Home — Essay Samples — Entertainment — Video Games — The Impact of Video Games on Violence

The Impact of Video Games on Violence
- Categories: Media Influence Video Games Violence in Video Games
About this sample

Words: 788 |
Published: Mar 25, 2024
Words: 788 | Pages: 2 | 4 min read
Table of contents
Introduction, body paragraphs, counterarguments.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Prof Ernest (PhD)
Verified writer
- Expert in: Sociology Entertainment Social Issues

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
5 pages / 2086 words
1 pages / 505 words
6 pages / 2508 words
6 pages / 2896 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Video Games
The notion that video games cause violence has been a topic of debate and concern for many years. However, a wealth of research challenges this belief, suggesting that the relationship between video games and violent behavior is [...]
The debate between video games and outdoor games as forms of recreation has become increasingly prominent in today's technology-driven society. Both types of games offer unique experiences and benefits, but they also present [...]
Video games have become an integral part of modern society, with millions of people around the world playing games on various devices. From consoles to mobile phones, video games have become ubiquitous and enjoyed by individuals [...]
Video games have become an integral part of modern society, with millions of people across the globe engaging in gaming activities. Despite the widespread popularity of video games, they are often criticized for their negative [...]
Mobile gaming is quite popular and it started with the first ever mobile game Tetris, this game was launched on the Hagenuk MT – 2000 phone in 1994. Although this was the first ever game it wasn’t as popular as Snake, this was [...]
It is very striking to see how technology has entered our lives and how sadly it is changing our traditions. In this case the theme of the games is presented, about how they have been breaking even in the lives of the youngest [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 13 March 2018
Does playing violent video games cause aggression? A longitudinal intervention study
- Simone Kühn 1 , 2 ,
- Dimitrij Tycho Kugler 2 ,
- Katharina Schmalen 1 ,
- Markus Weichenberger 1 ,
- Charlotte Witt 1 &
- Jürgen Gallinat 2
Molecular Psychiatry volume 24 , pages 1220–1234 ( 2019 ) Cite this article
546k Accesses
102 Citations
2348 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Neuroscience
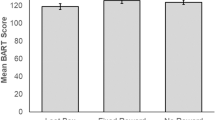
It is a widespread concern that violent video games promote aggression, reduce pro-social behaviour, increase impulsivity and interfere with cognition as well as mood in its players. Previous experimental studies have focussed on short-term effects of violent video gameplay on aggression, yet there are reasons to believe that these effects are mostly the result of priming. In contrast, the present study is the first to investigate the effects of long-term violent video gameplay using a large battery of tests spanning questionnaires, behavioural measures of aggression, sexist attitudes, empathy and interpersonal competencies, impulsivity-related constructs (such as sensation seeking, boredom proneness, risk taking, delay discounting), mental health (depressivity, anxiety) as well as executive control functions, before and after 2 months of gameplay. Our participants played the violent video game Grand Theft Auto V, the non-violent video game The Sims 3 or no game at all for 2 months on a daily basis. No significant changes were observed, neither when comparing the group playing a violent video game to a group playing a non-violent game, nor to a passive control group. Also, no effects were observed between baseline and posttest directly after the intervention, nor between baseline and a follow-up assessment 2 months after the intervention period had ended. The present results thus provide strong evidence against the frequently debated negative effects of playing violent video games in adults and will therefore help to communicate a more realistic scientific perspective on the effects of violent video gaming.
Similar content being viewed by others
No effect of short term exposure to gambling like reward systems on post game risk taking
Nicholas J. D’Amico, Aaron Drummond, … James D. Sauer
Increasing prosocial behavior and decreasing selfishness in the lab and everyday life
Andrew T. Gloster, Marcia T. B. Rinner & Andrea H. Meyer
Dynamics of the immediate behavioral response to partial social exclusion
J. F. Dewald-Kaufmann, T. Wüstenberg, … F. Padberg
The concern that violent video games may promote aggression or reduce empathy in its players is pervasive and given the popularity of these games their psychological impact is an urgent issue for society at large. Contrary to the custom, this topic has also been passionately debated in the scientific literature. One research camp has strongly argued that violent video games increase aggression in its players [ 1 , 2 ], whereas the other camp [ 3 , 4 ] repeatedly concluded that the effects are minimal at best, if not absent. Importantly, it appears that these fundamental inconsistencies cannot be attributed to differences in research methodology since even meta-analyses, with the goal to integrate the results of all prior studies on the topic of aggression caused by video games led to disparate conclusions [ 2 , 3 ]. These meta-analyses had a strong focus on children, and one of them [ 2 ] reported a marginal age effect suggesting that children might be even more susceptible to violent video game effects.
To unravel this topic of research, we designed a randomised controlled trial on adults to draw causal conclusions on the influence of video games on aggression. At present, almost all experimental studies targeting the effects of violent video games on aggression and/or empathy focussed on the effects of short-term video gameplay. In these studies the duration for which participants were instructed to play the games ranged from 4 min to maximally 2 h (mean = 22 min, median = 15 min, when considering all experimental studies reviewed in two of the recent major meta-analyses in the field [ 3 , 5 ]) and most frequently the effects of video gaming have been tested directly after gameplay.
It has been suggested that the effects of studies focussing on consequences of short-term video gameplay (mostly conducted on college student populations) are mainly the result of priming effects, meaning that exposure to violent content increases the accessibility of aggressive thoughts and affect when participants are in the immediate situation [ 6 ]. However, above and beyond this the General Aggression Model (GAM, [ 7 ]) assumes that repeatedly primed thoughts and feelings influence the perception of ongoing events and therewith elicits aggressive behaviour as a long-term effect. We think that priming effects are interesting and worthwhile exploring, but in contrast to the notion of the GAM our reading of the literature is that priming effects are short-lived (suggested to only last for <5 min and may potentially reverse after that time [ 8 ]). Priming effects should therefore only play a role in very close temporal proximity to gameplay. Moreover, there are a multitude of studies on college students that have failed to replicate priming effects [ 9 , 10 , 11 ] and associated predictions of the so-called GAM such as a desensitisation against violent content [ 12 , 13 , 14 ] in adolescents and college students or a decrease of empathy [ 15 ] and pro-social behaviour [ 16 , 17 ] as a result of playing violent video games.
However, in our view the question that society is actually interested in is not: “Are people more aggressive after having played violent video games for a few minutes? And are these people more aggressive minutes after gameplay ended?”, but rather “What are the effects of frequent, habitual violent video game playing? And for how long do these effects persist (not in the range of minutes but rather weeks and months)?” For this reason studies are needed in which participants are trained over longer periods of time, tested after a longer delay after acute playing and tested with broader batteries assessing aggression but also other relevant domains such as empathy as well as mood and cognition. Moreover, long-term follow-up assessments are needed to demonstrate long-term effects of frequent violent video gameplay. To fill this gap, we set out to expose adult participants to two different types of video games for a period of 2 months and investigate changes in measures of various constructs of interest at least one day after the last gaming session and test them once more 2 months after the end of the gameplay intervention. In contrast to the GAM, we hypothesised no increases of aggression or decreases in pro-social behaviour even after long-term exposure to a violent video game due to our reasoning that priming effects of violent video games are short-lived and should therefore not influence measures of aggression if they are not measured directly after acute gaming. In the present study, we assessed potential changes in the following domains: behavioural as well as questionnaire measures of aggression, empathy and interpersonal competencies, impulsivity-related constructs (such as sensation seeking, boredom proneness, risk taking, delay discounting), and depressivity and anxiety as well as executive control functions. As the effects on aggression and pro-social behaviour were the core targets of the present study, we implemented multiple tests for these domains. This broad range of domains with its wide coverage and the longitudinal nature of the study design enabled us to draw more general conclusions regarding the causal effects of violent video games.
Materials and methods
Participants.
Ninety healthy participants (mean age = 28 years, SD = 7.3, range: 18–45, 48 females) were recruited by means of flyers and internet advertisements. The sample consisted of college students as well as of participants from the general community. The advertisement mentioned that we were recruiting for a longitudinal study on video gaming, but did not mention that we would offer an intervention or that we were expecting training effects. Participants were randomly assigned to the three groups ruling out self-selection effects. The sample size was based on estimates from a previous study with a similar design [ 18 ]. After complete description of the study, the participants’ informed written consent was obtained. The local ethics committee of the Charité University Clinic, Germany, approved of the study. We included participants that reported little, preferably no video game usage in the past 6 months (none of the participants ever played the game Grand Theft Auto V (GTA) or Sims 3 in any of its versions before). We excluded participants with psychological or neurological problems. The participants received financial compensation for the testing sessions (200 Euros) and performance-dependent additional payment for two behavioural tasks detailed below, but received no money for the training itself.
Training procedure
The violent video game group (5 participants dropped out between pre- and posttest, resulting in a group of n = 25, mean age = 26.6 years, SD = 6.0, 14 females) played the game Grand Theft Auto V on a Playstation 3 console over a period of 8 weeks. The active control group played the non-violent video game Sims 3 on the same console (6 participants dropped out, resulting in a group of n = 24, mean age = 25.8 years, SD = 6.8, 12 females). The passive control group (2 participants dropped out, resulting in a group of n = 28, mean age = 30.9 years, SD = 8.4, 12 females) was not given a gaming console and had no task but underwent the same testing procedure as the two other groups. The passive control group was not aware of the fact that they were part of a control group to prevent self-training attempts. The experimenters testing the participants were blind to group membership, but we were unable to prevent participants from talking about the game during testing, which in some cases lead to an unblinding of experimental condition. Both training groups were instructed to play the game for at least 30 min a day. Participants were only reimbursed for the sessions in which they came to the lab. Our previous research suggests that the perceived fun in gaming was positively associated with training outcome [ 18 ] and we speculated that enforcing training sessions through payment would impair motivation and thus diminish the potential effect of the intervention. Participants underwent a testing session before (baseline) and after the training period of 2 months (posttest 1) as well as a follow-up testing sessions 2 months after the training period (posttest 2).
Grand Theft Auto V (GTA)
GTA is an action-adventure video game situated in a fictional highly violent game world in which players are rewarded for their use of violence as a means to advance in the game. The single-player story follows three criminals and their efforts to commit heists while under pressure from a government agency. The gameplay focuses on an open world (sandbox game) where the player can choose between different behaviours. The game also allows the player to engage in various side activities, such as action-adventure, driving, third-person shooting, occasional role-playing, stealth and racing elements. The open world design lets players freely roam around the fictional world so that gamers could in principle decide not to commit violent acts.
The Sims 3 (Sims)
Sims is a life simulation game and also classified as a sandbox game because it lacks clearly defined goals. The player creates virtual individuals called “Sims”, and customises their appearance, their personalities and places them in a home, directs their moods, satisfies their desires and accompanies them in their daily activities and by becoming part of a social network. It offers opportunities, which the player may choose to pursue or to refuse, similar as GTA but is generally considered as a pro-social and clearly non-violent game.
Assessment battery
To assess aggression and associated constructs we used the following questionnaires: Buss–Perry Aggression Questionnaire [ 19 ], State Hostility Scale [ 20 ], Updated Illinois Rape Myth Acceptance Scale [ 21 , 22 ], Moral Disengagement Scale [ 23 , 24 ], the Rosenzweig Picture Frustration Test [ 25 , 26 ] and a so-called World View Measure [ 27 ]. All of these measures have previously been used in research investigating the effects of violent video gameplay, however, the first two most prominently. Additionally, behavioural measures of aggression were used: a Word Completion Task, a Lexical Decision Task [ 28 ] and the Delay frustration task [ 29 ] (an inter-correlation matrix is depicted in Supplementary Figure 1 1). From these behavioural measures, the first two were previously used in research on the effects of violent video gameplay. To assess variables that have been related to the construct of impulsivity, we used the Brief Sensation Seeking Scale [ 30 ] and the Boredom Propensity Scale [ 31 ] as well as tasks assessing risk taking and delay discounting behaviourally, namely the Balloon Analogue Risk Task [ 32 ] and a Delay-Discounting Task [ 33 ]. To quantify pro-social behaviour, we employed: Interpersonal Reactivity Index [ 34 ] (frequently used in research on the effects of violent video gameplay), Balanced Emotional Empathy Scale [ 35 ], Reading the Mind in the Eyes test [ 36 ], Interpersonal Competence Questionnaire [ 37 ] and Richardson Conflict Response Questionnaire [ 38 ]. To assess depressivity and anxiety, which has previously been associated with intense video game playing [ 39 ], we used Beck Depression Inventory [ 40 ] and State Trait Anxiety Inventory [ 41 ]. To characterise executive control function, we used a Stop Signal Task [ 42 ], a Multi-Source Interference Task [ 43 ] and a Task Switching Task [ 44 ] which have all been previously used to assess effects of video gameplay. More details on all instruments used can be found in the Supplementary Material.
Data analysis
On the basis of the research question whether violent video game playing enhances aggression and reduces empathy, the focus of the present analysis was on time by group interactions. We conducted these interaction analyses separately, comparing the violent video game group against the active control group (GTA vs. Sims) and separately against the passive control group (GTA vs. Controls) that did not receive any intervention and separately for the potential changes during the intervention period (baseline vs. posttest 1) and to test for potential long-term changes (baseline vs. posttest 2). We employed classical frequentist statistics running a repeated-measures ANOVA controlling for the covariates sex and age.
Since we collected 52 separate outcome variables and conduced four different tests with each (GTA vs. Sims, GTA vs. Controls, crossed with baseline vs. posttest 1, baseline vs. posttest 2), we had to conduct 52 × 4 = 208 frequentist statistical tests. Setting the alpha value to 0.05 means that by pure chance about 10.4 analyses should become significant. To account for this multiple testing problem and the associated alpha inflation, we conducted a Bonferroni correction. According to Bonferroni, the critical value for the entire set of n tests is set to an alpha value of 0.05 by taking alpha/ n = 0.00024.
Since the Bonferroni correction has sometimes been criticised as overly conservative, we conducted false discovery rate (FDR) correction [ 45 ]. FDR correction also determines adjusted p -values for each test, however, it controls only for the number of false discoveries in those tests that result in a discovery (namely a significant result).
Moreover, we tested for group differences at the baseline assessment using independent t -tests, since those may hamper the interpretation of significant interactions between group and time that we were primarily interested in.
Since the frequentist framework does not enable to evaluate whether the observed null effect of the hypothesised interaction is indicative of the absence of a relation between violent video gaming and our dependent variables, the amount of evidence in favour of the null hypothesis has been tested using a Bayesian framework. Within the Bayesian framework both the evidence in favour of the null and the alternative hypothesis are directly computed based on the observed data, giving rise to the possibility of comparing the two. We conducted Bayesian repeated-measures ANOVAs comparing the model in favour of the null and the model in favour of the alternative hypothesis resulting in a Bayes factor (BF) using Bayesian Information criteria [ 46 ]. The BF 01 suggests how much more likely the data is to occur under the null hypothesis. All analyses were performed using the JASP software package ( https://jasp-stats.org ).
Sex distribution in the present study did not differ across the groups ( χ 2 p -value > 0.414). However, due to the fact that differences between males and females have been observed in terms of aggression and empathy [ 47 ], we present analyses controlling for sex. Since our random assignment to the three groups did result in significant age differences between groups, with the passive control group being significantly older than the GTA ( t (51) = −2.10, p = 0.041) and the Sims group ( t (50) = −2.38, p = 0.021), we also controlled for age.
The participants in the violent video game group played on average 35 h and the non-violent video game group 32 h spread out across the 8 weeks interval (with no significant group difference p = 0.48).
To test whether participants assigned to the violent GTA game show emotional, cognitive and behavioural changes, we present the results of repeated-measure ANOVA time x group interaction analyses separately for GTA vs. Sims and GTA vs. Controls (Tables 1 – 3 ). Moreover, we split the analyses according to the time domain into effects from baseline assessment to posttest 1 (Table 2 ) and effects from baseline assessment to posttest 2 (Table 3 ) to capture more long-lasting or evolving effects. In addition to the statistical test values, we report partial omega squared ( ω 2 ) as an effect size measure. Next to the classical frequentist statistics, we report the results of a Bayesian statistical approach, namely BF 01 , the likelihood with which the data is to occur under the null hypothesis that there is no significant time × group interaction. In Table 2 , we report the presence of significant group differences at baseline in the right most column.
Since we conducted 208 separate frequentist tests we expected 10.4 significant effects simply by chance when setting the alpha value to 0.05. In fact we found only eight significant time × group interactions (these are marked with an asterisk in Tables 2 and 3 ).
When applying a conservative Bonferroni correction, none of those tests survive the corrected threshold of p < 0.00024. Neither does any test survive the more lenient FDR correction. The arithmetic mean of the frequentist test statistics likewise shows that on average no significant effect was found (bottom rows in Tables 2 and 3 ).
In line with the findings from a frequentist approach, the harmonic mean of the Bayesian factor BF 01 is consistently above one but not very far from one. This likewise suggests that there is very likely no interaction between group × time and therewith no detrimental effects of the violent video game GTA in the domains tested. The evidence in favour of the null hypothesis based on the Bayes factor is not massive, but clearly above 1. Some of the harmonic means are above 1.6 and constitute substantial evidence [ 48 ]. However, the harmonic mean has been criticised as unstable. Owing to the fact that the sum is dominated by occasional small terms in the likelihood, one may underestimate the actual evidence in favour of the null hypothesis [ 49 ].
To test the sensitivity of the present study to detect relevant effects we computed the effect size that we would have been able to detect. The information we used consisted of alpha error probability = 0.05, power = 0.95, our sample size, number of groups and of measurement occasions and correlation between the repeated measures at posttest 1 and posttest 2 (average r = 0.68). According to G*Power [ 50 ], we could detect small effect sizes of f = 0.16 (equals η 2 = 0.025 and r = 0.16) in each separate test. When accounting for the conservative Bonferroni-corrected p -value of 0.00024, still a medium effect size of f = 0.23 (equals η 2 = 0.05 and r = 0.22) would have been detectable. A meta-analysis by Anderson [ 2 ] reported an average effects size of r = 0.18 for experimental studies testing for aggressive behaviour and another by Greitmeyer [ 5 ] reported average effect sizes of r = 0.19, 0.25 and 0.17 for effects of violent games on aggressive behaviour, cognition and affect, all of which should have been detectable at least before multiple test correction.
