- Privacy Policy

Home » How To Write A Proposal – Step By Step Guide [With Template]

How To Write A Proposal – Step By Step Guide [With Template]
Table of Contents

How To Write A Proposal
Writing a Proposal involves several key steps to effectively communicate your ideas and intentions to a target audience. Here’s a detailed breakdown of each step:
Identify the Purpose and Audience
- Clearly define the purpose of your proposal: What problem are you addressing, what solution are you proposing, or what goal are you aiming to achieve?
- Identify your target audience: Who will be reading your proposal? Consider their background, interests, and any specific requirements they may have.
Conduct Research
- Gather relevant information: Conduct thorough research to support your proposal. This may involve studying existing literature, analyzing data, or conducting surveys/interviews to gather necessary facts and evidence.
- Understand the context: Familiarize yourself with the current situation or problem you’re addressing. Identify any relevant trends, challenges, or opportunities that may impact your proposal.
Develop an Outline
- Create a clear and logical structure: Divide your proposal into sections or headings that will guide your readers through the content.
- Introduction: Provide a concise overview of the problem, its significance, and the proposed solution.
- Background/Context: Offer relevant background information and context to help the readers understand the situation.
- Objectives/Goals: Clearly state the objectives or goals of your proposal.
- Methodology/Approach: Describe the approach or methodology you will use to address the problem.
- Timeline/Schedule: Present a detailed timeline or schedule outlining the key milestones or activities.
- Budget/Resources: Specify the financial and other resources required to implement your proposal.
- Evaluation/Success Metrics: Explain how you will measure the success or effectiveness of your proposal.
- Conclusion: Summarize the main points and restate the benefits of your proposal.
Write the Proposal
- Grab attention: Start with a compelling opening statement or a brief story that hooks the reader.
- Clearly state the problem: Clearly define the problem or issue you are addressing and explain its significance.
- Present your proposal: Introduce your proposed solution, project, or idea and explain why it is the best approach.
- State the objectives/goals: Clearly articulate the specific objectives or goals your proposal aims to achieve.
- Provide supporting information: Present evidence, data, or examples to support your claims and justify your proposal.
- Explain the methodology: Describe in detail the approach, methods, or strategies you will use to implement your proposal.
- Address potential concerns: Anticipate and address any potential objections or challenges the readers may have and provide counterarguments or mitigation strategies.
- Recap the main points: Summarize the key points you’ve discussed in the proposal.
- Reinforce the benefits: Emphasize the positive outcomes, benefits, or impact your proposal will have.
- Call to action: Clearly state what action you want the readers to take, such as approving the proposal, providing funding, or collaborating with you.
Review and Revise
- Proofread for clarity and coherence: Check for grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors.
- Ensure a logical flow: Read through your proposal to ensure the ideas are presented in a logical order and are easy to follow.
- Revise and refine: Fine-tune your proposal to make it concise, persuasive, and compelling.
Add Supplementary Materials
- Attach relevant documents: Include any supporting materials that strengthen your proposal, such as research findings, charts, graphs, or testimonials.
- Appendices: Add any additional information that might be useful but not essential to the main body of the proposal.
Formatting and Presentation
- Follow the guidelines: Adhere to any specific formatting guidelines provided by the organization or institution to which you are submitting the proposal.
- Use a professional tone and language: Ensure that your proposal is written in a clear, concise, and professional manner.
- Use headings and subheadings: Organize your proposal with clear headings and subheadings to improve readability.
- Pay attention to design: Use appropriate fonts, font sizes, and formatting styles to make your proposal visually appealing.
- Include a cover page: Create a cover page that includes the title of your proposal, your name or organization, the date, and any other required information.
Seek Feedback
- Share your proposal with trusted colleagues or mentors and ask for their feedback. Consider their suggestions for improvement and incorporate them into your proposal if necessary.
Finalize and Submit
- Make any final revisions based on the feedback received.
- Ensure that all required sections, attachments, and documentation are included.
- Double-check for any formatting, grammar, or spelling errors.
- Submit your proposal within the designated deadline and according to the submission guidelines provided.
Proposal Format
The format of a proposal can vary depending on the specific requirements of the organization or institution you are submitting it to. However, here is a general proposal format that you can follow:
1. Title Page:
- Include the title of your proposal, your name or organization’s name, the date, and any other relevant information specified by the guidelines.
2. Executive Summary:
- Provide a concise overview of your proposal, highlighting the key points and objectives.
- Summarize the problem, proposed solution, and anticipated benefits.
- Keep it brief and engaging, as this section is often read first and should capture the reader’s attention.
3. Introduction:
- State the problem or issue you are addressing and its significance.
- Provide background information to help the reader understand the context and importance of the problem.
- Clearly state the purpose and objectives of your proposal.
4. Problem Statement:
- Describe the problem in detail, highlighting its impact and consequences.
- Use data, statistics, or examples to support your claims and demonstrate the need for a solution.
5. Proposed Solution or Project Description:
- Explain your proposed solution or project in a clear and detailed manner.
- Describe how your solution addresses the problem and why it is the most effective approach.
- Include information on the methods, strategies, or activities you will undertake to implement your solution.
- Highlight any unique features, innovations, or advantages of your proposal.
6. Methodology:
- Provide a step-by-step explanation of the methodology or approach you will use to implement your proposal.
- Include a timeline or schedule that outlines the key milestones, tasks, and deliverables.
- Clearly describe the resources, personnel, or expertise required for each phase of the project.
7. Evaluation and Success Metrics:
- Explain how you will measure the success or effectiveness of your proposal.
- Identify specific metrics, indicators, or evaluation methods that will be used.
- Describe how you will track progress, gather feedback, and make adjustments as needed.
- Present a detailed budget that outlines the financial resources required for your proposal.
- Include all relevant costs, such as personnel, materials, equipment, and any other expenses.
- Provide a justification for each item in the budget.
9. Conclusion:
- Summarize the main points of your proposal.
- Reiterate the benefits and positive outcomes of implementing your proposal.
- Emphasize the value and impact it will have on the organization or community.
10. Appendices:
- Include any additional supporting materials, such as research findings, charts, graphs, or testimonials.
- Attach any relevant documents that provide further information but are not essential to the main body of the proposal.
Proposal Template
Here’s a basic proposal template that you can use as a starting point for creating your own proposal:
Dear [Recipient’s Name],
I am writing to submit a proposal for [briefly state the purpose of the proposal and its significance]. This proposal outlines a comprehensive solution to address [describe the problem or issue] and presents an actionable plan to achieve the desired objectives.
Thank you for considering this proposal. I believe that implementing this solution will significantly contribute to [organization’s or community’s goals]. I am available to discuss the proposal in more detail at your convenience. Please feel free to contact me at [your email address or phone number].
Yours sincerely,
Note: This template is a starting point and should be customized to meet the specific requirements and guidelines provided by the organization or institution to which you are submitting the proposal.
Proposal Sample
Here’s a sample proposal to give you an idea of how it could be structured and written:
Subject : Proposal for Implementation of Environmental Education Program
I am pleased to submit this proposal for your consideration, outlining a comprehensive plan for the implementation of an Environmental Education Program. This program aims to address the critical need for environmental awareness and education among the community, with the objective of fostering a sense of responsibility and sustainability.
Executive Summary: Our proposed Environmental Education Program is designed to provide engaging and interactive educational opportunities for individuals of all ages. By combining classroom learning, hands-on activities, and community engagement, we aim to create a long-lasting impact on environmental conservation practices and attitudes.
Introduction: The state of our environment is facing significant challenges, including climate change, habitat loss, and pollution. It is essential to equip individuals with the knowledge and skills to understand these issues and take action. This proposal seeks to bridge the gap in environmental education and inspire a sense of environmental stewardship among the community.
Problem Statement: The lack of environmental education programs has resulted in limited awareness and understanding of environmental issues. As a result, individuals are less likely to adopt sustainable practices or actively contribute to conservation efforts. Our program aims to address this gap and empower individuals to become environmentally conscious and responsible citizens.
Proposed Solution or Project Description: Our Environmental Education Program will comprise a range of activities, including workshops, field trips, and community initiatives. We will collaborate with local schools, community centers, and environmental organizations to ensure broad participation and maximum impact. By incorporating interactive learning experiences, such as nature walks, recycling drives, and eco-craft sessions, we aim to make environmental education engaging and enjoyable.
Methodology: Our program will be structured into modules that cover key environmental themes, such as biodiversity, climate change, waste management, and sustainable living. Each module will include a mix of classroom sessions, hands-on activities, and practical field experiences. We will also leverage technology, such as educational apps and online resources, to enhance learning outcomes.
Evaluation and Success Metrics: We will employ a combination of quantitative and qualitative measures to evaluate the effectiveness of the program. Pre- and post-assessments will gauge knowledge gain, while surveys and feedback forms will assess participant satisfaction and behavior change. We will also track the number of community engagement activities and the adoption of sustainable practices as indicators of success.
Budget: Please find attached a detailed budget breakdown for the implementation of the Environmental Education Program. The budget covers personnel costs, materials and supplies, transportation, and outreach expenses. We have ensured cost-effectiveness while maintaining the quality and impact of the program.
Conclusion: By implementing this Environmental Education Program, we have the opportunity to make a significant difference in our community’s environmental consciousness and practices. We are confident that this program will foster a generation of individuals who are passionate about protecting our environment and taking sustainable actions. We look forward to discussing the proposal further and working together to make a positive impact.
Thank you for your time and consideration. Should you have any questions or require additional information, please do not hesitate to contact me at [your email address or phone number].
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Grant Proposal – Example, Template and Guide

How To Write A Business Proposal – Step-by-Step...

Business Proposal – Templates, Examples and Guide

How To Write A Research Proposal – Step-by-Step...

Proposal – Types, Examples, and Writing Guide

How to choose an Appropriate Method for Research?
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Business How to Write a Research Proposal: A Step-by-Step
How to Write a Research Proposal: A Step-by-Step
Written by: Danesh Ramuthi Nov 29, 2023

A research proposal is a structured outline for a planned study on a specific topic. It serves as a roadmap, guiding researchers through the process of converting their research idea into a feasible project.
The aim of a research proposal is multifold: it articulates the research problem, establishes a theoretical framework, outlines the research methodology and highlights the potential significance of the study. Importantly, it’s a critical tool for scholars seeking grant funding or approval for their research projects.
Crafting a good research proposal requires not only understanding your research topic and methodological approaches but also the ability to present your ideas clearly and persuasively. Explore Venngage’s Proposal Maker and Research Proposals Templates to begin your journey in writing a compelling research proposal.
What to include in a research proposal?
In a research proposal, include a clear statement of your research question or problem, along with an explanation of its significance. This should be followed by a literature review that situates your proposed study within the context of existing research.
Your proposal should also outline the research methodology, detailing how you plan to conduct your study, including data collection and analysis methods.
Additionally, include a theoretical framework that guides your research approach, a timeline or research schedule, and a budget if applicable. It’s important to also address the anticipated outcomes and potential implications of your study. A well-structured research proposal will clearly communicate your research objectives, methods and significance to the readers.

How to format a research proposal?
Formatting a research proposal involves adhering to a structured outline to ensure clarity and coherence. While specific requirements may vary, a standard research proposal typically includes the following elements:
- Title Page: Must include the title of your research proposal, your name and affiliations. The title should be concise and descriptive of your proposed research.
- Abstract: A brief summary of your proposal, usually not exceeding 250 words. It should highlight the research question, methodology and the potential impact of the study.
- Introduction: Introduces your research question or problem, explains its significance, and states the objectives of your study.
- Literature review: Here, you contextualize your research within existing scholarship, demonstrating your knowledge of the field and how your research will contribute to it.
- Methodology: Outline your research methods, including how you will collect and analyze data. This section should be detailed enough to show the feasibility and thoughtfulness of your approach.
- Timeline: Provide an estimated schedule for your research, breaking down the process into stages with a realistic timeline for each.
- Budget (if applicable): If your research requires funding, include a detailed budget outlining expected cost.
- References/Bibliography: List all sources referenced in your proposal in a consistent citation style.

How to write a research proposal in 11 steps?
Writing a research proposal in structured steps ensures a comprehensive and coherent presentation of your research project. Let’s look at the explanation for each of the steps here:
Step 1: Title and Abstract Step 2: Introduction Step 3: Research objectives Step 4: Literature review Step 5: Methodology Step 6: Timeline Step 7: Resources Step 8: Ethical considerations Step 9: Expected outcomes and significance Step 10: References Step 11: Appendices
Step 1: title and abstract.
Select a concise, descriptive title and write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology and expected outcomes. The abstract should include your research question, the objectives you aim to achieve, the methodology you plan to employ and the anticipated outcomes.
Step 2: Introduction
In this section, introduce the topic of your research, emphasizing its significance and relevance to the field. Articulate the research problem or question in clear terms and provide background context, which should include an overview of previous research in the field.
Step 3: Research objectives
Here, you’ll need to outline specific, clear and achievable objectives that align with your research problem. These objectives should be well-defined, focused and measurable, serving as the guiding pillars for your study. They help in establishing what you intend to accomplish through your research and provide a clear direction for your investigation.
Step 4: Literature review
In this part, conduct a thorough review of existing literature related to your research topic. This involves a detailed summary of key findings and major contributions from previous research. Identify existing gaps in the literature and articulate how your research aims to fill these gaps. The literature review not only shows your grasp of the subject matter but also how your research will contribute new insights or perspectives to the field.
Step 5: Methodology
Describe the design of your research and the methodologies you will employ. This should include detailed information on data collection methods, instruments to be used and analysis techniques. Justify the appropriateness of these methods for your research.
Step 6: Timeline
Construct a detailed timeline that maps out the major milestones and activities of your research project. Break the entire research process into smaller, manageable tasks and assign realistic time frames to each. This timeline should cover everything from the initial research phase to the final submission, including periods for data collection, analysis and report writing.
It helps in ensuring your project stays on track and demonstrates to reviewers that you have a well-thought-out plan for completing your research efficiently.
Step 7: Resources
Identify all the resources that will be required for your research, such as specific databases, laboratory equipment, software or funding. Provide details on how these resources will be accessed or acquired.
If your research requires funding, explain how it will be utilized effectively to support various aspects of the project.
Step 8: Ethical considerations
Address any ethical issues that may arise during your research. This is particularly important for research involving human subjects. Describe the measures you will take to ensure ethical standards are maintained, such as obtaining informed consent, ensuring participant privacy, and adhering to data protection regulations.
Here, in this section you should reassure reviewers that you are committed to conducting your research responsibly and ethically.
Step 9: Expected outcomes and significance
Articulate the expected outcomes or results of your research. Explain the potential impact and significance of these outcomes, whether in advancing academic knowledge, influencing policy or addressing specific societal or practical issues.
Step 10: References
Compile a comprehensive list of all the references cited in your proposal. Adhere to a consistent citation style (like APA or MLA) throughout your document. The reference section not only gives credit to the original authors of your sourced information but also strengthens the credibility of your proposal.
Step 11: Appendices
Include additional supporting materials that are pertinent to your research proposal. This can be survey questionnaires, interview guides, detailed data analysis plans or any supplementary information that supports the main text.
Appendices provide further depth to your proposal, showcasing the thoroughness of your preparation.

