- Find My Rep

You are here
How to Write Brilliant Psychology Essays
- Paul Dickerson - University of Roehampton, UK
- Description
“This book is one I wish I had bought at the start of my Psychology degree.” – Five-star review Essay writing is a key part of the Psychology degree and knowing how to write effective and compelling academic essays is key to success. Whether it's understanding how to implement feedback you receive on essays, how to stop procrastinating or what makes an effective introduction, this book covers it all. Drawing on insights derived from teaching thousands of students over a 25-year period How to Write Brilliant Psychology Essays provides the keys that will unlock your writing potential.
Ace your Assignment provide practical tips to help succeed
Exercises help try the theory out in practice
Take away points highlight the key learnings from each chapter
Online resources provide even more help and guidance.
Supplements
Paul Dickerson, Emma McDonald and Christian van Nieuwerburgh discuss study skills, wellbeing and employability and explore how university lecturers and student welfare teams can better support Psychology students through their university journey.
Students enjoyed this text - they found it easy to read and the author's dry sense of humour appealed to many. Not just for psychologists!
A really useful guide for students, breaking down the components of what constitutes a good essay and written from a subject-specific view - highly recommend
I have recommended this to my first year tutorial groups as it provides them with everything they need to know about producing an excellent psychology essay.
Preview this book
For instructors.
Please select a format:
Select a Purchasing Option
Order from:.
- VitalSource
- Amazon Kindle
- Google Play
Image Unavailable

- To view this video download Flash Player
Follow the author

How to Write Brilliant Psychology Essays 1st Edition
Purchase options and add-ons.
"This book is one I wish I had bought at the start of my Psychology degree." – Five-star review Essay writing is a key part of the Psychology degree and knowing how to write effective and compelling academic essays is key to success. Whether it′s understanding how to implement feedback you receive on essays, how to stop procrastinating or what makes an effective introduction, this book covers it all. Drawing on insights derived from teaching thousands of students over a 25-year period How to Write Brilliant Psychology Essays provides the keys that will unlock your writing potential.
Ace your Assignment provide practical tips to help succeed
Exercises help try the theory out in practice
Take away points highlight the key learnings from each chapter
Online resources provide even more help and guidance.
- ISBN-10 1526497301
- ISBN-13 978-1526497307
- Edition 1st
- Publisher SAGE Publications Ltd
- Publication date January 21, 2021
- Language English
- Dimensions 7.32 x 0.74 x 9.13 inches
- Print length 328 pages
- See all details

Editorial Reviews
About the author.
Paul Dickerson is Associate Professor at the University of Roehampton where he has taught for more than 25 years. His research has predominantly adopted a qualitative approach and has largely focused on issues of talk and interaction. He has previously written How to Write Brilliant Psychology Essays also published by Sage. Paul has written this book to enable you to immerse yourself in the exciting world of social psychology, to see its relevance in everyday life - as well as to support you in questioning its findings.
Product details
- Publisher : SAGE Publications Ltd; 1st edition (January 21, 2021)
- Language : English
- Paperback : 328 pages
- ISBN-10 : 1526497301
- ISBN-13 : 978-1526497307
- Item Weight : 1.32 pounds
- Dimensions : 7.32 x 0.74 x 9.13 inches
- #13,116 in Psychology (Books)
- #16,716 in Medical General Psychology
- #81,111 in Psychology & Counseling
About the author
Paul dickerson.
Don't read this if you prefer mediocre essays and uninspired psychology.
If you are still reading thank you!
The Social Psychology: Traditional and Critical Perspectives book aims to bring social psychology alive for you. How?
*By applying it to our world of AI, pandemics, troll farms and emojis.
*By evaluating the ideas that are covered - and supporting you in your evaluative writing.
*By including the broadest range of different perspectives - without losing depth of engagement.
The How to write Brilliant Psychology Essays book supports you in writing brilliant essays and doing brilliantly in your exams. How?
*By showing you what makes a brilliant essay.
*By showing you how to upgrade your writing in detailed steps.
*By tackling procrastination, critical evaluation, conclusion writing, unseen and seen exams and much more.
I have been teaching psychology to undergraduates and postgraduates for more or less, well, forever and I think these books can really help you to reach your full and amazing potential. BUT - if you prefer mediocrity please do not go any further, put the books down and step away carefully - they're not quite right for you.
Wishing you all success and joy
Customer reviews
Customer Reviews, including Product Star Ratings help customers to learn more about the product and decide whether it is the right product for them.
To calculate the overall star rating and percentage breakdown by star, we don’t use a simple average. Instead, our system considers things like how recent a review is and if the reviewer bought the item on Amazon. It also analyzed reviews to verify trustworthiness.
- Sort reviews by Top reviews Most recent Top reviews
Top reviews from the United States
Top reviews from other countries.
- Amazon Newsletter
- About Amazon
- Accessibility
- Sustainability
- Press Center
- Investor Relations
- Amazon Devices
- Amazon Science
- Sell on Amazon
- Sell apps on Amazon
- Supply to Amazon
- Protect & Build Your Brand
- Become an Affiliate
- Become a Delivery Driver
- Start a Package Delivery Business
- Advertise Your Products
- Self-Publish with Us
- Become an Amazon Hub Partner
- › See More Ways to Make Money
- Amazon Visa
- Amazon Store Card
- Amazon Secured Card
- Amazon Business Card
- Shop with Points
- Credit Card Marketplace
- Reload Your Balance
- Amazon Currency Converter
- Your Account
- Your Orders
- Shipping Rates & Policies
- Amazon Prime
- Returns & Replacements
- Manage Your Content and Devices
- Recalls and Product Safety Alerts
- Conditions of Use
- Privacy Notice
- Consumer Health Data Privacy Disclosure
- Your Ads Privacy Choices
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How to Write an Introduction for a Psychology Paper
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Emily is a board-certified science editor who has worked with top digital publishing brands like Voices for Biodiversity, Study.com, GoodTherapy, Vox, and Verywell.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Emily-Swaim-1000-0f3197de18f74329aeffb690a177160c.jpg)
- Writing Tips
If you are writing a psychology paper, it is essential to kick things off with a strong introduction. The introduction to a psychology research paper helps your readers understand why the topic is important and what they need to know before they delve deeper.
Your goal in this section is to introduce the topic to the reader, provide an overview of previous research on the topic, and identify your own hypothesis .
At a Glance
Writing a great introduction can be a great foundation for the rest of your psychology paper. To create a strong intro:
- Research your topic
- Outline your paper
- Introduce your topic
- Summarize the previous research
- Present your hypothesis or main argument
Before You Write an Introduction
There are some important steps you need to take before you even begin writing your introduction. To know what to write, you need to collect important background information and create a detailed plan.
Research Your Topic
Search a journal database, PsychInfo or ERIC, to find articles on your subject. Once you have located an article, look at the reference section to locate other studies cited in the article. As you take notes from these articles, be sure to write down where you found the information.
A simple note detailing the author's name, journal, and date of publication can help you keep track of sources and avoid plagiarism.
Create a Detailed Outline
This is often one of the most boring and onerous steps, so students tend to skip outlining and go straight to writing. Creating an outline might seem tedious, but it can be an enormous time-saver down the road and will make the writing process much easier.
Start by looking over the notes you made during the research process and consider how you want to present all of your ideas and research.
Introduce the Topic
Once you are ready to write your introduction, your first task is to provide a brief description of the research question. What is the experiment or study attempting to demonstrate? What phenomena are you studying? Provide a brief history of your topic and explain how it relates to your current research.
As you are introducing your topic, consider what makes it important. Why should it matter to your reader? The goal of your introduction is not only to let your reader know what your paper is about, but also to justify why it is important for them to learn more.
If your paper tackles a controversial subject and is focused on resolving the issue, it is important to summarize both sides of the controversy in a fair and impartial way. Consider how your paper fits in with the relevant research on the topic.
The introduction of a research paper is designed to grab interest. It should present a compelling look at the research that already exists and explain to readers what questions your own paper will address.
Summarize Previous Research
The second task of your introduction is to provide a well-rounded summary of previous research that is relevant to your topic. So, before you begin to write this summary, it is important to research your topic thoroughly.
Finding appropriate sources amid thousands of journal articles can be a daunting task, but there are several steps you can take to simplify your research. If you have completed the initial steps of researching and keeping detailed notes, writing your introduction will be much easier.
It is essential to give the reader a good overview of the historical context of the issue you are writing about, but do not feel like you must provide an exhaustive review of the subject. Focus on hitting the main points, and try to include the most relevant studies.
You might describe previous research findings and then explain how the current study differs or expands upon earlier research.
Provide Your Hypothesis
Once you have summarized the previous research, explain areas where the research is lacking or potentially flawed. What is missing from previous studies on your topic? What research questions have yet to be answered? Your hypothesis should lead to these questions.
At the end of your introduction, offer your hypothesis and describe what you expected to find in your experiment or study.
The introduction should be relatively brief. You want to give your readers an overview of a topic, explain why you are addressing it, and provide your arguments.
Tips for Writing Your Psychology Paper Intro
- Use 3x5 inch note cards to write down notes and sources.
- Look in professional psychology journals for examples of introductions.
- Remember to cite your sources.
- Maintain a working bibliography with all of the sources you might use in your final paper. This will make it much easier to prepare your reference section later on.
- Use a copy of the APA style manual to ensure that your introduction and references are in proper APA format .
What This Means For You
Before you delve into the main body of your paper, you need to give your readers some background and present your main argument in the introduction of you paper. You can do this by first explaining what your topic is about, summarizing past research, and then providing your thesis.
Armağan A. How to write an introduction section of a scientific article ? Turk J Urol . 2013;39(Suppl 1):8-9. doi:10.5152/tud.2013.046
Fried T, Foltz C, Lendner M, Vaccaro AR. How to write an effective introduction . Clin Spine Surg . 2019;32(3):111-112. doi:10.1097/BSD.0000000000000714
Jawaid SA, Jawaid M. How to write introduction and discussion . Saudi J Anaesth . 2019;13(Suppl 1):S18-S19. doi:10.4103/sja.SJA_584_18
American Psychological Association. Information Recommended for Inclusion in Manuscripts That Report New Data Collections Regardless of Research Design . Published 2020.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
Writing Guide for Psychologists
Staff Writers
Contributing Writer
Learn about our editorial process .
Updated August 17, 2022

