Global Banking and Finance Review is an online platform offering news, analysis, and opinion on the latest trends, developments, and innovations in the banking and finance industry worldwide. The platform covers a diverse range of topics, including banking, insurance, investment, wealth management, fintech, and regulatory issues. The website publishes news, press releases, opinion and advertorials on various financial organizations, products and services which are commissioned from various Companies, Organizations, PR agencies, Bloggers etc. These commissioned articles are commercial in nature. This is not to be considered as financial advice and should be considered only for information purposes. It does not reflect the views or opinion of our website and is not to be considered an endorsement or a recommendation. We cannot guarantee the accuracy or applicability of any information provided with respect to your individual or personal circumstances. Please seek Professional advice from a qualified professional before making any financial decisions. We link to various third-party websites, affiliate sales networks, and to our advertising partners websites. When you view or click on certain links available on our articles, our partners may compensate us for displaying the content to you or make a purchase or fill a form. This will not incur any additional charges to you. To make things simpler for you to identity or distinguish advertised or sponsored articles or links, you may consider all articles or links hosted on our site as a commercial article placement. We will not be responsible for any loss you may suffer as a result of any omission or inaccuracy on the website. .

The Rise of Mobile Banking: Challenges and Opportunities

By Dima Kats, CEO, Clear Junction
Mobile banking use is rapidly increasing worldwide. In the first half of 2020 alone, there were 26% more mobile banking app sessions globally than in 2019. Relative to even a few years ago, the number of people using mobile banking has skyrocketed. While the acceleration of mobile banking has indeed brought opportunity for financial institutions; it has also resulted in challenges.
There are significant security risks that arise from using mobile applications, including mobile banking apps. As businesses expand mobile payment capabilities, ensuring that business and customer payment data is safe is crucial.
With the growth of mobile and digital banking set to continue after the pandemic, banks must work to develop a seamless and secure environment for the future. Customer behaviour concerning mobile banking is changing, and businesses need to change too. Companies that fail to recognise this change will fall behind their competitors, while those who do adapt need to ensure they are putting appropriate security measures in place to protect their customers’ data.
How to profit from the benefits while avoiding security pitfalls
Mobile banking offers unparalleled convenience, speed and accessibility to consumers – no more closures on bank holidays, tiresome queues, or inscrutable statements. It’s no wonder people are adopting mobile payments and banking in droves; the benefits are enormous. While businesses rightly follow their customers in facilitating smooth mobile banking and payments, they must remain constantly vigilant to the security threats that mobile banking presents.

76% of mobile banking apps can be accessed by hackers, and with anyone from the app developers to the banks themselves capable of leaving vulnerabilities, it is easy for security to fall short at any stage.
Security and reliability are of paramount importance to mobile banking users. A substantial 62% of mobile banking users claim they would switch providers after a negative experience. With increased adoption and security risks tied to scalability, institutions need to be agile enough to embrace and scale their customer base while remaining vigilant about a smooth and secure service. Customers may abandon those who don’t.
Increasingly, mobile customers bring a range of new security issues to businesses. Companies wishing to future-proof their payments structure and match the customer demand for frictionless online payments can ensure success by working with payment experts. Partnering with a specialist team can ensure financial institutions are able to provide their customers with the best mobile banking experience, while keeping data safe and secure.
Preparing for the future
Financial institutions have been on a digital transformation journey for several years, but now is the time to turn this into a competitive advantage. 24% of UK residents use some form of digital wallet and in some countries, like Russia, banking customers are extensively using their phones to withdraw money from cash machines. The need for cards, let alone cash, is likely to wane in favour of mobile phones over the next few years.
However, the ever-increasing variety of choices regarding mobile banking support can leave businesses at a loss when it comes to setting up the right system for them. In areas of the world that suffer from slow or limited internet capacity, mobile phone ownership is still skyrocketing despite poor infrastructure.
To grasp this opportunity, businesses and banks need to make sure they are working with payment experts who have experience managing online transfers across the world safely and securely.
Companies like Clear Junction connect financial institutions to a secure, regulated and optimised payment infrastructure to help them overcome the barriers of digital transformation and challenges relating to banking and payments. Getting the digital foundation right the first time is a definitive way to remain a step ahead of competitors, retain customer loyalty and ensure future success.
Global Banking & Finance Review
Why waste money on news and opinions when you can access them for free?
Take advantage of our newsletter subscription and stay informed on the go!
Email (required) *
Example: Yes, I would like to receive emails from Global Banking & Finance Review. (You can unsubscribe anytime)
Recent Post

VistaCreate – No. One Design Assisstant For Businesses

How reforms and innovation have turned Uzbekistan into a global investment opportunity

Nektar Network begins Epoch 1 of Nektar Drops – Rewards for ongoing participation

Why it’s essential that merchants use acquirer agnostic PSPs
Privacy Overview
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
Mobile Banking
James Chen, CMT is an expert trader, investment adviser, and global market strategist.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/photo__james_chen-5bfc26144cedfd0026c00af8.jpeg)
What Is Mobile Banking?
Mobile banking is the act of making financial transactions on a mobile device (cell phone, tablet, etc.). This activity can be as simple as a bank sending fraud or usage activity to a client’s cell phone or as complex as a client paying bills or sending money abroad. Advantages to mobile banking include the ability to bank anywhere and at any time. Disadvantages include security concerns and a limited range of capabilities when compared to banking in person or on a computer.
Understanding Mobile Banking
Mobile banking is very convenient in today’s digital age with many banks offering impressive apps. The ability to deposit a check, to pay for merchandise, to transfer money to a friend or to find an ATM instantly are reasons why people choose to use mobile banking. However, establishing a secure connection before logging into a mobile banking app is important or else a client might risk personal information being compromised.
Mobile Banking and Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity has become increasingly important in many mobile banking operations. Cybersecurity encompasses a wide range of measures taken to keep electronic information private and avoid damage or theft. It is also used to make data is not misused, extending from personal information to complex government systems.
Three main types of cyber attacks can occur. These are:
- Backdoor attacks, in which thieves exploit alternate methods of accessing a system that doesn't require the usual means of authentication. Some systems have backdoors by design; others result from an error.
- Denial-of-service attacks prevent the rightful user from accessing the system. For example, thieves might enter a wrong password enough times that the account is locked.
- The direct-access attack includes bugs and viruses, which gain access to a system and copy its information and/or modify it.
Steps financial advisors can take to protect their clients against cyber attacks include:
- Helping educate clients about the importance of strong, unique passwords (e.g, not reusing the same one for every password-protected site), along with how a password manager like Valt or LastPass can add an extra layer of security.
- Never accessing client data from a public location, and being sure the connection is always private and secure.
Mobile Banking and Remittances
Remittances are funds that an expatriate sends to their country of origin via wire, mail, or mobile banking (online transfer). These peer-to-peer transfers of funds across borders have enormous economic significance for many of the countries that receive them – so much so that the World Bank and the Gates Foundation have set up complex tracking mechanisms. They estimate that remittances to developing countries amounted to $529 billion in 2018, up 9.6% from the previous record high $486 billion recorded in 2017.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/young-woman-using-smartphone-in-shopping-mall-981469094-28bcb62027334fd5848218d161bcc972.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
7 key benefits of mobile banking
Advertiser disclosure.
We are an independent, advertising-supported comparison service. Our goal is to help you make smarter financial decisions by providing you with interactive tools and financial calculators, publishing original and objective content, by enabling you to conduct research and compare information for free - so that you can make financial decisions with confidence.
Bankrate has partnerships with issuers including, but not limited to, American Express, Bank of America, Capital One, Chase, Citi and Discover.
How We Make Money
The offers that appear on this site are from companies that compensate us. This compensation may impact how and where products appear on this site, including, for example, the order in which they may appear within the listing categories, except where prohibited by law for our mortgage, home equity and other home lending products. But this compensation does not influence the information we publish, or the reviews that you see on this site. We do not include the universe of companies or financial offers that may be available to you.
- Share this article on Facebook Facebook
- Share this article on Twitter Twitter
- Share this article on LinkedIn Linkedin
- Share this article via email Email

