[FREE] Fun Math Games & Activities Packs
Always on the lookout for fun math games and activities in the classroom? Try our ready-to-go printable packs for students to complete independently or with a partner!
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
Stem & leaf plot

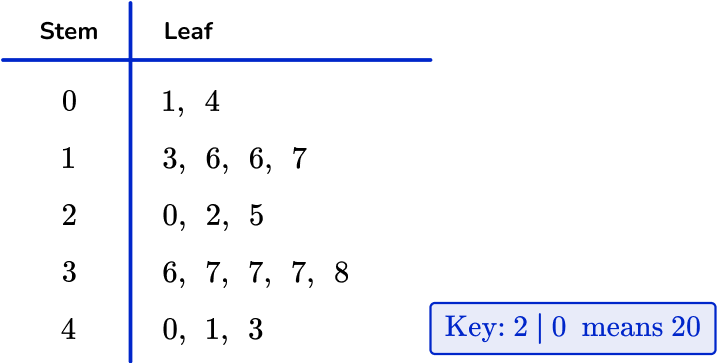
Stem and leaf plot
Here you will learn about stem and leaf plots, including drawing, interpreting, and comparing them.
Students will first learn about stem and leaf plots as part of statistics and probability in 7 th grade.
What is a stem and leaf plot?
A stem and leaf plot is a method of organizing numerical data based on the place value of the numbers.
Each number is split into two parts:
- The first digit(s) form the stem.
- The last digit forms the leaf.
The number of digits for the stem can vary, but the number of digits for the leaf should only ever contain a single digit.
For example, if the numerical data contains all whole numbers, the numbers in the tens place and greater would make up the stem values while all numbers in the ones place would make up the leaf values.
Each piece of numerical data will be written with the last digit to the right of a vertical line and all other digits to the left of the vertical line. For example, the number 154 would be split into two parts where the digits \bf{15} would be the stem and \bf{4} would be the leaf.

To set up a stem and leaf plot you need to:
- Organize the data into ascending order , smallest to largest.
- Determine how the numbers are split into 2 parts by writing a key for the stem and leaf plot.
- Write the values for the ‘stem’ into the stem and leaf plot.
- Write the values for the ‘leaf’ into the stem and leaf plot.
NOTE: A stem and leaf plot must have a key (sometimes referred to as a legend ). This explains how to convert the digits in the stem and leaf plot into a single data point.
You can use stem and leaf plots to calculate averages like the median, the mode and the mean, and to calculate measures of spread like the range and the interquartile range.
Dual stem and leaf plot
Comparing data sets is simplified by using a dual stem and leaf plot which have two sets of data represented back to back.
For example, here are two sets of data showing test scores of 20 males and 20 females.
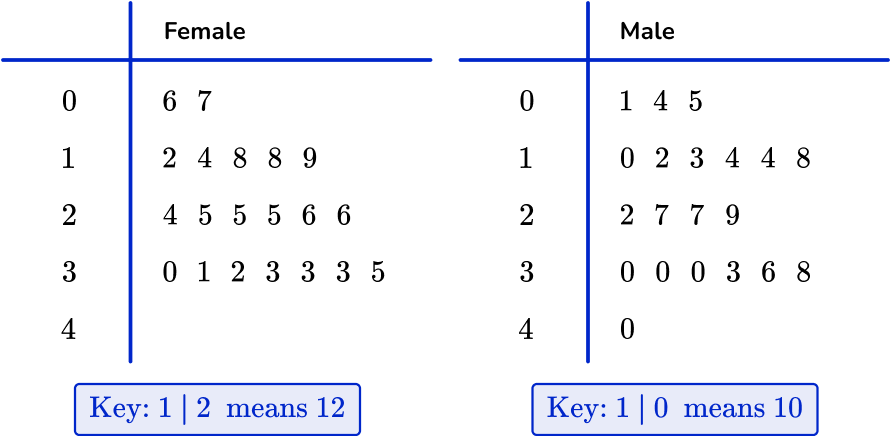
By combining them together to form one dual stem and leaf plot, you can directly compare the two sets of data.
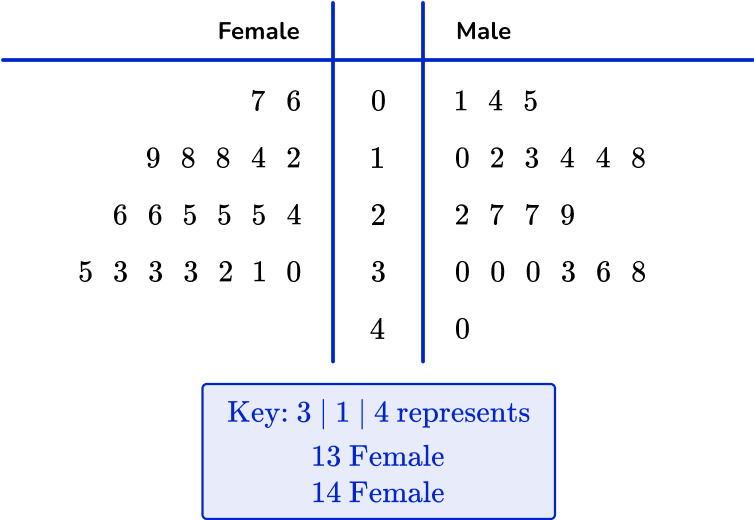
The data must be closely related for it to be compared effectively on the diagram. Note that the digits in the leaf for females is still in ascending order but from right to left , rather than left to right. Also, the key represents the data values for each side of the stem and leaf plot.
Common Core State Standards
How does this relate to 7 th grade math?
- Grade 7 – Statistics and Probability (7.SP.B.4) Use measures of center and measures of variability for numerical data from random samples to draw informal comparative inferences about two populations. For example, decide whether the words in a chapter of a seventh-grade science book are generally longer than the words in a chapter of a fourth-grade science book.
How to draw a stem and leaf plot
In order to draw a stem and leaf plot:
Order the numbers from smallest to largest.
Split the numbers into two parts; the last part must be one digit only.
Put the values into the diagram and create a key.
![week 2 assignment stem and leaf plots [FREE] Representing Data Check for Understanding (Grade 6 to 7)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/Representing-Data-listing-image.png)
[FREE] Representing Data Check for Understanding (Grade 6 to 7)
Use this quiz to check your grade 6th to 7th students’ understanding of representing data. 10+ questions with answers covering a range of 6th and 7th grade representing data topics to identify areas of strength and support!
Stem and leaf plot examples
Example 1: two digit numbers.
The data below shows the ages of people at a party.
35, \quad 50, \quad 37, \quad 44, \quad 53, \quad 41, \quad 39, \quad 45, \quad 48, \quad 56
Draw an ordered stem and leaf plot for the data. Remember to include a suitable key.
35, \quad 37, \quad 39, \quad 41, \quad 44, \quad 45, \quad 48, \quad 50, \quad 53, \quad 56
2 Split the numbers into two parts; the last part must be one digit only.
The numbers in the data will split into tens and ones, so 35 will be 3 and 5 ( 3 represents 30 or 3 tens, and 5 is 5 ones).
3 Put the values into the diagram and create a key.