Within the scope of the present study we tested the potential effects of playing the violent video game GTA V for 2 months against an active control group that played the non-violent, rather pro-social life simulation game The Sims 3 and a passive control group. Participants were tested before and after the long-term intervention and at a follow-up appointment 2 months later. Although we used a comprehensive test battery consisting of questionnaires and computerised behavioural tests assessing aggression, impulsivity-related constructs, mood, anxiety, empathy, interpersonal competencies and executive control functions, we did not find relevant negative effects in response to violent video game playing. In fact, only three tests of the 208 statistical tests performed showed a significant interaction pattern that would be in line with this hypothesis. Since at least ten significant effects would be expected purely by chance, we conclude that there were no detrimental effects of violent video gameplay.
This finding stands in contrast to some experimental studies, in which short-term effects of violent video game exposure have been investigated and where increases in aggressive thoughts and affect as well as decreases in helping behaviour have been observed [ 1 ]. However, these effects of violent video gaming on aggressiveness—if present at all (see above)—seem to be rather short-lived, potentially lasting <15 min [ 8 , 51 ]. In addition, these short-term effects of video gaming are far from consistent as multiple studies fail to demonstrate or replicate them [ 16 , 17 ]. This may in part be due to problems, that are very prominent in this field of research, namely that the outcome measures of aggression and pro-social behaviour, are poorly standardised, do not easily generalise to real-life behaviour and may have lead to selective reporting of the results [ 3 ]. We tried to address these concerns by including a large set of outcome measures that were mostly inspired by previous studies demonstrating effects of short-term violent video gameplay on aggressive behaviour and thoughts, that we report exhaustively.
Since effects observed only for a few minutes after short sessions of video gaming are not representative of what society at large is actually interested in, namely how habitual violent video gameplay affects behaviour on a more long-term basis, studies employing longer training intervals are highly relevant. Two previous studies have employed longer training intervals. In an online study, participants with a broad age range (14–68 years) have been trained in a violent video game for 4 weeks [ 52 ]. In comparison to a passive control group no changes were observed, neither in aggression-related beliefs, nor in aggressive social interactions assessed by means of two questions. In a more recent study, participants played a previous version of GTA for 12 h spread across 3 weeks [ 53 ]. Participants were compared to a passive control group using the Buss–Perry aggression questionnaire, a questionnaire assessing impulsive or reactive aggression, attitude towards violence, and empathy. The authors only report a limited increase in pro-violent attitude. Unfortunately, this study only assessed posttest measures, which precludes the assessment of actual changes caused by the game intervention.
The present study goes beyond these studies by showing that 2 months of violent video gameplay does neither lead to any significant negative effects in a broad assessment battery administered directly after the intervention nor at a follow-up assessment 2 months after the intervention. The fact that we assessed multiple domains, not finding an effect in any of them, makes the present study the most comprehensive in the field. Our battery included self-report instruments on aggression (Buss–Perry aggression questionnaire, State Hostility scale, Illinois Rape Myth Acceptance scale, Moral Disengagement scale, World View Measure and Rosenzweig Picture Frustration test) as well as computer-based tests measuring aggressive behaviour such as the delay frustration task and measuring the availability of aggressive words using the word completion test and a lexical decision task. Moreover, we assessed impulse-related concepts such as sensation seeking, boredom proneness and associated behavioural measures such as the computerised Balloon analogue risk task, and delay discounting. Four scales assessing empathy and interpersonal competence scales, including the reading the mind in the eyes test revealed no effects of violent video gameplay. Neither did we find any effects on depressivity (Becks depression inventory) nor anxiety measured as a state as well as a trait. This is an important point, since several studies reported higher rates of depressivity and anxiety in populations of habitual video gamers [ 54 , 55 ]. Last but not least, our results revealed also no substantial changes in executive control tasks performance, neither in the Stop signal task, the Multi-source interference task or a Task switching task. Previous studies have shown higher performance of habitual action video gamers in executive tasks such as task switching [ 56 , 57 , 58 ] and another study suggests that training with action video games improves task performance that relates to executive functions [ 59 ], however, these associations were not confirmed by a meta-analysis in the field [ 60 ]. The absence of changes in the stop signal task fits well with previous studies that likewise revealed no difference between in habitual action video gamers and controls in terms of action inhibition [ 61 , 62 ]. Although GTA does not qualify as a classical first-person shooter as most of the previously tested action video games, it is classified as an action-adventure game and shares multiple features with those action video games previously related to increases in executive function, including the need for hand–eye coordination and fast reaction times.
Taken together, the findings of the present study show that an extensive game intervention over the course of 2 months did not reveal any specific changes in aggression, empathy, interpersonal competencies, impulsivity-related constructs, depressivity, anxiety or executive control functions; neither in comparison to an active control group that played a non-violent video game nor to a passive control group. We observed no effects when comparing a baseline and a post-training assessment, nor when focussing on more long-term effects between baseline and a follow-up interval 2 months after the participants stopped training. To our knowledge, the present study employed the most comprehensive test battery spanning a multitude of domains in which changes due to violent video games may have been expected. Therefore the present results provide strong evidence against the frequently debated negative effects of playing violent video games. This debate has mostly been informed by studies showing short-term effects of violent video games when tests were administered immediately after a short playtime of a few minutes; effects that may in large be caused by short-lived priming effects that vanish after minutes. The presented results will therefore help to communicate a more realistic scientific perspective of the real-life effects of violent video gaming. However, future research is needed to demonstrate the absence of effects of violent video gameplay in children.
Anderson CA, Bushman BJ. Effects of violent video games on aggressive behavior, aggressive cognition, aggressive affect, physiological arousal, and prosocial behavior: a meta-analytic review of the scientific literature. Psychol Sci. 2001;12:353–9.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Anderson CA, Shibuya A, Ihori N, Swing EL, Bushman BJ, Sakamoto A, et al. Violent video game effects on aggression, empathy, and prosocial behavior in eastern and western countries: a meta-analytic review. Psychol Bull. 2010;136:151–73.
Article Google Scholar
Ferguson CJ. Do angry birds make for angry children? A meta-analysis of video game influences on children’s and adolescents’ aggression, mental health, prosocial behavior, and academic performance. Perspect Psychol Sci. 2015;10:646–66.
Ferguson CJ, Kilburn J. Much ado about nothing: the misestimation and overinterpretation of violent video game effects in eastern and western nations: comment on Anderson et al. (2010). Psychol Bull. 2010;136:174–8.
Greitemeyer T, Mugge DO. Video games do affect social outcomes: a meta-analytic review of the effects of violent and prosocial video game play. Pers Soc Psychol Bull. 2014;40:578–89.
Anderson CA, Carnagey NL, Eubanks J. Exposure to violent media: The effects of songs with violent lyrics on aggressive thoughts and feelings. J Pers Soc Psychol. 2003;84:960–71.
DeWall CN, Anderson CA, Bushman BJ. The general aggression model: theoretical extensions to violence. Psychol Violence. 2011;1:245–58.
Sestire MA, Bartholow BD. Violent and non-violent video games produce opposing effects on aggressive and prosocial outcomes. J Exp Soc Psychol. 2010;46:934–42.
Kneer J, Elson M, Knapp F. Fight fire with rainbows: The effects of displayed violence, difficulty, and performance in digital games on affect, aggression, and physiological arousal. Comput Hum Behav. 2016;54:142–8.
Kneer J, Glock S, Beskes S, Bente G. Are digital games perceived as fun or danger? Supporting and suppressing different game-related concepts. Cyber Beh Soc N. 2012;15:604–9.
Sauer JD, Drummond A, Nova N. Violent video games: the effects of narrative context and reward structure on in-game and postgame aggression. J Exp Psychol Appl. 2015;21:205–14.
Ballard M, Visser K, Jocoy K. Social context and video game play: impact on cardiovascular and affective responses. Mass Commun Soc. 2012;15:875–98.
Read GL, Ballard M, Emery LJ, Bazzini DG. Examining desensitization using facial electromyography: violent video games, gender, and affective responding. Comput Hum Behav. 2016;62:201–11.
Szycik GR, Mohammadi B, Hake M, Kneer J, Samii A, Munte TF, et al. Excessive users of violent video games do not show emotional desensitization: an fMRI study. Brain Imaging Behav. 2017;11:736–43.
Szycik GR, Mohammadi B, Munte TF, Te Wildt BT. Lack of evidence that neural empathic responses are blunted in excessive users of violent video games: an fMRI study. Front Psychol. 2017;8:174.
Tear MJ, Nielsen M. Failure to demonstrate that playing violent video games diminishes prosocial behavior. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e68382.
Tear MJ, Nielsen M. Video games and prosocial behavior: a study of the effects of non-violent, violent and ultra-violent gameplay. Comput Hum Behav. 2014;41:8–13.
Kühn S, Gleich T, Lorenz RC, Lindenberger U, Gallinat J. Playing super Mario induces structural brain plasticity: gray matter changes resulting from training with a commercial video game. Mol Psychiatry. 2014;19:265–71.
Buss AH, Perry M. The aggression questionnaire. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1992;63:452.
Anderson CA, Deuser WE, DeNeve KM. Hot temperatures, hostile affect, hostile cognition, and arousal: Tests of a general model of affective aggression. Pers Soc Psychol Bull. 1995;21:434–48.
Payne DL, Lonsway KA, Fitzgerald LF. Rape myth acceptance: exploration of its structure and its measurement using the illinois rape myth acceptance scale. J Res Pers. 1999;33:27–68.
McMahon S, Farmer GL. An updated measure for assessing subtle rape myths. Social Work Res. 2011; 35:71–81.
Detert JR, Trevino LK, Sweitzer VL. Moral disengagement in ethical decision making: a study of antecedents and outcomes. J Appl Psychol. 2008;93:374–91.
Bandura A, Barbaranelli C, Caprara G, Pastorelli C. Mechanisms of moral disengagement in the exercise of moral agency. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1996;71:364–74.
Rosenzweig S. The picture-association method and its application in a study of reactions to frustration. J Pers. 1945;14:23.
Hörmann H, Moog W, Der Rosenzweig P-F. Test für Erwachsene deutsche Bearbeitung. Göttingen: Hogrefe; 1957.
Anderson CA, Dill KE. Video games and aggressive thoughts, feelings, and behavior in the laboratory and in life. J Pers Soc Psychol. 2000;78:772–90.
Przybylski AK, Deci EL, Rigby CS, Ryan RM. Competence-impeding electronic games and players’ aggressive feelings, thoughts, and behaviors. J Pers Soc Psychol. 2014;106:441.
Bitsakou P, Antrop I, Wiersema JR, Sonuga-Barke EJ. Probing the limits of delay intolerance: preliminary young adult data from the Delay Frustration Task (DeFT). J Neurosci Methods. 2006;151:38–44.
Hoyle RH, Stephenson MT, Palmgreen P, Lorch EP, Donohew RL. Reliability and validity of a brief measure of sensation seeking. Pers Individ Dif. 2002;32:401–14.
Farmer R, Sundberg ND. Boredom proneness: the development and correlates of a new scale. J Pers Assess. 1986;50:4–17.
Lejuez CW, Read JP, Kahler CW, Richards JB, Ramsey SE, Stuart GL, et al. Evaluation of a behavioral measure of risk taking: the Balloon Analogue Risk Task (BART). J Exp Psychol Appl. 2002;8:75–84.
Richards JB, Zhang L, Mitchell SH, de Wit H. Delay or probability discounting in a model of impulsive behavior: effect of alcohol. J Exp Anal Behav. 1999;71:121–43.
Davis MH. A multidimensional approach to individual differences in empathy. JSAS Cat Sel Doc Psychol. 1980;10:85.
Google Scholar
Mehrabian A. Manual for the Balanced Emotional Empathy Scale (BEES). (Available from Albert Mehrabian, 1130 Alta Mesa Road, Monterey, CA, USA 93940); 1996.
Baron-Cohen S, Wheelwright S, Hill J, Raste Y, Plumb I. The “Reading the Mind in the Eyes” Test revised version: A study with normal adults, and adults with Asperger syndrome or high-functioning autism. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2001;42:241–51.
Buhrmester D, Furman W, Reis H, Wittenberg MT. Five domains of interpersonal competence in peer relations. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1988;55:991–1008.
Richardson DR, Green LR, Lago T. The relationship between perspective-taking and non-aggressive responding in the face of an attack. J Pers. 1998;66:235–56.
Maras D, Flament MF, Murray M, Buchholz A, Henderson KA, Obeid N, et al. Screen time is associated with depression and anxiety in Canadian youth. Prev Med. 2015;73:133–8.
Hautzinger M, Bailer M, Worall H, Keller F. Beck-Depressions-Inventar (BDI). Beck-Depressions-Inventar (BDI): Testhandbuch der deutschen Ausgabe. Bern: Huber; 1995.
Spielberger CD, Spielberger CD, Sydeman SJ, Sydeman SJ, Owen AE, Owen AE, et al. Measuring anxiety and anger with the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI) and the State-Trait Anger Expression Inventory (STAXI). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers; 1999.
Lorenz RC, Gleich T, Buchert R, Schlagenhauf F, Kuhn S, Gallinat J. Interactions between glutamate, dopamine, and the neuronal signature of response inhibition in the human striatum. Hum Brain Mapp. 2015;36:4031–40.
Bush G, Shin LM. The multi-source interference task: an fMRI task that reliably activates the cingulo-frontal-parietal cognitive/attention network. Nat Protoc. 2006;1:308–13.
King JA, Colla M, Brass M, Heuser I, von Cramon D. Inefficient cognitive control in adult ADHD: evidence from trial-by-trial Stroop test and cued task switching performance. Behav Brain Funct. 2007;3:42.
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc. 1995;57:289–300.
Wagenmakers E-J. A practical solution to the pervasive problems of p values. Psychon Bull Rev. 2007;14:779–804.
Hay DF. The gradual emergence of sex differences in aggression: alternative hypotheses. Psychol Med. 2007;37:1527–37.
Jeffreys H. The Theory of Probability. Oxford: Clarendon Press; 1961.
Raftery AE, Newton MA, Satagopan YM, Krivitsky PN. Estimating the integrated likelihood via posterior simulation using the harmonic mean identity. In: Bernardo JM, Bayarri MJ, Berger JO, Dawid AP, Heckerman D, Smith AFM, et al., editors. Bayesian statistics. Oxford: University Press; 2007.
Faul F, Erdfelder E, Lang A-G, Buchner A. G*Power3: a flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav Res Methods. 2007;39:175–91.
Barlett C, Branch O, Rodeheffer C, Harris R. How long do the short-term violent video game effects last? Aggress Behav. 2009;35:225–36.
Williams D, Skoric M. Internet fantasy violence: a test of aggression in an online game. Commun Monogr. 2005;72:217–33.
Teng SK, Chong GY, Siew AS, Skoric MM. Grand theft auto IV comes to Singapore: effects of repeated exposure to violent video games on aggression. Cyber Behav Soc Netw. 2011;14:597–602.
van Rooij AJ, Kuss DJ, Griffiths MD, Shorter GW, Schoenmakers TM, Van, de Mheen D. The (co-)occurrence of problematic video gaming, substance use, and psychosocial problems in adolescents. J Behav Addict. 2014;3:157–65.
Brunborg GS, Mentzoni RA, Froyland LR. Is video gaming, or video game addiction, associated with depression, academic achievement, heavy episodic drinking, or conduct problems? J Behav Addict. 2014;3:27–32.
Green CS, Sugarman MA, Medford K, Klobusicky E, Bavelier D. The effect of action video game experience on task switching. Comput Hum Behav. 2012;28:984–94.
Strobach T, Frensch PA, Schubert T. Video game practice optimizes executive control skills in dual-task and task switching situations. Acta Psychol. 2012;140:13–24.
Colzato LS, van Leeuwen PJ, van den Wildenberg WP, Hommel B. DOOM’d to switch: superior cognitive flexibility in players of first person shooter games. Front Psychol. 2010;1:8.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Hutchinson CV, Barrett DJK, Nitka A, Raynes K. Action video game training reduces the Simon effect. Psychon B Rev. 2016;23:587–92.
Powers KL, Brooks PJ, Aldrich NJ, Palladino MA, Alfieri L. Effects of video-game play on information processing: a meta-analytic investigation. Psychon Bull Rev. 2013;20:1055–79.
Colzato LS, van den Wildenberg WP, Zmigrod S, Hommel B. Action video gaming and cognitive control: playing first person shooter games is associated with improvement in working memory but not action inhibition. Psychol Res. 2013;77:234–9.
Steenbergen L, Sellaro R, Stock AK, Beste C, Colzato LS. Action video gaming and cognitive control: playing first person shooter games is associated with improved action cascading but not inhibition. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0144364.
Download references
Acknowledgements
SK has been funded by a Heisenberg grant from the German Science Foundation (DFG KU 3322/1-1, SFB 936/C7), the European Union (ERC-2016-StG-Self-Control-677804) and a Fellowship from the Jacobs Foundation (JRF 2016–2018).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Max Planck Institute for Human Development, Center for Lifespan Psychology, Lentzeallee 94, 14195, Berlin, Germany
Simone Kühn, Katharina Schmalen, Markus Weichenberger & Charlotte Witt
Clinic and Policlinic for Psychiatry and Psychotherapy, University Clinic Hamburg-Eppendorf, Martinistraße 52, 20246, Hamburg, Germany
Simone Kühn, Dimitrij Tycho Kugler & Jürgen Gallinat
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Simone Kühn .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary material, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Kühn, S., Kugler, D., Schmalen, K. et al. Does playing violent video games cause aggression? A longitudinal intervention study. Mol Psychiatry 24 , 1220–1234 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-018-0031-7
Download citation
Received : 19 August 2017
Revised : 03 January 2018
Accepted : 15 January 2018
Published : 13 March 2018
Issue Date : August 2019
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-018-0031-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
The effect of competitive context in nonviolent video games on aggression: the mediating role of frustration and the moderating role of gender.
- Jinqian Liao
- Yanling Liu
Current Psychology (2024)
Exposure to hate speech deteriorates neurocognitive mechanisms of the ability to understand others’ pain
- Agnieszka Pluta
- Joanna Mazurek
- Michał Bilewicz
Scientific Reports (2023)
The effects of violent video games on reactive-proactive aggression and cyberbullying
- Yunus Emre Dönmez
Current Psychology (2023)
Machen Computerspiele aggressiv?
- Jan Dieris-Hirche
Die Psychotherapie (2023)
Systematic Review of Gaming and Neuropsychological Assessment of Social Cognition
- Elodie Hurel
- Marie Grall-Bronnec
- Gaëlle Challet-Bouju
Neuropsychology Review (2023)
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Wiley-Blackwell Online Open

Violent video games exposure and aggression: The role of moral disengagement, anger, hostility, and disinhibition
Mengyun yao.
1 Faculty of Psychology, Southwest University, Chongqing China
2 Key Laboratory of Cognition and Personality, Ministry of Education, Southwest University, Chongqing China
Yuhong Zhou
Associated data.
