- Annual Meeting
- Member Login


About NCSSFL
The mission of NCSSFL is to provide leadership in facilitating and promoting policies and practices that support language education.
LinguaFolio ® Training Resources
Training modules to show how to implement LinguaFolio ®
1.6 Language Biography
The Language Biography is a record of personal, language-learning history . In this section of LinguaFolio, students are prompted to reflect on how they learn and to set learning goals. They evaluate their learning goals and reflect on language learning and cultural experiences. The Biography’s can-do statements help learners assess their language competencies and interactions in authentic cultural contexts. The Biography is the most important part in the formative assessment process.
Sometimes we wonder, why do students come to us and ask what their grade will be? Why don’t they know? It may be easy for us to evaluate our own proficiency, but students must have plenty of opportunities to practice self-assessment in order to form realistic and accurate evaluations of their abilities.
Parts of the Biography Learners use the three parts of the Language Biography to reflect on and document their overall language-learning processes.
PART 1: BACKGROUND INFORMATION In this part of the LinguaFolio Biography, language learners document personal language-learning history. They reflect on how they learn and complete a learning inventory.
PART 2: INTERCULTURAL ENCOUNTERS Learners evaluate their responses to various intercultural encounters and learn to react appropriately to a specific audience. Using cultural experiences as a starting point, students explore their feelings, perceptions, and goals.
PART 3: CHECKLISTS AND SELF-ASSESSMENT GRID The checklists and self-assessment grid are from the standard version of LinguaFolio — usually for students in heritage language programs, middle school language programs for high school credit, and high school or university language programs. When learners feel they can check off most of the can-do statements within a category, they summarize that ability in the Language Passport using the self-assessment grid indicators. A checklist sample and the self-assessment grid are both linked below.
The checklists are used by the learner for self-assessment but can also be used for peer- and teacher-assessment. The teacher may draw information from the Biography to guide instructional decisions.
In this video, teachers comment on the effect of the checklists in the language learning process . In your opinion, what are the three most important impacts?
Watch video here . Video transcript: “Language Biography Checklists” (pdf)
It is not unusual for a learner to be more competent in one area than another. For example, a learner may be intermediate-low in the speaking mode, but already at intermediate-mid in the interpretive mode.
Reaching consensus about where to place students in classes and when to move them to the next level is difficult. The checklists provide a unique opportunity to educators making these decisions. Using these checklists helps build a deeper understanding of proficiency levels, which can impact the expectations for the articulation sequence of a program at each level.
Also linked below is an example from LinguaFolio Junior that lists can-do statements for students in grades 3–5. Teachers can ask students to use a tool like this at the beginning, middle, and end of the school year. It is important that students realize that learning is a cyclical process; exposure to a new concept does not mean fluency. Plenty of opportunity to practice the new concept is essential to achieve proficiency.
The second page of the LinguaFolio Junior handout, geared toward students in grades 6–8, is a worksheet for students to keep track of dates they accomplish certain tasks. After winter or summer breaks — or even a week after a lesson — students may be unable to demonstrate previous learning. This ongoing check-up reinforces the fact that language learning is a process that requires continual use of skills until they are mastered. This worksheet also demonstrates how LinguaFolio creates opportunities to help students maintain what they have learned. What is a motivating factor for the student also functions as an accountability factor for the teacher — who is then encouraged to provide more language production situations.
Sample interpretive listening self-assessment checklist ( pdf )
Self-assessment grid ( pdf )
LinguaFolio Junior samples ( pdf )
Next: 1.7) Language Dossier

How to Write a Biography
Biographies are big business. Whether in book form or Hollywood biopics, the lives of the famous and sometimes not-so-famous fascinate us.
While it’s true that most biographies are about people who are in the public eye, sometimes the subject is less well-known. Primarily, though, famous or not, the person who is written about has led an incredible life.
In this article, we will explain biography writing in detail for teachers and students so they can create their own.
While your students will most likely have a basic understanding of a biography, it’s worth taking a little time before they put pen to paper to tease out a crystal-clear definition of one.

What Is a Biography?

A biography is an account of someone’s life written by someone else . While there is a genre known as a fictional biography, for the most part, biographies are, by definition, nonfiction.
Generally speaking, biographies provide an account of the subject’s life from the earliest days of childhood to the present day or, if the subject is deceased, their death.
The job of a biography is more than just to outline the bare facts of a person’s life.
Rather than just listing the basic details of their upbringing, hobbies, education, work, relationships, and death, a well-written biography should also paint a picture of the subject’s personality and experience of life.

Full Biographies
Teaching unit.
Teach your students everything they need to know about writing an AUTOBIOGRAPHY and a BIOGRAPHY.
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ ( 26 reviews )
Features of a Biography
Before students begin writing a biography, they’ll need to have a firm grasp of the main features of a Biography. An excellent way to determine how well they understand these essential elements is to ask them to compile a checklist like the one-blow
Their checklists should contain the items below at a minimum. Be sure to help them fill in any gaps before moving on to the writing process.
The purpose of a biography is to provide an account of someone’s life.
Biography structure.
ORIENTATION (BEGINNING) Open your biography with a strong hook to grab the reader’s attention
SEQUENCING: In most cases, biographies are written in chronological order unless you are a very competent writer consciously trying to break from this trend.
COVER: childhood, upbringing, education, influences, accomplishments, relationships, etc. – everything that helps the reader to understand the person.
CONCLUSION: Wrap your biography up with some details about what the subject is doing now if they are still alive. If they have passed away, make mention of what impact they have made and what their legacy is or will be.
BIOGRAPHY FEATURES
LANGUAGE Use descriptive and figurative language that will paint images inside your audience’s minds as they read. Use time connectives to link events.
PERSPECTIVE Biographies are written from the third person’s perspective.
DETAILS: Give specific details about people, places, events, times, dates, etc. Reflect on how events shaped the subject. You might want to include some relevant photographs with captions. A timeline may also be of use depending upon your subject and what you are trying to convey to your audience.
TENSE Written in the past tense (though ending may shift to the present/future tense)
THE PROCESS OF WRITING A BIOGRAPHY
Like any form of writing, you will find it simple if you have a plan and follow it through. These steps will ensure you cover the essential bases of writing a biography essay.
Firstly, select a subject that inspires you. Someone whose life story resonates with you and whose contribution to society intrigues you. The next step is to conduct thorough research. Engage in extensive reading, explore various sources, watch documentaries, and glean all available information to provide a comprehensive account of the person’s life.
Creating an outline is essential to organize your thoughts and information. The outline should include the person’s early life, education, career, achievements, and any other significant events or contributions. It serves as a map for the writing process, ensuring that all vital information is included.
Your biography should have an engaging introduction that captivates the reader’s attention and provides background information on the person you’re writing about. It should include a thesis statement summarising the biography’s main points.
Writing a biography in chronological order is crucial . You should begin with the person’s early life and move through their career and achievements. This approach clarifies how the person’s life unfolded and how they accomplished their goals.
A biography should be written in a narrative style , capturing the essence of the person’s life through vivid descriptions, anecdotes, and quotes. Avoid dry, factual writing and focus on creating a compelling narrative that engages the reader.
Adding personal insights and opinions can enhance the biography’s overall impact, providing a unique perspective on the person’s achievements, legacy, and impact on society.
Editing and proofreading are vital elements of the writing process. Thoroughly reviewing your biography ensures that the writing is clear, concise, and error-free. You can even request feedback from someone else to ensure that it is engaging and well-written.
Finally, including a bibliography at the end of your biography is essential. It gives credit to the sources that were used during research, such as books, articles, interviews, and websites.
Tips for Writing a Brilliant Biography
Biography writing tip #1: choose your subject wisely.
There are several points for students to reflect on when deciding on a subject for their biography. Let’s take a look at the most essential points to consider when deciding on the subject for a biography:
Interest: To produce a biography will require sustained writing from the student. That’s why students must choose their subject well. After all, a biography is an account of someone’s entire life to date. Students must ensure they choose a subject that will sustain their interest throughout the research, writing, and editing processes.
Merit: Closely related to the previous point, students must consider whether the subject merits the reader’s interest. Aside from pure labors of love, writing should be undertaken with the reader in mind. While producing a biography demands sustained writing from the author, it also demands sustained reading from the reader.
Therefore, students should ask themselves if their chosen subject has had a life worthy of the reader’s interest and the time they’d need to invest in reading their biography.
Information: Is there enough information available on the subject to fuel the writing of an entire biography? While it might be a tempting idea to write about a great-great-grandfather’s experience in the war. There would be enough interest there to sustain the author’s and the reader’s interest, but do you have enough access to information about their early childhood to do the subject justice in the form of a biography?
Biography Writing Tip #2: R esearch ! Research! Research!
While the chances are good that the student already knows quite a bit about the subject they’ve chosen. Chances are 100% that they’ll still need to undertake considerable research to write their biography.
As with many types of writing , research is an essential part of the planning process that shouldn’t be overlooked. If students wish to give as complete an account of their subject’s life as possible, they’ll need to put in the time at the research stage.
An effective way to approach the research process is to:
1. Compile a chronological timeline of the central facts, dates, and events of the subject’s life
2. Compile detailed descriptions of the following personal traits:
- Physical looks
- Character traits
- Values and beliefs
3. Compile some research questions based on different topics to provide a focus for the research:
- Childhood : Where and when were they born? Who were their parents? Who were the other family members? What education did they receive?
- Obstacles: What challenges did they have to overcome? How did these challenges shape them as individuals?
- Legacy: What impact did this person have on the world and/or the people around them?
- Dialogue & Quotes: Dialogue and quotations by and about the subject are a great way to bring color and life to a biography. Students should keep an eagle eye out for the gems that hide amid their sources.
As the student gets deeper into their research, new questions will arise that can further fuel the research process and help to shape the direction the biography will ultimately go in.
Likewise, during the research, themes will often begin to suggest themselves. Exploring these themes is essential to bring depth to biography, but we’ll discuss this later in this article.
Research Skills:
Researching for biography writing is an excellent way for students to hone their research skills in general. Developing good research skills is essential for future academic success. Students will have opportunities to learn how to:
- Gather relevant information
- Evaluate different information sources
- Select suitable information
- Organize information into a text.
Students will have access to print and online information sources, and, in some cases, they may also have access to people who knew or know the subject (e.g. biography of a family member).
These days, much of the research will likely take place online. It’s crucial, therefore, to provide your students with guidance on how to use the internet safely and evaluate online sources for reliability. This is the era of ‘ fake news ’ and misinformation after all!
COMPLETE TEACHING UNIT ON INTERNET RESEARCH SKILLS USING GOOGLE SEARCH