Example 2: three digit numbers
The data below shows the length in centimeters of 13 long jumps on a 9 th grade sports day.
153, 144, 148, 140, 149, 145, 144, \\\\ \quad 142, 158, 135, 140, 139, 160.
Draw an ordered stem and leaf plot for the following set of data. Remember to include a suitable key.
153, 144, 148, 140, 149, 145, 144, 142, 158, 135, 140, 139, 160
135, 139, 140, 140, 142, 144, 144, 145, 148, 149, 153, 158, 160.
The numbers in the data will be split into two parts: 148 will become 14 and 8 ( 14 represents 140 or 14 tens, and 8 represents 8 ones).
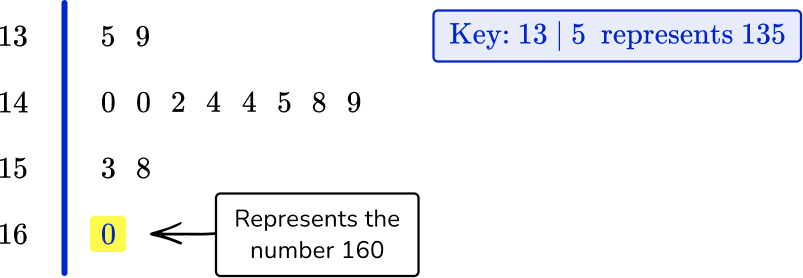
Example 3: decimal values
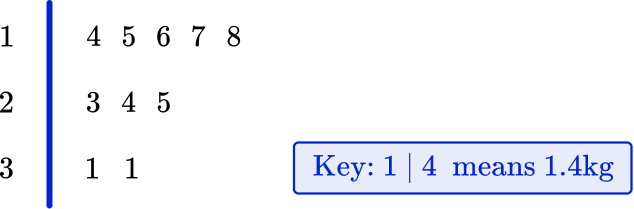
A group of students are making model gargoyles out of clay. The weight of each gargoyle is written below.
1.5 \, kg \quad 2.3 \, kg \quad 1.6 \, kg \quad 3.1 \, kg \quad 3.1 \, kg \\\\ 1.4 \, kg \quad 2.5 \, kg \quad 1.7 \, kg \quad 1.8 \, kg \quad 2.4 \, kg
Draw an ordered stem and leaf plot for data. Remember to include a suitable key.
1.5 \, kg , \, 2.3 \, kg, \, 1.6 \, kg, \, 3.1 \, kg, \, 3.1 \, kg, \, 1.4 \, kg, \, 2.5 \, kg, \, 1.7 \, kg, \, 1.8 \, kg, \, 2.4 \, kg
1.4 \, kg, \, 1.5 \, kg, \, 1.6 \, kg, \, 1.7 \, kg, \, 1.8 \, kg, \, 2.3 \, kg, \, 2.4 \, kg, \, 2.5 \, kg, \, 3.1 \, kg, \, 3.1 \, kg.
As the numbers are decimals, they are split like this – 1.4 \, kg splits into ones (1) and tenths (4).
How to interpret a stem and leaf plot
In order to interpret a stem and leaf plot:
Read the question(s).
Use the information in the stem and leaf plot to answer the question(s).
Example 4: answering questions using a stem and leaf plot
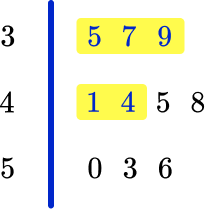
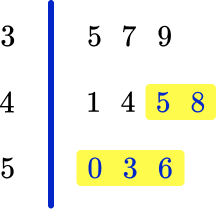
The stem and leaf plot below shows the ages of a group of people at a party.

(a) How many people are there in the group?
(b) What age is the youngest member of the group?
(c) What age is the oldest member of the group?
(d) How many people are under 45?
(e) How many people are 45 and over?
Count all the numbers in the leaf, so the answer is 10 people.
The first number in the leaf is the smallest value, so the answer is 35 years old.
The last number in the leaf is the largest value, so the answer is 56 years old.
Count all the values in the leaf that are less than 45, so the answer is 5 people.
Count all the people in the leaf that are 45 and above, so the answer is 5 people.
Example 5: calculating averages and the range from a stem and leaf plot
The stem and leaf plot below shows the weight of 10 puppies in kilograms.
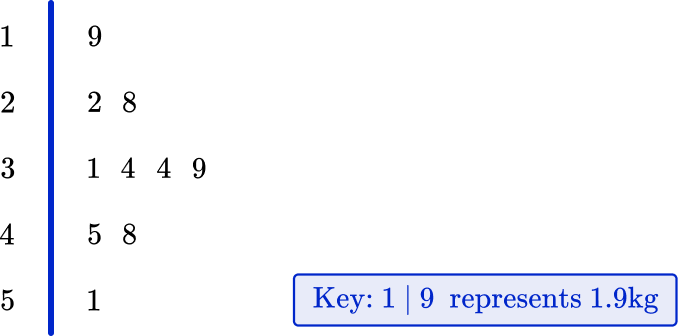
(a) What is the modal weight?
(b) What is the median weight?
(c) What is the range of the weights?
(d) What is the mean weight of the puppies?
The mode is the most frequent value, so the mode for this set of data is 3.4 \, kg, as it occurs twice.
The median is the middle value. As there are 10 values, the median is located in the position \cfrac{10+1}{2}=5.5.
Count 5 and a half places; in this case, that is between 3.4 and 3.4. So you would add them up and divide by 2, which gives you a median of 3.4 \, kg.
The range is calculated by subtracting the lowest value from the highest value.
5.1-1.9=3.2 \mathrm{~kg}
The mean is calculated by adding up all the numbers and dividing by the number of values. The sum of all 10 values is 35.1. Dividing by 10, you get a mean of 3.51 \, kg.
35.1 \div 10=3.51 \mathrm{~kg}
Example 6: dual stem and leaf plot
This dual stem and leaf plot shows test scores for the students in Miss Thomas’ class.
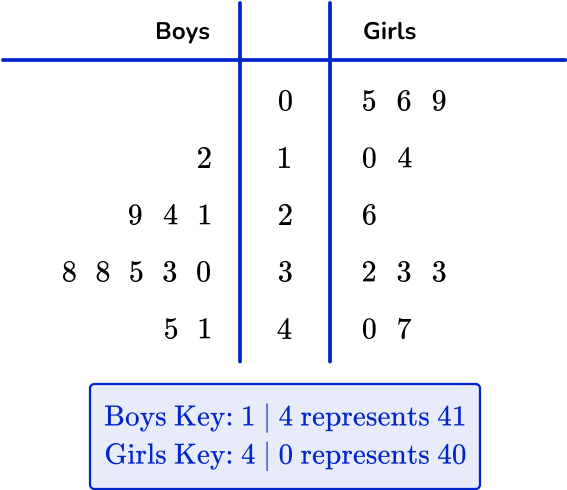
(a) What is the range of the boys’ scores?
(b) What is the median of the girls’ scores?
(c) What is the mode for the boys’ scores?
(d) Compare the median and range of the boys’ and girls’ scores.
The range is found by subtracting the lowest from the highest values on the ‘boys’ side of the diagram.
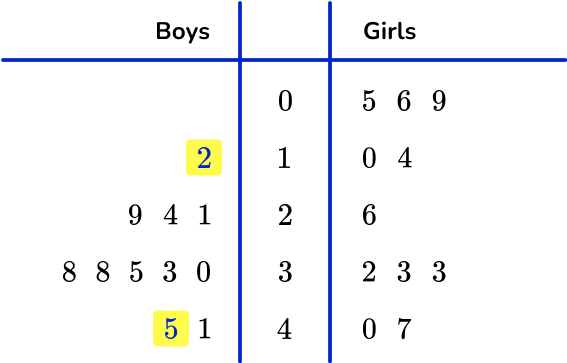
The range is 33.
The median is the middle value on the girls’ side of the diagram. There are 11 values, so the middle value is found by adding 1 and dividing by 2. 11+1 \div 2=6 \text{th} place. The median is therefore 26.
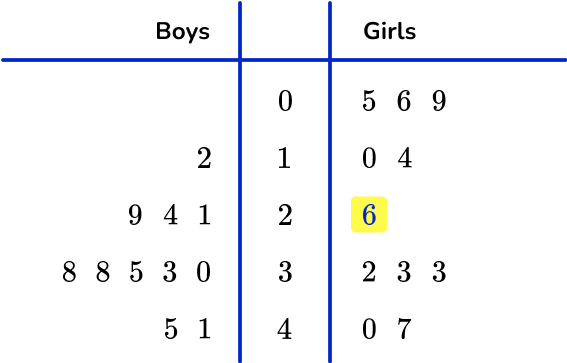
The mode is the most common number.
Here, the mode is 38 as it is the most frequent value for the boys.
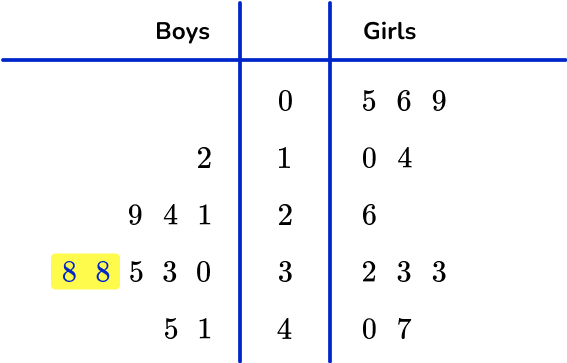
You need to compare the median and range for each set of data:
The boys did better on average (median =33 ) than the girls (median =26 ).
The girls’ scores (range =42 ) were more spread out than the boys (range =33 ).
Teaching tips for stem and leaf plot
- Start with simple data values ( 2 digit numbers whole numbers) and a clear explanation. Begin by explaining what a stem and leaf plot is and how it represents a set of data. Emphasize that it shows individual values split into stems (tens digit) and leaves (ones digit).
- Offer multiple guided examples where students can practice creating stem and leaf plots. Provide data sets and worksheets that gradually increase in complexity.
- Connect stem and leaf plots to real-life scenarios to make them more relatable. Use examples such as test scores, measurements, or survey data to show how stem and leaf plots can be used to analyze and interpret information.
- Provide visual aids or display examples around the classroom for students to differentiate between graph types including stem and leaf plots, bar graphs, histograms, and dot plots, and box plots.
Easy mistakes to make

