

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, where to find the best dbq examples.
Advanced Placement (AP)

One of the best ways to prepare for the DBQ (the "document-based question" on the AP European History, AP US History, and AP World History exams) is to look over sample questions and example essays. Doing this will help you to get a sense of what makes a good (and what makes a bad) DBQ response.
That said, not all DBQ essay examples are created equal. We'll briefly cover what makes a good DBQ example and then provide a list of example essays by course. Lastly, we'll give you some helpful tips on how to best use sample essays in your own preparation process.
What's a Good DBQ Example?
Without a doubt, the best sample resources come from the College Board . This is because they are the ones who design and administer the AP exams . This means the following:
Any DBQ essay example that the College Board provides will include a real DBQ prompt
All samples are real student responses from previous years , so you know they were written under the same conditions you'll have when you write your DBQ—in other words, they're authentic!
They not only have scores but also explanations of each essay's score , in accordance with the rubric
Each prompt includes several sample essays with a variety of scores
Some DBQ examples outside those available from the College Board might be worth looking at, particularly if they highlight how a particular essay could be improved. In general, though, a superior example will do the following:
Include the prompt and documents: It will be much easier for you to see how the information from the documents is integrated into the essay if you can actually look at the documents themselves!
Have a score: Seems simple, but you'd be surprised how many DBQ examples out there in the uncharted internet don't have one. Without a real, official score, it's hard to gauge how trustworthy a sample actually is.
With that in mind, I have compiled lists, organized by exam, of high-quality example DBQs below.

Don't spend all your study time on false starts with your practice DBQs.
Every DBQ Example Essay You Could Ever Need, by Exam
Here are your example essays! We'll start with AP US History, then move to AP European History, and finally wrap up with AP World History.
AP US History: Official College Board Examples
The APUSH test was redesigned in 2015 and again in 2018, so right now there are eight official College Board sets of sample essays you can use in your studies . Make sure to give yourself a 15-minute reading period and 45 minutes to write your answer. In addition, don't forget to use the current scoring guidelines when grading your own practice responses.
- 2023 Free-Response Questions | Scoring Guidelines 2023
- 2022 Free-Response Questions | Sample DBQ Responses 2022
- 2021 Free-Response Questions | Sample DBQ Responses 2021
- 2019 Free-Response Questions | Sample DBQ Responses 2019
- 2018 Free-Response Questions | Sample DBQ Responses 2018
- 2017 Free-Response Questions | Sample DBQ Responses 2017
- 2016 Free-Response Questions | Sample DBQ Responses 2016
- 2015 Free-Response Questions | Sample DBQ Responses 2015
If you want additional sample question sets, you can look at older College Board US History DBQ example response sets . To look at these, click "Free-Response Questions" for a given year. For the corresponding DBQ examples and scoring guidelines, click "Sample Responses Q1."
Note that these examples use the old rubric (which is integrated into the Scoring Guidelines for a given free-response section). General comments on the quality of the essay, outside information, and document analysis still apply, but the score is on a 9-point scale instead of the current 7-point scale, and some of the particulars will be different. Older DBQs had up to 12 documents, while the current format has seven documents.
If you do look at older DBQ examples, I recommend using the current rubric to re-grade the essays in the sample according to the 7-point scale. I'll also give more advice on how to use all these samples in your prep later on.

Mr. Bald Eagle is an AP US History DBQ grader in his spare time.
AP European History: Official College Board Examples
Unfortunately, there aren't as many sample resources for the AP Euro DBQ compared to the other AP history tests because 2016 was the first year the AP Euro test was administered in the new format . Since then, more minor changes have been made in terms of time (you now have an hour on the DBQ) and individual parts of the rubric (you can view the current scoring guidelines here ).
This means there are seven sets of official samples graded with the current 7-point rubric:
The rest of the existing available samples were graded in the old 9-point format instead of the 7-point format implemented in 2016.
In the old format, there were 6 "core" points and 3 additional points possible. The old rubric is integrated with the sample responses for each question, but we'll highlight some key differences between the old and current formats :
With the old format, you were given a brief "historical background" section before the documents
There were more documents—up to 12—but the current format has seven
There was an emphasis on "grouping" the documents that is not present in the current rubric
There was also explicit emphasis on correctly interpreting the documents that is not found in the current rubric
While the essential components of the DBQ are still the same between the two test formats, you should definitely refer to the current rubric if you decide to look at any old AP European History samples . You might find it useful to look at old essays and score them in accordance with the current rubric.
Here are the old sample DBQ questions and essays, organized by year:
- 2014 Free-Response Questions | Sample DBQ Responses 2014
- 2013 Free-Response Questions | Sample DBQ Responses 2013
- 2012 Free-Response Questions | Sample DBQ Responses 2012
- 2011 Free-Response Questions | Sample DBQ Responses 2011
You can get samples in the old format all the way back to 1999 from the College Board . (Click "Free -Response Questions" for the questions and "Sample Response Q1" for the samples.)

Consider how you might integrate this castle into the DBQ that is your life.
AP World History: Official College Board Examples
The World History AP exam transitioned to a new format to more closely resemble AP US History and AP European History for the 2017 test. This means that there are six past exams available that use the current DBQ format:
Note that starting with the 2020 exam, AP World History will only cover the years 1200 to the present instead of thousands of years of history. As a result, both the course and exam have been renamed AP World History: Modern (a World History: Ancient course is in the works). What this means for you is that previous DBQs might have to do with time periods you're no longer required to study, so just keep this in mind.
In the old format, there were 7 "core" points and 2 additional points possible. The old rubric is integrated with the sample responses for each question, but we'll highlight some key differences between the old and current formats :
There were more documents—up to 10—but the current format has seven
There was an emphasis on "grouping" the documents on the old rubric that is not present in the current rubric
- In the old rubric, you needed to identify one additional document that would aid in your analysis; the new rubric does not have this requirement
The essential components of the DBQ are still the same between the two formats, though you should definitely look at the current rubric if you study with any old AP World History questions and samples. You might find it useful to look at the old essays and score them according to the current rubric.
Here are old AP World History questions and DBQ sample responses , organized by year:

Don't worry, the old format isn't as old as this guy right here.
How Should I Use DBQ Examples to Prepare?
Now that you have all these examples, what should you do with them? In this section, we'll give you some tips on how to use example DBQs in your own AP history prep , including when to start using them and how many you should plan to review.
What Should I Do With These DBQs?
Official sample essay sets are a great way to test how well you understand the rubric. This is why we recommend that you grade a sample set early on in your study process—maybe even before you've written a practice DBQ .
Then, when you compare the scores you gave to the official scores and scoring notes given to the samples, you'll have a better idea of what parts of the rubric you don't really understand . If there are points you are consistently awarding differently than the graders, you’ll know those are skills you'll need to work on.
Keep giving points for the thesis and then finding out the sample didn't get those points? This tells you to work more on your thesis skills. Not giving points for historical context and then finding out the AP grader gave full credit? You need to work on recognizing what constitutes historical context according to the AP.
Check out my tips on building specific rubric-based skills in our guide on how to write a DBQ .
Once you've worked on some of those rubric skills you're weaker in, such as evaluating a good thesis or keeping track of how many documents were used, grade another sample set. This way you can see how your ability to grade the essays like an AP grader improves over time!
Obviously, grading sample exams is a much more difficult process if you're looking at examples in an old format. The old scores as awarded by the College Board will be helpful in establishing a ballpark —a 9 is still going to be a good essay using the current 7-point scale—but there may be some modest differences in grades between the two scales. (For example, maybe that perfect 9 is now more like a 6 out of 7 due to rubric changes.)
For practice grading with old samples, you might want to pull out two copies of the current rubric, recruit a trusted study buddy or academic advisor (or even two study buddies!), and have each of you re-grade the samples .
You can then discuss any major differences in the grades each of you awarded. Having multiple sets of eyes will help you determine whether the scores you're giving are reasonable, since you won’t have an official 7-point College Board score for comparison.

How Many Example DBQs Should I Be Using?
The answer to this question depends on your study plans.
If it's six months before the exam and you plan on transforming yourself into a hard diamond of DBQ excellence, you might do practice grading on a sample set every few weeks to a month to check your progress to being able to think like an AP grader. In this case, you would probably use six to nine official sample sets.
If, on the other hand, the exam is in a month and you're just trying to get in some extra skill-polishing, you might do a sample set every week to 10 days . It makes sense to check your skills more often when you have less time to study because you want to be sure that you are focusing your time on the skills that need the most work. For a short time frame, expect to use somewhere in the range of three to four official sample sets.
Either way, you should be integrating your sample essay grading with skills practice and doing some practice DBQ writing of your own .
Toward the end of your study time, you could even integrate DBQ writing practice with sample grading. Read and complete a timed prompt and then grade the sample set for that prompt, including yours! The other essays will help give you a sense of what score your essay might have received that year and any areas you might have overlooked.
There's no one-size-fits-all approach to using sample sets, but in general they are a useful tool for making sure you have a good idea what the DBQ graders will be looking for when you write your own DBQ on test day.

Hey, where can we find a good DBQ around here?
Closing Thoughts: Example DBQs for AP History Tests
Example DBQ essays are a valuable resource in your arsenal of study strategies for the AP history exams. Grading samples carefully will help you get a sense of your own blind spots so you'll know what skills to focus on in your prep.
That said, sample essays will be most useful when integrated with your own targeted skills prep . Grading 100 sample essays won't help you if you aren't practicing your skills; rather, you'll just keep making the same mistakes over and over again.
Make sure you aren't using sample essays to avoid writing practice DBQs either—you'll want to do at least a couple, even if you only have a month to practice.
And there you have it, folks. With this list of DBQ examples and tips on how to use them, you are all prepared to integrate samples into your study strategy!

What's Next?
Still not sure what a DBQ is? Check out my explanation of the DBQ to learn the basics.
Want tips on how to really dig in and study for AP history tests? We've got a complete how-to guide on preparing for and writing the DBQ .
If you're still studying for AP World History, check out our top AP World History study guide , or get more practice tests from our complete list .
Want more study material for AP US History? Look into this article on the best notes to use for studying from one of our experts. Also, read our review of the best AP US History textbooks !