- • Personal finance

- • Savings accounts
The Bankrate promise
At Bankrate we strive to help you make smarter financial decisions. While we adhere to strict editorial integrity , this post may contain references to products from our partners. Here's an explanation for how we make money .
Founded in 1976, Bankrate has a long track record of helping people make smart financial choices. We’ve maintained this reputation for over four decades by demystifying the financial decision-making process and giving people confidence in which actions to take next.
Bankrate follows a strict editorial policy , so you can trust that we’re putting your interests first. All of our content is authored by highly qualified professionals and edited by subject matter experts , who ensure everything we publish is objective, accurate and trustworthy.
Our banking reporters and editors focus on the points consumers care about most — the best banks, latest rates, different types of accounts, money-saving tips and more — so you can feel confident as you’re managing your money.
Editorial integrity
Bankrate follows a strict editorial policy , so you can trust that we’re putting your interests first. Our award-winning editors and reporters create honest and accurate content to help you make the right financial decisions. Here is a list of our banking partners .
Key Principles
We value your trust. Our mission is to provide readers with accurate and unbiased information, and we have editorial standards in place to ensure that happens. Our editors and reporters thoroughly fact-check editorial content to ensure the information you’re reading is accurate. We maintain a firewall between our advertisers and our editorial team. Our editorial team does not receive direct compensation from our advertisers.
Editorial Independence
Bankrate’s editorial team writes on behalf of YOU — the reader. Our goal is to give you the best advice to help you make smart personal finance decisions. We follow strict guidelines to ensure that our editorial content is not influenced by advertisers. Our editorial team receives no direct compensation from advertisers, and our content is thoroughly fact-checked to ensure accuracy. So, whether you’re reading an article or a review, you can trust that you’re getting credible and dependable information.
How we make money
You have money questions. Bankrate has answers. Our experts have been helping you master your money for over four decades. We continually strive to provide consumers with the expert advice and tools needed to succeed throughout life’s financial journey.
Bankrate follows a strict editorial policy , so you can trust that our content is honest and accurate. Our award-winning editors and reporters create honest and accurate content to help you make the right financial decisions. The content created by our editorial staff is objective, factual, and not influenced by our advertisers.
We’re transparent about how we are able to bring quality content, competitive rates, and useful tools to you by explaining how we make money.
Bankrate.com is an independent, advertising-supported publisher and comparison service. We are compensated in exchange for placement of sponsored products and services, or by you clicking on certain links posted on our site. Therefore, this compensation may impact how, where and in what order products appear within listing categories, except where prohibited by law for our mortgage, home equity and other home lending products. Other factors, such as our own proprietary website rules and whether a product is offered in your area or at your self-selected credit score range, can also impact how and where products appear on this site. While we strive to provide a wide range of offers, Bankrate does not include information about every financial or credit product or service.
Mobile banking has become the norm in many consumers’ daily lives. A report from the American Bankers’ Association found that 81 percent of consumers had managed their bank account from a mobile device at least once in the past month.
The allure, of course, is the convenience mobile banking offers: Consumers tote their smartphones virtually everywhere, so a mobile banking app can help them quickly take care of a range of financial needs whenever they wish. It’s essentially a bank in your pocket.
Having tools that make it easier to manage your finances is especially valuable at a time when most consumers are struggling to save. To put it in perspective, Bankrate’s 2024 emergency savings report found that 56 percent of Americans wouldn’t be able to pay for a $1,000 emergency expense with their savings. Mobile banking offers expense tracking, automated savings, account access for those who might not have a branch nearby and more to aid in your finances.
Key takeaways
- Expense tracking, automated savings and easy access to account information are a few features that make mobile banking an essential tool for managing finances in the modern world.
- Mobile banking apps also provide added security measures, such as encryption and biometric authentication, to protect sensitive financial information and prevent unauthorized access.
- Mobile banking can be especially helpful for underbanked or marginalized communities, as it offers tailored options and a sense of safety and convenience that traditional banks may not provide.
Advantages of mobile banking
Mobile banking apps can warn you when you spend more than you have in your account, automatically move money into savings on your payday and let you set controls on your cards to restrict spending. Banking apps can also make it easy to send money to friends and to reach a customer service representative with the tap of a button.
1. Accessing the bank 24/7
Unlike a bank branch, mobile banking conveniently gives you access to your account anytime you like — with some exceptions, such as planned maintenance updates and unexpected outages .
This ease of accessibility saves you time. Mobile check deposit, for example, a feature most banking apps offer, allows you to deposit a check on the go or from the comfort of your couch.
Mobile banking apps can also make it easy for users to schedule and pay bills at their convenience with features like bill pay and upcoming payment alerts. Customers can ensure bills are settled on time, regardless of whether it’s on the go or late at night.
2. Making it easier to save
The best mobile banking apps have evolved to help you manage your money with less effort. For example, the Ally Bank app offers several savings features, including automatic transfers to a savings account and round-ups that move rounded up change into your savings. The U.S. Bank app alerts customers when its algorithms spot money-saving opportunities or situations when an account is at risk of being overdrawn.
Some online-only banks are also offering innovative savings features through their apps. Varo Bank , a popular online bank, offers a Save Your Pay feature that automatically stashes away a pre-set percentage of your paycheck each time it deposits.
Spending alerts are another way mobile banking apps can help you optimize your money.
“You are seeing a lot of people say, ‘Hey, I want to know every time there is a transaction over $150 or over $250 or whatever that threshold the consumer happens to care about is,’” says Zach Bruhnke, co-founder at HMBradley, a challenger bank. “A lot of people want to go and understand things like, ‘What are my daily limits?’ Things you’d probably ask your banker or call a branch for, now you are [the] one to do it. The push is for more and more information to be available at customers’ fingertips prints,” Brunhke adds.
3. Paying IOUs
When you are logged into your mobile banking app, it’s easy to pay back someone you know.
Banks across the country partner with Zelle so that you can send someone money in minutes through the bank’s mobile app rather than paying people with cash or a check.
You only need to know recipients’ email addresses or phone numbers to send them money. If your bank doesn’t offer Zelle, it usually lets you transfer funds to someone else’s bank account if you know their routing and account numbers.
4. Strengthening security
Banks are in the business of guarding your assets — including transactions made using their mobile apps. Though nothing is foolproof, there are ways you can step up security precautions if you’re concerned about mobile banking security .
Financial institutions often require a username and password to sign into a mobile app and offer additional safety features to further safeguard your account. Multi-factor authentication , for example, requires at least two kinds of verification to prove that it’s really you. The first are the account credentials (your username and password) followed by a text with numeric code sent to your phone that needs to be submitted to gain access to the account.
Further, some mobile devices — and some bank apps — let you log in by scanning your face or fingerprint as yet another way to protect your digital bank account without trading convenience.
A growing number of banks, such as Wells Fargo, Ally Bank, Chase and Bank of America let you use their mobile apps to turn your debit or credit card off if it goes missing or is stolen. It’s a nice feature to help you feel instantly secure in a moment of panic. Calling a toll-free number is not required if you want to turn your card back on, either.
5. Offering clarity about where your financial data is going
Many consumers share bank data to use services like Venmo. Depending on how many outside apps you use, it can be quite taxing to remember which company has what bank data. So a number of banks are trying to help customers understand where it’s going by changing the way data is shared behind the scenes.
“We are seeing a lot more banks offer that functionality that gives consumers proactive control over where their data is going,” says Rob Morgan, senior vice president of emerging technologies at the American Bankers Association. “It’s not just the added security … but it’s also the importance of transparency so you see where your data is going, how it is being used and [controlled], the ability to turn off this thing when you are no longer using the service,” Morgan adds.
At Wells Fargo, for example, customers are able to see recurring payments connected to payment cards.
6. Tracking expenses
When it comes to managing and sticking to a budget, tracking all of your expenses is the part that requires the most labor, and it may lead you to give up on budgeting altogether. Mobile banking apps can do much of that labor for you, by keeping track of your expenses tied to a particular account and organizing them into spending categories. You can see a breakdown of total expenses for things like utilities, dining, transportation and more.
By reviewing your spending patterns, you should gain a clearer understanding of where your money is going and can identify areas where you may need to make adjustments.
Some apps even come with built-in budget creation. Regions Bank , for example, offers a suite of budgeting tools through a feature in its app called My GreenInsights. Users have the ability to set up a budget in the app, sync multiple accounts to it and monitor their spending progress.
Other banking apps allow you to set financial goals, such as saving for a vacation or paying down a debt. Ally Bank and Capital One are two banks that come with features that let users establish and track progress toward different savings goals.
7. Giving you tailored options
Mobile banking can offer services to those who might historically have been overlooked or who are untrusting of traditional banks.
Bliss, for example, is a mobile banking platform designed for the transgender community. It allows users to put their chosen name on their debit cards, regardless of whether it’s been legally updated, and contains a database of financial goals related to transitioning.
Meanwhile, those who are unbanked or underbanked might find that mobile-only banking providers can help them access important financial services. Chime is a fintech that offers a fee-free checking account and no balance minimums, which can be managed entirely through a mobile device. The account could serve as an alternative banking option to those in geographically remote areas or who have a lack of trust in traditional financial institutions.
There are also startups building mobile financial tools for Black communities, young adults, women and other groups.
Disadvantages of mobile banking
Technical interruptions.
Mobile banking relies heavily on the user’s mobile device and internet connectivity. If you don’t have your device or the network is slow, it can hinder your ability to perform mobile banking activities. Plus, not all mobile banking apps work well, and even the best ones encounter outages every now and then.
Difficulty using the app
As banks layer in more features, navigating the apps can feel daunting. It’s not always obvious what features are available or where they’re located within the app. The good news is that banks are working to make their designs more intuitive.
Lack of personal interaction
Mobile banking eliminates face-to-face interactions with bank tellers. While this might not be an issue for many customers, it can be a disadvantage for those who prefer assistance or have complex financial inquiries that require more in-depth guidance. However, some mobile banking apps may allow you to contact a banker over live chat or the phone from the app.

Highly rated mobile bank apps
In 2024, mobile banking apps with standout features let you automate money decisions, block your cards, quickly get answers to your questions and more. Here are some of Bankrate’s favorites.
- Ally Bank: The online-only bank offers the staples, such as finding nearby ATMs and transferring funds) and provides extra touches. You can use Ally Assist, a virtual assistant that can help initiate transfers and bill payments, as well as provide information on interest earned and patterns of spending and saving. You can also use the app to set up controls for your cards and create savings buckets to help organize your money.
- Bank of America: Among the standouts of the big bank’s app is Erica, a virtual assistant that can answer a wide range of financial questions. You can also use the mobile app to book an appointment with an in-person banker.
- Capital One: The Capital One app is easy to navigate, helps you save and includes Eno, a virtual assistant. Users can also add cash in store by getting a unique barcode through the app. They simply enter the amount of cash to deposit in the app, go to a nearby CVS and show the cashier the barcode to scan as confirmation.
- Chase: In addition to allowing you to send money to someone else and monitor your account, the Chase app shows you a simple daily snapshot of your spending and saving patterns. You can also set savings goals and track your progress.
- Chime: This challenger bank gives you daily balance alerts and allows you to block your card in-app. More impressively, it lets you set up rules to automatically save money and potentially get your payday up to two days early. You can also overdraw your account without paying a fee.
- Huntington : Rated the top regional bank for mobile banking in 2023 by J.D. Power , Huntington’s app is great for those who need to quickly check on their accounts. Users can view their account balance with one tap, without needing to log in. The app also offers bill pay, mobile check deposit, the ability to order checks and account alerts.
- Varo: This online-only bank’s app lets you track your spending with instant alerts, send money to friends and family, locate in-network ATMs and lock your debit card if it’s lost or stolen.
Is mobile banking safe?
A common concern among users is the safety of their financial information. Fortunately, banks have robust security measures in place to protect user data and money.
One of these measures is encryption technology. Encryption means that your sensitive information, such as login credentials and transaction details, remains confidential.
Mobile banking apps also incorporate multi-factor authentication (requiring users to provide multiple forms of identification to access accounts) or biometric authentication (requiring fingerprints or facial recognition to log in). Doing so adds an extra layer of protection against unauthorized access .
Still, there are some best practices to ensure you’re banking safely over a mobile device:
- Enable biometric authentication whenever possible.
- Regularly update your app. Developers often release updates that include security enhancements and bug fixes.
- Frequently check on your transaction history and account statements to quickly identify any unauthorized or suspicious activity.
- Avoid conducting mobile banking transactions on public Wi-Fi networks.
- Be cautious of phishing emails, messages or calls attempting to obtain your login information. Banks typically do not request sensitive information through these channels by reaching out to you first.
Bottom line
Mobile banking is designed to help you in all kinds of ways — some of which are fundamentally redefining the role of a bank. Thanks to 24/7 access to accounts and the ability to make transactions with the tap of a button, consumers have more control over their money management — making trips to the local bank — for many — a thing of the past.
— Mary Wisniewski wrote the original version of this story.

Related Articles

Best banks and credit unions for mobile banking

Worried about mobile banking security? Follow these best practices

Bank account alerts to help protect your money
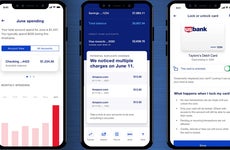
Best mobile banking features of 2024
To read this content please select one of the options below:
Please note you do not have access to teaching notes, mobile banking adoption: a systematic review.
International Journal of Bank Marketing
ISSN : 0265-2323
Article publication date: 28 December 2020
Issue publication date: 19 March 2021
This study is a systematic review of mobile banking services. Its main objective is to provide a state-of-the-art review of this particular growing type of services. It inventories and assesses the most significant determinants of and barriers to consumers' adoption of mobile banking. Moreover, it identifies the most common consequences of this adoption.
Design/methodology/approach
By using three major academic databases (ABI/INFORM global, Web of Science and Business Source Premier), this paper selected 76 manuscripts and produced a systematic review that exposes the main theories, conceptual frameworks and models used to explain consumers' adoption of mobile banking.
The results show that the TAM (technology of acceptance model), followed by the UTAUT (unified theory of acceptance and usage of technology), are still the main conceptual frameworks and models adopted and adapted by scholars to explain consumers' use or intention of using mobile banking. Using the vote counting method, a myriad of antecedents and consequences that are frequently used in the literature of mobile banking are reported. These were categorized into five main perspectives: (1) m-banking attributes-based perspective, (2) customer-based perspective, (3) social influence-based perspective, (4) trust-based perspective and (5) barriers-based perspective.
Originality/value
An integrated model regrouping and relating the five perspectives is proposed, leading to intriguing implications for both academics and practitioners.
- Systematic review
- Mobile banking
- Antecedents and consequences
Souiden, N. , Ladhari, R. and Chaouali, W. (2021), "Mobile banking adoption: a systematic review", International Journal of Bank Marketing , Vol. 39 No. 2, pp. 214-241. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJBM-04-2020-0182
Emerald Publishing Limited
Copyright © 2020, Emerald Publishing Limited
Related articles
We’re listening — tell us what you think, something didn’t work….
Report bugs here
All feedback is valuable
Please share your general feedback
Join us on our journey
Platform update page.
Visit emeraldpublishing.com/platformupdate to discover the latest news and updates
Questions & More Information
Answers to the most commonly asked questions here

As mobile surges, what’s the role of web banking?
Consumers have embraced banking apps as their main banking channel, even choosing their primary institutions based on user experience. at the same time, customers say that their apps still lag banking websites for some transactions and needs. how can banking sites play to these strengths.