- Miscounting A common error is to incorrectly count the numbers in a stem and leaf plot when calculating an average or range. It is a good idea to mark off each number to avoid missing a number.
- More than one digit for the leaf The leaf must only be one digit, otherwise the data can be greatly misinterpreted. Make sure that the smallest place value for the data is used for the leaf.
Related representing data lessons
- Representing data
- Interquartile range
- Scatterplot
- Two way tables
- Time series graph
Practice stem and leaf plot questions
1. Which stem and leaf plot matches this data?
29 \, cm \quad 60 \, cm \quad 51 \, cm \quad 34 \, cm \\\\ 42 \, cm \quad 61 \, cm \quad 46 \, cm \quad 36 \, cm
63 \, cm \quad 50 \, cm \quad 57 \, cm \quad 53 \, cm \quad \\\\ 60 \, cm \quad 39 \, cm \quad 47 \, cm \quad 40 \, cm
By checking the highest and lowest values from the list ( 29 is the lowest and 63 is the highest), you can see that the correct stem and leaf plot is:

2. The stem and leaf plot below shows heights of Mrs. Wilks’ flowers in centimeters.
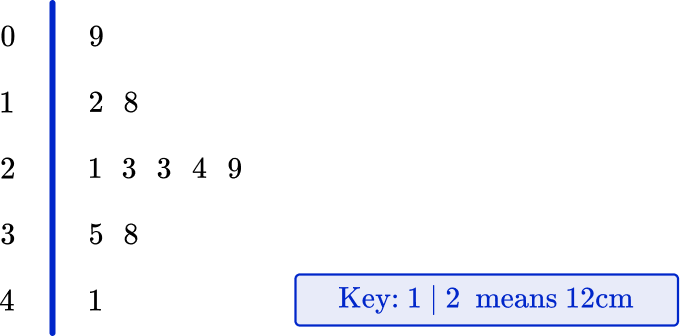
What is the range of the height of Mrs. Wilks’ flowers?
The range of the data is found by subtracting the lowest value from the highest value.
41-9=32 \mathrm{~cm}
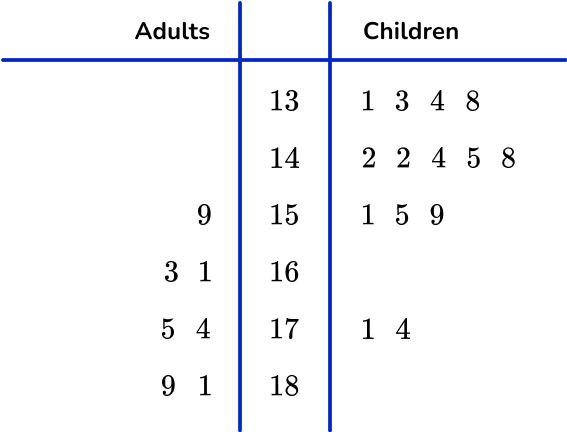
3. Below is a stem and leaf plot showing the scores of 18 javelin throws in a school sports day. The longest throw wins.
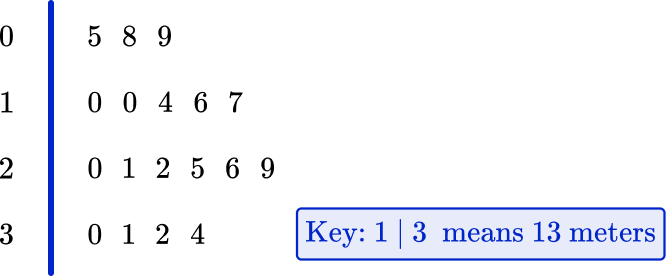
What was the mean distance thrown?
The mean is the sum of all the values, divided by the total number of values.
5+8+9+10+10+14+16+17+20+21+22+25+26+29+30+31+32+34=359 \, m
359 \div 18=19.9\overline{4} \mathrm{~m}=19.9 \mathrm{~m} \text { (to the nearest tenth) }
4. The stem and leaf plot below represents a sample of the lengths of leaves from a tree.
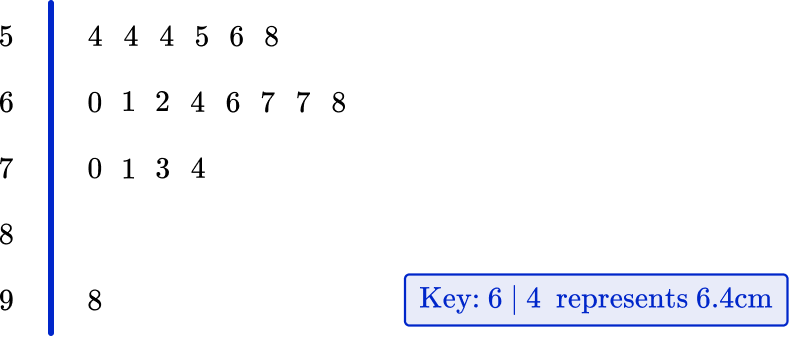
Which average would be the most suitable to represent the data?
As there is one value that is very large, this would affect the mean and the range. The mode is unsuitable because it does not use all of the data. The median is most suitable, as this is not affected as much as the mean when there are outliers.
5. The stem and leaf plot below shows the maximum weight of a deadlift lifted by each competitor in a weightlifting competition. Everyone managed to record at least one lift.
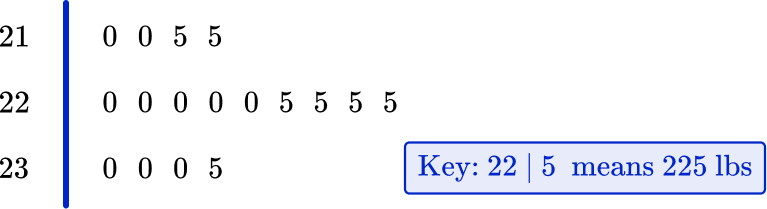
What was the median weight lifted?
The median is located at the middle position in the data.
17 \div 2=8.5^{\text {th }} value. This value lies between 220 \, lbs and 220 \, lbs.
As these two values are the same, the median is 220 \, lbs.
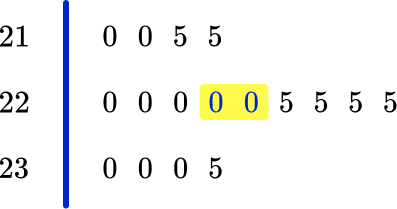
6. 42 people competed in a local 3 legged race. The time for each pair was recorded in a back to back stem and leaf plot.
Select the completed stem and leaf plot for the adult race using the results below.
16.3s \quad 18.1s \quad 15.9s \quad 16.1s \quad 17.4s \quad 18.9s \quad 17.5s
The values are written:
- In the correct row.
- In order (right to left) from the stem.
- On the left side of the stem and leaf plot and to the left of the vertical line.
Stem and leaf plot FAQs
A stem and leaf plot is a method of organizing numerical data based on the place value of the numbers. A stem and leaf plot can help visualize the shape of a distribution for quantitative data.
A stem and leaf plot may also be called a stem plot, a stem plot diagram, a stem and leaf diagram, or a stem and leaf display.
The next lessons are
- Frequency table
- Frequency graph
- Sampling methods
- Represent and interpret data
Still stuck?
At Third Space Learning, we specialize in helping teachers and school leaders to provide personalized math support for more of their students through high-quality, online one-on-one math tutoring delivered by subject experts.
Each week, our tutors support thousands of students who are at risk of not meeting their grade-level expectations, and help accelerate their progress and boost their confidence.

