- Product overview
- All features
- App integrations

CAPABILITIES
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- asana-intelligence icon Asana Intelligence
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Campaign management
- Creative production
- Content calendars
- Marketing strategic planning
- Resource planning
- Project intake
- Product launches
- Employee onboarding
- View all uses arrow-right icon
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- What's new Learn about the latest and greatest from Asana
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Support Need help? Contact the Asana support team
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
Featured Reads

- Business strategy |
- What is strategic planning? A 5-step gu ...
What is strategic planning? A 5-step guide

Strategic planning is a process through which business leaders map out their vision for their organization’s growth and how they’re going to get there. In this article, we'll guide you through the strategic planning process, including why it's important, the benefits and best practices, and five steps to get you from beginning to end.
Strategic planning is a process through which business leaders map out their vision for their organization’s growth and how they’re going to get there. The strategic planning process informs your organization’s decisions, growth, and goals.
Strategic planning helps you clearly define your company’s long-term objectives—and maps how your short-term goals and work will help you achieve them. This, in turn, gives you a clear sense of where your organization is going and allows you to ensure your teams are working on projects that make the most impact. Think of it this way—if your goals and objectives are your destination on a map, your strategic plan is your navigation system.
In this article, we walk you through the 5-step strategic planning process and show you how to get started developing your own strategic plan.
How to build an organizational strategy
Get our free ebook and learn how to bridge the gap between mission, strategic goals, and work at your organization.
What is strategic planning?
Strategic planning is a business process that helps you define and share the direction your company will take in the next three to five years. During the strategic planning process, stakeholders review and define the organization’s mission and goals, conduct competitive assessments, and identify company goals and objectives. The product of the planning cycle is a strategic plan, which is shared throughout the company.
What is a strategic plan?
![what is a strategic business plan for [inline illustration] Strategic plan elements (infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/7d1f14e4-b008-4ea6-9579-5af6236ce367/inline-business-strategy-strategic-planning-1-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
A strategic plan is the end result of the strategic planning process. At its most basic, it’s a tool used to define your organization’s goals and what actions you’ll take to achieve them.
Typically, your strategic plan should include:
Your company’s mission statement
Your organizational goals, including your long-term goals and short-term, yearly objectives
Any plan of action, tactics, or approaches you plan to take to meet those goals
What are the benefits of strategic planning?
Strategic planning can help with goal setting and decision-making by allowing you to map out how your company will move toward your organization’s vision and mission statements in the next three to five years. Let’s circle back to our map metaphor. If you think of your company trajectory as a line on a map, a strategic plan can help you better quantify how you’ll get from point A (where you are now) to point B (where you want to be in a few years).
When you create and share a clear strategic plan with your team, you can:
Build a strong organizational culture by clearly defining and aligning on your organization’s mission, vision, and goals.
Align everyone around a shared purpose and ensure all departments and teams are working toward a common objective.
Proactively set objectives to help you get where you want to go and achieve desired outcomes.
Promote a long-term vision for your company rather than focusing primarily on short-term gains.
Ensure resources are allocated around the most high-impact priorities.
Define long-term goals and set shorter-term goals to support them.
Assess your current situation and identify any opportunities—or threats—allowing your organization to mitigate potential risks.
Create a proactive business culture that enables your organization to respond more swiftly to emerging market changes and opportunities.
What are the 5 steps in strategic planning?
The strategic planning process involves a structured methodology that guides the organization from vision to implementation. The strategic planning process starts with assembling a small, dedicated team of key strategic planners—typically five to 10 members—who will form the strategic planning, or management, committee. This team is responsible for gathering crucial information, guiding the development of the plan, and overseeing strategy execution.
Once you’ve established your management committee, you can get to work on the planning process.
Step 1: Assess your current business strategy and business environment
Before you can define where you’re going, you first need to define where you are. Understanding the external environment, including market trends and competitive landscape, is crucial in the initial assessment phase of strategic planning.
To do this, your management committee should collect a variety of information from additional stakeholders, like employees and customers. In particular, plan to gather:
Relevant industry and market data to inform any market opportunities, as well as any potential upcoming threats in the near future.
Customer insights to understand what your customers want from your company—like product improvements or additional services.
Employee feedback that needs to be addressed—whether about the product, business practices, or the day-to-day company culture.
Consider different types of strategic planning tools and analytical techniques to gather this information, such as:
A balanced scorecard to help you evaluate four major elements of a business: learning and growth, business processes, customer satisfaction, and financial performance.
A SWOT analysis to help you assess both current and future potential for the business (you’ll return to this analysis periodically during the strategic planning process).
To fill out each letter in the SWOT acronym, your management committee will answer a series of questions:
What does your organization currently do well?
What separates you from your competitors?
What are your most valuable internal resources?
What tangible assets do you have?
What is your biggest strength?
Weaknesses:
What does your organization do poorly?
What do you currently lack (whether that’s a product, resource, or process)?
What do your competitors do better than you?
What, if any, limitations are holding your organization back?
What processes or products need improvement?
Opportunities:
What opportunities does your organization have?
How can you leverage your unique company strengths?
Are there any trends that you can take advantage of?
How can you capitalize on marketing or press opportunities?
Is there an emerging need for your product or service?
What emerging competitors should you keep an eye on?
Are there any weaknesses that expose your organization to risk?
Have you or could you experience negative press that could reduce market share?
Is there a chance of changing customer attitudes towards your company?
Step 2: Identify your company’s goals and objectives
To begin strategy development, take into account your current position, which is where you are now. Then, draw inspiration from your vision, mission, and current position to identify and define your goals—these are your final destination.
To develop your strategy, you’re essentially pulling out your compass and asking, “Where are we going next?” “What’s the ideal future state of this company?” This can help you figure out which path you need to take to get there.
During this phase of the planning process, take inspiration from important company documents, such as:
Your mission statement, to understand how you can continue moving towards your organization’s core purpose.
Your vision statement, to clarify how your strategic plan fits into your long-term vision.
Your company values, to guide you towards what matters most towards your company.
Your competitive advantages, to understand what unique benefit you offer to the market.
Your long-term goals, to track where you want to be in five or 10 years.
Your financial forecast and projection, to understand where you expect your financials to be in the next three years, what your expected cash flow is, and what new opportunities you will likely be able to invest in.
Step 3: Develop your strategic plan and determine performance metrics
Now that you understand where you are and where you want to go, it’s time to put pen to paper. Take your current business position and strategy into account, as well as your organization’s goals and objectives, and build out a strategic plan for the next three to five years. Keep in mind that even though you’re creating a long-term plan, parts of your plan should be created or revisited as the quarters and years go on.
As you build your strategic plan, you should define:
Company priorities for the next three to five years, based on your SWOT analysis and strategy.
Yearly objectives for the first year. You don’t need to define your objectives for every year of the strategic plan. As the years go on, create new yearly objectives that connect back to your overall strategic goals .
Related key results and KPIs. Some of these should be set by the management committee, and some should be set by specific teams that are closer to the work. Make sure your key results and KPIs are measurable and actionable. These KPIs will help you track progress and ensure you’re moving in the right direction.
Budget for the next year or few years. This should be based on your financial forecast as well as your direction. Do you need to spend aggressively to develop your product? Build your team? Make a dent with marketing? Clarify your most important initiatives and how you’ll budget for those.
A high-level project roadmap . A project roadmap is a tool in project management that helps you visualize the timeline of a complex initiative, but you can also create a very high-level project roadmap for your strategic plan. Outline what you expect to be working on in certain quarters or years to make the plan more actionable and understandable.
Step 4: Implement and share your plan
Now it’s time to put your plan into action. Strategy implementation involves clear communication across your entire organization to make sure everyone knows their responsibilities and how to measure the plan’s success.
Make sure your team (especially senior leadership) has access to the strategic plan, so they can understand how their work contributes to company priorities and the overall strategy map. We recommend sharing your plan in the same tool you use to manage and track work, so you can more easily connect high-level objectives to daily work. If you don’t already, consider using a work management platform .
A few tips to make sure your plan will be executed without a hitch:
Communicate clearly to your entire organization throughout the implementation process, to ensure all team members understand the strategic plan and how to implement it effectively.
Define what “success” looks like by mapping your strategic plan to key performance indicators.
Ensure that the actions outlined in the strategic plan are integrated into the daily operations of the organization, so that every team member's daily activities are aligned with the broader strategic objectives.
Utilize tools and software—like a work management platform—that can aid in implementing and tracking the progress of your plan.
Regularly monitor and share the progress of the strategic plan with the entire organization, to keep everyone informed and reinforce the importance of the plan.
Establish regular check-ins to monitor the progress of your strategic plan and make adjustments as needed.
Step 5: Revise and restructure as needed
Once you’ve created and implemented your new strategic framework, the final step of the planning process is to monitor and manage your plan.
Remember, your strategic plan isn’t set in stone. You’ll need to revisit and update the plan if your company changes directions or makes new investments. As new market opportunities and threats come up, you’ll likely want to tweak your strategic plan. Make sure to review your plan regularly—meaning quarterly and annually—to ensure it’s still aligned with your organization’s vision and goals.
Keep in mind that your plan won’t last forever, even if you do update it frequently. A successful strategic plan evolves with your company’s long-term goals. When you’ve achieved most of your strategic goals, or if your strategy has evolved significantly since you first made your plan, it might be time to create a new one.
Build a smarter strategic plan with a work management platform
To turn your company strategy into a plan—and ultimately, impact—make sure you’re proactively connecting company objectives to daily work. When you can clarify this connection, you’re giving your team members the context they need to get their best work done.
A work management platform plays a pivotal role in this process. It acts as a central hub for your strategic plan, ensuring that every task and project is directly tied to your broader company goals. This alignment is crucial for visibility and coordination, allowing team members to see how their individual efforts contribute to the company’s success.
By leveraging such a platform, you not only streamline workflow and enhance team productivity but also align every action with your strategic objectives—allowing teams to drive greater impact and helping your company move toward goals more effectively.
Strategic planning FAQs
Still have questions about strategic planning? We have answers.
Why do I need a strategic plan?
A strategic plan is one of many tools you can use to plan and hit your goals. It helps map out strategic objectives and growth metrics that will help your company be successful.
When should I create a strategic plan?
You should aim to create a strategic plan every three to five years, depending on your organization’s growth speed.
Since the point of a strategic plan is to map out your long-term goals and how you’ll get there, you should create a strategic plan when you’ve met most or all of them. You should also create a strategic plan any time you’re going to make a large pivot in your organization’s mission or enter new markets.
What is a strategic planning template?
A strategic planning template is a tool organizations can use to map out their strategic plan and track progress. Typically, a strategic planning template houses all the components needed to build out a strategic plan, including your company’s vision and mission statements, information from any competitive analyses or SWOT assessments, and relevant KPIs.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. business plan?
A business plan can help you document your strategy as you’re getting started so every team member is on the same page about your core business priorities and goals. This tool can help you document and share your strategy with key investors or stakeholders as you get your business up and running.
You should create a business plan when you’re:
Just starting your business
Significantly restructuring your business
If your business is already established, you should create a strategic plan instead of a business plan. Even if you’re working at a relatively young company, your strategic plan can build on your business plan to help you move in the right direction. During the strategic planning process, you’ll draw from a lot of the fundamental business elements you built early on to establish your strategy for the next three to five years.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. mission and vision statements?
Your strategic plan, mission statement, and vision statements are all closely connected. In fact, during the strategic planning process, you will take inspiration from your mission and vision statements in order to build out your strategic plan.
Simply put:
A mission statement summarizes your company’s purpose.
A vision statement broadly explains how you’ll reach your company’s purpose.
A strategic plan pulls in inspiration from your mission and vision statements and outlines what actions you’re going to take to move in the right direction.
For example, if your company produces pet safety equipment, here’s how your mission statement, vision statement, and strategic plan might shake out:
Mission statement: “To ensure the safety of the world’s animals.”
Vision statement: “To create pet safety and tracking products that are effortless to use.”
Your strategic plan would outline the steps you’re going to take in the next few years to bring your company closer to your mission and vision. For example, you develop a new pet tracking smart collar or improve the microchipping experience for pet owners.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. company objectives?
Company objectives are broad goals. You should set these on a yearly or quarterly basis (if your organization moves quickly). These objectives give your team a clear sense of what you intend to accomplish for a set period of time.
Your strategic plan is more forward-thinking than your company goals, and it should cover more than one year of work. Think of it this way: your company objectives will move the needle towards your overall strategy—but your strategic plan should be bigger than company objectives because it spans multiple years.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. a business case?
A business case is a document to help you pitch a significant investment or initiative for your company. When you create a business case, you’re outlining why this investment is a good idea, and how this large-scale project will positively impact the business.
You might end up building business cases for things on your strategic plan’s roadmap—but your strategic plan should be bigger than that. This tool should encompass multiple years of your roadmap, across your entire company—not just one initiative.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. a project plan?
A strategic plan is a company-wide, multi-year plan of what you want to accomplish in the next three to five years and how you plan to accomplish that. A project plan, on the other hand, outlines how you’re going to accomplish a specific project. This project could be one of many initiatives that contribute to a specific company objective which, in turn, is one of many objectives that contribute to your strategic plan.
What’s the difference between strategic management vs. strategic planning?
A strategic plan is a tool to define where your organization wants to go and what actions you need to take to achieve those goals. Strategic planning is the process of creating a plan in order to hit your strategic objectives.
Strategic management includes the strategic planning process, but also goes beyond it. In addition to planning how you will achieve your big-picture goals, strategic management also helps you organize your resources and figure out the best action plans for success.
Related resources

How to create a CRM strategy: 6 steps (with examples)
What is management by objectives (MBO)?

Write better AI prompts: A 4-sentence framework

What is content marketing? A complete guide
Essential Guide to the Strategic Planning Process
By Joe Weller | April 3, 2019 (updated March 26, 2024)
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
In this article, you’ll learn the basics of the strategic planning process and how a strategic plan guides you to achieving your organizational goals. Plus, find expert insight on getting the most out of your strategic planning.
Included on this page, you'll discover the importance of strategic planning , the steps of the strategic planning process , and the basic sections to include in your strategic plan .
What Is Strategic Planning?
Strategic planning is an organizational activity that aims to achieve a group’s goals. The process helps define a company’s objectives and investigates both internal and external happenings that might influence the organizational path. Strategic planning also helps identify adjustments that you might need to make to reach your goal. Strategic planning became popular in the 1960s because it helped companies set priorities and goals, strengthen operations, and establish agreement among managers about outcomes and results.
Strategic planning can occur over multiple years, and the process can vary in length, as can the final plan itself. Ideally, strategic planning should result in a document, a presentation, or a report that sets out a blueprint for the company’s progress.
By setting priorities, companies help ensure employees are working toward common and defined goals. It also aids in defining the direction an enterprise is heading, efficiently using resources to achieve the organization’s goals and objectives. Based on the plan, managers can make decisions or allocate the resources necessary to pursue the strategy and minimize risks.
Strategic planning strengthens operations by getting input from people with differing opinions and building a consensus about the company’s direction. Along with focusing energy and resources, the strategic planning process allows people to develop a sense of ownership in the product they create.

“Strategic planning is not really one thing. It is really a set of concepts, procedures, tools, techniques, and practices that have to be adapted to specific contexts and purposes,” says Professor John M. Bryson, McKnight Presidential Professor of Planning and Public Affairs at the Hubert H. Humphrey School of Public Affairs, University of Minnesota and author of Strategic Planning for Public and Nonprofit Organizations: A Guide to Strengthening and Sustaining Organizational Achievement . “Strategic planning is a prompt to foster strategic thinking, acting, and learning, and they all matter and they are all connected.”
What Strategic Planning Is Not
Strategic planning is not a to-do list for the short or long term — it is the basis of a business, its direction, and how it will get there.
“You have to think very strategically about strategic planning. It is more than just following steps,” Bryson explains. “You have to understand strategic planning is not some kind of magic solution to fixing issues. Don’t have unrealistic expectations.”
Strategic planning is also different from a business plan that focuses on a specific product, service, or program and short-term goals. Rather, strategic planning means looking at the big picture.
While they are related, it is important not to confuse strategic planning with strategic thinking, which is more about imagining and innovating in a way that helps a company. In contrast, strategic planning supports those thoughts and helps you figure out how to make them a reality.
Another part of strategic planning is tactical planning , which involves looking at short-term efforts to achieve longer-term goals.
Lastly, marketing plans are not the same as strategic plans. A marketing plan is more about introducing and delivering a service or product to the public instead of how to grow a business. For more about marketing plans and processes, read this article .
Strategic plans include information about finances, but they are different from financial planning , which involves different processes and people. Financial planning templates can help with that process.
Why Is Strategic Planning Important?
In today’s technological age, strategic plans provide businesses with a path forward. Strategic plans help companies thrive, not just survive — they provide a clear focus, which makes an organization more efficient and effective, thereby increasing productivity.