Based on the General Aggression Model (GAM), the current study investigated the interactive effect of personal factors (e.g., sensation‐seeking) and situational factors (e.g., violent video games exposure [VVGE]) on the trait aggressive behavior, and the mediating role of individual difference trait (e.g., moral disengagement, anger, and hostility). We recruited 547 undergraduates (48.45% male) from five Chinese universities. The results showed that VVGE was positively associated with moral disengagement, disinhibition, and the four aggressive traits (physical aggression, verbal aggression, anger, and hostility), which were positively associated with each other. Moral disengagement was positively associated with both the disinhibition and the four aggressive traits. Disinhibition was positively associated with the four aggressive traits as well. When controlled for gender, moral disengagement, anger, and hostility wholly mediated the relationship between VVGE and aggression, but the moderation effect of disinhibition was not significant. These findings support the framework of GAM and indicate that moral disengagement, anger, and hostility may be the factors that increase the risk of a higher level of aggression following repeated exposure to violent video games.
1. INTRODUCTION
Player Unknown's Battlegrounds (PUBG), a shooting game that Chinese players call “chicken dinner”, has recently become popular among young people, quickly overtaking Honor of Kings in terms of popularity. According to the China gaming industry report from January to June 2018, the top two games for sales in the mobile video games market were Action Role Playing Game (29.9%) and Multiplayer Online Battle Arena (MOBA; 17.4%), which accounted for nearly 50% of sales, and the proportion of Shooting Games has also increased significantly. Furthermore, the report showed that 35.9% of the game types were Shooting Games and 17.9% were MOBA in the Chinese client e‐sports game market (China Audio‐video & Digital Publishing Association Game Publishing Committee, 2018 ). Many games of such genres (e.g., PUBG) contain violent content (Teng, Li, & Liu, 2014 ), which explains to a certain extent the universality of violent video games.
Violent video games are those that depict intentional attempts by individuals (nonhuman cartoon characters, real persons, or anything in between) to inflict harm on others (Anderson & Bushman, 2001 ). The effects of violent video games have been a societal concern since the birth of the industry and have attracted much attention from researchers. A large body of research has found that violent video game exposure (VVGE) is associated with increased aggression among individuals at various ages (e.g., Gentile, Bender, & Anderson, 2017 ; Greitemeyer, 2018 ; Krahé, 2014 ; Teng et al., 2019 ; Velez, Greitemeyer, Whitaker, Ewoldsen, & Bushman, 2016 ). Also, some research has examined the pathways in the associations between VVGE and aggression; for instance, mediators such as hostile attribution bias, aggressive norms, and dehumanization (e.g., Anderson, Gentile, & Buckley, 2007 ; Gentile, Li, Khoo, Prot, & Anderson, 2014 ; Greitemeyer & McLatchie, 2011 ; Möller & Krahé, 2009 ), and moderators such as psychoticism, aggressive traits, neuroticism, and conscientiousness (e.g., Markey & Markey, 2010 ; Markey & Scherer, 2009 ). To the best of our knowledge, however, there have been few studies that have examined simultaneously the underlying mechanisms of the link between VVGE and aggression from the perspectives of social cognition (i.e., moral disengagement) and personality trait (i.e., sensation seeking, anger, hostility). Such a comprehensive study could help to develop interventions to reduce the relation between VVGE and aggressive behaviors from a theoretical perspective.
1.1. Violent video games exposure and aggression
Although some recent studies have not found a significant relationship between VVGE and aggression (Ferguson & Kilburn, 2010 ; McCarthy, Coley, Wagner, Zengel, & Basham, 2016 ; Pan, Gao, Shi, Liu, & Li, 2018 ), a relatively solid association has been established in experimental, cross‐sectional, and longitudinal studies in general. For example, most research in this area has found that violent video games increase aggressive thoughts, angry feelings, physiological arousal, and aggressive behaviors, and decrease empathic feelings and helping behaviors (e.g., Anderson et al., 2010 ; Gentile et al., 2017 ; Hasan, Bègue, & Bushman, 2012 ; Verheijen, Burk, Stoltz, Van, & Cillessen, 2018 ). In addition, some research in cognitive neuroscience has provided neuroimaging support for these effects (e.g., Gentile, Swing, Anderson, Rinker, & Thomas, 2016 ; Montag et al., 2012 ), and there are also meta‐analyses that have concluded that violent video games increase aggression (e.g., Bushman, 2016 ; Greitemeyer & Mügge, 2014 ).
How does VVGE affect individual aggression? The General Aggression Model (GAM), a general model to account for aggressive behavior, could answer this question. GAM consists of two major systems: personality development (distal processes) and social encounters (proximate processes). The proximate processes explain individual episodes of aggression using three stages, that is, personal and situational inputs influence internal states (cognition, affect, and arousal), which in turn affect appraisal and decision processes, which in turn influence aggressive and nonaggressive behavioral outcomes. Each cycle of the proximate processes serves as a learning trail that creates aggressive knowledge structures after many repetitions. Distal processes detail how biological and persistent environmental factors influence personality through changes in knowledge structures (aggressive beliefs and attitudes, aggressive perceptual schemata, aggressive expectation schemata, aggressive behavioral scripts, and aggression desensitization) and brain structure and function. The personality, in turn, influences personal and situational factors in a cyclical fashion (Allen, Anderson, & Bushman, 2018 ; Anderson & Bushman, 2002 ; Anderson & Bushman, 2018 ). VVGE has been assumed to be a situational input variable of proximal causal factors and an environmental factor of distal causal factors (Anderson & Bushman, 2018 ), that is, VVGE influences aggression through the two main systems of GAM.
Most violent video games primarily involve physical violence, and many of the multiplayer games also involve verbal violence (Adachi & Willoughby, 2016 ; Lemmens, Valkenburg, & Peter, 2011 ), therefore, we focused on self‐reported forms of physical aggression and verbal aggression in the current study.
1.2. Moral disengagement as a potential mediator
Moral disengagement is a cognitive predisposition that individuals reinterpret their immoral behaviors (Bandura, Barbaranelli, Caprara, & Pastorelli, 1996 ). In general, individuals have their own moral standards that inhibit them from engaging in immoral conduct (Bandura, 1990 ), but these standards can be deactivated selectively through eight moral disengagement mechanisms (Bandura, 1999 ). Thus, an individual's moral disengagement mechanisms may be exerted when they commit aggressive acts.
Previous research has supported the moral disengagement theory that moral disengagement mechanisms can make individuals reconstruct aggression cognitively; thus aggression is more likely to occur (Bandura et al., 1996 ). For instance, numerous cross‐sectional studies have found that moral disengagement is positively associated with various forms of aggressive behavior such as physical aggression, verbal aggression, and bullying (e.g., Bussey, Quinn, & Dobson, 2015 ; Gao, Weng, Zhou, & Yu, 2017 ; Obermann, 2011 ; Rubio‐Garay, Carrasco, & Amor, 2016 ). Also, this correlation was found to be significant in juvenile delinquent samples (Wang, Lei, Yang, Gao, & Zhao, 2016 ; Zapolski, Banks, Lau, & Aalsma, 2018 ). Moreover, longitudinal studies have found that initial moral disengagement can predict later aggression among adolescents (e.g., Barchia & Bussey, 2011 ; Hyde, Shaw, & Moilanen, 2010 ; Paciello, Fida, Tramontano, Lupinetti, & Caprara, 2008 ; Sticca & Perren, 2015 ). In addition, a recent meta‐analysis has reinforced this link (Gini, Pozzoli, & Hymel, 2014 ; Killer, Bussey, Hawes, & Hunt, 2019 ).
Moral disengagement is not only a powerful predictor of aggression but also a product of VVGE. Some longitudinal research has established a stable link between the two, indicating that frequent exposure to violent video games in early sessions can predict higher levels of moral disengagement in later sessions; however, this effect was not found to be significant when the position of these two variables was reversed (Teng, Nie, Pan, Liu, & Guo, 2017 ; Wang, Ryoo, Swearer, Turner, & Goldberg, 2017 ). In addition, some cross‐sectional studies have also found an association between VVGE and higher levels of moral disengagement (Gabbiadini, Andrighetto, & Volpato, 2012 ; Teng, Nie, Guo, & Liu, 2017 ).
As mentioned above, moral disengagement may be a potential mediator in the relationship between VVGE and aggression. Richmond and Wilson ( 2008 ) found that the relationship between violent media exposure frequency and aggression was mediated wholly by moral disengagement. As for violent video games in particular, research has found that dehumanization, one of the moral disengagement mechanisms, mediates the effect of VVGE on aggressive behavior (Greitemeyer & McLatchie, 2011 ). Teng et al. ( 2019 ) further demonstrated through a longitudinal study that moral disengagement mediates the link between VVGE and aggression, especially for early adolescents. However, as the research‐tested adolescents from the ages of 12–19 years, it is unclear whether the results can be generalized to adults.
Our research aimed to further test the role of moral disengagement in the relationship between VVGE and aggression among college students. Based on the literature reviewed above, it is reasonable to expect that moral disengagement would play a mediating role in the relationship. Thus we propose the following hypothesis:
H1 : Moral disengagement will play a mediating role in the relationship between VVGE and aggression.
1.3. Anger and hostility as potential mediators
Anger involves physiological arousal and preparation for aggression, representing the emotional or affective component of behavior, and hostility consists of feelings of ill will and injustice, representing the cognitive component of behavior (Buss & Perry, 1992 ). Research has explored the relationship between VVGE, anger, hostility, aggression, as follows. Anger moderated the relationship between VVGE and aggression (Engelhardt, Bartholow, & Saults, 2011 ; Giumetti & Markey, 2007 ), hostility mediated the relationship between VVGE and aggression (Adachi & Willoughby, 2016 ; Bartholow, Sestir, & Davis, 2005 ; Gentile, Lynch, Linder, & Walsh, 2004 ). But according to GAM, anger, and hostility may also be potential mediators.
According to the short‐term effects (proximal processes) of GAM, violent video gameplay, when combined with a provocation, may increase anger and hostility, thereby increasing the likelihood of subsequent aggressive behavior. The long‐term effects of GAM (distal processes) suggest that repeated exposure to violent video games changes aggressive knowledge structures, and finally contributing to enhanced aggressive personality (Anderson & Bushman, 2002 ; Anderson & Bushman, 2018 ). Rather trait anger and trait hostility are cognition correlated knowledge structures (Anderson & Bushman, 2001 ; Anderson et al., 2010 ). Therefore, according to GAM, anger, and hostility may be potential mediators. Thus, we propose the following hypothesis:
H2 : Anger and Hostility will play a mediating role in the relationship between VVGE and aggression.
1.4. Disinhibition as a potential moderator
Although VVGE has a significant effect on aggression, not all individuals are affected by VVGE in equal measure. Research has found that users with particular characteristics are more susceptible to VVGE effects than others (Exelmans, Custers, & Van den Bulck ( 2015 ); Markey & Markey, 2010 ; Markey & Scherer, 2009 ). According to the GAM, the interactive dynamics of personal and situational (i.e. VVGE) factors, of biological and environmental (i.e. VVGE) factors will influence an individual's aggressive behaviors. Based on this theory, users’ characteristics such as personality traits could moderate the association between VVGE and aggression.
Previous research has found that callous‐unemotional traits, psychoticism, aggressive traits, and empathy could moderate the relationship between VVGE and aggression (Gao et al., 2017 ; Krahé & Möller, 2010 ; Markey & Scherer, 2009 ; Rydell, 2016 ). As another form of personality trait, sensation‐seeking may also serve as a moderator between VVGE and aggression. Sensation seeking is defined by the seeking of varied, novel, complex and intense sensations and experiences, and the willingness to take physical, social, legal and financial risks for the sake of such experiences (Zuckerman, 1994 ). Sensation seeking has been identified as a moderator of the relationship between violent media content and aggression (Slater, Henry, Swaim, & Cardador, 2004 ). However, Bisch and Lee ( 2009 ) found that the interaction effect between violent video games and sensation seeking was not significant. Sensation seeking contains four subscales: thrills and adventure‐seeking; experience seeking; disinhibition; and boredom susceptibility. It may be that particular dimensions are the main factors in the effect of sensation seeking as a moderator.
The disinhibition dimension may be qualitatively different from the other three dimensions (Krcmar & Greene, 1999 ). Disinhibition represents the desire for social and sexual disinhibition as expressed in social drinking, partying, and variety in sexual partners (Zuckerman, 1994 ). It is the reverse of inhibition and describes how people reduce their public self‐awareness, have less concern about the judgment of others, and thus ignore conventional constraints (Lin & Tsai, 2002 ). Research has found that the disinhibition dimension and the experience‐seeking dimension are related to adolescents’ exposure to violent television positively and negatively, respectively (Krcmar & Greene, 1999 ). Additionally, Aluja‐Fabregat ( 2000 ) found a positive relation between disinhibition and exposure to violent films in 8th‐grade boys and girls. Moreover, a recent study that compared gamers (former and ongoing) with non‐gamers found an association between disinhibition and VVGE (Kimmig, Andringa, & Derntl, 2018 ). Consequently, it seems that disinhibition is the main factor in the moderation of the relationship between VVGE and aggression via sensation seeking.
However, although research has identified sensation seeking as a moderator in the relationship between violent media use and aggression, some studies have not found this effect with regard to VVGE. Given the findings cited above, it is reasonable to deduce that the disinhibition dimension may play a different role in the relationship between VVGE and aggression. Thus we propose the following hypothesis:
H3 : Disinhibition will moderate the relationship between violent video games exposure and aggression.
1.5. The present study
The aims of the present study were twofold: first, we aimed to examine the mediating effect of moral disengagement, anger, and hostility in the relationship between VVGE and aggression among college students. Second, we aimed to examine whether disinhibition dimension of sensation seeking plays a role as a moderator between VVGE and aggression. These two questions can address the mechanisms of both mediation (i.e., how does VVGE increase aggression), and moderation (i.e., when and for whom is the effect most potent) of the relationship between VVGE and aggression.
2. METHOD AND MATERIALS
2.1. participants.
The present study used convenient cluster sampling technology to recruit 855 college students from five universities in China as participants, based on the accessibility. We recovered 757 surveys, and among them were 547 valid responses (excluding incomplete surveys and false answers). The final sample included 265 males and 282 females. The participants’ ages ranged from 16 to 26 years ( M = 19.34; standard deviation = 1.01).
2.2. Measures
2.2.1. video game questionnaire.
To measure VVGE, we used the video game questionnaire adapted by Gentile et al. ( 2004 ) from Anderson and Dill ( 2000 ). Participants were asked to list their three favorite video games, including any games played on computers, video game consoles, hand‐held devices, or in video arcades. They were also asked to record the frequency of their play on a 7‐point scale for each game (1 = “rarely”, 7 = “often”). They then rated the extent of the violence of each game's content and graphics on a 7‐point scale (1 = “little or no violence”, 7 = “extremely violent”). The average rating of the video games was used as the overall index of the VVGE. The index was calculated as: ∑[(the content rating + the graphics rating) × (the weekday frequency × 5 + the weekend frequency × 2)] ÷ the number of games. And participants who never played video games were given a VVGE score of one. The higher the score is, the higher the level of VVGE will be. In the present study, Cronbach's α for the scale is 0.83.
2.2.2. Moral disengagement scale (MDS)
The MDS was used to measure moral disengagement (Bandura et al., 1996 ). The Chinese version has been demonstrated to be a reliable and valid measurement (Yang & Wang, 2012 ). The scale includes 32 items divided into eight mechanisms: moral justification, euphemistic language, advantageous comparison, displacement of responsibility, diffusion of responsibility, distorting consequences, attribution of blame, and dehumanization. All items use a 5‐point scale (1 = “strongly disagree”, 5 = “strongly agree”), and higher total scores indicate higher levels of moral disengagement. In the present study, Cronbach's α for the scale is 0.94.
2.2.3. Buss–Perry aggression questionnaire (BPAQ)
The BPAQ consists of 29 items, divided into four dimensions: physical aggression, verbal aggression, anger, and hostility (Buss & Perry, 1992 ). All items use a 5‐point scale (1 = “strongly disagree”, 5 = “strongly agree”). The Chinese version of BPAQ has high validity and reliability (Wang et al., 2016 ). In the present study, Cronbach's α for the scale is 0.91.
The present study used the physical aggression and verbal aggression subscales to assess the trait aggressive behavior, and anger and hostility subscales to access the trait anger and trait hostility. Higher scores indicate higher aggression trait, respectively. In the present study, Cronbach's α for the physical aggression subscale is 0.81, verbal aggression subscale is 0.74, anger subscale is 0.83; hostility subscale is 0.80.
2.2.4. Sensation‐seeking scale (SSS‐V)
The SSS‐V (Zuckerman, Eysenck, & Eysenck, 1978 ) consists of 40 items based on forced choice. Participants choose one statement from two options that best describes them and receive one point for each choice that corresponds to sensation seeking. The Chinese version of the SSS‐V (Wang et al., 2000 ) shows good validity and reliability and has been widely used. In the present study, Cronbach's α for the sensation‐seeking scale is 0.61. The study used the disinhibition subscale to measure disinhibition; higher disinhibition scores represent higher disinhibition tendencies. Cronbach's α for the disinhibition subscale is 0.52, higher disinhibition scores represent higher disinhibition tendencies.
2.3. Procedure and data analysis
The study was approved by the researchers’ University Ethics Committee. Before the investigation, all participants were told that the study was being conducted anonymously and that their information would remain confidential. We then obtained informed consent and participants completed the questionnaires, guided by trained researchers. All the participants were voluntary and they were free to withdraw from the study at any time.
Descriptive statistics, gender differences, correlation analysis, and regression analysis of main variables were conducted using SPSS 22.0. The mediation and moderation analysis was carried out using PROCESS macro (Hayes, 2013 ). The bootstrapping method (Hayes, 2013 ; Preacher & Hayes, 2004 ), which can attain robust standard errors for parameter estimation, was used to test the significance of the mediating effect and moderating effect. We set 5,000 bootstrapping samples and 95% bias‐corrected confidence intervals (CI). Cl containing zero indicated significant effects.
3.1. Preliminary analyses
The study used a self‐report design to collect data, which meant that common method variance may have existed. We used Harman's single‐factor test to test the common method bias. The test showed that there were 36 factors with eigenvalues greater than one, which together explained 65.24% of the total variance, with the largest single factor explaining 14.23% of the variance, which is less than the judgment standards of 40% (Podsakoff, Mackenzie, Lee, & Podsakoff, 2003 ). Therefore, the common method bias was not problematic in this study.