Teach your students ESSENTIAL SKILLS OF THE INFORMATION ERA to become expert DIGITAL RESEARCHERS.
⭐How to correctly ask questions to search engines on all devices.
⭐ How to filter and refine your results to find exactly what you want every time.
⭐ Essential Research and critical thinking skills for students.
⭐ Plagiarism, Citing and acknowledging other people’s work.
⭐ How to query, synthesize and record your findings logically.
BIOGRAPHY WRITING Tip #3: Find Your Themes In Biography Writing
Though predominantly a nonfiction genre, the story still plays a significant role in good biography writing. The skills of characterization and plot structuring are transferable here. And, just like in fiction, exploring themes in a biographical work helps connect the personal to the universal. Of course, these shouldn’t be forced; this will make the work seem contrived, and the reader may lose faith in the truthfulness of the account. A biographer needs to gain and maintain the trust of the reader.
Fortunately, themes shouldn’t need to be forced. A life well-lived is full of meaning, and the themes the student writer is looking for will emerge effortlessly from the actions and events of the subject’s life. It’s just a case of learning how to spot them.
One way to identify the themes in a life is to look for recurring events or situations in a person’s life. These should be apparent from the research completed previously. The students should seek to identify these patterns that emerge in the subject’s life. For example, perhaps they’ve had to overcome various obstacles throughout different periods of their life. In that case, the theme of overcoming adversity is present and has been identified.
Usually, a biography has several themes running throughout, so be sure your students work to identify more than one theme in their subject’s life.
BIOGRAPHY WRITING Tip: #4 Put Something of Yourself into the Writing
While the defining feature of a biography is that it gives an account of a person’s life, students must understand that this is not all a biography does. Relating the facts and details of a subject’s life is not enough. The student biographer should not be afraid to share their thoughts and feelings with the reader throughout their account of their subject’s life.
The student can weave some of their personality into the fabric of the text by providing commentary and opinion as they relate the events of the person’s life and the wider social context at the time. Unlike the detached and objective approach we’d expect to find in a history textbook, in a biography, student-writers should communicate their enthusiasm for their subject in their writing.
This makes for a more intimate experience for the reader, as they get a sense of getting to know the author and the subject they are writing about.
Biography Examples For Students
- Year 5 Example
- Year 7 Example
- Year 9 Example
“The Rock ‘n’ Roll King: Elvis Presley”
Elvis Aaron Presley, born on January 8, 1935, was an amazing singer and actor known as the “King of Rock ‘n’ Roll.” Even though he’s been dead for nearly 50 years, I can’t help but be fascinated by his incredible life!
Elvis grew up in Tupelo, Mississippi, in a tiny house with his parents and twin brother. His family didn’t have much money, but they shared a love for music. Little did they know Elvis would become a music legend!
When he was only 11 years old, Elvis got his first guitar. He taught himself to play and loved singing gospel songs. As he got older, he started combining different music styles like country, blues, and gospel to create a whole new sound – that’s Rock ‘n’ Roll!
In 1954, at the age of 19, Elvis recorded his first song, “That’s All Right.” People couldn’t believe how unique and exciting his music was. His famous hip-swinging dance moves also made him a sensation!
Elvis didn’t just rock the music scene; he also starred in movies like “Love Me Tender” and “Jailhouse Rock.” But fame came with challenges. Despite facing ups and downs, Elvis kept spreading happiness through his music.

Tragically, Elvis passed away in 1977, but his music and charisma live on. Even today, people worldwide still enjoy his songs like “Hound Dog” and “Can’t Help Falling in Love.” Elvis Presley’s legacy as the King of Rock ‘n’ Roll will live forever.
Long Live the King: I wish I’d seen him.
Elvis Presley, the Rock ‘n’ Roll legend born on January 8, 1935, is a captivating figure that even a modern-day teen like me can’t help but admire. As I delve into his life, I wish I could have experienced the magic of his live performances.
Growing up in Tupelo, Mississippi, Elvis faced challenges but found solace in music. At 11, he got his first guitar, a symbol of his journey into the world of sound. His fusion of gospel, country, and blues into Rock ‘n’ Roll became a cultural phenomenon.
The thought of being in the audience during his early performances, especially when he recorded “That’s All Right” at 19, sends shivers down my spine. Imagining the crowd’s uproar and feeling the revolutionary energy of that moment is a dream I wish I could have lived.
Elvis wasn’t just a musical prodigy; he was a dynamic performer. His dance moves, the embodiment of rebellion, and his roles in films like “Love Me Tender” and “Jailhouse Rock” made him a true icon.
After watching him on YouTube, I can’t help but feel a little sad that I’ll never witness the King’s live performances. The idea of swaying to “Hound Dog” or being enchanted by “Can’t Help Falling in Love” in person is a missed opportunity. Elvis may have left us in 1977, but he was the king of rock n’ roll. Long live the King!
Elvis Presley: A Teen’s Take on the Rock ‘n’ Roll Icon”
Elvis Presley, born January 8, 1935, was a revolutionary force in the music world, earning his title as the “King of Rock ‘n’ Roll.” Exploring his life, even as a 16-year-old today, I’m captivated by the impact he made.
Hailing from Tupelo, Mississippi, Elvis grew up in humble beginnings, surrounded by the love of his parents and twin brother. It’s inspiring to think that, despite financial challenges, this young man would redefine the music scene.
At 11, Elvis got his first guitar, sparking a self-taught journey into music. His early gospel influences evolved into a unique fusion of country, blues, and gospel, creating the electrifying genre of Rock ‘n’ Roll. In 1954, at only 19, he recorded “That’s All Right,” marking the birth of a musical legend.
Elvis wasn’t just a musical innovator; he was a cultural phenomenon. His rebellious dance moves and magnetic stage presence challenged the norms. He transitioned seamlessly into acting, starring in iconic films like “Love Me Tender” and “Jailhouse Rock.”
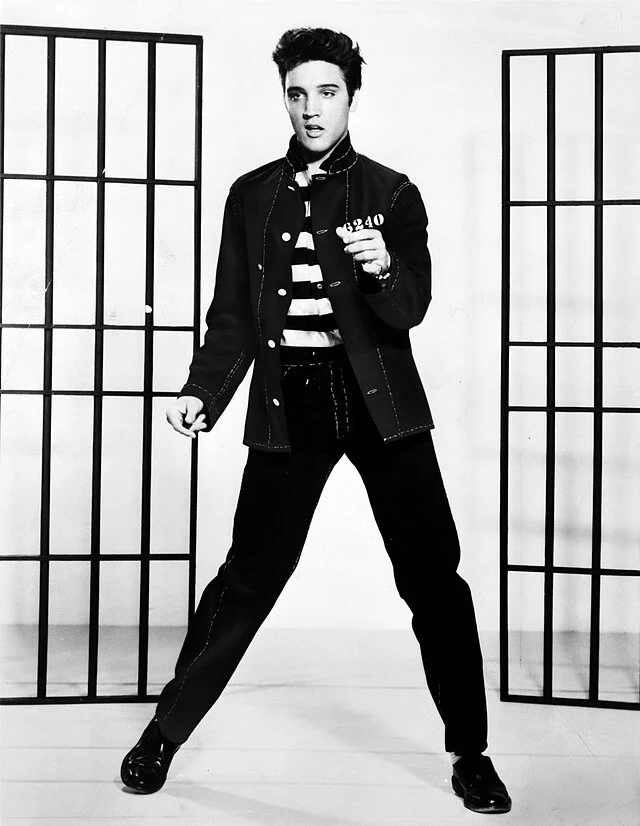

However, fame came at a cost, and Elvis faced personal struggles. Despite the challenges, his music continued to resonate. Even now, classics like “Hound Dog” and “Can’t Help Falling in Love” transcend generations.
Elvis Presley’s impact on music and culture is undeniable. He was known for his unique voice, charismatic persona, and electrifying performances. He sold over one billion records worldwide, making him one of the best-selling solo artists in history. He received numerous awards throughout his career, including three Grammy Awards and the Grammy Lifetime Achievement Award.
Elvis’s influence can still be seen in today’s music. Many contemporary artists, such as Bruno Mars, Lady Gaga, and Justin Timberlake, have cited Elvis as an inspiration. His music continues to be featured in movies, TV shows, and commercials.
Elvis left us in 1977, but his legacy lives on. I appreciate his breaking barriers and fearlessly embracing his artistic vision. Elvis Presley’s impact on music and culture is timeless, a testament to the enduring power of his artistry. His music has inspired generations and will continue to do so for many years to come.

Teaching Resources
Use our resources and tools to improve your student’s writing skills through proven teaching strategies.
BIOGRAPHY WRITING TEACHING IDEAS AND LESSONS
We have compiled a sequence of biography-related lessons or teaching ideas that you can follow as you please. They are straightforward enough for most students to follow without further instruction.
BIOGRAPHY LESSON IDEA # 1:
This session aims to give students a broader understanding of what makes a good biography.
Once your students have compiled a comprehensive checklist of the main features of a biography, allow them to use it to assess some biographies from your school library or on the internet using the feature checklist.
When students have assessed a selection of biographies, take some time as a class to discuss them. You can base the discussion around the following prompts:
- Which biographies covered all the criteria from their checklist?
- Which biographies didn’t?
- Which biography was the most readable in terms of structure?
- Which biography do you think was the least well-structured? How would you improve this?
Looking at how other writers have interpreted the form will help students internalize the necessary criteria before attempting to produce a biography. Once students have a clear understanding of the main features of the biography, they’re ready to begin work on writing a biography.
When the time does come to put pen to paper, be sure they’re armed with the following top tips to help ensure they’re as well prepared as possible.
BIOGRAPHY LESSON IDEA # 2:
This session aims to guide students through the process of selecting the perfect biography subject.
Instruct students to draw up a shortlist of three potential subjects for the biography they’ll write.
Using the three criteria mentioned in the writing guide (Interest, Merit, and Information), students award each potential subject a mark out of 5 for each of the criteria. In this manner, students can select the most suitable subject for their biography.
BIOGRAPHY LESSON IDEA # 3:
This session aims to get students into the researching phase, then prioritise and organise events chronologically.
Students begin by making a timeline of their subject’s life, starting with their birth and ending with their death or the present day. If the student has yet to make a final decision on the subject of their biography, a family member will often serve well for this exercise as a practice exercise.
Students should research and gather the key events of the person’s life, covering each period of their life from when they were a baby, through childhood and adolescence, right up to adulthood and old age. They should then organize these onto a timeline. Students can include photographs with captions if they have them.
They can present these to the class when they have finished their timelines.
BIOGRAPHY LESSON IDEA # 4:
Instruct students to look over their timeline, notes, and other research. Challenge them to identify three patterns that repeat throughout the subject’s life and sort all the related events and incidents into specific categories.
Students should then label each category with a single word. This is the thematic concept or the broad general underlying idea. After that, students should write a sentence or two expressing what the subject’s life ‘says’ about that concept.
This is known as the thematic statement . With the thematic concepts and thematic statements identified, the student now has some substantial ideas to explore that will help bring more profound meaning and wider resonance to their biography.
BIOGRAPHY LESSON IDEA # 5:
Instruct students to write a short objective account of an event in their own life. They can write about anyone from their past. It needn’t be more than a couple of paragraphs, but the writing should be strictly factual, focusing only on the objective details of what happened.
Once they have completed this, it’s time to rewrite the paragraph, but they should include some opinion and personal commentary this time.
The student here aims to inject some color and personality into their writing, to transform a detached, factual account into a warm, engaging story.
A COMPLETE UNIT ON TEACHING BIOGRAPHIES