Research proposal FAQs
1. how long should a research proposal be.
The length of a research proposal can vary depending on the requirements of the academic institution, funding body or specific guidelines provided. Generally, research proposals range from 500 to 1500 words or about one to a few pages long. It’s important to provide enough detail to clearly convey your research idea, objectives and methodology, while being concise. Always check
2. Why is the research plan pivotal to a research project?
The research plan is pivotal to a research project because it acts as a blueprint, guiding every phase of the study. It outlines the objectives, methodology, timeline and expected outcomes, providing a structured approach and ensuring that the research is systematically conducted.
A well-crafted plan helps in identifying potential challenges, allocating resources efficiently and maintaining focus on the research goals. It is also essential for communicating the project’s feasibility and importance to stakeholders, such as funding bodies or academic supervisors.

Mastering how to write a research proposal is an essential skill for any scholar, whether in social and behavioral sciences, academic writing or any field requiring scholarly research. From this article, you have learned key components, from the literature review to the research design, helping you develop a persuasive and well-structured proposal.
Remember, a good research proposal not only highlights your proposed research and methodology but also demonstrates its relevance and potential impact.
For additional support, consider utilizing Venngage’s Proposal Maker and Research Proposals Templates , valuable tools in crafting a compelling proposal that stands out.
Whether it’s for grant funding, a research paper or a dissertation proposal, these resources can assist in transforming your research idea into a successful submission.
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
Writing Your Research Proposal
5 Essentials You Need To Keep In Mind
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewer: Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) | June 2023
Writing a high-quality research proposal that “sells” your study and wins the favour (and approval) of your university is no small task. In this post, we’ll share five critical dos and don’ts to help you navigate the proposal writing process.
This post is based on an extract from our online course , Research Proposal Bootcamp . In the course, we walk you through the process of developing an A-grade proposal, step by step, with plain-language explanations and loads of examples. If it’s your first time writing a research proposal, you definitely want to check that out.
Overview: 5 Proposal Writing Essentials
- Understand your university’s requirements and restrictions
- Have a clearly articulated research problem
- Clearly communicate the feasibility of your research
- Pay very close attention to ethics policies
- Focus on writing critically and concisely
1. Understand the rules of the game
All too often, we see students going through all the effort of finding a unique and valuable topic and drafting a meaty proposal, only to realise that they’ve missed some critical information regarding their university’s requirements.
Every university is different, but they all have some sort of requirements or expectations regarding what students can and can’t research. For example:
- Restrictions regarding the topic area that can be research
- Restrictions regarding data sources – for example, primary or secondary
- Requirements regarding methodology – for example, qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods-based research
- And most notably, there can be varying expectations regarding topic originality – does your topic need to be super original or not?
The key takeaway here is that you need to thoroughly read through any briefing documents provided by your university. Also, take a look at past dissertations or theses from your program to get a feel for what the norms are . Long story short, make sure you understand the rules of the game before you start playing.

2. Have a clearly articulated research problem
As we’ve explained many times on this blog, all good research starts with a strong research problem – without a problem, you don’t have a clear justification for your research. Therefore, it’s essential that you have clarity regarding the research problem you’re going to address before you start drafting your proposal. From the research problem , the research gap emerges and from the research gap, your research aims , objectives and research questions emerge. These then guide your entire dissertation from start to end.
Needless to say, all of this starts with the literature – in other words, you have to spend time reading the existing literature to understand the current state of knowledge. You can’t skip this all-important step. All too often, we see students make the mistake of trying to write up a proposal without having a clear understanding of the current state of the literature, which is just a recipe for disaster. You’ve got to take the time to understand what’s already been done before you can propose doing something new.

3. Demonstrate the feasibility of your research
One of the key concerns that reviewers or assessors have when deciding to approve or reject a research proposal is the practicality/feasibility of the proposed research , given the student’s resources (which are usually pretty limited). You can have a brilliant research topic that’s super original and valuable, but if there is any question about whether the project is something that you can realistically pull off, you’re going to run into issues when it comes to getting your proposal accepted.
So, what does this mean for you?
First, you need to make sure that the research topic you’ve chosen and the methodology you’re planning to use is 100% safe in terms of feasibility . In other words, you need to be super certain that you can actually pull off this study. Of greatest importance here is the data collection and analysis aspect – in other words, will you be able to get access to the data you need, and will you be able to analyse it?
Second, assuming you’re 100% confident that you can pull the research off, you need to clearly communicate that in your research proposal. To do this, you need to proactively think about all the concerns the reviewer or supervisor might have and ensure that you clearly address these in your proposal. Remember, the proposal is a one-way communication – you get one shot (per submission) to make your case, and there’s generally no Q&A opportunity . So, make it clear what you’ll be doing, what the potential risks are and how you’ll manage those risks to ensure that your study goes according to plan.
If you have the word count available, it’s a good idea to present a project plan , ideally using something like a Gantt chart. You can also consider presenting a risk register , where you detail the potential risks, their likelihood and impact, and your mitigation and response actions – this will show the assessor that you’ve really thought through the practicalities of your proposed project. If you want to learn more about project plans and risk registers, we cover these in detail in our proposal writing course, Research Proposal Bootcamp , and we also provide templates that you can use.
Need a helping hand?
4. Pay close attention to ethics policies
This one’s a biggy – and it can often be a dream crusher for students with lofty research ideas. If there’s one thing that will sink your research proposal faster than anything else, it’s non-compliance with your university’s research ethics policy . This is simply a non-negotiable, so don’t waste your time thinking you can convince your institution otherwise. If your proposed research runs against any aspect of your institution’s ethics policies, it’s a no-go.
The ethics requirements for dissertations can vary depending on the field of study, institution, and country, so we can’t give you a list of things you need to do, but some common requirements that you should be aware of include things like:
- Informed consent – in other words, getting permission/consent from your study’s participants and allowing them to opt out at any point
- Privacy and confidentiality – in other words, ensuring that you manage the data securely and respect people’s privacy
- If your research involves animals (as opposed to people), you’ll need to explain how you’ll ensure ethical treatment, how you’ll reduce harm or distress, etc.
One more thing to keep in mind is that certain types of research may be acceptable from an ethics perspective, but will require additional levels of approval . For example, if you’re planning to study any sort of vulnerable population (e.g., children, the elderly, people with mental health conditions, etc.), this may be allowed in principle but requires additional ethical scrutiny. This often involves some sort of review board or committee, which slows things down quite a bit. Situations like this aren’t proposal killers, but they can create a much more rigid environment , so you need to consider whether that works for you, given your timeline.

5. Write critically and concisely
The final item on the list is more generic but just as important to the success of your research proposal – that is, writing critically and concisely .
All too often, students fall short in terms of critical writing and end up writing in a very descriptive manner instead. We’ve got a detailed blog post and video explaining the difference between these two types of writing, so we won’t go into detail here. However, the simplest way to distinguish between the two types of writing is that descriptive writing focuses on the what , while analytical writing draws out the “so what” – in other words, what’s the impact and relevance of each point that you’re making to the bigger issue at hand.
In the case of a research proposal, the core task at hand is to convince the reader that your planned research deserves a chance . To do this, you need to show the reviewer that your research will (amongst other things) be original , valuable and practical . So, when you’re writing, you need to keep this core objective front of mind and write with purpose, taking every opportunity to link what you’re writing about to that core purpose of the proposal.
The second aspect in relation to writing is to write concisely . All too often, students ramble on and use far more word count than is necessary. Part of the problem here is that their writing is just too descriptive (the previous point) and part of the issue is just a lack of editing .
The keyword here is editing – in other words, you don’t need to write the most concise version possible on your first try – if anything, we encourage you to just thought vomit as much as you can in the initial stages of writing. Once you’ve got everything down on paper, then you can get down to editing and trimming down your writing . You need to get comfortable with this process of iteration and revision with everything you write – don’t try to write the perfect first draft. First, get the thoughts out of your head and onto the paper , then edit. This is a habit that will serve you well beyond your proposal, into your actual dissertation or thesis.

Wrapping Up
To recap, the five essentials to keep in mind when writing up your research proposal include:
If you want to learn more about how to craft a top-notch research proposal, be sure to check out our online course for a comprehensive, step-by-step guide. Alternatively, if you’d like to get hands-on help developing your proposal, be sure to check out our private coaching service , where we hold your hand through the research journey, step by step.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Research Proposal Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

Thanks alot, I am really getting you right with focus on how to approach my research work soon, Insha Allah, God blessed you.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
11.2 Steps in Developing a Research Proposal
Learning objectives.
- Identify the steps in developing a research proposal.
- Choose a topic and formulate a research question and working thesis.
- Develop a research proposal.
Writing a good research paper takes time, thought, and effort. Although this assignment is challenging, it is manageable. Focusing on one step at a time will help you develop a thoughtful, informative, well-supported research paper.
Your first step is to choose a topic and then to develop research questions, a working thesis, and a written research proposal. Set aside adequate time for this part of the process. Fully exploring ideas will help you build a solid foundation for your paper.
Choosing a Topic
When you choose a topic for a research paper, you are making a major commitment. Your choice will help determine whether you enjoy the lengthy process of research and writing—and whether your final paper fulfills the assignment requirements. If you choose your topic hastily, you may later find it difficult to work with your topic. By taking your time and choosing carefully, you can ensure that this assignment is not only challenging but also rewarding.
Writers understand the importance of choosing a topic that fulfills the assignment requirements and fits the assignment’s purpose and audience. (For more information about purpose and audience, see Chapter 6 “Writing Paragraphs: Separating Ideas and Shaping Content” .) Choosing a topic that interests you is also crucial. You instructor may provide a list of suggested topics or ask that you develop a topic on your own. In either case, try to identify topics that genuinely interest you.
After identifying potential topic ideas, you will need to evaluate your ideas and choose one topic to pursue. Will you be able to find enough information about the topic? Can you develop a paper about this topic that presents and supports your original ideas? Is the topic too broad or too narrow for the scope of the assignment? If so, can you modify it so it is more manageable? You will ask these questions during this preliminary phase of the research process.
Identifying Potential Topics
Sometimes, your instructor may provide a list of suggested topics. If so, you may benefit from identifying several possibilities before committing to one idea. It is important to know how to narrow down your ideas into a concise, manageable thesis. You may also use the list as a starting point to help you identify additional, related topics. Discussing your ideas with your instructor will help ensure that you choose a manageable topic that fits the requirements of the assignment.
In this chapter, you will follow a writer named Jorge, who is studying health care administration, as he prepares a research paper. You will also plan, research, and draft your own research paper.
Jorge was assigned to write a research paper on health and the media for an introductory course in health care. Although a general topic was selected for the students, Jorge had to decide which specific issues interested him. He brainstormed a list of possibilities.
If you are writing a research paper for a specialized course, look back through your notes and course activities. Identify reading assignments and class discussions that especially engaged you. Doing so can help you identify topics to pursue.
- Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs) in the news
- Sexual education programs
- Hollywood and eating disorders
- Americans’ access to public health information
- Media portrayal of health care reform bill
- Depictions of drugs on television
- The effect of the Internet on mental health
- Popularized diets (such as low-carbohydrate diets)
- Fear of pandemics (bird flu, HINI, SARS)
- Electronic entertainment and obesity
- Advertisements for prescription drugs
- Public education and disease prevention
Set a timer for five minutes. Use brainstorming or idea mapping to create a list of topics you would be interested in researching for a paper about the influence of the Internet on social networking. Do you closely follow the media coverage of a particular website, such as Twitter? Would you like to learn more about a certain industry, such as online dating? Which social networking sites do you and your friends use? List as many ideas related to this topic as you can.
Narrowing Your Topic
Once you have a list of potential topics, you will need to choose one as the focus of your essay. You will also need to narrow your topic. Most writers find that the topics they listed during brainstorming or idea mapping are broad—too broad for the scope of the assignment. Working with an overly broad topic, such as sexual education programs or popularized diets, can be frustrating and overwhelming. Each topic has so many facets that it would be impossible to cover them all in a college research paper. However, more specific choices, such as the pros and cons of sexual education in kids’ television programs or the physical effects of the South Beach diet, are specific enough to write about without being too narrow to sustain an entire research paper.
A good research paper provides focused, in-depth information and analysis. If your topic is too broad, you will find it difficult to do more than skim the surface when you research it and write about it. Narrowing your focus is essential to making your topic manageable. To narrow your focus, explore your topic in writing, conduct preliminary research, and discuss both the topic and the research with others.
Exploring Your Topic in Writing
“How am I supposed to narrow my topic when I haven’t even begun researching yet?” In fact, you may already know more than you realize. Review your list and identify your top two or three topics. Set aside some time to explore each one through freewriting. (For more information about freewriting, see Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” .) Simply taking the time to focus on your topic may yield fresh angles.
Jorge knew that he was especially interested in the topic of diet fads, but he also knew that it was much too broad for his assignment. He used freewriting to explore his thoughts so he could narrow his topic. Read Jorge’s ideas.
Conducting Preliminary Research
Another way writers may focus a topic is to conduct preliminary research . Like freewriting, exploratory reading can help you identify interesting angles. Surfing the web and browsing through newspaper and magazine articles are good ways to start. Find out what people are saying about your topic on blogs and online discussion groups. Discussing your topic with others can also inspire you. Talk about your ideas with your classmates, your friends, or your instructor.
Jorge’s freewriting exercise helped him realize that the assigned topic of health and the media intersected with a few of his interests—diet, nutrition, and obesity. Preliminary online research and discussions with his classmates strengthened his impression that many people are confused or misled by media coverage of these subjects.
Jorge decided to focus his paper on a topic that had garnered a great deal of media attention—low-carbohydrate diets. He wanted to find out whether low-carbohydrate diets were as effective as their proponents claimed.
Writing at Work
At work, you may need to research a topic quickly to find general information. This information can be useful in understanding trends in a given industry or generating competition. For example, a company may research a competitor’s prices and use the information when pricing their own product. You may find it useful to skim a variety of reliable sources and take notes on your findings.
The reliability of online sources varies greatly. In this exploratory phase of your research, you do not need to evaluate sources as closely as you will later. However, use common sense as you refine your paper topic. If you read a fascinating blog comment that gives you a new idea for your paper, be sure to check out other, more reliable sources as well to make sure the idea is worth pursuing.
Review the list of topics you created in Note 11.18 “Exercise 1” and identify two or three topics you would like to explore further. For each of these topics, spend five to ten minutes writing about the topic without stopping. Then review your writing to identify possible areas of focus.
Set aside time to conduct preliminary research about your potential topics. Then choose a topic to pursue for your research paper.
Collaboration
Please share your topic list with a classmate. Select one or two topics on his or her list that you would like to learn more about and return it to him or her. Discuss why you found the topics interesting, and learn which of your topics your classmate selected and why.
A Plan for Research
Your freewriting and preliminary research have helped you choose a focused, manageable topic for your research paper. To work with your topic successfully, you will need to determine what exactly you want to learn about it—and later, what you want to say about it. Before you begin conducting in-depth research, you will further define your focus by developing a research question , a working thesis, and a research proposal.
Formulating a Research Question
In forming a research question, you are setting a goal for your research. Your main research question should be substantial enough to form the guiding principle of your paper—but focused enough to guide your research. A strong research question requires you not only to find information but also to put together different pieces of information, interpret and analyze them, and figure out what you think. As you consider potential research questions, ask yourself whether they would be too hard or too easy to answer.
To determine your research question, review the freewriting you completed earlier. Skim through books, articles, and websites and list the questions you have. (You may wish to use the 5WH strategy to help you formulate questions. See Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” for more information about 5WH questions.) Include simple, factual questions and more complex questions that would require analysis and interpretation. Determine your main question—the primary focus of your paper—and several subquestions that you will need to research to answer your main question.
Here are the research questions Jorge will use to focus his research. Notice that his main research question has no obvious, straightforward answer. Jorge will need to research his subquestions, which address narrower topics, to answer his main question.
Using the topic you selected in Note 11.24 “Exercise 2” , write your main research question and at least four to five subquestions. Check that your main research question is appropriately complex for your assignment.
Constructing a Working ThesIs
A working thesis concisely states a writer’s initial answer to the main research question. It does not merely state a fact or present a subjective opinion. Instead, it expresses a debatable idea or claim that you hope to prove through additional research. Your working thesis is called a working thesis for a reason—it is subject to change. As you learn more about your topic, you may change your thinking in light of your research findings. Let your working thesis serve as a guide to your research, but do not be afraid to modify it based on what you learn.
Jorge began his research with a strong point of view based on his preliminary writing and research. Read his working thesis statement, which presents the point he will argue. Notice how it states Jorge’s tentative answer to his research question.
One way to determine your working thesis is to consider how you would complete sentences such as I believe or My opinion is . However, keep in mind that academic writing generally does not use first-person pronouns. These statements are useful starting points, but formal research papers use an objective voice.
Write a working thesis statement that presents your preliminary answer to the research question you wrote in Note 11.27 “Exercise 3” . Check that your working thesis statement presents an idea or claim that could be supported or refuted by evidence from research.
Creating a Research Proposal
A research proposal is a brief document—no more than one typed page—that summarizes the preliminary work you have completed. Your purpose in writing it is to formalize your plan for research and present it to your instructor for feedback. In your research proposal, you will present your main research question, related subquestions, and working thesis. You will also briefly discuss the value of researching this topic and indicate how you plan to gather information.
When Jorge began drafting his research proposal, he realized that he had already created most of the pieces he needed. However, he knew he also had to explain how his research would be relevant to other future health care professionals. In addition, he wanted to form a general plan for doing the research and identifying potentially useful sources. Read Jorge’s research proposal.

