- Utility Menu

Violence Against Women Research Database
Publications by type: thesis.
http://digitalcommons.law.yale.edu/ylsd/3/
This thesis is born of the question: why do women suffer domestic violence disproportionately to any other group? Why does it continue, in the same form, with the same degree of pain, without rebate? And, if the same harm occurs over and over again, consistent through generations and uniform across borders, why then has the international community not yet developed effective means to address it? This thesis attempts to find a legal answer. This is prefaced, however, by the acknowledgement that the law is only one tool in an array of mechanisms, such as health, economics, and politics, which, if properly combined, could alleviate the pain and difficulties experienced by many victims of domestic violence. The area of law to which I look is international human rights law. My initial motivation for considering public international law arose from the repetition of similar forms of domestic violence around the globe. All over the world women suffer the same type of violence at the hands of their intimate partners and they endure the same feelings of helplessness and isolation when looking to the state for protection. If such violence is universal, it seems then, so too should be the solution. I propose in this thesis that international law, if properly fashioned, can be used effectively as part of this solution. In particular, I maintain that the authoritative enunciation of a norm against domestic violence in international law can improve the way states address domestic violence. I do not propose that individual abusers should be tried by international law. My focus instead is on the extent to which states fail consistently to alleviate domestic violence. This is important because many legal systems appreciate neither the exigency of extreme forms of domestic violence, nor the extent to which women as a group are disproportionately victims of this violence. The result of this lack of appreciation is an almost universal failure to police, prevent and punish domestic violence effectively.3 Due to the socialized normalcy of domestic violence, very few cases are reported or actually prosecuted. Where prosecutions do proceed, victims will often drop their complaints either because they have reconciled with, or because they fear recrimination from, their abuser. Given the disjuncture between the reality of domestic violence and the inefficacy of many legal systems to address it, a revision of the law vis-à-vis domestic violence is needed. Both national and international legal systems are in need of change. This thesis proposes that the international community should adopt a clear and authoritative articulation of a legal right against extreme and systemic forms of domestic violence and a corresponding duty of states to help remedy such violence. This proposition is made on the basis that international law currently does not contain an effective articulation of this right, and that adopting effective global standards in international law for addressing such violence would help improve state enforcement of this right. Under the current state of international law, it is difficult to convince states to prioritize its resources and infrastructures to protect abused women. Articulating clear and effective global standards in international law for addressing extreme forms of domestic violence would provide an important and practical benchmark against which domestic state legislation could be evaluated and re-shaped. Formulating such global standards could place pressure on states to take basic remedial steps against such violence, such as enacting legislation that allows for restraining orders to be made at the same time as a maintenance order, or creating accessible shelters, which will accommodate the divergent needs of women, including their children.
Filter by Type of Publication
- Book Chapter
- Conference Paper
- Government Report
- Journal Article
- Legal Ruling
Filter by Year
- Working Paper
- Latin America
- North America
By Type of Violence
- Access to Water/Sanitation/Hygiene
- Court System
- Domestic Violence
- Early/Child Marriage
- Family Violence
- Forced Marriage
- Forced Prostitution / Prostitution
- Forcible Sterilization
- Gender Based Violence
- Governmental/Police Violence
- Help seeking
- Honor Killings
- Indigenous Women
- Intimate Partner Violence
- Peace and Security
- Race/Racism
- Refuge/Shelter
- Reproductive Rights
- Trafficking
- VAW in Conflict
- Widows (of all ages)
- Workplace Violence
Filter by Country
Domestic violence & abuse: prevention, intervention and the politics of gender

This thesis foregrounds data from a survivor-led, qualitative study on domestic violence and abuse (DVA) prevention and intervention, set against the backdrop of UK austerity and the increasingly prominent political endorsement of a gender-neutral conceptualisation of DVA. The study charts how DVA prevention, victimhood and perpetration discourses might be productively reworked to shift the pervasive victim-blaming narratives patterning public understandings and intervention responses to DVA and violence against women (VAW). A key feature of this work entails expanding the scope of responsibility assigned to men for reducing DVA and men’s violence towards women, including within the context of the family. Using feminist, participatory based methods, the study elaborates a triangulated analysis of data from three participant groups: (i) women victim-survivors, (ii) women DVA practitioners, and (iii) ‘engaged men’ involved in efforts to address men’s violence. With analysis critically organised through the lens of the diverse lived experiences of victim-survivors, policy and practice implications are discussed in relation to four sociological domains: women’s lived experience of DVA; mothers and the family in which DVA is a feature; DVA, welfare reform and austerity; and men’s participation in the field of DVA or VAW. Analysis substantiates the imperative of earnestly listening to victim-survivors, and of recognising their experiences as a crucial component in the design of policy and sector responses to DVA. Accounts signal how typically gendered notions of ‘authentic victimhood’ are both routinely mobilised and fundamentally challenged, as victim-survivors engage in complex resistance work even in highly constrained and unsafe environments. Analysis also reveals the various ways in which welfare austerity exacerbates the harms associated with DVA, particularly for those living more marginal lives, closing down vital routes and opportunities for help-seeking and leave-seeking. The UK government’s commitment to tackling DVA is therefore severely undermined in this context. An examination of mothers’ experience of DVA further demonstrates how they are routinely failed by dominant (statutory) responses to DVA, cementing the urgent need for culture change and greater accountability and responsibility to be allocated to fathers who perpetrate DVA. Finally, data from across all three participant groups substantiates that men do and should have a role to play in addressing men’s violence towards women, at various scales, while also foregrounding the complexities associated with this work.
--> Final eThesis - complete (pdf) -->
Filename: WILD J._thesis_27Dec2020-correctversion.pdf

Embargo Date:
You do not need to contact us to get a copy of this thesis. Please use the 'Download' link(s) above to get a copy. You can contact us about this thesis . If you need to make a general enquiry, please see the Contact us page.