Teach your students to write AMAZING BIOGRAPHIES & AUTOBIOGRAPHIES using proven RESEARCH SKILLS and WRITING STRATEGIES .
- Understand the purpose of both forms of biography.
- Explore the language and perspective of both.
- Prompts and Challenges to engage students in writing a biography.
- Dedicated lessons for both forms of biography.
- Biographical Projects can expand students’ understanding of reading and writing a biography.
- A COMPLETE 82-PAGE UNIT – NO PREPARATION REQUIRED.
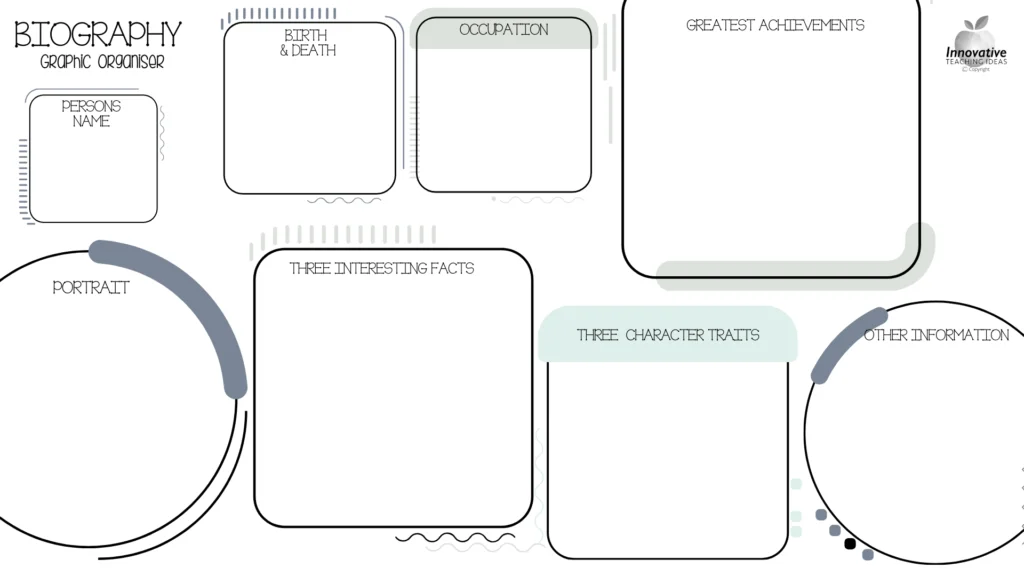
FREE Biography Writing Graphic Organizer
Use this valuable tool in the research and writing phases to keep your students on track and engaged.
WRITING CHECKLIST & RUBRIC BUNDLE

⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (92 Reviews)
To Conclude
By this stage, your students should have an excellent technical overview of a biography’s essential elements.
They should be able to choose their subject in light of how interesting and worthy they are, as well as give consideration to the availability of information out there. They should be able to research effectively and identify emerging themes in their research notes. And finally, they should be able to bring some of their personality and uniqueness into their retelling of the life of another.
Remember that writing a biography is not only a great way to develop a student’s writing skills; it can be used in almost all curriculum areas. For example, to find out more about a historical figure in History, to investigate scientific contributions to Science, or to celebrate a hero from everyday life.
Biography is an excellent genre for students to develop their writing skills and to find inspiration in the lives of others in the world around them.
HOW TO WRITE A BIOGRAPHY TUTORIAL VIDEO

OTHER GREAT ARTICLES RELATED TO BIOGRAPHY WRITING

How to write an Autobiography

How to Write a Historical Recount Text

15 Awesome Recount & Personal Narrative Topics

Personal Narrative Writing Guide
TRY OUR FREE APP
Write your book in Reedsy Studio. Try the beloved writing app for free today.
Craft your masterpiece in Reedsy Studio
Plan, write, edit, and format your book in our free app made for authors.

Blog • Perfecting your Craft
Posted on Jun 30, 2023
How to Write a Biography: A 7-Step Guide [+Template]
From time to time, nonfiction authors become so captivated by a particular figure from either the present or the past, that they feel compelled to write an entire book about their life. Whether casting them as heroes or villains, there is an interesting quality in their humanity that compels these authors to revisit their life paths and write their story.
However, portraying someone’s life on paper in a comprehensive and engaging way requires solid preparation. If you’re looking to write a biography yourself, in this post we’ll share a step-by-step blueprint that you can follow.
How to write a biography:
1. Seek permission when possible
2. research your subject thoroughly, 3. do interviews and visit locations, 4. organize your findings, 5. identify a central thesis, 6. write it using narrative elements, 7. get feedback and polish the text.

FREE RESOURCE
Biography Outline Template
Craft a satisfying story arc for your biography with our free template.
While you technically don’t need permission to write about public figures (or deceased ones), that doesn't guarantee their legal team won't pursue legal action against you. Author Kitty Kelley was sued by Frank Sinatra before she even started to write His Way , a biography that paints Ol Blue Eyes in a controversial light. (Kelley ended up winning the lawsuit, however).

Whenever feasible, advise the subject’s representatives of your intentions. If all goes according to plan, you’ll get a green light to proceed, or potentially an offer to collaborate. It's a matter of common sense; if someone were to write a book about you, you would likely want to know about it well prior to publication. So, make a sincere effort to reach out to their PR staff to negotiate an agreement or at least a mutual understanding of the scope of your project.
At the same time, make sure that you still retain editorial control over the project, and not end up writing a puff piece that treats its protagonist like a saint or hero. No biography can ever be entirely objective, but you should always strive for a portrayal that closely aligns with facts and reality.
If you can’t get an answer from your subject, or you’re asked not to proceed forward, you can still accept the potential repercussions and write an unauthorized biography . The “rebellious act” of publishing without consent indeed makes for great marketing, though it’ll likely bring more headaches with it too.
✋ Please note that, like other nonfiction books, if you intend to release your biography with a publishing house , you can put together a book proposal to send to them before you even write the book. If they like it enough, they might pay you an advance to write it.

Book Proposal Template
Craft a professional pitch for your nonfiction book with our handy template.
Once you’ve settled (or not) the permission part, it’s time to dive deep into your character’s story.
Deep and thorough research skills are the cornerstone of every biographer worth their salt. To paint a vivid and accurate portrait of someone's life, you’ll have to gather qualitative information from a wide range of reliable sources.
Start with the information already available, from books on your subject to archival documents, then collect new ones firsthand by interviewing people or traveling to locations.
Browse the web and library archives

Put your researcher hat on and start consuming any piece on your subject you can find, from their Wikipedia page to news articles, interviews, TV and radio appearances, YouTube videos, podcasts, books, magazines, and any other media outlets they may have been featured in.
Establish a system to orderly collect the information you find 一 even seemingly insignificant details can prove valuable during the writing process, so be sure to save them.
Depending on their era, you may find most of the information readily available online, or you may need to search through university libraries for older references.
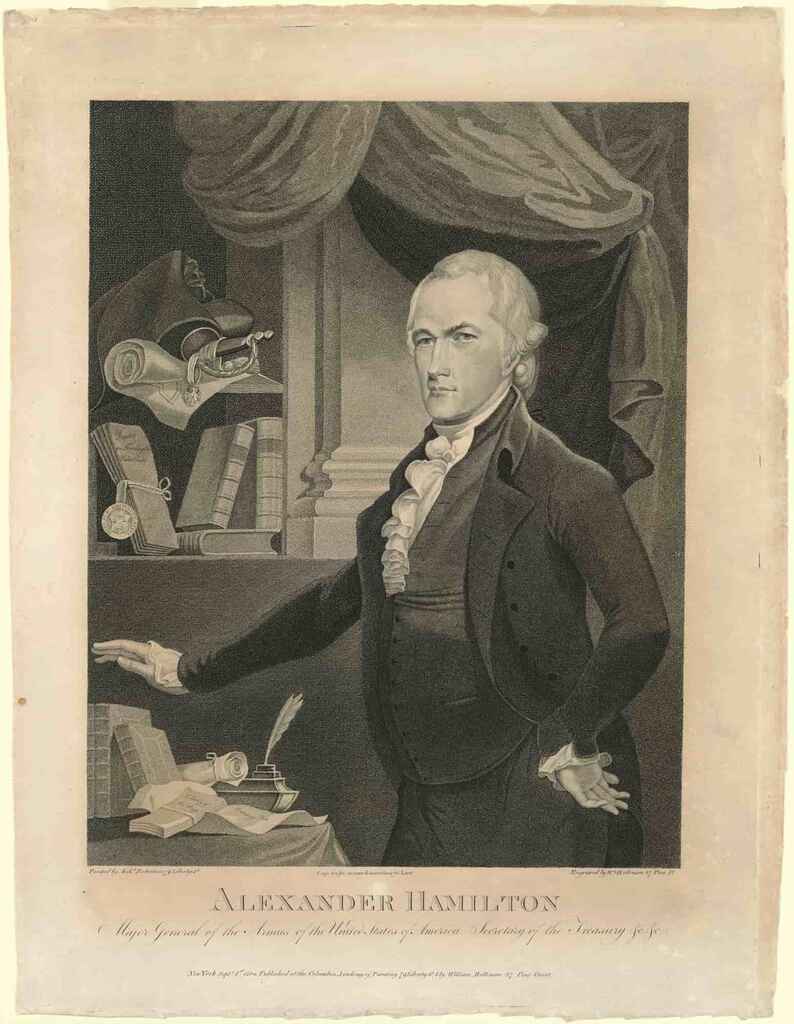

For his landmark biography of Alexander Hamilton, Ron Chernow spent untold hours at Columbia University’s library , reading through the Hamilton family papers, visiting the New York Historical Society, as well as interviewing the archivist of the New York Stock Exchange, and so on. The research process took years, but it certainly paid off. Chernow discovered that Hamilton created the first five securities originally traded on Wall Street. This finding, among others, revealed his significant contributions to shaping the current American financial and political systems, a legacy previously often overshadowed by other founding fathers. Today Alexander Hamilton is one of the best-selling biographies of all time, and it has become a cultural phenomenon with its own dedicated musical.
Besides reading documents about your subject, research can help you understand the world that your subject lived in.
Try to understand their time and social environment
Many biographies show how their protagonists have had a profound impact on society through their philosophical, artistic, or scientific contributions. But at the same time, it’s worth it as a biographer to make an effort to understand how their societal and historical context influenced their life’s path and work.
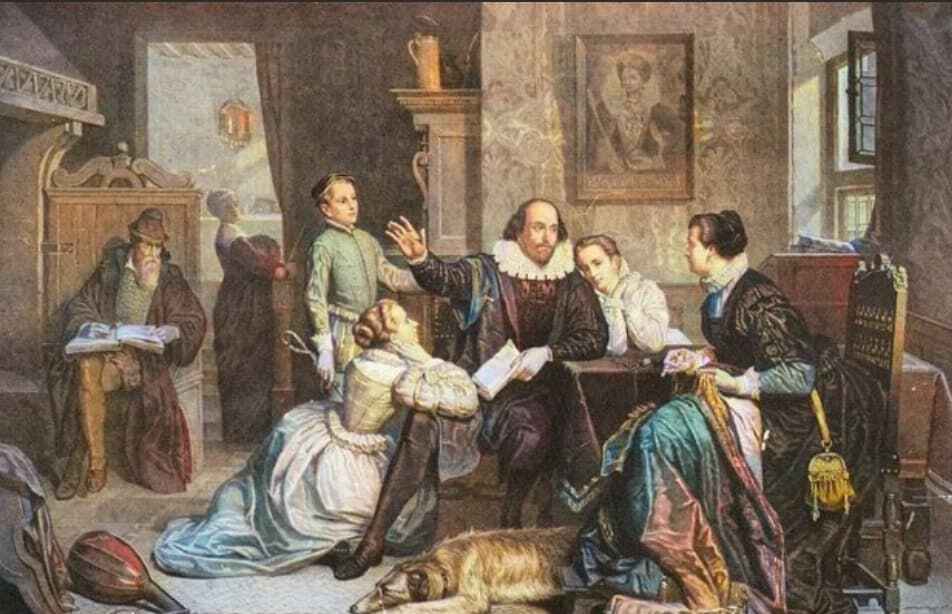
An interesting example is Stephen Greenblatt’s Will in the World . Finding himself limited by a lack of verified detail surrounding William Shakespeare's personal life, Greenblatt, instead, employs literary interpretation and imaginative reenactments to transport readers back to the Elizabethan era. The result is a vivid (though speculative) depiction of the playwright's life, enriching our understanding of his world.