Find out how we can help your students achieve success with our math tutoring programs .
[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (Grades 3 to 6)
Prepare for math tests in your state with these Grade 3 to Grade 6 practice assessments for Common Core and state equivalents.
40 multiple choice questions and detailed answers to support test prep, created by US math experts covering a range of topics!
Privacy Overview

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

2.8.4: Two-Sided Stem-and-Leaf Plots
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 5777
Two-Sided Stem-and-Leaf Plots
As you have learned in a previous section, stem-and-leaf plots are an excellent tool for organizing data. Remember that stem-and-leaf plots are a visual representation of grouped discrete data, but they can also be referred to as a modal representation. This is because by looking at a stem-and-leaf plot, we can determine the mode by quick visual inspection. The previous section was about single-sided stem-and-leaf plots. In this section, you will learn about two-sided stem-and-leaf plots , which are also often called back-to-back stem-and-leaf plots.
Interpreting Stem-and-Leaf Plots
The girls and boys in one of BDF High School's AP English classes are having a contest. They want to see which group can read the most number of books. Mrs. Stubbard, their English teacher, says that the class will tally the number of books each group has read, and the highest mode will be the winner. The following data was collected for the first semester of AP English:

a. Draw a two-sided stem-and-leaf plot for the data.
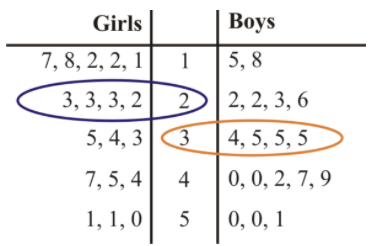
b. Determine the mode for each group.
The mode for the girls is 23 books. It is the number in the girls column that appears most often. The mode for the boys is 35 books. It is the number in the boys column that appears most often.
c. Help Mrs. Stubbard decide which group won the contest.
Mrs. Stubbard should decide that the boys group has won the contest.
Constructing a Two-Sided Stem-and-Leaf Plots
1. Mrs. Cameron teaches AP Statistics at GHI High School. She recently wrote down the class marks for her current grade 12 class and compared it to the previous grade 12 class. The data can be found below. Construct a two-sided stem-and-leaf plot for the data and compare the distributions.
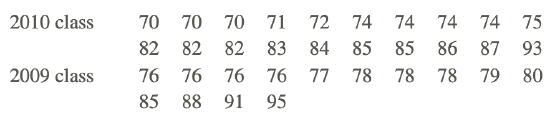
There is a wide variation in the marks for both years in Mrs. Cameron’s AP Statistics Class. In 2009, her class had marks anywhere from 76 to 95. In 2010, the class marks ranged from 70 to 100. The mode for the 2009 class was 76, but for the 2010 class, it was 74. It would seem that the 2009 class had, indeed, done slightly better than Mrs. Cameron’s current class.
2. The following data was collected in a survey done by Connor and Scott for their statistics project. The data represents the ages of people who entered into a new hardware store within its first half hour of opening on its opening weekend. The M's in the data represent males, and the F's represent females.

Construct a back-to-back stem-and-leaf plot showing the ages of male customers and the ages of female customers. Compare the distributions.
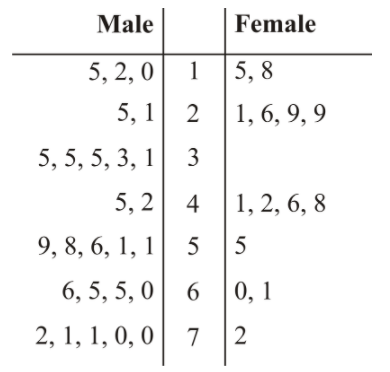
For the male customers, the ages ranged from 10 to 72. The ages for the male customers were spread out throughout this range, with the mode being age 35. In other words, for the males found to be at the store in the first half hour of opening day, there was no real age category where a concentration of males could be found.
For the female customers, the ages ranged from 15 to 72, but they were concentrated between 21 and 48. The mode for the ages of the female customers was 29 years of age.
Example
The boys and girls basketball teams at a high school had their heights measured at practice. The following data was recorded for their heights (in centimeters ):

Construct a two-sided stem-and-leaf plot for the data. Determine the median and mode using the two-sided stem-and-leaf plot for each distribution. What can you conclude from the distributions?
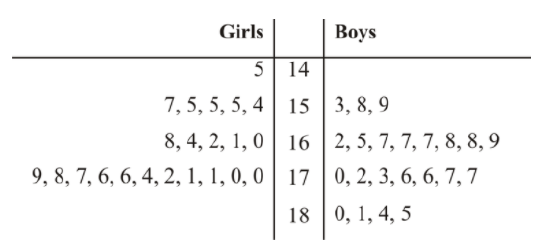
The data suggests that there is a slightly wider variation in the heights for the group of girls than for the group of boys. For the girls, the heights ranged from 145 to 179 centimeters , whereas for the boys, the heights ranged from 153 to 185 centimeters. The median for the girls group is at 168.5 centimeters, and the mode is at 155 centimeters. For the group of boys, however, the median is at 169.5 centimeters, and the mode is at 167 centimeters. The boys seem to be taller than the girls.
Review
The two-sided stem-and-leaf plot below shows the number of home runs hit by the members of 2 major league baseball teams. Use the two-sided stem-and-leaf plot to answer the following questions:

- What was the range for the number of home runs hit by the Mets? What was the range for the Phillies?
- What was the median for the number of home runs hit by the Mets? What was the median for the Phillies?
- What was the mode for the number of home runs hit by the Mets? What was the mode for the Phillies?
- Which team had more players hit 20 or more home runs?
30 girls and 35 boys participated in an intramural bowling league. The two-sided stem-and-leaf plot below shows the highest score of each of the participants. Use the two-sided stem-and-leaf plot to answer the following questions:
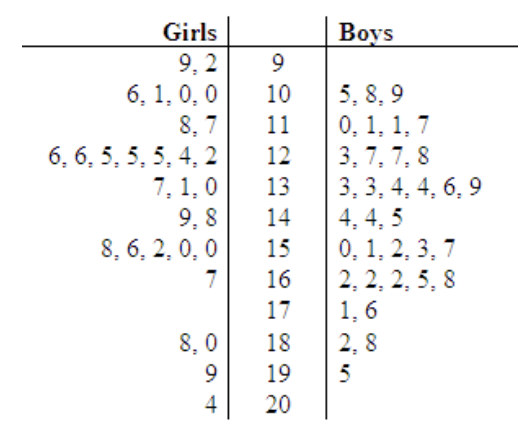
- What was the range for the highest scores for the girls? What was the range for the boys?
- What was the median for the highest scores for the girls? What was the median for the boys?
- What was the mode for the highest scores for the girls? What was the mode for the boys?
- Did a girl or a boy have the highest score in the intramural bowling league?
- Mr. Dugas, the senior high physical education teacher, is doing fitness testing this week in gym class. After each test, students are required to take their pulse rate and record it on the chart in the front of the gym. At the end of the week, Mr. Dugas looks at the data in order to analyze it. The data is shown below:

- Construct a two-sided stem-and-leaf plot for the data and compare the distributions.
- Starbucks prides itself on its low line-up times in order to be served. A new coffee house in town has also boasted that it will have your order in your hands and have you on your way quicker than the competition. The following data was collected for the line-up times (in minutes) for both coffee houses:

- Construct a two-sided stem-and-leaf plot for the data. Determine the median and mode using the two-sided stem-and-leaf plot. What can you conclude from the distributions?
Review (Answers)
To view the Review answers, open this PDF file and look for section 8.3.
Additional Resources
PLIX: Play, Learn, Interact, eXplore - Gamers
Video: Two Sided Stem and Leaf Plots Examples
Activities: Two-Sided Stem-and-Leaf Plots Discussion Questions
Lesson Plans: Two Sided Stem and Leaf Plots Lesson Plan
Practice: Two-Sided Stem-and-Leaf Plots
Real World: Two Sided Stem and Leaf Plots
2.1 Stem-and-Leaf Graphs (Stemplots), Line Graphs, and Bar Graphs
One simple graph, the stem-and-leaf graph or stemplot , comes from the field of exploratory data analysis. It is a good choice when the data sets are small. To create the plot, divide each observation of data into a stem and a leaf. The leaf consists of a final significant digit . For example, 23 has stem two and leaf three. The number 432 has stem 43 and leaf two. Likewise, the number 5,432 has stem 543 and leaf two. The decimal 9.3 has stem nine and leaf three. Write the stems in a vertical line from smallest to largest. Draw a vertical line to the right of the stems. Then write the leaves in increasing order next to their corresponding stem.
Example 2.1
For Susan Dean's spring pre-calculus class, scores for the first exam were as follows (smallest to largest): 33; 42; 49; 49; 53; 55; 55; 61; 63; 67; 68; 68; 69; 69; 72; 73; 74; 78; 80; 83; 88; 88; 88; 90; 92; 94; 94; 94; 94; 96; 100
The stemplot shows that most scores fell in the 60s, 70s, 80s, and 90s. Eight out of the 31 scores or approximately 26% ( 8 31 ) ( 8 31 ) were in the 90s or 100, a fairly high number of As.
For the Park City basketball team, scores for the last 30 games were as follows (smallest to largest): 32; 32; 33; 34; 38; 40; 42; 42; 43; 44; 46; 47; 47; 48; 48; 48; 49; 50; 50; 51; 52; 52; 52; 53; 54; 56; 57; 57; 60; 61 Construct a stem plot for the data.
The stemplot is a quick way to graph data and gives an exact picture of the data. You want to look for an overall pattern and any outliers. An outlier is an observation of data that does not fit the rest of the data. It is sometimes called an extreme value. When you graph an outlier, it will appear not to fit the pattern of the graph. Some outliers are due to mistakes (for example, writing down 50 instead of 500) while others may indicate that something unusual is happening. It takes some background information to explain outliers, so we will cover them in more detail later.
Example 2.2
The data are the distances (in kilometers) from a home to local supermarkets. Create a stemplot using the data: 1.1; 1.5; 2.3; 2.5; 2.7; 3.2; 3.3; 3.3; 3.5; 3.8; 4.0; 4.2; 4.5; 4.5; 4.7; 4.8; 5.5; 5.6; 6.5; 6.7; 12.3
Do the data seem to have any concentration of values?
The leaves are to the right of the decimal.
The value 12.3 may be an outlier. Values appear to concentrate at three and four kilometers.
The following data show the distances (in miles) from the homes of off-campus statistics students to the college. Create a stem plot using the data and identify any outliers:
0.5; 0.7; 1.1; 1.2; 1.2; 1.3; 1.3; 1.5; 1.5; 1.7; 1.7; 1.8; 1.9; 2.0; 2.2; 2.5; 2.6; 2.8; 2.8; 2.8; 3.5; 3.8; 4.4; 4.8; 4.9; 5.2; 5.5; 5.7; 5.8; 8.0
Example 2.3
A side-by-side stem-and-leaf plot allows a comparison of the two data sets in two columns. In a side-by-side stem-and-leaf plot, two sets of leaves share the same stem. The leaves are to the left and the right of the stems. Table 2.4 and Table 2.5 show the ages of presidents at their inauguration and at their death. Construct a side-by-side stem-and-leaf plot using this data.
The table shows the number of wins and losses the Atlanta Hawks have had in 42 seasons. Create a side-by-side stem-and-leaf plot of these wins and losses.
Another type of graph that is useful for specific data values is a line graph . In the particular line graph shown in Example 2.4 , the x -axis (horizontal axis) consists of data values and the y -axis (vertical axis) consists of frequency points . The frequency points are connected using line segments.
Example 2.4
In a survey, 40 mothers were asked how many times per week a teenager must be reminded to do his or her chores. The results are shown in Table 2.7 and in Figure 2.2 .
In a survey, 40 people were asked how many times per year they had their car in the shop for repairs. The results are shown in Table 2.8 . Construct a line graph.
Bar graphs consist of bars that are separated from each other. The bars can be rectangles or they can be rectangular boxes (used in three-dimensional plots), and they can be vertical or horizontal. The bar graph shown in Example 2.5 has age groups represented on the x -axis and proportions on the y -axis .
Example 2.5
By the end of 2011, Facebook had over 146 million users in the United States. Table 2.9 shows three age groups, the number of users in each age group, and the proportion (%) of users in each age group. Construct a bar graph using this data.
The population in Park City is made up of children, working-age adults, and retirees. Table 2.10 shows the three age groups, the number of people in the town from each age group, and the proportion (%) of people in each age group. Construct a bar graph showing the proportions.
Example 2.6
The columns in Table 2.11 contain: the race or ethnicity of students in U.S. Public Schools for the class of 2011, percentages for the Advanced Placement examine population for that class, and percentages for the overall student population. Create a bar graph with the student race or ethnicity (qualitative data) on the x -axis, and the Advanced Placement examinee population percentages on the y -axis.
Park city is broken down into six voting districts. The table shows the percent of the total registered voter population that lives in each district as well as the percent total of the entire population that lives in each district. Construct a bar graph that shows the registered voter population by district.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/introductory-statistics/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Barbara Illowsky, Susan Dean
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Introductory Statistics
- Publication date: Sep 19, 2013
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/introductory-statistics/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/introductory-statistics/pages/2-1-stem-and-leaf-graphs-stemplots-line-graphs-and-bar-graphs
© Jun 23, 2022 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
Module 2: Descriptive Statistics
Stem-and-leaf graphs (stemplots), learning outcomes.
- Display data graphically and interpret graphs: stemplots, histograms, and box plots
One simple graph, the stem-and-leaf graph or stemplot , comes from the field of exploratory data analysis. It is a good choice when the data sets are small. To create the plot, divide each observation of data into a stem and a leaf. The leaf consists of a final significant digit. For example, [latex]23[/latex] has stem two and leaf three. The number [latex]432[/latex] has stem [latex]43[/latex] and leaf two. Likewise, the number [latex]5,432[/latex] has stem [latex]543[/latex] and leaf two. The decimal [latex]9.3[/latex] has stem nine and leaf three. Write the stems in a vertical line from smallest to largest. Draw a vertical line to the right of the stems. Then write the leaves in increasing order next to their corresponding stem.
For Susan Dean’s spring pre-calculus class, scores for the first exam were as follows (smallest to largest): [latex]33[/latex]; [latex]42[/latex]; [latex]49[/latex]; [latex]49[/latex]; [latex]53[/latex]; [latex]55[/latex]; [latex]55[/latex]; [latex]61[/latex]; [latex]63[/latex]; [latex]67[/latex]; [latex]68[/latex]; [latex]68[/latex]; [latex]69[/latex]; [latex]69[/latex]; [latex]72[/latex]; [latex]73[/latex]; [latex]74[/latex]; [latex]78[/latex]; [latex]80[/latex]; [latex]83[/latex]; [latex]88[/latex]; [latex]88[/latex]; [latex]88[/latex]; [latex]90[/latex]; [latex]92[/latex]; [latex]94[/latex]; [latex]94[/latex]; [latex]94[/latex]; [latex]94[/latex]; [latex]96[/latex]; [latex]100[/latex]
The stemplot shows that most scores fell in the [latex]60[/latex]s, [latex]70[/latex]s, [latex]80[/latex]s, and [latex]90[/latex]s. Eight out of the [latex]31[/latex] scores or approximately [latex]26[/latex]% ([latex]\frac{8}{31}[/latex]) were in the [latex]90[/latex]s or [latex]100[/latex], a fairly high number of As.
For the Park City basketball team, scores for the last 30 games were as follows (smallest to largest):
[latex]32[/latex]; [latex]32[/latex]; [latex]33[/latex]; [latex]34[/latex]; [latex]38[/latex]; [latex]40[/latex]; [latex]42[/latex]; [latex]42[/latex]; [latex]43[/latex]; [latex]44[/latex]; [latex]46[/latex]; [latex]47[/latex]; [latex]47[/latex]; [latex]48[/latex]; [latex]48[/latex]; [latex]48[/latex]; [latex]49[/latex]; [latex]50[/latex]; [latex]50[/latex]; [latex]51[/latex]; [latex]52[/latex]; [latex]52[/latex]; [latex]52[/latex]; [latex]53[/latex]; [latex]54[/latex]; [latex]56[/latex]; [latex]57[/latex]; [latex]57[/latex]; [latex]60[/latex]; [latex]61[/latex]
Construct a stem plot for the data.
The stemplot is a quick way to graph data and gives an exact picture of the data. You want to look for an overall pattern and any outliers. An outlier is an observation of data that does not fit the rest of the data. It is sometimes called an extreme value . When you graph an outlier, it will appear not to fit the pattern of the graph. Some outliers are due to mistakes (for example, writing down [latex]50[/latex] instead of [latex]500[/latex]) while others may indicate that something unusual is happening. It takes some background information to explain outliers, so we will cover them in more detail later.
The data are the distances (in kilometers) from a home to local supermarkets. Create a stemplot using the data:
[latex]1.1[/latex]; [latex]1.5[/latex]; [latex]2.3[/latex]; [latex]2.5[/latex]; [latex]2.7[/latex]; [latex]3.2[/latex]; [latex]3.3[/latex]; [latex]3.3[/latex]; [latex]3.5[/latex]; [latex]3.8[/latex]; [latex]4.0[/latex]; [latex]4.2[/latex]; [latex]4.5[/latex]; [latex]4.5[/latex]; [latex]4.7[/latex]; [latex]4.8[/latex]; [latex]5.5[/latex]; [latex]5.6[/latex]; [latex]6.5[/latex]; [latex]6.7[/latex]; [latex]12.3[/latex]; Does the data seem to have any concentration of values?
The leaves are to the right of the decimal.
The value [latex]12.3[/latex] may be an outlier. Values appear to concentrate at three and four kilometers.
The following data show the distances (in miles) from the homes of off-campus statistics students to the college. Create a stem plot using the data and identify any outliers.
[latex]0.5[/latex]; [latex]0.7[/latex]; [latex]1.1[/latex]; [latex]1.2[/latex]; [latex]1.2[/latex]; [latex]1.3[/latex]; [latex]1.3[/latex]; [latex]1.5[/latex]; [latex]1.5[/latex]; [latex]1.7[/latex]; [latex]1.7[/latex]; [latex]1.8[/latex]; [latex]1.9[/latex]; [latex]2.0[/latex]; [latex]2.2[/latex]; [latex]2.5[/latex]; [latex]2.6[/latex]; [latex]2.8[/latex]; [latex]2.8[/latex]; [latex]2.8[/latex]; [latex]3.5[/latex]; [latex]3.8[/latex]; [latex]4.4[/latex]; [latex]4.8[/latex]; [latex]4.9[/latex]; [latex]5.2[/latex]; [latex]5.5[/latex]; [latex]5.7[/latex]; [latex]5.8[/latex]; [latex]8.0[/latex]
The value [latex]8.0[/latex] may be an outlier. Values appear to concentrate at one and two miles.
Watch this video to see an example of how to create a stem plot.
A side-by-side stem-and-leaf plot allows a comparison of the two data sets in two columns. In a side-by-side stem-and-leaf plot, two sets of leaves share the same stem. The leaves are to the left and the right of the stems. The two following tables show the ages of U.S. presidents at their inauguration and at their death. Construct a side-by-side stem-and-leaf plot using this data.
Presidents’ Ages at Inauguration:
Presidents’ Ages at Death:
The table shows the number of wins and losses the Atlanta Hawks have had in [latex]42[/latex] seasons. Create a side-by-side stem-and-leaf plot of these wins and losses.
Number of Losses
- OpenStax, Statistics, Stem-and-Leaf Graphs (Stemplots), Line Graphs, and Bar Graphs. Provided by : OpenStax. Located at : https://openstax.org/books/introductory-statistics/pages/2-1-stem-and-leaf-graphs-stemplots-line-graphs-and-bar-graphs . License : CC BY: Attribution . License Terms : Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/introductory-statistics/pages/1-introduction
- Introductory Statistics. Authored by : Barbara Illowsky, Susan Dean. Provided by : Open Stax. Located at : https://openstax.org/books/introductory-statistics/pages/1-introduction . License : CC BY: Attribution . License Terms : Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/introductory-statistics/pages/1-introduction
- Stem and Leaf Plots aka Stemplots. Authored by : patrickJMT. Located at : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=839OzHIsI-E . License : All Rights Reserved . License Terms : Standard YouTube License