Psychology.org is an advertising-supported site. Featured or trusted partner programs and all school search, finder, or match results are for schools that compensate us. This compensation does not influence our school rankings, resource guides, or other editorially-independent information published on this site.
Are you ready to discover your college program?
More so than other social science and science-related disciplines, psychology requires practitioners to engage in various types of writing throughout their academic and professional careers. Beginning with their college applications, prospective students must supply a writing sample to demonstrate their ability to convey ideas clearly and effectively. Throughout their time in school, learners hone writing skills by learning about various styles associated with essays, research papers, and exams. They also learn how to properly cite sources to avoid plagiarism.
Graduates use writing in a variety of important ways. Whether reviewing literature, contributing an article to an academic journal, writing a report about their own research, or keeping detailed client notes, psychologists continually use writing to advance both their careers and the profession as a whole. Psychology's precise nature requires practitioners to expertly convey nuance. The following guide highlights some of the types of writing aspiring psychologists engage in while at school, provides helpful information about common writing styles, and offers a number of resources for those looking to learn more.
Types of Writing Psychologists Will Do in School
Personal statements.
As the introduction between a college and you, personal statements serve an important function. Personal statements provide the space for applicants to differentiate themselves by sharing unique interests, accomplishments, and life experiences in a well-crafted essay. When reading personal statements, admissions panels look at what makes a student tick and, most importantly, why they fit within the program. Rather than submitting carbon-copy statements to every school, students should take time to personalize each statement.
Some of the common application essay prompts students may encounter include:
- Describe the background, interests, and talents that make you who you are.
- Can you name a time when you found yourself questioning or challenging an idea or belief that previously informed your worldview? What did that process look like?
When sitting down to write an essay, students must consider how to portray themselves.
According to Purdue University's Online Writing Lab , students should consider a number of approaches, including what's unique about their story, how their life story has been shaped, how they became interested in the field, and how they hope to use the degree. Above all, students should avoid writing a generic essay that could easily belong to another applicant. They should highlight their personality, as admissions specialists want a true sense of you. While not every school requires a personal statement, learners should take advantage of schools that provide the option of submitting one as it allows them to further establish what they bring to the table.
Once students reach college, professors expect them to embrace numerous psychology writing styles. Exams also require students to perfect their writing, as exams take the form of essays rather than multiple choice or short answer questions. Because students typically enter the exam without having first seen an essay prompt, they must develop a plan of action for whatever faces them on testing day. Aside from keeping up with all required reading, learners should spend time thinking about how to apply the knowledge gained to real-world questions.
When testing day arrives, remember to embrace all of the writing rules. After developing a solid thesis, create an outline of the three main points that you plan to convey and jot down notes to support the main argument. Take a moment to review the prompt once more, ensuring your argument and outline thoroughly answer each question. Remember to write each sentence in a way that supports the overarching thesis. While students should avoid rushing through the essay, they must also remember to leave ample time for proofreading, as careless mistakes cause point deductions.
Research Papers
Research papers provide another avenue for students to demonstrate their psychology writing style and skill. Unlike essays, which tend to rely heavily on the student's point of view, research papers call on learners to highlight the views of others and draw conclusions about existing primary and secondary sources.
When selecting a research topic, psychology provides students with a wide range of options. In addition to focusing on particular branches of the discipline, students also explore disorders, therapies, historical psychology figures, case studies, and literature reviews. After selecting a topic, learners must form an outline incorporating the various sections expected within a research paper. Professors set specific guidelines, but a standard assignment consists of an introduction, literature review, outline of methods, results of any findings, a discussion of the topic at hand, conclusion, and list of references.
When starting, learners should ensure that they fully understand the writing prompt and follow any guidelines. They should also select a sound thesis with qualitative evidence to back it up. Students then create a comprehensive outline of points and sub-points to guide the argument. When sitting down to write, use the active voice, follow style conventions, proofread, and make sure to write an accurate bibliography.
How Do You Write an Essay?
During the course of their college career, students come across various types of writing in psychology. Essays take multiple forms, making it imperative that students familiarize themselves with each.
- Collapse All
Narrative essays may initially seem like the easiest of all writing forms, but those who earn the highest scores recognize the importance of ensuring that the reader learns something new or thinks that the story provides an insightful angle. When writing a narrative essay, make full use of all five senses to draw the reader in and help them experience the setting.
Expository essays help students learn how to properly conduct research and express their findings in an academic arena. Rather than relying on existing knowledge, students should use these essays to fully delve into research and demonstrate how their findings helped them uncover a new perspective or way of looking at something. Although expository essays ultimately call on students to express their opinions, research should inform the opinions they form.
Persuasive essays require students to use evidence and reasoning skills to persuade the reader that their point of view represents a logical conclusion. When sitting down to write this type of essay, students need to ensure that their sources strongly support the argument they want to make.
Comparative
These types of essays call on the student to examine two topics and draw conclusions about their similarities and differences. Students should use qualitative research for each topic and craft a new, logical, and interesting argument.
Cause and Effect
As the name implies, cause and effect essays require students to examine a situation or event that caused something else to occur (i.e., the effect). One example might include an individual experiencing trauma (such as fighting in a war) and then developing post-traumatic stress disorder. When crafting this type of essay, students must establish a strong relation between the cause and the effect.
Featured Online Programs
Figuring out where to apply? These top, accredited schools offer a variety of online degrees. Consider one of these accredited programs, and discover their value today.
Citations Guide for Psychology Students
Learning how to properly attribute research articles and sources counts as one of the most important parts of becoming a psychologist . When students fail to acknowledge the ideas of others, they plagiarize by passing off someone else's work off as their own. Many students commit accidental plagiarism by failing to understand the rules of citations. If caught, students may face suspension or even expulsion, especially if it happens multiple times.
American Psychological Association (APA) Style
Established in 1929 by the American Psychological Association, APA Style serves as the primary style guideline for individuals working within the behavioral and social sciences. Whether writing an academic paper or compiling an article or literature review, APA Style provides all of the information needed to correctly cite sources and avoid plagiarism. Unlike citation forms that emphasize authorship, APA style emphasizes the date of publication to help readers ascertain how recent the research and ideas appear in the available literature.
Example: (Author last name, author first initial. (year of publication). Title of publication. Location of publication: publisher) Frankl, V.E. (2006). Man's search for meaning . Boston: Beacon Press.
Chicago Manual of Style (CMS)
A variety of disciplines use the Chicago Manual of Style (CMS) to bring uniformity and clarity to readers. Regardless of whether the text focuses on literature, history, the sciences, or medicine, CMS serves as a uniting form of citation that allows users to introduce both notes within the text and a full bibliography at the end of the work. Footnotes and endnotes count as common methods used by CMS. While they both add clarification to the main text, footnotes appear on the page at the bottom, and endnotes appear near the end of the work. User should use the 17th edition of the CMS, it's latest update.
Example: (Author last name, author first name. Title. City of publication: Publisher, Year of publication) Frankl, Viktor Emil. Man's Search for Meaning . Boston: Beacon Press, 2006.
Modern Language Association (MLA) Format
Created by the Modern Language Association (MLA), humanities students and scholars most commonly use this style of citation because it emphasizes authorship. When using MLA, writers cite the name of the author within the text and organize the bibliography (known as the Works Cited page) at the end of the paper. Disciplines commonly using this form of citation include English, history, anthropology, philosophy, and literature. Many high school teachers use MLA, meaning lots of students possess some familiarity with this style upon reaching college.
(Author last name, author first name. Title. Publisher, Release year) Frankl, Viktor Emil. Man's Search for Meaning. Boston: Beacon Press, 2006.
Associated Press (AP) Style
Associated Press Style (AP) caters to disciplines related to news writing and journalism. AP style focuses on numbers, dates, and abbreviations rather than end-of-chapter citations to ensure that writers maintain uniformity across publications. The Associated Press updates their style guides regularly, making it imperative for students and professionals alike to ensure that they follow the most recently established best practices.
The Best Writing Style for Psychology Majors
Students and scholars of psychology most commonly use the American Psychological Association writing style. Designed with psychology and other science-related disciplines in mind, APA style provides the clearest method for citing the types of materials typically encountered. Most psychology college professors require students to use APA style to prepare them for professional writing for psychology practice; however, some introductory classes may allow students to use MLA.
Common Writing Mistakes Students Make
Active vs. passive voice.
Writing in the active voice allows students to convey findings clearly and succinctly by calling on the subject of the sentence to perform the action. Passive sentence construction, conversely, allows the subject to receive the action. While not technically incorrect, passive sentences tend to weaken the persuasive nature of a sentence -- as they require more words (and prepositional phrases, in particular) -- and sometimes muddle a sentence's meaning. Understanding how to use active voice presents little difficulty, but executing active-voice sentences often requires sustained focus and practice. Examples of active and passive sentences include:
Passive: The man was scratched by a feral cat. Active: A feral cat scratched the man.
Passive: My shoe was left in the car by accident. Active: I left my shoe in the car by accident.
Passive: The picture has fallen off the wall. Active: The picture fell off the wall.
Punctuation
Students make a variety of punctuation and grammar errors. Some of the most common punctuation errors include the overuse or underuse of apostrophes and commas, adding unnecessary quotation marks, and failing to understand colon and semicolon rules. Examples of these mistakes include:
Apostrophes Incorrect: The professor took five point's off of your test. Correct: The professor took five points off of your test.
Incorrect: Its time to apply for graduation. Correct: It's time to apply for graduation
Quotation Marks Incorrect: The teaching assistant told me I wrote the "best paper he's ever read." Correct: The teaching assistant told me I wrote the best paper he's ever read.
Commas Incorrect: Within the field of psychology students are expected to use proper punctuation. Correct: Within the field of psychology, students are expected to use proper punctuation.
Incorrect: Today, we have a test. Correct: We have a test today.
Semicolons versus Colons Incorrect: I am interested in three types of psychology; developmental, school, and educational Correct: I am interested in three types of psychology: developmental, school, and educational.
Incorrect: I'm looking forward to summer break: I need time to rest. Correct: I'm look forward to summer break; I need time to rest.
Grammar mistakes take many forms, but students who closely observe the rules of writing quickly learn how to avoid them. Whether struggling with subject-verb agreement, unclear pronoun usage, or incorrectly using words, students can make easy repairs to these sentences. Examples of how to correct these common mistakes include:
Subject-verb agreement Incorrect: My colleague and I was happy with our grades. Correct: My colleague and I were happy with our grades.
Unclear pronoun usage Incorrect: Our professor told my colleague that he didn't like his writing style initially. Correct: Our professor encouraged my colleague by complimenting his improved writing style.
Incorrect word usage Incorrect: When they're group excepted our invitation, their were no spaces left for others. Correct: When their group accepted our invitation, there were no spaces left for others.
Writing Resources for Psychology Students
- Purdue Online Writing Lab : Every students seeking writing advice should bookmark Purdue University's OWL. The site provides endless resources to help them excel as writers both in college and beyond.
- APA Style : Psychology most commonly uses APA style for citations, and students should know the most updated rules. APA also provides several online and printed resources.
- Writing in Psychology Resources : The University of Connecticut offers an extensive list of resources for psychology students, including guides on how to read research articles, summarize reports, report statistics, and take examinations.
- Psychology Writing Resources : The University of Toronto offers help on APA style guidelines, scientific article writing, and best practices within the field.
- Tips and Advice for Writing Psychology Papers : Very Well Mind takes psychology students through the steps of learning to write great psychology papers and offers helpful tips and resources along the way.
Latest Posts
Introduction
Chapter outline.
Clive Wearing is an accomplished musician who lost his ability to form new memories when he became sick at the age of 46. While he can remember how to play the piano perfectly, he cannot remember what he ate for breakfast just an hour ago (Sacks, 2007). James Wannerton experiences a taste sensation that is associated with the sound of words. His former girlfriend’s name tastes like rhubarb (Mundasad, 2013). John Nash was a brilliant mathematician and Nobel Prize winner. However, while he was a professor at MIT, he would tell people that the New York Times contained coded messages from extraterrestrial beings that were intended for him. He also began to hear voices and became suspicious of the people around him. Soon thereafter, Nash was diagnosed with schizophrenia and admitted to a state-run mental institution (O’Connor & Robertson, 2002). Nash was the subject of the 2001 movie A Beautiful Mind . Why did these people have these experiences? How does the human brain work? And what is the connection between the brain’s internal processes and people’s external behaviors? This textbook will introduce you to various ways that the field of psychology has explored these questions.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Rose M. Spielman, William J. Jenkins, Marilyn D. Lovett
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Psychology 2e
- Publication date: Apr 22, 2020
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/1-introduction
© Jan 6, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 1. Introducing Psychology
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior . The word “psychology” comes from the Greek words “psyche,” meaning life , and “logos,” meaning explanation . Psychology is a popular major for students, a popular topic in the public media, and a part of our everyday lives. Television shows such as Dr. Phil feature psychologists who provide personal advice to those with personal or family difficulties. Crime dramas such as CSI , Lie to Me , and others feature the work of forensic psychologists who use psychological principles to help solve crimes. And many people have direct knowledge about psychology because they have visited psychologists, for instance, school counselors, family therapists, and religious, marriage, or bereavement counselors.
Because we are frequently exposed to the work of psychologists in our everyday lives, we all have an idea about what psychology is and what psychologists do. In many ways I am sure that your conceptions are correct. Psychologists do work in forensic fields, and they do provide counseling and therapy for people in distress. But there are hundreds of thousands of psychologists in the world, and most of them work in other places, doing work that you are probably not aware of.
Most psychologists work in research laboratories, hospitals, and other field settings where they study the behavior of humans and animals. For instance, my colleagues in the Psychology Department at the University of Maryland study such diverse topics as anxiety in children, the interpretation of dreams, the effects of caffeine on thinking, how birds recognize each other, how praying mantises hear, how people from different cultures react differently in negotiation, and the factors that lead people to engage in terrorism. Other psychologists study such topics as alcohol and drug addiction, memory, emotion, hypnosis, love, what makes people aggressive or helpful, and the psychologies of politics, prejudice, culture, and religion. Psychologists also work in schools and businesses, and they use a variety of methods, including observation, questionnaires, interviews, and laboratory studies, to help them understand behavior.
This chapter provides an introduction to the broad field of psychology and the many approaches that psychologists take to understanding human behavior. We will consider how psychologists conduct scientific research, with an overview of some of the most important approaches used and topics studied by psychologists, and also consider the variety of fields in which psychologists work and the careers that are available to people with psychology degrees. I expect that you may find that at least some of your preconceptions about psychology will be challenged and changed, and you will learn that psychology is a field that will provide you with new ways of thinking about your own thoughts, feelings, and actions.

Psychology is in part the study of behavior. Why do you think these people are behaving the way they are?
- Dominic Alves - Café Smokers - CC BY 2.0; Daniela Vladimirova - Reservoir Dogs debate, 3 in the morning - CC BY 2.0; Kim Scarborough - Old Ladies - CC BY-SA 2.0; Pedro Ribeiro Simões - Playing Chess - CC BY 2.0; epSos .de - Young Teenagers Playing Guitar Band of Youth - CC BY 2.0; Marco Zanferrari - 1... - CC BY-SA 2.0; CC BY 2.0 Pedro Ribeiro Simões - Relaxing - CC BY 2.0. ↵
Introduction to Psychology Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

Join Discovery, the new community for book lovers
Trust book recommendations from real people, not robots 🤓
Blog – Posted on Friday, Jan 07
25 best psychology books to read in 2024.

