- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences

The Truth About CSR
- V. Kasturi Rangan,
- Lisa Chase,
- Sohel Karim

Despite the widely accepted ideal of “shared value,” research led by Harvard Business School’s Kasturi Rangan suggests that this is not the norm—and that’s OK. Most companies practice a multifaceted version of CSR that spans theaters ranging from pure philanthropy to environmental sustainability to the explicitly strategic. To maximize their impact, companies must ensure that initiatives in the various theaters form a unified platform. Four steps can help them do so:
Pruning and aligning programs within theaters. Companies must examine their existing programs in each theater, reducing or eliminating those that do not address an important social or environmental problem in keeping with the firm’s business purpose and values.
Developing metrics to gauge performance. Just as the goals of programs vary from theater to theater, so do the definitions of success.
Coordinating programs across theaters. This does not mean that all initiatives necessarily address the same problem; it means that they are mutually reinforcing and form a cogent whole.
Developing an interdisciplinary CSR strategy. The range of purposes underlying initiatives in different theaters and the variation in how those initiatives are managed pose major barriers for many firms. Strategy development can be top-down or bottom-up, but ongoing communication is key.
These practices have helped companies including PNC Bank, IKEA, and Ambuja Cements bring discipline and coherence to their CSR portfolios.
Most of these programs aren’t strategic—and that’s OK.
Idea in Brief
The problem.
Many companies’ CSR initiatives are disparate and uncoordinated, run by a variety of managers without the active engagement of the CEO. Such firms cannot maximize their positive impact on the social and environmental systems in which they operate.
The Solution
Firms must develop coherent CSR strategies, with activities typically divided among three theaters of practice. Theater one focuses on philanthropy, theater two on improving operational effectiveness, and theater three on transforming the business model to create shared value.
Companies must prune existing programs in each theater to align them with the firm’s purpose and values; develop ways of measuring initiatives’ success; coordinate programs across theaters; and create an interdisciplinary management team to drive CSR strategy.
Most companies have long practiced some form of corporate social and environmental responsibility with the broad goal, simply, of contributing to the well-being of the communities and society they affect and on which they depend. But there is increasing pressure to dress up CSR as a business discipline and demand that every initiative deliver business results. That is asking too much of CSR and distracts from what must be its main goal: to align a company’s social and environmental activities with its business purpose and values. If in doing so CSR activities mitigate risks, enhance reputation, and contribute to business results, that is all to the good. But for many CSR programs, those outcomes should be a spillover, not their reason for being. This article explains why firms must refocus their CSR activities on this fundamental goal and provides a systematic process for bringing coherence and discipline to CSR strategies.
- VR V. Kasturi Rangan is a Baker Foundation Professor at Harvard Business School and a cofounder and cochair of the HBS Social Enterprise Initiative.
- Lisa Chase is a research associate at Harvard Business School and a freelance consultant.
- SK Sohel Karim is a cofounder and the managing director of Socient Associates, a social enterprise consulting firm.
Partner Center
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
5 Examples of Corporate Social Responsibility That Were Successful

- 06 Jun 2019
Business is about more than just making a profit. Climate change, economic inequality, and other global challenges that impact communities worldwide have compelled companies to be purpose-driven and contribute to the greater good .
In a recent study by Deloitte , 93 percent of business leaders said they believe companies aren't just employers, but stewards of society. In addition, 95 percent reported they’re planning to take a stronger stance on large-scale issues in the coming years and devote significant resources to socially responsible initiatives. With more CEOs turning their focus to the long term, it’s important to consider what you can do in your career to make an impact .
Access your free e-book today.
What Is Corporate Social Responsibility?
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) is a business model in which for-profit companies seek ways to create social and environmental benefits while pursuing organizational goals, like revenue growth and maximizing shareholder value .
Today’s organizations are implementing extensive corporate social responsibility programs, with many companies dedicating C-level executive roles and entire departments to social and environmental initiatives. These executives are commonly referred to as a chief officer of corporate social responsibility or chief sustainability officer (CSO).
There are many types of corporate social responsibility and CSR might look different for each organization, but the end goal is always the same: Do well by doing good . Companies that embrace corporate social responsibility aim to maintain profitability while supporting a larger purpose.
Rather than simply focusing on generating profit, or the bottom line, socially responsible companies are concerned with the triple bottom line , which considers the impact that business decisions have on profit, people, and the planet.
It’s no coincidence that some of today’s most profitable organizations are also socially responsible. Here are five examples of successful corporate social responsibility you can use to drive social change at your organization.
5 Corporate Social Responsibility Examples
1. lego’s commitment to sustainability.
As one of the most reputable companies in the world, Lego aims to not only help children develop through creative play, but foster a healthy planet.
Lego is the first, and only, toy company to be named a World Wildlife Fund Climate Savers Partner , marking its pledge to reduce its carbon impact. And its commitment to sustainability extends beyond its partnerships.
By 2030, the toymaker plans to use environmentally friendly materials to produce all of its core products and packaging—and it’s already taken key steps to achieve that goal.
Over the course of 2013 and 2014, Lego shrunk its box sizes by 14 percent , saving approximately 7,000 tons of cardboard. Then, in 2018, the company introduced 150 botanical pieces made from sustainably sourced sugarcane —a break from the petroleum-based plastic typically used to produce the company’s signature building blocks. The company has also recently committed to removing all single-use plastic packaging from its materials by 2025, among other initiatives .
Along with these changes, the toymaker has committed to investing $164 million into its Sustainable Materials Center , where researchers are experimenting with bio-based materials that can be implemented into the production process.
Through all of these initiatives, Lego is well on its way to tackling pressing environmental challenges and furthering its mission to help build a more sustainable future.
Related : What Does "Sustainability" Mean in Business?
2. Salesforce’s 1-1-1 Philanthropic Model
Beyond being a leader in the technology space, cloud-based software giant Salesforce is a trailblazer in the realm of corporate philanthropy.
Since its outset, the company has championed its 1-1-1 philanthropic model , which involves giving one percent of product, one percent of equity, and one percent of employees’ time to communities and the nonprofit sector.
To date, Salesforce employees have logged more than 5 million volunteer hours . Not only that, but the company has awarded upwards of $406 million in grants and donated to more than 40,000 nonprofit organizations and educational institutions.
In addition, through its work with San Francisco Unified and Oakland Unified School Districts, Salesforce has helped reduce algebra repeat rates and contributed to a high percentage of students receiving A’s or B’s in computer science classes.
As the company’s revenue continues to grow, Salesforce stands as a prime example of the idea that profit-making and social impact initiatives don’t have to be at odds with one another.
3. Ben & Jerry’s Social Mission
At Ben & Jerry’s, positively impacting society is just as important as producing premium ice cream.
In 2012, the company became a certified B Corporation , a business that balances purpose and profit by meeting the highest standards of social and environmental performance, public transparency, and legal accountability.
As part of its overarching commitment to leading with progressive values, the ice cream maker established the Ben & Jerry’s Foundation in 1985, an organization dedicated to supporting grassroots movements that drive social change.
Each year, the foundation awards approximately $2.5 million in grants to organizations in Vermont and across the United States. Grant recipients have included the United Workers Association, a human rights group striving to end poverty, and the Clean Air Coalition, an environmental health and justice organization based in New York.
The foundation’s work earned it a National Committee for Responsive Philanthropy Award in 2014, and it continues to sponsor efforts to find solutions to systemic problems at both local and national levels.
Related : How to Create Social Change: 4 Business Strategies
4. Levi Strauss’s Social Impact
In addition to being one of the most successful fashion brands in history, Levi’s is also one of the first to push for a more ethical and sustainable supply chain.
In 1991, the brand created its Terms of Engagement , which established its global code of conduct regarding its supply chain and set standards for workers’ rights, a safe work environment, and an environmentally-friendly production process.
To maintain its commitment in a changing world, Levi’s regularly updates its Terms of Engagement. In 2011, on the 20th anniversary of its code of conduct, Levi’s announced its Worker Well-being initiative to implement further programs focused on the health and well-being of supply chain workers.
Since 2011, the Worker Well-being initiative has been expanded to 12 countries and more than 100,000 workers have benefited from it. In 2016, the brand scaled up the initiative, vowing to expand the program to more than 300,000 workers and produce more than 80 percent of its product in Worker Well-being factories by 2025.
For its continued efforts to maintain the well-being of its people and the environment, Levi’s was named one of Engage for Good’s 2020 Golden Halo Award winners, which is the highest honor reserved for socially responsible companies.
5. Starbucks’s Commitment to Ethical Sourcing
Starbucks launched its first corporate social responsibility report in 2002 with the goal of becoming as well-known for its CSR initiatives as for its products. One of the ways the brand has fulfilled this goal is through ethical sourcing.
In 2015, Starbucks verified that 99 percent of its coffee supply chain is ethically sourced , and it seeks to boost that figure to 100 percent through continued efforts and partnerships with local coffee farmers and organizations.
The brand bases its approach on Coffee and Farmer Equity (CAFE) Practices , one of the coffee industry’s first set of ethical sourcing standards created in collaboration with Conservation International . CAFE assesses coffee farms against specific economic, social, and environmental standards, ensuring Starbucks can source its product while maintaining a positive social impact.
For its work, Starbucks was named one of the world’s most ethical companies in 2021 by Ethisphere.

The Value of Being Socially Responsible
As these firms demonstrate , a deep and abiding commitment to corporate social responsibility can pay dividends. By learning from these initiatives and taking a values-driven approach to business, you can help your organization thrive and grow, even as it confronts global challenges.
Do you want to gain a deeper understanding of the broader social and political landscape in which your organization operates? Explore our three-week Sustainable Business Strategy course and other online courses regarding business in society to learn more about how business can be a catalyst for system-level change.
This post was updated on April 15, 2022. It was originally published on June 6, 2019.

About the Author
Home — Essay Samples — Business — Corporate Social Responsibility — Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
Corporate Social Responsibility (csr)
- Categories: Corporate Social Responsibility Structure
About this sample

Words: 535 |
Published: Sep 25, 2018
Words: 535 | Page: 1 | 3 min read
Table of contents
Introduction, types of csr, importance of csr.