Ellen has extensive education mentorship experience and is deeply committed to helping students succeed in all areas of life. She received a BA from Harvard in Folklore and Mythology and is currently pursuing graduate studies at Columbia University.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
How to Write the Document Based Question (DBQ)
Do you know how to improve your profile for college applications.
See how your profile ranks among thousands of other students using CollegeVine. Calculate your chances at your dream schools and learn what areas you need to improve right now — it only takes 3 minutes and it's 100% free.
Show me what areas I need to improve
What’s Covered:
What is the document based question, steps to writing an effective dbq, how do ap scores affect my college chances.
If you’re taking a history AP exam, you’ll likely encounter the Document Based Question (DBQ). This essay question constitutes a significant portion of your exam, so it’s important that you have a good grasp on how best to approach the DBQ. In this post, we’ll cover what exactly a document based question is, and how to answer it successfully.
A Document Based Question (DBQ) is a measure of the skills you learned in your AP classes in regard to recalling history and analyzing related documents. These documents can be primary or secondary sources, and your responses are expected to be in the form of an essay. Your ability to relate the context of documents to concepts beyond the given text and creating meaningful connections between all your sources will help demonstrate your skills as a knowledgeable writer.
The number of documents for a DBQ varies from exam to exam, but typically will fall between five to seven documents. The following AP exams will require you to write a DBQ:
AP U.S. History
AP European History
AP World History
We’ve listed the formats for each exam below, and keep in mind that the number of documents is prone to changing from year to year:
- Up to seven Documents
- One hour recommended time (includes 15-minute reading period)
- Up to seven Documents
- 25% of total exam score
With that in mind, let’s jump right into how to craft a strong DBQ response!
We’ve summarized how to write an effective DBQ into the following five steps:
1. Read the prompt first
Though you may be tempted to jump into the documents right away, it’s very important that you first look at what exactly the prompt is asking for. This way, when you eventually look at the documents, your focus will be narrower. A DBQ tests your reading comprehension and analysis skills more than the content itself, making it very important to understand your prompt thoroughly.
2. Skim the document titles
Each document will contain vital information regarding the context, and it’s important to scout key words regarding dates, authors, and anything pertaining to the general sense of what the documents are about. Skimming through your documents like this could save time and allow you to form a more structurally sound thesis.
Let’s take a look at the following graph and figure out how to skim the figure:
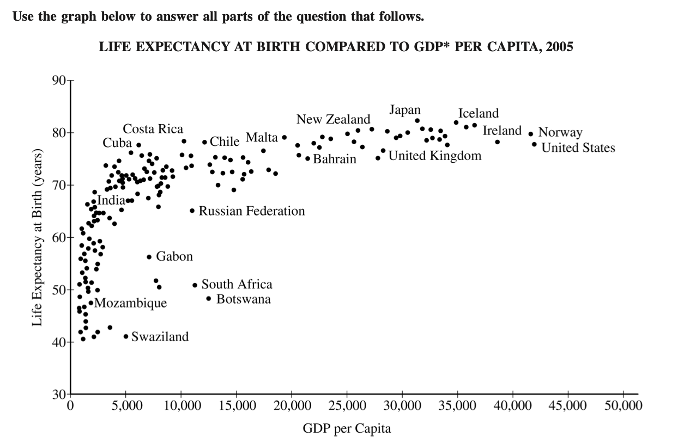
This document was in a real exam from the AP World History free response questions in 2019. It’s important to pay attention to data provided and what context can be drawn from it. In this case, we’re provided with a graph that displays the life expectancy of a country in relation to the GDP per capita of said country. Being able to skim this graph and notice the common trends in the data points could provide convenient information into the context of the document, without any further intensive reading.
For example, seeing how countries with a GDP below 4,000 to 5,000 have lower life expectancies already gives us a potential correlation between the two factors. We can use this information to start formulating a thesis, depending on what the prompt is specifically asking for.
Remember, just skim! Don’t worry about reading the entire document yet; this strategy can keep you calm and level-headed before tackling the rest of the document. Methods like this can make acing the AP World History DBQ less intimidating!
3. Formulate a tentative thesis
A thesis is a statement that should be proved and discussed upon. It’s important to have a strong thesis as the foundation of your DBQ, as it guides the rest of your response in relation to the context. Understanding the difference between weak and strong theses will be imperative to your success, so here is an example of a weak thesis:
“The Cold War originated from some scenarios of conflict between Soviets and some groups of oppressors.”
Such a thesis can be considered weak for its lack of specificity, focal point, and usability as a constructive tool to write further detail on the subject. This thesis does not take a clear stance or communicate to the reader what the essay will specifically focus on. Here’s how the same thesis can be restructured to be stronger and more useful:
“The Cold War originated from tense diplomatic conflicts relating to propaganda and conspiratorial warfare between the United States and the Soviet Union.”
The information that’s been included into the second thesis about the two groups involved with the Cold War gives you more room to build a structured essay response. In relation to the rubric/grading schema for this DBQ, forming a structurally sound thesis or claim is one of the seven attainable points. Being able to contextualize, analyze, and reason off of this thesis alone could provide for two to four points – this means that five out of seven of your points revolve around your thesis, so make sure that it’s strong! Doing all of this in your fifteen minute reading period is crucial as once this is set, writing your actual response will be much easier!
4. Actively read the documents
Simply reading a document doesn’t normally suffice for creating a well-written and comprehensive response. You should focus on implementing your active reading skills, as this will make a huge difference as to how efficient you are during your work process.
Active reading refers to reading with an intention to grab key words and fragments of important information, usually gone about by highlighting and separating important phrases. Annotations, underlining, and circling are all great ways to filter out important information from irrelevant text in the documents.
An example of where you might find important information via active reading is the description. Circle important names or dates to contextualize the document. If you still can’t find contextual value from the title, that’s totally fine! Just scope out the rest of the document in relevance to your thesis – that is, pinpoint the specific information or text that best supports your argument. Finding one or two solid points of interest from one document is usually enough to write about and expand upon within your essay.

Discover your chances at hundreds of schools
Our free chancing engine takes into account your history, background, test scores, and extracurricular activities to show you your real chances of admission—and how to improve them.

5. Make an Outline
If you like outlines, making one before writing your essay might prove helpful, just be aware of the time limit and act accordingly.
Start with your introduction, then work on the rest of your essay. This way, you can make sure your thesis is clear and strong, and it will help the graders form a clear view on what the general consensus of your paper is. Make sure to include evidence with your thesis within each paragraph and cite only relevant information, otherwise your citations could come across as filler as opposed to useful content. Every commentary or point you make should be tied in some way to the documents.
Format each body paragraph and organize your essay in a way that makes sense to you! The graders aren’t really looking at the structure of your essay; rather, they want to see that you analyzed the documents in a way that is supportive of your essay. As long as you have content from the documents which prove your thesis, the order or manner in which you present them doesn’t matter too much. What’s more important is that your essay is clear and comprehensive. As you write practice DBQs, try having someone else read your essays to make sure that the format is easy to follow.
Keep all these key details in mind as you construct your own DBQ response, and you’re well on your way to writing an effective essay!
Your chances of admission are actually not really impacted by your AP scores; however, the AP classes you take are more important than the exam scores themselves, meaning the impact of your AP scores isn’t as big as you think .
Instead, focusing on the AP classes on your transcript and the relevance of those classes to your future major is more impactful. For a further detailed understanding of the role AP classes play in regards to your college admissions, use CollegeVine’s free Admissions Calculator , which takes into account your GPA, standardized test scores, and more.
Additional Information
To dive deeper into DBQs, AP classes, and learning how to tackle each exam check out other resources at CollegeVine:
- Acing the Document Based Question on the AP US History Exam
- Acing the AP World History Document Based Question
- Ultimate Guide to the AP U.S. History Exam
- Ultimate Guide to the AP European History Exam
- Ultimate Guide to the AP World History Exam
Related CollegeVine Blog Posts