Many readers enjoy biographies that transport them to a time and place, so exploring a historical period through the lens of a character can be entertaining in its own right. The Diary of Samuel Pepys became a classic not because people were enthralled by his life as an administrator, but rather from his meticulous and vivid documentation of everyday existence during the Restoration period.
Once you’ve gotten your hands on as many secondary sources as you can find, you’ll want to go hunting for stories first-hand from people who are (or were) close to your subject.
With all the material you’ve been through, by now you should already have a pretty good picture of your protagonist. But you’ll surely have some curiosities and missing dots in their character arc to figure out, which you can only get by interviewing primary sources.
Interview friends and associates
This part is more relevant if your subject is contemporary, and you can actually meet up or call with relatives, friends, colleagues, business partners, neighbors, or any other person related to them.
In writing the popular biography of Steve Jobs, Walter Isaacson interviewed more than one hundred people, including Jobs’s family, colleagues, former college mates, business rivals, and the man himself.
🔍 Read other biographies to get a sense of what makes a great one. Check out our list of the 30 best biographies of all time , or take our 30-second quiz below for tips on which one you should read next.
Which biography should you read next?
Discover the perfect biography for you. Takes 30 seconds!
When you conduct your interviews, make sure to record them with high quality audio you can revisit later. Then use tools like Otter.ai or Descript to transcribe them 一 it’ll save you countless hours.
You can approach the interview with a specific set of questions, or follow your curiosity blindly, trying to uncover revealing stories and anecdotes about your subject. Whatever your method, author and biography editor Tom Bromley suggests that every interviewer arrives prepared, "Show that you’ve done your work. This will help to put the interviewee at ease, and get their best answers.”
Bromley also places emphasis on the order in which you conduct interviews. “You may want to interview different members of the family or friends first, to get their perspective on something, and then go directly to the main interviewee. You'll be able to use that knowledge to ask sharper, more specific questions.”
Finally, consider how much time you have with each interviewee. If you only have a 30-minute phone call with an important person, make it count by asking directly the most pressing questions you have. And, if you find a reliable source who is also particularly willing to help, conduct several interviews and ask them, if appropriate, to write a foreword as part of the book’s front matter .
Sometimes an important part of the process is packing your bags, getting on a plane, and personally visiting significant places in your character’s journey.
Visit significant places in their life
A place, whether that’s a city, a rural house, or a bodhi tree, can carry a particular energy that you can only truly experience by being there. In putting the pieces together about someone’s life, it may be useful to go visit where they grew up, or where other significant events of their lives happened. It will be easier to imagine what they experienced, and better tell their story.
In researching The Lost City of Z , author David Grann embarked on a trek through the Amazon, retracing the steps of British explorer Percy Fawcett. This led Grann to develop new theories about the circumstances surrounding the explorer's disappearance.
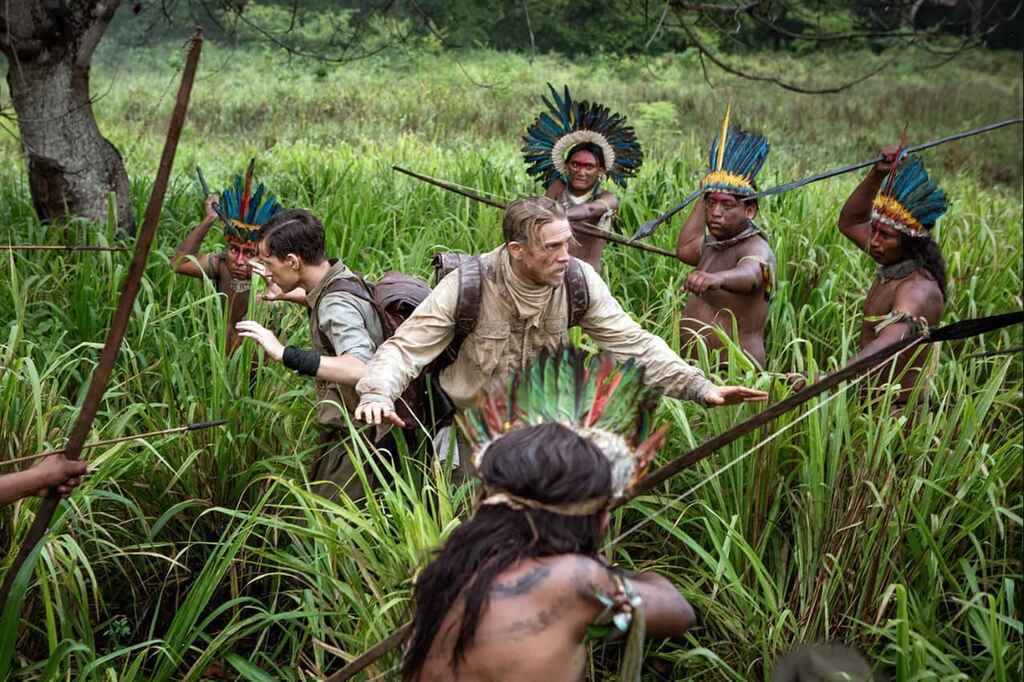

Hopefully, you won’t have to deal with jaguars and anacondas to better understand your subject’s environment, but try to walk into their shoes as much as possible.
Once you’ve researched your character enough, it’s time to put together all the puzzle pieces you collected so far.
Take the bulk of notes, media, and other documents you’ve collected, and start to give them some order and structure. A simple way to do this is by creating a timeline.
Create a chronological timeline
It helps to organize your notes chronologically 一 from childhood to the senior years, line up the most significant events of your subject’s life, including dates, places, names and other relevant bits.
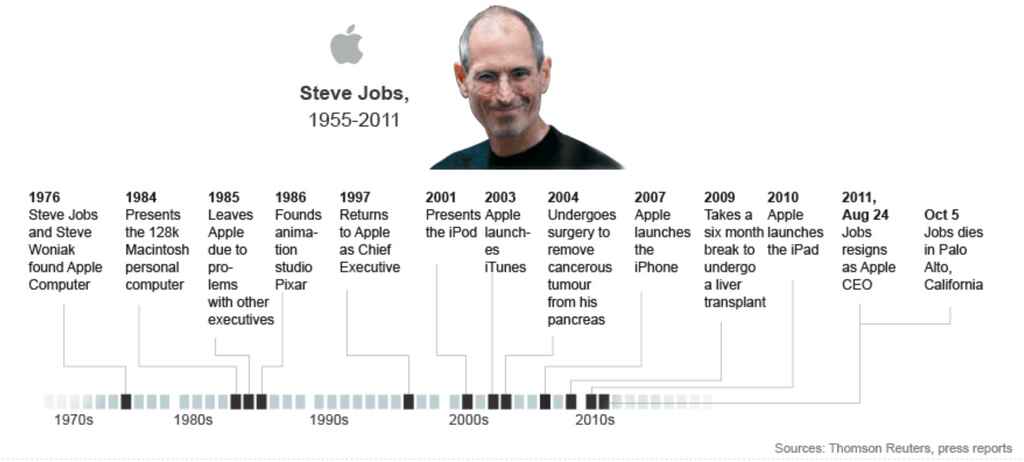
You should be able to divide their life into distinct periods, each with their unique events and significance. Based on that, you can start drafting an outline of the narrative you want to create.
Draft a story outline
Since a biography entails writing about a person’s entire life, it will have a beginning, a middle, and an end. You can pick where you want to end the story, depending on how consequential the last years of your subject were. But the nature of the work will give you a starting character arc to work with.
To outline the story then, you could turn to the popular Three-Act Structure , which divides the narrative in three main parts. In a nutshell, you’ll want to make sure to have the following:
- Act 1. Setup : Introduce the protagonist's background and the turning points that set them on a path to achieve a goal.
- Act 2. Confrontation : Describe the challenges they encounter, both internal and external, and how they rise to them. Then..
- Act 3. Resolution : Reach a climactic point in their story in which they succeed (or fail), showing how they (and the world around them) have changed as a result.
Only one question remains before you begin writing: what will be the main focus of your biography?
Think about why you’re so drawn to your subject to dedicate years of your life to recounting their own. What aspect of their life do you want to highlight? Is it their evil nature, artistic genius, or visionary mindset? And what evidence have you got to back that up? Find a central thesis or focus to weave as the main thread throughout your narrative.

Or find a unique angle
If you don’t have a particular theme to explore, finding a distinct angle on your subject’s story can also help you distinguish your work from other biographies or existing works on the same subject.
Plenty of biographies have been published about The Beatles 一 many of which have different focuses and approaches:
- Philip Norman's Shout is sometimes regarded as leaning more towards a pro-Lennon and anti-McCartney stance, offering insights into the band's inner dynamics.
- Ian McDonald's Revolution in the Head closely examines their music track by track, shifting the focus back to McCartney as a primary creative force.
- Craig Brown's One Two Three Four aims to capture their story through anecdotes, fan letters, diary entries, and interviews.
- Mark Lewisohn's monumental three-volume biography, Tune In , stands as a testament to over a decade of meticulous research, chronicling every intricate detail of the Beatles' journey.
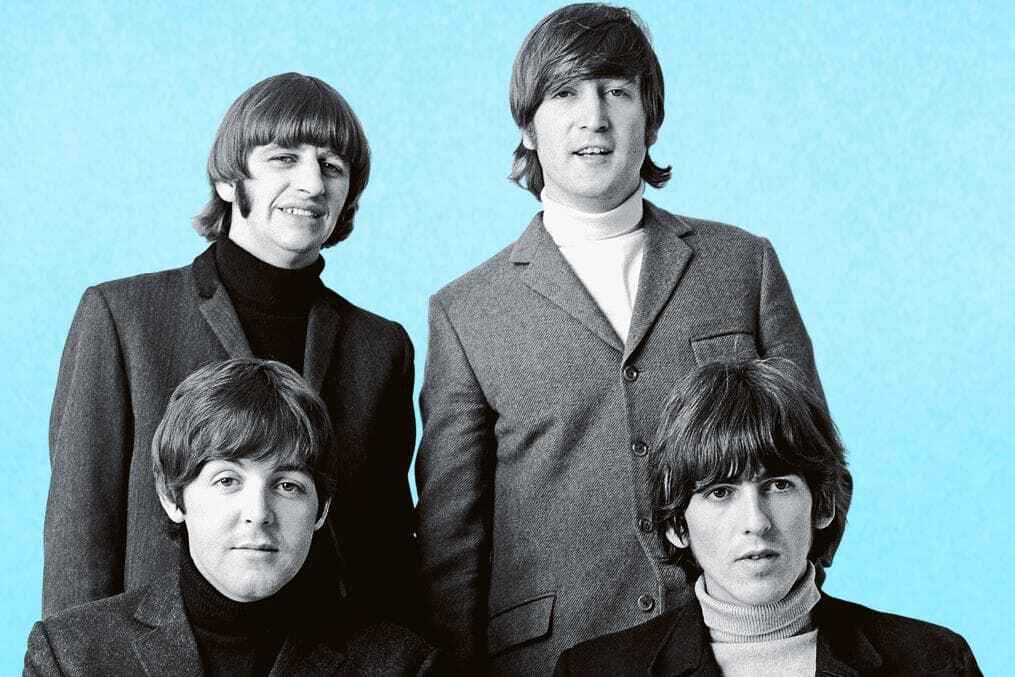

Finally, consider that biographies are often more than recounting the life of a person. Similar to how Dickens’ Great Expectations is not solely about a boy named Pip (but an examination and critique of Britain’s fickle, unforgiving class system), a biography should strive to illuminate a broader truth — be it social, political, or human — beyond the immediate subject of the book.
Once you’ve identified your main focus or angle, it’s time to write a great story.