- Environment-Focused Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) This type of CSR focuses on reducing detrimental effects of the corporation’s operations on the environment. The corporation innovates in its manufacturing stage to reduce the production of environment harming by-products. It also promotes the use of non-renewable energy sources to prevent harm caused to the environment by burning of fossil fuels.
- Community-Based Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) The corporation joins hands with other organizations (usually Non-Profit ones) to ensure the welfare of a local community’s people. These organizations either fund or receive funding from corporations to perform tasks that can improve the living conditions of the community’s people.
- Human Resource (HR)-Based Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Corporations focus on the well-being of their own staff and improve their living conditions. The companies may extend compassionate leaves like paternity leaves so that the employee can look after his newborn. They can also provide medical insurance to their employees to take care of accidents caused due to occupational hazards.
- Charity Based Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) In a charity-based CSR, corporations donate to organizations or individuals (usually through a charity partner) to improve their financial condition and for their general upliftment. This is the most common form of a CSR activity. Most corporations provide direct financial support to organizations or individuals who require such assistance.
- Increased employee’s loyalty and retention.
- Gaining legitimacy and access to markets.
- Less litigation
- Increased quality of products and services.
- Bolstering public image and enhanced brand value.
- Less volatile stock market.
- Avoiding state regulations.
- Increased customer loyalty.
- Improved quality of life and changing habits.
- Capacity building creates wealth and employment.
- Balanced eco-system.
- Waste management.
- Clean and green environment

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Prof Ernest (PhD)
Verified writer
- Expert in: Business

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
3 pages / 1171 words
1 pages / 499 words
3 pages / 1401 words
2 pages / 742 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Corporate Social Responsibility
Walmart, the world's largest retailer, has a unique business philosophy that has helped the company achieve remarkable success. This essay will explore Walmart's business philosophy and its impact on the company's operations and [...]
Augustine Medical is a company that specializes in developing and manufacturing advanced medical devices. The company has been at the forefront of innovation in the medical industry, and its products have been widely acclaimed [...]
Google, as one of the world's leading technology companies, has a wide range of stakeholders who have a significant impact on the company's operations, performance, and overall success. In this essay, we will conduct a [...]
Pfizer, one of the world's leading biopharmaceutical companies, has been at the forefront of developing innovative treatments for a wide range of diseases and health conditions. With a strong focus on research and development, [...]
The Toyota Motor Sales U.S.A., Inc. Mission and Vision Statements are as follows: Mission Statement: "To attract and attain customers with outstanding products and services and the most satisfying ownership experience in [...]
Individual Social Responsibility is a moral belief where we as individuals, have a responsibility toward society. Being “socially responsible” is about all individuals behaving ethically and sensitively towards social, economic, [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Portfolio Management
- Socially Responsible Investing
What Is Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/amilcar-AmilcarChavarria-7c0945d94896428a8f57a6a56d4710c8.jpeg)
How Corporate Social Responsibility Works
Benefits of corporate social responsibility, frequently asked questions (faqs).
Hero Images / Getty Images
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) is the business practice of joining environmental and social policies with a business’ economic goals and operations. It is based on the idea that businesses can reduce their adverse social and environmental impact on the world.
Key Takeaways
- Corporate social responsibility (CSR) involves actions taken when a company seeks to improve its environmental and societal impact.
- CSR also includes companies adopting fair and ethical business practices.
- Research suggests that a commitment to CSR can positively affect a company’s finances and employee morale.
- CSR is similar to ESG, a process by which investors make decisions based on CSR programs and a company's environmental impact.
Corporate social responsibility is a way of doing business that aims to increase a company's social impact while meeting business objectives such as growth and revenue goals. It can also refer to any effort to improve a company's eco-friendliness or carbon footprint. Companies can deploy CSR efforts as a standalone program or as part of a broader campaign.
Companies may create CSR programs that involve every part of their business and often have dedicated staff members and resources for CSR.
Types of Corporate Social Responsibility
In 1991, researcher Archie B. Carroll, came up with a 'pyramid of corporate social responsibility.' His pyramid included the four components of CSR – economic responsibility (make profits), legal responsibility (follow laws), ethical responsibility (be fair) and philanthropic responsibility (be charitable).
These components have evolved over time into the following types of CSR:
- Economic responsibility : According to Carroll, maximizing profits consistently was the firm's responsibility. Of course, that definition has evolved to include business practices that not only help maximize profits but help make an impact.
- Environmental responsibility : Efforts made by companies to adopt business practices keeping in mind their environmental impact. This could include companies committed to shirking their carbon footprint or working in other ways to mitigate adverse impacts of global warming and climate change.
- Ethical responsibility : Efforts made by companies to adopt fair and ethical business practices. That could mean anything from offering equal to or better than minimum wages to employees, to using ethically sourced raw material.
- Philanthropic responsibility : Some companies may opt to give away a portion of their earnings or executive time to charities or towards charitable causes. For example, in 1946, Target made a commitment to give away 5% of the company's profits back to the community.
Examples of Corporate Social Responsibility
CSR programs vary in scope, but a few examples might include:
- Giving to nonprofit groups, such as local food banks, by supplying volunteers or through monetary donations
- Offering job-training programs for those in need
- Pledging to ensure diversity in the workforce
- Focusing on shrinking the company’s carbon footprint through improved supply chain efficiency
For example, outdoor and sport apparel-maker Patagonia has a number of programs as a part of its CSR efforts. These include a living wage program, a migrant worker program, a fair trade program as well as a fair labor program among others.
Another example of a company's corporate social responsibility is Starbucks' commitment to global human rights. This commitment is spelled out in official corporate policy and includes compliance requirements across the firm's business units. From hiring to supply chain to the way the company works with its business partners, adhering to this social mission affects all levels of Starbucks' operations.
Though CSR programs are often the result of pressure from within the community , research shows that, once instilled, these programs often receive broad support from within the company, too.
One report found that 92% of S&P 500 and Russell 1000 companies published reports charting their efforts related to CSR and sustainability in 2020. In 2011, that figure was less than 20%.
There's little doubt that CSR programs should exist in every business. Companies with robust CSR programs can benefit from better public relations and have happier customers. Improved company profits usually result, in turn satisfying stakeholders.
In some cases, the positive financial impact of CSR is clear. For example, a shift toward renewable energy sources, like solar panels at corporate campuses, might result in lower electricity costs over time.
A report by Babson College reviewed hundreds of CSR program studies. The reviewers found that the programs can have a strong impact on a company's market value and brand and lower risk. The report's findings found that CSR programs have the potential to do the following:
- Increase market value by up to 6%
- Reduce systemic risk by up to 4%
- Reduce the cost of debt by 40% or more
- Raise price premium by up to 20%
- Reduce staff turnover rate by up to 50%
A lot of companies publish CSR reports and provide success metrics, however, it is very difficult to measure the actual impact of CSR activities beyond the numbers provided by the companies.
Corporate Social Responsibility vs. Environmental, Social, and Corporate Governance
CSR is similar to environmental, social, and corporate governance (ESG) principles. The leading difference is that CSR is an internal function, while ESG is an external one.
With CSR programs, it's up to those inside the company to measure the success of their actions. They decide which programs to continue, and rework those that aren't performing as well.
ESG, on the other hand, is a metric that outside analysts can use to compare the effect of different corporate efforts to address environmental and social issues.
Many investment groups gauge companies based on their pledge to integrate ESG criteria. Institutional investors and mutual fund companies may outline how ESG guidelines are incorporated into their philosophies in their annual reports.
The framework for ESG reporting stems from the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), which is a private standards body that seeks to standardize corporate sustainability reporting. It has been working toward this goal since the late 1990s.
In 2006, the United Nations launched the Principles for Responsible Investment (PRI), a program that institutional investors can use to merge ESG values into their decision-making process. More than 3,000 investors and groups have signed on to the PRI, pledging to stand by ESG six principles.
Individual investors may want their investments to reflect their values. They can buy into mutual funds and exchange traded funds (ETFs), grouped by their commitment to CSR. Examples of this include the iShares MSCI KLD 400 Social ETF (DSI) and the SPDR SSGA Gender Diversity Index Fund (SHE).
Why is corporate social responsibility important?
Big businesses committing to social and environmental causes can make a big a difference. However, CSR is important for businesses not just because it is good for their brand. Research suggests that CSR can potentially help companies increase their market value, reduce systemic risks and even retain employees. A 2019 survey suggested that 77% of consumers were motivated to give their business to companies committed to making the world a better place.
What is mainly driving the move toward more corporate social responsibility?
Companies moving towards practices aligned with environment, social and governance (ESG) criteria one of the driving forces behind CSR in recent years. While ESG has its roots in CSR, ESG is more focused on driving environmental impact, sustainability , and positive changes towards social justice.
Harvard Business School. " 5 Examples of Corporate Social Responsibility That Were Successful ."
Archie B. Carroll. " The Pyramid of Corporate Social Responsibility: Toward the Moral Management of Organizational Stakeholders ," Pages 40-43.
Target. " 2021 Target Corporate Social Responsibility Report ," Page 11.
Patagonia. " Social Responsibility. "
Starbucks.com. " Global Human Rights Statement ."
Porter Novelli. " PN Purpose Tracker: Employee Perspectives on Responsible Leadership During Crisis ," Page 3.
Governance & Accountability Institute. " 92% of S&P 500® Companies and 70% of Russell 1000® Companies Published Sustainability Reports in 2020, G&A Institute Research Shows ."
Babson College. " Project ROI: Defining the Competitive and Financial Advantages of Corporate Responsibility and Sustainability ," Page 3.
Global Reporting Initiative. " About GRI ."
Principles for Responsible Investment. " About the PRI ."
Aflac. " 2019 AFLAC CSR Survey ."
Dan Daugaard and Ashley Ding. "Global Drivers for ESG Performance: The Body of Knowledge."