Before you begin a new project at work, you may have to develop a project summary document that states the purpose of the project, explains why it would be a wise use of company resources, and briefly outlines the steps involved in completing the project. This type of document is similar to a research proposal. Both documents define and limit a project, explain its value, discuss how to proceed, and identify what resources you will use.
Writing Your Own Research Proposal
Now you may write your own research proposal, if you have not done so already. Follow the guidelines provided in this lesson.
Key Takeaways
- Developing a research proposal involves the following preliminary steps: identifying potential ideas, choosing ideas to explore further, choosing and narrowing a topic, formulating a research question, and developing a working thesis.
- A good topic for a research paper interests the writer and fulfills the requirements of the assignment.
- Defining and narrowing a topic helps writers conduct focused, in-depth research.
- Writers conduct preliminary research to identify possible topics and research questions and to develop a working thesis.
- A good research question interests readers, is neither too broad nor too narrow, and has no obvious answer.
- A good working thesis expresses a debatable idea or claim that can be supported with evidence from research.
- Writers create a research proposal to present their topic, main research question, subquestions, and working thesis to an instructor for approval or feedback.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
How to write a good research proposal (in 9 steps)
A good research proposal is one of the keys to academic success. For bachelor’s and master’s students, the quality of a research proposal often determines whether the master’s program= can be completed or not. For PhD students, a research proposal is often the first step to securing a university position. This step-by-step manual guides you through the main stages of proposal writing.
Disclosure: This post may contain affiliate links, which means I may earn a small commission if you make a purchase using the links below at no additional cost to you . I only recommend products or services that I truly believe can benefit my audience. As always, my opinions are my own.
1. Find a topic for your research proposal
2. develop your research idea, 3. conduct a literature review for your research proposal, 4. define a research gap and research question, 5. establish a theoretical framework for your research proposal, 6. specify an empirical focus for your research proposal, 7. emphasise the scientific and societal relevance of your research proposal, 8. develop a methodology in your research proposal, 9. illustrate your research timeline in your research proposal.
Finding a topic for your research is a crucial first step. This decision should not be treated lightly.
Writing a master’s thesis takes a minimum of several weeks. In the case of PhD dissertations, it takes years. That is a long time! You don’t want to be stuck with a topic that you don’t care about.
How to find a research topic? Start broadly: Which courses did you enjoy? What issues discussed during seminars or lectures did you like? What inspired you during your education? And which readings did you appreciate?
Take a blank piece of paper. Write down everything that comes to your mind. It will help you to reflect on your interests.
Then, think more strategically. Maybe you have a rough idea of where you would like to work after graduation. Maybe a specific sector. Or even a particular company. If so, you could strategically alight your thesis topic with an issue that matters to your dream employer. Or even ask for a thesis internship.
Once you pinpoint your general topic of interest, you need to develop your idea.
Your idea should be simultaneously original, make a scientific contribution, prepare you for the (academic) job market, and be academically sound.
Freaking out yet?! Take a deep breath.
First, keep in mind that your idea should be very focused. Master and PhD students are often too ambitious. Your time is limited. So you need to be pragmatic. It is better to make a valuable contribution to a very specific question than to aim high and fail to meet your objectives.
Second, writing a research proposal is not a linear process. Start slowly by reading literature about your topic of interest. You have an interest. You read. You rethink your idea. You look for a theoretical framework. You go back to your idea and refine it. It is a process.
Remember that a good research proposal is not written in a day.
And third, don’t forget: a good proposal aims to establish a convincing framework that will guide your future research. Not to provide all the answers already. You need to show that you have a feasible idea.

If you are looking to elevate your writing and editing skills, I highly recommend enrolling in the course “ Good with Words: Writing and Editing Specialization “, which is a 4 course series offered by the University of Michigan. This comprehensive program is conveniently available as an online course on Coursera, allowing you to learn at your own pace. Plus, upon successful completion, you’ll have the opportunity to earn a valuable certificate to showcase your newfound expertise!
Academic publications (journal articles and books) are the foundation of any research. Thus, academic literature is a good place to start. Especially when you still feel kind of lost regarding a focused research topic.
Type keywords reflecting your interests, or your preliminary research idea, into an academic search engine. It can be your university’s library, Google Scholar , Web of Science , or Scopus . etcetera.
Look at what has been published in the last 5 years, not before. You don’t want to be outdated.
Download interesting-sounding articles and read them. Repeat but be cautious: You will never be able to read EVERYTHING. So set yourself a limit, in hours, days or number of articles (20 articles, for instance).
Now, write down your findings. What is known about your topic of interest? What do scholars focus on? Start early by writing down your findings and impressions.
Once you read academic publications on your topic of interest, ask yourself questions such as:
- Is there one specific aspect of your topic of interest that is neglected in the existing literature?
- What do scholars write about the existing gaps on the topic? What are their suggestions for future research?
- Is there anything that YOU believe warrants more attention?
- Do scholars maybe analyze a phenomenon only in a specific type of setting?
Asking yourself these questions helps you to formulate your research question. In your research question, be as specific as possible.
And keep in mind that you need to research something that already exists. You cannot research how something develops 20 years into the future.

A theoretical framework is different from a literature review. You need to establish a framework of theories as a lens to look at your research topic, and answer your research question.
A theory is a general principle to explain certain phenomena. No need to reinvent the wheel here.
It is not only accepted but often encouraged to make use of existing theories. Or maybe you can combine two different theories to establish your framework.
It also helps to go back to the literature. Which theories did the authors of your favourite publications use?
There are only very few master’s and PhD theses that are entirely theoretical. Most theses, similar to most academic journal publications, have an empirical section.
You need to think about your empirical focus. Where can you find answers to your research question in real life? This could be, for instance, an experiment, a case study, or repeated observations of certain interactions.
Maybe your empirical investigation will have geographic boundaries (like focusing on one city, or one country). Or maybe it focuses on one group of people (such as the elderly, CEOs, doctors, you name it).
It is also possible to start the whole research proposal idea with empirical observation. Maybe you’ve come across something in your environment that you would like to investigate further.
Pinpoint what fascinates you about your observation. Write down keywords reflecting your interest. And then conduct a literature review to understand how others have approached this topic academically.
Both master’s and PhD students are expected to make a scientific contribution. A concrete gap or shortcoming in the existing literature on your topic is the easiest way to justify the scientific relevance of your proposed research.
Societal relevance is increasingly important in academia, too.
Do the grandparent test: Explain what you want to do to your grandparents (or any other person for that matter). Explain why it matters. Do your grandparents understand what you say? If so, well done. If not, try again.
Always remember. There is no need for fancy jargon. The best proposals are the ones that use clear, straightforward language.
The methodology is a system of methods that you will use to implement your research. A methodology explains how you plan to answer your research question.
A methodology involves for example methods of data collection. For example, interviews and questionnaires to gather ‘raw’ data.
Methods of data analysis are used to make sense of this data. This can be done, for instance, by coding, discourse analysis, mapping or statistical analysis.
Don’t underestimate the value of a good timeline. Inevitably throughout your thesis process, you will feel lost at some point. A good timeline will bring you back on track.
Make sure to include a timeline in your research proposal. If possible, not only describe your timeline but add a visual illustration, for instance in the form of a Gantt chart.
Master Academia
Get new content delivered directly to your inbox.
Subscribe and receive Master Academia's quarterly newsletter.
PhD thesis types: Monograph and collection of articles
Ten reasons not to pursue an academic career, related articles.

How to address data privacy and confidentiality concerns of AI in research

How to properly use AI in academic research

The best online courses for PhD researchers in 2024

Why and how to conduct a systematic literature review
- 301 Academic Skills Centre
- Study skills online
How to write a research proposal
Advice and guidance on writing a proposal for a student research project.