- Open access
- Published: 20 June 2023
A qualitative quantitative mixed methods study of domestic violence against women
- Mina Shayestefar 1 ,
- Mohadese Saffari 1 ,
- Razieh Gholamhosseinzadeh 2 ,
- Monir Nobahar 3 , 4 ,
- Majid Mirmohammadkhani 4 ,
- Seyed Hossein Shahcheragh 5 &
- Zahra Khosravi 6
BMC Women's Health volume 23 , Article number: 322 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
7459 Accesses
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
Violence against women is one of the most widespread, persistent and detrimental violations of human rights in today’s world, which has not been reported in most cases due to impunity, silence, stigma and shame, even in the age of social communication. Domestic violence against women harms individuals, families, and society. The objective of this study was to investigate the prevalence and experiences of domestic violence against women in Semnan.
This study was conducted as mixed research (cross-sectional descriptive and phenomenological qualitative methods) to investigate domestic violence against women, and some related factors (quantitative) and experiences of such violence (qualitative) simultaneously in Semnan. In quantitative study, cluster sampling was conducted based on the areas covered by health centers from married women living in Semnan since March 2021 to March 2022 using Domestic Violence Questionnaire. Then, the obtained data were analyzed by descriptive and inferential statistics. In qualitative study by phenomenological approach and purposive sampling until data saturation, 9 women were selected who had referred to the counseling units of Semnan health centers due to domestic violence, since March 2021 to March 2022 and in-depth and semi-structured interviews were conducted. The conducted interviews were analyzed using Colaizzi’s 7-step method.
In qualitative study, seven themes were found including “Facilitators”, “Role failure”, “Repressors”, “Efforts to preserve the family”, “Inappropriate solving of family conflicts”, “Consequences”, and “Inefficient supportive systems”. In quantitative study, the variables of age, age difference and number of years of marriage had a positive and significant relationship, and the variable of the number of children had a negative and significant relationship with the total score and all fields of the questionnaire (p < 0.05). Also, increasing the level of female education and income both independently showed a significant relationship with increasing the score of violence.
Conclusions
Some of the variables of violence against women are known and the need for prevention and plans to take action before their occurrence is well felt. Also, supportive mechanisms with objective and taboo-breaking results should be implemented to minimize harm to women, and their children and families seriously.
Peer Review reports
Violence against women by husbands (physical, sexual and psychological violence) is one of the basic problems of public health and violation of women’s human rights. It is estimated that 35% of women and almost one out of every three women aged 15–49 experience physical or sexual violence by their spouse or non-spouse sexual violence in their lifetime [ 1 ]. This is a nationwide public health issue, and nearly every healthcare worker will encounter a patient who has suffered from some type of domestic or family violence. Unfortunately, different forms of family violence are often interconnected. The “cycle of abuse” frequently persists from children who witness it to their adult relationships, and ultimately to the care of the elderly [ 2 ]. This violence includes a range of physical, sexual and psychological actions, control, threats, aggression, abuse, and rape [ 3 ].
Violence against women is one of the most widespread, persistent, and detrimental violations of human rights in today’s world, which has not been reported in most cases due to impunity, silence, stigma and shame, even in the age of social communication [ 3 ]. In the United States of America, more than one in three women (35.6%) experience rape, physical violence, and intimate partner violence (IPV) during their lifetime. Compared to men, women are nearly twice as likely (13.8% vs. 24.3%) to experience severe physical violence such as choking, burns, and threats with knives or guns [ 4 ]. The higher prevalence of violence against women can be due to the situational deprivation of women in patriarchal societies [ 5 ]. The prevalence of domestic violence in Iran reported 22.9%. The maximum of prevalence estimated in Tehran and Zahedan, respectively [ 6 ]. Currently, Iran has high levels of violence against women, and the provinces with the highest rates of unemployment and poverty also have the highest levels of violence against women [ 7 ].
Domestic violence against women harms individuals, families, and society [ 8 ]. Violence against women leads to physical, sexual, psychological harm or suffering, including threats, coercion and arbitrary deprivation of their freedom in public and private life. Also, such violence is associated with harmful effects on women’s sexual reproductive health, including sexually transmitted infection such as Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV), abortion, unsafe childbirth, and risky sexual behaviors [ 9 ]. There are high levels of psychological, sexual and physical domestic abuse among pregnant women [ 10 ]. Also, women with postpartum depression are significantly more likely to experience domestic violence during pregnancy [ 11 ].
Prompt attention to women’s health and rights at all levels is necessary, which reduces this problem and its risk factors [ 12 ]. Because women prefer to remain silent about domestic violence and there is a need to introduce immediate prevention programs to end domestic violence [ 13 ]. violence against women, which is an important public health problem, and concerns about human rights require careful study and the application of appropriate policies [ 14 ]. Also, the efforts to change the circumstances in which women face domestic violence remain significantly insufficient [ 15 ]. Given that few clear studies on violence against women and at the same time interviews with these people regarding their life experiences are available, the authors attempted to planning this research aims to investigate the prevalence and experiences of domestic violence against women in Semnan with the research question of “What is the prevalence of domestic violence against women in Semnan, and what are their experiences of such violence?”, so that their results can be used in part of the future planning in the health system of the society.
This study is a combination of cross-sectional and phenomenology studies in order to investigate the amount of domestic violence against women and some related factors (quantitative) and their experience of this violence (qualitative) simultaneously in the Semnan city. This study has been approved by the ethics committee of Semnan University of Medical Sciences with ethic code of IR.SEMUMS.REC.1397.182. The researcher introduced herself to the research participants, explained the purpose of the study, and then obtained informed written consent. It was assured to the research units that the collected information will be anonymous and kept confidential. The participants were informed that participation in the study was entirely voluntary, so they can withdraw from the study at any time with confidence. The participants were notified that more than one interview session may be necessary. To increase the trustworthiness of the study, Guba and Lincoln’s criteria for rigor, including credibility, transferability, dependability, and confirmability [ 16 ], were applied throughout the research process. The COREQ checklist was used to assess the present study quality. The researchers used observational notes for reflexivity and it preserved in all phases of this qualitative research process.
Qualitative method
Based on the phenomenological approach and with the purposeful sampling method, nine women who had referred to the counseling units of healthcare centers in Semnan city due to domestic violence in February 2021 to March 2022 were participated in the present study. The inclusion criteria for the study included marriage, a history of visiting a health center consultant due to domestic violence, and consent to participate in the study and unwillingness to participate in the study was the exclusion criteria. Each participant invited to the study by a telephone conversation about study aims and researcher information. The interviews place selected through agreement of the participant and the researcher and a place with the least environmental disturbance. Before starting each interview, the informed consent and all of the ethical considerations, including the purpose of the research, voluntary participation, confidentiality of the information were completely explained and they were asked to sign the written consent form. The participants were interviewed by depth, semi-structured and face-to-face interviews based on the main research question. Interviews were conducted by a female health services researcher with a background in nursing (M.Sh.). Data collection was continued until the data saturation and no new data appeared. Only the participants and the researcher were present during the interviews. All interviews were recorded by a MP3 Player by permission of the participants before starting. Interviews were not repeated. No additional field notes were taken during or after the interview.
The age range of the participants was from 38 to 55 years and their average age was 40 years. The sociodemographic characteristics of the participants are summarized in table below (Table 1 ).
Five interviews in the courtyards of healthcare centers, 2 interviews in the park, and 2 interviews at the participants’ homes were conducted. The duration of the interviews varied from 45 min to one hour. The main research question was “What is your experience about domestic violence?“. According to the research progress some other questions were asked in line with the main question of the research.
The conducted interviews were analyzed by using the 7 steps Colizzi’s method [ 17 ]. In order to empathize with the participants, each interview was read several times and transcribed. Then two researchers (M.Sh. and M.N.) extracted the phrases that were directly related to the phenomenon of domestic violence against women independently and distinguished from other sentences by underlining them. Then these codes were organized into thematic clusters and the formulated concepts were sorted into specific thematic categories.
In the final stage, in order to make the data reliable, the researcher again referred to 2 participants and checked their agreement with their perceptions of the content. Also, possible important contents were discussed and clarified, and in this way, agreement and approval of the samples was obtained.
Quantitative method
The cross-sectional study was implemented from February 2021 to March 2022 with cluster sampling of married women in areas of 3 healthcare centers in Semnan city. Those participants who were married and agreed with the written and verbal informed consent about the ethical considerations were included to the study. The questionnaire was completed by the participants in paper and online form.
The instrument was the standard questionnaire of domestic violence against women by Mohseni Tabrizi et al. [ 18 ]. In the questionnaire, questions 1–10, 11–36, 37–65 and 66–71 related to sociodemographic information, types of spousal abuse (psychological, economical, physical and sexual violence), patriarchal beliefs and traditions and family upbringing and learning violence, respectively. In total, this questionnaire has 71 items.
The scoring of the questionnaire has two parts and the answers to them are based on the Likert scale. Questions 11–36 and 66–71 are answered with always [ 4 ] to never (0) and questions 37–65 with completely agree [ 4 ] to completely disagree (0). The minimum and maximum score is 0 and 300, respectively. The total score of 0–60, 61–120 and higher than 121 demonstrates low, moderate and severe domestic violence against women, respectively [ 18 ].
In the study by Tabrizi et al., to evaluate the validity and reliability of this questionnaire, researchers tried to measure the face validity of the scale by the previous research. Those items and questions which their accuracies were confirmed by social science professors and experts used in the research, finally. The total Cronbach’s alpha coefficient was 0.183, which confirmed that the reliability of the questions and items of the questionnaire is sufficient [ 18 ].
Descriptive data were reported using mean, standard deviation, frequency and percentage. Then, to measure the relationship between the variables, χ2 and Pearson tests also variance and regression analysis were performed. All analysis were performed by using SPSS version 26 and the significance level was considered as p < 0.05.
Qualitative results
According to the third step of Colaizzi’s 7-step method, the researcher attempted to conceptualize and formulate the extracted meanings. In this step, the primary codes were extracted from the important sentences related to the phenomenon of violence against women, which were marked by underlining, which are shown below as examples of this stage and coding.
The primary code of indifference to the father’s role was extracted from the following sentences. This is indifference in the role of the father in front of the children.
“Some time ago, I told him that our daughter is single-sided deaf. She has a doctor’s appointment; I have to take her to the doctor. He said that I don’t have money to give you. He doesn’t force himself to make money anyway” (p 2, 33 yrs).
“He didn’t value his own children. He didn’t think about his older children” (p 4, 54 yrs).
The primary code extracted here included lack of commitment in the role of head of the household. This is irresponsibility towards the family and meeting their needs.
“My husband was fired from work after 10 years due to disorder and laziness. Since then, he has not found a suitable job. Every time he went to work, he was fired after a month because of laziness” (p 7, 55 yrs).
“In the evening, he used to get dressed and go out, and he didn’t come back until late. Some nights, I was so afraid of being alone that I put a knife under my pillow when I slept” (p 2, 33 yrs).
A total of 246 primary codes were extracted from the interviews in the third step. In the fourth step, the researchers put the formulated concepts (primary codes) into 85 specific sub-categories.
Twenty-three categories were extracted from 85 sub-categories. In the sixth step, the concepts of the fifth step were integrated and formed seven themes (Table 2 ).
These themes included “Facilitators”, “Role failure”, “Repressors”, “Efforts to preserve the family”, “Inappropriate solving of family conflicts”, “Consequences”, and “Inefficient supportive systems” (Fig. 1 ).
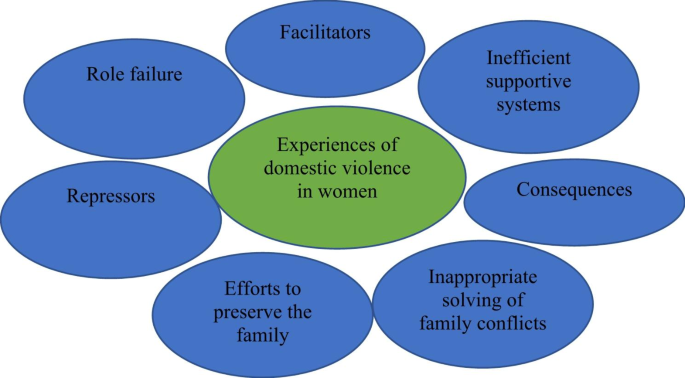
Themes of domestic violence against women
Some of the statements of the participants on the theme of “ Facilitators” are listed below:
Husband’s criminal record
“He got his death sentence for drugs. But, at last it was ended for 10 years” (p 4, 54 yrs).
Inappropriate age for marriage
“At the age of thirteen, I married a boy who was 25 years old” (p 8, 25 yrs).
“My first husband obeyed her parents. I was 12–13 years old” (p 3, 32 yrs).
“I couldn’t do anything. I was humiliated” (p 1, 38 yrs).
“A bridegroom came. The mother was against. She said, I am young. My older sister is not married yet, but I was eager to get married. I don’t know, maybe my father’s house was boring for me” (p 2, 33 yrs).
“My parents used to argue badly. They blamed each other and I always wanted to run away from these arguments. I didn’t have the patience to talk to mom or dad and calm them down” (p 5, 39 yrs).
Overdependence
“My husband’s parents don’t stop interfering, but my husband doesn’t say anything because he is a student of his father. My husband is self-employed and works with his father on a truck” (p 8, 25 yrs).
“Every time I argue with my husband because of lack of money, my mother-in-law supported her son and brought him up very spoiled and lazy” (p 7, 55 yrs).
Bitter memories
“After three years, my mother married her friend with my uncle’s insistence and went to Shiraz. But, his condition was that she did not have the right to bring his daughter with her. In fact, my mother also got married out of necessity” (p 8, 25 yrs).
Some of their other statements related to “ Role failure” are mentioned below:
Lack of commitment to different roles
“I got angry several times and went to my father’s house because of my husband’s bad financial status and the fact that he doesn’t feel responsible to work and always says that he cannot find a job” (p 6, 48 yrs).
“I saw that he does not want to change in any way” (p 4, 54 yrs).
“No matter how kind I am, it does not work” (p 1, 38 yrs).
Some of their other statements regarding “ Repressors” are listed below:
Fear and silence
“My mother always forced me to continue living with my husband. Finally, my father had been poor. She all said that you didn’t listen to me when you wanted to get married, so you don’t have the right to get angry and come to me, I’m miserable enough” (p 2, 33 yrs).
“Because I suffered a lot in my first marital life. I was very humiliated. I said I would be fine with that. To be kind” (p1, 38 yrs).
“Well, I tell myself that he gets angry sometimes” (p 3, 32 yrs).
Shame from society
“I don’t want my daughter-in-law to know. She is not a relative” (p 4, 54 yrs).
Some of the statements of the participants regarding the theme of “ Efforts to preserve the family” are listed below:
Hope and trust
“I always hope in God and I am patient” (p 2, 33 yrs).
Efforts for children
“My divorce took a month. We got a divorce. I forgave my dowry and took my children instead” (p 2, 33 yrs).
Some of their other statements regarding the “ Inappropriate solving of family conflicts” are listed below:
Child-bearing thoughts
“My husband wanted to take me to a doctor to treat me. But my father-in-law refused and said that instead of doing this and spending money, marry again. Marriage in the clans was much easier than any other work” (p 8, 25 yrs).
Lack of effective communication
“I was nervous about him, but I didn’t say anything” (p 5, 39 yrs).
“Now I am satisfied with my life and thank God it is better to listen to people’s words. Now there is someone above me so that people don’t talk behind me” (p 2, 33 yrs).
Some of their other statements regarding the “ Consequences” are listed below:
Harm to children
“My eldest daughter, who was about 7–8 years old, behaved differently. Oh, I was angry. My children are mentally depressed and argue” (p 5, 39 yrs).
After divorce
“Even though I got a divorce, my mother and I came to a remote area due to the fear of what my family would say” (p 2, 33 yrs).
Social harm
“I work at a retirement center for living expenses” (p 2, 33 yrs).
“I had to go to clean the houses” (p 5, 39 yrs).
Non-acceptance in the family
“The children’s relationship with their father became bad. Because every time they saw their father sitting at home smoking, they got angry” (p 7, 55 yrs).
Emotional harm
“When I look back, I regret why I was not careful in my choice” (p 7, 55 yrs).
“I felt very bad. For being married to a man who is not bound by the family and is capricious” (p 9, 36 yrs).
Some of their other statements regarding “ Inefficient supportive systems” are listed below:
Inappropriate family support
“We didn’t have children. I was at my father’s house for about a month. After a month, when I came home, I saw that my husband had married again. I cried a lot that day. He said, God, I had to. I love you. My heart is broken, I have no one to share my words” (p 8, 25 yrs).
“My brother-in-law was like himself. His parents had also died. His sister did not listen at all” (p 4, 54 yrs).
“I didn’t have anyone and I was alone” (p 1, 38 yrs).
Inefficiency of social systems
“That day he argued with me, picked me up and threw me down some stairs in the middle of the yard. He came closer, sat on my stomach, grabbed my neck with both of his hands and wanted to strangle me. Until a long time later, I had kidney problems and my neck was bruised by her hand. Given that my aunt and her family were with us in a building, but she had no desire to testify and was afraid” (p 3, 32 yrs).
Undesired training and advice
“I told my mother, you just said no, how old I was? You never insisted on me and you didn’t listen to me that this man is not good for you” (p 9, 36 yrs).