Find what you need to study
Score Higher on AP World History 2024: Tips for DBQs
1 min read • march 22, 2024
Exam simulation mode
Prep for the AP exam with questions that mimic the test!
This guide organizes advice from past students who got 4s and 5s on their exams. We hope it gives you some new ideas and tools for your study sessions. But remember, everyone's different—what works for one student might not work for you. If you've got a study method that's doing the trick, stick with it. Think of this as extra help, not a must-do overhaul.
- Students will be presented with seven documents that give various perspectives on a historical development or process and asked to develop an argument based on these documents and their own knowledge.
- 25% of Exam Score
- Recommended Time: 1 Hour (Includes a 15-minute reading period)
- Thesis/Claim (1)
- Contextualization (1)
- Evidence from 6 documents (2)
- Evidence beyond documents (1)
- Analyze 3 documents (1)
- Complexity (1)
💭 General Advice
Tips on mindset, strategy, structure, time management, and any other high level things to know
- You will technically have the DBQ and LEQ at the same time with 1 Hour and 40 Minutes total. However, the DBQ is worth more than the LEQ, so make sure to give yourself enough time to write your DBQ.
- A lot of students stress out over a DBQ because it has so many documents and seems so complex! To help mitigate this, try to think of this way the documents are helpful tools. You don't need to remember content, it's all right there for you! Don't stress over the outside evidence because it will come to you as you are using the documents and interacting with historical content.
- First, Source your documents in the thesis statement (ex: ...and resulted in a growth in capitalism (3, 4, 5), horrible working conditions (1, 2)... etc.).
- Do the same in your topic sentence of each body paragraph, and then, of course, source them when you refer to them the passage. Overall, you should source each document a total of 3 times.
- Secondly, include each source analysis "keyword" in your essay (ex: ...the POV of this document is.../the intended audience of this document is.../the historical context of this document is.../the purpose of this document is... ).
- Lastly, include the "keyword" of anything else you need to include in your essay (ex: "some outside historical evidence/knowledge that supports this is...").
- Make it clear to the reader/grader that you know what you are talking about and make it easy for them to check off every item from the rubric. This also helps you know if you completed everything you needed to get full points.
- Do a little extra in the essay as insurance. For example, instead of doing only 1 outside history evidence, do 2 or 3 in case you get one of them wrong. Do extra source analysis in case one of them isn't good enough, etc.
- It is essentially the "What?" and "Why?". Using a document's general idea to make your point not only helps organize your essay but makes it faster while writing it as well because most of the documents are linked in some way (same time period, about the same event, or an event that impacted another). So they will all often have a similar "What" and "Why," or any of the other big W's (who, what, when, where, why).
- Take a deep breath! Take your time reading through the documents and making the connections between each of them. You know more than you think!
🕛 Before You Write the DBQ
What should a student do in the first few minutes, before they start writing?
- Before you even look at the documents, you have to annotate the prompt! Make sure you know what it is asking, like is it an extent question? What’s the topic or the time period?
- Circle or underline certain different parts of the prompt just to make sure you understand.
- Skill of the prompt (what are they asking you to do with the topic?) This may be direct or vague - are they asking you to compare or contrast? Are they asking for a change or continuity? Are they asking for a cause or effect?
- READ THE PROMPT FIRST!!! You spend a lot of time reading through all of the documents and you NEED to know what you're looking for right from the start.
- Categorize the documents as you read. Based on the question, sort the documents based on their relevancy to your position or in any other way you see fit.
- When grouping/categorizing your documents ask yourself this question: Do those documents share the same value as the first document? If not, put them into a separate category and if they do put them in the same category as the first document! This will be the gateway into making your thesis with contrasting examples.
- Or if you’re a visual person, similar to the advice above, make a chart with two columns: one that is for the argument presented in the prompt and one that is against. It can be as simple as a check and and X. Organize the sources into which side they demonstrate best, then use the side that has more sources for your thesis and associated evidence, while the other side can be used in your counterclaim.
- While you're reading them, jot down ideas next to them. If you notice that Document 1 focuses on one perspective while Document 2 and 3 focus on another perspective, WRITE IT DOWN!!!
- Other things that you can note down is the purpose, perspective, biases, and context.
- Adding onto the above, being able to condense and re-express the documents is crucial to support whatever claim or main topic your essay will be about.
- When you are reading the documents, your eyes should ALWAYS go to the SOURCE FIRST!!! The source is so important. Many times the author, title, and especially the time period can tell you so much about the document BEFORE you even start reading.
- Take a few deep breaths and look at the documents. Make sure to comprehend the question first and then branch off on what possible controls can be used. If you have no idea what to do, gather evidence from the docs immediately and go from there.
- When reading look for key words in each document. Anything that sticks out to you can be underlined, such as who the document is addressed to, if it’s stated.
💡 Tips for Each DBQ Rubric Point
Thesis/claim.
- You can score up to 1 point for having this in your DBQ!
- After reading the question, take 30 seconds to think about how you plan to respond to the prompt.
- Before starting writing your introduction, write your claim off to the side so that you know what to write leading up to it.
- If time constraint is an issue for you, you can reduce it to 2 points as long as you make them strong. This is the foundation for the rest of your paper, so the thesis should be very clear on what it's about.
- Pick something defensible. You should be making your thesis after a strong understanding of what each of the documents says. Create a thesis that can be supported by at least 3 of the documents and don't be afraid to really flesh it out with the 'why' of your claim.
- “Within TIME PERIOD OF DBQ, three significant SKILL AND TOPIC OF PROMPT were the ARGUMENT/BP #1, ARGUMENT/BP #2 and ARGUMENT/BP #3.
Contextualization
- Before even looking at the documents, you need to brainstorm your contextualization! Nothing from the docs counts as context so it’s best to do it before, based on what the prompt is asking. Try to make a flow chart of at least 3 events that led up to the topic of the prompt and your context will already be done!