Have you ever found yourself trying to work out what mental processes lead humans to do what we do? Thanks to the internet, even in isolation we have a continual stream of information about what people are doing — and with this uniquely modern view of the world around us, we have more fodder than ever to think: “Hmm, I wonder why we do this or that?”
As a human, it’s natural to want to understand these things — not only about others, but also about yourself. In this post, we’ve put together a list of the 25 best psychology books you’ll definitely want to read to pursue that understanding! Whether you’re a beginner with a newfound interest in psychology or a seasoned psychology expert looking to branch out, we’ve got you covered.
1. The Happiness Hypothesis: Finding Modern Truth in Ancient Wisdom by Jonathan Haidt
A professor of social psychology, Jonathan Haidt wrote The Happiness Hypothesis as an accessible vessel for his research into moral foundations theory. In this book, Haidt takes the ancient wisdom, or “Great Ideas”, of historical thinkers — like Buddha, Plato, and even Jesus — and reveals their applications in light of contemporary psychological findings.
Haidt first describes the basic meanings of ancient lessons on happiness, virtue, and personal fulfillment. This leads into what Haidt extracted from these findings to develop his own “10 Great Ideas” about happiness and connect them to modern living. After all, while ancient wisdom is tried-and-tested, it’s essential to update old methods to match modern-day life — Plato, Jesus, and Buddha never spent hours doomscrolling or procrastinating on Instagram, for example.
2. Influence : The Psychology of Persuasion (New and Expanded) by PhD Robert B. Cialdini
Influence, New and Expanded is Dr. Robert B. Cialdini’s 2021 republication of his one of his acclaimed bestselling psychology books Influence (first published in 1984) — complete with new research, examples, and insights, especially regarding the age of the internet. Backed up by his 35 years of scientific research, Cialdini describes seven practicable principles of influence you can use in your everyday life (with the newest edition being “Unity”).
Each of the seven principles has a dedicated chapter to describe how it functions, where it’s most applicable, and — most importantly — how you apply it in your own life. If you’re looking for a book on psychology to help you learn more about the art of ethical persuasion in a modern context — and how to see through other people’s deceitful attempts — then this is the book for you.
3. Mistakes Were Made (but Not by Me) Third Edition: Why We Justify Foolish Beliefs, Bad Decisions, and Hurtful Acts by Carol Tavris
Ever been curious what causes people to deny vaccines, join cults, or engage in extremist behavior? The next entry on this list might clarify some of these seemingly illogical decisions: in Mistakes Were Made, Carol Tavris and Elliot Aronson discuss the systematic mental patterns which feed into development and radicalization of human beliefs. These include cognitive dissonance, confirmation bias, and positive feedback loops, among others.
To further explain how people’s attitudes can become so polarized, Tavris and Aronson walk readers through the effects of these mental patterns on people in various real-life cases and controversies. With its many compelling links to real-life events, this book is the perfect read for psychology and politics readers alike.
Looking for something new to read?
Trust real people, not robots, to give you book recommendations.
Or sign up with an email address
4. Upstream: How to Solve Problems Before They Happen by Dan Heath
Life can feel like we’re constantly sprinting to put out fires as they arise. But of course, endlessly reacting to problems without a second to breathe and prepare for the next is pretty exhausting. Dan Heath’s Upstream is his solution to breaking that cycle of reaction and starting to prevent problems before they start.
This begins with knowing the psychological forces that cause it. For example, one force that Heath attributes as a large factor is “problem blindness” — when a problem becomes so persistent that you start to register it as “normal” and therefore stop “seeing” it (or, naturally, trying to fix it). Heath shows how to step up and bolster your defenses against such problems by using real-life cases of individual thinkers, businesses, and even whole institutions that overcame their own. Thankfully, the uniting factor among these case studies is simple: all they had to do was change their mindset.
5. The School of Life: An Emotional Education by Alain de Botton
Many of us spend over a decade in school and, regardless of academic success, emerge feeling like something is missing. Sure, you can do complex algebra or give me an in-depth analysis of the symbolism of triads in Shakespeare — but can you navigate a workplace? Can you endure failure? Do you understand yourself? Whether you’re about to graduate or have been done with high school for years, you’ve probably found yourself wondering these things.
Aptly titled, The School of Life is Alain de Botton’s answer to questions like these — with the express aim of equipping people with the tools and self-knowledge to thrive in the modern world. From increasing your productivity at work to handling the dilemmas of interpersonal relationships, there’s a chapter for everything you need in The School of Life. This emotional education is sure to help you to develop resilience to life’s dilemmas and become a maven of emotional intelligence.
6. Noise: A Flaw in Human Judgement by Daniel Kahneman, Olivier Sibony, and Cass R. Sunstein
You may recognize authors Daniel Kahneman and Cass R. Sunstein from their respective bestsellers, Thinking, Fast and Slow and Nudge (or from a Reedsy Discovery post !). In a similar vein, Noise tackles the topic of variability in judgements and how we’re influenced by external factors. The overarching conclusion in Noise is that the majority of our decisions are unconsciously affected by the noise at different times and places.
The authors combine their scholarly expertise with additional research to deliver this in-depth guide outlining what we already know and their new theories about noise. For those interested in why we make decisions, this is one of the best psychology books to strengthen your understanding of the extraneous factors that can shape or bias decision-making, how to minimize those factors, and improve your thinking.