Table Table1 1 shows the correlations between the main variables with gender dummy coded. VVGE was positively associated with moral disengagement, disinhibition, and the four aggressive traits, which were positively correlated with each other. Moral disengagement was positively associated with both the disinhibition and the four aggressive traits. Disinhibition was positively associated with the four aggressive traits. Gender, as a covariate in subsequent analyses, was positively associated with every variable except trait anger.
Correlations and means of study variables
Abbreviation: VVGE, violent video games exposure.
3.2. The mediating effect of moral disengagement, anger, and hostility
To test Hypothesis 1 and Hypothesis 2 that moral disengagement, anger, and hostility would mediate the relationship between VVGE and aggression, we conducted the PROCESS macro Model 4 of SPSS (Hayes, 2013 ) with all data standardized. In the model, VVGE was entered as the predictor, moral disengagement, anger, and hostility as the mediators, aggressive behavior (the composite of physical aggression and verbal aggression) as the outcome variable, and gender was included as a covariate. The mediation effects of moral disengagement (0.03), anger (0.10), and hostility (0.02) were significant (see Table Table2, 2 , Table Table3, 3 , and Figure Figure1). 1 ). Moral disengagement, anger, and hostility accounted for 14.29, 47.62, and 9.52% of the total effect, respectively. When controlling for moral disengagement, anger, and hostility, the direct effect of VVGE on aggression was not significant ( β = 0.06; standard error = 0.03; 95% CI = [−0.001, 0.12]). Moral disengagement, anger, and hostility wholly mediated the relationship between VVGE and aggression with 71.43% of the total effect.
Testing the mediation effect of violent video games exposure on aggression (standardized coefficient)
Abbreviation: CI, confidence interval; VVGE, violent video games exposure.
The direct effect and the mediation effect of moral disengagement, anger, and hostility
Abbreviation: CI, confidence interval; ab, the mediation effect.

The relationship between VVGE, moral disengagement, anger, hostility, and aggressive behavior. VVGE, violent video games exposure
3.3. The moderating effect of disinhibition
To test Hypothesis 3 that disinhibition would moderate the relationship between VVGE and aggression, we conducted the PROCESS macro Model 1 of SPSS with disinhibition as a moderator, VVGE as the predictor, aggressive behavior as the outcome variable, gender as a covariate (Hayes, 2013 ). The results showed that the moderation effect of disinhibition was not significant ( β = −0.04, t = −0.90, 95% CI = [−0.12, 0.04]), see Table Table4 4 .
Testing the moderation effect of violent video games on aggression (standardized coefficient)
4. DISCUSSION
Consistent with H1, our study found that moral disengagement played a mediating role in the relationship between VVGE and aggression, suggesting that college students with high levels of VVGE are more likely to use moral disengagement mechanisms, further resulting in enhanced aggressive behavior trait. This finding is consistent with the research of Teng et al. ( 2019 ), indicating that the mediation effect of moral disengagement can be generalized to adult college students. The result also adds support for the GAM by the indication that VVGE influences an individual's internal state of cognition—specifically, the cognitive predisposition of moral disengagement (Bandura et al., 1996 )—and ultimately an individual's level of aggression (Anderson, & Bushman, 2002 ; Anderson, & Bushman, 2018 ).
Each of the separate links in the mediation model is noteworthy. VVGE was positively associated with moral disengagement, the first stage of the mediation process, and this result is consistent with previous research (e.g., Gabbiadini et al., 2012 ; Greitemeyer & McLatchie, 2011 ). Teng et al. ( 2017 ) explained this result by the use of Bandura's social cognitive theory; that is, VVGE as a contextual variable influences an individual's moral values and cognition, including moral disengagement (Bandura, 2001 ). Moral disengagement was positively associated with aggressive tendencies, the second stage of the mediation process, and this adds support for previous research (e.g., Paciello et al., 2008 ; Wang et al., 2016 ). Bandura's moral disengagement theory proposes that the eight moral disengagement mechanisms can encourage individuals to reconstruct aggression cognitively (e.g., by making the outcome of their behavior appear less harmful; by minimizing their role in the outcome; and by reducing their recognition for the victim), thus aggression is more likely to occur (Bandura et al., 1996 ). Shu, Gino, and Bazerman ( 2011 ) suggest that moral disengagement influences anticipatory guilt reactions, prosocial tendencies, and cognitive and affective reactions; effects that are conducive to immoral or antisocial behavior, such as aggression.
Consistent with H2, our study found that anger and hostility mediated the relationship between VVGE and aggression, suggesting that high level of VVGE is associated with increased anger and hostility in college students, which finally resulted in enhanced aggressive behavior trait. This is in line with the findings from some previous work (Adachi & Willoughby, 2016 ; Bartholow et al., 2005 ; Gentile et al., 2004 ). The result supports the long‐term effects (distal processes) of GAM (Anderson & Bushman, 2002 ; Anderson, & Bushman, 2018 ), that repeated VVGE over longer periods of time leads to elevations in more stable aggressive traits (trait anger, trait hostility), and such traits are part of aggression‐related knowledge structures. Finally, the reinforced knowledge structures contribute to the enhancement of aggressive personality, which further influence individuals’ decision together with situational variables.
With regard to H3, our study found that the moderation role of disinhibition, a dimension of sensation seeking, between VVGE and aggression was not significant. Disinhibition represents stimulation seeking through experiences with other individuals, using substances to feel disinhibited, and living a “hedonistic lifestyle” (Wilson & Scarpa, 2014 ). The characteristics of violent video games provide users with an opportunity for obtaining such experiences above. First, many violent video games are now large online multirole cooperative games, making them a kind of collective activity. Then, violent video games are full of violent and bloody content with immediate reinforcement (Teng et al., 2014 ) whilst a player can be anonymous; characteristics that make playing such games an unrestricted activity. Players of violent video games can do anything they want and perform acts that they cannot do in real life. And in this process, players are in an excited state with increased physiological arousal (Anderson et al., 2010 ); that is, through violent video gameplay, players can feel disinhibited and live a hedonistic lifestyle. These considerations help to explain the strong association between violent video games and disinhibition, but our results suggest that disinhibition is not the main factor in sensation seeking to moderate the relationship between VVGE and aggression. It may be due to the low reliability of sensation seeking scales and the disinhibition subscales. Actually, a few college students said they could not make a decision between some forced choices, because they never experienced some activities on the scale. Besides, some activities are forbidden (such as drugs) and some activities are not suitable to be discussed in public (such as sex) in China. So some items may not adapt to Chinese society situation and should be localized first. Or other materials to measure sensation seeking and inhibition should be considered.
The present study expands previous research by generalizing the mediation effect of moral disengagement to adult college students and exploring trait anger and trait hostility as the mediators in the relationship between VVGE and aggression. The results also add support for the social cognitive theory and the GAM to a certain extent. Reducing exposure to violent video games and the probability of moral standards being deactivated (Teng et al., 2019 ) may be an effective intervention to reduce aggression.
However, the study has several limitations. First, the datasets were collected through cross‐sectional methods, and this limits the inference of causal relationships. Longitudinal research should be conducted in the future. Second, we used self‐report questionnaires to gather the data. Although the common method bias was not problematic, as shown in the preliminary analysis, social desirability bias may exist. Moreover, players with higher levels of moral disengagement or aggression may evaluate the violence level of games lower than their counterparts. Future research could collect data from multiple informants and explore mediation and moderation effects through experimental research. Third, the research methods and sample (using only five universities in southwest China) may have influenced the size of the effects; selecting a more representative sample or improving the research methods may help to increase the size of the effects.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Supporting information
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This research was supported by the National Social Science Foundation of China (grant no. 14XSH013, Grant No. 19BSH112), Chongqing Research Program of Basic Research and Frontier Technology (cstc2018jcyjAX0480), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (grant no. SWU1909226).
Yao M, Zhou Y, Li J, Gao X. Violent video games exposure and aggression: The role of moral disengagement, anger, hostility and disinhibition . Aggr Behav . 2019; 45 :662–670. 10.1002/ab.21860 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Adachi, P. J. C. , & Willoughby, T. (2016). The longitudinal association between competitive video game play and aggression among adolescents and young adults . Child Development , 87 ( 6 ), 1877–1892. 10.1111/cdev.12556 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Allen, J. J. , Anderson, C. A. , & Bushman, B. J. (2018). The general aggression model . Current Opinion in Psychology , 19 , 75–80. 10.1016/j.copsyc.2017.03.034 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Aluja‐Fabregat, A. (2000). Personality and curiosity about TV and films violence in adolescents . Personality and Individual Differences , 29 ( 2 ), 379–392. 10.1016/S0191-8869(99)00200-7 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Anderson, C. A. , & Bushman, B. J. (2001). Effects of violent video games on aggressive behavior, aggressive cognition, aggressive affect, physiological arousal, and prosocial behavior: A meta‐analytic review of the scientific literature . Psychological Science , 12 , 353–359. 10.1111/1467-9280.00366 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Anderson, C. A. , & Bushman, B. J. (2002). Human aggression . Annual Review of Psychology , 53 , 27–51. 10.1146/annurev.psych.53.100901.135231 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Anderson, C. A. , & Bushman, B. J. (2018). Media violence and the general aggression model . Journal of Social Issues , 74 ( 2 ), 386–413. 10.1111/josi.12275 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Anderson, C. A. , & Dill, K. E. (2000). Video games and aggressive thoughts, feelings, and behavior in the laboratory and in life . Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 78 , 772–790. 10.1037//0022-3514.78.4.772 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Anderson, C. A. , Gentile, D. A. , & Buckley, K. E. (2007). Violent video game effects on children and adolescents: Theory, research, and public policy . Oxford University Press; 10.1111/j.1475-3588.2008.00486_3.x [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Anderson, C. A. , Shibuya, A. , Ihori, N. , Swing, E. L. , Bushman, B. J. , Sakamoto, A. , … Saleem, M. (2010). Violent video game effects on aggression, empathy, and prosocial behavior in eastern and western countries: A meta‐analytic review . Psychological Bulletin , 136 , 151–173. 10.1037/a0018251 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bandura, A. (1990). Selective activation and disengagement of moral control . Journal of Social Issues , 46 , 27–46. 10.1111/j.1540-4560.1990.tb00270.x [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bandura, A. (1999). Moral disengagement in the perpetration of inhumanities . Personality and Social Psychology Review , 3 , 193–209. 10.1207/s15327957pspr0303_3 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bandura, A. (2001). Social cognitive theory: An agentic perspective . Annual Review of Psychology , 52 , 1–26. 10.1146/annurev.psych.52.1.1 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bandura, A. , Barbaranelli, C. , Caprara, G. V. , & Pastorelli, C. (1996). Mechanisms of moral disengagement in the exercise of moral agency . Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 71 , 364–374. 10.1037//0022-3514.71.2.364 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Barchia, K. , & Bussey, K. (2011). Individual and collective social cognitive influences on peer aggression: Exploring the contribution of aggression efficacy, moral disengagement, and collective efficacy . Aggressive Behavior , 37 ( 2 ), 107–120. 10.1002/ab.20375 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bartholow, B. D. , Sestir, M. A. , & Davis, E. B. (2005). Correlates and consequences of exposure to video game violence: Hostile personality, empathy, and aggressive behavior . Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin , 31 ( 11 ), 1573–1586. 10.1177/0146167205277205 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bisch, S. J. , & Lee, M. J. (2009). Does violent video game play influence players' aggressive thoughts? An investigation based on sensation seeking tendency. Association for Education in Journalism and Mass Communication . Conference Paper.
- Bushman, B. J. (2016). Violent media and hostile appraisals: A meta‐analytic review . Aggressive Behavior , 42 , 605–613. 10.1002/ab.21655 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Buss, A. H. , & Perry, M. (1992). The aggression questionnaire . Journal of Personality & Social Psychology , 63 , 452–459. 10.1037//0022-3514.63.3.452 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bussey, K. , Quinn, C. , & Dobson, J. (2015). The moderating role of empathic concern and perspective taking on the relationship between moral disengagement and aggression . Merrill‐Palmer Quarterly , 61 , 10–29. 10.13110/merrpalmquar1982.61.1.0010 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- China Audio‐video and Digital Publishing Association Game Publishing Committee . (2018). China Gaming Industry Report . In Chinese.
- Engelhardt, C. R. , Bartholow, B. D. , & Saults, J. S. (2011). Violent and nonviolent video games differentially affect physical aggression for individuals high vs. low in dispositional anger . Aggressive Behavior , 37 ( 6 ), 539–546. 10.1002/ab.20411 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Exelmans, L. , Custers, K. , & Van den Bulck, J. (2015). Violent video games and delinquent behavior in adolescents: A risk factor perspective . Aggressive Behavior , 41 ( 3 ), 267–279. 10.1002/ab.21587 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ferguson, C. J. , & Kilburn, J. (2010). Much ado about nothing: The misestimation and overinterpretation of violent video game effects in Eastern and Western nations: Comment on Anderson et al. (2010) . Psychological Bulletin , 136 , 174–178. 10.1037/a0018566 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gabbiadini, A. , Andrighetto, L. , & Volpato, C. (2012). Brief report: Does exposure to violent video games increase moral disengagement among adolescents? Journal of Adolescence , 35 , 1403–1406. 10.1016/j.adolescence.2012.06.001 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gao, X. , Weng, L. , Zhou, Y. , & Yu, H. (2017). The influence of empathy and morality of violent video game characters on gamers' aggression . Frontiers in Psychology , 8 , 1863 10.3389/fpsyg.2017.01863 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gentile, D. A. , Bender, P. K. , & Anderson, C. A. (2017). Violent video game effects on salivary cortisol, arousal, and aggressive thoughts in children . Computers in Human Behavior , 70 , 39–43. 10.1016/j.chb.2016.12.045 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gentile, D. A. , Li, D. , Khoo, A. , Prot, S. , & Anderson, C. A. (2014). Mediators and moderators of long‐term effects of violent video games on aggressive behavior: Practice, thinking, and action . Jama Pediatrics , 168 , 450–457. 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2014.63 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gentile, D. A. , Lynch, P. J. , Linder, J. R. , & Walsh, D. A. (2004). The effects of violent video game habits on adolescent hostility, aggressive behaviors, and school performance . Journal of Adolescence , 27 ( 1 ), 5–22. 10.1016/j.adolescence.2003.10.002 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gentile, D. A. , Swing, E. L. , Anderson, C. A. , Rinker, D. , & Thomas, K. M. (2016). Differential neural recruitment during violent video game play in violent‐and nonviolent‐game players . Psychology of Popular Media Culture , 5 , 39–51. 10.1037/ppm0000009 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gini, G. , Pozzoli, T. , & Hymel, S. (2014). Moral disengagement among children and youth: A meta‐analytic review of links to aggressive behavior . Aggressive Behavior , 40 ( 1 ), 56–68. 10.1002/ab.21502 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Giumetti, G. W. , & Markey, P. M. (2007). Violent video games and anger as predictors of aggression . Journal of Research in Personality , 41 ( 6 ), 1234–1243. 10.1016/j.jrp.2007.02.005 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Greitemeyer, T. (2018). The spreading impact of playing violent video games on aggression . Computers in Human Behavior , 80 , 216–219. 10.1016/j.chb.2017.11.022 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Greitemeyer, T. , & McLatchie, N. (2011). Denying humanness to others: A newly discovered mechanism by which violent video games increase aggressive behavior . Psychological Science , 22 , 659–665. 10.1177/0956797611403320 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Greitemeyer, T. , & Mügge, D. O. (2014). Video games do affect social outcomes: A meta‐analytic review of the effects of violent and prosocial video game play . Personality & Social Psychology Bulletin , 40 , 578–589. 10.1177/0146167213520459 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hasan, Y. , Bègue, L. , & Bushman, B. J. (2012). Viewing the world through “blood‐red tinted glasses”: The hostile expectation bias mediates the link between violent video game exposure and aggression . Journal of Experimental Social Psychology , 48 , 953–956. 10.1016/j.jesp.2011.12.019 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hayes, A. F. (2013). Introduction to mediation, moderation, and conditional process analysis: A regression‐based approach . New York: Guilford Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hyde, L. W. , Shaw, D. S. , & Moilanen, K. L. (2010). Developmental precursors of moral disengagement and the role of moral disengagement in the development of antisocial behavior . Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology , 38 ( 2 ), 197–209. 10.1007/s10802-009-9358-5 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Killer, B. , Bussey, K. , Hawes, D. , & Hunt, C. (2019). A meta‐analysis of the relationship between moral disengagement and bullying roles in youth . Aggressive Behavior , 45 ( 4 ), 450–462. 10.1002/ab.21833 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kimmig, A. C. S. , Andringa, G. , & Derntl, B. (2018). Potential adverse effects of violent video gaming: Interpersonal‐affective traits are rather impaired than disinhibition in young adults . Frontiers in Psychology , 9 , 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.00736. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Krahé, B. (2014). Media violence use as a risk factor for aggressive behaviour in adolescence . European Review of Social Psychology , 25 ( 1 ), 71–106. 10.1080/10463283.2014.923177 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Krahé, B. , & Möller, I. (2010). Longitudinal effects of media violence on aggression and empathy among German adolescents . Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology , 31 ( 5 ), 401–409. 10.1016/j.appdev.2010.07.003 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Krcmar, M. , & Greene, K. (1999). Predicting exposure to and uses of television violence . Journal of Communication , 49 , 24–45. 10.1111/j.1460-2466.1999.tb02803.x [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lemmens, J. S. , Valkenburg, P. M. , & Peter, J. (2011). The effects of pathological gaming on aggressive behavior . Journal of Youth and Adolescence , 40 ( 1 ), 38–47. 10.1007/s10964-010-9558-x [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lin, S. S. J. , & Tsai, C. C. (2002). Sensation seeking and internet dependence of Taiwanese high school adolescents . Computers in Human Behavior , 18 , 411–426. 