“You are not going to go very far if you don’t have a strategic plan. You need to be able to show where you are going,” says Stefan Hofmeyer, an experienced strategist and co-founder of Global PMI Partners . He lives in the startup-rich environment of northern California and says he often sees startups fail to get seed money because they do not have a strong plan for what they want to do and how they want to do it.
Getting team members on the same page (in both creating a strategic plan and executing the plan itself) can be beneficial for a company. Planners can find satisfaction in the process and unite around a common vision. In addition, you can build strong teams and bridge gaps between staff and management.
“You have to reach agreement about good ideas,” Bryson says. “A really good strategy has to meet a lot of criteria. It has to be technically workable, administratively feasible, politically acceptable, and legally, morally, and ethically defensible, and that is a pretty tough list.”
By discussing a company’s issues during the planning process, individuals can voice their opinions and provide information necessary to move the organization ahead — a form of problem solving as a group.
Strategic plans also provide a mechanism to measure success and progress toward goals, which keeps employees on the same page and helps them focus on the tasks at hand.
When Is the Time to Do Strategic Planning?
There is no perfect time to perform strategic planning. It depends entirely on the organization and the external environment that surrounds it. However, here are some suggestions about when to plan:
If your industry is changing rapidly
When an organization is launching
At the start of a new year or funding period
In preparation for a major new initiative
If regulations and laws in your industry are or will be changing
“It’s not like you do all of the thinking and planning, and then implement,” Bryson says. “A mistake people make is [believing] the thinking has to precede the acting and the learning.”
Even if you do not re-create the entire planning process often, it is important to periodically check your plan and make sure it is still working. If not, update it.
What Is the Strategic Planning Process?
Strategic planning is a process, and not an easy one. A key is to make sure you allow enough time to complete the process without rushing, but not take so much time that you lose momentum and focus. The process itself can be more important than the final document due to the information that comes out of the discussions with management, as well as lower-level workers.

“There is not one favorite or perfect planning process,” says Jim Stockmal, president of the Association for Strategic Planning (ASP). He explains that new techniques come out constantly, and consultants and experienced planners have their favorites. In an effort to standardize the practice and terms used in strategic planning, ASP has created two certification programs .
Level 1 is the Strategic Planning Professional (SPP) certification. It is designed for early- or mid-career planners who work in strategic planning. Level 2, the Strategic Management Professional (SMP) certification, is geared toward seasoned professionals or those who train others. Stockmal explains that ASP designed the certification programs to add structure to the otherwise amorphous profession.
The strategic planning process varies by the size of the organization and can be formal or informal, but there are constraints. For example, teams of all sizes and goals should build in many points along the way for feedback from key leaders — this helps the process stay on track.
Some elements of the process might have specific start and end points, while others are continuous. For example, there might not be one “aha” moment that suddenly makes things clear. Instead, a series of small moves could slowly shift the organization in the right direction.
“Don’t make it overly complex. Bring all of the stakeholders together for input and feedback,” Stockmal advises. “Always be doing a continuous environmental scan, and don’t be afraid to engage with stakeholders.”
Additionally, knowing your company culture is important. “You need to make it work for your organization,” he says.
There are many different ways to approach the strategic planning process. Below are three popular approaches:
Goals-Based Planning: This approach begins by looking at an organization’s mission and goals. From there, you work toward that mission, implement strategies necessary to achieve those goals, and assign roles and deadlines for reaching certain milestones.
Issues-Based Planning: In this approach, start by looking at issues the company is facing, then decide how to address them and what actions to take.
Organic Planning: This approach is more fluid and begins with defining mission and values, then outlining plans to achieve that vision while sticking to the values.
“The approach to strategic planning needs to be contingent upon the organization, its history, what it’s capable of doing, etc.,” Bryson explains. “There’s such a mistake to think there’s one approach.”
For more information on strategic planning, read about how to write a strategic plan and the different types of models you can use.
Who Participates in the Strategic Planning Process?
For work as crucial as strategic planning, it is necessary to get the right team together and include them from the beginning of the process. Try to include as many stakeholders as you can.
Below are suggestions on who to include:
Senior leadership
Strategic planners
Strategists
People who will be responsible for implementing the plan
People to identify gaps in the plan
Members of the board of directors
“There can be magic to strategic planning, but it’s not in any specific framework or anybody’s 10-step process,” Bryson explains. “The magic is getting key people together, getting them to focus on what’s important, and [getting] them to do something about it. That’s where the magic is.”
Hofmeyer recommends finding people within an organization who are not necessarily current leaders, but may be in the future. “Sometimes they just become obvious. Usually they show themselves to you, you don’t need to look for them. They’re motivated to participate,” he says. These future leaders are the ones who speak up at meetings or on other occasions, who put themselves out there even though it is not part of their job description.
At the beginning of the process, establish guidelines about who will be involved and what will be expected of them. Everyone involved must be willing to cooperate and collaborate. If there is a question about whether or not to include anyone, it is usually better to bring on extra people than to leave someone out, only to discover later they should have been a part of the process all along. Not everyone will be involved the entire time; people will come and go during different phases.
Often, an outside facilitator or consultant can be an asset to a strategic planning committee. It is sometimes difficult for managers and other employees to sit back and discuss what they need to accomplish as a company and how they need to do it without considering other factors. As objective observers, outside help can often offer insight that may escape insiders.
Hofmeyer says sometimes bosses have blinders on that keep them from seeing what is happening around them, which allows them to ignore potential conflicts. “People often have their own agendas of where they want to go, and if they are not aligned, it is difficult to build a strategic plan. An outsider perspective can really take you out of your bubble and tell you things you don’t necessarily want to hear [but should]. We get into a rhythm, and it’s really hard to step out of that, so bringing in outside people can help bring in new views and aspects of your business.”
An outside consultant can also help naysayers take the process more seriously because they know the company is investing money in the efforts, Hofmeyer adds.
No matter who is involved in the planning process, make sure at least one person serves as an administrator and documents all planning committee actions.
What Is in a Strategic Plan?
A strategic plan communicates goals and what it takes to achieve them. The plan sometimes begins with a high-level view, then becomes more specific. Since strategic plans are more guidebooks than rulebooks, they don’t have to be bureaucratic and rigid. There is no perfect plan; however, it needs to be realistic.
There are many sections in a strategic plan, and the length of the final document or presentation will vary. The names people use for the sections differ, but the general ideas behind them are similar: Simply make sure you and your team agree on the terms you will use and what each means.
One-Page Strategic Planning Template
“I’m a big fan of getting a strategy onto one sheet of paper. It’s a strategic plan in a nutshell, and it provides a clear line of sight,” Stockmal advises.
You can use the template below to consolidate all your strategic ideas into a succinct, one-page strategic plan. Doing so provides you with a high-level overview of your strategic initiatives that you can place on your website, distribute to stakeholders, and refer to internally. More extensive details about implementation, capacity, and other concerns can go into an expanded document.
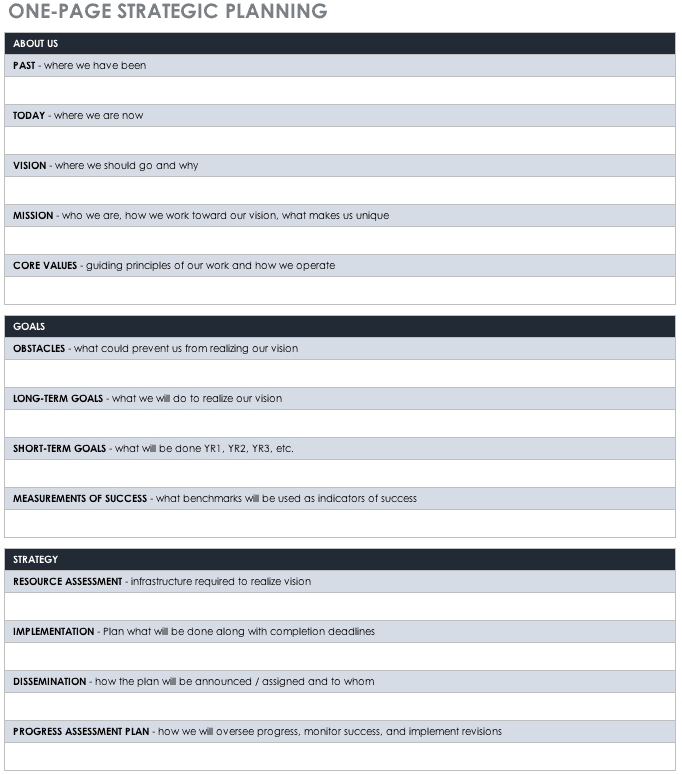
Download One-Page Strategic Planning Template Excel | Word | Smartsheet
The most important part of the strategic plan is the executive summary, which contains the highlights of the plan. Although it appears at the beginning of the plan, it should be written last, after you have done all your research.
Of writing the executive summary, Stockmal says, “I find it much easier to extract and cut and edit than to do it first.”
For help with creating executive summaries, see these templates .
Other parts of a strategic plan can include the following:
Description: A description of the company or organization.
Vision Statement: A bold or inspirational statement about where you want your company to be in the future.
Mission Statement: In this section, describe what you do today, your audience, and your approach as you work toward your vision.
Core Values: In this section, list the beliefs and behaviors that will enable you to achieve your mission and, eventually, your vision.
Goals: Provide a few statements of how you will achieve your vision over the long term.
Objectives: Each long-term goal should have a few one-year objectives that advance the plan. Make objectives SMART (specific, measurable, achievable, and time-based) to get the most out of them.
Budget and Operating Plans: Highlight resources you will need and how you will implement them.
Monitoring and Evaluation: In this section, describe how you will check your progress and determine when you achieve your goals.
One of the first steps in creating a strategic plan is to perform both an internal and external analysis of the company’s environment. Internally, look at your company’s strengths and weaknesses, as well as the personal values of those who will implement your plan (managers, executives, board members). Externally, examine threats and opportunities within the industry and any broad societal expectations that might exist.
You can perform a SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats) analysis to sum up where you are currently and what you should focus on to help you achieve your future goals. Strengths shows you what you do well, weaknesses point out obstacles that could keep you from achieving your objectives, opportunities highlight where you can grow, and threats pinpoint external factors that could be obstacles in your way.
You can find more information about performing a SWOT analysis and free templates in this article . Another analysis technique, STEEPLE (social, technological, economic, environmental, political, legal, and ethical), often accompanies a SWOT analysis.
Basics of Strategic Planning
How you navigate the strategic planning process will vary. Several tools and techniques are available, and your choice depends on your company’s leadership, culture, environment, and size, as well as the expertise of the planners.
All include similar sections in the final plan, but the ways of driving those results differ. Some tools are goals-based, while others are issues- or scenario-based. Some rely on a more organic or rigid process.
Hofmeyer summarizes what goes into strategic planning:
Understand the stakeholders and involve them from the beginning.
Agree on a vision.
Hold successful meetings and sessions.
Summarize and present the plan to stakeholders.
Identify and check metrics.
Make periodic adjustments.
Items That Go into Strategic Planning
Strategic planning contains inputs, activities, outputs, and outcomes. Inputs and activities are elements that are internal to the company, while outputs and outcomes are external.
Remember, there are many different names for the sections of strategic plans. The key is to agree what terms you will use and define them for everyone involved.
Inputs are important because it is impossible to know where you are going until you know what is around you where you are now.
Companies need to gather data from a variety of sources to get a clear look at the competitive environment and the opportunities and risks within that environment. You can think of it like a competitive intelligence program.
Data should come from the following sources:
Interviews with executives
A review of documents about the competition or market that are publicly available
Primary research by visiting or observing competitors
Studies of your industry
The values of key stakeholders
This information often goes into writing an organization’s vision and mission statements.
Activities are the meetings and other communications that need to happen during the strategic planning process to help everyone understand the competition that surrounds the organization.
It is important both to understand the competitive environment and your company’s response to it. This is where everyone looks at and responds to the data gathered from the inputs.
The strategic planning process produces outputs. Outputs can be as basic as the strategic planning document itself. The documentation and communications that describe your organization’s strategy, as well as financial statements and budgets, can also be outputs.
The implementation of the strategic plan produces outcomes (distinct from outputs). The outcomes determine the success or failure of the strategic plan by measuring how close they are to the goals and vision you outline in your plan.
It is important to understand there will be unplanned and unintended outcomes, too. How you learn from and adapt to these changes influence the success of the strategic plan.
During the planning process, decide how you will measure both the successes and failures of different parts of the strategic plan.
Sharing, Evaluating, and Monitoring the Progress of a Strategic Plan
After companies go through a lengthy strategic planning process, it is important that the plan does not sit and collect dust. Share, evaluate, and monitor the plan to assess how you are doing and make any necessary updates.
“[Some] leaders think that once they have their strategy, it’s up to someone else to execute it. That’s a mistake I see,” Stockmal says.
The process begins with distributing and communicating the plan. Decide who will get a copy of the plan and how those people will tell others about it. Will you have a meeting to kick off the implementation? How will you specify who will do what and when? Clearly communicate the roles people will have.
“Before you communicate the plan [to everyone], you need to have the commitment of stakeholders,” Hofmeyer recommends. Have the stakeholders be a part of announcing the plan to everyone — this keeps them accountable because workers will associate them with the strategy. “That applies pressure to the stakeholders to actually do the work.”
Once the team begins implementation, it’s necessary to have benchmarks to help measure your successes against the plan’s objectives. Sometimes, having smaller action plans within the larger plan can help keep the work on track.
During the planning process, you should have decided how you will measure success. Now, figure out how and when you will document progress. Keep an eye out for gaps between the vision and its implementation — a big gap could be a sign that you are deviating from the plan.
Tools are available to assist with tracking performance of strategic plans, including several types of software. “For some organizations, a spreadsheet is enough, but you are going to manually enter the data, so someone needs to be responsible for that,” Stockmal recommends.
Remember: strategic plans are not written in stone. Some deviation will be necessary, and when it happens, it’s important to understand why it occurred and how the change might impact the company's vision and goals.
Deviation from the plan does not mean failure, reminds Hofmeyer. Instead, understanding what transpired is the key. “Things happen, [and] you should always be on the lookout for that. I’m a firm believer in continuous improvement,” he says. Explain to stakeholders why a change is taking place. “There’s always a sense of re-evaluation, but do it methodically.”
Build in a schedule to review and amend the plan as necessary; this can help keep companies on track.
What Is Strategic Management?
Strategic planning is part of strategic management, and it involves the activities that make the strategic plan a reality. Essentially, strategic management is getting from the starting point to the goal effectively and efficiently using the ongoing activities and processes that a company takes on in order to keep in line with its mission, vision, and strategic plan.
“[Strategic management] closes the gap between the plan and executing the strategy,” Stockmal of ASP says. Strategic management is part of a larger planning process that includes budgeting, forecasting, capital allocation, and more.
There is no right or wrong way to do strategic management — only guidelines. The basic phases are preparing for strategic planning, creating the strategic plan, and implementing that plan.
No matter how you manage your plan, it’s key to allow the strategic plan to evolve and grow as necessary, due to both the internal and external factors.
“We get caught up in all of the day-to-day issues,” Stockmal explains, adding that people do not often leave enough time for implementing the plan and making progress. That’s what strategic management implores: doing things that are in the plan and not letting the plan sit on a shelf.
Improve Strategic Planning with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
The 5 steps of the strategic planning process
.jpg)
Starting a project without a strategy is like trying to bake a cake without a recipe — you might have all the ingredients you need, but without a plan for how to combine them, or a vision for what the finished product will look like, you’re likely to end up with a mess. This is especially true when working with a team — it’s crucial to have a shared plan that can serve as a map on the pathway to success.
Creating a strategic plan not only provides a useful document for the future, but also helps you define what you have right now, and think through and outline all of the steps and considerations you’ll need to succeed.
What is strategic planning?
While there is no single approach to creating a strategic plan, most approaches can be boiled down to five overarching steps:
- Define your vision
- Assess where you are
- Determine your priorities and objectives
- Define responsibilities
- Measure and evaluate results
Each step requires close collaboration as you build a shared vision, strategy for implementation, and system for understanding performance.
Related: Learn how to hold an effective strategic planning meeting
Why do I need a strategic plan?
Building a strategic plan is the best way to ensure that your whole team is on the same page, from the initial vision and the metrics for success to evaluating outcomes and adjusting (if necessary) for the future. Even if you’re an expert baker, working with a team to bake a cake means having a collaborative approach and clearly defined steps so that the result reflects the strategic goals you laid out at the beginning.
The benefits of strategic planning also permeate into the general efficiency and productivity of your organization as a whole. They include:
- Greater attention to potential biases or flaws, improving decision-making
- Clear direction and focus, motivating and engaging employees
- Better resource management, improving project outcomes
- Improved employee performance, increasing profitability
- Enhanced communication and collaboration, fostering team efficiency
Next, let’s dive into how to build and structure your strategic plan, complete with templates and assets to help you along the way.
Before you begin: Pick a brainstorming method
There are many brainstorming methods you can use to come up with, outline, and rank your priorities. When it comes to strategy planning, it’s important to get everyone’s thoughts and ideas out before committing to any one strategy. With the right facilitation , brainstorming helps make this process fair and transparent for everyone involved.
First, decide if you want to run a real-time rapid ideation session or a structured brainstorming . In a rapid ideation session, you encourage sharing half-baked or silly ideas, typically within a set time frame. The key is to just get out all your ideas quickly and then edit the best ones. Examples of rapid ideation methods include round robin , brainwriting , mind mapping , and crazy eights .
In a structured brainstorming session, you allow for more time to prepare and edit your thoughts before getting together to share and discuss those more polished ideas. This might involve brainstorming methods that entail unconventional ways of thinking, such as reverse brainstorming or rolestorming .
Using a platform like Mural, you can easily capture and organize your team’s ideas through sticky notes, diagrams, text, or even images and videos. These features allow you to build actionable next steps immediately (and in the same place) through color coding and tagging.
Whichever method you choose, the ideal outcome is that you avoid groupthink by giving everyone a voice and a say. Once you’ve reached a consensus on your top priorities, add specific objectives tied to each of those priorities.
Related: Brainstorming and ideation template
1. Define your vision
Whether it’s for your business as a whole, or a specific initiative, successful strategic planning involves alignment with a vision for success. You can think of it as a project-specific mission statement or a north star to guide employees toward fulfilling organizational goals.
To create a vision statement that explicitly states the ideal results of your project or company transformation, follow these four key steps:
- Engage and involve the entire team . Inclusivity like this helps bring diverse perspectives to the table.
- Align the vision with your core values and purpose . This will make it familiar and easy to follow through.
- Stay grounded . The vision should be ambitious enough to motivate and inspire yet grounded enough to be achievable and relevant.
- Think long-term flexibility . Consider future trends and how your vision can be flexible in the face of challenges or opportunities.
For example, say your vision is to revolutionize customer success by streamlining and optimizing your process for handling support tickets. It’s important to have a strategy map that allows stakeholders (like the support team, marketing team, and engineering team) to know the overall objective and understand the roles they will play in realizing the goals.
This can be done in real time or asynchronously , whether in person, hybrid, or remote. By leveraging a shared digital space , everyone has a voice in the process and room to add their thoughts, comments, and feedback.
Related: Vision board template
2. Assess where you are
The next step in creating a strategic plan is to conduct an assessment of where you stand in terms of your own initiatives, as well as the greater marketplace. Start by conducting a resource assessment. Figure out which financial, human, and/or technological resources you have available and if there are any limitations. You can do this using a SWOT analysis.
What is SWOT analysis?
SWOT analysis is an exercise where you define:
- Strengths: What are your unique strengths for this initiative or this product? In what ways are you a leader?
- Weaknesses: What weaknesses can you identify in your offering? How does your product compare to others in the marketplace?
- Opportunities: Are there areas for improvement that'd help differentiate your business?
- Threats: Beyond weaknesses, are there existing potential threats to your idea that could limit or prevent its success? How can those be anticipated?
For example, say you have an eco-friendly tech company and your vision is to launch a new service in the next year. Here’s what the SWOT analysis might look like:
- Strengths : Strong brand reputation, loyal customer base, and a talented team focused on innovation
- Weaknesses : Limited bandwidth to work on new projects, which might impact the scope of its strategy formulation
- Opportunities : How to leverage and experiment with existing customers when goal-setting
- Threats : Factors in the external environment out of its control, like the state of the economy and supply chain shortages
This SWOT analysis will guide the company in setting strategic objectives and formulating a robust plan to navigate the challenges it might face.
Related: SWOT analysis template
3. Determine your priorities and objectives
Once you've identified your organization’s mission and current standing, start a preliminary plan document that outlines your priorities and their corresponding objectives. Priorities and objectives should be set based on what is achievable with your available resources. The SMART framework is a great way to ensure you set effective goals . It looks like this:
- Specific: Set clear objectives, leaving no room for ambiguity about the desired outcomes.
- Measurable : Choose quantifiable criteria to make it easier to track progress.
- Achievable : Ensure it is realistic and attainable within the constraints of your resources and environment.
- Relevant : Develop objectives that are relevant to the direction your organization seeks to move.
- Time-bound : Set a clear timeline for achieving each objective to maintain a sense of urgency and focus.
For instance, going back to the eco-friendly tech company, the SMART goals might be:
- Specific : Target residential customers and small businesses to increase the sales of its solar-powered device line by 25%.
- Measurable : Track monthly sales and monitor customer feedback and reviews.
- Achievable : Allocate more resources to the marketing, sales, and customer service departments.
- Relevant : Supports the company's growth goals in a growing market of eco-conscious consumers.
- Time-bound : Conduct quarterly reviews and achieve this 25% increase in sales over the next 12 months.
With strategic objectives like this, you’ll be ready to put the work into action.
Related: Project kickoff template
4. Define tactics and responsibilities
In this stage, individuals or units within your team can get granular about how to achieve your goals and who'll be accountable for each step. For example, the senior leadership team might be in charge of assigning specific tasks to their team members, while human resources works on recruiting new talent.
It’s important to note that everyone’s responsibilities may shift over time as you launch and gather initial data about your project. For this reason, it’s key to define responsibilities with clear short-term metrics for success. This way, you can make sure that your plan is adaptable to changing circumstances.
One of the more common ways to define tactics and metrics is to use the OKR (Objectives and Key Results) method. By outlining your OKRs, you’ll know exactly what key performance indicators (KPIs) to track and have a framework for analyzing the results once you begin to accumulate relevant data.
For instance, if our eco-friendly tech company has a goal of increasing sales, one objective might be to expand market reach for its solar-powered products. The sales team lead would be in charge of developing an outreach strategy. The key result would be to successfully launch its products in two new regions by Q2. The KPI would be a 60% conversation rate in those targeted markets.
Related: OKR planning template
5. Manage, measure, and evaluate
Once your plan is set into motion, it’s important to actively manage (and measure) progress. Before launching your plan, settle on a management process that allows you to measure success or failure. In this way, everyone is aligned on progress and can come together to evaluate your strategy execution at regular intervals.
Determine the milestones at which you’ll come together and go over results — this can take place weekly, monthly, or quarterly, depending on the nature of the project.
One of the best ways to evaluate progress is through agile retrospectives (or retros) , which can be done in real time or asynchronously. During this process, gather and organize feedback about the key elements that played a role in your strategy.
Related: Retrospective radar template
Retrospectives are typically divided into three parts:
- What went well.
- What didn’t go well.
- New opportunities for improvement.
This structure is also sometimes called the “ rose, thorn, bud ” framework. By using this approach, team members can collectively brainstorm and categorize their feedback, making the next steps clear and actionable. Creating an action plan during a post-mortem meeting is a crucial step in ensuring that lessons learned from past projects or events are effectively translated into tangible improvements.
Another method for reviewing progress is the quarterly business review (QBR). Like the agile retrospective, it allows you to collect feedback and adjust accordingly. In the case of QBRs, however, we recommend dividing your feedback into four categories:
- Start (what new items should be launched?).
- Stop (what items need to be paused?).
- Continue (what is going well?).
- Change (what could be modified to perform better?).
Strategic planners know that planning activities continue even after a project is complete. There’s always room for improvement and an action plan waiting to be implemented. Using the above approaches, your team can make room for new ideas within the existing strategic framework in order to track better to your long-term goals.
Related: Quarterly business review template
Conclusions
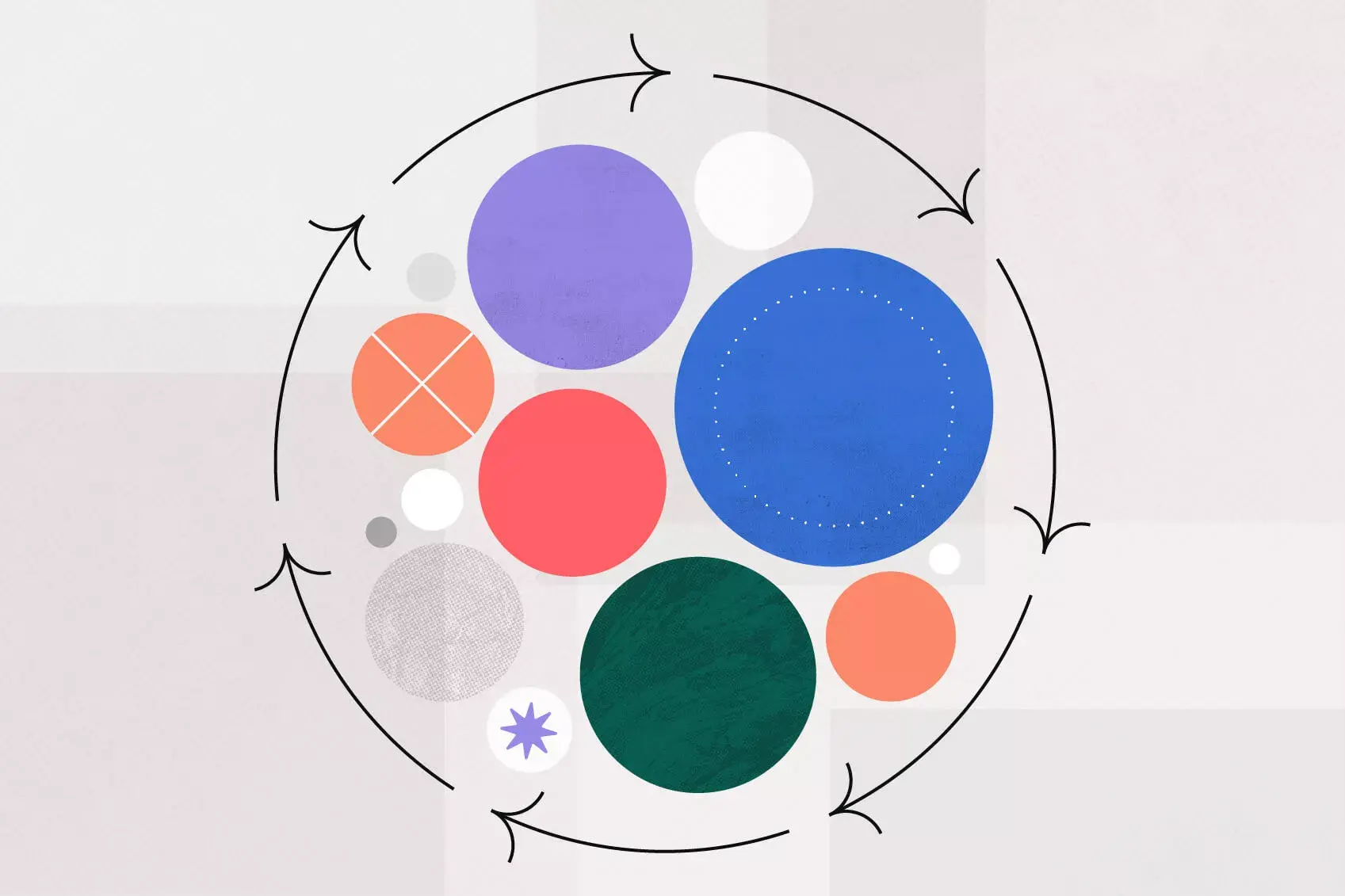
The beauty of the strategic plan is that it can be applied from the campaign level all the way up to organizational vision. Using the strategic planning framework, you build buy-in , trust, and transparency by collaboratively creating a vision for success, and mapping out the steps together on the road to your goals.
Also, in so doing, you build in an ability to adapt effectively on the fly in response to data through measurement and evaluation, making your plan both flexible and resilient.
Related: 5 Tips for Holding Effective Post-mortems
Why Mural for strategic planning
Mural unlocks collaborative strategic planning through a shared digital space with an intuitive interface, a library of pre-fab templates, and methodologies based on design thinking principles.
Outline goals, identify key metrics, and track progress with a platform built for any enterprise.
Learn more about strategic planning with Mural.
About the authors