While biographies are often highly informative, they do not have to be dry and purely expository in nature . You can play with storytelling elements to make it an engaging read.
You could do that by thoroughly detailing the setting of the story , depicting the people involved in the story as fully-fledged characters , or using rising action and building to a climax when describing a particularly significant milestone of the subject’s life.
One common way to make a biography interesting to read is starting on a strong foot…
Hook the reader from the start
Just because you're honoring your character's whole life doesn't mean you have to begin when they said their first word. Starting from the middle or end of their life can be more captivating as it introduces conflicts and stakes that shaped their journey.
When he wrote about Christopher McCandless in Into the Wild , author Jon Krakauer didn’t open his subject’s childhood and abusive family environment. Instead, the book begins with McCandless hitchhiking his way into the wilderness, and subsequently being discovered dead in an abandoned bus. By starting in medias res , Krakauer hooks the reader’s interest, before tracing back the causes and motivations that led McCandless to die alone in that bus in the first place.
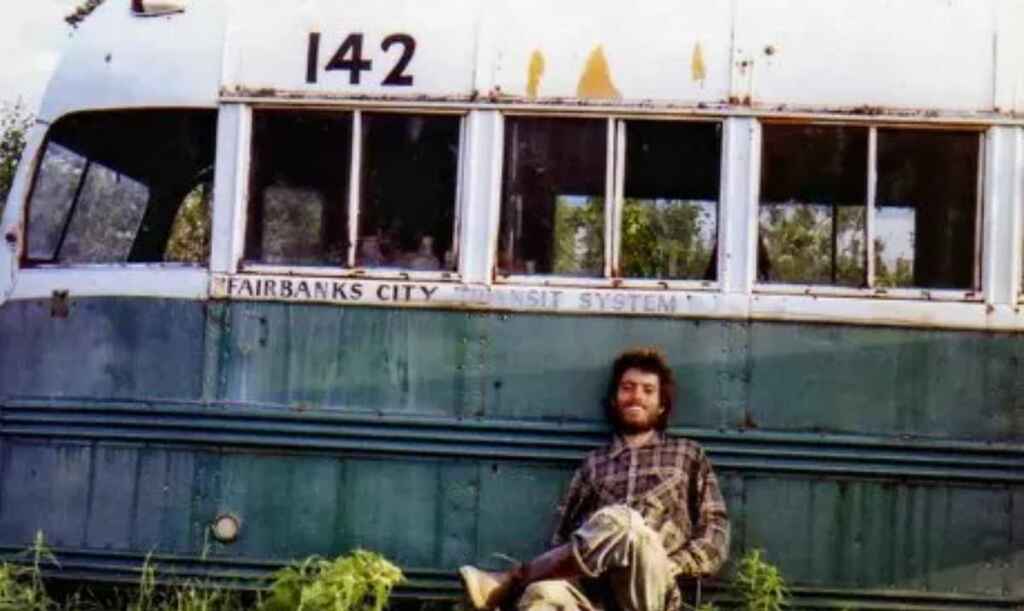

You can bend the timeline to improve the reader’s reading experience throughout the rest of the story too…
Play with flashback
While biographies tend to follow a chronological narrative, you can use flashbacks to tell brief stories or anecdotes when appropriate. For example, if you were telling the story of footballer Lionel Messi, before the climax of winning the World Cup with Argentina, you could recall when he was just 13 years old, giving an interview to a local newspaper, expressing his lifelong dream of playing for the national team.
Used sparsely and intentionally, flashbacks can add more context to the story and keep the narrative interesting. Just like including dialogue does…
Reimagine conversations
Recreating conversations that your subject had with people around them is another effective way to color the story. Dialogue helps the reader imagine the story like a movie, providing a deeper sensory experience.

One thing is trying to articulate the root of Steve Jobs’ obsession with product design, another would be to quote his father , teaching him how to build a fence when he was young: “You've got to make the back of the fence just as good looking as the front of the fence. Even though nobody will see it, you will know. And that will show that you're dedicated to making something perfect.”
Unlike memoirs and autobiographies, in which the author tells the story from their personal viewpoint and enjoys greater freedom to recall conversations, biographies require a commitment to facts. So, when recreating dialogue, try to quote directly from reliable sources like personal diaries, emails, and text messages. You could also use your interview scripts as an alternative to dialogue. As Tom Bromley suggests, “If you talk with a good amount of people, you can try to tell the story from their perspective, interweaving different segments and quoting the interviewees directly.”

FREE COURSE
How to Write Believable Dialogue
Master the art of dialogue in 10 five-minute lessons.
These are just some of the story elements you can use to make your biography more compelling. Once you’ve finished your manuscript, it’s a good idea to ask for feedback.
If you’re going to self-publish your biography, you’ll have to polish it to professional standards. After leaving your work to rest for a while, look at it with fresh eyes and self-edit your manuscript eliminating passive voice, filler words, and redundant adverbs.
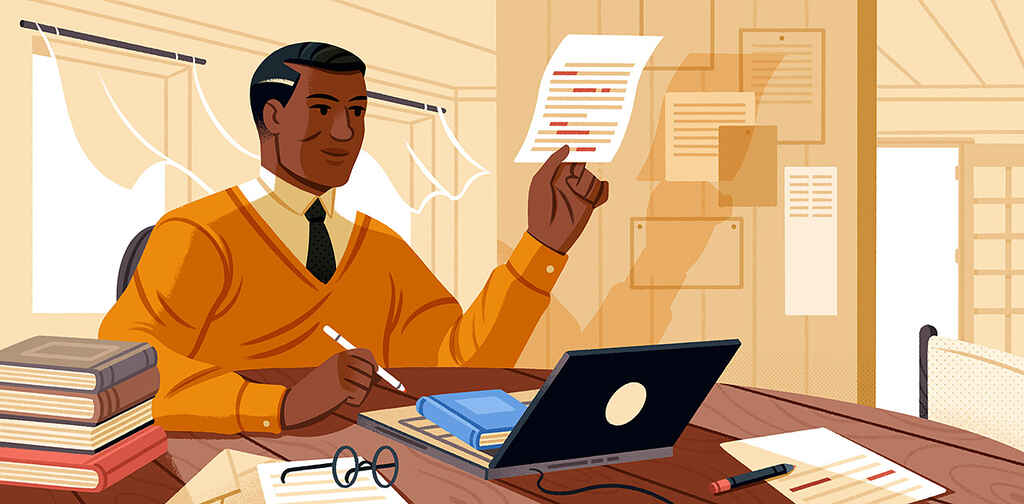

Then, have a professional editor give you a general assessment. They’ll look at the structure and shape of your manuscript and tell you which parts need to be expanded on or cut. As someone who edited and commissioned several biographies, Tom Bromley points out that a professional “will look at the sources used and assess whether they back up the points made, or if more are needed. They would also look for context, and whether or not more background information is needed for the reader to understand the story fully. And they might check your facts, too.”
In addition to structural editing, you may want to have someone copy-edit and proofread your work.

MEET EDITORS
Polish your book with expert help
Sign up, meet 1500+ experienced editors, and find your perfect match.
Importantly, make sure to include a bibliography with a list of all the interviews, documents, and sources used in the writing process. You’ll have to compile it according to a manual of style, but you can easily create one by using tools like EasyBib . Once the text is nicely polished and typeset in your writing software , you can prepare for the publication process.
In conclusion, by mixing storytelling elements with diligent research, you’ll be able to breathe life into a powerful biography that immerses readers in another individual’s life experience. Whether that’ll spark inspiration or controversy, remember you could have an important role in shaping their legacy 一 and that’s something not to take lightly.
Continue reading
Recommended posts from the Reedsy Blog

What is Tone in Literature? Definition & Examples
We show you, with supporting examples, how tone in literature influences readers' emotions and perceptions of a text.


Writing Cozy Mysteries: 7 Essential Tips & Tropes
We show you how to write a compelling cozy mystery with advice from published authors and supporting examples from literature.

Man vs Nature: The Most Compelling Conflict in Writing
What is man vs nature? Learn all about this timeless conflict with examples of man vs nature in books, television, and film.

The Redemption Arc: Definition, Examples, and Writing Tips
Learn what it takes to redeem a character with these examples and writing tips.

How Many Sentences Are in a Paragraph?
From fiction to nonfiction works, the length of a paragraph varies depending on its purpose. Here's everything you need to know.
Narrative Structure: Definition, Examples, and Writing Tips
What's the difference between story structure and narrative structure? And how do you choose the right narrative structure for you novel?
Join a community of over 1 million authors
Reedsy is more than just a blog. Become a member today to discover how we can help you publish a beautiful book.
We have an app for that
Build a writing routine with our free writing app.

1 million authors trust the professionals on Reedsy. Come meet them.
Enter your email or get started with a social account:

Oxford University Press's Academic Insights for the Thinking World

How to write a biography

Sorry About That: The Language of Public Apology
- By Edwin L. Battistella
- July 1 st 2018
This year I’ve been reading a lot of biographies and writing some short profile pieces. Both experiences have caused me to reflect back on a book-length biography I wrote a few years ago on the little-known educator Sherwin Cody .
I first learned about Sherwin Cody as an adolescent, when I spotted his “remarkable invention [that] has improved the speech and writing of thousands of people” in the back of a comic book. (It turned out to be a patented workbook of grammar exercises.) Many years later, reading about the history of writing instruction, I became fascinated by Cody’s life and career, so much so that I decided to tell his story. The rest is history, or more accurately, biography.
Writing a book-length biography was a new experience for me at the time. I learned a lot along the way. Here are a few tips based on my experience.
Start small —A good way to begin is by writing a short profile of your subject in no more than 1,000 words. Imagine it as a short encyclopedia piece or obituary of the person that encapsulates the basic story (the who, what, where, when and how ) along with discussion of significant accomplishments and challenges. The profile will tell you if you know enough to write more and also help you to clarify your stance toward the subject. If you feel too strongly about your subject you may not be the ideal person to write a biography. There may be a temptation to adulate or unmask.
Figure out the contexts— Spend some time studying the individual’s era. What was the state of the world during the person’s lifetime, and how did major events intersect with your subject’s life. The context can be large-scale, taking in the sweep of history over several generations, or finely grained, covering one life span. But understanding the world as it was will give you a sense of how your subject may have seen it.
If you are writing about someone who has already been the subject of biographical work, you also need to consider the context of what other writers have said. How does your effort add to the story? Do you have new material? Has there been a re-evaluation of the individual? Has society changed in such a way that the person has new relevance? Is there an anniversary on the horizon? (You’ll want to plan way ahead for that last one!)
Develop a research network— As you dig into your work, be on the lookout for new material. Is archival material coming available? Are there family members who have recollections or bits of ephemera? Can you find some librarians or archivists or historical society staffers who share your interest? Some of this research may involve travel and/or copying fees, so keep that cost in mind.
Engage the backstory— Part of the enjoyment of writing a biography is that it allows you to put together a mystery not just out of large events, but out of small puzzle pieces as well. A description of some event during a person’s college years or on a vacation, for example, can illustrate their personality just as well as a large life event does, and it can make the subject relatable to readers who may have had a similar experience. Finding the sweet spot between too much digression and just enough backstory will not come immediately but it is worth the effort.
Be open to refocusing your idea— As you write and learn more about your subject, it may turn out that the story you are writing is not really about just one person. Perhaps it is a story about an ensemble of like-minded people, or a movement, and perhaps the stories of others are just as fascinating and important. Your work could turn out to be about a group working together or in opposition, or about people set in different times or places brought together by common thread. It may not be a biography in the strict sense and that’s fine. You can adjust.
Writing a biography can take an author anywhere. If there is someone whose life fascinates you and that you are in a position to illuminate as a researcher and writer, jump in.
Featured image credit: Epicantus by Daria. CC-BY-2.0 via Flickr .
Edwin L. Battistella teaches linguistics and writing at Southern Oregon University in Ashland, where he has served as a dean and as interim provost. He is the author of Do You Make These Mistakes in English? (OUP, 2009), Bad Language (OUP, 2005), and The Logic of Markedness (OUP, 1996). He is also the author of Sorry About That: The Language of Public Apology .