10.1016/S0747-5632(01)00056-5 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Markey, P. M. , & Markey, C. N. (2010). Vulnerability to violent video games: A review and integration of personality research . Review of General Psychology , 14 ( 2 ), 82–91. 10.1037/a0019000 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Markey, P. M. , & Scherer, K. (2009). An examination of psychoticism and motion capture controls as moderators of the effects of violent video games . Computers in Human Behavior , 25 ( 2 ), 407–411. 10.1016/j.chb.2008.10.001 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McCarthy, R. J. , Coley, S. L. , Wagner, M. F. , Zengel, B. , & Basham, A. (2016). Does playing video games with violent content temporarily increase aggressive inclinations? A preregistered experimental study . Journal of Experimental Social Psychology , 67 , 13–19. 10.1016/j.jesp.2015.10.009 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Möller, I. , & Krahé, B. (2009). Exposure to violent video games and aggression in German adolescents: A longitudinal analysis . Aggressive Behavior , 35 ( 1 ), 75–89. 10.1002/ab.20290 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Montag, C. , Weber, B. , Trautner, P. , Newport, B. , Markett, S. , Walter, N. T. , … Reuter, M. (2012). Does excessive play of violent first‐person‐shooter‐video‐games dampen brain activity in response to emotional stimuli? Biological Psychology , 89 , 107–111. 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2011.09.014 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Obermann, M. L. (2011). Moral disengagement in self‐reported and peer‐nominated school bullying . Aggressive Behavior , 37 ( 2 ), 133–144. 10.1002/ab.20378 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Paciello, M. , Fida, R. , Tramontano, C. , Lupinetti, C. , & Caprara, G. V. (2008). Stability and change of moral disengagement and its impact on aggression and violence in late adolescence . Child Development , 79 , 1288–1309. 10.1111/j.1467-8624.2008.01189.x [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pan, W. , Gao, X. , *Shi, S. , Liu, F. , & Li, C. (2018). Spontaneous brain activity did not show the effect of violent video games on aggression: A resting‐state fMRI study . Frontiers in Psychology , 8 , 2219 10.3389/fpsyg.2017.02219 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Podsakoff, P. M. , Mackenzie, S. B. , Lee, J. Y. , & Podsakoff, N. P. (2003). Common method biases in behavioral research: A critical review of the literature and recommended remedies . Journal of Applied Psychology , 88 , 879–903. 10.1037/0021-9010.88.5.879 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Preacher, K. J. , & Hayes, A. F. (2004). SPSS and SAS procedures for estimating indirect effects in simple mediation models . Behavior Research Methods, Instruments, & Computers: A Journal of the Psychonomic Society, Inc , 36 , 717–731. 10.3758/bf03206553 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Richmond, J. , & Wilson, J. C. (2008). Are graphic media violence, aggression and moral disengagement related? Psychiatry Psychology & Law , 15 , 350–357. 10.1080/13218710802199716 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rubio‐Garay, F. , Carrasco, M. A. , & Amor, P. J. (2016). Aggression, anger and hostility: Evaluation of moral disengagement as a mediational process . Scandinavian Journal of Psychology , 57 ( 2 ), 129–135. 10.1111/sjop.12270 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rydell, A. M. (2016). Violent media exposure, aggression and CU traits in adolescence: Testing the selection and socialization hypotheses . Journal of Adolescence , 52 , 95–102. 10.1016/j.adolescence.2016.07.009 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Shu, L. L. , Gino, F. , & Bazerman, M. H. (2011). Dishonest deed, clear conscience: When cheating leads to moral disengagement and motivated forgetting . Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin , 37 ( 3 ), 330–349. 10.1177/0146167211398138 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Slater, M. D. , Henry, K. L. , Swaim, R. C. , & Cardador, J. M. (2004). Vulnerable teens, vulnerable times: How sensation seeking, alienation, and victimization moderate the violent media content‐aggressiveness relation . Communication Research , 31 , 642–668. 10.1177/0093650204269265 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sticca, F. , & Perren, S. (2015). The chicken and the egg: Longitudinal associations between moral deficiencies and bullying: A parallel process latent growth model . Merrill‐Palmer Quarterly , 61 , 85–100. 10.13110/merrpalmquar1982.61.1.0085 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Teng, Z. , Li, Y. , & Liu, Y. (2014). Online gaming, internet addiction, and aggression in Chinese male students: The mediating role of low self‐control . International Journal of Psychological Studies , 6 ( 2 ), 89 10.5539/ijps.v6n2p89 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Teng, Z. , Nie, Q. , Guo, C. , & Liu, Y. (2017). Violent video game exposure and moral disengagement in early adolescence: The moderating effect of moral identity . Computers in Human Behavior , 77 , 54–62. 10.1016/j.chb.2017.08.031 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Teng, Z. , Nie, Q. , Guo, C. , Zhang, Q. , Liu, Y. , & Bushman, B. J. (2019). A longitudinal study of link between exposure to violent video games and aggression in Chinese adolescents: The mediating role of moral disengagement . Developmental Psychology , 55 ( 1 ), 184–195. 10.1037/dev0000624 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Teng, Z. , Nie, Q. , Pan, Y. , Liu, Y. , & Guo, C. (2017). A cross‐lagged model of the relationship between violent video game exposure and moral disengagement in middle school and high school students . Children and Youth Services Review , 81 , 117–123. 10.1016/j.childyouth.2017.07.029 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Velez, J. A. , Greitemeyer, T. , Whitaker, J. L. , Ewoldsen, D. R. , & Bushman, B. J. (2016). Violent video games and reciprocity: The attenuating effects of cooperative game play on subsequent aggression . Communication Research , 43 ( 4 ), 447–467. 10.1177/0093650214552519 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Verheijen, G. P. , Burk, W. J. , Stoltz, S. E. M. J. , van den Berg, Y. H. M. , & Cillessen, A. H. N. (2018). Friendly fire: Longitudinal effects of exposure to violent video games on aggressive behavior in adolescent friendship dyads . Aggressive Behavior , 44 , 257–267. 10.1002/ab.21748 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wang, C. , Ryoo, J. H. , Swearer, S. M. , Turner, R. , & Goldberg, T. S. (2017). Longitudinal relationships between bullying and moral disengagement among adolescents . Journal of Youth and Adolescence , 46 ( 6 ), 1304–1317. 10.1007/s10964-016-0577-0 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wang, W. , Wu, Y. X. , Peng, Z. G. , Lu, S. W. , Yu, L. , Wang, G. P. , … Wang, Y. H. (2000). Test of sensation seeking in a Chinese sample . Personality & Individual Differences , 28 , 169–179. 10.1016/s0191-8869(99)00092-6 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wang, X. , Lei, L. , Yang, J. , Gao, L. , & Zhao, F. (2016). Moral disengagement as mediator and moderator of the relation between empathy and aggression among Chinese male juvenile delinquents . Child Psychiatry & Human Development , 48 , 316–326. 10.1007/s10578-016-0643-6 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wilson, L. C. , & Scarpa, A. (2014). Aggressive behavior: An alternative model of resting heart rate and sensation seeking . Aggressive Behavior , 40 , 91–98. 10.1002/ab.21504 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yang, J. P. , & Wang, X. C. (2012). Effect of moral disengagement on adolescents’ aggressive behavior: Moderated mediating effect . Acta Psychologica Sinica , 44 , 1075–1085. 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2012.01075 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zapolski, T. C. , Banks, D. E. , Lau, K. S. , & Aalsma, M. C. (2018). Perceived police injustice, moral disengagement, and aggression among juvenile offenders: Utilizing the general strain theory model . Child Psychiatry & Human Development , 49 ( 2 ), 290–297. 10.1007/s10578-017-0750-z [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zuckerman, M. (1994). Behavioral expressions and biosocial bases of sensation seeking . Cambridge University Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Zuckerman, M. , Eysenck, S. , & Eysenck, H. J. (1978). Sensation seeking in England and America: Cross‐cultural, age, and sex comparisons . Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology , 46 , 139–149. 10.1037//0022-006x.46.1.139 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]

- Computational and Systems Biology
- Neuroscience
Empathy: Exploring the impact of violence in video games
- Open access
- Copyright information
- Comment Open annotations (there are currently 0 annotations on this page).
- 1,174 views
Share this article
Cite this article.
- Nicolas Roy
- Michel-Pierre Coll
- Copy to clipboard
- Download BibTeX
- Download .RIS
- École de Psychologie, Université Laval, Canada ;
- Centre interdisciplinaire de recherche en réadaptation et intégration sociale, Canada ;
The release of Grand Theft Auto III in 2001 marked a turning point in the public discussion around video games ( McLaughlin, 2008 ). With graphics more lifelike than ever, the game allowed players to act as criminals free to roam a city and commit senseless acts of violence against its population. Inevitably, social and research questions were raised regarding how this type of media could impact social and emotional wellbeing, in particular in the young men who form most of the gaming community. How would playing highly realistic games that allow the gratuitous murder and exploitation of others impact their psychological functioning?
This question has been notoriously difficult to answer scientifically, and it remains harshly debated ( Devilly et al., 2023 ; Bushman and Anderson, 2021 ). Indeed, both real world observations and lab-based experiments have limitations when trying to assess how gaming may impact emotional, neural and behavioral mechanisms. Observational studies, which rely on measuring these processes without influencing them, are confounded by the fact that violent games tend to attract individuals who already have specific personality and social profiles ( Braun et al., 2016 ). In contrast, experimental work is restricted by practical considerations; in the laboratory, participants can only be exposed to games for short periods, for example. It has also been hindered by inadequate study design, with experiments featuring control conditions that fail to effectively isolate violent content, or recruiting participants who have extensive experience with violent games. Now, in eLife, Claus Lamm and colleagues at the University of Vienna and Karolinska Institutet – including Lukas Lengersdorff as first author – report having designed an experimental study that overcomes many of these limitations ( Lengersdorff et al., 2023 ).
The team recruited 89 young men with little gaming experience and no previous exposure to Grand Theft Auto V (GTA V). Half the participants were assigned to play a normal version of the game and incentivized to kill as many people as possible; the other half accessed a modified version of GTA V devoid of all violent content and got rewarded for taking pictures of other characters. Both groups played for seven hours over two weeks in a supervised lab setting. In addition, the participants’ neural and behavioral responses to images of people in pain or in emotionally charged situations were measured at the start and the end of the study, with Lengersdorff et al. using well-established fMRI and behavioral approaches to measure empathy and emotional reactivity ( Singer et al., 2004 ).
The results showed that the two groups showed no neural or behavioural differences in the response to the distress of others. Additionally, statistical analyses using Bayesian techniques further suggested that playing a violent or non-violent version of the game had no effect on empathy for pain or emotional reactivity. Overall, these analyses provide solid evidence that men with little gaming experience do not get desensitised to the emotions of others after using violent games for a short period.
As Lengersdorff et al. highlight, however, the tightly controlled nature of this lab-based study may limit the generalization of the findings to other demographics or more typical video game use. For example, it remains unclear if the same results would emerge in people of different genders or those already drawn to violent games. The relatively short gaming period used in the study may also not accurately represent the habits of habitual gamers, who, on average, engage in gaming for about 16 hours a week over many years ( Clement, 2021 ).
Nevertheless, the findings of Lengersdorff et al. align with accumulating evidence that playing violent video games has, by itself, little to no substantial impact on emotional and social functioning ( Ferguson et al., 2020 ; Kühn et al., 2019 ). Although these studies do not imply that consuming this type of media is never problematic, they do suggest it can be a part of a healthy lifestyle. More than two decades after the release of GTA III, it may be time to move beyond the moral panic and the simplistic assumption that violent video games are inherently damaging. Future scientific research should aim to delineate the specific circumstances under which this type of media may contribute to psychological distress and antisocial behaviours without neglecting the idea that it might, in some cases, offer positive benefits to players ( Etchells, 2019 ).
- Google Scholar
- Anderson CA
- Copenhaver A
- Ferguson CJ
- Weichenberger M
- Lengersdorff LL
- Sastre-Yagüe D
- McLaughlin R
- O’Doherty J

Article and author information
Author details.
Nicolas Roy is in the École de Psychologie, Université Laval and the Centre interdisciplinaire de recherche en réadaptation et intégration sociale, Québec, Canada
Competing interests
Michel-Pierre Coll is in the École de Psychologie, Université Laval and the Centre interdisciplinaire de recherche en réadaptation et intégration sociale, Québec, Canada
For correspondence
Publication history.
- Version of Record published: January 16, 2024 (version 1)
© 2024, Roy and Coll
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use and redistribution provided that the original author and source are credited.
- 1,174 Page views
- 61 Downloads
- 0 Citations
Article citation count generated by polling the highest count across the following sources: Crossref , PubMed Central , Scopus .
Download links
Downloads (link to download the article as pdf).
- Article PDF
Open citations (links to open the citations from this article in various online reference manager services)
Cite this article (links to download the citations from this article in formats compatible with various reference manager tools), categories and tags.
- violent video games
- emotional reactivity
- desensitization
Research organism
Neuroimaging and behavioral evidence that violent video games exert no negative effect on human empathy for pain and emotional reactivity to violence, further reading.
Influential accounts claim that violent video games (VVGs) decrease players’ emotional empathy by desensitizing them to both virtual and real-life violence. However, scientific evidence for this claim is inconclusive and controversially debated. To assess the causal effect of VVGs on the behavioral and neural correlates of empathy and emotional reactivity to violence, we conducted a prospective experimental study using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). We recruited 89 male participants without prior VVG experience. Over the course of two weeks, participants played either a highly violent video game or a non-violent version of the same game. Before and after this period, participants completed an fMRI experiment with paradigms measuring their empathy for pain and emotional reactivity to violent images. Applying a Bayesian analysis approach throughout enabled us to find substantial evidence for the absence of an effect of VVGs on the behavioral and neural correlates of empathy. Moreover, participants in the VVG group were not desensitized to images of real-world violence. These results imply that short and controlled exposure to VVGs does not numb empathy nor the responses to real-world violence. We discuss the implications of our findings regarding the potential and limitations of experimental research on the causal effects of VVGs. While VVGs might not have a discernible effect on the investigated subpopulation within our carefully controlled experimental setting, our results cannot preclude that effects could be found in settings with higher ecological validity, in vulnerable subpopulations, or after more extensive VVG play.
Disrupting abnormal neuronal oscillations with adaptive delayed feedback control
Closed-loop neuronal stimulation has a strong therapeutic potential for neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease. However, at the moment, standard stimulation protocols rely on continuous open-loop stimulation and the design of adaptive controllers is an active field of research. Delayed feedback control (DFC), a popular method used to control chaotic systems, has been proposed as a closed-loop technique for desynchronisation of neuronal populations but, so far, was only tested in computational studies. We implement DFC for the first time in neuronal populations and access its efficacy in disrupting unwanted neuronal oscillations. To analyse in detail the performance of this activity control algorithm, we used specialised in vitro platforms with high spatiotemporal monitoring/stimulating capabilities. We show that the conventional DFC in fact worsens the neuronal population oscillatory behaviour, which was never reported before. Conversely, we present an improved control algorithm, adaptive DFC (aDFC), which monitors the ongoing oscillation periodicity and self-tunes accordingly. aDFC effectively disrupts collective neuronal oscillations restoring a more physiological state. Overall, these results support aDFC as a better candidate for therapeutic closed-loop brain stimulation.
- Cancer Biology
Unveiling the signaling network of FLT3-ITD AML improves drug sensitivity prediction
Currently, the identification of patient-specific therapies in cancer is mainly informed by personalized genomic analysis. In the setting of acute myeloid leukemia (AML), patient-drug treatment matching fails in a subset of patients harboring atypical internal tandem duplications (ITDs) in the tyrosine kinase domain of the FLT3 gene. To address this unmet medical need, here we develop a systems-based strategy that integrates multiparametric analysis of crucial signaling pathways, and patient-specific genomic and transcriptomic data with a prior knowledge signaling network using a Boolean-based formalism. By this approach, we derive personalized predictive models describing the signaling landscape of AML FLT3-ITD positive cell lines and patients. These models enable us to derive mechanistic insight into drug resistance mechanisms and suggest novel opportunities for combinatorial treatments. Interestingly, our analysis reveals that the JNK kinase pathway plays a crucial role in the tyrosine kinase inhibitor response of FLT3-ITD cells through cell cycle regulation. Finally, our work shows that patient-specific logic models have the potential to inform precision medicine approaches.
Be the first to read new articles from eLife


Handbook of Anger, Aggression, and Violence pp 1–22 Cite as
Violent Video Games and Aggression
A discussion based on the main theoretical frameworks
- H. Andaç Demirtaş-Madran 4
- Living reference work entry
- First Online: 23 November 2022
157 Accesses
Whether or not exposure to violent media is a risk factor for aggressive behavior has been the subject of numerous studies over many years. Research, which was mostly focused on the effects of television during the first decades, started to shift its focus in the 1980s to video games. The interactive and rewarding nature of video gaming and the active role it imposes on players not only facilitates the comprehension of educational content, but also accelerates the modeling and reinforcement of negative orientations. Studies have generally shown that violent video games can trigger harmful effects in physical, cognitive, emotional, and behavioral terms. This chapter presents an overview of current findings from experiments, longitudinal and cross-sectional studies, meta-analyses, and conclusions based on the main theoretical frameworks. Initially, a comparison of the effects of violent video games and violent television is presented. Then, research findings concerning the effects of violent video game and theoretical explanations of the underlying processes are reviewed in detail. This is followed by a summary of research findings concerning the effect of violent video games on aggressive tendencies in accordance with the main theoretical frameworks and ongoing academic conflicts based on disagreements in method, tool, sampling, and statistical dimensions. Finally, a comprehensive discussion is presented along with various recommendations.