Quantitative results
In the present study, 376 married women living in Semnan city participated in this study. The mean age of participants was 38.52 ± 10.38 years. The youngest participant was 18 and the oldest was 73 years old. The maximum age difference was 16 years. The years of marriage varied from one year to 40 years. Also, the number of children varied from no children to 7. The majority of them had 2 children (109, 29%). The sociodemographic characteristics of the participants are summarized in the table below (Table 3 ).
The frequency distribution (number and percentage) of the participants in terms of the level of violence was as follows. 89 participants (23.7%) had experienced low violence, 59 participants (15.7%) had experienced moderate violence, and 228 participants (60.6%) had experienced severe violence.
Cronbach’s alpha for the reliability of the questionnaire was 0.988. The mean and standard deviation of the total score of the questionnaire was 143.60 ± 74.70 with a range of 3-244. The relationship between the total score of the questionnaire and its fields, and some demographic variables is summarized in the table below (Table 4 ).
As shown in the table above, the variables of age, age difference and number of years of marriage have a positive and significant relationship, and the variable of number of children has a negative and significant relationship with the total score and all fields of the questionnaire (p < 0.05). However, the variable of education level difference showed no significant relationship with the total score and any of the fields. Also, the highest average score is related to patriarchal beliefs compared to other fields.
The comparison of the average total scores separately according to each variable showed the significant average difference in the variables of the previous marriage history of the woman, the result of the previous marriage of the woman, the education of the woman, the education of the man, the income of the woman, the income of the man, and the physical disease of the man (p < 0.05).
In the regression model, two variables remained in the final model, indicating the relationship between the variables and violence score and the importance of these two variables. An increase in women’s education and income level both independently show a significant relationship with an increase in violence score (Table 5 ).
The results of analysis of variance to compare the scores of each field of violence in the subgroups of the participants also showed that the experience and result of the woman’s previous marriage has a significant relationship with physical violence and tradition and family upbringing, the experience of the man’s previous marriage has a significant relationship with patriarchal belief, the education level of the woman has a significant relationship with all fields and the level of education of the man has a significant relationship with all fields except tradition and family upbringing (p < 0.05).
According to the results of both quantitative and qualitative studies, variables such as the young age of the woman and a large age difference are very important factors leading to an increase in violence. At a younger age, girls are afraid of the stigma of society and family, and being forced to remain silent can lead to an increase in domestic violence. As Gandhi et al. (2021) stated in their study in the same field, a lower marriage age leads to many vulnerabilities in women. Early marriage is a global problem associated with a wide range of health and social consequences, including violence for adolescent girls and women [ 12 ]. Also, Ahmadi et al. (2017) found similar findings, reporting a significant association among IPV and women age ≤ 40 years [ 19 ].
Two others categories of “Facilitators” in the present study were “Husband’s criminal record” and “Overdependence” which had a sub-category of “Forced cohabitation”. Ahmadi et al. (2017) reported in their population-based study in Iran that husband’s addiction and rented-householders have a significant association with IPV [ 19 ].
The patriarchal beliefs, which are rooted in the tradition and culture of society and family upbringing, scored the highest in relation to domestic violence in this study. On the other hand, in qualitative study, “Normalcy” of men’s anger and harassment of women in society is one of the “Repressors” of women to express violence. In the quantitative study, the increase in the women’s education and income level were predictors of the increase in violence. Although domestic violence is more common in some sections of society, women with a wide range of ages, different levels of education, and at different levels of society face this problem, most of which are not reported. Bukuluki et al. (2021) showed that women who agreed that it is good for a man to control his partner were more likely to experience physical violence [ 20 ].
Domestic violence leads to “Consequences” such as “Harm to children”, “Emotional harm”, “Social harm” to women and even “Non-acceptance in their own family”. Because divorce is a taboo in Iranian culture and the fear of humiliating women forces them to remain silent against domestic violence. Balsarkar (2021) stated that the fear of violence can prevent women from continuing their studies, working or exercising their political rights [ 8 ]. Also, Walker-Descarte et al. (2021) recognized domestic violence as a type of child maltreatment, and these abusive behaviors are associated with mental and physical health consequences [ 21 ].
On the other hand and based on the “Lack of effective communication” category, ignoring the role of the counselor in solving family conflicts and challenges in the life of couples in the present study was expressed by women with reasons such as lack of knowledge and family resistance to counseling. Several pathologies are needed to investigate increased domestic violence in situations such as during women’s pregnancy or infertility. Because the use of counseling for couples as a suitable solution should be considered along with their life challenges. Lin et al. (2022) stated that pregnant women were exposed to domestic violence for low birth weight in full term delivery. Spouse violence screening in the perinatal health care system should be considered important, especially for women who have had full-term low birth weight infants [ 22 ].
Also, lack of knowledge and low level of education have been found as other factors of violence in this study, which is very prominent in both qualitative and quantitative studies. Because the social systems and information about the existing laws should be followed properly in society to act as a deterrent. Psychological training and especially anger control and resilience skills during education at a younger age for girls and boys should be included in educational materials to determine the positive results in society in the long term. Manouchehri et al. (2022) stated that it seems necessary to train men about the negative impact of domestic violence on the current and future status of the family [ 23 ]. Balsarkar (2021) also stated that men and women who have not had the opportunity to question gender roles, attitudes and beliefs cannot change such things. Women who are unaware of their rights cannot claim. Governments and organizations cannot adequately address these issues without access to standards, guidelines and tools [ 8 ]. Machado et al. (2021) also stated that gender socialization reinforces gender inequalities and affects the behavior of men and women. So, highlighting this problem in different fields, especially in primary health care services, is a way to prevent IPV against women [ 24 ].
There was a sub-category of “Inefficiency of social systems” in the participants experiences. Perhaps the reason for this is due to insufficient education and knowledge, or fear of seeking help. Holmes et al. (2022) suggested the importance of ascertaining strategies to improve victims’ experiences with the court, especially when victims’ requests are not met, to increase future engagement with the system [ 25 ]. Sigurdsson (2019) revealed that despite high prevalence numbers, IPV is still a hidden and underdiagnosed problem and neither general practitioner nor our communities are as well prepared as they should be [ 26 ]. Moreira and Pinto da Costa (2021) found that while victims of domestic violence often agree with mandatory reporting, various concerns are still expressed by both victims and healthcare professionals that require further attention and resolution [ 27 ]. It appears that legal and ethical issues in this regard require comprehensive evaluation from the perspectives of victims, their families, healthcare workers, and legal experts. By doing so, better practical solutions can be found to address domestic violence, leading to a downward trend in its occurrence.
Some of the variables of violence against women have been identified and emphasized in many studies, highlighting the necessity of policymaking and social pathology in society to prevent and use operational plans to take action before their occurrence. Breaking the taboo of domestic violence and promoting divorce as a viable solution after counseling to receive objective results should be implemented seriously to minimize harm to women, children, and their families.
Limitations
Domestic violence against women is an important issue in Iranian society that women resist showing and expressing, making researchers take a long-term process of sampling in both qualitative and quantitative studies. The location of the interview and the women’s fear of their husbands finding out about their participation in this study have been other challenges of the researchers, which, of course, they attempted to minimize by fully respecting ethical considerations. Despite the researchers’ efforts, their personal and professional experiences, as well as the studies reviewed in the literature review section, may have influenced the study results.
Data Availability
Data and materials will be available upon email to the corresponding author.
Abbreviations
Intimate Partner Violence
Human Immunodeficiency Virus
Organization WH. Violence against women prevalence estimates, 2018: global, regional and national prevalence estimates for intimate partner violence against women and global and regional prevalence estimates for non-partner sexual violence against women. World Health Organization; 2021.
Huecker MR, Malik A, King KC, Smock W. Kentucky Domestic Violence. StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL) ineligible companies. Disclosure: Ahmad Malik declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies. Disclosure: Kevin King declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies. Disclosure: William Smock declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.: StatPearls Publishing Copyright © 2023, StatPearls Publishing LLC.; 2023.
Gandhi A, Bhojani P, Balkawade N, Goswami S, Kotecha Munde B, Chugh A. Analysis of survey on violence against women and early marriage: Gyneaecologists’ perspective. J Obstet Gynecol India. 2021;71(Suppl 2):76–83.
Article Google Scholar
Sugg N. Intimate partner violence: prevalence, health consequences, and intervention. Med Clin. 2015;99(3):629–49.
Google Scholar
Abebe Abate B, Admassu Wossen B, Tilahun Degfie T. Determinants of intimate partner violence during pregnancy among married women in Abay Chomen district, western Ethiopia: a community based cross sectional study. BMC Womens Health. 2016;16(1):1–8.
Adineh H, Almasi Z, Rad M, Zareban I, Moghaddam A. Prevalence of domestic violence against women in Iran: a systematic review. Epidemiol (Sunnyvale). 2016;6(276):2161–11651000276.
Pirnia B, Pirnia F, Pirnia K. Honour killings and violence against women in Iran during the COVID-19 pandemic. The Lancet Psychiatry. 2020;7(10):e60.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Balsarkar G. Summary of four recent studies on violence against women which obstetrician and gynaecologists should know. J Obstet Gynecol India. 2021;71:64–7.
Ellsberg M, Jansen HA, Heise L, Watts CH, Garcia-Moreno C. Intimate partner violence and women’s physical and mental health in the WHO multi-country study on women’s health and domestic violence: an observational study. The lancet. 2008;371(9619):1165–72.
Chasweka R, Chimwaza A, Maluwa A. Isn’t pregnancy supposed to be a joyful time? A cross-sectional study on the types of domestic violence women experience during pregnancy in Malawi. Malawi Med journal: J Med Association Malawi. 2018;30(3):191–6.
Afshari P, Tadayon M, Abedi P, Yazdizadeh S. Prevalence and related factors of postpartum depression among reproductive aged women in Ahvaz. Iran Health care women Int. 2020;41(3):255–65.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Gebrezgi BH, Badi MB, Cherkose EA, Weldehaweria NB. Factors associated with intimate partner physical violence among women attending antenatal care in Shire Endaselassie town, Tigray, northern Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study, July 2015. Reproductive health. 2017;14:1–10.
Duran S, Eraslan ST. Violence against women: affecting factors and coping methods for women. J Pak Med Assoc. 2019;69(1):53–7.
PubMed Google Scholar
Devries KM, Mak JY, Garcia-Moreno C, Petzold M, Child JC, Falder G, et al. The global prevalence of intimate partner violence against women. Science. 2013;340(6140):1527–8.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Mahapatro M, Kumar A. Domestic violence, women’s health, and the sustainable development goals: integrating global targets, India’s national policies, and local responses. J Public Health Policy. 2021;42(2):298–309.
Lincoln YS, Guba EG. Naturalistic inquiry: sage; 1985.
Colaizzi PF. Psychological research as the phenomenologist views it. 1978.
Mohseni Tabrizi A, Kaldi A, Javadianzadeh M. The study of domestic violence in Marrid Women Addmitted to Yazd Legal Medicine Organization and Welfare Organization. Tolooebehdasht. 2013;11(3):11–24.
Ahmadi R, Soleimani R, Jalali MM, Yousefnezhad A, Roshandel Rad M, Eskandari A. Association of intimate partner violence with sociodemographic factors in married women: a population-based study in Iran. Psychol Health Med. 2017;22(7):834–44.
Bukuluki P, Kisaakye P, Wandiembe SP, Musuya T, Letiyo E, Bazira D. An examination of physical violence against women and its justification in development settings in Uganda. PLoS ONE. 2021;16(9):e0255281.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Walker-Descartes I, Mineo M, Condado LV, Agrawal N. Domestic violence and its Effects on Women, Children, and families. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2021;68(2):455–64.
Lin C-H, Lin W-S, Chang H-Y, Wu S-I. Domestic violence against pregnant women is a potential risk factor for low birthweight in full-term neonates: a population-based retrospective cohort study. PLoS ONE. 2022;17(12):e0279469.
Manouchehri E, Ghavami V, Larki M, Saeidi M, Latifnejad Roudsari R. Domestic violence experienced by women with multiple sclerosis: a study from the North-East of Iran. BMC Womens Health. 2022;22(1):1–14.
Machado DF, Castanheira ERL, Almeida MASd. Intersections between gender socialization and violence against women by the intimate partner. Ciência & Saúde Coletiva. 2021;26:5003–12.
Holmes SC, Maxwell CD, Cattaneo LB, Bellucci BA, Sullivan TP. Criminal Protection orders among women victims of intimate Partner violence: Women’s Experiences of Court decisions, processes, and their willingness to Engage with the system in the future. J interpers Violence. 2022;37(17–18):Np16253–np76.
Sigurdsson EL. Domestic violence-are we up to the task? Scand J Prim Health Care. 2019;37(2):143–4.
Moreira DN, Pinto da Costa M. Should domestic violence be or not a public crime? J Public Health. 2021;43(4):833–8.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors of this study appreciate the Deputy for Research and Technology of Semnan University of Medical Sciences, Social Determinants of Health Research Center of Semnan University of Medical Sciences and all the participants in this study.
Research deputy of Semnan University of Medical Sciences financially supported this project.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Allied Medical Sciences, Semnan University of Medical Sciences, Semnan, Iran
Mina Shayestefar & Mohadese Saffari
Amir Al Momenin Hospital, Social Security Organization, Ahvaz, Iran
Razieh Gholamhosseinzadeh
Department of Nursing, Faculty of Nursing and Midwifery, Semnan University of Medical Sciences, Semnan, Iran
Monir Nobahar
Social Determinants of Health Research Center, Semnan University of Medical Sciences, Semnan, Iran
Monir Nobahar & Majid Mirmohammadkhani
Clinical Research Development Unit, Kowsar Educational, Research and Therapeutic Hospital, Semnan University of Medical Sciences, Semnan, Iran
Seyed Hossein Shahcheragh
Student Research Committee, School of Allied Medical Sciences, Semnan University of Medical Sciences, Semnan, Iran
Zahra Khosravi
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
M.Sh. contributed to the first conception and design of this research; M.Sh., Z.Kh., M.S., R.Gh. and S.H.Sh. contributed to collect data; M.N. and M.Sh. contributed to the analysis of the qualitative data; M.M. and M.Sh. contributed to the analysis of the quantitative data; M.SH., M.N. and M.M. contributed to the interpretation of the data; M.Sh., M.S. and S.H.Sh. wrote the manuscript. M.Sh. prepared the final version of manuscript for submission. All authors reviewed the manuscript meticulously and approved it. All names of the authors were listed in the title page.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Mina Shayestefar .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
This article is resulted from a research approved by the Vice Chancellor for Research of Semnan University of Medical Sciences with ethics code of IR.SEMUMS.REC.1397.182 in the Social Determinants of Health Research Center. The authors confirmed that all methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations. All participants accepted the participation in the present study. The researchers introduced themselves to the research units, explained the purpose of the research to them and then all participants signed the written informed consent. The research units were assured that the collected information was anonymous. The participant was informed that participating in the study was completely voluntary so that they can safely withdraw from the study at any time and also the availability of results upon their request.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
All authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Shayestefar, M., Saffari, M., Gholamhosseinzadeh, R. et al. A qualitative quantitative mixed methods study of domestic violence against women. BMC Women's Health 23 , 322 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12905-023-02483-0
Download citation
Received : 28 April 2023
Accepted : 14 June 2023
Published : 20 June 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12905-023-02483-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Domestic violence
- Cross-sectional studies
- Qualitative research
BMC Women's Health
ISSN: 1472-6874
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Research Thesis on Effects Of Gender Based Violence Among Students In Masinde Muliro University, Kakamega, Kenya