7. The Lucifer Effect: Understanding How Good People Turn Evil by Philip G. Zimbardo
The Lucifer Effect is Professor Philip Zimbardo’s first detailed account of his infamous Stanford Prison Experiment and the conclusions he took from it. The Stanford Prison Experiment was Zimbardo’s 1971 study looking into the effects of different situational factors on conformity by putting college student volunteers into a fake prison environment for -2 weeks. Without giving too much away, the experiment ran into some serious roadblocks that meant it had to be discontinued after only six days. (The controversy was such that there was even a mostly-accurate movie dramatization released in 2015!)
Zimbardo’s thoughts on the experiment are interesting not only because he conducted it, but because he was a part of it, acting as the prison warden — which, needless to say, has serious ethical connotations. The following chapters discuss the study’s effect on the decades of subsequent research into psychological and social variables that cause “average” people to commit immoral acts — making it one of the most influential books on psychology you can pick up today. Most people with an interest in psychology might have an idea of the original experiment, but the research afterwards should definitely not be overlooked!
8. The Psychopath Test: A Journey Through the Madness Industry by Jon Ronson
Put simply, The Psychopath Test takes us through the modern-day mental health system, asking us to think more deeply about whom it labels “psychopathic”. Jon Ronson starts with a man who faked madness to escape a prison sentence, his method being to act charming, glib, and well-presented in contrast to other patients in the psychiatric hospital. Ronson takes these alleged tell-tale signs of psychopathy and applies them to people in other walks of life, making the startling discovery that psychopaths appear everywhere.
This is where the doors to the so-called “industry of madness” are truly flung open. How many of our most influential CEOs, researchers, and world leaders are psychopaths? Can any good come of our newfound access to the best psychology books or theories if they facilitate diagnoses of strangers based on their “maddest” parts? If these questions interest you, pick up The Psychopath Test and see what you think.
9. Games People Play: The Psychology of Human Relationships by Eric Berne
We’ve mostly talked about complex mental health issues so far in this post—but maybe you want to know about the psychology behind our most basic social interactions. If so, Eric Berne’s description of functional and dysfunctional social interactions in Games People Play will be right up your alley. Berne claims that we play “social games” all of the time, be that power games against authority, sexual games, marital games, or competitive games within friendships.
Berne divulges the types of mind games that everyone can fall victim to indulging: in status contests, the game becomes a back and forth game of “I know better”, and couples are prone to playing mental games claiming each is holding the other back. Berne doesn’t just name these interactions, but he also exposes the meaning behind them as unconscious ploys and maneuvers that rule our lives. It’s these creatively poised insights that make this book on psychology an influential and striking bestseller.
10. The Body Keeps the Score: Mind, Brain and Body in the Transformation of Trauma by Bessel Van Der Kolk
Described as “the Bible of trauma” for struggling readers, The Body Keeps the Score is the culmination of Dr Bessel Van Der Kolk’s entire career. One of the world’s leading experts on traumatic stress, Van Der Kolk highlights the clear effects that trauma has on literally reshaping the body and brain. Drawing on his status as an active therapist, continually learning from what works for his patients best, Van Der Kolk delivers a wonderfully personal yet analytic approach to trauma recovery. Considering the frustrating physical effects of trauma related by his patients, Van Der Kolk suggests a fresh paradigm for treatment.
The ideological heart of this method is to make it safe for trauma survivors to inhabit their own bodies by moving away from the “standard” combination of talking therapies or drug therapies and instead using a new approach that heals the mind, brain, and body. One size never fits all, but Van Der Kolk suggests that therapeutic interventions like neurofeedback, theater, meditation, play, or yoga may play a larger part than first thought in healing. The Body Keeps the Score provides a unique perspective on trauma and recovery relayed in a compassionate yet truthful voice, making it accessible to readers of all levels.
11. The Comfort Book by Matt Haig
Ever just really felt like you needed a hug? The Comfort Book answers that craving: it is a warm and personal hug in the form of a book — something even the best psychology books haven't focused on before. If you’re looking for a guide to self-love, contentment, and emotional strength, then Matt Haig’s reflections on the conflicting feelings that come with being alive are for you.
The essence of this book is that many of our best and clearest revelations are made when at our lowest — but we also shouldn’t have to figure everything out ourselves, especially when we’re suffering. Haig’s reflections are built on what he’s learned in hard times, with the hope that they can get you through similar situations. It’s a great comfort to know that you’re not the only one that’s dealt with something hard, and Haig understands that. Drawing on maxims, meditations, and inspirational lives of others, he aims to nurture your inner strength and deliver advice like a wise, commiserative old friend.
12. The Oracle of Night: The History and Science of Dreams by Sidarta Ribeiro
What really makes a dream, why do we have them, and how do they affect us? Sidarta Ribeiro takes these questions and uses them as a springboard for his completely fresh and enthralling study of dreams, tracing them all the way back to our ancient ancestors. It’s in the earliest cave paintings that Ribeiro finds the first traces of human dreams and begins unlocking revolutionary conclusions about the role of dreams in human evolution.
Some will also know that contemporary neuroscience and psychology have uncovered many findings about dreams, such as their role in healing trauma or in consolidating what we learned in the day prior. The Oracle of Night then explains Ribeiro’s advancements on these topics: the role of dreaming in memory recall and transformation, and, startlingly, their oracular nature as confirmed by new research — making this a great book club book to ignite a conversation! Ribeiro combines his absolute authority on the topic with a clear, compelling writing style to make this book a page-turner from the first page to the last.
13. Everyday Vitality: Turning Stress into Strength by Samantha Boardman
Psychiatrist Samantha Boardman believes that an essential factor in healthy aging and overall well-being is a sense of vitality. Which is to say: knowing that you’re up to a task both physically and mentally. This belief is the jumping-off point for Everyday Vitality, a book full of strategies for cultivating vitality by focusing on improving a little every day, instead of reacting to fix what’s wrong as it arises.
While vitality wellness is often associated with managing aging, Boardman posits that vitality can help all of us no matter our age. Whether you’re eighteen or eighty, you may recall times you’ve felt mentally exhausted from the constant barrage of media every day, or physically drained after a long day at a desk. Boardman explains three routes to better vitality for everyone: meaningfully connecting with others, taking on experiences that push your limits, and contributing to something beyond just you. If you want to cultivate your own wellness, why not pick up this book and discuss it with someone you love?
14. Survival of the Friendliest: Understanding Our Origins and Rediscovering Our Common Humanity by Brian Hare and Vanessa Woods
Humanity’s success as a species has developed in leaps and bounds during our relatively short time on Earth. Many people have hypothesized what might be the cause of these advancements: is it our strength, intellect, curiosity, or something else completely? Authors — and husband-and-wife duo — Brian Hare and Vanessa Woods believe in the latter, making the case in this book that humanity’s progression is actually because of our “friendliness”.
Combining their respective expertise in cognitive neuroscience, research science, and journalism, Hare and Wood have come up with a theory about this evolutionary friendliness. The theory is elegantly termed “self-domestication” — a remarkable propensity to coordinate and communicate with others. Instead of coveting our individual successes, we often share them with others to help advance and protect each other. This capability, Hare and Wood argue, has allowed us to achieve the impressive cultural and technical marvels that we’ve culminated today. However, this friendliness may come at a cost: when threats to those we love become a target for our worst instincts, our evolutionary propensity for bond-making may be a double-edged sword.
15. Blink: The Power of Thinking Without Thinking by Malcolm Gladwell
In Blink, critically acclaimed author and journalist Malcolm Gladwell hopes to revolutionize your understanding of how you (and others) think. Why, for example, are some people exceptionally fast decision-makers, when others choke under pressure? Why does “following your gut” work perfectly for some, while others fall short? And do situational variables like our immediate surroundings affect our abilities to make these decisions?
Gladwell posits that a key factor towards people’s ability to make better decisions is “thin-slicing”: the unconscious ability to analyze patterns in scenarios based on brief flashes of experience, and come to a conclusion based on that knowledge. Gladwell draws on real-life examples to illustrate these ideas: from a psychologist who could predict whether a marriage would last from just a brief interaction with the couple, to antiquities experts who only need to glance at an object to tell it’s a fake. Put simply, Blink proves that the main difference between a good and a bad decision-maker is their mastery of “thin-slicing.” Can you learn to do it, too?
16. The Paradox of Choice: Why More Is Less by Barry Schwartz
Have you ever walked into a clothing store and found yourself overwhelmed by choices among different shirts, skirts, or jeans, all of which look eerily similar? Not to mention the stress of weaving through other shoppers, worrying about prices, and working out your size. Barry Schwartz believes that this abundance of choices to make “no longer liberates, but debilitates” shoppers with consumer anxiety. The solution? Eliminating consumer choices (within reason).
Of course, Schwartz acknowledges that autonomy and freedom of choice are still critical to our well-being. It’s just that, while modern Americans may technically have more choice than ever before, they are no longer benefiting from it psychologically. The Paradox of Choice neatly establishes the psychology behind why choice overload makes us suffer — constant comparison, opportunity hunting, and buyer’s remorse, for example — and how to avoid consumer anxiety in the first place.
17. Explaining Humans: What Science Can Teach Us about Life, Love and Relationships by Camilla Pang
Explaining Humans is an intriguing in-depth exploration of the complexities of human behavior, as explained by hard science. Diagnosed with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) at an early age, author and scientist Dr Camilla Pang struggled to untangle the mess of the world around her — even asking her mother if she could find an instruction manual for humans. When she found that not even the best psychology books of the time provided such a manual, the only solution was to write her own.
Backed up with copious amounts of scientific research and her own hard-won expertise, this book on psychology examines obscure social customs, what it means to be human in different cultures, and where proteins and molecular chemistry fit into all of this. What does it mean to understand someone? How do we recognize people’s motivations or expressions, and what dictates them to begin with? Whether this all feels foreign or far too familiar to you, Pang is sure to deliver some surprises.
18. Rationality: What It Is, Why It Seems Scarce, Why It Matters by Steven Pinker
The goal of Rationality is to make you more rational and help you understand why there is so much irrationality in the world. You may think that sounds pretty lofty, but try reading author and cognitive psychologist Steven Pinker’s analysis before making concrete judgements!
Pinker rejects the cliché idea that humans are an irrational species — how could any species discover and achieve so much without being inherently rational? Despite this, we live in a dichotic age of rationality vs. intense irrationality. Pinker’s explanation is that humans tend to think within the context of the low-tech settings in which we spend the majority of our lives. As a result, we don’t take advantage of the tools that our best thinkers discovered previously: critical thinking, logic, probability, correlation vs. causation, and ways to update our beliefs individually are not a part of our education. Fortunately, you can find these tools (and analyses of the crippling effects of irrationality) presented clearly and with good humor in Rationality !
19. Rapport: The Four Ways to Read People by Emily and Laurence Alison
We’ve all had to interact with difficult people before, whether that’s an annoying customer, a high-maintenance friend, or even a demanding stranger on the train. But imagine you had to deal with some of the most difficult people possible, managing extremely high-stress interactions: criminal interrogations. These interactions are a specialty of forensic psychologists Emily and Laurence Alison: they advise and train police, security companies, and even secret services on how to maneuver interviews with dangerous suspects.
After experiences over the past thirty years that the “average” person could only imagine, the author duo have developed a revolutionary model for interpersonal communication. According to them, every interaction follows one of four types: Control (the lion), Capitulate (the mouse), Confront (the Tyrannosaur) and Co-operate (the monkey). It might sound abstract now, but once you’ve been taken through these types in Rapport, you’ll understand why they’re so praised. Learn to understand and apply them to your own goals and you can shape any conversation at will.
20. Authentic Happiness: Using the New Positive Psychology to Realise Your Potential for Lasting Fulfilment by Martin E. P. Seligman
You may have heard of this entry after its launch in 2004 caused international debate over the nature of real happiness. Authentic Happiness was the starting point for the science of Positive Psychology and the discussion of happiness in a scientific way.
According to Martin Seligman, happiness has less to do with factors such as genes or luck, and more to do with focusing on your internal strengths rather than weaknesses. This isn’t to say that situational factors based on your genes wouldn’t impact you, or that being lucky enough to win the lottery wouldn’t change your life. Seligman’s point is that maintaining a positive mindset and building on one’s strengths is the most dependable route to long-lived happiness. To that end, Seligman supplies exercises, brief tests, and interesting programs that will help you identify your virtues and use them most efficiently.
21. Emotional Intelligence: Why It Can Matter More Than IQ by Daniel Goleman
It’s no secret that a high IQ doesn’t automatically make a person smart or good (not to mention the long-standing debate over the reliability and biases of IQ tests). That said, what actually makes a person smart or good? Daniel Goleman’s innovative analyses in Emotional Intelligence certainly brings us closer to understanding. This book breaks down human processes into “two minds”, the rational and the emotional, to detail how they together shape the ways that we move through the world.
Goleman draws on contemporary cognitive and behavioral research to show the factors that make higher IQ flounder where those with average IQ excel. The factors that go into this disparity are: self-awareness, self-discipline, and empathy, and their presence adds up to a completely different manner of intelligence. Luckily, this kind of emotional intelligence can be developed and strengthened at every age to ultimately benefit our health, work, and relationships.
22. The Psychology of Pandemics: Preparing for the Next Global Outbreak of Infectious Disease by Steven Taylor
Published in October 2019, just before the COVID-19 pandemic, Steven Taylor’s book about the importance of psychology in curbing the spread of deadly pandemics — stating that, at the time, the next pandemic could be soon — turned out to be frighteningly prophetic. Taylor posits that, while vaccinations and behavioral methods are crucial for stemming infection rates, psychological elements are equally important.
The Psychology of Pandemics explains psychology’s role in nonadherence to vaccination and hygiene programs and in mental health as people cope with the threat and loss of life. Taylor talks through every reason why understanding psychology is essential to managing societal problems that go hand-in-hand with pandemics. You need only consult a few history books to see that the same problems recurr every time we face a pandemic. These problems range from excessive fear to maladaptive behaviours to the xenophobia that occurs when people feel threatened by infection. Sound familiar? If you want to understand why the COVID-19 pandemic unfolded in the way it did, this is definitely on the list of the best psychology books to try.
23. Human Givens : A New Approach to Emotional Health and Clear Thinking by Joe Griffin and Ivan Tyrrell
Feeling like something a little more laidback? Human Givens is a guide to emotional and physical health, as well as education, using the “human givens” approach. Authors Joe Griffin and Ivan Tyrrell chronicle what some call the best psychological insight of this age — that we are all born with innate knowledge patterns known as “human givens”. These givens are experienced as physical and emotional needs, and only when those needs are met can one reach their full mental and physical potential.
Griffin and Tyrrell suggest that how your innate needs connect with the world can shape not just your own health and happiness, but that of your family and friends. Human Givens takes this idea and looks at what every person needs to flourish, as well as how to actively pursue those things. Of course, this isn’t all just speculation: Griffin and Tyrell back up their approach with new scientific findings and ideas about how the mind works — as well as how to use those ideas to overcome the anxieties of the modern world.
24. Obedience to Authority: An Experimental View by Stanley Milgram
The next book on our list is what some might call a psychology classic. Psychologist Stanley Milgram performed a series of famous experiments in the 1960s with the view to better understanding obedience to authority, after numerous war criminals on trial had claimed they were “just following orders”.
The experiments were controversial at the time, because they involved volunteer subjects being instructed to administer what they thought were progressively more painful shocks to another human being — the aim of this was to see how far people would obey orders even when they knew them to be morally gray. Though Milgram’s experiment was criticized for being immoral itself, it has since been vindicated as a breakthrough in understanding both obedience and psychology as a whole. Obedience to Authority has long been thought of as one of the best psychology books, offering Milgram’s personal insight into his groundbreaking methods, theories, and post-experiment conclusions.
25. Consciousness and the Social Brain by Michael S. A. Graziano
The final entry on our list delves into one of the great mysteries of the human race: the brain. How are we conscious, what is consciousness, and how does the brain create it? Why do some people have more of a constant running internal monologue than others? These are the big questions that Michael S. A. Graziano aims to tackle in Consciousness and the Social Brain.
The human brain has evolved a vastly complicated circuitry which allows it to be socially intelligent — one function of which is to be aware of others socially, to understand when someone other than oneself is thinking or feeling. Graziano’s theory is that the brain’s internal machinery that allows it to be aware of others also allows self awareness. The crux is that human awareness is layers upon layers of information that the brain has gathered, processed, and rendered — a wholly physical phenomena in the same way that generating heat or electricity might be. This is, of course, a hotly debated topic, with many people believing that to reduce the brain to only physicality would be reductive. Regardless of what you believe, Graziano’s scientific journey is a thrill to the last page!
Seeking more answers about human interaction? Check out our lists of the 60 Best Nonfiction Books of the 21st Century or the 40 Best Leadership Books of All Time !
Continue reading
More posts from across the blog.
20 Addictive Urban Fantasy Books
Urban fantasy is no doubt one of the most fascinating genres in modern literature. For those who may not know what it is, you can head to this post for a great guide on
The 10 Best Books Like Outlander To Make You Swoon
Whether you’re a history buff
50 Best Stephen King Books, Ranked By Horror Readers
Stephen King has published over 130 short stories and 61 novels. So how do you start reading him? Why not start with our list of the best Stephen Kings books, ranked from least most popular.
Heard about Reedsy Discovery?
Or sign up with an
Or sign up with your social account
- Submit your book
- Reviewer directory