Digital banking solutions, specifically mobile and web-based platforms, have gained widespread adoption in the past ten years, as bank branches become less and less utilized. However, a pertinent question arises: Are consumers still actively utilizing web banking services, or has mobile banking emerged as the dominant preference, rendering web banking obsolete? Should banking institutions favor, innovate and push one platform over the other?
In research exclusive to The Financial Brand conducted by Rivel in March 2024, among a national sample of banking consumers, mobile banking usage is a clear favorite with 58% using their phone to bank most or all the time. The numbers are even more stark when Rivel looks at the results by generation: 33% of Millennials use their mobile app exclusively and Gen Z comes in at 38% mobile app primary usage.
A crazy stat:
A shocking 14% of Baby Boomers do not use their bank’s digital tools at all.
How are banks preparing for the slow decline of the web interface and how can they effectively position their mobile solutions?
Related Articles

Key insights from the 2024 Digital Banking Performance Metrics Report

Don’t just follow the latest (business book) fad

Innovative approach to savings benefits members and local charities

Navigating credit union challenges: Insights gained from core consulting
Stay connected to the credit union community with our free newsletter.
Delivered to the inboxes of thousands of credit union leaders daily.
You have Successfully Subscribed!
Impacts of Mobile Banking
Introduction.
As a result of the advent of mobile banking, which fundamentally revolutionized and redefined how banks previously conducted their business, technology is now considered the key contributor to the success of organizations and one of their core competencies. With the help of their mobile phones or personal digital assistants, customers of a financial institution can perform a wide range of financial operations (Kumar et al., 2020). Banking and financial services are available and accessed via mobile phones and other wireless devices. Services may include banking and trading capabilities, account management, and customized data displays based on user preferences. An example of an innovation that has spread across multiple economic and industrial sectors is the concept of mobile banking. To promote economic growth, healthy banking conditions are universally recognized as both a prerequisite and a key factor (Ho et al., 2020). This paper explores the impacts of mobile banking technology on the financial sector.
Ways in Which Mobile Banking Has Changed the Financial Industry
Mobile banking can improve bank performance by increasing market share, customer satisfaction, product variety, individualized goods, and responsiveness to customer demands. Mobile banking has been and will be used as a strategic tool to influence the revenue structures of banks ever since it was introduced (Garzaro et al., 2021). Over time, profitability can be traced back to a strategy that effectively maintained or grew the customer base. Banking institutions can benefit from mobile banking and mobile money by increasing their market share, fostering customer loyalty, reducing operational expenses, and fulfilling governmental service obligations.
Mobile banking provides financial institutions with numerous opportunities to develop new revenue streams. Among these are capitalizing on customer analytics, improving customers’ access to products and services in real-time, and using the data banks collect about their customers’ preferences to create more personalized marketing campaigns (Khoa, 2021). Previous research into the concept of branchless banking has identified the crucial role that mobile phones play in specific models. These match the expectations that electronic money will bring greater efficiencies and lower transaction costs. Theoretically, The provision of mobile banking services is expected to increase profits for banks in the form of commission incomes and to gradually reduce the costs of overhead operations, both of which positively impact financial performance as a whole.
Mobile banking has wholly revolutionized the money transfer industry and spawned additional innovations that have reduced transaction costs for customers and banks alike. As a result of this change, financial institutions are making more money and more profit from the money transfer market (Samsudeen et al., 2021). Worldwide, there has been a shift toward doing a growing share of retail business via mobile devices. Customers can move funds between their checking and savings accounts and electronic money accounts, and vice versa. The improvement of mobile money services has increased the velocity and circulation of money in the country, leading to higher commission incomes for banks.
Branchless banking, such as mobile banking and mobile payments, is a way to cut down on the expenses of catering to low-income customers. Financial institutions that have had difficulty serving customers with low incomes in a viable manner through more conventional distribution routes will find this an attractive proposition (Rajaobelina et al., 2021). Mobile banking has matured into its channel and is no longer seen as an add-on to online banking; it is now called the “fifth channel” of banking. Because of this, there is now tighter coordination between mobile banking and traditional bank servers. This has allowed financial institutions access to the tools necessary to increase their customer base and revenue by bringing previously unbanked individuals into the banking system.
Drawbacks of Mobile Banking
Specific smartphone devices can only use a subset of the available apps. It is also possible that your device is incompatible with the platform the app was made for (Samsudeen et al., 2022). Typically, financial services on the go are reserved for the more high-tech mobile devices. A stable internet connection is also essential for your program to run smoothly and effectively.
Many security issues plague today’s bank-specific software, beginning with inadequate data encryption and ending with data leakage. If this is the case, hackers and other online peril can easily compromise these programs (Shankar et al., 2020). If hackers determine that your account has sensitive data, they may attempt to gain access to it. In order to avoid falling victim to scammers, you should never give out your password or any other financial details. If you lose your device, criminals may be able to access your financial information.
Mobile banking apps are not a good fit for corporations because they can only process small deposits simultaneously. When your account reaches the maximum amount, you must visit the branch to make a new deposit (Çera et al., 2020). The computer scanning software may be unable to identify some types of checks. As a result, you should set aside a considerable amount of time for this procedure.
While it may be possible to keep tabs on your accounts and investments even when you are on the go, getting your hands on that cash will still take some time. Experts scrutinize each deposit and transfer of funds before being granted (Zhang and Kim, 2020). It follows that you must keep waiting till the approval is granted. The ramifications of this technique affect virtually all financial institutions.
A mobile banking application’s numerous advantages and functions make it a helpful tool. You have total flexibility and freedom to manage your money and access banking services whenever and wherever you like. While using a mobile banking app, it is essential to prevent it from illegal use by taking measures such as protecting your login information and password security. Though mobile banking eliminates several inconvenient steps, it still has its challenges. Carefully consider an app’s potential drawbacks and advantages before installing it on your device. Do not let yourself become a victim of cybercriminals by forgetting to take precautions. Keeping up standards requires that service providers manage issues such as network oscillations, the impact of lost or stolen mobile phones, unauthorized access, and the possibility of improper transfers.
Reference List
Çera, G., Pagria, I., Khan, K.A. and Muaremi, L., 2020. Mobile banking usage and gamification: the moderating effect of generational cohorts. Journal of Systems and Information Technology .
Ho, J.C., Wu, C.G., Lee, C.S. and Pham, T.T.T., 2020. Factors affecting the behavioural intention to adopt mobile banking: An international comparison. Technology in Society , 63 , p.101360.
Rajaobelina, L., Brun, I., Line, R. and Cloutier-Bilodeau, C., 2021. Not all elderly are the same: fostering trust through mobile banking service experience. International Journal of Bank Marketing , 39 (1), pp.85-106.
Samsudeen, S.N., Hilmy, M.H.A. and Gunapalan, S., 2020. Islamic banking customers’ intention to use mobile banking services: A Sri Lankan study.
Samsudeen, S.N., Selvaratnam, G. and Hayathu Mohamed, A.H., 2022. Intention to use mobile banking services: An Islamic banking customers’ perspective from Sri Lanka. Journal of Islamic Marketing , 13 (2), pp.410-433.
Shankar, A., Jebarajakirthy, C. and Ashaduzzaman, M., 2020. How do electronic word-of-mouth practices contribute to mobile banking adoption? Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services , 52 , p.101920.
Zhang, L.L. and Kim, H., 2020. The influence of financial service characteristics on use intention through customer satisfaction with mobile fintech. Journal of System and Management Sciences , 10 (2), pp.82-94.
Khoa, B.T., 2020. The impact of the personal data disclosure’s tradeoff on the trust and attitude loyalty in mobile banking services. Journal of Promotion Management , 27 (4), pp.585-608.
Garzaro, D.M., Varotto, L.F. and Pedro, S.D.C., 2021. Internet and mobile banking: the role of engagement and experience on satisfaction and loyalty. International Journal of Bank Marketing , 39 (1), pp.1-23.
Kumar, A., Dhingra, S., Batra, V. and Purohit, H., 2020. A framework of mobile banking adoption in India. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity , 6 (2), p.40.
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing style below:
Related Essays
Organisations and systems, leveraging big data and analytics for improved logistics and supply chain management: a case study, leadership failure in an organization, brand loyalty among millennials (generation y) and generation z, ethical leadership: the case of dennis kozlowski – the ceo of tyco international, technology and innovation in banking/finance, popular essay topics.
- American Dream
- Artificial Intelligence
- Black Lives Matter
- Bullying Essay
- Career Goals Essay
- Causes of the Civil War
- Child Abusing
- Civil Rights Movement
- Community Service
- Cultural Identity
- Cyber Bullying
- Death Penalty
- Depression Essay
- Domestic Violence
- Freedom of Speech
- Global Warming
- Gun Control
- Human Trafficking
- I Believe Essay
- Immigration
- Importance of Education
- Israel and Palestine Conflict
- Leadership Essay
- Legalizing Marijuanas
- Mental Health
- National Honor Society
- Police Brutality
- Pollution Essay
- Racism Essay
- Romeo and Juliet
- Same Sex Marriages
- Social Media
- The Great Gatsby
- The Yellow Wallpaper
- Time Management
- To Kill a Mockingbird
- Violent Video Games
- What Makes You Unique
- Why I Want to Be a Nurse
- Send us an e-mail
A Marketing Research on Mobile Banking Essay
Research problem, research objective, research hypothesis, research plan, data collection, data analysis, conclusion and recommendations.
The study plans to bridge the gap of knowledge in the acceptance and adoption of mobile banking among the consumers. The research will be an exploratory research. The reason for the choice of this methodology is due to its innovation of novel ideas that is required in the mobile banking market. Through exploratory study will provide new and clear concepts explaining the dynamics of mobile banking consumption.
The realization that the technology plays a critical role in the development of banking have adverse effects on the performance of the banking institutions and has led to reorganizations of the operation process and as well as the way banking processes are conducted. The most affected process is the customer services.
Technological developments have caused banks to move from the traditional queuing services to the modern day where customers can reach banks at any place and at any time. In fact technological development has revolutionized the banking industry. One of the areas that have been affected is the communication. Technology is utilized by banks to enhance connectivity and communication as well as in other business processes including customer services.
Mobile technology is one of the technological developments used by banks to increase the customer services. Currently, banks utilize mobile technology to allow their clients pay bills, receive updates in, plan payments as well as other aspects of consumer services while in their private life.
The major issue is whether the consumers have adopted the technological developments in banking. Banks have not established whether the consumers have adopted the new electronic payment services as in mobile banking. In addition, it has not been established what factors affect the mobile adoption. These are the problems and relations that will be examined in this research study.
The research study has the following objectives:
- To investigate the adoption of mobile banking by the consumers
- To establish specific factors affecting the mobile banking adoption by the consumers.
- To formulate appropriate recommendations to the banking institutions and the industry regarding strategies that may enhance the adoption of mobile banking.
This study will test the following hypothesis:
- H1: mobile banking is effectively adopted by the consumers and not influenced by many factors
- Ho: mobile banking is not effectively adopted by the consumers and influenced by many factors
For this research to meet its obligations, it will be an exploratory research. The reason for the choice of this methodology is due to its innovation of novel ideas that is required in the mobile banking market. Through exploratory, the research will come up with new and clear concepts explaining the dynamics of mobile banking consumption, set up main concerns, build up on operational explanations and improve on the final research design.
The study is both qualitative and quantitative. The qualitative part will be based on the literature review while the quantitative will be based on data collected through a survey. The survey will consist of a questionnaire that will be administered to the sampled population of both mobile banking users and non-users.
As a field survey, the information concerning mobile adoption and the factors afecting the adoption will be collected through administering properly designed research questionnaires, observation alongside conducting well-structured in-depth interviews to the unbiased selected users and non-users of mobile banking.
The well-designed research questionnaire will be administered to 60 users and 40 non-users. Each part of the questionnaire will constitute key items that suitably attend to the research questions. For instance, part one will constitute whether the consumer have embraced the mobile technology in banking services while part two will elicit factors that may have contributed their adoption or not of the mobile banking.
Other parts will generate insights amidst offering recommendations to the organization to adopt or abandon the employees training strategy to augment success. Some items in the questionnaire will throw light on the mobile banking services and its impact on the consumers along with the consumer knowledge of existence of such services.
The questionnaire will thus be made of both open and closed ended research questions and this is believed to be of great significance to the researcher since it will assist in performing data analysis. Minor research tools namely direct observations, personal in-depth interviews and occasional conversation will be used to collect primary data.
Conversely, secondary research data will be acquired from the banking institutions, industry records, and other documents, which contain mobile banking information as well as its successes. For this particular case, the researcher intends to trace the mobile banking history and its adoption successes over the past years from the research secondary sources. Different scales will however be applied in the survey questionnaire during data collection to ensure the scales reliability and validity of some research questions.
For example, ordinary scale will be applicable in various research questions given that most questions will measure knowledge, feelings and experience. In contrast, the scale reliability will be made certain via applying the repeatability and internal consistency concepts. This implies that, the questionnaire will comprise of different questions asking about the same thing yet in a very different way. Finally, split half technique will be applied to attain internal consistency.
In order to ensure logical completeness as well as response consistency, the acquired data will be edited by the researcher each day to be able to identify the ensuing data gaps or any mistakes that needs instant rectification.
When data editing is completed, the collected research information will definitely be analyzed qualitatively and quantitatively. For example, any data that will have been collected through in-depth interviews and secondary sources such as the mobile banking files and the banking organizations documents will be analyze by means of content analysis along with the logical analysis techniques.
Furthermore, from the acquired independent variables values such the number of customers using the mobile banking services and the institutional success measured in terms of total output or general productivity, regression analysis will be applied to establish the correlation that exist between mobile banking services and the success of those institutions.
To obtain the best correlation approximation values, the study quantitative data analysis will be carried out by utilizing the integrated approach. Further quantitative data analysis techniques including percentages, frequency distribution and deviations will be used to determine the research respondents’ proportions that chose various responses.
The method will be applied for each group of items available in the questionnaire that ideally corresponds to the formulated research question and objectives. Line graphs, tables as well as statistical bar charts will be used to maker sure quantitative data analysis is simply comprehensible.
The findings indicate mobile bank services, in delivering the services to the clients, try to eliminate the impediments that the customers face from the conventional banking delivering of the services. The obstacles were identified to be from a diverse combination of items that are replicated from the obstacles in supply part of services. In addition, the hurdles are reflected from the obstacles associated with the purpose of cell phones as a means of conveying information from the part of the client in the delivery of services.
The study also indicated that mobile banking has achieved tremendous acceptance among consumers compared to other ways of banking such as internet banking that is still at its developing phase. Consequently, consumers have perceived mobile banking as the best way of carrying out banking transactions. According to the institutional studies, 80% agree that the mobile banking sector has made major strides in the delivery of services due to the rapid acceptance by majority of consumers.
However, the approval pace of mobile banking among consumers is not equivalent to the rate at which technology advances. Therefore, many factors were found to have a strong influence on the way consumers perceive and adopt mobile banking.
The impact of the increased technological advancement has compromised the proficiency of service superiority because services are initiated in the premature phases due competitiveness as well as outlay constraints. Consequently, the clients’ responses to the consumption of services are low because they think their needs are not considered. For instance, the customers feel that the adaptability of sustaining item services is inadequate.
Moreover, emphasis on expertise has an impact of overlooking basic requirements for approval in the provision of services. Technology has enabled mediums of creating new supply channels as well as communicating attributes of technology. Conversely, delivery involving technical knowledge comes with its own shortcomings. For example, there is lack of composition of service delivery and worth creation. In addition, customers have to know how to use technology-based electronics to achieve optimal usage.
An additional drawback in mobile banking is the functionality of cell phones in transacting banking services. Customers feel that the mobile phones are not effective in banking because for example, the cell phones have small keyboards leading to errors while accessing the services.
Further, studies show that consumers are dissatisfied by the confusing nature of the mobile phones while transacting banking services. Moreover, increasing concerns by consumers about transacting banking through wireless ways due to safety as well as significance of the services has had negative impacts acceptance of the service.
Results show that service providers must recognize the importance of client requirements when devising innovative services and products. Additionally, execution of information from familiarity of wireless banking should not be directed to the clients. As a result, banks have been able to make well-versed judgments in distributing assets as well as reduction of expenses.
It is evident that cell phones bear a huge ability of enabling success in accomplishing monetary operations and has led to the attainment of expansion in the financial sector with ease and less expenses. Therefore, it is essential for banks to expand their banking services to enable accessibility of their services.
As a result, government, supervisory bodies, service providers and all the stakeholders have easy access to the banking services from all regions. Further, implementing mobile banking services will bring on board non-bankers in the financial system. In addition, through creation of the understanding of mobile banking services among the people, they are able to embrace its use for personal gains.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2020, January 13). A Marketing Research on Mobile Banking. https://ivypanda.com/essays/a-marketing-research-on-mobile-banking/
"A Marketing Research on Mobile Banking." IvyPanda , 13 Jan. 2020, ivypanda.com/essays/a-marketing-research-on-mobile-banking/.
IvyPanda . (2020) 'A Marketing Research on Mobile Banking'. 13 January.
IvyPanda . 2020. "A Marketing Research on Mobile Banking." January 13, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/a-marketing-research-on-mobile-banking/.
1. IvyPanda . "A Marketing Research on Mobile Banking." January 13, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/a-marketing-research-on-mobile-banking/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "A Marketing Research on Mobile Banking." January 13, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/a-marketing-research-on-mobile-banking/.
- Exploratory Research in Organizational Leadership
- Leadership Preferences in Japan: an Exploratory Study
- Exploratory, Descriptive, and Causal Research Designs - Compare & Contrast
- Methods of Conducting Exploratory Marketing Research
- Visual Display of Data: Exploratory Data Analysis
- How to Become a Successful Athlete? Exploratory Essay
- Mobile Banking Adoption: Challenges and Solutions
- Applying a Gender Perspective to Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): An Exploratory Study in the United Arab Emirates
- Exploratory Research Assignment: Sportsmanship
- Principal Components and Exploratory Factor Analysis
- What Are Some of the Product and Industry Characteristics Affecting EC Success?
- Keys to Be Successful Online
- Security and Privacy Issues in E-Commerce
- Mobile Commerce Technology
- Virtual Corporations: Article Analysis

