

Law Firm Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky

Law Firm Plan
Over the past 20+ years, we have helped over 1,000 lawyers to create business plans to start and grow their law firms. On this page, we will first give you some background information with regards to the importance of business planning. We will then go through a law firm business plan template step-by-step so you can create your plan today.
Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here >
What is a Law Firm Business Plan?
A business plan provides a snapshot of your law firm as it stands today, and lays out your growth plan for the next five years. It explains your business goals and your strategy for reaching them. It also includes market research to support your plans.
Why You Need a Business Plan for a Law Firm
If you’re looking to start a law firm, or grow your existing law firm, you need a business plan. A business plan will help you raise funding, if needed, and plan out the growth of your law firm in order to improve your chances of success. Your law firm plan is a living document that should be updated annually as your company grows and changes.
Sources of Funding for Law Firms
With regards to funding, the main sources of funding for a law firm are personal savings, credit cards and bank loans. With regards to bank loans, banks will want to review your business plan and gain confidence that you will be able to repay your loan and interest. To acquire this confidence, the loan officer will not only want to confirm that your financials are reasonable, but they will also want to see a professional plan. Such a plan will give them the confidence that you can successfully and professionally operate a business.
Finish Your Business Plan Today!
How to write a business plan for a law firm.
If you want to start a law firm or expand your current one, you need a business plan. Below are links to each section of your law firm plan template:
Executive Summary
Your executive summary provides an introduction to your business plan, but it is normally the last section you write because it provides a summary of each key section of your plan.
The goal of your Executive Summary is to quickly engage the reader. Explain to them the type of law firm you are operating and the status. For example, are you a startup, do you have a law firm that you would like to grow, or are you operating law firms in multiple cities?
Next, provide an overview of each of the subsequent sections of your plan. For example, give a brief overview of the law firm industry. Discuss the type of law firm you are operating. Detail your direct competitors. Give an overview of your target customers. Provide a snapshot of your marketing plan. Identify the key members of your team. And offer an overview of your financial plan.
Company Analysis
In your company analysis, you will detail the type of law firm you are operating.
For example, you might operate one of the following types of law firms:
- Commercial Law : this type of law firm focuses on financial matters such as merger and acquisition, raising capital, IPOs, etc.
- Criminal, Civil Negligence, and Personal Injury Law: this type of business focuses on accidents, malpractice, and criminal defense.
- Real Estate Law: this type of practice deals with property transactions and property use.
- Labor Law: this type of firm handles everything related to employment, from pensions/benefits, to contract negotiation.
In addition to explaining the type of law firm you will operate, the Company Analysis section of your business plan needs to provide background on the business.
Include answers to question such as:
- When and why did you start the business?
- What milestones have you achieved to date? Milestones could include the number of clients served, number of cases won, etc.
- Your legal structure. Are you incorporated as an S-Corp? An LLC? A sole proprietorship? Explain your legal structure here.
Industry Analysis
In your industry analysis, you need to provide an overview of the law firm industry.
While this may seem unnecessary, it serves multiple purposes.
First, researching the law firm industry educates you. It helps you understand the market in which you are operating.
Secondly, market research can improve your strategy, particularly if your research identifies market trends.
The third reason for market research is to prove to readers that you are an expert in your industry. By conducting the research and presenting it in your plan, you achieve just that.
The following questions should be answered in the industry analysis section of your law firm plan:
- How big is the law firm industry (in dollars)?
- Is the market declining or increasing?
- Who are the key competitors in the market?
- Who are the key suppliers in the market?
- What trends are affecting the industry?
- What is the industry’s growth forecast over the next 5 – 10 years?
- What is the relevant market size? That is, how big is the potential market for your law firm? You can extrapolate such a figure by assessing the size of the market in the entire country and then applying that figure to your local population.
Customer Analysis
The customer analysis section of your law firm plan must detail the customers you serve and/or expect to serve.
The following are examples of customer segments: businesses, households, and government organizations.
As you can imagine, the customer segment(s) you choose will have a great impact on the type of law firm you operate. Clearly, households would respond to different marketing promotions than nonprofit organizations, for example.
Try to break out your target customers in terms of their demographic and psychographic profiles. With regards to demographics, include a discussion of the ages, genders, locations and income levels of the customers you seek to serve. Because most law firms primarily serve customers living in their same city or town, such demographic information is easy to find on government websites.
Psychographic profiles explain the wants and needs of your target customers. The more you can understand and define these needs, the better you will do in attracting and retaining your customers.
Finish Your Law Firm Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Competitive Analysis
Your competitive analysis should identify the indirect and direct competitors your business faces and then focus on the latter.
Direct competitors are other law firms.
Indirect competitors are other options that customers have to purchase from that aren’t direct competitors. This includes accounting firms or human resources companies. You need to mention such competition as well.
With regards to direct competition, you want to describe the other law firms with which you compete. Most likely, your direct competitors will be law firms located very close to your location.
For each such competitor, provide an overview of their businesses and document their strengths and weaknesses. Unless you once worked at your competitors’ businesses, it will be impossible to know everything about them. But you should be able to find out key things about them such as:
- What types of customers do they serve?
- What types of cases do they accept?
- What is their pricing (premium, low, etc.)?
- What are they good at?
- What are their weaknesses?
With regards to the last two questions, think about your answers from the customers’ perspective. And don’t be afraid to ask your competitors’ customers what they like most and least about them.
The final part of your competitive analysis section is to document your areas of competitive advantage. For example:
- Will you provide better legal advice and services?
- Will you provide services that your competitors don’t offer?
- Will you provide more responsive customer interactions?
- Will you offer better pricing or flexible pricing options?
Think about ways you will outperform your competition and document them in this section of your plan.
Marketing Plan
Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P’s: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. For a law firm plan, your marketing plan should include the following:
Product : In the product section, you should reiterate the type of law firm company that you documented in your Company Analysis. Then, detail the specific products you will be offering. For example, in addition to in-person consultation, will you provide virtual meetings, or any other services?
Price : Document the prices you will offer and how they compare to your competitors. Essentially in the product and price sub-sections of your marketing plan, you are presenting the products and services you offer and their prices.
Place : Place refers to the location of your law firm company. Document your location and mention how the location will impact your success. For example, is your law firm located in a busy business district, office building, etc. Discuss how your location might be the ideal location for your customers.
Promotions : The final part of your law firm marketing plan is the promotions section. Here you will document how you will drive customers to your location(s). The following are some promotional methods you might consider:
- Advertising in local papers and magazines
- Reaching out to local websites
- Social media marketing
- Local radio advertising
Operations Plan
While the earlier sections of your business plan explained your goals, your operations plan describes how you will meet them. Your operations plan should have two distinct sections as follows.
Everyday short-term processes include all of the tasks involved in running your law firm, including filling and filing paperwork, researching precedents, appearing in court, meeting with clients, etc.
Long-term goals are the milestones you hope to achieve. These could include the dates when you expect to file your 100th lawsuit, or be on retainer with 25 business clients, or when you hope to reach $X in revenue. It could also be when you expect to expand your law firm to a new city.
Management Team
To demonstrate your law firm’ ability to succeed, a strong management team is essential. Highlight your key players’ backgrounds, emphasizing those skills and experiences that prove their ability to grow a company.
Ideally you and/or your team members have direct experience in managing law firms. If so, highlight this experience and expertise. But also highlight any experience that you think will help your business succeed.
If your team is lacking, consider assembling an advisory board. An advisory board would include 2 to 8 individuals who would act like mentors to your business. They would help answer questions and provide strategic guidance. If needed, look for advisory board members with legal experience or with a track record of successfully running small businesses.
Financial Plan
Your financial plan should include your 5-year financial statement broken out both monthly or quarterly for the first year and then annually. Your financial statements include your income statement, balance sheet and cash flow statements.
Income Statement : an income statement is more commonly called a Profit and Loss statement or P&L. It shows your revenues and then subtracts your costs to show whether you turned a profit or not.
In developing your income statement, you need to devise assumptions. For example, will you file 25 lawsuits per month or sign 5 retainer contracts per month? And will sales grow by 2% or 10% per year? As you can imagine, your choice of assumptions will greatly impact the financial forecasts for your business. As much as possible, conduct research to try to root your assumptions in reality.
Balance Sheets : Balance sheets show your assets and liabilities. While balance sheets can include much information, try to simplify them to the key items you need to know about. For instance, if you spend $50,000 on building out your law firm, this will not give you immediate profits. Rather it is an asset that will hopefully help you generate profits for years to come. Likewise, if a bank writes you a check for $50,000, you don’t need to pay it back immediately. Rather, that is a liability you will pay back over time.
Cash Flow Statement : Your cash flow statement will help determine how much money you need to start or grow your business, and make sure you never run out of money. What most entrepreneurs and business owners don’t realize is that you can turn a profit but run out of money and go bankrupt.
In developing your Income Statement and Balance Sheets be sure to include several of the key costs needed in starting or growing a law firm:
- Location build-out including design fees, construction, etc.
- Cost of licensing, software, and office supplies
- Payroll or salaries paid to staff
- Business insurance
- Taxes and permits
- Legal expenses
Attach your full financial projections in the appendix of your plan along with any supporting documents that make your plan more compelling. For example, you might include your office location lease or your certificate of admission to the bar.
Putting together a business plan for your law firm is a worthwhile endeavor. If you follow the template above, by the time you are done, you will truly be an expert and know everything you need about starting a law firm business plan; once you create your plan, download it to PDF to show banks and investors. You will really understand the law firm industry, your competition, and your customers. You will have developed a marketing plan and will really understand what it takes to launch and grow a successful law firm.
Law Firm Business Plan FAQs
What is the easiest way to complete my law firm business plan.
Growthink's Ultimate Business Plan Template allows you to quickly and easily complete your Law Firm Business Plan.
What is the Goal of a Business Plan's Executive Summary?
The goal of your Executive Summary is to quickly engage the reader. Explain to them the type of law firm you are operating and the status; for example, are you a startup, do you have a law firm that you would like to grow, or are you operating a chain of law firms?
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your Law Firm business plan?
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies who have gone on to achieve tremendous success. Click here to see how Growthink’s professional business plan consulting services can create your business plan for you.
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates


Latest Blogs
5 ways lexis+ ai’s second-generation legal ai assistant will....
By Alison Manchester The commercial launch of Lexis+ AI in October 2023 was a watershed moment in the legal industry, introducing the first comprehensive legal research platform powered by generative...
GC Guardrails for Gen AI Adoption
By Geoffrey D. Ivnik, Esq. | Director of Large Markets, LexisNexis Corporate legal departments are not standing on the sidelines and waiting to see how the adoption of generative artificial intelligence...
Law Firms: Ask Your Clients About AI Expectations
By Geoffrey D. Ivnik, Esq. | Director of Large Markets, LexisNexis Corporate counsel have made it clear they are expecting their outside counsel to become more efficient in their operations by leveraging...
ESG, DEI and CSR: What In-House Counsel Need to Know
Casual observers of business trends can be forgiven for being puzzled by the alphabet soup of acronyms used in the legal space, but in-house counsel don’t have the same luxury when it comes to the...
Corporate Legal Departments Are Seizing the GenAI Opportunit...
By Geoffrey D. Ivnik, Esq. | Director of Large Markets, LexisNexis Every corner of the legal profession has explored the potential uses of generative artificial intelligence (Gen AI) technology in the...
How to Draft a Law Firm Business Plan
Law firms are something more than a business. Law firms and the lawyers within them are engaged in a profession, with obligations that go beyond purely commercial concerns.
Listen to this article: Click here to play this audio clip
This truth can obscure the need for lawyers to pay attention to the business management side of their practices: their finances, marketing plans, business development efforts, IT purchases, lease terms and capital needs. For the highly trained lawyer, such concerns may feel at best like an afterthought, or at worst a nuisance that steals time from their true occupation: the “practice of law.”
And yet, those annoying business details are responsible for keeping the lights on. While law firms may be more than a business, there is, in fact, a large and necessary business element to them. For solo practices and small firms in particular, investing time into the business management side of legal practice can make a major difference in the financial rewards they derive from it—or even their survival. Firms that have failed to do so in the past (and even those that haven’t) can get a handle on their law practice business management by taking the step of drafting a business plan.
THE POINT OF A BUSINESS PLAN
We’ll discuss the components of a business plan in a moment, but first, let’s talk about why this exercise is valuable. For another type of business, a business plan may be useful in attracting investors or securing financing. Law firms should not think of their business plans as utilitarian documents in that sense (although someday one could prove helpful in obtaining a line of credit, say, or attracting lateral partners). Instead, the primary value of the business plan, particularly for the solo practice or small firm drafting one for the first time, lies in the fact that it forces the firm to think about business issues that it otherwise would not have considered.
As the D.C. Bar says in its advice to startup law offices : “The act of planning helps you think things through thoroughly, study and research if you are not sure of the facts, and look at your ideas critically. It takes time now, but avoids costly, perhaps disastrous, mistakes later.”
Of course, a business plan does little for anyone if it is quickly forgotten. But the mere act of generating a business plan gives a firm a direction to head in and goals to point toward. If the firm makes it a practice to revisit the business plan on an annual basis (if not more regularly), its business considerations will stay top-of-mind and the firm will continually refine them in ways that improve its performance.
THE CONTENTS OF A BUSINESS PLAN
Creating a strong business plan will require an investment of time and energy. At the same time, no one wants to write, or read, a massive document. To improve the chances that the project gets done, and gets read, it is best to keep a business plan to a reasonable length. Anything over 20 pages may stretch attention spans to the breaking point, and there’s no harm in going shorter if you have covered all the territory you need to by that point.
So, what, exactly, is the territory that you should cover? Most authorities agree that a sound business plan for a law firm should address the following broad areas:
- Overview of the Firm
This section should include basic information about the firm: its name, legal structure, practice areas and leadership positions. It should also contain some deeper information about the firm's identity and aspirations.
This would include:
A mission statement about the firm’s purpose
A vision statement or recitation of medium- and long-term goals for the firm
Important aspects of the firm’s history
Any important philosophies that the firm brings to legal practice
- Market Analysis
This section should discuss the business trends affecting the firm’s important practice areas and clients. It should evaluate any technologies that are affecting your practice area and consider how the firm may leverage or keep up with them. This section should also devote substantial energy to identifying the firm’s major competitors in each of its important practice areas and comparing their services to the firm’s.
In this section, identify the firm’s major clients, breaking them down by important characteristics like size, location, industry and practice groups used. Go through a similar exercise for major client prospects and targets. It’s worth examining how the firm can improve its relationships with both of these groups.
Important financial information includes the firm’s fixed and variable costs, backward- and forward-looking revenue, realization rate, collection rate, monthly overhead, assets and liabilities. A 12-month profit and loss projection should be included and could be considered the heart of the business plan.
There is a great amount of detail that any firm could get into on this front. Don’t get overwhelmed by it; at the same time, this is some of the most important information in the business plan, so it’s not advisable to gloss over it.
This section will address key operational issues like the office lease, equipment purchases and technology plans. You may assign roles to various staff members for operational issues.
Think about what marketing the firm currently performs, how it obtains clients and what marketing goals it wants to set for the future.
After completing these and any other sections the firm might want to address, then go back and draft an executive summary to be included at the beginning of the business plan document. The summary should be professional, but don’t be afraid to give it some optimistic energy. After all, with your eyes on the business management fundamentals of your firm, things should be looking up for the future.
- Growing Your Business
- Law Practice Management

