Tax Planning Knowledge Diffusion via the Labor Market
We examine the extent to which the labor market facilitates the diffusion of tax planning knowledge across firms. Using a novel dataset of tax department employee movements between S&P 1500 firms, we find that firms experience an increase in their tax planning after hiring a tax employee from a tax aggressive firm. This finding is robust to various research designs and specifications. Consistent with tax planning knowledge driving this result, we find that the tax planning benefit of hiring an employee from a tax aggressive firm is stronger when the employee has more tax experience and is hired into a senior tax department role, and when the hiring firm likely had less tax planning knowledge prior to the hire. Further tests suggest that tax planning knowledge is highly specific in nature: the increase in tax avoidance is larger when the hiring and former firms are similar (i.e., operating in the same sector or having similar foreign operations), and firms are more likely to hire tax department employees from firms with similar characteristics. Our study documents the first-order role of the labor market in the diffusion of tax planning knowledge across firms, and suggests that tax department human capital is a central determinant of tax planning outcomes.
The authors thank Kathleen Andries, Mary Billings, Jennifer Blouin, Jenny Brown, Ted Christensen, Scott Dyreng, Merle Erickson, Michelle Hanlon, Martin Jacob, April Klein, Eva Labro, Petro Lisowsky, Ed Maydew, Stephanie Sikes, Terry Shevlin, Jaron Wilde, Xiang Zheng, and seminar participants at the Frankfurt School of Finance and Management, University of Georgia, MIT, New York University, and the University of Pennsylvania for helpful comments. The authors thank Belle Zhang and Peter Banks for their excellent research assistance. The authors gratefully acknowledge the Accounting Research Center's support, the Charles E. Merrill Faculty Research Fund, and the Centel Foundation/Robert P. Reuss Fund at the University of Chicago Booth School of Business. The views expressed herein are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Bureau of Economic Research.
MARC RIS BibTeΧ
Download Citation Data

Published Versions
John M. Barrios & John Gallemore, 2024. " Tax Planning Knowledge Diffusion via the Labor Market, " Management Science, vol 70(2), pages 1194-1215.
Working Groups
More from nber.
In addition to working papers , the NBER disseminates affiliates’ latest findings through a range of free periodicals — the NBER Reporter , the NBER Digest , the Bulletin on Retirement and Disability , the Bulletin on Health , and the Bulletin on Entrepreneurship — as well as online conference reports , video lectures , and interviews .

tax planning Recently Published Documents
Total documents.
- Latest Documents
- Most Cited Documents
- Contributed Authors
- Related Sources
- Related Keywords
PENGARUH PERENCANAAN PAJAK, STRUKTUR MODAL DAN KEPEMILIKAN MANAJERIAL TERHADAP NILAI PERUSAHAAN DENGAN TRANSPARANSI PERUSAHAAN SEBAGAI VARIABEL MODERASI
This study aims to identify and prove empirically the effect of Tax Planning, Capital Structure and Managerial Ownership on Firm Value with Corporate Transparency as a moderating variable. This type of research is quantitative approach research with explanatory research and associative methods. Samples were taken using the purposive sampling technique using Eviews 9 software for data analysis. The sample consists of 60 data from 12 property and real estate subsector manufacturing companies listed on the Indonesia Stock Exchange in 2016-2020. The results show that Tax Planning, Capital Structure and Managerial Ownership simultaneously affect the value of the company which is moderated by corporate transparency, tax planning has no effect on firm value, the capital structure does not affect firm value, managerial ownership does not affect firm value, and corporate transparency does not. effect on firm value, corporate transparency is unable to moderate the relationship between tax planning and firm value, corporate transparency is unable to moderate the relationship between capital structure and firm value, and corporate transparency is unable to moderate the relationship between managerial ownership and firm value.
Determinan Perencanaan Pajak Perusahaan Pertambangan di Indonesia
This research aims to determine the effect of corporate governance as measured by institutional ownership, the proportion of independent commissioners, audit committee, and board of director also solvability, profitability, company size, growth opportunity, and capital intensity ratio on tax planning. The population in this research were all mining companies listed on Indonesia stock exchange for the 2015-2018 with the sampling technique used was purposive sampling. This type of research was causal associative, with data analysis method, namely confirmatory factor analysis and then continued with multiple regression analysis. The result of the factor test indicate that the audit committee is not a determinant of tax planning. Based on the results of regression analysis shows that simultaneously, institutional ownership, the proportion of independent commissioners, board of directors, solvency, profitability, company size, growth opportunity, and capital intensity ratio have an effect on tax planning. While partially, the results of the study indicate that institutional ownership, profitability, growth opportunity, and capital intensity ratio can be determinants that affect corporate tax planning. Meanwhile, the proportion of independent commissioners, board of directors, solvency, and company size partially not influence the company to do the tax planning. From results of this research, the government is expected will pay more attention to the grey area that can be used by companies as a gap to reduce tax payments which results in reduced state revenues.
¿Influyen los auditores en la agresividad fiscal de sus clientes? Evidencia empírica en las compañías españolas no cotizadas
The purpose of our study was to carry out an empirical test of the extent to which auditors have an influence on the tax practices of the audited firm. Based on a wide sample of Spanish non-listed companies for the period 2009-2017, we have obtained consistent empirical evidence revealing that the choice of a high-quality auditor has a significant impact on the tax planning strategy of the firm. Companies show a greater tax planning aggressiveness when they are audited by one of the Big Four. Notwithstanding, leverage and the existence of tax credits are factors mitigating that aggressiveness. Moreover, abnormally higher audit fees do not seem to be an incentive for the auditor to cooperate in the tax strategies of the audited company. Our results are robust and remain unaltered after adjusting for the potential heterogeneity inherent to auditor’s choice and using alternative variable specifications. Nuestro estudio tiene por objeto verificar empíricamente en qué medida los auditores influyen en las prácticas fiscales de sus clientes. Tomando una amplia muestra representativa de compañías españolas no cotizadas para el periodo comprendido entre 2009 y 2017, hemos documentado resultados empíricos que dejan constancia de que la elección de un auditor de calidad induce un significativo impacto en las estrategias de planificación fiscal de las empresas, que muestran una mayor agresividad tributaria cuando son auditadas por una Big Four. No obstante esta evidencia, el endeudamiento y la presencia de créditos fiscales pendientes de aprovechamiento se erigen como factores mitigantes de esta conducta. Además, la percepción por el auditor de un nivel de honorarios anormalmente elevados no parece generar incentivos para cooperar en las estrategias fiscales de la compañía auditada. Los resultados que hemos documentado son robustos y se mantienen inalterados tras corregir la posible endogeneidad inherente a la elección del auditor y ensayar con especificaciones alternativas de variables.
AN ANALYTICAL STUDY OF TAXATION LITERACY AMONG INDIVIDUALS
Over the recent years, taxation literacy has become a major area of concern for governments, banks, community service groups, other similar organizations, and people in India. People largely lack basic knowledge about financial matters, required to take household decisions, day-to-day money management as well as saving for the long term. Taxation literacy is defined as the knowledge which an individual should possess to manage the issues concerning personal taxation effectively. It helps the individuals in assessing their tax liability, tax management, and tax planning too. Lack of financial and taxation literacy often makes people vulnerable to a financial crisis. It also adversely affects market operations and competitive forces. On the other hand, people who are well informed and well knowledgeable can help to create a more competitive and more efficient financial and tax planning system. The basic purpose of this study is to determine the relationship between financial and taxation literacy among the people, the impact of various government awareness programs on salaried individuals. An illiterate person may arise issues related to tax evasion which is illegal in Indian perspectives. Descriptive type of research will be used to describe the meaning of taxation literacy and review various research papers. Data will be collected from secondary sources. The later section of this review paper observes the views of the different researchers on taxation literacy and will give valued suggestions and future viewpoints on the same. KEYWORDS: Taxation Literacy, Financial Literacy, Tax Management, Tax Planning, People
Tax Planning, Solvabilitas, Nilai Perusahaan, dan Ukuran Perusahaan sebagai Variabel Moderasi
AbstrakTujuan dari penelitian ini adalah untuk menguji pengaruh Tax Planning dan Solvabilitas terhadap Nilai Perusahaan dan menguji Ukuran Perusahaan apakah akan memperkuat pengaruh masing-masing variabel. Variabel independen dalam penelitian ini adalah Tax Planning dan Solvabilitas. Kemudian variabel dependennya adalah nilai perusahaan. Penelitian ini juga menggunakan Ukuran Perusahaan sebagai variabel moderasi. Hipotesis yang akan dibuktikan dalam penelitian ini adalah Tax Planning tidak berpengaruh terhadap Nilai Perusahaan, Solvabilitas berpengaruh terhadap Nilai Perusahaan, Ukuran Perusahaan tidak mampu memoderasi Tax Planning dengan Nilai Perusahaan, dan terakhir Ukuran Perusahaan mampu memperkuat pengaruh Solvabilitas dengan Nilai Perusahaan. Penelitian ini menggunakan MRA (Moderated Regression Analysis). MRA merupakan suatu bentuk regresi yang pada hakikatnya dirancang untuk mengetahui hubungan antara dua variabel yang dipengaruhi oleh variabel ketiga/moderator, suatu persamaan regresi yang mengandung unsur-unsur atau interaksi perkalian antara dua atau lebih variabel independen. Populasi penelitian ini adalah seluruh perusahaan real estate dan kontraktor yang terdaftar di Bursa Efek Indonesia (BEI) periode 2018-2020. Metode pengambilan sampel yang digunakan adalah purposive sampling. Hasil dari penelitian ini membuktikan seluruh hipotesis yang dibangun dapat diterima.AbstractThe purpose of this study are examine the effect of Tax Planning and Solvability on Firm Value and to test whether firm size will strengthen the influence of each variable. The independent variables in this study are Tax Planning and Solvability. Then the dependent variable is firm value. This study also using firm size as a moderating variable. The hypothesis that will be proven in this study is Tax Planning has no effect on Firm Value, Solvability has no effect on Firm Value, Firm Size could not moderate Tax Planning with Firm Value, and finally Firm Size could strengthen the effect of Solvability with Firm Value. This study using MRA (Moderated Regression Analysis). MRA is a form of regression which essentially designed to determine the relationship between two variables that influenced by a third/moderator variable, a regression equation consist of elements or multiplication interactions between two or more independent variables. The population of this study are all real estate companies and contractors listed on the Indonesia Stock Exchange (IDX) for the 2018-2020 period. The method of this sampling is purposive sampling. The results of this study prove that all hypotheses are acceptable.