- If you get stuck/start blanking out about the time period, work backwards! First pick a year and then start jotting down key historical events/figures of that time. From there, you will be able to remember a lot of important topics that are relevant to the contextualization. Make sure that it is complete but do not spend too much time on it or going too far back. 2 sentences is plenty for contextualization.
- One thing: if you use information in your contextualization, you are no longer allowed to reuse it for outside evidence.
- Go 50-100 years back from the time of the prompt, but make sure that the information is relevant and does not go back further than a century.
- If you have been doing vocab lists throughout the year try and use some of those words (around 3-4) in this section. Think about the era of the DBQ and what major shifts had occurred or are in the process of occurring during that time period. This means that for this point periodization is an important skill to have for each unit. However, if you are extremely lost on the DBQ there are ways to try and earn the contextualization point by picking up on cultural norms or political tensions from the sources.
- When coming up with contextualization, you need to really think about telling a story. What major events led to the event/topic that is the focus of my essay?
- One way to think about it was like an upside-down pyramid where your most broad evidence goes at the top and your most specific evidence goes at the bottom, right before your thesis. Ideally, one should have about 3-4 good pieces of information in contextualization. 4 is recommended in case something is not correct. It's the same reason why you'd want to do extra HIPPs just in case you mess up.
- Another way to think of this is if it was a 'on last weeks episode' recap. So what happened to cause this or what were some developments that contributed to this topic? Or it’s similar to a lawsuit, there are a series of events that lead to the trial. There are always a set of factors or events that create the path to a certain development, which is easily applicable to the content in AP World.
- Context should never be more than two sentences. Pay attention to the time period given in the prompt and make a general statement describing what was going on before or during this time period. Don’t be too general and instead focus on information relevant to the prompt. For example, if the prompt asks about the Ottomans in the 1800s, you can contextualize by mentioning the Ottomans in the 1700s and how they had changed by the 1800s.
- As far as organization, contextualization can fit nicely after your thesis and before evidence since it offers background information. To write a more complex essay it is critical that your context matches the theme within the argument you are making.
Evidence from the Documents
- You can score up to 2 points for having this in your DBQ!
- Briefly review the documents prior to starting the essay and label which specific documents will support your thesis.
- Make note of the date!! If you misattribute a document to an incorrect time period, you will lose a lot of points.
- Remember to condense each document into a 1-2 sentence commentary in your own words, which will make drawing from each document much easier.
- Then you need to connect it to your argument. You can accomplish by saying “This shows or this illustrates” and then how it connect a to your argument. This is a format that you can use “Document X explains blah blah blah. This shows that blah blah blah”.
Evidence from Beyond the Documents
- Study and learn as much general knowledge as you can about Women’s’ Suffrage, WWI and WWII and big, HUGE events and timeframes like those because when it comes to their evidence, it will be a lot easier to connect it to topics like this in order to get points.
- There's not much to this other than knowing each of your units really well. If you have a solid foundation of the entire curriculum, this will not be particularly difficult. It is always worth the time to work backward and write down the key events/figures from a given period and then use that to support your claim.
- Cram sheets helps a lot for this because if you’re on a time crunch, knowing basic knowledge can help a lot on DBQ’s. With the help of a mentor (teacher), remember key units that are mentioned in the exam a lot like the Industrial Revolution or Pre-Modern Era. If you have more time in your hands, take a practice DBQ from the previous years found in college board and try to think of outside evidence on the spur of the moment to train yourself.
- If you know quite literally anything about the topic, just shove it in. The only requirement is that it must be relative to the prompt! Don't know what's going on with women in Cuba? Then say what's going on with women in America! It's much better than nothing. The good thing about AP World is that your range of usable information is much broader than in AP Euro or APUSH.
Document Analysis
- FRAME OF REFERENCE This is influenced by a person's gender, occupation, class, education, religion, personal interests, and other aspects of their being.
- HISTORICAL SITUATION This is made up of society's influences on a person. It can be societal values, economic pressures, political conditions, or other things which influence society. Examples: gas prices, war, theocratic government, revolution, etc.
- Having some kind of paper aside can help you the most on my exam. Write what your claim is, your 2/3 points, and the document you’d like to use. Then list 1-7 for each document provided on this aside and write POV, Purpose, Context, and Intended audience per document. This makes it clear on how to set up your essay and when to use what document.
- Remember, you don't need these specific analysis points for every single document. Usually, you unconsciously think through things like POV, purpose, context, and intended audience while reading. If one factor jumps out at you while reading, WRITE IT DOWN! It shouldn't be a stretch to make these analysis points work, most of the time they just make sense to include while paraphrasing evidence or when providing explanation.
- The idea is to put it in the form of "While [counter argument], it was ultimately [main argument]".
- For example, "While the Mongols played a large role in spreading the bubonic plague, it was ultimately trade routes such as the Silk Roads that were the main cause of the Black Death". Then, you can easily add a paragraph at the end discussing your counterargument, which counts as considering multiple perspectives!
- The easiest ways to get complexity is by introducing counterarguments and weaving together multiple pieces of evidence to create a narrative. The documents are intentionally supposed to contain views from many points, and by comparing the documents and doing sourcing to assess their validity, you have a very good shot of earning the complexity point.
- Adding onto the point above, if you have enough time, try to write a counterargument against your thesis that you then disprove. You can do this by bringing up the counterargument and then saying "while this and this may be true, my point is better due to this and this." If the rest of your DBQ is solid, then you have a very good shot of getting the complexity point with this format.