Bryan Kitch
Tagged Topics
Related blog posts
%20(2).jpg)
How to hold effective strategic planning meetings
%20(2).jpg)
Tactical vs. strategic planning: Why you need both
%20(2).jpg)
5 effective strategic planning models for your business
Related blog posts.

Don't do this when using a flowchart builder

How Mural links design thinking and Agile
%20(3).jpg)
A guide to the Agile development lifecycle
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading Change and Organizational Renewal
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
How to Set Strategic Planning Goals

- 29 Oct 2020
In an ever-changing business world, it’s imperative to have strategic goals and a plan to guide organizational efforts. Yet, crafting strategic goals can be a daunting task. How do you decide which goals are vital to your company? Which ones are actionable and measurable? Which goals to prioritize?
To help you answer these questions, here’s a breakdown of what strategic planning is, what characterizes strategic goals, and how to select organizational goals to pursue.
Access your free e-book today.
What Is Strategic Planning?
Strategic planning is the ongoing organizational process of using available knowledge to document a business's intended direction. This process is used to prioritize efforts, effectively allocate resources, align shareholders and employees, and ensure organizational goals are backed by data and sound reasoning.
Research in the Harvard Business Review cautions against getting locked into your strategic plan and forgetting that strategy involves inherent risk and discomfort. A good strategic plan evolves and shifts as opportunities and threats arise.
“Most people think of strategy as an event, but that’s not the way the world works,” says Harvard Business School Professor Clayton Christensen in the online course Disruptive Strategy . “When we run into unanticipated opportunities and threats, we have to respond. Sometimes we respond successfully; sometimes we don’t. But most strategies develop through this process. More often than not, the strategy that leads to success emerges through a process that’s at work 24/7 in almost every industry."
Related: 5 Tips for Formulating a Successful Strategy
4 Characteristics of Strategic Goals
To craft a strategic plan for your organization, you first need to determine the goals you’re trying to reach. Strategic goals are an organization’s measurable objectives that are indicative of its long-term vision.
Here are four characteristics of strategic goals to keep in mind when setting them for your organization.

1. Purpose-Driven
The starting point for crafting strategic goals is asking yourself what your company’s purpose and values are . What are you striving for, and why is it important to set these objectives? Let the answers to these questions guide the development of your organization’s strategic goals.
“You don’t have to leave your values at the door when you come to work,” says HBS Professor Rebecca Henderson in the online course Sustainable Business Strategy .
Henderson, whose work focuses on reimagining capitalism for a just and sustainable world, also explains that leading with purpose can drive business performance.
“Adopting a purpose will not hurt your performance if you do it authentically and well,” Henderson says in a lecture streamed via Facebook Live . “If you’re able to link your purpose to the strategic vision of the company in a way that really gets people aligned and facing in the right direction, then you have the possibility of outperforming your competitors.”
Related: 5 Examples of Successful Sustainability Initiatives
2. Long-Term and Forward-Focused
While strategic goals are the long-term objectives of your organization, operational goals are the daily milestones that need to be reached to achieve them. When setting strategic goals, think of your company’s values and long-term vision, and ensure you’re not confusing strategic and operational goals.
For instance, your organization’s goal could be to create a new marketing strategy; however, this is an operational goal in service of a long-term vision. The strategic goal, in this case, could be breaking into a new market segment, to which the creation of a new marketing strategy would contribute.
Keep a forward-focused vision to ensure you’re setting challenging objectives that can have a lasting impact on your organization.
3. Actionable
Strong strategic goals are not only long-term and forward-focused—they’re actionable. If there aren’t operational goals that your team can complete to reach the strategic goal, your organization is better off spending time and resources elsewhere.
When formulating strategic goals, think about the operational goals that fall under them. Do they make up an action plan your team can take to achieve your organization’s objective? If so, the goal could be a worthwhile endeavor for your business.
4. Measurable
When crafting strategic goals, it’s important to define how progress and success will be measured.
According to the online course Strategy Execution , an effective tool you can use to create measurable goals is a balanced scorecard —a tool to help you track and measure non-financial variables.
“The balanced scorecard combines the traditional financial perspective with additional perspectives that focus on customers, internal business processes, and learning and development,” says HBS Professor Robert Simons in the online course Strategy Execution . “These additional perspectives help businesses measure all the activities essential to creating value.”
The four perspectives are:
- Internal business processes
- Learning and growth

The most important element of a balanced scorecard is its alignment with your business strategy.
“Ask yourself,” Simons says, “‘If I picked up a scorecard and examined the measures on it, could I infer what the business's strategy was? If you've designed measures well, the answer should be yes.”
Related: A Manager’s Guide to Successful Strategy Implementation
Strategic Goal Examples
Whatever your business goals and objectives , they must have all four of the characteristics listed above.
For instance, the goal “become a household name” is valid but vague. Consider the intended timeframe to reach this goal and how you’ll operationally define “a household name.” The method of obtaining data must also be taken into account.
An appropriate revision to the original goal could be: “Increase brand recognition by 80 percent among surveyed Americans by 2030.” By setting a more specific goal, you can better equip your organization to reach it and ensure that employees and shareholders have a clear definition of success and how it will be measured.
If your organization is focused on becoming more sustainable and eco-conscious, you may need to assess your strategic goals. For example, you may have a goal of becoming a carbon neutral company, but without defining a realistic timeline and baseline for this initiative, the probability of failure is much higher.
A stronger goal might be: “Implement a comprehensive carbon neutrality strategy by 2030.” From there, you can determine the operational goals that will make this strategic goal possible.
No matter what goal you choose to pursue, it’s important to avoid those that lack clarity, detail, specific targets or timeframes, or clear parameters for success. Without these specific elements in place, you’ll have a difficult time making your goals actionable and measurable.
Prioritizing Strategic Goals
Once you’ve identified several strategic goals, determine which are worth pursuing. This can be a lengthy process, especially if other decision-makers have differing priorities and opinions.
To set the stage, ensure everyone is aware of the purpose behind each strategic goal. This calls back to Henderson’s point that employees’ alignment on purpose can set your organization up to outperform its competitors.
Calculate Anticipated ROI
Next, calculate the estimated return on investment (ROI) of the operational goals tied to each strategic objective. For example, if the strategic goal is “reach carbon-neutral status by 2030,” you need to break that down into actionable sub-tasks—such as “determine how much CO2 our company produces each year” and “craft a marketing and public relations strategy”—and calculate the expected cost and return for each.

