Compare and Contrast Rubric


About this printout
Students and teachers can use this rubric when doing writing that compares and contrasts two things, as well as when assessing the writing.
Teaching with this printout
More ideas to try.
When assigning a compare and contrast writing assignment, students need to be aware of what makes an outstanding written work. This rubric is a great tool to show students what is expected of them in a concrete way. Additionally, this rubric will help teachers assess this student writing and inform further instruction. This Comparison and Contrast Rubric is also a great way to introduce different rubrics that are used to assess student writing on many state tests.
- Have students work with a partner or a group and grade each others' papers using the rubric (the entire group should grade the same paper at one time). Students can then compare their scores with those of other students, as well as the author, to see how they are similar and different. Feedback from group members will help students when editing their own papers and looking to see if they have included what is required of the assignment.
- Before turning in the writing assignment, have students assess his/her own writing using the rubric. After the teacher has assessed the assignment, the student and teacher could have a one-on-one conference to discuss how their assessed rubrics differ and what improvements could be made.
- Print this resource
Explore Resources by Grade
- Kindergarten K
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Comparing and contrasting in an essay | Tips & examples
Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay | Tips & Examples
Published on August 6, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
Comparing and contrasting is an important skill in academic writing . It involves taking two or more subjects and analyzing the differences and similarities between them.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
When should i compare and contrast, making effective comparisons, comparing and contrasting as a brainstorming tool, structuring your comparisons, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about comparing and contrasting.
Many assignments will invite you to make comparisons quite explicitly, as in these prompts.
- Compare the treatment of the theme of beauty in the poetry of William Wordsworth and John Keats.
- Compare and contrast in-class and distance learning. What are the advantages and disadvantages of each approach?
Some other prompts may not directly ask you to compare and contrast, but present you with a topic where comparing and contrasting could be a good approach.
One way to approach this essay might be to contrast the situation before the Great Depression with the situation during it, to highlight how large a difference it made.
Comparing and contrasting is also used in all kinds of academic contexts where it’s not explicitly prompted. For example, a literature review involves comparing and contrasting different studies on your topic, and an argumentative essay may involve weighing up the pros and cons of different arguments.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
As the name suggests, comparing and contrasting is about identifying both similarities and differences. You might focus on contrasting quite different subjects or comparing subjects with a lot in common—but there must be some grounds for comparison in the first place.
For example, you might contrast French society before and after the French Revolution; you’d likely find many differences, but there would be a valid basis for comparison. However, if you contrasted pre-revolutionary France with Han-dynasty China, your reader might wonder why you chose to compare these two societies.
This is why it’s important to clarify the point of your comparisons by writing a focused thesis statement . Every element of an essay should serve your central argument in some way. Consider what you’re trying to accomplish with any comparisons you make, and be sure to make this clear to the reader.
Comparing and contrasting can be a useful tool to help organize your thoughts before you begin writing any type of academic text. You might use it to compare different theories and approaches you’ve encountered in your preliminary research, for example.
Let’s say your research involves the competing psychological approaches of behaviorism and cognitive psychology. You might make a table to summarize the key differences between them.
Or say you’re writing about the major global conflicts of the twentieth century. You might visualize the key similarities and differences in a Venn diagram.
These visualizations wouldn’t make it into your actual writing, so they don’t have to be very formal in terms of phrasing or presentation. The point of comparing and contrasting at this stage is to help you organize and shape your ideas to aid you in structuring your arguments.
When comparing and contrasting in an essay, there are two main ways to structure your comparisons: the alternating method and the block method.
The alternating method
In the alternating method, you structure your text according to what aspect you’re comparing. You cover both your subjects side by side in terms of a specific point of comparison. Your text is structured like this:
Mouse over the example paragraph below to see how this approach works.
One challenge teachers face is identifying and assisting students who are struggling without disrupting the rest of the class. In a traditional classroom environment, the teacher can easily identify when a student is struggling based on their demeanor in class or simply by regularly checking on students during exercises. They can then offer assistance quietly during the exercise or discuss it further after class. Meanwhile, in a Zoom-based class, the lack of physical presence makes it more difficult to pay attention to individual students’ responses and notice frustrations, and there is less flexibility to speak with students privately to offer assistance. In this case, therefore, the traditional classroom environment holds the advantage, although it appears likely that aiding students in a virtual classroom environment will become easier as the technology, and teachers’ familiarity with it, improves.
The block method
In the block method, you cover each of the overall subjects you’re comparing in a block. You say everything you have to say about your first subject, then discuss your second subject, making comparisons and contrasts back to the things you’ve already said about the first. Your text is structured like this:
- Point of comparison A
- Point of comparison B
The most commonly cited advantage of distance learning is the flexibility and accessibility it offers. Rather than being required to travel to a specific location every week (and to live near enough to feasibly do so), students can participate from anywhere with an internet connection. This allows not only for a wider geographical spread of students but for the possibility of studying while travelling. However, distance learning presents its own accessibility challenges; not all students have a stable internet connection and a computer or other device with which to participate in online classes, and less technologically literate students and teachers may struggle with the technical aspects of class participation. Furthermore, discomfort and distractions can hinder an individual student’s ability to engage with the class from home, creating divergent learning experiences for different students. Distance learning, then, seems to improve accessibility in some ways while representing a step backwards in others.
Note that these two methods can be combined; these two example paragraphs could both be part of the same essay, but it’s wise to use an essay outline to plan out which approach you’re taking in each paragraph.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
Some essay prompts include the keywords “compare” and/or “contrast.” In these cases, an essay structured around comparing and contrasting is the appropriate response.
Comparing and contrasting is also a useful approach in all kinds of academic writing : You might compare different studies in a literature review , weigh up different arguments in an argumentative essay , or consider different theoretical approaches in a theoretical framework .
Your subjects might be very different or quite similar, but it’s important that there be meaningful grounds for comparison . You can probably describe many differences between a cat and a bicycle, but there isn’t really any connection between them to justify the comparison.
You’ll have to write a thesis statement explaining the central point you want to make in your essay , so be sure to know in advance what connects your subjects and makes them worth comparing.
Comparisons in essays are generally structured in one of two ways:
- The alternating method, where you compare your subjects side by side according to one specific aspect at a time.
- The block method, where you cover each subject separately in its entirety.
It’s also possible to combine both methods, for example by writing a full paragraph on each of your topics and then a final paragraph contrasting the two according to a specific metric.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay | Tips & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 15, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/compare-and-contrast/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write an expository essay, how to write an argumentative essay | examples & tips, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, what is your plagiarism score.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write a Compare and Contrast Essay
Last Updated: May 12, 2023 Approved
This article was co-authored by Megan Morgan, PhD . Megan Morgan is a Graduate Program Academic Advisor in the School of Public & International Affairs at the University of Georgia. She earned her PhD in English from the University of Georgia in 2015. wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. This article has 29 testimonials from our readers, earning it our reader-approved status. This article has been viewed 3,101,165 times.
The purpose of a compare and contrast essay is to analyze the differences and/or the similarities of two distinct subjects. A good compare/contrast essay doesn’t only point out how the subjects are similar or different (or even both!). It uses those points to make a meaningful argument about the subjects. While it can be a little intimidating to approach this type of essay at first, with a little work and practice, you can write a great compare-and-contrast essay!
Formulating Your Argument

- You could pick two subjects that are in the same “category” but have differences that are significant in some way. For example, you could choose “homemade pizza vs. frozen grocery store pizza.”
- You could pick two subjects that don’t appear to have anything in common but that have a surprising similarity. For example, you could choose to compare bats and whales. (One is tiny and flies, and the other is huge and swims, but they both use sonar to hunt.)
- You could pick two subjects that might appear to be the same but are actually different. For example, you could choose "The Hunger Games movie vs. the book."

- For example, ask yourself: What can we learn by thinking about “The Hunger Games” and “Battle Royale” together that we would miss out on if we thought about them separately?
- It can be helpful to consider the “So what?” question when deciding whether your subjects have meaningful comparisons and contrasts to be made. If you say “The Hunger Games and Battle Royale are both similar and different,” and your friend asked you “So what?” what would your answer be? In other words, why bother putting these two things together?

- A “Venn diagram” can often be helpful when brainstorming. This set of overlapping circles can help you visualize where your subjects are similar and where they differ. In the outer edges of the circle, you write what is different; in the overlapping middle area, you write what’s similar. [2] X Trustworthy Source University of North Carolina Writing Center UNC's on-campus and online instructional service that provides assistance to students, faculty, and others during the writing process Go to source
- You can also just draw out a list of all of the qualities or characteristics of each subject. Once you’ve done that, start looking through the list for traits that both subjects share. Major points of difference are also good to note.

- For example, if you are comparing and contrasting cats and dogs, you might notice that both are common household pets, fairly easy to adopt, and don’t usually have many special care needs. These are points of comparison (ways they are similar).
- You might also note that cats are usually more independent than dogs, that dogs may not provoke allergies as much as cats do, and that cats don’t get as big as many dogs do. These are points of contrast (ways they are different).
- These points of contrast can often be good places to start thinking about your thesis, or argument. Do these differences make one animal a superior type of pet? Or a better pet choice for a specific living situation (e.g., an apartment, a farm, etc.)?

- Show readers why one subject is more desirable than the other. Example: "Cats are better pets than dogs because they require less maintenance, are more independent, and are more adaptable."
- Help readers make a meaningful comparison between two subjects. Example: "New York City and San Francisco are both great cities for young professionals, but they differ in terms of their job opportunities, social environment, and living conditions."
- Show readers how two subjects are similar and different. Example: "While both The Catcher in the Rye and To Kill a Mockingbird explore the themes of loss of innocence and the deep bond between siblings, To Kill a Mockingbird is more concerned with racism while The Catcher in the Rye focuses on the prejudices of class."
- In middle school and high school, the standard format for essays is often the “5-paragraph form,” with an introduction, 3 body paragraphs, and a conclusion. If your teacher recommends this form, go for it. However, you should be aware that especially in college, teachers and professors tend to want students to break out of this limited mode. Don’t get so locked into having “three main points” that you forget to fully explore your topic.
Organizing Your Essay

- Subject by subject. This organization deals with all of the points about Topic A, then all of the points of Topic B. For example, you could discuss all your points about frozen pizza (in as many paragraphs as necessary), then all your points about homemade pizza. The strength of this form is that you don’t jump back and forth as much between topics, which can help your essay read more smoothly. It can also be helpful if you are using one subject as a “lens” through which to examine the other. The major disadvantage is that the comparisons and contrasts don’t really become evident until much further into the essay, and it can end up reading like a list of “points” rather than a cohesive essay. [4] X Trustworthy Source University of North Carolina Writing Center UNC's on-campus and online instructional service that provides assistance to students, faculty, and others during the writing process Go to source
- Point by point. This type of organization switches back and forth between points. For example, you could first discuss the prices of frozen pizza vs. homemade pizza, then the quality of ingredients, then the convenience factor. The advantage of this form is that it’s very clear what you’re comparing and contrasting. The disadvantage is that you do switch back and forth between topics, so you need to make sure that you use transitions and signposts to lead your reader through your argument.
- Compare then contrast. This organization presents all the comparisons first, then all the contrasts. It’s a pretty common way of organizing an essay, and it can be helpful if you really want to emphasize how your subjects are different. Putting the contrasts last places the emphasis on them. However, it can be more difficult for your readers to immediately see why these two subjects are being contrasted if all the similarities are first.

- Introduction. This paragraph comes first and presents the basic information about the subjects to be compared and contrasted. It should present your thesis and the direction of your essay (i.e., what you will discuss and why your readers should care).
- Body Paragraphs. These are the meat of your essay, where you provide the details and evidence that support your claims. Each different section or body paragraph should tackle a different division of proof. It should provide and analyze evidence in order to connect those proofs to your thesis and support your thesis. Many middle-school and high-school essays may only require three body paragraphs, but use as many as is necessary to fully convey your argument.
- Acknowledgement of Competitive Arguments/Concession. This paragraph acknowledges that other counter-arguments exist, but discusses how those arguments are flawed or do not apply.
- Conclusion. This paragraph summarizes the evidence presented. It will restate the thesis, but usually in a way that offers more information or sophistication than the introduction could. Remember: your audience now has all the information you gave them about why your argument is solid. They don’t need you to just reword your original thesis. Take it to the next level!

- Introduction: state your intent to discuss the differences between camping in the woods or on the beach.
- Body Paragraph 1 (Woods): Climate/Weather
- Body Paragraph 2 (Woods): Types of Activities and Facilities
- Body Paragraph 3 (Beach): Climate/Weather
- Body Paragraph 4 (Beach): Types of Activities and Facilities

- Introduction

- Body Paragraph 1: Similarity between woods and beaches (both are places with a wide variety of things to do)
- Body Paragraph 2: First difference between woods and beaches (they have different climates)
- Body Paragraph 3: Second difference between woods and beaches (there are more easily accessible woods than beaches in most parts of the country)
- Body Paragraph 4: Emphasis on the superiority of the woods to the beach

- Topic sentence: This sentence introduces the main idea and subject of the paragraph. It can also provide a transition from the ideas in the previous paragraph.
- Body: These sentences provide concrete evidence that support the topic sentence and main idea.
- Conclusion: this sentence wraps up the ideas in the paragraph. It may also provide a link to the next paragraph’s ideas.
Putting It All Together

- If you are having trouble finding evidence to support your argument, go back to your original texts and try the brainstorming process again. It could be that your argument is evolving past where it started, which is good! You just need to go back and look for further evidence.

- For example, in a body paragraph about the quality of ingredients in frozen vs. homemade pizza, you could close with an assertion like this: “Because you actively control the quality of the ingredients in pizza you make at home, it can be healthier for you than frozen pizza. It can also let you express your imagination. Pineapple and peanut butter pizza? Go for it! Pickles and parmesan? Do it! Using your own ingredients lets you have fun with your food.” This type of comment helps your reader understand why the ability to choose your own ingredients makes homemade pizza better.

- Reading your essay aloud can also help you find problem spots. Often, when you’re writing you get so used to what you meant to say that you don’t read what you actually said.

- Avoid bias. Don't use overly negative or defamatory language to show why a subject is unfavorable; use solid evidence to prove your points instead.
- Avoid first-person pronouns unless told otherwise. In some cases, your teacher may encourage you to use “I” and “you” in your essay. However, if the assignment or your teacher doesn’t mention it, stick with third-person instead, like “one may see” or “people may enjoy.” This is common practice for formal academic essays.
- Proofread! Spelling and punctuation errors happen to everyone, but not catching them can make you seem lazy. Go over your essay carefully, and ask a friend to help if you’re not confident in your own proofreading skills.
Sample Body Paragraphs

- "When one is deciding whether to go to the beach or the woods, the type of activities that each location offers are an important point to consider. At the beach, one can enjoy the water by swimming, surfing, or even building a sandcastle with a moat that will fill with water. When one is in the woods, one may be able to go fishing or swimming in a nearby lake, or one may not be near water at all. At the beach, one can keep one's kids entertained by burying them in sand or kicking around a soccer ball; if one is in the woods, one can entertain one's kids by showing them different plans or animals. Both the beach and the woods offer a variety of activities for adults and kids alike."

- "The beach has a wonderful climate, many activities, and great facilities for any visitor's everyday use. If a person goes to the beach during the right day or time of year, he or she can enjoy warm, yet refreshing water, a cool breeze, and a relatively hot climate. At the beach, one can go swimming, sunbathe, or build sandcastles. There are also great facilities at the beach, such as a changing room, umbrellas, and conveniently-located restaurants and changing facilities. The climate, activities, and facilities are important points to consider when deciding between the beach and the woods."
Sample Essay Outline

Community Q&A
- Collect your sources. Mark page numbers in books, authors, titles, dates, or other applicable information. This will help you cite your sources later on in the writing process. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 2
- Don't rush through your writing. If you have a deadline, start early. If you rush, the writing won't not be as good as it could be. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Use reputable sources. While Wikipedia may be an easy way to start off, try to go to more specific websites afterwards. Many schools refuse to accept Wikipedia as a valid source of information, and prefer sources with more expertise and credibility. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

- If you have external sources, make sure you always cite them. Otherwise, you may be guilty of plagiarism. Thanks Helpful 3 Not Helpful 0
You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://writingcenter.unc.edu/handouts/comparing-and-contrasting/
- ↑ http://www.readwritethink.org/files/resources/interactives/compcontrast/
About This Article

To write a compare and contrast essay, try organizing your essay so you're comparing and contrasting one aspect of your subjects in each paragraph. Or, if you don't want to jump back and forth between subjects, structure your essay so the first half is about one subject and the second half is about the other. You could also write your essay so the first few paragraphs introduce all of the comparisons and the last few paragraphs introduce all of the contrasts, which can help emphasize your subjects' differences and similarities. To learn how to choose subjects to compare and come up with a thesis statement, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Huma Bukhari
Feb 16, 2019
Did this article help you?

Alain Vilfort
Mar 2, 2017
Aida Mirzaie
Aug 19, 2018
Michaela Mislerov
Apr 2, 2017
Subhashini Gunasekaran
Jul 31, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
GPB Originals
Browse by genre, featured programs, featured programs & series, more gpb news, for kids & teachers, ghsa sports, high school football, browse by type, browse by category, for parents & caregivers, support gpb, tagged as: .
- English Language Arts
Essay Structure for Compare and Contrast - High School
Share this page.
- Let's Learn GA! - Model Lessons
In this episode of Let's Learn GA! , high school English teacher Dana Cole discusses different structures on writing compare and contrast essays.
For this lesson you will need:
- something to write with
Georgia Standards of Excellence
English arts.
Develop claim(s) and counterclaims fairly, supplying evidence for each while pointing out the strengths and limitations of both in a manner that anticipates the audience's knowledge level and concerns.
Introduce a topic; organize complex ideas, concepts, and information to make important connections and distinctions; include formatting (e.g., headings), graphics (e.g., figures, tables), and multimedia when useful to aiding comprehension.
Develop the topic with well-chosen, relevant, and sufficient facts, extended definitions, concrete details, quotations, or other information and examples appropriate to the audience's knowledge of the topic.
Produce clear and coherent writing in which the development, organization, and style are appropriate to task, purpose, and audience. (Grade-specific expectations for writing types are defined in Standards 1–3 above.)
Let's Learn GA! - Model Lessons Segments
Let's Learn GA! is series of video lessons for grades K-12 taught by Georgia teachers. The videos in this collection are aligned to the Georgia Standards of Excellence for English language arts (ELA). Let's Learn GA! is a collaboration between GPB and the Georgia Department of Education (GaDOE) to support both in-person and remote learning plans. Check back for more ELA lessons coming soon.
Rhyming - Kindergarten

Literature Connections - 1st Grade

Informational Writing - 1st Grade

Narrative Writing - 1st Grade

Opinion Writing - 2nd Grade

You may also enjoy ...