- Violent media
- Video games
Violent video games
- Media effects
- Video game effects
- Violent video game effects
- Violent games
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Abbreviations
Adachi T, Willoughby T (2011) The effect of violent video games on aggression. Is it more than just the violence? Aggress Violent Behav 16:55–62
Article Google Scholar
Addo PC, Fang J, Kulbo NB et al (2021) Violent video games and aggression among young adults: the moderating effects of adverse environmental factors. Cyberpsychol Behav Soc Netw 24(1):17–23. https://doi.org/10.1089/cyber.2020.0018
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Anderson CA, Berkowitz L, Donnerstein E (2003) The influence of media violence on youth. Psychol Sci Public Interest 4(3):81–110. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1529-1006.2003.pspi_1433.x
Anderson CA (2002) Violent video games and aggressive thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. In: Calvert SL, Jordan AB, Cocking RR (eds) Children in the digital age. Praeger, Westport, pp 101–119
Google Scholar
Anderson CA, Bushman BJ (2001) Effects of violent video games on aggressive behavior, aggressive cognition, aggressive affect, physiological arousal, and prosocial behavior: a meta-analytic review of the scientific literature. Psychol Sci 12:353–359
Anderson CA, Bushman BJ (2002) The effects of media violence on society. Science 295(5564):2377–2379. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1070765
Anderson CA, Carnagey NL (2004) Violent evil and the general aggression model. In: Miller A (ed) The social psychology of good and evil. Guilford, New York, pp 168–192
Anderson CA, Carnagey NL (2009) Causal effects of violent sports video games on aggression: is it competitiveness or violent content? J Exp Soc Psychol 45:731–739
Anderson CA, Dill KE (2000) Video games and aggressive thoughts, feelings, and behavior in the laboratory and in life. J Pers Soc Psychol 78:772–790
Anderson CA, Carnagey NL, Flanagan M et al (2004) Violent video games: specific effects of violent content on aggressive thoughts and behavior. In: Zanna MP (ed) Advances in experimental social psychology, vol 36. Elsevier Academic Press, pp 199–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2601(04)36004-1
Chapter Google Scholar
Anderson CA, Gentile DA, Buckley KE (2007) Violent video game effects on children and adolescents: theory, research, and public policy. Oxford University Press, New York
Book Google Scholar
Anderson CA, Shibuya A, Ihori N et al (2010) Violent video game effects on aggression, empathy, and prosocial behavior in eastern and western countries: a meta-analytic review. Psychol Bull 136(2):151–173. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0018251
Anderson CA, Suzuki K, Swing EL et al (2017) Media violence and other aggression risk factors in seven nations. Personal Soc Psychol Bull 43(7):986–998. https://doi.org/10.1177/0146167217703064
Ballard ME, Lineberger R (1999) Video game violence and confederate gender: effects on reward and punishment given by college males. Sex Roles 41:541–558
Ballard ME, Wiest JR (1996) Mortal Kombat (TM): the effects of violent video game play on males’ hostility and cardiovascular responding. J Appl Soc Psychol 26:717–730
Bandura A (1986) Social foundations of thought and action: a social cognitive theory. Prentice Hall
Bandura A (2001) Social cognitive theory: an agentic perspective. Annu Rev Psychol 52:1–26. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.psych.52.1.1
Barlett CP, Harris RJ, Baldassaro R (2007) Longer you play, the more hostile you feel: examination of first person shooter video games and aggression during video game play. Aggress Behav 33(6):486–497. https://doi.org/10.1002/ab.20227
Barlett CP, Branch O, Rodeheffer C et al (2009) How long do the short-term violent video game effects last? Aggress Behav 35(3):225–236. https://doi.org/10.1002/ab.20301
Bartholow BD, Bushman BJ, Sestir MA (2006) Chronic violent video game exposure and desensitization to violence: behavioral and event-related brain potential data. J Exp Soc Psychol 42(4):532–539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jesp.2005.08.006
Bender PK, Plante C, Gentile DA (2018) The effects of violent media content on aggression. Curr Opin Psychol 19:104–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copsyc.2017.04.003
Bensley L, Van Eenwyk J (2001) Video games and real-life aggression: review of the literature. J Adolesc Health 29(4):244–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1054-139x(01)00239-7
Bleakley A, Vaala S, Jordan AB et al (2017) The Annenberg media environment survey: media access and use in US homes with children and adolescents. In: Jordan AB, Romer D (eds) Media and the well-being of children and adolescents. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 1–19
Bond RM, Bushman BJ (2017) The contagious spread of violence among US adolescents through social networks. Am J Public Health 107(2):288–294. https://doi.org/10.2105/AJPH.2016.303550
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Bryant J, Zillmann D, Oliver MB (eds) (2002) Media effects, advances in theory and research, 2nd edn. Routledge, New York. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781410602428
Bushman BJ (1998) Effects of television violence on memory for commercial messages. J Exp Psychol Appl 4(4):291–307. https://doi.org/10.1037/1076-898X.4.4.291
Bushman BJ, Huesmann LR (2001) Effects of televised violence on aggression. In: Singer DG, Singer JL (eds) Handbook of children and the media. Sage, Thousand Oaks, pp 223–254
Bushman BJ, Newman K, Calvert SL et al (2016) Youth violence: what we know and what we need to know. Am Psychol 71:17–39. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0039687
Carnagey NL, Anderson CA (2004) Violent video game exposure and aggression: a literature review. Minerva Psichiatr 45(1):1–18
Carnagey NL, Anderson CA (2005) The effects of reward and punishment in violent video games on aggressive affect, cognition, and behavior. Psychol Sci 16(11):882–889. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9280.2005.01632.x
Crick NR (1995) Relational aggression: the role of intent attributions, feelings of distress, and provocation type. Dev Psychopathol 7(2):313–322. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954579400006520
Delhove M, Greitemeyer T (2021) Violent media use and aggression: two longitudinal network studies. J Soc Psychol 161(6):697–713. https://doi.org/10.1080/00224545.2021.1896465
Donnerstein E, Slaby RG, Eron LD (1994) The mass media and youth aggression. In: Eron LD, Gentry JH, Schlegel P (eds) Reason to hope: a psychosocial perspective on violence & youth. American Psychological Association, Washington, DC, pp 219–250. https://doi.org/10.1037/10164-010
Drew B, Waters J (1986) Video games: utilization of a novel strategy to improve perceptual motor skills and cognitive functioning in the non-institutionalized elderly. Cogn Rehab 4(2):26–31
Drummond A, Sauer JD, Garea SS (2018) The infamous relationship between violent video game use and aggression: uncharted moderators and small effects make it a far cry from certain. In: Ferguson CJ (ed) Video game influences on aggression, cognition, and attention. Springer, Cham, pp 23–40
Elson M, Mohseni MR, Breuer J et al (2014) Press CRTT to measure aggressive behavior: the unstandardized use of the competitive reaction time task in aggression research. Psychol Assess 26(2):419–432. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0035569
Evra JV (2004) Television and child development. Lawrence Erlbaum, Hillsdale
Ferguson CJ (2015) Do angry birds make for angry children? A meta-analysis of video game influences on children’s and adolescents’ aggression, mental health, prosocial behavior, and academic performance. Perspect Psychol Sci 10(5):646–666. https://doi.org/10.1177/1745691615592234
Ferguson CJ, Beresin E (2017) Social science’s curious war with pop culture and how it was lost: the media violence debate and the risks it holds for social science. Prev Med Int J Devot Pract Theory 99:69–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ypmed.2017.02.009
Ferguson CJ, Colwell J (2017) Understanding why scholars hold different views on the influences of video games on public health. J Commun 67:305–327. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcom.12293
Ferguson CJ, Kilburn J (2010) Much ado about nothing: the misestimation and overinterpretation of violent video game effects in Eastern and Western nations: comment on Anderson et al. (2010). Psychol Bull 136(2):174–178. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0018566
Ferguson CJ, Wang JC (2019) Aggressive video games are not a risk factor for future aggression in youth: a longitudinal study. J Youth Adolesc 48(8):1439–1451
Ferguson CJ, Rueda S, Cruz A et al (2008) Violent video games and aggression: causal relationship or byproduct of family violence and intrinsic violence motivation? Crim Justice Behav 35:311–332
Ferguson CJ, Ivory JD, Beaver KM (2013) Genetic, maternal, school, intelligence and media use predictors of adult criminality: a longitudinal test of the catalyst model in adolescence through early adulthood. J Aggress Maltreat Trauma 22:447–460
Ferguson CJ, Copenhaver A, Markey P (2020) Reexamining the findings of the American Psychological Association’s 2015 task force on violent media: a meta-analysis. Perspect Psychol Sci 15(6):1423–1443. https://doi.org/10.1177/1745691620927666
Ferguson CJ, Gryshyna A, Kim JS et al (2022) Video games, frustration, violence, and virtual reality: two studies. Br J Soc Psychol 61(1):83–99. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjso.12471
Feshbach S (1955) The drive-reducing function of fantasy behavior. J Abnorm Soc Psychol 50(1):3–11. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0042214
Gardner H (1991) The unschooled mind: how children think and how schools should teach. Basic Books, New York
Geen RG, Donnerstein E (eds) (1998) Human aggression: theories, research, and implications for social policy. Academic Press, Cambridge, MA
Gentile DA (ed) (2003) Media violence and children: a complete guide for parents and professionals. Praeger/Greenwood, Santa Barbara
Gentile DA, Anderson CA (2003) Violent video games: The newest media violence hazard. In: Gentile DA (ed) Media violence and children: A complete guide for parents and professionals. Praeger Publishers/Greenwood Publishing Group, pp 131–152
Gentile DA, Anderson CA (2006) Video games. In: Salkind NJ (ed) Encyclopedia of human development, vol 3. Sage, Thousand Oaks, pp 1303–1307
Gentile DA, Gentile RJ (2008) Violent video games as exemplary teachers: a conceptual analysis. J Youth Adolesc 37:127–141
Gentile DA, Lynch PJ, Linder JR et al (2004) The effects of violent video game habits on adolescent hostility, aggressive behaviors, and school performance. J Adolesc 27(1):5–22
Gentile DA, Li D, Khoo A et al (2014) Mediators and moderators of long-term effects of violent video games on aggressive behavior: practice, thinking, and action. JAMA Pediatr 168(5):450–457. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapediatrics.2014.63
Gerbner G, Gross L, Morgan M et al (1994) Growing up with television: the cultivation perspective. In: Bryant J, Zillmann D (eds) Media effects: advances in theory and research. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc., pp 17–41
Graybill D, Kirsch JR, Esselman ED (eds) (1985) Effects of playing violent versus non-violent video games on the aggressive ideation of children. Child Study J 15:199–205
Greitemeyer T (2014) Intense acts of violence during video game play make daily life aggression appear innocuous: a new mechanism why violent video games increase aggression. J Exp Soc Psychol 50:52–56
Greitemeyer T (2018) The spreading impact of playing violent video games on aggression. Comput Hum Behav 80:216–219
Greitemeyer T (2019) The contagious impact of playing violent video games on aggression: longitudinal evidence. Aggress Behav 45(6):635–642. https://doi.org/10.1002/ab.21857
Greitemeyer T (2022) The dark and bright side of video game consumption: effects of violent and prosocial video games. Curr Opin Psychol 46:101326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copsyc.2022.101326
Greitemeyer T, McLatchie N (2011) Denying humanness to others: a newly discovered mechanism by which violent video games increase aggressive behavior. Psychol Sci 22(5):659–665. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797611403320
Greitemeyer T, Mügge DO (2014) Video games do affect social outcomes: a meta-analytic review of the effects of violent and prosocial video game play. Personal Soc Psychol Bull 40(5):578–589. https://doi.org/10.1177/0146167213520459
Greitemeyer T, Osswald S (2010) Effects of prosocial video games on prosocial behavior. J Pers Soc Psychol 98(2):211–221. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0016997
Griffiths MD, Hunt N (1998) Dependence on computer games by adolescents. Psychol Rep 82(2):475–480. https://doi.org/10.2466/pr0.1998.82.2.475
Gunter B (2016) Does playing video games make players more violent? Springer, London
Harris RJ (2004) A cognitive psychology of mass communication. Lawrence Erlbaum, Mahwah
Hilgard J, Engelhardt CR, Rouder JN (2017) Overstated evidence for short-term effects of violent games on affect and behavior: a reanalysis of Anderson et al. (2010). Psychol Bull 143:757–774. https://doi.org/10.1037/bul0000074
Huesmann LR (1986) Psychological processes promoting the relation between exposure to media violence and aggressive behavior by the viewer. J Soc Issues 42(3):125–139
Huesmann LR (1988) An information processing model for the development of aggression. Aggress Behav 14:13–24
Huesmann LR (2010) Nailing the coffin shut on doubts that violent video games stimulate aggression: comment on Anderson et al. (2010). Psychol Bull 136(2):179–181. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0018567
Huesmann LR (2018) An integrative theoretical understanding of aggression: a brief exposition. Curr Opin Psychol 19:119–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copsyc.2017.04.015
Huesmann LR, Miller LS. Long-term effects of repeated exposure to media violence in childhood. In Huesmann LR. Aggressive behavior: current perspectives. Plenum Press; 1994, p. 153–186 https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4757-9116-7_7
Ihori N, Sakamoto A, Kobayashi K et al (2003) Does video game use grow children’s aggressiveness?: results from a panel study. In: Arai K (ed) Social contributions and responsibilities of simulation and gaming. Japan Association of Simulation and Gaming, Tokyo, pp 221–230
Kestenbaum GI, Weinstein L (1985) Personality, psychopathology, and developmental issues in male adolescent video game use. J Am Acad Child Psychiatry 24(3):329–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0002-7138(09)61094-3
Király O, Griffiths MD, King DL et al (2018) Policy responses to problematic video game use: a systematic review of current measures and future possibilities. J Behav Addict 7(3):503–517. https://doi.org/10.1556/2006.6.2017.050
Kirsh SJ (1998) Seeing the world through mortal Kombat-colored glasses: violent video games and the development of a short-term hostile attribution bias. Childhood 5:177–184
Kirsh SJ, Olczak PV, Mounts JRW (2005) Violent video games induce an affect processing bias. J Media Psychol 7:239–250
Krahé B (2013) The social psychology of aggression, 2nd edn. Psychology Press, Hove. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315804521
Kühn S, Kugler DT, Schmalen K et al (2019) Does playing violent video games cause aggression? A longitudinal intervention study. Mol Psychiatry 24(8):1220–1234
Lynch PJ (1994) Type A behavior, hostility, and cardiovascular function at rest and after playing video games in teenagers. Psychosom Med 56:152
Lynch PJ (1999) Hostility, type a behavior, and stress hormones at rest and after playing violent video games in teenagers. Psychosom Med 61:113
Lynch PJ, Gentile DA, Olson AA et al (2001) The effects of violent video game habits on adolescent aggressive attitudes and behaviors. Biennial Conference of the Society for Research in Child Development, Minneapolis. http://www.eric.ed.gov/PDFS/ED461420.pdf
Milani L, Camisasca E, Caravita SCS et al (2015) Violent video games and children’s aggressive behaviors: an Italian study. SAGE Open 5(3). https://doi.org/10.1177/2158244015599428
Mullin CR, Linz D (1995) Desensitization and resensitization to violence against women: effects of exposure to sexually violent films on judgments of domestic violence victims. J Pers Soc Psychol 69(3):449–459. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.69.3.449
Olson CK, Kutner LA, Warner DE (2008) The role of violent video game content in adolescent development: boys’ perspectives. J Adolesc Res 23(1):55–75. https://doi.org/10.1177/0743558407310713
Paik H, Comstock G (1994) The effects of television violence on antisocial behavior: a meta-Analysis1. Commun Res 21(4):516–546. https://doi.org/10.1177/009365094021004004
Palaus M, Marron EM, Viejo-Sobera R et al (2017) Neural basis of video gaming: a systematic review. Front Hum Neurosci 22(11):248. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2017.00248
Prot S, Anderson CA, Gentile DA et al (2014) The positive and negative effects of video game play. In: Jordan AB, Romer D (eds) Media and the well-being of children and adolescents. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 109–128
Sestir MA, Bartholow BD (2010) Violent and nonviolent video games produce opposing effects on aggressive and prosocial outcomes. J Exp Soc Psychol 46(6):934–942
Shao R, Wang Y (2019) The relation of violent video games to adolescent aggression: an examination of moderated mediation effect. Front Psychol 10:384. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00384
Sherry JL (2001) The effects of violent video games on aggression: a meta analysis. Hum Commun Res 27(3):409–431
Sherry JL (2004) Media effects theory and the nature/nurture debate: a historical overview and directions for future research. Media Psychol 6:83–109. https://doi.org/10.1207/s1532785xmep0601_4
Shibuya A, Sakamoto A, Ihori N et al (2008) The effects of the presence and contexts of video game violence on children: a longitudinal study in Japan. Simul Gaming 39(4):528–539. https://doi.org/10.1177/1046878107306670
Silvern SB, Williamson PA (1987) The effects of video game play on young children’s aggression, fantasy and prosocial behavior. J Appl Dev Psychol 8:453–462
Smith SL, Donnerstein E. Harmful effects of exposure to media violence: learning of aggression, emotional desensitization, and fear. In Geen RG, Donnerstein E, edıtors. Human aggression: Theories, research, and implications for social policy. Academic Press; 1998, p. 167–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-012278805-5/50008-0
Statista (2022). https://www.statista.com/statistics/748044/number-video-gamers-world/ . Accessed April 2022
Tannenbaum PH, Zillmann D (1975) Emotional arousal in the facilitation of aggression through communication. In: Berkowitz L (ed) Advances in experimental social psychology, vol VIII. Academic Press, New York, pp 149–192
Tian Y, Gao M, Wang P et al (2020) The effects of violent video games and shyness on individuals’ aggressive behaviors. Aggress Behav 46(1):16–24. https://doi.org/10.1002/ab.21869
Unsworth G, Devilly GJ, Ward T (2007) The effect of playing violent video games on adolescents: should parents be quaking in their boots? Psychol Crime Law 13(4):383–394
Van Schie EG, Wiegman O (1997) Children and videogames: leisure activities, aggression, social integration, and school performance. J Appl Soc Psychol 27(13):1175–1194
Warburton WA, Anderson CA (2015) Social psychology of aggression. In: Wright J, Berry J (eds) International encyclopedia of social and behavioral sciences, vol 1, 2nd edn. Elsevier, Oxford, pp 373–380
Wiederhold BK (2021) Violent video games: harmful trigger or harmless diversion? Cyberpsychol Behav Soc Netw 24(1):1–2. https://doi.org/10.1089/cyber.2020.29203
Wiegman O, Van Schie EGM (1998) Video game playing and its relations with aggressive and prosocial behavior. Br J Soc Psychol 37:367–368
Winkel M, Novak DM, Hopson H (1987) Personality factors, subject gender, and the effects of aggressive video games on aggression in adolescents. J Res Pers 21(2):211–223
Zhang Q, Cao Y, Tian J (2021) Effects of violent video games on aggressive cognition and aggressive behavior. Cyberpsychol Behav Soc Netw 24(1):5–10. https://doi.org/10.1089/cyber.2019.0676
Zheng X, Chen H, Wang Z et al (2021) Online violent video games and online aggressive behavior among Chinese college students: the role of anger rumination and self-control. Aggress Behav 47(5):514–520. https://doi.org/10.1002/ab.21967
Zillmann D (2002) Exemplification theory of media influence. In: Bryant J, Zillmann D (eds) Media effects: advances in theory and research. Lawrence Erlbaum, Hillsdale, pp 19–41
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Faculty of Comm, Başkent University, Ankara, Turkey
H. Andaç Demirtaş-Madran
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to H. Andaç Demirtaş-Madran .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Institute for Clinical and Applied Health Research, University of Hull, Hull, UK
Colin Martin
King's College London, London, UK
Victor R. Preedy
University of Westminster, London, UK
Vinood B. Patel
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Demirtaş-Madran, H.A. (2022). Violent Video Games and Aggression. In: Martin, C., Preedy, V.R., Patel, V.B. (eds) Handbook of Anger, Aggression, and Violence. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-98711-4_21-1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-98711-4_21-1
Received : 26 May 2022
Accepted : 12 June 2022
Published : 23 November 2022
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-98711-4
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-98711-4
eBook Packages : Springer Reference Behavioral Science and Psychology Reference Module Humanities and Social Sciences Reference Module Business, Economics and Social Sciences
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

Pushing Buttons: Why linking real-world violence to video games is a dangerous distraction
In this week’s newsletter: Tragic shootings in the US have resurrected the disproven theory games turn people into killers. Why does this myth persist?