ESSAY SAUCE
FOR STUDENTS : ALL THE INGREDIENTS OF A GOOD ESSAY
Essay: Mobile banking
Essay details and download:.
- Subject area(s): Finance essays
- Reading time: 26 minutes
- Price: Free download
- Published: 28 September 2015*
- File format: Text
- Words: 6,940 (approx)
- Number of pages: 28 (approx)
Text preview of this essay:
This page of the essay has 6,940 words. Download the full version above.
Over the last few years, the mobile and wireless market has been one of the fastest growing markets in the world and it is still growing at a fast space. Mobile phones have become an essential part in the communication tools for almost every individual. Advent of M commerce has managed to take mobile VAS to next level. Mobile banking is an integral part of the M commerce. It has become popular among mobile users from 2007. It creates a new communication and fast financial transactional channel for mobile user’s .Checking account information, available balance, , cheque , alerts, reminders, locating ATMs, mini statement etc are some of the services offered in mobile banking. The multiple access channels such as SMS, downloadable client, mobile Internet mobile banking is providing mobile users more to explore the service. Simple transactions including querying balances, are common, but there is huge opportunity to bring a vast array of financial services, everything from personal loans to investment products, to remote parts of India with mobile banking.(Mobile banking in India – Perception and Statistics, 2008) Mobile banking is becoming more and more prevalent in India due to the convenience factor. As per Reserve bank of India data, a total of 3.7 crore mobile transactions took place between Feb and Nov 2012. These transactions saw an increase in value over the same period. Increased use of Smartphone and initiatives such as media promotions and customer education programmes for mobile banking has led to this uptrend. For customers, mobile banking is convenient while banks benefit through a low-cost channel. With the mobile phone penetration reaching over 80 per cent, India has great potential for mobile banking. But on the global space, mobile payments have to go a long way in India. According to the MasterCard Mobile Payments Readiness Index (MPRI), India is ranked 21st among 34 countries with the score of 31.4 on a scale of 100 by the MasterCard Mobile Payments Readiness index. The index relies on an analysis of 34 countries and their readiness to use three types of mobile payments: person to person, mobile e-commerce and mobile payments at the point of sale .The index shows that consumers in India have not yet fully accepted mobile payments. (business today, 2013) Recent statistics indicate that m-banking is catching on in India. According to Reserve Bank. Mobile-based banking transactions grew from Rs 190 crores in January 2012 to Rs 624 crores in January 2013. M-banking in India has not reached to its full capability. It’s important to think why in spite of having more than 800 million mobile phone connections and 90 per cent handsets capable of basic financial transactions there are barriers to adopt m-banking in India.. Also, they can now avail of the security of regulated services and avoid the more risky unlicensed operators. This makes m-banking a safe and efficient procedure.(business line, 2013) Despite continued growth of the mobile money industry in the world, we will see that, however, there remain significant obstacles to its sustained growth and to the value it brings to the poor and unbanked.. This is the kind of new banking system that sought to develop Bank, one of the main microfinance actors in the Philippines in 2012 by inserting itself in the market for retail microfinance using the mobile phone as the primary channel. This initiative has emerged a new bank of microfinance which allowed customers to pay, save, and use credit services and insurance products directly by their mobile phone. Indeed, the m-banking affects the heart business of microfinance institutions and their way of serving customers, as well as new business models emerge gradually.(planet finance group, 2013) A phenomenon that is picking up speed worldwide, Mobile Banking is now also reaching out to millions of customers across India. Some recent stats on mobile banking are- 45 million registered mobile banking users,5 million regular mobile banking users,52 banks with mobile banking license,300 Per cent annual growth of mobile banking, Total transaction value to be dollar 245 million by 2014,40 Per cent of India’s mobile users have used a Smartphone for online banking and financial activities.50 Per cent have used a Smartphone to make a purchase., Interbank Mobile Payment Service was used for over 10000 transactions..Mobile banker transfer limit of Rs. 50000 has been recently removed by the RBI, enabling customers to transfer bigger amounts through their mobile phone. (thinkpod turn it) Customer adoption has been one of the key challenges with most of the mobile banking implementations across the globe. Customer adoption has to a function of the following: Product, which should be compelling and easy to use, Delivery, which channel and hand set education, through agents and call centre. The Reserve Bank of India has reported that the number of mobile banking transactions in India has increased by 6.39 Per cent to 47, 20,871 during the month of November 2012. While India’s mobile population is growing at rapid rate. It is estimated to be over 775 million strong; the percentage of these connections using banking services on the mobile is small. The reason is the fact that over 40 per cent of the adult population in India lacks a bank account. By end 2010, only about 1 Per cent of bank account holders were registered as mobile banking customers. (state of indian mobile banking, 2011) CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW 2.1 IMPORTANCE OF LITERATURE REVIEW Literature review is important due to the following reasons: 1) A literature review gives more knowledge about the area in which the research is conducted 2) It helps to refine the research topic by determining the research gap. 3) It helps to avoid errors of duplication 4) It helps to identify the contribution that one’s research will make and also provides a justification for the study. 5) It will help in understanding how already existing research findings have been presented in that particular area. 2.2 HOW THE REVIEW HAS BEEN DONE The review has been conducted in the following manner: 1) First, several literature sources in the area of behavioural finance were identified and studied. 2) The topic was then narrowed down upon as there were several discussions on the various factors 3) Therefore, I decided to study all such factors and read more articles on this topic which completed the literature review. 2.3 LITERATURE REVIEW Dasgupta Siddhartha, Paul, Fuloria &Sanjay (2011).The study was conducted to understand the behavioural intention of mobile banking usage of Indian customers. Research methods like the Factor analysis and a multiple regression analysis were done in order to determine the extent of impact the antecedents have over the behavioural intentions of mobile banking usage. The results of the study showed that other than the traditional variables like Perceived Usefulness and Perceived Ease of Use, factors like Perceived Image, Perceived Value, Self Efficacy, Perceived Credibility and Tradition all significantly affects Behavioural Intentions towards mobile banking usage. Palani and Yasodha P. (Apr 2012) The research paper is focused on customer’s perceptions on mobile banking offered by Indian Overseas Bank and it also focuses on the various drivers that drive mobile banking consumers.. The results of this study showed that gender, education and income of the consumers play an important role in usage of mobile banking. Most of the researches are focused on the acceptance of the mobile banking technology due to which not much research has been conducted on people. The research reveals that if skills can be upgraded among the consumers there will be greater willingness on the part of consumers toward the use of Mobile banking. Some the factors like security trust, gender, education, religion, and price can have minimal effect on consumer mindset towards Mobile banking compared to the other factors. Thakur, Rakhi; Srivastava, Mala. (2013) The paper studies the factors influencing the adoption intention of mobile commerce. Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use and social influence are found to be significant dimensions of technology adoption readiness to use mobile commerce while facilitating conditions were not found to be significant. The results of the research study also indicate the perceived credibility risk defined by security risk and privacy risk are significantly associated with behavioural intention in negative relation, which indicates that security and privacy concerns are important in deterring customers from using mobile commerce. This research study developed an integrated model for behavioural intention towards financial innovations. Practical implications of this study is one of the few empirical studies which have investigated the adoption of mobile commerce in India, which is considered one of the fastest growing countries in terms of mobile usage. The study relates to inclusion of both utilitarian and credibility aspect of adoption intention. It gives an empirical basis on which mobile and banking companies can base their mobile payments marketing strategy. Kumar, Reji G; Rejikumar, G; Ravindran, D Sudharani. This research paper examines the factors influencing the continuance decisions of the early adopters of m-banking services in Kerala, India. The study used constructs adopted from Technology Acceptance Model along with constructs of perceived service quality, perceived credibility and perceived risk to empirically establish the influence on satisfaction and continuance usage intentions. The study confirmed that after adoption of the technology, the customer finds satisfaction in the quality parameters of the service. Perceptions about the risks involved in m-banking had adverse impact on service quality and satisfaction. Kalaiarasi, H & Srividya, V. 3 (Jul-Sep 2012): Mobile banking as a new channel to the existing banking channels provides convenient and cost efficient banking services anytime anywhere. It is observed that, though India has strong potential for mobile banking only 5% of mobile subscribers are registered users of mobile banking. Attracting the new customers may not be easy than retaining the existing mobile banking customers 2009). Hence the current research focuses on the factors influencing actual usage of mobile banking services. The results shows that, Indians mobile banking usage is influenced by ease of mobile banking technology, its suitability to the user’s lifestyle and the benefits like mobility and mobile transactions. However customer’s perception towards security of mobile transactions and privacy fears demotivates actual usage. Tenkasi Taluk &Devasena, S Valli, (Jan 2012) Banking system is the backbone of the economy and Information Technology (IT) in turn has become the backbone of banking activities. Technology, which was playing a supportive role in banking, has come to the forefront with the ever-increasing challenges and requirements. Technology to start with was a business enabler and now has become a business driver. The Banks cannot think of introducing a financial product without IT support. Be it customer service, transactions, remittances, audit, marketing, pricing or any other activity in the Banks, IT plays an important role not to complete the activity with high efficiency but also has the potential to innovate and meet the future requirements. The Banking Sector was early adopter of technology and in that way set an example to the other industries the need to opt for automation for taking full advantage in operational efficiency. Laukkanen &Tommie (2007).The aim of the paper is to explore and compare customer value perceptions in internet and mobile banking. The results indicate that customer value perceptions in banking actions differ between internet and mobile channels. The findings suggest that efficiency, convenience and safety are salient in determining the differences in customer value perceptions between internet and mobile banking. By understanding how and what kind