Purpose of a Research Proposal
A research proposal should describe what you will investigate, why it is important to the discipline and how you will conduct your research.
Simply put, it is your plan for the research you intend to conduct. All research proposals are designed to persuade someone about how and why your intended project is worthwhile.
In your proposal you will need to explain and defend your choices. Always think about the exact reasons why you are making specific choices and why they are the best options available to you and your project.
Your research proposal aims should be centred on:
- Relevance - You want to convince the reader how and why your research is relevant and significant to your field and how it is original. This is typically done in parts of the introduction and the literature review.
- Context - You should demonstrate that you are familiar with the field, you understand the current state of research on the topic and your ideas have a strong academic basis (i.e., not simply based on your instincts or personal views). This will be the focus of your introduction and literature review.
- Approach - You need to make a case for your methodology, showing that you have carefully thought about the data, tools and procedures you will need to conduct the research. You need to explicitly defend all of your choices. This will be presented in the research design section.
- Feasibility - You need to demonstrate clearly that your project is both reasonable and feasible within the practical constraints of the course, timescales, institution or funding. You need to make sure you have the time and access to resources to complete the project in a reasonable period.
301 Recommends:
Our Research Writing workshop will look at some of the main writing challenges associated with writing a large-scale research project and look at strategies to manage your writing on a day-to-day basis. It will identify ways to plan, organise and map out the structure of your writing to allow you to develop an effective writing schedule and make continuous progress on your dissertation project.
Proposal format
The format of a research proposal varies between fields and levels of study but most proposals should contain at least these elements: introduction, literature review, research design and reference list.
Generally, research proposals can range from 500-1500 words or one to a few pages long. Typically, proposals for larger projects such as a PhD dissertation or funding requests, are longer and much more detailed.
Remember, the goal of your research proposal is to outline clearly and concisely exactly what your research will entail and accomplish, how it will do so and why it is important. If you are writing to a strictly enforced word count, a research proposal can be a great test of your ability to express yourself concisely!
Introduction
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project, so make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why. In other words, this is where you answer the reader’s “so what?” It should typically include: introducing the topic , outlining your problem statement and research question(s) and giving background and context. Some important questions to shape your introduction include:
- Who has an interest in the topic (e.g. scientists, practitioners, policymakers, particular members of society)?
- How much is already known about the problem and why is it important?
- What is missing from current knowledge and why?
- What new insights will your research contribute?
- Why is this research worth doing?
If your proposal is very long, you might include separate sections with more detailed information on the background and context, problem statement, aims and objectives, and importance of the research.
Literature Review
It’s important to show that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review convinces the reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory (i.e. how it relates to established research in the field).
Your literature review will also show that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said. This is also where you explain why your research is necessary. You might want to consider some of the following prompts:
- Comparing and contrasting: what are the main theories, methods, debates and controversies?
- Being critical: what are the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches?
- Showing how your research fits in: how will you build on, challenge or synthesise the work of others?
- Filling a gap in the existing body of research: why is your idea innovative?
Research design and methods
Following the literature review, it is a good idea to restate your main objectives, bringing the focus back to your own project. The research design/ methodology section should describe the overall approach and practical steps you will take to answer your research questions. You also need to demonstrate the feasibility of the project keeping in mind time and other constraints.
You should definitely include:
- Qualitative vs quantitative research? Combination?
- Will you collect original data or work with primary/secondary sources?
- Is your research design descriptive, correlational or experimental? Something completely different?
- If you are undertaking your own study, when and where will you collect the data? How will you select subjects or sources? Ethics review? Exactly what or who will you study?
- What tools and procedures will you use (e.g. systematic reviews, surveys, interviews, observation, experiments, bibliographic data) to collect your data?
- What tools/methods will you use to analyse your data?
- Why are these the best methods to answer your research question(s)? This is where you should justify your choices.
- How much time will you need to collect the data?
- How will you gain access to participants and sources?
- Do you foresee any potential obstacles and if so, how will you address them?
Make sure you are not simply compiling a list of methods. Instead, aim to make an argument for why this is the most appropriate, valid and reliable way to approach answering your question. Remember you should always be defending your choices!
Implications and Contributions to Knowledge
To ensure you finish your proposal on a strong note, it is a good idea to explore and/or emphasise the potential implications of the research. This means: what do you intend to contribute to existing knowledge on the topic?
Although you cannot know the results of your research until you have actually done the work, you should be going into the project with a clear idea of how your work will contribute to your field. This section might even be considered the most critical to your research proposal’s argument because it expresses exactly why your research is necessary.
You should consider covering at least some of the following topics:
- Ways in which your work can challenge existing theories and assumptions in your field.
- How your work will create the foundation for future research and theory.
- The practical value your findings will provide to practitioners, educators and other academics in your field.
- The problems or issues your work can potentially help to resolve.
- Policies that could be impacted by your findings.
- How your findings can be implemented in academia or other settings and how this will improve or otherwise transform these settings.
This part is not about stating the specific results that you expect to obtain but rather, this is the section where you explicitly state how your findings will be valuable.
This section is where you want to wrap it all up in a nice pretty bow. It is just like the concluding paragraph that you would structure and craft for a typical essay. You should briefly summarise your research proposal and reinforce your research purpose.
Reference List or Bibliography
Your research proposal MUST include proper citations for every source you have used and full references. Please consult your departmental referencing styles to ensure you are citing and referencing in an appropriate way.
Common mistakes to avoid
Try and avoid these common pitfalls when you are writing your research proposal:
- Being too wordy: Remember formal does not mean flowery or pretentious. In fact, you should really aim to keep your writing as concise and accessible as possible. The more economically you can express your goals and ideas, the better.
- Failing to cite relevant information/sources: You are adding to the existing body of knowledge on the subject you are covering. Therefore, your research proposal should reference the main research pieces in your field (while referencing them correctly!) and connect your proposal to these works in some way. This does not mean just communicating the relevance of your work, it should explicitly demonstrate your familiarity with the field.
- Focusing too much on minor issues: Your research is most likely important for so many great reasons. However, they do not all need to be listed in your research proposal. Generally, including too many questions and issues in your research proposal can serve as a red flag and detract from your main purpose(s). This will in turn weaken your proposal. Only involve the main/key issues you plan to address.
- Failing to make a strong argument for your research: This is the simplest way to undermine your proposal. Your proposal is a piece of persuasive and critical writing . This means that, although you are presenting your proposal in an academic and hopefully objective manner, the goal is to get the reader to say ‘yes’ to your work.
- Not polishing your writing : If your proposal has spelling or grammatical errors, an inconsistent or inappropriate tone or even just awkward phrasing it can undermine your credibility. Check out some of these resources to help guide you in the right direction: Manchester Academic Phrasebank , Proofreading Guide , Essay Checklist and Grammar Guide . Remember to double and triple check your work.
Links and Resources
You might also need to include a schedule and/or a budget depending on your requirements. Some tools to help include:
- Manchester University Academic Phrasebank
- Leeds Beckett Assignment Calculator
- Calendarpedia
Related information
Dissertation planning
Writing a literature review
Research methods

Be the first to hear about our new and upcoming workshops!
The 301 Academic Skills Centre newsletter is a fortnightly email for study skills, mathematics and statistics.
Be the first to find out about our:
- new and upcoming workshops,
- special events and programmes, and
- new and relevant online materials and resources.
- Utility Menu
GA4 tracking code

- CARAT (Opportunities Database)
- URAF Application Instructions
- URAF Calendar
Writing Research Proposals
The research proposal is your opportunity to show that you—and only you!—are the perfect person to take on your specific project. After reading your research proposal, readers should be confident that…
- You have thoughtfully crafted and designed this project;
- You have the necessary background to complete this project;
- You have the proper support system in place;
- You know exactly what you need to complete this project and how to do so; and
- With this funding in hand, you can be on your way to a meaningful research experience and a significant contribution to your field.
Research proposals typically include the following components:
- Why is your project important? How does it contribute to the field or to society? What do you hope to prove?
- This section includes the project design, specific methodology, your specific role and responsibilities, steps you will take to execute the project, etc. Here you will show the committee the way that you think by explaining both how you have conceived the project and how you intend to carry it out.
- Please be specific in the project dates/how much time you need to carry out the proposed project. The scope of the project should clearly match the timeframe in which you propose to complete it!
- Funding agencies like to know how their funding will be used. Including this information will demonstrate that you have thoughtfully designed the project and know of all of the anticipated expenses required to see it through to completion.
- It is important that you have a support system on hand when conducting research, especially as an undergraduate. There are often surprises and challenges when working on a long-term research project and the selection committee wants to be sure that you have the support system you need to both be successful in your project and also have a meaningful research experience.
- Some questions to consider are: How often do you intend to meet with your advisor(s)? (This may vary from project to project based on the needs of the student and the nature of the research.) What will your mode of communication be? Will you be attending (or even presenting at) lab meetings?
Don’t be afraid to also include relevant information about your background and advocate for yourself! Do you have skills developed in a different research experience (or leadership position, job, coursework, etc.) that you could apply to the project in question? Have you already learned about and experimented with a specific method of analysis in class and are now ready to apply it to a different situation? If you already have experience with this professor/lab, please be sure to include those details in your proposal! That will show the selection committee that you are ready to hit the ground running!
Lastly, be sure to know who your readers are so that you can tailor the field-specific language of your proposal accordingly. If the selection committee are specialists in your field, you can feel free to use the jargon of that field; but if your proposal will be evaluated by an interdisciplinary committee (this is common), you might take a bit longer explaining the state of the field, specific concepts, and certainly spelling out any acronyms.
- Getting Started
- Application Components
- Interviews and Offers
- Building On Your Experiences
- Applying FAQs
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research process
A Beginner's Guide to Starting the Research Process

When you have to write a thesis or dissertation , it can be hard to know where to begin, but there are some clear steps you can follow.
The research process often begins with a very broad idea for a topic you’d like to know more about. You do some preliminary research to identify a problem . After refining your research questions , you can lay out the foundations of your research design , leading to a proposal that outlines your ideas and plans.
This article takes you through the first steps of the research process, helping you narrow down your ideas and build up a strong foundation for your research project.
Table of contents
Step 1: choose your topic, step 2: identify a problem, step 3: formulate research questions, step 4: create a research design, step 5: write a research proposal.
First you have to come up with some ideas. Your thesis or dissertation topic can start out very broad. Think about the general area or field you’re interested in—maybe you already have specific research interests based on classes you’ve taken, or maybe you had to consider your topic when applying to graduate school and writing a statement of purpose .
Even if you already have a good sense of your topic, you’ll need to read widely to build background knowledge and begin narrowing down your ideas. Conduct an initial literature review to begin gathering relevant sources. As you read, take notes and try to identify problems, questions, debates, contradictions and gaps. Your aim is to narrow down from a broad area of interest to a specific niche.
Make sure to consider the practicalities: the requirements of your programme, the amount of time you have to complete the research, and how difficult it will be to access sources and data on the topic. Before moving onto the next stage, it’s a good idea to discuss the topic with your thesis supervisor.
>>Read more about narrowing down a research topic
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
So you’ve settled on a topic and found a niche—but what exactly will your research investigate, and why does it matter? To give your project focus and purpose, you have to define a research problem .
The problem might be a practical issue—for example, a process or practice that isn’t working well, an area of concern in an organization’s performance, or a difficulty faced by a specific group of people in society.
Alternatively, you might choose to investigate a theoretical problem—for example, an underexplored phenomenon or relationship, a contradiction between different models or theories, or an unresolved debate among scholars.
To put the problem in context and set your objectives, you can write a problem statement . This describes who the problem affects, why research is needed, and how your research project will contribute to solving it.
>>Read more about defining a research problem
Next, based on the problem statement, you need to write one or more research questions . These target exactly what you want to find out. They might focus on describing, comparing, evaluating, or explaining the research problem.
A strong research question should be specific enough that you can answer it thoroughly using appropriate qualitative or quantitative research methods. It should also be complex enough to require in-depth investigation, analysis, and argument. Questions that can be answered with “yes/no” or with easily available facts are not complex enough for a thesis or dissertation.
In some types of research, at this stage you might also have to develop a conceptual framework and testable hypotheses .
>>See research question examples
The research design is a practical framework for answering your research questions. It involves making decisions about the type of data you need, the methods you’ll use to collect and analyze it, and the location and timescale of your research.
There are often many possible paths you can take to answering your questions. The decisions you make will partly be based on your priorities. For example, do you want to determine causes and effects, draw generalizable conclusions, or understand the details of a specific context?
You need to decide whether you will use primary or secondary data and qualitative or quantitative methods . You also need to determine the specific tools, procedures, and materials you’ll use to collect and analyze your data, as well as your criteria for selecting participants or sources.
>>Read more about creating a research design
Finally, after completing these steps, you are ready to complete a research proposal . The proposal outlines the context, relevance, purpose, and plan of your research.
As well as outlining the background, problem statement, and research questions, the proposal should also include a literature review that shows how your project will fit into existing work on the topic. The research design section describes your approach and explains exactly what you will do.
You might have to get the proposal approved by your supervisor before you get started, and it will guide the process of writing your thesis or dissertation.
>>Read more about writing a research proposal
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, dissertation & thesis outline | example & free templates, how to write a thesis or dissertation introduction, more interesting articles.
- How to Choose a Dissertation Topic | 8 Steps to Follow
- How to Define a Research Problem | Ideas & Examples
- How to Write a Problem Statement | Guide & Examples
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
- Relevance of Your Dissertation Topic | Criteria & Tips
- What Is a Fishbone Diagram? | Templates & Examples
- What Is Root Cause Analysis? | Definition & Examples
- Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples


Preparing Proposals

- Consultants (Proposal)
- Cost Sharing or Matching
- Description of the Project
- Direct Costs
- Formal Proposal
- Fringe Benefits (Proposal)
- Indirect Costs (Proposal)
- Informal Inquiry
- Other Direct Costs (Proposal)
- Permanent Equipment
- Personnel (Proposal)
- Proposal Content
- Publications (Proposal)
- Supplies and Expendable Equipment
- Travel (Proposal)

- Request Info
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.
Sandeep Kashyap
How to write a perfect project proposal in 2024?