2014, EFFECTS OF GENDER BASED VIOLENCE AMONG STUDENTS N MASINDE MULIRO UNIVERSITY, KAKAMEGA, KENYA
Background: A recent global review of 50 population-based studies carried out in 36 countries indicates that between 10 and 60% of women who have ever been married or partnered have experienced at least one incident of physical violence from a current or former intimate partner (Heise.L, 2009). Kenya‟s Demographic and Health Survey in 2003 found that 44 percent of married, divorced or separated women aged 15–49 report they had been physically or sexually violated at least once by their husbands or partners. Purpose of the study: This research however not only focused on the general overview of GBV but specifically arrowed on the effects of GBV amongst campus students in Masinde Muliro University. No such research had been conducted in Masinde Muliro Univeristy and any other public university in Kenya but there was evidence in written articles of the existence of GBV victims amongst the students courtesy of reports from I Choose Life Africa –Masinde Muliro chapter. Methodology: A cross sectional quantitative explorative study design was employed which combined both quantitative and qualitative enquiries. The study was conducted in Masinde Muliro University main campus as the study site with the target population of this study being both the male and female students of Masinde Muliro University. Results: From the results, it was quiet evident that the Females were the ones who faced Gender Based violence more at 96% as opposed to the male who only had 4% of the cases. Conclusion: From the findings and analysis of these results; this research came to the conclusion that GBV is present in MMUST majorly physical abuse of the students by their partners and psychological abuse from the university staff and their colleagues. It also established that There was a correlation between substance abuse and instances of GBV hence curbing substance abuse would help curb GBV.
Related Papers
Wafula J. A.
Dr. Judith A D I K I N Y I Wafula
Studies reveal that Gender-Based Violence (GBV) is increasingly becoming a crisis. This is despite the development spirit entrenched in making the world a global village, Education for All plans and Vision 2030. This paper examines the challenges faced by universities in Kenya in the fight against GBV experienced by their students. It emanates from a study that involved 662 students; 144 lecturers; five deans of students and heads of student counselling; four student leaders and vice chancellors from six universities in Kenya which revealed that universities face challenges that require concerted efforts in tackling. Universities in Kenya have been growing at a rapid pace, from one national university to university colleges and fully fledged universities at varied counties. This expansion bears challenges and the fight against GBV is not exempt. The challenges run from the family structure as evidenced by domestic quarrels, fights and even murders that render it dysfunctional. The genesis of GBV resides in the underlying norm and value systems that make it necessary and legitimate subverting prevention and response efforts [1]. Consequently, GBV is exposed as a display of socio-cultural tendencies that influence the perceptions of gender and is sustained by a culture of silence and denial [2]. Further revelations from UNFPA show that biological factors have no bearing in the intense differences in the behaviours of men and women indicating that the differences are based on the socialization process. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates show that at least one in every three women experience GBV in their lifetime. Additionally, it was found that male survivors experience similar physical, social and psychological violations only that they are less likely to seek medical help due to stigma and prejudice regarding male sexuality or masculinity [3]. Therefore, the paper addresses the challenges and provides recommendations in dealing with the vice. Devolved governments are in a very strategic position of involvement in curbing the vice.
World Journal of Public Health
MICHAEL AVWERHOTA
BMC women's health
Ikeola Adeoye
In Nigeria, there is paucity of information on the IPV burden and experience among young women in courtship and dating relationships. This study assesses the prevalence and correlates of IPV in female undergraduate and postgraduate students in a tertiary institution. The study was a cross-sectional survey. A four-stage sampling technique was used to select 1,100 undergraduate and 255 postgraduate female students from the University of Ibadan, Nigeria. Data was collected using a 43-item self-administered structured questionnaire. Descriptive statistics and multivariate analyses were carried out at 0.05 level of significance. The life-time prevalence of IPV was 42.3% (postgraduate: 34.5%, undergraduate: 44.1%; P < 0.05). Lifetime experience of psychological, physical and sexual IPV were 41.8%, 7.9% and 6.6% respectively. Recent experience (within the previous 12 months) of violence was also more frequently reported by respondents who had a previous history of physical (62.5%) (OR =...
Melak Mengistab Gebresilassie
Gender based violence is one of the most frequent type of human rights violation against girls and women. Having this background, the major objectives of this research was investigating the types, cause and consequences of this gender based violence against female students in Bahir Dar University. A qualitative study has been used predominantly to have a deep in-sight about the experiences of female students with regard to gender based violence (GBV). A case study design has been used, whereby the researcher investigates the respondents’ perspectives on their experience of GBV. A focus group discussion has also been employed to give depth to the study through analyzing groups’ consensus. Furthermore, in-depth interviews with key informants have been conducted to gather data on the prevailing norms and practices of the University in relation to GBV. Finally, beside the above major techniques, questionnaires have been distributed to female and male students to supplement the qualitative data with quantitative results. The out come of the research confirmed that, different sorts of GBV are committed against female students in Bahir Dar University. Sexual harassment is the most frequent form of sexual violence perpetrated against female students. In addition, attempted rape and rape too were perpetrated against female students mainly outside of the University. Psychological and emotional violence are also inflicted against female students through insult, humiliation and embarrassment. Economic violence, denial of liberty and discrimination in the form of giving priority to male students, are the other types of GBV observed in Bahir Dar University. Female students are also victims of physical violence through slap, battering and kicking. The causes for such types of violence were identified as legal and structural constraints. The legal challenges associated with the University which failed to have a specific policy on the rights of girls and its failure in incorporating the rights of girls within the existing senate legislation. Furthermore, absence of any nationwide law that protects girls against campus based GBV is another challenge. The structural constraints include the discriminatory culture, and poverty which are related to the society. The physical environment, alcoholism and drugs abuses are the other challenges related to the University and the students, respectively. GBV has various consequences on female students’ physical, emotional and psychological health and educational achievements. The study showed that GBV is one the major cause for female students’ lower academic achievements. Finally, the study points out some recommendations.
Busola Odubela Ajibola
Gender-based violence (GBV) is globally recognized as a public health issue. The specific focus of this research is violence against women (VAW), as statistics continue to show that women are more likely to fall victims of violence by virtue of their gender. This study investigates the prevalence, pattern and causal factors for violence against female undergraduates in Moshood Abiola Polytechnic, Abeokuta, Nigeria. In addition, the study examines the causes and effects of this malaise on victims. Possible ways of reducing occurrence of VAW against female undergraduates are also proffered. The study is cross-sectional, analytical and descriptive, in nature. It made use of secondary data source like; academic papers, newspaper publications, online publications ands so on. Data were collected with a pilot tested, semi-structured questionnaire; self-administered by the respondents. Data were analyzed with the Epi. Info software. Respondents were selected using a 3-level multistage sampling technique. Results and conclusion are based on valid responses only.
Science Journal of Public Health
kassahun Gebeyehu
Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences
Zarina Mohd Zain
https://www.ijhsr.org/IJHSR_Vol.7_Issue.11_Nov2017/IJHSR_Abstract.031.html
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research (IJHSR)
Background: Studies have shown that violence against women which is manifested in multiple forms is increasingly seen as a major public health concern. The findings from a study conducted in Kenya indicated that 46% of ever-married women have experienced any type of intimate partner violence. This is a problem affecting people from all walks of life, in Kenya, information on most aspects of gender based violence is inadequate and there is great need for research on all aspects gender based violence and therefore this research seeks to fill this gap by assessing the predisposing factors attending the Nairobi women's hospital, in Nairobi Kenya. Objective: Assessing the predisposing factors associated with Gender-based violence amongst married women attending Nairobi Women's Hospital. Methodology: The study was a hospital based cross-sectional study conducted at gender violence and recovery Centre of Nairobi Women's Hospital in Nairobi, Kenya, where 325 gender based violence victims visiting the facility were recruited to participate in the study. Data was collected using questionnaires and focus group discussions and the predisposing factors to be analyzed were age, marital status, economic status and education level. The data from the questionnaire forms were coded and entered in the Ms-Access, which was then analyzed using STATA version 13and the association was tested using chi-square at 5%confidence level. Data collected from Focus Group Discussions was sorted manually based on themes developed from issues arising from responses, transcribed translated and coded. Results: Age (P<0.0001), marital status (p=0.015), whether the victim was alone during the incidence (P<0.0001), drinking habit of the victim (P=0.011), and whether perpetrator was drunk during the incidence (P=0.026) individually showed statistically significant association with the forms of violence experienced while highest level of education (P=0.575) and occupation (P=0.101) individually showed no statistical association with the forms of violence. Conclusion: Women experience gender-based violence in a number of contexts and roles, and many have accepted their situation and therefore prevention strategies should be implemented to address the spectrum of GBV women victims. Recommendation: Active campaigns to sensitize the community against gender based violence
International Journal of Health Research
Dr. Endalew G E M E C H U Sendo
Background: Sexual harassment has posed a tremendous challenge to African women both in the workplace and educational setting, and this problem has impacted women's self-esteem as well as their academic, social, and psychological wellbeing. One in five college women are victims of acquaintance rape during their academic career and less than 5% of college women who are victims of sexual assault report their victimization. However, there is limited data on sexual violence in the context of higher education in Ethiopia particularly in the study setting. This study, therefore, determined the prevalence and its associated factors among female students of Hawassa University in Ethiopia. Methods: Institution-based cross-sectional descriptive study was conducted from April to June 2013. A multistage sampling technique was used. A total of 336 female students registered as 2nd year and above were involved in the study. Data was collected using anonymous self-administered structured questionnaire. Results: A total of 336 female students took part in the study. Majority of the study participants (N = 298; 88.7%) were in the age range of 20-34 years. The mean age and standard deviation of the respondents were 21.3 ± 1.7 years. Regarding the marital status of the respondents, 307 (91.4%) of them were single. We found that, while 14.3% reported having experienced completed rape since being admitted to the university, 3% had the experience in the past years. Conclusions: This study showed a high prevalence of sexual violence against female students of Hawassa University in Ethiopia. Interventions are, therefore, required by university authorities and other stakeholders, to create a safe learning environment for female students through primary prevention of sexual violence and rehabilitation programs for the victims.
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- My Shodhganga
- Receive email updates
- Edit Profile
Shodhganga : a reservoir of Indian theses @ INFLIBNET
- Shodhganga@INFLIBNET
- Amity University, Noida
- Amity Law School
Items in Shodhganga are licensed under Creative Commons Licence Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0).