- Between the Lines with Edwin Battistella
- Linguistics
Our Privacy Policy sets out how Oxford University Press handles your personal information, and your rights to object to your personal information being used for marketing to you or being processed as part of our business activities.
We will only use your personal information to register you for OUPblog articles.
Or subscribe to articles in the subject area by email or RSS
Related posts:
No related posts.
Recent Comments
Every biography hide a lot of failure behind success
Writing a biography is not difficult but you should have to make sure about its points, instructions very carefully so readers might be interested in the book while they read.
[…] How to write a biography, July 2018 […]
Comments are closed.

How to Write a Biography in English With Example

At some point in your education career, you will be asked to write a biography about yourself or someone else. Writing a biography is not a difficult task if you know what biography is then you can easily write. If you don’t know how to write a biography in English, read carefully the following article.
How to Write a Biography in English
A biography is a detailed description or account of a person’s life. It entails more than basic facts (education, work, relationship, and death). A biography also explains the subject’s experience of these events. Like a profile or curriculum vitae (resume).
A biography presents a subject’s life story, highlighting various aspects of his or her life, including intimate details of experience, and may include an analysis of a subject’s personality.
Biographical works are usually non-fiction, but fiction can also be used to portray a person’s life. One in-depth form of biographical coverage is called legacy writing. Biographical works in diverse media—from literature to film—from the genre known as a biography.
Biography of General Muhammad Musa
General Musa Khan Hazara (H.PK., HJ, HQA, MBE, PSC 1908 – 1991) was the commander in chief of Pakistan Army. He succeeded Filed Marshal Ayub Khan, who assumed the presidency of Pakistan.
He was the eldest son of Sardar Yazdan Khan, born on 20 October 1908 in a Hazara Shia Muslim family in Quetta. He was from the Sardar family of the Hazara tribe in Baluchistan, Pakistan. He was a Naik (Junior Non-commissioned Office) in the 106 th Hazara Pioneers, went to the Indian Military Academy in Dehra Dun as a cadet, and graduated with the first batch of British Indian commissioned officer on 1 February 1935.
He was posted to the 6 th Royal Battalion, the 13 th frontier Force Rifles as a platoon commander in 1936. He took part in the Waziristan Operations in 1936-1938 and in World War 2, where he served in North Africa. He served with distinction in the Pakistan Army and rose to the rank of the commander in chief of Pakistan Armed Forces during President Muhammad Ayub Khan’s regime (1958-1969).
His promotion to commander in chief saw the suppression of two seniors: Major General Sher Ali Khan and Major General Latif Khan, both Sandhurst graduated in 1933.
General Muhammad Musa commanded the Army in the Indo-Pakistan war of 1965 and had overall responsibility for operations throughout the conflict. As army chief, he was criticized for not anticipating an assault across the international border. However, he was given credit for blunting the Indian offensive towards Sialkot during the Battle of Chawinda.
He has narrated the events and experiences of the war his book” My Vision”. In the book, he was given accounts of the secret war that was going on in Kashmir between the two countries, long before the real war actually began.
General Musa is the author or his autobiography, “Jawan to General” in which he describes his life experiences from a simple foot-soldier rising to the rank of a general.
After the retirement from Pakistan Army, President Ayub Khan appointed him as the Governor of West Pakistan (now Bangladesh) from 1967 to 1979. After serving for few years, he retired and settled in Karachi.
In 1987, he was once again involved in politics. He was appointed as Governor of Baluchistan Province by then president General Zia-ul-Haq. In Baluchistan, Governor General (Retd) Musa dissolved the provincial assembly in December 1988. However, the Baluchistan High court restored the assembly amid public condemnation of Governor’s move. The step towards dissolving the assembly was believed to have been taken with the consent to the president and prime minister.
He died on 12 March 1991 at Governor House in Quetta.
Conclusion:
I hope now you know how to write a biography in English. If you have any question please don’t hesitate to comment it in the comment section below.
Also, read: How To Write An Autobiography In English
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
Related posts
Top 10 essay writing mistakes, what are the qualities of a great teacher, most common english idioms native speakers use, leave a comment cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Learn How to Write a Biography: A Step-by-Step Guide.
- Self Publishing Guide
Human lives are intricate tapestries woven with experiences, emotions, challenges, and triumphs. Biographies and autobiographies serve as windows into these remarkable stories, offering insight into the lives of individuals who have left their mark on history or those who wish to chronicle their own journeys.
I n this guide, we will explore the art of writing biographies and autobiographies, delving into the nuances of both genres and providing valuable tips on how to craft compelling narratives.
Understanding Biography and Autobiography
- Biography: Exploring Lives Beyond the Surface A biography is a literary exploration that unveils the intricate layers of a person’s existence, transcending the mere listing of events. It provides a comprehensive account of an individual’s life, offering insights into their achievements, struggles, societal impact, and distinct qualities that define them. These narratives serve as windows into history, allowing readers to traverse time and understand the legacy left by remarkable individuals. Biographies are usually crafted by biographers, individuals skilled in research and storytelling. They undertake a meticulous journey of gathering information from diverse sources, such as historical records, interviews, letters, and secondary literature. The biographer’s role is to curate these fragments of information into a coherent narrative, painting a vivid portrait of the subject. This comprehensive approach lends credibility and depth to the portrayal, enriching the reader’s understanding of the subject’s contributions and character. Example: Consider the biography of Mahatma Gandhi. A biographer compiling his life story would explore not only his role in India’s fight for independence but also his principles of nonviolence, his experiments with truth, and his impact on the world’s political landscape. By presenting a holistic view of Gandhi’s life, the biography reveals the nuances of his personality, beliefs, and the larger context in which he operated.
- Autobiography: The Intimate Dialogue of Self-Discovery An autobiography is a narrative journey undertaken by the subject themselves—a profound sharing of one’s life experiences, emotions, and reflections. This genre provides readers with an intimate insight into the subject’s psyche, allowing them to witness their life’s trajectory through personal recollections. Autobiographies carry a unique authenticity, as they are composed from the vantage point of the person who lived those moments, providing a firsthand account of their journey. Autobiographies draw from the subject’s reservoir of memories, emotions, and introspections. This self-exploration leads to a narrative that is often more than a linear chronicle; it becomes a tapestry woven with the threads of emotions, thoughts, and personal revelations. By directly communicating with the reader, the autobiographer creates a powerful connection, allowing readers to step into their shoes and experience their story from within. Example: A notable example of an autobiography is “The Diary of a Young Girl” by Anne Frank. Written during her time in hiding during World War II, the book offers a candid portrayal of Anne’s life, fears, hopes, and dreams. Through her own words, readers gain a deep understanding of the challenges faced by Jews during the Holocaust, as well as the resilience and humanity that Anne exudes even in the face of adversity.
Writing a Biography:
Research: The Foundation of a Compelling Biography Thorough research is the cornerstone of a captivating biography. Delve into reputable sources like books, articles, interviews, and archives to gather a comprehensive view of your subject’s life. By immersing yourself in these materials, you gain insights into their experiences, motivations, and contributions. Scrutinise the historical context to understand the era’s impact on their journey. Successful research forms the bedrock of your biography, enabling you to present an accurate and nuanced portrayal that resonates with readers. It’s through meticulous research that you uncover the hidden stories and connect the dots, allowing the subject’s essence to shine through the pages.
Selecting a Focus: Defining the Narrative Scope Choosing a focal point is essential for a well-structured biography. Decide whether to cover the subject’s entire life or concentrate on specific periods or achievements. This decision shapes the narrative’s trajectory, preventing it from becoming overwhelming or disjointed. A focused approach allows you to delve deeply into pivotal moments, providing a more profound understanding of the subject’s journey. By clarifying the scope, you enable readers to follow a coherent storyline, making it easier for them to engage with the subject’s life in a meaningful way.
Structuring the Biography: Chronology and Themes The organisation of your biography greatly impacts its readability. Structure your work into logical sections or chapters, employing either a chronological or thematic arrangement. Begin with an engaging introduction that captures readers’ attention and provides essential context. A chronological structure follows the subject’s life in sequential order, offering a clear timeline of events. Alternatively, a thematic structure groups events by themes, allowing you to explore different facets of the subject’s life. A well-structured biography guides readers smoothly through the subject’s experiences, fostering a deeper connection and understanding.
Show, Don’t Tell: Evocative Storytelling Vivid descriptions, anecdotes, and quotes breathe life into your biography. Rather than merely listing facts, employ descriptive language to recreate scenes and emotions, allowing readers to immerse themselves in the subject’s world. Use anecdotes to illustrate key moments, capturing the essence of the subject’s character and the impact of events on their journey. Integrating quotes from the subject, contemporaries, or relevant sources adds authenticity and depth. Through this technique, you transport readers into the subject’s experiences, enabling them to witness the moments that shaped their lives.
Balanced Perspective: Portraying Strengths and Flaws A balanced portrayal adds credibility and depth to your biography. While it’s tempting to focus solely on accomplishments, a well-rounded view includes the subject’s strengths and flaws. This authenticity humanises the subject, making it relatable and multidimensional. By acknowledging both successes and challenges, readers gain a more honest understanding of their journey. Balancing positives and negatives helps readers empathise with the subject, connecting them on a deeper level and offering a more genuine insight into their lives.
Engaging Emotions: Creating Emotional Resonance Emotions are a potent tool in biography writing. Delve into the subject’s feelings, struggles, and aspirations to create an emotional connection with readers. By tapping into their emotional experiences, you make the narrative relatable and engaging. Sharing personal challenges and triumphs allows readers to empathise and reflect on their own lives. This emotional resonance elevates the biography from a mere factual account to a compelling and moving story that lingers in readers’ minds, leaving a lasting impact.
Citing Sources: Ensuring Accuracy and Credibility Accurate information is vital in biography writing. Properly cite your sources to maintain credibility and integrity. Clear citations not only lend authority to your work but also provide readers with the opportunity to explore further if they desire. Accurate referencing safeguards against misinformation and ensures that your portrayal is based on reliable evidence. In addition to enhancing your credibility, thorough citations demonstrate your commitment to thorough research and ethical writing practises, contributing to the overall trustworthiness of your biography.