IMPROVING TAXATION, ACCOUNTING, TAX REPORTING AND CONTROL OF VALUE ADDED TAX TO IMPROVE TAX PLANNING AT THE ENTERPRISE
Tax planning, corporate governance and financial performance of selected quoted non-financial companies in nigeria (2007–2018).
This study examines the interactive effect of tax planning and corporate governance on the financial performance of 50 non-financial quoted companies in Nigeria between 2007 and 2018. The study sample that covers 9 sectors was selected purposively through stratified random sampling. Data used were collected from the audited annual reports and accounts of selected quoted companies in Nigeria and fact books published by the Nigeria Stock Exchange. A system GMM was employed to estimate the dynamic models, and results show that ownership structure (OS) and capital intensity (CI) exerted a significant and positive impact on the returns on assets. This implies that OS plays a significant role to ensure that CI triggers an increase in the return on assets of the quoted Nigerian companies. However, board diversity and thin capitalization wielded a significant and negative influence on return on assets. This study thus recommends that companies should put in place a strong corporate governance mechanism that will monitor, check and balance tax planning activities and strategies adopted by the management of quoted companies in Nigeria.
Intelligent tax planning model of aircraft leasing based on big data mining algorithm
Tax planning measures among individual taxable assessees: an exploration of the age effect, planejamento tributário em uma indústria de confecções.
A presente pesquisa teve por objetivo identificar o regime tributário que fosse menos oneroso à uma indústria de confecções, ou seja, ocasionando a menor carga tributária. Com a finalidade de realizar o planejamento tributário, foram efetuadas diversas consultas em pesquisas existentes e nas legislações aplicáveis, para que tudo fosse praticado por meios legais, sendo caracterizada pela elisão fiscal, trata-se de uma pesquisa qualitativa, onde os dados da pesquisa foram coletados através do sistema eletrônico de processamento de dados, relatórios, balanços e demonstrações contábeis. O período analisado refere-se ao ano de 2018, pelo qual foram efetuados os cálculos pelo regime tributário Lucro Real o pela contabilidade responsável pela empresa. Foram comparados os valores dos tributos de PIS, COFINS, IRPJ, CSLL, ICMS, IPI e CPP, onde ocorreu os comparativos entre os regimes de tributação Lucro Real e Lucro Presumido, com a finalidade de demonstrar o melhor regime aplicável. Os resultados indicam que o melhor regime tributário para o período analisado foi o Lucro Real, identificando que está enquadrada na melhor forma de apuração. Palavras-Chave: Lucro Real. Lucro Presumido. Regime Tributário. Tributos. Abstract: The present research aimed to identify the tax regime that would be less costly to a clothing industry, that is, causing the lowest tax burden. In order to carry out tax planning, several consultations were carried out in existing research and in the applicable legislation, so that everything could be practiced by legal means, being characterized by tax avoidance, it is a qualitative research, where the research data were collected through the electronic data processing system, reports, balance sheets and financial statements. The period analyzed refers to the year 2018, where calculations have already been made under the taxable profit regime by the accounting responsible for the company. The values of the PIS, COFINS, IRPJ, CSLL, ICMS, IPI and CPP taxes were compared, where the comparisons between the taxable income tax system and the presumed income tax occurred, in order to demonstrate the best applicable regime. The results indicate that the best tax regime for the period analyzed is the Real Profit, identifying that it is framed in the best form of calculation. Keywords: Real Profit. Presumed profit. Tax regime. Taxes.
Export Citation Format
Share document.
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
Missed Tax Day? File as soon as possible to limit penalties. Try our fast, hassle-free tax filing. It's just $50.
Missed Tax Day? Try our fast, hassle-free tax filing. It's just $50.
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
Tax Planning: 7 Tax Strategies and Concepts to Know

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
Tax planning is the analysis and arrangement of a person's financial situation to maximize tax breaks and minimize tax liabilities in a legal and an efficient manner.
Tax rules can be complicated, but taking some time to know and use them for your benefit can change how much you end up paying (or getting back) when you file on tax day .
Here are some key tax planning and tax strategy concepts to understand before you make your next money move.
Understand your tax bracket
Learn how tax credits and deductions work
Decide between the standard deduction and itemizing
Take advantage of popular tax credits and deductions
Keep good records
Tweak your W-4 if you need to
Leverage tax-advantaged accounts
Simple tax filing with a $50 flat fee for every scenario
With NerdWallet Taxes powered by Column Tax, registered NerdWallet members pay one fee, regardless of your tax situation. Plus, you'll get free support from tax experts. Sign up for access today.
for a NerdWallet account
Transparent pricing
Maximum refund guaranteed
Faster filing
*guaranteed by Column Tax
1. Tax planning starts with understanding your tax bracket
You can’t really plan for the future if you don’t know where you are today. So the first tax planning tip is to figure out what federal tax bracket you’re in.
The United States has a progressive tax system. That means people with higher taxable incomes are subject to higher tax rates, while people with lower taxable incomes are subject to lower tax rates. There are seven federal income tax brackets: 10%, 12%, 22%, 24%, 32%, 35% and 37%.
No matter which bracket you’re in, you probably won’t pay that rate on your entire income. There are two reasons:
You get to subtract tax deductions to determine your taxable income (that’s why your taxable income usually isn’t the same as your salary or total income).
You don’t just multiply your tax bracket by your taxable income. Instead, the government divides your taxable income into chunks and then taxes each chunk at the corresponding rate.
Example: Let’s say you’re a single filer with $32,000 in taxable income. That puts you in the 12% tax bracket for the 2023 tax year (taxes filed in 2024). But do you pay 12% on all $32,000? No. Actually, you pay only 10% on the first $11,000; you pay 12% on the rest.
» MORE: See what tax bracket you’re in
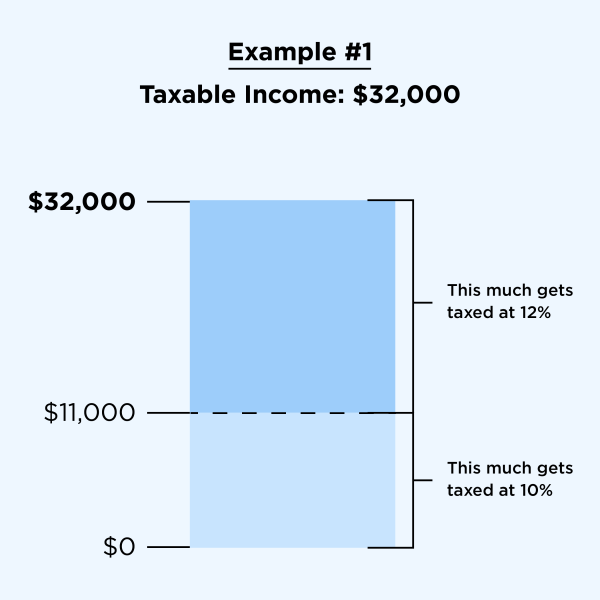
2. The difference between tax deductions and tax credits
Tax deductions and tax credits may be the best part of preparing your tax return. Both reduce your tax bill but in very different ways. Knowing the difference can create some very effective tax strategies that reduce your tax bill.
Tax deductions are specific expenses you’ve incurred that you can subtract from your taxable income. They reduce how much of your income is subject to taxes.
Tax credits are even better — they give you a dollar-for-dollar reduction in your tax bill. For instance, a tax credit valued at $1,000 lowers your tax bill by $1,000.
3. Taking the standard deduction vs. itemizing
Deciding whether to itemize or take the standard deduction is a big part of tax planning because the choice can make a huge difference in your tax bill.
What is the standard deduction?
Basically, it’s a flat-dollar, no-questions-asked tax deduction. Taking the standard deduction makes tax prep go a lot faster, which is probably a big reason why many taxpayers do it instead of itemizing.
Congress sets the amount of the standard deduction, and it’s typically adjusted every year for inflation. The standard deduction that you qualify for depends on your filing status , as the table below shows.
What does 'itemize' mean?
Instead of taking the standard deduction, you can itemize your tax return, which means taking all the individual tax deductions that you qualify for, one by one.
Generally, people itemize if their itemized deductions add up to more than the standard deduction. A key part of their tax planning is to track their deductions through the year.
The drawback to itemizing is that it takes longer to do your taxes, and you have to be able to prove you qualified for your deductions.
You use IRS Schedule A to claim your itemized deductions.
Some tax strategies may make itemizing especially attractive. For example, if you own a home, your itemized deductions for mortgage interest and property taxes may easily add up to more than the standard deduction. That could save you money.
You might be able to itemize on your state tax return even if you take the standard deduction on your federal return.
The good news: Tax software or a good tax preparer can help you figure out which deductions you’re eligible for and whether they add up to more than the standard deduction.