Essay on Corporate Social Responsibility
This report provides information on whether the benefits of CSR outweigh the drawbacks. The report shows that the benefits of CSR are more than the drawbacks and managers should consider implementing the strategy. The research utilizes the use of secondary resources to conclude. Most of the authors used in this report show that CSR has more advantages such as consumer satisfaction, financial performance, productivity, and promotes relationships among the companies, the stakeholders, and society. This research informs the managers on the benefits of executing CSR in their companies. More so, it provides information on few drawbacks that the managers should be prepared to experience. The study adds new information concerning the comparison of advantages and disadvantages of CSR which makes it easier to determine if the strategy should be implemented in companies.
Corporate Social Responsibility
Introduction
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) is a self-controlling model of business that helps business organizations to be socially accountable to the public, stakeholders, and self. Through CSR, companies have conscious of how that affects society environmentally, socially, and economically as they do their businesses (Basuony et al., 2014). Engaging in CSR means that companies are operating in ways that improve society and its environment. As much as CSR influences companies to translate the principles into practical activities, some of the researchers show that CSR may harm companies, stakeholders, and consumers.
Research Questions
Do the positive impacts outweigh the negative effects of CSR among the companies?
Despite some of the researchers revealing the negative impacts of CSR, there are many positive influences that companies, stakeholders, and consumers experience. Companies should ensure that they are responsible for themselves, society, stakeholders, and consumers. This promotes the positive impact of business in society without other people suffering the implications of unethical business activities. However, it is linked to few drawbacks such as costs, conflicts in the profit motive, and “green washing” of customers.
Methodology
This report will utilize secondary sources for review to come up with conclusions. Articles that are less than 10 years old will be used to develop conclusions on whether CSR is effective among companies and if the benefits outweigh the drawbacks.
Literature Review
Based on a substantiation from Mena country, Basuony et al. (2014) state that CSR promotes the performance of business organizations. The stakeholder theory suggests that organizations have to manage relationships with other groups and stakeholders which influences the effectiveness of business decisions. Despite making entrepreneurship progress, businesses that pay attention to the needs of society are successful. For example, branding is effective when a business organization protects the environment and takes part in social activities such as the construction of schools. Most of the researches in this article show that CSR influences business performance through market orientation and consumer satisfaction and financial performance. In research done by Newman et al. (2018), shows that CSR has an independent positive influence on the level of firms efficacy- increased productivity influenced by high effective business engagement. Increased company involvement in community initiatives is a great influence for success in business due to customers’ and stakeholders’ trust.
The concept of the future of CSR presented by Archie Caroll shows that as companies continue to apply CSR, benefits such as stakeholders engagement, increased productivity due to employees being the driving force of business and the enhancement of power among ethically sensitive customers and the client will be experienced (Agudelo et al., 2019). The concept influences effective governance criteria, environmental responsibility, corporate citizenship, the establishment of shared business values, and social performance. However, CSR is linked to various negative impacts. Mahmood et al. (2020) suggest that CSR influences negativity through abusive supervision while valuing employees’ conducts. As much as CSR influences minimization of negative employees’ behavior, it also influences negative conduct when there is abusive supervision. More so, the implementation of CSR needs money. Especially for small businesses, CSR is not affordable to be allocated in the budget. The conflict of the profit motive is also established in CSR as the focus on societal benefits may influence losses to companies. Greenwashing of consumers is linked to CSR. For example, labeling products to be organic to attract consumers.
Implications
This exploration has implications for both bodies of knowledge and management. The research used in this report shows that as much as CSR may have various drawbacks, the benefits outweighs the disadvantages. It contributes to the existing body of knowledge by showing that CSR has more benefits and companies should consider its application in business. The limitations of the current study are the use of secondary sources and few articles to provide more evidence. More so, the articles used in this report do not include cultural factors such as religion which are significant in understanding CSR and the involved activities in the society. The discussion concerning the link between CSR and corporate governance is not provided. Therefore, further research should be done to evaluate this link and its impact on the performance of the company and the experiences of the stakeholders and customers. More so, the research provides a key takeaway for managers which is mainly the benefits of executing CSR in companies to influence performance. The managers should know that despite the presence of drawbacks linked to CSR, there are many advantages such as consumer satisfaction, effective branding, establishing trust, and financial performance.
Based on the previous research used in this report, it is evident that CSR has many advantages. These pros include consumer satisfaction, productivity, good relationships with society and stakeholders, financial performance, and effective branding. These advantages overpower the drawbacks which include costs, conflicts in the profit motive, and “green washing” of customers. However, the limitations of the research include the inclusion of fewer articles and a lack of cultural factors in the research. Therefore, this study concludes that the benefits of CSR outweigh the disadvantages. The implication of the literature is informing managers to execute CSR which promotes productivity and financial performance.
Agudelo, M. A. L., Jóhannsdóttir, L., & Davídsdóttir, B. (2019). A literature review of the history and evolution of corporate social responsibility. International Journal of Corporate Social Responsibility , 4 (1), 1-23.
Basuony, M. A., Elseidi, R. I., & Mohamed, E. K. (2014). The impact of corporate social responsibility on firm performance: Evidence from a MENA country. Corporate Ownership & Control , 12 (1-9), 761-774.
Mahmood, F., Qadeer, F., Abbas, Z., Hussain, I., Saleem, M., Hussain, A., & Aman, J. (2020). Corporate social responsibility and employees’ negative behaviors under abusive supervision: A multilevel insight. Sustainability , 12 (7), 2647.
Newman, C., Rand, J., Tarp, F., & Trifkovic, N. (2020). Corporate social responsibility in a competitive business environment. The Journal of Development Studies , 56 (8), 1455-1472.
Cite this page
Similar essay samples.
- Situational Analysis Spotify
- Jus Cogens are the highest source of international law to which all st...
- DETERMINANTS OF AUDITING FEES AMONG UK FIRMS
- Essay on Should Abortion Be Legalized or Not?
- Police Wearing Body Worn Cameras
- Press Release
Advertisement
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Implementation: A Review and a Research Agenda Towards an Integrative Framework
- Review Paper
- Published: 02 February 2022
- Volume 183 , pages 105–121, ( 2023 )
Cite this article

- Tahniyath Fatima ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2383-3390 1 &
- Said Elbanna ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5891-8258 1
85k Accesses
104 Citations
2 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
In spite of accruing concerted scholarly and managerial interest since the 1950s in corporate social responsibility (CSR), its implementation is still a growing topic as most of it remains academically unexplored. As CSR continues to establish a stronger foothold in organizational strategies, understanding its implementation is needed for both academia and industry. In an attempt to respond to this need, we carry out a systematic review of 122 empirical studies on CSR implementation to provide a status quo of the literature and inform future scholars. We develop a research agenda in the form of an integrated framework of CSR implementation that pronounces its multi-dimensional and multi-level nature and provides a snapshot of the current literature status of CSR implementation. Future research avenues relating to multi-level studies, theoretically supported research models, developing economy settings, and more are recommended. Practitioners can also benefit through utilizing the holistic framework to attain a bird’s eye view and proactively formulate and implement CSR strategies that can be facilitated by collaborations with CSR scholars and experts.
Similar content being viewed by others
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): The Role of Government in promoting CSR

Mandatory CSR and sustainability reporting: economic analysis and literature review

Meta-analyses on Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): a literature review
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Advocates of corporate social responsibility (hereafter referred to as CSR) propose devising and implementing CSR strategies as an opportunity for organizations. When CSR is looked at from a strategic perspective, it emanates from top management’s vision and values and is not considered an expense but a strategic initiative readily adopted by organizations to differentiate themselves from their competition (Beji et al., 2021 ; Porter & Kramer, 2006 ; Serra-Cantallops et al., 2018 ). The organization’s ulterior motive to receive something in return for going out of its way to do better for the direct and indirect stakeholders indicates extrinsic CSR practices, i.e., strategic CSR (Story & Neves, 2015 ). Currently, CSR is predominantly being viewed as a strategic issue (Zerbini, 2017 ), and such a strategic interest of organizations towards CSR needs to be addressed by scholars when we take into consideration the significant time and resources invested in implementing CSR strategically within the organization (Bansal et al., 2015 ). While CSR has been under the limelight in the academic as well as the industrial sectors since the 1950s, its implementation, however, had not received as much attention (Klettner et al., 2014 ). Furthermore, implementation of CSR like any other strategy implementation is of crucial importance to ensure the successful attainment of one’s goals. Accordingly, an increasing number of academicians, over the past decade, have started focusing on how CSR is implemented in organizations, thereby paving a way for future research (Baumann-Pauly et al., 2013 ; Du & Vieira, 2012 ).
CSR implementation as indicated by Lindgreen, Swaen, et al. ( 2009 ) is a budding field of research and has seen profound growth since they called attention to it in the special issue of Journal of Business Ethics. Although, various empirical papers have proposed CSR implementation frameworks to assist practitioners in implementing and formulating CSR strategies (Baumann-Pauly et al., 2013 ; Ingham & Havard, 2017 ; Lindgreen et al., 2011 ), none of the review studies exclusively looked at CSR implementation from a multi-level and a multi-dimensional perspective. In this study, we define CSR implementation as the process that an organization undertakes to increase the awareness levels of CSR issues and CSR strategies, embed CSR values within the organization, communicate CSR initiatives internally and externally, and evaluate the progress of CSR strategies. The very few scholars who have produced reviews on CSR implementation look at specific dimensions of CSR implementation such as communication (Crane & Glozer, 2016 ) or ways of CSR implementation such as CSR washing (Pope & Wæraas, 2016 ). Therefore, conducting a review such as ours at this stage would allow researchers to attain a better idea on the overall progress of research in CSR implementation literature and provide a clearer perspective on future prospects, thereby filling in an important knowledge gap. In regard to facilitating this main research objective, this review paper proposes an integrative framework for CSR implementation and answers the call for a two-stage systematic review on CSR implementation (Lattemann et al., 2009 ; Lindgreen & Swaen, 2010 ). Hence, through the integrative framework, we illustrate what has been done in CSR implementation literature and how can it be enhanced further.