The ROI formula is typically written as:
ROI = (Net Profit / Cost of Investment) x 100
In project management, the formula uses slightly different terms:
ROI = [(Financial Value - Project Cost) / Project Cost] x 100
An estimate can be a valuable piece of information when deciding which goals to pursue. Although not all strategic goals need to yield a high return on investment, it’s in your best interest to calculate each objective's anticipated ROI so you can compare them.
Consider Current Events
Finally, when deciding which strategic goal to prioritize, the importance of the present moment can’t be overlooked. What’s happening in the world that could impact the timeliness of each goal?
For example, the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic and the ever-intensifying climate change crisis have impacted many organizations’ strategic goals in 2020. Often, the goals that are timely and pressing are those that earn priority.

Learn to Plan Strategic Goals
As you set and prioritize strategic goals, remember that your strategy should always be evolving. As circumstances and challenges shift, so must your organizational strategy.
If you lead with purpose, a measurable and actionable vision, and an awareness of current events, you can set strategic goals worth striving for.
Do you want to learn more about strategic planning? Explore our online strategy courses and download our free flowchart to determine which is right for you and your goals.
This post was updated on November 16, 2023. It was originally published on October 29, 2020.

About the Author
What is a Business Plan? Definition and Resources

9 min. read
Updated May 10, 2024
If you’ve ever jotted down a business idea on a napkin with a few tasks you need to accomplish, you’ve written a business plan — or at least the very basic components of one.
The origin of formal business plans is murky. But they certainly go back centuries. And when you consider that 20% of new businesses fail in year 1 , and half fail within 5 years, the importance of thorough planning and research should be clear.
But just what is a business plan? And what’s required to move from a series of ideas to a formal plan? Here we’ll answer that question and explain why you need one to be a successful business owner.
- What is a business plan?

A business plan lays out a strategic roadmap for any new or growing business.
Any entrepreneur with a great idea for a business needs to conduct market research , analyze their competitors , validate their idea by talking to potential customers, and define their unique value proposition .
The business plan captures that opportunity you see for your company: it describes your product or service and business model , and the target market you’ll serve.
It also includes details on how you’ll execute your plan: how you’ll price and market your solution and your financial projections .
Reasons for writing a business plan
If you’re asking yourself, ‘Do I really need to write a business plan?’ consider this fact:
Companies that commit to planning grow 30% faster than those that don’t.
Creating a business plan is crucial for businesses of any size or stage. It helps you develop a working business and avoid consequences that could stop you before you ever start.
If you plan to raise funds for your business through a traditional bank loan or SBA loan , none of them will want to move forward without seeing your business plan. Venture capital firms may or may not ask for one, but you’ll still need to do thorough planning to create a pitch that makes them want to invest.
But it’s more than just a means of getting your business funded . The plan is also your roadmap to identify and address potential risks.
It’s not a one-time document. Your business plan is a living guide to ensure your business stays on course.
Related: 14 of the top reasons why you need a business plan
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy

What research shows about business plans
Numerous studies have established that planning improves business performance:
- 71% of fast-growing companies have business plans that include budgets, sales goals, and marketing and sales strategies.
- Companies that clearly define their value proposition are more successful than those that can’t.
- Companies or startups with a business plan are more likely to get funding than those without one.
- Starting the business planning process before investing in marketing reduces the likelihood of business failure.
The planning process significantly impacts business growth for existing companies and startups alike.
Read More: Research-backed reasons why writing a business plan matters
When should you write a business plan?
No two business plans are alike.
Yet there are similar questions for anyone considering writing a plan to answer. One basic but important question is when to start writing it.
A Harvard Business Review study found that the ideal time to write a business plan is between 6 and 12 months after deciding to start a business.
But the reality can be more nuanced – it depends on the stage a business is in, or the type of business plan being written.
Ideal times to write a business plan include:
- When you have an idea for a business
- When you’re starting a business
- When you’re preparing to buy (or sell)
- When you’re trying to get funding
- When business conditions change
- When you’re growing or scaling your business
Read More: The best times to write or update your business plan
How often should you update your business plan?
As is often the case, how often a business plan should be updated depends on your circumstances.
A business plan isn’t a homework assignment to complete and forget about. At the same time, no one wants to get so bogged down in the details that they lose sight of day-to-day goals.
But it should cover new opportunities and threats that a business owner surfaces, and incorporate feedback they get from customers. So it can’t be a static document.
Related Reading: 5 fundamental principles of business planning
For an entrepreneur at the ideation stage, writing and checking back on their business plan will help them determine if they can turn that idea into a profitable business .
And for owners of up-and-running businesses, updating the plan (or rewriting it) will help them respond to market shifts they wouldn’t be prepared for otherwise.
It also lets them compare their forecasts and budgets to actual financial results. This invaluable process surfaces where a business might be out-performing expectations and where weak performance may require a prompt strategy change.
The planning process is what uncovers those insights.
Related Reading: 10 prompts to help you write a business plan with AI
- How long should your business plan be?
Thinking about a business plan strictly in terms of page length can risk overlooking more important factors, like the level of detail or clarity in the plan.
Not all of the plan consists of writing – there are also financial tables, graphs, and product illustrations to include.
But there are a few general rules to consider about a plan’s length:
- Your business plan shouldn’t take more than 15 minutes to skim.
- Business plans for internal use (not for a bank loan or outside investment) can be as short as 5 to 10 pages.
A good practice is to write your business plan to match the expectations of your audience.
If you’re walking into a bank looking for a loan, your plan should match the formal, professional style that a loan officer would expect . But if you’re writing it for stakeholders on your own team—shorter and less formal (even just a few pages) could be the better way to go.
The length of your plan may also depend on the stage your business is in.
For instance, a startup plan won’t have nearly as much financial information to include as a plan written for an established company will.
Read More: How long should your business plan be?
What information is included in a business plan?
The contents of a plan business plan will vary depending on the industry the business is in.
After all, someone opening a new restaurant will have different customers, inventory needs, and marketing tactics to consider than someone bringing a new medical device to the market.
But there are some common elements that most business plans include:
- Executive summary: An overview of the business operation, strategy, and goals. The executive summary should be written last, despite being the first thing anyone will read.
- Products and services: A description of the solution that a business is bringing to the market, emphasizing how it solves the problem customers are facing.
- Market analysis: An examination of the demographic and psychographic attributes of likely customers, resulting in the profile of an ideal customer for the business.
- Competitive analysis: Documenting the competitors a business will face in the market, and their strengths and weaknesses relative to those competitors.
- Marketing and sales plan: Summarizing a business’s tactics to position their product or service favorably in the market, attract customers, and generate revenue.
- Operational plan: Detailing the requirements to run the business day-to-day, including staffing, equipment, inventory, and facility needs.
- Organization and management structure: A listing of the departments and position breakdown of the business, as well as descriptions of the backgrounds and qualifications of the leadership team.
- Key milestones: Laying out the key dates that a business is projected to reach certain milestones , such as revenue, break-even, or customer acquisition goals.
- Financial plan: Balance sheets, cash flow forecast , and sales and expense forecasts with forward-looking financial projections, listing assumptions and potential risks that could affect the accuracy of the plan.
- Appendix: All of the supporting information that doesn’t fit into specific sections of the business plan, such as data and charts.
Read More: Use this business plan outline to organize your plan
- Different types of business plans
A business plan isn’t a one-size-fits-all document. There are numerous ways to create an effective business plan that fits entrepreneurs’ or established business owners’ needs.
Here are a few of the most common types of business plans for small businesses:
- One-page plan : Outlining all of the most important information about a business into an adaptable one-page plan.
- Growth plan : An ongoing business management plan that ensures business tactics and strategies are aligned as a business scales up.
- Internal plan : A shorter version of a full business plan to be shared with internal stakeholders – ideal for established companies considering strategic shifts.
Business plan vs. operational plan vs. strategic plan
- What questions are you trying to answer?
- Are you trying to lay out a plan for the actual running of your business?
- Is your focus on how you will meet short or long-term goals?
Since your objective will ultimately inform your plan, you need to know what you’re trying to accomplish before you start writing.
While a business plan provides the foundation for a business, other types of plans support this guiding document.
An operational plan sets short-term goals for the business by laying out where it plans to focus energy and investments and when it plans to hit key milestones.
Then there is the strategic plan , which examines longer-range opportunities for the business, and how to meet those larger goals over time.
Read More: How to use a business plan for strategic development and operations
- Business plan vs. business model
If a business plan describes the tactics an entrepreneur will use to succeed in the market, then the business model represents how they will make money.
The difference may seem subtle, but it’s important.
Think of a business plan as the roadmap for how to exploit market opportunities and reach a state of sustainable growth. By contrast, the business model lays out how a business will operate and what it will look like once it has reached that growth phase.
Learn More: The differences between a business model and business plan
- Moving from idea to business plan
Now that you understand what a business plan is, the next step is to start writing your business plan .
The best way to start is by reviewing examples and downloading a business plan template. These resources will provide you with guidance and inspiration to help you write a plan.
We recommend starting with a simple one-page plan ; it streamlines the planning process and helps you organize your ideas. However, if one page doesn’t fit your needs, there are plenty of other great templates available that will put you well on your way to writing a useful business plan.
Tim Berry is the founder and chairman of Palo Alto Software , a co-founder of Borland International, and a recognized expert in business planning. He has an MBA from Stanford and degrees with honors from the University of Oregon and the University of Notre Dame. Today, Tim dedicates most of his time to blogging, teaching and evangelizing for business planning.

Table of Contents
- Reasons to write a business plan
- Business planning research
- When to write a business plan
- When to update a business plan
- Information to include
- Business vs. operational vs. strategic plans
Related Articles

13 Min. Read
How to Write a Nonprofit Business Plan

7 Min. Read
Target Market Examples

8 Min. Read
How to Forecast Personnel Costs in 3 Steps

6 Min. Read
Differences Between Single-Use and Standing Plans Explained
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
How to write a strategic plan and what it should include
As Abraham Lincoln once said, “Give me six hours to chop down a tree and I will spend the first four sharpening the axe.”
Whether you’re a lumberjack or not, there’s a powerful truth to Lincoln’s wise words. And that’s the importance of planning.
Coming up with a solid strategic plan is a crucial aspect of any business. How can you expect to achieve your objectives if you don’t know what you’re aiming for? And how can you efficiently reach your goals without deciding on the appropriate method first?
You need a plan. More specifically, you need a strategic plan.
Sharpen your axes and get comfortable because we’re going to give you a step-by-step guide on how to write a strategic plan like a total boss.
- What is a strategic plan?
A strategic plan is a document that lays out how an organization plans to realize its long-term ambitions. Think of it as your roadmap. It establishes the direction a company is going to take by considering its goals and objectives. But it also includes the specific actions you are going to take to achieve your goal.
A strategic plan should essentially answer three questions:
- Where are we now?
- Where do we want to go?
- How will we get there?