» MORE: Find the right tax software for your tax situation this year
4. Keep an eye on popular tax deductions and credits
Hundreds of possible deductions and credits are available, and there are rules about who’s allowed to take them. Here are some big ones (click on the links to learn more).
» MORE: See a list of 20 common tax breaks
5. Know what tax records to keep
Keeping tax returns and the documents you used to complete them is critical if you’re ever audited . Typically, the IRS has three years to decide whether to audit your return, so keep your records for at least that long. You also should hang on to tax records for three years if you file a claim for a credit or refund after you've filed your original return.
Keep records longer in certain cases — if any of these circumstances apply, the IRS has a longer limit on auditing you:
Six years: If you underreported your income by more than 25%.
Seven years: If you wrote off the loss from a “worthless security.”
Indefinitely: If you committed tax fraud or you didn’t file a tax return.
» MORE: See more about how long to keep your tax records
6. Tweak your W-4
A W-4 tells your employer how much tax to withhold from your paycheck. Your employer remits that tax to the IRS on your behalf.
Here's how to use the W-4 for tax planning.
If you got a huge tax bill when you filed and don’t want to relive that pain, you may want to increase your withholding. That could help you owe less (or nothing) next time you file.
If you got a huge refund last year and would rather have that money in your paycheck throughout the year, do the opposite and reduce your withholding.
You probably filled out a W-4 when you started your job, but you can change your W-4 at any time. Just download it from the IRS website, fill it out and give it to your human resources or payroll team at work. You may also be able to adjust your W-4 directly through your employment portal if you have one.
» MORE: Learn how FICA and other payroll taxes work
7. Tax strategies to shelter income or cut your tax bill
Deductions and credits are a great way to cut your tax bill, but there are other tax planning strategies that can help with tax planning. Here are some popular strategies.
Put money in a 401(k)
Your employer might offer a 401(k) savings and investing plan that gives you a tax break on money you set aside for retirement.
The IRS doesn’t tax what you divert directly from your paycheck into a 401(k). In 2024, you can funnel up to $23,000 per year into an account. If you’re 50 or older, you can contribute up to $30,500.
While these retirement accounts are usually sponsored by employers, self-employed people can open their own 401(k)s .
If your employer matches some or all of your contribution, you’ll get free money to boot.
» MORE: Calculate how much you should put in your 401(k)
Put money in an IRA
Outside of an employer-sponsored plan, there are two major types of individual retirement accounts : Roth IRAs and traditional IRAs.
You have until the tax deadline to fund your IRA for the previous tax year, which gives you extra time to do some tax planning and take advantage of this strategy.
The tax advantage of a traditional IRA is that your contributions may be tax-deductible. How much you can deduct depends on whether you or your spouse is covered by a retirement plan at work and how much you make. You pay taxes when you take distributions in retirement (or if you make withdrawals prior to retirement).
The tax advantage of a Roth IRA is that your withdrawals in retirement are not taxed. You pay the taxes upfront; your contributions are not tax-deductible.
Earnings on your investments grow tax-free in a Roth and tax-deferred in a traditional IRA.
This table illustrates these accounts in action.
» MORE: How to find the right kind of IRA for you
Open a 529 account
These savings accounts, operated by most states and some educational institutions, help people save for college.
You can’t deduct contributions on your federal income taxes, but you might be able to on your state return if you’re putting money into your state’s 529 plan.
There may be gift-tax consequences if your contributions plus any other gifts to a particular beneficiary exceed $17,000 in 2023 or $18,000 in 2024.
» MORE: Learn more about how 529s work
Fund your flexible spending account (FSA)
If your employer offers a flexible spending account , take advantage of it to lower your tax bill. The IRS lets you funnel tax-free dollars directly from your paycheck into your FSA every year. In 2024, the limit is $3,200.
You’ll have to use the money during the calendar year for medical and dental expenses, but you can also use it for related everyday items such as bandages, sunscreen and glasses for yourself and your qualified dependents. You may lose what you don’t use, so take time to calculate your expected medical and dental expenses for the coming year.
Some employers might let you carry over up to $640 to the next year.
Use dependent care flexible spending accounts (DCFSAs)
This FSA with a twist is another handy way to reduce your tax bill — if your employer offers it.
The IRS will exclude up to $5,000 of your pay that you have your employer divert to a dependent care FSA account, which means you’ll avoid paying taxes on that money. That can be huge for parents, because before- and after-school care, day care, preschool and day camps are usually allowed uses. Elder care may be included, too.
What’s covered can vary among employers, so check out your plan’s documents.
Maximize health savings accounts (HSAs)
Health savings accounts are tax-exempt accounts you can use to pay medical expenses.
Contributions to HSAs are tax-deductible, and the withdrawals are tax-free, too, so long as you use them for qualified medical expenses.
If you have self-only high-deductible health coverage, you can contribute up to $4,150 in 2024. If you have family high-deductible coverage, you can contribute up to $8,300 in 2024. If you're 55 or older, you can put an extra $1,000 in your HSA.
Your employer may offer an HSA, but you can also start your own account at a bank or other financial institution.
» MORE: See the tax benefits of FSAs and HSAs
On a similar note...

Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Income Tax Planning with respect to Individual Assessee

- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
A Systems View Across Time and Space
- Open access
- Published: 16 February 2021
Factors influencing taxpayers to engage in tax evasion: evidence from Woldia City administration micro, small, and large enterprise taxpayers
- Erstu Tarko Kassa ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8199-4910 1
Journal of Innovation and Entrepreneurship volume 10 , Article number: 8 ( 2021 ) Cite this article
72k Accesses
15 Citations
6 Altmetric
Metrics details
The main purpose of this paper is to investigate factors that influence taxpayers to engage in tax evasion. The researcher used descriptive and explanatory research design and followed a quantitative research approach. To undertake this study, primary and secondary data has been utilized. From the target population of 4979, by using a stratified and simple random sampling technique, 370 respondents were selected. To verify the data quality, the exploratory factor analysis (EFA) was conducted for each variable measurements. After factor analysis has been done, the data were analyzed by using Pearson correlation and multiple regression analysis. The finding of the study revealed that the relationship between the study independent variables with the dependent variable was positive and statistically significant. The regression analysis also indicates that tax fairness, tax knowledge, and moral obligation significantly influence taxpayers to engage in tax evasion, and the remaining moral obligation and subjective norms were not statistically significant to influence taxpayers to engage in tax evasion.
Introduction
In developed and developing countries, business owners, government workers, service providers, and other organizations are forced by the government to pay a tax for a long period in human being history, and no one can escape from the tax of the country. To support this, there is an interesting statement mentioned by Benjamin Franklin “nothing is certain except death and taxes”. This statement confirmed that every citizen should be subjected to the law of tax, and they are obliged to pay the tax from their income. To build large dams, to construct transportation infrastructures, and to provide quality social services for the community, collecting a tax from citizens plays a significant role for the governments (Saxunova and Szarkova, 2018 ).
Tax is the benchmark and turning point of the country’s overall development and changing the livelihoods and enhancing per capital income of the individuals. The gross domestic product of the developed countries and average revenue ratio were 35% in the year 2005, whereas in developing countries the share was 15% and in third world countries also not more than 12% (Mughal, 2012 ).
In the developing world, countries have no system to collect a sufficient amount of tax from their taxpayers. The expected amount of revenue cannot be enhanced due to different reasons. Among the reasons tax operation of the system may not be smooth, tax evasion and lack of awareness creation for the taxpayers are common in the developing world, and citizens are not committed to paying the expected amount of tax for their countries (Fagbemi et al., 2010 ). In today’s world, this remains very much the same as persons now pay taxes to their governments. As the world has evolved, tax compliance has taken a back seat with tax avoidance and tax evasion being at the forefront of the taxpayer’s main objective. Tax avoidance is the use of legal means to reduce one’s tax liability while tax evasion is the use of illegal means to reduce that tax liability (Alleyne & Harris, 2017 ). Tax evasion is a danger to the community; the countries and international organizations have been making an effort to fight undesirable phenomena related to taxation, the tax evasion, or tax fraud (Saxunova and Szarkova, 2018 ).
Tax evasion may brings a devastating loss for the country's GDP at the micro level, and it became a debatable and a special concern for tax collector authorities (Aumeerun et al., 2016 ). The participants in tax evasion activity critized by different individuals and groups by considering the loss that brings to the country economy (Alleyne & Harris, 2017 ).
According to Dalu et al., ( 2012 ) state that in the Zimbabwe tax system there are identical devils tax evasion and tax avoidance that create a problem for the government to collect a tax from taxpayers. Like Zimbabwe, many nations have faced challenges to cover the annual budget and to construct different infrastructures due to the budget deficit created by tax evasion (Alleyne & Harris, 2017 ; Turner, 2010 ).
Scholars especially economists agreed that tax evasion may be considered a technical problem that exists in the tax collection system, whereas psychologists believed that tax evasion is a social problem for the countries (Terzić, 2017 ).
Tax evasion practices are more worsen in developing countries than when we compare against the developed countries. Tax evasion is like a pandemic for the countries because they are unable to control it. Therefore, governments were negatively affected by tax evasion to improve the life standard of its citizens and to allocate a budget for public expenditure, and it became a disease for the country’s economy and estimated to cost 20% of income tax revenue (Ameyaw et al., 2015 ; degl’Innocenti & Rablen, 2019 ; Palil et al., 2016 ).
Several factors may lead taxpayers to engage in tax evasion. Among the factors, tax knowledge, tax morale, tax system, tax fairness, compliance cost, attitudes toward the behavior, subjective norms, perceived behavioral control, and moral obligation are major factors (Alleyne & Harris, 2017 ; Rantelangi & Majid, 2018 ). Other factors have also a significant effect on taxpayers to engage in tax evasion practice such as capital intensity, leverage, fiscal loss, compensation, profitability, contextual tax awareness, interest rate, inflation, average tax rate, gender, and ethical tax awareness on tax evasion (Annan et al., 2014 ; AlAdham et al., 2016 ; Putra et al., 2018 ).
