AP Macroeconomics Practice Tests
The AP Macroeconomics Exam includes 60 multiple-choice questions and 3 free-response questions. See the table below:
If you are a mobile user, click here: Do AP Macroeconomics Practice Questions .

AP Macroeconomics Multiple-Choice Practice Tests
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test: Pacing Drills
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test: Basic Macroeconomics Concepts
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test: Aggregate Demand
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test: Fiscal Policy
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test: Deficits, Inflation, Unemployment
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test 1
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test 2
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test 3
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test 4
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test 5
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test: Fundamental Economic Issues
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test: The National Economic Accounts
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test: Inflation and Unemployment
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test: Aggregate Supply and Aggregate Demand
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test: Keynes' Remedy for the Great Depression
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test: Money and Banking
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test: Monetary Policy
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test: Economic Growth
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test: International Trade and Exchange
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test 6
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test 7
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test 8
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test 9
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test 10
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test: Fundamentals of Economic Analysis
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test: Demand, Supply, Market Equilibrium, and Welfare Analysis
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test: Macroeconomic Measures of Performance
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test: Consumption, Saving, Investment, and the Multiplier
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test: Fiscal Policy, Economic Growth, and Productivity
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test: Money, Banking, and Monetary Policy
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test: International Trade
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test 11
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test 12
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test 13
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test 14
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test 15
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test 16
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test 17
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test 18
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test 19
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test 20
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test 21
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test 22
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test 23
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test 24
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test 25
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test 26
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test 27
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Test 28
AP Macroeconomics Free-Response Practice Tests
- AP Macroeconomics Free-Response Practie Test 1
- AP Macroeconomics Free-Response Practie Test 2
- AP Macroeconomics Free-Response Practie Test 3
- AP Macroeconomics Free-Response Practie Test 4
- AP Macroeconomics Free-Response Practie Test 5
- AP Macroeconomics Free-Response Practie Test 6
- AP Macroeconomics Free-Response Practice Test 1
- AP Macroeconomics Free-Response Practice Test 2
- AP Macroeconomics Free-Response Practice Test 3
- AP Macroeconomics Free-Response Practice Test 4: The National Economic Accounts
- AP Macroeconomics Free-Response Practice Test 5: Inflation and Unemployment
- AP Macroeconomics Free-Response Practice Test 6: Money and Banking
- AP Macroeconomics Free-Response Practice Test 7: Monetary Theory
- AP Macroeconomics Free-Response Practice Test 8: Aggregate Supply and Aggregate Demand
AP Macroeconomics Flashcards
- AP Macroeconomics Flashcards Set 1
- AP Macroeconomics Flashcards Set 2
- AP Macroeconomics Flashcards Set 3
- AP Macroeconomics Flashcards Set 4
- AP Macroeconomics Flashcards Set 5
- AP Macroeconomics Flashcards Set 6
- AP Macroeconomics Flashcards Set 7
- AP Macroeconomics Flashcards Set 8
- AP Macroeconomics Flashcards Set 9
- AP Macroeconomics Flashcards Set 10
- AP Macroeconomics Flashcards Set 11
- AP Macroeconomics Flashcards Set 12
- AP Macroeconomics Flashcards Set 13
- AP Macroeconomics Flashcards Set 14
- AP Macroeconomics Flashcards Set 15
- AP Macroeconomics Flashcards Set 16
- AP Macroeconomics Flashcards Set 17
- AP Macroeconomics Flashcards Set 18
AP Macroeconomics Downloads
- More AP Macroeconomics Downloads

Tips for writing economics essays
Some tips for writing economics essays Includes how to answer the question, including right diagrams and evaluation – primarily designed for A Level students.
1. Understand the question
Make sure you understand the essential point of the question. If appropriate, you could try and rephrase the question into a simpler version.
For example:
Q. Examine the macroeconomic implications of a significant fall in UK House prices, combined with a simultaneous loosening of Monetary Policy.
In plain English.
- Discuss the effect of falling house prices on the economy
- Discuss the effect of falling interest rates (loose monetary policy) on economy
In effect, there are two distinct parts to this question. It is a valid response, to deal with each separately, before considering both together.
It helps to keep reminding yourself of the question as you answer. Sometimes candidates start off well, but towards the end forget what the question was. Bear in mind, failure to answer the question can lead to a very low mark.
2. Write in simple sentences
For clarity of thought, it is usually best for students to write short sentences. The main thing is to avoid combining too many ideas into one sentence. If you write in short sentences, it may sound a little stilted; but it is worth remembering that there are no extra marks for a Shakespearian grasp of English. (at least in Economics Exams)
Look at this response to a question:
Q. What is the impact of higher interest rates?
Higher interest rates increase the cost of borrowing. As a result, those with mortgages will have lower disposable income. Also, consumers have less incentive to borrow and spend on credit cards. Therefore consumption will be lower. This fall in consumption will cause a fall in Aggregate Demand and therefore lead to lower economic growth. A fall in AD will also reduce inflation.
I could have combined 1 or 2 sentences together, but here I wanted to show that short sentences can aid clarity of thought. Nothing is wasted in the above example.
Simple sentences help you to focus on one thing at once, which is another important tip.
3. Answer the question
Quite frequently, when marking economic essays, you see a candidate who has a reasonable knowledge of economics, but unfortunately does not answer the question. Therefore, as a result, they can get zero for a question. It may seem harsh, but if you don’t answer the question, the examiner can’t give any marks.
At the end of each paragraph you can ask yourself; how does this paragraph answer the question? If necessary, you can write a one-sentence summary, which directly answers the question. Don’t wait until the end of the essay to realise you have answered a different question.
Discuss the impact of Euro membership on UK fiscal and monetary policy?
Most students will have revised a question on: “The benefits and costs of the Euro. Therefore, as soon as they see the Euro in the title, they put down all their notes on the benefits and costs of the Euro. However, this question is quite specific; it only wishes to know the impact on fiscal and monetary policy.
The “joke” goes, put 10 economists in a room and you will get 11 different answers. Why? you may ask. The nature of economics is that quite often there is no “right” answer. It is important that we always consider other points of view, and discuss various different, potential outcomes. This is what we mean by evaluation.
Macro-evaluation
- Depends on the state of the economy – full capacity or recession?
- Time lags – it may take 18 months for interest rates to have an effect
- Depends on other variables in the economy . Higher investment could be offset by fall in consumer spending.
- The significance of factors . A fall in exports to the US is only a small proportion of UK AD. However, a recession in Europe is more significant because 50% of UK exports go to EU.
- Consider the impact on all macroeconomic objectives . For example, higher interest rates may reduce inflation, but what about economic growth, unemployment, current account and balance of payments?
- Consider both the supply and demand side . For example, expansionary fiscal policy can help to reduce demand-deficient unemployment, however, it will be ineffective in solving demand-side unemployment (e.g. structural unemployment)
Example question :
The effect of raising interest rates will reduce consumer spending.
- However , if confidence is high, higher interest rates may not actually discourage consumer spending.
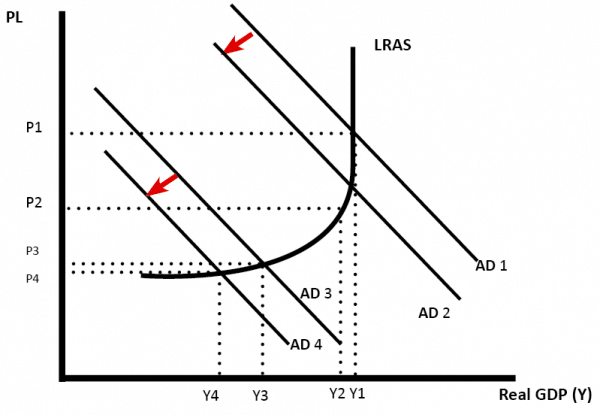
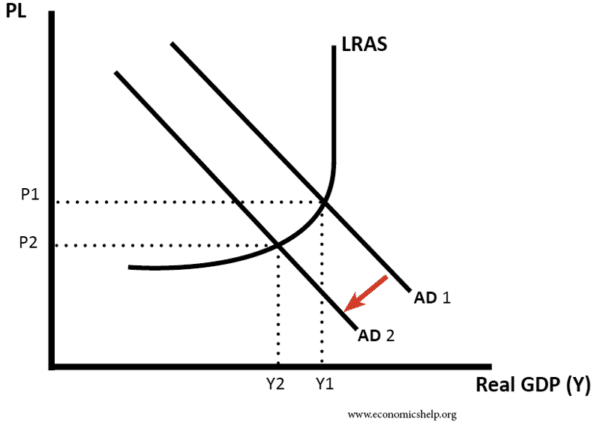
If the economy is close to full capacity a rise in interest rates may reduce inflation but not reduce growth. (AD falls from AD1 to AD2)
- However , if there is already a slowdown in the economy, rising interest rates may cause a recession. (AD3 to AD3)
Micro-evaluation
1. The impact depends on elasticity of demand
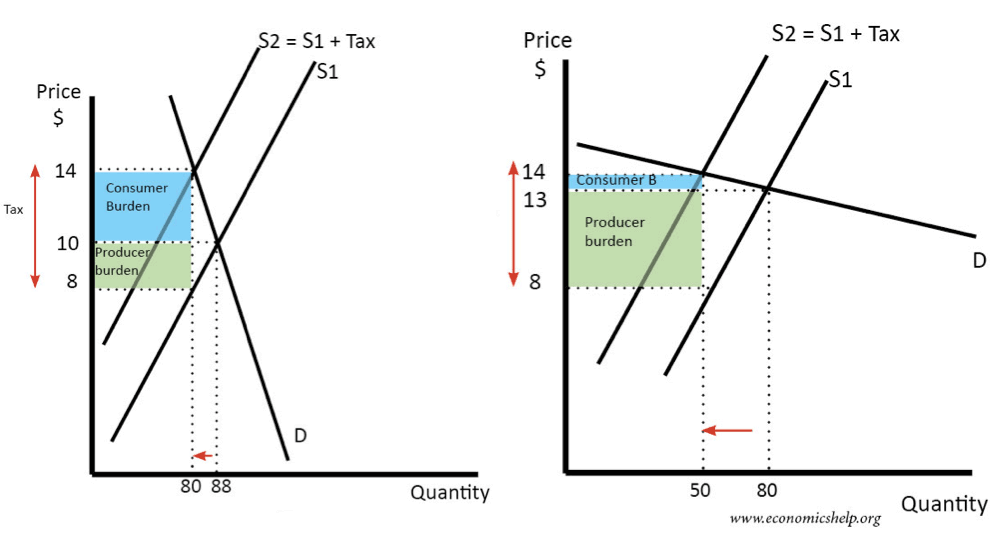
In both diagrams, we place the same tax on the good, causing supply to shift to the left.
- When demand is price inelastic, the tax causes only a small fall in demand.
- If demand is price elastic, the tax causes a bigger percentage fall in demand.
2. Time lag
In the short term, demand for petrol is likely to be price inelastic. However, over time, consumers may find alternatives, e.g. they buy electric cars. In the short-term, investment will not increase capacity, but over time, it may help to increase a firms profitability. Time lags.
3. Depends on market structure
If markets are competitive, then we can expect prices to remain low. However, if a firm has monopoly power, then we can expect higher prices.
4. Depends on business objectives
If a firm is seeking to maximise profits, we can expect prices to rise. However, if a firm is seeking to maximise market share, it may seek to cut prices – even if it means less profit.
5. Behavioural economics
In economics, we usually assume individuals are rational and seeking to maximise their utility. However, in the real world, people are subject to bias and may not meet expectations of classical economic theory. For example, the present-bias suggest consumers will give much higher weighting to present levels of happiness and ignore future costs. This may explain over-consumption of demerit goods and under-consumption of merit goods. See: behavioural economics

Exam tips for economics – Comprehensive e-book guide for just £5
8 thoughts on “Tips for writing economics essays”
I really want to know the difference between discussion questions and analysis questions and how to answer them in a correct way to get good credit in Economics
Analysis just involves one sided answers while Discussion questions involve using two points of view
This is a great lesson learnd by me
how can I actually manage my time
The evaluation points in this article are really useful! The thing I struggle with is analysis and application. I have all the knowledge and I have learnt the evaluation points like J-curve analysis and marshall learner condition, but my chains of reasoning are not good enough. I will try the shorter sentences recommended in this article.
What kind of method for costing analysis is most suitable for a craft brewery, in order to analyze the cost of production of different types of beer_
Really useful!Especially for the CIE exam papers
Does anyone know how to evaluate in those advantages/disadvantages essay questions where you would basically analyse the benefits of something and then evaluate? Struggling because wouldn’t the evaluation just be the disadvantages ?? Like how would you evaluate without just stating the disadvantage?
Leave a comment Cancel reply
AP Macroeconomics Practice Exams
Below you will find links to free AP Macroeconomics practice exams. Hundreds of free practice questions with detailed explanations. Start your exam prep right here!
Official 2012 Practice Test
Practice ap macro questions, khan academy, albert’s ap macroeconomics, varsity tutors, practice test, mankiw textbook quizzes, mcconnell textbook quizzes, flashcard review, exam review, vocabulary quiz.
AP Macroeconomics | Practice Exams | Free Response | Notes | Videos | Study Guides
Scarcity means human wants for goods and services exceed the available supply. Supply is limited because resources are limited. Demand, however, is virtually unlimited. Whatever the supply, it seems human nature to want more.
100 people / 10 people per ham = a maximum of 10 hams per month if all residents produce ham. Since consumption is limited by production, the maximum number of hams residents could consume per month is 10.
She is very productive at her consulting job, but not very productive growing vegetables. Time spent consulting would produce far more income than it what she could save growing her vegetables using the same amount of time. So on purely economic grounds, it makes more sense for her to maximize her income by applying her labor to what she does best (i.e. specialization of labor).
The engineer is better at computer science than at painting. Thus, his time is better spent working for pay at his job and paying a painter to paint his house. Of course, this assumes he does not paint his house for fun!
There are many physical systems that would work, for example, the study of planets (micro) in the solar system (macro), or solar systems (micro) in the galaxy (macro).
Draw a box outside the original circular flow to represent the foreign country. Draw an arrow from the foreign country to firms, to represents imports. Draw an arrow in the reverse direction representing payments for imports. Draw an arrow from firms to the foreign country to represent exports. Draw an arrow in the reverse direction to represent payments for imports.
There are many such problems. Consider the AIDS epidemic. Why are so few AIDS patients in Africa and Southeast Asia treated with the same drugs that are effective in the United States and Europe? It is because neither those patients nor the countries in which they live have the resources to purchase the same drugs.
Public enterprise means the factors of production (resources and businesses) are owned and operated by the government.
The United States is a large country economically speaking, so it has less need to trade internationally than the other countries mentioned. (This is the same reason that France and Italy have lower ratios than Belgium or Sweden.) One additional reason is that each of the other countries is a member of the European Union, where trade between members occurs without barriers to trade, like tariffs and quotas.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/principles-macroeconomics-2e/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Steven A. Greenlaw, David Shapiro
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Principles of Macroeconomics 2e
- Publication date: Oct 11, 2017
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/principles-macroeconomics-2e/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/principles-macroeconomics-2e/pages/chapter-1
© Jun 15, 2022 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
Live revision! Join us for our free exam revision livestreams Watch now →
Reference Library
Collections
- See what's new
- All Resources
- Student Resources
- Assessment Resources
- Teaching Resources
- CPD Courses
- Livestreams
Study notes, videos, interactive activities and more!
Economics news, insights and enrichment
Currated collections of free resources
Browse resources by topic
- All Economics Resources
Resource Selections
Currated lists of resources
Economics Revision Essay Plans
Last updated 17 Dec 2019
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share by Email
This series of resources provides revision essay plans for a wide variety of essay topics, including synoptic questions.
For the 2019 papers check out our collection of videos on building A* evaluation into your answers
Have you tried our series of more than 50 Quizlet revision activities? Click here to access!
Essay Plan: Limits on Monopoly Power
Topic Videos
Chains of Reasoning and Evaluation: Fuel Prices in the UK
Exam Support
EU Customs Union Membership (Revision Essay Plan)
Practice Exam Questions
Market for Electric Vehicles (Revision Essay Plan)
Mergers and consumer welfare (revision essay plan), air pollution and policies to control (revision essay plan), policies to improve competitiveness (revision essay plan), economic effects of higher interest rates (revision essay plan), current account deficit & policies (revision essay plan), unemployment and policy trade-offs (revision essay plan), case for cutting the national debt (revision essay plan), micro-finance (2019 revision update), essay on advertising and economic welfare, essay on oligopoly and collusion, policies to control inflation.
Study Notes
Why is high inflation a problem?
Revision essay: exchange rate depreciation and macroeconomic objectives, to what extent should full-employment be the main macro policy objective, housing supply (revision essay plan), minimum alcohol pricing (revision essay plan), oligopoly and collusion (revision essay plan), building confidence in writing synoptic 25 mark essays (edexcel), behavioural and neo-classical economics (revision essay plan), barriers to entry and economic profit (revision essay plan), micro and macro impact of a plastic tax (revision essay plan), edge revision webinar: market failure and government intervention, farm subsidies (revision essay plan), competitiveness of the uk motor industry (revision essay plan), labour migration (revision essay plan), financial market failure (revision essay plan), tariff on chinese steel (revision essay plan), policies to improve food affordability (revision essay plan), reducing a trade deficit (revision essay plan), museums and government subsidy (revision essay plan), fiscal policy and inequality (revision essay plan), globalisation and inequality (revision essay plan), economic inactivity (revision essay plan), competition and consumer welfare (essay technique video), essay plan: is the euro the main cause of the crisis in greece and italy, china: successes and failures essay plan, our subjects.
- › Criminology
- › Economics
- › Geography
- › Health & Social Care
- › Psychology
- › Sociology
- › Teaching & learning resources
- › Student revision workshops
- › Online student courses
- › CPD for teachers
- › Livestreams
- › Teaching jobs
Boston House, 214 High Street, Boston Spa, West Yorkshire, LS23 6AD Tel: 01937 848885
- › Contact us
- › Terms of use
- › Privacy & cookies
© 2002-2024 Tutor2u Limited. Company Reg no: 04489574. VAT reg no 816865400.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.

AP®︎/College Macroeconomics
Course: ap®︎/college macroeconomics > unit 1.
- Quiz 1 Basic economics concepts

A-Level Economics Model Answers (for Edexcel Past Papers)
Download A-Level Economics Model Answers for Edexcel past papers below for A2 and AS. These candidate responses were extracted from Edexcel exam board’s examiners’ reports and were graded by Edexcel examiners. All new specification Economics papers and their model answers are now available including Paper 1 (Microeconomics), Paper 2 (Macroeconomics) and Paper 3 (Synoptic).
Relevant resources: Download Edexcel A2 Economics past papers for students studying A2 Economics in their second year. Download Edexcel AS Economics past papers for students studying AS Economics in their first year. Visit our Edexcel Economics notes & questions by topic for practicing and revising certain areas of the course.
Economics Model Answers for A2 (Year 2)
Edexcel 2018 Economics A Paper 1 Model Answers Download
Edexcel 2018 Economics A Paper 2 Model Answers Download
Edexcel 2017 Economics A Paper 1 Model Answers Download
Edexcel 2017 Economics A Paper 2 Model Answers Download
Economics Model Answers for AS (Year 1)
Edexcel 2018 AS Economics A Paper 1 Model Answers Download
Edexcel 2017 AS Economics A Paper 1 Model Answers Download
Edexcel 2016 AS Economics A Paper 1 Model Answers Download
Need help with these Edexcel Economics past papers? Ask our Economics Tutor a free question or get a personalised 1 to 1 online lesson with us today. Alternatively, check out our Edexcel Economics revision notes to refresh your memory.
Other Resources
Looking for the full version of the Examiner Reports and more? You can find more Economics past papers and mark schemes on Edexcel’s resource page . Copyright for these examination papers belongs to their respective examination boards but not Qurious Education Ltd.
You may also like

AQA A-Level Economics Past Papers
Download A2 AQA Economics past papers for Paper 1 (Microeconomics), Paper 2 (Macroeconomics) and Paper 3 (Synoptic) from 2017 to 2019 below. […]

Economics A-Level Syllabus (Edexcel)
Please see the Economics A-Level syllabus and curriculum for the Edexcel exam board below, extracted directly from the Edexcel A-Level specification for […]

Phillips Curve Notes & Questions (A-Level, IB Economics)
Relevant Exam Boards: A-Level (Edexcel, OCR, AQA, Eduqas, WJEC), IB, IAL, CIE Edexcel Economics Notes Directory | AQA Economics Notes Directory | […]

Demand/Supply-side Policies Notes (A-Level, IB)
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Example 15 mark essay in style of IB Economics Paper 1
How should you structure a 15 mark question?
Because of multiple requests from students, I have created a 15 mark model answer in style of IB Economics paper 1.
This is based on the new IBDP Economics syllabus.
For 24 model answers to 15 mark paper 1 questions, check out the links below:
For more exam tips for IB Economics HL, check out the links below:
Question for model answer
Here is a practice question I have created:
Using real world examples, evaluate the effectiveness of contractionary monetary policy in reducing inflation (15 marks)
Brief essay plan
Here is a quick plan:
- Point 1: Effect of higher interest rates on consumption, investment and AD and hence inflation.
- Evaluation 1: But this depends on the importance of interest rate decisions for (consumption /) investment decisions.
- Point 2: Effect on exchange rates and net exports
- Evaluation 2: But depends on what happens to other interest rates around the world e.g. US rising rates.
- Point 3 (optional): Effect of quantitative tightening (opposite of quantitative easing) on investment and AD and hence inflation.
- Evaluation 3 (optional): But this depends on the level of spare capacity.
- Examples: UK interest rate rises / inflation, US interest rate rises, UK quantitative tightening.
Example model answer
Contractionary monetary policy includes raising interest rates and reversing quantitative easing. Interest rates are the cost of borrowing and the reward from saving. Interest rates are currently rising in the UK in response to high inflation.
Higher interest rates are likely to reduce aggregate demand. Interest rates increased from 0.25% to 3% in the UK over 2022. Higher interest rates increase the reward for saving, increasing the incentive to save. So saving increases and consumption falls. Higher interest rates increase the cost of borrowing, so consumers who borrow e.g. with a mortgage face higher bills and so are more likely to cut consumption. As a result of higher borrowing costs, firms are less likely to borrow to invest, which reduces investment. As consumption and investment are components of aggregate demand (AD=C+I+G+X-M), AD falls and shifts left from AD to AD1. There could also be a negative multiplier effect, where a one off fall in AD leads to a further fall in AD and real GDP, as shown by the shift left in AD from AD1 to AD2. This is because, for example, reduced investment means reduced profits for other firms, who cut workers’ wages. Workers then go on to cut their own consumer spending, reducing the incomes for local shop owners and so on. This means real GDP falls from Y to Y2 and there is a decrease in the price level from PL to PL2. This is likely to reduce the rate of inflation.

But this depends on the importance of interest rate changes for consumption and investment decisions. For example most mortgages in the UK are fixed rate mortgages rather than variable rate mortgages, with 82% of mortgage borrowing on fixed rates in the UK. Those on fixed rate mortgages may face less of an immediate increase in mortgage borrowing costs as interest rates rise, as the rates are likely to have been fixed in advance of the rate rise. Though many fixed rate mortgages may be short term, so these fixed rate mortgages are likely to be renewed with updated rates, with most mortgages expected to be renewed before 2025. While some mortgage holders may be protected in the short run, higher interest rates are likely to have a significant effect through mortgage costs.
A higher interest rate, relative to rates in other economies, leads to a higher rate of return on assets or savings in the UK. This leads to hot money flows into the UK economy. To buy UK assets or to put money in a UK bank, international investors are likely to need to convert currency into pounds. This increases demand for the currency, which shifts right from D to D1 leading to an appreciation of the pound from P to P1. This makes exports more expensive and imports cheaper, reducing export demand and increasing import demand. Provided the Marshall-Lerner condition holds, that the PED of exports and the PED of imports sum to 1 or more, this will result in reduced net exports, leading to lower AD as net exports is a component of AD. This will cause reduced real GDP and reduced employment because demand for workers is derived from demand for goods and services. Employment is most likely to fall particularly in industries that export heavily, such as gold, cars, airplanes, pharmaceuticals and oil – these exports account for nearly 28% of UK exports.

But this depends on what happens to other interest rates around the world. At the same time, we have also seen rising interest rates in the US, as the Federal Reserve central bank also tries to control inflation. This means there may be less of a difference in the US and UK rates of return, reducing the likelihood of significant hot money flows to the UK as a result of higher interest rates. Indeed we have seen increased strength of the US dollar relative to the pound in September 2022, which may have resulted from hot money flows into the US. So higher interest rates in the UK are unlikely to have a significant positive effect on net exports.
Quantitative tightening is the reverse of quantitative easing. Quantitative tightening means the central bank, for example the Bank of England, sells government bonds (that it had previously purchased with digitally created money). This increases the supply of government bonds, reducing their price and increasing their quantity. Reducing the bond price raises interest rates on government bonds. Bondholders such as commercial banks now receive a higher return on holding bonds relative to giving out loans. This means banks buy more bonds, leaving reduced cash available for lending, and so commercial banks reduce the supply of loanable funds, reducing the amount of total investment in the economy. This will reduce aggregate demand and hence inflation.The total value of assets under the quantitative easing scheme in the U.K. reached £895 billion. The Bank of England plans to engage in quantitative tightening of about £80 billion in 2023.
But this depends on the position of the economy on the Keynesian LRAS. If the economy has high spare capacity, then the economy is on the horizontal part of the Keynesian LRAS curve. This means a shift left in AD leads to a significant fall in real GDP and little change in inflation. The Bank of England currently judges there is little spare capacity in November 2022 but over the medium term weak demand is likely to mean higher spare capacity. So in the medium term quantitative tightening may have less of an effect on reducing inflation.
Overall contractionary monetary policy is likely to reduce inflation, reduce real GDP and reduce employment. While the direction of the effects is mostly clear, the magnitude is less clear. The most important effect is through the mortgage market, which is likely to be larger in the medium term rather than the short run as consumers renew their fixed mortgages. The effects of contractionary monetary policy also depend on the stance of fiscal policy. If fiscal policy is expansionary, e.g. increased government spending without higher taxes, then this may negate the effect of contractionary monetary policy on inflation. As interest rates rise in the UK, fiscal policy was briefly expansionary with announcements of tax cuts and spending on the energy support scheme, yet the fiscal policy has become less expansionary under Chancellor Jeremy Hunt, with tax rises for example on middle and higher earners announced. This means monetary policy is likely to be more effective in reducing inflation.
This answer features detailed analysis, with use of graphs.
There are real world examples throughout. Here I have mainly focussed on the UK example. But you can tailor your answer to another country.
For data on the UK economy, I recommend two sources: Trading Economics and the Bank of England’s monetary policy reports .
There is also evaluation and a solid conclusion.
There are also some definitions of key terms where relevant.
This answer would likely score full marks or close to it.
Other questions
How many words / how much time for a 15 mark question in ib economics paper 1.
The word count is somewhat arbitrary – it depends on how succinctly you can express ideas.
Given the time limits in the exam, most top 15 mark answers I observe reach a word count between 700 and 1100 words..
I recommend spending 45 minutes on the 15 mark question. I also recommend a quick plan in this time (just so you know the points, evaluation and example(s) you will use.
Note the timing and requirements may be different for questions in papers 2 and 3.
How should I structure a 15 marker for paper 1 IB?
- Introduction
- Point 1 (analysis and example)
- Evaluation 1
- Point 2 (analysis and example)
- Evaluation 2
- [Optional: third point and evaluation, depending on length of first two points].
How do you write conclusions in IB Economics?
There are a few key steps for conclusions:
- Pick a side / answer the question!
- Justify your decision.
- Bring in context.
- Bring in one other evaluative point on which your answer may depend.
What are the most common mistakes to avoid?
- Forgetting application – make sure to revise your real-world examples. Include your real world examples in your plan.
- Forgetting evaluation or not knowing the evaluation points to write . Practise the most common evaluation points. Here for example, spare capacity is a key evaluation point you can use for any AD shift.
- Analysis issues in particular graph sketching . Practise graphs so that you have the key graphs memorised. This includes supply and demand, cost and benefit, cost and revenue, AS-AD and tariff diagrams. Analysis issues are harder to solve – you have to understand the content well and practise key chains of analysis for each key area of the course.
- Poor conclusion . A poor conclusion may just summarise the arguments already made (adding no value). Alternatively it may not answer the question given. Remember to start with a decision on the question and justify it. I recommend practising using the conclusion framework above.
Related posts
For more resources on economics university applications or economics exam technique, check out the links below:
Latest posts
- 12 Practice Papers for A Level Economics 2024
- The economics of why people give gifts
- 11 Practice Questions in style of Edexcel Economics Paper 2
- What economic theory says about immigration
- 25 Practice Questions in style of Edexcel Economics Paper 1
About the author
Helping economics students online since 2015. Previously an economist and economics tutor, I now focus on providing economics resources on tfurber.com . Read more about me here .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Download free-response questions from past exams along with scoring guidelines, sample responses from exam takers, and scoring distributions. If you are using assistive technology and need help accessing these PDFs in another format, contact Services for Students with Disabilities at 212-713-8333 or by email at [email protected]. The ...
Questions Macroeconomics (with answers) ... Stephen Dobson and Susan Palfreman: Introduction to Economics, Oxford University Press, Oxford / New York 1999, ISBN 978--19-877565-2, pp. 207 to 234 1 Consumption, investment and saving (neither government nor foreign trade) A consumption function ( Questions 1.1 - 1.10) 50 10 Aggregate demand ...
There are from 10 to 40 questions in each pool. The exam on Blackboard will randomly select 2 or 3 questions from each pool for each question covered on an exam. The multiple-choice exam is an open book, open note exam which will be taken on-line outside of class time. The three midterm multiple-choice exams will consist of between 30 and 50 ...
SAMPLE EXAM QUESTIONS . Notes: - Many of these questions are drawn from past Econ 134 exams. - The instructions accompanying some of the questions take the form, "Decide whether the statement is true, false, or uncertain and explain why. Your explanation determines your grade; you will receive no credit for an answer without an explanation.
PRINCIPLES OF MACROECONOMICS. INSTRUCTOR: JAMES SONDGEROTH . For the essay and multiple choice parts of the exam, students will be allowed to use one sheet of paper (8.5 X 11) with handwritten notes on both sides of it. This information sheet must be turned in with the exam. Answers to the essay questions must be written in a Blue Book.
Humorous. Top 10 Reasons For Studying Economics. Inflation explained by Victor Borge. Funny Exam Answers. Humorous look at Subprime crisis. A collection of macro-economic essays on topics Inflation, Economic growth, government borrowing, balance of payments. Evaluation and critical analysis of all latest issues of the current day.
AP Macroeconomics Free-Response Practice Test 4: The National Economic Accounts. AP Macroeconomics Free-Response Practice Test 5: Inflation and Unemployment. AP Macroeconomics Free-Response Practice Test 6: Money and Banking. AP Macroeconomics Free-Response Practice Test 7: Monetary Theory.
You will only earn credit for what you write in the separate Free Response booklet. 1. Assume the United States economy is in short-run macroeconomic equilibrium at an output level greater than potential output. Draw a correctly labeled graph of the aggregate demand, short-run aggregate supply, and long-run aggregate supply curves, and show ...
Some tips for writing economics essays Includes how to answer the question, including right diagrams and evaluation - primarily designed for A Level students. 1. Understand the question. Make sure you understand the essential point of the question. If appropriate, you could try and rephrase the question into a simpler version.
GDP $550. (a) Draw a correctly labeled graph of the aggregate demand, short-run aggregate supply, and long-run aggregate supply curves, and show each of the following. (i) The current equilibrium real output and price level, labeled. Y 1 (ii) The full-employment output, labeled.
Nominal interest rate (↓) = Real interest rate + Inflation rate (↓) 2. fQuestion 3. a) 'In the long run, "money is neutral.". (ii) The long‐run aggregate supply curve is vertical. Changes in the supply of money affect nominal variables, but not real variables. b) Firms and workers often reach agreements under which nominal wages are.
Vocabulary Quiz. This AP Macro vocab quiz has a total of 275 terms to review. A very thorough review. | | | | |. Work through dozens of challening exam questions on these AP Macroeconomics practice tests. Includes AP Macro multiple choice and free response questions.
Introduction to Demand and Supply; 3.1 Demand, Supply, and Equilibrium in Markets for Goods and Services; 3.2 Shifts in Demand and Supply for Goods and Services; 3.3 Changes in Equilibrium Price and Quantity: The Four-Step Process; 3.4 Price Ceilings and Price Floors; 3.5 Demand, Supply, and Efficiency; Key Terms; Key Concepts and Summary; Self-Check Questions; Review Questions
QMACR1.DOC. Page 1 (of 2) 1 GDP and living standard. 08/06/2016. Value added. Calculate the value added, used for calculating GDP: Input goods 60. Output 230. Pollution due to the production process (estimated) 5. Investment.
Economics Revision Essay Plans. This series of resources provides revision essay plans for a wide variety of essay topics, including synoptic questions. For the 2019 papers check out our collection of videos on building A* evaluation into your answers. Have you tried our series of more than 50 Quizlet revision activities?
The AP Macroeconomics Exam includes two sections. The first section contains 60 multiple-choice questions. The second section is the free-response section, which includes one long question and two short questions. Below is a detailed breakdown of both the multiple choice and free-response sections. Starting with the 2023 exam, a four-function ...
Quiz 1. Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more. Khan Academy is a nonprofit with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere.
GCSE Economics. Our extensive collection of resources is the perfect tool for students aiming to ace their exams and for teachers seeking reliable resources to support their students' learning journey. Here, you'll find an array of revision notes, topic questions, fully explained model answers, past exam papers and more, meticulously organized ...
Free economics essay outlines and templates by topic. CIE and AQA economics model essays for A level, AS level, GCSE, IGCSE and O level. All questions are taken from past papers and Solutions are included. Relevant for years 10, 11, 12 and 13. Questions and answers are classified by topic.
PRINCIPLES OF MACROECONOMICS. INSTRUCTOR: JAMES SONDGEROTH . For the essay and multiple choice parts of the exam, students will be allowed to use one sheet of paper (8.5 X 11) with handwritten notes on both sides of it. This information sheet must be turned in with the exam. Answers to the essay questions must be written in a Blue Book.
Find step-by-step solutions and answers to Macroeconomics - 9781464119828, as well as thousands of textbooks so you can move forward with confidence. ... Questions for Review. Page 128: Problems and Applications. Page 132: More Problems and Applications. Exercise 1. Exercise 2. Exercise 3. Exercise 4. Exercise 5. Exercise 6. Exercise 7.
Download A-Level Economics Model Answers for Edexcel past papers below for A2 and AS. These candidate responses were extracted from Edexcel exam board's examiners' reports and were graded by Edexcel examiners. All new specification Economics papers and their model answers are now available including Paper 1 (Microeconomics), Paper 2 ...
Here is a quick plan: Point 1: Effect of higher interest rates on consumption, investment and AD and hence inflation. Evaluation 1: But this depends on the importance of interest rate decisions for (consumption /) investment decisions. Point 2: Effect on exchange rates and net exports. Evaluation 2: But depends on what happens to other interest ...