- Bibliography
- More Referencing guides Blog Automated transliteration Relevant bibliographies by topics
- Automated transliteration
- Relevant bibliographies by topics
- Referencing guides
Dissertations / Theses on the topic 'Sexual and Gender-Based Violence'
Create a spot-on reference in apa, mla, chicago, harvard, and other styles.
Consult the top 50 dissertations / theses for your research on the topic 'Sexual and Gender-Based Violence.'
Next to every source in the list of references, there is an 'Add to bibliography' button. Press on it, and we will generate automatically the bibliographic reference to the chosen work in the citation style you need: APA, MLA, Harvard, Chicago, Vancouver, etc.
You can also download the full text of the academic publication as pdf and read online its abstract whenever available in the metadata.
Browse dissertations / theses on a wide variety of disciplines and organise your bibliography correctly.
Underwood, Jennifer W. "Impacts of Gender-Based Violence and Harassment on Graduate Student Academic Functioning." VCU Scholars Compass, 2019. https://scholarscompass.vcu.edu/etd/5761.
Nemeth, Julianna Maria. "Intimate Partner and/or Sexual Gender-based Violence and Smoking in Ohio Appalachia." The Ohio State University, 2015. http://rave.ohiolink.edu/etdc/view?acc_num=osu1429731984.
Hudepohl, Adam David. "Determinants of Group Perpetrated Violence Based on Sexual Orientation." Digital Archive @ GSU, 2009. http://digitalarchive.gsu.edu/psych_theses/56.
Nordby, Linda. "Gender-based violence in the refugee camps in Cox Bazar : -A case study of Rohingya women’s and girls’ exposure to gender-based violence." Thesis, Uppsala universitet, Teologiska institutionen, 2018. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:uu:diva-353891.
Burn, Jessica Ashley. "Advancing the girl child movement: a potential mechanism to curtail sexual gender-based violence against women in South Africa." Master's thesis, Faculty of Law, 2019. http://hdl.handle.net/11427/31340.
Newton, Kerwin Mel. "Sexual and gender-based violence in international refugee law- examining whether women are effectively protected." University of Western Cape, 2021. http://hdl.handle.net/11394/7936.
Sandrine, Ndayambaje. "Sexual and Reproductive Health and Rights : - A catalysis to combat Gender-based violence in South Africa?" Thesis, Uppsala universitet, Teologiska institutionen, 2020. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:uu:diva-412211.
Wilder, Shannon Marie Johnson. "Resilience from Violence in the Transgender Community." Ohio University / OhioLINK, 2018. http://rave.ohiolink.edu/etdc/view?acc_num=ohiou1530112472869158.
Silva, Jessica. "Refugee Women's Experiences With Sexual Violence and Their Post-Migration Needs in Canada." Thesis, Université d'Ottawa / University of Ottawa, 2015. http://hdl.handle.net/10393/33163.
Olusegun, Adefolalu Adegoke. "Delayed disclosure of sexual violence incidents among victims in Newcastle, Kwazulu-Natal." Thesis, University of the Western Cape, 2010. http://etd.uwc.ac.za/index.php?module=etd&action=viewtitle&id=gen8Srv25Nme4_5849_1298535106.
The aim of this study was to identify factors associated with reporting incidents of sexual violence after seventy-two hours at the sexual assault service centre in Newcastle, KwaZulu-Natal. This descriptive study was based on retrospective analysis of 534 medical records of victims of sexual violence at the Newcastle hospital between 2005 and 2009. A data collection sheet was designed to extract information from three sources namely: the victimsâ hospital files, J88 forms and specific hospital forms that were completed for sexual assault victims. The collected data were entered into and processed for analysis using EPI INFO statistical package. Frequencies, means and standard deviations were calculated for the data set. Test of significance was also done using the Chi-square test and presented using odds ratios with 95% CI and p-value of < 0.05. The victimsâ age range was 2-81years (mean= 18.84, &sigma =13.25). Approximately 87% were female and 59.4% of the victims were aged 0-17 years. One in five victims (19.7%) was HIV positive, and most (74.4%) reported rape with vaginal penetration. Fifty-nine percent reported within 72 hours of being assaulted. The most common reason for delayed reporting (21.5%) was fear of the perpetrator. Most of the sexual assaults were committed by male (96%) and single perpetrator (90%). Nearly a third (32.4%) of the sexual violence occurred within intimate relationships and more than two-thirds (68%) knew the perpetrators. In all, 35% sustained injuries during the assault and a third (34.5%) reported the use of weapons during the assault. Nearly half of the victims (48.7%) were referred to hospital by their relatives who also accompanied them to the facility (42.1%). Of the 198 victims that were offered post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP), 87% collected the full 28-day course.
Hill, Deborah L. "Gender, Athlete Status, and Bystander Intervention in Situations of Sexual Violence." Thesis, University of Louisiana at Lafayette, 2015. http://pqdtopen.proquest.com/#viewpdf?dispub=1585859.
The prevalence of sexual violence on college campuses has reached an alarming level. With some reports indicating that almost 20% of women experience attempted or completed rape after entering college, the call for intervention is at an all-time high (Krebs et al., 2009). One of the more recent and successful interventions has come in the form of bystander intervention, which calls upon the people around when the potential for a sexually violent situation develops and encourages them to step up and intervene (Banyard, Plante, Moynihan, 2005). This study looked into how college student athletes were different than their non-athlete peers on measures of willingness to intervene and actual intervention behaviors in situations of sexual violence. Intervention behavior was measured in terms of total opportunities to intervene, total intervention actions, total inactions, the proportion of actions per opportunity, and the proportion of inactions per opportunity. For any effect of athlete status on bystander intention or behavior, these potential mediators were investigated: drinking behavior, rape supportive attitudes, exposure to sexual violence education, and social connectedness. A two-way analysis of variance indicated gender and athlete status main effects and interactions. Several regression models explored the relationships of the potential mediating variables with these effects. Athletes were less willing to intervene but reported more frequent intervention behavior than non-athletes. Drinking behavior mediated the relationship between athlete status and willingness to intervene. These results indicate the field of bystander intervention should tailor intervention techniques to fit the student athlete population, and further to include in this intervention a discussion of how drinking behavior inhibits willingness to intervene in situations of sexual violence.
Nyberg, Björn. "Sociological Perspectives on Gender and Sexual Violence in The Handmaid's Tale." Thesis, Umeå universitet, Institutionen för språkstudier, 2018. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:umu:diva-151322.
Nordquist, Angelica. "Sexual Violence in South Africa : Religious leaders as local norm entrepreneurs." Thesis, Linnéuniversitetet, Institutionen för samhällsstudier (SS), 2021. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:lnu:diva-105249.
Alexandersson, Hanna. "Indian male voices on gender equality and sexual violence : a qualitative study." Thesis, Ersta Sköndal högskola, Institutionen för socialvetenskap, 2013. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:esh:diva-2437.
Nyman, Mikaela. "‘It is just culture’ : Eight young people’s perception of the gender roles in Zambia." Thesis, Linköpings universitet, Institutionen för kultur och kommunikation, 2013. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:liu:diva-97614.
Lindsey, Rose. "Nationalism and gender : a study of war-related violence against women." Thesis, University of Southampton, 2000. http://ethos.bl.uk/OrderDetails.do?uin=uk.bl.ethos.326731.
Proulx, Geneviève. "Male Sexual and Gender-Based Violence in Schools: Barriers to Community Action and Strategies for Change. The Case of Awaso, Ghana." Thèse, Université d'Ottawa / University of Ottawa, 2012. http://hdl.handle.net/10393/20569.
Burke, Megan. "Gender and Time." Thesis, University of Oregon, 2015. http://hdl.handle.net/1794/19262.
Holmström, Elin. "Dimensions of power and gender based violence in post-disaster societies : A case study on Haiti after the 2010 earthquake." Thesis, Linnéuniversitetet, Institutionen för samhällsstudier (SS), 2018. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:lnu:diva-76343.
Odabashian, Gavin M. "“To Live Confidently, Courageously, and Hopefully": Challenging Patriarchy and Sexual Violence at Scripps College." Scholarship @ Claremont, 2013. http://scholarship.claremont.edu/scripps_theses/247.
Gilkes, Madeleine. "'There was no one who could escape this horrible situation' : gender-based violence in the American-Viet Nam war, 1954-1975." Thesis, University of York, 2000. http://etheses.whiterose.ac.uk/14040/.
Carroll, Emma. ""Was It Good For You?"/Is It Good for Us?: Implications of Sexual Scripting for Pleasure and Violence." The Ohio State University, 2019. http://rave.ohiolink.edu/etdc/view?acc_num=osu1563287501358132.
Scheer, Jillian Ryan. "Trauma-Informed Care for Sexual and Gender Minority Survivors of Intimate Partner Violence." Thesis, Boston College, 2018. http://hdl.handle.net/2345/bc-ir:107451.
Anthony, Elizabeth Ruth. "Normative Violence? The Impact of Gender-neutral Language on Self-reported Rates of Sexual Violence Victimization and Perpetration." Digital Archive @ GSU, 2008. http://digitalarchive.gsu.edu/psych_theses/52.
Souza, Cesário da Silva. "Caracterização da violência sexual em mulheres na cidade de Ribeirão Preto - SP." Universidade de São Paulo, 2012. http://www.teses.usp.br/teses/disponiveis/17/17139/tde-11082015-131209/.
Cima, Samantha. "Expanding Posttraumatic Growth: An Examination of Male Survivors of Sexual Violence." Thesis, Université d'Ottawa / University of Ottawa, 2019. http://hdl.handle.net/10393/39549.
Svensson, Julia. "Responsibility to Represent : Representation of conflict related sexual and gender-based violence; a thematic analysis of World Bank and ICRC documents." Thesis, Uppsala universitet, Teologiska institutionen, 2019. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:uu:diva-389700.
Hargis, Kathleen J. "Contextualizing Empowerment Discourse in Eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo: A Case Study of the Ushindi Project." Ohio University / OhioLINK, 2012. http://rave.ohiolink.edu/etdc/view?acc_num=ohiou1338573094.
Gammon, J. D. "Ravishment and ruin : the construction of stories of sexual violence in England, c.1640-1820." Thesis, University of Essex, 2000. http://ethos.bl.uk/OrderDetails.do?uin=uk.bl.ethos.326830.
Saxena, Anshul. "Theory of Gender and Power: Intimate Partner Violence, HIV Status and Sexual Risk Behaviors in Haitian Women." FIU Digital Commons, 2017. http://digitalcommons.fiu.edu/etd/3200.
Mazimhaka, Anne P. Inturire. "Much to be done: towards an effective transitional justice model for dealing with conflict-related crimes of sexual and gender-based violence." Master's thesis, University of Cape Town, 2014. http://hdl.handle.net/11427/4719.
McGraw, Lora K. "Challenging masculinities: a program analysis of male-based university sexual violence prevention programs." Thesis, Kansas State University, 2017. http://hdl.handle.net/2097/35389.
Liljeroos, Thea. "Caring for migrant women affected by sexual and gender-based violence: Experiences of healthcare providers in Europe and North America : A meta-synthesis." Thesis, Uppsala universitet, Internationell mödra- och barnhälsovård (IMCH), 2019. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:uu:diva-387825.
Walsh, Brian P. "The rape of Tokyo| Legends of mass sexual violence and exploitation during the occupation of Japan." Thesis, Princeton University, 2016. http://pqdtopen.proquest.com/#viewpdf?dispub=10120354.
Much recent writing on the Occupation of Japan has challenged the traditional picture of a well-disciplined American army laying the groundwork for Japan’s transition to democracy by the example of its behavior. Instead it depicts the Occupation, especially its opening phase, as marred by the widespread rape of Japanese women by American servicemen. In addition, many writers claim the United States encouraged, requested or even ordered the Japanese government to establish brothels for its troops. Copious documentation of American behavior from both Japanese and American sources does not support such claims. Rather, it makes very clear that though there were a fair number of reported rapes of Japanese women by American and other Allied servicemen, stories of mass rape during any period of the Occupation, including its opening phase, are simply not credible. In addition the contemporary record suggests that American authorities regarded prostitution not as a benefit for their troops, but as an entrenched social problem which they tolerated reluctantly. This raises the question of how such stories became incorporated into the mainstream. Part of the reason for this was the psychic environment in which these stories were originally created. There is an innate and deep-seated association between rape and war in the human psyche. The Japanese understanding of war in the mid-twentieth century reinforced this association. Rape also served as a metaphor for the American conquest of Japan. GHQ robbed Japanese men of their control of women’s sexuality. Many women then used their sexual autonomy to consort with American soldiers. To many this seemed like a hypocritical seizure of Japanese women, a rape of sorts. Shortly after the Occupation ended a leftist anti-American propaganda campaign and a boom in exploitation literature coincided to produce a great number of works purporting to be true exposes of American cruelties. Though these books are wholly unreliable, and contradict contemporary evidence, many have been incorporated into mainstream history. This is an error. Stories of mass rape and organized sexual exploitation during the Occupation are better understood as metaphoric expressions of the humiliation of defeat, occupation and continuing diplomatic subordination, than as history.
Back, Madeleine. "Determinants of Intimate Partner SexualViolence against Women in India." Thesis, Mittuniversitetet, Institutionen för hälsovetenskap, 2020. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:miun:diva-41032.
Betyg i Ladok 201214.
Kumar, Megha. "Communal riots, sexual violence and Hindu nationalism in post-independence Gujarat (1969-2002)." Thesis, University of Oxford, 2009. http://ora.ox.ac.uk/objects/uuid:2b06b4e0-afac-4571-ab46-44968d36b17c.
Pia, Christina Kalus. "Redressing female victims of sexual violence: possibilities for gender-specific reparations at the International Criminal Court." Thesis, University of the Western Cape, 2011. http://etd.uwc.ac.za/index.php?module=etd&action=viewtitle&id=gen8Srv25Nme4_1824_1373278492.
This paper is about the reparations regime of the International Criminal Court and reparations possibilities for victims of sexual violence. It will contain a legal analysis of the reparations system of the Court, including the Trust Fund for Victims of the International Criminal Court. In a second step, the needs of women who experienced conflict related violence will be examined. The central question, which this paper will try to answer, is whether the ICC reparations regime has the ability to provide gender-sensitive reparations and thus make a contribution to the improvement of women&rsquo s lives in post-conflict societies.
Gomes, Melissa Elisabete Silva Lopez. "Mulheres refugiadas na União Europeia : políticas, percursos e violência de género." Master's thesis, Instituto Superior de Economia e Gestão, 2020. http://hdl.handle.net/10400.5/20942.
Källvik, Emma. "A Critical Discourse Analysis of Sexual Violence and Power : #metoo in Swedish media." Thesis, Linköpings universitet, Tema Genus, 2018. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:liu:diva-149794.
Mbesherubusa, Mittag Danielle. "Persistent, ‘Me Too’? Voices from the Past : An Analysis of Testimonials on Sexual and Gender-Based Violence in the Congo Free State (1885-1908)." Thesis, Malmö universitet, Institutionen för konst, kultur och kommunikation (K3), 2021. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:mau:diva-45698.
Ozel, Gulen. "Sexual Violence Against Women In Civil Wars: An Analysis Of Yugoslavian Civil War." Master's thesis, METU, 2006. http://etd.lib.metu.edu.tr/upload/12607244/index.pdf.
Engström, Sara. "The Narrative of Conflict Minerals : An Exploration of Sexual Gender-Based Violence and Socioeconomic Impacts of the Dodd-Frank Act in the Eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo." Thesis, Uppsala universitet, Statsvetenskapliga institutionen, 2017. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:uu:diva-324548.
Hamel, Marie-Eve. "Mediated voices : nation/state-building, NGOs and survivors of sexual violence in postconflict Rwanda and Bosnia-Herzegovina." Thesis, University of Edinburgh, 2016. http://hdl.handle.net/1842/23509.
Melake, Yordanos. "Women in Conflict: The Relationship between Female Participation in Non-State Armed Groups and Sexual Violence." Thesis, Uppsala universitet, Institutionen för freds- och konfliktforskning, 2019. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:uu:diva-385112.
Peltola, Larissa. "Rape and Sexual Violence Used as a Weapon of War and Genocide." Scholarship @ Claremont, 2018. http://scholarship.claremont.edu/cmc_theses/1965.
Kline, Kathleen Elizabeth. "Collegiate dating violence: A quantitative analysis of attachment style and help -seeking behavior by gender and sexual orientation." ScholarWorks, 2009. https://scholarworks.waldenu.edu/dissertations/726.
Krolnik, Campos Monica. "The Impact of Sexual Assault Training and Gender on Rape Attitudes." CSUSB ScholarWorks, 2019. https://scholarworks.lib.csusb.edu/etd/796.
Coleman, Anne M. "The clinician's experience of working in complex psychological trauma (CPT), gender based violence/childhood sexual abuse : an interpretative phenomenological analysis of the impact of CPT work." Thesis, Glasgow Caledonian University, 2015. https://ethos.bl.uk/OrderDetails.do?uin=uk.bl.ethos.743884.
Schmitz, Kelsey Catherine. "Shut Up and Play, or Get Out: A Pedagogy of Gendered Digital Identities in Video Gaming." Thesis, Université d'Ottawa / University of Ottawa, 2018. http://hdl.handle.net/10393/38053.
Andrade, Adathiane Farias de. "Rompendo o silêncio: uma análise sobre as histórias de meninas com vivências de abuso sexual atendidas pelo CREAS do município de João Pessoa." Universidade Federal da Paraíba, 2011. http://tede.biblioteca.ufpb.br:8080/handle/tede/7224.
University of South Florida
Main Navigation