According to Woldia City Administration Revenue Office annual report ( 2019/2020 ) from July 1, 2019, to June 30, 2020, 232,757,512 birr was planned to be collected from taxpayers; however, the office was able to collect only 198,537,785.25 birr; however, the remaining 34,219,726.75 birr have not been collected by the office from the taxpayers. The reason behind this was there might be some factors that lead to taxpayers not to pay the annual tax from their annual income. Based on the review of the previous studies and by diagnosing the tax collection system in the city administration, the researcher identified the gaps. The first gap that motivated the researcher to undertake this study is that the prior studies did not address the factors that influence the tax collection system of Ethiopia, specifically, there is no research result that was able to show which factors influence taxpayers to engage in tax evasion in the Woldia city administration. The other gap is the previous study focused on the demographic, economic, social, and other factors. However, this study mainly focused on the behavioral and other factors that lead taxpayers to engage in tax evasion.
To indicate the benefit of this study, the study specifies on which critical factors the authority will focus on to enhance annual revenue and to aware tax payers of the devastating impact of tax evasion. Moreover, the paper may bring new insights on tax evasion influential non-economic factors that the researchers may give more emphasis on the upcoming researches. This paper will also contribute innovative ways to know the reasons why tax payers engage in tax evasion and inform the authority at which factors they will struggle to reduce their influence and to enhance revenue. The study can be an evidence that the tax authority should launch innovative techniques to control tax evasion practices. Moreover, applying fair tax system in the collectors’ side, the enterprises become innovative and will expand their business.
To sum up, in this study, the researcher examined which factor (tax knowledge, tax fairness, subjective norms, moral obligation, and attitude towards the behavior) influences taxpayers to engage in tax evasion activities. Based on the above discussion, the objective of the study is to examine factors that influence taxpayers to engage in tax evasion in Woldia city administration.

Literature review
Tax and tax evasion.
Tax is charged by the government to the business, governmental organization, and individual without any return forwarded from the authority. Tax can be categorized as direct tax which is collected from the profit of the companies and the incomes of individuals, and the other category of tax is an indirect tax collected from consumers’ payment (James and Nobes, 1999 ).
Tax evasion is a word explaining individuals, groups, and companies rejecting the expected amount of payment for the authority. It is a criminal offense on the view of law (Nangih & Dick, 2018 ). The overall procedure of tax collection faced different challenges especially tax evasion the most important one. Tax evasion is done intentionally by taxpayers by avoiding and hiding different documents that become evidence for the tax collection authorities. It is simply an illegal act to pay the true amount of the tax (Aumeerun et al., 2016 ; Storm, 2013 ). Tax evasion is a crime that is able to distort the overall economic, political, and social system of the country. The economic aspect of tax evasion affects fair distribution of wealth for the citizens. The social aspect also creates different social groups motivated by tax evasion discouraged by these individuals due to unfair competition (AlAdham et al., 2016 ). Tax evasion is a mal-activity that reduces the amount of tax paid by the payers. Perhaps the taxpayers who engaged in evasion activity may be supported by the legislative of the country (Kim, 2008 ; Putra et al., 2018 ; Allingham & Sandmo, 1972 ). According to Al Baaj et al. ( 2018 ) argument, there are two types of tax evasions. The first one is the legal evasion or tax avoidance which is supported by the legislation of the countries and the right is given for the taxpayer, but it is not constitutional (Gallemore & Labro, 2015 ; Zucman, 2014 ).
Theoretical reviews on factors affecting tax evasion
The illegal activity done by taxpayers has many determinants that lead them to engage in tax evasion. Among the factors that trigger taxpayers who participate in this activity are the economic factors. Under the economic factors, business sanctions, business stagnation, and the amount of tax burden are considered as influential factors. On the other hand, legal factors, social factors, demographic factors, mental factors, and moral factors are the most important factors (Saxunova and Szarkova, 2018 ). Many factors determine the taxpayers’ interest to engage in tax evasion. Among the factors, the following are considered under this review.
The factors that able to influence taxpayers to engage in tax evasion are moral obligation . It is a principle and a duty of taxpayers by paying a reasonable amount of tax for the tax authorities without the enforcement of others. It is an intrinsic motivation of payers paying the tax (Sadjiarto et al., 2020 ). When taxpayers have low tax morals, they will become negligent to pay their allotted tax, and they will engage in tax evasion (Alm & Torgler, 2006 ; Frey & Oberholzer-Gee, 1997 ; Torgler et al., 2008 ). According to Feld and Frey ( 2007 ), when tax officials are responsible and provide respect in their duties toward taxpayers, tax morale or the honesty of taxpayers will increase. Tax morals may be affected by a demographic and another factor like income level, marital status, and religion (Rantelangi & Majid, 2018 ). It is the determinant behavior of tax payers whether they participate or not. Tax morals can affect positively taxpayers to engage in tax evasion (Nangih & Dick, 2018 ; Terzić, 2017 ). It is known that taxes levied by the concerned authority are ethical. As cited by Ozili ( 2020 ), McGee ( 2006 ) argues that there are three basic views on the ethics and moral of tax evasion. The first view is tax evasion is unethical and should not be practice by any payer, the second argument deals that the state is illegal and has no moral authority to take anything from anyone, and the last argument is tax evasion can be ethical under some conditions and unethical under other situations; therefore, the decision to evade tax is an ethical dilemma which considers several factors (Robert, 2012 ). Therefore, the discussion leads to the following hypothesis:
H 1 . Moral obligation has a negative influence on taxpayers to engage in tax evasion.
The other factor that influences taxpayers to engage in tax evasion is tax fairness . Tax fairness is a non-economic factor that determines the tax collection of the country (Alkhatib et al., 2019 ). It is known that the tax collection procedures, principles, and implementation must be fair. Unethical behavior may happen due to the unfairness of the tax collection process. The fairness of tax may influence payers positively to pay the tax. When the tax rate is not reasonable and fair, the payers will regret to engage in the tax evasion practices and they will inform authorities their annual income without denying the exact amount. Considering the ability of paying or acceptable tax rates helps to maintain the fairness of the taxation system (Rantelangi & Majid, 2018 ). The governments choose to levy in what amounts and on whom will pay a high tax rate (Thu, 2017 ). The tax rate is a factor that induces taxpayers to pay less amount from their income. The rate of tax should be fair and reasonable for the payers (Ozili, 2020 ). As cited by Gandhi et al. ( 1995 ) the Allingham and Sandmo’s model, Allingham and Sandmo ( 1972 ) shows that the tax rate on payment can be positive, zero, or negative, which implies that an increase in the tax rate may cause the tax payment to increase, remain the same, or decrease. The theoretical literature could not evidence the claim that an increase in the tax rate will lead to an increase in tax evasion (Gandhi et al., 1995 ). The fairness of tax is controversial and argumentative because there may not happen a similar amount of tax for all payers (Abera, 2019 ). Thus, based on this ground the study hypothesis would be:
H 2 . Tax fairness has a positive influence on taxpayers to engage in tax evasion.
Tax knowledge is vital for taxpayers to know the cause and effect brought to them to engage in tax evasion. If tax payers are well informed about tax evasion, their participation in tax evasion would be infrequent; the reverse is true for a taxpayer who is not well informed. Tax-related information should give more emphasis to enhance the knowledge of taxpayers and experts of the authority (Poudel, 2017 ). Tax knowledge is a means to enhance the revenue of the country from the side of tax payers (Sadjiarto et al., 2020 ). If the authorities cascade different training for taxpayers about tax evasion and other tax-related issues, taxpayers become reluctant to engage in tax evasion (Rantelangi & Majid, 2018 ). Tax knowledge is a determinant factor for the taxpayer to engage and retain from the tax evasion activities (Abera, 2019 ). When taxpayers are undertaking their routine tasks without tax knowledge, they may involve in certain risks that expose them to engage in tax evasion (Thu, 2017 ). Thus, the discussion leads to the following hypothesis:
H 3 . Tax knowledge has a negative influence on taxpayers engaged in tax evasion.
The stakeholders, government experts, families, individuals, groups, and peers influence taxpayers whether they engaged in tax evasion or not (Alleyne & Harris, 2017 ). As cited by Alkhatib et al. ( 2019 ), the influence of peer groups on tax taxpayers is high, thus affecting the taxpayers’ preferences, personal values, and behaviors to engage in tax evasion (Puspitasari & Meiranto, 2014 ). The stakeholders around the taxpayers might be motivators to push taxpayers in the criminal act of tax evasion. This act called subjective norms meant that the payers are influenced by peers and other stakeholders. When the tax payer is reluctant to pay a tax for the authority, his/her friends are more likely to hide tax. As cited by Abera ( 2019 ), there is a strong relationship between social norms and subjective norms with tax evasion and affects the small business taxpayers (Nabaweesi, 2009 ). The above discussion can support the following hypothesis of the study:
H 4 . Subjective norms have a positive influence on taxpayers to engage in tax evasion.
The other factor that influences taxpayers to engage in tax evasion is an attitude towards the behavior of taxpayers. Attitude is a means of evaluating the activities whether they are positive or negative of any object. Many studies have been done by different scholars by defining and identifying the relationship between the attitudes of taxpayers with tax evasion (Alleyne & Harris, 2017 ). If the attitude of taxpayers towards taxation is negative, they will be reluctant to pay their obligation to the authority; the reverse is true when taxpayers have positive attitudes towards taxation (Abera, 2019 ). Based on the above discussion, the hypothesis of the study would be as follows:
H 5 . Tax payers’ attitude towards the behavior has a positive influence on taxpayers to engage in tax evasion.