Complete Guide to Write a Biography. Start Writing Your Biography Now
Writing an Autobiography:
Reflecting on Significant Moments and Experiences Initiating an autobiography involves introspection into your life’s pivotal moments. Delve into memories that have influenced your journey, such as turning points, challenges, relationships, and achievements. Reflect on these experiences, dissecting their impact on your personal growth and development. By contemplating these key events, you gain insight into the narrative threads that weave your life story together. This reflective process sets the foundation for an authentic autobiography that resonates with readers on a profound level.
Developing Your Unique Voice and Tone Crafting an autobiography demands a consistent voice and tone that reflect your personality. Write in a way that feels true to you, capturing your unique perspective and emotions. Authenticity is key, as it allows readers to connect with your narrative on a personal level. Whether your tone is introspective, humorous, or contemplative, ensure it aligns with the essence of your experiences. By embracing your genuine voice, you create an autobiography that not only tells your story but also conveys the essence of who you are.
Structured Storytelling for Engagement While autobiographies can be more flexible in structure compared to biographies, organising your narrative into coherent sections or themes enhances its readability. By grouping related experiences together, you provide readers with a clearer understanding of the themes that have shaped your life. This structure helps maintain their engagement by guiding them through your journey in a logical and compelling manner. While allowing for creativity, a structured approach ensures that your autobiography remains focused and accessible.
Embracing honesty and authenticity Honesty is the bedrock of an impactful autobiography. Share not only your triumphs but also your mistakes and failures. Authenticity creates relatability, allowing readers to connect with your humanity and vulnerabilities. Your journey’s challenges and setbacks are just as integral to your story as your successes. By being candid about your experiences, you demonstrate resilience and growth, inspiring readers to reflect on their own paths. This level of authenticity fosters a deeper connection, making your autobiography a source of empathy and encouragement.
Adding Depth Through Reflection Incorporate reflection to imbue your autobiography with depth and meaning. Explore the lessons you’ve learned from your experiences and the transformations they’ve prompted. Delve into how these moments shaped your beliefs, values, and perspective on life. By offering insights gained from introspection, you provide readers with wisdom and a broader understanding of your journey. Reflection transforms your autobiography from a chronicle of events into a thoughtful exploration of personal growth and the profound impact of life’s moments.
Creating vivid details for immersion Immerse readers in your world by employing sensory details and vivid descriptions. Paint a picture with words, allowing readers to visualise the scenes and emotions you’re describing. By incorporating sensory elements like sights, sounds, smells, and feelings, you transport readers into the moments you’re recounting. This immersive experience draws them closer to your story, fostering a stronger connection. Vivid details not only make your autobiography more engaging but also enable readers to forge a deeper connection with your experiences and emotions.
In the realm of literature, biographies and autobiographies stand as powerful testaments to the diversity and richness of human existence. Whether you’re capturing the life of a historical figure or penning your own life story, the art of writing these genres involves meticulous research, introspection, and a keen understanding of human emotions.
Through carefully chosen words and evocative storytelling, biographers and autobiographers alike can craft narratives that resonate with readers and offer a deeper understanding of the human experience. So, whether you’re writing about the extraordinary or the everyday, embrace the challenge and privilege of narrating lives through the written word.
Publish your book with BlueRoseONE and become a bestselling author . Don’t let your dream of becoming an author fade away, grab the opportunity now and publish your book – be it fiction, non fiction, poetry or more.
- About The Author
- Latest Posts
Mansi Chauhan

You May Also Like

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Teaching primary
Working with biographies
The biography section of portfolios is a documentation of the learners' personal language learning history and can include, for example, a short narrative about the summer camp they attended and for which they may include a certificate of attendance in the passport section.

This biography lends itself well to ‘show and tell’ sessions when learners can talk to the class about their own experiences. In this section too, learners may include any plans they have for taking an English exam, visiting an English-speaking country, or having English-speaking visitors at home.
Age: Older primary
The type of things which learners can include in their biography are:
- Learner checklist
- A narrative about a trip to an English-speaking country
- The day an English-speaking friend came to stay
- Plans for the future
- I start the class by putting some pictures on the board and tell the class I’m going to tell them about my trip to an English-speaking country. The pictures include some famous landmarks, photos of my friends there and a picture of myself on the trip.
- I ask the class to guess which country I visited and then brainstorm any information they know about the city. I put vocabulary on the board which will help in the following task. This activates top-down knowledge, personalizes the task and gives the group time to think about their own experiences.
- We then read the story of my trip to Liverpool together. At this stage I point out that the story is in the past, that it is divided into three parts and that each part is a paragraph.
- There are lots of ways to check comprehension, sometimes I ask questions as we go along, or ask the class to answer questions at the end of the reading task.
- Finally, using my story as a model I ask the group to write about their own trip.
Of course there are many children in the class who won’t have visited an English-speaking country or were too young to remember the trip. I tell them they can write about someone they know who went abroad or about an English-speaking visitor to their home.
One of the objectives of working with portfolios is to raise learners' awareness of the many different ways English can be learnt and practised. It tries to move away from the idea that it is a school subject and that it is useful and necessary outside the classroom.
Finally, it's always a good idea to put work up around the class for the group to read at the end of the activity. It’s a valuable activity for children to share their experiences and find out about what others do. Also, reading about their own classmates’ stories in English is useful for reviewing grammar and vocabulary.
Research and insight
Browse fascinating case studies, research papers, publications and books by researchers and ELT experts from around the world.
See our publications, research and insight
- AI Content Shield
- AI KW Research
- AI Assistant
- SEO Optimizer
- AI KW Clustering
- Customer reviews
- The NLO Revolution
- Press Center
- Help Center
- Content Resources
- Facebook Group
How to Write Your Own Biography
Table of Contents
It’s an experience we can all relate to. We agonize over how to write a bio that doesn’t sound too self-promotional. Or worse — how do we write a personal bio that doesn’t fall flat with modesty.
We are not talking about an autobiography here, folks. A personal bio is about the author’s professional history. It shows which school they went to, how did they learn what they know, what experiences they have had, and more.
To remain competitive in today’s market, one must learn how to write a personal bio.
Using a few straightforward tips will make writing an exciting and concise personal bio simpler. It is intended to depict their lived experiences and basic information like education and employment.
It can be challenging to write a professional and engaging biography. Optimizing it for better search engine visibility may make your work even more difficult. That’s why we decided to dedicate today’s article to how to write your own biography . If this sounds interesting, stay tuned!
What Exactly Is a Personal Bio?

A personal biography is a concise introduction that summarizes your qualifications and education. As well as other details that define you and your professional accomplishments. We frequently use personal bios when looking for work to give hiring managers a summary of why you are the best applicant.
They can also be applied to business websites and networking platforms.
Starting to write your biography is one of the most challenging steps. Give yourself enough time to concentrate so that you can convey all the information you want clearly and effectively.
Why Are Personal Bios Important?
A professional bio might be how a potential client, employer, or networking contact first comes into contact with you. People should clearly understand who you are and what you stand for from your professional bio, which should be extensive and thorough. After reading it, the reader of your professional biography ought to have a strong familiarity with you. Not only that but also an understanding of the advantages of working with you. Even though a well-written resume is essential, HR won’t notice if your personal bio isn’t up to par.
A strong bio goes further than a resume; it provides information about your personality, credentials, background, and relationship to your industry. A bio fulfills all the criteria for a resume and then some; think of it as a more approachable version of a resume. And even better, a bio goes places that a resume cannot. These bios are distributed at networking events and on marketing materials, but not just when applying for work.
A personal bio is a special account of your life story. As such, it allows you to connect with the audience in a special way that a resume doesn’t allow. On a personal bio page, you can share your character a little to give people an idea of who the real you really is.
How to Write Your Own Biography?
To write a personal bio that will grab the attention of potential employers , abide by these rules!
At the start of your bio, give a brief introduction of yourself. Your name should come first; then, you should highlight a few essential details like your education, credentials, or accomplishments.
After a strong introduction, mention your passions, ethical standards, and outlook on life by considering the following four aspects of who you are:
- How valuable are your skills to a given position or company? What do you have training or expertise in?
- What qualities contribute to your success in your field?
- Which principle or personal value has influenced who you are today the most?
- What do you value most about the organization you work for professionally? What are the objectives you want to achieve in your career?
Include any additional relevant information, such as your current employment title, the economic sector you work in, and the scope of your duties. These specifics are crucial for potential employers searching for you on professional websites.
Make a word count before you begin. Depending on the objective and focus of the biography, it may differ, but setting a word limit can help you organize your content. The biography section of a resume or for an individual shouldn’t contain more than one or two concise paragraphs that describe who they are. This type of biography should be between 300 and 500 words in length.
The purpose of shorter biographies is to pique the reader’s curiosity and encourage them to read the rest of your resume. Be straightforward and exciting.
If you’re writing it for your personal website, your bio should be 1,500 and 2,000 words long. While including as many as you can, keep your details brief and concise.
What Should Your Bio Include?
The critical components of your bio should be:
Why did you decide to write your biography? to speak with clients and shoppers? Find employment? What do you want readers of your bio to take away from it?
What professional objectives have you accomplished? Have you received any awards? Did you carry out your duties effectively and efficiently?
What elements of your personal history led you to this point in your life? Which personal experiences most significantly influenced your career course?
Remember, the topics are not optional for the writer. Your personal bio should include all of these topics, from start to finish. You want the reader to know almost everything about you by reading this small snippet.
To encourage readers to keep reading, prioritize the essential information, and delete details unrelated to the goal of your bio. It should be noted as someone else is writing about you.
Writing in the third person allows you to include your full name, even though some first-person biographies can be influential. Because it informs search engines that the article is about you, this tactic is better for SEO.
When writing in the third person, it’s important not to overuse your name. It ought to appear as if you naturally included it.
Where to Find Examples of Personal Bios?
Examples can help you understand the phenomenon a lot better instead of talking about it. There are many different mediums to find examples of personal bios on the Internet.
Our favorite is LinkedIn. You all know LinkedIn; it’s Facebook, but for professionals. On that platform, you can find everything you need regarding personal bios, including many examples that you can use.
Just look at the profile of your favorite professional in the field. More likely than not, they have a great personal bio in writing that you can use to write your own.
Another place to look at would be the personal websites of professionals you admire. They will have their life story up there as an example, not only their personal bio you could use.
Final Thoughts
So, how to write your own biography ? Writing a personal bio is one of those things that are unexpectedly challenging. After all, it is the writer who knows the most about — himself! However, it’s still strange to write about yourself as another person to a foreign audience.
In any case, we need to write a good story about ourselves. Hiring managers these days are flooded with job applications. Without a good personal biography, they won’t even take a good look at your resume.
After looking at this list of tips and tricks, if you are still having difficulty with writing your own biography, there is another way. Many people in a similar spot as you are, get help from personal biography generators. These tools are assisted by artificial intelligence to ensure that the content is 100% original. By employing the help of AI, you can write your biography in no time without needing to worry!
Our AI-powered writing assistant also has a personal bio generator tool that you can use! You just write your important personal information, previous life experiences, education, and so on. Finally, if you want, you can also ask INK to write your bio in a specific tone! If you are applying for jobs in a formal environment, you can use a serious tone for the reader!
In the end, whichever method you choose, it’s important to remember that your bio tells everything about you in a quick glance! It makes hiring managers’ work that much easier!
If you liked our guide on how to write your own biography, consider sharing this piece with your friends!