Privacy Policy
Stem-and-Leaf Plot Questions with Data Counts of About 25 (A)
Welcome to The Stem-and-Leaf Plot Questions with Data Counts of About 25 (A) Math Worksheet from the Statistics Worksheets Page at Math-Drills.com. This math worksheet was created or last revised on 2014-12-12 and has been viewed 10 times this week and 588 times this month. It may be printed, downloaded or saved and used in your classroom, home school, or other educational environment to help someone learn math.
Teacher s can use math worksheets as test s, practice assignment s or teaching tool s (for example in group work , for scaffolding or in a learning center ). Parent s can work with their children to give them extra practice , to help them learn a new math skill or to keep their skills fresh over school breaks . Student s can use math worksheets to master a math skill through practice, in a study group or for peer tutoring .
Use the buttons below to print, open, or download the PDF version of the Stem-and-Leaf Plot Questions with Data Counts of About 25 (A) math worksheet . The size of the PDF file is 23104 bytes . Preview images of the first and second (if there is one) pages are shown. If there are more versions of this worksheet, the other versions will be available below the preview images. For more like this, use the search bar to look for some or all of these keywords: math, statistics, data, management, stem-and-leaf, plot, mean, median, mode, range .
Print Full Version
Open Full Version
Download Full Version
Print Student Version
Open Student Version
Download Student Version
The Print button initiates your browser's print dialog. The Open button opens the complete PDF file in a new browser tab. The Download button initiates a download of the PDF math worksheet. Teacher versions include both the question page and the answer key. Student versions, if present, include only the question page.

Other Versions:
More Statistics Worksheets
Copyright © 2005-2024 Math-Drills.com You may use the math worksheets on this website according to our Terms of Use to help students learn math.
Scholarly Tutorials
Email us :- [email protected]
[Solved] MATH399N Week 2 Assignment: Creating and Interpreting Stem-and-leaf plots and Dot plots
A set of data is summarized by the stem and leaf plot below.
In the scenario above, what is the least number of textbooks brought home per student on a Friday?
A college student records the number of textbooks that are brought home on a Friday from a random sample of 20 history majors. Below is the data.
Make a dot plot which represents the textbook data.
A mathematics professor created a test that was supposed to be mostly easy except for two challenging problems. The scores of the students are shown in the dot plot below. What is the range of the scores? Do not include the percent sign in your answer.
A dot plot has a horizontal axis labeled Test Score Percentage from 70 to 100 in increments of 5. Columns of dots are plotted over horizontal coordinates with heights as follows, where the horizontal coordinate is listed first and the number of dots in the column is listed second: 70, 1; 71, 1; 74, 1; 75, 2; 76, 2; 77, 3; 78, 2; 79, 4; 80, 5; 81, 5; 82, 6; 83, 7; 84, 7; 85, 9; 86, 11; 87, 13; 88, 14; 89, 15; 90, 14; 91, 13; 92, 2; 93, 2.
Describe the shape of the given dot plot.
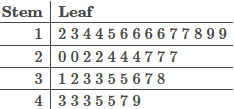
Answer: There are 14 values in the data set which are greater than or equal to 10 and less than or equal to 19 . There are 9 values in the data set which are greater than or equal to 30 and less than or equal to 39 . There are 7 values in the data set which are greater than or equal to 40 and less than or equal to 49 .
Remember that every entry in the leaf column corresponds to a value in the data set. To see …………….please follow the link below to purchase the solution at $4
Click one of our contacts below to chat on WhatsApp
Social Chat is free, download and try it now here!
Scholarly Guider
Email us : [email protected]
[Answered] MATH 225N Week 2 Assignment: Stem and Leaf plots -(2023)
Math 225n statistical reasoning for the health sciences.
Instructions
- Question: A set of data is summarized by the stem and leaf plot below.
- Question: A set of data is… by the stem and leaf plot below. Ch 5.2.3: stem and leaf plots
- Question: A set of data is … by the stem and leaf plot below.
- Question: Which data set is … by this stem-and-leaf plot?
- Question: The ages of United States’ presidents … in the 20th century are … by the stem and leaf plot below.
- Question: Which of the following statements are true? Choose all answers that apply.
- Question: A set of data is … by the stem and leaf plot below. Stem 1 Leaf 266888999 Stem 2 Leaf 00112455567
- Question: The data below shows the stem and leaf plot of the number of counties in some U.S. states in 2013. Which of the following statements are true? Select all that apply
- Question: Which of the following statements are true? Select all that apply
- Question: A set of data is … by the stem and leaf plot below……
There are 8 values in the data set which are greater than or equal to 20 and less than or equal to 29 . There are 6 values in the data set which are greater than or equal to 10 and less than or equal to 19 . There are 14 values in the data set which are greater than or equal to 40 and less than or equal to 49 .
……..please click the icon below to purchase the solution at $10
GradesBooster
Your shopping cart is empty!
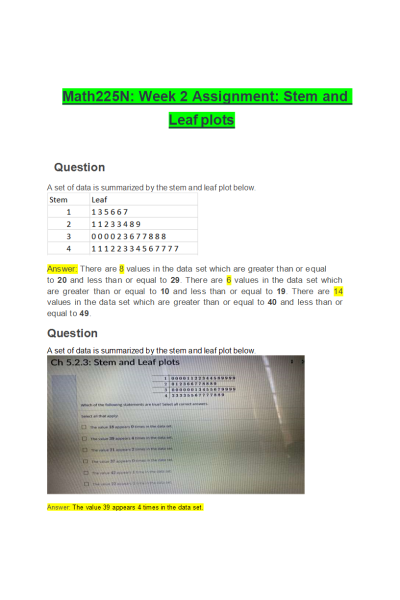
MATH 225N Week 2 Assignment; Stem and Leaf plots
- Description
- Question: A set of data is summarized by the stem and leaf plot below.
Related Products