Conceptual framework of the study
The researcher identified the variables and presented the relationship between independent and dependent variables as follows (Fig. 1 ):
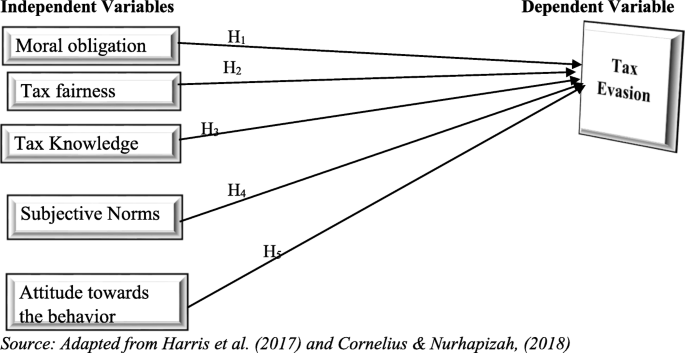
Conceptual framework of the study. Adapted from Alleyne and Harris ( 2017 ) and Rantelangi and Majid ( 2018 )
Materials and methods
The researcher applied descriptive and explanatory research design to carry out this study. The explanatory research design enables the researcher to show the cause and effect relationship between independent and dependent variables, and the descriptive research also helps to describe the event as it is. The quantitative approach has been followed by the researcher to analyze and interpret the numerical data collected from the respondents. The researcher used primary and secondary data. The primary data was collected from the respondents by using questionnaires, and the secondary data was also collected from the reports, websites, and other sources.
The target population of the study was 4979 taxpayers (micro, small, and large enterprises). From the total taxpayers, 377 are categorized under level “A,” 207 are under level “B,” and the remaining 4395 taxpayers are categorized under level “C”. From the target population by using a stratified sampling technique, the respondents have been selected. The target population has been divided by the level of taxpayers; after dividing the population by level, the researcher applied a simple random sampling technique to select respondents. To identify the target participants or sample size in this study, the researcher used Yamane’s ( 1967 ) formula. Hence, the formula is described as follows:
where N = target population, n = sample size, e = error term
Based on the sample size, the respondents have participated proportionally as follows from each level. The total population was divided by strata based on the level categorized by the authorities. By using a simple random sampling technique, 28 respondents were from level “A,” 15 respondents from level “B,” and 327 respondents from level “C” have participated.
Regarding data collection instruments , the data was collected by self-administered standardized questionnaires. The variable of the study a moral obligation was measured by 4 items; after conducting factor analysis, the fourth variable or questionnaire has been removed and after that correlation and regression analysis has been done for 3 items; the value of Cronbach’s alpha was .711; the other factor attitude towards the behavior was measured by 4 items with a value of .804 Cronbach’s alpha; the third variable subjective norms was also measured by 4 items; the value of Cronbach’s Alpha was .887, and tax evasion was measured by 5 items; the Cronbach’s alpha value was .868. For the above-listed variables, the questionnaires were adapted from Alleyne and Harris ( 2017 ), and the remaining variable tax fairness was measured by 7 items, the Cronbach’s alpha value was .905, the items were adapted from Benk et al. ( 2012 ), and the last variable tax knowledge was measured by 5 items. However, after conducting factor analysis, the fifth item has been removed due to low value of the variable. After the removal of the fifth item, the Cronbach’s alpha value for the remaining items was .800, the items were adapted from Poudel ( 2017 ). For all variables, the researcher has used a five-point Likert scale from strongly agree to strongly disagree.
To analyze the collected data, the researcher used descriptive statistics analysis, factor analysis, correlation analysis, and multiple regression analysis to know the result of variables by using SPSS Version 22. Moreover, the model of the study is described as follows:
where Y = tax evasion, X 1 = moral obligation, X 2 = tax fairness, X 3 = tax knowledge, X 4 = subjective norms, and X 5 = attitude towards the behavior, β = beta coefficient, B 0 = constant, e = other factors not included in the study (0.05 random error).
Results and discussion
Level of respondents.
As indicated in Table 1 from the total respondents, 88.4% are categorized under level “C,” 4.1% are leveled under “B,” and the remaining 7.6% of respondents have been categorized under level “A”.
Factor analysis of the study variables
To undertake exploratory factor analysis, the data should fulfill the following assumptions. The first assumption is the variables should be ratio, interval, and ordinal; the second one is within the variables there should be linear associations; the third assumption is a simple size should range from 100 to 500; and the last assumption is the data without outliers. Thus, this study data have been checked by the researcher whether the data meets the assumption or not. After checking the assumptions, factor analysis was conducted as follows.
KMO and Bartlett’s test
Conducting KMO and Bartlett’s test is a precondition to conduct the factor analysis of the study measuring variables. KMO measures the adequacy of the sample of the study. In the result reported in Table 2 , the value was 0.883 and enough for the factor analysis. Related with Bartlett test as shown in Table 2 , the value is 5727.623 ( p < 0.001), which reveals the adequacy of data using factor analysis.
As shown in Table 3 , factors were extracted from study data; there was a linear relationship between variables. From the table, we can understand that 6 variables have more than one eigenvalue. The first factor scored the value 31.782 of the variance, the second value is 11.739 of the variance, the third factor scored 8.246 of the variance, the fourth factor accounts for 6.725 of the variance, the fifth factor also accounts for 5.233, and the last factor scored 4.123 of the variance. All six factors were explained cumulatively by 67.85% of the variance.
As shown in the Fig. 2 , the scree plot starts to turn down slowly at the low eigenvalue which is less than 1. The six factors eigenvalue is greater than one.
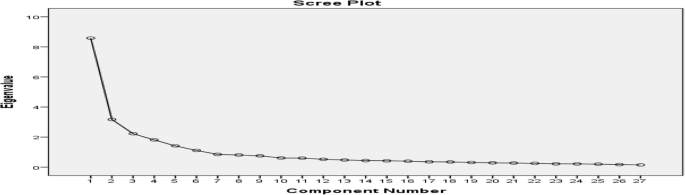
Scree plot. Source: own survey (2020)
The pattern matrix is shown in Table 4 which is able to show the loading of each variable and the relationship of variables in the study. The highest value among the factors measured the variable considerably. The cutoff point of loading was set at .35 and above. Based on the loading cutoff point except two factors, all are significant and analyzed under this study. From the six variables (five independent and one dependent) incorporated under this study, the identified factors show that how significantly enough to measure the situation. These factors have scored greater than 1 eigenvalue and able to explain 67.85% of the variance. In general, the detail variables and their factor are described as follows:
The first component tax fairness has 7 factors; the eigenvalue is 8.58 and able to explain 31.78 of the total variance. In this component, the highest contributed factor was item TF3 (weight = .925), TF5 (weight = .865), TF1 (weight = .859), TF2 (weight = .778), TF4 (.668), TF6 (weight = .614), and TF7 (weight = .568). The second component was tax evasion and has 5 items; the eigenvalue is 3.17 and explaining 11.73 of the variance. The factor weight of the items, TE4 (factor weight = .860), TE5 (factor weight = .810), TE3 (factor weight = .730), TE2 (factor weight = .650), and the last one is TE1 (factor weight = .606). The third component was subjective norms; it has 4 factors the weight of each factor described as follows. The first item SNS1 weight = .898, SNS2 factor weight = .887, SNS4 factor weight = .846, and SNS3 factor weight = .820. Moreover, the eigenvalue of this component is 2.226 and explained 8.246 of the variance of the study. The fourth component is an attitude towards the behavior. This variable has four factors that have 1.816 eigenvalue and explained 6.725 of the total variance. Among the items, ATB2 factor weight = .863, ATB1 factor weight = .792, ATB3 factor weight = .791 and the last factor is ATB4 factor weight = .500. The fifth component of the study is tax knowledge; at the very beginning of this variable, the researcher adapted five items. However, one item (TK5) was not significant and removed from this analysis. In this component, the highest value was scored by TK3 (factor weight = .866), the second highest TK2 (factor weight = .801), the third highest factor weight (weight = .700), and the last factor is TK4 (weight = .690). The eigenvalue of this component was 1.413 and explained 5.233% of the variance. The last component is a moral obligation; like tax knowledge, the researcher adapted for this variable 4 items, though, one item (MO4) was not significant and removed from the items list. The eigenvalue of this component was 1.113 and explained 4.123 of the variance. From the items, MO1 scored the highest factor weight of .891, the second highest weight in this component was MO3 with a factor weight of .854, and the third highest factor weight was scored by MO3 with a value of .508.
Association analysis of the study variables
To analyze the correlation between variables as shown in the Table 5 , the relation between subjective norms with taxpayers engaged in tax evasion is r = 0.240 ( p < 0.05); this indicates that there is a statistically significant relationship between the two variables. The relationship between ATB with TE, MO with TE, TK with TE, and TF with TE, the Pearson correlation result is r = 0.318 ( p < 0.05), r = 0.371 ( p < 0.05), .446, and r = 0.691 ( p < 0.05) respectively and statistically significant. It implies that the independent variables have a positive relationship with the dependent variable of the study with a statistically significant level of p < 0.05 and n = 370.
Effect analysis of the study variables
As shown in Table 6 , the study independent variables (SNS, ATB, MO, TK, and TF) explained the study dependent variable (TE) by 54.9%. This result indicates that there are other variables that explain the dependent variable by 45.1% which has not been investigated under this study.