Abir Ghenaiet
Abir is a data analyst and researcher. Among her interests are artificial intelligence, machine learning, and natural language processing. As a humanitarian and educator, she actively supports women in tech and promotes diversity.
Explore All Personal Bio Generator Articles
Describing someone in a unique way.
We value and care the people in our lives for various reasons. But sometimes it can be challenging to explain…
- Personal Bio Generator
Tips for Writing a Bio for Artists
Your artist bio should connect emotionally with the reader and provide a glimpse into your personality. It allows you to…
Saddest Bios You Can Use for Facebook
Facebook offers many advantages to businesses, whether you have a Facebook page or have sparked a personal page. One of…
Coolest Insta Bios For Software Engineers
It’s a pretty cool to be a software engineer. You have the fun and challenge of writing code for a…
Best Instagram Bios for Singers’ Pages
Writing a singer or musician’s biography can be challenging, especially for press materials and Instagram. Writing a compelling musician bio…
Freshest Instagram Bios for Nature Lovers
Being a lover of nature makes you want to observe the beauty of nature all the time. The various hues…
Published In: Brief
How to Write a Biography (Examples & Templates)
A biography is a written account of a person’s life that details their life in chronological order. Another person usually writes this detailed account, and it contains reports of their childhood, career, major life events, relationships, and social impact. It also details their relationships with their family, children, and life accomplishments.
The best way to find out more about a popular figure is through reading their biographies, so you need to make sure you get the correct information. Before writing a biography, you need to do a lot of research and interviews to represent a person’s life accurately.
Types of Biography
A biography is the story of someone’s life as written by another writer. Most biographies of popular figures are written years, or even decades, after their deaths. Authors write biographies of popular figures due to either a lack of information on the subject or personal interest.
A biography aims to share a person’s story or highlight a part of their life.
There are different types of biographies, depending on the story. Some biographies are written true to the story, while some are written as fictional works. Biographies can give you true understanding of a person on an internal as well as external level along with a lot of life lessons.
Autobiography
An autobiography is different from a biography because it is written by the subject of the story, themselves. The author writes in the first-person narrative, and it flows step-by-step like a story of their life. Autobiographies contain personal accounts of the subject’s life, along with their perspectives and opinions on events in their life.
How To Write a Biography
Pick a subject.
Picking a subject is the first step in writing a biography. You can pick an already famous person or a relatively unknown person with a great life story. If you already have a few in mind, you can start by asking yourself some questions such as;
- What has the subject accomplished that makes them a good subject?
- Have they had an impact on society?
- Is the subject a celebrity or a well-known personality?
- Will the biography appeal to a wide audience?
Get Permission
When you pick a subject, the next thing to do is to get permission from them or their family or rights owners. Although, with some historical figures, there may not be any need for permission. Getting permission from your subject makes it easier for you to get stories to put into your book. You can get the chance to obtain additional personal stories and anecdotes that will make your book more interesting by doing so as well.
Do The Research
Research is the most important part of a biography’s process as the entire content of the book is dependent on it. Irrespective of what you know about the subject, you need to carry out as much research as possible to get the story’s facts precisely.
Biography research comes from various sources, depending on the book’s subject. Firsthand reports from family, friends, or personal accounts from the subjects are primary sources. They are usually the most accurate and reliable, and they are crucial for a biography. Secondary sources come from other sources like magazines or documentaries.
Pick a Format
Biographies come in various formats, with each of them having their pros and cons. A typical biography will start at the beginning, usually with the birth and childhood of the subject. Yet, if the biography’s theme involves a different event in their life, the author may want to explore the flashback option or one with concurrent events from different times.
Usually, biographies have a theme or a general life lesson at the center. The author’s role is to tell the subject’s story leading up to the major event.
Which-ever format you choose should place the theme at the center, with the other events detailing the journey.
Create a Timeline Of The Story
Since a biography takes place in chronological order, there needs to be a timeline of the events in the right order. The timeline should contain the key events in the subject’s life, in the order the author plans on revealing them. A great way to declutter the story and keep it interesting is to use flashbacks . This way, the author can introduce past events and explain later events excluding the element of monotony.
Add In Your Thoughts
The good thing about biographies is that you don’t have to stick to the hard facts only. As the author, you can share your opinions and emotions in writing. The author has the freedom to do this by commenting on a significant action by the subject in a manner that describes why they feel the subject may have done what they did.
The author can also include commentary on events depicted in the biography – how it was influenced society or its impact on the lives around them. Recounting these events through a different perspective can make the biography more relatable and interesting to read.
FAQ’s
Why is a biography template important.
A biography template has an outline that makes the writing easier for the author. Biography templates usually contain a sample timeline, format, and questions that provide more information about the subject. With a great biography template, you can cut your writing time in half and spend less time coming up with an outline.
How are biographies better in comparison to autobiographies
Since a different person writes biographies, they tend to be more objective and somewhat accurate than autobiographies. An autobiography tells things from the author’s perspective, so their views and perspective cloud it. Thus, a biography will likely tell a more factual story.
These are the important steps you need to take to help you write a great biography. Now, to make things easier for you, we have a free customizable autobiography and biography template that you can use to start your first book. Get the template and start writing today
What are some of the most important elements to keep in consideration while writing a biography?
Any author looking to write a biography must consider the factors below. They aren’t the only important factors, but a biography isn’t complete without them. • Date and place of their birth • Academic background • Professional expertise • Death, if deceased • Facts and anecdotes about the person • Main accomplishments • Detailed accounts of their child and adult life
Biographies tell the untold stories of some incredibly relevant people in the world. But biographies are not always strictly accurate. So, every biographer needs to follow the necessary steps to provide a biography with all the requirements.
Related Documents

COMMENTS
With the information provided in your Language Biodata Form, write your Language. Biography, which is a paragraph that tells the story of your languages. My Language Biography. My name is Trisha Mae L. Jalimao, 20 years old and studying at Mabini Colleges, Inc. I am currently studying for a Bachelor of Science in Accountancy.
1.6 Language Biography. The Language Biography is a record of personal, language-learning history. In this section of LinguaFolio, students are prompted to reflect on how they learn and to set learning goals. They evaluate their learning goals and reflect on language learning and cultural experiences. The Biography's can-do statements help ...
Linguistic Autobiography In a narrative essay between 500 and 700 words, write about your language history in a "linguistic autobiography." A "linguistic autobiography" is a first-person narrative essay in which a writer reflects on the history of his or her relationship with language.
A Language Biography encourages you to think about your use of language, whether for personal communication or, for example, in conjunction with applications for employment. There are sections which focus on. your progress. how you learn. your ability and what you can do with your language.
The Language Biography facilitates the learner's involvement in planning, reflecting upon and assessing his or her learning process and progress. The Language Biography contains goal-setting and self-assessment checklists that expand on the summary descriptors contained in the Self-assessment Grid. The Language Biography also encourages the ...
BIOGRAPHY FEATURES. LANGUAGE Use descriptive and figurative language that will paint images inside your audience's minds as they read. Use time connectives to link events. PERSPECTIVE Biographies are written from the third person's perspective.. DETAILS: Give specific details about people, places, events, times, dates, etc. Reflect on how events shaped the subject.
Conduct relevant interviews. Whenever possible, seek firsthand accounts from those who knew or interacted with the subject. Conduct interviews with family members, friends, colleagues, or experts in the field. Their insights and anecdotes can provide a deeper understanding of the person's character and experiences.
the process of writing her language biography helped her to rediscover and valorize her own linguistic resources, to enhance her language awareness and to develop metalinguistic skills useful for her professional work as a teacher as well as for her personal development towards multilingualism.
See why leading organizations rely on MasterClass for learning & development. Biographies are how we learn information about another human being's life. Whether you want to start writing a biography about a famous person, historical figure, or an influential family member, it's important to know all the elements that make a biography worth ...
11 Some Elements of Family History and Language Biography; 12 My Trajectory in Languages and Language Learning; 13 Multilingualism as Norm; 14 From Patois to Inter-comprehension Issues; 15 Biography, Linguistic Coexistence, and Epistemological Reflection; 16 Fighting off Zombies in France's Multilingual Education
Facebook. These are just some of the story elements you can use to make your biography more compelling. Once you've finished your manuscript, it's a good idea to ask for feedback. 7. Get feedback and polish the text. If you're going to self-publish your biography, you'll have to polish it to professional standards.
Here are a few tips based on my experience. Start small —A good way to begin is by writing a short profile of your subject in no more than 1,000 words. Imagine it as a short encyclopedia piece or obituary of the person that encapsulates the basic story (the who, what, where, when and how) along with discussion of significant accomplishments ...
A biography is a detailed description or account of a person's life. It entails more than basic facts (education, work, relationship, and death). A biography also explains the subject's experience of these events. Like a profile or curriculum vitae (resume). A biography presents a subject's life story, highlighting various aspects of his ...
language related to the biography. Sample Text-Based Writing Prompts. Prompt 1: Write a letter to the subject . of the biography. Be sure your comments and questions respond to the content of the biography. Prompt 2: Find a picture of the subject of the biography. Write a physical description of that person. In a second
The organisation of your biography greatly impacts its readability. Structure your work into logical sections or chapters, employing either a chronological or thematic arrangement. Begin with an engaging introduction that captures readers' attention and provides essential context.
Direction: With the information provided in your Language Biodata Form, write your Language Biography, which is a paragraph that tells the story of your languages.Your output graded base from the rubric below. My Language Biography I am 21 yrs. Old. I speak three languages; Cebuano or Bisaya, Filipino and English language. My first language or my mother tongue is Cebuano or Bisaya.
Working with biographies. The biography section of portfolios is a documentation of the learners' personal language learning history and can include, for example, a short narrative about the summer camp they attended and for which they may include a certificate of attendance in the passport section. This biography lends itself well to 'show ...
This type of biography should be between 300 and 500 words in length. The purpose of shorter biographies is to pique the reader's curiosity and encourage them to read the rest of your resume. Be straightforward and exciting. If you're writing it for your personal website, your bio should be 1,500 and 2,000 words long.
A biography is the story of someone's life as written by another writer. Most biographies of popular figures are written years, or even decades, after their deaths. Authors write biographies of popular figures due to either a lack of information on the subject or personal interest. A biography aims to share a person's story or highlight a ...
The process of writing a biography can be easier with a map to follow. You can follow these steps to write a biography: 1. Research your subject. The first step to writing a great biography is to spend time conducting extensive research on the person you're writing about, their career, their family and other information about them.
With the information provided in your Language Biodata Form, write your Language Biography, which is a paragraph that tells the story of your languages. My Language Biography I'm 19 years old and was born in Taguig city, Manila. Since then, most of the people speak in Tagalog and English.
With the information provided in your language Biodata Form, write your Language Biography, which is a paragraph that tells the story of your languages. Your paragraph should be in 100 - 120 words only. IMPORTANT NOTES: Write down your ideas comfortably like you are having a conversation. For now, Grammar will not be checked strictly. That ...