- Don’t get Pushing Buttons delivered to your inbox? Sign up here
Welcome to Pushing Buttons, the Guardian’s gaming newsletter. If you’d like to receive it in your inbox every week, just pop your email in below – and check your inbox (and spam) for the confirmation email.
Remember how, in the wake of yet more awful shootings in the US this month, Fox News decided to blame video games rather than, you know, the almost total absence of meaningful gun control? Remember how I said last week that the video-games-cause-violence “argument” was so mendacious and nakedly manipulative that I wasn’t going to dignify it with a response?
Well, here I am, responding, because the supposed link between video games and real-life violence is one of the most persistent myths that I’ve encountered over the course of my career, and it has an interesting (if also infuriating) history.
Many video games have violent content, just as many films and TV series have violent content (and of course many books, as anyone who has endured a Bret Easton Ellis novel will attest). And it makes intuitive sense that the interactivity of games – especially shooting games – might appear more troubling, from the outside, than passive media such as film. (I gotta say, though, that in 25 years of playing video games I have never seen a scene as violent or upsetting as, say, a Quentin Tarantino movie.)
But the idea that exposure to these violent games turns people into killers in real life is comprehensively false – and it deflects attention from the actual drivers of real-world violence, from inequality to access to firearms to online radicalisation. It is a very politically motivated argument, and one that makes me instantly suspicious of the person wielding it. The NRA, for instance, trots it out on the regular . Donald Trump, inciter of actual real-life violent riots, was fond of it too. Why might that be, I wonder?
First, the facts: there is no scientifically credible link between video games and real-life violence. A lot of the studies around this issue are, in a word, bad – small sample sizes, lab conditions that have no relation to how people engage with games in the real world – but the best we have show either no link at all between violent games and violent thoughts or behaviour, or a positive correlation so minuscule as to be meaningless. A review of the science in 2020 , which looked at and re-evaluated 28 global studies of video games and violence, found no cumulative harm, no long-term effect, and barely even any short-term effect on aggression in the real world. It concluded that the “long-term impacts of violent games on youth aggression are near zero”.
This seems self-evident: video games have been a part of popular culture for at least 50 years, since Pong, and violent games have existed in some form since Space Invaders, though they’ve gotten more visually realistic over time. If video games were in some way dangerous – if they significantly affected our behaviour, our emotional responses – you would expect to have seen widespread, cross-cultural changes in how we act. That is demonstrably not the case. Indeed, overall, violent crime has been decreasing for more than 20 years, the exact period of time during which games have become ubiquitous. Though it would be unscientific to credit video games with that effect, you would think that if the generations of people who’ve now played Doom or Call of Duty or Grand Theft Auto were warped by it, we might be seeing some evidence of that by now.
It is true that some perpetrators of mass murders – such as the Columbine shooters – were fans of video games. But given that the great majority of teenagers are fans of video games, that doesn’t mean much. More often than a fixation on violent media – of all kinds – mass shooters display an obsession with weapons or explosives or real-life killers, an interest in extremist views, social ostracisation. These are not otherwise well-adjusted people suddenly compelled to real-world violence by a game, or a film, or a Marilyn Manson album.
The history of the “video games cause violence” argument goes back even further than video games themselves: it’s an extension of the panic that flares up whenever a new and supposedly morally abject form of youth culture emerges. In the 1940s, when New York’s mayor ordered 2,000 pinball machines to be seized so that he could performatively smash them up , it was arcades; during the satanic panic of the 1980s and beyond, it was metal music . Since the mid to late 90s, it’s been video games, and no amount of studies debunking any link between them and real-world violence seems to make a difference.
So why does this argument keep showing up? In short: because it’s an easy scapegoat that ties into older generations’ instinctive wariness of technology, screen time and youth culture, and it greatly benefits institutions like the NRA and pro-gun politicians to have a scapegoat. Whenever video games are implicated in a violent event, there is usually stunning hypocrisy on display. After the El Paso shooting in 2019, Walmart removed violent video game displays from its stores – but continued to sell actual guns . Fox News, the TV network that platforms Tucker Carlson and the great replacement theory with him, is happy to point out that the perpetrator of a mass shooting played video games, while remaining oddly quiet on the racist ideas that show up in these shooters’ manifestos.
I’m not saying that we shouldn’t examine video game violence at all, or question it. Does every game that involves sneaking up on enemies need a gratuitous neck-breaking animation when you succeed in overpowering a guard? Why do games so often resort to violence as the primary method of interaction with a virtual world? Do we really need more violent media – couldn’t we be playing something more interesting than another military shooter? These are valid and interesting questions. But they have nothing to do with real-world violence.
What to play

Back in 1994, video game magazine Edge ended its review of Doom with this infamous line: “If only you could talk to these creatures, then perhaps you could try and make friends with them, form alliances… Now that would be interesting.” Nearly 30 years later, “talk to the monsters” jokes and memes still crop up, even if nobody remembers where it originally came from.
Turns out that reviewer had a point, though, as proved by 2015’s Undertale , probably the most interesting anti-violent video game I’ve played. In this lo-fi role-playing game, you get into fights with plenty of monsters, but instead of battering them into submission you can win them over by talking them down and showing them mercy, which is often the more difficult option. In most games, there’s no question about what you do when a monster turns up in your path: this one makes you interrogate yourself. I interpreted it at the time as social commentary on pacifism and community, and looking back, I don’t think that was too much of an overreach.
Available on: PC, PlayStation 4, Xbox One, Nintendo Switch Approximate play time: 6-10 hours
What to read
I’m going to start with a book this time: Lost in a Good Game: Why We Play Video Games and What They Can Do For Us, by Pete Etchells. A researcher and lecturer in biological psychology, Etchells’ perspective on video games is both relatable and extremely well-informed. He looks at the evidence (or lack of evidence) behind all the most pervasive beliefs about video games, and in the end he makes the case that most of the effects that they have on individuals and society are actually positive. It’s a reassuring read that I often recommend to worried parents who don’t play games themselves.
Grand Theft Auto V, perhaps the poster child for morally bankrupt video games that supposedly corrupt the youth, has now sold 165 million copies , following its launch on PS5 and Xbox Series X earlier this year. This makes it one of the most popular entertainment products of all time in any medium, and yet strangely, in the nine years since it was released, we have not seen the emergence of roving gangs of teenagers looking to act out their chaotic GTA Online shootouts in real life. Funny that.
What to click
Gibbon: Beyond the Trees review – short, simple and lovely to play
Activision Blizzard’s Raven Software workers vote to form industry’s first union
Question Block
Will return next week. If you have anything you’d like me to answer, just email me on [email protected]!
- Pushing Buttons newsletter
- newsletters
Most viewed
60 Violence in Video Games Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
🏆 best violent games essay topics and examples, 📌 most interesting video game argument topics, 🎮 video games cause violence – essay topics, ❓ research questions about video games and violence.
- The Negative Effects of Video Games on Children Essay Development of knuckle pads in children is associated with addiction to playing video games. Most of the young children tend to think that what they see in video games is a reality.
- Do Violent Video Games Contribute to Youth Violence? The violence and aggression that stains the youth of today, as a result of these video games, is unquestionably a cancer that ought to be uprooted or at least contained by parents, school leaders, governments […] We will write a custom essay specifically for you by our professional experts 808 writers online Learn More
- Video Games and Violent Behavior As opposed to watching the violence on TV, in these video games the player is the one who commits the acts of violence. In the survey, a group of 10 young men were allowed to […]
- Examining the Perception of Violence in Video Games To examine the perception of violence in video games and their effects a survey was conducted addressing the current view on video games in general and the visualized violence in particular.
- Violence in Video Games To conclude, it is assumed that the dispute among researchers, the public, and authorities on the question of the relationship between violent video games and aggressive behavior may not have a universal answer.
- Does Violence in Video Games Affect Youth? Our concern in this paper is to concentrate on the violent video games, the effects to the youths through participation in the violent video games, the counter arguments and finally the remarks or conclusion.
- Research of Violence in the Media The left frontal lobe of the participants was analyzed and found to be more active in the control group than in the exposed group. Exposure of children to violence in the mass media leads to […]
- Violent Video Games and How They Affect Youth Violence However, despite the overwhelming outcry against the youth playing violent video games, there are a number of researchers and advocates who oppose the idea of directly linking the exposure of young adults to violent scenes […]
- Violence exposure in real-life, video games, television, movies, and the internet: Is there desensitization? The article under consideration entitled “Violence exposure in real-life, video games, television, movies, and the internet: Is there desensitization?” investigates the links between the violent content of TV programs, video games and the increase of […]
- Do Violent Video Games Lead to Aggressive Behavior? Everyone is however in agreement that the violent video games are in compromise of morals and expose the young kids to in appropriate content.
- Video Games and Violence in Children There have been arguments that such behavior is as a result of a pre-disposition to violence in the media as well as in video games.
- A Look at the Violence in Video Games, Movies and Music: A Bad Influence on Our Children
- An Analysis of the Negative Effects of Violence in Video Games
- An Analysis of Violence in Video Games and Violence in Teens
- An Argument Against the Claim That Violence in Video Games Promote Violence in Real Life
- An Argument Against the Opinion on Effects of Violence in Video Games
- Blame Games: Does Violence In Video Games Influence Players To Commit Mass Shootings
- Children And Violence in Video Games
- Critical Argumentations on Violence in Video Games
- Dangers in Media: How Violence in Video Games Affects the Youth
- Does Violence In Video Games Affect Children’s Behavior
- Does Violence in Video Games Contribute to Misconduct
- How Does the Portrayal of Violence in Video Games Influence Children
- Increase In Violence In Video Games Targeted At Children
- Legal and Ethical Issues Concerning Violence in Video Games
- Positive Influence of Violence in Video Games
- Presence Of Sex And Violence In Video Games
- The Consequences Of Video Game Violence In Video Games
- The Debate over Whether the Government Should Restrict Violence in Video Games
- The Depiction of Violence in Video Games
- The Impact of Violence in Video Games on the Intellectual Development of Young People: Grand Theft Auto
- The Problem of Violence in Video Games
- The Use Of Violence In Video Games And Its Impact On Young
- The Vehement Vilification Of Violence In Video Games
- Violence In Video Games and Aggression
- Violence in Video Games and the Role of the Government
- Violence in Video Games Can Be Transferred to the Children’s Real-Life Attitudes and Behaviors
- Violence in Video Games Does Not Create Violence
- Violence in Video Games Do Not Affect Agression
- Violence in Video Games Increases Violence in Children
- What Is Your Take on Violence in Video Games, Movies, and Music?
- Can Violence in Video Games Have a Bad Influence on Our Children?
- What Could Be the Analysis of the Negative Consequences of Violence in Video Games?
- What Argument Can Be Made Against the Claim?
- Violence in Video Games Contributes to Violence in Real Life?
- What Are the Arguments Against the Opinion About the Consequences of Violence in Video Games?
- Does Violence in Video Games Affect Children?
- How Does Violence in Video Games Relate to Violence in Reality?
- Can Video Game Violence Affect Players in Mass Shootings?
- Can Violence in Video Games Encourage Misconduct?
- How Do Video Game Depictions of Violence Can Affect Children?
- What Are the Legal and Ethical Aspects of Violence in Video Games?
- What Is the Connection Between Video Game Violence and Future Technology?
- How Is Youth Aggression Related to Video Game Violence?
- How Negatively Does Aggression in Video Games Affect Today’s Youth?
- How Does Violence in Video Games Cause Ethical Issues?
- What Can Be Done To Prevent the Development of Violence in Children?
- How Can Parents Influence the Development of Violence in Children?
- How Does Violence in Video Games Affect the Maladaptive?
- How Does Violence in Video Games Generally Affect Society?
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, November 30). 60 Violence in Video Games Essay Topic Ideas & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/violence-in-video-games-essay-examples/
"60 Violence in Video Games Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." IvyPanda , 30 Nov. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/violence-in-video-games-essay-examples/.
IvyPanda . (2023) '60 Violence in Video Games Essay Topic Ideas & Examples'. 30 November.
IvyPanda . 2023. "60 Violence in Video Games Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." November 30, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/violence-in-video-games-essay-examples/.
1. IvyPanda . "60 Violence in Video Games Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." November 30, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/violence-in-video-games-essay-examples/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "60 Violence in Video Games Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." November 30, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/violence-in-video-games-essay-examples/.
- Video Game Topics
- Media Violence Titles
- Entertainment Ideas
- Domestic Violence Paper Topics
- Juvenile Delinquency Essay Titles
- Child Development Research Ideas
- Youth Violence Research Topics
- Computers Essay Ideas
- Bullying Research Topics
- Cognitive Development Essay Ideas
- School Violence Ideas
- Censorship Essay Ideas
- Critical Thinking Essay Ideas
- Emotional Development Questions
- Human Behavior Research Topics
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
What Research Says About Video Games And Violence In Children
President Trump held a roundtable at the White House Thursday to discuss violent video games and how they relate to school shootings. NPR's Ari Shapiro speaks with Douglas Gentile, psychology professor at Iowa State University, about what research tells us about video games and violence in children.
ARI SHAPIRO, HOST:
President Trump has held a series of White House meetings on gun violence, and the focus of today's was video games. Lawmakers, parent advocates and people from video game companies were invited to talk with the president. The press was not allowed in. Trump has been focused on this subject for a while now. Here's what he said a couple weeks ago.
(SOUNDBITE OF ARCHIVED RECORDING)
PRESIDENT DONALD TRUMP: I'm hearing more and more people say the level of violence on video games is really shaping young people's thoughts.
SHAPIRO: The central question at the heart of this White House meeting is, does playing violent video games turn people into real-life shooters? Douglas Gentile has researched this issue. He's a psychology professor at Iowa State University. Thanks for joining us.
DOUGLAS GENTILE: My pleasure.
SHAPIRO: If you could just begin with the conclusion of your research - if every violent video game disappeared tomorrow, would there be fewer mass shootings?
GENTILE: We don't know the answer to that, but that's because aggression is actually very complicated. It's multi-causal. No one single thing causes it. And when we've had a school shooting, we usually ask the wrong question. We ask, what was the cause? And then we point around at different things such as mental health or violent video games or poverty or whatever. And none of them is it. What is it is when you put them all together. And so would it reduce the risk - yes. How much - we don't know.
SHAPIRO: So if we take a step back from mass shootings and say how much does playing violent video games increase real-life violence and aggression, do we have a clear answer to that?
GENTILE: We have a clear answer when we're talking about aggression. So aggression is any behavior - that could be a verbal behavior, a physical behavior or a relational behavior - that is intended to harm someone else. So if you give someone the cold shoulder, that is aggressive. But that's different from violence, which is only physical and extreme such that if successful, it would cause severe bodily damage or death. And the research on media violence and aggression seems pretty clear - that the more children consume media violence, whether that's in video games, TV or movies, they do become more willing to behave aggressively when provoked.
SHAPIRO: You sort of conflated video games, TV, movies there. In a video game, you're pretending to be the shooter. You're interacting with a virtual world. TV or movies is much more passive. Is there an important distinction there, or is violence violence in media no matter whether it's interactive or passive?
GENTILE: We used to think that video games would have a much larger effect than passive media like TV or movies. But the research has not seemed to bear that out. It seems to be about the same size effect, which is somewhat surprising because they are active, and you are being rewarded for it. But basically what we're coming down to is learning. We can learn from all of these different ways. And it seems we don't learn particularly differently from video games than from TV or movies.
SHAPIRO: Some people have offered a theory that videogames can be catharsis, and expressing violent impulses in a virtual world helps people not express those in the real world. Has that been disproven?
GENTILE: That has been disproven. So how do you memorize a phone number? You repeat it. Does seeing it one more time take it out of your brain? That would be the catharsis idea, right?
SHAPIRO: (Laughter) Right.
GENTILE: But, no, each new time you see it burns it in a little deeper. So in fact, there's no possible way that catharsis can happen, at least not nearly the way people like to talk about it.
SHAPIRO: Do you think the premise of this White House meeting is flawed? I mean, should video games be one focus of this debate over gun violence in America?
GENTILE: I do think it's flawed. I think the problem is that we're seeking a simple solution to a complex problem. And I noticed there are no real aggression researchers at this White House meeting. So we're not even getting the real picture. What we're getting is just a very one-sided and very limited look into only one of the risk factors for aggression.
SHAPIRO: Professor Gentile, thanks very much.
GENTILE: My pleasure.
SHAPIRO: Psychology professor Douglas Gentile of Iowa State University.
Copyright © 2018 NPR. All rights reserved. Visit our website terms of use and permissions pages at www.npr.org for further information.
NPR transcripts are created on a rush deadline by an NPR contractor. This text may not be in its final form and may be updated or revised in the future. Accuracy and availability may vary. The authoritative record of NPR’s programming is the audio record.
- Entertainment
- Environment
- Information Science and Technology
- Social Issues
Home Essay Samples Crime
Essay Samples on Violence in Video Games
Do violent video games cause behavior problems.
A very big debate about video games has been going on where people argue about whether video games cause behavioral problems or not. I claim that video games don’t cause problems because they improve brain capacity rather than causing behavioral problems, Video games unite people...
- Impact of Video Games
- Video Games
- Violence in Video Games
Are Video Games Doing More Harm Than Good
Video games are one of the most popular sources of entertainment in today’s world, there are many different types of games made for people of different ages. As technology gets more advanced, these games get better and more interesting. Some people believe that video is...
- Youth Violence
The Negative Impact Of Video Games On Children
Video games are the games played by electronically manipulating images produced by a computer program on a monitor or other display (Oxford advance learner’s dictionary, 1948). The Scholars mentioned that violent video games cause short-term or long-term increases in aggression and violent behavior of children with different...
Effects Of Violent Video Gaming On Human Behavior
There are many various kinds of games and consoles within the world and vying worldwide. Video play has become a very common trade all over the world and has been growing exceptionally throughout the past twenty years. Gamers that are obsessed with online play are...
The Rise Of Gun Violence Because Of Video Game Violence
A constant threat of violence lurked from January 2019 to May 2019. A ridiculous eight school shootings would occur, each varying in intensity. The United States was on edge, looking for a reason why their children had to risk their lives in order to pursue...
