How to Introduce Yourself in a Presentation in Class.

Instead, you probably want to add in a fun way to start a speech . For example, instead of introducing yourself in your class speech and starting in an awkward way, start with a startling statistic. Or start with a summary of your conclusion. Or, you could start the presentation with an inspirational quote.
Each of these presentation starters will help you lower your nervousness and decrease your awkwardness.
If you are delivering a speech in a speech competition or to an audience who doesn’t know you try this technique. Just introduce yourself by saying your name , the school you represent , and your topic . Make it easy. This way you get to your content more quickly and lower your nervousness.
Typically, after you get the first few sentences out of the way, your nervousness will drop dramatically. Since your name, school, and topic should be very easy to remember, this takes the pressure off you during the most nervous moments.
Obviously, follow the guidelines that your teacher or coach gives you. (The competition may have specific ways they want you to introduce yourself.)
How to Introduce Yourself in a Business Presentation — A Step-by-Step Guide.

In a professional setting, when new people walk into a meeting and don’t know what to expect, they will feel uncomfortable. The easiest way to ease some of that tension is to chat with your audience as they come into the room.
By the way, if you are looking for a template for an Elevator Speech , make sure to click this link.
Step #1: Start with your name and company name (or organization).
This one is easy. Just tell your audience your name and the organization that you are representing. If your organization is not a well-known brand name, you might add a short clarifying description. For instance, most people outside of the training industry have never heard of The Leader’s Institute ®. So, my step #1 might sound something like…
Hi, I’m Doug Staneart with The Leader’s Institute ®, an international leadership development company…
Still short and sweet, but a little more clear to someone who has never heard of my company.
Should you give your job title? Well… Maybe and sometimes. Add your title into the introduction only if your title adds to your credibility.
For example, if you are delivering a financial presentation and you are the Chief Financial Officer (CFO) of your company, you might mention that. Your title adds to your credibility. However, if the CFO is delivering a presentation about the value of joining a trade association, the CFO title adds little credibility. So, there is very little value in adding the title.
Step #2: Tell your audience what problem you can solve for them.