There are a lot of terms around strategic plans that sound similar. But it’s important for your team to understand what each of them means and how they are different. Let’s clarify some common terms:
- Strategic plan is your roadmap document.
- Strategic planning is the process of developing your strategic plan.
- Strategic planning meeting is the session or event during which strategic planning takes place.
- Strategic planning frameworks are the tools and methodologies to help your team develop different elements of your strategic plan.
- Strategic planning model is the overarching approach for how you are going to structure your strategic ideas. You should decide on which model you are going to use before you begin the strategic planning process.
- Why is a strategic plan important?
Now you know what a strategic plan is. But why do you need one? Here are just some of the reasons developing a strategic plan is so important to your organization
Helps you come up with goals that direct your actions
How can you expect to get anywhere if you don’t know where you’re going? A key aspect of the strategic planning process is establishing goals and objectives. These goals will help build momentum within your team and keep them focused on the overarching goal of the business.
Keeps you on track toward achieving your goals
A well-written strategic business plan gives your organization direction. As well as what you want to achieve, strategic plans require you to get specific about how you are going to achieve your goals. Having this plan of action in one consolidated document helps your team stay on track and achieve their goals faster and with more efficiency.
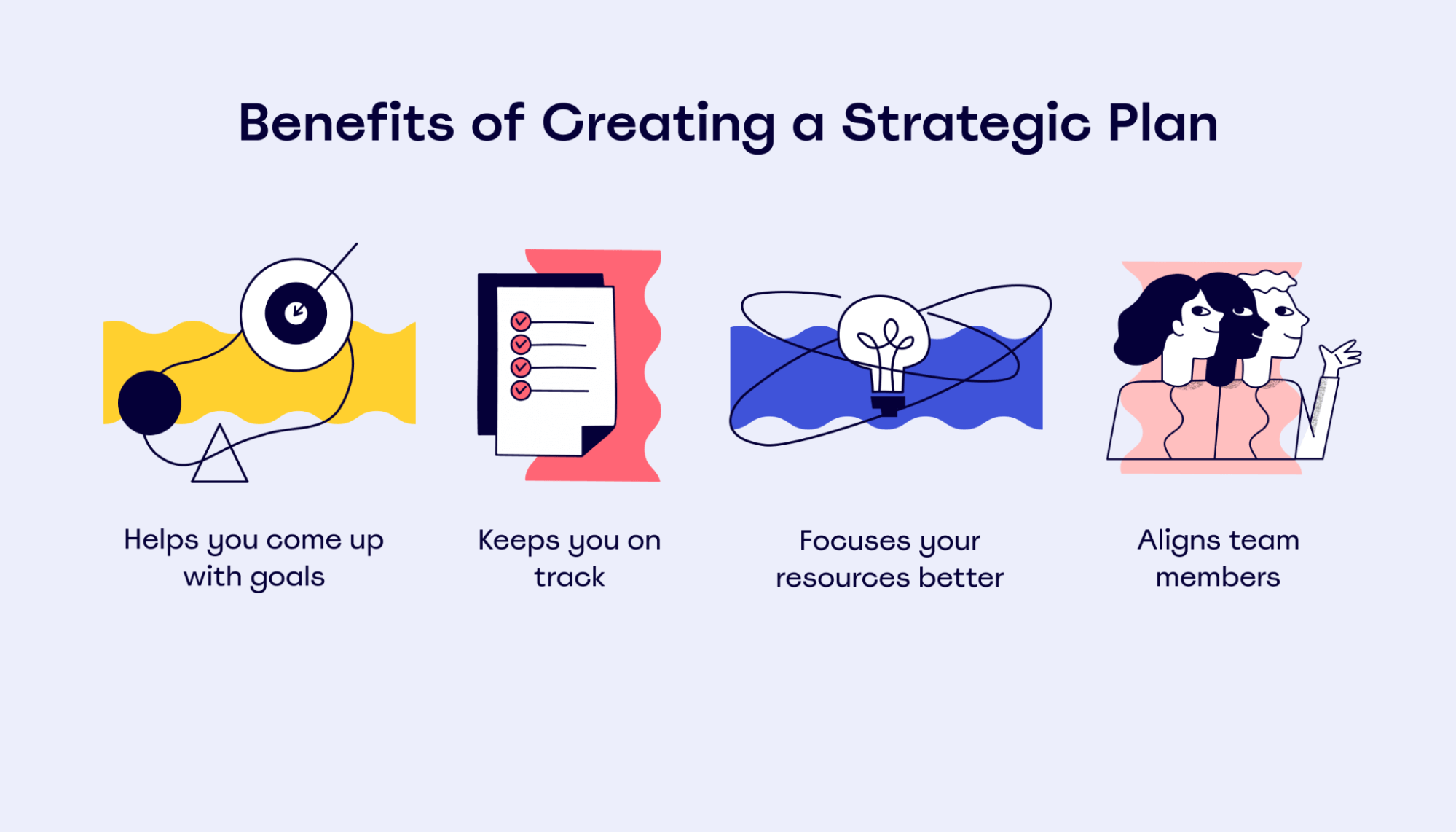
Focus your resources better
Taking the time to write a well-thought-out strategic plan means carefully considering what actions are going to best serve your company. This prevents wasting time, money, and effort on projects that are not going to take your business to where it wants to go.
The clarity that comes from a strategic plan sets you up for successful resource allocation, which is essential for growing your business.
Aligns team members
A robust strategic plan becomes a source of truth for your team. It keeps all team members on the same page regarding the company’s mission and strategy. When confused about why they are doing something or how they fit into the bigger picture, they can refer to the team’s strategic plan.
As well as team members, a strategic plan keeps stakeholders in the know. They should be involved in the development of the strategic plan so that the goals and strategies are aligned with their expectations.
- What is included in a strategic plan?
These are the key elements that make up a strategic plan.
Vision statement
The vision statement gives a clear picture of what your organization wants to achieve in the long run. It is an aspirational statement that describes the ideal future state of your business.
Many great vision statements use emotional language to paint a picture of what impact the group hopes to make on the world. For example, IKEA’s vision statement is “To create a better everyday life for the many people.”
Mission statement
While a vision statement looks toward the future, a mission statement considers the present. It should describe the core purpose of the company and why it exists. Your mission statement should provide context for all other goals and actions.
IKEA’s mission statement is “to offer a wide range of well-designed, functional home furnishing products at prices so low that as many people as possible will be able to afford them.”
Your objectives are what you plan to achieve. They are the specific results that your organization wants to accomplish within a certain time frame. Strategic objectives aim to bridge the gap between your overall vision and the goals needed to achieve it.
Strategic objectives can be financial, growth-related, or customer-related. An example of a strategic objective is “Enter three new foreign markets in the next five years.”
This section of your strategic plan is where you turn the focus from your vision to execution. Your strategy is the blueprint for how to achieve your goals and objectives.
If your objective is to “Enter three new foreign markets in the next five years,” you need to develop a strategy for how you are going to do this. Which markets are you going to target? What products or services are you going to introduce? What are the current market trends? Asking and answering these questions will help you design a specific market entry strategy.
This is where strategic planning frameworks become so useful. For example, the Ansoff Matrix helps you evaluate opportunities for growth. Also known as the product-market expansion grid, the Ansoff Matrix helps you review the potential risks and opportunities of each growth plan option.
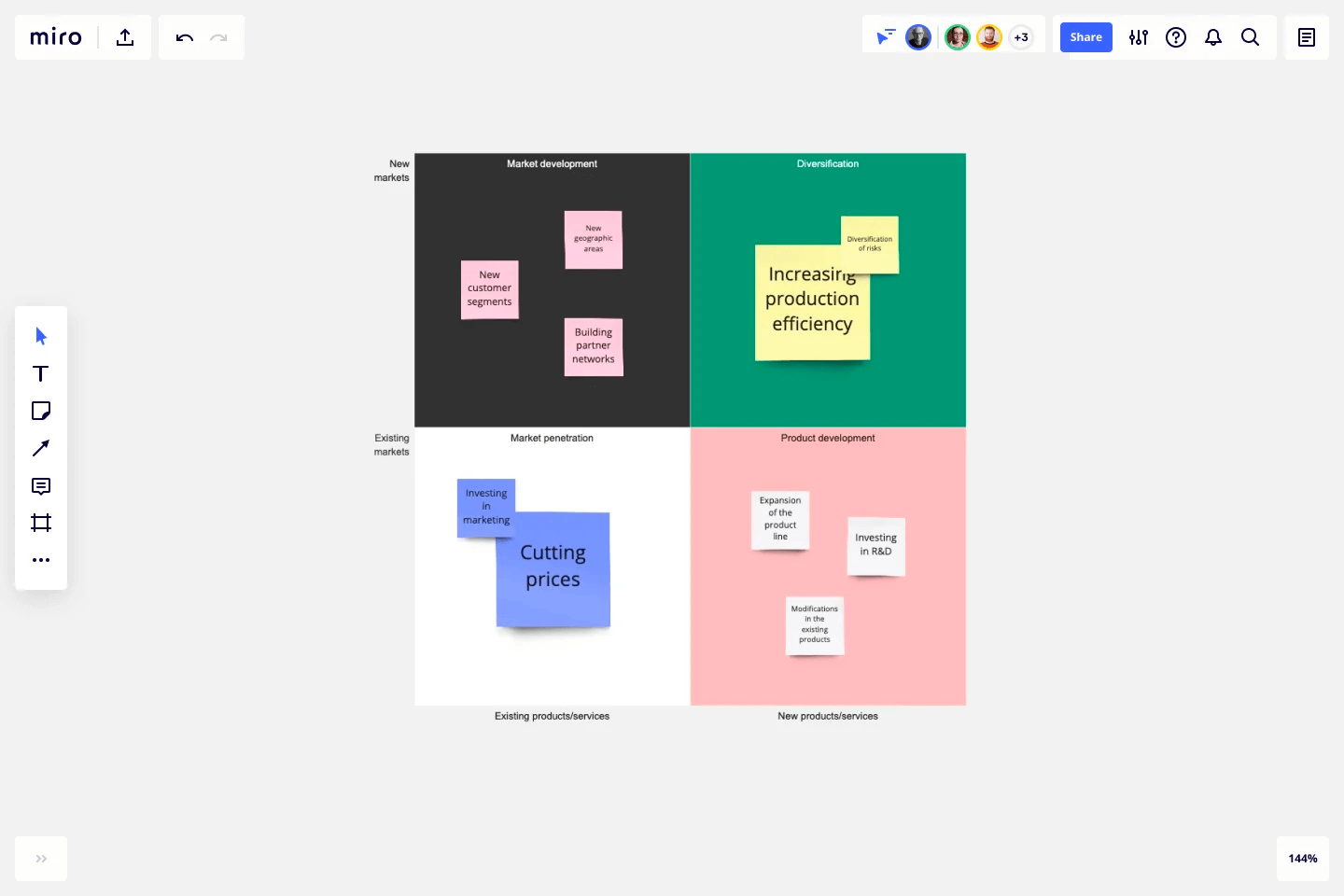
By using frameworks like the Ansoff Matrix, you can analyze each strategic option. All the data gathered and your team’s insights on this data will help determine your strategic approach.
After writing a strategic plan and implementing it, you need to track its progress. Metrics are a way for you to measure the success of your actions. If you find that your strategic plan isn’t giving you the results you expected, you can make changes to your strategic approach.
Metrics can be milestones, such as launching a product or completing a certain project. Or your metrics can be quantifiable performance measures, like KPIs.
- How to write a strategic plan
Now that you know what a strategic plan should include, here’s a step-by-step guide on how to write a strategic plan for your business.
1. Hold a strategic planning meeting
No man is an island, especially in the realm of strategic planning. You want to get your entire team involved in the strategic planning process. To ensure everyone is part of the process, you need to hold a strategic planning meeting . This meeting is about collaboration and openly sharing ideas around your strategic plan.
Start by making an invite list and sending out calendar invites to the people you want to attend the session. This should include people from different departments, executives, and stakeholders.
2. Use a template
To save you time and hassle, use a customizable Strategic Planning Template . Businesses have been writing strategic plans for years and years, so there’s no need to reinvent the wheel. Using a template will also help ensure that you don’t miss out on any important aspects of the strategic planning process.
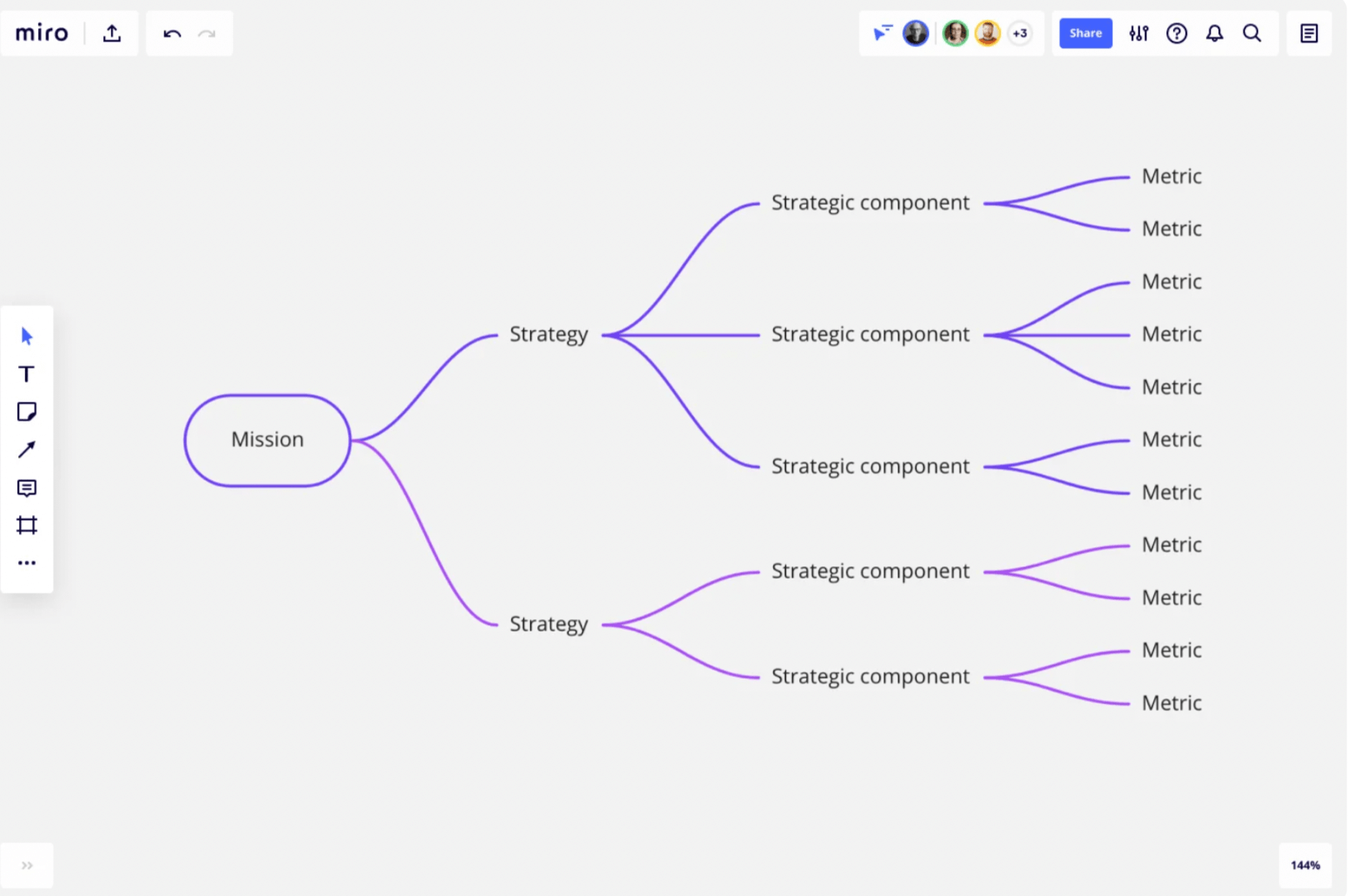
3. Determine your position
Before you look towards the future about where you want to be, you need to understand where you currently stand. This means looking internally at who you are as a company and conducting market and competitor analysis to fully understand your external environment.
A popular method for taking stock of your company’s current position is a SWOT analysis . This framework helps you map out the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of your business.
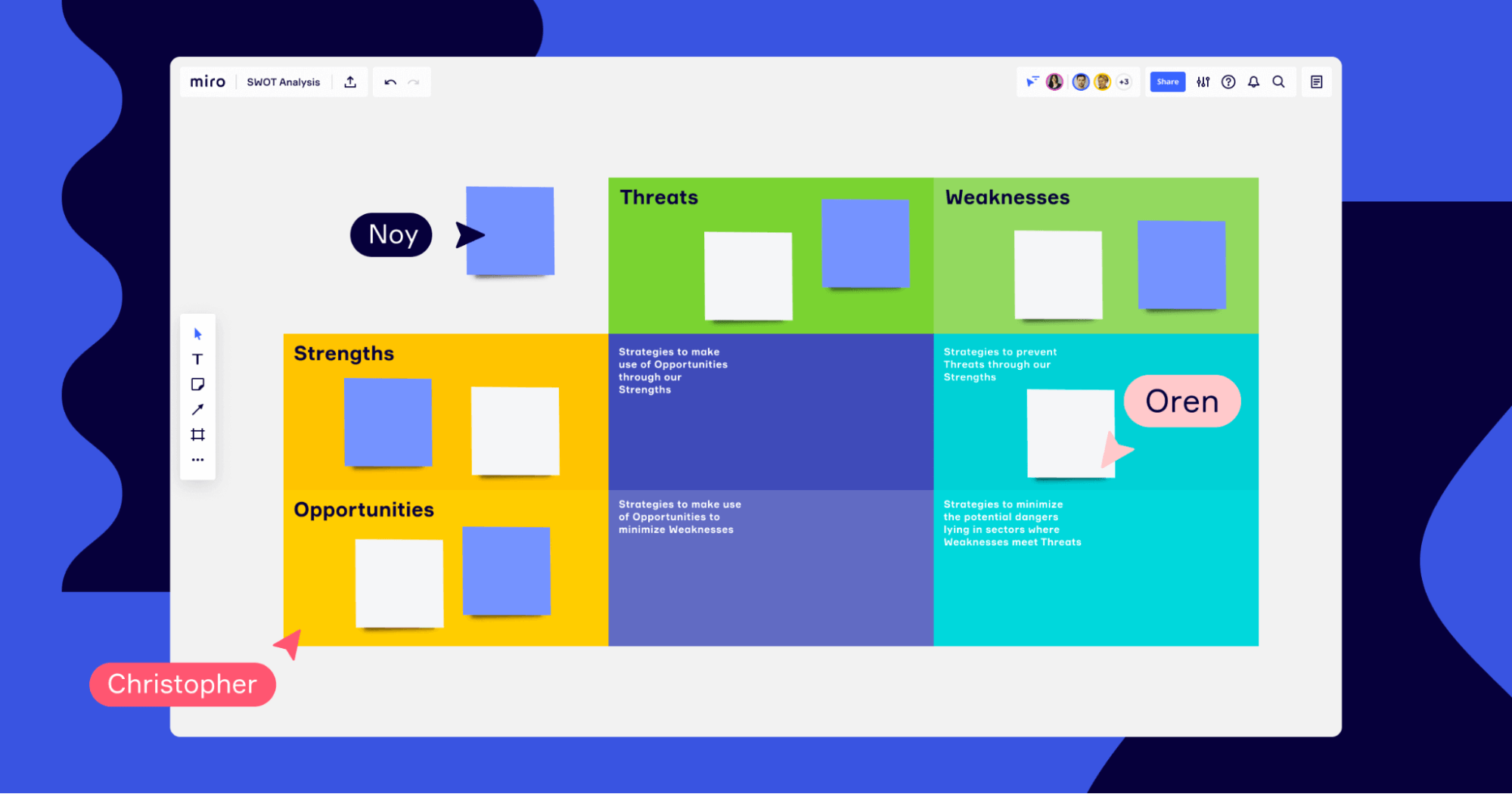
4. Decide where you want to go
Now it’s time to look toward the future and decide on what you are aiming for. This is where you articulate what you want to achieve. Some examples of thought-provoking questions to ask your team include:
- What do we want to accomplish?
- Where do we want to be?
- How many products would we sell?
- How many countries will we be based in?
- Who would our customers be?
This part of writing a strategic plan is where you develop the strategic objectives, goals, and action items. We’re big fans of setting OKRs: Objectives and their related Key Results. This OKR Template will ensure your business goals are structured and clearly defined.
5. Decide how you are going to get there
Now that you know where you’re going, you need to decide how to get there. This phase involves deciding how you’re going to make your goals a reality. And that means coming up with an action plan.
An action plan is a detailed set of lists outlining the steps you are going to take to complete your objectives. Our Action Plan Template promotes clarity and transparency around assigned tasks. As a team, you need to decide who needs to do what and by when. Everyone should be aware of their role in executing the overall strategic plan.
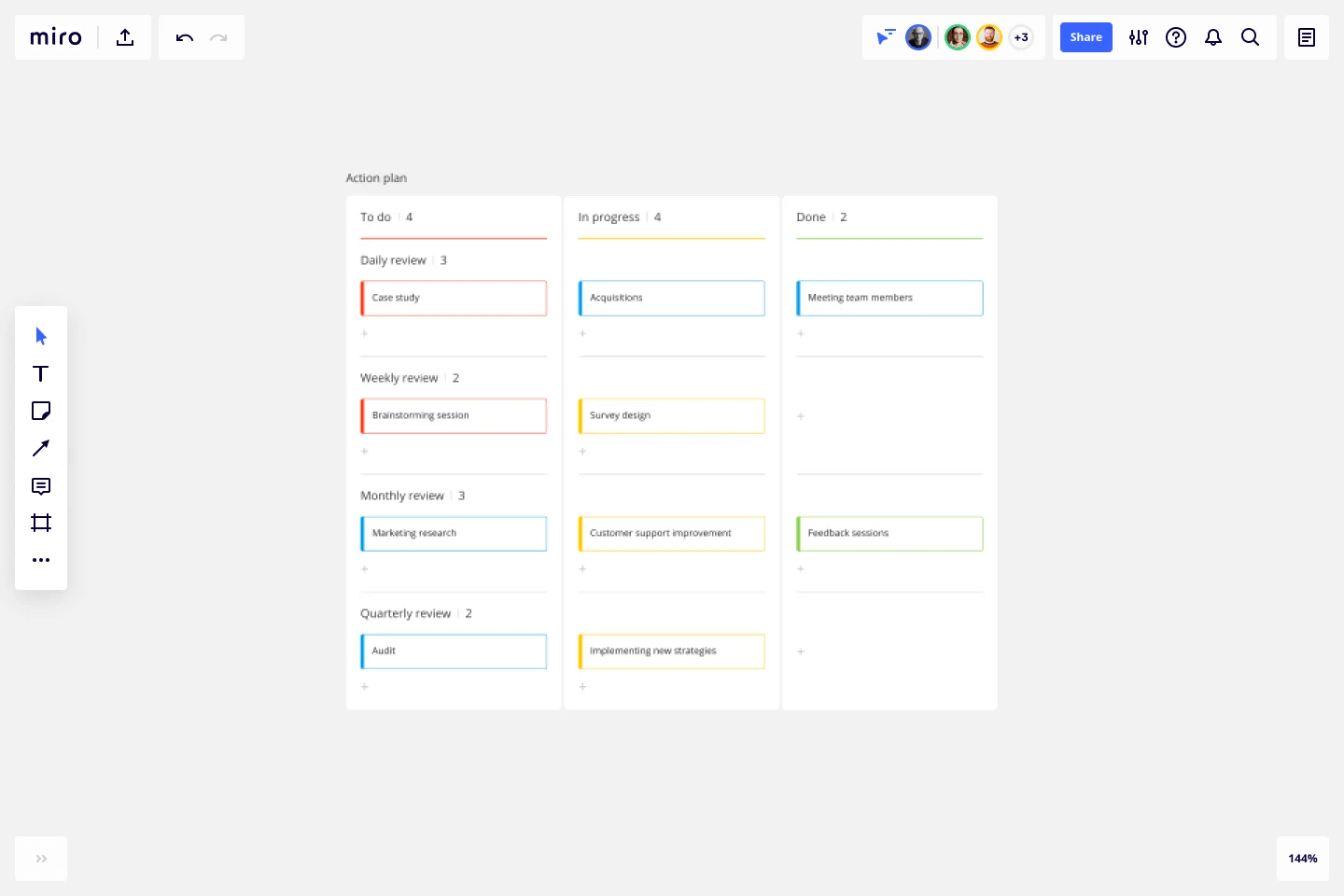
- Tips for writing a strategic plan
Keep these tips in mind when writing your strategic plan to make the process more efficient.
Use the right tools
Developing a strategic plan has a lot of moving parts. From running a strategic planning session to capturing your team’s ideas, there’s a lot to stay on top of. But an online collaborative tool like Miro can make the process a whole lot easier.
With Miro, you collaborate with your team from anywhere, at any time. Not to mention safely store all your mindmaps , boards, and diagrams in one consolidated place. To get a real sense of what’s possible, have a look at our list of features .
Be SMART with your goals
Whenever you create goals or objectives, ensure that they are SMART . This means they should be specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound. It’s no use coming up with a long list of impressive goals that aren’t realistic or focused.
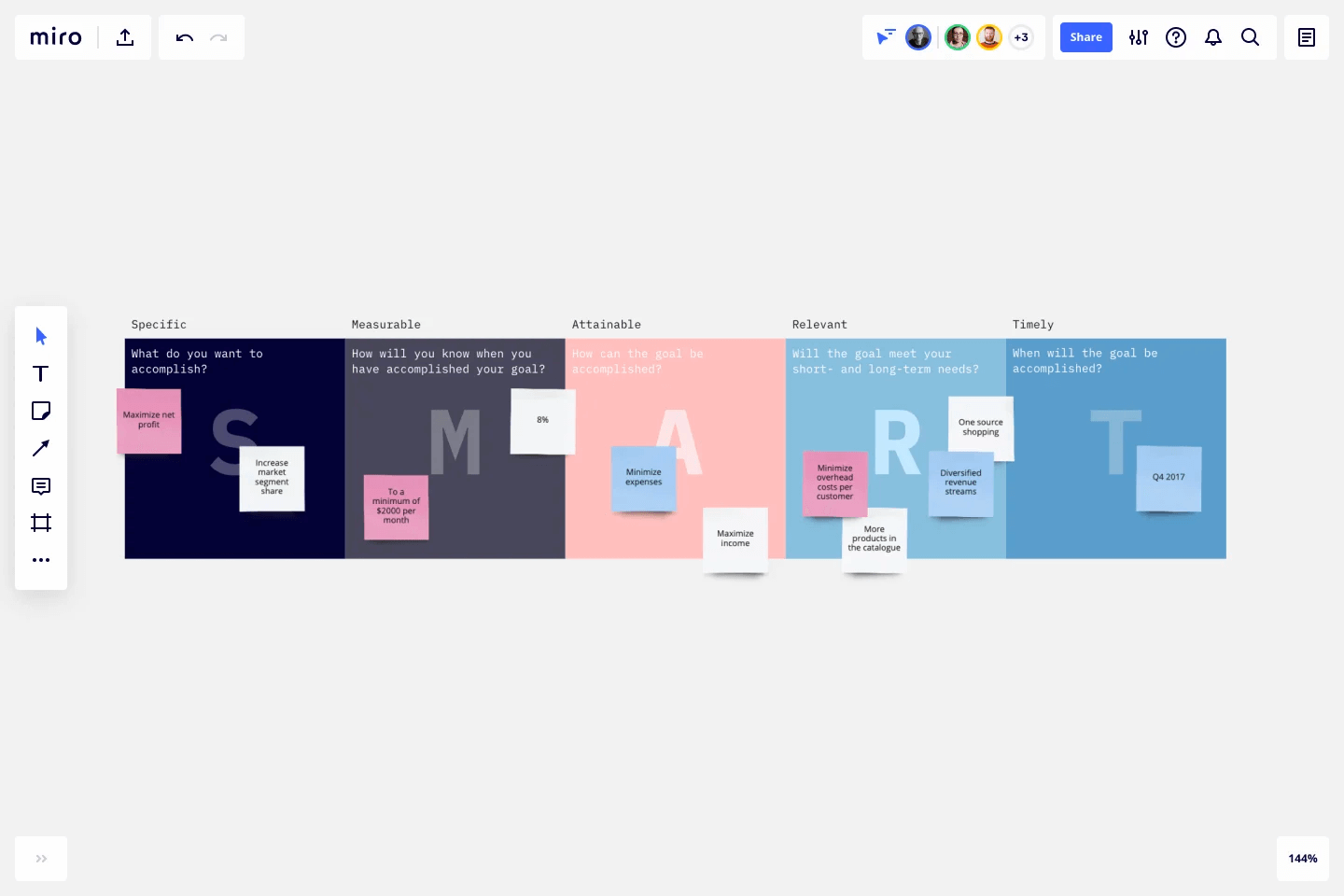
Don’t be afraid to change your plan
Strategic plans aren’t set in stone. They should be used more as a guideline that is adjusted as needed. Your company will no doubt face new challenges or identify new opportunities as time goes on. So it’s important to revisit your strategic plan and make necessary adjustments based on changes in your organization’s environment and situation.
Strategic plans are usually developed for the next two to five-year period. Some companies reconsider their strategic plan every year, while others hold strategic planning sessions every quarter.
It’s up to you and your team how often you revisit your strategic plan, but the key takeaway is that you should be open to changing your plan.
- Get starting writing your strategic plan
We’re not going to lie to you — creating a strategic plan isn’t the easiest process to execute. From capturing your company’s vision to measuring your strategy’s success, there’s a lot to do. But that shouldn’t deter you.
Knowing how to write a strategic plan is a valuable skill to have, no matter what industry you’re in. And tools like Miro are there to make the process a whole lot easier and more efficient.
Miro is your team's visual platform to connect, collaborate, and create — together.
Join millions of users that collaborate from all over the planet using Miro.
Keep reading
11 must-read books for developing and shipping better products.