Stay Connected
© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.
AP® and SAT® are trademarks registered by the College Board, which is not affiliated with, and does not endorse this website.

AP® US History
Ensuring your students earn the contextualization point on the dbq.
- The Albert Team
- Last Updated On: March 1, 2022

The redesign has brought a great deal of uncertainty and confusion amongst APUSH teachers. In many ways, we are all “rookie” teachers, as all of us have the challenge of implementing fundamental curricular and skills-based changes into our classrooms.
One of the more significant changes is to the structure of one essay on the AP® exam, the Document Based question (DBQ). The rubric for the DBQ was previously a more holistic essay that combined a strong thesis, and use of documents and outside information to support the argument. This has been transformed into a much more structured and formulaic skills-based rubric. The change has led to a healthy debate about the pros and cons of both types of essays, but in general the core of the essay has remained the same: write a thesis and support it with evidence in the form of documents and outside information. If students continue to apply these basic writing skills, they are likely to earn 3 or 4 out of the seven total points for the Document Based Question .
In this post, we will explore one of these points students will be looking to earn to help their chances at passing the APUSH exam this May: the Contextualization point.
What is Contextualization?
According to the College Board, contextualization refers to a:
Historical thinking skill that involves the ability to connect historical events and processes to specific circumstances of time and place as well as broader regional, national, or global processes. ( College Board AP® Course and Exam Description, AP® US History, Fall 2015 )
Contextualization is a critical historical thinking skill that is featured in the newly redesigned course. In my opinion, this is a skill of fundamental importance for students to utilize in the classroom. Often times, students find history difficult or boring because they don’t see connections between different historical time periods and the world they live in today. They assume that events occur in a vacuum, and don’t realize that the historical context is critical in helping explain people’s beliefs and points of view in that period of time. Putting events into context is something I always thought was important, but now that the College Board explicitly has established the skill, it has forced me to be more proactive in creating lessons and assignments that allow students to utilize this way of thinking.
The place that contextualization is most directly relevant on the actual AP® exam itself is the Document Based Question. In order to earn the point for contextualization, students must:
Situate historical events, developments, or processes within the broader regional, national, or global context in which they occurred in order to draw conclusions about their relative significance. (College Board AP® Course and Exam Description, AP® US History, Fall 2015)
In other words, students are asked to provide background before jumping right into their thesis and essay and paint a picture of what is going on at the time of the prompt. Although there is no specific requirement as to where contextualization should occur, it makes natural sense to place it in the introduction right before a thesis point. Placing this historical background right at the beginning sets the stage for the argument that will occur in the body of the essay, and is consistent with expectations many English teachers have in how to write an introduction paragraph.
I explain contextualization to students by using the example of Star Wars. Before the movie starts, the film begins with “A long time ago in a galaxy far, far away…” and continues with background information on the characters, events, and other information that is crucial to understanding the film. Without this context, the viewer would not know what is going on, and might miss key events or be lost throughout the film. This is what contextualization aims to do in student essays. It sets the stage for their thesis, evidence, and argument that is to follow.
Contextualization vs. Historical Context
One aspect of the DBQ rubric that can be a bit confusing initially is that students are asked to do this contextualization, but there is also another area which gives them the option to use historical context. So what is the difference?
Contextualization refers to putting the entire essay into a broader context (preferably in the introduction). However, when writing their essays, students are also required to analyze four of the documents that they utilize by either examining the author’s point of view, describing the intended audience of the source, identifying the author’s purpose or putting the source into historical context. The latter sounds similar to contextualization (and it is essentially the same skill), but historical context is only focused on the specific document being analyzed, not the entire essay, like the contextualization point. For example, if a document is a map that shows slavery growing dramatically from 1820 to 1860, a student might point out that this growth can be explained in the context of the development of the cotton gin, which made the production of cotton much more profitable and let to the spread of slavery in the Deep South. While essentially the same skill, historical context focuses on one specific document’s background.
Examples of Successful Student Contextualization Points
One of the biggest pitfalls that prevent students from earning the contextualization point is that they are too brief or vague. In general, it would be difficult for students to earn the point if they are writing only a sentence or two. Early in the year, I assigned students a DBQ based on the following prompt:
Evaluate the extent in which the Civil War was a turning point in the lives of African Americans in the United States. Use the documents and your knowledge of the years 1860-1877 to construct your response.