We made a writing app for you
Yes, you! Write. Format. Export for ebook and print. 100% free, always.
Essays About Psychology: Top 12 Examples and Prompts
Need a psychology research paper idea? Check out these provoking example essays about psychology to get your writing started.
Psychology is a broad field focusing on the mind and behavior. It’s also concerned with individuals’ consciousness and subconscious. This branch of science has many subdivisions, such as developmental, social, forensic, and cognitive. Because it’s applicable in various fields, psychology is one of the most popular college courses in the US .
If you are studying psychology in college, the odds are high that you will need to complete an essay or research paper at some point in your education. Consider these twelve essay examples and eighteen prompts to get inspired and start writing your essay.
For help with your essays, check out our round-up of the best essay checkers .
12 Example Essays About Psychology
1. the epidemic of mental illness: why by marcia angell, 2. is the internet making us crazy what the new research says by tony dukoupil, 3. the dark psychology of social networks by jonathan haidt and tobias rose-stockwell, 4. the benjamin franklin effect by david mcraney, 5. caring for your introvert by jonathan rauch, 6. the stanford prison experiment by dr. saul mcleod, 7. why your brain is not a computer by matthew cobb, 8. introduction to psychology by seema r, 9. meaning and definition of industrial psychology by shreyas kammar, 10. do not let negative feelings destroy our lives by anonymous on papersowl, 11. psychology. health behavior change & reflection coursework by anonymous on ivypanda, 12. fields of psychology by seema r, essay prompts about psychology, 1. what is antisocial personality disorder, and how is it treated, 2. the rise of schizophrenia or other serious mental disorders, 3. the role of media and video games in violent behavior, 4. the main factors that impact problem-solving abilities in child development, 5. can serious physical illnesses cause post-traumatic stress disorder, 6. the impact of parenting styles on human development, 7. what stops panic attacks effectively, 8. what is causing the rise in anorexia among children, 9. do teenagers face anxiety in high school, 10. how does low self-confidence hurt athletes, 11. my favorite branch of psychology, 12. psychological disorders: definitions and treatments, 13. how do religious beliefs affect someone’s behavior, 14. analyzation of a psychology theory or experiment, 15. the different careers in psychology, 16. do family relationships affect a child’s behavioral development, 17. effects of racism , 18. a historical figure in psychology.
“It seems that Americans are in the midst of a raging epidemic of mental illness, at least as judged by the increase in the numbers treated for it. The tally of those who are so disabled by mental disorders that they qualify for Supplemental Security Income (SSI) or Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) increased nearly two and a half times between 1987 and 2007—from one in 184 Americans to one in seventy-six. The rise is even more startling for children—a thirty-five-fold increase in the same two decades.”
Angell describes the realities behind mental illness statistics. She then explores why problems like anxiety disorders, depression, and similar issues are rising. Finally, she proposes that they are possibly being diagnosed more frequently than before, more so than becoming more prevalent. You might find our list of books on psychology for beginners helpful.
“The first good, peer-reviewed research is emerging, and the picture is much gloomier than the trumpet blasts of Web utopians have allowed. The current incarnation of the Internet—portable, social, accelerated, and all-pervasive—may be making us not just dumber or lonelier but more depressed and anxious, prone to obsessive-compulsive and attention-deficit disorders, even outright psychotic. Our digitized minds can scan like those of drug addicts, and normal people are breaking down in sad and seemingly new ways.”
In this essay, Dukoupil points out the mental health concerns of constant exposure to social media and other technology. He explores new research into the abnormal psychology disorders this exposure is creating.
“The problem may not be connectivity itself but rather the way social media turns so much communication into a public performance. We often think of communication as a two-way street. Intimacy builds as partners take turns, laugh at each other’s jokes, and make reciprocal disclosures. What happens, though, when grandstands are erected along both sides of that street and then filled with friends, acquaintances, rivals, and strangers, all passing judgment and offering commentary?”
Social media has a dark side, which is what Haidt and Rose-Stockwell explore in this essay. What started as a positive way to build social connections has turned into a public facade that pushes people toward mental health issues. You might also be interested in these essays about sociology .
“The Misconception: You do nice things for the people you like and bad things to the people you hate. The Truth: You grow to like people for whom you do nice things and hate people you harm. Benjamin Franklin knew how to deal with haters.”
In this social psychology essay, McRaney explores how Benjamin Franklin’s people skills created a psychological phenomenon known as the Benjamin Franklin Effect. This theory says that a person who has done someone a favor is more likely to do that person another favor than they would be had they received a favor . McRaney delves into the psychology behind this theory.
“My name is Jonathan, and I am an introvert. Oh, for years I denied it. After all, I have good social skills. I am not morose or misanthropic. Usually. I am far from shy. I love long conversations that explore intimate thoughts or passionate interests. But at last I have self-identified and come out to my friends and colleagues. In doing so, I have found myself liberated from any number of damaging misconceptions and stereotypes. Now I am here to tell you what you need to know in order to respond sensitively and supportively to your own introverted family members, friends, and colleagues.”
Rauch, a self-proclaimed introvert, explores what it means to be one and how people can best care for one. After reading this article, you will be well-equipped for any social interaction involving an introvert.
“The study may also lack population validity as the sample comprised US male students. The study’s findings cannot be applied to female prisons or those from other countries. For example, America is an individualist culture (were people are generally less conforming) and the results may be different in collectivist cultures (such as Asian countries).”
This informative essay talks about the Stanford Prison Experiment and how it impacted the field of psychology as a whole. McLeod also provides some critical evaluation of the study and its findings.
“There are indeed theoretical approaches to brain function, including to the most mysterious thing the human brain can do – produce consciousness. But none of these frameworks are widely accepted, for none has yet passed the decisive test of experimental investigation. It is possible that repeated calls for more theory may be a pious hope. It can be argued that there is no possible single theory of brain function, not even in a worm, because a brain is not a single thing. (Scientists even find it difficult to come up with a precise definition of what a brain is.).”
In this essay, Cobb takes on the ideology that the brain is nothing more than a complex computer. He looks at the current research and draws an opinion on how much more complex the human brain is than simply calling it a computer.
“Psychology is relatively a young science and yet within a brief span it has made tremendous progress. Psychology touches almost every facet of our lives. There is hardly any single aspect of human life where psychology has not made its contribution.”
Unlike most psychology introductions with a direct description and definition, this short essay shows the importance of the subject. Seema R makes this possible by talking about essential industries where psychology makes a unique contribution and how psychologists define behavior. Seema’s findings include behavior is a physical and mental process that helps people adapt to different situations in their environment.
“It is the study of people at work. It deals with the aptitudes, attitudes, and interests of the people at work… It studies the varied methods of performing manual operations for the better utilisation and the least waste of efforts through human engineering.”
This essay aims to understand the importance of industrial psychology in handling human relations in the workplace. Kammar begins the piece by sharing psychology’s exact meaning and follows it with other definitions from prominent industrial psychology textbook authors. The author then concludes that industrial psychology is research done in a company to create ways to improve industrial workers’ efficiency.
“The World Health Organization has said that depression is a common illness worldwide, with more than 300 million affected… Negative feelings are harmful to our mental health and take away the ability to enjoy our lives.”
The author’s purpose for writing the essay is to let everyone know what and how to deal with negative feelings. In addition, it is to prevent these feelings from worsening and turning into depression. To strengthen the credibility of the essay, the author uses statistics from the World Health Organization and a popular movie related to the topic, “ I Have a Black Dog ” by Will Hutchinson.
“Being mindful of my health habits also enabled me to cultivate self-monitoring techniques and, more importantly, to make health-enhancing behavior. This approach worked because the energy and determination of behavior change came from deep within my heart.”
The essay differs from the examples in this list as it’s from the author’s own experience and how psychology played a role in their journey to becoming a better person. The author shares their drive to improve and maintain healthy behaviors for a better, more active, happier life. The essay starts with the author sharing the cause and effect of their unhealthy habits, what methods they used, and the struggles they faced along the way. The writer also identifies what helped them the most to achieve a positive change in their behavior.
“Psychology is no longer a subject of academic interest taught in colleges and universities, but its impact has been felt in business, industry, clinics, guidance centers, and education. Psychologists do many things depending on their field of specialization”
Psychology is a vast field of behavioral study that shows constant growth and development in its subfields. The work and method that the psychologist will use depend on what field they belong to. To help readers better understand the difference between prominent fields of psychology, Seema R writes an informative essay that defines and differentiates each area of specialization of the subject. You might also be interested in our round-up of the best Carl Jung books .
If you are looking for psychology essay topics, here are some prompts for inspiration.
If you are looking for informative essay topic ideas, you could build an exciting essay around defining and exploring treatments for antisocial personality disorder. This disorder, sometimes called sociopathy, causes the individual to ignore the needs and feelings of others and show no remorse for doing wrong. Many serial killers have this disorder, one of the most damaging psychological disorders. Your essay could explore causes and treatments.
Are severe mental disorders, like schizophrenia, on the rise? First, research this topic and then build an essay around it. You will find that rates of this mental disorder are on the rise. After doing the research, determine why this increase might be happening. Then, explore ideas for treatment that might help combat the issue.
Do violent video games and movies cause violent behavior? Do they hurt the development of a child’s psychological well-being enough that the child can commit atrocious crimes? The APA warns that it is a risk factor for aggressive behavior. Answering these questions in your essay could address an important social issue while helping you craft a topical piece, as this type of media is an integral part of modern society.
What factors support children in becoming problem solvers and improve their critical thinking skills? Some research indicates that the school setting is primarily the most impactful. Still, you will also find some research that says parents and familial upbringing play a significant role. After researching, decide what you feel is the most crucial factor. Then, build your paper around that thesis as you prove your choice. You can also provide practical advice to help teachers and parents better teach problem-solving to the children they impact.
Many people think of PTSD as affecting people who have been to war or suffered a traumatic accident or incident, but some research has found that chronic illness can lead to PTSD symptoms . You could build an essay around this, discussing why this is and how doctors could better serve patients by understanding the connection. With an understanding of the link between PTSD and chronic illness, doctors may be able to help their patients not only recover from physical diseases but also the psychological effects of those illnesses.
Parents come in all shapes and sizes, and all have distinct parenting styles. Explore how different parenting techniques impact a child’s development. You can choose a selection of well-researched parenting styles and compare the outcomes with regard to child development. You may also choose to compare your findings to your own upbringing.
A panic attack can stop you in your tracks and make normal functioning impossible. Knowing how to stop a panic attack is vital to protecting the health and well-being of the individual. Explore various ideas for controlling a panic attack and helping someone achieve a positive mental state, such as deep breathing, meditation, or even taking a walk. Discuss why these tactics work and how someone can remember to use them during an attack.
Over half of all teenage girls and a third of adolescent boys have an eating disorder, and most suffer from anorexia. Explore what factors make teens more likely to try to control their weight in this unhealthy manner. Is it our growing dependence on social media and the perfect body image it portrays, or is it a change in our biological makeup? The statistics surrounding teen eating disorders are clear and established, but the cause is not. Consider using your essay to explore the potential causes of this serious issue.
High school is a challenging time for teenagers growing into adults and facing increasing academic pressure, which can result in anxiety. According to the National Institutes of Health , one out of three teenagers will suffer an anxiety disorder. This statistic shows that teenagers do, in fact, face anxiety in high school. Your essay could explore why this is true, include strategies teachers could use to reduce stress and comment on the overall impact of this anxiety on developing adolescents.
Sports psychology can be interesting to explore. In one study , researchers found that athletes’ physical prowess helped their athletic ability between 45% and 48%, while psychological health increased their ability by 79% to 85%. Based on statistics like this, create an essay that explores the impact of self-confidence on performance.
Psychology has many branches. Choose what interests you the most and tell your readers why you find the field interesting. You can also include how the field’s lessons can be applied in everyday life. Always remember to have a good structure and do proper research to understand the topic and clearly explain it to your readers.
Personality, anxiety, PTSD, and depression are the most common psychological disorders many individuals experience. Writing an essay about these conditions is an excellent way to show how psychology helps people overcome their disorders. In using this prompt, add relevant information such as signs one is suffering from the condition or how to support someone with the illness. If you choose depression as a topic, see our guide on how to write essays about depression.
Beliefs have a significant impact on a person’s behavior. Use this prompt to give your perspective or share your experience on how an individual’s religious beliefs can affect how they think and shape the way they live. In addition, you can delve into the psychological impacts of religion and discuss whether it helps or hinders a person’s mental well-being.
Writing an essay about theories and experiments in psychology is challenging. For this prompt, you will not only choose a popular psychology theory to write about, such as “ Piaget’s Theory of Development ” or the “ Kohlberg’s Theory of Moral Development ,” but also experiments conducted worldwide to discover how the brain works and why psychological disorders exist. Consider commenting on how well the theory has been absorbed into our society and whether it remains credible.
Since psychology is a popular course, writing about different careers in psychology is an exciting topic. Include jobs such as a forensic psychologist, child psychologist, trauma counselor, or behavioral therapist. Use this prompt to write about a psychologist’s typical duties and responsibilities in a specific field. You can also add how much they earn and what other job opportunities become available through psychology. This topic can encourage your readers to pick a psychology career they want to pursue.
Teenage pregnancy, rebellion, mental illness, and falling into bad habits are often the result of broken families and bad parenting. Use this prompt to show how vital a good family relationship is in a child’s development. You can add news, blogs, or interview someone willing to share their experiences to make your essay more credible.
Do you need topics on writing about family? Then, check out our 20 engaging essay topics about family.
Racism is a timely and controversial topic in social psychology. Use this prompt to show the effects of racism on an individual or country and add positive initiatives to reduce the violence it causes.
Essay writing tips : Add statistics and recent or popular news about racism to make your arguments reasonable and your essay credible.
Writing about a pertinent person in the history of psychology is one of the most straightforward but fascinating prompts. You should gather the person’s biography and professional history as well as their theories and influence on the subject. Consider famous individuals like Harry Harlow, Sigmund Freud, and other renowned psychologists of which the general public is already aware.
If you are interested in learning more, check out our essay writing tips!
APA References Page Formatting and Example
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
The APA reference page (also called the reference list) is the final page of your paper where all sources you cited in the main text are listed.
It should include the full details of all sources you cited in the main text, arranged A-Z alphabetically by author’s surname.
Everything cited in the text must appear in the reference list, and everything on your reference page must be something you have referred to in the text. Make sure you don”t have anything in one place that isn’t in the other.
Reference Page vs. Bibliography
A reference list includes all works that have been cited in the assignment. A bibliography is a detailed list of references cited in your work, plus the background readings or other material you may have read, but not cited.
Note : This page reflects the latest version of the APA Publication Manual (i.e., APA 7), which released in October 2019.
Reference Page: Basic Rules
List references on a new page. Type “References” as page heading, written in boldface, at the top center of the page. Use double spacing. Reference list entries should be alphabetized by the last name of the first author of each work. For multiple articles by the same author, list the entries in chronological order, from earliest to most recent. Indent second and subsequent lines of each entry using a hanging indent of 5-7 spaces (by pressing Ctrl + T on a PC, or Command (⌘) + T on a Mac). All references in APA end with a full stop except when the reference ends with a URL or a DOI.
APA Reference List Example

Journal Article Reference in APA Format
- Author or authors. The surname is followed by a comma and the first initials.
- Year of publication of the article (in parentheses). End with a period.
- Article title. Capitalize only the first letter of the first word. End with a period.
- Capitalize all major words in the title of the journal, followed by a comma.
- Italicize journal title and volume number. Do not put a space between in the volue number and the parentheses around the issue number.
- Issue number of journal in parentheses (no italics) followed by a comma.
- Page range of article. Use an en dash (not a hyphen); do not put spaces around the dash. End with a period.
- Include a DOI (digital object identifier) for all works that have one (i.e. online journal articles). Do not put a period after the DOI url.
Journal Article (Online): One Author
Author, A. A. (Year). Title of article. Title of Journal, volume number (issue number), page numbers. doi: or URL of the journal’s home page
Matsunaga, M. (2011). Underlying circuits of social support for bullied victims: An appraisalbased perspective on supportive communication and postbullying adjustment. Human Communication Research, 37 (2), 174-206. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2958.2010.01398.x
Journal Article (Online): 2-7 Authors
Author, A. A., Author, A. A., Author, A. A., Author, A. A., & Author, A. A. (Year). Title of article. Title of Journal, volume number (issue number), page numbers. doi: or URL of the journal’s home page
Williams, S. L., & Mickelson, K. D. (2008). A paradox of support seeking and rejection among the stigmatized. Personal Relationships, 15 (4), 493-509. doi:10.1111/j.1475-6811.2008.00212.x
Book Reference in APA Format
- Book title (in italics ). Capitalize only the first letter of the first word. End with a period.
- Edition (in parentheses), if other than first. Position this after the title but before the period.
- Incude the name of the publisher, followed by a period. Do not include the publisher location.
- Include a DOI for all workds that have one, regardless of whether you used the online version or print version. Do not put a period after the DOI url.
Book: One Author
Author, A. A., & Author, B. B. (Year). Title of the work . Publisher.
Fletcher, D. P. (2018). Disrupters: Success strategies for women who break the mold . Entrepreneur Press.
Book: Two Authors, and Edition
Author, A. A., & Author, B. B. (Year). Title of the work (edition). Publisher.
Moran, A., & Toner, J. (2017). A critical introduction to sport psychology (3rd ed.). Routledge.
- Chapter in an Edited Book: One Author
Author, A. A. (Year). Title of chapter. In A. Editor & B. Editor (Eds.), Title of the book (pages of chapter). Publisher.
Haybron, M. D. (2008). Philosophy and the science of the subjective well-being. In M. Eid & R. J. Larsen (Eds.), The science of subjective well-being (pp. 17-43). Guilford Press.
Reference for a Chapter in Edited Book in APA Format
- Title of the book chapter. Capitalize only the first letter of the first word. End with a period.
- Write the word “In” and the initials and last name (not inverted) of each editor. Use “(Ed.)” for one editor or “(Eds.)” for multiple editors. End with a comma.
- Write “pp.” and include the chapter page range (in parentheses). End with a period.
- Include a DOI if available. Do not put a period after the DOI url.
Reference for a Website in APA Format
- Year, Month Day of publication (in parentheses). Use the most exact date possible. End with a period.
- Title (in italics ). End with a period.
- Website name. Capitalize all major words. End with a period.
- Website URL. Do not put a period after the url.
APA Website Reference Example
McLeod, S. A. (2019, September 29). APA reference page formatting and example . Simply Psychology. www.www.www.www.www.www.simplypsychology.org/apa-reference-page.html
Further Information
- APA Style 7th Edition Quick Reference Guide
- APA Style Citations & References
Related Articles