Introduction
The primary purpose of writing a project proposal is to secure funding, gain approval, or secure resources from the most important stakeholders of a project.
For that, you need to explain the following in simple terms in a project proposal:
- What do you want to do and what are your goals for the project?
- How are you going to achieve your goals?
- How are stakeholders going to benefit from the project?
- What do you want from stakeholders?
- How are you going to use the money and resources granted by stakeholders?
In this post, we will learn about all these about writing a perfect project proposal in 2024. We will look at different types of project proposals, a project proposal template, and a real-world example of a project proposal.
What is a project proposal?
A project proposal is a project management document that outlines a project’s objectives, timeline, budget, goals, and requirements.
It is primarily written for stakeholders to secure funding, gain approval, and secure resources. However, other types of project proposals are also sent to win projects from clients.
A project manager should have a good understanding of the project and its key stakeholders for writing an effective project proposal. It is because a manager needs to get into the heads of the project’s stakeholders to understand what they expect from a project and write an effective project proposal accordingly to ensure buy-in for the project.
Benefits of writing a strong project proposal
Writing a strong project proposal offers a surprising number of benefits beyond simply securing funding or approval. Here are five key benefits of writing an effective project proposal:
- Clearly defines the project to increase the chances of success
- Makes it easy for stakeholders to mutually understand the project
- Ensures everyone involved is on the same page about goals, roles, and expectations
- Helps identify potential roadblocks early for proactive planning of solutions
- It can attract funding, and talent, and even serve as a marketing tool
Difference between a project proposal, a project charter, and a project plan
It is important to note that a project proposal is different from a project charter and project plan. Let’s understand the difference between these terms.
Project proposal vs. project charter
A project charter is a formal document that outlines the project’s goals, objectives , and resource requirements for a shared understanding of the team. It can’t be created until the project proposal is approved. Whereas a project proposal is written during the initiation phase.
Project proposal vs. project plan
A project plan is a detailed guide that provides step-by-step instructions for executing, monitoring, and managing the approved project. It is created during the planning stage after the project charter and project scope is defined. Whereas, a project proposal is a persuasive tool for securing project approval and resources.
Read more: Project management plan – everything you need to know about
Project proposal types
Project proposals are of six different types. Each has a different goal. A manager may have to write a project proposal for external and internal stakeholders to run a project successfully. Therefore, it is important to know about the different types of project proposals.
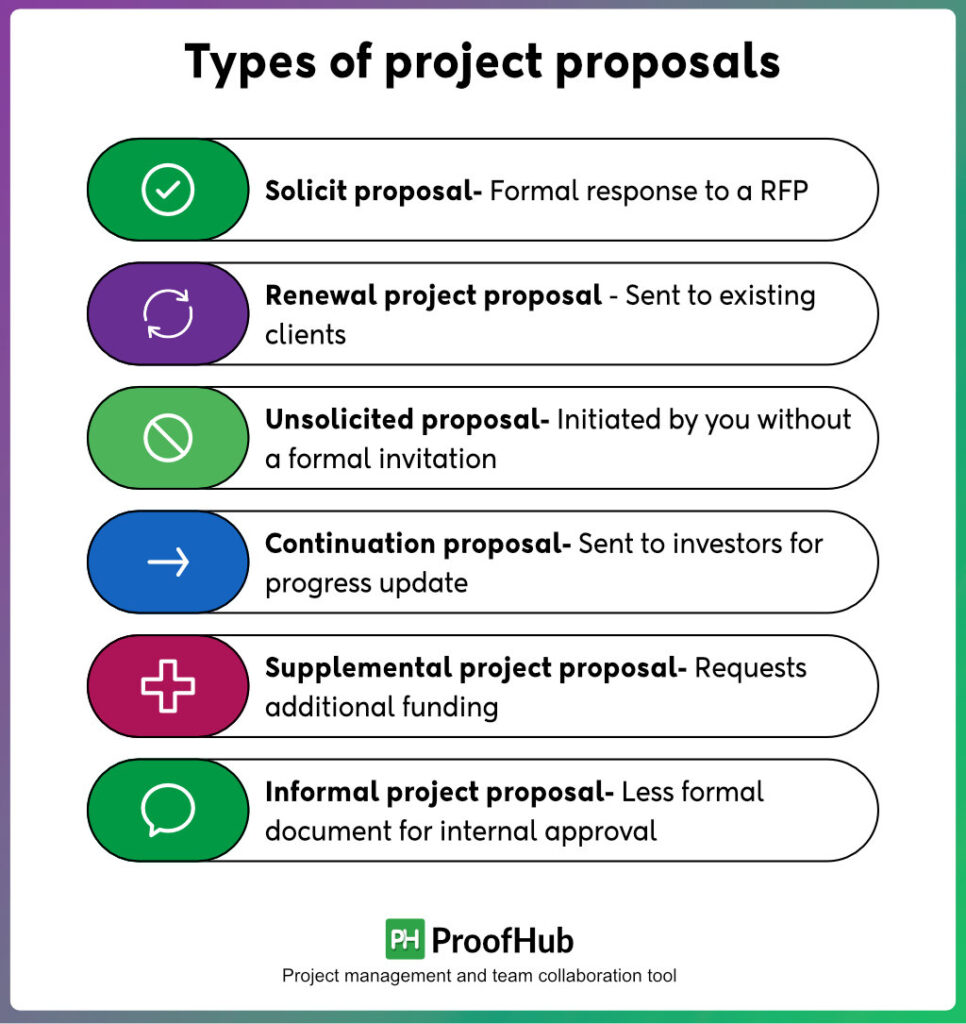
1. Solicited project proposal
A solicited project proposal is sent in response to a request for proposal (RFP). RFP is a document sent by a company to vendors to seek out resources required for a project. It includes the details of the scope of the work and the payment company pays for the resources.
RFP is sent to many vendors. Thus, while writing a solicited project proposal, you need to keep in mind that you may be competing against other vendors to secure a project. Thus, you need to keep your tone persuasive.
2. Unsolicited project proposal
This type of proposal is sent without having received a request for a proposal (RFP). A company has not sent a request for proposal to vendors but you know that the company is seeking resources from third-party vendors. You may or may not be competing against the other vendors in this type of proposal.
3. Informal project proposal
It is a type of project proposal that is created when a client makes an informal request for a project proposal from vendors. It means there is no formal RFP. Thus, the rules for writing a project proposal are less concrete. You can follow any format that can secure you a project.
4. Renewal project proposal
A project manager writes this type of proposal to existing clients to extend their services to the client. In this type of proposal, you focus on highlighting past achievements to secure a renewal for the future.
5. Continuation project proposal
The purpose of the continuation project proposal is to inform the client that the project is beginning and communicate the progress. You are not persuading the client with this type of proposal.
6. Supplemental project proposal
As the name suggests, this type of proposal is sent to the stakeholders who are already involved in a project to secure additional resources. The purpose is to convince the client to invest additional resources during the project execution phase.
How to write a winning project proposal?
You need to include certain elements in the project proposal to make sure it is good. Have a look at the steps to learn how to format a project proposal.

A. Pre-writing stage
The pre-writing stage is crucial for creating a compelling and successful project proposal. Here’s a breakdown of the key steps involved:
1. Understanding the audience
The first step is to identify decision-makers and understand the mindset of the audience for which you are writing a proposal. Thoroughly research the client’s needs, goals, and expectations. This includes understanding their industry, current challenges, and past projects.
Determine who will be reviewing and approving the proposal. This will help you adjust the tone, level of detail, and overall focus to cater to their expertise and interests. Tailor your proposal to directly address their specific concerns and priorities.
2. Project requirements gathering
To create an effective project proposal that has a higher chance of getting accepted, gather the project requirements. Usually, it is mentioned in the Request for Proposal (RFP) where specific requirements, evaluation criteria, submission deadlines, and any other instructions are provided.
If there is no RFP, schedule meetings or interviews with key stakeholders to gain a deeper understanding of the project requirements. This allows you to ask clarifying questions, gather feedback, and ensure your proposal aligns perfectly with their expectations.
3. Team brainstorming
Writing a project proposal is teamwork. Involve your team in brainstorming sessions to make a strong proposal. When a team is involved, it diversifies perspectives and expertise, leading to a more comprehensive and well-rounded proposal. Discuss the project goals, potential solutions, and resource needs with your team. Refine the proposal concept based on the collective knowledge and ensure everyone is aligned on the final approach.
B. Writing the proposal
1. start with writing an executive summary .
An executive summary is a concise overview of what a project is all about. It talks about the most important details or information of the project.
It primarily talks about the problem a project will solve, the solution a project will provide, and the benefits stakeholders will get from investing in this project.
It is important to keep in mind to explain these items briefly as you are going to explain the problem and solution in detail later in your proposal.
The purpose of writing an executive summary is to pique the interest of the stakeholders in a project. It is like the elevator pitch of an entrepreneur whose purpose is to attract the stakeholders for further discussion.
2. Explain the problem in the project background
The project background is a one-page section that focuses on highlighting the opportunity by talking about the project problems you are going to solve. It talks about the problem and its history such as statistics, references, and start date.
It discusses what has been done so far to solve the problem by others or earlier projects. What is the current state of the problem, and how your project will focus on solving it?
This section indicates the opportunity and the next section of vision explains how you are going to seize the opportunity.
3. Project vision and solution
Project vision is the section where you present the solution to the problem. Vision statement defines your vision for the project, the solution you are going to work on, and how it will solve the problems.
This section tells what goals and objectives you are going to achieve from the project. Thus, it also acts as a north star or success criterion for your project.
Now, stakeholders know what a project is all about; the problems, the solution, and the objectives. And they are interested to know how you will achieve the proposed objectives of a project.
The next sections of a project proposal talk about the project approach, scope, deliverables, milestones, budget, resources, and timeline.
Read more: Project objectives: learn how to write them for business growth
4. Project scope and deliverables
This section describes all the work items you need to work on a project. It involves breaking a large project into small tasks so that stakeholders can easily understand the project scope.
It also includes describing key milestones and project deliverables during the execution phase of your project life cycle.
The purpose is to provide stakeholders with enough information to make decisions about funding and resources.
5. Project timeline
Project stakeholders have a clear idea about the scope of the project. But the very next question that comes to stakeholders’ minds is how much time a project will take to complete.
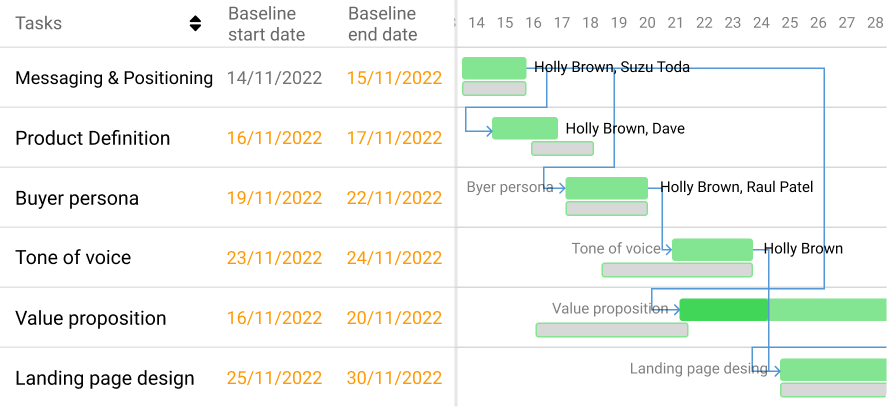
You need to propose an estimated timeline for the project describing when the key deliverables and milestones will be delivered and achieved.
6. Project methodology
With every project, the risks of cost, scope, time, and quality are associated. Thus, you need an effective project management approach to manage these risks.
In this section, you explain to stakeholders about the project approach you are going to use for project management . It includes defining project management methodology, tools, and governance for your project.
79% of teams worldwide use digital collaboration tools . The choice of your project management tool is going to influence how the project will be planned, executed, and managed and its potential risks are identified and mitigated successfully.
ProofHub is an all-in-one project management and team collaboration software that provides you with a centralized platform to collaborate with a team on a project proposal.
ProofHub strengthens your project proposal’s “Implementation Plan” by providing a platform to meticulously define tasks, assign roles, and track progress . Its work plan section allows for a detailed breakdown of the project with clear task dependencies and time estimates, visualized through a Gantt chart .
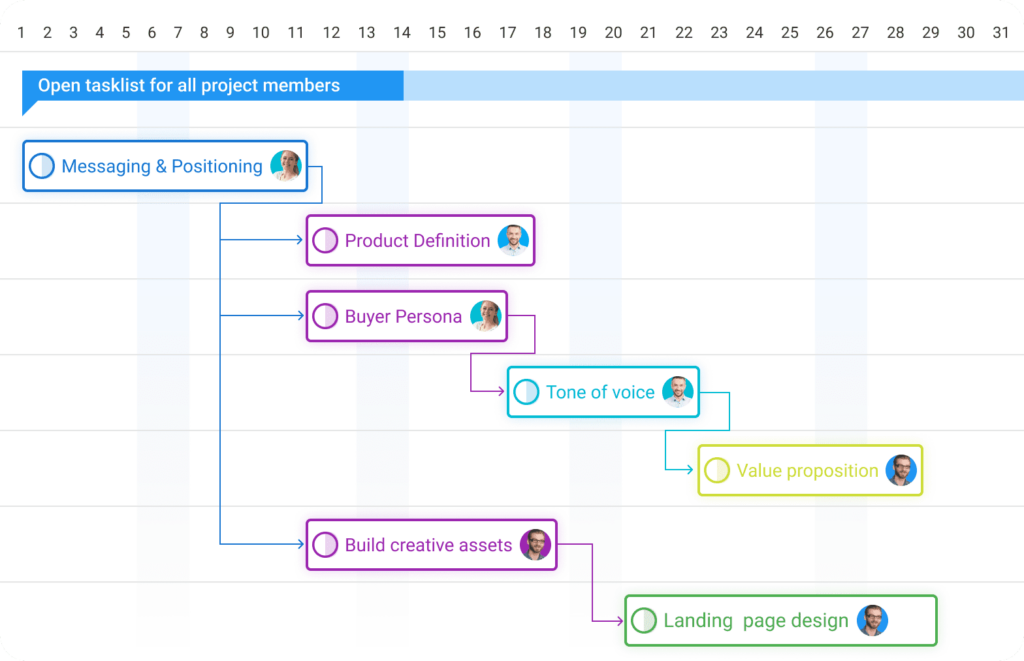
Team members can be assigned to specific tasks, ensuring accountability, while resource allocation demonstrates a well-planned approach.
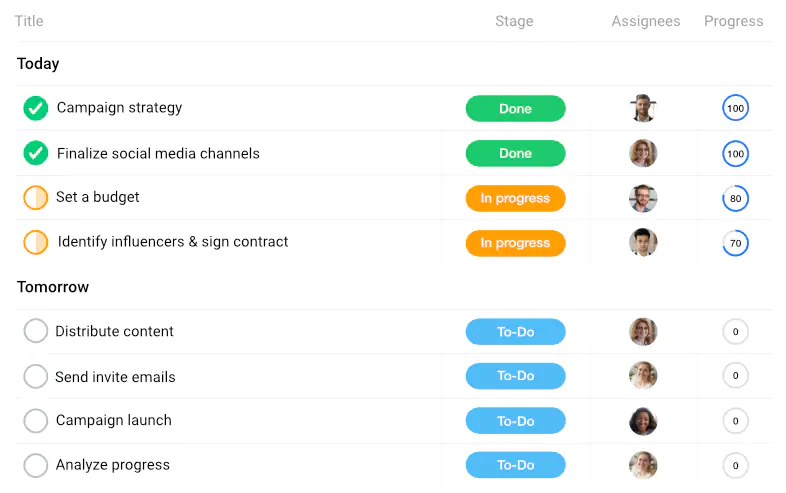
Real-time progress updates, collaborative discussions within tasks, and reporting capabilities showcase transparency and proactive management.
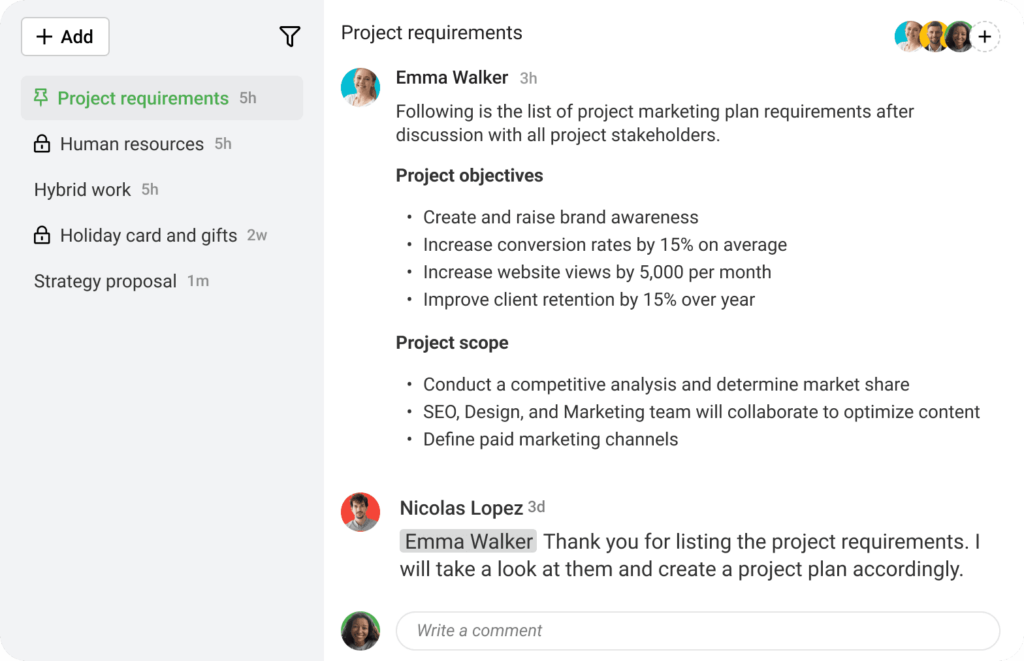
By incorporating ProofHub, your proposal presents a clear picture of efficient execution, giving the reader confidence in your ability to deliver the project successfully.
Learn more about ProofHub’s collaboration capabilities !
7. Project resource requirements
Project resource requirements talk about the resources you need to complete your project which includes materials, human resources, and technology. It is a key section that is crucial for the success of the project because every project needs resources to convert a plan into action.
This section of the project proposal briefly describes the project resources you need for the project and how you are going to utilize these resources.
It does not explain the nitty gritty details of resource allocation. But, it gives a fair idea of why you need specific resources for your project and how these will be utilized.
Read more: 2024 guide to project resource management: processes, challenges & tools
8. Estimate project costs and budget
Project resources come at a price. Thus, in this section, you will define the project costs and create a project budget. It is the responsibility of a project manager to write this section in such a way that it covers all the project expenses.
At the same time, it also provides the opportunity for stakeholders to jump in and help you mitigate unexpected costs.
It also includes estimating project costs everything from the cost of project technology to team salaries and materials.
9. Closing statement
At this point of a project proposal, stakeholders have complete information about the project: scope, cost, time, objectives, and impact. You just have to briefly summarize the problem your project addresses and remind stakeholders about the benefits they will get from this project.
You can use cost-benefit analysis to demonstrate why your project is profitable. Thus, in this section, you wrap up your project proposal with a persuasive and confident conclusion to convince stakeholders to close the deal.
I hope these steps help you write a winning project proposal. Now, let’s have a look at some practical tips from experts to write a winning proposal.
Additional tips to write a perfect project proposal
Here are the five practical project proposal tips for writing a proposal:
- Clarity and conciseness: Do not use jargon or make your proposal overly complex. Keep it simple so that project sponsors can understand it easily.
- Strong value proposition: You want your project proposal to be accepted. Give strong emphasis on the benefits of your project and how it addresses the existing problems.
- Compelling visuals: Make your proposal compelling so that project sponsors read it. If it is not persuasive and visually interesting, project sponsors may not read it.
- Proofreading and editing: Do not make silly grammatical mistakes and fact check and proofread your proposal. Wherever required provide statistics to back your claims.
- Use collaboration tools: A project proposal involves explaining about project scope, cost, time, and resources. Use a project management tool like ProofHub to create a plan and collaborate with a team to create an effective project proposal.
Project proposal examples
A project proposal in project management is primarily sent to the stakeholders to secure funding, gain approvals, and request resources from stakeholders.
Here is a real-world example to get an idea of how to write a proposal for a project:
Project Proposal: Implementation of a CRM System to manage company customers, prospects, and leads
1. Executive
The Customer Success Manager at XYZ Corporation is proposing the implementation of a new Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system.
Currently, the company is using a legacy system that makes it difficult to manage data and ensure the alignment between the sales and marketing teams. It results in poor customer service to the customer and missed opportunities.
The new CRM system streamlines the company’s customer interactions, improves data management, and enhances overall customer satisfaction.
This results in enhanced customer relationships, improved operational efficiency, and increased business growth.
2. Background
- Lack of centralized data management system
- Lack of alignment between marketing and sales departments
- Not able to provide exceptional customer experience due to operational inefficiencies
3. Vision
- Implementing CRM to improve customer data management by centralizing all customer information into a single database
- Enhance communication and collaboration among sales, marketing, and customer service teams
- Increase customer satisfaction and retention through personalized and timely interaction
4. Project scope
- Researching and selecting a suitable CRM solution based on the specific needs and requirements of XYZ Corporation.
- Customizing the CRM system to align with the company’s business processes and workflows.
- Migrating existing customer data from legacy systems into the new CRM platform.
- Phase 1: Research and Selection (1 week)
- Phase 2: Customization and Configuration (2 weeks)
- Phase 3: Data Migration (1 week)
- Phase 4: Training and Adoption (2 weeks)
- Phase 5: Go-Live and Deployment (2 weeks)
5. Project management approach
Hybrid project management : Waterfall during the planning of each phase of the project and Agile during the implementation of the CRM.
6. Project resource and budget
The estimated budget for the CRM implementation project is $50,000, including software licensing fees, customization costs, training expenses, and implementation services.
7. Project risks and mitigation
- Potential resistance from employees toward adopting new technology
- Integration challenges with existing systems and applications:
Mitigation:
- Addressed through providing training sessions for employees to ensure hassle-free adoption of the CRM system.
- Managed through careful planning and coordination with IT vendors and stakeholders.
8. Conclusion
The implementation of a CRM system for XYZ Corporation enhances customer relationships, improves operational efficiency, and drives business growth. We seek approval from the executive management team to proceed with the implementation of the CRM system as outlined in this proposal.
Project management proposal template
Trying to manage a project without project management is like trying to play a football game without a game plan. – Karen Tate
A project management proposal template provides the framework and detailed proposal outlining to create a project proposal. It outlines the sections you need to include in a project proposal and the instructions in each section. By following the instructions in the template, you know how to make a project proposal, customized to your business needs.
Here is the project management proposal template:
1. Executive Summary
In this section, you will summarize the complete project proposal and add the most important details of the project.
Outline the following details in brief in the executive summary:
- Project background and vision
- Project goals and deliverables
- Project budget, timeframe, resource, and success criteria
2. Project Background
In this section, you will talk about the problem a project is going to solve or the business opportunity a project intends to grab. Explain it in-depth because it forms the basis of the project.
Here is what you need to include:
- Project history and stats of similar projects
- The basis upon which the project is created
3. Project vision
This section includes the project vision statement. You explain the solution to the project problem and define the goals of the project.
Here is what you need to do:
- Write a project vision
- Present a solution
- Write the SMART goals you want to achieve
4. Project plan
It includes multiple sections as below:
4.1 Project scope and deliverables
Project scope defines all the work you need to do to complete the project.
Project deliverable is something that is of the end-user or customer value.
4.2 Project timeline
Every project has a start and an end date. Similarly, there is a timeframe for each task and deliverable.
4.3 Project approach
Every project follows an approach to project management and uses project management tools. For example, construction projects follow the Waterfall methodology whereas software development projects follow the Agile methodology.
4.4 Project risks
A project risk is something that can impact the cost, time, and scope of the project.
List here all the project risks, likelihood, impact, mitigation plan, and risk owners in a table.
4.5 Project resource requirements
Project sponsors need to know about the details of the resources required to approve the budget for the Project Proposal.
Define the project resource requirements here in the table:
- Technology requirements
- Human resources requirements
- Material requirements
4.6 Project estimated cost and return on investment
A project sponsor wants to know the project costs and return on investments.
4.7 Project ownership and communication plan
This section includes the details of the key stakeholders of the project.
- Project sponsor: who owns the project
- Project customer: who the project is being delivered to
- Manager: who is responsible for managing the project and informing the status to stakeholders
5. Call to action
In this section, provide your contact details for the client to get in touch with any questions or allow the project sponsor to authorize the project if they are happy with the project proposal.
It is important to keep in mind the above-mentioned are the standard sections that are included in most project proposals. If you want to add some other elements to your project proposal, you can add the sections as per your needs to format a project proposal.
Create a winning project proposal with the right tool
A good project proposal convinces stakeholders why the project should be carried out. It should clearly describe project problems, project objectives, benefits for stakeholders, your requirements from stakeholders, and how you will utilize the secured resources. You need to have a good understanding of the project and project sponsors and stakeholders before writing a project proposal.
To create an effective project proposal, you need cross-collaboration between departments to gather key details and project management software to plan a project.
That’s where a feature-rich project management software, ProofHub, comes into play. It helps you with team collaboration and project planning for the project proposal. You can create a project plan using a Gantt chart , create tasks using task management software , and collaborate with the team using chat and a centralized file-sharing system .
Organize, manage, and collaborate seamlessly with ProofHub – All-in-one solution for projects, tasks, and teams
Related articles
- How to manage projects with a tool like ProofHub
- 10 Common project management challenges (and How to solve them)
- Project objectives: learn how to write them for business growth
- The 11 best project management software for your team
How long should a project proposal be?
A project proposal should not be too long. Ideally, a project proposal should take 1-2 pages but it also depends on the complexity of the project and the format you choose.
What section of a proposal presents a list of project costs?
Project costs are briefly covered in the Project Cost section. However, it depends on the template you choose. The detailed breakdown of the project costs is attached with the project proposal in the reference document.
What section of a proposal identifies the key issues and discusses the project goals?
Project background and project vision are the sections that talk about the key issues and project goals. However, it is explained in brief in the executive summary also.