This was the third DBQ we had written, and students were now getting brave enough to move beyond a thesis and document analysis and started attempting to tackle the contextualization point. However, the attempts were all over the map. One student wrote:
The Civil War was a bloody event that led to the death of thousands of Americans.
Of course this is a true statement, but is extremely vague. What led to the Civil War? Why was it so deadly? Without any specific detail, this student could not earn the contextualization point.
Another student wrote:
Slavery had existed for hundreds of years in the United States. It was a terrible thing that had to be abolished.
Again, this is a drive-by attempt at earning contextualization. It mentions things that are true, but lacks any meaningful details or explanation that would demonstrate understanding of the time period in discussion. What led to the beginning of slavery in the colonies? How did it develop? What made it so horrible? How did individuals resist and protest slavery? These are the types of details that would add meaning to contextualization.
One student nailed it. She wrote:
The peculiar institution of slavery had been a part of America’s identity since the founding of the original English colony at Jamestown. In the early years, compromise was key to avoiding the moral question, but as America entered the mid 19th century sectional tensions and crises with popular sovereignty, Kansas, and fugitive slaves made the issue increasingly unavoidable. When the Civil War began, the war was transformed from one to simply save the Union to a battle for the future of slavery and freedom in the United States.
Now THAT is contextualization! It gives specific details about the beginning of slavery and its development. It discusses attempts at compromise, but increasing sectional tensions that led to the Civil War. The writer paints a vivid and clear picture of the situation, events, and people that set the stage for the Civil War. Students don’t want to write a 6-8 sentence paragraph (they will want to save time for their argument in the body), but they need to do more than write a vague sentence that superficially addresses the era.
Strategies for Teaching Contextualization to Students
Analyze Lots of Primary Sources One of the best ways to prepare for the DBQ is for students to practice reading and comprehending primary source texts, particularly texts that are written by people who use very different language and sentence structure from today. This helps them understand and analyze documents, but it also can be helpful in practicing contextualization. Looking at different perspectives and points of view in the actual historical time periods they are learning is key in allowing students to understand how the era can impact beliefs, values and events that occur.
Assign Many DBQ Assessments and Share Specific Examples The more often students write DBQs, the more comfortable students will get with the entire process and skill set involved, including contextualization. One thing that has been especially successful in my classroom is to collect a handful of student attempts at the contextualization point and share them with students. Students then get to examine them and look at effective and less effective attempts at earning contextualization. Often the best way for students to learn what to do or how to improve is to see what their classmates have done.
Incorporating In-Class Activities The course is broken into nine distinct time periods from 1491 to present. In each period or unit students are assigned activities that force them to put a specific policy, event, or movement into context. For example, we did lecture notes on the presidency of JFK, learning about the Man on the Moon Speech, Cuban Missile Crisis, and creation of the Peace Corps. Students had to write 3-4 sentences that asked them to put these events in historical context using the Cold War. This allowed students to understand that each of these seemingly unrelated historical events were shaped by the tension between the United States and Soviet Union: winning the space race, stopping a communist nuclear threat less than 100 miles from Florida, and spreading goodwill into nations that might otherwise turn to communism all are strategies the United States used to thwart the Soviet threat. By doing this activity, students gain an appreciation for how historical context shapes events and decisions of the day.

Teach Cause and Effect in United States History It is very easy to get caught up as a teacher in how to best get lots of minutia and factoids into students heads quickly and efficiently. However, if we can teach history not as a series of independent and unrelated events, but as a series of events that have a causal relationship that impact what happens next, this helps students grasp and understand contextualization. For example, in the lead-up to World War I, students create a timeline of events that led to America entering the conflict. As students examine the torpedoing of the Lusitania, unrestricted submarine warfare, the Zimmermann telegram, etc., they gain an understanding that it was not a random decision by President Wilson, but rather a series of events that precipitated the declaration of war. This is what contextualization is: the background that sets the stage for a particular moment in American history.
Examine Contextualization with Current Events I know what you are thinking, I have one school year (less if your school year starts in September) to get through 1491 to Present and now I am supposed to make this a current events class as well? The answer is yes and no. Will stuff from the news pages be content the students need to know for the exam: absolutely not. However, it is a great opportunity for students to understand that our past explains why our country is what it is today.
For example, President Obama’s decision to work towards normalizing relations with Cuba makes more sense if students think about it through the lens of contextualization. The United States invaded Cuba in 1898 in the Spanish-American War and set up a protectorate. Cubans, upset with what they perceived as U.S. meddling and intervention led a communist revolution in 1959, ousting the American-backed government and setting the stage for one of the scariest moments in the Cold War : the Cuban Missile Crisis. Looking at how the past shapes current events today helps students understand this skill, and it also helps them gain a deeper appreciation of how important history is in shaping the world around them.

Any time changes happen, there is a temptation to be reactionary and reject them. I have found that by being more deliberate about helping students understand historical context, their engagement and understanding have improved significantly. Teachers always are fighting that battle between covering the content (which is daunting in an AP® course) and helping students understand the “so what?” question. Why does this matter to me? By making connections, students can see that history does not every happen in a vacuum. Our shared narrative is a series of events and ideas that continuously evolve and build off of each other. When students gain a firm understanding of how the past impacts their lives today, it makes learning way more meaningful and fun.
Contextualization is tough for students at first, but it is a skill application that can be perfected and improved to maximize your students’ chances of earning that point and rocking the AP® exam.
Looking for AP® US History practice?
Kickstart your AP® US History prep with Albert. Start your AP® exam prep today .
We also go over five-steps to writing effective FRQs for AP® US History in this video:

Ben Hubing is an educator at Greendale High School in Greendale, Wisconsin. Ben has taught AP® U.S. History and AP® U.S. Government and Politics for the last eight years and was a reader last year for the AP® U.S. History Short Answer. Ben earned his Bachelors degree at The University of Wisconsin-Madison and Masters degree at Cardinal Stritch University in Milwaukee, Wisconsin.
Interested in a school license?
4 thoughts on “ensuring your students earn the contextualization point on the dbq”.
great very helpful!
Glad it helped!
Very useful, thank you.
Glad it was helpful!
Comments are closed.
Popular Posts

AP® Score Calculators
Simulate how different MCQ and FRQ scores translate into AP® scores

AP® Review Guides
The ultimate review guides for AP® subjects to help you plan and structure your prep.

Core Subject Review Guides
Review the most important topics in Physics and Algebra 1 .