3 steps to go from customer interviews to a customer journey map
4 Business Canvases in one place

More Like this
What is the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan.
It is not uncommon that the terms ‘strategic plan’ and ‘business plan’ get confused in the business world. While a strategic plan is a type of business plan, there are several important distinctions between the two types that are worth noting. Before beginning your strategic planning process or strategy implementation, look at the article below to learn the key difference between a business vs strategic plan and how each are important to your organization.
Definition of a business plan vs. a strategic plan
A strategic plan is essential for already established organizations looking for a way to manage and implement their strategic direction and future growth. Strategic planning is future-focused and serves as a roadmap to outline where the organization is going over the next 3-5 years (or more) and the steps it will take to get there.
Get the Free Guide for Setting OKRs that Work (with 100 examples!)
A strategic plan serves 6 functions for an organization that is striving to reach the next level of their growth:.
- Defines the purpose of the organization.
- Builds on an organization’s competitive advantages.
- Communicates the strategy to the staff.
- Prioritizes the financial needs of the organization.
- Directs the team to move from plan to action.
- Creates long-term sustainability and growth impact
Alternatively, a business plan is used by new businesses or organizations trying to get off the ground. The fundamentals of a business plan focus on setting the foundation for the business or organization. While it looks towards the future, the focus is set more on the immediate future (>1 year). Some of the functions of a business plan may overlap with a strategic plan. However, the focus and intentions diverge in a few key areas.
A business plan for new businesses, projects, or organizations serves these 5 functions:
- Simplifies or explains the objectives and goals of your organization.
- Coordinates human resource management and determines operational requirements.
- Secures funding for your organization.
- Evaluates potential business prospects.
- Creates a framework for conceptualizing ideas.
In other words, a strategic plan is utilized to direct the momentum and growth of an established company or organization. In contrast, a business plan is meant to set the foundation of a newly (or not quite) developed company by setting up its operational teams, strategizing ways to enter a new market, and obtaining funding.
A strategic plan focuses on long-term growth and the organization’s impact on the market and its customers. Meanwhile, a business plan must focus more on the short-term, day-to-day operational functions. Often, new businesses don’t have the capacity or resources to create a strategic plan, though developing a business plan with strategy elements is never a bad idea.
Business and strategic plans ultimately differ in several key areas–timeframe, target audience, focus, resource allocation, nature, and scalability.
While both a strategic and business plan is forward-facing and focused on future success, a business plan is focused on the more immediate future. A business plan normally looks ahead no further than one year. A business plan is set up to measure success within a 3- to 12-month timeframe and determines what steps a business owner needs to take now to succeed.
A strategic plan generally covers the organizational plan over 3 to 5+ years. It is set with future expansion and development in mind and sets up roadmaps for how the organization will reach its desired future state.
Pro Tip: While a vision statement could benefit a business plan, it is essential to a strategic plan.
Target Audience
A strategic plan is for established companies, businesses, organizations, and owners serious about growing their organizations. A strategic plan communicates the organization’s direction to the staff and stakeholders. The strategic plan is communicated to the essential change makers in the organization who will have a hand in making the progress happen.
A business plan could be for new businesses and entrepreneurs who are start-ups. The target audience for the business plan could also be stakeholders, partners, or investors. However, a business plan generally presents the entrepreneur’s ideas to a bank. It is meant to get the necessary people onboard to obtain the funding needed for the project.
A strategic plan provides focus, direction, and action to move the organization from where they are now to where they want to go. A strategic plan may consist of several months of studies, analyses, and other processes to gauge an organization’s current state. The strategy officers may conduct an internal and external analysis, determine competitive advantages, and create a strategy roadmap. They may take the time to redefine their mission, vision, and values statements.
Alternatively, a business plan provides a structure for ideas to define the business initially. It maps out the more tactical beginning stages of the plan.
Pro Tip: A mission statement is useful for business and strategic plans as it helps further define the enterprise’s value and purpose. If an organization never set its mission statement at the beginning stages of its business plan, it can create one for its strategic plan.
A strategic plan is critical to prioritizing resources (time, money, and people) to grow the revenue and increase the return on investment. The strategic plan may start with reallocating current financial resources already being utilized more strategically.
A business plan will focus on the resources the business still needs to obtain, such as vendors, investors, staff, and funding. A business plan is critical if new companies seek funding from banks or investors. It will add accountability and transparency for the organization and tell the funding channels how they plan to grow their business operations and ROI in the first year of the business.
The scalability of a business plan vs. strategic plan
Another way to grasp the difference is by understanding the difference in ‘scale’ between strategic and business plans. Larger organizations with multiple business units and a wide variety of products frequently start their annual planning process with a corporate-driven strategic plan. It is often followed by departmental and marketing plans that work from the Strategic Plan.
Smaller and start-up companies typically use only a business plan to develop all aspects of operations of the business on paper, obtain funding and then start the business.
Why understanding the differences between a business plan vs a strategic plan matters
It is important to know the key differences between the two terms, despite often being used interchangeably. But here’s a simple final explanation:
A business plan explains how a new business will get off the ground. A strategic plan answers where an established organization is going in the future and how they intend to reach that future state.
A strategic plan also focuses on building a sustainable competitive advantage and is futuristic. A business plan is used to assess the viability of a business opportunity and is more tactical.
10 Comments
I agree with your analysis about small companies, but they should do a strategic plan. Just check out how many of the INC 500 companies have an active strategic planning process and they started small. Its about 78%,
Strategic management is a key role of any organization even if belong to small business. it help in growth and also to steam line your values. im agree with kristin.
I agree with what you said, without strategic planning no organization can survive whether it is big or small. Without a clear strategic plan, it is like walking in the darkness.. Best Regards..
Vision, Mission in Business Plan VS Strategic Plan ?
you made a good analysis on strategic plan and Business plan the difference is quite clear now. But on the other hand, it seems that strategic plan and strategic management are similar which I think not correct. Please can you tell us the difference between these two?. Thanks
Thank you. I get points to work on it
super answer Thanking you
Hi. I went through all the discussions, comments and replies. Thanks! I got a very preliminary idea about functions and necessity of Strategic Planning in Business. But currently I am looking for a brief nice, flowery, juicy definition of “Business Strategic Planning” as a whole, which will give anyone a fun and interesting way to understand. Can anyone help me out please? Awaiting replies…… 🙂
that was easy to understand,
Developing a strategic plan either big or small company or organization mostly can’t achieve its goal. A strategic plan or formulation is the first stage of the strategic management plan, therefore, we should be encouraged to develop a strategic management plan. We can develop the best strategic plan but without a clear plan of implementation and evaluation, it will be difficult to achieve goals.
Comments Cancel
Join 60,000 other leaders engaged in transforming their organizations., subscribe to get the latest agile strategy best practices, free guides, case studies, and videos in your inbox every week..

Leading strategy? Join our FREE community.
Become a member of the chief strategy officer collaborative..
Free monthly sessions and exclusive content.
Do you want to 2x your impact.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, how often should a business plan be updated, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, How To Create One
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One CURRENT ARTICLE
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons
- Best Startup Business Loans
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros & Cons, and Differences From an LLC
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types
- What is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
Strategic planning — what it is and how to do it well

It can be difficult to reach your business goals and ambitions, regardless of what preparation you’ve done. But if you have a strategic plan in place, you’ll be more likely to achieve a favorable outcome.
This post will explain the importance of strategic planning, when and how to make a strategic plan, and how to manage it and stay on course. It will allow the audience to move forward with their planning efforts.
Read on to learn:
- What strategic planning is
Benefits of strategic planning
- When you should do strategic planning
Steps in strategic planning
- What strategic management is
Strategic mapping
What is strategic planning.
Strategic planning is the process of defining your business’s direction and outlining a path toward a preferred future. The goal of a strategic plan is to capture an organization’s mission and core principles — to envision the fulfillment of these ideals. Strategic planning is both conceptual and practical, as it presents both high-level goals and specific approaches to achieve them.
A strategic plan needs to answer the following questions:
- Where are we now?
- Where are we going?
- How do we get there?
Strategic planning helps businesses set and maintain a clear vision and ensure they’re moving in the right direction. Once the plan has been put in place, it helps maintain alignment between various stakeholders and teams within your business. This plan can make resource allocation simpler — by determining if certain resources are being used in ways that don’t align with the broader strategic plan.
Running a business without a strategic plan is like planning a vacation with no destination in mind. How will you get there? What do you need to bring with you? The same applies to planning for your business. Strategic planning:
- Gives a sense of purpose and direction. A strategic plan provides a clear goal and end result so all other business functions can work to get you closer to that outcome. This clarity helps keep employees aligned on their efforts, make better decisions, and work towards a shared goal.
- Makes you aware of opportunities for success. Tying your plans to strategy helps your organization identify opportunities that you discover along your journey. If you find an opportunity that aligns with your strategy — and desired outcomes — you can more easily adapt to take advantage of the situation.
- Alerts you to risks to avoid. Part of the strategic planning process is scanning the external environment and competitive landscape, which allows you to identify potential roadblocks you may encounter.
- Helps you understand what resources you will need. When you have a strategic plan in place, you can more effectively allocate your resources. By aligning resources with strategic goals, businesses can focus on the initiatives, projects, and investments that maximize their ROI.
- Helps prioritize critical tasks. When deciding which tasks are most important and which can be put on hold, a strategic plan streamlines that decision making. Tasks that don’t contribute to your mission can wait, while mission-critical tasks get prioritized.
- Fosters teamwork and communication. Without a strategic plan, team members can feel isolated and siloed. However, when that strategic plan is clearly communicated to everyone, your team will feel more connected as they work towards a common goal.
- Increases motivation. And when your team understands the desired outcomes and bigger goals behind their daily tasks, they’ll be more motivated to do high-quality work in a timely manner.
- Helps measure and evaluate results. Because you’ve likely identified key performance indicators (KPIs) in your planning process, you’ll have an easier time tracking your progress. When you measure your progress, you can more easily identify areas for improvement and make changes on the fly.
When should you do strategic planning?
When and how often your business does strategic planning depends on the size and stage of your company, the speed of your business, and the scope of the projects you’re working on. Strategic planning should not be a one-time event. It should be an iterative process with continuous monitoring, evaluation, and adjustment.
If you’re a new business, you’ll want to create a business plan first, before you move into strategic planning. Once your business is established you can then set a strategic plan to outline your goals and manage your business’s strategic direction. For planning more short-term projects, use a project plan .
Once you’ve created a strategic plan, you should review it regularly — quarterly and yearly, for example — to make sure it is still aligned with your business’s goals and industry landscape. Generally, you should create a new strategic plan every 3–5 years. However, newer or faster-moving companies may need to create a new strategic plan every 1–2 years. Another scenario when you should rework your strategic plan is when you’re preparing to make a major pivot in your business.
How to write a strategic plan for a project
Learn how to write a strategic plan, why you need to create one, and the topics it should cover.