Hypothesis test
The proposed hypothesis of the study has been tested based on the coefficient of regression and the “ p ” value of the study variables. The detail result is described as follows:
As shown in Table 7 , moral obligation influences positively the taxpayers to engage in tax evasion activities with a beta value of .177 and p < .05. This result entails that the taxpayers are influenced by other stakeholders to engage in tax evasion, and they have low moral value to pay the tax levied by the government. This result is supported by the finding of Alleyne and Harris ( 2017 ), Rantelangi and Majid ( 2018 ), and Sadjiarto et al. ( 2020 ). Thus, the hypothesis related to this variable has been rejected because moral obligation influences positively taxpayers to engage in tax evasion.
H 2 . Tax fairness has a positive influence on taxpayers to engage in tax evasion
To minimize the participation of taxpayers engaged in tax evasion, tax fairness plays a significant role. The regression result indicates in Table 7 that tax fairness positively influences the taxpayers to engage in tax evasion. This result is similar to the finding of Majid et al., ( 2017 ) and contradicts with the finding of Rantelangi and Majid ( 2018 ) and Alkhatib et al. ( 2019 ). Accordingly, the proposed hypothesis has been accepted because the beta value is .563 and the p value is less than .05.
H 3 . Tax knowledge has a negative influence on taxpayers to engage in tax evasion
Table 7 shows that tax knowledge influences the taxpayers positively to engaged in tax evasion. The beta value is .183 and the value is p = 0.00. It is known that when the taxpayers were not well informed about the importance of tax for the country development and the devastating issues of tax evasion, they will be forced to engage in tax evasion. This finding contradicts the finding of Rantelangi and Majid ( 2018 ) and is supported by the finding of AlAdham et al. ( 2016 ). To conclude, the proposed hypothesis rejected because tax knowledge positively influenced the taxpayers to engage in tax evasion.
H 4 . Subjective norms have a positive influence on taxpayers engaged in tax evasion
Table 7 indicates that subjective norms have not been significantly influenced positively by the taxpayers engaged in tax evasion, which means taxpayers were not influenced by others to participate in tax evasion activities. This result is consistent with the finding of Alleyne and Harris ( 2017 ). Thus, the proposed hypothesis is rejected because the variable of subjective norms was not statistically significant with a p value of .099.
H 5 . Tax payers’ attitude towards the behavior has a positive influence on taxpayers to engage in tax evasion
As indicated in Table 7 , attitudes toward the behavior were not significantly influencing the taxpayers to participate in tax evasion with the p value of .985. However, according to the study conducted by Alleyne and Harris ( 2017 ), attitude toward the behavior significantly predicts the intentions of taxpayers to engage in tax evasion. This finding contradicts with this study result. To conclude, the proposed hypothesis has been rejected because the variable is not statistically significantly influencing the taxpayers to engage in tax evasion activities.
According to Table 7 through the examination of coefficients, moral obligation had a positive effect on tax evasion having a coefficient of .197. This means that a 1% change in moral obligation keeping the other things remain constant can result to motivate taxpayers to engage in tax evasion by 19.7% in the same direction. This finding is similar to the result of Alleyne and Harris ( 2017 ), Nangih and Dick ( 2018 ), Rantelangi and Majid ( 2018 ), and Sadjiarto et al. ( 2020 ). Tax knowledge had a positive effect on tax evasion having a coefficient of .174. This indicates that a 1% change in tax knowledge keeping the other things constant can result in a change in taxpayers to engage in tax evasion by 17.4% in the same direction. This finding contradicts the finding of Rantelangi and Majid ( 2018 ) and is similar to the finding of AlAdham et al. ( 2016 ) and Thu ( 2017 ). Tax fairness also had a positive effect on tax evasion having a coefficient of .468. This implies that a 1% change in tax fairness keeping the other things remain constant can result in a change in taxpayers engage in tax evasion by .468% in the same direction. This result is similar to the finding of Majid et al. ( 2017 ) and contradicts the finding of Alkhatib et al. ( 2019 ) and Rantelangi and Majid ( 2018 ). Thus, the final model of the study would be:
Tax evasion = .623 + .197MO + .174TK + .468TF
To generalize, the standardized beta coefficient indicates that tax fairness highly affects taxpayers to engage in tax evasion by 56.3%, tax knowledge affects secondly taxpayers to engage in tax evasion by 18.3%, and moral obligation affects taxpayers to engage in tax evasion by 17.7%. The remaining variables subjective norms and attitude towards the behavior were not statistically significant.
Conclusion and recommendations
Every citizen of the country was subjected to pay the tax of the country levied by the authority that administered the revenue. However, the taxpayer may be reluctant to pay a tax based on their revenue. There are push factors that instigate payers to engage in tax evasion. Sometimes the payers may be convinced themselves that being engaged in tax evasion is ethical, others may consider it unethical. They may argue “I Do Not Receive Benefits, Therefore I Do Not Have to Pay” (Robert, 2012 ). This study tried to examine the factors that influence taxpayers to engage in tax evasion by identifying five factors namely moral obligation , tax fairness , tax knowledge , subjective norms , and taxpayers’ attitude towards the behavior . The study findings based on the result analysis described as follows.
The correlation analysis of the study shows that there was a positive and statistically significant relationship between independent variables with the dependent variable (tax evasion). The regression result, on the other hand, revealed that tax knowledge affects taxpayers to participate in tax evasion activities with a statistically significant level. This finding can be evidence that the knowledge of the taxpayers regarding the importance of tax is limited. Because according to the regression result, they engaged in the tax evasion activities in the study area. The other factor that affects taxpayers to engage in tax evasion is tax fairness. The regression result of tax fairness supported that taxpayers have been affected by the fairness of the tax system in the study area to participate in tax evasion. The finding confirms that the tax charged by the government is not fair for payers. Thus, we can conclude that due to the absence of tax fairness taxpayers are engaged in tax evasion in the city administration. The other variable moral obligation regression result confirms that moral obligation affects positively taxpayers to engage in tax evasion. This is signal that taxpayers did not know the moral value of retaining from tax evasion that is why the moral obligation results in positive and statistical significance. Generally, tax fairness highly affects taxpayers to evade taxes, tax knowledge affects secondly, and moral obligation affected tax payers thirdly to evade tax in the city administration.
Based on the findings, the following recommendations have been forwarded by the researcher. The first one is creating a fair tax payment system, or charging fair tax for the payers helps to reduce the participation of payers in tax evasion. The second recommendation is cascading different training related to tax will help taxpayers to pay a tax based on their annual income. The last recommendation is related to tax moral or moral obligation. The moral is an abounding rule for human beings to know the right and wrong activities. The authority is better to strive to recognize the payers about the moral obligations of the payers and better to inform to the payers to think about the shattering effect of tax evasion for the country development and city as well.
Further future lines of research will attempt to:
Investigate the employees’ side of tax authority and the perception of the community towards tax evasion.
Explore other influencing factors that affect tax payers to engage in tax evasion which are not incorporated under this study.
Conducting a comparative study on one city, region, and country with others.
Suggestion for future study
This study addresses only one city administration in Amhara region; other researchers are better to undertake the study on one more cities.
Availability of data and materials
All data are included in the manuscript and available on hand too.
Abbreviations
Attitude towards the behavior
- Moral obligation
Micro and small enterprises
Subjective norms
- Tax evasion
- Tax fairness
- Tax knowledge
Abera, A. A. (2019). Factors affecting presumptive tax collection in Ethiopia: Evidence from category “C” taxpayers in Bahir Dar City. Journal of Tax Administration , 5 (2), 74–96.
Google Scholar
Al Baaj, Q. M. A., Al Marshedi, A. A. S., & Al-Laban, D. A. A. (2018). The impact of electronic taxation on reducing tax evasion methods of Iraqi companies listed in the Iraqi stock exchange. Academy of Accounting and Financial Studies Journal , 22 (4) Retrieved from: www.abacademies.org/articles/ .
AlAdham, M. A. A., Abukhadijeh, M. A., & Qasem, M. F. (2016). Tax evasion and tax awareness evidence from Jordan. International Business Research , 9 (12) https://doi.org/10.5539/ibr.v9n12p65 .
Alkhatib, A. A., Abdul-Jabbar, H., Abuamria, F., & Rahhal, A. (2019). The effects of social influence factors on income tax evasion among the Palestinian SMEs. International Journal of Advanced Science and Technology , 28 (17), 690–700.
Alleyne, P., & Harris, T. (2017). Antecedents of taxpayers’ intentions to engage in tax evasion: Evidence from Barbados. Journal of Financial Reporting and Accounting (Emerald Publishing Limited) , 15 (1), 2–21 https://doi.org/10.1108/JFRA-12-2015-0107 .
Article Google Scholar
Allingham, M. G., & Sandmo, A. (1972). Income tax evasion: a theoretical analysis. Journal of Public Economics , 1 (3-4), 323–338.
Alm, J., & Torgler, B. (2006). Culture differences and tax morale in the United States and in Europe. Journal of Economic Psychology , 27 (2), 224–246.
Ameyaw, B., Addai, B., Ashalley, E., & Quaye, I. (2015). The effects of personal income tax evasion on socio-economic development in Ghana: A case study of the informal sector. British Journal of Economics, Management & Trade (Sciencedomain international) , 10 (4), 1–14 https://doi.org/10.9734/BJEMT/2015/19267 .
Annan, B., Bekoe, W., & Nketiah-Amponsah, E. (2014). Determinants of Tax Evasion in Ghana: 1970-2010. International Journal of Economic Sciences and Applied Research , 6 ( 3 ), 97 – 121 .
Aumeerun, B., Jugurnath, & Soondrum, H. (2016). Tax evasion: Empirical evidence from sub-Saharan Africa. Journal of Accounting and Taxation (Academic Journals) , 8 (7), 70–80 https://doi.org/10.5897/JAT2016.022 .