Student Resources
How To Cite A YouTube Video In APA Style – With Examples

How to Write an Abstract APA Format

APA Title Page (Cover Page) Format, Example, & Templates

How do I Cite a Source with Multiple Authors in APA Style?
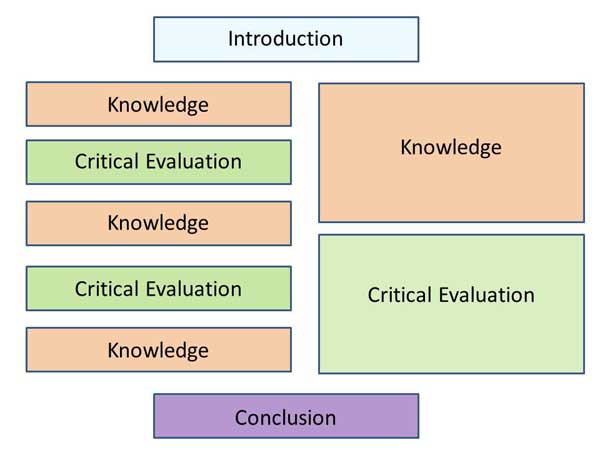
How to Write a Psychology Essay

Lab Report Format: Step-by-Step Guide & Examples

A block party during Carnival in Belo Horizonte, Brazil; 11 February 2024. Photo by Washington Alves/Reuters
Learning to be happier
In order to help improve my students’ mental health, i offered a course on the science of happiness. it worked – but why.
by Bruce Hood + BIO
In 2018, a tragic period enveloped the University of Bristol, when several students killed themselves related to work stress. Suicide is usually the ultimate culmination of a crisis in mental health, but these students weren’t alone in feeling extreme pressure: across the campus there was a pervasive sense that the general student body was not coping with the demands of higher education. My own tutee students, whom I met on a regular basis, were reporting poor mental health or asking for extensions because they were unable to meet deadlines that were stressing them out. They were overly obsessed with marks and other performance outcomes, and this impacted not only on them, but also on the teaching and support staff who were increasingly dealing with alleviating student anxiety. Students wanted more support that most felt was lacking and, in an effort to deal with the issue, the university had invested heavily, making more provision for mental health services. The problem with this strategy, however, is that by the time someone seeks out professional services, they are already at a crisis point. I felt compelled to do something.
At the time, Bristol University was described in the British press as a ‘toxic’ environment, but this was an unfair label as every higher education institution was, and still is, experiencing a similar mental health crisis. Even in the Ivy League universities in the United States, there was a problem, as I discovered when I became aware of a course on positive psychology that had become the most popular at Yale in the spring of 2018. On reading about the course, I was somewhat sceptical that simple interventions could make much difference until I learned that Yale’s ‘Psychology and the Good Life’ course was being delivered by a colleague of mine, Laurie Santos, who I knew would not associate herself with anything flaky.
That autumn term of 2018, I decided to try delivering a free lunchtime series of lectures, ‘The Science of Happiness’, based on the Yale course. Even though this pilot was not credit-bearing, more than 500 students gave up their Wednesday lunchtimes to attend. That was unusual as, in my experience, students rarely give up time or expend effort to undertake activities unless they are awarded credit or incentives. There would be 10 lectures, and everyone was requested to fill in self-report questionnaires assessing various mental health dimensions both before and after the course, to determine whether there had been any impact and, if so, how much.
The Science of Happiness had clearly piqued interest as indicated by the audience size, but I was still nervous. This was not my area of academic expertise and there was heightened sensitivity following the media attention over recent tragic events on campus. What were the students’ expectations? Talking about mental health seemed hazardous. Would I trigger adverse reactions simply by discussing these issues?
D espite my initial reservations, the final feedback after the course ended was overwhelmingly positive. That was gratifying but, as a scientist, I like hard evidence. What would the questionnaires tell us? The analysis of the before and after scores revealed that there had been a 10-15 per cent positive increase in mental wellbeing across the different measures of wellbeing, anxiety and loneliness. That may not sound much but it was the average, and a significant impact in the field of interventions. Who wouldn’t want to be 15 per cent happier, healthier or wealthier? I was no longer a sceptic; I was a convert. I would stop focusing on developmental psychology, my own area of research, and concentrate on making students happier. Even a 15 per cent improvement might lead to a degree of prevention that was better than dealing with a student who was already struggling.
The following year, we launched a credit-bearing course for first-year students who had room in their curriculum schedule to take an open unit, which has now been running for five years. These psychoeducational courses are not new and predate my efforts by at least a decade. But what makes the Bristol psychoeducational course unique (and I believe this is still the case) is that we persuaded the university to allow a credit-bearing course that had no graded examinations but was accredited based on engagement alone. Not only was I convinced by compelling arguments for why graded assessment is the wrong way to educate, but it would have been hypocritical of me to lecture about the failings of an education system based solely on assessment, and then give students an exam to determine if they had engaged. Rather, engagement required regular weekly attendance, meeting in peer-mentored small groups, but also undertaking positive psychology exercises and journaling about their experiences so that we could track progress. Again, to test the impact of the course, students were asked to fill in the various psychometric questionnaires to give us an insight to impact.
Meditation stops you thinking negative thoughts. Not exactly a scientific explanation
We now have five years’ worth of data and have published peer-reviewed scientific papers on evaluation of the course. As with the initial pilot, the consistent finding is that there is, on average, a 10-15 per cent significant increase in positive mental wellbeing over the duration of the course. The course improves mental wellbeing but there are limitations. Our most recent analysis over the longer term shows that the positive benefits we generate during the course, and the two months after, are lost within a year, returning to previous baseline scores, unless the students maintain some of the recommended activities. However, in those students who kept practising at least one of the positive psychology interventions (PPIs) such as journaling, meditation, exercise, expressing gratitude or any of the other evidence-based activities, they maintained their benefits up to two years later.
Why do interventions work and why do they stop working? As to the first question, there are countless self-help books promoting PPIs, but the level of explanation is either missing or tends to be circular. Acts of kindness work because they make you feel better. Meditation calms the mind and stops you thinking negative thoughts. Not exactly a scientific explanation or revelation. Even though I had largely put my experimental work with children on hold because of the demands of teaching such a large course, I was still intellectually intrigued by the same basic theoretical question that has always motivated my research. What is the mechanism underlying positive psychology?
T here are several plausible hypotheses out there from established academics in the field that explain some of the activities, but they lack a unifying thread that I thought must be operating across the board. I started considering the wide and diverse range of PPIs to see if there was any discernible pattern that might suggest underlying mechanisms. Two years ago, I had an insight and I think the answer can be found in the way we focus on our self.
In my role as a developmental psychologist, I see change and continuity everywhere in relation to human thought and behaviour. For some time, I have been fascinated by the concept of the self and how it emerges but must change over the course of a lifetime. I believe earlier childhood notions lay the foundation for later cognition which is why development is so critical to understanding adults. My most recent work concentrated on how ownership and possessions play major roles in our concept of self, and I was particularly interested in acts of sharing among children. Specifically, we had completed a set of studies demonstrating that, when children are instructed to talk about themselves, they thought about their own possessions differently and became less willing to share with others. Emphasising their self had made these children more selfish. This got me thinking about the role of self-focus in happiness.
The most pernicious aspect of self-focus is the tendency to keep comparing ourselves to others
Infants start off with an egocentric view of the world – a term and concept introduced by the psychologist Jean Piaget. Egocentric individuals tend to perceive the world from their own perspective, and many studies have shown that young children are egocentric in the way they see the world, act, talk, think and behave with others. Normal development requires adopting a more allocentric – or other-based perspective in order to be accepted. The sense of self changes from early ebullient egocentrism to an increasing awareness of one’s relative position in the social order. Children may become more other-focused but that also includes unfavourable comparisons. They increasingly become self-aware and concerned about what others think about them – a concern that transitions into a preoccupation when they enter adolescence that never really goes away. As for adults, like many features of the human mind, earlier ways of thinking are never entirely abandoned. This is why our self-focus can become a ‘curse’, as the psychologist Mark Leary describes , feeding the inner critic who is constantly negatively evaluating our position in life.
One reason that self-focus can become a curse is that we are ignorant of the biases our brains operate with that lead us to make wrong decisions and comparisons. When it comes to happy choices, we want something because we think it will make us happy, but our predictions are inaccurate. We think events will be more impactful than they turn out to be, and we fail to appreciate how fast we get used to things, both good and bad. This is called a failure of affective forecasting which is why the psychologist Dan Gilbert explains that our tendency to ‘stumble on happiness’ is because our emotional predictions are so way off. We don’t take into consideration how future circumstances will differ because we focus on just one element and we also forget how quickly we adapt to even the most pleasurable experiences. But the most pernicious aspect of self-focus is the tendency to keep comparing ourselves to others who seem to be leading happier lives. Social media is full of images of delicious plates of food, celebrity friends, exotic holidays, luxurious products, amazing parties and just about anything that qualifies as worthy of posting to bolster one’s status. Is it any wonder that the individuals who are the most prone to social comparison are the ones who feel the worst after viewing social media? As Gore Vidal once quipped: ‘Every time a friend succeeds, I die a little.’
If egocentric self-focus is problematic then maybe positive psychology works by altering our perspective to one that is more allocentric or ‘other-focused’? To do so is challenging because it is not easy to step out of ourselves under normal circumstances. Our stream of conscious awareness is from the first-person, or egocentric, perspective and, indeed, it is nigh-on-impossible to imagine an alternative version because our sensory systems, thought processes and representation of our selves are coded as such to enable us to interact within the world as coherent entities.
M any PPIs such as sharing, acts of kindness, gratitude letters or volunteering are clearly directed towards enriching the lives of others, but how can we explain the benefits of solitary practices where the self seems to be the focus of attention? The explanation lies with the self-representation circuitry in the brain known as the default mode network (DMN). One of the surprising discoveries from the early days of brain imaging is that, when we are not task-focused, rather than becoming inactive, the brain’s DMN goes into overdrive. Mind-wandering is commonly reported during bouts of DMN activity and, although that may be associated with positive daydreaming, we are also ruminating about unresolved problems that continue to concern us. According to one influential study that contacted people at random points of the day to ask them about what they were doing, what they were thinking and how they were feeling, people were more likely to be unhappy when their minds were wandering, which was about half of the waking day. Probably because they were focusing on their own predicaments.
If you focus on your problems, this can become difficult to control. There’s no point trying to stop yourself ruminating because the very act of trying not to think about a problem increases the likelihood that this becomes the very thought that occupies your mind. This was first described in an 1863 essay by Fyodor Dostoyevsky, when he observed the effect of trying not to think; he wrote: ‘Try to pose for yourself this task: not to think of a polar bear, and you will see that the cursed thing will come to mind every minute.’ My late colleague Dan Wegner would go on to study this phenomenon called ironic thought suppression , which he explained resulted from two mechanisms: the tendency to increase the strength of the representation of a thought by the act of trying to suppress it, and a corresponding increased vigilance to monitor when the thought comes to the fore in consciousness. Ironic thought suppression is one reason why it can be so difficult to fall asleep. This is why one of our recommended activities on our Science of Happiness course is to journal on a regular basis because this helps to process information in a much more controlled and objective way, rather than succumbing to the torment of automatic thinking.
Could the long-term benefits be something to do with altering the ego?
Other recommended activities that calibrate the level of self-focus also attenuate DMN activity. For example, mindfulness meditation advocates not trying to suppress spontaneous thoughts but rather deliberately turning attention to bodily sensations or external sounds. In this way, the spotlight of attention is directed away from the internal dialogue one is having with oneself. It is during such states that brain imaging studies reveal that various solitary interventions we recommend on the course – such as meditation or taking a walk in the country – are associated with lowered DMN activity and, correspondingly, less negative rumination. This is why achieving absorption or full immersion during optimal states of flow draws conscious awareness and attention out of egocentric preoccupation. To achieve states of flow, we recommend that students engage in activities that require a challenge that exceeds their skill level to an extent that they rise to the task, but do not feel overwhelmed by it. When individuals achieve flow states, their sense of self, and indeed time itself, appears to evaporate.
There are other more controversial ways to alter the egocentric self into one that is more allocentric. Currently, there is a growth in the use of psychedelics as a treatment for intractable depression and, so far, the initial findings from this emerging field are highly encouraging. One clinical study has shown that psychedelic-assisted therapy produced significant improvement in nearly three-quarters of patients who previously did not respond to conventional antidepressants. The primary mechanism of action of psychedelics is upon serotonin (5-HT 2A ) receptors within the DMN which, in turn, produce profound alterations of consciousness, including modulations in the sense of self, sensory perception and emotion. Could the long-term benefits be something to do with altering the ego? One of the most common reports from those who have undergone psychedelic-assisted therapy, aside from euphoria and vivid hallucinations, is a lasting, profound sense of connection to other people, the environment, nature and the cosmos. Across a variety of psychedelics, the sense of self becomes more interconnected, which is why a recent review concluded that there was consistent acute disruption in the resting state of the DMN.
I f chemically induced states of altered consciousness through psychedelics (which is currently still illegal in most places) is not your thing, then there are other ways to redress the balance between egocentrism and allocentrism. Engaging in group activities that generate synchronicity – such as rituals, dancing or singing in choirs – alter the sense of self and increase connection with others. But if group activities or psychedelic trips don’t work for you, then take a rocket trip. One of the most moving emotional and lasting experiences, known as ‘ the overview effect ’, occurs to those lucky individuals given the opportunity to view our planet from outer space. As the astronaut Edgar Mitchell described it, it creates an ‘explosion of awareness’ and an ‘overwhelming sense of oneness and connectedness … accompanied by an ecstasy … an epiphany.’
Back down on Earth, we can be happier when we simply acknowledge that we are all mortal, interconnected individuals who suffer personal losses and tragedies. No one’s life is perfect, and indeed you need to experience unhappiness in order recognise when things are going well. As the Stoic philosopher Epictetus put it: ‘Men are disturbed not by things, but by the views which they take of things.’ In other words, it’s not what happens to you, but how you respond, that matters, and that’s where positive psychology can make a difference – but only if you keep reminding yourself to get out of your own head.
Happiness hack
How to shift your egocentric self to one that is more allocentric using language
Consider a problem that is currently bothering you. A real problem – not a hypothetical one or a world problem beyond your control. Find something that makes you unhappy and then say to yourself: ‘I am worried about [whatever it is] because [whatever the reason may be] and this makes me upset.’ Now repeat the exercise but this time don’t use egocentric or first-person terms such as ‘I’ or ‘me’. Rather use your name and non-first-person language such as: ‘Bruce is worried about his [whatever it is] problem and this makes him upset.’
Speaking in non-first-person language should automatically transpose you out of the egocentric perspective to one that is other or allocentric, making the problem seem less.