of value different service channels provide for customers service providers are better enabled to create actions to enhance internet and mobile banking adoption. The contribution of the paper lies in achieving a more profound understanding on consumer value perceptions to internet and mobile banking. Goswami, Divakar; Raghavendran, Satish. (2009)The research is conducted to determine the potential that mobile banking provides for both the banks and the mobile carriers. After the secondary research the report gives an insight into the best-practices based on a critical evaluation of partnership models. Banks and mobile carriers have tested these waters timidly, and many of the resulting offerings were expensive to the banks and mobile carriers and less than enticing to their customers. This report weeds out ineffective partnering models that companies stumble into on their way to developing mobile-banking and identifies the keys to successful partnerships. Dr. Vinod Kumar Gupta Renu Bagoria & Neha Bagoria . This research paper try s to identify and investigate the various factors which influence the customer’s decision to use a specific form of mobile banking and specially focus on the evaluation of SMS-based mobile banking in India. The study also plans to connect the gap of research in the acceptance of mobile banking among the customers. The main challenges involved in the adoption of mobile banking are related to the Positive and Negative factors which influence the adoption of SMS-based mobile banking .Second challenge is Focused on the adoption of mobile banking services by customers and usage of mobile banking in India. Third is related to the different Technologies behind Mobile Banking. The study has its own limitations but the implications and conclusion from the results can provide practical recommendations to the banking areas and banking industries. It can also provide directions for further work Prerna Sharma Bamoriya(2011) The study was conducted to identify certain issues relating to banks, mobile handsets and telecom operators, mobile handset operability, security/privacy, standardization of services, customization, Downloading & installing application software and Telecom services quality. For this purpose a descriptive design was adopted to empirically explore the selected issues. Study suggested that from consumers ‘perspective mobile handset operability security or privacy and standardization of services are the critical issues. The objective of the research is to study the selected issues in mobile banking form urban customers’ perspective and to explore the perceived utility of mobile banking in comparison to retail banking and online banking among the mobile banking users and non-users. The study is aimed to evaluate perceptions and opinions of urban mobile banking users. For this purpose a cross sectional descriptive design was adopted with ad-hoc quota sampling. Sample for the study comprised of 50 mobile banking users and 50 non-users in Indore city, India. Achana Sharma (2011) this paper examines consumer adopting mobile banking as a new electronic payment service .It also focuses on the various factors influencing the adoption of mobile banking in India. When it comes to the research methodology used in the study, data collected has been grouped into two main categories – primary and secondary data. The secondary data have been collected from the newspapers, journals, magazines, internet and also various other research papers..In case of questionnaires the has been targeted on user and non user of mobile banking which included the Businessmen, servicemen, professionals, students etc. The primary data for the study is extracted from a survey conducted in Ghaziabad in U.P, India. The research had a total of 100 respondents participating in the data collection for understanding the use of Mobile banking. From the data collected it was possible to make projections in the research. Ashish Adholiya, Pankaj Dave, Shilpa Adholiya (2012) this paper investigates the determinants influencing the customer satisfaction for mobile banking users. Customer satisfaction is one of the fundamental marketing constrain in the last three decades. This research is focused to those respondents who are using the mobile banking services by their service provider. For the research100 respondents are identified. The respondents belong from both private and public sector banks of Udaipur, Rajasthan. The opinions of the respondents were collected using structured questionnaire. Data collected were analyzed using tools like factor analysis, chi-square and correlation analysis. In factor analysis varimax rotation is used and correlation matrix is used for identifying the relationship between the service quality, perceived value , flexibility, technological innovation, brand perception, strategic endorsement and functional performance of mobile banking service with customer satisfaction. CHAPTER 3 RESEARCH Methodology 3.1 STATEMENT OF PROBLEM Mobile banking in a service that provides the individuals with a platform to carry out financial transactions through a mobile. Even though it’s a convenient service for the customers it still has to gain the popularity among the users. There are still bank users who have a mobile but not making use of the mobile banking service. The usages of the mobile banking services by the customers are dependent on certain factors. As it’s an emerging concept in the field of banking the customers perception and the quality of on the mobile banking services provided bank has a huge impact on the adoption of this service by the customers. The quality of service provided by the banks has a great impact on the extent to which customers adopt this service. So in order to provide the best possible services to meet the needs and wants of the customers the banks should have an idea of what these factors are and how much the these factors individually contribute towards the usage of mobile banking. It is also important to understand to what extent these factors impact on the customer satisfaction. The study will help in understanding theses factors that influence Customer’s perception on the use of mobile banking and which of these factors are the major contributors towards the service adoption .It will also help in understanding what kind of positive or negative effect these factors will have on customer satisfaction towards mobile banking service. 3.2 VARIABLES OF THE STUDY There are two kinds of variables in this study- Dependent variable and the independent variable 3.2.1 DEPENDENT VARIABLE Dependent variables are those whose value is dependent on the value of the others. In this study the dependent variable is customer satisfaction 3.2.2 INDEPENDENT VARIABLES Independent variables are any variable whose value determines that of others. The following are the independent variables of the study 1) Time factor 2) Flexibility factor 3) Reliability factor 4) cost factor 5) convenience factor 6) Security factor 3.3 OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY 1. To Identify the extent to which Gender and profession influence customers in adopting mobile banking services. 2. To understand the customer perception towards adopting mobile banking 3. To identify the factors effecting the adoption of mobile banking by mobile banking customers 4. To analyse the impact of mobile banking on the customer satisfaction 3.4 HYPOTHESIS Ho1: There is no significant effect of profession on the usage of mobile banking H11: There is significant effect of profession on the usage of mobile banking Ho2: There is no significant effect of and gender on the usage of mobile banking H12: There is significant effect of gender on the usage of mobile banking H02: There is no significant effect for time saving factor on the use of mobile banking H12: There is significant effect for time saving factor on customer on the use of mobile banking H03: There is no significant effect for cost factor on the use of mobile banking H13: There is significant effect for cost factor on customer on the use of mobile banking H04: There is no significant effect for convenience factor on the use of mobile banking H14: There is significant effect for convenience factor on customer on the use of mobile banking H05: There is no significant effect for security factor on the use of mobile banking H15: There is significant effect for security factor on customer on the use of mobile banking H05: There is no significant effect for reliability factor on the use of mobile banking H15: There is significant effect for reliability factor on customer on the use of mobile banking H06: There is no significant effect for flexibility factor on the use of mobile banking H16: There is significant effect for flexibility factor on customer on the use of mobile banking 3.5 DESIGN OF THE STUDY 3.5.1 TYPE OF INVESTIGATION The research that is being conducted is Descriptive in nature where we are trying to establish a relationship between dependent and independent variable. 3.5.2 DATA COLLECTION METHOD A questionnaire will be developed where respondents will answer the questions which will help in understanding the extent to which the factors affect the use of mobile banking and how these factors have an end effect on the level of customer satisfaction. The questionnaire will also include the basic personal details of the respondents like their name, address, age, qualification, job profile, income etc. The data collected using these questionnaires will be further analysed using the statistical tools that are covered later on. 3.6 SAMPLING PROCEDURE 3.6.1 SAMPLING METHOD The sampling will be a judgment sampling as it is necessary to administer the questionnaires only to such people who are actually having mobile connections and who hold a bank account as well. 3.6.2 SAMPLE SIZE The research will be based on a minimum of 100 respondents. The respondents will be from Bangalore city ranging between the age group of 20 years to 40 years. The sample will include both females and males. 3.7 TOOLS USED IN THE STUDY The following are tools used in the study to analyse the collected data: 1) Regression analysis: statistical process for estimating the relationships among variables. It includes number of techniques which are used to model and analyze different variables, when we need to focus on the relationship between dependent variable and one or more independent variables. More precisely, regression analysis helps us to understand how the value of the dependent variable changes as and when any one of the independent variables is changed, while the other independent variables are remaining fixed. 