Benk, S., Budak, T., & Cakmak, A. F. (2012). Tax professionals’ perceptions of tax fairness: Survey evidence in Turkey. International Journal of Business and Social Science , 3 (2) Centre for Promoting Ideas, USA.
Dalu, T., Maposa, V. G., Pabwaungana, S., & Dalu, T. (2012). The impact of tax evasion and avoidance on the economy: a case of Harare, Zimbabwe. African Journal Economic and Sustainable Development , 1 (3), 284–296.
degl’Innocenti, D. G., & Rablen, M. D. (2019). Tax evasion on a social network. Journal of Economic Behavior and Organization (Elsevier B.V) , 79–91 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jebo.2019.11.001 .
Fagbemi, T. O., Uadiale, O. M., & Noah, A. O. (2010). The ethics of tax evasion: Perceptual evidence from Nigeria. European Journal of Social Sciences , 17 ( 3 ).
Feld, L. P., & Frey, B. S. (2007). Tax Compliance as the Result of a Psychological Tax Contract: The Role of Incentives and Responsive Regulation. Law & Policy , 29 (1), 102–120.
Frey, B. S., & Oberholzer-Gee, F. (1997). The Cost of Price Incentives: An Empirical Analysis of Motivation Crowding- Out. The American Economic Review , 87 (4), 746–755.
Gallemore, J., & Labro, E. (2015). The importance of the internal information environment for tax avoidance. Journal of Accounting and Economics , 60 (1), 149–167.
Gandhi, V. P., Edrill, L. P., Mackenzie, G. A., Manas-Anton, L. A., Modi, J. R., Richupan, S., … Shome, P. (1995). Supply-side tax policy: Its relevance to developing countries . International Monteray Fund.
James, S. R., & Nobes, C. (1999). The Economics of Taxation: Principles, Policy, and Practice , (vol. 7). Financal Times Management.
Kim, S. (2008). Does political intention affect tax evasion? Journal of Policy Modeling , 30 (3), 401–415.
Majid, N., Rantelangi, C., & Iskandar (2017). Tax evasion: Is it ethical or unethical? (based on Samarinda taxpayers’ perception). In Mulawarman international conference on economics and business (MICEB 2017) , (pp. 13–18). Atlantis Press http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ .
McGee, R. W. (2006). Three views on the ethics of tax evasion. Journal of Business Ethics , 67 (1), 15–35.
Mughal, M. M. (2012). Reasons of Tax Avoidance and Tax Evasion: Reflections from Pakistan. Journal of Economics and Behavioral Studies , 4 (4), 217–222.
Nabaweesi, J. (2009). Social norms and tax compliance among small business enterprises in Uganda (Master’s thesis) . Retrieved from http://makir.mak.ac.ug/handle/10570/2525
Nangih, E., & Dick, N. (2018). An empirical review of the determinants of tax evasion in Nigeria: Emphasis on the informal sector operators in Port Harcourt Metropolis. Journal of Accounting and Financial Management , 4 (3) http://www.iiardpub.org/ .
Ozili, P. K. (2020). Tax evasion and financial instability. Journal of Financial Crime. Emerald Publishing Limited , 27 (2), 531–539 https://doi.org/10.1108/JFC-04-2019-0051 .
Palil, M. R., Malek, M. M., & Jaguli, A. R. (2016). Issues, challenges and problems with tax evasion: The institutional factors approach. Gadjah Mada International Journal of Busines , 18 (2), 187–206.
Poudel, R. L. (2017). Tax knowledge among university teachers in Pokhara. The Journal of Nepalese Bussiness Studies , 10 ( 1 ).
Puspitasari, E., & Meiranto, W. (2014). Motivational postures in tax compliance decisions: An experimental studies. International Journal of Business, Economics and Law , 5 (1), 100–110.
Putra, P. D., Syah, D. H., & Sriwedari, T. (2018). Tax avoidance: Evidence of as a proof of agency theory and tax planning. International Journal of Research and Review , 5 (9), 2454–2223.
Rantelangi, C., & Majid, N. (2018). Factors that influence the taxpayers’ perception on the tax evasion. In Advances in economics, business and management research (AEBMR) , (p. 35). Atlantis Press.
Robert, W. M. G. (2012). The ethics of tax evasion; perspectives in theory and practice . North Miami: Springer Science+Business Media https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-1287-8 .
Sadjiarto, A., Susanto, A. N., Yuniar, E., & Hartanto, M. G. (2020). Factors affecting perception of tax evasion among Chindos. In Advances in economics, business and management research:23rd Asian Forum of Business Education(AFBE 2019),144 , (pp. 487–493). Atlantis Press SARL.
Saxunova, D., & Szarkova, R. (2018). Global Efforts of Tax Authorities and Tax Evasion Challenge. Journal of Eastern Europe Research in Business and Economics , 2018 , 1–14.
Storm, A. (2013). Establishing The Link Between Money Laundering And Tax Evasion. International Business & Economics Research Journal (IBER) , 12 (11), 1437.
Terzić, S. (2017). Model for determining subjective and objective factors of tax evasion. Notitia - Journal for Economic, Business and Social Issues, Notitia Ltd. , 1 (3), 49–62.
Thu, H. N. (2017). Determinants to tax evasion behavior in Vietnam. Journal of Management and Sustainability Canadian Center of Science and Education. https://doi.org/10.5539/jms.v7n4p123 .
Torgler, B., Demir, I. C., Macintyre, A., & Schaffner, M. (2008). Causes and Consequences of Tax Morale: An Empirical Investigation. Economic Analysis and Policy , 38 (2), 313–339.
Turner, Sean C. (2010). Essays on Crime and Tax Evasion . Dissertation, Georgia State University, 2010. https://scholarworks.gsu.edu/econ_diss/64
Woldia City Administration Revenue Office (2019/2020). 2012E.C annual report. Woldia .
Yamane, T. (1967). Statistics: An Introductory Analysis , (2nd ed., ). New York: Harper and Row.
Zucman, G. (2014). Taxing accross borders: Tracking personal wealth and corporate profits. The Journal of Economic Perspectives , 28 (4), 121–148.
Download references
Acknowledgements
I am grateful to all anonymous reviewers, my respondents, and Woldia City administration revenue office experts sharing the required information.
The author has not received a fund from any organization.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Woldia University, Woldia, Ethiopia
Erstu Tarko Kassa
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
The research was done independently. I have carried out the whole work of the study. The author read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Erstu Tarko Kassa .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The author declares that there are no competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Kassa, E.T. Factors influencing taxpayers to engage in tax evasion: evidence from Woldia City administration micro, small, and large enterprise taxpayers. J Innov Entrep 10 , 8 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13731-020-00142-4
Download citation
Received : 01 October 2020
Accepted : 09 December 2020
Published : 16 February 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13731-020-00142-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- How it works

Useful Links
How much will your dissertation cost?
Have an expert academic write your dissertation paper!
Dissertation Services

Get unlimited topic ideas and a dissertation plan for just £45.00
Order topics and plan

Get 1 free topic in your area of study with aim and justification
Yes I want the free topic

50+ Focused Taxation Research Topics For Your Dissertation
Published by Ellie Cross at December 29th, 2022 , Revised On May 2, 2024
A thorough understanding of taxation involves drawing from multiple sources to understand its goals, strategies, techniques, standards, applications, and many types. Tax dissertations require extensive research across a variety of areas and sources to reach a conclusive result. It is important to understand and present tax dissertation themes well since they deal with technical matters.
Choosing the right topic in the area of taxation can assist students in understanding how much insight and knowledge they can contribute and the tools they will need to authenticate their study.
If you are not sure what to write about, here are a few top taxation dissertation topics to inspire you .
The Most Pertinent Taxation Topics & Ideas
- The effects of tax evasion and avoidance on and the supporting data
- How does budgeting affect the management of tertiary institutions?
- How does intellectual capital affect the development and growth of huge companies, using Microsoft and Apple as examples?
- The importance and function of audit committees in South Africa and China: similarities and disparities
- How taxation can aid in closing the fiscal gap in the UK economy’s budget
- A UK study comparing modern taxation and the zakat system
- Is it appropriate to hold the UK government accountable for subpar services even after paying taxes?
- Taxation’s effects on both large and small businesses
- The impact of foreign currencies on the nation’s economy and labour market and their detrimental effects on the country’s tax burden
- A paper explaining the importance of accounting in the tax department
- To contribute to the crucial growth of the nation, do a thorough study on enhancing tax benefits among American residents
- A thorough comparison of current taxes and the Islamic zakat system is presented. Which one is more beneficial and effective for reducing poverty?
- According to the most recent academic study on tax law, what essential improvements are needed to implement tax laws in the UK?
- A thorough investigation of Australian tax department employees’ active role in assisting residents of all Commonwealth states to pay their taxes on time.
- Why establishing a taxation system is essential for a country’s growth
- What is the tax system’s greatest benefit to the poor?
- Is it legitimate to lower the income tax so that more people begin paying it?
- What is the most significant investment made using tax revenue by the government?
- Is it feasible for the government to create diverse social welfare policies without having the people pay the appropriate taxes?
- How tax avoidance by people leads to an imbalance in the government budget
- What should deter people from trying to avoid paying taxes on time?
- Workers of the tax department’s role in facilitating tax evasion through corruption
- Investigate the changes that should be made to the current taxation system. A case study based on the most recent UK tax studies
- Examine the variables that affect the amount of income tax UK people are required to pay
- An analysis of the effects of intellectual capital on the expansion and development of large businesses and multinationals. An Apple case study
- A comparison of the administration and policy of taxes in industrialised and emerging economies
- A detailed examination of the background and purposes of international tax treaties. How successful were they?