This review study is guided by three developments: (1) the growing amount of time and efforts organizations are putting in towards implementing CSR, (2) an upsurge in organizations’ interests towards strategic CSR, and (3) recognition among CSR scholars of the need to understand how strategies are implemented (Elbanna et al., 2016 ). The structure of this review study is as follows: “ Defining CSR Implementation ” section begins with the theoretical development of the constructs under study and is followed by “ Review Methodology ” section on methodology that outlines the steps taken to initiate the systematic review and sets the stage for this review study. “ Trends in CSR Implementation Research ” section proceeds to discuss the trends discovered through descriptively analyzing the sampled studies. It also portrays the findings of reviewing the CSR implementation literature in six established categories, namely, level of analysis, research methods, theories being used, geographical focus, journal distribution with years of publication, and time lapse of CSR implementation topics. “ Thematic Analysis: An Integrative Framework of CSR Implementation ” section introduces an integrative CSR implementation framework that thematically distributes the CSR implementation literature and proposes a future research agenda. We conclude with “ Conclusion ” section that provides a summarized overview on theoretical and practical implications of this study.
Defining CSR Implementation
The first step of a systematic review entertains a repetitive process of defining, clarifying, and refining (Tranfield et al., 2003 ). As such, we scoured the CSR implementation literature to find any existing conceptual definitions that can support our review process. In our search for what it means to implement CSR, we found two empirical studies which developed CSR implementation frameworks. We used these studies as the foundation to build our own CSR implementation definition, which is supported with the theory of business citizenship as discussed later in this section. The first study was carried out by Maon et al. ( 2009 ), where a nine-stage integrative framework was developed, based on data collected from case studies and theoretically grounded on Lewin’s change model. The second study of Baumann-Pauly et al. ( 2013 ) regarded the process nature of CSR implementation construct, but generalized it into three separate dimensions; (1) commitment to CSR, (2) internal structures and procedures, and (3) external collaboration. Accordingly, these two frameworks were analyzed to procure specific lenses that can entail a better understanding of CSR implementation process. This phase contributed towards attaining richer and micro-level insights on CSR implementation. In addition, we theoretically based our dimensions of CSR implementation on the theory of business citizenship proposed by Logsdon and Wood ( 2002 ). This theory looks into the ethical, social, and political issues surrounding organizations. According to this theory, an organization can be viewed as a citizen such that there exists moral and structural ties among business organizations, humans, and social institutions where social control is exercised by the society on organizations, thereby protecting and enhancing public welfare and private interests.
As such, we identified four distinct dimensions of CSR implementation that concisely portray the CSR implementation process outlined in the two frameworks proposed by Maon et al. ( 2009 ) and Baumann-Pauly et al. ( 2013 ) and are based on the theory of business citizenship that views a corporation as a citizen, where the responsibilities associated with such citizenship towards society and environment come into play. According to Maon et al. ( 2009 ), CSR design and implementation constitute of nine steps. These are (1) raising CSR awareness, (2) assessing organizational purpose in a societal context, (3) establishing a CSR definition and vision, (4) assessing current status of CSR, (5) developing a CSR strategy, (6) implementing the CSR strategy, (7) communicating about CSR strategy, (8) evaluating CSR strategy, and (9) institutionalizing CSR policy. However, Baumann-Pauly et al. ( 2013 ) consider CSR implementation to comprise three dimensions, namely, commitment to CSR, embedding CSR, and external collaboration.
Of the nine steps proposed by Maon et al. ( 2009 ), we considered steps 1 (raising CSR awareness), 5 (embedding CSR), 6 (implementing CSR activities), 7 (communicating about CSR), and 8 (evaluating CSR) for inclusion in CSR implementation. It is worth noting that though step 5 dealt with formulating CSR strategy, a sub-part of this step (5.2) constituted of embedding CSR in the organization, which is also proposed as a CSR implementation dimension by Baumann-Pauly et al. ( 2013 ). Hence, we included step 5 in our typology of CSR implementation dimensions. Similarly, the commitment to CSR dimension proposed by Baumann-Pauly et al. ( 2013 ) takes into consideration the awareness that organizational members show towards CSR as included in step 1 of Maon et al. ( 2009 ). Although, CSR evaluation (step 8) is primarily not a constituent of strategy implementation process, scholars have begun to indicate its importance in the implementation process, where managers monitor strategy progress and take relevant steps for further improvements in CSR implementation (Graafland & Smid, 2019 ; Laguir et al., 2019 ; Rama et al., 2009 ). Steps 2, 3, and 4 are not considered in this study as they represent a part of CSR design, while step 9 identifies with post-implementation. Hence, the four dimensions relate to the need for an organization to accrue sufficient (1) CSR awareness which manifests itself in the form of organization’s commitment to CSR through (2) communicating and (3) embedding CSR , and placing systematic processes in place to (4) evaluate CSR . Overall, these dimensions entail interactions with various external stakeholders and are not restricted to interorganizational dynamics (Baumann-Pauly et al., 2013 ).
CSR awareness includes the act of raising sensitivity of an organization and its members towards CSR issues, where it may be initiated by managers (top-down approach) or employees (bottom-up approach) for strategic or altruistic reasons and includes commitment to CSR through integrating it into policy documents (Baumann-Pauly et al., 2013 ; Maon et al., 2009 ). Further, CSR communication is directed towards both internal and external stakeholders, where the means or nature of communication and its content need to be identified (Maon et al., 2009 ). The different ways of communication include meetings, corporate internal newsletters, and trainings for internal stakeholders such as employees and board members, while the social and environmental performance of an organization may be disclosed in the form of annual reports or CSR reports and advertisements to external stakeholders.
Embedding CSR entails instilling CSR values among organizational members using tools such as CSR policies, procedures, mission, and vision to reinforce a CSR compliant behavior in operational functions (Baumann-Pauly et al., 2013 ; Maon et al., 2009 ). Lastly, CSR evaluation includes the measurement of how well the CSR objectives have been met, monitoring the progress of these CSR objectives, and exploring ways to improve CSR performance (Maon et al., 2009 ).
Review Methodology
We utilized a systematic literature approach to accomplish our research goal of surveying the literature on CSR implementation. Systematic reviews are commonly used to ensure transparency and replicability in the review process (Hossain, 2018 ). Given that it is imperative to outline the scope of one’s search prior to ensuing the data collection process (George et al., 2019 ; Tranfield et al., 2003 ), we restricted our range to any research study that exclusively focused on the concept of CSR implementation or its four dimensions, namely, CSR awareness, CSR communication, CSR embedding, and CSR evaluation. The concept of CSR has taken various titular forms in literature, where overlapping constructs like corporate sustainability, corporate social performance, and corporate citizenship have been proposed and are now interchangeably used by researchers (Albinger & Freeman, 2000 ; Evans & Davis, 2014 ; Matten & Crane, 2005 ; Pedersen et al., 2018 ; Wood, 1991 ). However, the terminology of CSR had been most widely used by researchers (Matten & Crane, 2005 ), and as such is adopted in this study. Furthermore, we do not include research examining the concept of sustainability or corporate sustainability as it is an overarching concept that incorporates two different topics of CSR and corporate responsibility (see Fig. 1 ). As such, CSR acts as an intermediary tool that examines the efforts of organizations aimed at balancing the triple bottom line (van Marrewijk, 2003 ).
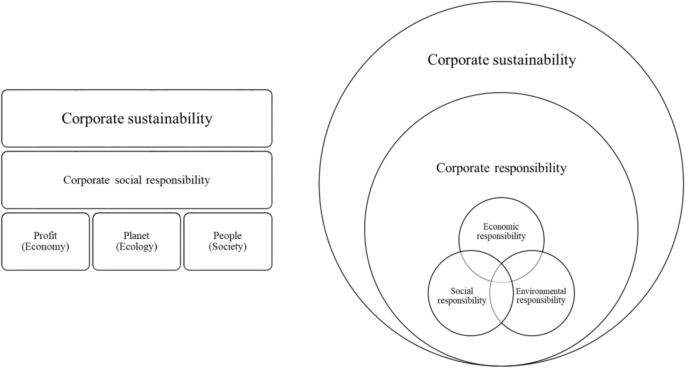
Mapping of corporate sustainability, CSR, and corporate responsibility (adapted from van Marrewijk, 2003 )
Three databases, namely, EBSCO, Science Direct, and ABI/Inform (ProQuest), were searched with the following set of keywords: “CSR awareness,” “CSR implementation,” “CSR sensitiveness,” “commitment to CSR,” “CSR integration,” “initiating CSR,” “CSR issues,” “CSR communication,” “CSR disclosure,” “CSR report,” “CSR value,” “embedding CSR,” “CSR policies,” “CSR procedure,” “CSR vision,” “CSR mission,” “evaluating CSR,” and “monitoring CSR.” We also took into account different occurrences of the keywords such as “implementing CSR,” “sensitivity to CSR,” and “CSR policy.” Further, our inclusion criteria did not include any time restriction as this would have limited our analysis and inferences of understanding the literature conducted so far on CSR implementation. However, in order to ensure quality of our findings and development of a relevant agenda for future research, we included peer-reviewed journal articles that were published in journals with a rating of at least B and above as per the 2019 ABDC ranking and 3 and above for the 2021 AJG ranking (Hoque, 2014 ). Imposition of the above strict criteria led to collection of 168 research articles. These papers were further analyzed to assess if the focus of their study was related to our research objective. Thus, the selection of the studies was contingent on the main topic of the study in question being either CSR implementation or one of the four dimensions (CSR awareness, CSR communication, CSR embedding, and CSR evaluation). In applying this criteria, we were able to shortlist 140 research studies.