Client Management
Case management, billing & payments, accounting & report, e-signature.
- Help Center
Starting a law firm can be a rewarding and lucrative venture, but it requires careful planning and strategy. A well-crafted business plan is a crucial tool for any law firm looking to establish itself, secure funding, or grow its practice. The business plan will serve as a roadmap, outlining the law firm’s objectives, strategies, and unique selling proposition
Why Every Law Firm Needs a Business Plan
A well-structured business plan is imperative for every law firm, regardless of its size or specialization. While legal expertise is undoubtedly crucial, having a clear vision and strategic direction is equally essential. A business plan serves as a guiding light, defining the firm’s mission, values, and long-term goals. This clarity is vital for aligning the entire firm towards a common purpose, ensuring that everyone understands the objectives and the path to achieving them. Without a business plan, a law firm may find itself navigating uncertain waters, reacting to circumstances rather than proactively pursuing its ambitions.
The Key Components of a Law Firm Business Plan
A well-structured law firm business plan consists of several key components, each playing a crucial role in guiding the firm’s operations and ensuring its long-term success. Here are the essential elements of a comprehensive law firm business plan:
- Executive summary
- Law firm description
- Market analysis
- Organization and management
- Services
- Marketing Strategy
- Financial plan
- Start-up budget
Section One: Executive Summary
The executive summary is arguably the most critical section of your law firm’s business plan. While it appears at the beginning, it is often written last, as it serves as a concise yet comprehensive overview of your entire plan. This section should capture the reader’s attention, providing them with a clear understanding of your law firm’s essence, mission, and what to expect from the rest of the document. In your executive summary:
- Introduce your law firm: Briefly describe your law firm’s name, location, and legal specialization.
- Mission and vision: State your firm’s mission and vision, highlighting your commitment to serving clients’ legal needs effectively.
- Your unique selling proposition: Clearly state your USP, and present what is unique about your firm that will ensure success.
The executive summary sets the stage for your entire business plan. It should be a concise yet compelling introduction to your firm’s mission, values, and potential. If crafted well, it can grab the reader’s attention and encourage them to explore other sections in detail. If you feel overwhelmed by this, you can write this section last.
Section Two: Law Firm Description
This section of your business plan provides a deeper dive into your firm’s background, history, legal specializations, and legal structure and ownership. This section should provide a concise yet informative overview of your firm’s identity and history. Here’s what this section should cover:
- Mission Statement: Briefly reiterate your law firm’s mission statement. This statement should encapsulate your firm’s overarching purpose and guiding principles.
- Geographic Location: State out the physical location of your law firm’s office(s). This should include the city or region where your primary office is situated.
- Legal Structure and Ownership: State the legal structure of your law firm, whether it’s an LLC, S-Corp, or another legal entity. This choice is a fundamental aspect of your business model, influencing ownership, liability, and taxation. If your firm’s ownership is not that of a sole proprietorship, provide details on the ownership structure. Explain how the chosen structure aligns with your firm’s business model, decision-making processes, and long-term goals.
- Firm History: Provide the history of your law firm. Highlight key milestones, achievements, and notable moments in your firm’s journey. If your firm is well-established, briefly summarize its history, showcasing your accomplishments and contributions to the legal field.
Remember that brevity is key in this section. Don’t spend too much time, just touch on important points and achievements.
Section Three: Market Analysis
A well-conducted market analysis will not only demonstrate your understanding of the legal industry but also inform your law firm’s strategies and decision-making. It goes beyond understanding your competition; it delves deep into your potential clients’ needs and expectations.
Through market analysis, you can segment your target market based on demographics, industry, legal needs, and preferences. This segmentation allows you to tailor your services to meet the specific needs of different client groups. It also helps you identify the pain points and challenges that potential clients face. By understanding their concerns, you can offer solutions that directly address these pain points.
Your market analysis should also reveal the pricing strategies of your competitors. By benchmarking your pricing against theirs, you can position your services competitively. You can choose to price higher if you offer unique value or lower if you aim to attract price-sensitive clients. Your market analysis should reveal areas where your competitors may be falling short. Use this information to frame your services as the solution to these weaknesses. For example, if competitors have slow response times, emphasize your firm’s commitment to timely communication.
Showcase your firm’s USPs that directly address client needs and preferences. If you excel in a particular practice area, have a reputation for excellent client service, or offer innovative fee structures, use these strengths to attract your preferred clientele. Ultimately, a well-documented market analysis not only informs your law firm’s business model but also guides your approach to client acquisition, pricing, and service delivery. It ensures that your legal services align with client expectations and positions your firm for success in a competitive legal industry
Section Four: Organization and Management
Image Source – Creately
This section provides a clear picture of your firm’s internal structure and leadership. Name the key stakeholders in your law firm and what they bring to the table. Highlight any unique experiences or expertise that each partner brings to the firm. This could include prior work at prestigious law firms, involvement in landmark cases, or specialized knowledge in a specific area of law. Explain how these experiences set your firm apart and enhance its capabilities. You can also include an organizational chart that visually represents your law firm’s structure. This chart should showcase the hierarchy, roles, and reporting lines within the firm. By including the names, educational backgrounds, unique experiences, and organizational chart, you paint a comprehensive picture of your law firm’s leadership and structure. This not only builds confidence in your team’s capabilities but also showcases the depth and expertise of your staff to potential clients, partners, or investors.
Section Five: Services
This section is the core of your law firm business plan. Here, you will go into detail about all aspects of your services. Present in simple words:
- The problem(s) your law firm is addressing and your approach to how to alleviate those pain points? Answer these questions, and provide in detail how your firm is in the best position to tackle this problem.
- The solution(s) you are providing. This should describe how your law firm resolves your prospective market’s needs. This should include the work you do, and the benefits that each client will receive if they work with your firm.
- Your law firm competition. This should describe what advantages your law firm has over your competitors? What you do differently when providing your solutions and how your clients will gain additional benefits when they work with your law firm.
Section Six: Marketing Strategy
As you craft your business plan, keep these four essential questions in mind:
- What Is Your Firm’s Value Proposition? Clearly define what sets your law firm apart from others. This should guide your marketing and sales strategies, emphasizing the unique value you offer to clients.
- Who Is Your Target Audience? Identify your ideal client profile. Understanding your target audience helps tailor your marketing efforts to reach those most likely to benefit from your services.
- What Are Your Growth Goals? Set specific, measurable growth goals for your firm. These goals should inform your sales and marketing strategies, outlining how you plan to achieve them.
- How Will You Measure Success? Determine key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the success of your marketing and sales efforts. Whether it’s tracking client acquisition rates, website traffic, or revenue growth, having measurable metrics will help you gauge your progress and make informed adjustments.
It is also valuable to perform a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) to assess your law firm’s internal and external factors. Describe your online marketing efforts, including your website, social media presence, and email marketing campaigns. Explain how you plan to leverage marketing to reach and engage potential clients effectively. You should also define your pricing structure and fee arrangements. This may include hourly rates for specific legal services, retainer agreements for ongoing representation, or flat fees for standardized services.
Section Seven: Financial Plan
If you want to expand your law firm and ensure a steady income, it’s essential to create a financial strategy for your practice. While you might not have all the answers regarding your firm’s finances, provide comprehensive details. Your goal should be to establish a financial plan, particularly for the initial year of your firm’s operation.
Provide comprehensive financial projections that cover the anticipated income, expenses, and cash flow for your law firm. These forecasts should offer a clear picture of how your firm expects to perform financially. You should also Incorporate income statements, which show your firm’s revenue and expenses, balance sheets that detail your assets and liabilities, and cash flow projections, which illustrate how money moves in and out of your business. These financial statements offer a holistic view of your firm’s financial health.
Explain the assumptions underlying your financial projections. This may include factors like growth rates, market trends, client acquisition strategies, and pricing models. Describe your strategies for achieving growth and how they translate into financial outcomes. This section is critical for demonstrating your law firm’s financial preparedness and sustainability. Investors, lenders, or partners will scrutinize these sections to assess the viability of your firm, making it essential to provide detailed and well-supported financial information.
Section Eight: Start-up Budget
When developing a business plan for your law firm, it is essential to create a realistic startup budget. This involves carefully considering various initial and ongoing expenses and factoring them into your revenue objectives. Here are some instances of expenses to incorporate into your budget:
- Hardware costs, such as laptops, printers, scanners, and office furniture.
- Office space expenses, whether you plan to rent space or work from home.
- Malpractice insurance fees.
- Staff salaries, including potential hires like administrative assistants or paralegals.
- Utility expenses, covering phone and internet services, among others.
- Expenses on practice management software or other tech tools
After itemizing these costs, review them thoroughly. Clearly state the total amount of funding you require to start and sustain your law firm. Explain how this funding will be allocated, including how much goes into covering startup costs and how much is reserved for ongoing operations. Be specific about the purpose of each funding component.
Additionally, explore tools and solutions that can streamline non-billable tasks, freeing up more time for your legal practice. This not only enhances your overall productivity but also allows you to allocate more time to your legal practice. One exceptional solution that can significantly benefit your law firm operations is a legal practice management software.
DigitsLaw: The Legal Practice Management Software for Law Firms
DigitsLaw is an all-in-one practice management software that streamlines and simplifies the day-to-day operations of a law firm. Whether you are a small firm or you have law firms in major cities, DigitsLaw can meet the unique needs of your legal practice. Our simple and intuitive tool offers a wealth of features that can make a substantial difference in the success and efficiency of your firm.
Here’s how DigitsLaw can help your new law firm scale:
- Effortless Case Management: DigitsLaw simplifies case management by centralizing all your client information, documents, and communications in one secure location. This ensures that you have easy access to everything you need, right at your fingertips.
- Time Tracking and Billing: With DigitsLaw, tracking billable hours and generating invoices is seamless. You can accurately record your time, expenses, and activities, allowing for transparent and error-free billing processes.
- Conflict Check: DigitsLaw provides a robust conflict check system that assists law firms in maintaining ethical standards and preventing conflicts of interest. By incorporating DigitsLaw conflict check capabilities into your law firm’s workflow, you can enhance your due diligence processes, reduce the risk of conflicts of interest, and uphold the highest ethical standards in your legal practice.
- Client Collaboration: Foster better client relationships through DigitsLaw’s client portal . Clients can securely access case information, share documents, and communicate with your firm, enhancing transparency and trust.
- Legal Document Management: Say goodbye to the hassle of paper documents and disorganized files. DigitsLaw enables efficient document storage, organization, and collaboration, saving you time and reducing the risk of errors.
- Secure and Compliant: DigitsLaw prioritizes security and compliance, ensuring that your client data and sensitive information are protected at the highest standards.
By leveraging DigitsLaw’s capabilities, you can significantly reduce administrative overhead, minimize errors, and provide a more streamlined and responsive experience for your clients. It’s a strategic investment that will pay dividends as your firm grows and prospers.
Sample Business Plan and Fillable Template
If you’re in the early stages of creating your business plan, we’ve prepared an example that can serve as a reference. You can also download a blank version of our template here. Remember to tailor your plan to your specific requirements and objectives.
Download your copy of our law firm business plan template HERE
Final thoughts.
In conclusion, crafting a law firm business plan is not just a formality; it’s a roadmap that guides your firm toward success. Whether you’re launching a new law firm or seeking to revitalize an existing one, a well-thought-out plan helps you. From defining your firm’s mission and values to conducting a thorough market analysis every section of your plan plays a crucial role in shaping your law firm’s journey. It’s not just about impressing potential investors; it’s about setting clear goals, making informed decisions, and ensuring that your firm is well-prepared for the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
As you start planning, remember that your business plan is a living document. It should evolve and adapt as your firm grows and the legal industry changes. Regularly revisit and update your plan to stay aligned with your mission, serve your clients better, and achieve your long-term vision.

Share this post
Latest Writings
The latest news and resources from our team
Our Integrations
It is the easiest and most organized way to manage your law firm, clients, cases, billing, accounting and more.
Get the app
© 2023 Digitslaw. All rights reserved.


A Complete Strategy for Creating a Law Firm Business Plan
You’ve invested so much time into completing and graduating from law school and studying and passing the state bar exam. Maybe you spent years working at law firms, in government, or in corporate law. Now you’re ready to open your own firm, and you want to do it right so all those years of hard work pay off. You need a law firm business plan.
But do you know where to begin? What should your business plan include? What are the challenges you know and, most importantly, what don’t you know?
Start with the basics. What are your values? What do you want to achieve with your law firm? What will make your firm stand out?
Understanding your “why” will prepare you to open your firm and establish its operations—from case and document management to checking your firm’s growth profile. Well-defined goals, plenty of preparation, and the right tools can help you get answers to your business questions and create the best business plan for your law firm.
What Is a Law Firm Business Plan?
A business plan is a roadmap that accounts for your milestones, potential setbacks, and the overall growth of your brand. You may want to include strategies for marketing, finance, sales, and partnerships.
Generally speaking, it’s a summary of what goals you want to achieve as a brand. If you’re not sure of where you’d like to start with your business plan, think about:
- The purpose of your firm and what you want to do
- How you see your firm in five, ten, or twenty years
- The type of working environment you want to provide
- Management and organization of the firm
- What do you want to see come out of your firm financially
While considering each of these factors, keep your target clientele in mind. Consider your demographic, their needs, and expectations. This way of thinking can help keep you focused on providing top-notch client care.
Why Is a Law Firm Business Plan Important?
Making a business plan is a guiding principle for your goals and success. This way, you’ll be less likely to lose sight of your goal. When managing a firm, you have to worry about yourself, your staff, the brand and business as a whole, your partners, competitors, and of course, your clients. With all this responsibility, losing track of your mission seems almost inevitable. However, it doesn’t have to be. Referring to your firm’s values, your long- and short-term objectives, and your financial projections can help prevent you from falling behind.
Your firm is a business, so you must manage it as such.
Even though you should follow your law firm’s business plan, that doesn’t mean your goals won’t or shouldn’t change. Sometimes, things don’t go as intended, and you must adapt. For example, some marketing strategies may not be as popular with your target audience as intended. In that case, it’s time to go back to the drawing board and see how you can appeal to them.
How Do I Start a Law Firm Business Plan?
Getting started is almost always the hardest part of anything. However, if you start small, it’s easy to build.
When creating your law firm business plan, follow these steps:
Define Your Goals
Having defined goals sets the tone for how you manage and market your business. It may seem obvious to you, but when prospects do a search and land on your website , that might not be the case for them. When you articulate what drives you, these potential clients may be more inclined to look into what you can offer them.
If you’re unsure how to explain your goals for the firm, maybe come back to that later. Figuring out your services, marketing strategies, financial projections, management, and operations may help you come to a more concise conclusion.
Revenue/Value Estimation
Whether you’re asking for funding or want to build the firm from the ground up, you must figure out how to keep the lights on.
You’ll want to have an answer for the following:
- What are the costs associated with starting a law firm?
- What is the number of cases you need to break even? Make a profit?
- What is your profit-loss estimation?
Be precise with these numbers. That way, you can better gauge your success or lack thereof.
Billing Structure
Creating a comprehensive legal billing policy at the beginning will save your law firm a vast amount of non-billable hours and money .
First, you’ll want to get clear on items like your fees. Some firms charge a flat fee. Others charge by the hour. The fee structure can vary depending on the area of practice . For example, if you’re working in personal injury law , especially, you may go the contingency fee route.
Once you figure out which payment structure to use, you’ll want to create a process for how you’ll get paid. Automating your billing with legal workflows is a simple way to standardize the processes. This workflow should outline items like the invoice creation process, modes of sending the invoice, and how the client will pay.
PracticePanther’s automated legal workflows can be customized to trigger events throughout the billing cycle so you never have to worry about missing a step.
Identify the Risks
Just like the risk assessment you give your clients, the same should be done when starting a law firm. Identifying potentials risk during the planning process will help inform your business decision. While risks are not always avoidable, being proactive can limit the shock associated with surprise risks.
A few potential risks for law firms:
- Market share
- Pros and cons of your pricing structure
- Demand of services
What Is in a Law Firm Business Plan?
There’s no set formula for creating a picture-perfect business plan. However, these things may put you on the road to success:
Executive Summary
This section gives an overall view of your plan. It includes:
- Mission statement, noting your inspiration and drive for your law firm
- Core values, describing what you’ll use to serve your clients
- How you stand out, discussing what you’ll bring to the table that others may not
- A company description, articulating how you got started in law, your educational and professional background, etc.
Refrain from making general, overstated platitudes. Every other firm promises how they’ll strive to deliver the results their clients need. Be specific and tell them how you will act.
Market Analysis
Who will you represent, and how will you get paid? These questions can help you determine how you’ll carry out a market analysis:
- Target clientele: What demographic do you want to serve? Think of age, location, status, occupation, or gender.
- Financial projections: How much would this demographic reasonably spend on your services?
- Industry: What are the trends in this industry? What’s the market size? What’s its potential for growth or lack thereof?
- Competition: Who are your main competitors? What are their/your strengths and weaknesses?
Law Firm Billing and Finances
What are budgets and revenue going to look like? Think about how much money you’ll need to start up and keep the firm running every month. How many cases will allow you to break even or make a profit?
Assess how much you project to make this year and every year thereafter.
Management Structure
Now is the time to think about how you’ll operate. Yes, you want to create a healthy work environment, but how will you do that?
If you’re opening this firm, you probably have the educational background and experience to hit the ground running.
However, serving clients and running operations are two different things. Are you the right person to manage the firm as a whole? It’s okay if you’re not sure. Maybe you would benefit from hiring an office manager or other employees to keep things running.
Legal Technology
The more clients you take, the more paperwork, documents, and overall assistance you’ll need. You may not need to hire an employee to take care of such matters per se. As such, you may want to consider purchasing law practice management software to keep track of every detail of your business operations. These cloud-based solutions make it easy to work from anywhere while maintaining collaboration with staff or outsourced workers.
Managing your law firm is made easy with an all-in-one solution . PracticePanther comes equipped with all of the resources your need to efficiently manage a profitable law firm. Native features like custom reporting to track expenses or cash flow, legal document management for accessibility and paperless filing, legal billing software to accurately manage your billing and invoicing, case management to streamline your cases, eSignature to quickly send documents for electronic signature , and online payment processing to get paid faster and enhance the client experience.
Other law practice management platforms may require costly monthly subscriptions for essential business features like online payment processing or eSignature. With PracticePanther — they’re free to activate and included with your account.
Legal Services
Your services are the bread and butter of your firm. What problems are your potential clients experiencing, and how will you help them?
Here, you can also differentiate yourself from your competitors and discuss the advantages of hiring you.
Law Firm Marketing
When you market your firm, think about how you will present it and entice a prospect to hire you. What services will you provide, and at what cost? Show potential clients that your firm is worth every penny and that you will go above and beyond for them.
Creating a law firm marketing strategy with proven tactics and goals is key. Traditionally, firms have relied on word of mouth. However, to remain profitable — law firms should utilize modern channels such as social media, paid advertising, and search engine optimization or SEO.
Use your executive summary and market analysis as an initial guide for your marketing strategy then continue to measure and adjust your strategy.
Sample Law Firm Business Plan
Organizing your law firm’s business plan can seem like a big maze. However, if you have a document template that allows you to break everything down step by step, it won’t be as scary.
PracticePanther offers a white-label template for you to write out your goals for your firm. You can even customize it with your logo, ensuring your professionalism and brand recognition. This feature also stores your business plan in one place.
What’s more, if you have several potential business plans, you can easily store them within PracticePanther as a template or file . This way, if you need to adjust your plan (which is highly recommended that you monitor your business plan) you can easily access it.
Outlook on the Business of a Law Firm
It’s great to have short-and long-term goals and objectives when you’re forming a law firm business plan. Still, these plans should be flexible and adapt to the market.
Having an understanding of how to scale and market your law firm with modern processes will ensure the overall profitability of your business. With PracticePanther’s five-minute law firm growth quiz , you can find your growth profile along with a strategic growth roadmap for success.
Modern legal technology makes it easier than ever to practice and manage a law firm today. Ready to get started? You can schedule a custom demo with PracticePanther to see how our features support your firm’s success.
Download as PDF
Want a copy of this article? Download it for free!
Related Articles
8 legal podcasts to help grow your law practice.
Legal podcasts offer excellent content for legal professionals to stay current on tre...
5 Organization Tips for Lawyers to Stay Productive
Lawyers have a lot on their plates every day — managing casework, keeping track of de...
How to Write a Legal Cover Letter for Lawyers That Stands Out
Whether you’re a fresh grad just starting out or a legal professional seeking a new r...