- An examination of the effects of taxation on small and medium-sized enterprises compared to giant corporations
- An examination of the effects of tax avoidance and evasion. An analysis of the worldwide Panama crisis and how tax fraud was carried out through offshore firms
- A critical analysis of how the administration of higher institutions is impacted by small business budgeting
- Recognising the importance of foreign currency in a nation’s economy. How can foreign exchange and remittances help a nation’s finances?
- An exploration of the best ways tax professionals may persuade customers to pay their taxes on time
- An investigation of the potential impact of tax and accounting education on the achievement of the nation’s leaders
- How the state might expand its revenue base by focusing on new taxing areas. Gaining knowledge of the digital content creation and freelance industries
- An evaluation of the negative impacts of income tax reduction. Will it prompt more people to begin paying taxes?
- A critical examination of the state’s use of tax revenue for human rights spending. A UK case study
- A review of the impact of income tax on new and small enterprises. Weighing the benefits and drawbacks
- A comprehensive study of managing costs so that money may flow into the national budget without interruption. A study of Norway as an example
- An overview of how effective taxes may contribute to a nation’s development of a welfare state. A study of Denmark as an example
- What are the existing problems that prevent the government systems from using the tax money they receive effectively and completely?
- What are people’s opinions of those who frequently avoid paying taxes?
- Explain the part tax officials play in facilitating tax fraud by accepting small bribes
- How do taxes finance the growth and financial assistance of the underprivileged in the UK?
- Is it appropriate to criticise the government for not providing adequate services when people and businesses fail to pay their taxes?
- A comprehensive comparison of current taxes and the Islamic zakat system is presented. Which one is more beneficial and effective for reducing poverty?
- A critical evaluation of the regulatory organisations was conducted to determine the tax percentage on different income groups in the UK.
- An investigation into tax evasion: How do wealthy, influential people influence the entire system?
- To contribute to the crucial growth of the nation, conduct a thorough investigation of enhancing tax benefits among British nationals.
- An assessment of the available research on the most effective ways to manage and maintain an uninterrupted flow of funds for a better economy.
- The effect and limitations of bilateral and multilateral tax treaties in addressing double taxation and preventing tax evasion.
- Assess solutions: OECD/G20 Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (BEPS) project and explore the implications for multinational corporations.
- The Impact of Tax cuts in Obtaining Social, monetary, and Aesthetic Ends That Benefit the Community.
- Exploring the Effect of Section 1031 of the Tax Code During Transactions on Investors and Business People.
- Investigating the role of environmental taxes and incentives in addressing global environmental challenges.
- Evaluating the impact of increased transparency on multinational enterprises and global efforts to combat tax evasion and illicit financial flows.
- Exploring the health and financial effects of a proposed policy to increase the excise tax on cigarettes.
Hire an Expert Writer
Orders completed by our expert writers are
- Formally drafted in an academic style
- Free Amendments and 100% Plagiarism Free – or your money back!
- 100% Confidential and Timely Delivery!
- Free anti-plagiarism report
- Appreciated by thousands of clients. Check client reviews

We hope that you will be able to write a first-class dissertation or thesis on one of the issues identified above at your own pace and submit a solid draft. If you wish to use any of the above taxation dissertation topics directly, you may do so. Many people, however, prefer tailor-made topics that meet their specific needs. If you need help with topics or a taxation dissertation, you can also use our dissertation writing services . Place your order now !
Free Dissertation Topic
Phone Number
Academic Level Select Academic Level Undergraduate Graduate PHD
Academic Subject
Area of Research
Frequently Asked Questions
How to find taxation dissertation topics.
To find taxation dissertation topics:
- Study recent tax reforms.
- Analyse cross-border tax issues.
- Explore digital taxation challenges.
- Investigate tax evasion or avoidance.
- Examine environmental tax policies.
- Select a topic aligned with law, economics, or business interests.
You May Also Like
Need interesting and manageable law dissertation topics or thesis? Here are the trending law dissertation titles so you can choose the most suitable one.
The study of cognitive psychology focuses on how the brain processes and stores information. The underlying mechanisms are investigated using experimental methods, computer modeling, and neuropsychology.
Are you looking for unique and intriguing branding dissertation topics, ideas and topic examples? If yes, continue reading this article because it provides several branding dissertation topic suggestions for your consideration.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In this paper, we have attempted to shed light on the notion of tax planning through a rich theoretical approach. Th us, we have based our analysis on the postulates of tax
Reviews on the Measurement of Tax Planning. 1) T he effective tax rate method. The most widely existing calculat ion method for tax planning is the effective tax rate method (ETR), because. of the ...
To calibrate the growing interest in AFIT research, we searched thetitles of papers published during the last decade in the . Journal of Accounting and Economics, the . Journal of Accounting Research, and . The Accounting Review. for the word "tax" or any variant. We find that 35% of the "tax" papers from 2004-2008 address AFIT
Tax Planning: Theory and Modeling. Saadia Kouroub, Lahcen Oubdi. Published in Journal of Applied Business… 30 August 2022. Economics, Law, Business. The majority of taxpayers, whether individuals or corporations, seek to reduce their tax burden or to benefit from a certain tax saving. In this sense, taxpayers resort to various legal or even ...
We use data envelopment analysis (DEA) to develop a measure of effective tax planning that is theoretically aligned with the Scholes-Wolfson paradigm and captur ... Brian, Effective Tax Planning (February 7, 2021). The Accounting Review, Forthcoming, Kelley School of Business Research Paper No. 2021-23, Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com ...
While many researchers hypothesize that reputational concerns affect the degree to which managers engage in tax planning, this hypothesis is difficult to test with archival data. ... Evidence from the Field (November 11, 2013). The Accounting Review, Vol. 89, No. 3, pp. 991-1023, May 2014, MIT Sloan Research Paper No. 4990-12, Available at SSRN ...
State of research within IB literature on MNEs and corporate tax planning. Because our paper adopts an IB perspective, we commence with a review of the existing relevant IB literature. We examine the contribution of IB papers and how they interact to provide a view of MNEs and their tax planning strategies. ... Recently, this qualitative ...
View PDF. Journal of Applied Business, Taxation and Economics Research (JABTER) P-ISSN 2828-4976 E-ISSN 2808-263X Vol. 1, No. 6, August 2022 (Page: 594-613) DOI: 10.54408/jabter.v1i6.100 Tax Planning: Theory and Modeling Saadia Kouroub1*, Lahcen Oubdi2 1*,2 ENCG Agadir, Ibn Zohr University, Morocco Corresponding Author: [email protected] ...
Working Paper 28775. DOI 10.3386/w28775. Issue Date May 2021. We examine the extent to which the labor market facilitates the diffusion of tax planning knowledge across firms. Using a novel dataset of tax department employee movements between S&P 1500 firms, we find that firms experience an increase in their tax planning after hiring a tax ...
It's important to follow proven steps for conducting tax research. Following a trusted process can help you make sure you've done your due diligence when researching tax issues. The steps for tax research include: Identifying and defining the facts and issues. Collecting relevant authorities.
Other supportive research. also conducted by Hidayat & Pesudo (2019) revealed. that tax planning has a positive effect on firm value, managerial ownership has a negative eff ect on firm. value ...
This paper reviews the literature that deals with international tax avoidance techniques by highlighting tax planning measurements in the empirical literature. The methodology used is the narrative approach of literature review, which consists on assembling and synthesizing previously published research. The paper concludes that there are ...
Tax planning means deferring and flat out avoiding tax by taking advantages of beneficial tax-law provision increasing, an accelerating tax deductions and tax credits, and generally making maximum use of ... Lack of previous experience in doing research was another difficulty. VIII. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY FOLLOWED IN THE PRESENT STUDY 2.1 POPULATION
Corporate Transparency . The Relationship. This study aims to identify and prove empirically the effect of Tax Planning, Capital Structure and Managerial Ownership on Firm Value with Corporate Transparency as a moderating variable. This type of research is quantitative approach research with explanatory research and associative methods.
That means people with higher taxable incomes are subject to higher tax rates, while people with lower taxable incomes are subject to lower tax rates. There are seven federal income tax brackets ...
An overview of the evolution of tax planning research is the goal of this study. Corporate tax planning, or the capacity of the corporation to plan its tax affairs, refers to the use of a variety ...
Period of the study opted was 1984-85 to 1997-. 98. The study revealed while the progressive tax rate structure was followed in the case of individual taxpayers in all these countries but the tax rates were found to be higher in developed countries than that of developing 88 countries. The level of income at which the maximum marginal rate was ...
By diverting the income to Mr. C, Mr. A has resorted to Tax Avoidance. 1.3.4 Tax Planning Tax Planning has been described as a refined form of 'tax avoidance' and implies arrangement of a person's financial affairs in such a way that it reduces the tax liability.
The main purpose of this paper is to investigate factors that influence taxpayers to engage in tax evasion. The researcher used descriptive and explanatory research design and followed a quantitative research approach. To undertake this study, primary and secondary data has been utilized. From the target population of 4979, by using a stratified and simple random sampling technique, 370 ...
Accordingly, this paper employs the narrative approach of literature review, which consists on assembling and synthesizing previously published research on international tax planning.
To find taxation dissertation topics: Study recent tax reforms. Analyse cross-border tax issues. Explore digital taxation challenges. Investigate tax evasion or avoidance. Examine environmental tax policies. Select a topic aligned with law, economics, or business interests.
This study. focusses on income tax p lanning for individuals f or the assessment y ear 2021-2022. Objective of the Study: Th e main objective of the study is to give ideas to minimise the tax ...