- Physical Health and Wellness
- Professional Learning
Sharing Our Stories Through StoryCorps and The Great Thanksgiving Listen
Join GPB Education as we explore the inspiring teaching tools surrounding The Great Thanksgiving Listen from StoryCorps, a national storytelling project that invites us all to share our unique voices and build connections within our communities in order to create a more just and compassionate world. Participants will discuss how our stories can help us build empathy and community, invite courageous conversations in our schools and classrooms, and inspire our students to share their own unique stories.

Literacy Shorts
Discover literacy teaching strategies with these bite-sized videos.

We Are Courageous: A PBS American Portrait Series for Georgia Educators
Join GPB Education as we explore the inspiring teaching tools surrounding PBS American Portrait, a national storytelling project that invites us all to share our voices in response to a number of thought-provoking prompts. Participants will discuss how our stories can help us build empathy and community, invite courageous conversations in our schools and classrooms, and inspire our students to create their own unique American portraits.
Connect with GPB Education

ChatGPT for Teachers
Trauma-informed practices in schools, teacher well-being, cultivating diversity, equity, & inclusion, integrating technology in the classroom, social-emotional development, covid-19 resources, invest in resilience: summer toolkit, civics & resilience, all toolkits, degree programs, trauma-informed professional development, teacher licensure & certification, how to become - career information, classroom management, instructional design, lifestyle & self-care, online higher ed teaching, current events, compare-and-contrast essays: 3 keys to helping students get better grades on compositions.
Whether they’re comparing a book to a film adaptation or contrasting two speeches, students inevitably get many compare-and-contrast essay assignments throughout their academic careers.
Students need to do more than report on how things are similar or different: The compare-and-contrast essay requires a sophisticated analysis of the source materials.
I’ve found that teaching students to prepare via prewriting, developing arguments and careful outlining helps them write much better compare-contrast essays.
Planning ahead with prewriting
Before writing the essay, students should take notes on the two source pieces they are comparing. That means setting up their notes in two columns so they can examine specific elements side-by-side before generating broader arguments.
For instance, if comparing a book to a film adaptation, students might want to compare elements such as plot, characters and story arc. A two-column note page allows them to comment on each one of these elements individually.
Students’ notes could compare and contrast how a particular character is portrayed and do the same with other plot elements they have selected. Having notes on each element they are comparing helps them develop stronger, more sophisticated arguments. This in turn helps set the stage for comparing and contrasting the overall source documents.
Developing an argument: Start narrow and go broad
After taking notes, students are ready to develop their arguments by comparing and contrasting individual elements in the source materials they are analyzing. Rather than saying all the characters are flat in the film adaptation, for example, students could look at each character and see what makes that character flat, or what part of their characterization makes that the case. Completing this process for each element gives students the evidence they need to review the bigger picture and develop their arguments.
How does this work in practice? The student might argue that while the film version ultimately presented the plot in a different order, the overall impact was the same because the film stayed true to the characters and the overall message of the original text.
Outlining the essay
After finalizing their notes and developing arguments, students need to determine how they will write the essay. Many students struggle with these types of arguments because they get too bogged down in the individual elements that are different and fail to present a cohesive thesis. Or they focus on the large picture and fail to substantiate their claims with evidence.
To avoid these problems, students need to develop a strong outline that presents the specific elements they want to compare. First, students must determine the small arguments about particular elements: “The film version of the book preluded the ending first, which ultimately grabbed the attention of the audience visually.”
From there, students can pull direct evidence from their notes to adequately support their claims. Their notes should detail the visual elements in both the film and the text.
This process helps them prove to the reader how the two differ and lets them develop deeper analysis. Students can actually point to how one representation is more meaningful than the other, which helps them to connect all their ideas together and support the thesis more thoroughly.
Compare-and-contrast essay assignments are so common in high school and college that they seem fairly obvious and easy to write at first glance. But students don’t always have an intuitive grasp that they need to do more than simply report — they need to analyze and look at the larger picture. That’s why it’s so important to teach them how to review the evidence carefully, build arguments, outline the text and push their analysis to the next level.
Caitrin Blake has a BA in English and Sociology from the University of Vermont and a master’s degree in English literature from the University of Colorado Denver. She teaches composition at Arapahoe Community College.
You may also like to read
- 5 Tips for Teachers Assigning Essays to High School Students
- 4 Math Software Programs for Students
- How Grade Inflation Hurts Students
- Students Evaluating Teachers: What Educators Need to Know
- First Generation College Students Graduation Rates
- Popular Science Websites for Students
Categorized as: Tips for Teachers and Classroom Resources
Tagged as: High School (Grades: 9-12) , Middle School (Grades: 6-8) , Professional Development
- Online & Campus Bachelor's Degrees in Educati...
- Online & Campus Master's in Elementary Educat...
- PhD Programs for Education
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
FREE Poetry Worksheet Bundle! Perfect for National Poetry Month.
80 Intriguing Compare and Contrast Essay Topics for Kids and Teens
Android vs. iPhone? Capitalism vs. communism? Hot dog vs. taco?

In compare and contrast essays , writers show the similarities and differences between two things. They combine descriptive writing with analysis, making connections and showing dissimilarities. Remind students that in this type of writing, they’re not necessarily trying to sway the reader to one opinion or another—they’re just presenting and analyzing facts. These compare and contrast essay topics will give them plenty of practice.
- School and Life Essay Topics
- Entertainment Essay Topics
- History and Politics Essay Topics
- Just for Fun Essay Topics
School and Life Compare and Contrast Essay Topics
- Public and private schools
- Online school and in-person school
- Any two schools or colleges
- Going to college vs. starting work full-time

- Working your way through college as you go or taking out student loans
- Parents and grandparents
- Elementary school and high school
- Learning to read vs. learning to write
- The importance of any two school subjects
- Wearing glasses vs. having braces
- You and your best friend
- Friendship vs. romantic love

- Group work and individual work
- Only child vs. having siblings
- Nature vs. nurture
- Anxiety and depression
- Old friends and new friends
- Your teacher vs. your parent/guardian
- Car ownership and public transportation

- Learning to ride a bike vs. learning to drive a car
Entertainment Compare and Contrast Essay Topics
- iPhone vs. Android
- Instagram vs. Twitter (or choose any other two social media platforms)
- Xbox vs. PlayStation

- Any two sports, like American football vs. soccer
- Cooking at home and dining out
- A movie based on a book and the book it was based on
- Reading and watching TV
- Opera music and pop music (or any two music genres)
- Vegetarian and vegan

- Giving and receiving gifts
- Going to a play vs. going to a movie
- Playing a video game and watching a movie
- Horse racing vs. NASCAR
- Laptop vs. tablet
- Sprint vs. marathon
- Poetry and rap music
- Ping-Pong vs. tennis
- DC vs. Marvel
- Netflix and YouTube
- Shopping online and shopping in person

History and Politics Compare and Contrast Essay Topics
- Capitalism vs. communism
- Socialism vs. communism
- Monarchy/dictatorship and democracy
- Two political candidates in a current race

- Spanish flu pandemic vs. COVID-19 pandemic
- World War I and World War II
- American pioneers vs. first space explorers
- Gen X vs. Gen Z
- Abraham Lincoln vs. Barack Obama (or any other two presidents)
- Any two U.S. states

- Any two historic eras
- Queen Elizabeth I vs. Queen Elizabeth II
- Republicans and Democrats
- Hitler and Stalin
- The first airplane flight vs. the first manned spaceflight
- American president vs. U.K. prime minister

- Fox News vs. CNN
- Legislative branch and executive branch and/or judicial branch
- Equality and equity
- Elected politicians vs. lobbyists
Just for Fun Compare and Contrast Essay Topics
- Dogs vs. cats as pets

- Paper books or e-books
- Hot dogs vs. tacos
- Summer and winter
- Fall and spring
- Big Mac vs. Whopper
- Coke vs. Pepsi
- Chocolate shake vs. hot chocolate
- Any two superheroes or villains
- Mondays and Fridays
- Mornings vs. evenings

- First day of school vs. last day of school
- Christmas vs. birthdays
- Hurricane vs. tornado
- Birthday as a kid and birthday as an adult
- Going barefoot vs. wearing shoes
- Appetizers and desserts

- Phone calls and texting
- Pants vs. skirts
- Electric cars vs. gas-powered cars
What are some of your favorite compare and contrast essay topics? Come share your prompts on the WeAreTeachers HELPLINE group on Facebook .
Plus, check out the big list of essay topics for high school (100+ ideas).

You Might Also Like

34 Compelling Compare and Contrast Essay Examples
Topics cover education, technology, pop culture, sports, animals, and more. Continue Reading
Copyright © 2023. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256
Compare and Contrast Essay: Full Writing Guide and 150+ Topics

Compare and contrast essays are academic papers in which a student analyses two or more subjects with each other. To compare means to explore similarities between subjects, while to contrast means to look at their differences. Both subjects of the comparison are usually in the same category, although they have their differences. For example, it can be two movies, two universities, two cars etc.
Good compare and contrast papers from college essay writer focus on a central point, explaining the importance and implications of this analysis. A compare and contrast essay thesis must make a meaningful comparison. Find the central theme of your essay and do some brainstorming for your thesis.
This type of essay is very common among college and university students. Professors challenge their students to use their analytical and comparative skills and pay close attention to the subjects of their comparisons. This type of essay exercises observance and analysis, helps to establish a frame of reference, and makes meaningful arguments about a subject. Let's get deeper on how to write a compare and contrast essay with our research writing services .
How to Start a Compare and Contrast Essay: Brainstorm Similarities and Differences
Now that you know what is compare and contrast essay and are set with your topic, the first thing you should do is grab a piece of paper and make a list with two columns: similarities and differences. Jot down key things first, the most striking ones. Then try to look at the subjects from a different angle, incorporating your imagination.
If you are more of a visual learner, creating a Venn diagram might be a good idea. In order to create it, draw two circles that overlap. In the section where it overlaps, note similarities. Differences should be written in the part of the circle that does not overlap.
Let’s look at a simple example of compare and contrast essay. Let one of the subjects be oranges, and the other one be apples. Oranges have thick peel, originally from India, and are tropical fruit. These characteristics pertain only to oranges and should be in the part of the circle that does not overlap. For the same section on apples, we put thin peel, originated in Turkey or Kazakhstan, and moderate to subtropical. In the section that overlaps, let’s say that they are both fruit, can be juiced, and grow on trees. This simple, yet good example illustrates how the same concept can be applied to many other complicated topics with additional points of comparison and contrast.

This format of visual aid helps to organize similarities and differences and make them easier to perceive. Your diagram will give you a clear idea of the things you can write about.
Another good idea for brainstorming in preparation for your comparison contrast essay is to create a list with 2 columns, one for each subject, and compare the same characteristics for each of them simultaneously. This compare and contrast format will make writing your comparison contrast paper argument a breeze, as you will have your ideas ready and organized.
One mistake you should avoid is simply listing all of the differences or similarities for each subject. Sometimes students get too caught up in looking for similarities and differences that their compare and contrast essays end up sounding like grocery lists. Your essay should be based on analyzing the similarities and differences, analyzing your conclusions about the two subjects, and finding connections between them—while following a specific format.
Compare and Contrast Essay Structure and Outline
So, how do you structure this compare and contrast paper? Well, since compare and contrast essay examples rely heavily on factual analysis, there are two outline methods that can help you organize your facts. You can use the block method, or point-by-point method, to write a compare and contrast essay outline.
While using the block structure of a compare and contrast essay, all the information is presented for the first subject, and its characteristics and specific details are explained. This concludes one block. The second block takes the same approach as the first for the second subject.
The point-by-point structure lists each similarity and difference simultaneously—making notes of both subjects. For example, you can list a characteristic specific to one subject, followed by its similarity or difference to the other subject.
Both formats have their pros and cons. The block method is clearly easier for a compare and contrast essay writer, as you simply point out all of the information about the two subjects, and basically leave it to the reader to do the comparison. The point-by-point format requires you to analyze the points yourself while making similarities and differences more explicit to the reader for them to be easier to understand. Here is a detailed structure of each type presented below.
Point-by-Point Method
- Introduce the topic;
- Specify your theme;
- Present your thesis - cover all areas of the essay in one sentence.
Example thesis: Cars and motorcycles make for excellent means of transportation, but a good choice depends on the person’s lifestyle, finances, and the city they live in.
Body Paragraph 1 - LIFESTYLE
- Topic Sentence: Motorcycles impact the owner’s lifestyle less than cars.
- Topic 1 - Motorcycles
- ~ Argument: Motorcycles are smaller and more comfortable to store.
- ~ Argument: Motorcycles are easy to learn and use.
- Topic 2 - Cars
- ~ Argument: Cars are a big deal - they are like a second home.
- ~ Argument: It takes time to learn to become a good driver.
Body Paragraph 2 - FINANCES
- Topic sentence: Cars are much more expensive than motorcycles
- ~ Argument: You can buy a good motorcycle for under 300$.
- ~ Argument: Fewer parts that are more accessible to fix.
- ~ Argument: Parts and service are expensive if something breaks.
- ~ Argument: Cars need more gas than motorcycles.
Body Paragraph 3 - CITY
- Topic sentence: Cars are a better option for bigger cities with wider roads.
- ~ Argument: Riding motorcycles in a big city is more dangerous than with cars.
- ~ Argument: Motorcycles work great in a city like Rome, where all the streets are narrow.
- ~ Argument: Big cities are easier and more comfortable to navigate by car.
- ~ Argument: With a car, traveling outside of the city is much easier.
- Sum up all you wrote in the article.
Block Method
- Thesis — cover all areas of the essay in one sentence
Body Paragraph 1
- Topic Sentence: Motorcycles are cheaper and easier to take care of than cars.
- Aspect 1 - Lifestyle
- Aspect 2 - Finances
- ~ Argument: Fewer parts, easier to fix.
- Aspect 3 - City
- ~ Argument: Riding motorcycles in a big city is more dangerous than cars.
Body Paragraph 2
- Topic sentence: Cars are more expensive but more comfortable for a big city and for travelling.
- ~ Argument: Cars are a big deal—like a second home.
- ~ Argument: With a car, traveling outside the city is much more comfortable.
Body Paragraph 3
Use the last paragraph to evaluate the comparisons and explain why they’re essential. Giving a lot of facts can be intense. To water it down, try to give the reader any real-life applications of these facts.
Depending on the structure selected, you can begin to create an outline for your essay. The typical comparison essay follows the format of having an introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion — though, if you need to focus on each subject in more detailed ways, feel free to include an extra paragraph to cover all of the most important points.
To make your compare and contrast essay flow better, we recommend using special transition words and phrases. They will add variety and improve your paper overall.
For the section where you compare two subjects, you can include any of the following words: similarly, likewise, also, both, just like, similar to, the same as, alike, or to compare to. When contrasting two subjects, use: in contrast, in comparison, by comparison, on the other hand, while, whereas, but, to differ from, dissimilar to, or unlike.
Show Your Evidence
Arguments for any essay, including compare and contrast essays, need to be supported by sufficient evidence. Make good use of your personal experiences, books, scholarly articles, magazine and newspaper articles, movies, or anything that will make your argument sound credible. For example, in your essay, if you were to compare attending college on campus vs. distance-based learning, you could include your personal experiences of being a student, and how often students show up to class on a daily basis. You could also talk about your experience taking online classes, which makes your argument about online classes credible as well.
Helpful Final Tips
The biggest tip dissertation writing services can give you is to have the right attitude when writing a compare contrast essay, and actively engage the reader in the discussion. If you find it interesting, so will your reader! Here are some more compare and contrast essay tips that will help you to polish yours up:

- Compare and contrast essays need powerful transitions. Try learning more about writing transition sentences using the words we provided for you in the 'Compare and Contrast Structure and Outline' section.
- Always clarify the concepts you introduce in your essay. Always explain lesser known information—don’t assume the reader must already know it.
- Do not forget to proofread. Small mistakes, but in high quantities, can result in a low grade. Pay attention to your grammar and punctuation.
- Have a friend or family member take a look at your essay; they may notice things you have missed.
Compare and Contrast Essay Examples
Now that you know everything there is to know about compare and contrast essays, let’s take a look at some compare and contrast examples to get you started on your paper or get a hand from our essay helper .
Different countries across the world have diverse cultural practices, and this has an effect on work relationships and development. Geert Hofstede came up with a structured way of comparing cultural dimensions of different countries. The theory explains the impacts of a community’s culture on the values of the community members, and the way these values relate to their behaviors. He gives scores as a way to help distinguish people from different nations using the following dimensions: long-term orientation, individualism, power distance, indulgence, necessity avoidance, and masculinity. Let us examine comparisons between two countries: the United Kingdom and China — based on Hofstede’s Six Dimensions of Culture.
Over the last two decades, the demand from consumers for organic foods has increased tremendously. In fact, the popularity of organic foods has exploded significantly with consumers, spending a considerably higher amount of money on them as compared to the amount spent on inorganic foods. The US market noted an increase in sales of more than 10% between 2014 and 2015 (Brown, n.p). The increase is in line with the views of many consumers that organic foods are safer, tastier, and healthier compared to the inorganic foods. Furthermore, considering the environmental effects of foods, organic foods present less risk of environmental pollution — compared to inorganic foods. By definition, organic foods are those that are grown without any artificial chemical treatment, or treatment by use of other substances that have been modified genetically, such as hormones and/or antibiotics (Brown, n.p).
Still feeling confused about the complexities of the compare and contrast essay? Feel free to contact our paper writing service to get a professional writing help.
Finding the Best Compare and Contrast Essay Topics For You
When choosing a topic for your comparison essay, remember that subjects cannot be drastically different, because there would be little to no points of comparison (similarities). The same goes for too many similarities, which will result in poor contrasts. For example, it is better to write about two composers, rather than a composer and a singer.
It is extremely important to choose a topic you are passionate about. You never want to come across something that seems dull and uninspiring for you. Here are some excellent ways to brainstorm for a topic from essay writer :
- Find categories: Choose a type (like animals, films or economics), and compare subjects within that category – wild animals to farm animals, Star Wars to Star Trek, private companies to public companies, etc.
- Random Surprising Fact: Dig for fun facts which could make great topics. Did you know that chickens can be traced back to dinosaurs?
- Movie vs. Book: Most of the time, the book is better than the movie — unless it’s Blade Runner or Lord of the Rings. If you’re a pop culture lover, compare movies vs. books, video games, comics, etc.
Use our rewrite essay service when you need help from professionals.
How to Choose a Great Compare and Contrast Topic
College students should consider providing themselves with a chance to use all topic examples. With enough revision, an advantage is gained. As it will be possible to compare arguments and contrast their aspects. Also, discuss numerous situations to get closer to the conclusion.
For example:
- Choose a topic from the field of your interests. Otherwise you risk failing your paper.
- It is a good idea to choose a topic based upon the class subject or specialist subject. (Unless the requirements say otherwise.)
- Analyze each argument carefully. Include every detail for each opposing idea. Without doing so, you can definitely lower grades.
- Write a conclusion that summarizes both arguments. It should allow readers to find the answer they’re looking for.
- It is up to you to determine which arguments are right and wrong in the final conclusion.
- Before approaching the final conclusion, it’s important to discuss each argument equally. It is a bad idea to be biased, as it can also lower grades.
Need a Great Essay From Us?
Our professionals are ready to help you asap! Contact us 24/7.
150 Compare and Contrast Essay Topics to Consider
Choosing a topic can be a challenging task, but there are plenty of options to consider. In the following sections, we have compiled a list of 150 compare and contrast essay topics to help you get started. These topics cover a wide range of subjects, from education and technology to history and politics. Whether you are a high school student or a college student, you are sure to find a topic that interests you. So, read on to discover some great compare and contrast essay ideas.
Compare and Contrast Essay Topics For College Students
When attending a college, at any time your professor can assign you the task of writing this form of an essay. Consider these topics for college students from our team to get the grades you deserve.
- Attending a College Course Vs. Distance-Based Learning.
- Writing a Research Paper Vs. Writing a Creative Writing Paper. What are the differences and similarities?
- The differences between a Bachelor’s Degree and a Master’s Degree.
- The key aspects of the differences between the US and the UK education systems.
- Completing assignments at a library compared with doing so at home. Which is the most efficient?
- The similarities and differences in the behavior among married and unmarried couples.
- The similarities and differences between the EU (European Union) and ASEAN (The Association of Southeast Asian Nations)?
- The similarities and significant differences between American and Canadian English.
- Writing an Internship Report Vs. Writing a Research Paper
- The differences between US colleges and colleges in the EU?
Interesting Compare and Contrast Essay Topics
Some topics for the compare and contrast essay format can be boring. To keep up motivation, doing a research , have a look at these topics. Maybe they can serve you as research paper help .
- Public Transport Vs. Driving A Car. Which is more efficient?
- Mandarin Vs. Cantonese: What are the differences between these Chinese languages?
- Sports Cars Vs. Luxurious Family Cars
- Wireless Technology Vs. Wired Devices
- Thai Food Vs. Filipino Cuisine
- What is the difference and similarities between a register office marriage and a traditional marriage?
- The 2000s Vs. The 2010s. What are the differences and what makes them similar?
- Abu Dhabi Vs. Dubai. What are the main factors involved in the differences?
- What are the differences between American and British culture?
- What does the New York Metro do differently to the London Underground?
Compare and Contrast Essay Topics for High School Students
When writing essays for high school, it is good to keep them informative. Have a look at these compare and contrast sample topics.
- Highschool Life Vs. College Life
- Paying College Fees Vs. Being Awarded a Scholarship
- All Night Study Sessions Vs. Late Night Parties
- Teenager Vs. Young Adult Relationships
- Being in a Relationship Vs. Being Single
- Male Vs. Female Behavior
- The similarities and differences between a high school diploma and a college degree
- The similarities and differences between Economics and Business Studies
- The benefits of having a part-time job, instead of a freelance job, in college
- High School Extra Curricular Activities Vs. Voluntarily Community Services
Compare and Contrast Essay Topics for Science
At some point, every science student will be assigned this type of essay. To keep things at flow, have a look at best compare and contrast essay example topics on science:
- Undiscovered Species on Earth Vs. Potential Life on Mars: What will we discover in the future?
- The benefits of Gasoline Powered Cars Vs. Electric Powered Cars
- The differences of the Milky Way Vs. Centaurus (Galaxies).
- Earthquakes Vs. Hurricanes: What should be prepared for the most?
- The differences between our moon and Mars’ moons.
- SpaceX Vs. NASA. What is done differently within these organizations?
- The differences and similarities between Stephen Hawking and Brian Cox’s theories on the cosmos. Do they agree or correspond with each other?
- Pregnancy Vs. Motherhood
- Jupiter Vs. Saturn
- Greenhouse Farming Vs. Polytunnel Farming
Sports & Leisure Topics
Studying Physical Education? Or a gym fanatic? Have a look at our compare and contrast essay topics for sports and leisure.
- The English Premier League Compared With The Bundesliga
- Real Madrid Vs. Barcelona
- Football Vs. Basketball
- Walking Vs. Eating Outside with Your Partner
- Jamaica Team Vs. United States Team: Main Factors and Differences
- Formula One Vs. Off-Road Racing
- Germany Team Vs. Brazil Team
- Morning Exercise Vs. Evening Exercise.
- Manning Team Vs. Brazil Team
- Swimming Vs. Cycling
Topics About Culture
Culture can have several meanings. If you’re a Religious Studies or Culture student, take a look at these good compare and contrast essay topics about culture.
- The fundamental similarities and differences between Pope Francis and Tawadros II of Alexandria
- Canadian Vs. Australian Religion
- The differences between Islamic and Christian Holidays
- The cultural similarities and differences between the Native Aboriginals and Caucasian Australians
- Native American Culture Vs. New England Culture
- The cultural differences and similarities between Italians and Sicilians
- In-depth: The origins of Buddhism and Hinduism
- In-depth: The origins of Christianity and Islam
- Greek Gods Vs. Hindu Gods
- The Bible: Old Testament Vs. New Testament
Unique Compare and Contrast Essay Topics
What about writing an essay which is out of the ordinary? Consider following these topics to write a compare and contrast essay on, that are unique.
- The reasons why some wealthy people pay extortionate amounts of money for gold-plated cell phones, rather than buying the normal phone.
- The differences between Lipton Tea and Ahmad Tea
- American Football Vs. British Football: What are their differences?
- The differences and similarities between France and Britain
- Fanta Vs. 7Up
- Traditional Helicopters Vs. Lifesize Drones
- The differences and similarities between Boston Dynamics and the fictional equivalent Skynet (From Terminator Movies).
- Socialism Vs. Capitalism: Which is better?
- Curved Screen TVs’ Vs. Regular Flat Screen TVs’: Are they really worth big bucks?
- Is it better to wear black or white at funerals?
Good Compare and Contrast Essay Topics
Sometimes, it may be a requirement to take it back a notch. Especially if you’re new to these style of writing. Consider having a look at these good compare and contrast essay topics that are pretty easy to start off.
- Is it a good idea to work on weekdays or weekends?
- Black of White Coffee
- Becoming a teacher or a doctor? Which career choice has more of an impact on society?
- Air Travel Vs. Sea Travel: Which is better?
- Rail Travel Vs. Road Travel: Which is more convenient?
- What makes Europe far greater than Africa? In terms of financial growth, regulations, public funds, policies etc…
- Eating fruit for breakfast Vs. cereals
- Staying Home to Read Vs. Traveling the World During Holidays. Which is more beneficial for personal growth?
- Japanese Vs. Brazilian Cuisine
- What makes ASEAN Nations more efficient than African Nations?
Compare and Contrast Essay Topics About TV Shows, Music and Movies
We all enjoy at least one of these things. If not, all of them. Why not have a go at writing a compare and contrast essay about what you have been recently watching or listening to?
- Breaking Bad Vs. Better Call Saul: Which is more commonly binge watched?
- The differences between Dance Music and Heavy Metal
- James Bond Vs. Johnny English
- Iron Man Vs. The Incredible Hulk: Who would win?
- What is done differently in modern movies, compared to old black and white movies?
- Dumber and Dumber 2 Vs. Ted: Which movie is funnier?
- Are Horror movies or Action Movies best suited to you?
- The differences and similarities between Mozart and Beethoven compositions.
- Hip Hop Vs. Traditional Music
- Classical Music Vs. Pop Music. Which genre helps people concentrate?
Topics About Art
Sometimes, art students are required to write this style of essay. Have a look at these compare and contrast essay topics about the arts of the centuries.
- The fundamental differences and similarities between paintings and sculptures
- The different styles of Vincent Van Gogh and Leonardo Da Vinci.
- Viewing Original Art Compared With Digital Copies. How are these experiences different?
- 18th Century Paintings Vs. 21st Century Digitally Illustrated Images
- German Art Vs. American Art
- Modern Painting Vs. Modern Photography
- How can we compare modern graphic designers to 18th-century painters?
- Ancient Greek Art Vs. Ancient Egyptian Art
- Ancient Japanese Art Vs. Ancient Persian Art
- What 16th Century Painting Materials were used compared with the modern day?
Best Compare and Contrast Essay Topics
Almost every student at any stage of academics is assigned this style of writing. If you’re lacking inspiration, consider looking at some of the best compare and contrast essay topics to get you on track with your writing.
- The United States and North Korea Governmental Conflict: What is the reason behind this phenomenon?
- In the Early Hours, Drinking Water is far healthier than consuming soda.
- The United States Vs. The People’s Republic of China: Which economy is the most efficient?
- Studying in Foreign Countries Vs. Studying In Your Hometown: Which is more of an advantage?
- Toast Vs. Cereal: Which is the most consumed in the morning?
- Sleeping Vs. Daydreaming: Which is the most commonly prefered? And amongst who?
- Learning French Vs. Chinese: Which is the most straightforward?
- Android Phones Vs. iPhones
- The Liberation of Slaves Vs. The Liberation of Women: Which is more remembered?
- The differences between the US Dollar and British Pound. What are their advantages? And How do they correspond with each other?
Easy Compare and Contrast Essay Topics
In all types of academics, these essays occur. If you’re new to this style of writing, check our easy compare and contrast essay topics.
- The Third Reich Vs. North Korea
- Tea Vs. Coffee
- iPhone Vs. Samsung
- KFC Vs. Wendy’s
- Laurel or Yanny?
- Healthy Lifestyle Vs. Obese Lifestyle
- Forkes Vs. Sporks
- Rice Vs. Porridge
- Roast Dinner Vs. Chicken & Mushroom Pie
- What’s the difference between apples and oranges?

Psychology Compare and Contrast Essay Topics
Deciding upon good compare and contrast essay topics for psychology assignments can be difficult. Consider referring to our list of 10 psychology compare and contrast essay topics to help get the deserved grades.
- What is a more severe eating order? Bulimia or Anorexia
- Modern Medicine Vs. Traditional Medicine for Treating Depression?
- Soft Drugs Vs. Hard Drugs. Which is more dangerous for people’s psychological well-being?
- How do the differences between Lust and Love have an effect on people’s mindsets?
- Ego Vs. Superego
- Parents Advice Vs. Peers Advice amongst children and teens.
- Strict Parenting Vs. Relaxed Parenting
- Mental Institutions Vs. Stress Clinics
- Bipolar Disorder Vs. Epilepsy
- How does child abuse affect victims in later life?
Compare and Contrast Essay Topics for Sixth Graders
From time to time, your teacher will assign the task of writing a compare and contrast essay. It can be hard to choose a topic, especially for beginners. Check out our easy compare and contrast essay topics for sixth graders.
- Exam Preparation Vs. Homework Assignments
- Homeschooling Vs. Public Education
- High School Vs. Elementary School
- 5th Grade Vs. 6th Grade: What makes them different or the same?
- Are Moms’ or Dads’ more strict among children?
- Is it better to have strict parents or more open parents?
- Sandy Beaches Vs. Pebble Beaches: Which beaches are more popular?
- Is it a good idea to learn guitar or piano?
- Is it better to eat vegetable salads or pieces of fruit for lunch?
- 1st Grade Vs. 6th Grade
Funny Compare and Contrast Essay Topics
Sometimes, it is good to have a laugh. As they always say : 'laughter is the best medicine'. Check out these funny compare and contrast essay topics for a little giggle when writing.
- What is the best way to waste your time? Watching Funny Animal Videos or Mr. Bean Clips?
- Are Pug Dogs or Maltese Dogs crazier?
- Pot Noodles Vs. McDonalds Meals.
- What is the difference between Peter Griffin and Homer Simpson?
- Mrs. Doubtfire Vs. Mrs. Brown. How are they similar?
- Which game is more addictive? Flappy Bird or Angry Birds?
- Big Shaq Vs. PSY
- Stewie Griffin Vs. Maggie Simpson
- Quarter Pounders Vs. Big Macs
- Mr. Bean Vs. Alan Harper
Feeling Overwhelmed While Writing a COMPARE AND CONTRAST ESSAY?
Give us your paper requirements, set the deadline, choose a writer and chill while we write an original paper for you.
Which Is The Most Effective Topic For A Compare-and-contrast Essay?
How to start a compare and contrast essay, how to write a thesis for a compare and contrast essay, related articles.
%20(2).webp)
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Mentor Texts
Writing Comparative Essays: Making Connections to Illuminate Ideas
Breathing new life into a familiar school format, with the help of Times journalism and several winning student essays.

By Katherine Schulten
Our new Mentor Text series spotlights writing from The Times and from our student contests that teenagers can learn from and emulate.
This entry aims to help support those participating in our Third Annual Connections Contest , in which students are invited to take something they are studying in school and show us, via parallels found in a Times article, how it connects to our world today. In other words, we’re asking them to compare ideas in two texts.
For even more on how to help your students make those kinds of connections, please see our related writing unit .
I. Overview
Making connections is a natural part of thinking. We can’t help doing it. If you’re telling a friend about a new song or restaurant or TV show you like, you’ll almost always find yourself saying, “It’s like _________” and referencing something you both know. It’s a simple way of helping your listener get his or her bearings.
Journalists do it too. In fact, it’s one of the main tools of the trade to help explain a new concept or reframe an old one. Here are just a few recent examples:
A science reporter explains the behavior of fossilized marine animals by likening them to humans making conga lines.
A sportswriter describes the current N.B.A. season by framing it in terms of Broadway show tunes.
An Op-Ed contributor compares today’s mainstreaming of contemporary African art to “an urban neighborhood undergoing gentrification.”
Sometimes a journalist will go beyond making a simple analogy and devote a whole piece to an extended comparison between two things. Articles like these are real-world cousins of that classic compare/contrast essay you’ve probably been writing in school since you could first hold a pen.
For example, take a look at how each of the Times articles below focuses on a comparison, weaving back and forth between two things and looking at them from different angles:
Consider a classic sports debate: Jordan vs. James. See how this 2016 piece explores what the two have in common — as well as how they differ.
Or, check out this 2019 piece that argues that “ Friendsgiving Has Become Just as Fraught as Thanksgiving ,” and compares the two to determine which has become “a bigger pain in the wishbone.”
Though written as a list rather than an essay, this fun piece from the Watching section in 2018 contends that “ ‘Die Hard’ Never Died, It Just Turned 30 and Had Cinematic Children ” by comparing the original to heirs like “Speed” and “Home Alone.” Read it to notice how, in just a paragraph per movie, the writer still manages to provide plenty of evidence to make each comparison work.
To find real-world examples that are closer to what you’re asked to do in school, look to Times sections that feature in-depth writing, like the Sunday Review and the Times Magazine . Both often publish pieces that connect some aspect of the past to an event, issue or trend today. For example:
“ What Quakers Can Teach Us About the Politics of Pronouns ” suggests lessons for “today’s egalitarians” by making a link to the 17th-century Quakers, “who also suspected that the rules of grammar stood between them and a society of equals.”
Other recent pieces focus on historical comparisons, including “ Early Motherhood Has Always Been Miserable ,” “ Donald Trump, Meet Your Precursor ” and a satirical video Op-Ed, “ Here’s What Cancel Culture Looked Like in 1283 .”
The 1619 Project , a Times Magazine initiative observing the 400th anniversary of the beginning of American slavery, is an especially rich example of this kind of connection-making. It reframes American history by “placing the consequences of slavery and the contributions of black Americans at the very center of the story we tell ourselves about who we are” — and uses that frame to look at issues including today’s prison system, health care, the wealth gap, the sugar industry and traffic jams in Atlanta.
Now, are all of these pieces structured exactly like that essay you have to write for your English class comparing a contemporary work to “Romeo and Juliet?” Does each have a clear thesis statement in the last line of the first paragraph and three body paragraphs that begin with topic sentences?
Of course not. They were written for an entirely different audience and purpose than the essay you might have to write, and most of them resist easy categorization into a specific “text type.”
But these pieces are full of craft lessons that can make your own writing more artful and interesting. And if you are participating in our annual Connections Contest , the essays we feature below will be especially helpful, since they focus on doing just what you’ll be doing — making a comparison between something you’re studying in school and some event, issue, trend, person, problem or concept in the news today.
First you’ll consider one excellent Times essay that does pretty much exactly what we’re asking you to do.
Next, we’ve supplied examples from over a dozen previous student winners to help guide you through the basic elements of any comparative analysis. Whether you’re writing for our contest or not, we hope you’ll find plenty of strategies to borrow.
II. Looking at Structure Over All: One Times Mentor Text
Take a look at the essay the Times book critic Michiko Kakutani wrote in the first weeks of the Trump administration. Just as many of you will do for our contest, she examines how a classic literary work can take on new significance when considered in light of real-world events.
Whether you agree with her analysis or not, notice how “ Why ‘1984’ Is a 2017 Must-Read ” is structured. You might highlight three categories — places where she’s writing chiefly about “1984”; places where she’s writing chiefly about our world today; and places where the two merge.
Here is how her piece, a Critic’s Notebook essay, begins:
The dystopia described in George Orwell’s nearly 70-year-old novel “1984” suddenly feels all too familiar. A world in which Big Brother (or maybe the National Security Agency) is always listening in, and high-tech devices can eavesdrop in people’s homes. (Hey, Alexa, what’s up?) A world of endless war, where fear and hate are drummed up against foreigners, and movies show boatloads of refugees dying at sea. A world in which the government insists that reality is not “something objective, external, existing in its own right” — but rather, “whatever the Party holds to be truth is truth.”
How does the first line set up the comparison?
How does the writer weave back and forth between today’s world and the world of “1984”? For example, what is she doing the two times she uses parentheses?
After you read the full essay, you might then consider:
Over all, what did you notice about the structure of this piece? How does it emphasize the parallels between the world of “1984” and the world of January 2017?
Is it effective? What is this writer’s thesis? Does she make her case, in your opinion? What specific lines, or points of comparison, do that especially well?
What transitional words and phrases does the writer use to move between her two topics? For example, in the second paragraph she writes “It was a phrase chillingly reminiscent …” as a bridge. What other examples can you find?
How does she sometimes merge her two topics — for example in the phrase “make Oceania great again”?
What else do you notice or admire about this review? What lessons might it have for your writing?
III. Elements of Effective Comparative Analyses: Great Examples From Students
Our Connections Contest asks students to find and analyze parallels, just as Ms. Kakutani does in her essay on Orwell — though she had some 1,200 words to build a case and students participating in our contest have only 450.
But if you look at the examples below from our 2017 and 2018 winners, you’ll see that it’s possible to make a rich connection in just a few paragraphs, and you’ll find plenty of specific strategies to borrow in constructing your own.
Here are some tips, with student examples to illustrate each.
1. Make sure you’re focusing on a manageable theme or idea.
One of the first ways to get on the wrong track in writing a comparative essay is to take on something too big for the scope of the assignment. Say, for example, you’re studying the Industrial Revolution and you realize you can compare it to today’s digital revolution in an array of ways, including worker’s rights, the upheaval of traditional industries and the impact on everyday lives. Where do you even begin?
That’s more or less the problem Alex Iyer, a student winner of our 2018 contest, had after reading “The Odyssey” in class, and noticing connections between the tale of that famous wanderer and today’s global refugee crisis. What can you possibly say in 450 words to connect two enormous topics, both of which have been the subject of innumerable scholarly books?
Notice how this student focuses. Instead of starting with a broad thesis like “We can see many parallels between the themes of ‘The Odyssey’ and our world today,” he looks only at how the Greek concept of xenia echoes today — and does so by examining just one article about Uganda. Below are the first two paragraphs, but we suggest you read the entire essay , paying close attention to how he describes both texts solely through this lens.
Try this: Once you choose a manageable focus, make sure all your details and examples support it.
Example: Alex Iyer, Geneva School of Boerne, San Antonio: Homer’s “The Odyssey” and “ As Rich Nations Close the Door on Refugees, Uganda Welcomes Them ”
In literature, we learned that in Homer’s epic poem “The Odyssey,” Homer uses the tribulations of the hero Odysseus to illustrate the Ancient Grecian custom of xenia. This custom focused on extending hospitality to those who found themselves far from home. As Odysseus navigates the treacherous path back to his own home, he encounters both morally upstanding and malevolent individuals. They range from a charitable princess who offers food and clothing, to an evil Cyclops who attempts to murder the hero and his fellow men. In class, we agreed that Homer employs these contrasting characters to exemplify not only proper, but also poor forms of xenia. For the people of its time, “The Odyssey” cemented the idea that xenia was fundamental for good character, resulting in hospitality becoming ingrained in the fabric of Ancient Grecian society. I saw a parallel to this in a New York Times article called “As Rich Nations Close the Door on Refugees, Uganda Welcomes Them” published on October 28, 2018. Similar to the prevalent custom of xenia in Ancient Greece, Uganda has made hosting refugees a national policy. The country is now occupied by up to 1.25 million refugees, many of whom are fleeing the violent unrest of South Sudan.
2. Introduce and briefly explain the significance of the connection.
We know it’s tempting to resort to a generic statement like, “In this essay I will compare and contrast _________ and _________ to show that …”
Not only is that deadly dull, but if you are participating in our contest, you also don’t want to waste any of your 450 words on a sentence that doesn’t say much.
Consider, instead, four more powerful ways to introduce the two things you’ll be connecting, and show right away how they work together.
Try this: Pose a question or questions that both texts are asking.
Example: Connor Stevens, Sunset High School, Portland, Ore.: Comparing “Fahrenheit 451” by Ray Bradbury and “ How Egypt Crowdsources Censorship ” ( Read the full student essay .)
How can you control ideas? In today’s world, you scroll through feeds, finding any information available: government trade deals, local restaurants, movies, and TV shows. We are in an age where the power to find any fact, answer or piece of information that floats into question is available anywhere. If this privilege was stripped by a bodying government, how would freedom of information change?
Try this: Make a statement that is true for both, and then explain why briefly.
Example: Jack Magner, Flint Hill School, Oakton, Va.: Comparing biological feedback loops and homeostasis with “ After #MeToo, the Ripple Effect ” ( Read the full student essay .)
All it takes is a single action to spark innumerable reactions. In the case of Jessica Bennett’s “After #MeToo, the Ripple Effect,” it is the publishing of a 2017 article in the Times that launches a revolution, changing the treatment and recognition of women for the better. In the case of AP Biology, it is the connection of a ligand to a receptor protein or a drastic change to an organism’s environment that sends millions of signals that protect the organism from harm.
Try this: Explain how or why you’ll look at a classic work through a new lens.
Example: Zaria Roller, Verona Area High School, Wis.: Comparing “Things Fall Apart” by Chinua Achebe and “ The Boys Are Not All Right ” ( Read the full student essay .)
Colonial-age Nigeria and modern day Western society have more in common than one would think. Although the buzz phrase “toxic masculinity” did not exist at the time Chinua Achebe’s “Things Fall Apart” was written, its protagonist, Okonkwo, might as well be the poster boy for it.
Try this: Trace your thinking about how you came to connect the two things. Please note: For this contest, use of the word “I” is not only permitted but also encouraged if it helps you explore your ideas.
Example: Alexa Bolnick, Indian Hills High School, Franklin Lakes, N.J.: “Death of a Salesman” by Arthur Miller and “ A Lack of Respect for the Working Class in America Today ” ( Read the full student essay .)
Last year, reading the play “Death of a Salesman,” I couldn’t understand why salesman Willy Loman refused to accept his son’s desire to perform manual labor for a living. If working on a ranch made him happy, then why couldn’t Willy let his son go.
Example: Isabella Picillo, 17, Oceanside High School: “The Scarlet Letter” and “ Judge Partially Lifts Trump Administration Ban on Refugees ” ( Read the full student essay .)
I stumble upon a New York Times article, “Judge Partially Lifts Trump Administration Ban on Refugees,” that makes me wonder if Hawthorne, the literary genius, is wrong.
3. Use transition words and phrases to pivot between the two works.
When you’re discussing two works in the same piece, you’ll find yourself needing to switch gears regularly. How do you do that gracefully?
Try this: Explore a connection by choosing transition words that emphasize commonality.
Here are some sentences, all from our 2018 winners , with examples of those words in bold:
— “ Similar to the prevalent custom of xenia in Ancient Greece, Uganda has made hosting refugees a national policy.” — “John Steinbeck’s classic novel ‘The Grapes of Wrath,’ which chronicles the struggles of the Joad family during the Great Depression, documents a similar reality.” — “Republican anti-Trump attitudes echo those of their nineteenth century counterparts, such as Carl Schulz, who wrote, ‘Our duty to the country … is … paramount to any duty we may owe to the party.’” — “ Paralleling the same theme, the short story ‘Harrison Bergeron’ by Kurt Vonnegut describes a future in which absolute equality has become the obsession of society.” — “This phenomenon mirrors that of negative feedback loops in biology, in which a stimulus triggers a biological response designed to keep a biological system at equilibrium.”
4. Acknowledge important contrasts between the two things you are connecting.
Part of comparing two things is contrasting them — showing where the commonalities end and explaining why the differences are significant.
But your essay shouldn’t just be a list of all the things the two texts have in common vs. all the things they don’t. Instead, you need to use the contrasts to acknowledge obvious differences, but still further your point about how and why the two ideas work together.
For example, the article comparing LeBron James and Michael Jordan makes the crucial distinction that they played in different eras — and thus it’s hard to compare them since we remember Jordan through “rose-colored” memories, while James, playing today, is considered by many “the most scrutinized and criticized American athlete, much of the naysaying unwarranted and aggravated by the polarizing effects of social media” that didn’t exist in Jordan’s heyday.
Keep in mind that since our contest emphasizes connections, not all of our previous winners have done this — but those who did only strengthened their cases.
Try this: Point out that surface differences are less important than the underlying message.
Example: Megan Lee, West Windsor Plainsboro High School North, Plainsboro, N.J.: “Harrison Bergeron” by Kurt Vonnegut and “ The Curse of Affirmative Action ” ( Read the full student essay .)
Although the “Harrison Bergeron” is a heavily exaggerated piece of fiction writing while “The Curse of Affirmative Action” was written to denounce a real world policy, both allude to the delicacy of equality.
Try this: Use a contrast to illuminate a bigger point — in this case that the ways in which the #MeToo movement is different than a biological feedback loop is also what makes it so “revolutionary.”
Example: Jack Magner, Flint Hill School, Oakton, Va.: Biological feedback loops and homeostasis and “ After #MeToo, the Ripple Effect ” ( Read the full student essay .)
#MeToo and feedback loops are extremely interconnected, but there is one key difference in the #MeToo movement that makes it so dynamic and revolutionary. In biology, feedback responses are developed slowly and organically over millions of years of evolution. Environments select for these responses, and a species’s fitness increases as a result. The #MeToo movement is the exact opposite, attacking the perceived natural order that our environment has selected for at the expense the “fittest” members of society: powerful men. This positive feedback loop does not run in concurrence with the already-established negative feedback loop. It instead serves as its foil, aiming to topple the destructive systems for which hyper-masculine society has selected for over thousands of years.
5. End in a way that sums up and says something new.
We could repeat this piece of advice in every edition of our Mentor Text series regardless of genre: No matter what you’re writing about, don’t waste your conclusion by just lazily restating what you’ve already said.
Instead, keep your readers thinking. Pose a new question, use a fresh quote that sums up your main idea, give some surprising new information, or tell a fitting final story.
In other words, no “In conclusion, I have shown how _________ and _________ have many similarities and many differences.”
Instead you could …
Try this: Draw a final lesson, takeaway or “moral” that the two together express.
Example: Samantha Jones, 16, Concord Carlisle Regional High School: “Walden” and “ Dropping Out of College Into Life ” ( Read the full student essay .)
The moral is clear: there are gaps in our education system, and because of these gaps students aren’t adequately prepared for their own futures. In his book Walden, Thoreau elaborates on the ideas Stauffer touches on in her article. As stated before, he believed learning through experience was exponentially better than a in classroom. When a rigid curriculum with expectations is set in place, students aren’t given the same hands on learning as they would be without one. Just as Stauffer embraced this learning style in the New School, Thoreau did so in Walden Woods …
Example: Robert McCoy, Whippany Park High School, Whippany, N.J.: Gilded Age Mugwumps and “ Republicans for Democrats ” ( Read the full student essay .)
The parallels in the Mugwump and Never Trump movements demonstrate the significance of adhering to a strict moral standard, despite extreme partisan divides …
Try this: Raise a new question or idea suggested by the comparison.
In this essay, Sebastian Zagler compares the ways that both a famous mathematical problem and the issue of climate change will require new innovation and collaboration to solve. But he ends the essay by engaging a new, related question: Why would anyone want to take on such “impossible problems” in the first place?
Example: Sebastian Zagler, John T. Hoggard High School, Wilmington, N.C.: the Collatz, or 3n+1, conjecture, a mathematical problem that has produced no mathematical proof for over 80 years, and “ Stopping Climate Change Is Hopeless. Let’s Do It. ” ( Read the full student essay .)
What draws mankind to these impossible problems, whether it be solving the Collatz conjecture or reversing climate change? Fighting for a common cause brings people together, making them part of something greater. Even fighting a “long defeat” can give one a sense of purpose — a sense of belonging …
Try this: End with an apt quote that applies to both.
Here are Sebastian Zagler’s last two lines:
There is a beauty in fighting a losing battle, as long as a glimmer of hope remains. And as Schendler and Jones write, “If the human species specializes in one thing, it’s taking on the impossible.”
And here are Samantha Jones’s:
For that is all Walden really is; Thoreau learning from nature by immersing himself in it, instead of seeing it on the pages of a book. A quote from Walden most fitting is as follows, “We boast of our system of education, but why stop at schoolmasters and schoolhouses? We are all schoolmasters, and our schoolhouse is the universe”
In both cases, the quotes are inspiring, hopeful and get at truths their essays worked hard to demonstrate.
Additional Resources
In our description of Unit 3 of our writing curriculum you can find much, much more, including related writing prompts and a series of lesson plans that can help teachers teach with our Connections Contest.

6 compare and contrast essay topics | Homeschool high school writing ideas
by Kim Kautzer | May 13, 2019 | High school , Writing & Journal Prompts

Compare and contrast essays don’t have to be dull and tedious! Homeschool high school students will be sure to enjoy a few of this week’s lighthearted topics.
Help teens stay focused with a four-paragraph outline: introduction, similarities, differences, and conclusion . Motivated writers may need two paragraphs for the comparisons or two paragraphs for the contrasts, and that’s fine, too!
1. Fashion Statement
It makes us laugh and makes us cry; it fills our closets and empties our wallets. Fashion, past and present, can be fun to study and even more fun to wear! Compare and contrast the clothing styles of today with the styles from a twentieth-century decade of your choice.
2. All in the Family
Family reunions tend to occur at the time of births, weddings, and funerals . Choose two of these three events to compare and contrast.
3. Saved by the Bell?
Some people procrastinate every assignment and always arrive five minutes late. Others rise before dawn, meet deadlines early , and arrive at meetings with a quarter hour to spare. You know both types, so it’s time to immortalize them in a compare/contrast essay.
4. Behind Closed Doors
Imagine two modest-sized houses: the first belongs to a young pair of newlyweds, and the other is owned by an elderly couple. Compare and contrast these two homes , including the furniture styles, the gadgets and appliances, and the number of items stored in garages, drawers, and closets.
5. Bucket Lists and Dirty Floors
How does it feel to experience something the very first time ? How do your feelings change when the activity becomes an old routine ? Think about an experience such as driving a car, going camping, baking a cake, or practicing an instrument. Compare and contrast the first time you tried it with your most recent experience.
6. Cheaper by the Dozen
Piles of laundry, noise levels, schedules, routines—we see so many differences between large and small families . Contrast a few of the differences you’ve noticed, and compare several things that both kinds of families have in common.
A Venn diagram is the perfect compare-contrast brainstorming tool! Students who prefer using a laptop over pencil and paper might enjoy this cool tool from Canva for creating Venn diagrams online —for free!

Easy-to-Teach Essay and Creative Writing Curriculum
For homeschool teens.
If you’re looking for an easy-to-teach homeschool writing curriculum for your teens, consider our WriteShop program :
- WriteShop I
- WriteShop II
Download free sample lessons here .
Let’s Stay Connected!
Subscribe to our newsletter.

- Gift Guides
- Reluctant or Struggling Writers
- Special Needs Writers
- Brainstorming Help
- Editing & Grading Help
- Encouragement for Moms
- Writing Games & Activities
- Writing for All Subjects
- Essays & Research Papers
- College Prep Writing
- Grammar & Spelling
- Writing Prompts
Recent Posts
- An exciting announcement!
- 10 Stumbling Blocks to Writing in Your Homeschool
- Help kids with learning challenges succeed at homeschool writing
- How to correct writing lessons without criticizing your child
101 Compare and Contrast Essay Topics
Great Ideas for Essays
- Teaching Resources
- An Introduction to Teaching
- Tips & Strategies
- Policies & Discipline
- Community Involvement
- School Administration
- Technology in the Classroom
- Teaching Adult Learners
- Issues In Education
- Becoming A Teacher
- Assessments & Tests
- Elementary Education
- Secondary Education
- Special Education
- Homeschooling
- M.Ed., Curriculum and Instruction, University of Florida
- B.A., History, University of Florida
Compare and contrast essays are taught in school for many reasons. For one thing, they are relatively easy to teach, understand, and format. Students can typically understand the structure with just a short amount of instruction. In addition, these essays allow students develop critical thinking skills to approach a variety of topics.
Brainstorming Tip
One fun way to get students started brainstorming their compare and contrast essays is to create a Venn diagram , where the overlapping sections of the circle contain similarities and the non-overlapping areas contain the differing traits.
Following is a list of 101 topics for compare and contrast essays that you are welcome to use in your classroom. As you look through the list you will see that some items are academic in nature while others are included for interest-building and fun writing activities.
- Apple vs. Microsoft
- Coke vs. Pepsi
- Renaissance Art vs. Baroque Art
- Antebellum Era vs. Reconstruction Era in American History
- Childhood vs. Adulthood
- Star Wars vs. Star Trek
- Biology vs. Chemistry
- Astrology vs. Astronomy
- American Government vs. British Government (or any world government)
- Fruits vs. Vegetables
- Dogs vs. Cats
- Ego vs. Superego
- Christianity vs. Judaism (or any world religion )
- Republican vs. Democrat
- Monarchy vs. Presidency
- US President vs. UK Prime Minister
- Jazz vs. Classical Music
- Red vs. White (or any two colors)
- Soccer vs. Football
- North vs. South Before the Civil War
- New England Colonies vs. Middle Colonies OR vs. Southern Colonies
- Cash vs. Credit Cards
- Sam vs. Frodo Baggins
- Gandalf vs. Dumbledore
- Fred vs. Shaggy
- Rap vs. Pop
- Articles of Confederation vs. U.S. Constitution
- Henry VIII vs. King Louis XIV
- Stocks vs. Bonds
- Monopolies vs. Oligopolies
- Communism vs. Capitalism
- Socialism vs. Capitalism
- Diesel vs. Petroleum
- Nuclear Power vs. Solar Power
- Saltwater Fish vs. Freshwater Fish
- Squids vs. Octopus
- Mammals vs. Reptiles
- Baleen vs. Toothed Whales
- Seals vs. Sea Lions
- Crocodiles vs. Alligators
- Bats vs. Birds
- Oven vs. Microwave
- Greek vs. Roman Mythology
- Chinese vs. Japanese
- Comedy vs. Drama
- Renting vs. Owning
- Mozart vs. Beethoven
- Online vs. Traditional Education
- North vs. South Pole
- Watercolor vs. Oil
- 1984 vs. Fahrenheit 451
- Emily Dickinson vs. Samuel Taylor Coleridge
- W.E.B. DuBois vs. Booker T. Washington
- Strawberries vs. Apples
- Airplanes vs. Helicopters
- Hitler vs. Napoleon
- Roman Empire vs. British Empire
- Paper vs. Plastic
- Italy vs. Spain
- Baseball vs. Cricket
- Jefferson vs. Adams
- Thoroughbreds vs. Clydesdales
- Spiders vs. Scorpions
- Northern Hemisphere vs. Southern Hemisphere
- Hobbes vs. Locke
- Friends vs. Family
- Dried Fruit vs. Fresh
- Porcelain vs. Glass
- Modern Dance vs. Ballroom Dancing
- American Idol vs. The Voice
- Reality TV vs. Sitcoms
- Picard vs. Kirk
- Books vs. Movies
- Magazines vs. Comic Books
- Antique vs. New
- Public vs. Private Transportation
- Email vs. Letters
- Facebook vs. Twitter
- Coffee vs. an Energy Drink
- Toads vs. Frogs
- Profit vs. Non-Profit
- Boys vs. Girls
- Birds vs. Dinosaurs
- High School vs. College
- Chamberlain vs. Churchill
- Offense vs. Defense
- Jordan vs. Bryant
- Harry vs. Draco
- Roses vs. Carnations
- Poetry vs. Prose
- Fiction vs. Nonfiction
- Lions vs. Tigers
- Vampires vs. Werewolves
- Lollipops vs. popsicles
- Summer vs. Winter
- Recycling vs. Landfill
- Motorcycle vs. Bicycle
- Halogen vs. Incandescent
- Newton vs. Einstein
- . Go on vacation vs. Staycation
- Rock vs. Scissors
- Write a Compare and Contrast Essay
- Beef Up Critical Thinking and Writing Skills: Comparison Essays
- How to Teach the Compare and Contrast Essay
- Topical Organization Essay
- Writing About Literature: Ten Sample Topics for Comparison & Contrast Essays
- Comparing and Contrasting in English
- 25 Essay Topics for American Government Classes
- Expository Essay Genre With Suggested Prompts
- Venn Diagrams to Plan Essays and More
- Teaching Comparative and Superlative Forms to ESL Students
- Cause and Effect Essay Topics
- Comparative and Superlatives for Beginners
- How to Teach Topic Sentences Using Models
- Exercise in Using the Comparative and Superlative Forms of Adjectives
- Climate in the Northern vs Southern Hemispheres
- Miss Nelson Is Missing Lesson Plan
Compare and Contrast
The ability to compare and contrast is critical for comprehending literary and informational texts—and for writing them. Learners practice this skill via compare and contrast worksheets, graphic organizers and Venn diagrams, paired texts, reading response sheets, close reading activities, and report writing.
TRY US RISK-FREE FOR 30 DAYS!
ADD TO YOUR FILE CABINET
THIS RESOURCE IS IN PDF FORMAT
Printable Details
- Number of pages:
- Guided Reading Level:
- Common Core:
- Open access
- Published: 15 April 2024
Demuxafy : improvement in droplet assignment by integrating multiple single-cell demultiplexing and doublet detection methods
- Drew Neavin 1 ,
- Anne Senabouth 1 ,
- Himanshi Arora 1 , 2 ,
- Jimmy Tsz Hang Lee 3 ,
- Aida Ripoll-Cladellas 4 ,
- sc-eQTLGen Consortium ,
- Lude Franke 5 ,
- Shyam Prabhakar 6 , 7 , 8 ,
- Chun Jimmie Ye 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 ,
- Davis J. McCarthy 13 , 14 ,
- Marta Melé 4 ,
- Martin Hemberg 15 &
- Joseph E. Powell ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5070-4124 1 , 16
Genome Biology volume 25 , Article number: 94 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
Recent innovations in single-cell RNA-sequencing (scRNA-seq) provide the technology to investigate biological questions at cellular resolution. Pooling cells from multiple individuals has become a common strategy, and droplets can subsequently be assigned to a specific individual by leveraging their inherent genetic differences. An implicit challenge with scRNA-seq is the occurrence of doublets—droplets containing two or more cells. We develop Demuxafy, a framework to enhance donor assignment and doublet removal through the consensus intersection of multiple demultiplexing and doublet detecting methods. Demuxafy significantly improves droplet assignment by separating singlets from doublets and classifying the correct individual.
Droplet-based single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) technologies have provided the tools to profile tens of thousands of single-cell transcriptomes simultaneously [ 1 ]. With these technological advances, combining cells from multiple samples in a single capture is common, increasing the sample size while simultaneously reducing batch effects, cost, and time. In addition, following cell capture and sequencing, the droplets can be demultiplexed—each droplet accurately assigned to each individual in the pool [ 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 ].
Many scRNA-seq experiments now capture upwards of 20,000 droplets, resulting in ~16% (3,200) doublets [ 8 ]. Current demultiplexing methods can also identify doublets—droplets containing two or more cells—from different individuals (heterogenic doublets). These doublets can significantly alter scientific conclusions if they are not effectively removed. Therefore, it is essential to remove doublets from droplet-based single-cell captures.
However, demultiplexing methods cannot identify droplets containing multiple cells from the same individual (homogenic doublets) and, therefore, cannot identify all doublets in a single capture. If left in the dataset, those doublets could appear as transitional cells between two distinct cell types or a completely new cell type. Accordingly, additional methods have been developed to identify heterotypic doublets (droplets that contain two cells from different cell types) by comparing the transcriptional profile of each droplet to doublets simulated from the dataset [ 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 ]. It is important to recognise that demultiplexing methods achieve two functions—segregation of cells from different donors and separation of singlets from doublets—while doublet detecting methods solely classify singlets versus doublets.
Therefore, demultiplexing and transcription-based doublet detecting methods provide complementary information to improve doublet detection, providing a cleaner dataset and more robust scientific results. There are currently five genetic-based demultiplexing [ 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 16 ] and seven transcription-based doublet-detecting methods implemented in various languages [ 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 ]. Under different scenarios, each method is subject to varying performance and, in some instances, biases in their ability to accurately assign cells or detect doublets from certain conditions. The best combination of methods is currently unclear but will undoubtedly depend on the dataset and research question.
Therefore, we set out to identify the best combination of genetic-based demultiplexing and transcription-based doublet-detecting methods to remove doublets and partition singlets from different donors correctly. In addition, we have developed a software platform ( Demuxafy ) that performs these intersectional methods and provides additional commands to simplify the execution and interpretation of results for each method (Fig. 1 a).
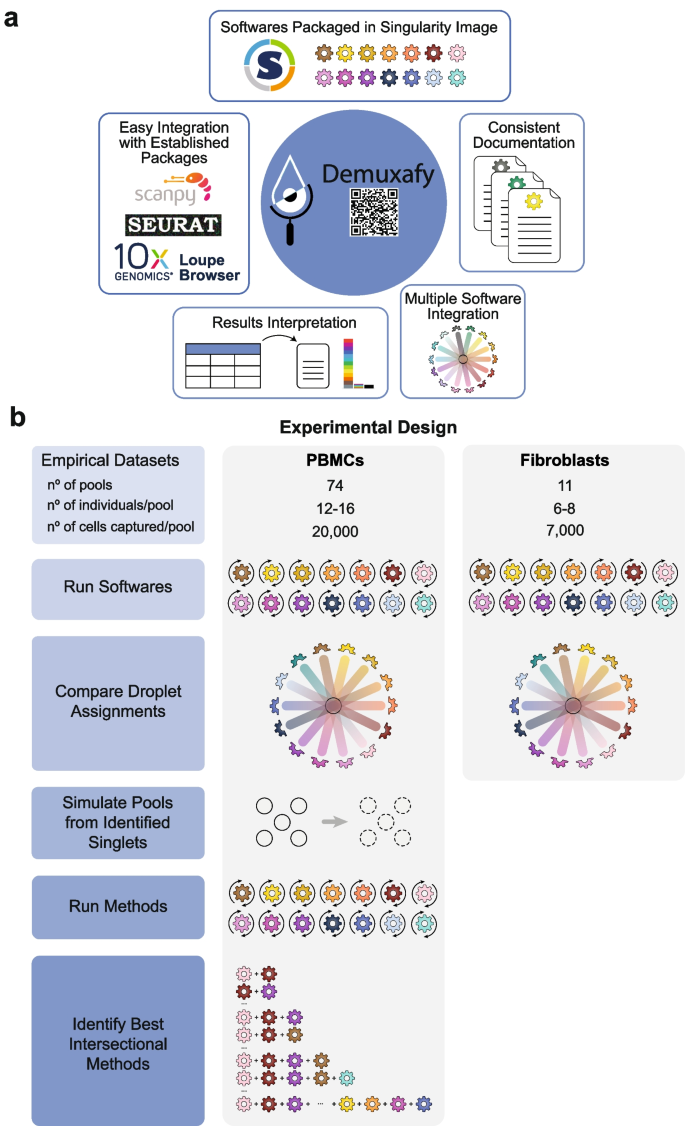
Study design and qualitative method classifications. a Demuxafy is a platform to perform demultiplexing and doublet detecting with consistent documentation. Demuxafy also provides wrapper scripts to quickly summarize the results from each method and assign clusters to each individual with reference genotypes when a reference-free demultiplexing method is used. Finally, Demuxafy provides a script to easily combine the results from multiple different methods into a single data frame and it provides a final assignment for each droplet based on the combination of multiple methods. In addition, Demuxafy provides summaries of the number of droplets classified as singlets or doublets by each method and a summary of the number of droplets assigned to each individual by each of the demultiplexing methods. b Two datasets are included in this analysis - a PBMC dataset and a fibroblast dataset. The PBMC dataset contains 74 pools that captured approximately 20,000 droplets each with 12-16 donor cells multiplexed per pool. The fibroblast dataset contains 11 pools of roughly 7,000 droplets per pool with sizes ranging from six to eight donors per pool. All pools were processed by all demultiplexing and doublet detecting methods and the droplet and donor classifications were compared between the methods and between the PBMCs and fibroblasts. Then the PBMC droplets that were classified as singlets by all methods were taken as ‘true singlets’ and used to generate new pools in silico. Those pools were then processed by each of the demultiplexing and doublet detecting methods and intersectional combinations of demultiplexing and doublet detecting methods were tested for different experimental designs
To compare the demultiplexing and doublet detecting methods, we utilised two large, multiplexed datasets—one that contained ~1.4 million peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from 1,034 donors [ 17 ] and one with ~94,000 fibroblasts from 81 donors [ 18 ]. We used the true singlets from the PBMC dataset to generate new in silico pools to assess the performance of each method and the multi-method intersectional combinations (Fig. 1 b).
Here, we compare 14 demultiplexing and doublet detecting methods with different methodological approaches, capabilities, and intersectional combinations. Seven of those are demultiplexing methods ( Demuxalot [ 6 ], Demuxlet [ 3 ], Dropulation [ 5 ], Freemuxlet [ 16 ], ScSplit [ 7 ], Souporcell [ 4 ], and Vireo [ 2 ]) which leverage the common genetic variation between individuals to identify cells that came from each individual and to identify heterogenic doublets. The seven remaining methods ( DoubletDecon [ 9 ], DoubletDetection [ 14 ], DoubletFinder [ 10 ], ScDblFinder [ 11 ], Scds [ 12 ], Scrublet [ 13 ], and Solo [ 15 ]) identify doublets based on their similarity to simulated doublets generated by adding the transcriptional profiles of two randomly selected droplets in the dataset. These methods assume that the proportion of real doublets in the dataset is low, so combining any two droplets will likely represent the combination of two singlets.
We identify critical differences in the performance of demultiplexing and doublet detecting methods to classify droplets correctly. In the case of the demultiplexing techniques, their performance depends on their ability to identify singlets from doublets and assign a singlet to the correct individual. For doublet detecting methods, the performance is based solely on their ability to differentiate a singlet from a doublet. We identify limitations in identifying specific doublet types and cell types by some methods. In addition, we compare the intersectional combinations of these methods for multiple experimental designs and demonstrate that intersectional approaches significantly outperform all individual techniques. Thus, the intersectional methods provide enhanced singlet classification and doublet removal—a critical but often under-valued step of droplet-based scRNA-seq processing. Our results demonstrate that intersectional combinations of demultiplexing and doublet detecting software provide significant advantages in droplet-based scRNA-seq preprocessing that can alter results and conclusions drawn from the data. Finally, to provide easy implementation of our intersectional approach, we provide Demuxafy ( https://demultiplexing-doublet-detecting-docs.readthedocs.io/en/latest/index.html ) a complete platform to perform demultiplexing and doublet detecting intersectional methods (Fig. 1 a).
Study design
To evaluate demultiplexing and doublet detecting methods, we developed an experimental design that applies the different techniques to empirical pools and pools generated in silico from the combination of true singlets—droplets identified as singlets by every method (Fig. 1 a). For the first phase of this study, we used two empirical multiplexed datasets—the peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) dataset containing ~1.4 million cells from 1034 donors and a fibroblast dataset of ~94,000 cells from 81 individuals (Additional file 1 : Table S1). We chose these two cell systems to assess the methods in heterogeneous (PBMC) and homogeneous (fibroblast) cell types.
Demultiplexing and doublet detecting methods perform similarly for heterogeneous and homogeneous cell types
We applied the demultiplexing methods ( Demuxalot , Demuxlet , Dropulation , Freemuxlet , ScSplit , Souporcell , and Vireo ) and doublet detecting methods ( DoubletDecon , DoubletDetection , DoubletFinder , ScDblFinder , Scds , Scrublet , and Solo ) to the two datasets and assessed the results from each method. We first compared the droplet assignments by identifying the number of singlets and doublets identified by a given method that were consistently annotated by all methods (Fig. 2 a–d). We also identified the percentage of droplets that were annotated consistently between pairs of methods (Additional file 2 : Fig S1). In the cases where two demultiplexing methods were compared to one another, both the droplet type (singlet or doublet) and the assignment of the droplet to an individual had to match to be considered in agreement. In all other comparisons (i.e. demultiplexing versus doublet detecting and doublet detecting versus doublet detecting), only the droplet type (singlet or doublet) was considered for agreement since doublet detecting methods cannot annotate donor assignment. We found that the two method types were more similar to other methods of the same type (i.e., demultiplexing versus demultiplexing and doublet detecting versus doublet detecting) than they were to methods from a different type (demultiplexing methods versus doublet detecting methods; Supplementary Fig 1). We found that the similarity of the demultiplexing and doublet detecting methods was consistent in the PBMC and fibroblast datasets (Pearson correlation R = 0.78, P -value < 2×10 −16 ; Fig S1a-c). In addition, demultiplexing methods were more similar than doublet detecting methods for both the PBMC and fibroblast datasets (Wilcoxon rank-sum test: P < 0.01; Fig. 2 a–b and Additional file 2 : Fig S1).
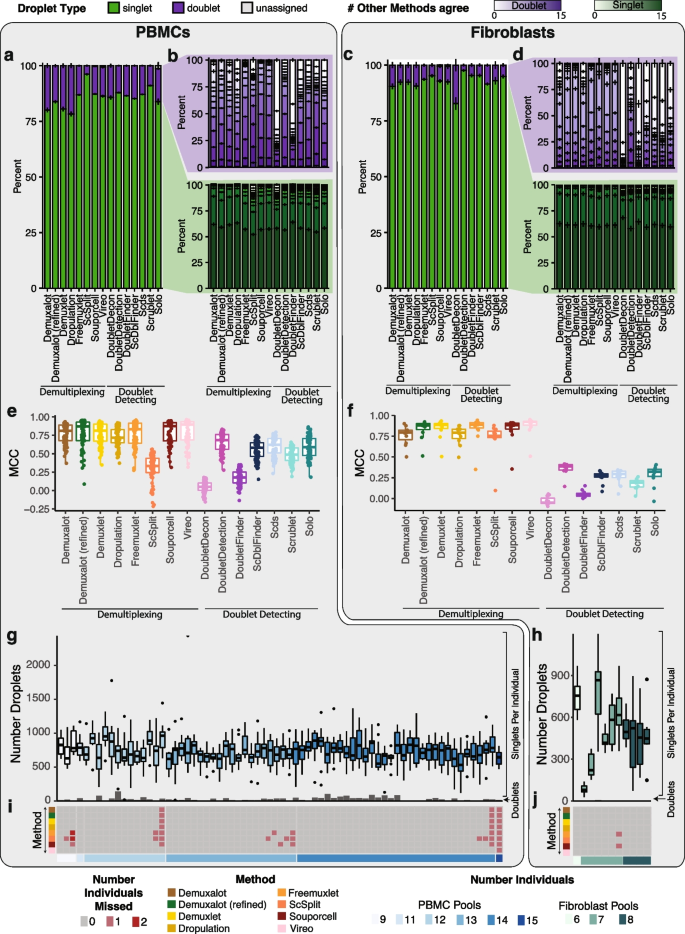
Demultiplexing and Doublet Detecting Method Performance Comparison. a The proportion of droplets classified as singlets and doublets by each method in the PBMCs. b The number of other methods that classified the singlets and doublets identified by each method in the PBMCs. c The proportion of droplets classified as singlets and doublets by each method in the fibroblasts. d The number of other methods that classified the singlets and doublets identified by each method in the fibroblasts. e - f The performance of each method when the majority classification of each droplet is considered the correct annotation in the PBMCs ( e ) and fibroblasts ( f ). g - h The number of droplets classified as singlets (box plots) and doublets (bar plots) by all methods in the PBMC ( g ) and fibroblast ( h ) pools. i - j The number of donors that were not identified by each method in each pool for PBMCs ( i ) and fibroblasts ( j ). PBMC: peripheral blood mononuclear cell. MCC: Matthew’s correlationcoefficient
The number of unique molecular identifiers (UMIs) and genes decreased in droplets that were classified as singlets by a larger number of methods while the mitochondrial percentage increased in both PBMCs and fibroblasts (Additional file 2 : Fig S2).
We next interrogated the performance of each method using the Matthew’s correlation coefficient (MCC) to calculate the consistency between Demuxify and true droplet classification. We identified consistent trends in the MCC scores for each method between the PBMCs (Fig. 2 e) and fibroblasts (Fig. 2 f). These data indicate that the methods behave similarly, relative to one another, for heterogeneous and homogeneous datasets.
Next, we sought to identify the droplets concordantly classified by all demultiplexing and doublet detecting methods in the PBMC and fibroblast datasets. On average, 732 singlets were identified for each individual by all the methods in the PBMC dataset. Likewise, 494 droplets were identified as singlets for each individual by all the methods in the fibroblast pools. However, the concordance of doublets identified by all methods was very low for both datasets (Fig. 2 e–f). Notably, the consistency of classifying a droplet as a doublet by all methods was relatively low (Fig. 2 b,d,g, and h). This suggests that doublet identification is not consistent between all the methods. Therefore, further investigation is required to identify the reasons for these inconsistencies between methods. It also suggests that combining multiple methods for doublet classification may be necessary for more complete doublet removal. Further, some methods could not identify all the individuals in each pool (Fig. 2 i–j). The non-concordance between different methods demonstrates the need to effectively test each method on a dataset where the droplet types are known.
Computational resources vary for demultiplexing and doublet detecting methods
We recorded each method’s computational resources for the PBMC pools, with ~20,000 cells captured per pool (Additional file 1 : Table S1). Of the demultiplexing methods, ScSplit took the most time (multiple days) and required the most steps, but Demuxalot , Demuxlet , and Freemuxlet used the most memory. Solo took the longest time (median 13 h) and most memory to run for the doublet detecting methods but is the only method built to be run directly from the command line, making it easy to implement (Additional file 2 : Fig S3).
Generate pools with known singlets and doublets
However, there is no gold standard to identify which droplets are singlets or doublets. Therefore, in the second phase of our experimental design (Fig. 1 b), we used the PBMC droplets classified as singlets by all methods to generate new pools in silico. We chose to use the PBMC dataset since our first analyses indicated that method performance is similar for homogeneous (fibroblast) and heterogeneous (PBMC) cell types (Fig. 2 and Additional file 2 : Fig S1) and because we had many more individuals available to generate in silico pools from the PBMC dataset (Additional file 1 : Table S1).
We generated 70 pools—10 each of pools that included 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, or 128 individuals (Additional file 1 : Table S2). We assume a maximum 20% doublet rate as it is unlikely researchers would use a technology that has a higher doublet rate (Fig. 3 a).
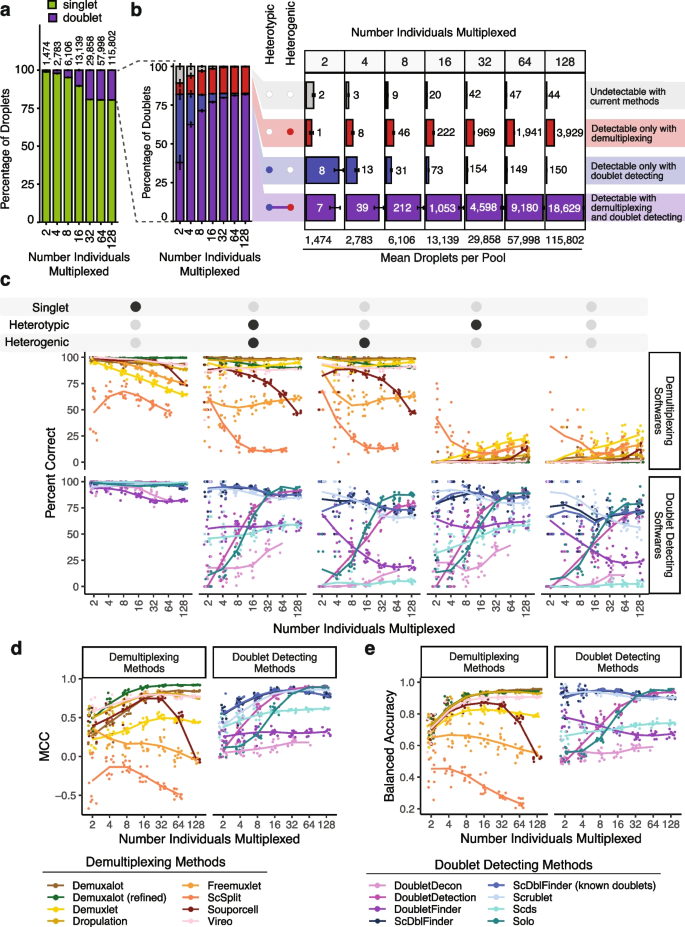
In silico Pool Doublet Annotation and Method Performance. a The percent of singlets and doublets in the in -silico pools - separated by the number of multiplexed individuals per pool. b The percentage and number of doublets that are heterogenic (detectable by demultiplexing methods), heterotypic (detectable by doublet detecting methods), both (detectable by either method category) and neither (not detectable with current methods) for each multiplexed pool size. c Percent of droplets that each of the demultiplexing and doublet detecting methods classified correctly for singlets and doublet subtypes for different multiplexed pool sizes. d Matthew’s Correlation Coefficient (MCC) for each of the methods for each of the multiplexed pool sizes. e Balanced accuracy for each of the methods for each of the multiplexed pool sizes
We used azimuth to classify the PBMC cell types for each droplet used to generate the in silico pools [ 19 ] (Additional file 2 : Fig S4). As these pools have been generated in silico using empirical singlets that have been well annotated, we next identified the proportion of doublets in each pool that were heterogenic, heterotypic, both, and neither. This approach demonstrates that a significant percentage of doublets are only detectable by doublet detecting methods (homogenic and heterotypic) for pools with 16 or fewer donors multiplexed (Fig. 3 b).
While the total number of doublets that would be missed if only using demultiplexing methods appears small for fewer multiplexed individuals (Fig. 3 b), it is important to recognise that this is partly a function of the ~732 singlet cells per individual used to generate these pools. Hence, the in silico pools with fewer individuals also have fewer cells. Therefore, to obtain numbers of doublets that are directly comparable to one another, we calculated the number of each doublet type that would be expected to be captured with 20,000 cells when 2, 4, 8, 16, or 32 individuals were multiplexed (Additional file 2 : Fig S5). These results demonstrate that many doublets would be falsely classified as singlets since they are homogenic when just using demultiplexing methods for a pool of 20,000 cells captured with a 16% doublet rate (Additional file 2 : Fig S5). However, as more individuals are multiplexed, the number of droplets that would not be detectable by demultiplexing methods (homogenic) decreases. This suggests that typical workflows that use only one demultiplexing method to remove doublets from pools that capture 20,000 droplets with 16 or fewer multiplexed individuals fail to adequately remove between 173 (16 multiplexed individuals) and 1,325 (2 multiplexed individuals) doublets that are homogenic and heterotypic which could be detected by doublet detecting methods (Additional file 2 : Fig S5). Therefore, a technique that uses both demultiplexing and doublet detecting methods in parallel will complement more complete doublet removal methods. Consequently, we next set out to identify the demultiplexing and doublet detecting methods that perform the best on their own and in concert with other methods.
Doublet and singlet droplet classification effectiveness varies for demultiplexing and doublet detecting methods
Demultiplexing methods fail to classify homogenic doublets.
We next investigated the percentage of the droplets that were correctly classified by each demultiplexing and doublet detecting method. In addition to the seven demultiplexing methods, we also included Demuxalot with the additional steps to refine the genotypes that can then be used for demultiplexing— Demuxalot (refined). Demultiplexing methods correctly classify a large portion of the singlets and heterogenic doublets (Fig. 3 c). This pattern is highly consistent across different cell types, with the notable exceptions being decreased correct classifications for erythrocytes and platelets when greater than 16 individuals are multiplexed (Additional file 2 : Fig S6).
However, Demuxalot consistently demonstrates the highest correct heterogenic doublet classification. Further, the percentage of the heterogenic doublets classified correctly by Souporcell decreases when large numbers of donors are multiplexed. ScSplit is not as effective as the other demultiplexing methods at classifying heterogenic doublets, partly due to the unique doublet classification method, which assumes that the doublets will generate a single cluster separate from the donors (Table 1 ). Importantly, the demultiplexing methods identify almost none of the homogenic doublets for any multiplexed pool size—demonstrating the need to include doublet detecting methods to supplement the demultiplexing method doublet detection.
Doublet detecting method classification performances vary greatly
In addition to assessing each of the methods with default settings, we also evaluated ScDblFinder with ‘known doublets’ provided. This method can take already known doublets and use them when detecting doublets. For these cases, we used the droplets that were classified as doublets by all the demultiplexing methods as ‘known doublets’.
Most of the methods classified a similarly high percentage of singlets correctly, with the exceptions of DoubletDecon and DoubletFinder for all pool sizes (Fig. 3 c). However, unlike the demultiplexing methods, there are explicit cell-type-specific biases for many of the doublet detecting methods (Additional file 2 : Fig S7). These differences are most notable for cell types with fewer cells (i.e. ASDC and cDC2) and proliferating cells (i.e. CD4 Proliferating, CD8 Proliferating, and NK Proliferating). Further, all of the softwares demonstrate high correct percentages for some cell types including CD4 Naïve and CD8 Naïve (Additional file 2 : Fig S7).
As expected, all doublet detecting methods identified heterotypic doublets more effectively than homotypic doublets (Fig. 3 c). However, ScDblFinder and Scrublet classified the most doublets correctly across all doublet types for pools containing 16 individuals or fewer. Solo was more effective at identifying doublets than Scds for pools containing more than 16 individuals. It is also important to note that it was not feasible to run DoubletDecon for the largest pools containing 128 multiplexed individuals and an average of 115,802 droplets (range: 113,594–119,126 droplets). ScDblFinder performed similarly when executed with and without known doublets (Pearson correlation P = 2.5 × 10 -40 ). This suggests that providing known doublets to ScDblFinder does not offer an added benefit.
Performances vary between demultiplexing and doublet detecting method and across the number of multiplexed individuals
We assessed the overall performance of each method with two metrics: the balanced accuracy and the MCC. We chose to use balanced accuracy since, with unbalanced group sizes, it is a better measure of performance than accuracy itself. Further, the MCC has been demonstrated as a more reliable statistical measure of performance since it considers all possible categories—true singlets (true positives), false singlets (false positives), true doublets (true negatives), and false doublets (false negatives). Therefore, a high score on the MCC scale indicates high performance in each metric. However, we provide additional performance metrics for each method (Additional file 1 : Table S3). For demultiplexing methods, both the droplet type (singlet or doublet) and the individual assignment were required to be considered a ‘true singlet’. In contrast, only the droplet type (singlet or doublet) was needed for doublet detection methods.
The MCC and balanced accuracy metrics are similar (Spearman’s ⍴ = 0.87; P < 2.2 × 10 -308 ). Further, the performance of Souporcell decreases for pools with more than 32 individuals multiplexed for both metrics (Student’s t -test for MCC: P < 1.1 × 10 -9 and balanced accuracy: P < 8.1 × 10 -11 ). Scds , ScDblFinder , and Scrublet are among the top-performing doublet detecting methods Fig. 3 d–e).
Overall, between 0.4 and 78.8% of droplets were incorrectly classified by the demultiplexing or doublet detecting methods depending on the technique and the multiplexed pool size (Additional file 2 : Fig S8). Demuxalot (refined) and DoubletDetection demonstrated the lowest percentage of incorrect droplets with about 1% wrong in the smaller pools (two multiplexed individuals) and about 3% incorrect in pools with at least 16 multiplexed individuals. Since some transitional states and cell types are present in low percentages in total cell populations (i.e. ASDCs at 0.02%), incorrect classification of droplets could alter scientific interpretations of the data, and it is, therefore, ideal for decreasing the number of erroneous assignments as much as possible.
False singlets and doublets demonstrate different metrics than correctly classified droplets
We next asked whether specific cell metrics might contribute to false singlet and doublet classifications for different methods. Therefore, we compared the number of genes, number of UMIs, mitochondrial percentage and ribosomal percentage of the false singlets and doublets to equal numbers of correctly classified cells for each demultiplexing and doublet detecting method.
The number of UMIs (Additional file 2 : Fig S9 and Additional file 1 : Table S4) and genes (Additional file 2 : Fig S10 and Additional file 1 : Table S5) demonstrated very similar distributions for all comparisons and all methods (Spearman ⍴ = 0.99, P < 2.2 × 10 -308 ). The number of UMIs and genes were consistently higher in false singlets and lower in false doublets for most demultiplexing methods except some smaller pool sizes (Additional file 2 : Fig S9a and Additional file 2 : Fig S10a; Additional file 1 : Table S4 and Additional file 1 : Table S5). The number of UMIs and genes was consistently higher in droplets falsely classified as singlets by the doublet detecting methods than the correctly identified droplets (Additional file 2 : Fig S9b and Additional file 2 : Fig S10b; Additional file 1 : Table S4 and Additional file 1 : Table S5). However, there was less consistency in the number of UMIs and genes detected in false singlets than correctly classified droplets between the different doublet detecting methods (Additional file 2 : Fig S9b and Additional file 2 : Fig S10b; Additional file 1 : Table S4 and Additional file 1 : Table S5).
The ribosomal percentage of the droplets falsely classified as singlets or doublets is similar to the correctly classified droplets for most methods—although they are statistically different for larger pool sizes (Additional file 2 : Fig S11a and Additional file 1 : Table S6). However, the false doublets classified by some demultiplexing methods ( Demuxalot , Demuxalot (refined), Demuxlet , ScSplit , Souporcell , and Vireo ) demonstrated higher ribosomal percentages. Some doublet detecting methods ( ScDblFinder , ScDblFinder with known doublets and Solo) demonstrated higher ribosomal percentages for the false doublets while other demonstrated lower ribosomal percentages ( DoubletDecon , DoubletDetection , and DoubletFinder ; Additional file 2 : Fig S11b and Additional file 1 : Table S6).
Like the ribosomal percentage, the mitochondrial percentage in false singlets is also relatively similar to correctly classified droplets for both demultiplexing (Additional file 2 : Fig S12a and Additional file 1 : Table S7) and doublet detecting methods (Additional file 2 : Fig S12b). The mitochondrial percentage for false doublets is statistically lower than the correctly classified droplets for a few larger pools for Freemuxlet , ScSplit , and Souporcell . The doublet detecting method Solo also demonstrates a small but significant decrease in mitochondrial percentage in the false doublets compared to the correctly annotated droplets. However, other doublet detecting methods including DoubletFinder and the larger pools of most other methods demonstrated a significant increase in mitochondrial percent in the false doublets compared to the correctly annotated droplets (Additional file 2 : Fig S12b).
Overall, these results demonstrate a strong relationship between the number of genes and UMIs and limited influence of ribosomal or mitochondrial percentage in a droplet and false classification, suggesting that the number of genes and UMIs can significantly bias singlet and doublet classification by demultiplexing and doublet detecting methods.
Ambient RNA, number of reads per cell, and uneven pooling impact method performance
To further quantify the variables that impact the performance of each method, we simulated four conditions that could occur with single-cell RNA-seq experiments: (1) decreased number of reads (reduced 50%), (2) increased ambient RNA (10%, 20% and 50%), (3) increased mitochondrial RNA (5%, 10% and 25%) and 4) uneven donor pooling from single donor spiking (0.5 or 0.75 proportion of pool from one donor). We chose these scenarios because they are common technical effects that can occur.
We observed a consistent decrease in the demultiplexing method performance when the number of reads were decreased by 50% but the degree of the effect varied for each method and was larger in pools containing more multiplexed donors (Additional file 2 : Fig S13a and Additional file 1 : Table S8). Decreasing the number of reads did not have a detectable impact on the performance of the doublet detecting methods.
Simulating additional ambient RNA (10%, 20%, or 50%) decreased the performance of all the demultiplexing methods (Additional file 2 : Fig S13b and Additional file 1 : Table S9) but some were unimpacted in pools that had 16 or fewer individuals multiplexed ( Souporcell and Vireo ). The performance of some of the doublet detecting methods were impacted by the ambient RNA but the performance of most methods did not decrease. Scrublet and ScDblFinder were the doublet detecting methods most impacted by ambient RNA but only in pools with at least 32 multiplexed donors (Additional file 2 : Fig S13b and Additional file 1 : Table S9).
Increased mitochondrial percent did not impact the performance of demultiplexing or doublet detecting methods (Additional file 2 : Fig S13c and Additional file 1 : Table S10).
We also tested whether experimental designs that pooling uneven proportions of donors would alter performance. We tested scenarios where either half the pool was composed of a single donor (0.5 spiked donor proportion) or where three quarters of the pool was composed of a single donor. This experimental design significantly reduced the demultiplexing method performance (Additional file 2 : Fig S13d and Additional file 1 : Table S11) with the smallest influence on Freemuxlet . The performance of most of the doublet detecting methods were unimpacted except for DoubletDetection that demonstrated significant decreases in performance in pools where at least 16 donors were multiplexed. Intriguingly, the performance of Solo increased with the spiked donor pools when the pools consisted of 16 donors or less.
Our results demonstrate significant differences in overall performance between different demultiplexing and doublet detecting methods. We further noticed some differences in the use of the methods. Therefore, we have accumulated these results and each method’s unique characteristics and benefits in a heatmap for visual interpretation (Fig. 4 ).
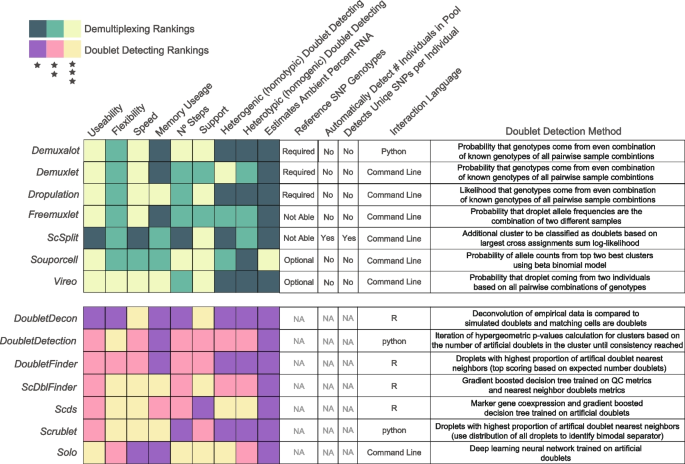
Assessment of each of the demultiplexing and doublet detecting methods. Assessments of a variety of metrics for each of the demultiplexing (top) and doublet detecting (bottom) methods
Framework for improving singlet classifications via method combinations
After identifying the demultiplexing and doublet detecting methods that performed well individually, we next sought to test whether using intersectional combinations of multiple methods would enhance droplet classifications and provide a software platform— Demuxafy —capable of supporting the execution of these intersectional combinations.
We recognise that different experimental designs will be required for each project. As such, we considered this when testing combinations of methods. We considered multiple experiment designs and two different intersectional methods: (1) more than half had to classify a droplet as a singlet to be called a singlet and (2) at least half of the methods had to classify a droplet as a singlet to be called a singlet. Significantly, these two intersectional methods only differ when an even number of methods are being considered. For combinations that include demultiplexing methods, the individual called by the majority of the methods is the individual used for that droplet. When ties occur, the individual is considered ‘unassigned’.
Combining multiple doublet detecting methods improve doublet removal for non-multiplexed experimental designs
For the non-multiplexed experimental design, we considered all possible method combinations (Additional file 1 : Table S12). We identified important differences depending on the number of droplets captured and have provided recommendations accordingly. We identified that DoubletFinder , Scrublet , ScDblFinder and Scds is the ideal combination for balanced droplet calling when less than 2,000 droplets are captured. Scds and ScDblFinder or Scrublet , Scds and ScDblFinder is the best combination when 2,000–10,000 droplets are captured. Scds , Scrublet, ScDblFinder and DoubletDetection is the best combination when 10,000–20,000 droplets are captured and Scrublet , Scds , DoubletDetection and ScDblFinder . It is important to note that even a slight increase in the MCC significantly impacts the number of true singlets and true doublets classified with the degree of benefit highly dependent on the original method performance. The combined method increases the MCC compared to individual doublet detecting methods on average by 0.11 and up to 0.33—a significant improvement in the MCC ( t -test FDR < 0.05 for 95% of comparisons). For all combinations, the intersectional droplet method requires more than half of the methods to consider the droplet a singlet to classify it as a singlet (Fig. 5 ).
Recommended Method Combinations Dependent on Experimental Design. Method combinations are provided for different experimental designs, including those that are not multiplexed (left) and multiplexed (right), including experiments that have reference SNP genotypes available vs those that do not and finally, multiplexed experiments with different numbers of individuals multiplexed. The each bar represents either a single method (shown with the coloured icon above the bar) or a combination of methods (shown with the addition of the methods and an arrow indicating the bar). The proportion of true singlets, true doublets, false singlets and false doublets for each method or combination of methods is shown with the filled barplot and the MCC is shown with the black points overlaid on the barplot. MCC: Matthew’s Correlation Coefficient
Demuxafy performs better than Chord
Chord is an ensemble machine learning doublet detecting method that uses Scds and DoubletFinder to identify doublets. We compared Demuxafy using Scds and DoubletFinder to Chord and identified that Demuxafy outperformed Chord in pools that contained at least eight donors and was equivalent in pools that contained less than eight donors (Additional file 2 : Fig S14). This is because Chord classifies more droplets as false singlets and false doublets than Demuxafy . In addition, Chord failed to complete for two of the pools that contained 128 multiplexed donors.
Combining multiple demultiplexing and doublet detecting methods improve doublet removal for multiplexed experimental designs
For experiments where 16 or fewer individuals are multiplexed with reference SNP genotypes available, we considered all possible combinations between the demultiplexing and doublet detecting methods except ScDblFinder with known doublets due to its highly similar performance to ScDblFinder (Fig 3 ; Additional file 1 : Table S13). The best combinations are DoubletFinder , Scds , ScDblFinder , Vireo and Demuxalot (refined) (<~5 donors) and Scrublet , ScDblFinder , DoubletDetection , Dropulation and Demuxalot (refined) (Fig. 5 ). These intersectional methods increase the MCC compared to the individual methods ( t -test FDR < 0.05), generally resulting in increased true singlets and doublets compared to the individual methods. The improvement in MCC depends on every single method’s performance but, on average, increases by 0.22 and up to 0.71. For experiments where the reference SNP genotypes are unknown, the individuals multiplexed in the pool with 16 or fewer individuals multiplexed, DoubletFinder , ScDblFinder, Souporcell and Vireo (<~5 donors) and Scds , ScDblFinder , DoubletDetection , Souporcell and Vireo are the ideal methods (Fig. 5 ). These intersectional methods again significantly increase the MCC up to 0.87 compared to any of the individual techniques that could be used for this experimental design ( t -test FDR < 0.05 for 94.2% of comparisons). In both cases, singlets should only be called if more than half of the methods in the combination classify the droplet as a singlet.
Combining multiple demultiplexing methods improves doublet removal for large multiplexed experimental designs
For experiments that multiplex more than 16 individuals, we considered the combinations between all demultiplexing methods (Additional file 1 : Table S14) since only a small proportion of the doublets would be undetectable by demultiplexing methods (droplets that are homogenic; Fig 3 b). To balance doublet removal and maintain true singlets, we recommend the combination of Demuxalot (refined) and Dropulation . These method combinations significantly increase the MCC by, on average, 0.09 compared to all the individual methods ( t -test FDR < 0.05). This substantially increases true singlets and true doublets relative to the individual methods. If reference SNP genotypes are not available for the individuals multiplexed in the pools, Vireo performs the best (≥ 16 multiplexed individuals; Fig. 5 ). This is the only scenario in which executing a single method is advantageous to a combination of methods. This is likely due to the fact that most of the methods perform poorly for larger pool sizes (Fig. 3 c).
These results collectively demonstrate that, regardless of the experimental design, demultiplexing and doublet detecting approaches that intersect multiple methods significantly enhance droplet classification. This is consistent across different pool sizes and will improve singlet annotation.
Demuxafy improves doublet removal and improves usability
To make our intersectional approaches accessible to other researchers, we have developed Demuxafy ( https://demultiplexing-doublet-detecting-docs.readthedocs.io/en/latest/index.html ) - an easy-to-use software platform powered by Singularity. This platform provides the requirements and instructions to execute each demultiplexing and doublet detecting methods. In addition, Demuxafy provides wrapper scripts that simplify method execution and effectively summarise results. We also offer tools that help estimate expected numbers of doublets and provide method combination recommendations based on scRNA-seq pool characteristics. Demuxafy also combines the results from multiple different methods, provides classification combination summaries, and provides final integrated combination classifications based on the intersectional techniques selected by the user. The significant advantages of Demuxafy include a centralised location to execute each of these methods, simplified ways to combine methods with an intersectional approach, and summary tables and figures that enable practical interpretation of multiplexed datasets (Fig. 1 a).
Demultiplexing and doublet detecting methods have made large-scale scRNA-seq experiments achievable. However, many demultiplexing and doublet detecting methods have been developed in the recent past, and it is unclear how their performances compare. Further, the demultiplexing techniques best detect heterogenic doublets while doublet detecting methods identify heterotypic doublets. Therefore, we hypothesised that demultiplexing and doublet detecting methods would be complementary and be more effective at removing doublets than demultiplexing methods alone.
Indeed, we demonstrated the benefit of utilising a combination of demultiplexing and doublet detecting methods. The optimal intersectional combination of methods depends on the experimental design and capture characteristics. Our results suggest super loaded captures—where a high percentage of doublets is expected—will benefit from multiplexing. Further, when many donors are multiplexed (>16), doublet detecting is not required as there are few doublets that are homogenic and heterotypic.
We have provided different method combination recommendations based on the experimental design. This decision is highly dependent on the research question.
Conclusions
Overall, our results provide researchers with important demultiplexing and doublet detecting performance assessments and combinatorial recommendations. Our software platform, Demuxafy ( https://demultiplexing-doublet-detecting-docs.readthedocs.io/en/latest/index.html ), provides a simple implementation of our methods in any research lab around the world, providing cleaner scRNA-seq datasets and enhancing interpretation of results.
PBMC scRNA-seq data
Blood samples were collected and processed as described previously [ 17 ]. Briefly, mononuclear cells were isolated from whole blood samples and stored in liquid nitrogen until thawed for scRNA-seq capture. Equal numbers of cells from 12 to 16 samples were multiplexed per pool and single-cell suspensions were super loaded on a Chromium Single Cell Chip A (10x Genomics) to capture 20,000 droplets per pool. Single-cell libraries were processed per manufacturer instructions and the 10× Genomics Cell Ranger Single Cell Software Suite (v 2.2.0) was used to process the data and map it to GRCh38. Cellbender v0.1.0 was used to identify empty droplets. Almost all droplets reported by Cell Ranger were identified to contain cells by Cellbender (mean: 99.97%). The quality control metrics of each pool are demonstrated in Additional file 2 : Fig S15.
PBMC DNA SNP genotyping
SNP genotype data were prepared as described previously [ 17 ]. Briefly, DNA was extracted from blood with the QIAamp Blood Mini kit and genotyped on the Illumina Infinium Global Screening Array. SNP genotypes were processed with Plink and GCTA before imputing on the Michigan Imputation Server using Eagle v2.3 for phasing and Minimac3 for imputation based on the Haplotype Reference Consortium panel (HRCr1.1). SNP genotypes were then lifted to hg38 and filtered for > 1% minor allele frequency (MAF) and an R 2 > 0.3.
Fibroblast scRNA-seq data
The fibroblast scRNA-seq data has been described previously [ 18 ]. Briefly, human skin punch biopsies from donors over the age of 18 were cultured in DMEM high glucose supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), L-glutamine, 100 U/mL penicillin and 100 μg/mL (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA).
For scRNA-seq, viable cells were flow sorted and single cell suspensions were loaded onto a 10× Genomics Single Cell 3’ Chip and were processed per 10× instructions and the Cell Ranger Single Cell Software Suite from 10× Genomics was used to process the sequencing data into transcript count tables as previously described [ 18 ]. Cellbender v0.1.0 was used to identify empty droplets. Almost all droplets reported by Cell Ranger were identified to contain cells by Cellbender (mean: 99.65%). The quality control metrics of each pool are demonstrated in Additional file 2 : Fig S16.
Fibroblast DNA SNP genotyping
The DNA SNP genotyping for fibroblast samples has been described previously [ 18 ]. Briefly, DNA from each donor was genotyped on an Infinium HumanCore-24 v1.1 BeadChip (Illumina). GenomeStudioTM V2.0 (Illumina), Plink and GenomeStudio were used to process the SNP genotypes. Eagle V2.3.5 was used to phase the SNPs and it was imputed with the Michigan Imputation server using minimac3 and the 1000 genome phase 3 reference panel as described previously [ 18 ].
Demultiplexing methods
All the demultiplexing methods were built and run from a singularity image.
Demuxalot [ 6 ] is a genotype reference-based single cell demultiplexing method. Demualot v0.2.0 was used in python v3.8.5 to annotate droplets. The likelihoods, posterior probabilities and most likely donor for each droplet were estimated using the Demuxalot Demultiplexer.predict_posteriors function. We also used Demuxalot Demultiplexer.learn_genotypes function to refine the genotypes before estimating the likelihoods, posterior probabilities and likely donor of each droplet with the refined genotypes as well.
The Popscle v0.1-beta suite [ 16 ] for population genomics in single cell data was used for Demuxlet and Freemuxlet demultiplexing methods. The popscle dsc-pileup function was used to create a pileup of variant calls at known genomic locations from aligned sequence reads in each droplet with default arguments.
Demuxlet [ 3 ] is a SNP genotype reference-based single cell demultiplexing method. Demuxlet was run with a genotype error coefficient of 1 and genotype error offset rate of 0.05 and the other default parameters using the popscle demuxlet command from Popscle (v0.1-beta).
Freemuxlet [ 16 ] is a SNP genotype reference-free single cell demultiplexing method. Freemuxlet was run with default parameters including the number of samples included in the pool using the popscle freemuxlet command from Popscle (v0.1-beta).
Dropulation
Dropulation [ 5 ] is a SNP genotype reference-based single cell demultiplexing method that is part of the Drop-seq software. Dropulation from Drop-seq v2.5.1 was implemented for this manuscript. In addition, the method for calling singlets and doublets was provided by the Dropulation developer and implemented in a custom R script available on Github and Zenodo (see “Availability of data and materials”).
ScSplit v1.0.7 [ 7 ] was downloaded from the ScSplit github and the recommended steps for data filtering quality control prior to running ScSplit were followed. Briefly, reads that had read quality lower than 10, were unmapped, were secondary alignments, did not pass filters, were optical PCR duplicates or were duplicate reads were removed. The resulting bam file was then sorted and indexed followed by freebayes to identify single nucleotide variants (SNVs) in the dataset. The resulting SNVs were filtered for quality scores greater than 30 and for variants present in the reference SNP genotype vcf. The resulting filtered bam and vcf files were used as input for the s cSplit count command with default settings to count the number of reference and alternative alleles in each droplet. Next the allele matrices were used to demultiplex the pool and assign cells to different clusters using the scSplit run command including the number of individuals ( -n ) option and all other options set to default. Finally, the individual genotypes were predicted for each cluster using the scSplit genotype command with default parameters.
Souporcell [ 4 ] is a SNP genotype reference-free single cell demultiplexing method. The Souporcell v1.0 singularity image was downloaded via instructions from the gihtub page. The Souporcell pipeline was run using the souporcell_pipeline.py script with default options and the option to include known variant locations ( --common_variants ).
Vireo [ 2 ] is a single cell demultiplexing method that can be used with reference SNP genotypes or without them. For this assessment, Vireo was used with reference SNP genotypes. Per Vireo recommendations, we used model 1 of the cellSNP [ 20 ] version 0.3.2 to make a pileup of SNPs for each droplet with the recommended options using the genotyped reference genotype file as the list of common known SNP and filtered with SNP locations that were covered by at least 20 UMIs and had at least 10% minor allele frequency across all droplets. Vireo version 0.4.2 was then used to demultiplex using reference SNP genotypes and indicating the number of individuals in the pools.
Doublet detecting methods
All doublet detecting methods were built and run from a singularity image.
DoubletDecon
DoubletDecon [ 9 ] is a transcription-based deconvolution method for identifying doublets. DoubletDecon version 1.1.6 analysis was run in R version 3.6.3. SCTransform [ 21 ] from Seurat [ 22 ] version 3.2.2 was used to preprocess the scRNA-seq data and then the Improved_Seurat_Pre_Process function was used to process the SCTransformed scRNA-seq data. Clusters were identified using Seurat function FindClusters with resolution 0.2 and 30 principal components (PCs). Then the Main_Doublet_Decon function was used to deconvolute doublets from singlets for six different rhops—0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9, 1.0 and 1.1. We used a range of rhop values since the doublet annotation by DoubletDecon is dependent on the rhop parameter which is selected by the user. The rhop that resulted in the closest number of doublets to the expected number of doublets was selected on a per-pool basis and used for all subsequent analysis. Expected number of doublets were estimated with the following equation:
where N is the number of droplets captured and D is the number of expected doublets.
DoubletDetection
DoubletDetection [ 14 ] is a transcription-based method for identifying doublets. DoubletDetection version 2.5.2 analysis was run in python version 3.6.8. Droplets without any UMIs were removed before analysis with DoubletDetection . Then the doubletdetection.BoostClassifier function was run with 50 iterations with use_phenograph set to False and standard_scaling set to True. The predicted number of doublets per iteration was visualised across all iterations and any pool that did not converge after 50 iterations, it was run again with increasing numbers of iterations until they reached convergence.
DoubletFinder
DoubletFinder [ 10 ] is a transcription-based doublet detecting method. DoubletFinder version 2.0.3 was implemented in R version 3.6.3. First, droplets that were more than 3 median absolute deviations (mad) away from the median for mitochondrial per cent, ribosomal per cent, number of UMIs or number of genes were removed per developer recommendations. Then the data was normalised with SCTransform followed by cluster identification using FindClusters with resolution 0.3 and 30 principal components (PCs). Then, pKs were selected by the pK that resulted in the largest BC MVN as recommended by DoubletFinder. The pK vs BC MVN relationship was visually inspected for each pool to ensure an effective BC MVN was selected for each pool. Finally, the homotypic doublet proportions were calculated and the number of expected doublets with the highest doublet proportion were classified as doublets per the following equation:
ScDblFinder
ScDblFinder [ 11 ] is a transcription-based method for detecting doublets from scRNA-seq data. ScDblFinder 1.3.25 was implemented in R version 4.0.3. ScDblFinder was implemented with two sets of options. The first included implementation with the expected doublet rate as calculated by:
where N is the number of droplets captured and R is the expected doublet rate. The second condition included the same expected number of doublets and included the doublets that had already been identified by all the demultiplexing methods.
Scds [ 12 ] is a transcription-based doublet detecting method. Scds version 1.1.2 analysis was completed in R version 3.6.3. Scds was implemented with the cxds function and bcds functions with default options followed by the cxds_bcds_hybrid with estNdbl set to TRUE so that doublets will be estimated based on the values from the cxds and bcds functions.
Scrublet [ 13 ] is a transcription-based doublet detecting method for single-cell RNA-seq data. Scrublet was implemented in python version 3.6.3. Scrublet was implemented per developer recommendations with at least 3 counts per droplet, 3 cells expressing a given gene, 30 PCs and a doublet rate based on the following equation:
where N is the number of droplets captured and R is the expected doublet rate. Four different minimum number of variable gene percentiles: 80, 85, 90 and 95. Then, the best variable gene percentile was selected based on the distribution of the simulated doublet scores and the location of the doublet threshold selection. In the case that the selected threshold does not fall between a bimodal distribution, those pools were run again with a manual threshold set.
Solo [ 15 ] is a transcription-based method for detecting doublets in scRNA-seq data. Solo was implemented with default parameters and an expected number of doublets based on the following equation:
where N is the number of droplets captured and D is the number of expected doublets. Solo was additionally implemented in a second run for each pool with the doublets that were identified by all the demultiplexing methods as known doublets to initialize the model.
In silico pool generation
Cells that were identified as singlets by all methods were used to simulate pools. Ten pools containing 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64 and 128 individuals were simulated assuming a maximum 20% doublet rate as it is unlikely researchers would use a technology that has a higher doublet rate. The donors for each simulated pool were randomly selected using a custom R script which is available on Github and Zenodo (see ‘Availability of data and materials’). A separate bam for the cell barcodes for each donor was generated using the filterbarcodes function from the sinto package (v0.8.4). Then, the GenerateSyntheticDoublets function provided by the Drop-seq [ 5 ] package was used to simulate new pools containing droplets with known singlets and doublets.
Twenty-one total pools—three pools from each of the different simulated pool sizes (2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64 and 128 individuals) —were used to simulate different experimental scenarios that may be more challenging for demultiplexing and doublet detecting methods. These include simulating higher ambient RNA, higher mitochondrial percent, decreased read coverage and imbalanced donor proportions as described subsequently.
High ambient RNA simulations
Ambient RNA was simulated by changing the barcodes and UMIs on a random selection of reads for 10, 20 or 50% of the total UMIs. This was executed with a custom R script that is available in Github and Zenodo (see ‘Availability of data and materials’).
High mitochondrial percent simulations
High mitochondrial percent simulations were produced by replacing reads in 5, 10 or 25% of the randomly selected cells with mitochondrial reads. The number of reads to replace was derived from a normal distribution with an average of 30 and a standard deviation of 3. This was executed with a custom R script available in Github and Zenodo (see ‘Availability of data and materials’).
Imbalanced donor simulations
We simulated pools that contained uneven proportions of the donors in the pools to identify if some methods are better at demultiplexing pools containing uneven proportions of each donor in the pool. We simulated pools where 50, 75 or 95% of the pool contained cells from a single donor and the remainder of the pool was even proportions of the remaining donors in the pool. This was executed with a custom R script available in Github and Zenodo (see ‘Availability of data and materials’).
Decrease read coverage simulations
Decreased read coverage of pools was simulated by down-sampling the reads by two-thirds of the original coverage.
Classification annotation
Demultiplexing methods classifications were considered correct if the droplet annotation (singlet or doublet) and the individual annotation was correct. If the droplet type was correct but the individual annotation was incorrect (i.e. classified as a singlet but annotated as the wrong individual), then the droplet was incorrectly classified.
Doublet detecting methods were considered to have correct classifications if the droplet annotation matched the known droplet type.
All downstream analyses were completed in R version 4.0.2.
Availability of data and materials
All data used in this manuscript is publicly available. The PBMC data is available on GEO (Accession: GSE196830) [ 23 ] as originally described in [ 17 ]. The fibroblast data is available on ArrayExpress (Accession Number: E-MTAB-10060) [ 24 ] and as originally described in [ 18 ]. The code used for the analyses in this manuscript are provided on Github ( https://github.com/powellgenomicslab/Demuxafy_manuscript/tree/v4 ) and Zenodo ( https://zenodo.org/records/10813452 ) under an MIT Open Source License [ 25 , 26 ]. Demuxafy is provided as a package with source code available on Github ( https://github.com/drneavin/Demultiplexing_Doublet_Detecting_Docs ) and instructions on ReadTheDocs ( https://demultiplexing-doublet-detecting-docs.readthedocs.io/en/latest/ ) under an MIT Open Source License [ 27 ]. Demuxafy is also available on Zenodo with the link https://zenodo.org/records/10870989 [ 28 ].
Zheng GXY, Terry JM, Belgrader P, Ryvkin P, Bent ZW, Wilson R, et al. Massively parallel digital transcriptional profiling of single cells. Nat Commun. 2017;8:1–12.
Article Google Scholar
Huang Y, McCarthy DJ, Stegle O. Vireo: Bayesian demultiplexing of pooled single-cell RNA-seq data without genotype reference. Genome Biol. 2019;20:273.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Kang HM, Subramaniam M, Targ S, Nguyen M, Maliskova L, McCarthy E, et al. Multiplexed droplet single-cell RNA-sequencing using natural genetic variation. Nat Biotechnol. 2018;36:89–94.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Heaton H, Talman AM, Knights A, Imaz M, Gaffney DJ, Durbin R, et al. Souporcell: robust clustering of single-cell RNA-seq data by genotype without reference genotypes. Nat Methods. 2020;17:615–20.
Wells MF, Nemesh J, Ghosh S, Mitchell JM, Salick MR, Mello CJ, et al. Natural variation in gene expression and viral susceptibility revealed by neural progenitor cell villages. Cell Stem Cell. 2023;30:312–332.e13.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Rogozhnikov A, Ramkumar P, Shah K, Bedi R, Kato S, Escola GS. Demuxalot: scaled up genetic demultiplexing for single-cell sequencing. bioRxiv. 2021;2021.05.22.443646.
Xu J, Falconer C, Nguyen Q, Crawford J, McKinnon BD, Mortlock S, et al. Genotype-free demultiplexing of pooled single-cell RNA-seq. Genome Biol. 2019;20:290.
What is the maximum number of cells that can be profiled?. Available from: https://kb.10xgenomics.com/hc/en-us/articles/360001378811-What-is-the-maximum-number-of-cells-that-can-be-profiled -
DePasquale EAK, Schnell DJ, Van Camp PJ, Valiente-Alandí Í, Blaxall BC, Grimes HL, et al. DoubletDecon: deconvoluting doublets from single-cell RNA-sequencing data. Cell Rep. 2019;29:1718–1727.e8.
McGinnis CS, Murrow LM, Gartner ZJ. DoubletFinder: doublet detection in single-cell RNA sequencing data using artificial nearest neighbors. Cell Syst. 2019;8:329–337.e4.
Germain P-L, Lun A, Meixide CG, Macnair W, Robinson MD. Doublet identification in single-cell sequencing data. 2022;
Bais AS, Kostka D. Scds: Computational annotation of doublets in single-cell RNA sequencing data. Bioinformatics. 2020;36:1150–8.
Wolock SL, Lopez R, Klein AM. Scrublet: computational identification of cell doublets in single-cell transcriptomic data. Cell Syst. 2019;8:281–291.e9.
Shor, Jonathan. DoubletDetection. Available from: https://github.com/JonathanShor/DoubletDetection .
Bernstein NJ, Fong NL, Lam I, Roy MA, Hendrickson DG, Kelley DR. Solo: doublet identification in single-cell RNA-Seq via semi-supervised deep learning. Cell Syst. 2020;11:95–101.e5.
popscle. Available from: https://github.com/statgen/popscle .
Yazar S, Alquicira-Hernandez J, Wing K, Senabouth A, Gordon MG, Andersen S, et al. Single-cell eQTL mapping identifies cell type–specific genetic control of autoimmune disease. Science. 2022;376:eabf3041.
Neavin D, Nguyen Q, Daniszewski MS, Liang HH, Chiu HS, Senabouth A, et al. Single cell eQTL analysis identifies cell type-specific genetic control of gene expression in fibroblasts and reprogrammed induced pluripotent stem cells. Genome Biol. 2021;1–19.
Hao Y, Hao S, Andersen-Nissen E, Mauck WM, Zheng S, Butler A, et al. Integrated analysis of multimodal single-cell data. Cell. 2021;184:3573–3587.e29.
Huang X, Huang Y. Cellsnp-lite: an efficient tool for genotyping single cells. bioRxiv. 2021;2020.12.31.424913.
Hafemeister C, Satija R. Normalization and variance stabilization of single-cell RNA-seq data using regularized negative binomial regression. bioRxiv. 2019;576827.
Stuart T, Butler A, Hoffman P, Hafemeister C, Papalexi E, Mauck WM, et al. Comprehensive integration of single-cell data. Cell. 2019;177:1888–1902.e21.
Powell JE. Single-cell eQTL mapping identifies cell type specific genetic control of autoimmune disease. Datasets. Gene Expression Omnibus. 2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE196830 .
Nguyen Q, Powell JE. scRNA-seq in 79 fibroblast cell lines and 31 reprogrammed induced pluripotent stem cell lines for sceQTL analysis. Datasets. ArrayExpress. 2021. https://www.ebi.ac.uk/biostudies/arrayexpress/studies/E-MTAB-10060?query=E-MTAB-10060 .
Neavin DR. Demuxafy analyses. Github. 2024. https://github.com/powellgenomicslab/Demuxafy_manuscript/tree/v4 .
Neavin DR. Demuxafy analyses. Zenodo. 2024. https://zenodo.org/records/10813452 .
Neavin D. Demuxafy. Github. 2024. https://github.com/drneavin/Demultiplexing_Doublet_Detecting_Docs .
Neavin D. Demuxafy. Zenodo. 2024. https://zenodo.org/records/10870989 .
McCaughey T, Liang HH, Chen C, Fenwick E, Rees G, Wong RCB, et al. An interactive multimedia approach to improving informed consent for induced pluripotent stem cell research. Cell Stem Cell. 2016;18:307–8.
Download references
Authors’ Twitter handles
Twitter handles: @drneavin (Drew Neavin), @thjimmylee (Jimmy Tsz Hang Lee), @marta_mele_m (Marta Melé)
Peer review information
Wenjing She was the primary editor of this article and managed its editorial process and peer review in collaboration with the rest of the editorial team.
Review history
The review history is available as Additional file 3 .
This work was funded by the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) Investigator grant (1175781), and funding from the Goodridge foundation. J.E.P is also supported by a fellowship from the Fok Foundation.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Garvan-Weizmann Centre for Cellular Genomics, Garvan Institute for Medical Research, Darlinghurst, NSW, Australia
Drew Neavin, Anne Senabouth, Himanshi Arora & Joseph E. Powell
Present address: Statewide Genomics at NSW Health Pathology, Sydney, NSW, Australia
Himanshi Arora
Wellcome Sanger Institute, Wellcome Genome Campus, Hinxton, UK
Jimmy Tsz Hang Lee
Life Sciences Department, Barcelona Supercomputing Center, Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain
Aida Ripoll-Cladellas & Marta Melé
Department of Genetics, University of Groningen, University Medical Center Groningen, Groningen, The Netherlands
Lude Franke
Spatial and Single Cell Systems Domain, Genome Institute of Singapore (GIS), Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR), Singapore, Republic of Singapore
Shyam Prabhakar
Population and Global Health, Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, Republic of Singapore
Cancer Science Institute of Singapore, National University of Singapore, Singapore, Republic of Singapore
Bakar Institute for Computational Health Sciences, University of California, San Francisco, CA, USA
Chun Jimmie Ye
Institute for Human Genetics, University of California, San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, USA
Division of Rheumatology, Department of Medicine, University of California, San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, USA
Chan Zuckerberg Biohub, San Francisco, CA, USA
Bioinformatics and Cellular Genomics, St Vincent’s Institute of Medical Research, Fitzroy, Australia
Davis J. McCarthy
Melbourne Integrative Genomics, School of BioSciences–School of Mathematics & Statistics, Faculty of Science, University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia
Present address: The Gene Lay Institute of Immunology and Inflammation, Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
Martin Hemberg
UNSW Cellular Genomics Futures Institute, University of New South Wales, Kensington, NSW, Australia
Joseph E. Powell
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
sc-eQTLGen Consortium
Contributions.
DRN and JEP conceived the project idea and study design. JTHL, AR, LF, SP, CJY, DJM, MM and MH provided feedback on experimental design. DRN carried out analyses with support on coding from AS. JTHL and AR tested Demuxafy and provided feedback. DRN and JEP wrote the manuscript. All authors reviewed and provided feedback on the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Drew Neavin or Joseph E. Powell .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Briefly, all work was approved by the Royal Hobart Hospital, the Hobart Eye Surgeons Clinic, Human Research Ethics Committees of the Royal Victorian Eye and Ear Hospital (11/1031), University of Melbourne (1545394) and University of Tasmania (H0014124) in accordance with the requirements of the National Health & Medical Research Council of Australia (NHMRC) and conformed with the Declaration of Helsinki [ 29 ].
Consent for publication
No personal data for any individual requiring consent for publication was included in this manuscript.
Competing interests
C.J.Y. is founder for and holds equity in DropPrint Genomics (now ImmunAI) and Survey Genomics, a Scientific Advisory Board member for and holds equity in Related Sciences and ImmunAI, a consultant for and holds equity in Maze Therapeutics, and a consultant for TReX Bio, HiBio, ImYoo, and Santa Ana. Additionally, C.J.Y is also newly an Innovation Investigator for the Arc Institute. C.J.Y. has received research support from Chan Zuckerberg Initiative, Chan Zuckerberg Biohub, Genentech, BioLegend, ScaleBio and Illumina.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: supplementary tables and legends., additional file 2: supplementary figures and legends., additional file 3..
Review history.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Neavin, D., Senabouth, A., Arora, H. et al. Demuxafy : improvement in droplet assignment by integrating multiple single-cell demultiplexing and doublet detection methods. Genome Biol 25 , 94 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-024-03224-8
Download citation
Received : 07 March 2023
Accepted : 25 March 2024
Published : 15 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-024-03224-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Single-cell analysis
- Genetic demultiplexing
- Doublet detecting
Genome Biology
ISSN: 1474-760X
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Recognizing comparison/contrast in assignments. Some assignments use words—like compare, contrast, similarities, and differences—that make it easy for you to see that they are asking you to compare and/or contrast. Here are a few hypothetical examples: Compare and contrast Frye's and Bartky's accounts of oppression.
Use transitional words when writing a compare-contrast assignment to show the relationship between your ideas and to connect your main points. Transitional Words showing Comparison: in comparison. in the same way. comparably. equally. equivalently. in a similar manner. likewise.
Teaching with this printout. When assigning a compare and contrast writing assignment, students need to be aware of what makes an outstanding written work. This rubric is a great tool to show students what is expected of them in a concrete way. Additionally, this rubric will help teachers assess this student writing and inform further instruction.
Making effective comparisons. As the name suggests, comparing and contrasting is about identifying both similarities and differences. You might focus on contrasting quite different subjects or comparing subjects with a lot in common—but there must be some grounds for comparison in the first place. For example, you might contrast French ...
Matt Ellis. Updated on June 2, 2022 Students. A compare-and-contrast essay is a style of essay that points out the similarities and differences between two or more subjects. It's ideal for showing what separates and unites related things or concepts, particularly if the subjects are often confused for each other or unjustly lumped together.
Use Clear Transitions. Transitions are important in compare and contrast essays, where you will be moving frequently between different topics or perspectives. Examples of transitions and phrases for comparisons: as well, similar to, consistent with, likewise, too. Examples of transitions and phrases for contrasts: on the other hand, however ...
A good compare/contrast essay doesn't only point out how the subjects are similar or different (or even both!). ... In middle school and high school, the standard format for essays is often the "5-paragraph form," with an introduction, 3 body paragraphs, and a conclusion. ... However, if the assignment or your teacher doesn't mention it ...
Compare and contrast essays examine topics from multiple viewpoints. This kind of essay, often assigned in middle school and high school, teaches students about the analytical writing process and prepares them for more advanced forms of academic writing. Compare and contrast essays are relatively easy to write if you follow a simple step-by-step approach.
In this episode of Let's Learn GA!, high school English teacher Dana Cole discusses different structures on writing compare and contrast essays. ... Essay Structure for Compare and Contrast - High School From Let's Learn GA! - Model Lessons, English Language Arts. Essay Structure for Compare and Contrast - High School ...
Students need to take notes, develop arguments and craft an effective outline to succeed at the compare-and-contrast essay assignment. MENU. Menu ... Compare-and-contrast essay assignments are so common in high school and college that they seem fairly obvious and easy to write at first glance. But students don't always have an intuitive grasp ...
Step 1. Discuss practical reasons for comparing and contrasting. Discuss reasons for learning to write about similarities and differences. Selecting subjects that matter to students is critical for this step. For example, one might be to compare two models of cars and then write a letter to a benefactor who might buy them one.
Learning to read vs. learning to write. The importance of any two school subjects. Wearing glasses vs. having braces. You and your best friend. Friendship vs. romantic love. Group work and individual work. Only child vs. having siblings. Nature vs. nurture. Anxiety and depression.
Compare and Contrast Essay Topics for High School Students. When writing essays for high school, it is good to keep them informative. Have a look at these compare and contrast sample topics. Highschool Life Vs. College Life; Paying College Fees Vs. Being Awarded a Scholarship; All Night Study Sessions Vs. Late Night Parties; Teenager Vs.
COMPARE AND CONTRAST The Writing Centre Department of English 1 Comparison Emphasizes the similarities between two things, ideas, concepts, or points of view. Contrast ... assignment. In high school, however, an assignment is worth only 5% to 20% of a student's final grade. In college, an assignment is worth 25% or as much as 50% of a student ...
Comparing and Contrasting. This tutorial will give you some guidelines and practice for organizing an essay by comparing— explaining the similarities between things—and/or contrasting— explaining the differences. Although you may not have received an essay assignment that specifically asks you to compare and/or contrast two or more things ...
Here are some tips, with student examples to illustrate each. 1. Make sure you're focusing on a manageable theme or idea. One of the first ways to get on the wrong track in writing a comparative ...
Compare and contrast essays don't have to be dull and tedious! Homeschool high school students will be sure to enjoy a few of this week's lighthearted topics.. Help teens stay focused with a four-paragraph outline: introduction, similarities, differences, and conclusion.Motivated writers may need two paragraphs for the comparisons or two paragraphs for the contrasts, and that's fine, too!
Recycling vs. Landfill. Motorcycle vs. Bicycle. Halogen vs. Incandescent. Newton vs. Einstein. Go on vacation vs. Staycation. Rock vs. Scissors. Cite this Article. These compare and contrast essay topics provide teachers and students with great and fun ideas for home and class work.
This collection of activity sheets will teach your students how to compare and contrast ideas, stories, and statements. In addition to evaluating whole works, your students will learn which words are used to signal either a comparison or a contrast. Answer keys are provided. Project Idea: Have your students pull similar item descriptions from ...
Recognizing comparison/contrast in assignments. Some assignments use words—like compare, contrast, similarities, and differences—that make it easy for you to see that they are asking you to compare and/or contrast. Here are a few hypothetical examples: Compare and contrast Frye's and Bartky's accounts of oppression.
The ability to compare and contrast is critical for comprehending literary and informational texts—and for writing them. Learners practice this skill via compare and contrast worksheets, graphic organizers and Venn diagrams, paired texts, reading response sheets, close reading activities, and report writing. Scholastic Teachables—, lesson ...
Discuss the specific vocabulary associated with the compare/contrast genre. Familiarize students with key transition words. In a compare/contrast essay, writers use specific transition words or phrases to denote similarities and differences. Transition words, typically followed by a comma, are like bridges that provide a structure, convey sequence,
It is a time of change, growth, and newfound independence. High school life and university life are two distinct phases that offer unique experiences and challenges. This essay examines the differences between high school life and university life, exploring the shift from structured routines to autonomous decision-making, the academic demands ...
Recent innovations in single-cell RNA-sequencing (scRNA-seq) provide the technology to investigate biological questions at cellular resolution. Pooling cells from multiple individuals has become a common strategy, and droplets can subsequently be assigned to a specific individual by leveraging their inherent genetic differences. An implicit challenge with scRNA-seq is the occurrence of ...