2) Percentage analysis: The percentage analysis will help in understanding the percentage contribution of each factors 3) Chi square test: Chi-square is a statistical test commonly used to compare observed data with data we would expect to obtain according to a particular hypothesis. The chi-square test is used to find out whether there is a significant difference between the expected frequencies and the observed frequencies in one or more categories 3.8 LIMITATIONS OF THE STUDY 1) The sample size consists of data collected from Bangalore city which might not reflect the proper opinion of the entire population 2) The research is conducted in a limited time period 3) The data is collected from a very small portion of the population hence the study cannot be applied on the entire population 4) The interpretation and suggestions are based on the assumption that the information provided by the respondents is genuine. CHAPTER 4 INDUSTRY OVERVIEW A bank is a financial institution that provides banking and other financial services. From the word ‘bank’ it is generally understood as an institution that holds a Banking Licenses. Financial supervision authorities grants Banking licenses and provide the rights to conduct fundamental banking services of accepting deposits and making loans. Without meeting the legal definition of a bank, there are some financial institutions that provide certain banking services which are known as the so called ‘non banks’ For the purpose of ensuring that banks are focusing on building that reach irrespective of profitability considerations, the government of India went through two rounds of nationalization of banks. ‘ In 1969, 14 major Indian commercial banks were centralized ‘ Six more banks were nationalized in the year1980 SBI, its subsidiaries, and 20 nationalized banks are generally referred to as public sector banks. As per the reserve bank of India’s supervision other private sector banks were allowed to continue as private entities . These are mostly referred to as the old private sector banks. Foreign banks that were operating in the country were similarly allowed to continue as private entities. Ownership of the regional rural banks is shared between three stake holders’ viz. Central government, concerned state government and the bank which sponsors the RRB. The sponsoring bank is expected to assist the RRB in operations. Another vehicle for local reach are the co-operative banks, which have an existence for over last century. They were registered under the act co-operative societies Act of 1960 and were supervised under the guidelines of banking regulations Act 1949 and banking laws act, 1956.Several states have their own regulations. Modern Banking in India originated in the last decades of the 18th century. Bank of Hindustan (1770-1829) and The General Bank of India, were the first banks established in 1786. State bank of India is the oldest bank that exists in the country. State bank originated as Bank of Calcutta in June 1806, which immediately became Bank of Bengal. For many years the presidency banks acted as a quasi-central bank, as done by their successors. The 3 banks merged in 1921 to form the Imperial bank of India which, after independence, became the State bank of India in 1955 The Indian banking industry has shown consistent growth during the last few decades, with banks with their customers accepting the robust systems and the existing process. This industry has marked a consistent rise in the number of reporting offices in last few years. With RBI stressing on its policy of financial inclusion, there is a large emphasis on rural expansion. However, still a large part of Indian village population remains without banks. Further expansions are required from the Indian banks to raise the penetration levels of banking services in rural areas of the country, which is home to more than 65% of Indian population. The Indian banking industry experienced a slowdown in financial year 2013. Persistent high inflation forced the RBI to maintain the benchmark interest rate at a higher level. This slowed down the credit off take in the country, which led to an industrial slowdown. All other sectors recorded subdued loan growth, except for agricultural loans and personal loans. High inflation led to reduction in domestic savings which resulted in a lower rate of deposit growth. However, when the interest rates are high and volatile conditions in the market attracts more depositors towards high yield and risk free term deposits of scheduled commercial banks. The prevailing adverse economic conditions deteriorated the asset quality of all commercial banks, especially public sector banks. Higher interest rates during this period triggered to an increase in non-performing assets in public sector banks, this increase brings threat to the profitability of the bank. The government of India has emphasized upon a need-based recapitalization of public sector banks so that they can comply with ‘Basel III norms’. These norms will be fully implemented in by 31/3/ 2018.Recently the Reserve Bank of India finalized the guidelines on licensing of new banks in the private sectors. They also invited applications in regards to licenses from eligible promoters with a cut-off date which was specifies as 1/7/2013. Ever since, the long term outlook of the Indian banking sector is in a stable state because of a large no: of non-banking population, increasing per capita income and a fast developing middle class. Emergence of new players and technology upgrades will further add to the growth of this sector. One of the most preferred employment destinations in India is the banking sector. Banking sector index has grown at an annual rate of 51% since the year 2001.The industry is recruiting in huge numbers and in the next 5 years, banks will have to recruit almost ‘7.5 lakh people’ Along with the regular banking activities, now, the banks have diversified to new products and services which includes opportunities in credit cards, wealth management, consumer finance, investment banking, mutual funds, life and general insurance, stock brokering, custodian services etc. Further most of the banks are setting up offices in foreign countries as a part of going global. The expansion and convergence with the other financial sectors such as the NBFCs, insurance and capital markets, retirement of employees and financial inclusion has created more opportunities in the banking sector. Some of the areas which require specialization are infrastructures, Risk managements, banking and financial service, MIS and CRM. Currently the industry is going through a transition phase. On one hand, the public sector banks are in the process of reducing their excessive manpower, non Performing assets and government equitys. While on the other hand the Private sector banks are consolidating themselves through mergers and Acquisitions. The public sector banks which form 78% of the total banking industry assets are troubled with non performing assets, reduced revenues from the traditional sources, lack of latest technology and excessive workforce. Whereas the private banks are moving ahead of the public sectors banks by changing the traditional banking model with innovation and service. The private banks however cannot match up to the great reach, size and access to low cost deposits of the public sector banks. Hence one of the means adopted by the private players to combat the public players has been through the mergers and acquisitions route. Over the past two years, the industry has witnessed several such instances. For instance, HDFC Merger with ‘Times Bank.’Private sector Banks have are experts in the field of internet banking, mobile banking, anywhere anytime banking, debit and credit cards, ATMs and combined various other services and collaborated them into the mainstream banking arena, while the public sector banks are still struggling with disgruntled employees in the aftermath of successful VRS schemes. Talks of government diluting their equity from 51% to 33 %in November 2000 have also opened up a new opportunity for the takeover of even the PSBs. Banks in India have been allowed to provide fee-based insurance services without risk participation invest in an insurance company for providing infrastructure and services support and set up of a separate joint venture insurance company with risk participation. CHAPTER 5 Data Analysis and Interpretation DATA INTERPRETATION User * Gender Cross tabulation Gender Total Male Female User Yes Count 29 13 42 % within User 69.0% 31.0% 100.0% No Count 25 33 58 % within User 43.1% 56.9% 100.0% Total Count 54 46 100 % within User 54.0% 46.0% 100.0% Comparing between male and females using mobile banking from the above table it can be seen that the percentage of male users are more compared to females. There are more of female non users than male non users. CHI SQUARE TEST Chi square test for finding the effect of profession and gender on the usage of mobile banking User * Profession Cross tabulation Profession Total student Employees businessman Teacher Others User Yes Count 6 7 13 3 13 42 Expected Count 8.8 8.4 12.2 2.1 10.5 42.0 No Count 15 13 16 2 12 58 Expected Count 12.2 11.6 16.8 2.9 14.5 58.0 Total Count 21 20 29 5 25 100 Expected Count 21.0 20.0 29.0 5.0 25.0 100.0 Chi-Square Tests Value df Asymp. Sig. (2-sided) Pearson Chi-Square 3.743a 4 .442 Likelihood Ratio 3.794 4 .435 Linear-by-Linear Association 3.264 1 .071 N of Valid Cases 100 Cases Valid Missing Total N Percent N Percent N Percent User * Gender 100 99.0% 1 1.0% 101 100.0% User * Gender Crosstabulation Gender Total Male Female User Yes Count 29 13 42 Expected Count 22.7 19.3 42.0 No Count 25 33 58 Expected Count 31.3 26.7 58.0 Total Count 54 46 100 Expected Count 54.0 46.0 100.0 Value df Asymp. Sig. (2-sided) Exact Sig. (2-sided) Exact Sig. (1-sided) Pearson Chi-Square 6.601a 1 .010 Continuity Correctionb 5.598 1 .018 Likelihood Ratio 6.718 1 .010 Fisher’s Exact Test .015 .009 Linear-by-Linear Association 6.535 1 .011 N of Valid Cases 100 a. 0 cells (.0%) have expected count less than 5. The minimum expected count is 19.32. b. Computed only for a 2×2 table Symmetric Measures Value Approx. Sig. Nominal by Nominal Phi .257 .010 Cramer’s V .257 .010 N of Valid Cases 100 INTERPRETATION From the above results it can be observed that the difference between actual and expected is not so significant in case of profession and usage of mobile banking. Greater the difference between the actual and expected greater will be the chi square value. In this case the difference is not significant and also the significance level is less than .05 hence there is no significant impact of profession on the use of mobile banking. In case of gender we can see that there is reasonably significant difference between the actual and the expected and significance level is less than .005. This implies that gender has significant impact on the use of mobile banking. Ho1: There is no significant relationship between professions on the usage of mobile banking H11: There is significant relationship between professions on the usage of mobile banking Hence Ho1 is accepted proving that profession does not have significant impact on mobile banking usage Ho2: There is no significant relationship between gender on the usage of mobile banking H12: There is significant relationship between gender on the usage of mobile banking Hence Ho1 is rejected proving that gender has significant impact on mobile banking usage Chi-Square Tests(Time factor) Value df Asymp. Sig. (2-sided) Exact Sig. (2-sided) Exact Sig. (1-sided) Pearson Chi-Square 4.433a 1 .035 Continuity Correctionb 3.503 1 .061 Likelihood Ratio 4.395 1 .036 Fisher’s Exact Test .060 .031 Linear-by-Linear Association 4.389 1 .036 N of Valid Cases 100 a. 0 cells (.0%) have expected count less than 5. The minimum expected count is 10.50. b. Computed only for a 2×2 table Chi-Square Tests( cost factor) Value df Asymp. Sig. (2-sided) Exact Sig. (2-sided) Exact Sig. (1-sided) Pearson Chi-Square 5.332a 1 .021 Continuity Correctionb 4.434 1 .035 Likelihood Ratio 5.364 1 .021 Fisher’s Exact Test .026 .017 Linear-by-Linear Association 5.278 1 .022 N of Valid Cases 100 a. 0 cells (.0%) have expected count less than 5. The minimum expected count is 19.32. b. Computed only for a 2×2 table Chi-Square Tests(flexibility) Value df Asymp. Sig. (2-sided) Exact Sig. (2-sided) Exact Sig. (1-sided) Pearson Chi-Square .164a 1 .685 Continuity Correctionb .041 1 .839 Likelihood Ratio .164 1 .685 Fisher’s Exact Test .840 .420 Linear-by-Linear Association .163 1 .687 N of Valid Cases 100 a. 0 cells (.0%) have expected count less than 5. The minimum expected count is 21.00. b. Computed only for a 2×2 table Chi-Square Tests(Ease factor) Value df Asymp. Sig. (2-sided) Exact Sig. (2-sided) Exact Sig. (1-sided) Pearson Chi-Square .312a 1 .577 Continuity Correctionb .125 1 .724 Likelihood Ratio .311 1 .577 Fisher’s Exact Test .682 .362 Linear-by-Linear Association .309 1 .579 N of Valid Cases 100 a. 0 cells (.0%) have expected count less than 5. The minimum expected count is 17.64. b. Computed only for a 2×2 table Chi-Square Tests(security) Value df Asymp. Sig. (2-sided) Exact Sig. (2-sided) Exact Sig. (1-sided) Pearson Chi-Square .828a 1 .363 Continuity Correctionb .494 1 .482 Likelihood Ratio .826 1 .363 Fisher’s Exact Test .412 .041 Linear-by-Linear Association .820 1 .365 N of Valid Cases 100 a. 0 cells (.0%) have expected count less than 5. The minimum expected count is 16.80. b. Computed only for a 2×2 table Chi-Square Tests(reability) Value df Asymp. Sig. (2-sided) Exact Sig. (2-sided) Exact Sig. (1-sided) Pearson Chi-Square 1.175a 1 .278 Continuity Correctionb .772 1 .380 Likelihood Ratio 1.182 1 .277 Fisher’s Exact Test .310 .040 Linear-by-Linear Association 1.163 1 .281 N of Valid Cases 100 a. 0 cells (.0%) have expected count less than 5. The minimum expected count is 17.64. b. Computed only for a 2×2 table Chi-Square Tests(others) Value df Asymp. Sig. (2-sided) Exact Sig. (2-sided) Exact Sig. (1-sided) Pearson Chi-Square 3.525a 1 .060 Continuity Correctionb 2.604 1 .107 Likelihood Ratio 3.752 1 .053 Fisher’s Exact Test .070 .190 Linear-by-Linear Association 3.490 1 .062 N of Valid Cases 100 a. 0 cells (.0%) have expected count less than 5. The minimum