- Gun Violence
Stressed out with your paper?
Consider using writing assistance:
- 100% unique papers
- 3 hrs deadline option
The Violence Of Video Games And Reasons To Avoid Playing It
In the article “videogames and violence” the passage explains many of the reasons for the evidence against video games and why it is supposably the cause of so much violence among us all. It gives plenty of facts upon the subject and events from the...
Correlation Between Violence in Video Games and Violence in Real Life
As the age of gaming continues with the evolution and advancement of technology, gaming continues to become more and more advanced. This advancement is clear, as seen in such items such as consoles, graphics, story, etc. Unfortunately, the gaming industry seems to have taken a...
- Correlation
The Effects Violent Video Games Have on Children
We live in a world with everyday violence. Can we truly say that the violent things that we see in our everyday lives are dehumanizes us? Absolutely. Researchers say that too much of savage video gaming can cause an increase in violent actions. Video games...
Studies that Prove Violent Video Games Cause Real Life Violence
Violent video games are causing more bullying, fighting and aggression in kids and teens. 60% of middle school boy and 40% of middle school girls who have played at least one Mature-rated game hit or beat up someone. That’s compared with 39% of boys and...
Looking for Connections Between Real Life Violent Events and Video Games
With all the recent tragedies in the news, people are looking for answers on why this is happening. Many people have their own theories, but a popular one perpetuated is that violent video games are causing real life violence. Even the president of the United...
Pros and Cons of Video Games and How They Affect Children and Teens
Does it seem dull and boring waiting for time to pass by? Even though some have better plans to do, there are some that do not have the same plans to do. For the time to pass by, the other thing they can do is...
Rogerian Argument on Video Games: The Effect Violent Video Games Have on Teenagers
The gaming industry is a growing population with approximately 2.5 billion video gamers all over the world (The European Mobile Game Market, 2016). With the popularity of video games, they are bound to be held accountable for the negative actions of gamers. The most recent...
- Rogerian Argument
Best topics on Violence in Video Games
1. Do Violent Video Games Cause Behavior Problems
2. Are Video Games Doing More Harm Than Good
3. The Negative Impact Of Video Games On Children
4. Effects Of Violent Video Gaming On Human Behavior
5. The Rise Of Gun Violence Because Of Video Game Violence
6. The Violence Of Video Games And Reasons To Avoid Playing It
7. Correlation Between Violence in Video Games and Violence in Real Life
8. The Effects Violent Video Games Have on Children
9. Studies that Prove Violent Video Games Cause Real Life Violence
10. Looking for Connections Between Real Life Violent Events and Video Games
11. Pros and Cons of Video Games and How They Affect Children and Teens
12. Rogerian Argument on Video Games: The Effect Violent Video Games Have on Teenagers
- Drinking and Driving
- Jeffrey Dahmer
- Animals Testing
- Serial Killer
- Crime Prevention
- Drug Trafficking
Need writing help?
You can always rely on us no matter what type of paper you need
*No hidden charges
100% Unique Essays
Absolutely Confidential
Money Back Guarantee
By clicking “Send Essay”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement. We will occasionally send you account related emails
You can also get a UNIQUE essay on this or any other topic
Thank you! We’ll contact you as soon as possible.
Do Video Games Cause Violence Essay: Separating Fact from Fiction
Video games have become an integral part of modern entertainment, captivating people of all ages with their immersive experiences and interactive gameplay. However, the question of whether video games cause violence has sparked a heated debate that continues to generate headlines and discussions.
In this comprehensive article, we’ll delve into the complexities of the “ Do video games cause violence essay ” debate, examining various viewpoints, credible research studies, and expert opinions to provide you with a well-rounded understanding of the topic.
We recently just wrote an article that teaches everything you need to know about DBQ essays “ Expert Tips For Writing A Compelling DBQ Essay Introduction ” you can do well to check it out.
Introduction: Understanding the Controversy
In recent years, concerns about the potential link between video games and violent behavior have gained traction. The argument centers around whether engaging in violent video games can influence real-life aggression and aggression-related outcomes. As technology advances and video game narratives become more intricate, the debate becomes increasingly nuanced.
Do Video Games Cause Violence? Analyzing the Evidence
The core question of whether video games directly cause violence remains a topic of rigorous investigation. To understand the complexities, let’s explore the key points:
The Role of Aggressive Content in Video Games
The portrayal of violence in video games is undeniably prevalent, but does exposure to aggressive content equates to violent behavior in reality? Research indicates that the relationship between violent video games and aggression is more intricate than a simple cause-and-effect scenario. While short-term increases in aggressive thoughts and behaviors have been observed after playing violent games, long-term effects are less clear.
Psychological Factors and Individual Differences
Psychologists emphasize the significance of individual differences in determining the impact of video games. Factors such as personality traits, family environment, and mental health play crucial roles in shaping a person’s reaction to gaming. A well-adjusted individual is less likely to display aggressive behavior due to video games compared to someone with pre-existing behavioral issues.
Correlation vs. Causation
It’s essential to distinguish between correlation and causation. While studies have identified a correlation between playing violent video games and increased aggression, it doesn’t definitively prove causation. Other factors, such as socio-economic status and peer influences, could contribute to aggressive behavior.
Longitudinal Studies: Unraveling the Long-Term Effects
Longitudinal studies provide a deeper understanding of the long-term impact of video games. A study by Ferguson et al. (2018) followed participants over several years and found no significant link between playing violent video games and subsequent aggression . This suggests that any short-term effects might dissipate over time.
The question of whether video games cause violence has been a longstanding and contentious topic. The debate centers around whether the consumption of violent video games leads to an increase in aggressive or violent behavior in real life. While the issue is complex and multi-faceted, several key points can help shed light on this matter.
Empirical Research: Numerous studies have attempted to investigate the relationship between video game violence and real-world aggression. Some research suggests a correlation between exposure to violent video games and short-term increases in aggressive thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. However, the majority of studies have failed to establish a clear causal link between playing violent video games and committing actual acts of violence. It’s important to note that aggression is a multifaceted behavior influenced by various factors beyond just media consumption.
Theoretical Perspectives: Different psychological theories have been put forth to explain the potential influence of video games on behavior. Social learning theory posits that individuals learn behavior through observation and imitation. Critics of this theory argue that people are able to differentiate between fantasy and reality, preventing a direct emulation of in-game violence. The catharsis hypothesis suggests that violent video games can provide an outlet for pent-up aggression, reducing real-world aggressive tendencies. However, research on this theory remains inconclusive.
Individual Variation: The impact of video game violence can vary significantly among individuals. Factors such as personality traits, family environment, mental health, and social support play crucial roles in mediating any potential influence. Not everyone who plays violent video games exhibits aggressive behavior, highlighting the importance of considering personal differences.
Positive Aspects of Gaming: Video games are not solely associated with negative effects. They can promote cognitive development, problem-solving skills, and teamwork. Multiplayer games encourage collaboration and communication, fostering social skills. Some video games are even used in educational and therapeutic contexts to enhance learning and address mental health issues.
Media Literacy and Responsibility: Rather than placing the blame solely on video games, promoting media literacy and responsible gaming is essential. Teaching individuals, especially young players, to critically evaluate the content they consume can help them distinguish between fiction and reality.
Prominent researchers and experts have weighed in on the do video games cause violence essay debate, offering valuable insights.
Do Video Games Cause Violence Example Essay (500 words)
Video games, a captivating and diverse form of entertainment, have been at the center of an ongoing debate surrounding their potential influence on real-life violence. The question of whether video games cause aggression and violent behavior has sparked intense discussions among researchers, policymakers, parents, and gamers themselves. This essay delves into the complex interplay between video games and aggression, exploring the various perspectives and evidence surrounding this contentious issue.
Empirical Research: One of the central points of contention is the empirical research on the correlation between video game violence and real-world aggression. Numerous studies have investigated this relationship, with some suggesting a short-term increase in aggressive thoughts and feelings after playing violent video games. However, the majority of studies have failed to establish a clear causal link between virtual violence and actual violent behavior. It’s important to recognize that aggression is a multifaceted behavior influenced by a variety of factors beyond media consumption.
Theoretical Frameworks: Psychological theories play a crucial role in understanding the potential effects of video game violence. The social learning theory asserts that individuals learn behavior through observation and imitation, leading to concerns that players might emulate violent actions. However, critics of this theory argue that people are capable of distinguishing between fantasy and reality, mitigating the direct replication of in-game violence. The catharsis hypothesis suggests that violent video games might serve as an outlet for pent-up aggression, potentially reducing real-world aggressive tendencies. However, the validity of this theory remains inconclusive.
Individual Variation: A significant factor in this debate is the role of individual differences in determining the impact of video game violence. Psychological traits, family environments, mental health conditions, and social support systems can all mediate any potential influence. It’s essential to note that not everyone who engages with violent video games displays aggressive behavior. This underscores the importance of acknowledging the complex interplay of factors at play.
Positive Aspects of Gaming: While the debate often focuses on the negative aspects, it’s crucial to recognize that video games offer numerous positive effects as well. They can enhance cognitive abilities, problem-solving skills, and strategic thinking. Multiplayer games encourage collaboration, teamwork, and communication, fostering social skills in an online context. Furthermore, video games have been adapted for educational and therapeutic purposes, aiding in learning and addressing mental health concerns.
Media Literacy and Responsibility: Rather than vilifying video games outright, an effective approach involves promoting media literacy and responsible gaming. Educating individuals, particularly young players, about critically evaluating the content they consume can help them differentiate between fiction and reality. This empowerment equips individuals with the skills to engage with media in a balanced and informed manner.
Conclusion: In conclusion, the question of whether video games cause violence is a complex and multifaceted issue. While research has not definitively established a causal link between video game violence and real-world aggression, the debate remains relevant due to its societal implications. Recognizing that video games are just one piece of a larger puzzle and understanding the various psychological, contextual, and individual factors at play is vital. Addressing this issue requires a comprehensive and balanced approach that acknowledges both the potential risks and benefits of video game engagement.
Addressing Common Misconceptions
Misconception 1: all video games are equally violent.
Video games have become an integral part of modern entertainment and culture, but they often fall victim to misconceptions and stereotypes. Here are some common misconceptions about video games, along with explanations to provide a more accurate perspective:
1. Video Games are Only for Kids: Misconception : Video games are often associated with children, and some believe they are exclusively designed for young audiences. Explanation : Video games cater to a diverse range of players, spanning various age groups and demographics. From complex strategy games to immersive role-playing adventures, the industry offers a wide spectrum of experiences that appeal to adults and even seniors.
2. Video Games are a Waste of Time: Misconception : Many people perceive playing video games as unproductive and time-consuming. Explanation : Video games can offer cognitive benefits such as improved problem-solving skills, strategic thinking, and hand-eye coordination. Moreover, like any form of entertainment, they provide relaxation and enjoyment, contributing to overall well-being.
3. Video Games Foster Isolation: Misconception : Playing video games is often thought to encourage social isolation and hinder face-to-face interactions. Explanation : While excessive gaming can lead to isolation, many video games promote social interactions. Multiplayer games encourage collaboration and teamwork, and online communities allow players to connect, communicate, and form friendships with people from around the world.
4. Video Games are Violent and Aggressive: Misconception : The belief that all video games promote violence and aggressive behavior. Explanation : Video games encompass a wide array of genres, including puzzle games, simulation games, and adventure games that do not involve violence. While some games may contain violent content, studies have not definitively proven a direct causal link between playing violent video games and real-world aggression.
5. Video Games Are Only for Couch Potatoes: Misconception : Playing video games is often associated with a sedentary lifestyle. Explanation : The gaming industry has evolved to include active and fitness-oriented games that encourage physical movement. These games utilize motion controls and augmented reality technology to promote exercise and active engagement.
6. Video Games are Addictive Like Drugs: Misconception : Video games are frequently compared to addictive substances, suggesting they can lead to similar harmful effects. Explanation : While some individuals may develop problematic gaming habits, the vast majority of players engage in gaming without experiencing addiction-like symptoms. Research shows that moderate gaming can be a normal and enjoyable leisure activity.
7. Video Games Have No Educational Value: Misconception : Video games are often dismissed as devoid of educational benefits. Explanation : Many video games incorporate educational elements such as historical settings, problem-solving challenges, and science-based content. “Edutainment” games explicitly aim to educate players while entertaining them.
FAQs about Video Games and Violence
Are there any benefits to playing video games.
Yes, research suggests that video games can enhance cognitive skills, problem-solving abilities, and even social interactions when played in moderation.
How can parents ensure responsible gaming for their children?
Parents should be actively involved in their children’s gaming habits, setting time limits, selecting age-appropriate games, and fostering open communication about the content.
Can video games be used as therapy?
Absolutely, video games are increasingly used as therapeutic tools for various conditions, including stress, anxiety, and even pain management.
Do video game age ratings effectively protect young players from violent content?
Age ratings provide guidance, but parental involvement and awareness are crucial in ensuring children are exposed to suitable content.
What does current research tell us about the long-term effects of violent video games?
While short-term effects can include increased aggression, long-term effects on real-world violence are inconclusive and require more extensive research.
Are there any regulations on the sale of violent video games?
Many countries have regulations in place that restrict the sale of violent video games to minors. However, enforcement varies.
Final Verdicts
In the do video games cause violence essay debate, it’s essential to approach the topic with a balanced perspective. While research acknowledges potential short-term effects, attributing real-world violence solely to video games oversimplifies the issue. As technology evolves and research advances, our understanding of this intricate relationship will likely continue to evolve.
Remember, video games are just one facet of a multifaceted society, and the impact they have on individuals depends on a myriad of factors. Responsible gaming, open conversations, and critical thinking are key to navigating the world of video games while enjoying their benefits and avoiding their potential pitfalls.
Related: Should Marijuana Be Legalized Essay +Example
👋 Hi! I’m your smart assistant Amy!
Don’t know where to start? Type your requirements and I’ll connect you to an academic expert within 3 minutes.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This trend suggests that video games are not a primary driver of violent behavior and that other factors, such as improved social programs and law enforcement, may be contributing to the decline in violence. Cross-cultural research further undermines the claim that video games cause violence. Countries such as South Korea and Japan, which have ...
Meta‐analyses have shown that violent video game play increases aggression in the player. The present research suggests that violent video game play also affects individuals with whom the player is connected. A longitudinal study ( N = 980) asked participants to report on their amount of violent video game play and level of aggression as well ...
Long Essay on Violence in Video Games 500 Words in English. Long Essay on Violence in Video Games is usually given to classes 7, 8, 9, and 10. The internet is filled with articles about the side effects of playing online, multiplayer games. Online gaming and video games started to have fun online and have now grown to become a community.
Their research article "Violent Video Game Effects on Aggression, Empathy, and Prosocial Behavior in Eastern and Western Countries: A Meta-Analytic Review" demonstrates that the period spent on playing video games is a leading factor in aggressive behavior (Sandra et al. 2017). They use the meta-analytic procedures as their primary approach.
It is a widespread concern that violent video games promote aggression, reduce pro-social behaviour, increase impulsivity and interfere with cognition as well as mood in its players. Previous ...
1.1. Violent video games exposure and aggression. Although some recent studies have not found a significant relationship between VVGE and aggression (Ferguson & Kilburn, 2010; McCarthy, Coley, Wagner, Zengel, & Basham, 2016; Pan, Gao, Shi, Liu, & Li, 2018), a relatively solid association has been established in experimental, cross‐sectional, and longitudinal studies in general.
The case that violent video game play increases aggressive behavior has been made most forcefully by Anderson et al. (6; see also refs.7 and 8).Specifically, these authors undertook a comprehensive metaanalysis of the literature on the impact of violent video game play on six categories of aggressive response: cognition, affect, arousal, empathy/sensitization to violence, overt aggressive ...
Empathy: Exploring the impact of violence in video games. eLife 13 :e94949. The release of Grand Theft Auto III in 2001 marked a turning point in the public discussion around video games ( McLaughlin, 2008 ). With graphics more lifelike than ever, the game allowed players to act as criminals free to roam a city and commit senseless acts of ...
Violent video games. Games designed to encourage players to harm other characters. Ongoing debates exist regarding alternative descriptors such as aggressive video games, kinetic video games, and conflict-oriented games. ... (2017) Overstated evidence for short-term effects of violent games on affect and behavior: a reanalysis of Anderson et al ...
A review of the science in 2020, which looked at and re-evaluated 28 global studies of video games and violence, found no cumulative harm, no long-term effect, and barely even any short-term ...
The violence and aggression that stains the youth of today, as a result of these video games, is unquestionably a cancer that ought to be uprooted or at least contained by parents, school leaders, governments […] We will write. a custom essay specifically for you by our professional experts. 809 writers online.
The global video game industry was worth contributing $159.3 billion in 2020, a 9.3% increase of 9.3% from 2019. Violent video games have been blamed for school shootings, increases in bullying, and violence towards women. Critics argue that these games desensitize players to violence, reward players for simulating violence, and teach children ...
WASHINGTON — Violent video game play is linked to increased aggression in players but insufficient evidence exists about whether the link extends to criminal violence or delinquency, according to a new American Psychological Association task force report. "The research demonstrates a consistent relation between violent video game use and ...
The advent of video games raised new questions about the potential impact of media violence, since the video game player is an active participant rather than merely a viewer. 97% of adolescents age 12-17 play video games—on a computer, on consoles such as the Wii, Playstation, and Xbox, or on portable devices such as Gameboys, smartphones, and tablets.
ARI SHAPIRO, HOST: President Trump has held a series of White House meetings on gun violence, and the focus of today's was video games. Lawmakers, parent advocates and people from video game ...
A more nuanced view. In recent years, however, other researchers have challenged the popular view that violent video games are harmful. Several of them contributed papers to a special issue of the Review of General Psychology, published in June 2010 by the American Psychological Association.. In one paper, Dr. Christopher Ferguson, a psychology professor at Texas A&M International University ...
Negative Effects Article 1: "Violent Video Game Effects on Aggression, Empathy, and Prosocial Behavior in Eastern and Western Countries: A Meta-Analytic Review" This is a scholarly article published by the American Psychological Association and written by Craig Anderson and seven other reputable researchers in the psychology field.
Studies that Prove Violent Video Games Cause Real Life Violence. Violent video games are causing more bullying, fighting and aggression in kids and teens. 60% of middle school boy and 40% of middle school girls who have played at least one Mature-rated game hit or beat up someone. That's compared with 39% of boys and...
In this comprehensive article, we'll delve into the complexities of the "Do video games cause violence essay" debate, ... Some research suggests a correlation between exposure to violent video games and short-term increases in aggressive thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. However, the majority of studies have failed to establish a clear ...