Mental health
The last great stigma
Workers with mental illness experience discrimination that would be unthinkable for other health issues. Can this change?
Pernille Yilmam
Quantum theory
Quantum dialectics
When quantum mechanics posed a threat to the Marxist doctrine of materialism, communist physicists sought to reconcile the two
Jim Baggott

Nations and empires
A United States of Europe
A free and unified Europe was first imagined by Italian radicals in the 19th century. Could we yet see their dream made real?
Fernanda Gallo

Stories and literature
On Jewish revenge
What might a people, subjected to unspeakable historical suffering, think about the ethics of vengeance once in power?
Shachar Pinsker

Building embryos
For 3,000 years, humans have struggled to understand the embryo. Now there is a revolution underway
John Wallingford

Design and fashion
Sitting on the art
Given its intimacy with the body and deep play on form and function, furniture is a ripely ambiguous artform of its own
Emma Crichton Miller

- Published: 4 June 2024
- ISBN: 9780241638682
- Imprint: Dorling Kindersley
- Format: Hardback
- RRP: $42.99
- Self-help & personal development
The Psychology Book
Big Ideas Simply Explained
DK's best-selling guide to the history of psychology – now fully revised and updated
How do our minds influence the way we behave? How do our bodies and minds work together? Do we have free will?
Exploring and explaining the big ideas and groundbreaking theories in the field of psychology in a clear and simple way, The Psychology Book answers these questions and more besides, and is the perfect introduction to the subject. Untangling knotty theories and shedding light on abstract concepts, entries unpack each complex idea with a combination of easy-to-follow explanations and innovative graphics.
Delve into the history of psychology, from its roots in philosophy right up to modern studies of autism and psychiatry across all of the key fields of study, from psychotherapy to cognitive psychology and behaviourism. And discover the groundbreaking ideas of great thinkers, from Sigmund Freud and Carl Jung to Noam Chomsky and Daniel Kahneman, along the way.
Fully revised and updated with eight brand-new pages of content, The Psychology Book is an essential and accessible introduction to a fascinating subject.
Related titles
Our top books, exclusive content and competitions. straight to your inbox..
Sign up to our newsletter using your email.
By clicking subscribe, I acknowledge that I have read and agree to Penguin Books Australia’s Terms of Use and Privacy Policy .
Thank you! Please check your inbox and confirm your email address to finish signing up.
The Book “Too Scared to Cry” by Lenore Terr Essay
Description, self-reflection.
Lenore Terr’s Too scared to cry: Psychic trauma in childhood is a psychology book that discusses various real-life scenarios when children were exposed to traumatic events and their response to those situations. Initially, the author explores and defines childhood trauma and what factors may cause it. She provides examples of older adults who were harassed and hence developed an aversion to sex. Furthermore, she presents the story of a young boy who was kidnapped and raped by a middle-aged man. In this case, the child seems to have a poor recollection of that event because it happened when he was three. Additionally, the author tells about a group of kidnapped schoolchildren who were buried alive and, fortunately, survived (Terr, 2008). In the subsequent chapters, Terr (2008) presents a range of responses to traumatic events that include terror, rage, numbing, denial, grief, shaming, and guilt. Furthermore, the author discusses how these emotions affect a person for the rest of one’s life if left unresolved. Lastly, the book presents treatment methods available for patients with traumatic life experiences.
Childhood trauma is a severe and often poorly discussed topic, resulting in many untreated traumatized adults that project their issues onto their families and other people. Too scared to cry can be related to three concepts in A guide to crisis intervention textbook: situational crisis, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and trauma-informed care. Situational crises are unexpected and often negative experiences and events that a person cannot control or prevent (Kanel, 2019). PTSD is a clinical diagnosis established for individuals in the state of pathologic grief after the loss or death of a loved one longer than six months (Kanel, 2019). The PTSD diagnosis also applies to those who have flashbacks about a traumatic event for an extended period of time (Kanel, 2019). Trauma-informed care focuses on ensuring a person’s physical and emotional safety, providing collaboration, and empowering the victim (Kanel, 2019). PTSD and other psychological traumas are the consequences of inciting events known as crises, resulting in a wide range of healthy and unhealthy coping mechanisms among individuals.
The response of victims of assault, neglect, or sexual abuse varies depending on the age of exposure to that type of violence. The sooner a child is removed from an unfavorable environment, the higher the chance one has to leave a traumatic event in the past and continue developing normally if exposed to trauma-informed care. Although Terr (2008) admits that not all traumatized children remember their issues vividly for their entire lifetime, she believes that it shapes their relationship style, methods of communication, and overall reaction to various external stressors. The author claims that many people remain paralyzed for a long time after being raped, while some displace their anger on objects or people. The latter usually results from cases when a child was continuously abused in one’s family or school.
I chose this book for reading and reflection because it is an essential and painful topic for me because I know many individuals who carry their childhood traumas with them. I am certainly not an exception because the author of the book showed that all adults were traumatized at some point in their lives, but they respond differently. Undoubtedly, the reaction varies depending on the type of crisis. Still, in all of these cases, the only solution is to help these individuals understand their psychological problems, accept them, and eventually heal.
Terr, L. (2008). Too scared to cry: Psychic trauma in childhood . Basic Books.
Kanel, K. (2019). A guide to crisis intervention . Cengage Learning.
- "The Raven" by Edgar Allan Poe Analysis
- The Lifespan Theory Applied to a Grieving Case
- "The Raven" by Edgar Allan Poe: Poem Analysis
- Safety Standards for Children Playgrounds
- Child Psychoanalysis: Freud's Contributions
- Children's Behavior and Development
- Early Childhood Trauma, Neglect, and Abuse
- COVID-19 Social-Emotional Impact on Young Children
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, May 26). The Book "Too Scared to Cry" by Lenore Terr. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-book-too-scared-to-cry-by-lenore-terr/
"The Book "Too Scared to Cry" by Lenore Terr." IvyPanda , 26 May 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/the-book-too-scared-to-cry-by-lenore-terr/.
IvyPanda . (2024) 'The Book "Too Scared to Cry" by Lenore Terr'. 26 May.
IvyPanda . 2024. "The Book "Too Scared to Cry" by Lenore Terr." May 26, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-book-too-scared-to-cry-by-lenore-terr/.
1. IvyPanda . "The Book "Too Scared to Cry" by Lenore Terr." May 26, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-book-too-scared-to-cry-by-lenore-terr/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "The Book "Too Scared to Cry" by Lenore Terr." May 26, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-book-too-scared-to-cry-by-lenore-terr/.

- Relationships
The Lives of Sea Turtles and Why They Matter
Marine biologist christine figgener on the oldest living creatures on earth..
Posted May 23, 2024 | Reviewed by Lybi Ma
- Why Relationships Matter
- Find counselling to strengthen relationships
- Figgener highlights the biology and ecology of sea turtles and showcases the complexity of threats.
- Her book could motivate people to do more and entirely fall in love with these prehistoric creatures.

I love sea turtles but don't know much about them. Christine Figgener's new book My Life with Sea Turtles: A Marine Biologist’s Quest to Protect One of the Most Ancient Animals on Earth answers many questions. I couldn't be happier after I read it and agree with part of the book's description: "Filled with reverence and wonder for the natural world, this captivating book reveals the secret life of sea turtles, one of the oldest living creatures on Earth, alongside one female scientist’s fight to save their future." Her video of the painful removal of a plastic straw from a sea turtle's nose went viral and catalyzed the global debate about single-use plastics that led to them being banned in many countries. Here's what she had to say about her passionate and important book.
Marc Bekoff: Why did you write My Life with Sea Turtles ?
Christine Figgener: I wrote My Life with Sea Turtles, first and foremost, to express my love and enthusiasm for sea turtles and their oceanic habitat, including the biology and ecology that have ensured their survival for millions of years. But this book was also born out of my concerns for the future of our sea turtles and oceans, which I want to share with more people.
We are currently experiencing a sixth mass extinction of species due solely to our human existence and lifestyle. Because of us, many species face unprecedented threats and only have a chance of survival if we drastically change how we live and actively do something to prevent their extinction. Despite the sad topics I address, it is still a plea for hope, optimism , and community.
By sharing my personal life journey with sea turtles, which took me from a small inland town in Germany to studying marine biology and working with sea turtles in Central America, I want to encourage and empower particularly young people to dedicate their lives to nature conservation. If there is a next generation of conservationists and sea turtle enthusiasts we will continue to have sea turtles and other animals on our planet.
I hope to motivate many people to do more and, if they haven't, entirely fall in love with these prehistoric creatures.
MB: How does your book relate to your background and general areas of interest?
CF: I have been an avid reader ever since I started reading. As a child, books let me travel into the densest jungles and deepest marine trenches without leaving the confinement of my room. I have always been a storyteller by heart, loving to write essays and short stories in school, but as I became a scientist, my storytelling had to change somewhat to comply with the rigor of the scientific method. However, I have always dreamed about writing a book about things I deeply care about and hopefully inspire others to care. With this book, I combined my love of storytelling, including photography, with my passion for science and sea turtles.
MB: Who do you hope to reach?
CF: People who wouldn't generally read a popular science book. I don't want to preach to the choir. We have an incredible global conservation community. While I appreciate my friends and colleagues reading my book, I would like people outside our usual bubble to pick it up. It is not my friends and colleagues I need to educate about the plight of sea turtles and our oceans, but people who have never before thought about it. Sea turtles are charismatic animals; some might even say magical. I hope their unique charm will help me convince people that they and their oceanic habitat are worthy of our protection and that we need all hands on deck for it.

MB: What are some of the major topics you consider?
CF: Besides highlighting extraordinary sea turtle biology and ecology, I primarily want to showcase the complexity of threats they and their oceanic habitat face. We won't save sea turtles just by banishing plastic straws or eating fish. There is so much going on, from direct exploitation to climate change , pollution, and invasive species, and all of this needs to be addressed and hopefully solved if sea turtles are meant to have a future on this planet.
Other topics near and dear to me are general issues in the conservation sector (and academia), ranging from low pay and little available funding to low diversity and neocolonial structures that many people might not be aware of. I am also talking about the importance of data-driven conservation measures to maximize their impact and outcome while being limited by funding and what it is like to have two hearts beating in my chest, that of a cool-headed scientist and a hot-blooded activist. I write from my perspective as a female scientist and conservationist, which might provide some insights into the unique challenges women face and how we navigate this world.

MB: How does your book differ from others that are concerned with some of the same general topics?
CF: When I set out to write this book, I didn't want to write another popular science book about sea turtles with fact after fact after fact. I want to reach audiences beyond those who usually pick up these books. I want people of all ages, who like the ocean and perhaps even sea turtles, those who like a good read about an interesting topic, to be drawn into the world of sea turtles, my work with them, and learning a good amount on the side. Having written this book as part memoir, part adventure-travel book, and part popular science book, it hopefully provides the right mix to keep people engaged.