- Share on LinkedIn
- Email this Page
- Share on Facebook
- Share on WhatsApp
Try ProofHub, our powerful project management and team collaboration software, for free !
No per user fee. No credit card required. Cancel anytime.
How to create a successful website design proposal
Follow this end-to-end guide to win your next client with a compelling website design proposal.

Illustration by Ashger Zamana.

Aaron Gelbman
14 min read
Every web design business has the potential for success, whether that means growing its earnings, client roster or portfolio. As long as you have a steady flow of new projects, all of this is within reach. But to win those new design projects and clients, you first have to win the pitch.
Creating a persuasive web design proposal can help you demonstrate why you’re the right professional for the job. Get the proposal right, and you’re that much closer to your next signed contract.
Below, we take you through everything you need to know about writing a thorough web design proposal that will resonate with your could-be client. Plus, you’ll hear from Tiereny Allen-Green, founder of Scopetheory , a design and consulting agency that has been creating winning web design proposals for more than a decade.
Create an account on Wix Studio, the web creation platform for designers and agencies.
Why do I need to create a web design proposal?
A web design proposal is a document that presents a designer’s or agency’s credentials and expertise to win a new client’s project. Before jumping into any new web design project, a client needs to find a designer or agency whose services match the project’s needs. But keep in mind that a client is likely going to receive many proposals and only pick one. Your proposal needs to therefore make a strong first impression and display your commitment to quality work and client service. “Don’t confuse your proposal with a portfolio,” advises Allen-Green. “Our most successful proposals were simple black text on white pages.”
Think of your proposal as a project plan, which helps to:
Clarify project objectives and align both parties from the outset on what you’ll help the client achieve.
Outline the scope of work, namely which activities and deliverables are or aren’t included, and thus avoid “ scope creep ” that introduces unexpected deliverables and costs.
Detail the design process, offering transparency into how you work to foster trust and credibility with the client, while also differentiating your process from that of competing proposals.
Establish timelines and deadlines so that both you and the client know when to fulfill your responsibilities as needed for the project to succeed.
Provide an accurate quote that fits your client’s budget and ensures that you’re fairly compensated for your services.
Act as a legal document so that, in case of disputes, your proposal can protect you by serving as evidence of agreed-upon terms.
A well-crafted website design proposal can be the deciding factor between winning a new client or watching them go to a competitor. “When you’re talking about five to six figure projects, the proposal is critical,” explains Allen-Green. “It very accurately shows what we [at Scopetheory] bring to the table value-wise. For [the client], it provides a level of assurance to see in writing what they receive so they can be sound on the investment they are about to make.”

How to create a website design proposal: the 3 main stages
The perfect website design proposal doesn’t just rely on great writing. It also hinges on how it’s presented to—and ultimately approved by—a potential client. Guide yourself through the end-to-end process by moving through these three distinct phases:
01. Research : Gather information and data that will serve as the building blocks for your proposal.
02. Writing : The seven-part formula below provides the structure for your proposal and the recommended content for each section.
03. Presenting : One size does not fit all, and each proposal you create might fit a different presentation method to suit each client and each project.

How to conduct research for your proposal
Research is the critical first phase in which you gather all the necessary information about your client's business, their core values , their target audience and their objectives. This helps tailor your proposal to their unique needs and goals.
At this stage, you’ll want to read up on your client's industry, competitors and market position. Ask your client questions to understand what they want to achieve with their website, and determine the challenges they’re facing with their current website or online presence.
“We have refined a very methodical intake process that allows us to extract key info and cater each proposal to a very specific set of outcomes for the client,” says Allen-Green. “It makes it almost impossible for them to say ‘no,’ which is why we have an exceptionally high close rate. Because we infuse [the client’s] key wants into the proposals…they’ve already bought in by the end of the intake call. At this point, the proposal is almost like a confirmation or formality.”
7 things to include in your web design proposal
With this information in hand, you can move on to the next step and write the key components of your website design proposal:
01. Overview
03. solution, 04. schedule.
07. Call-to-Action (CTA)

As you’ll see below, a helpful guide throughout this process is to frame each section of your proposal as an answer to a question, such as, “Why?” or “How?”
This first section of your web design proposal should answer the question, “Why?” Why is this client looking for web design services and why are you the right person or team for the job?
Why the client needs web design services can sometimes be more easily articulated when framed as the “problem” or “challenge.” What is the client unable to achieve right now and what is getting in their way?
Why you are right for the job should highlight the results you’ve delivered to past clients. Don’t simply focus on the names of companies you’ve worked with or how many sites you’ve made. Describe the impact that your work had on these businesses, such as an increase in site traffic, sales or engagement.
The overview is just an introduction to your agency, so keep it short and treat it like an executive summary that you’ll expand on later in the proposal. Bear in mind that this overview sets the tone for the rest of your proposal, so make sure your positive attitude comes across—clients want to work with a partner that brings the right chemistry and collaboration to the project.
In this section, you are answering the “What?” of the proposal. Whereas in the overview you outlined the client’s problems, here you set a North Star for your project. What does your client want to achieve? What will the client gain from working with you? Below are a few examples of different goals that can all apply to a single project:
Marketing: To increase the site’s organic ranking on Google to a top three position
Product: To test which product features generate the most site engagement
Sales: To increase the amount sold to each customer by 20%
Operations: To enable the marketing team to make site content updates without requiring layout changes
Once you’ve completed the project and the new site has been live for some time, these goals can become your KPIs (or key performance indicators). You'll want to measure your progress towards these goals to determine if you’ve achieved them. If yes, then this is a great case study for your portfolio. If not, you have a chance to pivot your strategy to help meet these goals.
Learn more about Wix Studio's marketing integrations with leading analytics tools.
This section addresses the “how.” As Allen-Greene puts it, “Your job in a proposal is to effectively show how you will execute your project and get the client to a desired outcome.” This section should outline two important elements: the process and the deliverables.
The process is like your ownable IP. It’s your unique way of working—the steps, tools and people you bring together like no other designer or agency can. As much as we like to feel that we bring a certain magic to the table, your client wants transparency to feel confident that they’re investing in an experienced agency and a reliable process. When writing about your process, be sure to address:
Steps: This helps your client understand how each action affects the next step of the project, and what they need to do to keep things moving.
Tools: Some clients will request a specific tool—such as a website built specifically on Wix Studio —and others will rely on you to make a recommendation.
People: It’s important to outline the owner(s) of each step, especially for your client to know their responsibilities in driving the project to completion. This is also where you introduce your team members and their expertise for the project.
The deliverables are the items you will produce and hand over to your client as part of the project. Think of them as all of the items that go into the shopping bag after a purchase. Depending on the nature of your proposal, the deliverables could be delivered in phases—such as at the end of each step—or in one handoff at the end of the project. The deliverables could be for the client’s internal use, such as a strategic positioning presentation, or for the client’s go-to-market needs, like a live website with multiple sub-pages, including all the produced imagery and text.
Don’t over-promise when writing this section. Clients will often refer back to this section to make sure you're on track (and to follow up on anything missing along the way).
Learn more about client management tools on Wix Studio .
Now you will outline “when” this project is going to start and end, including the project milestones along the way. This is often a balance between when your client needs to go live with their new website—for example, maybe they want to time it with a new product launch—and the time that your team needs to get the work done.
It’s important to outline:
Where and how the schedule will be accessed and managed . For example, will you collaborate on an online task management program like Monday.com?
Key dates or milestones, including client presentations, client feedback, final approvals and live dates.