Of the total 140 identified studies, we analyzed the nature of their research and found 18 papers were theoretical in nature. One of the theoretical papers was an editorial and was excluded. The remaining 122 empirical studies Footnote 1 are considered for further review, while the 17 theoretical papers are used to supplement the analysis and findings attained from this systematic review. We now discuss the findings attained from conducting our two-staged narrative synthesis analysis that provides the reader with a descriptive and thematic outlook of CSR implementation literature. In utilizing a narrative synthesis approach, we are able to efficiently provide a narrative on the CSR implementation literature through the use of statistical data (Popay et al., 2006 ). The first stage detailed in Sect. Trends in CSR Implementation Research analyzes the entire empirical literature descriptively (123 studies) and discusses the underlying trends on the basis of the (1) level of analysis, (2) research methods, (3) theories being used, (4) geographical focus, (5) journal distribution with years of publication, and (6) time lapse of CSR implementation topics. The second stage brings a more nuanced understanding of the empirical literature where the literature is analyzed with respect to a comprehensive outlook of CSR implementation in Sect. Thematic Analysis: An Integrative Framework of CSR Implementation .
Trends in CSR Implementation Research
Upon analyzing the empirical literature on CSR implementation, we were able to make several inferences that would shed light on research gaps not yet covered in the CSR implementation literature. We followed established review studies in CSR literature (Aguinis & Glavas, 2012 ; Pisani et al., 2017 ) and focused on six aspects to attain a general purview of CSR implementation research conducted to date. First, with respect to the level of analysis , CSR implementation literature, unlike the general CSR literature, does not seem to suffer from lack of focus on individual-level research. However, majority of the empirical research conducted on CSR implementation is at the firm level (refer to Table 1 ). In addition to that, multi-level studies are quite rare with only 8 papers analyzing CSR implementation at multiple levels, e.g., a combination of individual, firm, institutional, industry, and country levels with a combination of at most three levels (Ettinger et al., 2021 ; Helmig et al., 2016 ; Lattemann et al., 2009 ; Lindgreen, Antioco, et al., 2009 a; Lu & Wang, 2021 ; Pomering & Dolnicar, 2009 ; Shen & Benson, 2016 ; Zamir & Saeed, 2020 ). In spite of acknowledging the multi-dimensional nature of CSR implementation (Lindgreen, Swaen, et al., 2009 b), majority of the scholars have failed to conceptualize and operationalize CSR implementation at a multi-dimensional basis. Accordingly, future research needs to take into consideration the multi-dimensional nature of CSR implementation and conduct scientific research that is not limited to a single level of analysis. Other empirical studies looked at various levels of analyses such as advertisement level (Green & Peloza, 2015 ), project level (Rama et al., 2009 ), activity level (Jong & Meer, 2017 ), and interaction level (Muthuri et al., 2009 ).
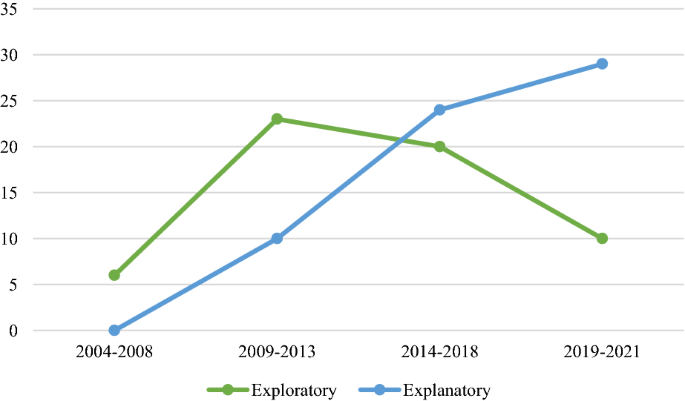
Second, the CSR implementation literature uses a wide variety of research methods . 36% of the research studies used qualitative research methods, 53% used quantitative methods, and only 11% of the studies have used mixed methods. The use of qualitative methods can be explained by the exploratory nature of the studies, which accounted for 49% of the empirical research, while a majority of 51% studies were explanatory in nature. However, given the growing adoption of CSR by different organizations across industries and countries, scholars have delved into examining implementation of CSR from a more explanatory nature as the trend line shows in Fig. 2 . Further, scholars can utilize mixed method studies in future to attain an insightful and a holistic empirical understanding of their research topic. This would allow the research findings to have both theoretical and geographical validity.
Trend of CSR implementation studies’ nature
Third, the theoretical underpinning of research on CSR implementation is still emergent, where a considerable proportion of the empirical literature, approximately 45%, was missing a theoretical foundation. Having a proper theory is quite essential to easily illustrate complex concepts (Frynas & Yamahaki, 2016 ), thereby indicating scope for future research to have richer theoretical support. Of the remaining 67 research studies that had theoretical support (54% of total empirical literature), a considerable proportion of research (42%) resorted to the use of multiple theories to substantiate their proposed frameworks. The most commonly used theory was stakeholder theory inclusive of its use in research studies with multiple theories (28%, 19 out of 67 papers) (e.g., Ettinger et al., 2018 ; Lindgreen et al., 2011 ; Park & Ghauri, 2015 ; Zheng et al., 2015 ). Lastly, as depicted in Fig. 3 , the remaining 31 research studies (46%) used a diverse range of theories from other disciplines like psychology (theory of planned behavior, balance theory, attribution theory, and social identity theory), communications (diffusion theory, inoculation theory), sociology (systems theory, social exchange theory, social identity theory), and biology (signaling theory).
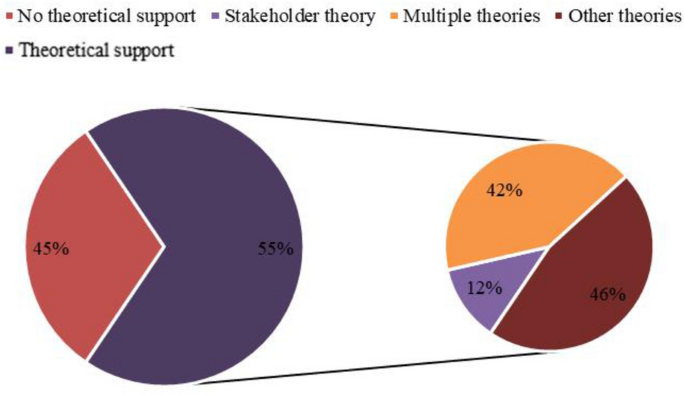
Theoretical orientations in CSR implementation literature
Fourth, in terms of geographical locations being studied, majority of empirical studies were based on samples obtained from European (37%) and North American regions (22%) with only a small portion of research (16%) constituting samples from Asian countries. Further, only few studies examined other regions, such as Oceania (4%), United Kingdom (3%), Africa (1%), and South America (1%). However, the proportion of studies using samples from multiple regions was comparatively higher at around 16%. Hence, future research needs to study the less researched regions to better understand the role of context in CSR implementation. Further, given the emerging nature of cross-country research in CSR implementation (Lattemann et al., 2009 ), an additional scope exists for researchers to compare different regions in their future research.
Fifth, CSR implementation research, since the special issue in Journal of Business Ethics (Lindgreen, Swaen, et al., 2009 b) has been under the research limelight. The first empirical research conducted on CSR implementation in our collection of articles appeared in 2004, however, focus on CSR implementation has drastically improved since 2009 such that approximately 81% of CSR implementation literature has been published in 2010 and onwards. Moreover, Journal of Business Ethics is the highest contributing journal with a major share of 49% of the research studies. This was closely followed by Journal of Business Research (7%), Business Ethics: A European Review (5%), Business and Society (3%), and Business Strategy and the Environment (3%) while the remaining 32% was distributed among 28 journals. Interestingly, other top journals in the field of business ethics and CSR, such as Business Ethics Quarterly and Corporate Social Responsibility and Management were not reflected in our list of reviewed studies. This could be explained due to the absence of studies relevant to our research topic of CSR implementation and the inability of the journal to meet our selection criteria. While, other journals exclusively focusing on ethics and CSR constituted majority of the CSR implementation research, however, this topic seems relatively unexplored and under-published in general management and accounting focused journals.
Lastly, the ingrained analysis of empirical research concerning CSR implementation has shed the much needed light on how this research has changed over the years. For example, we find that while CSR communication has seen constant growth over the years, other dimensions of CSR implementation have experienced uneven growth and decline in research attention (see Fig. 4 ). The comparatively high focus placed on CSR communication brings into question the negligence of other crucial facets of CSR implementation such as CSR embedding and CSR evaluation. Overall, CSR implementation literature that covered either the entire process of CSR implementation in general or more than one dimension of CSR implementation has been gradually on the rise since 2009–2013. While the latest year indicates low publication rates, this may be attributed to the incompleteness of the time period. Upon learning from the insights gained in this descriptive analysis, we proposed a comprehensive framework to better portray the current status of CSR implementation literature and highlight more nuanced directions for future research.
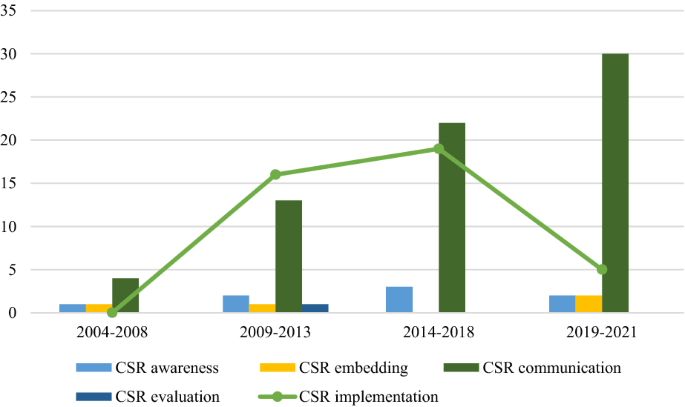
CSR implementation trends over the years
Thematic Analysis: An Integrative Framework of CSR Implementation
The question that comes to mind at this moment in time is: What can we learn more about CSR implementation? We adapt an approach similar to that taken up by researchers who developed various integrative CSR implementation frameworks based on empirical data (Baumann-Pauly et al., 2013 ; Maon et al., 2009 ; Yin & Jamali, 2016 ). However, our integrative framework is built upon the analytical insights attained from the selected 140 research studies and keeping in mind our purpose of aiding academicians and practitioners in understanding the complex multi-level nature of CSR implementation. Hence, this review tries to learn from the findings attained in descriptively analyzing the 122 empirical studies in the previous section and proposes directions for future research using a macroscopic lens with the aid of an integrative multi-level CSR implementation framework (see Fig. 5 ) that can have both research and practical implications.