Emanuelle M. Dias, PhD, MPH, CPH. (Photo courtesy of Dias)
From tragedy to triumph: One alum’s path to the U.S. Army
- Liz Bannon, College of Public Health
- April 19, 2024
- Alumni & Development
USF College of Public Health (COPH) alumna Emanuelle Dias is a proud native Floridian who grew up in South Florida. When she was 14 years old, her mother passed away from breast cancer which inspired her healing journey through education, research and cancer prevention.
Dias began her education at the University of Florida as a pre-med student. She was halfway through her first year when she started exploring different paths. “I took an introduction to health disparities class and knew in that moment it was exactly what I wanted to have a career in,” she said.
After graduating, Dias decided to pursue her master of public health at the COPH. “I knew that it was the number one program in the state and I would be able to work with my mentor, former COPH professor Dr. Alicia Best,” Dias said. “We had very similar backgrounds, both losing our mothers to breast cancer, and that was part of our public health journey that connected us. It just felt right to be at USF.”
Dias said one of the most memorable experiences she had was in March of 2019 with the International Health Service Collaborative , a group of USF Health students, faculty and professionals focused on promoting sustainable health in underserved communities abroad.
“We went on a medical mission trip to Jamaica for a week during spring break,” she said. “It was incredible because one of the students was from Jamaica and helped make many connections and contacts there for us. We were able to squeeze in some fun time too.”