SAT® Score Calculator
See how scores on each section impacts your overall SAT® score

ACT® Score Calculator
See how scores on each section impacts your overall ACT® score

Grammar Review Hub
Comprehensive review of grammar skills

AP® Posters
Download updated posters summarizing the main topics and structure for each AP® exam.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Let's take a look at a sample AP World History DBQ question and techniques to construct a solid thesis. Using the following documents, analyze how the Ottoman government viewed ethnic and religious groups within its empire for the period 1876-1908. Identify an additional document and explain how it would help you analyze the views of the ...
To answer the AP World History DBQ, you'll have to read through all seven documents and write an argumentative essay that answers the prompt. So not only will you have to come up with an arguable point, you'll have to prove that thesis using evidence contained in at least three of the seven documents.
AP World DBQ Contextualization and Thesis Practice. Practicing DBQ prompts is a great way to prep for the AP exam! Review practice writing samples of the opening paragraph of a DBQ and corresponding feedback from Fiveable teachers Melissa Longnecker, Eric Beckman, and Evan Liddle.
The intent of this question was to assess students' ability to articulate and defend an argument based on evidence provided by a select set of historical documents. The Document-Based Question (DBQ) asked students to evaluate the extent to which European imperialism had an impact on the economies of Africa and/or Asia.
The DBQ, or document-based-question, is a somewhat unusually-formatted timed essay on the AP History Exams: AP US History, AP European History, and AP World History. Because of its unfamiliarity, many students are at a loss as to how to even prepare, let alone how to write a successful DBQ essay on test day. Never fear!
If you're taking AP World History or AP United States History and feel unsure about how to approach the DBQ thesis, you've come to the right place! In this post, you'll learn about a DBQ thesis formula that you can use to: A) consistently earn the thesis point and
Resources from Heimler's History: To master all the WRITING SKILLS you need, get my ESSAY CRAM COURSE: +AP Essay CRAM Course (DBQ, LEQ, SAQ Help): https://bi...
Step 2: Plan Your Response. Next, take time to plan your response. Focus on formulating a strong thesis, and check your plan against the six DBQ requirements. See the sample plan that a high-scoring writer might make. Scoring requirements are written in bold for reference; note that the writer includes six of the seven documents and plans to ...
The foreign influence from close and a far sparked revolts from the native people of China and allowed foreigners to manipulate the system. First, a main factor of the collapse of the Qing dynasty was the European involvement and influence on the economy and politics. An example was the Opium trade.
Question 1: Document-Based Question, Economic Factors in the Mexican Revolution 7 points General Scoring Notes • Except where otherwise noted, each point of these rubrics is earned independently; for example, a student could earn a point for evidence without earning a point for thesis/claim.
Evan Liddle. M. Melissa Longnecker. DBQ Practice is very important when preparing for the AP World exam. It is recommended to write a short brief outline of your argument before writing your body paragraph. Your task: In 20 minutes or less, read the documents and: Outline arguments you would make, using LESS than a full sentence for each.
DBQ Strategy 1: Analyze the Prompt. Most prompts will test one of the following historical reasoning skills: causation, continuity and change over time, or comparison. Look for keywords in the prompt that indicate which skill is being tested (for instance, "changes" often indicates continuity and change over time, while phrases such as ...
One of the best ways to prepare for the DBQ (the "document-based question" on the AP European History, AP US History, and AP World History exams) is to look over sample questions and example essays. Doing this will help you to get a sense of what makes a good (and what makes a bad) DBQ response. That said, not all DBQ essay examples are created equal.
You will have 45 minutes total to analyze documents and write your essay, and 5 minutes to upload your response. A good breakdown would be. 15 min. (reading & analysis) + 30 min. (writing) = 45 min. + 5 min. (upload) The DBQ is scored on a rubric out of seven points and is weighted at 25% of your overall exam score.
The following AP exams will require you to write a DBQ: AP U.S. History; AP European History; AP World History We've listed the formats for each exam below, and keep in mind that the number of documents is prone to changing from year to year: AP U.S. History. Up to seven Documents; One hour recommended time (includes 15-minute reading period)
AP ® World History: Modern Sample Student Responses and Scoring Commentary Set 2 ... Document-Based Question 5 Scoring Guidelines 5 Student Samples 5 Scoring Commentary . ... The thesis or claim must consist of one or more sentences located in one place, either in the introduction or the conclusion (which may not be limited to ...
Flag every directive word or key phrase in the question prompt. 3. Plan out your response BEFORE you start writing. 4. Double check you've made explicit references to connections in your writing. 5. Practice, practice, and then practice some more. 37 AP® World History and Politics FRQ Tips to Scoring a 4 or 5.
Document-Based Question ... AP® WORLD HISTORY 2018 SCORING GUIDELINES ©2018 The College Board Visit the College Board on the Web: www.collegeboard.org Question 1 — Document-Based Question . ... 1918." Points Rubric Notes A: Thesis/Claim (0-1) Responds to the prompt with a historically defensible thesis/claim that establishes a line of
Overview. The intent of this question was to assess students' ability to articulate and defend an argument based on historical documents. This DBQ asked students to evaluate the extent to which states and religions differed in their views regarding wealth accumulation in both the classical and post-classical eras.
Basic WHAP DBQ Thesis Formula "Within TIME PERIOD OF DBQ, three significant SKILL AND TOPIC OF PROMPT were the ARGUMENT/BP #1, ARGUMENT/BP #2 and ARGUMENT/BP #3. Contextualization. You can score up to 1 point for having this in your DBQ! Before even looking at the documents, you need to brainstorm your contextualization!
Use the documents and your knowledge of the years 1860-1877 to construct your response. This was the third DBQ we had written, and students were now getting brave enough to move beyond a thesis and document analysis and started attempting to tackle the contextualization point. However, the attempts were all over the map.
c) Explain ONE way in which changes in Eurasian societies' subsistence patterns altered their political or social structures in the period circa 10,000 B.C.E. to 600 B.C.E. Answer all parts of the question that follows. 4. a) Identify ONE economic change in the period 1750-1900 that led to the formation of new elites.
Created by an experienced AP U.S. History teacher and AP test grader, this PowerPoint® presentation shows students a step-by-step method for formulating and composing a well-written response to the AP U.S. History DBQ. The first part of the presentation lays out a method for breaking down the process of