Kamron Sanders
Kamron Sanders is the Senior Content Marketing Specialist at PracticePanther, an all-in-one legal practice management software. She is responsible for creating engaging content across multiple channels including social media, articles, videos, and more. Kamron views marketing through a customer-focused lens and equips legal professionals with the information and tools to automate their practice.
Subscribe for Updates
Learn how to grow your firm and get tips to save you time and automate your work, straight to your inbox.

Download PDF
Submit this form to download this article as a PDF file.
- First Name *
- Last Name *
- Firm Name *
By submitting this form, you are agreeing to our Terms of Service and Privacy Policy
Start your free trial today
PracticePanther is the leading legal practice management software. Start a free trial today and discover the power of automation at your firm.
By creating an account, you are agreeing to our Terms of Service and Privacy Policy

Download the Buyer's Guide to Law Firm Software
Maximize the security of your law firm's confidential information and improve productivity with the right law firm software. Explore crucial features to look for when choosing your law firm software.
Law practice management software made easy
We help you do right by your clients and get you home for dinner on time. Win-win.
Already have an account? Login

Free Download
Law Firm Business Plan Template
Download this free law firm business plan template, with pre-filled examples, to create your own plan..
Or plan with professional support in LivePlan. Save 50% today
Available formats:
What you get with this template
A complete business plan.
Text and financials are already filled out and ready for you to update.
- SBA-lender approved format
Your plan is formatted the way lenders and investors expect.
Edit to your needs
Download as a Word document and edit your business plan right away.
- Detailed instructions
Features clear and simple instructions from expert business plan writers.
All 100% free. We're here to help you succeed in business, no strings attached.
Get the most out of your business plan example
Follow these tips to quickly develop a working business plan from this sample.
1. Don't worry about finding an exact match
We have over 550 sample business plan templates . So, make sure the plan is a close match, but don't get hung up on the details.
Your business is unique and will differ from any example or template you come across. So, use this example as a starting point and customize it to your needs.
2. Remember it's just an example
Our sample business plans are examples of what one business owner did. That doesn't make them perfect or require you to cram your business idea to fit the plan structure.
Use the information, financials, and formatting for inspiration. It will speed up and guide the plan writing process.
3. Know why you're writing a business plan
To create a plan that fits your needs , you need to know what you intend to do with it.
Are you planning to use your plan to apply for a loan or pitch to investors? Then it's worth following the format from your chosen sample plan to ensure you cover all necessary information.
But, if you don't plan to share your plan with anyone outside of your business—you likely don't need everything.
More business planning resources

How to Write a Business Plan for Investors

How to Write a Business Plan

Industry Business Planning Guides

How to Start a Business With No Money

Business Plan Template

How to Write a Law Firm Business Plan

10 Qualities of a Good Business Plan

Simple Business Plan Outline
Download your template now
Need to validate your idea, secure funding, or grow your business this template is for you..
- Fill-in-the-blank simplicity
- Expert tips & tricks
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .
Not ready to download right now? We'll email you the link so you can download it whenever you're ready.
Download as Docx
Download as PDF

Finish your business plan with confidence
Step-by-step guidance and world-class support from the #1 business planning software

From template to plan in 30 minutes
- Step-by-step guidance
- Crystal clear financials
- Expert advice at your fingertips
- Funding & lender ready formats
- PLUS all the tools to manage & grow

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
Log in to Lawyerist.com
Not a Subscriber yet? Register here. (It's free!)
Username or Email Address
Remember Me
Forgot your password? Reset it here.
Subscribe to Lawyerist
Back to login.
- Hidden Date MM slash DD slash YYYY
- Name * First Last
- Password * Enter Password Confirm Password
- United States
- Which state is your firm's primary location? * Pick one. Alabama Alaska American Samoa Arizona Arkansas California Colorado Connecticut Delaware District of Columbia Florida Georgia Guam Hawaii Idaho Illinois Indiana Iowa Kansas Kentucky Louisiana Maine Maryland Massachusetts Michigan Minnesota Mississippi Missouri Montana Nebraska Nevada New Hampshire New Jersey New Mexico New York North Carolina North Dakota Northern Mariana Islands Ohio Oklahoma Oregon Pennsylvania Puerto Rico Rhode Island South Carolina South Dakota Tennessee Texas Utah U.S. Virgin Islands Vermont Virginia Washington West Virginia Wisconsin Wyoming Armed Forces Americas Armed Forces Europe Armed Forces Pacific State
- Which province is your firm's primary location? * Pick one. Alberta British Columbia Manitoba New Brunswick Newfoundland and Labrador Northwest Territories Nova Scotia Nunavut Ontario Prince Edward Island Quebec Saskatchewan Yukon Province
- What is the size of your firm? * Pick one. Solo practice Small firm (2–15 lawyers) Medium or large firm (16+ lawyers) I do not work at a law firm
- What is your role at your firm? * Pick one. Owner/partner Lawyer Staff Vendor (web designer, consultant, etc.) I do not work at a law firm
- What is your primary practice area? * Pick one. Bankruptcy Civil litigation (non-PI) Class Action Collections Corporate Criminal Education Employment Estate planning, probate, or elder Family General practice Immigration International Landlord/Tenant Mediation/ADR Personal injury Real estate Small business Sports/Entertainment Tax Trademark/IP Other I do not work in law
- Legal Technology Products and Services
- Building a Healthy Firm
- Comments This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
You have read all five of your free articles this month. To read this article, log in or register.
- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Part of the ‘Lawyerist Healthy Law Firm’
Legal product reviews and business guidance from industry experts.
Chapter 3/6
Developing a Business Plan for a New Law Firm
How to Start a Law Firm
10 min read

Guides Parent Form
Already an Insider? Log in to your account to receive your e-book!
Previous Chapter
Next Chapter
A law firm business plan is the foundation for everything your business does. Without a solid foundation, your firm will lack direction from the very beginning.
Starting a Law Firm Business Plan
A good business plan includes:
- Vision. Create a picture of what you’re building.
- Values. Identify the rules to guide your team’s important work.
- Law Firm Business Model. What you offer, who you offer it to, and how you’ll deliver your services.
- Targets and Priorities. Clarify metrics that indicate success.
Law Firm Vision
We worked with a lawyer who was stressed out about his vision. He spent weeks on the assignment because he couldn’t think of a statement that would make his entire office happy.
During one coaching session , he got that lightbulb moment when we told him that he was making too big of a deal of it. You don’t have to create the most amazing vision that perfectly captures everything you are hoping to build. You do need to start mapping out what you are (and aren’t) trying to create.
Picture these two lawyers:
- Lawyer 1 wants to double the size of his team in the next two years so he can handle more cases, help more people, and make more money.
- Lawyer 2 does not enjoy managing people. She wants to build a technology-based solution that she can offer clients with a recurring monthly price and that is delivered using a few key team members.
Neither vision is wrong. But, how each lawyer will make decisions to build a profitable business will look very different. You need to get a sense if you are trying to build something that looks more like Lawyer 1, Lawyer 2, or Lawyers 3-8. Get it?
Jot down thoughts now so you know where you’re headed and can start building the guardrails for future decisions.
Law Firm Values
Your values are a living embodiment of the firm culture you’re hoping to create and the approach to work your team shares. They are the guardrails of your business.
From hiring to client management to a marketing strategy, every decision you make comes from your values.
Your values are typically 3-6 factual statements that are authentically you.
Here are some tips on crafting great values:
- Your values must concretely point to your business. You want achievable values that set your business up for success .
- Your values must have actual meaning. Like the “be the best lawyer” example, you want to avoid the obvious. Sure, every firm wants to be the best. But what, precisely, does your firm want to do that sets you apart from the crowd?
- Finally, avoid table stakes values. Honesty, integrity, and hard work are all good works that all companies should have. But, they have nothing to do with your specific goals vs. any other firm.
As an example, here are Lawyerist’s values :
- Build an Inclusive Community.
- Experiment Like a Lobster.
- Grab the Marker.
- Seek Candor.
- Grow as People.
Each of these represents the culture of our company (even “ Experiment Like a Lobster ,” which describes our playful and out-of-the-box thinking process). We use these values for all of our decisions, especially hiring. When we evaluate a candidate, we study their fit: Are they open to experimenting? Are they willing to help us build an inclusive community ? Are they eager to lean into candor and compassion ?
Building your vision and values is an essential first step for your business. We can’t tell you how much easier other decisions will flow once you have these documented. You will make better decisions and alleviate some of the anxiety of decision fatigue.
Law Firm Business Model
One of the biggest perks of starting your firm is deciding your law firm business plan and model. You get to take everything you learned in school and while working at other organizations and implement the parts you like. Even better, you get to leave out the details that stressed you out.
This is an excellent place to review your vision and values. Take the time to dream about this. This is often the most rewarding part for new law firm owners. With a smart strategy, you can build your dream firm.
Ask yourself:
- What kind of place do I want to work in every day?
- What kind of clients do I want to serve? Who is my ideal client ?
- What type of pricing model do I want?
- What kind of access to justice issues do I want to tackle?
You get the gist. The questions you can ask yourself here are endless, but use your vision and values to inform your model. For example, if one of your values is “ grow as people ,” you might offer education opportunities for clients in areas related to their cases.
The important part is, it’s all up to you. This is yours. You get to decide.
Competitive Analysis
As part of finalizing your law firm business model, it can be very helpful to complete a competitive analysis. A competitive analysis not only forces you to define who your competitors are, it gives you a chance to determine what may be missing in the market so that you can address it.
Lawyers often assume as long as they practice law, there’s a market for what they want to do. Or they think they’re only competing against other lawyers when clients are often drawn to non-law solutions.
These lawyers are missing a huge opportunity. They aren’t asking clients how they heard about their firm. They’re not trying to figure out what other solutions their clients tried first. They aren’t looking at what clients want and how the market is attempting to respond.
Here are some tips for putting together a competitive analysis:
- Make a list of competitors. Simple, right? List firms in your practice area/location, your jurisdiction, and who may be serving your ideal client base.
- List the other ways your clients are solving their problems . Are they use an online service to create their will? Are they asking their cousin’s nephew’s wife, who once worked at a law firm in 1988, for advice? Get creative.
- Do field research . Ask your friends, family, and current clients what they do when they have a potential legal problem.
Once you’ve collected the data, you can begin the analysis. Think about the strengths and weaknesses of each competitor and the solution you’ve collected. Compare pricing, accessibility, marketing messages, and client service. How does it all compare to your firm? What do you do better? What could you improve?
And keep in mind: This isn’t a one-time deal. You’ll want to stay on top of competitive solutions through Google or social media alerts or by subscribing to industry emails and newsletters. At least once a year, do a complete forensic competitive analysis to see where things have changed.
Targets and Priorities
When you’re first starting a law firm business plan, you may just have a goal of “get my firm up and running.” A good goal! But, as you dream on your initial strategy, it’s helpful to set some initial short-term and excellent long-term goals. Yes, these goals may change as you learn and grow. But, setting goals upfront will give you a path to get started.
Short-term Goals
Look to your initial vision and values for your first goals. If you’re a family law firm that wants to do low-conflict divorces, you might have a client acquisition goal aligned with this.
For example, you could say: In the first six months of my firm opening, I want 50% of my new clients to be low-conflict separations and divorces. You’ll see this goal follows the S.M.A.R.T. formula: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-Bound.
Another short-term goal might be systems-oriented: I want a written client onboarding process documented in my first three months. (If not implemented.)
Think through all the different parts of your business and see if you can achieve one short-term goal.
Long-term Goals
Long-term goals can be a little trickier when you’re first starting. Thinking one, two, or even five years out might seem impossible. But this is where you can begin to dream a little.
A long-term goal might be that in three years, you want a staff of five people, a complete operations manual, 50 new clients a year, and Fridays off each week.
Remember, these goals might—and likely will—change. But give yourself something to work with in the beginning.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
As you’re starting a law firm business plan, you’ll need a way to measure your firm’s health. These measurements are called KPIs. They track goals in all parts of your business, from marketing to finances to client acquisition .
Measuring and monitoring your KPIs will allow you to:
- Monitor the health of your firm . KPIs will enable you to see how well your law firm is performing. For example, KPIs make it easy to track your finances and your firm’s monthly growth. You’ll see problems and successes quickly and be able to take action by creating new goals or redirecting your team’s efforts.
- Simplify decision-making . Armed with the above information, you can make informed, rational decisions for everything in your business. You don’t have to guess if a decision is the right one. Instead, you can (and should) measure all variables to make the best decision for your firm’s future.
- Track your wins. By tracking your KPIs, you track your wins. Monitoring law firm data makes it simple to incentivize your staff’s hard work. After all, when you meet your numbers, everyone benefits.
For example, at Lawyerist, we track KPIs with a color-coded system.
Green means hitting our goal, yellow means we’re on the cusp, and red means not hitting the number. We track weekly, which means when something goes yellow, we can analyze and plan before it goes red.
And, because we track weekly, a one-week red doesn’t mean an emergency. It means we need to take time to discuss, find a cause, and make a plan.
Types of KPIs for Successful Firms
KPIs can cover all aspects of your business, including your finances, client satisfaction, marketing, and business development. Keep in mind, as you start your firm, KPIs will be new to you and can feel overwhelming. So, keep it simple in the beginning.
Start by picking three business questions you want answered. Find a way to measure that answer that you can track and update without too much work regularly. Then, start measuring. As your firm grows, you’ll develop your KPIs.
Let’s look at some examples.
Financial KPIs
Want to increase your revenue or improve your law firm’s financial health? You’ll want to track some financial KPIs , including (but not limited to):
- Revenue (cash collected)
- Monthly amount invoiced to clients
- Accounts receivable (amount clients owe you)
- Budgeted expenses
Regardless of your goals, we recommend tracking some basic financial data to keep an eye on the health of your firm. For a quick win, narrow down your financial KPIs to the top three financial numbers needed to understand your business.
Client Satisfaction KPIs
Your clients are your most valuable assets. Firm success requires that you watch specific metrics involving your clients.
Client satisfaction KPIs connect to several key law firm growth goals. These include increasing referrals, increasing revenue (happy clients are loyal clients), and improving overall client experience.
Examples of KPIs to track include:
- Net Promoter Score (NPS)
- Client retention rate
- Speed at which you close cases
Your Net Promoter Score measures whether current or former clients would recommend your legal services to others. A satisfied client is more likely to do so. This metric is most often gathered using a survey at the final delivery of your services.
Other measures, such as closing speed and retention, can give you insights into how happy your clients are with your services. Do you have a lower NPS than you expect? Are you losing clients? If so, your client satisfaction is low, and you could take action to improve it.
Marketing and Business Development KPIs
Is your current marketing strategy working? Without measuring KPIs, there’s no way of knowing. By tracking marketing metrics for your firm, you can see your marketing strategy’s performance and tweak where needed.
Some of these metrics include:
- Organic traffic to your website
- Number of leads generated
- Conversion rates
- Acquisition costs/return on investment (ROI)
For example, if you see your website traffic trending down, some fresh content might do the trick. Or, if you see low conversion rates yet high traffic, your website isn’t inspiring potential clients to give you a call. You might need to change your call-to-actions or refresh your website.
Marketing and business development go hand-in-hand—as they’re both critical to achieving long-term growth goals.
Some examples of business development metrics to track include:
- Number of new clients each month
- Competitor pricing
- Sales cycle length
- Number of leads that turn into consultations
Profitability KPIs and Law Firm Financial Ratios
Every law firm should have a documented long-term financial strategy and profitability model. Any healthy business has a written plan to forecast revenue, expenses, net profit, and cash reserves. To ensure you follow through with your plan, track your firm’s profitability and financial KPIs.
And where should you track these KPIs? Don’t think too hard on that one. At Lawyerist, we use a Google Sheets spreadsheet with a few simple formulas. Track anywhere that makes sense for your firm .
Next, we’ll outline how to use legal technology successfully.
Download the Full Guide on How to Start a Law Firm
With this guide, you’ll have the tools to plan, strategize, organize, finance, brand, launch, market, and run a new firm.
- Product Reviews
The original content within this website is © 2024. Lawyerist, Lawyerist Lab, TBD Law, Small Firm Dashboard, and
The Small Firm Scorecard are trademarks registered by Lawyerist Media, LLC.
Privacy policy // XML sitemap // Page ID: 1405448
How to Create a Law Firm Business Plan Aimed at Success
Want a successful law firm? Start with a solid business plan. Our guide covers everything that will help you create a roadmap for success.
A firm exists to serve people- so its business plan must take into account those it aims to help. A law firm's business plan lays out the key pillars that will support a practice, from operational details to marketing strategies to financial projections. Furthermore, it should provide a clear roadmap for where the firm hopes to be in the coming years.
In this blog, we will guide you through the process of creating a comprehensive law firm business plan that will help you achieve your goals . Additionally, in our latest Grow Law Firm podcast, our host Sasha Berson conversed with Omar Ochoa, the founding attorney of Omar Ochoa Law Firm, to discuss the topic of creating a law firm business plan aimed at success.
Why Is a Business Plan Important for Law Firms?
A business plan is a vital tool for any law firm to achieve success. It outlines goals, strategies, and the feasibility of business ideas, providing a clear direction and focus for the firm. The plan can be used to secure funding from investors or financial institutions by demonstrating the potential for growth and profitability.