Dias, pictured front row and second from the left, conducted a one-week medical mission trip to Montego Bay, Jamaica in March 2019 with the International Health Service Collaboration. (Photo courtesy of Dias)
Dias points to two people who inspired her during her time at the COPH.
“ Dr. Dinorah "Dina" Martinez Tyson embodies being a community-engaged researcher. Her cancer survivorship camp motivated and inspired me to be the type of researcher that I'm still working on being. The kind of public health professional that I strive to be,” Dias said. “Then, Dr. Mahmooda Pasha believed in me and encouraged me to take on a PhD.”
Dias also participated in a leadership training that promoted Latino researchers to get their PhD's in public health. “After that, I knew I wanted to do research in the cancer prevention space,” she said. Dias became involved with the Florida Prevention Research Center with Dr. Pasha and Professor Dr. Claudia Parvanta . “The center allowed me to build strong research experience, work on presentations and publications and allowed me to become a competitive applicant going into a PhD program,” Dias said. Dias was accepted to the University of Texas Health Science Center in Houston for her PhD where she is currently residing. “Houston is very much a cancer prevention research hub,” Dias said. “It aligned with my journey and so I grew my research skills, solidified myself as a scientist and was able to expand and become a research professional.”
During her PhD program, Dias said she was funded by a National Cancer Institute predoctoral fellowship, which allowed her to focus on her dissertation.
Dias graduated in December 2023 with a PhD in public health, with a focus in health promotion and behavioral sciences.
“After I graduated, I had to decide what was next,” she said. “I could have gone the typical route and stayed in academia and go through with the postdoctoral fellowship, but I decided to leave to explore some other sectors.”
In January 2024, Dias was offered a position as an Oak Ridge Institute for Science and Education fellow with the U.S. Department of the Army.
“This was something I honestly never envisioned myself doing. No one in my family has been enlisted and I don’t know a lot of Army folks, but it has been a really rewarding experience. I’ve even visited Washington, D.C., and the Pentagon through my work!”

D ias, pictured front row on the far left, in the Pentagon Library and Conference Center, March 2024 with the Integrated Prevention Advisory Group, the U.S. Army's new primary prevention workforce. (Photo courtesy of Dias)
“I'm part of an integrated prevention division,” Dias said. “We are working on preventing harmful behaviors including sexual assault, suicide, substance misuse, child mistreatment and domestic partnership violence.” “I’m working at the strategic level to build this workforce,” Dias said. “This infrastructure is solidifying a research agenda. As this has never existed, we're starting from scratch. I’ve been working on literature review and scanning strategic initiatives at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and other government organizations to align with our organization.” For the future, Dias says she will most likely stay in the government sector but she’s also interested in going into the private sector, like a research institution. No matter where she ends up, she says the journey she started after her mom’s passing feels complete.
“There's so much opportunity and public health continues to grow. The U.S. Army is developing a public health infrastructure, and I know we will continue to see these various roles across different sectors.”

Dias presented a poster exploring the association between maternal and paternal characteristics and the risk of colorectal cancer in adult offspring at the American Society of Preventive Oncology in March 2023 in San Diego, California. (Photo courtesy of Dias)
Fast Five What did you dream of becoming when you were young? I wanted to be a medical doctor. Where would we find you on the weekend? I am very active, so I love weightlifting and yoga.
What is the last book you read? “Everything I Know About Love” by Dolly Alderton. What superpower would you like to have? Teleportation, so I can get to places quickly.
What is your all-time favorite movie? “The Proposal” with Sandra Bullock. It’s one of the last movies that I watched with my mom before she passed.
Return to article listing
Emanuelle Dias
Explore More Categories
- Awards & Honors
- College News
- Community Engagement
- In the Media
- Research & Innovation
- Student Life
- USF SafetyFlorida
About Department News
Welcome to the USF COPH news page. Our marketing and communications team is entrusted with storytelling. Through written stories, photography, video and social media we highlight alumni, faculty, staff and students who are committed to passionately solving problems and creating conditions that allow every person the universal right to health and well-being. These are our stories.
Evan Stark, who expanded definition of domestic violence, dies at 82
By explaining the patterns of domination often at the root of domestic violence, the sociologist helped improve services for victims as well as their treatment under the law.

Evan Stark, a sociologist who helped broaden the definition of domestic violence beyond physical assault to include the patterns of domination often at its root, a shift that improved services for victims as well as their treatment under the law, died March 17 at his home in Woodbridge, Conn. He was 82.
His wife and academic collaborator, Anne Flitcraft, confirmed his death. He was on a Zoom call with domestic violence advocates in British Columbia when he had an apparent heart attack, Flitcraft said.
Dr. Stark was a self-described “veteran radical sociologist” who participated in the civil rights movement and led protests against the Vietnam War before turning his attention to domestic violence — “an epidemic problem that has been invisible,” he once said — when a friend in Minnesota helped open one of the country’s first shelters for battered women in the 1970s.
As a sociologist, author, expert witness and advocate, Dr. Stark challenged pervasive misconceptions about domestic violence, which is primarily, although not universally, inflicted upon women. One of the most pernicious myths is the notion that women who remain in abusive relationships do so willingly.
“You would never ask why a hostage or kidnapping victim stays — or why they finally retaliate,” Dr. Stark once said.
In the 1980s, advocates created a diagram known as the “Power and Control Wheel” to represent the tactics often employed by abusers to keep their victims from leaving. Those tactics might include belittling a woman to degrade her self-esteem, isolating her from her friends and family, limiting her access to money, surveilling her activities and threatening violence on her or her children.
Dr. Stark encapsulated such behaviors under the term “coercive control,” a concept he outlined in books including “Coercive Control: The Entrapment of Women in Personal Life” (2007) and “Children of Coercive Control” (2023).
“He singularly articulated the real double binds that define the lives of battered women,” said Nancy Grigsby, a member of the advisory group for the Battered Women’s Justice Project and a longtime domestic violence advocate in Ohio.
With his work, she continued, Dr. Stark helped demonstrate that “battered women live in a landscape where their daily choices are defined and confined by the possible consequences that their partners might impose.”
For example, shelters and protective orders do little to help women who live in justified fear of availing themselves of such options. Informed by the concept of coercive control, advocates expanded their efforts beyond the immediate prevention of homicide and injury to also address the underlying forces that keep women in relationships of physical violence — and to help them get out.
Dr. Stark often testified as an expert witness in court, notably in a federal class-action suit brought in New York on behalf of abused women whose children were forcibly placed in foster care by New York City’s Administration for Children’s Services on the grounds that the women had neglected their children by keeping them in violent situations.
In his expert report, Dr. Stark argued that “removal of a young child from its primary caretaker can be particularly traumatic where domestic violence has occurred and should be used only as a last resort and in the face of evidence that the child faces imminent harm.”
Regarding the abused mothers, he “talked about coercive control … though he did not call it that in the context of this lawsuit,” Jill M. Zuccardy, one of the lead lawyers for the plaintiffs, wrote in an email. “He understood at a time when many did not that domestic violence was so much more than just violence.”
Judge Jack B. Weinstein of the U.S. District Court in Brooklyn found in favor of the women in 2002, writing that “the pitiless double abuse of these mothers is not malicious, but is due to benign indifference, bureaucratic inefficiency, and outmoded institutional biases.”
Sharwline Nicholson, the lead plaintiff in the case, was a 32-year-old mother of two when the father of her younger child attacked her in 1999, leaving her bleeding from the head and with a broken arm and fractured ribs.
She asked a trusted neighbor to care for her children before calling an ambulance for herself. At a hospital, she learned that authorities had taken custody of them. Her children were placed in foster case — initially with no legal authorization — where they remained for several weeks.
“The blame from the city was more to the woman,” Nicholson said in a telephone interview after Dr. Stark’s death. “Evan Stark came in and explained where a woman’s mind-set would be after they had been beaten or were a victim of violence,” she continued, adding that “he made things even clearer for survivors themselves.”
Early activism
Evan David Stark was born in Manhattan on March 10, 1942, and grew up in Queens, the Bronx and Yonkers, N.Y. His father was a novelist, poet and professor at the City College of New York, and his mother did administrative work for the Brotherhood of Sleeping Car Porters, the African American labor union.
Dr. Stark joined the civil rights movement as a member of the Congress of Racial Equality. He received an undergraduate degree from Brandeis University in Waltham, Mass., in 1963, before entering a graduate sociology program at the University of Wisconsin at Madison.
In 1967, he helped lead a demonstration at Madison against on-campus recruiting by Dow Chemical, a manufacturer of napalm. The protest, which left dozens injured when police used nightsticks and tear gas to break it up, attracted national attention.
Dr. Stark had received his master’s degree at that point but left Madison after the protest, suspending his doctoral studies. He lived briefly in Canada before returning to the United States, where he did antipoverty work in Minnesota and helped lead the Honeywell Project, a protest campaign against Honeywell Inc., one of the state’s largest employers, over its manufacture of antipersonnel fragmentation bombs.
In the 1970s, Dr. Stark and Flitcraft were living in New Haven, Conn., where she was a medical student at Yale University. They became involved in domestic violence advocacy and opened their home to women fleeing abusive relationships.
Flitcraft pursued a thesis examining the medical profession’s treatment of domestic violence victims. Recalling the language used at the time, she said in an interview that a typical patient chart might note that a woman had been “hit in the head by a glass ashtray,” without noting who had thrown the object at her.
Furthermore, Flitcraft said, many physicians failed to understand the recurrent nature of much domestic abuse. When a patient returned again and again with injuries, the hospital treated each incident separately, without addressing the blatant pattern of abuse.
At the time, Dr. Stark was employed at Yale’s Institution for Social and Policy Studies. Working together, he and his wife received a grant from the National Institute of Mental Health to expand on Flitcraft’s study.
The result of their work, an article titled “Medicine and Patriarchal Violence: The Social Construction of a ‘Private’ Event,” was published in the International Journal of Health Services in 1979. Having examined the records of 481 women treated at a New Haven hospital for a total of more than 1,400 cases of trauma, they determined that battering was approximately 10 times more common than doctors acknowledged.
With his wife, Dr. Stark later wrote the book “Women at Risk: Domestic Violence and Women’s Health” (1996).
Dr. Stark received a PhD in sociology in 1984 from Binghamton University, part of the State University of New York, according to his wife. He spent much of the rest of his career at Rutgers University in New Jersey, where he taught in fields including public health and women’s studies. His degrees also included a master’s of social work from Fordham University in 1991.
His marriage to Sally Connolly ended in divorce. Besides his wife, of Woodbridge, survivors include a son from his first marriage, Aaron Stark of New Haven, Conn.; three sons from his second marriage, Sam Stark of Cambridge, Mass., Daniel Stark of Jacksonville, Fla., and Eli Stark of Holyoke, Mass.; a sister; and three grandchildren.
Working with local advocates, Dr. Stark helped persuade numerous nations to criminalize coercive control in recent years. England and Wales, Ireland and Scotland were among the first international jurisdictions to take that step.
In the United States, only Hawaii “followed suit in the criminal law,” but several states “have incorporated coercive control into the civil law with his help,” according to Joan S. Meier, director of the National Family Violence Law Center at George Washington University’s law school.
“Domestic abuse is a crime against the whole community because the community cannot thrive without women’s full participation,” Dr. Stark once said in a speech. He hoped, he remarked in another , to “have made significant inroads into ending violence against women and children.”