expected count is 7.56. b. Computed only for a 2×2 table INTERPRETATION The chi square test was conducted to find out how much the factors like time, cost, flexibility, ease, reliably, security and other factors influence the usage of mobile banking. It can be seen that for factors like time, reliability, security and cost the significance level is less than .05 hence showing that they have significant impact on the usage of mobile banking. This indicates that the null hypothesis will be rejected .Implying that these following factors have significant level of impact on the mobile banking usage by the customers. The rest of the factors ease flexibility and others are not having significant impact as the the significance level found through the test is greater than 0.05 which mean accept null hypothesis. That implies that are not having significant impact. Since the significance level of these factors are less than 0.05 it implies that the null hypothesis is rejected and these factos have strong impact on the usage of mobile banking/ factors that motivated to open account in mobile banking Frequency Percent Valid Percent Cumulative Percent Valid self motivation 30 29.7 30.0 30.0 advertisement 16 15.8 16.0 46.0 Friends 31 30.7 31.0 77.0 Internet 19 18.8 19.0 96.0 Others 4 4.0 4.0 100.0 Total 100 99.0 100.0 Missing System 1 1.0 Total 101 100.0 INTERPRETATION From the various factors listed as the motivator for usage of mobile banking services by customers it can be observed that after using frequency test we can say that the highest percent of respondent’s i.e 31% have selected friends as the common motivator. We can also see that self motivation is also having response of closely 30% .Hence it can be concluded that the biggest motivator for using mobile banking services are self-motivation and friends. REASONS BEHIND YOUR DISSATISFACTION Frequency Percent Valid Percent Cumulative Percent Valid service quality 7 6.9 7.0 7.0 low safety 32 31.7 32.0 39.0 reliability 24 23.8 24.0 63.0 difficult to understand 33 32.7 33.0 96.0 Others 4 4.0 4.0 100.0 Total 100 99.0 100.0 Missing System 1 1.0 Total 101 100.0 INTERPRETAION The respondents were given five factors to choose from which has caused dissatisfaction for them during the usage of mobile banking service. From the results of descriptive analysis it is observed that low safety and difficulty in usage are the two main factors chosen. 32% and 33% of the respondents chose low safety and difficulty in use. These are the highest contributor for dissatisfaction in the case of mobile banking usage Rank the services provided on the basis of the frequency of their usage(Fund transfer) Frequency Percent Valid Percent Cumulative Percent Valid first rank 21 20.8 21.0 21.0 second rank 27 26.7 27.0 48.0 third rank 30 29.7 30.0 78.0 fourth rank 15 14.9 15.0 93.0 fifth rank 3 3.0 3.0 96.0 sixth rank 4 4.0 4.0 100.0 Total 100 99.0 100.0 Missing System 1 1.0 Total 101 100.0 Rank the services provided on the basis of the frequency of their usage (IMPS) Frequency Percent Valid Percent Cumulative Percent Valid first rank 6 5.9 6.0 6.0 second rank 15 14.9 15.0 21.0 third rank 22 21.8 22.0 43.0 fourth rank 25 24.8 25.0 68.0 fifth rank 19 18.8 19.0 87.0 sixth rank 8 7.9 8.0 95.0 seventh rank 2 2.0 2.0 97.0 eight rank 3 3.0 3.0 100.0 Total 100 99.0 100.0 Missing System 1 1.0 Total 101 100.0 Rank the services provided on the basis of the frequency of their usage(enquiry) Frequency Percent Valid Percent Cumulative Percent Valid first rank 24 23.8 24.0 24.0 second rank 16 15.8 16.0 40.0 third rank 15 14.9 15.0 55.0 fourth rank 18 17.8 18.0 73.0 fifth rank 1 1.0 1.0 74.0 sixth rank 16 15.8 16.0 90.0 seventh rank 10 9.9 10.0 100.0 Total 100 99.0 100.0 Missing System 1 1.0 Total 101 100.0 Rank the services provided on the basis of the frequency of their usage(demat) Frequency Percent Valid Percent Cumulative Percent Valid first rank 2 2.0 2.0 2.0 second rank 5 5.0 5.0 7.0 third rank 3 3.0 3.0 10.0 fourth rank 4 4.0 4.0 14.0 fifth rank 15 14.9 15.0 29.0 sixth rank 9 8.9 9.0 38.0 seventh rank 23 22.8 23.0 61.0 eight rank 39 38.6 39.0 100.0 Total 100 99.0 100.0 Missing System 1 1.0 Total 101 100.0 Rank the services provided on the basis of the frequency of their usage(request) Frequency Percent Valid Percent Cumulative Percent Valid first rank 26 25.7 26.0 26.0 second rank 20 19.8 20.0 46.0 third rank 9 8.9 9.0 55.0 fourth rank 14 13.9 14.0 69.0 fifth rank 9 8.9 9.0 78.0 sixth rank 10 9.9 10.0 88.0 seventh rank 8 7.9 8.0 96.0 eight rank 4 4.0 4.0 100.0 Total 100 99.0 100.0 Missing System 1 1.0 Total 101 100.0 Rank the services provided on the basis of the frequency of their usage(bill pay) Frequency Percent Valid Percent Cumulative Percent Valid first rank 18 17.8 18.0 18.0 second rank 12 11.9 12.0 30.0 third rank 15 14.9 15.0 45.0 fourth rank 10 9.9 10.0 55.0 fifth rank 11 10.9 11.0 66.0 sixth rank 24 23.8 24.0 90.0 seventh rank 5 5.0 5.0 95.0 eight rank 5 5.0 5.0 100.0 Total 100 99.0 100.0 Missing System 1 1.0 Total 101 100.0 Rank the services provided on the basis of the frequency of their usage(top up) Frequency Percent Valid Percent Cumulative Percent Valid first rank 18 17.8 18.0 18.0 second rank 12 11.9 12.0 30.0 third rank 15 14.9 15.0 45.0 fourth rank 10 9.9 10.0 55.0 fifth rank 11 10.9 11.0 66.0 sixth rank 24 23.8 24.0 90.0 seventh rank 5 5.0 5.0 95.0 eight rank 5 5.0 5.0 100.0 Total 100 99.0 100.0 Missing System 1 1.0 Total 101 100.0 Enquiry Request Fund transfer INTERPRETATION Out of the 8 services commonly provided through mobile banking i.e. fund transfer, IMPS, enquiry, Demat , request, bill pay ,Top-up and m commerce it is observed that the customers are most aware of the request services which was raked top by majority of the respondents and demat service was ranked least out of the 8 by majority of the respondents. The top three services that are the customers are aware of can be concluded as request, fund transfer and enquiry. TIMEFACTOR frequency percent valid percent cumulative percent valid no 25 24.8 25.0 25.0 time 75 74.3 75.0 100.0 total 100 99.0 100.0 missing system 1 1.0 total 101 100.0 COSTFACTOR frequency percent valid percent cumulative percent valid no 46 45.5 46.0 46.0 cost 54 53.5 54.0 100.0 total 100 99.0 100.0 missing system 1 1.0 total 101 100.0 FLEXIBILITYFACTOR frequency percent valid percent cumulative percent valid no 50 49.5 50.0 50.0 flexibility 50 49.5 50.0 100.0 total 100 99.0 100.0 missing system 1 1.0 total 101 100.0 EASEFACTOR frequency percent valid percent cumulative percent valid no 42 41.6 42.0 42.0 ease 58 57.4 58.0 100.0 total 100 99.0 100.0 missing system 1 1.0 total 101 100.0 SECURITYFACTOR frequency percent valid percent cumulative percent valid no 40 39.6 40.0 40.0 security 60 59.4 60.0 100.0 total 100 99.0 100.0 missing system 1 1.0 total 101 100.0 RLIABILITYFACTOR frequency percent valid percent cumulative percent valid no 42 41.6 42.0 42.0 reliability 58 57.4 58.0 100.0 total 100 99.0 100.0 missing system 1 1.0 total 101 100.0 OTHERFACTOR frequency percent valid percent cumulative percent valid no 82 81.2 82.0 82.0 other 18 17.8 18.0 100.0 total 100 99.0 100.0 missing system 1 1.0 total 101 100.0 INTERPRETATION For a question related to choosing the factors that affect the opening of mobile banking account it was found that time factor were chosen by 75% of the respondents, cost factor was chosen by 54%,flexibility by 50% respondents, ease factor by 58% , security factor by 60%,reliability by 58% and other factors were chosen by 18% respondents. From the responses it can be inferred that the biggest factor that contributes towards opening a mobile banking account was time saving factor. Ease, security and reliability were also other major contributors. REGRESSION ANALYSIS Descriptive Statistics Mean Std. Deviation N User 1.5800 .49604 100 mobile banking is time saving than conventional banking? 1.7300 .56595 100 mobile banking is cost saving than conventional banking? 2.0600 .70811 100 mobile banking is flexible than conventional banking? 2.2200 .56102 100 mobile banking is easy to than conventional banking? 3.3300 4.12202 100 mobile banking is secure than conventional banking? 2.8800 .81995 100 mobile banking is reliable than conventional banking? 3.0600 .82658 100 mobile banking has better problem handling capacity than conventional banking? 3.0400 .89803 100 mobile banking has full filled my expectations than conventional banking? 2.8600 .95367 100 Model Summary Model R R Square Adjusted R Square Std. Error of the Estimate 1 . 058a .607 -.016 .49988 b. Dependent Variable: User ANOVAb Model Sum of Squares df Mean Square F Sig. 1 Regression 1.621 8 .203 .811 .044a Residual 22.739 91 .250 Total 24.360 99 b. Dependent Variable: User INTERPRETATION R=0.58 R square=.607 Anova=.044 The value of R should be closer to 1 in Oder to have a significant impact. Here we can see that the value is closer to 1 therefore it implies that the factors have significant relation to the dependent variable square value should be above 50% and here in the results its 60% .This implies there exists a significant affect of variables on dependent variable . The anova significance should ideally be less than 0.05 and this results we can see its 0.044 which indicated that factors have strong impact on dependent variables. Therefore the regression analysis states that the factors are significant and have a significant impact on deciding the usage of mobile banking. CHAPTER 6 FINDINGS, CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS FINDINGS AND CONCLUSIONS 1. From the sample size it was observed that the usage of mobile banking was more among the male respondents compared to that of female respondents. More than 60% of the male respondents were mobile banking users and more than 50% of females were non users. 2. It is also found from the responses that the most number of users belonged to the businessman category. 3. After conducting the Chi square test it was found that profession does not have significant impact on mobile banking usage 4. The chi square test proved that gender has significant impact on the usage of mobile banking. 5. Out of the six factors time saving, cost, reliability, security, ease , flexibility and others it was found that except for ease factor, flexibility factor and other factors rest of the 3 factors have significant impact on influencing the customers in opening a mobile banking account in their respective bank 6. The chi square test was conducted to find the service which the customers are most aware of in mobile banking service. It was found that the respondents ranked fund transfer, request service and enquiries as the top services that they are aware of. The least ranked service was demat services implying that the customers are not so aware of this particular services provided through mobile banking. 7. Time, cost, reliability, security, ease, flexibility are having significant impact on the decision of becoming a mobile banking user. These factors contribute significantly towards the level of satisfaction a customer has from the usage this mobile banking service.
...(download the rest of the essay above)
About this essay:
If you use part of this page in your own work, you need to provide a citation, as follows:
Essay Sauce, Mobile banking . Available from:<https://www.essaysauce.com/finance-essays/essay-mobile-banking/> [Accessed 05-05-24].
These Finance essays have been submitted to us by students in order to help you with your studies.
* This essay may have been previously published on Essay.uk.com at an earlier date.
Essay Categories:
- Accounting essays
- Architecture essays
- Business essays
- Computer science essays
- Criminology essays
- Economics essays
- Education essays
- Engineering essays
- English language essays
- Environmental studies essays
- Essay examples
- Finance essays
- Geography essays
- Health essays
- History essays
- Hospitality and tourism essays
- Human rights essays
- Information technology essays
- International relations
- Leadership essays
- Linguistics essays
- Literature essays
- Management essays
- Marketing essays
- Mathematics essays
- Media essays
- Medicine essays
- Military essays
- Miscellaneous essays
- Music Essays
- Nursing essays
- Philosophy essays
- Photography and arts essays
- Politics essays
- Project management essays
- Psychology essays
- Religious studies and theology essays
- Sample essays
- Science essays
- Social work essays
- Sociology essays
- Sports essays
- Types of essay
- Zoology essays