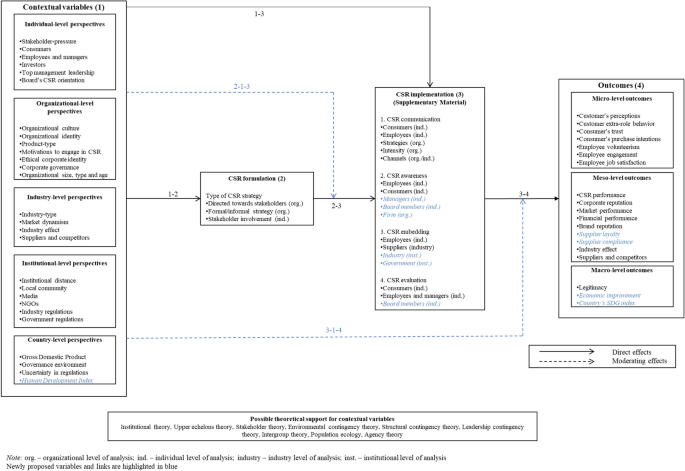
An integrative multi-level CSR implementation framework
The remaining of this section will discuss the four components of our proposed framework: (1) CSR implementation, (2) CSR formulation, (3) CSR outcomes, and (4) CSR context. The main focus is placed on CSR implementation, as it is the main core of this review paper. We discuss the inherent complexity of the CSR implementation construct and how extant literature has conceptualized it, setting the stage to examine two distinct attributes of CSR implementation, namely, its multi-dimensional and multi-level nature. Given the capacity and scope of this study, which is centered on CSR implementation, we lightly touch on the other three components, namely, formulation, outcomes, and context to provide an overview on the whole CSR implementation framework. In discussing CSR formulation, we unravel its absence in studies that have examined CSR implementation and illustrate different ways that future scholars can incorporate it henceforth given the strong link that exists between strategy formulation and implementation. Additionally, the next sub-section on the effect of CSR implementation provides a snapshot on how the CSR implementation literature has heavily examined organizational outcomes, particularly, non-financial, and explains the potential of studying organizational performance comprehensively along with macro-level outcomes. We then conclude this section by extrapolating on the importance of identifying and accounting for contextual variables when studying CSR implementation that may inhibit or drive the implementation process and even potentially moderate the relationship of CSR implementation with CSR formulation and CSR outcomes.
CSR Implementation Construct
CSR implementation is characterized by complexity, where the organization has to deal with different stakeholders, internally and externally. Further, this complexity of CSR implementation is pronounced with its contextual nature across industries, countries, time, and pool of stakeholders (Kleine & Hauff, 2009 ). In spite of CSR implementation experiencing complexity in these varied manners, research studies have so far neglected this aspect (Dobele et al., 2014 ). For example, Luo et al. ( 2017 ) indicate how organizations vary in their CSR disclosure based on their linkages to the central government, highlighting the underlying institutional complexity. On the other hand, Marano and Kostova ( 2016 ) examine how various countries’ institutional forces affect the adoption of CSR practices by various multi-national corporations (MNCs) indicating the presence of transnational complexity (refer to Fig. 5 , link 1-3). Similarly, Polonsky and Jevons ( 2009 ) assert that global brands face three different kinds of complexity when implementing CSR, namely, social issue complexity, organizational complexity, and communication complexity. Communication complexity is the complexity that arises regarding the type of information that needs to be communicated, the consistency that needs to be maintained across the messages and in ensuring that the organizations are also walking the walk and not just talking the talk (Baumann-Pauly et al., 2013 ; Brunton et al., 2017 ). Along these lines, a series of research articles have examined the concepts of CSR walk and CSR talk, where the former represents actual CSR implementation while the latter focuses on CSR communication (Graafland & Smid, 2019 ; Schoeneborn et al., 2020 ; Wickert et al., 2016 ). Further, Graafland and Smid ( 2019 ) found that the overall impact of CSR implementation on the society and environment is dampened in the presence of incongruency between CSR activities being communicated and CSR activities actually being implemented.
Adding to its complex nature, CSR implementation has escaped conceptualization by most of the studies under review (Klettner et al., 2014 ; Peloza et al., 2009 ; Risi & Wickert, 2017 ; Skouloudis & Evangelinos, 2014 ). On the other hand, researchers who did attempt to conceptualize the construct of CSR implementation either did so from a limited perspective of how CSR implementation occurred in the presence of stakeholder management (Osagie et al., 2016 ; Subramaniam et al., 2017 ), capacity development (Rama et al., 2009 ), social partnerships (Seitanidi & Crane, 2009 ), and employee participation (Bolton et al., 2011 ; Kim et al., 2010 ) or examined CSR implementation on the basis of the different types of CSR activities implemented by organizations (Khan et al., 2015 ; Quintana-García et al., 2018 ; Russo & Tencati, 2009 ). Although extant research has identified CSR implementation as a process comprising various stages (Farmaki, 2019 ), it falls short in operationalizing CSR implementation in a similar manner; rather, the studies were found to resort to using existing CSR scales for measuring CSR implementation (Helmig et al., 2016 ). Similar lack in exploring and discussing the process of CSR implementation was also observed among organizations (Klettner et al., 2014 ; Skouloudis & Evangelinos, 2014 ). Hence, as we acknowledge the existence of complexity in CSR implementation and the prevalent absence in conceptualizing CSR implementation, we need to understand the factors that contribute towards the aforesaid complexity of CSR implementation and how can we deal with these factors. To do so, we try to explain the inherent complexity of CSR implementation by exploring its multi-dimensional and multi-level facets that can assist future studies in better conceptualizing CSR implementation.
Multi-dimensional Nature
First and foremost, much of complexity in CSR implementation arises due to its multi-dimensional nature. Multi-dimensionality refers to information that is distributed over multiple dimensions due to its inability to align together in a single dimension such that the information is uniquely sorted into these various dimensions (Bucaro et al., 2020 ; Spalding & Murphy, 1996 ). Although extant research acknowledges the multi-dimensional nature of CSR implementation (Lindgreen, Swaen, et al., 2009 b), many have failed to conceptualize and operationalize it in such a manner, except for a few scholars. Primarily, these authors have assessed CSR implementation on the basis of the traditional classification of stakeholder theory, i.e., implementing CSR strategies directed towards society, environment, and employees (Muller & Kolk, 2009 ; Reimer et al., 2018 ; Shen & Benson, 2016 ) or as per the triple bottom line approach of economy, ecology, and society (Quintana-García et al., 2018 ; Stekelorum et al., 2019 ). However, the above conceptualizations of CSR implementation resonate with the conceptualization of the generic CSR concept itself, where CSR has been conceptualized in terms of stakeholders being targeted at or the nature of responsibility an organization holds towards its society such as economic, ethical, legal, and discretionary (Maignan & Ferrell, 2000 ; Turker, 2009 ). In the same vein, Frynas and Yamahaki ( 2016 ) suggest that CSR scholars need to diversify their usage of theories and restrict themselves from focusing only on the stakeholder view. Hence, researchers need to properly distinguish between the CSR strategy and its implementation.
Accordingly, our proposed conceptualization of CSR implementation can aid scholars and organizations in perceiving the multi-dimensional nature of CSR implementation by focusing on the four dimensions proposed in Sect. 2 . Future research can also test whether these four dimensions are practiced with equal fervor across and within organizations and industries (Walters & Anagnostopoulos, 2012 ). This will enable CSR implementation research to extend beyond CSR communication, which majority of identified empirical research in this study focused exclusively on with very little focus being placed on other CSR implementation dimensions or the construct as a whole. While CSR communication plays an important role in the implementation process, it, however, does not necessarily ensure that these practices are in fact carried out in reality (Arvidsson, 2010 ; Fassin, 2008 ).
CSR communication literature has seen a rich growth over the years (see Fig. 4 ) and as such has diversified into various sub-topics, with CSR disclosure or reporting being the most researched form of CSR communication, particularly in the accounting literature (Gödker & Mertins, 2018 ). Scholars have extensively examined the antecedents and outcomes of CSR disclosure on various fronts: individual, organizational, and country levels (Bucaro et al., 2020 ; DeTienne & Lewis, 2005 ; Lu & Wang, 2021 ; Tan et al., 2020 ; Zhang et al., 2021 ). Further, CSR communication has now diversified into the arena of social media where direct and frequent interactions with customers have heightened (Chu et al., 2020 ; Saxton et al., 2021 ). In addition to customers, CSR communication research seems to have predominantly focused on external stakeholders in general, including investors (Bucaro et al., 2020 ; Hockerts & Moir, 2004 ). Consequently, no research in our shortlisted set of studies examined CSR communication from an internal perspective. A study by Schaefer et al. ( 2019 ) does examine the impact of CSR advertisements on embedding CSR values in employees of an European energy provider, however, the CSR communication under assessment is targeted at external stakeholders. Given the strong inter-relations that exist among actions and communication of CSR activities, examining CSR communication from an interorganizational perspective can tap into the unexplored avenue of its effect on employee involvement in the CSR implementation process (Schoeneborn et al., 2020 ; Sendlhofer, 2020 ; Tourky et al., 2020 ).
Multi-level Nature
Second, while examining different dimensions of CSR implementation surely gives one the wholesome picture, one cannot ignore the multiple levels involved as the above four dimensions of CSR implementation are considered. However, as per our review only a small fraction of the empirical research on CSR implementation (6%) had conducted multi-level research. Hence, academicians have not managed to pay attention to the multiple levels that are in-built when implementing CSR. In referring to the concept of multi level, we propose that CSR implementation involves actors and characteristics at various levels in its environment such that employees, customers, and managers form individual level, while organizational characteristics such as firm size, age, ownership constitute organizational level, and so on. The conceptualization of CSR implementation in our study as discussed in Sect. 2 shows its inherent multi-level nature, where for instance, CSR values may be embedded in the form of CSR vision and mission at organizational level, while CSR awareness initiated by managers or employees occurs at individual level.