MATH 225N Week 2 Discussion: Graphing and Describing Data in Everyday Life

MATH 225N Week 6 Discussion: Confidence Intervals

MATH 225N Week 7 Discussion; Hypothesis Testing

MATH 225N Week 6 Statistics Quiz

MATH 225N Week 6 Question-Answers on Confidence Intervals

MATH 225N Week 3 Lab Assignment; Adolescents First Tobacco Products

MATH 225N Week 3 Lab Assignment; Article on Concussions

MATH 225N Week 3 Lab Assignment; Diabetic Patients

MATH 225N Week 3 Lab Assignment; Article on Blood Pressure

MATH 225N Week 2 Quiz

MATH 225N Week 5 Discussion; The Normal Distribution

MATH 225N Week 5 Lab Assignment: Height of 10 out of 50 Nurses: August Term


MATH 225N Week 5 Lab Assignment: November Term

MATH 225N Week 5 Lab Assignment: Height of 10 Female Friends

MATH 225N Week 7 Lab Assignment

MATH 225N Week 7 Lab Assignment; Closing the Ductus Arteriosus in Premature Infa

MATH 225N Week 8 Discussion; Correlation and Regression (v1)

MATH 225N Week 8 Discussion; Correlation and Regression (v2)

MATH 225N Week 8 Final Exam (Version 1)

MATH 225N Week 8 Final Exam (Version 2)

MATH 225N Week 7 Assignment; Developing Hypothesis and Understanding Possible Co

MATH 225N Week 8 Assignment; Multivariate Relationships

MATH 225N Week 8 Assignment; Performing Linear Regressions with Technology - Exe

MATH 225N Week 8 Assignment; Predictions Using Linear Regression (Collection)

MATH 225N Week 2 Assignment; Frequency Tables and Histograms

MATH 225N Week 2 Assignment; Frequency Tables

MATH 225N Week 2 Assignment; Line and Bar Graphs

MATH 225N Week 2 Quiz; Answer Score 96%

MATH 225N Week 3 Assignment; Distribution Shape

MATH 225N Week 3 Assignment; Measures of Central Tendency

MATH 225N Week 3 Assignment; Quartiles and Box Plots

MATH 225N Week 3 Assignment; Standard Deviation

MATH 225N Week 3 Assignment; Understanding Measures of Central Tendency

MATH 225N Week 3 Lab Assignment; Adolescents First Tobbacco Products

MATH 225N Week 3 Lab Assignment; Article from Demographic, Parental, and Persona

MATH 225N Week 5 Assignment; Applications of the Normal Distribution - Excel

MATH 225N Week 5 Assignment; Central Limit Theorem for Means

MATH 225N Week 5 Assignment; Central Limit Theorem for Proportions

MATH 225N Week 5 Assignment; Evaluating Probability Using the Normal Distributio

MATH 225N Week 5 Assignment; Understanding Normal Distribution

MATH 225N Week 6 Assignment; Confidence Interval for Mean – Population Standar

MATH 225N Week 6 Assignment; Confidence Intervals – Empirical Rule

MATH 225N Week 6 Assignment; Estimating Sample Size for a PopulationProportion

MATH 225N Week 6 Assignment; Point Estimates, Margins of Error, and Confidence I

MATH 225N Week 6 Assignment; Understanding Confidence Intervals - Excel

MATH 225N Week 7 Assignment; Construct Hypothesis Test for Proportions - Excel

MATH 225N Week 7 Assignment; Hypothesis Test for Mean; Population Standard Devia

MATH 225N Week 7 Assignment; Hypothesis Test for the Mean - Population Standard

MATH 225N Week 8 Assignment; Coefficient of Determination

MATH 225N Week 8 Assignment; Correlation and Causation

MATH 225N Week 8 Assignment; Linear Regression Equations

MATH 225N Week 8 Assignment; Performing Linear Regressions with Technology – E

MATH 225N Week 8 Assignment; Predictions Using Linear Regression

MATH 225N Week 8 Final Exam (Scored 120 out of 160 = 80%)

MATH 225N Week 2 Quiz Review

MATH 225N Week 3 Lab Assignment (Including Selected Article)

MATH 225N Week 4 Quiz; Professor Review Notes

MATH 225N Week 1 Assignment; Comparing Sampling Methods

MATH 225N Week 1 Assignment; Evidence, Claims, and Types
MATH 225N Week 1 Assignment; Sampling Methods
MATH 225N Week 1 Assignment; Variables and Measures of Data

MATH 225N Week 1 Discussion; Basic Statistics Data Used in Everyday Life - # of

MATH 225N Week 1 Discussion; Basic Statistics Data Used in Everyday Life - Quant

MATH 225N Week 3 Lab Assignment; Article COVID-19 Vaccine Hesitancy and Attitude

MATH 225N Week 3 Lab Assignment; Review of COVID-19 Vaccine Hesitancy and Attitu
MATH225N WEEK 2 ASSIGNMENT: STEM AND LEAF PLOTS QUESTION AND ANSW ... $10.00 Add to Cart
Math225N Week 2 Assignment: Stem And Leaf Plots Question And Answers
Preview 3 out of 7 pages

Generating Your Document
You are viewing 3 pages of the document titled: Math225N Week 2 Assignment: Stem and Leaf plots Question and Answers . Purchase the document to get full access instantly
- Trusted by 40,000+ Students
- Money Back Guarantee 24/7
- Download is directly available
Report Copyright Violation
Attached Document Preview (unformatted)
Document details.
Add To Cart
Add To Wishlist Remove from wishlist
- Trusted by 40,000+ Students
- Money Back Guarantee 24/7
- Download is directly available
Specifications
Seller details.