Moreover, a business plan supports decision-making by evaluating the feasibility of new ventures and assessing potential risks and rewards. It helps to manage resources effectively by setting financial goals and tracking progress, ensuring the firm is making the most of its resources and achieving objectives.
Lastly, a law firm's business plan enables growth by identifying new opportunities and developing strategies to capitalize on them. By planning for the future and setting realistic growth targets, law firms can take their businesses to the next level. Overall, a well-developed business plan is critical for success in the legal industry, providing direction and focus, supporting decision-making, managing resources effectively, and enabling growth.
General Tips for Creating an Attorney Business Plan

Building a business plan for law firms is not an easy or intuitive process. By considering the following issues before opening your doors to clients, you have a much better chance of having a stable firm that matches your values and has a clear set of goals.
— Stay Focused
Forming a law firm can feel overwhelming. You have a lot of freedom and can easily get sidetracked into issues that either can wait or do not deserve your attention.
If having a strong law firm website design is important enough for you to include in your plan, you will spend time on that instead of less important matters.
A plan also includes a budget. The process of planning your firm's finances can ensure that you do not overspend (or underspend) as you start your own firm.
The attention to detail that comes from having a plan will help you avoid spreading yourself too thin by focusing on every issue or the wrong issues. Instead, you will maintain your focus on the important issues.
Whether you have law partners or develop a solo law firm business plan, the plan will help you stay focused on your end goals.
— Keep Track of Goals and Results
It is easy to set goals when you start a law firm and then promptly forget about them.
Your plan will set out your goals and the metrics you will use to determine your progress toward meeting them. The plan should also explain how you will know when you have met them.
For example, you might have a growth goal of reaching five lawyers within two years. Or you might have a revenue goal of collecting $200,000 your first year.
Too many businesses, including law firms, meander on their developmental path. By setting goals and the path for meeting them, you will have guardrails to keep your firm on track.
"If you want to be the number one law firm in the country by revenue right in a 20 year time period, have that be your goal and everything that you do right is in service of that goal. You might not get there, but you're gonna find that you're gonna be very successful either way."
"If you want to be the number one law firm in the country by revenue right in a 20 year time period, have that be your goal and everything that you do right is in service of that goal. You might not get there, but you're gonna find that you're gonna be very successful either way." — Omar Ochoa
— Sort Out Your Own Law Firm Strategy
Developing a clear vision is important for establishing a strategic law firm plan aimed at long-term goals . As Omar Ochoa discusses in the podcast, having very specific milestone visions like where you want to be in five, ten, or fifteen years helps drive the strategy and actions needed to get there.
It's easy to say that you'll run your law firm better. But a plan actually helps you identify how to improve by articulating a concrete strategy. The process of creating the plan will help you pinpoint problems and solutions.
A plan forces consideration of operational details often overlooked. It equates to defining your firm's purpose and then pursuing that vision with purpose-driven strategies and actions. As Omar notes, marrying vision to action through knowledge of other successful law firm models is key to achieving goals.
One area that is frequently overlooked in plans is the inclusion of law firm marketing strategies . Developing this aspect is critical for attracting clients and sustaining growth.
Level Up Your Brand
Book a Free Consultation
— Move Forward
You should view your plan as a law firm business development plan that will guide the formation and growth of your firm .
You can review the document periodically to remind you and your law partners of your growth and expansion projections. After this review, you can ensure your growth and expansion remain on track to carry you to your goals.
The review will also tell you whether you need to update your firm's goals. When you started your law firm, you might have been unduly pessimistic or optimistic in your projections. Once you have some time to operate according to your plan, you can update your goals to keep them realistic. You can also update your processes to focus on what works and discard what does not.
The review can provide your projections for what you hope to accomplish and the roadmap for accomplishing it.
Law Firm Business Plan Template

Each of the websites below includes at least one attorney business development plan template:
- Business Plan Workbook
- PracticePro
- Smith & Jones, P.A.
- Wy'East Law Firm
You can use a law firm strategic plan example from these sites to start your firm's plan, then turn the plan into a document unique to your circumstances, goals, and needs.
What to Consider before Starting Law Firm Business Plans
Before starting a law firm business plan, think through a few key issues, including:
— Setting the Goals
Reflect deeply on your firm's purpose. Think about who you represent and how you can best meet their needs. A law firm exists for its clients. As you think about your law firm goals , think about goals for providing legal services to your clients.
"We continue to try to have the biggest impact that we can because ultimately, in my opinion at least, that's what lawyers are for, is to be able to help people and be able to move us forward." — Omar Ochoa
You need to set realistic and achievable goals. These goals should reflect your reasons for starting your law firm. Thus, if you started your law firm because you expected to make more money on your own than working for someone else, set some goals for collections.
While you are setting your goals, think about how you will reach them and the ways you will measure your success. For example, if you want to expand to include ten lawyers within three years, think about intermediate goals at the end of years one and two. This helps measure your progress.
— Choosing Partnership Structure
For lawyers considering a partnership structure, it's important to select partners that complement each other's strengths and weaknesses to help the firm function effectively.
There are 2 main partnership structure options:
- A single-tier model provides equal decision-making power and liability between partners.
- Meanwhile, a two-tier structure offers tiers like equity and non-equity partners, providing flexibility and career progression opportunities.
While similarly skilled individuals may clash, partners with differing abilities can succeed together. Some attorneys also choose to run their own firm for flexibility. This allows them to leverage different specialists through occasional joint ventures tailored for specific cases, without the constraints of a single long-term partnership. Furthermore, it highlights how the law firm partnership structures impacts freedom and sustainability.
— Thinking of the Revenue You Need
Calculate how much revenue you need to cover your overhead and pay your salary. Suppose your expenses include:
- $2,000 per month for office rent
- $36,000 per year for a legal assistant salary
- $600 per month for courier expenses
- $400 per month for a copier lease

Assume you want the median annual salary for lawyers of $127,990. You need $199,990 per year in revenue to cover your salary and expenses.
But revenue is not the end of the story. Your landlord, vendors, and employees expect to get paid monthly. So, you should also calculate how much cash flow you need each month to cover your hard expenses.
You also need a reserve. Clients expect you to front expenses like filing fees. Make sure you have a reserve to pay these costs and float them until clients reimburse you.
— Defining the Rate of Payment
You need to make some difficult decisions when it comes to setting your own fee structure. If you choose a higher billing rate, you will need to work less to meet your revenue goals. But you might not find many clients who are able to pay your fees.
Whether you charge a flat fee, contingent fee, or hourly fee, you should expect potential clients to compare your fees to those of your direct and indirect competitors. Remember, your firm competes against other lawyers, online services like LegalZoom , and do-it-yourself legal forms books.
Finally, you need to comply with your state's rules of professional conduct when setting your fees. The ABA's model rules give eight factors to determine the reasonableness of a fee. These factors include the customary fee for your location and the skill required to provide the requested legal services.
— Making the Cases in Your Law Practice Meet the Revenue Needs
Figure out how much you need to work to meet your revenue target . If you charge a flat fee, you can simply divide your revenue target by your flat fee.
Hourly fee lawyers can calculate the number of hours they need to bill and collect. However, law firm owners rarely bill 100% of the hours they work due to the administrative tasks they perform to run a firm. Also, you will probably not collect 100% of your billings, and clients could take 90 days or longer to pay.
Contingency fee lawyers will find it nearly impossible to project the cases they need. You have no way of knowing the value of your cases in advance. You also have no idea when your cases will settle. You could work on a case for years before you finally get paid.
Parts of a Business Plan for Law Firm Formation: Structure
A law firm business plan is a written document that lays out your law firm goals and strategies.
For many businesses, a business plan helps secure investors. But the ethical rules prohibit law firms from seeking funding from outside investors or non-lawyer shareholders .

Your business plan is for you and your law partners. It will help you manage everyone's expectations and roles in the firm. Here is a law firm business plan example to help you see the parts and pieces in action.
— Executive Summary
An executive summary combines the important information in the business plan into a single-page overview. Your plan will include details like projections, budgets, and staffing needs. This section highlights the conclusions from those detailed analyses.
Your executive summary should include :
- A mission statement explaining the purpose of your firm in one or two sentences
- A list of the core values that your firm will use whenever it makes decisions about its future
- The firm's overarching goals for itself, its lawyers, and the clients it serves
- The unique selling proposition that sets your firm apart from other firms in the legal industry
You should think of this section as a quick way for people like lenders, potential law partners, and merger targets, to quickly understand the principles that drive your firm.
— Law Firm Description and Legal Structure
First, you will describe what your law firm does. You will describe your law practice and the clients you expect to serve.
Second, you will describe how your firm operates. The organization and management overview will explain your legal structure and the management responsibilities of you and your law partners.
This section should fill in the details about your firm's operation and structure by:
- Describing the scope of the legal services you offer and your ideal clients
- Restating your mission statement and core values and expanding upon how they will guide your firm
- Explaining your location and where your clients will come from
- Describing your business entity type and management structure
- Detailing your unique selling proposition , including the features that distinguish your firm from your competitors
When someone reads this section, they should have a clear picture of what you will create.
— Financial Calculations
Your attorney business plan explains where your firm's revenue comes from and where it goes. This is where your skills as a lawyer begin to diverge from your skills as a business owner. You may need to learn a few new accounting concepts so you can perform the analyses expected in a financial plan.
You will need a financial plan for at least the first year.
If you plan to seek a bank loan or line of credit, your bank may need a financial plan that covers three years or longer.
You will need more than a few rough numbers for a useful business plan. Instead, you will need to estimate your expenses and revenues as accurately as possible.
"Take some financial statements courses, take some managerial accounting courses that teach you how to track costs, how to frame costs in a way that you're looking at the important costs." — Omar Ochoa
You might need to contact vendors and service providers to get precise costs. You will probably need to track your billings with your prior firm to predict your revenues. If you are opening a law firm after law school or an in-house job, you may need a competitive analysis to show what similar law firms earn in your location and practice area.
Some reports you may need in your business plan include:
- Revenue analysis listing the fees you will collect each month
- Budget describing your monthly and annual expenses
- Financial projections combining the revenue analysis and budgeted expenses to predict your profit margins
- Cash flow statement showing how your revenues and expenses affect your cash on hand.
Your cash flow statement might be the most important financial report because it explains how your bank balance will fluctuate over time. If your clients take too long to pay their bills or you have too many accounts payable due at the same time, your cash flow statement will show you when money might get tight.
— Market Analysis
A market analysis will tell you where you fit into the legal market in your location and field. You need a competitive analysis to understand the other lawyers and law firms that will compete with you for potential clients. You can also analyze their marketing messages to figure out how to stand out from the competition.
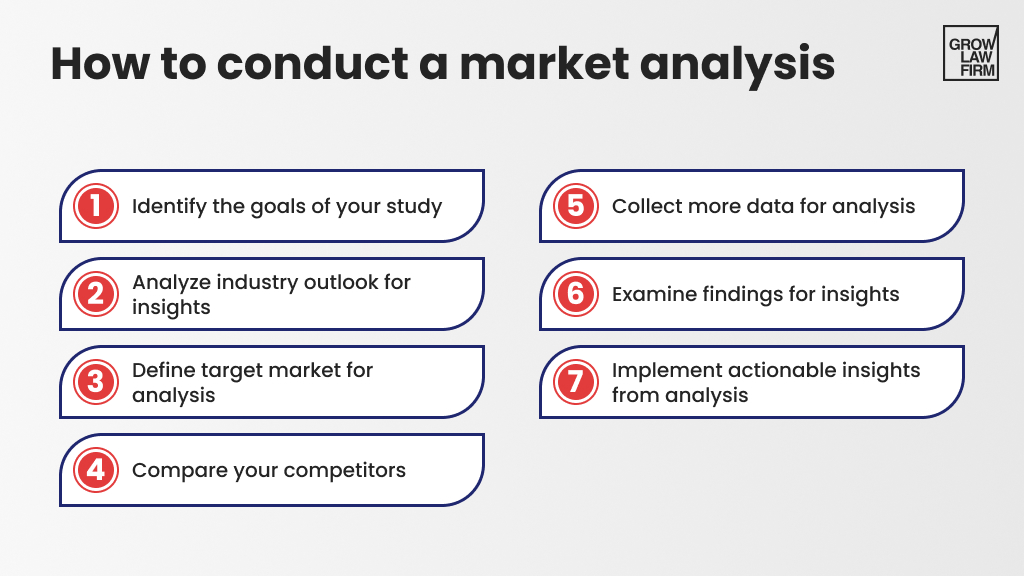
A competitive analysis will tell you what services other firms offer, how much they charge, and what features help your competitors succeed.
Your analysis should include a discussion about your :
- Ideal clients and what you can do to help them
- Market size and whether you offer something clients need
- Competitors and what they offer to clients
- Competitive advantages and how you can market them to potential clients
You can also develop and hone your marketing strategy based on the benefits you offer to clients over your competitors. Finally, a market analysis can tell you the locations and practice areas in which your firm may expand in the future.
Your market analysis helps you focus your efforts on your legal niche.
— Marketing Plan
A marketing plan sets out the steps you will take to reach your target market. Your marketing strategy will take your market analysis and turn it into a plan of action.
You will start with the results of your market analysis identifying your clients, your competitors, and your competitive advantages. You will then discuss the message you can deliver to potential clients that captures the advantages you have over your competition.

Some advantages you might have over other lawyers and law firms might include tangible benefits like lower billing rates or local office locations. Other advantages might provide some intangible benefits like more years of experience or state-bar-certified specialists in those states that allow specialization.
You will then discuss your marketing plan. A marketing plan explains :
- Characteristics of the target market you want to reach
- What your competition offers
- The distinct benefits you offer
- A message you can use to explain what separates you from your competition
- Your action plan for delivering your message
- Your goals for your action plan, such as the number of client leads, new clients, or new cases per month
Your action plan will include the marketing channels you want to use to spread your message. Marketing specialists can help you identify the best channels for your marketing message and client base.
For example, if you practice intellectual property law, you need to reach business owners and in-house lawyers who want to protect their companies' brands, inventions, artistic works, and trade secrets. A marketing agency may help you create a marketing strategy geared toward trade publications and business magazines.
However, IP lawyers require an entirely different marketing strategy than firms that practice family law. Family lawyers need to market to individuals and will tailor their marketing efforts toward different marketing channels and messages.
Even if you expect most of your client leads to come from referrals, you still need brand recognition for those leads to find you. You should consider a website, basic SEO, legal directory, and bar association listings.
— Your Law Firm Services
You will outline the services your law firm offers to clients. Lawyers with established clients and an existing legal practice can simply describe what they already do.
Any new law firm or lawyer transitioning from other practice areas should consider:
- Practice areas you know and enjoy
- Overlapping practice fields that will not require extra staff, such as personal injury and workers' comp
- Related legal services your clients may need, such as wills and guardianship
By offering needed services you can competently provide, you can gain clients and avoid referring existing clients out to other lawyers.
— Your Law Firm Budget
You should approach your budget as a living document. You will spend more money as you add more lawyers and staff members to your firm. But you can also look for ways to reduce your operating costs through investments in technology services and other cost-saving measures .
Your budget should set out the amount you expect to initially spend on start-up expenses. As you create your start-up budget, remember many of these expenses are not recurring. Furniture, computers, and office space build-outs can last several years. In short, your budget should answer the question, "What do you need to open a law firm?"
It should also lay out the amount you plan to spend each month to operate your firm. Here, you will include your recurring expenses, such as rent, staff salaries, insurance premiums, and equipment leases.
Using your operating budget, you will determine the amount of money you need to start and run your firm. This, in turn, will tell you whether you need to take out a loan or tap into your savings to start your law firm. You will need a plan for paying your expenses and day-to-day costs while your firm gets onto its feet.

Let us help you create a digital marketing strategy and a growth plan
.webp)
Some Useful Tips on Creating a Business Plan for Law Firm Creation and Development
As you draft your law firm business plan, you should focus on the process. By putting your thoughts down in writing, you will often identify issues you had not previously considered.
Some other tips for drafting your business plan include:
— Describe Both Strengths and Weaknesses
You want to project confidence as you prepare your business plan. Remember, you will use this plan to approach potential law partners, lenders, and merger targets. You need to show that you have a solid plan backed up by your financial projections.
At the same time, you need to remain realistic. Write a business plan that describes your business challenges as well as your competitive advantages.
For example, if you have a strong competitor that has a solid law firm reputation management and many of the clients you will target, acknowledge the difficulty of getting those clients to switch law firms. Describe your marketing strategies for approaching and pitching your law firm to those clients.
— Think Ahead
Remember that your business plan sets out the roadmap for both the establishment and operation of your law firm . Think about issues that could arise as your firm grows and matures.
For example, you may have a goal of reaching ten lawyers in three years. But as your staff grows, you may need a human resources manager. You may also seek to handle your payroll in-house instead of outsourcing it to a payroll provider. These changes will create ripple effects throughout your business plans. You will incur costs when you add staff members. You will also realize benefits like increased attorney efficiency.
At the same time, any projections more than five years into the future will likely be useless. Your firm and its clients will evolve, and technology will change how you practice law.
— Be Clear about Your Intentions
As you develop your plan, you should keep its purpose in mind. First, you want to outline your core values and goals for your law firm. Set out the reasons why you started your law firm and what you intend to accomplish with it.
"You can't just be doing something because you want prestige. There's gotta be more to that, right? You have to have a purpose that you're following. And if you've got that, that purpose is like gravity, right? You will always be grounded." — Omar Ochoa
Second, you set out your path to achieving those goals. This will include boring technical information like how much you spend on legal research every month. But it will also explain your approach to solving problems consistent with your mission statement and philosophy for law firm management.
— Consult and Update If Necessary
Your plan should guide you as you build your firm. It contains your goals and the roadmap for reaching them. But your plan is not carved in stone.
As you face challenges, you will consult your plan to make sure you approach these challenges in a way consistent with achieving your goals. But under some circumstances, you might find that the plan no longer provides the right solution.
As you work with your firm and your law partners, your goals, processes, and solutions to problems may evolve. The technology your firm uses may change. Your law firm's costs may go up with inflation or down as you realize economies of scale. You should update your plan when this happens.
Final Steps
There is no recipe for creating a business plan for law firm development. What goes into your mission statement and plan will depend on several factors, including your law firm's business model. But this is a feature, not a bug of developing a business plan.
The process of business planning will help you develop solutions to issues you might have overlooked. If you have law partners, just going through the process of creating a law firm business plan can ensure that everyone is on the same page.
As you create your plan, the process itself should provoke thoughts and ideas so you can have a unique law firm tailored to your goals and values. This will help you get exactly what you wanted when you started in the legal industry.
To learn how to expand your client base as your firm grows, check out Grow Law Firm, a professional law firm SEO agency .
Founder of Omar Ochoa Law Firm
Omar Ochoa is a founding attorney with extensive experience in complex litigation, including antitrust, class actions, and securities cases. He has recovered hundreds of millions of dollars for clients and has been nationally recognized as one of the best young trial lawyers in the country.
Omar graduated from the University of Texas at Austin with degrees in business administration, accounting, and economics. He later earned his law degree from the university, serving as editor-in-chief of the Texas Law Review. He has clerked for two federal judges and has worked at the prestigious law firm Susman Godfrey L.L.P. Omar is dedicated to seeking excellence. He has been recognized for his outstanding achievements in antitrust litigation.