Stanford Humanities Today
Arcade: a digital salon.

Hope: The Future of an Idea | 2024 Spring Salon
Where is hope in humanities research? Perhaps it's a concept with a particular history, perhaps a force whose effects are latent or invisible; or it may be absent altogether for reasons to explain. Does hope motivate one's work? What does hope mean intellectually and personally?
Please join us for brief responses to these questions by current fellows, followed by a general discussion with Q&A moderated by SHC Director Roland Greene . The event will conclude with a reception.
About the Speakers
Samia Errazzouki (Mellon Postdoctoral Fellow) is a historian of early Northwest Africa. She holds a PhD in history from the University of California, Davis and an MA in Arab Studies from Georgetown University. Her research and teaching focuses on trans-regional histories of racial capitalism, slavery, and empire. Errazzouki formerly worked as a Morocco-based journalist with the Associated Press, and later, with Reuters. She is currently a co-editor of Jadaliyya and assistant editor of The Journal of North African Studies .
Jisha Menon (Violet Andrews Whittier Internal Fellow) is Professor of Theater and Performance Studies, and, by courtesy, of Comparative Literature at Stanford University. She is the author of Brutal Beauty: Aesthetics and Aspiration in Urban India (Northwestern UP, 2021) and The Performance of Nationalism: India, Pakistan and the Memory of Partition (Cambridge UP, 2013). She is also co-editor of two volumes: Violence Performed: Local Roots and Global Routes of Conflict (Palgrave-Macmillan Press, 2009) and Performing the Secular: Religion, Representation, and Politics (Palgrave Macmillan, 2017).
Joseph Wager (SHC Dissertation Prize Fellow) is a PhD Candidate in Iberian and Latin American Cultures at Stanford University. He is writing a dissertation focused on the form of the stories about desaparecidos, what is said about desaparecidos, in contemporary Colombia and Mexico. The dissertation places social-scientific inquiry, the work of activists and collectives, and legal instruments in dialogue with art installations, film, novels, performances, and poems. Underpinning this combination is 1. the idea that human-rights changes stem from how individual and collective actions resist institutionalization or translate into institutions and 2. that cultural products (e.g., art) and their form are crucial to the understanding of such processes.
Ya Zuo (External Faculty Fellow) is an associate professor of History at University of California, Santa Barbara. She is a cultural historian of middle and late imperial China. She is the author of Shen Gua’s Empiricism (Harvard University Press, 2018) and a range of articles on subjects such as theory of knowledge, sensory history, medical history, book history, and the history of emotions.

Stanford Humanities Center 424 Santa Teresa Street
Also online via Zoom

Discovering Humanities Research at Stanford

Stanford Humanities Center
Advancing Research in the Humanities
Humanities Research for a Digital Future

The Humanities in the World
- Annual Reports
- Humanitrees
- Humanities Center Fellows
- Advisory Council
- Director's Alumni Cabinet
- Honorary Fellows
- Hume Honors Fellows
- International Visitors
- Workshop Coordinators
- Why Humanities Matter
- Fellowships for External Faculty
- Fellowships for Stanford Faculty
- Mellon Fellowship of Scholars in the Humanities
- Dissertation Fellowships FAQs
- Career Launch Fellowships
- Fellowships for Stanford Undergraduates
- International Visitors Program
- FAQ Mellon Fellowship
- Faculty Fellowships FAQ
- Events Archive
- Public Lectures
- Checklist for Event Coordinators
- Facilities Guidelines
- co-sponsorship from the Stanford Humanities Center
- Call for Proposals
- Manuscript Workshops
- Past Workshops
- Research Workshops

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This thesis foregrounds data from a survivor-led, qualitative study on domestic violence and abuse (DVA) prevention and intervention, set against the backdrop of UK austerity and the increasingly prominent political endorsement of a gender-neutral conceptualisation of DVA. The study charts how
Dissertation Advisor: Dr. S. Bryn Austin Avanti Adhia Predictors and Consequences of Intimate Partner Violence Impacting Children and Youth Abstract Intimate partner violence (IPV) is a substantial public health problem in the United States with profound implications for the health and well-being of individuals. This dissertation
interpersonal violence and one-fifth are attributed war. New scholarship has shown how violence can spread across populations temporally and spatially. Yet the link between armed conflict and postconflict interpersonal violence is poorly documented. Methods: This dissertation will use multilevel modeling to assess the link between levels of armed
Chapter 1: Introduction to the Thesis 1 Aim and structure of Thesis 12 Chapter 2: The association between adolescents' attitudes towards adolescent intimate partner violence and reported perpetration and/or victimisation among community samples: A Systematic Review. 14 Chapter 2 rationale 14 Abstract 15 Introduction 16 Method 24 Results 44
Niaosong Dist., Kaohsiung City 833, Taiwan. 2 College of Nursing, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung City 807, Taiwan. * Correspondence: [email protected]; Tel.: +886-7-3121101 (ext. 2625 ...
This thesis focuses on police response to domestic violence and in so doing addresses some of the more fundamental issues associated with the subject. The research draws heavily on Evan Stark's (2007) articulation of a typology of domestic violence which has 'coercive control' as its most insidious element. Coercive control is:
PhD Thesis, London: London Metropolitan University. Available at: ... As a result, research on domestic and sexual violence is subject to obstructive intervention by RECs (Downes et al., ...
Publications by Type: Thesis. Download Citations. 2016. Meyersfield B. A Theory of Domestic Violence in International Law. Yale Law School Dissertations. 2016; (3). Publisher's Version Abstract.
violence, are used in the thesis to broaden the scope of what nonviolence might mean. Following from this, the project looks at three different concrete ways in which violence, and definitions of ... myself for writing this thesis. A PhD is, for better and worse, a fairly unique process, and for me there have definitely been a good amount of ...
For her PhD thesis entitled "Sexual Violence in Armed Conflict: Threat, Mobilization and Gender Norms," she received the 2020 Christiane Rajewsky Prize for junior conflict researchers from the German Association for Peace and Conflict Studies. References. Boesten, Jelke, and Marsha Henry. 2018. "Between Fatigue and Silence: The Challenges ...
This literature review of research in the past 30 years on domestic violence. against women focuses on the cycle of violence within abusive relationships, why women. so frequently stay in abusive relationships,'and what is the most helpful in allowing them. to leave.
Utuza, Aimée Josephine, "Gender-Based Violence among Women and Girls with Disabilities in Sub-Saharan African Countries: A Scoping Review of the Literature" (2021). Electronic Thesis and Dissertation Repository. 8189. https://ir.lib.uwo.ca/etd/8189 This Dissertation/Thesis is brought to you for free and open access by Scholarship@Western.
The dissertation argues for the inclusion of other key factors, namely narratives, leadership and organisation. These three factors are important for explaining the 'how' and 'why' within the political trajectories of the Ogoni and Ijaw in terms of nonviolence and violence. This more nuanced
Thesis Summary Victim blaming and self-blame are common experiences for women who have been subjected to sexual violence and abuse. This thesis employs a comprehensive mixed-methods approach from ...
This thesis foregrounds data from a survivor-led, qualitative study on domestic violence and abuse (DVA) prevention and intervention, set against the backdrop of UK austerity and the increasingly prominent political endorsement of a gender-neutral conceptualisation of DVA. The study charts how DVA prevention, victimhood and perpetration discourses might be productively reworked to shift the ...
ISS 23343745 197 Februar 2019 PERSPECTIVES ON TERRORISM Volume 13, Issue 1 475 Academic Theses (Ph.D. and MA) on Countering Violent Extremism (CVE), Preventing Violent Extremism (PVE) and
Yamawaki N., Ostenson J., Brown C. (2009). The functions of gender role traditionality, ambivalent sexism, injury, and frequency of assault on domestic violence perception: A study between Japanese and American college students. Violence against Women 15(9): 1126-1142.
This thesis has been submitted to fulfill requirements for a Bachelor of International and Global Studies (Honours) in Government and International Relations. Word Count: 19,501 Gender-Based Violence Crimes in Conflict: A Discourse Analysis of International Justice Mechanisms By Charlotte Carney SID: 460 366 030
Violence against women is one of the most widespread, persistent and detrimental violations of human rights in today's world, which has not been reported in most cases due to impunity, silence, stigma and shame, even in the age of social communication. Domestic violence against women harms individuals, families, and society. The objective of this study was to investigate the prevalence and ...
application of violence. This doctoral thesis reports on the findings derived as part of an action research conducted in two secondary schools in Zimbabwe, urban and rural respectively, with young ... motivated me and reminded me that the PhD was within my reach, I had to be patient, resilient and overcome my challenges. ...
Gibbons, R.E. (2010) Violence against women on the college campus: Evaluating anti-violence programming (unpublished dissertation). Heise L. Violence against women: global organizing for change. In: Edleson JL, Eisikovits ZC, editors. Future interventions with battered women and their families. Thousand Oaks, California: Sage Publications, 1996.
The Shodhganga@INFLIBNET Centre provides a platform for research students to deposit their Ph.D. theses and make it available to the entire scholarly community in open access. Shodhganga@INFLIBNET. Amity University, Noida. Amity Law School.
Thesis (PhD) — Boston College, 2018 Submitted to: Boston College. Lynch School of Education ... In each conflict that is examined in this thesis, sexual violence is used against civilian populations for the specific purpose of genocide. 46 Kline, Kathleen Elizabeth. "Collegiate dating violence: A quantitative analysis of attachment style and ...
During her PhD program, Dias said she was funded by a National Cancer Institute predoctoral fellowship, which allowed her to focus on her dissertation. Dias graduated in December 2023 with a PhD in public health, with a focus in health promotion and behavioral sciences. ... child mistreatment and domestic partnership violence." "I'm ...
By Emily Langer. April 17, 2024 at 3:05 a.m. EDT. Sociologist Evan Stark died March 17 at his home in Woodbridge, Conn. (Family photo) Evan Stark, a sociologist who helped broaden the definition ...
She is also co-editor of two volumes: Violence Performed: Local Roots and Global Routes of Conflict (Palgrave-Macmillan Press, 2009) and Performing the Secular: Religion, Representation, and Politics (Palgrave Macmillan, 2017). Joseph Wager (SHC Dissertation Prize Fellow) is a PhD Candidate in Iberian and Latin American Cultures at Stanford ...