For instance, if my topic is how to deliver presentations, I have to determine why the audience would care. What problem will they have that I can help them with? For my audiences, the problem that I most often help people with is how to eliminate public speaking fear. Once I have the problem, I add that to my introduction by using the words, “I help people…”
Hi, I’m Doug Staneart with The Leader’s Institute ®, an international leadership development company, and I help people eliminate public speaking fear.
However, if my topic is How to Close a Higher Percentage of Sales Presentations , I’d likely want to alter my introduction a little. I might say something like…
Hi, I’m Doug Staneart with The Leader’s Institute ®, an international leadership development company, and I help people design more persuasive sales presentations.
I have expertise in both areas. However, I focus my introduction on just the expertise that is applicable to this audience. If I gave the first introduction to the second audience, they will likely respond by thinking, well, I don’t really get nervous speaking, so I guess I can tune out of this speech .
So, create a problem statement starting with, “I help people…” Make the statement apply to what your audience really wants.
Step #3: Share some type of proof (social proof works best) that you can solve this problem.
By the way, if you just do steps #1 and #2, your introduction will be better than most that you will hear. However, if you add Step #3, you will gain more respect (and attention) from your audience. Without adding some type of proof that you can solve this problem, you are just giving your opinion that you are an expert. However, if you can prove it, you are also proving that you are an expert.
This is the tricky part. For some reason, most people who get to this part feel like they haven’t accomplished great things, so they diminish the great accomplishments that they do have.
For instance, an easy way to offer proof is with a personal story of how you have solved that problem in the past.
A Few Examples of How to Introduce Yourself Before a Presentation.
For instance, one of my early clients was a young accountant. When I was working with him, he came up with the following introduction, “I’m Gary Gorman with Gorman and Associates CPA’s, and I help small businesses avoid IRS audits.” It was a great, audience-focused attention-getter. (No one wants to get audited.) However, as an accountant, it wasn’t like his company was getting a lot of five-star reviews on Yelp! So, he was kind of struggling with his social proof. So, I asked him a series of questions.
Me, “How many clients do you have?”
Gary, “Over 300.”
Me, “How many small business tax returns have you processed?”
Gary, “Well, at least a couple hundred a year for 15 years.”
Me, “So, at least 3000?” He nodded. “How many of your 300 clients have been audited since you have been representing them?”
He looked at me and said, “Well, none.”
So, we just added that piece of proof to his talk of introduction.
I’m Gary Gorman with Gorman and Associates CPA’s, and I help small businesses avoid IRS audits. In fact, in my career, I’ve helped clients complete over 3000 tax returns, and not a single one has ever been audited.
Here Is How I Adjust My Introduction Based on What I Want the Audience to Do.
For my proof, I have a number of options. Just like Gary, I have had a lot of clients who have had great successes. In addition, I have published two best-selling books about public speaking. I also have hundreds of thousands of people who listen to my podcast each week. So, I can pick my evidence based on what I want my audience to do.
For instance, if I’m speaking at a convention, and I want the audience to come by my booth to purchase my books, my introduction might sound like this.
Hi, I’m Doug Staneart with The Leader’s Institute ®, an international leadership development company, and I help people eliminate public speaking fear. One of the things that I’m most know for is being the author of two best-selling books, Fearless Presentations and Mastering Presentations.
However, if I’m leading a webinar, I may want the audience to purchase a seat in one of my classes. In that case, my introduction might sound like this.
Hi, I’m Doug Staneart with The Leader’s Institute ®, an international leadership development company, and I help people eliminate public speaking fear. For instance, for the last 20 years, I’ve taught public speaking classes to over 20,000 people, and I haven’t had a single person fail to reduce their nervousness significantly in just two days.
If my goal is to get the audience to subscribe to my podcast, my intro might sound like…
Hi, I’m Doug Staneart with The Leader’s Institute ®, an international leadership development company, and I help people eliminate public speaking fear. One of the ways that I do this is with my weekly podcast called, Fearless Presentations, which has over one million downloads, so far.
Use the Form Below to Organize How to Introduce Yourself in a Presentation.
The point is that you want to design your introduction in a way that makes people pause and think, “Really? That sounds pretty good.” You want to avoid introductions that make your audience think, “So what?”
If you have a speech coming up and need a good introduction, complete the form below. We will send you your answers via email!
Can You Replace Your Introduction with a PowerPoint Slide?
Is it okay to make your first slide (or second slide) in your presentation slides an introduction? Sure. A good public speaker will often add an introduction slide with a biography, portrait, and maybe even contact information. I sometimes do this myself.
However, I NEVER read the slide to my audience. I often just have it showing while I deliver the short introduction using the guide above. This is a great way to share more of your work experience without sounding like you are bragging.
For tips about how many powerpoint slides to use in a presentation , click here.
Remember that There Is a Big Difference Between Your Introduction in a Presentation and Your Presentation Starter.
When you introduce yourself in a presentation, you will often just use a single sentence to tell the audience who you are. You only use this intro if the audience doesn’t know who you are. Your presentation starter, though, is quite different. Your presentation starter should be a brief introduction with relevant details about what you will cover in your presentation.
For details, see Great Ways to Start a Presentation . In that post, we show ways to get the attention of the audience. We also give examples of how to use an interesting hook, personal stories, and how to use humor to start a presentation.

Podcasts , presentation skills
View More Posts By Category: Free Public Speaking Tips | leadership tips | Online Courses | Past Fearless Presentations ® Classes | Podcasts | presentation skills | Uncategorized