- Easy steps you can take to bring in more clients and up this year’s revenue
- The top website and marketing mistakes holding your law firm back

Find out how much demand there is in your geographical area

To view the calculation tailored to your law firm's needs, please provide your email address below

Consult with Sasha Berson, a legal marketing expert , to address your marketing needs.
You May Also Like

Law Firm Marketing Budget: How Much Should You Spend?

Unlocking the Secrets of Law Firm Partnership Structures: A Must-Read Guide for Success-Driven Lawyers

Lawyers Against Unbillable Hours: Joshua Lennon Maximizes Attorney Billable Hours

How to Start a Law Firm in 2024 and Succeed

Starting a Law Firm: LLP vs. PC

Don't just wait for clients, attract them!
Get our FREE Marketing Audit to find bold new ways to boost your caseload.
Contact us today to speak with one of our experts and learn more about how we can help you grow your firm.

Stay ahead of the competition!
Compare your law firm's performance to Local competitors with our instant assessment tool
Get a clear picture of your firm's performance
Boost your online presence
.webp)

Home Committees, Members & Career Services Small Law Firm Center Overview Small Firm Resources Writing a Business Plan for Law Firm – Law Firm Business Plan Sample
Writing a Business Plan for Law Firm – Law Firm Business Plan Sample
Business plans for lawyers.
New York City Bar Association Small Law Firm Committee
Writing a Business Plans for Lawyers – The Non-Financial Side
1 Why write a law firm business plan?
First and foremost, it’s a Management Tool, It f orces you to think through important issues you may not otherwise consider The recipe to grow your law practice
- A roadmap, albeit a changing one, with milestones to help reach goals you already know and have yet to define
- A sales tool to obtain financing
- A sales tool when looking to form a partnership or join one
- Some parts of a business plan include stating the obvious, but should not be overlooked because they still form a part of the whole
- As you write it, ideas come, strategies unfold, beliefs you may have had change
- It also changes your mindset. You’re no longer thinking about starting a business, you’re now in the process of starting a business.
- If you write a business plan and put it away in a drawer you have not written one that is feasible or is going to do you any good. Continual updating – whether semi-annual, annual, biennial, whichever is best for you – is your own set of checks and balances.
If you are going to buy a book, look for one that offers general advice and suggestions applicable to all businesses. And, if you choose a software package, eliminate the “techy” things like their numbering system; that is a dead giveaway that you’re using a software program. Also, eliminate sections that are irrelevant!
Suggestion: Don’t just buy one from an online bookstore. Take the time go through a table of contents and thumb through.
Examples available from Barnes & Noble:
- Alpha Teach Yourself – Business Plans in 24 Hours by Michael Miller
- Successful Business Planning in 30 Days TM, 3/ed, Peter Patsula
- The Executive Summary
- Analysis of Your Market
- Description of Your Firm
- Competitors
- Your Marketing Strategy
No set formula for a successful practice
Before developing a plan for a lawyer, answer the following:
- Identify your practice niche(s)
- What skills and experience you bring to your practice
- What legal structure to use: sole proprietorship, PC, partnership, LLP, etc.
- What clients you currently have and might potentially acquire
- What clients you want
- What business and social contacts you have
- What other attorneys you can call upon to fill in practice gaps
- How your firm’s records will be kept
- What equipment and supplies will be needed
- What library and other information sources will be needed
- What insurance will be needed
- What other resources will be needed
- How you will compensate yourself
- Review your current finances re assets, current cash flow, expenses
- What financing may be needed
- What financial assets do you have
- What banking accounts will be needed
- Review your current non non-financial resources
- Identify your market
- Describe your startup plans
- Where will your office be located
- What will the name of your firm be
2 The Executive Summary
For some businesses this is the most important part of the business plan because it summarizes what the company does, where it is going and how to get there. Therefore, it must describe the company, the “product” and the market opportunities concisely.
It is written after the plan is complete but is the first and, sometimes, most important part read by investors.
How important this is for a legal business plan depends on your long and short term goals, e.g., whether they are to grow a partnership, join a firm, build up a practice that is enticing for acquisition by a larger firm, etc.
In order to provide that summary, go through a number of exercises:
- Mission statement – the firm’s purpose and what it will do
- Major goals
- Objectives/milestones needed to achieve those goals
- Vision statement – where you want to go and what you want your firm to become, not just 20 years down the road but where you want to be three or five years from now
- List what is out of your control e.g., nature of the law business, direction of the marketplace, competition, mergers and acquisitions among clients, and competitors, attorneys and firms already in place
- Analyze opportunities to face and threats
- List your firm’s specific capabilities and whatever you believe you can offer that is unique
- If you are not a solo practitioner, who is the management
- What is the legal organization
- What technology will you be capitalizing on
- What is the marketing potential
- Describe your basic strategies based on the information you have learned about the legal business, your competition and applicable markets within your field.
- Provide the basis for why you believe your strategy is the right one for your firm.
- What markers will you use to change direction
- Outline what your firm needs to make that strategy succeed
- Financial projections
- Back up of those projections with assumptions (so that they can be adjusted as necessary)
- Summary of revenues by month for at least three years
- Balance sheet
- Cash flow statement
- What actions you’re going to take to carry out the plan
- What changes will be needed or skills acquired to put the plan to work
3 Analysis of Your Market: The Legal “Business” that Affects You
Purpose: an accurate understanding of trends affecting law practice in general and your specializations, client demographics, client universe.
Keep track of impact factors, obstacles, opportunities and threats to better forecast and build the strategies.
- Identify who and what firms dominate and where they are
- What new technologies have already and may yet change the way your practice is done
- What laws and regulations have and may yet change your practice
- Describe the overall demand for your specialties
- What else besides price affects your client decisions to use your services
- What clients (people or companies) can influence your areas of practice
- Large firms, mid size, boutiques, solo practitioners
- In-house attorneys
- Government attorneys
- Divide into primary, secondary and, if necessary, tertiary levels
- Is there substitution, e.g., do it yourself or outsourcing to India
- List what is available and how it affects your practice
- Describe how technology is affecting your kind of practice
- Describe who controls the technologies that affect
- Describe how you keep up with new technology
- List all the things that will make it difficult for you to practice in your expertise and locale
- List the things that will make your exit from you area of expertise or your transition to a different one difficult
- What can relationships with suppliers do for you
- Could a supplier become a competitor, e.g.; for articles you write
- Colleagues and competitors
- Professional associations
- Community associations
- Social and business organizations
- Current and former clients
- Former employment colleagues
- Pro bono colleagues
- What ways improve your position with clients
- Does pricing affect
- What else affects your relationship
- What kind of follow up do you do after meeting someone who may be a potential client or who can introduce you
- Writing articles
- Giving speeches
- How can you use your other relationships
- What are the overall costs that affect your hourly, daily or matter rates?
- Profit margins
- What do suppliers of your technology, research, information, etc. offer by way of pricing, discounts
- Are there long term agreements that can be to your advantage/disadvantage
- Elasticity of demand for the rates you charge
- If on a regular retainer, are you realizing 100% of your hourly rate, or more/less
- Identify where the biggest costs of your practice come from
- Identify fixed and variable costs
- How to gain economies of scale
- Identify where you can lower costs
- Is the profit margin you’re working with the right one for your practice
- Describe the size of your primary market
- List the niche markets that can use your expertise
- Is your kind of practice a growing or shrinking market
- Identify new growth opportunities in your areas of expertise
- Economic slowdowns
- Changing statutes, regulations and decisions
- Social pressures
- By product, industry, size, geography
- Membership lists of trade organizations
- List of conference attendees
- By referral of current clients
- By referral of colleagues, bar association, etc.
- By referral from competitors with conflicts
- What untapped market is there
- What underserved market is there
- Trade associations made of small companies in the same field
- Part time general counsel for small companies
- Trade associations you can join and committees you can volunteer for
4 Describing and Analyzing Your Own Firm
- It’s not just a law firm.
- What’s the general history
- When was it formed and why
- What is your mission
- What are your goals
- What direct experience do you have? Your partners?
- How relevant is your experience to the current world?
- How often do you talk to prospective clients
- What do you current clients feel about you
- What is the maximum amount of business you can handle yourself without farming it out
- To whom can you farm
- Who is your backup when you are too busy, traveling on business, on vacation, sick
- What is unique about you or your practice
- Describe the areas you focus on and want to focus on
- What are the ancillary areas of law that often or usually involved or triggered by your focus area
- What need does your expertise serve
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of your areas of expertise
- Identify your own strengths and weaknesses
- Who are your clients
- Who among your clients makes the decisions to use your services
- What stage of business development are your clients in
- How sophisticated/knowledgeable are your clients
- Are your clients street smart and/or business savvy
- Do they use more than one lawyer at a time
- Long term objectives
- Short term objectives
- What problems do you face
- What problems do your clients face
- What do you consider milestones
- What are the legal (statutory, regulatory & case law) trends that will affect it
- What are the technological trends that will affect it
- What are the economic trends that will affect it
- What potential risks and opportunities to be faced?
- Do you use innovative technology
- Do you offer superior client care/service
- Is your hourly, daily, or matter pricing lower than the “norm”
- Is there a small group of firms or attorneys who offer the same expertise or specialization
- Are you well known for a book, a speech, an article, news coverage, etc.
- Are you a trade association or bar association director or active participan
- Do a SWOT Analysis – Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats
Strengths & Weaknesses are vis à vis your competitors, rather than your own history Focus on current competition and potential competition
- Are there advantages to your expertise areas
- What do you enjoy doing
- What resources to you have access to
- What do others see as your strengths
- What can you improve
- What don’t you do well
- What should you avoid
- Do others perceive a weakness you don’t agree with
- Are your competitors doing better than you
- How can you meet a potential client
- What are the good opportunities – are they new areas, new statutes & regulations, etc.
- How can changes in technology help you
- How can changes (or no changes) in government policy affect your area of expertise
- Are there changes in social patterns or lifestyle that can help
- What opportunities can open if a weakness is eliminated
- Family/emotional/physical challenges
- Technological challenges
- What is your competition doing you are not
- How can technological changes threaten you
5 Competitive Analysis and Target Market
- List law firm/solo practice trends
- List direct competition
- List indirect competition
- Describe the extent of the unserved market for your kind of legal services
- Who is your client/customer
- What is your price
- Profile your primary customer
- Traits: geographics, demographics, psychograhics
- List client needs
- Describe how your fill those needs
- List primary, secondary and tertiary competitors
- What services do they offer in addition to yours
- What do they charge
- How do competitor firms sell their services
- What are the competitor strengths
- What are the competitor weaknesses
- What size competes with you
- What other specialties do they offer
- Who are they representing
- What is their pricing
- What are their operational strengths and weaknesses
- Are they adequately financed
- How do your competitors advertise or promote themselves
- What are their conflicts
- How does your competition market itself
- Competitive Identification
- Direct competitor – offers the same benefit
- Indirect competitor – services the client can get instead of yours
- Visit and read competitor websites and their advertising, including separate websites by individual partners
- Subscribe to competitor law firm online or other newsletters
- Does it use innovative technology
- Does it offer superior client care/service
- Is its hourly, daily, or matter pricing lower than the “norm”
- Are they well known for a book, a speech, an article, news coverage, etc.
- Are they trade association or bar association directors or active participants
Generate similar info for potential clients to help identify the target that will be most interested in you
A marketing plan must have a detailed description of the target market for your services, an analysis of the trends and conditions of that marketplace and how the trends affect that marketplace
- Total size of targeted market
- Historical current and projected growth rates
- What social, economic &political changes could affect it and your services
- Describe recent developments in the law that affect your areas of expertise
- Are there identifiable niches
- What or will be your clients’ needs and wants
- How will potential customers find out about you
- What kind of marketing, if any, are your clients and potential clients receptive to
- What do existing clients like best about your services
- Are your target clients consumers, businesses or both
- Demographics, psychographics, legal service purchasing habits
- When and how does the client decide to use a lawyer & find a lawyer
- Does your potential client use the Internet, bar association, trade association, business referral, family referral, friend referral, etc. to find a lawyer
- What is your client’s level of education and occupation
- Are they Fortune 1000,500, 100, mid size or smaller
- Is your client industry specialized and do you know that industry
- Does the client use more than one lawyer or law firm
- How long does the client take to decide to use a lawyer
- Does more than one person at the client make the decisions to use a lawyer, and if so who are they
- Is the person who decides who is going to provide legal services the one who is going to receive those services
- What influences your client’s decision to retain a lawyer
- Is using a lawyer optional, a necessity or a luxury
- Is a lawyer needed all year round, seasonal or ad hoc
- How and how well do your clients market themselves
6 Marketing & Strategy
Once you analyze your client needs you can build a comprehensive marketing strategy,
- What is it you intend to accomplish
- What is the amount of increase in clients and/or billing that you want to achieve
- Make each goal measurable and explain each one specifically
- Set each goal to a planned schedule
- Be able and prepared to assess all components to revise when necessary
- Compare these goals to what you believe your competitors’ goals to be
- Tactical objectives = measurable tasks
- Create client value
- Name recognition among your clients and potential clients
- Client retention
- Attracting partners or merging into a bigger firm
- Create a timeline for the objectives or events
- Determine the time frame for the plan, e.g., every six months, every year, etc.
- Describe the need for your services from the client’s POV
- Define the impact on the client of your services
- Ask whether your clients currently obtain this service more cost-effectively than you can provide it
- Describe what would compel clients to change from the lawyers they are using to you or to add you to their lawyer rosters
- E.g., how you will use that list of relationships
- Marketing Mix – Networking, Advertising, Promotion, PR
- Inserts in papers
- Bus, taxi, etc. ads
- Space in professional and trade publications
- Street banners
- New resident welcome kits
- Trade and trade association show directories and handouts
- Trade and trade association show sponsorships
- Coupon mailers
- Press releases
- Sponsorship
- CRM (customer relationship marketing)
- Cost based = cost plus profit margin
- Cost plus profit = cost plus fixed percentage markup
- Market based = use the market norm and add or subtract
- Ask what the highest price your target market can bear
- Determine the price elasticity for your kind of legal services
- Should you offer an introductory rate
- Age of business
- Premises/location
- Competition
- Cost to acquire a client

- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.
Upmetrics AI Assistant: Simplifying Business Planning through AI-Powered Insights. Learn How
Entrepreneurs & Small Business
Accelerators & Incubators
Business Consultants & Advisors
Educators & Business Schools
Students & Scholars
AI Business Plan Generator
Financial Forecasting
AI Assistance
Ai Pitch Deck Generator
Strategic Planning
See How Upmetrics Works →
- Sample Plans
- WHY UPMETRICS?
Customer Success Stories
Business Plan Course
Small Business Tools
Strategic Planning Templates
E-books, Guides & More
- Sample Business Plans
Law Firm Business Plan
If you are a lawyer, chances are you have thought of owning a law firm at least once if not more.
After all, having your firm gives you the freedom of taking up projects that you like and working at flexible hours.
But with freedom comes responsibility, and most of us find the thought of doing everything from onboarding clients to taking care of every detail of their case at least in the initial days quite overwhelming.
But don’t worry! It isn’t as scary as it looks. All you need to run a successful law firm is your sharp wit to deal with cases and a well-written law firm business plan to deal with the business side of your profession.