While every strategic plan might look a little different depending on the organization, industry, and other context, there is still a general outline of the process that you can follow to get you started.
Before you get started, there are a few preliminary steps you can take to make sure your planning process goes smoothly. You need to decide who is involved in the process and what documentation they’ll need. You’ll also want to revisit your company’s vision and mission statements which define where your business is aiming to go.
These are the steps you can take to create a strategic plan for your business:
1. Identify and assess your current position
To understand where you’re headed, you first need to look at where you are now. I n this stage you should:
- Collect customer and employee feedback to understand what is working well for you and what could use improvement.
- Perform a needs assessment or SWOT analysis to understand more about the current state of your business.
- Assess your available resources so you can understand what you have enough of and what you may need to reach your goals.
2. Set goals
Next, you can set goals that you’d like your business to achieve over the short and long term. It’s important to choose goals that align with your company mission and vision. You can use marketing and sales forecasts to give you an idea of what types of goals are realistic. In this phase you’ll also want to prioritize the goals you set — so you know which to choose if conflicts arise.
When setting goals, remember to set SMART goals that are specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time bound.
3. Develop your plan
In this phase it’s time to put your plan together and map out a project roadmap. This is where your plan becomes clearer both to your planning committee and to your team members who will execute based on the plan.
You want to make sure that your plan is achievable with your current resources — so that you aren’t setting yourself up for failure. You’ll also want to set measurable milestones so you can track your progress along the way. You also need to set KPIs so you have objective numbers to determine if you’re heading in the right direction.
When developing your plan, you should make sure that any short-term action items align with long-term goals. And finally, you’ll need to get approval from leadership and stakeholders.
4. Implement your plan
Now that you’ve created your strategic plan it’s time to act. In fact, the first step of implementation is creating a strategic action plan. Your action plan will outline the specific tactics you’ll use to execute your strategic plan.
In this phase, you’ll also assign tasks to your team members so everyone knows what they are responsible for and what they will be contributing to your mission. It’s important to distribute and communicate your plan across your organization. This helps encourage transparency and will drive buy-in from everyone on your team.
As you are executing on your plan, you should rely on metrics and KPIs to track your performance.
5. Revise your plan as necessary
Next, you’ll want to revise your plan as you encounter roadblocks or market changes. Even the best strategic plans will change as you gather more data or feedback. Using tools — like a project management solution — can help you monitor the progress your team is making. You should schedule periodic evaluations to see which parts of the plan are going well and which need to be revised or reevaluated.
You can conduct reviews on a quarterly basis, so you have information at the end of the year to revise your plan if needed. Even if things are going well, you should make minor adjustments every year to keep your teams aligned and your strategy up to date. Any major revisions you make will require a new planning process — because a major adjustment could derail the rest of your strategic plan.
What is strategic management?
Strategic management is the process of formulating, implementing, and evaluating strategies to achieve the larger goals and objectives of an organization. It can sometimes be used interchangeably with the term strategic planning — but within strategic planning, strategic management means managing the plan being put into action.
Part of strategic management is being adaptive and adjusting to headwinds or organizational changes. You’ll also need to maintain a strong team culture, so your plan stays on track and team members stay engaged.
There are several models that strategic management can follow. Each takes a different approach to the management process, and how it solves problems that may arise.
One of these frameworks is the balanced scorecard method. This method looks at the strategic measures of a business beyond just financial metrics to get a more “balanced” look at performance. The phrase “balanced scorecard” refers to the management report that leaders may use to drive decision making within the business, since this approach looks at more than just numbers, it provides a more wholistic view of a business.
A strategic map is a visual representation of a business’s strategic objectives and their cause-and-effect relationships between each objective. This diagram helps visualize the strategic plan and understand which tasks are dependent on others. This map should be drawn during the development of the strategic plan to get a better understanding of how things should get done and in what order.
Strategic mapping can turn complex strategic plans into easily understandable visual representations. These can be helpful tools for communicating your strategy more clearly to team members and stakeholders within your organization. Strategic maps also help organizations identify success factors, prioritize initiatives, allocate resources, and monitor progress.
A strategic map can be designed in several ways, but needs to address the four main facets of business:

- Financial. This section of the map should identify how the strategy helps meet the financial goals of the business.
- Customer. This section should address the benefits that the customer will see from the specific strategy.
- Internal business processes (IBPs). This section shares the benefits of the strategy to the processes of the business and their efficiency.
- Learning and growth. This section will address how the business’s capabilities and knowledge will improve by using a given strategy.
Getting started with strategic planning
Strategic planning is a helpful tool for aligning everyone in your organization with your objectives and long-term goals. It can also help you gain a better understanding of your place in the market and how you can improve your business outcomes.
When you’re ready to get started, assemble your leadership team, draft your mission and vision statements, and begin by assessing the current state of your business. But you can’t get the most out of your strategic plan without a platform to drive the process forward.
That’s where Adobe Workfront can help. Workfront is an enterprise work management tool that connects work to strategy and drives better collaboration to deliver measurable business outcomes. It integrates people, data, processes, and technology across an organization so you can manage the entire lifecycle of projects from start to finish. By centralizing digital projects, cross-functional teams can connect, collaborate, and execute from anywhere to help them do their best work.
Take a product tour or watch an overview video to see how Workfront can help you execute on your strategic plan to improve your business outcomes.
https://business.adobe.com/blog/perspectives/workfront-and-the-employee-experience
https://business.adobe.com/blog/perspectives/get-the-most-out-of-workfront-discovery-by-avoiding-common-challenges
https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/annual-planning

What Is a Strategic Business Plan?
- Small Business
- Business Planning & Strategy
- Strategic Business Plans
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Pinterest" aria-label="Share on Pinterest">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Reddit" aria-label="Share on Reddit">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Flipboard" aria-label="Share on Flipboard">
Objectives in Workforce Planning
Projected profit and loss statement, rationales for marketing strategies.
- How to Find a DSL Modem's IP Address
- Why Is the Business Research Process Necessary to Assist Managers?
Long-term strategic business planning is necessary for company growth and success, explains Entrepreneur magazine . Business plans provide companies with the tools to track growth, establish a budget and prepare for unforeseen changes in the market place. A strategic business plan focuses on long-term growth objectives, rather than near-term operating goals and addresses different business strategy types.
A strategic plan includes many elements a business can utilize to attract financing and manage company objectives. To optimize strategic business planning, businesses must clearly define company goals and conduct extensive research to properly understand industry trends. Looking at different strategic planning models will help you decide how to set long-term goals for your small business.
What is a Strategic Business Plan?
A strategic business plan is a written document that pairs the objectives of a company with the needs of the market place. Although a strategic business plan contains similar elements of a traditional plan, a strategic plan takes planning a step further by not only defining company goals but utilizing those goals to take advantage of available business opportunities.
This is achieved by carefully analyzing a particular business industry and being honest about your company's strength and weakness in meeting the needs of the industry. A strategic business plan is followed by tactical plans to help achieve the strategic goals.
Reasons for Strategics Plans
A strategic business plan is necessary to optimize market research and to attain optimum market share for your business. The plan allows businesses to focus on a particular niche in the marketplace, which makes sales, advertising and customer management more effective. The plan allows a company to know as much as possible about the needs of its customers and gaps in the marketplace that need to be filled. A strategic business plan helps a company provide better, more targeted service to its clients.
Strategy vs. Tactics
A strategic business plan might set a goal of diversification for the business. Tactics for achieving this strategic goal might include acquiring a business with different product lines, or adding new products to the company's line. For example, a tennis racquet manufacturer might decided to add strings to its product line, either acquiring a string maker or sourcing its own strings.
A strategic business plan includes extensive market research, industry trends and competitor analyses. A strategic plan will include the components of a traditional plan, such as an executive summary, marketing analysis and financial statements, but a strategic plan will be more specific on how the company will go about achieving company goals.
For example, a strategic business plan will attempt to identify a target market, narrow it down to a manageable size, and establish a strategy for acquiring those customers.
Benefits of Strategic Business Plans
Writing a strategic business plan has many advantages. The plan can serve as an outline for successful completion of company milestones. Company owners are in a better position to not only understand their business but become experts in their industries.
A strategic plan helps executives understand the direction in which their company is headed by reviewing past progress and making changes to improve and grow. The plan is an organizational tool that helps to keep a company on track to meet growth and financial objectives.
Misconceptions About These Plans
Many small business owners feel that strategic business plans are for large companies and big businesses. However, according to the U.S. Small Business Administration, a strategic business plan can benefit companies of all sizes and can be a great advantage to small businesses. Small businesses may utilize different types of planning activities to develop the strategies necessary to attract and retain the customers it needs to succeed.
- Entrepreneur.com: Building a Strategy Pyramid
Sherrie Scott is a freelance writer in Las Vegas with articles appearing on various websites. She studied political science at Arizona State University and her education has inspired her to write with integrity and seek precision in all that she does.
Related Articles
Why create a business plan, business planning & analysis, the importance of a business plan, what is the meaning of corporate planning, differences between strategy, plans and tactics, difference between business plan & strategic plan, tactical and operational planning, how does a business strategy differ from strategic marketing management, business enterprise planning, most popular.
- 1 Why Create a Business Plan?
- 2 Business Planning & Analysis
- 3 The Importance of a Business Plan
- 4 What Is the Meaning of Corporate Planning?
EY must ‘work through’ strategic questions after split plan shelved, says firm’s Irish head
Big four firm grew irish business despite ‘difficult market’, says ey uk and ireland managing partner frank o’keeffe.
EY Ireland managing partner Frank O'Keeffe said the firm did not reduce its Irish headcount last year despite market challenges. Photograph: EY Ireland
Strategic questions that EY attempted to answer by splitting its audit and consulting businesses globally remain unanswered and future options are “under review” after being shelved last spring, the big four accounting firm’s UK and Ireland managing partner has said.
Dubbed Project Everest, the plan to hive off and explore a stock market listing for EY’s lucrative global advisory business received the green light from EY leaders in September 2022.
However, the carve out was scuppered by disagreements between EY partners in the US about how much of its tax practice would be retained within the newly separated accounting arm and issues of compensation.
Frank O’Keeffe, managing partner of EY UK and Ireland, said while the plan was “stopped” last spring, the “strategic question” that prompted the proposed separation of its audit and advisory businesses “will remain and we will have to work our way through as to what is the right answer.”
Dublin’s student accommodation shortage offers investors lucrative opportunity
:quality(70)/cloudfront-eu-central-1.images.arcpublishing.com/irishtimes/DH7Q22MD6VFDNGM34KRA3UWRBU.jpg)
Connacht’s female entrepreneurs: ‘Making a living from clothing in Ireland is not easy’
:quality(70)/cloudfront-eu-central-1.images.arcpublishing.com/irishtimes/RFX5VNB2A5AW7G2EADMRJBNJ6Y.jpg)
US investor to offload Cork’s Blackpool Shopping Centre at heavily discounted €49.5m
:quality(70)/cloudfront-eu-central-1.images.arcpublishing.com/irishtimes/TKX5XW2XIQPLWCYC643XIWBOMI.jpg)
Private investor closing in on deal for McKillen jnr’s Lucky Duck pub
:quality(70)/cloudfront-eu-central-1.images.arcpublishing.com/irishtimes/VLOVQXV6FFFQTG5YD53QXLHCMQ.jpg)
He praised incoming EY global chief executive Janet Truncale, who is set to replace Carmine Di Sibio upon his retirement in July, for her clarity in telling EY partners globally that “if we decide to do this, we will do it together at the right time.”
“So what that really means for us is we will keep things under review,” Mr O’Keeffe said. “And we will consider that over the next few years.”
When it comes to middle market transactions, the movement of money, it’s been slower. The pickup has been slower. I wouldn’t say it’s recessionary
Mr O’Keeffe, who was speaking to The Irish Times in Cape Town last week where was attending the annual EY Entrepreneur of the Year (EoY) executive retreat, said EY Ireland continued to grow its headcount and revenues last year despite market challenges.
Bloomberg reported earlier this year that EY’s global business had tapped a $700 million (€644 million) credit line to prepare for the split, contributing to cost pressures which forced its UK and US affiliates to trim their headcounts and cut spending. EY told Bloomberg in February: “The costs incurred during Project Everest will be almost entirely paid down by July 1st, 2024.”
Yet, Mr O’Keeffe said EY Ireland did not reduce its headcount over the past year despite a slowdown in deal-making and business levels generally due to macroeconomic pressures. He said the business grew in a “more difficult market” over the past 11 months.
“When it comes to middle market transactions, the movement of money, it’s been slower. The pickup has been slower. I wouldn’t say it’s recessionary,” he said.
[ Shortlist for 2024 EY Entrepreneur of the Year awards revealed ]
“We would all know that the capital markets have been quieter, interest rates have bitten. Staff salaries – you have to make sure they’re going in the right direction. Cost of living has been more expensive and that impacts our clients too.”
Mr O’Keeffe said EY’s Irish clients are also doing business in a more geopolitically fraught and “polarised” world than they were even a few years ago. “What we have to do is to really spend a lot of time with our clients around their strategy, from supply chain right into new markets.”
More than 100 Irish entrepreneurs travelled to Cape Town last week for the retreat, a centrepiece of the year-long EoY programme. It was the first time in the competition’s 27-year history that the retreat took place in Africa.
- Sign up for Business push alerts and have the best news, analysis and comment delivered directly to your phone
- Join The Irish Times on WhatsApp and stay up to date
- Our Inside Business podcast is published weekly – Find the latest episode here
Ian Curran is a Business reporter with The Irish Times
IN THIS SECTION
Can the ai boom halt the tech exodus from san francisco, salesforce forecasts second quarter revenue, profit below estimates on soft cloud demand, bank of ireland files court proceedings against former davy shareholders’ company, european stocks slip as us bond sales struggle amid concerns over fed rate cuts, conor pope’s guide to getting the most bang for your summer holiday buck, ‘my brother is meeting fabulous women, but they leave because he does not want more children’, de niro held, questioned in paris over vice ring, delivery of new national children’s hospital set to be further delayed, holidaymakers warned over complex scams after almost €100m stolen last year, roy keane left ‘in shock’ after being allegedly ‘headbutted’ through doors, court told, latest stories, twelve ‘critically endangered’ curlew chicks hatch at fota wildlife park, jurors in trump ‘hush money’ trial end first day of deliberations without reaching verdict, gavin robinson says he will ‘continue irish sea border fight’ as he’s ratified as dup leader.
:quality(70)/cloudfront-eu-central-1.images.arcpublishing.com/irishtimes/VR3765MFOBH2NMV2QNICYDF67M.png)
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Information
- Cookie Settings
- Community Standards
American Airlines CEO admits the airline messed up its plan to disrupt how tickets are sold
- American Airlines slashed its revenue and margin outlook for Q2 2024 on Tuesday.
- The airline also announced the departure of chief commercial officer Vasu Raja.
- American's CEO said part of its struggles is due to recent changes in ticket sales strategy.

American Airlines lowered its earnings outlook for the second quarter of 2024 and announced the departure of its Chief Commercial Officer on Tuesday.
Speaking at an event on Wednesday, CEO Robert Isom said the lower earnings guidance can be attributed to a weaker-than-expected marketplace and the airline's weaker-than-expected performance.
A key factor behind lower bookings is the airline's recent changes to ticket sales strategy, Isom said.
That's a not-so-tacit admission that the airline's recent shake-up of its corporate ticket sales and third-party ticket sales strategy quarterbacked by the outgoing CCO, Vasu Raja, has not worked.
"We are adapting our distribution strategy," Isom said at the event, which was hosted by Bernstein. "We moved faster than we should have and we didn't execute well."
Related stories
In February, American Airlines announced changes to its ticket distribution strategy, including new rules that limit the accrual of loyalty points needed to achieve elite status to tickets purchased from the airline and through select approved travel agencies.
The strategy encouraged customers to buy directly from the carrier instead of third-party websites and travel agencies.
Last year, American gutted its corporate sales team, responsible for managing business travel needs for its major corporate clients.
Isom said that American is reevaluating its distribution strategy to make it easier for travel agencies, corporate clients, and customers in general to interact with the airline. This includes pausing some of the policy changes announced in February.
"Our approach has driven customers away from American and we are unequivocally committed to getting those customers back," Isom added.
In a regulatory filing, the airline said it now expects profit margins for the current quarter to be 1% lower than it had predicted in April. In addition, American expects second-quarter revenue to be as much as 6% lower than the same period in 2023.
Raja, who joined the company in 2004 and took over as CCO in 2022, will officially leave the company in June.
Shares of American Airlines fell more than 13% in trading on Wednesday.
- Main content
$532 million committed to National Battery Strategy, but no plan yet on how to reclaim supply chain
More than half a billion dollars of federal government funds have been set aside to encourage production of batteries in Australia, but exactly how the scheme will work has not yet been figured out.
A new National Battery Strategy has been released, aiming to make the country a globally competitive battery maker for domestic use and as an export opportunity.
It is part of the government's Future Made in Australia policy, which aims to grasp the economic opportunities of the global transition to net zero emissions, as well as ensuring China does not control the supply chain.
The centrepiece of the strategy is $532 million in financial incentives for the production of batteries. Announced in the budget earlier this month, the funding would be spread over seven years and administered by the Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA).
But the scheme, dubbed "Battery Breakthrough", has not yet been formulated, despite funding due to commence in the coming financial year.
"The government will work closely with industry and other stakeholders to design, develop and deliver the Battery Breakthrough," the strategy reads.
From 'dig and ship' to 'renewable energy superpower'
The National Battery Strategy focuses on areas the federal government sees Australia having a competitive advantage, including turning raw minerals into substances used in the global electric vehicle supply chain.
The other areas of focus are large-scale energy storage for the electricity grid, building batteries for industrial uses and developing technical and safety standards.
In a statement, Industry and Science Minister Ed Husic said Australia could become a "renewable energy superpower" by "moving beyond a 'dig and ship' economy".
"It's inexcusable that we supply half the global supply of lithium but produce less than one per cent of the world's processed battery components," he said.
"Australia is a pioneer of battery tech, yet for too long we've sent our ideas offshore and lost the good jobs they create.
"The global clean energy transition is happening — and we've got a once-in-a-lifetime opportunity for Australia to create more well-paid, secure jobs."
There is also potential for households to benefit from more batteries being made locally.
In 2023, 3.7 million homes in Australia had rooftop solar, but only 250,000 had batteries.
The National Battery Strategy suggests the new funding will mean "Australian manufacturers can meet the growing demand for stationary energy [and] provide more choice to consumers".
The 'one country' controlling the global battery supply chain
While the National Battery Strategy does not mention China directly, it notes that "one country" dominates global processing and manufacturing of batteries.
From small vehicle-based batteries to large-scale industrial batteries, "supply chains are highly concentrated, with more than 75 per cent of supply coming from one country", the strategy reads.
"As this market evolves, it's important to ensure Australia builds sovereign capabilities where it is a necessary and efficient way to strengthen Australian economic resilience or security," the strategy reads.
"Building this industry now will ensure Australia can develop and access the newest battery technologies, securing the economy and helping protect against potential market shocks."
Other nations are also moving to build up or protect their own battery-making capacity from China's dominance.
The United States introduced manufacturing tax credits for batteries and related components as part of its Inflation Reduction Act in 2022.
Last week, the US went further, raising tariffs on lithium-ion batteries and related parts from 7.5 per cent to 25 per cent.
Tariffs of 25 per cent were also announced for a range of critical minerals, graphite and permanent magnets.
The Future Made in Australia policy has similar aims to the US's Inflation Reduction Act, with battery production central to both schemes.
"We want to make more things here and with global demand for batteries set to quadruple by 2030, Australia must be a player in this field," Prime Minister Anthony Albanese said in a statement.
"Batteries are a critical ingredient in Australia's clean energy mix. Together with renewable energy, green hydrogen, and critical minerals, we will meet Australia's emission reduction targets and create a strong clean energy manufacturing industry."
- X (formerly Twitter)
Related Stories
To the untrained eye it looks like any ordinary rock, but what it can produce is 'critical' to our future.
'Half of the world's lithium is in the country of kangaroos': Indonesia looks to Australia to realise EV battery plans
- Alternative Energy
- Federal Government
- Government and Politics
- Manufacturing
VMware: Business Simplification, Portfolio Innovation and Ecosystem Standardization