It’s standard to include a clause in this section that warns about the domino effect of missing milestones, such as a delay in receiving client feedback that pushes out subsequent steps. But you should always expect the unexpected and pad your timeline so that both you and your client are working together comfortably.
Finally, you’re ready to address the question of “How much?” There are different approaches on web design pricing , including charging by hour, charging by deliverable and others. Whichever approach you choose, this is the section where you should provide all the details on your team’s project fee, as well as any hard costs specific to the project.
The project fee covers the costs of your or your employees’ time to complete the client’s project. For a web design project, this would typically include a designer and a writer, and then depending on the project scope you might include a web developer, an SEO specialist, a video editor or others. Each individual working directly on the project should be listed in this section of the proposal for full transparency.
Hard costs relate to expenses outside of your team or agency that are unique to this project. This could include image licensing, domain registration, website plugins, etc. Present these as an itemized list and indicate which of these costs will recur monthly or annually.

The terms and conditions of your web design proposal must protect both you and your client—not only you. It's good practice to work with a lawyer who specializes in creative or digital agencies, and to establish terms that you can use repeatedly and adapt as needed to each new proposal.
When writing these terms, make sure to highlight:
Scope of work: You’ve already listed the deliverables and timing, so here is where you’ll want to mention the implications of additional deliverables or working days, such as additional fees.
Revisions policy : Manage the client feedback process , in particular the number of rounds of revisions and how these are communicated to you. For example, require revisions in writing over email to ensure that you have a paper trail of all the client’s requests.
Payments: Break down how much of your project fee is due and when. One standard procedure is to receive one payment before the project begins and then a final payment when the project is completed. However, you should also consider that a project might be terminated before completion; stipulate the amount you still require as a “cancel fee,” which will compensate you for finished work (or for any income lost because of projects you turned down during this time).
Again, these are only a few of the items you want to consider for your terms and conditions, so speak with a legal expert to assist you in the process.
07. Call-to-action (CTA)
Your potential client has finished reading the web design proposal. Make it clear what should happen next.
When do you want a response by? In a designer’s perfect world, the client will immediately tell you if they accept your proposal or not, but this is often not the case. It’s common practice for a proposal to include an expiration date, i.e., that your services and the price quote as included are available and valid only until this specified date. This can create a healthy and professional sense of urgency—if the proposal expires, your team can take on other projects and you are no longer held to your proposal.
How does the client confirm? Do you want the client to sign the proposal immediately? Or is sending the proposal the start of a negotiation? Whichever it is, make sure that what you want from the client is obvious and easy—you can include a link to schedule a meeting or for an electronic signature, as examples. You also want it to be easy for the client to reach you, so include any relevant contact details here.
Who will take the next step? Even though your proposal is now in the client’s hands, you’ll want to follow up after a few days if they leave you hanging. You can do so gently via an email or phone call reminding them of the confirmation deadline. (Not sure what to do if a client ghosts you ? Read these tips to address the problem.)
How to format your website proposal
There are a few different web design proposal formats, each with its own advantages. At Scopetheory, explains Allen-Green, “Our most successful proposals are five simple pages or less (including a cover page), and guide the client through their journey with us, covering key details like deliverables, timing and pricing. Even for us, we don’t particularly focus on deliverables. Instead, we place more emphasis on results and outcomes.”

Below are different options, starting with the most simple formats and ending with the most detailed ones.
Outline format
This simple approach presents the proposal as a structured outline, broken down by the sections of your proposal. It provides a clear and concise overview of the proposal's contents, making it easy for clients to read and understand the proposed project plan. This format works best for simple projects; for more complex projects with numerous dependencies and customizations, consider one of the more detailed formats below.
Narrative format
Just like its name, this format is more detailed and structured like a story, covering the client's current situation, challenges, proposed solutions and anticipated outcomes. It's written in a conversational tone, allowing for a more engaging presentation of ideas while still maintaining a professional demeanor.
Visual presentation format
This format is ideal for showcasing design aesthetics and functionality in a compelling and even interactive manner. More visually rich, this presentation format relies heavily on visual aids like a presentation deck or an interactive landing page. It might include images, graphics or mockups to visually demonstrate the proposed design concepts, UI elements and user flow. Platforms like Wix Studio make it easy to create low-fidelity designs for visual presentations, thanks to wireframe templates and AI tools that generate responsive layouts and website text.
Technical specification format
The most detailed approach, this format delves into the technical aspects of the proposed website design, detailing specifications such as programming languages, frameworks, content management systems , hosting requirements and security measures. It's geared towards clients who have complex needs—for example, web apps or digital products—or who better understand web development and prefer a more detailed breakdown of the technical implementation. Here you’ll call out any tools or systems you recommend and align with the client before the project kicks off.
Learn more about Wix Studio’s development tools and capabilities.
How to present a web design proposal to a client
After all the time you spent crafting a persuasive web design proposal, consider the best way to present it to the client for the most impact.
Online meetings are the status quo these days, making in-person meetings much stronger for first impressions. Plus, it’s a great way to immediately assess the chemistry. Meeting in person allows for real-time interaction, clarification of any questions and the opportunity to gauge the client's reactions and feedback.
Online meeting
Since many agencies now work with clients in other states or countries, in-person meetings are not often a practical option. In that case, arrange a video call to present the proposal virtually. This approach still enables a real-time discussion and review of the proposal.
Send the proposal
Sometimes it’s perfectly acceptable to send a proposal over email, either because you have a good history with the client or because you already aligned on the proposal contents in prior conversations. When sending a proposal over email, include a short note about what you’re including, what the client should do and any deadlines—for example, “Attached please find a link to download the web design proposal as well as a link to an interactive prototype. This proposal is valid through the end of the week, so we will follow up with you by then if we haven’t received a response.”
Even when emailing a proposal, suggest meeting the client face-to-face or scheduling a virtual meeting. It’s a strong gesture that shows your professionalism.

Web design proposal templates and tools
Crafting a website design proposal from scratch each time isn’t necessary. The structure of a web design proposal is relatively standard across projects, so using an external template or creating your own template will save you time and effort.
“Over the years, we’ve refined a pared-back outline that reflects what we discussed in our inquiry call [with the client] but in the client's words, which is incredibly important,” says Allen-Greene. “It also covers all the information a client needs to make an educated decision. We’ve taken this outline and created a template in Canva.”
Building on that point, you also need to consider where you want to create your proposal. You can use various tools to your advantage:
Free templates: These can be a good option for freelancers or small agencies who are starting a web design business for the first time. Free templates often cover the basics and easily integrate into platforms like Google Docs and Figma. But don’t forget to customize it if possible with your own branding.
Premium templates : For a more polished look and advanced features, premium templates can be worth the investment. They often come with additional support and customization options. PandaDoc and Better Proposals both offer free templates with paid plans that unlock advanced features.
Proposal generators : Online tools that help you create proposals by simply inputting your information into a pre-designed format can also be useful. ClientManager and Proposable are two tools that include helpful prompts and sections that ensure you cover all necessary information.
When using any template or generative tool for the first time, it’s a good idea to run your proposal by a legal professional to make sure it’s legally sound. And remember to personalize a template to each client and their specific needs. This personal touch shows that you're not just using a one-size-fits-all approach but did the research to understand their business and needs.
How to create a proposal for a website redesign
Not all web design proposals are for entirely new work. Sometimes a business decides to revamp its existing website, and the project could range from a few new page layouts to a full reconstruction.
First, you’ll determine the scope of the project—during research—before you even start to write it. In the case of a website redesign, be sure to ask your client about any historical website data; this can give you insights into what did or didn’t work well on the previous site, so your proposal will be more informed and relevant.
In the case of a redesign, there are a few unique questions to ask your potential client as you develop your proposal:
Why aren’t you working with your previous designer? This will give you clues into what didn’t work with the previous processes or personalities. You’ll want to make sure that you can offer a better experience and solution.
What can’t you do with your existing site? This will tell you how limited or wide the new project will be, whether new plugins could fix certain functional gaps or an entirely new website infrastructure needs to be implemented. Keep in mind that this could include external, site visitor limitations (e.g., poor mobile experience) as well as internal, client-side limitations (e.g., CMS ease-of-use).
Is there anything you want to keep? This helps you by creating a focus for your proposal and setting boundaries for your work, whether the client wants to keep all the current branding or all of the current backend systems.
Why now? It helps to know the pressures driving your client to act right now. If there is a new brand identity or if the company suffered a data breach, you’ll better understand the urgency or impetus for the project and reflect this in your proposal.
Design a site on Wix Studio and create an account today .
RELATED ARTICLES
.png)
How to pitch Wix Studio to different types of clients
JOE O CONNOR
.png)
Why clients and prospects ghost (and how to make sure it never happens again)
IDO LECHNER

How much to charge for a website: a pricing guide for web designers
REBECCA STREHLOW
Find new ways FWD
Thanks for submitting!
By subscribing, you agree to receive the Wix Studio newsletter and other related content and acknowledge that Wix will treat your personal information in accordance with Wix's Privacy Policy .
Do brilliant work—together
Collaborate and share inspiration with other pros in the Wix Studio community.


Collaborative Calls for Proposals Home Agreements Collaborative Calls for Proposals
Call for proposals fapesp and king’s college london – 2024 versão em português.
1. Introduction
The São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) and King’s College London (King’s) are pleased to launch this new call for joint research projects. The aim is to promote and strengthen collaboration between researchers affiliated with Higher Education and Research Institutions in State of São Paulo and researchers working for King’s College London.
2. Research Themes
The present call invites research proposals in any discipline.
3. Funding and duration
FAPESP and King’s will each fund selected projects with an equivalent total of up to USD 50,000 per project for projects with a duration of two (2) years , without extensions. A single joint project may therefore receive up to USD 100,000 in total through this funding call over a two-year period.
A total of two (2) proposals will be funded for this call.
FAPESP will fund the research team based in the State of São Paulo and King’s will fund the UK research team.
4. Eligibility criteria and funding principals
It is envisaged that applications will be for a balanced partnership. Each proposal should include one Principal Investigator (PI) from the State of São Paulo and one from King’s who join their strengths to execute a joint research project. Applicants are expected to propose a coherent research project, in which the added value of both partners, and the complementarity of both teams, is clearly shown. The proposals must aim to respect the principle of reciprocity with regards to academic qualifications of those who will take part in the exchange activities.
4.1 FAPESP:
a) Eligibility: The PI must be employed by a public or private Higher Education or Research Institution in the State of São Paulo and must meet the rules from Auxílio à Pesquisa Regular . Each PI can only submit one proposal.
b) Funding: Proposals must meet the rules and instructions of Auxílio à Pesquisa Regular , with the exceptions of funding (item 3).
4.2 King’s:
a) Eligibility: The PI should be an academic staff member or post-doctoral researcher at King’s with a contract of employment for the full length of the proposed project.
b) Funding: King’s will arrange the internal transfer of funds over two years, with the total amount of funds to be transferred split equally between the 1 st and 2 nd years of the project.
5. Submission
Proposals, in English, and prepared by both research teams (maximum of 15 pages) must contain a clear description of the planned collaboration (distribution of work and methods of implementation) and the added value to be expected from the collaboration. A budget summary table (template available) to indicate funds requested to FAPESP and King’s must also be prepared.
5.1 Submission and documents required by FAPESP will follow the general rules for Auxílio à Pesquisa Regular and will be available for consultation in the SAGe system.
5.2 Submission and documents required by King’s: research proposal; research proposal submission form; budget summary table; and CV of the PI.
Proposals must be submitted to FAPESP and King’s, as specified in item 6.
6. How to apply
6.1. Proposals must be submitted by 12 August 2024 (11h59 pm local time for FAPESP) to FAPESP by the PI from the State of São Paulo and to King’s by the PI from the UK.
a) FAPESP submission
- The proposal must be submitted through the SAGe platform. The specific path for this Call is: Nova Proposta Inicial > + Outras Linhas de Fomento > + Acordos de Cooperação> + KCL - King's College London > + KCL - Projeto de Pesquisa - Regular > + Chamada de Propostas (2024)
- The PI from King’s must create a SAGe login and confirm participation in the project online . Please see the annex at the end of the document for more information. It is strongly recommended to complete and submit the proposal well in advance
b) King’s Submission
- The PI from King’s must submit the documents itemised in 5.2 to the Global Engagement team, by email, to [email protected] .
6.2. No proposal will be accepted after the closing date for submission, nor will any addendum or explanation be accepted, unless those explicitly and formally requested by FAPESP or King’s.
6.3. Proposals submitted by any other means will not be accepted.
7. Analysis and selection
7.1. Each Party will select the proposals according to its own procedures. Only the proposals selected by both Parties will be funded.
7.2. Beyond regular review procedures by each Party, the evaluation criteria include:
- scientific quality and innovativeness of the research plan;
- feasibility of the research plan;
- competence and expertise of the applicants from both countries;
- added value generated by UK-Brazilian research collaboration.
The mobility of researchers will also be considered in the review.
7.3. Proposals that do not comply with the terms of this Call will not qualify for analysis.
7.4. Considering the final results announced under this call for proposals, FAPESP and King’s College London will not accept reconsideration requests.
8. Intellectual Property
In case of approval, a Letter of Agreement (or “Consortium Agreement”) should be signed between the partner Host Institutions establishing how Intellectual Property rights, confidentiality and publications will be treated jointly, in observance of the policies of each funding Party. The presentation of this document is not mandatory for signing the Grant Term, however, FAPESP can request its presentation at any time.
9. Matchmaking
Foreign researchers interested in finding partners in the state of São Paulo can use the Virtual Library of FAPESP . It is possible to search for information regarding Grants and Scholarships awarded by FAPESP, including abstracts, as well as the names of participating researchers and their institutions. The Global Engagement team at King’s can also be contacted for support with matchmaking between King’s and São Paulo state institutions via [email protected] .
10. Contact
All questions related to this Call for Proposals must be directed to:
FAPESP: [email protected]
King’s College London: [email protected]
7 Government Small Business Grants to Apply For in May 2024
Seeking funding is a right of passage for many small business owners. While there are endless private and government-backed loans to choose from, if you’re looking to evade strict repayment terms and steep interest rates, it could be worth considering government business grants.
Government business grants are financial awards issued by federal, state, or local authorities. There are thousands of grants up for grabs through government website portals, but since this type of financing is designed to support the public, their eligibility criteria tend to be quite specific.
If you’re interested in pursuing this type of finance, we round up some government grants small businesses can apply for in May, including their specialisms, funding limits, and deadlines. We also offer some advice for writing your application, to make sure your proposal is as competitive as possible.
In this guide:
Government Small Business Grants to Apply For in May 2024
Tips for perfecting your government grant application.
Get the latest tech news, straight to your inbox
Don't miss out on the top business tech news with Tech.co's weekly highlights reel
By signing up to receive our newsletter, you agree to our Privacy Policy . You can unsubscribe at any time.
There are thousands of government funds to apply for. If you want to cut through the noise, take a look at some of the most popular options below:
- Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) program
- Small Business Technology Transfer (STTR) program
- Women-Owned Small Business (WOSB) Federal Contracting program
- 8(a) Business Development Program
- HUBZone Program
- Small State Business Credit Initiative (SSBCI)
- U.S. Department of Commerce Minority Business Development Agency (MBDA)

1. Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) program
- For: Small businesses interested in carrying out innovation research
- Funding limit: Over $2 million
- Deadline: September 5, January 5, and April 5
The Small Business Innovation Research program was designed by the Small Business Administration to encourage US businesses to engage in Federal research and development. The competitive program is open to select small businesses and specifically encourages participation from women and socially or economically disadvantaged persons.
To be eligible for the SBIR program, your business must be for profit, be over 50% owned by permanent residents of the US, and have fewer than 500 employees. To apply for the grant, you need to register your business with SBIR, if you haven’t already, submit a proposal before one of the program’s tri-annual deadlines, and then respond to feedback and refine your concept if necessary.
Learn more about the SBIR grant, and how to apply here .
2. Small Business Technology Transfer (STTR) programs
- For: Small businesses that have paired up with a research institution
Like the SBIR, the Small Business Technology Transfer program is a government program focused on developing innovative solutions to pressing problems across the US. This type of funding aims to facilitate cooperative research and development efforts research between small business concerns and non-profit US research institutions, with the potential for commercialization of innovative technological solutions.
However, unlike the SBIR, this program requires the small business applicant to be teamed up with a non-profit research institution already, which typically takes the form of a university or Federal Laboratory. The STTR program is also focused on the transfer of technology from the research institution, rather than just the research alone.
Aside from being paired with a research institution, STTR’s eligibility criteria are nearly identical to SBIR’s.
Learn more about the STTR grant, and how to apply here .
3. Women-Owned Small Business (WOSB) Federal Contracting Program
- For: Women-owned businesses
- Funding limit: $4 million for service contracts and $6.5 million for manufacturing contracts
- Deadline: Rolling
The Women-Owned Small Business Federal Contracting Program was designed to build a level playing field for female business owners. The contracts are designated for specific industries where female-owned businesses are underrepresented. You can see which industries are eligible for the grant program here .
To be eligible for this program, you need to run a small business, have the business be at least 51% owned and controlled by US women, and have an economically disadvantaged woman manage the day-to-day operations and make long-term decisions.
Learn more about WOSB, and how to apply here.
4. 8(a) Business Development Program
- For: Socially and economically disadvantaged business owners
- Funding limit: $7 million for acquisitions assigned manufacturing NAICS codes and $4.5 million for all other acquisitions
The 8(a) program is a nine-year program created by the SBA to financially support firms owned and controlled by socially and economically disadvantaged individuals. It’s designed to span nine years and helps eligible businesses access new business paths from government contracting.
Since the creation of the program in 1970, it has helped disadvantaged businesses gain access to billions of dollars in funding. To be eligible for the government grant, you must run a small business, be at least 51% owned and controlled by US citizens who are socially and economically disadvantaged, have a personal net worth of under $805 thousand, and demonstrate good character.
Learn more about the 8(a) business development program, and how to apply here .
5. HUBZone Program
- For: Small businesses in historically under-utilized business zones
- Funding limit: $3.5 million for products and services, and $5.5 million per contract for manufacturing
The HUBZone program is a SBA initiative designed to promote economic development and job growth in historically underutilized business zones (HUBZones). The program does so by offering financial grants to business owners operating within these communities.
To be eligible for this business grant you need to run a small business, have the business be at least 51% owned and controlled by a Community Development Corporation, an agricultural cooperative, an Alaska Native corporation, a Native Hawaiian organization, or an Indian tribe, have its main office located in a HUBZone, and have at least 35% of it employees living in the HUBZone for at least 45 days before applying.
Learn more about the HUBZone program, and how to apply here .
6. Small State Business Credit Initiative (SSBCI)
- For: Small businesses run by socially and economically disadvantaged individuals
- Funding limit: $20 million
The Small State Business Credit Initiative is a federal program designed to support entrepreneurship across the US. The grant program is provided by the US Department of the Treasury and was expanded by President Biden’s American Rescue Plan Act in 2021, providing an extra $10 billion in funding to eligible businesses.
In addition to providing capital support to small businesses, SSBCI can also provide technical assistance to eligible businesses through its Technical Assistance (TA) Grant Program. The SSBCI is available to businesses owner-occupied small businesses with 500 employees or less, and is specifically tailored to small businesses owned and controlled by socially and economically disadvantaged (SEDI) owners and very small businesses with less than 10 employees.
Learn more about the SSBCI program, and apply here .
7. U.S. Department of Commerce Minority Business Development Agency (MBDA)
- For: Small businesses run by minorities
- Funding limit: Up to $350,000 for the first 10 months
The U.S. Department of Commerce Minority Business Development Agency (MBDA) is a Federal grants program designed to promote the growth of minority-owned businesses. The ultimate aim of the program is to provide minority business enterprises (MBEs) with access to funds, contracts, and market opportunities both in the US and globally.
To be eligible for MBDA assistance, a business must be owned or controlled by one or more socially or economically disadvantaged persons. The majority of business owners must also identify as racial minorities.
To apply for an MBDA business grant, you need to register your business with SAM.gov and Grants.gov if you haven’t already, align your proposal with the stated requirements, and submit your application before the deadline.
Learn more about the grant, and how to apply here .
Government grants offer a golden opportunity to businesses looking to grow or recover their business. However, due to the competitive nature of the financing, you need to ensure your grant proposal is polished and stands out from the crowd.
We understand that writing a grant application might seem like a daunting process, especially if you’re a first-timer. So, to give your proposal the best chance possible of succeeding, take heed of these pointers below.
- Give yourself enough time – You don’t want to be writing a grant application against the clock. Writing a proposal can take much longer than you expect, so to account for unexpected hold-ups we recommend giving yourself at least 45 days to complete your written application.
- Follow the instructions carefully – Don’t go off-piste when writing your application. Make sure you include all the information requested by the agency, and present it in the correct format.
- Be as concise and clear as possible – Ensure your application is written in clear, simple language, and use as many candid examples as possible to paint a clear image for your reader. If you use any graphs or imagery, make sure you label them clearly as well.
- Keep the audience in mind – The likelihood is that the reviewer won’t already be familiar with your business. To make sure you won’t gloss over necessary information write the proposal for an audience that’s hearing about your business for the first time.
- Develop a proofreading strategy – You don’t want to hamper your application’s success with silly mistakes like typos or grammatical errors. So, to ensure your proposal looks polished carefully proofread the application or outsource the service to a professional.
Stay informed on the top business tech stories with Tech.co's weekly highlights reel.
We're sorry this article didn't help you today – we welcome feedback, so if there's any way you feel we could improve our content, please email us at [email protected]
Written by:

11 Small Business Grants and Loans to Apply For in 2024
Getting a financial boost could be easier than you think,...

Company Offering $10K for a 30 Day Phone Detox, Apply Now
If you think you've got what it takes to do a one-month...

9 Innovative Startups To Watch Out For in 2024
Discover the startups that have triumphed over adversity in...

Claude 2.1: Anthropic’s ChatGPT Rival Gets New Killer Feature
As OpenAI hits the headlines for all the wrong reasons,...

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management" Example research proposal #2: "Medical Students as Mediators of ...
Here is an explanation of each step: 1. Title and Abstract. Choose a concise and descriptive title that reflects the essence of your research. Write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes. It should provide a brief overview of your proposal. 2.
Make sure you can ask the critical what, who, and how questions of your research before you put pen to paper. Your research proposal should include (at least) 5 essential components : Title - provides the first taste of your research, in broad terms. Introduction - explains what you'll be researching in more detail.
1. Title Page: Include the title of your proposal, your name or organization's name, the date, and any other relevant information specified by the guidelines. 2. Executive Summary: Provide a concise overview of your proposal, highlighting the key points and objectives.
Step 1: Title and Abstract. Select a concise, descriptive title and write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology and expected outcomes . The abstract should include your research question, the objectives you aim to achieve, the methodology you plan to employ and the anticipated outcomes.
The purpose of the research proposal (its job, so to speak) is to convince your research supervisor, committee or university that your research is suitable (for the requirements of the degree program) and manageable (given the time and resource constraints you will face). The most important word here is "convince" - in other words, your ...
2. Have a clearly articulated research problem. As we've explained many times on this blog, all good research starts with a strong research problem - without a problem, you don't have a clear justification for your research. Therefore, it's essential that you have clarity regarding the research problem you're going to address before you start drafting your proposal.
Key Takeaways. Developing a research proposal involves the following preliminary steps: identifying potential ideas, choosing ideas to explore further, choosing and narrowing a topic, formulating a research question, and developing a working thesis. A good topic for a research paper interests the writer and fulfills the requirements of the ...
Conduct a literature review for your research proposal. 4. Define a research gap and research question. 5. Establish a theoretical framework for your research proposal. 6. Specify an empirical focus for your research proposal. 7. Emphasise the scientific and societal relevance of your research proposal.
Are you writing a research proposal to get funding or approval for your project? In this video, you'll learn the four aims of a research proposal, and how to...
A research proposal outline's content typically varies in length, from 3 to 35 pages, with references (and appendices, if necessary). But like any academic activity, start the research proposal template writing process by first carefully reading the instructions.
Hannah Skaggs. Hannah, a writer and editor since 2017, specializes in clear and concise academic and business writing. She has mentored countless scholars and companies in writing authoritative and engaging content. Write a research proposal with purpose and accuracy. Learn about the objective, parts, and key elements of a research proposal in ...
The format of a research proposal varies between fields and levels of study but most proposals should contain at least these elements: introduction, literature review, research design and reference list. Generally, research proposals can range from 500-1500 words or one to a few pages long. Typically, proposals for larger projects such as a PhD ...
Writing Research Proposals. The research proposal is your opportunity to show that you—and only you!—are the perfect person to take on your specific project. After reading your research proposal, readers should be confident that…. You have thoughtfully crafted and designed this project; You have the necessary background to complete this ...
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: 'A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management'.
A proposal needs to show how your work fits into what is already known about the topic and what new paradigm will it add to the literature, while specifying the question that the research will answer, establishing its significance, and the implications of the answer. [ 2] The proposal must be capable of convincing the evaluation committee about ...
To begin with, the introduction must set context for your research by mentioning what is known about the topic and what needs to be explored further. In the introduction, you can highlight how your research will contribute to the existing knowledge in your field and to overall scientific development. The introduction must also contain a ...
institution you are applying to. However, if you are not given any guidelines on how to format your research proposal, you could adopt the suggested structure below. This is also relevant if you are applying for external funding or asking your employer to sponsor you to undertake a research degree. Suggested structure for a research proposal:
The proposal outlines the context, relevance, purpose, and plan of your research. As well as outlining the background, problem statement, and research questions, the proposal should also include a literature review that shows how your project will fit into existing work on the topic. The research design section describes your approach and ...
Consultants (Proposal)Cost Sharing or MatchingDescription of the ProjectDirect CostsFacilitiesFormal ProposalFringe Benefits (Proposal)Indirect Costs (Propo ...
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue.
The first step is to identify decision-makers and understand the mindset of the audience for which you are writing a proposal. Thoroughly research the client's needs, goals, and expectations. This includes understanding their industry, current challenges, and past projects. ... B. Writing the proposal 1. Start with writing an executive summary .
It's common practice for a proposal to include an expiration date, i.e., that your services and the price quote as included are available and valid only until this specified date. This can create a healthy and professional sense of urgency—if the proposal expires, your team can take on other projects and you are no longer held to your proposal.
Launch of call: Monday, 13 May 2024 Closing date for submission of proposals: Monday, 12 August 2024 Announcement of results: 2 December 2024 Start of projects: 1 January 2025 End of projects: January 2025 1. Introduction The São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) and King's College London (King's) are pleased to launch this new call for joint research projects. The aim is ...
1. Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) program. For: Small businesses interested in carrying out innovation research; Funding limit: Over $2 million; Deadline: September 5, January 5, and ...