Free Law Firm Business Plan Template
Download our free business plan template now and pave the way to success. Let’s turn your vision into an actionable strategy!
- Fill in the blanks – Outline
- Financial Tables
Industry Overview
The global legal services market was valued at a whopping sum of 849.28 billion dollars in 2020 and is expected to rise at a high rate going forward too.
The main changes in the legal industry have been brought about by the introduction of AI which does proofreading and data research jobs with higher efficiency. This lets the lawyers focus on what really matters.
Also, the security and access systems have become loads better due to cloud computing.
What is Law Firm Business Plan?
A law firm business plan is a document that outlines your business goals and strategies to achieve those goals. It includes your law firm overview, your reason to start your firm, the services you will offer, a budget or funding requirements, and strategies to get and manage your clients.
Why Law Firm Business Plan is Important?
A business plan would help you understand what sets you apart from your competitors, and how you can market your USP to your clients.
It also helps you design strategies to reach out to your clients and manage them. It comes in extremely handy for analyzing the loopholes in your business structure.
Moreover, it helps you identify your strengths and work on your weaknesses.
All in all, It can make managing your business a hassle-free and less chaotic process.
Things to Consider Before Writing a Law Firm Business Plan
Focus on your expertise.
Between juggling business and practice, it is natural that practice gets neglected more often than not. But always keep in mind that though focusing on your business is important it shouldn’t come at the cost of skills you need to develop and upgrade to do well as a lawyer.
Also, it is important to decide on a niche so you can dig deeper and become an expert at handling cases of that kind.
Create a proper website
In today’s world being present and active on the internet is as important for your business as being good at what you do.
A strong web presence helps you reach out to your customers as well as builds your reliability for them.
Build your network
Networking is an important aspect of being a lawyer. From getting new customers, getting updates on the legal world, and even collecting evidence if you are a criminal lawyer, a good network can work wonders for your legal business.
The kind of circle you belong to also has an impact on your reputation and image as a lawyer.
Develop soft skills
We all know that confidence and intellect are a lawyer’s best friends. And although it is an ongoing process to develop these skills, it is good to get a head start before you start your business.
Intellect helps you upgrade and pay attention to detail, and confidence helps you sound more convincing and reliable. Both of which are foundational to a legal business.
How to Write a Law Firm Business Plan?
A law firm business plan would be a combination of segments common to all business plans and segments specific to a law firm.
Before you start writing your business plan for your new law firm, spend as much time as you can reading through some examples of consulting-related business plans .
Reading some sample business plans will give you a good idea of what you’re aiming for. It will also show you the different sections that different entrepreneurs include and the language they use to write about themselves and their business plans.
We have created this sample law firm business plan for you to get a good idea about how a perfect law firm business plan should look like and what details you will need to include in your stunning business plan.

Chalking out Your Business Plan
Starting your own law firm is an exciting prospect for any lawyer. Having your firm gives you more independence, lets you implement ideas you want to, and most importantly, you get to deal with clients firsthand.
And if you plan on starting your own, do so with a proper business plan.
But you might wonder, why do I need a business plan as a lawyer, isn’t my legal knowledge and years of work enough?
The answer is no.
To run a law firm you need a law degree, but to run a successful business you need a business plan alongside your degree.
Law Firm Business Plan Outline
This is the standard law firm business plan outline which will cover all important sections that you should include in your business plan.
- Mission Statement
- Vision Statement
- Financial Summary
- 3 Year profit forecast
- Business Structure
- Startup cost
- Market Analysis
- Market Trends
- Target Market
- Market Segmentation
- Sales Strategy
- Marketing Strategy
- Pricing Strategy
- Personnel Plan
- Financial Plan
- Important Assumptions
- Brake-even Analysis
- Profit Yearly
- Gross Margin Yearly
- Projected Cash Flow
- Projected Balance Sheet
- Business Ratios
Say goodbye to boring templates
Build your business plan faster and easier with AI
Plans starting from $7/month

Now, let’s understand how you can complete each section of your business plan.
1. Executive Summary
The executive summary forms the first page of your business plan. It acts as a pitch for your business to potential investors and should consist of the following sections.
- Objective: This gives an overview of what you wish to accomplish with your business. The objective should be clear and solve an existing problem in the market.
- Vision Statement: This should state what vision you have for your business. How do you want it to function and how far do you expect to reach with it. You can also include how your vision sits with the current market situation.
- Financial Summary: This section should ideally consist of the history of your finances and their current state. A proper financial summary helps you gain an investor’s confidence and makes it easier for your business to get funded.
2. Company Summary
Next up we have the company summary section, this segment provides an overview of your company’s structure and its functioning.
This section provides a brief description of the following:
- Legal Structure: This section would describe the legal terms and conditions your firm functions on, as well as the ownership structure of your firm.
- USP: This would consist of points that set your firm apart from your competitor’s firm.
- Services: This section will include the services you offer, the legal procedures you are well versed in, all in all, the client base you cater to.
- Location: This segment covers your area of service and the location of your firm. A clearly stated area of service, helps you reach the right audience.
3. Market analysis
This segment consists of a thorough analysis of the market situation. It can be split up into the following sub-segments.
- Market Trends: This would consist of all the prevailing trends in the market. It is important to know market trends because it helps your business keep up with the evolving market.
- Target Market: This section would consist of a summary of the market you cater to. Clearly defining your niche helps you reach out to your desired customer base.
- Market Segmentation: In this section, note down the segments present in the market, as well as what segment of the market your business would fit in. This would help you narrow down the number of competitors you have, the strategies you must follow, and the major and additional services you should offer.
4. Strategy and implementations
In this section, you would include various business strategies like:
- Marketing strategy You can formulate a marketing strategy depending on your target audience and the easiest and most effective ways of reaching out to them. It is important to formulate your marketing strategy based on your USP and your vision statement.
- Pricing Strategy It is important to formulate a pricing strategy based on the market trends, the nature of the work, and your target audience.
- Milestones This segment would consist of the various milestones your business would have to reach to achieve your goal and the strategies to help you reach them.
5. Financial Plan
The financial section of your business plan would consist of the following information regarding your business.
- Financial history
- Current State of finances
- Profit and loss
Download a sample law firm business plan
Need help writing your business plan from scratch? Here you go; download our free law firm business plan pdf to start.
It’s a modern business plan template specifically designed for your law firm business. Use the example business plan as a guide for writing your own.
The Quickest Way to turn a Business Idea into a Business Plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
Law Firm Business Plan Summary
All of the above segments would help you in creating a well-rounded business plan. Starting your law firm with a well-written business plan can make your growth process faster and smoother.
After getting started with Upmetrics , you can copy this law firm business plan example into your business plan and modify the required information and download your law firm business plan pdf or doc file.
It’s the fastest and easiest way to start writing your business plan.
Related Posts
Law Firm Financial Plan
How to Write a Business Plan Step by Step
Notary Business Plan
Bookkeeping Business Plan
About the Author
Upmetrics Team
Upmetrics is the #1 business planning software that helps entrepreneurs and business owners create investment-ready business plans using AI. We regularly share business planning insights on our blog. Check out the Upmetrics blog for such interesting reads. Read more
Plan your business in the shortest time possible
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
Popular Templates

Create a great Business Plan with great price.
- 400+ Business plan templates & examples
- AI Assistance & step by step guidance
- 4.8 Star rating on Trustpilot
Streamline your business planning process with Upmetrics .

Trending News

Related Practices & Jurisdictions
- Law Office Management
- Corporate & Business Organizations
- All Federal

Lawyers often approach their work with a strong focus on client advocacy, research and legal strategy. While these are crucial aspects of practicing law, it’s equally important to recognize that running a law firm effectively requires a business-oriented mindset. Operating your law practice like a business not only ensures financial stability but also fosters growth, efficiency and long-term success. In this blog post, I’ll explore various ways in which lawyers can successfully manage their practices by adopting a more business-centric approach.
1. Develop a Clear Business Plan: Just as any successful business starts with a well-defined business plan, your law practice should have a strategic roadmap. Your plan should outline your practice’s mission, goals, target clients, practice areas, financial projections and marketing strategies. Having a clear plan provides direction and helps you make informed decisions for the growth of your practice.
2. Effective Financial Management: Managing the finances of your law practice is essential. This includes budgeting, tracking expenses, setting pricing structures and managing cash flow. Implement accounting software or hire a professional accountant to maintain financial records and provide insights on optimizing your practice’s profitability.
3. Marketing and Branding: Effective marketing is key to attracting and retaining clients. Invest in building a strong online presence, including a professional website and active social media profiles. Develop a consistent brand image and engage in content marketing, including blog posts, articles and social media updates that showcase your expertise.
4. Client Relationship Management: Building strong client relationships is essential for repeat business and referrals. Communicate clearly, set expectations and provide exceptional client service. Regularly solicit feedback from clients to improve your services and address any issues promptly.
5. Invest in Technology: Embrace technology to streamline your operations and improve efficiency. Practice management software, document management systems and legal research tools can help you save time and enhance your service delivery.
6. Efficient Time Management: Time is a valuable resource, and effective time management is crucial. Implement time tracking software to understand how you spend your work hours and identify areas where you can be more productive. Delegate tasks when appropriate to free up your time for high-value legal work.
7. Networking and Business Development: Build a strong professional network within the legal industry and your specific practice area. Attend legal conferences, join bar associations, and participate in local business organizations. Networking can lead to referrals and valuable connections.
8. Embrace Innovation: Stay up-to-date with legal technology trends and innovations. Explore alternative fee structures, such as flat fees or subscription models, to provide clients with flexible options while ensuring steady income for your practice.
9. Measure Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Identify and track key performance indicators that are relevant to your practice. These may include client acquisition cost, client retention rates, billable hours and revenue growth. Regularly review your KPIs to assess the health and progress of your practice.
10. Continuous Learning and Professional Development: In the legal profession, staying current with legal developments and professional standards is vital. Invest in your ongoing education, attend relevant seminars, and pursue advanced certifications or specialization.
By adopting a business-oriented approach to your law practice, you’ll be better positioned to achieve your goals, provide excellent legal services, and ensure the long-term success and sustainability of your practice. Remember that while legal expertise is your foundation, a strong business mindset will empower you to thrive in an increasingly competitive legal landscape.
Key Takeaways
- Business Mindset Matters: Operating your law practice like a business is crucial for long-term success. A business-oriented approach helps you make informed decisions, achieve financial stability and foster growth.
- Develop a Strategic Plan: Start with a clear business plan that outlines your mission, goals, target clients, practice areas and marketing strategies. A well-defined plan provides direction and focus.
- Effective Financial Management: Properly manage your finances, including budgeting, expense tracking, pricing and cash flow management. Seek professional help when necessary to optimize profitability.
- Invest in Marketing: Building a strong online presence and consistent branding is essential for attracting and retaining clients. Create content pieces and leverage social media to showcase your expertise.
- Nurture Client Relationships: Exceptional client service and clear communication are key to building strong client relationships. Solicit feedback to continuously improve your services.
- Leverage Technology: Embrace legal technology to streamline operations and improve efficiency. Practice management software and document management systems can save time and enhance service delivery.
- Time Management: Efficiently manage your time, delegate tasks when possible and prioritize high-value legal work.
- Network and Build Connections: Cultivate a strong professional network within the legal industry and your practice area. Networking can lead to referrals and valuable connections.
- Embrace Innovation: Stay current with legal tech trends and explore alternative fee structures to adapt to evolving client needs.
- Measure Performance: Identify and track key performance indicators (KPIs) relevant to your practice. Regularly assess your KPIs to monitor progress and make data-driven decisions.
- Continuous Learning: Commit to ongoing education and professional development to stay up-to-date with legal developments and industry standards.
By combining your legal expertise with a business-oriented mindset, you’ll not only provide exceptional legal services but also ensure the sustainability and success of your law practice in an increasingly competitive legal landscape.
Current Legal Analysis
More from stefanie marrone consulting, upcoming legal education events.

Sign Up for e-NewsBulletins
Seven Sample Attorney Business Plans: Why Attorneys Must Have Business Plans
Share this article
Print/Download PDF

By Harrison Barnes
Rate this article
2443 Reviews Average: 5 out of 5
- Business plans are a dying art, especially in the legal profession.
- Needless to say, business plans are also essential for a lawyer’s career.
- As the adage goes, if you don't plan your career, someone else will plan it for you.

Many of you work in firms that don't have a business plan for the firm as a whole , let alone your practice group or individual attorneys. And some of you are not privy to the firm's plan, even if there is one.
- If you are interested in seeing the elements of a lateral partner business plan click here: Partner Business Plans: Key Elements
Even so, that's no reason to forgo developing a plan for yourself. Remember, if you don't plan your career, someone else will plan it for you.
Have no fear. Personal business planning is not about writing a 50-page manifesto outlining every detail of every day of your professional life for the next 10 years . In fact, personal business planning can be as simple as you want to make it, as you can see here with this sample business plan for law practice PDF . You don't even have to call it a business plan -- call it a career plan if you prefer.
No matter how simple you make it or what you call it, personal business planning is about taking inventory of where you are , determining where you want to go and building a roadmap for getting there. Once you have the plan in writing, all you have to do is revisit it periodically to check your course and make any necessary adjustments.

Also, when it comes to planning, the biggest land mines are complexity and procrastination. Try to avoid creating a plan that overwhelms you or anyone you tell about it. And remember that any plan is better than no plan at all.
Strive to keep your plan simple and start taking action. As an attorney, you're well-versed in the areas of analysis and logic. In every work matter, you look at the situation and connect the dots to accomplish the desired objective. Apply the same approach to personal business planning and the dots you connect will lead you to the career you've always wanted.
- See 30 Ways to Generate Business as an Attorney for more information.
Business Plan For A Law Firm
How do i write a business plan for a law firm, what goes into a business plan, overview of the firm.
- A mission statement about the firm’s purpose.
- A vision statement or recitation of medium- and long-term goals for the firm.
- Important aspects of the firm’s history.
- Any important philosophies that the firm brings to legal practice.
Market Analysis
Do lawyers write business plans, 1. what are your goals.
- What do I want to achieve by starting my own law firm ?
- What is the impact I want to have?
- What am I good at?
- How do I want to service my clients?
- What problems do I want to help solve?
- What does success look like after starting this law firm?
2. Consider how much revenue you will need.
3. setting your fee structure, 4. determine how many cases you need to meet that revenue goal, how to create a law firm business plan, 1. executive summary.
- Mission statement: One or two sentences describing your firm’s purpose.
- Core values: What values are most important to the firm?
- Major goals: What are your firm’s overarching goals and objectives?
- Unique selling proposition: What sets your firm apart from other firms?
2. Firm Description
- Service(s): What type of law do you practice? What types of clients do you serve?
- Firm values: Restate your mission statement and core values.
- Legal structure: What sort of business entity are you? Are you in a sole proprietorship or a limited liability partnership?
- Location: Where is the office geographically located? What areas does the firm serve?
- Unique selling proposition: What makes your firm stand out? What technology or services give your firm an edge?
3. Market Analysis
- Ideal client: What demographics (like location, age, occupation), needs, and motivations would signify the best client match for your firm, and why?
- Industry description: What is the current and projected size of the market your firm is in? What are the trends in your legal niche?
- Competitive analysis: Who are your direct and indirect competitors, and how are they serving your target market? Where do your competitors succeed? What opportunities are there for your firm?
- Projections: How much can your ideal clients spend on legal services? How much can you charge?
4. Organization and Management Overview
- Describe what makes you unique and what sets you apart from other applicants.
- If applicable, include what makes each member of your team suitable for their particular roles.
- The organizational chart is a great visual aid if you have a larger practice.
5. Services
- What problems do your potential clients need your help with?
- How can your services uniquely help your clients solve their problems?
- What is the benefit of your services to clients?
- Why would potential clients choose your firm over another firm?
6. Marketing Strategy
- Ideal client: Where would you find your ideal client?
- Marketing goals: Detail what specific outcomes you hope to accomplish through marketing. Goals should include tactical objectives (more clients? Higher billing rates?) and overall objectives (like increased name recognition).
- Unique selling proposition: Restate what sets you apart and makes you uniquely able to best serve your clients.
- Competition: Detail who your competition is—and what they are doing to gain clients. Analyze their marketing strategies and assess where the cost of your services fits in with your competitors.
- Action plan: List the specific actions your firm will take to reach your target market and achieve your marketing goals (this could include a media/advertising strategy).
7. Financial Plan
- Revenue goal: How much money you want to make broken down by month.
- Financial projections: What you will really expect to earn, how many cases you think you will have the capacity to take on, and what you will be charging each client each month.
- Budget: A breakdown of your expenses and what your money will be going towards each month.
- Cash flow statement: What you actually earned and spent each month. This is different from your projections and budget and should be updated as the year progresses. You will find that you may have budgeted for something that cost you much less than you originally thought or made more in a month than you projected, these discrepancies should be recorded in your cash flow statement.
8. Start-Up Budget
- Hardware (laptops, printers, scanners, office furniture, etc.)
- Office space (Will you rent, or work from home?)
- Malpractice insurance
- Staff salaries (Are you planning to hire an administrative assistant or paralegal?)
- Utilities (Phone, internet, etc.)
- Practice management software or other technology services
- Partner Business Plans: Key Elements
- You Need to be Self-Managing and Responsible
- The Importance of Finding and Creating Demand
- The Importance of Asking the Right Questions, Self Improvement and Perception
- Attorney Business Plan Sample 1
- Attorney Business Plan Sample 2
- Attorney Business Plan Sample 3
- Attorney Business Plan Sample 4
- Attorney Business Plan Sample 5
- Attorney Business Plan Sample 6
- Attorney Business Plan Sample 7
Want to continue reading?
Become a free bcg attorney search subscriber..
Once you become a subscriber you will have unlimited access to all of BCG’s articles.
There is absolutely no cost!
Harrison Barnes does a weekly free webinar with live Q&A for attorneys and law students each Wednesday at 10:00 am PST. You can attend anonymously and ask questions about your career, this article, or any other legal career-related topics. You can sign up for the weekly webinar here: Register on Zoom
Harrison also does a weekly free webinar with live Q&A for law firms, companies, and others who hire attorneys each Wednesday at 10:00 am PST. You can sign up for the weekly webinar here: Register on Zoom
You can browse a list of past webinars here: Webinar Replays
You can also listen to Harrison Barnes Podcasts here: Attorney Career Advice Podcasts
You can also read Harrison Barnes' articles and books here: Harrison's Perspectives
Harrison Barnes is the legal profession's mentor and may be the only person in your legal career who will tell you why you are not reaching your full potential and what you really need to do to grow as an attorney--regardless of how much it hurts. If you prefer truth to stagnation, growth to comfort, and actionable ideas instead of fluffy concepts, you and Harrison will get along just fine. If, however, you want to stay where you are, talk about your past successes, and feel comfortable, Harrison is not for you.
Truly great mentors are like parents, doctors, therapists, spiritual figures, and others because in order to help you they need to expose you to pain and expose your weaknesses. But suppose you act on the advice and pain created by a mentor. In that case, you will become better: a better attorney, better employees, a better boss, know where you are going, and appreciate where you have been--you will hopefully also become a happier and better person. As you learn from Harrison, he hopes he will become your mentor.
To read more career and life advice articles visit Harrison's personal blog.
Article Categories
- Legal Recruiter ➝
- Harrison's Perspectives ➝
- Career Advice for Attorneys
Do you want a better legal career?
Hi, I'm Harrison Barnes. I'm serious about improving Lawyers' legal careers. My only question is, will it be yours?