The multi-level studies under examination in this review examined CSR implementation at different levels, namely, country, institutional, industry, organizational, and individual. These studies examined (1) drivers of CSR implementation (refer Fig. 5 , link 1-3) like corporate governance and culture background (Lu & Wang, 2021 ), organizational location and distribution of country income (Zamir & Saeed, 2020 ), stakeholders and their pressures (Helmig et al., 2016 ; Pomering & Dolnicar, 2009 ), country governance, industry effect, and organizational characteristics (Lattemann et al., 2009 ); and (2) outcomes of CSR implementation including market performance (Helmig et al., 2016 ), customer attitudes (Ettinger et al., 2021 ), customer perceptions (Lindgreen, Antioco, et al., 2009 a), and employee work behavior (Shen & Benson, 2016 ). Hence, our integrative multi-level framework of CSR implementation considers the five levels discussed above as shown in Fig. 5 .
While researchers have used institutional-level interchangeably with country level due to institutionalized practices of governments or economies (Pisani et al., 2017 ), institutionalization can occur at an industry level as well (O'Connor & Shumate, 2010 ) indicating the need to distinguish institutional level of analysis. While country-level perspective pertains to factors such as government regulations and policies (Pisani et al., 2017 ), institutional-level factors, on the other hand, include institutionalized practices in the economy or corporations (O'Connor & Shumate, 2010 ). Conclusively, industry-level perspective consists of factors such as industry type (Lattemann et al., 2009 ), organizational-level perspective pertains to firm characteristics (Lattemann et al., 2009 ), and individual level refers to employees and managers (Graafland & Zhang, 2014 ; Helmig et al., 2016 ).
CSR Formulation: An Overlooked Antecedent of CSR Implementation
CSR strategy implementation is preceded by its formulation, which consists of decision making upon attaining and interpreting information (Khan, 2018 ). Given the integrative nature of this multi-level framework of CSR implementation, it becomes crucial to consider its critical antecedent, i.e., CSR formulation. Maon et al. ( 2009 ), in their CSR design and implementation framework, identified various steps involved in the formulation of CSR strategies; understanding organization’s societal purpose, identifying its stakeholders, defining CSR vision and mission, assessing current CSR practices, benchmarking with competition and developing the CSR strategy. Additionally, higher CSR orientation of board members also ensures higher proactivity in forming and implementing firm’s CSR strategy, as we identify through the links 1-2 and 1-3 in Fig. 5 (Shaukat et al., 2016 ). On the other hand, various researchers have focused on the sense making concept and linked it to how managers make sense of CSR (as opposed to having planned goals) and accordingly formulate CSR strategies, thereby dictating their implementation as depicted in links 1-2 and 2-3 in Fig. 5 (Hanke & Stark, 2009 ; Jiang et al., 2018 ; Khan, 2018 ). While the presence of stakeholders in CSR strategy formulation was found to positively influence CSR implementation (van Tulder et al., 2009 ), their real world presence in CSR formulation seems to be minimal (Trapp, 2014 ). Accordingly, future research can examine the barriers to stakeholder involvement in CSR formulation and propose ways in which organizations can enhance their involvement (link 1-2, Fig. 5 ). Moreover, scholars can also run comparative studies through collecting field data to test the difference in effectiveness of CSR implementation among organizations that involved stakeholders in formulating CSR versus organizations that had no stakeholder involvement.
Furthermore, very few researchers consider the formulation of CSR as an antecedent or control for its effect in their research studies when studying CSR implementation (Baumann-Pauly et al., 2013 ; Maon et al., 2009 ). Instead several researchers have focused directly on examining various other antecedents of CSR implementation. Accordingly, one can examine if the mediation of CSR formulation can change the impact of certain antecedents like lack of top management commitment, lack of CSR knowledge and skills, and uncertain government regulations (Graafland & Zhang, 2014 ; Luo et al., 2019 ) on CSR implementation from negative to positive. Hence, linking CSR formulation with its implementation can provide a richer feedback as it gives deeper insights into the successful execution of the formulated strategy, where successful CSR implementation can be treated as a dependent variable.
The Impact of CSR Implementation
The outcomes in CSR research have prominently focused on organizational outcomes with special attention being given to financial performance, thereby ignoring the appropriate assessment of the success of a CSR strategy by looking at its non-financial performance indicators such as employees’ extra-role behavior, consumer’s perceptions, and social and environmental performance impact (Fatima & Elbanna, 2020 ). On the other end, CSR implementation, the subset of CSR research literature, has focused exclusively on the non-financial indicators including corporate reputation (Axjonow et al., 2018 ; Kim, 2019 ), consumer purchase intentions (Bartikowski & Berens, 2021 ; Groza et al., 2011 ), and various stakeholder satisfaction such as consumers (Cantrell et al., 2015 ) and employees (Brunton et al., 2017 ; Peloza et al., 2009 ). Comparatively, only four research papers by Helmig et al. ( 2016 ), Rhou et al. ( 2016 ), Pham and Tran ( 2020 ), and Platonova et al. ( 2018 ) have looked at financial indicators. Further, the measurement of CSR performance in CSR literature has been used interchangeably to reflect the construct of CSR (Beji et al., 2021 ; Ge & Li, 2021 ; Öberseder et al., 2014 ), thereby creating a conundrum when it comes to assessing the comprehensive impact of CSR implementation strategies. Consequently, CSR implementation research requires clarification in understanding the nature of its impact on organizational performance, where it may also act as a mediator between CSR formulation and CSR impact (Graafland & Smid, 2019 ).
Future research, hence, needs to consider both financial and non-financial indicators when examining the organizational performance outcome of CSR implementation. This can be achieved, for example, through adopting the sustainability balanced scorecard perspective when measuring organizational outcomes of CSR implementation (Elbanna et al., 2015 ; Fatima & Elbanna, 2020 ). In doing so, organizations can effectively assess the overall impact of CSR implementation on CSR performance constituting social, environmental, and financial performance. In addition to examining these micro-level and meso-level (industry level, institutional level) outcomes, future research can also explore how implementation of CSR strategies within organizations and industries can lead to a macro-level sustainability impact such as the country’s economic and sustainable development (Verk et al., 2021 ) through improvement of Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) index (a standard indicator of country’s sustainability performance developed by United Nations ( 2020 )) (refer to link 3-4, Fig. 5 ).
The Context Matters
Referring to the integrative multi-level framework shown in Fig. 5 , we can clearly see how various factors interact with each other at several levels during CSR formulation and implementation. This framework provides a multi-dimensional view of CSR implementation, examines the nature of interconnectivity among the antecedents and consequences of CSR implementation, and presents CSR implementation in a multi-level manner. While, we do not push for the scholarly need to examine and account for all the variables depicted in Fig. 5 , however, we do aim to bring forth the need for future scholars to consider the context of their study and account for the impact of certain variables that may confound their results when studying CSR implementation. The various perspectives under contextual variables relate to five different levels of analysis highlighted previously in Sect. 5.1.2 (individual, firm, industry, institutional, and country levels). The categorization of these various levels has been done based on the context as per the extant literature review on CSR implementation (Helmig et al., 2016 ; Lattemann et al., 2009 ; Lindgreen, Antioco, et al., 2009 a; Shen & Benson, 2016 ). For ease of understanding, each level is listed under a stand-alone perspective that portrays various items CSR implementation scholars can explore. For instance, items such as pressure from or involvement of stakeholders like customers, employees, managers, board members, etc., relate to individual-level characteristics.
As per our earlier discussion, CSR formulation has been neglected to a certain extent by CSR implementation scholars, where significant research scope also exists in understanding if certain situations or characteristics can impact the CSR formulation–CSR implementation relationship (link 2-1-3 in Fig. 5 ). For example, to what extent organizational size or industry type and stakeholder pressures (Helmig et al., 2016 ) strengthen or weaken this relationship? Our knowledge of extant theories such as institutional theory and stakeholder theory posit for the prevalence of a positive moderation effect. The institutional theory leads to the process of ‘isomorphism’ which can be defined as a process that constrains a unit in a particular set of environmental conditions to resonate with other units existing in similar situations (DiMaggio & Powell, 1983 ). As leading organizations in controversial industries such as oil and mining respond to concerns on their societal and environmental impact (Dobele et al., 2014 ; Du & Vieira, 2012 ), other organizations are complied to follow suit to maintain legitimacy, thereby eliciting the potential role of industry type in moderating the relationship between CSR formulation and implementation. Additionally, Miska et al. ( 2016 ) found that home country characteristics played a pivotal role in shaping the type of CSR strategy that MNCs engaged in. Thus, the effect of institutional level of indicators need to be accounted for when examining the link between CSR formulation and implementation.
Similarly, stakeholder theory emphasizes an organization’s relationships with other stakeholders consisting of employees, customers, suppliers, society, and others by stressing on the importance of satisfying relevant stakeholders (Jamali, 2008 ; Zerbini, 2017 ). As organizations in the current century face rising pressures from various stakeholders to depict socially responsible behavior (Erdiaw-Kwasie et al., 2017 ; Shahzad & Sharfman, 2017 ), they are bound by normative pressure as per institutional theory to comply with these stakeholder needs to establish a sense of legitimacy among their stakeholders. Thus, through building upon the interplay of these three theories, namely, institutional theory, legitimacy theory, and stakeholder theory, future research can probe into the following research question: Are larger organizations or manufacturing industries or higher stakeholder pressures more prone to having a stronger CSR formulation–implementation relationship, in comparison to smaller organizations or service industries or lower stakeholder pressures?