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
How to create an engaging introduction. Consider using the tips below to engage your audience before your next presentation: 1. Tell your audience who you are. Introduce yourself, and then once your audience knows your name, tell them why they should listen to you. Example: "Good morning. My name is Miranda Booker, and I'm here today to ...
introduction should constitute about 10% to 20% of the length of your presentation. So if you are presenting for 10 minutes, your introduction should be between 1 to 2 minutes, no more. 1) Capture your audience's interest This is a sentence or two that you use to get people's attention and draw their interest. It could be a question or a
6/ Engage Emotionally. Connect emotional levels with your audience by appealing to their aspirations, fears, desires, or values. They help create a deeper connection and engagement from the very beginning. Make sure your introduction is concise and to the point. Avoid unnecessary details or lengthy explanations.
1. Give your presentation an introduction, a main message, and a conclusion. Some people summarise this as 'say what you're going to say, say it, then say what you've said'. However, that is not the whole story. Your introduction needs to 'set the scene' a bit and give a broad outline of what you are going to cover in your presentation.
Organize notes and other content. 9 Tips on Openings and How to Start Presentation Introduction. 1-know your audience. 2-Have an exciting start with attracting attention. 3-Choose your opening sentences carefully. 4-Use visual aids. 5-Compliment your audience. 6-Use an anecdote or a quick story. 7-Ask for audience participation.
Read through your introduction and make sure it is clear, concise, and interesting. Avoid giving too much detail - that will go into the body of the presentation. Your introduction should make your audience curious and want to hear more. With this step-by-step guide, you will be well-prepared to create a powerful introduction for your presentation.
Ask a question and get your audience to respond by raising hands. Get the complete Presentations in English Series: Part 1: How to Prepare for Your Presentation in English. Part 2: How to Start with a Great Introduction in Your Presentation. Part 3: How to Organize Your Presentation in English.
Your presentation, like a written assignment, should include an introduction, body, and conclusion. These components serve much the same purpose as they do in a written assignment. The introduction engages the audience's attention, introduces the topic, and sets the tone for what is to come.
Here are the basic elements you can apply to make a particularly impactful introduction: Speak in a calm, clear, and confident manner. Welcome the audience members and thank them for their presence and attention. Introduce yourself and the reason for your presentation. Provide a brief outline of the topic your presentation addresses.
It consists of five steps: Attention: Gain the attention of your audience by telling a story, using a startling fact/statistic, posing a question/rhetorical situation, using visuals, etc. Need: Show that there is a need for change and that the situation at hand is dire by using statistics, examples, testimony, etc.
A good introduction to the delivery of your presentation is extremely important. The first minute or so sets the stage for the rest of your talk. You should start with an upbeat, positive mood. The first impression you make lasts. You want to quickly gain the attention, interest, and respect of your audience. Your first words should be lively ...
Step 1: Open PowerPoint and Select a Theme. Choose a theme that aligns with the topic of your presentation. Selecting a theme is the first step because it sets the visual tone for your presentation. The theme should be professional yet engaging, and it should complement, not distract from, your introduction.
This clarifies the overall purpose of your talk and reinforces your reason for being there. Follow these steps: Signal that it's nearly the end of your presentation, for example, "As we wrap up/as we wind down the talk…". Restate the topic and purpose of your presentation - "In this speech I wanted to compare…". 5.
Length and Structure. The main part should make up about 70% of the presentation and also include a clear structure. Explain your ideas in detail and build them up logically. It should be organized chronologically, by priority or by topic. There should be a smooth transition between the individual issues.
First things first: the date's in the diary and you need to prepare. Let's break it down. 1. Preparing your presentation. Imagine you're a designer in the automotive industry and your boss has asked you to give a presentation. The subject: the future of the car and how it will fit with all the other modes of transport.
3. State your Main Point. When considering time constraints you may state your central idea at the very beginning of your presentation. You need not make your audience think first then realize the gist of your presentation eventually. This is apt to the kind of audience that is busy and prefers directness. 4.
Financial PowerPoint Template with Calculator by SlideModel. 5. Use the Word "Imagine". "Imagine," "Picture This," and "Think of" are better word choices for when you plan to begin your presentation with a quick story. Our brain loves interacting with stories. In fact, a captivating story makes us more collaborative.
Join online writing groups or forums to share your writing and get feedback from native speakers. This can improve your writing skills and confidence. Use Presentation Templates: Utilise presentation templates and tools, like PowerPoint or Google Slides, which can help you structure your content effectively and visually enhance your presentations.
A strong introduction will also make the audience aware of the purpose of the presentation. Have you ever sat through a speech wondering what the point was? Or perhaps you have listened to a presentation and had no clue what the speaker was talking about. An introduction is important because it makes the audience fully aware of the topic, why ...
Images or pictures should be big (perhaps 20-25% of the page), bold, and have a clear purpose that complements the slide's text. Layout: Don't overcrowd your slides with too much information.
Oral presentations are a common feature of many courses at university. They may take the form of a short or longer presentation at a tutorial or seminar, delivered either individually or as part of a group. You may have to use visual aids such as PowerPoint slides. Researching, planning and structuring an oral presentation is similar to the ...
Find the most important idea—the main thing you want to tell your audience. Make sure it's clear, short and something they'll find interesting. Recheck your ideas and remove anything that doesn't match your main message or the people you're talking to. Create a Skeleton Outline.
Step #2: Tell your audience what problem you can solve for them. This is where all of the pre-work comes into play. In this step, you will use the answers to one of those questions that you answered earlier. For instance, if my topic is how to deliver presentations, I have to determine why the audience would care.