About Harrison Barnes
Harrison is the founder of BCG Attorney Search and several companies in the legal employment space that collectively gets thousands of attorneys jobs each year. Harrison is widely considered the most successful recruiter in the United States and personally places multiple attorneys most weeks. His articles on legal search and placement are read by attorneys, law students and others millions of times per year.
Find Similar Articles:
- Legal Job Market
- Business Development
- Generate Business
- Legal Career
- Develop Additional Business
- Partner Resources
- Attorney Business Plans
- Partner Business Plans
- Lateral Partner Business Plan
- Business Plans
- Personal Business Planning
Active Interview Jobs
Featured jobs.
Location: California - Beverly Hills
Location: Massachusetts - Yarmouth Port
Location: New Jersey - Roseland
Most Viewed Jobs
Location: Oregon - Salem
Location: New York - New York City
Location: California - Santa Ana
Upload Your Resume
Upload your resume to receive matching jobs at top law firms in your inbox.
Additional Resources
- Harrison's Perspectives
- Specific Practice Areas
- The Winning Mindset
BCG Reviews
Responsive company.
Russell Klein
Columbia University School of Law, Class Of 2006
I like BCG because I felt like, well I am going to direct my comments toward my legal placement professional because I r.... Read more >
Katherine Thornton
Vanderbilt University Law School, Class Of 2011
Brian placed me at a top law firm, and I would highly recommend them to anyone seeking an excellent legal job. My goal w.... Read more >
Alyssa Ohanian
UC Berkeley - School of Law, Class Of 2014
It is with great pleasure that I can say that I have a job I love. BCG Attorney Search and my recruiter have a great rol.... Read more >
Darren Watson
Harvard Law School, Class Of 1991
My favorite thing about working with BCG was my legal placement professional. She was very invested in my search and got.... Read more >
Mauricio Gonzalez
Cornell, Class Of 2003
She never gave up on me. There was definitely a lot of effort put in for me. I liked how every so often I would get new .... Read more >
Rose Nankervis
St. John's University School of Law, Class Of 2016
Popular Articles by Harrison Barnes
- What is Bar Reciprocity and Which States Allow You to Waive Into the Bar?
- What Do Law Firm Titles Mean: Of Counsel, Non-Equity Partner, Equity Partner Explained
- Top 6 Things Attorneys and Law Students Need to Remove from Their Resumes ASAP
- Why Going In-house Is Often the Worst Decision a Good Attorney Can Ever Make
- Top 9 Ways For Any Attorney To Generate a Huge Book of Business
Helpful Links
- The BCG Attorney Search Guide to Basic Law Firm Economics and the Billable Hour: What Every Attorney Needs to Understand to Get Ahead
- Quick Reference Guide to Practice Areas
- Refer BCG Attorney Search to a Friend
- BCG Attorney Search Core Values
- Recent BCG Attorney Search Placements
- What Makes a World Class Legal Recruiter
- What Makes BCG Attorney Search The Greatest Recruiting Firm in the World
- Top 10 Characteristics of Superstar Associates Who Make Partner
- Off-the-Record Interview Tips From Law Firm Interviewers
- Relocating Overseas
- Writing Samples: Top-12 Frequently Asked Questions
- The 'Dark Side' of Going In-house
- "Waive" Goodbye To Taking Another Bar Exam: Typical Requirements and Tips to Effectively Manage the Waive-in Process
- Changing Your Practice Area
- Moving Your Career to Another City
- A Comprehensive Guide to Working with a Legal Recruiter
- A Comprehensive Guide to Bar Reciprocity: What States Have Reciprocity for Lawyers and Allow You to Waive into The Bar
Related Articles

Important Questions Attorneys Need to Ask Themselves Before ....
The Importance of a Great Business Plan

No Job Offer in Hand? Then You Need a Plan

Business Plans Revealed
When you use BCG Attorney Search you will get an unfair advantage because you will use the best legal placement company in the world for finding permanent law firm positions.
Don't miss out!
Submit Your Resume for Review
Register for Unlimited Access to BCG
Sign-up to receive the latest articles and alerts
Already a subscriber? Sign in here.

Virtual Legal Staffing
- Social Media
Organic Marketing
Law Firm Growth
- Social Media Management
- LS Press Release
- Press Release
Success in Overseas Staffing: A Conversation with Hamid Kohan of Legal Soft

Law Firm Incubation: The Future of Legal Entrepreneurship

Making Your Website Mobile-Friendly and Why You Need It

How to Grow a Small Law Firm: A Guide for Success (Part 2)

How to Manage a Small Law Firm: A Guide for Success (Part 1)

2024’s Blueprint for Success: Innovative Trends in Law Firm Marketing
We will contact you as soon as possible, speak with a representative.
- I Work at a Law Firm
- I'm a Virtual Assistant
Book A Demo Now
- Testimonials
Virtual Staffing
- Legal Virtual Assistants
- Virtual Demand Writer
- Virtual Marketing Specialist
- Virtual Assistant Smart Device
Branding and Outreach
- Mobile Apps
- Website Development & Maintenance
- Client Survey
- Attorneys Newsletter
- GMB Optimizations
- SMS Campaigns
- Directory Listing
- Website Development
- Legal Virtual Assistant
- Practice Growth
- Practice Setup
- Practice Management
- Lead Generation & Management
- Automated Intake Forms
- Intake Set up
- [email protected]
- (424) 341-4917
Subscribe to Our Newsletter!
- 21731 Ventura Blvd. Suite 100, Woodland Hills, CA 91364
Ⓒ 2023 Legal Soft - All Rights Are Reserved
- Legal Research

LAW FIRM GUIDES AND TEMPLATES
- For Legal Professionals
- Member Support
- Practice Management Assistance
Business Plan Template
Guides and templates from the wsba.
These resources are developed to help you navigate law firm business ownership. If you have any questions, please send us an email or schedule a free telephone consultation .
Document Retention │ Disaster Planning & Recovery │ Cybersecurity │ Hanging Your Own Shingle
Document retention.

View the guide .
Disaster Planning & Recovery

Cybersecurity

Hanging Your Own Shingle

All Guides and Templates
Nwsidebar blog washington state bar news magazine.

Toll-free: 800-945-9722 Local: 206-443-9722 Admissions: 206-727-8209 Ethics Line: 206-727-8284 Email: [email protected] Webmaster: [email protected] Washington State Bar Association 1325 Fourth Ave., Suite 600, Seattle, WA 98101-2539
© 2023 Washington State Bar Association, all rights reserved.
Business Plan for Investors
- Bank/SBA Business Plan
- Operational/Strategic Planning Services
- L1 Visa Business Plan
- E1 Treaty Trader Visa Business Plan
- E2 Treaty Investor Visa Business Plan
- EB-1 Business Plan
- EB-2 NIW Business Plan
- EB-5 Business Plan
- Innovator Founder Visa Business Plan
- Start-Up Visa Business Plan
- Expansion Worker Visa Business Plan
- Manitoba MPNP Visa Business Plan
- Nova Scotia NSNP Visa Business Plan
- British Columbia BC PNP Visa Business Plan
- Self-Employed Visa Business Plan
- OINP Entrepreneur Stream Business Plan
- LMIA Owner Operator Business Plan
- ICT Work Permit Business Plan
- LMIA Mobility Program – C11 Entrepreneur Business Plan
- USMCA (ex-NAFTA) Business Plan
- Franchise Business Plan
- Landlord business plan
- Nonprofit Start-Up Business Plan
- USDA Business Plan
- Cannabis business plan
- Ecommerce business plan
- Online boutique business plan
- Mobile application business plan
- Daycare business plan
- Restaurant business plan
- Food delivery business plan
- Real estate business plan
- Business Continuity Plan
- Pitch Deck Consulting Services
- Financial Due Diligence Services
- ICO whitepaper
- ICO consulting services
- Confidential Information Memorandum
- Private Placement Memorandum
- Feasibility study
- Fractional CFO
- How it works
- Business Plan Examples
Law Firm Business Plan Sample
JUN.03, 2018

Do you want to start a law firm business?
Do you plan to start a law firm business? There is no doubt this is an awesome business venture with amazing potential. In recent years, the law firm industry has been experiencing a steady growth of more than 15% per annum. The need for individuals, businesses and companies seeking for lawyer services in order not to get into legal problems has greatly increased. Today, there are many niches you can choose to start your practice on. All you need to have is the right qualification and target the right customers for your law firm business plan .
Executive Summary
2.1 the business.
The law firm will be registered under the names Raymond Associates, and will be situated in Houston, Texas. The law firm will be owned and managed by Alex Raymond who is a lawyer by profession.
2.2 Management Team
Alex Raymond is a lawyer by professional who has worked in the legal industry for more than fifteen years. Before coming up with a law firm business model, Alex worked for many to law firms across the United States and is an accomplished legal business service expert .
2.3 Customer Focus
Raymond Associates plans to offer different top notch legal services to customers in Houston, Texas. The customer focus will cater for different age groups and working class.
Once you have figured out how to start your own law firm, having an idea of the customer you intend to target is important. The customers you plan to target is essential for the growth of the business.
2.4 Business Target
Raymond Associates intends to offer services to a wide range of clientele keen on seeking legal services for their various needs. For a business to grow, it is important to carry out an in-depth research to target the right clientele.

Company Summary
3.1 company owner.
Alex Raymond is a lawyer professional who has worked with famous legal firms in the United States. In the course of his career, he ascended to the position of a seasoned attorney and took the lead role in planning the law firm operations and overseeing all management related aspects.
3.2 Aim of Starting the Business
After having been in the career long enough, Alex noticed there was a lot of potential in the legal industry in his home town Houston. That is the when he decided to move back to home and start a business plan for law firms . With a good business plan for law firms , Raymond Associates will indeed be one of the best law firms in Houston.
3.3 How the Business will be Started
As an expert in legal services, Alex understands what he needs to start the law firm. To set his idea into action, he has worked closely with businesses set-up experts to develop a financial plan for the law firm.

Services for Customers
Raymond Associates is focused on offering professional legal services to different type of clients. According to the starting a law firm business plan, the business is focused on offering the following services:
- Provide property law services to people facing mortgage, foreclosure and other property acquisition.
- Offer legal services to people suffering from personal injury. Employees’ injuries at work are extremely sensitive and need a qualified lawyer to intervene.
- Provide legal services to couples going through a divorce.
- Offer legal services to people buying and selling businesses – acquisitions and mergers.
Marketing Analysis for Law Firm Business
For Raymond Associates to meet its market obligations, a detailed market analysis was done to help the business establish itself in the industry and adequately serve the needs of client. This law firm business plan explains the strategy the business will follow to attain its goals. Given the rising demand for various legal services, there is a great opportunity for Raymond Associates to meet its objectives.
5.1 Market Segmentation
Given the increasing popularity of law firms industry, Raymond Associates understands the value of coming up with sustainable marketing strategies to acquire a larger market share. Being one of the largest cities in the United States, Houston is a business hub with many individuals and companies looking for legal services. Based on the market findings and law firm business plan template, the law firm intends to target the following potential customers.

excellent work
excellent work, competent advice. Alex is very friendly, great communication. 100% I recommend CGS capital. Thank you so much for your hard work!
5.1.1 Couples
Marriage is a good thing but a time comes in life where people want to depart for various reasons. Nowadays, there is a high divorce rate in Texas, and for this reason Alex so it necessary to start a law office business plan to provide divorce legal services. When going through a divorce, you want to use a law firm that know how to handle sensitive issues. Raymond Associates highly trained attorneys and family law professionals will be dedicated to help people going through divorce to successfully navigate the family courts. If you have a family law case, it can be frustrating to sort through the maze of paperwork required to finish your case. Raymond Associates is ready to help though all the steps if filing a divorce, spousal support orders or custody issues among other services listed in the law firm business plan sample.
5.1.2 Property Owners
One of the main services offered by Raymond Associates is foreclosure and mortgage legal services. Whether it is mortgage, foreclosure or other property acquisition, Raymond Associates lawyers will help you go through that. The lawyers will offer the best advice and assist you throughout the whole process. The law firm will help file necessary documents and go through disputes that may arise between the transactions.
5.1.3 Employees
With so many companies and organization in Houston, Raymond Associates sample law firm business plan will target employees. When it comes to legal services involving employee injuries at work, these cases are usually sensitive and need a qualified lawyer to intervene. In most cases, employees feel oppressed in matters in regards to compensation and opt to use a lawyer. This is why Raymond Associates has a well inclusive personal injury law firm business plan to cater for such cases.
5.1.4 Businesses
According to the law firm marketing plan template, Raymond Associates will offer legal services to businesses to buying and selling businesses – acquisitions and mergers. With many individuals buying and selling businesses, it is important to use the services of a lawyer. A good law office will help you minimize taxes and potential liability issues for buyers and sellers figuring out how to structure a deal.
5.2 Business Target
Raymond Associates is getting into a highly competitive environment considering there are a high number of law firms in Houston. However, this small law firm business plan outlines the plan the business intends to use to acquire clients and propel business growth. It is costly to set up a fully functioning law firm, but adequate strategies have been put in place to help the business fully recover its initial capital. After finalizing the starting a law firm business and rolling out operations, the call centerexpects to recoup its initial investment in three years based on a projected 30-40% annual sales growth.
5.3 Product Pricing
While strategizing on how to start a law firm business plan , Alex Raymond together with the assistance of experts has come up with a competitive pricing structure tailored for different services. At the beginning, the call center intends to offer various incentives to attract clients.
When planning to start a law office, you need to come up with a great business development strategy . Alex Raymond has engaged experts to formulate a call center strategy that will be instrumental to steer business growth. He has also invested time to studying law firm proposal examples. The following is Raymond Associates law firm sales strategy.
6.1 Competitive Analysis
Raymond Associates has deployed the latest telemarketing technologies to boost efficiency and seamlessly handle multiple clients without compromising quality. After completing the procedures of how to build a law firm, the business anticipates high competition considering there are numerous similar establishments in Houston.
6.2 Sales Strategy
For Raymond Associates to achieve its intended targets and create a successful law office which is popular with clients, the following sales strategy will be implemented.
- Hire professional marketing agencies to help advertise the law firm and reach out to potential clients.
- Organize an official opening party and welcome top industry stakeholders to create awareness about the business
- Advertise on digital media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter and Instagram
- Use local media channels such as Television and newspapers to advertise the business
6.3 Sales Forecast
Raymond Associates law firm has put in place various sales strategies in order to meet its targets. According to the law firm business plan example, the sales forecast looks promising for the business.
Personnel Plan
Raymond Associates provides diverse services in order to boost the company’s income. When coming up with a business plan for law firms , it is vital to focus on having a good personnel team to handle business operations.
7.1 Personnel Plan
The law firm is owned by Alex Raymond who will be the overall firm manager for the business. The law office intends to hire the following staff to enable the business carry out its operations.
- Administrator
- Operations Manager
- Two Marketing Executives
- Five Lawyers
- Three Advocates
Successful candidates will undergo intensive training to understand procedures and expectations.
7.2 Average Staff Salaries
Raymond Associates law office plans to pay its staff the following salaries in the first three years of operations.
Financial Plan
Alex Raymond law firm has formulated a financial plan that will steer the path to business success. To the business, Alex will use his personal savings and funds from two investors. A loan will be sought to help raise startup capital for the business. Crucial financial information for the business has been indicated in the law firm business plan template free.
8.1 Important Assumptions
Financial forecast for Raymond Associates law firm will be based on the following assumptions.
8.2 Brake-even Analysis
Raymond Associates Brake-even Analysis is indicated in the graph below.

8.3 Projected Profit and Loss
Profit and Loss information for Raymond Associates calculated on a monthly and annual basis is shown below.
8.3.1 Monthly Profit

8.3.2 Yearly Profit

8.3.3 Monthly Gross Margin

8.3.4 Yearly Gross Margin

Below is the profit and Loss Analysis for Raymond Associates law firm.
8.4 Projected Cash Flow
The diagram below is a summary of subtotal cash spent, subtotal cash from operations, subtotal cash spent on operations, subtotal cash received and pro forma cash flow.

8.5 Projected Balance Sheet
The following is a Projected Balance Sheet for Raymond Associates law firm that shows capital, assets, long term assets, liabilities and current liabilities.
8.6 Business Ratios
Raymond Associates law firm Business Ratios, Ratio Analysis and Business Net Worth are shown below.
Download Law Firm Business Plan Sample in pdf
OGS capital professional writers specialized also in themes such as financial due diligence, technical due diligence , due diligence of the enterprise , due diligence template , etc.
OGSCapital’s team has assisted thousands of entrepreneurs with top-rate business plan development, consultancy and analysis. They’ve helped thousands of SME owners secure more than $1.5 billion in funding, and they can do the same for you.