11532 documents uploaded
148 documents sold
Recommended documents
Math225n week 2 assignment: stem and le ..., math225n week 4 discussion answer, week four: individual assignment: evolu ..., bus 7320 week 1 - assignment: draft a r ..., week 8 assignment: correlation and caus ..., week two: individual assignment: evolvi ..., week 4 assignment: evaluating probabili ..., issc 499 week 5 assignment: strategic s ..., week four assignment: local, regional, ..., mba 555 week 4 assignment: change manag ..., busn100 week 7 assignment: a company-wi ..., week 6 assignment: academic success pla ..., nrnp 6665 week 7 assignment:neuro devel ..., bus 7320 week 6 - assignment: evaluate ..., nrnp 6665 week #9 assignment: dissociat ..., week 5 assignment: production costs to: ..., week 2- assignment:develop a powerpoint ..., what students are saying about us.
PaperStoc is my best source of study materials. I usually buy all my exams here. So nicely done and their support is awesome. I will be back for more… Thanks…
Liberty University Sam W
I was looking for an example essay to help me write my own. Luckily, I found the exact paper on PaperStoc, and it was all great.
This website is my go-to place when am looking for exam / quiz solution. They have all the exams questions and answers and some even include explanations. PaperStoc is my best study resource center… Keep up the great work
Arizona Global Martin J
I needed help urgently and PaperStoc came through for me. Besides the authentic documents, they have experts who can help you deal with difficult homework questions.
UOP Prince E
PaperStoc, is my best study resource provider so far, I am confident of finding the best essays, notes and summaries done by my fellow students. Thanks and keep up the great work…
Walden Christinna F
I find PaperStoc easy to use and most resourceful. They have a variety of study resources and documents. Besides, their support team is awesome and are available 24/7
Southern New Hampshire Mike T
For long, I had been search for a website that do cheap essays. Now that I found PaperStoc, My mind is at peace. They did my paper very well and it was All Ace...
Southern New Hampshire Alice
I find Paperstoc to be authentic, easy to use and a community with quality notes and study tips. Now is my chance to help others.
University Of Arizona Mike T
Register a free account
- Follow us on
- Copyright © 2024 | All rights reserved

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Southern New Hampshire University MAT- Week 2 Notes. Stem and Leaf Display. One simple way to visualize small data sets is a stem-and-leaf plot. The stem-and-leaf plot is a tool of exploratory data analysis (EDA) that seeks to reveal essential data features in an intuitive way.
For example, the number 154 154 would be split into two parts where the digits \bf {15} 15 would be the stem and \bf {4} 4 would be the leaf. To set up a stem and leaf plot you need to: Organize the data into ascending order, smallest to largest. 2 2 parts by writing a key for the stem and leaf plot. Write the values for the 'stem' into the ...
Construct a two-sided stem-and-leaf plot for the data and compare the distributions. There is a wide variation in the marks for both years in Mrs. Cameron's AP Statistics Class. In 2009, her class had marks anywhere from 76 to 95. In 2010, the class marks ranged from 70 to 100. The mode for the 2009 class was 76, but for the 2010 class, it ...
Expert Answer. 56 Count number of 6 in Leaf corresponding to stem 5. We see that 6 appears 2 times corr …. -61323 > Modules > Week 2 Assignment: Creating and Interpreting Stem-and-leaf plots and Dot plots Week 2 Assignment: Creating and Interpreting Stem-and-leaf plots and Dot plots Stem Leaf 1 00111 2 2 2 3 3 455 78 99 2 003 6 78 8999 3 ...
Stem-and-leaf plots. We learn how to interpret a stem-and-leaf plot using basketball scores as an example. The video demonstrates how to read the plot, translate it into individual scores, and then use those scores to calculate the team's total points. This method provides a clear view of data distribution and makes it easier to understand the ...
Instead, you can use a histogram or box plot. To make a stem and leaf plot, split each data point into a stem and leaf value. The stem values divide the data points into groups. The stem value contains all the digits of a data point except the final number, which is the leaf. For example, if a data point is 42, the stem is 4 and the leaf is 2.
Math; Statistics and Probability; Statistics and Probability questions and answers; Week 2 Assignment: Stem and Leaf plots Due Sunday by 11:59pm Points 10 Submitting an external tool Question A set of data is summarized by the stem and leaf plot below.
A side-by-side stem-and-leaf plot allows a comparison of the two data sets in two columns. In a side-by-side stem-and-leaf plot, two sets of leaves share the same stem. The leaves are to the left and the right of the stems. Table 2.4 and Table 2.5 show the ages of presidents at their inauguration and at their death. Construct a side-by-side stem-and-leaf plot using this data.
Transcript. A stem and leaf plot displays data by breaking each data point into two parts: the "stem" and the "leaf." Each stem represents a range of values (e.g. if the stem is 2, the corresponding leaves might be data points in the 20s). Each leaf typically represents the last digit of a data point (e.g. if the leaf is 6 next to a stem of 2 ...
Creating a stem and leaf plot. Here's how to make a stem and leaf plot step by step. We'll use the same dataset as before. Here it is again: 17 , 18 , 20 , 25 , 28 , 34 , 34 , 37 , 38 , 50. Step 1: Split each data point into a stem and a leaf. The stem is everything before the final digit, and the leaf is the final digit.
STAT280 | Week 2 | Stem and Leaf Plot and Histogram. Learn how to construct stem and leaf plots and analyze histograms in this educational video. The video s...
Math225N: Week 2 Assignment: Stem and Leaf plots Question A set of data is summarized by the stem and leaf plot below. Answer: There are 8 values in the data set which are greater than or equal to 20 and less than or equal to 29 .
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like A group of high school students reported the typical number of hours spent studying each week: 4, 20, 20, 19, 7, 20 Construct a stem-and-leaf plot to represent this set of data., The test scores of a group of students are shown below: 81, 73, 75, 88, 90, 71, 81, 90 Construct a stem-and-leaf plot to represent this set of data ...
One simple graph, the stem-and-leaf graph or stemplot, comes from the field of exploratory data analysis. It is a good choice when the data sets are small. To create the plot, divide each observation of data into a stem and a leaf. The leaf consists of a final significant digit. For example, 23 23 has stem two and leaf three.
Welcome to The Stem-and-Leaf Plot Questions with Data Counts of About 25 (A) Math Worksheet from the Statistics Worksheets Page at Math-Drills.com. This math worksheet was created or last revised on 2014-12-12 and has been viewed 277 times this week and 569 times this month. It may be printed, downloaded or saved and used in your classroom, home school, or other educational environment to help ...
Join Nagwa Classes. Attend live sessions on Nagwa Classes to boost your learning with guidance and advice from an expert teacher! This lesson plan includes the objectives, prerequisites, and exclusions of the lesson teaching students how to use stem-and-leaf plots to organize data sets and interpret stem and leaf plots to answer questions.
[Solved] MATH399N Week 2 Assignment: Creating and Interpreting Stem-and-leaf plots and Dot plots. Question. A set of data is summarized by the stem and leaf plot below. Question. A set of data is summarized by the stem and leaf plot below. Question. In the scenario above, what is the least number of textbooks brought home per student on a ...
Question: odules Week 2 Assignment: Creating and Interpreting Stem-and-leaf plots and Dot plots Eek 2 Assignment: Creating and Interpreting Stem-and-leaf plots and Dot plots Question A factory records the number of malfunctions per machine over a one year period. Below is the data. Make a dot plot which represents the machine malfunction data.
Instructions Question: A set of data is summarized by the stem and leaf plot below. Question: A set of data is… by the stem and leaf plot below.Ch 5.2.3: stem and leaf plots; Question: A set of data is … by the stem and leaf plot below. Question: Which data set is … by this stem-and-leaf plot? Question: The ages of United States' presidents … in the 20th century are … by the stem ...
MATH 225N Week 2 Assignment; Stem and Leaf plots. $20.00; Add to Cart. Term/Session: Summer 2021: Course: MATH 225N Statistical Reasoning for the Health Sciences: Contributor: Patricia: Description; Question: A set of data is summarized by the stem and leaf plot below.
Week 2 Assignment Stem and Leaf Plot.pdf - Week 2 Stem and... Doc Preview. Pages 1. Total views 18. Distance Learning Centre. EDUCATIONS. EDUCATIONS 123. allisongordon12. 11/18/2021. View full document. Students also studied. Quiz 8.docx. Solutions Available. American Military University. SCIN 130. test prep.
This document Contains Math225N Week 2 Assignment: Stem and Leaf plots Question and Answers Math225N: Week 2 Assignment: Stem and Leaf plotsQuestionA set o. login ; 0. Shopping cart 0 item(s) $0.00. Checkout . Homework Help ; Sell ; login ; 0. Shopping cart 0 item(s) $0.00. Checkout .
Question: which were A Set Of Duta Sumarted by the end Week 2 Assignment: Creating and Interpreting Stem-and-leaf plots and Dot plots Due Sunday by 11:59pm Points 10 ...