- Share "VMware: Business Simplification, Portfolio Innovation and Ecosystem Standardization" on Twitter
- Share "VMware: Business Simplification, Portfolio Innovation and Ecosystem Standardization" on Facebook
- Share "VMware: Business Simplification, Portfolio Innovation and Ecosystem Standardization" on LinkedIn
Change is never easy. Since the completion of Broadcom’s acquisition of VMware, we have been all about change. For the VMware Cloud Foundation division, all of this change was necessary to transform our business to deliver faster innovation with more value to customers, and even better profitability and market opportunity for our partners. So, what's changed now, post-acquisition, and why will this benefit your organization?
- Business model transition to subscription licensing which is the standard in the industry
- Radical simplification across our portfolio, go-to-market and organizational structure to make it easier to do business with us.
- Standardization across our ecosystem to drive value through distributors/resellers, Cloud Service Providers, Hyperscalers and technology partners.
Business Transformation: A Strategy Summarized in One Word - Simplification
To recap, we’ve completed our transition from selling perpetual software to subscription licensing only; streamlined what, how, and through whom we will sell our software going forward; and reorganized internally around our VMware Cloud Foundation strategy to streamline execution.
First, subscription is the model all major enterprise software providers are on today. Subscription software is the right model for fueling continuous innovation for customers. This past quarter we finalized the switch fully to subscription software, just like everyone else. We immediately turned this transformation into net new value for our customers. How? Do you want to have deployment flexibility? Now you can. When you purchase VMware Cloud Foundation, you get license portability. This means you will be able to deploy on-premises and then take your subscription at any time to a supported Hyperscaler or VMware Cloud Services Provider environment as desired. You retain your license subscription as you move. Google Cloud will be the first to support VMware Cloud Foundation license portability with other Hyperscaler and partner clouds expected to follow. Read the full Google Cloud announcement here .
How about that portfolio? Offering a few offerings that are lower in price on the high end and are packed with more value for the same or less cost on the lower end makes business sense for customers, partners and VMware. We’re putting all our R&D investment towards fewer offerings, which is a double win for customers.
Finally, we’ve brought all of the product teams into the VMware Cloud Foundation division. We are now better positioned to deliver a single, integrated product across all core technologies with a single vision for where we are taking the VMware Cloud Foundation platform. We also have professional services and global support practically sitting right next to R&D inside the same business division. This gives us a laser focus on building one product with the services and support needed to drive maximum value.
Three changes, but massive impact.
Portfolio Transformation: Fueling an Engine of Innovation
We are now focusing our innovation engine on VMware Cloud Foundation and VMware vSphere Foundation, along with some very strategic add-ons related to security, ransomware protection and recovery, application platform services, and private AI.
VMware Cloud Foundation helps organizations modernize their infrastructure with the best possible TCO. It’s fully software-defined compute, network, storage with automated and simplified operations. VMware Cloud Foundation enables a cloud operating model that provides the benefit of public cloud with the security and performance of on-premises private clouds.
VMware Cloud Foundation provides developers a self-service private cloud experience, which results in greater productivity. Development teams can leverage the embedded Kubernetes runtime and a self-service cloud consumption interface to deploy infrastructure as code. This results in frictionless deployment of business-critical and cloud-native applications. IT teams can maintain compliance against security requirements by building security into the policies deployed with every cluster.
VMware Cloud Foundation provides enterprise-grade resiliency and security. Customers can scale infrastructure and applications seamlessly through a hardened platform that has built-in resilience to ensure mission-critical apps are always available. The intrinsic security built into VMware Cloud Foundation helps significantly reduce the attack surface for lateral threats, and our disaster and ransomware recovery capabilities help customers rapidly and efficiently recover from cyber threats.
Through all of this change we’ve not stopped innovating. Here are updates to both the core platform and our add-on services that we have recently made available or will deliver throughout the rest of Broadcom’s Q2FY24.
VMware Cloud Foundation Core Platform Enhancements
Automation for Infrastructure and Application Services: In response to a growing need from VMware customers to deliver and support next-gen cloud-native and AI-powered applications across their private and hybrid clouds, are announcing three new automation capabilities:
- Automation for Data Services: available today, VMware Cloud Foundation provides a native infrastructure automation and management experience for data services. This enables IT to offer self-service, enterprise-hardened Postgres, MySQL, and Google AlloyDB Omni (tech preview) to their teams, boosting developer innovation, reducing IT costs, and ensuring data resilience. For more details read the blog here .
- Automation for Load Balancing Services: through built-in VMware Cloud Foundation capabilities, cloud admins will be able to offer application teams self-service access to L4-L7 load balancing services. This will enable application and infrastructure teams to immediately deploy load balancing at the time of application provisioning, with minimal know-how of load balancing technology or the need to create manual tickets. These capabilities will be available to support the VMware Avi Load Balancer add-on starting in a few months.
- Automation Services for Private AI : customers will be able to use capabilities built into VMware Cloud Foundation to automate private AI service setup and provisioning of GPU-enabled machines for ML workloads when VMware Private AI Foundation with NVIDIA add-on becomes available this quarter.
Integrated Network Operations Capabilities: The latest integrated network operations capabilities offered exclusively as part of VMware Cloud Foundation help IT users improve their network visibility, gain insights into network performance, and quickly identify and resolve network issues. These new enhancements are available today. Read about them here .
VMware Cloud Foundation Add-On Services Updates
Unified Ransomware and Disaster Recovery : With VMware Live Recovery, customers can protect applications and data from modern ransomware and other disasters across on-premises and public clouds with flexible licensing for changing business needs and threats. VMware Live Recovery will bring together the existing capabilities of VMware Cloud DR, VMware Ransomware Recovery, and VMware Site Recovery Manager, and add new capabilities such as enhanced vSphere replication (1-minute RPO) and seamless extension of on-premises disaster recovery to the public cloud with ransomware recovery. All of this will be delivered with a unified management experience and available through a single add-on subscription for VMware Cloud Foundation, which is expected to become available in Q2FY24.
VMware Private AI Foundation with NVIDIA : unveiled at VMware Explore 2023 Las Vegas , VMware and NVIDIA are working to deliver this new add-on service to VMware Cloud Foundation. We’re almost there, and you can expect an update on availability of the solution this quarter. But you don’t have to wait to learn more. Join the team online for AI Field Day 4 on February 21 from 08:00-10:00 PST to get an update on the capabilities we’re driving and the use cases we’re seeing emerge for VMware Private AI Foundation with NVIDIA.
Ecosystem Transformation: Standardization Drives a Better Experience
Broadcom’s strategy is to drive adoption of our full stack VMware Cloud Foundation as the best subscription-based private cloud platform for innovation. We will rely heavily on partners to transition our broad customer base to the new subscription model and help them transform their business with our private cloud infrastructure. This quarter we are welcoming thousands of partners across all routes to market into the Broadcom Advantage Partner Program .
In the channel, we are standardizing pricing so that everyone knows what to expect, all partners are on a level playing field, and partners are competing on value-added differentiation. This will deliver a better customer experience. We’ve also implemented a new customer segmentation model aligned with our simplified portfolio strategy. Here are some important things to know about our customer segmentation model:
- Partners have opportunities across all segments including the strategic segment.
- VMware will have deeper direct relationships with its most strategic customers, in order to accelerate the adoption of VMware Cloud Foundation in these accounts.
It makes business sense for Broadcom to have close relationships with its most strategic VMware customers to make sure VMware Cloud Foundation is being adopted, used and providing customer value. However, we expect there will be a role change in accounts that will have to be worked through so that both Broadcom and our partners are providing the most value and greatest impact to strategic customers. And, partners will play a critical role in adding value beyond what Broadcom may be able to offer itself.
VMware Cloud Service Provider partners will help take VMware Cloud Foundation to an even broader set of corporate and commercial customers and deliver it as a managed service. And because not all customers are ready to consume VMware Cloud Foundation, our thousands of reseller partners will drive adoption of VMware vSphere Foundation. In the corporate segment, we support co-selling with our CSP partners. And our commercial segment is 100% owned and led by reseller partners. This should help reduce channel conflict, which partners have said was an ongoing challenge previously.
Good Business Hygiene is Never Easy
When you acquire a company, you look at everything. Broadcom identified things that needed to change, and as a responsible company, made the changes quickly and decisively. The changes that have taken place over the past 60+ days were absolutely necessary. We understand this massive transformation and simplification of the portfolio and our business model has raised many questions and concerns as you continue to evaluate how to maximize value from your VMware software investments. We are proactively working with the sales teams and channel partners to help customers make this transition and encourage customers to engage them to work through the best approach for their businesses.
One thing has not changed…delivering value to you, our customers. You are the reason we build and deliver great software. You drive our innovation. The new VMware Cloud Foundation is the best platform for deploying a private cloud infrastructure that is ubiquitous, flexible and integrated across cloud endpoints.
It will only get better.
About the Author

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Step 1: Assess your current business strategy and business environment. Before you can define where you're going, you first need to define where you are. Understanding the external environment, including market trends and competitive landscape, is crucial in the initial assessment phase of strategic planning.
Strategic planning is the art of creating specific business strategies, implementing them, and evaluating the results of executing the plan, in regard to a company's overall long-term goals or desires.
Strategic management is part of a larger planning process that includes budgeting, forecasting, capital allocation, and more. There is no right or wrong way to do strategic management — only guidelines. The basic phases are preparing for strategic planning, creating the strategic plan, and implementing that plan.
A well-done strategic plan turns an enterprise strategy into a clear roadmap of initiatives, actions and investments required to execute the strategy and meet business goals. Functional strategic plans document the choices and actions needed for the function to move from the current state to the desired end state, and contribute effectively to ...
Putting your strategic plan into practice (our final step) is the key to making it all work during the strategy implementation plan, and getting these details 80% right in a timely fashion is much more important than getting them 100% right in a year. 3. Putting your strategic plan into practice.
Growth-business plan. A growth-business plan is a strategic plan that outlines how a company plans to expand its business. It helps business owners identify new market opportunities and increase revenue and profitability. The primary purpose of a growth-business plan is to provide a roadmap for the company's expansion and growth.
A strategic plan is more than just a business tool, it also plays a key role in defining operational, cultural, and workplace ethics. Here are some of the key aspects of the importance of strategic planning: 1. Provides a unified goal . A strategic plan is like a unified action plan for the whole company in order to achieve common outcomes.
How to Create a Strategic Plan for Your Business in 5 Steps. The most successful small businesses, corporations, and organizations never remain static for long. Their leaders continually look to the future, pursuing a slate of both short-term goals and long-term goals while angling for competitive advantages over rivals.
Using the above approaches, your team can make room for new ideas within the existing strategic framework in order to track better to your long-term goals. Related: Quarterly business review template Conclusions. The beauty of the strategic plan is that it can be applied from the campaign level all the way up to organizational vision.
What is a strategic business plan? A strategic business plan is a comprehensive document that outlines a company's vision, mission statement, and goals, coupled with a detailed roadmap to achieve those objectives.The plan takes account of the current business environment, provides insights into a company's competitive advantages, and helps identify key performance indicators (KPIs).
An annual strategic business plan should include 8 key sections. Follow these steps to write an effective annual strategic business plan: State information that defines the company. Perform a SWOT analysis. Identify business goals. Identify key performance indicators. Perform and summarize market research. Outline the business marketing plan.
A strategic plan for a business will include the company's mission and vision statement, as well as its goals and objectives and the action plans to achieve them. The strategic plan is different from a business plan. The business plan is typically used to help start the business and acquire the necessary funds to open the doors.
What Is Strategic Planning? Strategic planning is the ongoing organizational process of using available knowledge to document a business's intended direction. This process is used to prioritize efforts, effectively allocate resources, align shareholders and employees, and ensure organizational goals are backed by data and sound reasoning.
A business plan lays out a strategic roadmap for any new or growing business. Any entrepreneur with a great idea for a business needs to conduct market research, analyze their competitors, validate their idea by talking to potential customers, and define their unique value proposition.
This part of writing a strategic plan is where you develop the strategic objectives, goals, and action items. We're big fans of setting OKRs: Objectives and their related Key Results. This OKR Template will ensure your business goals are structured and clearly defined. Make your goals measurable using Miro's OKR Template. 5.
A strategic plan answers where an established organization is going in the future and how they intend to reach that future state. A strategic plan also focuses on building a sustainable competitive advantage and is futuristic. A business plan is used to assess the viability of a business opportunity and is more tactical.
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
Strategic planning is the process of defining your business's direction and outlining a path toward a preferred future. The goal of a strategic plan is to capture an organization's mission and core principles — to envision the fulfillment of these ideals. Strategic planning is both conceptual and practical, as it presents both high-level ...
What is a strategic plan? In contrast to a business plan, a strategic plan sets out a company's goals and defines the actions it takes to get there. The audience is your own team. Its key purpose is to build alignment and decision-making capacity to ready your company for the future. For example, if a company's business model is ...
A strategic business plan is a written document that pairs the objectives of a company with the needs of the market place. Although a strategic business plan contains similar elements of a ...
Strategic planning is a must for every business, big and small. It's a process to figure out where your company is going and how to get there—but it's also so much more. A strategic plan defines who you are as a business and lists concrete actions to achieve your goals. When the unexpected occurs, a strategic plan helps your business ...
A strategic plan for your company is one of the best ways to ensure that every move you make gets you closer to your business goals. Forbes Business Development Council is an invitation-only ...
A business plan is a written document that defines your business goals and the tactics to achieve those goals. A business plan typically explores the competitive landscape of an industry, analyzes a market and different customer segments within it, describes the products and services, lists business strategies for success, and outlines ...
The company plans to begin a "strategic transformation plan" to bring back customers and improve business by driving relevancy, delivering food and an experience guests love, and growing ...
Template #1: Strategic Communication Plan. Strategic communication plans are essential documents that corporations, organizations and companies use to maintain stable and constant communication with their audiences. Below is an example of a communication plan template you can use to streamline communication.
Strategic questions that EY attempted to answer by splitting its audit and consulting businesses globally remain unanswered and future options are "under review" after being shelved last ...
The true impact of this strategic release will likely be negligible, oil market experts said - and the sale was mandated by Congress earlier this year.
American Airlines CEO admits the airline messed up its plan to disrupt how tickets are sold. Benjamin Zhang. May 29, 2024, 2:36 PM PDT. Shares of American Airlines closed down more than 13% ...
The National Battery Strategy focuses on areas the federal government sees Australia having a competitive advantage, including turning raw minerals into substances used in the global electric ...
Business Transformation: A Strategy Summarized in One Word - Simplification. To recap, we've completed our transition from selling perpetual software to subscription licensing only; streamlined what, how, and through whom we will sell our software going forward; and reorganized internally around our VMware Cloud Foundation strategy to ...