Add comment
E-mail is already registered on the site. Please use the Login form or enter another .
You entered an incorrect username or password
Comments (0)
mentioned in the press:
Search the site:
OGScapital website is not supported for your current browser. Please use:

EU Adopts Mandatory Rules on Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence That Will Apply to Many US Companies
On 24 April 2024, the European Parliament voted to adopt the Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CSDDD), meaning it will now become law and necessitate a shift in corporate attitudes to responsible business conduct. The CSDDD will apply to European Union (EU) and non-EU companies with activities in the EU meeting the thresholds outlined below. For the first time, it will introduce comprehensive mandatory human rights and environmental due diligence obligations, with significant financial penalties and civil liability for companies that do not fully comply. It also will create a new obligation for companies to adopt and put into effect a climate transition plan, as well as a requirement for companies to report on their due diligence processes. This will likely be a heavy lift for most in-scope businesses, as these requirements reframe existing international soft laws [1] as mandatory obligations. Companies not in scope but in the value chains of businesses that are in scope also will feel the effects of the law, and can expect increasing sustainability-related information requests, contractual requirements and climate-related transition requests.
The new due diligence obligations created by the CSDDD will apply in addition to other more specific due diligence obligations introduced under the EU’s Conflict Minerals Regulation , the EU’s Batteries Regulation , the EU’s Deforestation Regulation and the new procedures companies will have to adopt to ensure compliance with the EU’s ban on products made with forced labour , which also was approved by the European Parliament this week.
Which companies does the CSDDD apply to?
The CSDDD applies to EU and non-EU companies, including most regulated financial undertakings, that satisfy the turnover and employee thresholds. It also applies to ultimate parent companies of groups that satisfy the same thresholds on a consolidated group basis.
The EU has adopted a phased-in approach for the CSDDD with the obligations applying between three and five years from the date the law enters into force.
The CSDDD only applies to those companies that meet the relevant thresholds for two consecutive years.
We also will be closely tracking national implementation of the CSDDD into the laws of the EU member states, since EU member states are permitted to bring additional companies in scope of the CSDDD and/or require compliance sooner.
Franchisors and licensors
Lower financial thresholds apply to companies that rely on franchise or license models where the company’s or group’s agreements with third parties ensure a common identity, a common business concept and the application of uniform business methods.
What does the CSDDD require in-scope entities to do?
Mandatory climate transition plans.
The CSDDD will require all in-scope companies to adopt and put into effect a climate transition plan which aims to ensure, through best efforts, that the business model and strategy of the company is compatible with all of the following:
- Limiting global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius in line with the Paris Agreement.
- The EU’s objective of achieving climate net zero greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by 2050, including all related interim targets for 2030 (i.e., a reduction of net GHG emissions by at least 55% compared to 1990 levels) and 2040.
- A transition to a sustainable economy.
A company’s climate transition plan must include, amongst other things, science-based, time-bound targets covering Scope 1, 2 and 3 GHG emissions for 2030 – and every five years after until 2050. The transition plan needs to be updated annually and must contain a description of the progress the company has made towards achieving its targets. For those companies in scope of the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD), their plan will be subject to audit. The 2030 emissions target will, in practice, require many companies to take steps to comply before the CSDDD fully applies to them, otherwise they risk not being able to achieve the target set.
Critically, this is an obligation of means and not of results. While the CSDDD recognizes that specific circumstances may lead to companies not being able to reach their targets, for traded companies, in particular, there remains a risk of securities litigation where targets disclosed in regulated filings go unmet. Even for nonlisted companies, there are risks of claims being brought under new EU green claims rules if reported targets are known to be unachievable (and therefore potentially misleading).
Mandatory human rights and environmental due diligence
Under the CSDDD, companies also will be required to identify and, where necessary, prioritize, prevent, mitigate, bring to an end, minimize and remediate potential and actual adverse human rights and environmental impacts whilst engaging in stakeholder consultation throughout. Companies will need to refresh their mandatory human rights and environmental due diligence assessments at minimum every 12 months and, where not already required to report on their processes under the CSRD, they will be required to publish an annual statement on their due diligence processes.
In-scope companies’ due diligence efforts must cover their own operations, the operations of their subsidiaries, and operations carried out by direct and indirect business partners in their ‘chain of activities’. A company’s ‘chain of activities’ covers the upstream activities connected to a company’s product or service – including design, extraction, sourcing, and manufacture of raw materials and products. It also covers certain downstream activities, including the distribution, transport and storage of products, but not their disposal or end use.
As the downstream impacts of services are entirely excluded, regulated financial undertakings are therefore only subject to due diligence obligations for the upstream part of their chain of activities. However, the CSDDD envisages the possible introduction of sustainability due diligence requirements for the financial services industry as early as 2026.
What does mandatory human rights and environmental due diligence require in practice?
In practice, this means companies will need to:
1. Integrate mandatory human rights and environmental due diligence into their policies and risk management systems at all relevant levels of operation.
These policies must be developed in consultation with the company’s employees and representatives and must be updated periodically.
2. Identify and assess actual and potential adverse human rights and environmental impacts.
Adverse human rights and environmental impacts include, for example, forced labour, pollution and biodiversity loss, and must be assessed throughout a company’s own operations, those of its subsidiaries and, where related to its chain of activities, those of its business partners. This will require companies to map their chain of activities and carry out in-depth assessments in those areas where adverse impacts are most likely to occur and/or are most severe. Mandatory stakeholder consultation is a critical part of this identification and assessment process.
3. Prevent – or, where not possible, mitigate – potential adverse impacts and where impacts are identified, bring them to an end.
The CSDDD provides for risk-based due diligence, aligned with the UNGPs’ focus on severity and likelihood. These obligations are not obligations of result but obligations of means (i.e., companies are not expected to guarantee that adverse impacts will never occur or that they will always be stopped). Companies must nevertheless take appropriate measures that are capable of effectively addressing adverse impacts identified in a manner commensurate to the nature of the adverse impact. Measures might include cascading contractual clauses or targeted support for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in the form of training or even targeted financial aid. As a last resort, where efforts to prevent or mitigate have been unsuccessful, companies may be required to terminate their business relationship. Stakeholder consultation will play an important role in each instance to inform and support a company’s decisions and actions.
4. Provide remediation where the company causes or causes jointly with subsidiaries or business partners (e.g., by facilitating or incentivizing) an actual adverse impact.
Remediation here means the restitution of affected persons, communities or the environment to a situation equivalent to or as close as possible to the position they would have been in had the adverse impact not materialized. Where a company neither causes nor contributes to the impact arising in its chain of activities, the company is nevertheless expected to use its influence to bring to an end or minimize the extent of the impact.
5. Prioritize where necessary.
Companies should prioritize adverse impacts based on their severity and likelihood without regard to business-related factors, such as the company’s potential liability or the leverage the company might have. Once the most salient adverse impacts have been addressed, companies must then address those less salient.
6. Engage in stakeholder consultation.
The CSDDD mandates ‘meaningful’ stakeholder engagement throughout the due diligence process. Stakeholders include individuals and communities whose rights or interests are or could be impacted, as well as civil society organizations. Companies are expected to pay particular attention to the needs of vulnerable stakeholders and must address barriers to engagement.
7. Establish and maintain a notification mechanism and complaints procedure.
These processes must be publicly available and transparent, and they must enable impacted persons, trade unions and civil society to submit legitimate concerns regarding actual or potential adverse impacts.
8. Do more than rely on contractual assurances alone.
Companies will not be able to rely on cascading contractual assurances alone to satisfy their due diligence obligations under the CSDDD. Where used, contractual assurances must be accompanied by ‘appropriate measures’ to verify compliance and should be designed to ensure that responsibilities are shared appropriately by the company and the relevant business partner and avoid the complete transfer of due diligence obligations. The European Commission is expected to publish voluntary model contract clauses before the end of 2026.
Enforcement
The CSDDD will be enforced nationally by the authorities of the EU member states. Companies that do not comply with the CSDDD may face sanctions from national administrative authorities – including fines of up to 5% of their global turnover.
New civil liability regime
The CSDDD introduces a civil liability regime whereby companies could be liable for damages where they ‘intentionally or negligently’ failed to prevent, mitigate, bring to an end or minimize an adverse human rights impact which led to damage. The civil liability is subject to a five-year limitation period and excludes damage caused solely by the activities of a company’s business partners. Civil society and nongovernmental organizations will be able to bring claims for collective redress on behalf of victims. National courts also are expected to implement mechanisms to address procedural barriers for claimants.
Exclusion from public tenders
It also is possible that national authorities will make compliance with the CSDDD a criterion for the award of public contracts and concessions.
Next steps?
The CSDDD enters into force 20 days after its publication in the Official Journal of the EU. Prior to publication, the CSDDD will need to be formally approved by the European Council (expected 23 May). This means that the CSDDD will likely enter into force during Q3 2024. Member states will have two years after entry into force to transpose the legislation into national law, and the requirements will start to apply to companies three, four and five years after entry into force, depending on the size of the company.
We will be closely tracking national implementation of the CSDDD and how it impacts existing national due diligence regimes in the EU – e.g., the German Supply Chain Due Diligence Act (LkSG) and the French law on the duty of vigilance – already in force, along with proposed regimes – e.g., the Dutch Child Labour Due Diligence Act. Member states have discretion under the CSDDD to expand the scoping thresholds, the downstream activities in scope and the measures available for remediation.
If you have any questions or would like support understanding the implications of this new regime, please contact a member of Cooley’s international ESG and sustainability advisory team .
[1] The CSDDD is broadly aligned with the United Nations’ Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights (UNGPs) and the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development’s Guidelines for Multinational Enterprises (OECD guidelines).
Related insights
Related services, related contacts.

This content is provided for general informational purposes only, and your access or use of the content does not create an attorney-client relationship between you or your organization and Cooley LLP, Cooley (UK) LLP, or any other affiliated practice or entity (collectively referred to as “Cooley”). By accessing this content, you agree that the information provided does not constitute legal or other professional advice. This content is not a substitute for obtaining legal advice from a qualified attorney licensed in your jurisdiction and you should not act or refrain from acting based on this content. This content may be changed without notice. It is not guaranteed to be complete, correct or up to date, and it may not reflect the most current legal developments. Prior results do not guarantee a similar outcome. Do not send any confidential information to Cooley, as we do not have any duty to keep any information you provide to us confidential. This content may be considered Attorney Advertising and is subject to our legal notices .
Most Companies Plan to Voluntarily Disclose Climate Rules Data
By David Hood

Almost nine in ten companies say they’ll disclose extensive carbon-footprint data even beyond what many are required to produce, according to a new study by global consulting firm Workiva.
In the US, 86% of respondents in the survey released Tuesday said they plan to voluntarily comply with all or part with Europe’s Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive even though they don’t have to.
European Union requirements ask companies that have subsidiaries in the bloc to discuss their impact on the communities where they operate plus other details on fair labor practices. Those reporting requirements could start as soon as 2026.
The US Securities and Exchange Commission also plans to require companies to disclose their climate impact, but its significantly watered down rules for reporting on greenhouse gas emissions have been put on hold amid litigation.
Voluntarily compliance with rules—especially disclosures—isn’t normal, Andie Wood, vice president for regulatory strategy for Workiva said. Massive investor demand and competition among peer businesses are driving companies to offer the information, she said.
“There are certainly a number of companies, whilst they’re not necessarily shouting as loudly, they’re still looking to provide good data in some context or another,” Wood said. “If they are going to disclose something, it’s important that it is robust and comparable.”
The survey polled environmental, social and governance practitioners across 2,204 companies worldwide with at least 250 employees and $250 million or more in recurring annual revenue. About 660 were US-based.
The survey also showed companies have faith in the accuracy of the data they’re supplying voluntarily but are less sure about their ability to properly report information required under EU government regulations. Nearly all practitioners indicated full confidence in their own data while 83% said collecting accurate data to meet EU requirements will be a challenge to their organization.
That, Wood said, indicates how difficult it is to collect, distill and report the data as required. There’s a lot of pressure to disclose the right information in the right ways, Wood said.
“It tells us that they’re confident in what they’re putting out, but they know that there’s more that could be done and that it could be done more efficiently,” she said.
To contact the reporter on this story: David Hood in Washington at [email protected]
To contact the editors responsible for this story: Jeff Harrington at [email protected] ; Amelia Gruber Cohn at [email protected]
Learn more about Bloomberg Law or Log In to keep reading:
Learn about bloomberg law.
AI-powered legal analytics, workflow tools and premium legal & business news.
Already a subscriber?
Log in to keep reading or access research tools.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
4. Determine how many cases you need to meet that revenue goal. If you are only handling two or three cases per month, the number you came up with above might look outrageous. It's not. For example, let's use the 2023 median pay of $126,930 a year in annual revenue as our goal, with a flat fee of $3,000 per client.
Law Firm Plan. Over the past 20+ years, we have helped over 1,000 lawyers to create business plans to start and grow their law firms. On this page, we will first give you some background information with regards to the importance of business planning. We will then go through a law firm business plan template step-by-step so you can create your ...
It should also contain some deeper information about the firm's identity and aspirations. This would include: A mission statement about the firm's purpose. A vision statement or recitation of medium- and long-term goals for the firm. Important aspects of the firm's history. Any important philosophies that the firm brings to legal practice.
Every new law practice needs a business plan. This is a guide to creating one. Here is what should go in your business plan once you've decided about your law firm business model. Section One: Executive Summary. This section provides a succinct overview of your full plan. It should also include the following: Mission statement.
Download your free law firm sample business plan. Download our law firm sample business plan for free right now and use it for reference as you write your own plan. You can even copy and paste sections from the sample plan and customize them for your business. Just make sure you're taking the time to do your own research.
Starting a law firm can be a rewarding and lucrative venture, but it requires careful planning and strategy. A well-crafted business plan is a crucial tool for any law firm looking to establish itself, secure funding, or grow its practice. The business plan will serve as a roadmap, outlining the law firm's objectives, strategies, and unique selling proposition
The lawyer or lawyers who will make up the firm at the time of launch. The location of the firm and the areas it serves. The general approach the firm takes when representing clients. 3. Market Analysis. A competitive analysis is one of the most compelling components of well-written business plans.
Explore a real-world law firm business plan example and download a free template with this information to start writing your own business plan. Don't bother with copy and paste. ... 4.2 Service Business Analysis. The technology law practice is fairly competitive in Portland. Most larger, more prestigious firms have attorneys who specialize in ...
A detailed law firm business plan can set you on the road to success. Gain an understanding of the essentials of a law firm business plan. Pricing ... Kamron Sanders is the Senior Content Marketing Specialist at PracticePanther, an all-in-one legal practice management software. She is responsible for creating engaging content across multiple ...
Follow these tips to quickly develop a working business plan from this sample. 1. Don't worry about finding an exact match. We have over 550 sample business plan templates. So, make sure the plan is a close match, but don't get hung up on the details. Your business is unique and will differ from any example or template you come across.
A good business plan includes: Vision. Create a picture of what you're building. Values. Identify the rules to guide your team's important work. Law Firm Business Model. What you offer, who you offer it to, and how you'll deliver your services. Targets and Priorities. Clarify metrics that indicate success.
By planning for the future and setting realistic growth targets, law firms can take their businesses to the next level. Overall, a well-developed business plan is critical for success in the legal industry, providing direction and focus, supporting decision-making, managing resources effectively, and enabling growth.
How important this is for a legal business plan depends on your long and short term goals, e.g., whether they are to grow a partnership, join a firm, build up a practice that is enticing for acquisition by a larger firm, etc. ... Purpose: an accurate understanding of trends affecting law practice in general and your specializations, client ...
A law firm business plan is a document that outlines your business goals and strategies to achieve those goals. It includes your law firm overview, your reason to start your firm, the services you will offer, a budget or funding requirements, and strategies to get and manage your clients.
In fact, it is a mirror of your entire business plan. You will set goals, establish strategies, plan actions steps, and allow for review. The primary goals of a sales and advertising plan are: 1) To build a strong identity; 2) To build a strong client base; and, 3) To build continuously increasing collections.
1. Develop a Clear Business Plan: Just as any successful business starts with a well-defined business plan, your law practice should have a strategic roadmap. Your plan should outline your ...
Personal business planning is not about writing a 50-page manifesto outlining every detail of every day of your professional life for the next 10 years. In fact, personal business planning can be as simple as you want to make it, as you can see here with this sample business plan for law practice PDF. You don't even have to call it a business ...
Key Elements of Creating a Business Plan for Solo Practitioners. For solo practitioners in the legal profession, having a well-crafted solo law firm business plan is essential for long-term success. A business plan provides a roadmap to guide your practice, establish goals, and outline strategies for growth and profitability.
List of all of the practice management guides available from the WSBA. ... These resources are developed to help you navigate law firm business ownership. ... Resources. Business Plan Template Apr 27, 2017, 14:08 PM by User Not Found Download (pdf) 582 KB. Disaster Planning & Recovery. View the guide. Resources. Business Plan Template ...
Services. This section is the core of your solo law practice business plan. Here, you need to dive into the services that your firm provides, in every aspect of them. Mention your practice areas ...
As an expert in legal services, Alex understands what he needs to start the law firm. To set his idea into action, he has worked closely with businesses set-up experts to develop a financial plan for the law firm. Start-up Expenses. Legal. $7,000. Consultants. $5,000. Insurance. $20,000.
Across the legal industry, there's been a significant shift to cloud-based solutions in the last several years. According to the International Legal Technology Association's 2023 Technology Survey, which tallied input from more than 500 law firms and 150,000 attorneys, 80 percent of respondents said their email was in the cloud or headed there within the next year, up from 74 percent in ...
It also will create a new obligation for companies to adopt and put into effect a climate transition plan, as well as a requirement for companies to report on their due diligence processes. This will likely be a heavy lift for most in-scope businesses, as these requirements reframe existing international soft laws [1] as mandatory obligations.
Almost nine in ten companies say they'll disclose extensive carbon-footprint data even beyond what many are required to produce, according to a new study by global consulting firm Workiva. In the US, 86% of respondents in the survey released Tuesday said they plan to voluntarily comply with all or part with Europe's Corporate Sustainability ...
Trevor Varnes, formerly with Perkins Coie LLP for more than two decades across two stints, is joining BCLP, formerly Bryan Cave Leighton Paisner, as its firmwide CFO, the law firm announced April ...