MB: Are you hopeful that as people learn more about turtles, they will treat them with more compassion and respect?
CF: You only protect what you love, and you only love what you know. After reading my book, people will know more about sea turtles and their state in our world. Time will tell if this will also lead to a love for them and more compassion and respect.
In conversation with Dr. Christine Figgener . Christine has lived and worked in Costa Rica since 2007, researching sea turtles and fighting for their protection. She is a Time magazine Next Generation Leader and her research and advocacy efforts have been featured in the BBC and National Geographic . Currently, she leads research projects in Costa Rica dedicated to empowering local conservation initiatives. Her video of the painful removal of a plastic straw from a sea turtle's nose went viral and catalyzed the global debate about single-use plastics that led to them being banned in many countries.
Endangered Turtles Offer Hope In an Era of Despair .

Marc Bekoff, Ph.D. , is professor emeritus of ecology and evolutionary biology at the University of Colorado, Boulder.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- International
- New Zealand
- South Africa
- Switzerland
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

At any moment, someone’s aggravating behavior or our own bad luck can set us off on an emotional spiral that threatens to derail our entire day. Here’s how we can face our triggers with less reactivity so that we can get on with our lives.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
- Experiential Learning
- Human Subject Pool
- Student Associations
- Student Research
- PhD Program
- Behavioural Neuroscience
- Cognitive Science
- Developmental
- Quantitative Methods
- Social & Personality
- Opportunities
- Research Streams
- Participate
- Postdoctoral Research
- PSYC240: Research Experience
- Newsletters
- Pets of UBC Psych
- EDI Committee
- EDI Strategy, Goals & Initiatives
- EDI Involvement
- EDI Resources & Support
- EDI Funding
- EDI Research
- Diversity Mentorship Program
- Equity, Diversity, and Inclusion
- Psychology Clinic
- Community Pantry
- Job Opportunities
- Sustainability
New book by Dr. Wolfgang Linden examines how to stop controlling the uncontrollable
May 27, 2024
On June 16, 2024, Professor Emeritus Dr. Wolfgang Linden’s new book The Illusion of Control: A Practical Guide to Avoid Futile Struggles will be released.
Based on scientific evidence and real-life experience, the book makes a well-justified case that people grossly overestimate how much power they have over others and simultaneously miss out on opportunities to enjoy and exploit the power they have over themselves.
Dr. Linden joins us for a Q&A where he shares personal anecdotes, examples of missed opportunities, and what readers can learn from his book.
What inspired you to write “Illusions of Control”? Was there a particular event or realization that sparked the idea for the book? I thought about that; it is the kind of question a psychologist asks. There was no specific event that served as a trigger. But I do think my motives and objectives are fairly clear, at least to myself. At my age, you care about legacy and this is a legacy project; it ties together a huge amount of what I am, what I believe, what I advocate for, and why! And, as you know, as scientists we write articles in journals that must be concise and narrow; no opportunity here for world views and tangents, and lovely analogies. Even when you get to write a textbook (as Paul Hewitt and I did, 3rd edition in the works), you are told to some degree by reviewers and acquisition editors what needs to be covered. Mind you, there was quite a bit more room in the textbook to develop and share a personal style, be a bit more chatty. Also, writing this book is part of the legacy I like to leave, where I feel guilty (and my wife shares that with me, another psychologist sort of retired) that it is just wrong for us to retire and not share what we have learned. Failures can be learned about and told to prevent others from doing it, and success strategies must be shared of course, too. In the book, you discuss the idea of missed opportunities to enjoy and exploit the power individuals have over themselves. Could you provide some examples of these missed opportunities? There is lots here. For one thing, I believe you can learn and make new experiences as long as you breathe, there is no age limit. My wife and I just got back from three week in Colombia where we stayed with a local family and took Spanish courses in the morning. And people who make new experiences can share these with friend and families and don’t not need to repeat the same war stories a hundred times. We have lots of control over our behaviour: yes, we can be scared of heights and still book a flight in a hot air balloon (done this). We can make friend at all ages and enjoy their company. We can create joyous events at will whereas problems are often out our control, but the joy makes the problem solving easier. What do you hope readers will take away from your book? Are there any specific insights or perspectives you aim to impart? Oh yes, there’s lots here. Learn when to invest and engage and know when to stop. Stop trying to convince other people that you are right and they are wrong. Unsolicited advice is rarely appreciated. Create your fun, the sky is the limit. Make sure there is meaning to your life; give to others, engage with politics you believe in. Learn active listening: great for friendships, marriages, political engagement. Can you share any personal anecdotes or experiences that influenced the themes explored in “Illusions of Control”? I listed some of those above already. But, of course there are more: I have learned and accept that there is more joy in making new experiences than in buying new gadgets or cars or whatever. I try (and of course sometimes fail) to not repeat myself more than once. If these two attempts did not work, walk away or change tactics.
About the Author
Dr. Wolfgang Linden is a Professor Emeritus in Clinical and Health Psychology at the University of British Columbia in Vancouver, Canada. He is a scientist practitioner with expertise in the reduction of health risk behaviours, stress management, eating disorders, treatment of hypertension, psychosocial cardiac rehabilitation, and psychological factors in cancer care. Dr. Linden has written over 170 peer-reviewed articles and book chapters and six books, three of which were also published in German, Turkish, Chinese, and Korean. For the last four decades he has worked as an advocate for improved mental health care, and has recently focused on trying to minimize the long-term consequences of adverse childhoods.
Recent News
Spotlight: class of 2024.

Congratulations to our graduate students crossing the stage this week

UBC-led psychology research reveals one daily act of kindness fights loneliness


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
through, step by step, the process of writing an essay or term paper in psychology. The section on Academic Honesty in Writing reinforces information you have previously received about using sources responsibly (and avoiding plagiarism). The Do's and Don'ts for Effective Writing in Psychology include examples of common mistakes made by
Essay writing is a key part of the Psychology degree and knowing how to write effective and compelling academic essays is key to success. Whether it's understanding how to implement feedback you receive on essays, how to stop procrastinating or what makes an effective introduction, this book covers it all.
Identify the subject of the essay and define the key terms. Highlight the major issues which "lie behind" the question. Let the reader know how you will focus your essay by identifying the main themes to be discussed. "Signpost" the essay's key argument, (and, if possible, how. this argument is structured).
"This book is one I wish I had bought at the start of my Psychology degree." - Five-star review Essay writing is a key part of the Psychology degree and knowing how to write effective and compelling academic essays is key to success. Whether it′s understanding how to implement feedback you receive on essays, how to stop procrastinating or what makes an effective introduction, this book ...
the ideas and direction in this book. To guide the discussion, I will assume that you've been assigned to write a typical psychology research paper. In this kind of paper, you focus on a single idea—for example, the bio-logical basis of obsessive-compulsive disorder—and you review, eval-uate, and synthesize the research on the topic.
"This book is one I wish I had bought at the start of my Psychology degree." - Five-star review Essay writing is a key part of the Psychology degree and knowing how to write effective and compelling academic essays is key to success. Whether it′s understanding how to implement feedback you receive on essays, how to stop procrastinating or what makes an effective introduction, this book ...
"This book is one I wish I had bought at the start of my Psychology degree." - Five-star review Essay writing is a key part of the Psychology degree and knowing how to write effective and compelling academic essays is key to success. Whether it′s understanding how to implement feedback you receive on essays, how to stop procrastinating or what makes an effective introduction, this book ...
Hero Images / Getty Images. Writing in psychology is formal, concise, and straightforward. When writing a psychology paper, avoid using metaphors, anecdotes, or narrative. Your paper should be well-cited and the point should be clear. In almost all cases, you will need to structure your paper in a specific way and follow the rules of APA format.
Description. Through the use of clearly defined instructions and examples, How to Write in Psychology is a concise and comprehensive guide for the well-prepared student on the principles of writing essays and research papers for psychology. Presents everything the well-prepared student needs to know about the principles and practice of writing ...
Remember to follow APA format as you write your paper and include in-text citations for any materials you reference. Make sure to cite any information in the body of your paper in your reference section at the end of your document. Writing a psychology research paper can be intimidating at first, but breaking the process into a series of ...
Tips for Writing Your Psychology Paper Intro . Use 3x5 inch note cards to write down notes and sources. Look in professional psychology journals for examples of introductions. Remember to cite your sources. Maintain a working bibliography with all of the sources you might use in your final paper. This will make it much easier to prepare your ...
Writing Guide for Psychologists. by. Staff Writers. Updated August 17, 2022. Use this guide to learn about types of writing aspiring psychologists, helpful information about common writing styles, and a number of resources for those looking to learn more. Credit: Integrity Pictures Inc / Royalty-free Collection: The Image Bank / Getty Image.
LEARNING OBJECTIVES. Describe the purpose of writing and presenting in the context of a psychology degree. Describe some of the diferent types of psychology assignment formats including laboratory reports, essay, reviews, and presentations. Identify the sections of this book that will help you to complete diferent types of psychology assignments.
Psychology 2e is designed to meet scope and sequence requirements for the single-semester introduction to psychology course. The book offers a comprehensive treatment of core concepts, grounded in both classic studies and current and emerging research. The text also includes coverage of the DSM-5 in examinations of psychological disorders.
About the Series. Essays in Cognitive Psychology is designed to meet the need for rapid publication of brief volumes in cognitive psychology. Primary topics include perception, movement and action, attention, memory, mental representation, language and problem solving. Furthermore, the series seeks to define cognitive psychology in its broadest ...
Chapter Outline. 1.1 What Is Psychology? Clive Wearing is an accomplished musician who lost his ability to form new memories when he became sick at the age of 46. While he can remember how to play the piano perfectly, he cannot remember what he ate for breakfast just an hour ago (Sacks, 2007).
Chapter 1. Introducing Psychology. Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. The word "psychology" comes from the Greek words "psyche," meaning life, and "logos," meaning explanation. Psychology is a popular major for students, a popular topic in the public media, and a part of our everyday lives.
This book contains two comprehensive essays that delve into the depths of analytical psychology. The first essay explores the role of the unconscious in the human psyche, discussing its influence on dreams, mythology, and mental illnesses. The second essay delves into the process of individuation, which is the psychological process of ...
Influence, New and Expanded is Dr. Robert B. Cialdini's 2021 republication of his one of his acclaimed bestselling psychology books Influence (first published in 1984) — complete with new research, examples, and insights, especially regarding the age of the internet.Backed up by his 35 years of scientific research, Cialdini describes seven practicable principles of influence you can use in ...
In this essay, Dukoupil points out the mental health concerns of constant exposure to social media and other technology. He explores new research into the abnormal psychology disorders this exposure is creating. 3. The Dark Psychology of Social Networks by Jonathan Haidt and Tobias Rose-Stockwell.
Type "References" as page heading, written in boldface, at the top center of the page. Use double spacing. Reference list entries should be alphabetized by the last name of the first author of each work. For multiple articles by the same author, list the entries in chronological order, from earliest to most recent.
Recently published articles from subdisciplines of psychology covered by more than 90 APA Journals™ publications. For additional free resources (such as article summaries, podcasts, and more), please visit the Highlights in Psychological Research page.
His most recent book is The Science of Happiness: Seven Lessons for Living Well (2024). Edited by Nigel Warburton. 2,900 words. Syndicate this essay. In 2018, a tragic period enveloped the University of Bristol, when several students killed themselves related to work stress. Suicide is usually the ultimate culmination of a crisis in mental ...
And discover the groundbreaking ideas of great thinkers, from Sigmund Freud and Carl Jung to Noam Chomsky and Daniel Kahneman, along the way. Fully revised and updated with eight brand-new pages of content, The Psychology Book is an essential and accessible introduction to a fascinating subject. Read more. DK's best-selling guide to the history ...
Description. Lenore Terr's Too scared to cry: Psychic trauma in childhood is a psychology book that discusses various real-life scenarios when children were exposed to traumatic events and their response to those situations. Initially, the author explores and defines childhood trauma and what factors may cause it. She provides examples of older adults who were harassed and hence developed an ...
Moral psychology is a field of study in both philosophy and psychology.Historically, the term "moral psychology" was used relatively narrowly to refer to the study of moral development. Moral psychology eventually came to refer more broadly to various topics at the intersection of ethics, psychology, and philosophy of mind. Some of the main topics of the field are moral judgment, moral ...
1689 - John Locke published An Essay Concerning Human Understanding, which claims that the human mind is a Tabula Rasa at birth. 18th century. 1701 - Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz published the Law of Continuity, which he applied to psychology, becoming the first to postulate an unconscious mind; he also introduced the concept of threshold.
Figgener highlights the biology and ecology of sea turtles and showcases the complexity of threats. Her book could motivate people to do more and entirely fall in love with these prehistoric ...
About the Author. Dr. Wolfgang Linden is a Professor Emeritus in Clinical and Health Psychology at the University of British Columbia in Vancouver, Canada. He is a scientist practitioner with expertise in the reduction of health risk behaviours, stress management, eating disorders, treatment of hypertension, psychosocial cardiac rehabilitation, and psychological factors in cancer care. Dr ...