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
76% of mobile banking apps can be accessed by hackers, and with anyone from the app developers to the banks themselves capable of leaving vulnerabilities, it is easy for security to fall short at any stage.. Security and reliability are of paramount importance to mobile banking users. A substantial 62% of mobile banking users claim they would switch providers after a negative experience.
The Importance of Mobile Banking. Mobile banking allows consumers to be able to access banking services from anywhere. Businesses and business owners are now able to save time by making use of mobile applications to process their payments or even receive funds from clients directly to their phone numbers. It is particularly popular among small ...
Mobile banking is the most popular and powerful mode of service delivery, which ensures the delivery of banking services anywhere and anytime. This article attempts to analyse the current status of research on mobile banking in order to identify the themes to be explored by future researchers. With the deft use of different inclusion and ...
Mobile banking refers to banking activities that are carried out using mobile devices, for instance, cell phones and tablets (Market Reports 2015). Mobile banking has transformed the way people conduct business transactions by eliminating the inherent need for face-to-face transactions. Mobile banking, also known as m-banking, enables users to ...
Adoption of mobile banking services has been. tremendously increased in past few years. The. purpose of this study is to find out the factors which. influence in adoptio n of Mob ile banking among ...
of mobile banking. Academic papers provide prior research in related fields and offer their conclusions. All references in this paper have been of great value and have stirred ... Mobile banking was first introduced in the late 90s-early 2000s when the Internet began to gain popularity. A few select large banks like Wachovia and Wells Fargo started
The mobile banking innovation is in tandem with these legal requirements to avoid court cases. For instance, mobile banking innovation has put measures in place to address the issue of infringing on other people's rights. Mobile banking innovation has managed to comply with them. Suitability of Mobile Banking: SWOT Analysis
transactions using a mobile phone" Mobile banking is the act of doing financial transactions on a. mobile device (cell phone, tablet, etc ).and using software usually called an app provided by ...
Literature review of mobile banking and individual performance. August 2017. International Journal of Bank Marketing 35 (1):00-00. DOI: 10.1108/IJBM-09-2015-0143. Authors: Carlos Tam. Universidade ...
Mobile banking is the act of doing financial transactions on a mobile device (cell phone, tablet, etc.). This activity can be as simple as a bank sending fraud or usage activity to a client's ...
1. Accessing the bank 24/7. Unlike a bank branch, mobile banking conveniently gives you access to your account anytime you like — with some exceptions, such as planned maintenance updates and ...
Purpose. This study is a systematic review of mobile banking services. Its main objective is to provide a state-of-the-art review of this particular growing type of services. It inventories and assesses the most significant determinants of and barriers to consumers' adoption of mobile banking. Moreover, it identifies the most common ...
Search for more papers by this author. Book Author(s): Sankar Krishnan, Sankar Krishnan. ... Share a link. Share on. Facebook; Twitter; Linked In; Reddit; Wechat; The Power of Mobile Banking: How to Profit from the Revolution in Retail Financial Services. Related; Information; Close Figure Viewer. Return to Figure. Previous Figure Next Figure ...
Imperative #2: Designing-In Fraud Assurance. Banks already do plenty to identify and prevent fraudulent activity related to mobile banking—but it clearly hasn't eliminated consumers ...
Digital banking solutions, specifically mobile and web-based platforms, have gained widespread adoption in the past ten years, as bank branches become less and less utilized. However, a pertinent ...
Facts. Mobile banking is well utilized in countries of Europe and even Japan, yet it is slow to catch up in America. A study by Forrester Research found that only 10% of Americans like the idea of m banking while 35% already bank online. Citibank had designed its own mobile banking software that can be downloaded and installed on more than 100 ...
Ways in Which Mobile Banking Has Changed the Financial Industry. Mobile banking can improve bank performance by increasing market share, customer satisfaction, product variety, individualized goods, and responsiveness to customer demands. Mobile banking has been and will be used as a strategic tool to influence the revenue structures of banks ...
2. Round-the-clock availability even functional and holidays. 3. Provides a variety of banking and value-added service. 4. In Mobile banking there is not GPRS required; works only on voice ...
Mobile Banking Essay. For nearly 30 years, financial institutions have been on consistently trying to satisfy their customers' need for more convenience. The automated teller machines (ATM) were the first to change the scenario with technology bringing in better convenience, which was introduced by Chemical Bank in New York in 1969.
A Marketing Research on Mobile Banking Essay. The study plans to bridge the gap of knowledge in the acceptance and adoption of mobile banking among the consumers. The research will be an exploratory research. The reason for the choice of this methodology is due to its innovation of novel ideas that is required in the mobile banking market.
Abstract. The aged have unique challenges when using mobile banking applications and financial institutions need to adapt and incorporate security into mobile banking application design according to the unique needs of this demographic.
Meaning of Mobile Banking. In a layman's context, the term Mobile Banking means; "Execution of Banking and Financial transactions using a Mobile phone" or "Availing banking services through a medium of cellular phone, without visiting the bank's branch". SMSs sent by bank on withdrawal and deposit transactions, credit card and ATM ...
In India, we have more than 900 million mobile users but still mobile banking is used by 40 million customers approximately. There can be various reasons behind this, such as need of active ...
Mobile Banking Essay. Decent Essays. 873 Words. 4 Pages. Open Document. Essay Sample Check Writing Quality. Show More. Trends and Issues on Mobile Banking Applications in the Developing Countries. Security and privacy aspects of the customer is the main thing from the adoption of the latest technologies for banks and financial institutions ...
Essay: Mobile banking. 28 September 2015 by Essay Sauce. Essay details and download: Subject area(s): Finance essays; Reading time: 26 minutes; Price: Free download; Published: 28 September 2015* File format: Text; Words: 6,940 (approx) Number of pages: 28 (approx) Text preview of this essay: