Home — Essay Samples — Education — Teaching Philosophy — My teaching philosophy

My Teaching Philosophy
- Categories: Teaching Philosophy
About this sample

Words: 673 |
Published: Mar 25, 2024
Words: 673 | Page: 1 | 4 min read
Teaching Philosophy: Fostering Lifelong Learning and Critical Thinking Skills

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Education

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 807 words
4 pages / 1847 words
1 pages / 624 words
7 pages / 3286 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Teaching Philosophy
In conclusion, with the possibility of sounding cliché, I must say that being a teacher is my calling. I love the idea of being the person that inspires young children (and not only) to be better and seek knowledge and success. [...]
Dewey, John. Democracy and Education: An Introduction to the Philosophy of Education. Free Press, 1997.
Philosophy, often considered an abstract and esoteric discipline, plays a crucial role in shaping society and individual beliefs. By exploring fundamental questions, major movements, ethical and moral dilemmas, and the nature of [...]
In the realm of education, fostering a strong and collaborative working relationship between teachers and parents is paramount to the holistic development of students. This essay explores various strategies that educators can [...]
There is a new crisis in modern society that has endured from skepticism about the legitimacy and importance of the discipline of philosophy itself when science can provide all the answers. Why should people even care about [...]
Teachers reflect on the year and often redesign and perfect their teaching strategies and plans. In essence, they get back to the basics of what they believe is the best way to inspire learning in their students. In other words, [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
4 Teaching Philosophy Statement Examples
ThoughtCo / J.R. Bee
- Becoming A Teacher
- Assessments & Tests
- Elementary Education
- Secondary Education
- Special Education
- Homeschooling
- M.S., Education, Buffalo State College
- B.S., Education, Buffalo State College
A teaching philosophy statement, or an educational philosophy statement, is a brief essay that nearly all prospective teachers must write when applying for an academic position. The statement generally reflects on the writer's teaching beliefs and includes concrete examples of how those beliefs have informed the writer's teaching practices.
A well-crafted teaching statement gives a clear and unique portrait of the writer as a teacher. Teaching philosophy statements are important because a clear teaching philosophy can lead to a change in teaching behavior and foster professional and personal growth. As a result, it can also be effective for practicing teachers to conceptualize their teaching approaches by writing a statement—even if they aren't applying for another teaching role.
Examples of Teaching Philosophy Statements
This passage is an example of a strong statement of teaching philosophy because it puts students at the front and center of the teacher's focus. An author who writes such a statement will likely always ensure student needs are the primary focus of all lessons and schoolwork.
"My philosophy of education is that all children are unique and must have a stimulating educational environment where they can grow physically, mentally, emotionally, and socially. It is my desire to create this type of atmosphere where students can meet their full potential. I will provide a safe environment where students are invited to share their ideas and take risks.
"I believe that there are five essential elements that are conducive to learning. (1) The teacher's role is to act as a guide. (2) Students must have access to hands-on activities. (3) Students should be able to have choices and let their curiosity direct their learning. (4) Students need the opportunity to practice skills in a safe environment. (5) Technology must be incorporated into the school day."
The following statement is a good example of a teaching philosophy because the author emphasizes that all classrooms and students are unique, with specific learning needs and styles. A teacher with this philosophy is likely to ensure they spend time helping each student achieve their highest potential.
"I believe that all children are unique and have something special that they can bring to their own education. I will assist my students to express themselves and accept themselves for who they are, as well embrace the differences of others.
"Every classroom has its own unique community; my role as the teacher will be to assist each child in developing their own potential and learning styles. I will present a curriculum that will incorporate each different learning style, as well as make the content relevant to the students' lives. I will incorporate hands-on learning, cooperative learning, projects, themes, and individual work to engage and activate students learning."
This statement provides a solid example because the author emphasizes the moral objective of teaching: She will hold each student to the highest expectations and ensure each one is diligent in their studies. This statement also implies the teacher will not give up on any student.
"I believe that a teacher is morally obligated to enter the classroom with only the highest of expectations for each and every one of her students. Thus, the teacher maximizes the positive benefits that naturally come along with any self-fulfilling prophecy. With dedication, perseverance, and hard work, her students will rise to the occasion."
"I aim to bring an open mind, a positive attitude, and high expectations to the classroom each day. I believe that I owe it to my students, as well as the community, to bring consistency, diligence, and warmth to my job in the hope that I can ultimately inspire and encourage such traits in the children as well."
The following statement takes a slightly different approach. It states that classrooms should be warm and caring communities, and unlike the first two sample statements, it focuses more on community-based learning, as opposed to an individualized approach. The teaching strategies mentioned, such as morning meetings and community problem-solving, follow this community-based philosophy.
"I believe that a classroom should be a safe, caring community where children are free to speak their mind, blossom, and grow. I will use strategies to ensure our classroom community will flourish, like the morning meeting, positive vs. negative discipline, classroom jobs, and problem-solving skills.
"Teaching is a process of learning from your students, colleagues, parents, and the community. This is a lifelong process where you learn new strategies, new ideas, and new philosophies. Over time, my educational philosophy may change, and that's okay. That just means that I have grown and learned new things."
Components of a Teaching Philosophy Statement
A teaching philosophy statement should include an introduction, body, and conclusion—just as you would expect of your students if they were writing a paper. But there are other specific components that you need to include:
Introduction: This should be your thesis statement where you discuss your general belief about education (such as: "I believe all students have a right to learn"), as well as your teaching ideals. Consider what students will have learned once they depart your class, and what those lessons learned say about your teaching philosophy and strategies.
Body: In this part of the statement, discuss what you see as the ideal classroom environment and how it makes you a better teacher, addresses student needs, and facilitates interactions between parents and their children. Discuss how you would facilitate age-appropriate learning and involve students in the assessment process . Explain how you would put your educational ideals into practice.
Clearly state your goals and objectives for students. Layout specifically what you hope your teaching will help students to accomplish. Be specific by telling a story or detailing a teaching strategy you've used. Doing so helps your reader understand how your teaching philosophy would play out in the classroom.
Conclusion : In this section, talk about your goals as a teacher, how you have been able to meet them in the past, and how you can build on them to meet future challenges. Focus on your personal approach to pedagogy and classroom management, as well as what makes you unique as an educator, and how you wish to advance your career.
Cite your sources. Explain where your teaching philosophy originated—for example, from your experiences as an undergraduate, from a faculty mentor you worked with during your teacher-training program, or perhaps from books or articles on teaching that had a particular influence on you.
Formatting Your Statement
There are some general rules to follow when writing a teaching philosophy statement.
Keep it brief. The statement should be no more than one-to-two pages, double-spaced.
Use present tense , and write the statement in the first person, as the previous examples illustrate.
Avoid jargon. Use common, everyday language, and not technical terms. If you must use jargon, explain what you're writing about in everyday terms as well.
Be personal. Make sure you talk about your experiences and beliefs, and ensure your statement is original and truly describes the methods and philosophy you would employ in teaching.
Vanderbilt University. " Teaching Statements ."
The Chronicle of Higher Education. " 4 Steps to a Memorable Teaching Philosophy ."
The Ohio State University. " Philosophy of Teaching Statement ."
- 10 Questions to Ask Yourself to Design Your Educational Philosophy
- How to Write a Philosophy of Education for Elementary Teachers
- Educational Philosophy Basics
- Top Tips for Acing a Teacher Interview
- How to Write a Homeschooling Philosophy Statement
- Student Welcome Letter
- Building a Classroom Community
- What is a Waldorf School?
- 5 Keys to Being a Successful Teacher
- 4 Tips for Effective Classroom Management
- Problems for Teachers That Limit Their Overall Effectiveness
- Teacher Interview Questions and Suggested Answers
- Medical School Personal Statement Examples and Analysis
- An Educational Leadership Philosophy for School Leaders
- Strategies for Teachers to Develop Positive Relationships With Students
- The Law School Applicant’s Guide to the Diversity Statement
- MyU : For Students, Faculty, and Staff
- Academic Leaders
- Faculty and Instructors
- Graduate Students and Postdocs
Center for Educational Innovation
- Campus and Collegiate Liaisons
- Pedagogical Innovations Journal Club
- Teaching Enrichment Series
- Recorded Webinars
- Video Series
- All Services
- Teaching Consultations
- Student Feedback Facilitation
- Instructional Media Production
- Curricular and Educational Initiative Consultations
- Educational Research and Evaluation
- Thank a Teacher
- All Teaching Resources
- Aligned Course Design
- Active Learning
- Team Projects
- Active Learning Classrooms
- Leveraging the Learning Sciences
- Inclusive Teaching at a Predominantly White Institution
- Strategies to Support Challenging Conversations in the Classroom
- Assessments
- Online Teaching and Design
- AI and ChatGPT in Teaching
- Documenting Growth in Teaching
- Early Term Feedback
- Scholarship of Teaching and Learning
- Writing Your Teaching Philosophy
- All Programs
- Assessment Deep Dive
- Designing and Delivering Online Learning
- Early Career Teaching and Learning Program
- International Teaching Assistant (ITA) Program
- Preparing Future Faculty Program
- Teaching with Access and Inclusion Program
- Teaching for Student Well-Being Program
- Teaching Assistant and Postdoc Professional Development Program
Your teaching philosophy is a self-reflective statement of your beliefs about teaching and learning. It's a one to two page narrative that conveys your core ideas about being an effective teacher in the context of your discipline. It develops these ideas with specific, concrete examples of what the teacher and learners will do to achieve those goals. Importantly, your teaching philosophy statement also explains why you choose these options.
+ Getting Started
Your reasons for writing a teaching philosophy may vary. You might be writing it as an exercise in concisely documenting your beliefs so that you can easily articulate them to your students, peers, or a search committee. It might serve as the introduction to your teaching portfolio. Or, it can serve as a means of professional growth as it requires you to give examples of how you enact your philosophy, thus requiring you to consider the degree to which your teaching is congruent with your beliefs.
Generating ideas
Teaching philosophies express your values and beliefs about teaching. They are personal statements that introduce you, as a teacher, to your reader. As such, they are written in the first person and convey a confident, professional tone. When writing a teaching philosophy, use specific examples to illustrate your points. You should also discuss how your values and beliefs about teaching fit into the context of your discipline.
Below are categories you might address with prompts to help you begin generating ideas. Work through each category, spending time thinking about the prompts and writing your ideas down. These notes will comprise the material you’ll use to write the first draft of your teaching philosophy statement. It will help if you include both general ideas (‘I endeavor to create lifelong learners’) as well as specifics about how you will enact those goals. A teaching philosophy template is also available to help you get started.
Questions to prompt your thinking
Your concept of learning.
What do you mean by learning? What happens in a successful learning situation? Note what constitutes "learning" or "mastery" in your discipline.
Your concept of teaching
What are your values, beliefs, and aspirations as a teacher? Do you wish to encourage mastery, competency, transformational learning, lifelong learning, general transference of skills, critical thinking? What does a perfect teaching situation look like to you and why? How are the values and beliefs realized in classroom activities? You may discuss course materials, lesson plans, activities, assignments, and assessment instruments.
Your goals for students
What skills should students obtain as a result of your teaching? Think about your ideal student and what the outcomes of your teaching would be in terms of this student's knowledge or behavior. Address the goals you have for specific classes or curricula and that rational behind them (i.e., critical thinking, writing, or problem solving).
Your teaching methods
What methods will you consider to reach these goals and objectives? What are your beliefs regarding learning theory and specific strategies you would use, such as case studies, group work, simulations, interactive lectures? You might also want to include any new ideas or strategies you want to try.
Your interaction with students
What are you attitudes towards advising and mentoring students? How would an observer see you interact with students? Why do you want to work with students?
Assessing learning
How will you assess student growth and learning? What are your beliefs about grading? Do you grade students on a percentage scale (criterion referenced) or on a curve (norm referenced)? What different types of assessment will you use (i.e. traditional tests, projects, portfolios, presentations) and why?
Professional growth
How will you continue growing as a teacher? What goals do you have for yourself and how will you reach them? How have your attitudes towards teaching and learning changed over time? How will you use student evaluations to improve your teaching? How might you learn new skills? How do you know when you've taught effectively?
+ Creating a Draft
Two ways of organizing your draft.
Now that you've written down your values, attitudes, and beliefs about teaching and learning, it's time to organize those thoughts into a coherent form. Perhaps the easiest way of organizing this material would be to write a paragraph covering each of the seven prompts you answered in the Getting Started section. These would then become the seven major sections of your teaching philosophy.
Another way of knitting your reflections together—and one that is more personal—is to read through your notes and underscore ideas or observations that come up more than once. Think of these as "themes" that might point you toward an organizational structure for the essay. For example, you read through your notes and realize that you spend a good deal of time writing about your interest in mentoring students. This might become one of the three or four major foci of your teaching philosophy. You should then discuss what it says about your attitudes toward teaching, learning, and what's important in your discipline.
No matter which style you choose, make sure to keep your writing succinct. Aim for two double-spaced pages. And don't forget to start with a "hook." Your job is to make your readers want to read more; their level of engagement is highest when they read your opening line. Hook your readers by beginning with a question, a statement, or even an event from your past.
Using specific examples
Remember to provide concrete examples from your teaching practice to illustrate the general claims you make in your teaching philosophy. The following general statements about teaching are intended as prompts to help you come up with examples to illustrate your claims about teaching. For each statement, how would you describe what happens in your classroom? Is your description specific enough to bring the scene to life in a teaching philosophy?
"I value helping my students understand difficult information. I am an expert, and my role is to model for them complex ways of thinking so that they can develop the same habits of mind as professionals in the medical field."
"I enjoy lecturing, and I'm good at it. I always make an effort to engage and motivate my students when I lecture."
"It is crucial for students of geology to learn the techniques of field research. An important part of my job as a professor of geology is to provide these opportunities."
"I believe that beginning physics students should be introduced to the principles of hypothesis generation, experimentation, data collection, and analysis. By learning the scientific method, they develop critical thinking skills they can apply to other areas of their lives. Small group work is a crucial tool for teaching the scientific method."
"As a teacher of writing, I am committed to using peer review in my classes. By reading and commenting on other students' work in small cooperative groups, my students learn to find their voice, to understand the important connection between writer and audience, and to hone their editing skills. Small group work is indispensible in the writing classroom."
Go back to the notes you made when getting started and underline the general statements you’ve made about teaching and learning. As you start drafting, make sure to note the specific approaches, methods, or products you use to realize those goals.
+ Assessing Your Draft
Assessing your draft teaching philosophy.
According to a survey of search committee chairs by the University of Michigan Center for Research on Learning and Teaching, there are five elements that are shared by strong teaching philosophy statements:
- They offer evidence of practice (specific examples)
- They are student-centered
- They demonstrate reflectiveness
- They demonstrate that the writer values teaching
- They are well written, clear, and readable
Now that you’ve completed an initial draft, ask whether your statement captures these elements and how well you articulate them.
You might find it useful to compare your draft to other teaching philosophies in your discipline. It can also be useful to have a colleague review your draft and offer recommendations for revision. Consider printing out a teaching philosophy rubric from our “Rubrics and Samples” tab to provide your reviewer with guidelines to assess your draft. These exercises will give you the critical distance necessary to see your teaching philosophy objectively and revise it accordingly.
+ Rubrics and Samples
Rubrics and sample teaching philosophies.
Here are links to three teaching philosophy rubrics to help you assess your statement. We have included four different rubrics for you to choose from. These rubrics cover similar elements, and one is not necessarily better than the other. Your choice of which to use should be guided by how comfortable you feel with the particular instrument and how usable you find it.
- Teaching Philosophy Rubric 1 This rubric allows a reader to rate several elements of persuasiveness and format on a scale of 1 to 5.
- Teaching Philosophy Rubric 2 This rubric contains prompts for assessing purpose and audience, voice, beliefs and support, and conventions.
- Teaching Philosophy Rubric 3 This rubric contains prompts for assessing content, format, and writing quality.
- Rubric for Statements of Teaching Philosophy This rubric was developed by Kaplan et. al. from the University of Michigan.
- Marisol Brito – philosophy
- Benjamin Harrison – biology
- Jamie Peterson – psychology
- The University of Michigan has a wide variety of samples organized by field of study.
- Caroline Hilk
- Research and Resources
- Why Use Active Learning?
- Successful Active Learning Implementation
- Addressing Active Learning Challenges
- Why Use Team Projects?
- Project Description Examples
- Project Description for Students
- Team Projects and Student Development Outcomes
- Forming Teams
- Team Output
- Individual Contributions to the Team
- Individual Student Understanding
- Supporting Students
- Wrapping up the Project
- Addressing Challenges
- Course Planning
- Working memory
- Retrieval of information
- Spaced practice
- Active learning
- Metacognition
- Definitions and PWI Focus
- A Flexible Framework
- Class Climate
- Course Content
- An Ongoing Endeavor
- Learn About Your Context
- Design Your Course to Support Challenging Conversations
- Design Your Challenging Conversations Class Session
- Use Effective Facilitation Strategies
- What to Do in a Challenging Moment
- Debrief and Reflect On Your Experience, and Try, Try Again
- Supplemental Resources
- Align Assessments
- Multiple Low Stakes Assessments
- Authentic Assessments
- Formative and Summative Assessments
- Varied Forms of Assessments
- Cumulative Assessments
- Equitable Assessments
- Essay Exams
- Multiple Choice Exams and Quizzes
- Academic Paper
- Skill Observation
- Alternative Assessments
- Assessment Plan
- Grade Assessments
- Prepare Students
- Reduce Student Anxiety
- SRT Scores: Interpreting & Responding
- Student Feedback Question Prompts
- Research Questions and Design
- Gathering data
- Publication
- GRAD 8101: Teaching in Higher Education
- Finding a Practicum Mentor
- GRAD 8200: Teaching for Learning
- Proficiency Rating & TA Eligibility
- Schedule a SETTA
- TAPD Webinars
What Is a Teaching Philosophy? Examples and Prompts

The life of a teacher is an extremely busy one. From early morning until long after dark, teachers dedicate the better part of their day to their students. Amid the lesson planning, the snack breaks, the recess duty, grading and the myriad other daily tasks, it can be easy to lose sight of the why of teaching.
Why are you drawn to the classroom, and what is it about your love of teaching that makes it a fulfilling career? What’s the overarching philosophy that guides your teaching practice? Even on the busiest school days, every teacher should be able to explain their “why” by returning to their teaching philosophy.
What Is a Teaching Philosophy Statement?
Teaching philosophy prompts, components of a teaching philosophy statement, formatting your teaching philosophy statement [plus best practices], teaching philosophy examples , faqs about teaching philosophies, helpful resource links.
Simply put, a teaching philosophy is a written statement that includes:
- Your core belief(s) about the purpose of teaching and learning
- A high-level description of how you teach
- An explanation of why you teach that way
- Any primary specializations
- Examples of your teaching philosophy in practice in the classroom (if space allows)
A teaching philosophy statement should demonstrate that you are purposeful, reflective and goal-oriented each time you stand at the front of your class. Not only does committing this statement to writing help to solidify your own beliefs — it can help you collaborate with other teachers, apply for jobs and even write grant proposals. Ideally, evidence of your philosophy will be apparent in your resume and portfolio content.
Depending on the context, a teaching philosophy statement can be several sentences or several pages long. You will occasionally be asked to provide some form of this statement when applying for certain academic or administrative positions. Versions of it may also appear as the introduction to your teaching portfolio, as your LinkedIn bio, your resume objective statement or your bio for any accreditations (such as for contributions to a publication, awards, volunteer work, etc.).
You will likely never be asked to recite it. That said, when sitting for interviews, teaching applicants should demonstrate a clear teaching philosophy through their answers.
Think about your teaching philosophy as your teaching portrait.
Portraits can look different depending on the subject’s age and life experiences, and a teaching philosophy is no different. Younger teachers may focus on their goals and any areas of interest they studied in college. More senior teachers may update their philosophy statements to reflect their lived experiences in the classroom and how those experiences informed (or resulted from) their teaching philosophy.
The clearer and more crystallized your teaching philosophy is, the easier it will be to draw upon it in the classroom. Use any combination of the following prompts — organized from immediate to future-facing — to begin writing your own philosophy statement.
The basics
Why did you decide to become a teacher?
What teaching methods do you use?
How do you assess your students’ learning and growth?
Do you follow certain standards?
What are your strongest qualities as a teacher?
Do you have an academic specialization?
Why do you like to teach certain subjects?
How do you use technology in the classroom ?
How do you incorporate new techniques, activities, curriculum and technology into your teaching?
Student advocacy
How do you motivate your students?
How do you think students learn best?
How do you approach learners who are struggling?
How do you promote and maintain educational equity ?
How would you describe your interactions with your students?
Preservation in the classroom
What’s your classroom management style ?
How do you handle stress ?
Describe a time you handled a challenging situation.
The Big Questions
How do you define learning?
How do you define teaching?
What is the purpose of education?
How does education improve society?
Do you believe all students can learn?
What does it take to be a good teacher?
Looking ahead
What goals do you have for your students?
What goals do you have for yourself?
What achievements do you like to see at the end of every school year?
Why do you continue to want to teach?
How will you continue to grow professionally?
Just like leading students through an essay prompt, begin by creating an outline around a single thesis statement. Build a case for your core belief by giving specific examples and demonstrating an in-depth knowledge of pedagogy. Be sure to connect philosophical statements to practical outcomes or examples; otherwise, you risk the “word salad” problem, wherein the statement sounds nice but means very little to the average reader. (See Formatting Your Teaching Philosophy Statement [Plus Best Practices] below for more tips.)
>>Related Reading: 5 Reasons Why Continuing Education Matters for Educators
Be prepared for your philosophy to change over time — it’s not meant to live in stone! If you feel you need to re-write it, follow the prompts above to recrystallize your beliefs and objectives.
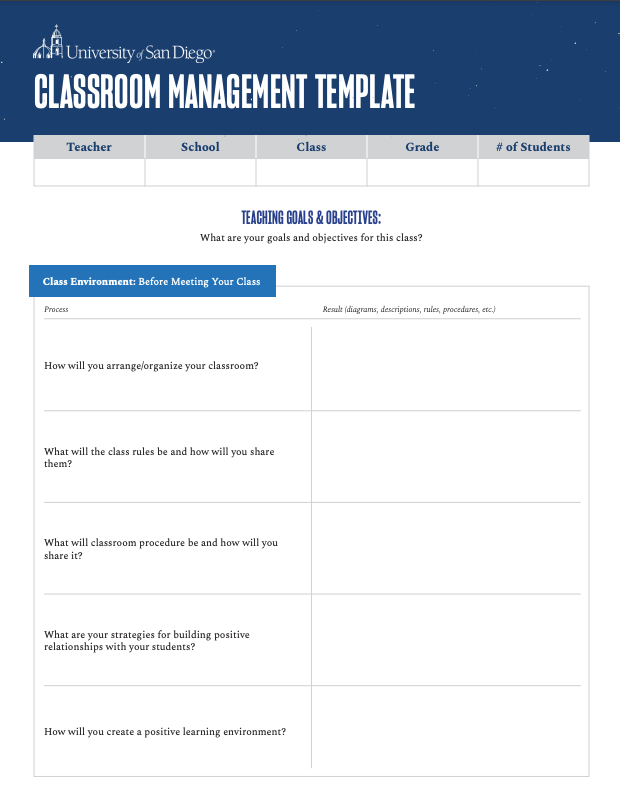
CLASSROOM MANAGEMENT TEMPLATE [FREE TEACHING TOOL]
Use our handy 3-page Classroom Management Template to create a plan for everything that goes into successfully operating a classroom.
In a one- or two-sentence teaching philosophy statement, you’ll likely touch on your experience, grade and subject specialization, preferred methods and high-level goals. When crafting a longer statement, it should contain some specific components that paint the clearest picture of your teaching style.
According to the University of Minnesota , strong teaching philosophy statements share the following elements:
- Offer evidence of practice (specific examples)
- Are student-centered
- Demonstrate reflectiveness
- Demonstrate that the writer values teaching
- Are well written, clear and readable
Long-form teaching philosophy statements should follow the same tried-and-true format as a well-crafted student essay:
Introduction
This first section should include mention of:
- Your teaching methods
- Any subject or pedagogical specialties
- Your preferred method of assessment
- Your high-level goals for all students
As you go into more detail about your experience and teaching practice, it’s a good idea to give examples that support your philosophy. If you choose to cite any educational researchers or studies, be sure you credit your sources. You may want to touch upon:
- A list of courses you have taught
- A list or short descriptions of effective learning engagements
- What you consider the ideal classroom environment
- Your personal approach to classroom management
- How you facilitate age-appropriate learning
- How you facilitate learning for students of differing abilities
- How you involve students in their own learning and assessment
- An example of a challenge you solved in the classroom
Conclusion
A good teacher is never done growing and learning. Wrap up your philosophy statement by describing your objectives, which should include student-oriented academic goals, professional development goals and the ideal outcomes of your teaching career. Your conclusion could include:
- content mastery
- discovery and knowledge generation
- critical thinking
- problem solving
- individual fulfillment
- self-directed learning
- experiential learning
- engaged citizenship
- …or something else?
- The goals you’ve already achieved as a teacher, as well as those in progress
- What makes you unique as an educator
If you are asked for supplemental materials as part of a teaching job application, you can provide:
- Peer reviews
- Letters of recommendation
- Students’ comments
- Performance ratings
- Lesson plans
- Teaching activities
Your teaching philosophy is unique to you, so there is no right or wrong way to go about it. That said, there are some best practices to follow when it comes to formatting and readability to make it easy for potential employers and others to read.
Write in the first person: You’re writing about your own goals, vision and philosophy — it’s okay to use “I” statements!
Write in the present tense: Your philosophy statement should reflect your current views and experience level, not those you hope to have someday.
Avoid wordiness: Your teaching philosophy should be easy enough for an eighth-grade reader to understand, barring any pedagogical terminology. Making simple concepts more complicated for show is an easy way to lose your reader. Unless you’re going for a university lecturer position, avoid the AP-level vocabulary words on principle.
Use specific examples: Potential employers — or readers of your academic papers — want to know how your philosophy plays out in the classroom. Your expertise in project-based learning (PBL) will carry more weight if you can describe a specific assignment you designed around PBL, and what the outcome was.
Skip the clichés: If you say you want to teach to “change the world,” or that you believe “children are our future,” be prepared to give concrete examples of what you mean. Teaching philosophies are not meant to be abstract or even overly aspirational — leave this to motivational posters.
If you find you are struggling to craft your ideal philosophy statement, ask a colleague to review and highlight possible areas for expansion or clarification. You can even ask this colleague to note any recurring themes they notice, so you can mention them briefly in your introduction. Compare your draft to others in your field with similar specialities or levels of experience and make changes as necessary.
The easiest way to maintain and share your philosophy statement and portfolio is to keep everything in a digital format. Whether that’s an editable PDF you can make small changes or updates to, or a cloud-based folder you can invite others to view, digital is the safest and most portable format.
Here are some examples of teaching philosophy statements from real teachers. Note that each statement will not follow all of the prompts above, but this is because each statement should be unique and personal to each educator.
“My philosophy of education is that all children are unique and must have a stimulating educational environment where they can grow mentally, emotionally, and socially. It is my desire to create this type of atmosphere where students can meet their full potential. I will provide a safe environment where students are invited to share their ideas and take risks. They should be able to have choices and let their curiosity direct their learning as I operate as a facilitator.” Mr. B., Language Arts, 5th & 6th grade
Do I need a teaching philosophy to get a teaching job?
Most teachers who earn master’s degrees are asked to write a philosophy statement as part of their program. Whether or not you have a master’s degree in education, you may be asked to provide some form of a teaching philosophy statement when applying for certain academic or administrative positions. You may also want to craft a version of this statement as the introduction to your teaching portfolio, as your LinkedIn bio, your resume objective statement or your bio for any accreditations (such as for contributions to a publication, awards, volunteer work, etc.).
You will likely never be asked to recite your teaching philosophy, and a lack of a formal written philosophy should not bar you from consideration for teaching jobs. That said, when sitting for interviews, teaching applicants should demonstrate a clear teaching philosophy through their answers.
Can I change my teaching philosophy?
Yes! In fact, teachers should expect their philosophy to change with time, experience, and professional and personal development. If at any point you feel you need to re-write your philosophy statement, follow the prompts in this article to recrystallize your beliefs and objectives.
Effective Classroom Management Solutions Certificate
Addressing topics like teaching positive social skills, diverse learners and restorative justice, this certificate helps current educators strengthen their overall classroom management approach.
Professional Teachers Program Series
A series of self-paced courses covering remote teaching, student anxiety, educational equity and homeschooling, all designed for the mid-career to veteran teacher.
Using Inquiry, Discussion, and Experience to Develop Critical Thinkers and Inspire Lifelong Learning
How can you authentically engage students while ensuring they receive the education they require? This course presents new ways to approach tired subjects, and capture students’ interest along the way.
Curriculum covered in this article
Educator Programs – 25% Off Teachers Appreciation Sale
Valid May 1, 2024 – May 31, 2024
Some restrictions apply. Offer valid only during sale dates. Not all courses apply. **Only one discount can be applied per course.**
Be Sure To Share This Article
- Share on Twitter
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Your Salary
Browse over 500+ educator courses and numerous certificates to enhance your curriculum and earn credit toward salary advancement.
My Teaching Philosophy Statement
This essay about a teaching philosophy emphasizes innovation, empathy, and empowerment as foundational elements for a dynamic learning environment. It advocates for active student participation, diversity, and the practical application of knowledge. The approach promotes critical thinking, a growth mindset, and meaningful feedback, aiming to develop lifelong learners and compassionate leaders. The philosophy embodies collaboration, inclusivity, and engagement with the wider world as key components.
How it works
In my educational approach, I blend the art of teaching with the science of inspiration, weaving together elements of innovation, empathy, and empowerment to create a dynamic tapestry of learning experiences where each student can truly flourish. Rather than simply delivering information, I see myself as a catalyst for intellectual and personal growth, igniting the flames of curiosity within each learner.
At the heart of my pedagogy lies a deep commitment to fostering student agency. I recognize that every student brings a rich diversity of backgrounds and perspectives to the classroom, and I strive to create an environment where they are active participants in their own educational journey.
Through collaborative projects, spirited discussions, and immersive activities, I aim to cultivate a culture of inquiry and exploration, where questions are celebrated and curiosity is nurtured.
Equally essential to my philosophy is the promotion of inclusivity and belonging. I firmly believe that diversity is not only a strength but a fundamental aspect of our humanity, and I work tirelessly to create a space where every voice is heard and every identity is respected. By fostering empathy, understanding, and open dialogue, I seek to build a community where students feel empowered to express themselves authentically and engage with one another in meaningful ways.
Moreover, I am deeply passionate about bridging the gap between theory and practice. I firmly believe that education should extend beyond the walls of the classroom, and I strive to integrate real-world relevance into my teachings. Whether through hands-on experiences, real-life case studies, or project-based learning, I aim to inspire students to see the connections between their studies and the world around them, motivating them to become proactive agents of change in their communities.
Furthermore, I am committed to nurturing critical thinking skills and fostering a growth mindset. In an age inundated with information, the ability to analyze, synthesize, and evaluate is more important than ever. Through thought-provoking discussions, challenging assignments, and opportunities for reflection, I aim to instill in my students a deep sense of intellectual curiosity and a willingness to explore new ideas, equipping them with the skills they need to thrive in an ever-changing world.
Finally, I believe in the transformative power of feedback and assessment as tools for growth and development. Rather than viewing assessment as a mere judgment, I see it as an opportunity for learning and improvement. By providing timely and constructive feedback, I empower my students to reflect on their progress, identify areas for growth, and set meaningful goals for their continued development.
In essence, my teaching philosophy is a mosaic of collaboration, inclusivity, relevance, critical thinking, and growth. By creating an environment where students are encouraged to take ownership of their learning, embrace diversity, and engage with the world around them, I hope to inspire a lifelong love of learning, compassionate leadership, and global citizenship.
Cite this page
My Teaching Philosophy Statement. (2024, Apr 29). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/my-teaching-philosophy-statement/
"My Teaching Philosophy Statement." PapersOwl.com , 29 Apr 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/my-teaching-philosophy-statement/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). My Teaching Philosophy Statement . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/my-teaching-philosophy-statement/ [Accessed: 18 May. 2024]
"My Teaching Philosophy Statement." PapersOwl.com, Apr 29, 2024. Accessed May 18, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/my-teaching-philosophy-statement/
"My Teaching Philosophy Statement," PapersOwl.com , 29-Apr-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/my-teaching-philosophy-statement/. [Accessed: 18-May-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). My Teaching Philosophy Statement . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/my-teaching-philosophy-statement/ [Accessed: 18-May-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
Win 10 Summer Reading Books from ThriftBooks 📚!
40 Philosophy of Education Examples, Plus How To Write Your Own
Learn how to define and share your teaching philosophy.

These days, it’s become common for educators to be asked what their personal teaching philosophy is. Whether it’s for a job interview, a college class, or to share with your principal, crafting a philosophy of education can seem like a daunting task. So set aside some time to consider your own teaching philosophy (we’ll walk you through it), and be sure to look at philosophy of education examples from others (we’ve got those too!).
What is a philosophy of education?
Before we dive into the examples, it’s important to understand the purpose of a philosophy of education. This statement will provide an explanation of your teaching values and beliefs. Your teaching philosophy is ultimately a combination of the methods you studied in college and any professional experiences you’ve learned from since. It incorporates your own experiences (negative or positive) in education.
Many teachers have two versions of their teaching philosophy: a long form (a page or so of text) and a short form. The longer form is useful for job application cover letters or to include as part of your teacher portfolio. The short form distills the longer philosophy into a couple of succinct sentences that you can use to answer teacher job interview questions or even share with parents.
What’s the best teaching philosophy?
Here’s one key thing to remember: There’s no one right answer to “What’s your teaching philosophy?” Every teacher’s will be a little bit different, depending on their own teaching style, experiences, and expectations. And many teachers find that their philosophies change over time, as they learn and grow in their careers.
When someone asks for your philosophy of education, what they really want to know is that you’ve given thought to how you prepare lessons and interact with students in and out of the classroom. They’re interested in finding out what you expect from your students and from yourself, and how you’ll apply those expectations. And they want to hear examples of how you put your teaching philosophy into action.
What’s included in strong teaching philosophy examples?
Depending on who you ask, a philosophy of education statement can include a variety of values, beliefs, and information. As you build your own teaching philosophy statement, consider these aspects, and write down your answers to the questions.
Purpose of Education (Core Beliefs)
What do you believe is the purpose of teaching and learning? Why does education matter to today’s children? How will time spent in your classroom help prepare them for the future?
Use your answers to draft the opening statement of your philosophy of education, like these:
- Education isn’t just about what students learn, but about learning how to learn.
- A good education prepares students to be productive and empathetic members of society.
- Teachers help students embrace new information and new ways of seeing the world around them.
- A strong education with a focus on fundamentals ensures students can take on any challenges that come their way.
- I believe education is key to empowering today’s youth, so they’ll feel confident in their future careers, relationships, and duties as members of their community.
- Well-educated students are open-minded, welcoming the opinions of others and knowing how to evaluate information critically and carefully.
Teaching Style and Practices
Do you believe in student-led learning, or do you like to use the Socratic method instead? Is your classroom a place for quiet concentration or sociable collaboration? Do you focus on play-based learning, hands-on practice, debate and discussion, problem-solving, or project-based learning? All teachers use a mix of teaching practices and styles, of course, but there are some you’re likely more comfortable with than others. Possible examples:
- I frequently use project-based learning in my classrooms because I believe it helps make learning more relevant to my students. When students work together to address real-world problems, they use their [subject] knowledge and skills and develop communication and critical thinking abilities too.
- Play-based learning is a big part of my teaching philosophy. Kids who learn through play have more authentic experiences, exploring and discovering the world naturally in ways that make the process more engaging and likely to make a lasting impact.
- In my classroom, technology is key. I believe in teaching students how to use today’s technology in responsible ways, embracing new possibilities and using technology as a tool, not a crutch.
- While I believe in trying new teaching methods, I also find that traditional learning activities can still be effective. My teaching is mainly a mix of lecture, Socratic seminar, and small-group discussions.
- I’m a big believer in formative assessment , taking every opportunity to measure my students’ understanding and progress. I use tools like exit tickets and Kahoot! quizzes, and watch my students closely to see if they’re engaged and on track.
- Group work and discussions play a major role in my instructional style. Students who learn to work cooperatively at a young age are better equipped to succeed in school, in their future careers, and in their communities.
Students and Learning Styles
Why is it important to recognize all learning styles? How do you accommodate different learning styles in your classroom? What are your beliefs on diversity, equity, and inclusion? How do you ensure every student in your classroom receives the same opportunities to learn? How do you expect students to behave, and how do you measure success?
Sample teaching philosophy statements about students might sound like this:
- Every student has their own unique talents, skills, challenges, and background. By getting to know my students as individuals, I can help them find the learning styles that work best for them, now and throughout their education.
- I find that motivated students learn best. They’re more engaged in the classroom and more diligent when working alone. I work to motivate students by making learning relevant, meaningful, and enjoyable.
- We must give every student equal opportunities to learn and grow. Not all students have the same support outside the classroom. So as a teacher, I try to help bridge gaps when I see them and give struggling students a chance to succeed academically.
- I believe every student has their own story and deserves a chance to create and share it. I encourage my students to approach learning as individuals, and I know I’m succeeding when they show a real interest in showing up and learning more every day.
- In my classroom, students take responsibility for their own success. I help them craft their own learning goals, then encourage them to evaluate their progress honestly and ask for help when they need it.
- To me, the best classrooms are those that are the most diverse. Students learn to recognize and respect each other’s differences, celebrating what each brings to the community. They also have the opportunity to find common ground, sometimes in ways that surprise them.
How do I write my philosophy of education?
Think back to any essay you’ve ever written and follow a similar format. Write in the present tense; your philosophy isn’t aspirational, it’s something you already live and follow. This is true even if you’re applying for your first teaching job. Your philosophy is informed by your student teaching, internships, and other teaching experiences.
Lead with your core beliefs about teaching and learning. These beliefs should be reflected throughout the rest of your teaching philosophy statement.
Then, explain your teaching style and practices, being sure to include concrete examples of how you put those practices into action. Transition into your beliefs about students and learning styles, with more examples. Explain why you believe in these teaching and learning styles, and how you’ve seen them work in your experiences.
A long-form philosophy of education statement usually takes a few paragraphs (not generally more than a page or two). From that long-form philosophy, highlight a few key statements and phrases and use them to sum up your teaching philosophy in a couple of well-crafted sentences for your short-form teaching philosophy.
Still feeling overwhelmed? Try answering these three key questions:
- Why do you teach?
- What are your favorite, tried-and-true methods for teaching and learning?
- How do you help students of all abilities and backgrounds learn?
If you can answer those three questions, you can write your teaching philosophy!
Short Philosophy of Education Examples
We asked real educators in the We Are Teachers HELPLINE group on Facebook to share their teaching philosophy examples in a few sentences . Here’s what they had to say:
I am always trying to turn my students into self-sufficient learners who use their resources to figure it out instead of resorting to just asking someone for the answers. —Amy J.

My philosophy is that all students can learn. Good educators meet all students’ differentiated learning needs to help all students meet their maximum learning potential. —Lisa B.
I believe that all students are unique and need a teacher that caters to their individual needs in a safe and stimulating environment. I want to create a classroom where students can flourish and explore to reach their full potential. My goal is also to create a warm, loving environment, so students feel safe to take risks and express themselves. —Valerie T.
In my classroom, I like to focus on the student-teacher relationships/one-on-one interactions. Flexibility is a must, and I’ve learned that you do the best you can with the students you have for however long you have them in your class. —Elizabeth Y
I want to prepare my students to be able to get along without me and take ownership of their learning. I have implemented a growth mindset. —Kirk H.
My teaching philosophy is centered around seeing the whole student and allowing the student to use their whole self to direct their own learning. As a secondary teacher, I also believe strongly in exposing all students to the same core content of my subject so that they have equal opportunities for careers and other experiences dependent upon that content in the future. —Jacky B.

All children learn best when learning is hands-on. This works for the high students and the low students too, even the ones in between. I teach by creating experiences, not giving information. —Jessica R.
As teachers, it’s our job to foster creativity. In order to do that, it’s important for me to embrace the mistakes of my students, create a learning environment that allows them to feel comfortable enough to take chances, and try new methods. —Chelsie L.
I believe that every child can learn and deserves the best, well-trained teacher possible who has high expectations for them. I differentiate all my lessons and include all learning modalities. —Amy S.
All students can learn and want to learn. It is my job to meet them where they are and move them forward. —Holli A.
I believe learning comes from making sense of chaos. My job is to design work that will allow students to process, explore, and discuss concepts to own the learning. I need to be part of the process to guide and challenge perceptions. —Shelly G.

I want my students to know that they are valued members of our classroom community, and I want to teach each of them what they need to continue to grow in my classroom. —Doreen G.
Teach to every child’s passion and encourage a joy for and love of education and school. —Iris B.
I believe in creating a classroom culture of learning through mistakes and overcoming obstacles through teamwork. —Jenn B.
It’s our job to introduce our kids to many, many different things and help them find what they excel in and what they don’t. Then nurture their excellence and help them figure out how to compensate for their problem areas. That way, they will become happy, successful adults. —Haley T.
Longer Philosophy of Education Examples
Looking for longer teaching philosophy examples? Check out these selections from experienced teachers of all ages and grades.
- Learning To Wear the Big Shoes: One Step at a Time
- Nellie Edge: My Kindergarten Teaching Philosophy
- Faculty Focus: My Philosophy of Teaching
- Robinson Elementary School: My Teaching Philosophy
- David Orace Kelly: Philosophy of Education
- Explorations in Higher Education: My Teaching Philosophy Statement
- University of Washington Medical School Faculty Teaching Philosophy Statements
Do you have any philosophy of education examples? Share them in the We Are Teachers HELPLINE Group on Facebook!
Want more articles and tips like this be sure to subscribe to our newsletters to find out when they’re posted..

You Might Also Like
15 Inspiring Teaching Portfolio Examples (Plus How To Create Your Own)
Show them what you've got. Continue Reading
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256
59 Teaching Philosophy Statement Examples

A statement of teaching philosophy is a requirement for all teachers.
This statement shows future employers, parents and colleagues what you value as an educator and what your teaching skills are .
Examples of things to emphasize in a teaching philosophy statement include:
- A student-centered approach to education.
- A focus on active learning.
- High expectations for yourself and your students.
- Your ideal learning environment.
- Your approach to technology in the classroom.
- How you motivate your students.
- Your approach to assessment.
Here are 57 teaching philosophy statement examples that you could get some ideas from.
Teaching Philosophy Statement Examples
1. you create a student-centered learning environment.
- “I aspire to create student-centered learning environments in which the student is in the driving seat of their own learning.”
- “My classrooms are always focused on the specific needs of my students. I work hard to differentiate learning so that each student’s unique skills are emphasized.”
“I always ensure that my lessons involve multiple learning modalities so that students learn through their preferred learning style.”
- “Central to my pedagogy is a focus on the needs of students. I embrace Vygotsky’s Zone of Proximal Development as a key pedagogical tool to ensure all students are taught content that is achievable yet challenging.”
- “For me, the ideal classroom environment is student-centered. I strive to create learning scenarios where the students are undertaking group projects while I move between groups facilitating discussions.”
2. You have a Focus on Active Learning
- “I embrace a Constructivist pedagogy that emphasizes active discovery learning on the part of my students. All my lessons are designed to have students learning through doing: trial-and-error, solving problems, and creating new solutions.”
- “My classrooms are spaces for exploration and discovery. I favor practical lessons in which students get hands-on experience of the subjects under analysis.”
“Students learn best when they are actively engaged in their own learning. Passive approaches where students take notes and listen during teacher-centered lessons are not as conducive to deep learning as lessons in which students are learning through discovery.”
- “One example teaching strategy that I often employ is the guided practice or ‘I do, we do, you do’ method . This approach starts with teacher modelling a practice but involves the gradual release of responsibility to the student until the student can undertake tasks on their own.”
Read Also: 47 One-Sentence Teacher Vision Statements
3. You Set High Expectations
- “While I like to see students enjoying themselves in class, I also insist on hard work and focus on the task at hand.”
- “I set high standards and high expectations by promoting growth mindsets among my students. All my students know that I expect them to try their hardest and strive for improvement every day.”
“I always expect my students to come to class ready to focus and engage. I often ask my students to set their own goals and take steps toward achieving their goals every day.”
- “I encourage students to walk into the classroom with a positive attitude toward learning. The best classes occur when students know that they are expected to do their best each and every day.”
- “Students enter my classroom with the knowledge that I expect them to engage with the learning materials. I keep a strong focus on creating a serious learning environment. This starts with me insisting on focus and engagement from the minute students walk in the door.”
4. You are a Community Engaged Teacher
- “I strive to develop connections between students and the school community. When community members come into the classroom, students not only learn about people from various walks of life. They also get to see role models of different shapes and sizes around the community.”
“I like to invite parents into my classrooms so they can feel that they are a partner in teaching. I set myself goals to contact all parents throughout the school term to listen to them and learn from their deep knowledge of their own children.”
- “In this culturally diverse area, I make every effort to expose my students to community members from diverse cultural backgrounds. It is important to me that students feel a connection to the rich local community in which they learn.”
5. Learning Environment Statements
- “I aim to create learning environments that are rich in resources so that students can learn through practical learning scenarios.”
“I create classrooms that empower students to make decisions for themselves so that they develop self-confidence and thinking skills .”
- “I develop learning environments that have multiple workstations in which students can work in groups to solve problems. I find group-based classroom layouts (through table seating) help children to communicate and learn from one another while learning.”
6. You have a Holistic Approach
- “I follow a holistic approach to child development. Educators need to pay attention to students’ social, physical, emotional and cognitive development equally to help raise balanced children for the 21st Century.”
“I do my best to get to know my students so I can best meet their needs. I focus on not only their cognitive development but also their emotional and social wellbeing , which is equally necessary for learning to occur.”
- “My teaching philosophy is strongly influenced by Abraham Maslow’s humanist approach and in particular his Hierarchy of Needs. I aim to ensure students’ basic needs are met in the classroom so that they feel happy, comfortable, safe and welcomed into the classroom. When students’ basic needs are met, they can focus on learning and personal development.”
7. You Promote Critical Thinking
- “I write my lessons to target higher-order thinking skills from Bloom’s Taxonomy, for example ‘creating’, ‘inquiring’ and ‘critiquing’. I aim to have all my students think critically about themselves and the world around them.”
- “It is my goal to have my students think outside the box, critique the everyday assumptions they take for granted, and leave my classes with more questions than answers.”
“I aspire to be a teacher who instils a love of learning, analysis and critical thinking in all the students I encounter.”
- “I believe students of the 21st Century need more than just knowledge. Students need to have critical and creative thinking skills so that they can compete for the jobs of the future. To encourage a critical thinking approach, I consistently ask my students to analyse concepts that I teach from multiple competing perspectives.”
- “I help my students to develop metacognitive skills so they can reflect on their own learning and identify ways they can learn more effectively and efficiently.”
Read Also: Education Slogans, Taglines and Mottos that Pop!
8. You Support Authentic Learning Experiences
- “My credo is to prioritize authentic learning situations where students learn through solving real-world problems. In this way, I help my students understand the connection between what they’re learning and life beyond the four walls of the classroom.”
“I believe students learn best when they learn in authentic contexts. By learning through real-world problem solving, they discover the value in knowledge.”
- “To me, students should learn through experience. I aim to create experiences in the classroom that are as authentic as possible to mimic real-life application of knowledge.”
9. You Embrace Social Learning
- “I encourage students to learn in groups because I believe conversation with others helps students to express, challenge and refine their thought processes. By listening to peers, students can also hear new perspectives that may broaden their horizons and deepen their own knowledge.”
“I follow a sociocultural teaching philosophy inspired by Lev Vygotsky. This philosophy is heavily focused on having students communicate with “ more knowledgeable others ” and learn challenging but achievable tasks that are within their “Zone of Proximal Development”.
- “I embrace a situated learning theory approach to teaching. This theory emphasizes the importance of learning from experts in the contexts in which learning is applied. To this end, I encourage students to take up apprenticeships and go on many field trips so my students can learn by working with professionals.”
10. You Emphasize Communication Skills
- “In the 21st Century, it is more important than ever for students to develop effective communication skills. I help students develop communication skills such as teamwork, negotiation and self-expression in every lesson through the consistent use of guided group work lessons.”
“Students need to become clear and confident communicators of their knowledge. I often create assessments that require students to express themselves in written and verbal formats to help them develop their communication capacities.”
- “Communication skills are vital for students to become effective self-advocates. I aim to teach students to become confident communicators by giving ample opportunities to work in groups, report their research to their classmates, and perform in front of their families.”
11. You Create Inquiry and Problem Based Learning Lessons
- “I embrace an inquiry based learning approach whereby I start with a higher-order thinking question and students come up with hypotheses for answering the questions. Through this approach, students exercise skills like ‘predicting’ and ‘testing’ to seek knowledge.”
“I focus on problem based learning experiences where students are presented with a problem that they need to overcome. In overcoming the problems, students must use research skills to figure out solutions and apply them to their scenarios.”
- “I encourage students to use scientific methods to solve problems. Through scientific inquiry, students do not simply learn new information, but learn how to go about seeking truths through accurate and reliable testing methods.”
12. Mention your Assessment Style
- “I use creative assessment practices that go beyond standardized assessment. I like to assess students’ practical applications of knowledge rather than simply their written knowledge of information. When students are assessed on their practical skills, they focus on how to put knowledge into action and reaching mastery of their content.”
“I have a strong focus on formative assessment so that I have a finger on the pulse of my students’ progress. I do not shy away from altering my teaching following formative assessments to ensure my students do not fall through the gaps.”
- “Assessment is important to me as a teacher because it helps me to measure my own teaching efficacy. I often use students’ assessment results to reflect upon how I taught the content, what areas of weakness appeared across a cohort, and how to teach to those areas of weakness more effectively in years to come.”
13. You Motivate Your Students
- “I believe students learn best when they are intrinsically motivated . I therefore focus on creating lessons that are engaging, relevant to my students’ real lives, and encourage active discovery.”
- “To motivate my students, I aim to tie my lessons to their interests and hobbies. This requires me to build strong rapport and relationships with my students so I know how I can tailor my lessons for them.”
“Students who are motivated and inspired to learn will come to school with a positive mindset. I work hard to promote student self-motivation by giving them agency to explore areas of interest within the curriculum.”
- “I believe motivated students are engaged, spend more time on task, and cause less disruption to their peers. I therefore work hard to motivate students by modelling an inspired, positive outlook to education every day.
14. Education is Important to You
- “Education is the foundation for a child’s future. As a teacher, I take pride in my profession as someone who shepherds the future generations. To do this effectively, I strive to …”
“Teaching is one of the most important professions in the world. Teachers need to work hard to produce ethically and critically thinking leaders of tomorrow…”
- “It is a great pleasure to work every day to help raise confident future citizens who will solve the problems of the future. Education is incredibly important for all students’ futures. …”
15. You Promote Play-Based Learning
- “I use a play-based learning approach in my early years classroom. I follow Froebel’s approach that states “play is the highest form of learning”. Play help students learn through trial-and-error, discovery and exploration.”
“When students learn by doing rather than listening, they tend to store information in their minds more effectively. This is why I use a play-based learning approach. I create play-based learning situations where students can play in parallel , learn from one another, and make new discoveries through the use of all their senses.”
- “I encourage cooperative play in my classrooms so that my students can learn with and from one another. By playing together, young children develop important communication and group work skills. Furthermore, they can pick up new information and ways of playing from friends which can enhance their cognitive development.”
16. You Incorporate Educational Technologies
- “I am competent with 21st century technologies and use them regularly in my teaching. I believe technology is deeply important for students as it is a requirement for most jobs of the 21st Century.”
“Through the use of technology, I encourage students to learn from, research about and engage with the world around them. The internet, in particular, is an excellent pedagogical resource for students to learn.”
- “While I regularly use technology in the classroom, I first reflect on how to use technology to help extend learning. I see technology as a ‘ cognitive tool ’ that shouldn’t be used just as a gimmick. Rather, I use technology when it can help students to extend their thinking and learn more than if they hadn’t had technology in the lessons.”

17. Mention your Classroom Management Style
- “I believe classroom and behavior management is about ensuring students are focused on their learning materials. My first step for classroom management is to make my lessons engaging and motivating. I find that this is the best way to minimize disruptions and promote learning.”
“Following the assertive discipline theory, I believe strong classroom management skills are essential. Disruptive students violate the rights of other students to learn, so I ensure classes are controlled and ordered at all time to protect well-behaved students’ rights to a positive learning space.”
- “I employ an authoritative approach to classroom management. This authoritative style focuses on gaining respect and rapport from students by being firm but fair at all times and ensuring all students know I have their best interests at heart.”
To go deeper on this, see: List of Classroom Management Styles
Final Thoughts
Your teaching philosophy statement needs to be your own. It should reflect your own personality and approach to education.
The above teaching philosophy statement examples give you a good idea about the sorts of things you can start talking about in your teaching philosophy.

Follow-up your statements of beliefs with examples from your own practice.
You might also want to zoom-in on subject-specific approaches . If you are writing a teaching philosophy as a Mathematics teacher, for example, you will need to narrow down on specifically how you teach math.
Aim for your teaching philosophy statement to be a maximum of two pages long and ensure it shows both your personality and your knowledge of pedagogy skills or learning theories .

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 15 Animism Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 10 Magical Thinking Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Social-Emotional Learning (Definition, Examples, Pros & Cons)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is Educational Psychology?
6 thoughts on “59 Teaching Philosophy Statement Examples”
This is very helpful. I appreciate the wide variety of examples as well as the final thoughts at the end. Yet, did you mean, “59 Teaching Philosophy Statement Examples” (rather than 57)?

Two bonus ones 🙂 I think you’re the first person to have counted the list! I updated the title to 59.
Thanks! Chris
Very inspiring and insightful. It really helped me a lot in my studies. Looking forward for more.
Thank you Chris.
Great insight, as a basketball coach and athletic director of my youth football program I agree with mostly all of your points. As an ELA teacher it is easy to implement a lot of my coaching qualities into my teaching. Just as in the classroom students are on different skill levels while also learning and comprehending information differently. Providing skills base learning within the lesson is a much better approach instead of continuing to drill skills over and over. A lot of students may lose interest in the activity due to that skills approach. Do you believe a skills-based approach would also benefit students in the classroom
Hi Chris, This is very informative indeed.Thank you. Regards, Chamila
Thank you for a very informative materials shared and it’s a very helpful to me, I learned and refreshed from this. I love to read , review and apply this in my classroom.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

1000-Word Philosophy: An Introductory Anthology
Philosophy, One Thousand Words at a Time
How to Write a Philosophical Essay
Authors: The Editors of 1000-Word Philosophy [1] Category: Student Resources Word Count: 998
If you want to convince someone of a philosophical thesis, such as that God exists , that abortion is morally acceptable , or that we have free will , you can write a philosophy essay. [2]
Philosophy essays are different from essays in many other fields, but with planning and practice, anyone can write a good one. This essay provides some basic instructions. [3]

1. Planning
Typically, your purpose in writing an essay will be to argue for a certain thesis, i.e., to support a conclusion about a philosophical claim, argument, or theory. [4] You may also be asked to carefully explain someone else’s essay or argument. [5]
To begin, select a topic. Most instructors will be happy to discuss your topic with you before you start writing. Sometimes instructors give specific prompts with topics to choose from.
It’s generally best to select a topic that you’re interested in; you’ll put more energy into writing it. Your topic will determine what kind of research or preparation you need to do before writing, although in undergraduate philosophy courses, you usually don’t need to do outside research. [6]
Essays that defend or attack entire theories tend to be longer, and are more difficult to write convincingly, than essays that defend or attack particular arguments or objections: narrower is usually better than broader.
After selecting a topic, complete these steps:
- Ensure that you understand the relevant issues and arguments. Usually, it’s enough to carefully read and take notes on the assigned readings on your essay’s topic.
- Choose an initial thesis. Generally, you should choose a thesis that’s interesting, but not extremely controversial. [7] You don’t have to choose a thesis that you agree with, but it can help. (As you plan and write, you may decide to revise your thesis. This may require revising the rest of your essay, but sometimes that’s necessary, if you realize you want to defend a different thesis than the one you initially chose.)
- Ensure that your thesis is a philosophical thesis. Natural-scientific or social-scientific claims, such as that global warming is occurring or that people like to hang out with their friends , are not philosophical theses. [8] Philosophical theses are typically defended using careful reasoning, and not primarily by citing scientific observations.
Instructors will usually not ask you to come up with some argument that no philosopher has discovered before. But if your essay ignores what the assigned readings say, that suggests that you haven’t learned from those readings.
2. Structure
Develop an outline, rather than immediately launching into writing the whole essay; this helps with organizing the sections of your essay.
Your structure will probably look something like the following, but follow your assignment’s directions carefully. [9]
2.1. Introduction and Thesis
Write a short introductory paragraph that includes your thesis statement (e.g., “I will argue that eating meat is morally wrong”). The thesis statement is not a preview nor a plan; it’s not “I will consider whether eating meat is morally wrong.”
If your thesis statement is difficult to condense into one sentence, then it’s likely that you’re trying to argue for more than one thesis. [10]
2.2. Arguments
Include at least one paragraph that presents and explains an argument. It should be totally clear what reasons or evidence you’re offering to support your thesis.
In most essays for philosophy courses, you only need one central argument for your thesis. It’s better to present one argument and defend it well than present many arguments in superficial and incomplete ways.
2.3. Objection
Unless the essay must be extremely short, raise an objection to your argument. [11] Be clear exactly which part of the other argument (a premise, or the form) is being questioned or denied and why. [12]
It’s usually best to choose either one of the most common or one of the best objections. Imagine what a smart person who disagreed with you would say in response to your arguments, and respond to them.
Offer your own reply to any objections you considered. If you don’t have a convincing reply to the objection, you might want to go back and change your thesis to something more defensible.
2.5. Additional Objections and Replies
If you have space, you might consider and respond to the second-best or second-most-common objection to your argument, and so on.
2.6. Conclusion
To conclude, offer a paragraph summarizing what you did. Don’t include any new or controversial claims here, and don’t claim that you did more than you actually accomplished. There should be no surprises at the end of a philosophy essay.
Make your writing extremely clear and straightforward. Use simple sentences and don’t worry if they seem boring: this improves readability. [13] Every sentence should contribute in an obvious way towards supporting your thesis. If a claim might be confusing, state it in more than one way and then choose the best version.
To check for readability, you might read the essay aloud to an audience. Don’t try to make your writing entertaining: in philosophy, clear arguments are fun in themselves.
Concerning objections, treat those who disagree with you charitably. Make it seem as if you think they’re smart, careful, and nice, which is why you are responding to them.
Your readers, if they’re typical philosophers, will be looking for any possible way to object to what you say. Try to make your arguments “airtight.”
4. Citations
If your instructor tells you to use a certain citation style, use it. No citation style is universally accepted in philosophy. [14]
You usually don’t need to directly quote anyone. [15] You can paraphrase other authors; where you do, cite them.
Don’t plagiarize . [16] Most institutions impose severe penalties for academic dishonesty.
5. Conclusion
A well-written philosophy essay can help people gain a new perspective on some important issue; it might even change their minds. [17] And engaging in the process of writing a philosophical essay is one of the best ways to develop, understand, test, and sometimes change, your own philosophical views. They are well worth the time and effort.
[1] Primary author: Thomas Metcalf. Contributing authors: Chelsea Haramia, Dan Lowe, Nathan Nobis, Kristin Seemuth Whaley.
[2] You can also do some kind of oral presentation, either “live” in person or recorded on video. An effective presentation, however, requires the type of planning and preparation that’s needed to develop an effective philosophy paper: indeed, you may have to first write a paper and then use it as something like a script for your presentation. Some parts of the paper, e.g., section headings, statements of arguments, key quotes, and so on, you may want to use as visual aids in your presentation to help your audience better follow along and understand.
[3] Many of these recommendations are, however, based on the material in Horban (1993), Huemer (n.d.), Pryor (n.d.), and Rippon (2008). There is very little published research to cite about the claims in this essay, because these claims are typically justified by instructors’ experience, not, say, controlled experiments on different approaches to teaching philosophical writing. Therefore, the guidance offered here has been vetted by many professional philosophers with a collective hundreds of hours of undergraduate teaching experience and further collective hundreds of hours of taking philosophy courses. The editors of 1000-Word Philosophy also collectively have thousands of hours of experience in writing philosophy essays.
[4] For more about the areas of philosophy, see What is Philosophy? by Thomas Metcalf.
[5] For an explanation of what is meant by an “argument” in philosophy, see Arguments: Why Do You Believe What You Believe? by Thomas Metcalf.
[6] Outside research is sometimes discouraged, and even prohibited, for philosophy papers in introductory courses because a common goal of a philosophy paper is not to report on a number of views on a philosophical issue—so philosophy papers usually are not “research reports”—but to rather engage a specific argument or claim or theory, in a more narrow and focused way, and show that you understand the issue and have engaged in critically. If a paper engages in too much reporting of outside research, that can get in the way of this critical evaluation task.
[7] There are two reasons to avoid extremely controversial theses. First, such theses are usually more difficult to defend adequately. Second, you might offend your instructor, who might (fairly or not) give you a worse grade. So, for example, you might argue that abortion is usually permissible, or usually wrong, but you probably shouldn’t argue that anyone who has ever said the word ‘abortion’ should be tortured to death, and you probably shouldn’t argue that anyone who’s ever pregnant should immediately be forced to abort the pregnancy, because both of these claims are extremely implausible and so it’s very unlikely that good arguments could be developed for them. But theses that are controversial without being implausible can be interesting for both you and the instructor, depending on how you develop and defend your argument or arguments for that thesis.
[8] Whether a thesis is philosophical mostly depends on whether it is a lot like theses that have been defended in important works of philosophy. That means it would be a thesis about metaphysics, epistemology, value theory, logic, history of philosophy, or something therein. For more information, see Philosophy and Its Contrast with Science and What is Philosophy? both by Thomas Metcalf.
[9] Also, read the grading rubric, if it’s available. If your course uses an online learning environment, such as Canvas, Moodle, or Schoology, then the rubric will often be visible as attached to the assignment itself. The rubric is a breakdown of the different requirements of the essay and how each is weighted and evaluated by the instructor. So, for example, if some requirement has a relatively high weight, you should put more effort into doing a good job. Similarly, some requirement might explicitly mention some step for the assignment that you need to complete in order to get full credit.
[10] In some academic fields, a “thesis” or “thesis statement” is considered both your conclusion and a statement of the basic support you will give for that conclusion. In philosophy, your thesis is usually just that conclusion: e..g, “Eating meat is wrong,” “God exists,” “Nobody has free will,” and so on: the support given for that conclusion is the support for your thesis.
[11] To be especially clear, this should be an objection to the argument given for your thesis or conclusion, not an objection to your thesis or conclusion itself. This is because you don’t want to give an argument and then have an objection that does not engage that argument, but instead engages something else, since that won’t help your reader or audience better understand and evaluate that argument.
[12] For more information about premises, forms, and objections, see Arguments: Why do You Believe What You Believe? by Thomas Metcalf.
[13] For a philosophical argument in favor of clear philosophical writing, and guidance on producing such writing, see Fischer and Nobis (2019).
[14] The most common styles in philosophy are APA (Purdue Online Writing Lab, n.d.a) and Chicago (Purdue Online Writing Lab, n.d.b.).
[15] You might choose to directly quote someone when it’s very important that the reader know that the quoted author actually said what you claim they said. For example, if you’re discussing some author who made some startling claim, you can directly quote them to show that they really said that. You might also directly quote someone when they presented some information or argument in a very concise, well-stated way, such that paraphrasing it would take up more space than simply quoting them would.
[16] Plagiarism, in general, occurs when someone submits written or spoken work that is largely copied, in style, substance, or both, from some other author’s work, and does not attribute it to that author. However, your institution or instructor may define “plagiarism” somewhat differently, so you should check with their definitions. When in doubt, check with your instructor first.
[17] These are instructions for relatively short, introductory-level philosophy essays. For more guidance, there are many useful philosophy-writing guides online to consult, e.g.: Horban (1993); Huemer (n.d.); Pryor (n.d.); Rippon (2008); Weinberg (2019).
Fischer, Bob and Nobis, Nathan. (2019, June 4). Why writing better will make you a better person. The Chronicle of Higher Education .
Horban, Peter. (1993). Writing a philosophy paper. Simon Fraser University Department of Philosophy .
Huemer, Michael. (N.d.). A guide to writing. Owl232.net .
Pryor, Jim. (N.d.). Guidelines on writing a philosophy paper. Jimpryor.net .
Purdue Online Writing Lab. (N.d.a.). General format. Purdue Online Writing Lab .
Purdue Online Writing Lab. (N.d.b.). General format. Purdue Online Writing Lab .
Rippon, Simon. (2008). A brief guide to writing the philosophy paper. Harvard College Writing Center .
Weinberg, Justin. (2019, January 15). How to write a philosophy paper: Online guides. Daily Nous .
Related Essays
Arguments: Why do You Believe What You Believe? by Thomas Metcalf
Philosophy and its Contrast with Science by Thomas Metcalf
What is Philosophy? By Thomas Metcalf
Translation
Pdf download.
Download this essay in PDF .
Follow 1000-Word Philosophy on Facebook and Twitter and subscribe to receive email notifications of new essays at 1000WordPhilosophy.com .
Share this:.

Teaching Philosophy
Ai generator.

Teaching philosophy is grounded in one’s beliefs, core values , and views on teaching , learning , and action plan for educators . Whether you adhere to a single approach or adapt over time, understanding diverse perspectives on teaching philosophy is invaluable. This article explores various teaching philosophies, offering insights into how different educators approach their practice, and highlighting the importance of reflecting on and articulating one’s own teaching philosophy. By examining these different views, teachers can gain a broader understanding of effective teaching strategies and the underlying principles that guide them.
What is Teaching Philosophy?
A teaching philosophy statement in simple terms is principle-based mainly on how a person views teaching. Teaching philosophy statements are written documents that describe personal values , professional values, personal beliefs, and personal and professional views. This is regarding both teaching and learning.
Teaching Philosophy Statement Examples
1. student-centered learning.
“I believe that education should be student-centered, focusing on each student’s unique learning style and strengths. My goal is to create a classroom environment where students feel valued and motivated to engage deeply with the material.”
2. Active Learning
“My teaching philosophy is rooted in active learning. I strive to create interactive lessons that encourage students to participate, ask questions, and collaborate with their peers. This approach helps students develop critical thinking skills and retain information more effectively.”
3. Inclusive Education
“I am committed to creating an inclusive classroom where all students feel welcome and supported. I use diverse teaching strategies to accommodate different learning needs and ensure that every student has the opportunity to succeed.”
4. Growth Mindset
“I believe in fostering a growth mindset in my students. I encourage them to view challenges as opportunities for growth and to persist in the face of difficulties. By promoting a positive attitude towards learning, I help students build resilience and confidence.”
5. Real-World Connections
“My teaching philosophy emphasizes the importance of connecting classroom learning to real-world experiences. I incorporate practical examples and hands-on activities to help students see the relevance of what they are learning and apply it to their lives.”
6. Collaborative Learning
“I believe that learning is a social process. I create a collaborative classroom environment where students work together on projects, share ideas, and learn from each other. This approach not only enhances their understanding but also develops their communication and teamwork skills.”
7. Critical Thinking
“My goal as a teacher is to develop my students’ critical thinking skills. I encourage them to question assumptions, analyze information, and consider multiple perspectives. By fostering a critical mindset, I prepare students to become thoughtful and informed citizens.”
8. Reflective Practice
“I believe that reflection is a key component of learning. I regularly ask my students to reflect on their learning experiences, set goals, and identify areas for improvement. This practice helps them take ownership of their education and become self-directed learners.”
9. Technology Integration
“I integrate technology into my teaching to enhance student learning and engagement. I use a variety of digital tools and resources to create interactive lessons, provide immediate feedback, and facilitate collaboration. Technology also allows me to differentiate instruction and meet the diverse needs of my students.”
10. Culturally Responsive Teaching
“I am dedicated to culturally responsive teaching. I incorporate diverse perspectives into my curriculum and create a classroom environment that respects and values cultural differences. By doing so, I help students develop a deeper understanding of the world and prepare them to thrive in a multicultural society.”
11. Hands-On Learning
“I believe in the power of hands-on learning. I design lessons that involve experiments, projects, and real-life applications to make learning more engaging and meaningful. This approach helps students develop practical skills and a deeper understanding of the subject matter.”
12. Lifelong Learning
“I aim to instill a love of learning in my students. I encourage curiosity, exploration, and a willingness to take risks. By modeling a passion for learning myself, I inspire students to become lifelong learners who continuously seek knowledge and personal growth.”
13. Supportive Environment
“My teaching philosophy centers on creating a supportive and nurturing classroom environment. I build strong relationships with my students, provide emotional support, and create a safe space where they feel comfortable taking risks and expressing themselves.”
14. Interdisciplinary Approach
“I believe in an interdisciplinary approach to teaching. I connect concepts from different subjects to help students see the interconnectedness of knowledge. This approach not only broadens their understanding but also encourages them to think critically and creatively.”
15. Assessment for Learning
“I use assessment as a tool for learning rather than just a measure of performance. I provide regular, formative feedback to help students understand their progress and identify areas for improvement. This approach encourages a growth mindset and helps students take charge of their learning.
Teaching Philosophy Examples for Elementary
Example 1: student-centered learning.
My teaching philosophy centers around the belief that each child is unique and learns in their own way. I strive to create a classroom environment where students feel safe, valued, and empowered to explore their interests and strengths. By incorporating hands-on activities, collaborative projects, and individualized instruction, I aim to foster a love of learning and encourage critical thinking. I believe in the importance of building strong relationships with my students and their families to support their educational journey and help them reach their full potential.
Example 2: Holistic Development
I believe in nurturing the whole child, focusing not only on academic growth but also on social, emotional, and physical development. My classroom is a place where children learn to respect themselves and others, develop resilience, and become responsible citizens. I integrate social-emotional learning into my curriculum and provide opportunities for students to practice empathy, cooperation, and problem-solving skills. By creating a supportive and inclusive classroom community, I aim to help students develop a strong sense of self and a lifelong love of learning.
Example 3: Inquiry-Based Learning
My teaching philosophy is grounded in the principles of inquiry-based learning. I encourage students to ask questions, explore, and engage with the material in a meaningful way. By designing lessons that are open-ended and student-driven, I aim to cultivate curiosity and a deeper understanding of the subject matter. I believe that when students are active participants in their learning, they develop critical thinking skills and a sense of ownership over their education. My goal is to create a classroom where students feel confident to take risks, make mistakes, and learn from them.
Example 4: Inclusive Education
I believe that every child deserves an education that meets their individual needs and respects their unique background and experiences. My teaching philosophy emphasizes the importance of inclusive education, where all students, regardless of their abilities or differences, are welcomed and supported. I use differentiated instruction, assistive technology, and collaborative teaching strategies to ensure that every student can access the curriculum and achieve success. By fostering a culture of acceptance and diversity, I aim to help students develop a positive self-image and an appreciation for the differences in others.
Example 5: Constructivist Approach
I subscribe to a constructivist approach to teaching, where students build their own understanding and knowledge through experiences and reflections. I see my role as a facilitator, guiding students as they construct meaning and make connections between new information and their prior knowledge. My classroom is a dynamic environment where students are encouraged to experiment, discuss, and collaborate. Through project-based learning and real-world applications, I aim to make learning relevant and engaging, helping students to see the value and purpose of their education.
Example 6: Growth Mindset
My teaching philosophy is inspired by the concept of a growth mindset, the belief that abilities and intelligence can be developed through dedication and hard work. I strive to instill this mindset in my students by creating a positive and encouraging classroom atmosphere. I celebrate effort, perseverance, and improvement, and I help students understand that mistakes are an essential part of the learning process. By setting high expectations and providing the support needed to meet them, I aim to help students develop resilience, confidence, and a lifelong love of learning.
Example 1: Holistic Development
Philosophy Statement: I believe that education should foster the holistic development of students, addressing their intellectual, emotional, social, and ethical growth. My teaching aims to create a supportive and nurturing environment where students can develop critical thinking skills, emotional intelligence, and a strong sense of ethics.
Implementation:
- Integrated Curriculum: I design my curriculum to include elements that promote not just academic learning but also personal growth, such as ethical discussions, emotional regulation strategies, and social skills development.
- Mentorship: I view my role as a mentor who guides students not just academically but also in their personal development, offering advice and support on a range of issues.
- Community Engagement: I incorporate service-learning projects that encourage students to engage with and contribute to their communities, fostering a sense of social responsibility and ethical awareness.
Example 2: Culturally Responsive Teaching
Philosophy Statement: I believe that culturally responsive teaching is essential in today’s diverse educational landscape. My goal is to create an inclusive learning environment that respects and values the diverse cultural backgrounds of my students, integrating their experiences and perspectives into the learning process.
- Diverse Content: I include diverse voices and perspectives in my curriculum, ensuring that students see themselves reflected in the course material and learn about cultures different from their own.
- Inclusive Pedagogy: I use teaching methods that are inclusive and adaptable to different cultural contexts, such as storytelling, collaborative learning, and culturally relevant examples.
- Student Voice: I encourage students to share their cultural experiences and perspectives in class discussions and assignments, fostering a richer and more inclusive learning environment.
Example 3: Research-Driven Instruction
Philosophy Statement: I believe that integrating research into the teaching process enhances learning by encouraging students to engage deeply with the subject matter and develop critical thinking skills. My approach emphasizes the importance of research and evidence-based learning.
- Research Projects: I design assignments that require students to conduct their own research, analyze data, and present their findings. This helps them develop essential skills in inquiry and analysis.
- Evidence-Based Teaching: I base my teaching strategies on current educational research, continuously updating my methods to incorporate the latest findings in pedagogy.
- Research Mentorship: I mentor students in their research projects, providing guidance and support throughout the research process, from formulating questions to presenting results.
Example 4: Lifelong Learning and Adaptability
Philosophy Statement: I believe that education should prepare students for lifelong learning and adaptability in an ever-changing world. My teaching philosophy focuses on equipping students with the skills and mindset needed to continuously learn, adapt, and thrive in their personal and professional lives.
- Skill Development: I emphasize the development of transferable skills such as critical thinking, problem-solving, and effective communication that students can apply in various contexts.
- Adaptability: I incorporate flexible and adaptive learning activities that encourage students to embrace change and uncertainty, preparing them for the dynamic nature of the modern world.
- Continuous Improvement: I model a commitment to lifelong learning by continuously seeking professional development opportunities and staying current with advancements in my field.
Example 5: Reflective Practice
Philosophy Statement: I believe that reflective practice is key to effective learning and teaching. By encouraging students to reflect on their experiences and learning processes, I help them develop self-awareness and a deeper understanding of the material.
- Reflective Assignments: I include assignments that require students to reflect on their learning experiences, such as reflective journals, self-assessments, and reflective essays.
- Feedback Loops: I provide regular, constructive feedback and encourage students to reflect on this feedback and use it to improve their performance.
- Metacognitive Strategies: I teach metacognitive strategies that help students become more aware of their learning processes and develop skills to monitor and regulate their own learning.
Example 6: Problem-Based Learning
Philosophy Statement: I believe that problem-based learning (PBL) is an effective way to engage students and develop their critical thinking and problem-solving skills. By presenting students with real-world problems, I encourage them to apply their knowledge and skills in meaningful ways.
- Real-World Problems: I design course activities and assignments around real-world problems that are relevant to the course content, encouraging students to apply what they have learned in practical contexts.
- Collaborative Learning: I use group work and collaborative projects as a key component of PBL, helping students learn to work effectively with others and leverage diverse perspectives.
- Facilitative Teaching: I take on the role of a facilitator, guiding students through the problem-solving process and providing support and resources as needed, rather than simply delivering information.
Teaching Philosophy Examples for Higher Education
Teaching philosophy examples for high school, example 1: growth mindset and resilience.
Teaching Philosophy:
I believe that fostering a growth mindset is crucial for students’ academic and personal development. In my classroom, I emphasize the value of effort, perseverance, and learning from mistakes. I create a supportive environment where students are encouraged to take risks and view challenges as opportunities to grow. By modeling resilience and a positive attitude towards learning, I help students build the confidence and grit necessary to overcome obstacles and achieve their goals.
Example 2: Real-World Connections
Education should connect students to the real world, making learning relevant and meaningful. I design my lessons to bridge the gap between classroom concepts and real-life applications. Through project-based learning, community involvement, and interdisciplinary approaches, I aim to show students the practical significance of their studies. This approach not only enhances engagement but also helps students develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills that are essential for their future careers and everyday lives.
Example 3: Collaborative Learning
Collaboration is a key component of effective learning. I believe that students learn best when they work together, share ideas, and support each other’s growth. In my classroom, I encourage group activities, peer tutoring, and cooperative projects. By fostering a collaborative learning environment, I help students develop communication, teamwork, and leadership skills. This not only enhances their academic performance but also prepares them for success in a collaborative world.
Example 4: Individualized Instruction
Every student is unique, with their own strengths, interests, and learning needs. My teaching philosophy revolves around individualized instruction, where I tailor my teaching strategies to meet the diverse needs of my students. By using formative assessments, differentiated instruction, and personalized feedback, I ensure that each student receives the support and challenge they need to thrive. My goal is to help every student reach their full potential and develop a lifelong love of learning.
Example 5: Integrating Arts and Creativity
Creativity and the arts play a vital role in education, enhancing students’ cognitive abilities and emotional well-being. I integrate arts and creative activities into my teaching to make learning more engaging and enjoyable. Whether through visual arts, music, drama, or creative writing, I encourage students to express themselves and explore their creativity. This approach not only enriches their learning experience but also helps them develop critical thinking, empathy, and a deeper appreciation for the world around them.
Teaching Philosophy Essay
Fostering a Growth Mindset
Central to my teaching philosophy is the concept of a growth mindset, as advocated by psychologist Carol Dweck. I believe that intelligence and abilities are not fixed traits but can be developed through dedication and hard work. This perspective is essential in encouraging students to embrace challenges, persist in the face of setbacks, and view effort as a pathway to mastery. To nurture a growth mindset, I emphasize the importance of effort, strategy, and progress over innate ability. I provide constructive feedback that focuses on specific strategies and behaviors, rather than labeling students’ abilities, and celebrate improvements and perseverance alongside achievements.
Creating an Inclusive and Supportive Classroom Environment
An inclusive and supportive classroom environment is vital for student engagement and success. I am committed to creating a space where all students feel valued, respected, and empowered to express their ideas and perspectives. This involves recognizing and addressing diverse learning needs, backgrounds, and experiences. I employ differentiated instruction strategies to cater to varied learning styles and provide multiple means of engagement, representation, and expression. By fostering a culture of mutual respect and collaboration, I encourage students to learn from one another and develop a sense of community and belonging.
Integrating Real-World Applications
Connecting classroom learning to real-world applications is crucial in making education relevant and meaningful. I strive to bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical experience by incorporating real-life examples, case studies, and problem-solving activities into my lessons. This approach not only enhances students’ understanding and retention of concepts but also equips them with critical thinking and problem-solving skills essential for their future endeavors. By demonstrating the practical implications of academic content, I aim to inspire students to see the value and relevance of their education beyond the classroom.
Reflective Practice and Continuous Improvement
As an educator, I am committed to reflective practice and continuous improvement. I regularly assess and refine my teaching methods based on feedback from students, colleagues, and self-reflection. I stay informed about current educational research and best practices and seek professional development opportunities to enhance my skills and knowledge. By modeling a commitment to lifelong learning, I aim to inspire my students to adopt a similar mindset.
In conclusion, my teaching philosophy is grounded in the belief that every student has the potential to succeed when provided with a supportive, inclusive, and engaging learning environment. By fostering a growth mindset, creating a sense of community, integrating real-world applications, and continuously reflecting on and improving my practice, I strive to empower my students to become confident, curious, and capable learners. Education is not merely about imparting knowledge but about inspiring a lifelong love of learning and equipping students with the skills and mindset needed to navigate and contribute to an ever-changing world.
How to Write a Teaching Philosophy?
1. reflect on your beliefs about teaching and learning.
Consider what you believe about:
- The purpose of education.
- How students learn best.
- The role of a teacher in the learning process.
- The most important outcomes of education.
2. Identify Your Teaching Methods
Think about the strategies and techniques you use or plan to use:
- How do you engage students?
- How do you assess student understanding and progress?
- What instructional methods do you prefer (e.g., lectures, group work, hands-on activities)?
3. Provide Examples
Use specific examples to illustrate your teaching methods and beliefs:
- Describe a successful lesson or activity.
- Share anecdotes or experiences that highlight your approach.
- Explain how you’ve adapted to meet the needs of diverse learners.
4. Discuss Your Goals for Students
What do you hope students gain from your teaching?
- Critical thinking skills .
- Subject-specific knowledge.
- Lifelong learning habits.
5. Explain How You Assess and Reflect on Your Teaching
How do you measure your effectiveness as a teacher?
- Student feedback.
- Self-reflection.
- Professional development activities.
6. Keep It Personal and Specific
Your teaching philosophy should reflect your unique approach and experiences. Avoid generic statements; instead, focus on what makes your teaching style distinctive.
7. Structure Your Statement
A well-organized teaching philosophy might include:
- Introduction : Brief overview of your teaching beliefs.
- Body : Detailed description of your teaching methods, goals, and examples.
- Conclusion : Summary of your teaching philosophy and its implications for your future practice.
8. Revise and Edit
- Ensure clarity and coherence.
- Seek feedback from colleagues or mentors.
- Revise for conciseness and impact.
Why teaching Philosophy is Important?
A teaching philosophy is important for several reasons, serving as a foundational element for educators. Here are key reasons why it’s important:
1. Clarifies Your Teaching Approach
- Articulates Beliefs : It helps you articulate your beliefs about education, learning, and teaching.
- Defines Methods : It clarifies the methods and strategies you use in the classroom.
2. Guides Professional Development
- Reflection : Writing a teaching philosophy encourages self-reflection on your teaching practices and experiences.
- Improvement : It highlights areas for professional growth and improvement.
3. Enhances Communication
- Transparency : It provides transparency to students, colleagues, and administrators about your approach to teaching.
- Expectations : It sets clear expectations for your students about what they can expect from you as an educator.
4. Supports Career Advancement
- Job Applications : A well-crafted teaching philosophy is often required in job applications for teaching positions.
- Promotion and Tenure : It can be a critical component of promotion and tenure dossiers in academic settings.
5. Improves Student Learning
- Consistency : A teaching philosophy helps maintain consistency in teaching practices, which can improve student learning outcomes.
- Alignment : It ensures that your teaching methods are aligned with your educational goals and objectives.
1. Teaching Philosophy Template
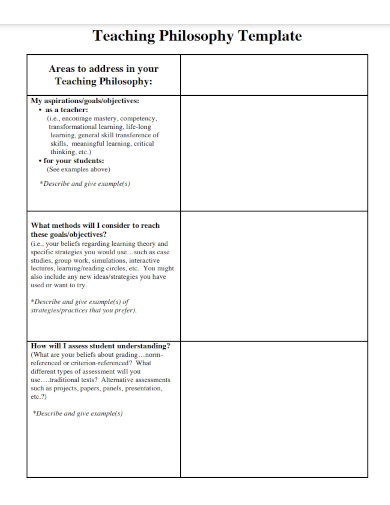
2. Teaching Philosophy Sample

3. Teaching Philosophy Statement

4. Components of Teaching Philosophy Statement

A teaching philosophy is a reflective statement outlining an educator’s beliefs, values, and practices about teaching and learning.
It guides instructional strategies, shapes classroom environment, and communicates teaching values to students and colleagues.
Reflect on your teaching beliefs, methods, and goals. Begin with a clear introduction stating your educational principles.
Typically, a teaching philosophy is 1-2 pages long, concisely covering key points.
It provides a consistent, thoughtful approach to teaching, enhancing student learning and engagement.
Yes, it evolves with new experiences, reflections, and educational advancements.
Yes, concrete examples illustrate your teaching practices and philosophy in action.
Revisit and update it annually or when significant teaching experiences occur.
Use it in job applications, tenure dossiers, and as a reflective tool for continuous improvement.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
As an educator, my teaching philosophy is centered around the belief that education is not just about imparting knowledge, but about equipping students with the skills they need to become lifelong learners and critical thinkers. In this essay, I will explore the key components of my teaching philosophy, including its history, development, and ...
Sample 1. This passage is an example of a strong statement of teaching philosophy because it puts students at the front and center of the teacher's focus. An author who writes such a statement will likely always ensure student needs are the primary focus of all lessons and schoolwork. "My philosophy of education is that all children are unique ...
Your teaching philosophy reflects your fundamental beliefs and values regarding: your role as a teacher; students (and their families); knowledge and curriculum; classroom practices; classroom management; professionalism; and equity. Compose an essay discussing and explaining your teaching philosophy at this moment in your pre-service teaching ...
Writing Your Teaching Philosophy. Your teaching philosophy is a self-reflective statement of your beliefs about teaching and learning. It's a one to two page narrative that conveys your core ideas about being an effective teacher in the context of your discipline. It develops these ideas with specific, concrete examples of what the teacher and ...
Long-form teaching philosophy statements should follow the same tried-and-true format as a well-crafted student essay: Introduction. This first section should include mention of: Your teaching methods; Any subject or pedagogical specialties ... "My philosophy of education is that all children are unique and must have a stimulating educational ...
field of education. My philosophy of education is based on what I know and have experienced at this point in my career. I am sure that my teaching philosophy will change as I learn more as a young professional. That's one of the gifts of being human; we can make mistakes, or learn something new, and make a change for the better.
HOW RESEARCH RELATES TO YOUR TEACHING ONLY TEACHING RESEARCH + TEACHING Your EXPERIENCE with research will help you bring real-world examples into your instruction. You are KNOWLEDGEABLE about current findings in your field. You can help TRAIN students to think like a scientist. Your RESEARCH RESULTS can be discussed in your
Follow these seven steps to write your teaching philosophy statement: 1. Consider your audience. Before you begin writing your teaching philosophy statement, begin by considering your audience and what may be of greatest importance to them. If you're writing for a hiring committee, know that they may be interested in both the internal and ...
Your teaching philosophy is what you believe is the best way to reach that purpose, and why. Your ideas about education and teaching should come from reflecting on your past experiences with education and the educational theories you have learned in your education courses. Beliefs, attitudes, values, and experiences influence a person's ...
This essay about a teaching philosophy emphasizes innovation, empathy, and empowerment as foundational elements for a dynamic learning environment. It advocates for active student participation, diversity, and the practical application of knowledge. The approach promotes critical thinking, a growth mindset, and meaningful feedback, aiming to ...
the teaching components of graduate school or the teaching position you're applying for. In this handout, you will learn some strategies for writing your teaching philosophy. COMPOSITION EXAMPLE I believe that good writing, like learning, is inherently social: we write with an audience in mind, in response to what others have written. Thus ...
My Teaching Philosophy Essay. Decent Essays. 564 Words. 3 Pages. Open Document. My Teaching Philosophy I believe that education extends far beyond the classroom walls, and involves many more people than students and teachers. People should be learning wherever they go, and should continue learning long after they've graduated from high school ...
Cite this essay. Download. As a teacher, my philosophy statement is that I believe that education is important for all. Children have many differences and each child has special characteristics that they can apply toward their individual education. As a teacher I will help guide my students so that they learn to express themselves, and learn ...
Play-based learning is a big part of my teaching philosophy. Kids who learn through play have more authentic experiences, exploring and discovering the world naturally in ways that make the process more engaging and likely to make a lasting impact. In my classroom, technology is key.
Bradley Coleman, PhD Director HMS Curriculum Fellows Program. [email protected]. September 24th, 2020. Objectives. By the end of. this 90 minute workshop, participants will. recognize the role of a teaching statement in an academic portfolio or job application. identify the views and experiences that influence their own philosophy ...
Teaching Philosophy Statement Examples. 1. You Create a Student-Centered Learning Environment. "I aspire to create student-centered learning environments in which the student is in the driving seat of their own learning.". "My classrooms are always focused on the specific needs of my students. I work hard to differentiate learning so that ...
The teaching philosophy is the teacher-educator personal view on ideal teaching and learning, and it is a reflection of personal experiences (Bowne, 2017). The context of teaching, personal and ...
Example 1: A safe learning environment. The classroom is a haven from the world outside. My sixth-grade students are discovering so much about themselves. Right now, few spaces in their lives may allow them to focus on learning and growth rather than social pressure.
1. Planning. Typically, your purpose in writing an essay will be to argue for a certain thesis, i.e., to support a conclusion about a philosophical claim, argument, or theory.[4] You may also be asked to carefully explain someone else's essay or argument.[5] To begin, select a topic. Most instructors will be happy to discuss your topic with ...
arguments or theories in philosophy papers, you must always practice philosophy. This means that you should explain the argument in your own words and according to your own understanding of the steps involved in it. You will need to be very clear on the precise logical structure of an author's argument (N.B. this may not be
My Teaching Philosophy Essay. My Teaching Philosophy I believe that education extends far beyond the classroom walls, and involves many more people than students and teachers. People should be learning wherever they go, and should continue learning long after they've graduated from high school or college.
Teaching Philosophy Essay Teaching is a dynamic and transformative endeavor, grounded in the belief that education is the cornerstone of personal and societal growth. My teaching philosophy is rooted in the conviction that every student possesses the potential to learn and thrive when provided with the right environment, support, and encouragement.