Figure 5 portrays various variables under each of the five perspectives or levels that can either act as drivers or inhibitors towards implementation of CSR. Scholars can accordingly utilize this framework to attain a holistic view and empirically examine how these contextual variables may impact CSR implementation strategies of their sample under study and control for the relevant contextual variables. For instance, CSR scholars have found top managerial characteristics played a significant role towards implementation (Rodríguez Bolívar et al., 2015 ). Scholars can further extend this finding to examine if top management characteristics have a differential impact on CSR implementation dimensions, where the type of leadership may have an effect on the nature of CSR values (strategic or normative) being embedded in the organization’s employees (link 2-1-3). The upper echelons theory which states that an organization is a function of its leaders’ beliefs and thoughts as these leaders make most of the important organizational strategic decisions (Quintana-García et al., 2018 ) finds support for the above proposed moderating impact. Ethical leadership style, for instance, can instill a sense of ethical behavior among employees (Hansen et al., 2016 ) through posing as social learning models and establishing a reward system for ethically appropriate behavior (Fatima, 2020 ).
Further, as per our findings from reviewing the CSR implementation literature, some industries have rarely been studied with respect to their CSR implementation strategies such as the sports and gaming industry (link 1-3). Accordingly, future research can actively collaborate with practitioners to conduct field studies and longitudinal studies, where practitioners can execute and examine CSR implementation, while CSR scholars can act as consultants and conduct quality research. Additionally, with the influx of COVID-19 pandemic, the topical nature of CSR implementation has heightened such that organizations are now actively focusing towards building their social performance to build a safe and healthy organizational work environment and image (Donthu & Gustafsson, 2020 ; He & Harris, 2020 ). This reaction of organizations also finds theoretical support in literature as per the environmental contingency theory that asserts the influence of environment on various characteristics of the organization, such as strategy, task uncertainty, size, and technology (Hatch & Cunliffe, 2013 , p. 98). Hence, scholars can effectively conduct prospective research as opposed to the retrospective research by studying the actions taken by organizations towards their CSR implementation strategies in response to such environmental changes in real time.
Considerable number of studies have managed to study the contextual nature of CSR implementation by examining the presence of mediating and moderating variables (Eberle et al., 2013 ; Ginder et al., 2021 ; Karaosmanoglu et al., 2016 ; Lecuyer et al., 2017 ; Skard & Thorbjørnsen, 2014 ; Vlachos et al., 2009 ). It is worthy to note that all of these research studies have examined mediators and moderators only at individual level and firm level, with an exception of Thorne et al. ( 2017 ) who carried out a cross-country comparison on CSR disclosures. Our framework indicates that multiple perspectives can have a moderating impact on the relationship between CSR implementation and outcomes (refer to link 3-1-4 in Fig. 5 ). For instance, referring to our earlier discussion of stakeholder and institutional theories, future researchers can also examine whether the presence of stakeholder pressures in the form of governmental regulations, active NGOs, and media positively strengthen the relationship between CSR implementation dimensions like CSR awareness, CSR embedding, CSR communication, and outcomes like organizational legitimacy, customer’s perceptions, and organizational performance (Du & Vieira, 2012 ; Pomering & Dolnicar, 2009 ; Rhou et al., 2016 ).
Moreover, given the relatively low level of research being conducted in developing regions such as South America, Asia, and Africa, future research can study whether uncertain regulations weaken the relationship between CSR embedding in suppliers and supplier loyalty or supplier compliance through weakening the coercive pressures felt by organizations in compliance with institutional theory (Boyd et al., 2007 ; Lim & Phillips, 2008 ). Further research ideas can also be attained through scrutinizing our proposed framework where CSR implementation researchers can expand their theoretical support from merely focusing on stakeholder and legitimacy theory to other theories such as structural contingency theory for industry perspective, leadership contingency theory for individual perspective, intergroup theory for CSR embedding, population ecology for institutional perspective, agency theory for the relationship between CSR formulation and CSR implementation in SMEs and so on.
While it is difficult to ensure that one research study covers various levels as depicted in the CSR implementation framework, it, however, becomes easier to realize the presence of multiple factors that may affect CSR implementation–outcomes relationship. With this knowledge at hand, academicians can account and control for the factors, when applicable. Similarly, practitioners can also utilize this framework to get an overarching purview of CSR implementation and better understand the various factors that may positively or adversely impact the different outcomes of CSR implementation, and accordingly, take the necessary proactive decisions.
Upon analyzing the empirical literature trends on CSR implementation in Sect. 4 , several suggestions for future research were made pertaining to the nature of research, level of analysis, theoretical support, and geographical expansion. Further insights were gained through the depiction of an integrative multi-level CSR implementation framework developed in the previous section of thematic analysis. In doing so, this research study has made several theoretical and practical implications, as discussed below.
In terms of theoretical implications, first, we found that scholars have placed a considerable amount of focus towards examining the factors impacting implementation of CSR (antecedents, mediators, and moderators) and the organizational-level consequences of CSR implementation. In comparison, fewer studies have looked at non-organizational consequences or carried out field studies or longitudinal case studies to examine the implementation of complete CSR strategies. Hence, one of the prime insights for future research involve attaining deeper insights into how organizations implement CSR with respect to CSR awareness, CSR embedding, CSR communication, and CSR evaluation. In doing so, researchers would be able to examine CSR implementation from multi-dimensional and multi-level perspectives.
Second, one of the prominent difficulties encountered by organizations when implementing CSR relates to prioritizing stakeholders’ interests (Lee, 2011 ; Porter & Kramer, 2006 ). Different organizations place importance on different stakeholders and as such, a universal solution to prioritize stakeholders becomes difficult. We attempt to resolve this dilemma by proposing a CSR implementation definition (outlined in Sect. 2 ) that indicates the process of CSR implementation as an integrated and a comprehensive process which entails coordinated involvement of all stakeholders at different degrees throughout the four dimensions of CSR implementation.
Third, enhancing from the above research agenda, scholars could also link how multiple dimensions of CSR implementation relate to each other. For instance, Pomering and Dolnicar ( 2009 ) examined whether CSR communication by organizations leads to higher CSR awareness of customers. Furthermore, within the field of CSR implementation, some of its dimensions have not been as heavily researched as the rest; CSR communication has been of prime focus for several academicians. However, only three studies were found to study CSR evaluation as a part of the implementation process (Cowper-Smith & de Grosbois, 2011 ; Schaefer et al., 2019 ; Vlachos et al., 2009 ). Evaluating CSR in the implementation phase resonates with assessing the extent to which CSR objectives are met. However, CSR evaluation has mostly focused on assessing CSR performance using secondary databases like Kinder, Lyndenberg, and Domini (Rhou et al., 2016 ). Thus, to examine CSR evaluation as a part of the implementation phase, researchers need to study other internal stakeholders in addition to employees, such as way of monitoring CSR strategies by both board members and top managements. Accordingly, examining other CSR implementation dimensions in detail, specifically perceiving them from a different lens would enrich the extant knowledge on CSR implementation.
Fourth, most of the CSR implementation–performance literature has looked at organizational and individual-level outcomes. Given the very nature of an organization is to ensure profitability, the prime focus has been placed by researchers in identifying how CSR implementation impacts organizational outcomes such as organizational reputation and CSR performance. Similarly, customers are deemed as the most important stakeholder given their direct impact on organization’s profitability, and thereby, its sustenance. Accordingly, most prior studies have examined the impact of CSR strategy implementation on customer perceptions and behaviors. However, a research gap exists with regard to studying the impact on other external stakeholders like suppliers’ loyalty and suppliers’ compliance. Moreover, the impact of organization’s CSR implementation has been restricted to micro-level and meso-level, where country-level impacts such as on economic improvement and increase in sustainability index have not yet been studied. Therefore, researchers need to examine meso-level and macro-level impacts of implementing CSR strategies. Understandably, the absence of studies examining macro-level outcomes of CSR maybe due to the exclusion of sustainability construct from our literature search which is more prominently linked with country-level outcomes like sustainable development goals. Future reviews can, as such, consider the prospect of examining implementation of sustainability strategies as opposed to the concept of CSR which was the focus in this review.
The restrictive journal criteria used in this systematic review pose a constricted presentation of the CSR implementation literature. However, we followed the standard journal selection criteria used widely across general business and management reviews. Further, we aimed to examine high-quality research on CSR implementation, thereby justifying our usage of a restricted journal criteria. In order to attain a more general view and to better understand the research trends of a vast literature of CSR implementation that includes research in established ethics and CSR focused journals like Journal of Cleaner Production and Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management, future scholars can conduct bibliometric analysis or meta-analysis with a more relaxed journal criteria.
This research study also produces various implications for practitioners regarding CSR implementation. First, practitioners can make use of the proposed CSR implementation dimensions that stresses on its multi-level and multi-dimensional nature and identifies it as a process that is not restricted to a stakeholder view. Accordingly, managers can make appropriate decisions to ensure CSR strategies are properly implemented in their organizations and are not solely restricted to financial investments. Second, top management and policy makers can utilize the CSR implementation framework for a bird’s eye view on the potential factors that can impact CSR implementation and the possible outcomes of CSR implementation. In doing so, organizations can pay heed to contextual factors that may impede or promote implementation of CSR and its relationship with different outcomes. Third, practitioners, upon realizing the multi-level impact of CSR implementation, which goes beyond the individual and organizational levels, can reflect upon their current organizational CSR strategies and accordingly, revise or formulate better versions.
To sum, CSR implementation has come a long way in the past decade and still has a long way to go. This review paper attempts to enlighten the research community with insights on the progress of CSR implementation research and how it can be further improved to enrich our understanding of the concept of CSR implementation. With the proposition of CSR implementation dimensions that facilitate the review of literature, an integrative multi-level CSR implementation framework has been developed to assist future research on CSR implementation in getting closer to reality by portraying the interconnectivity in implementing any organizational strategic decision. With the above research contributions, this study attempted to set the stage for future research to build upon by conducting richer and deeper empirical studies that examine CSR implementation in the right light.
A table reviewing the literature on CSR implementation has been submitted as supplementary material due to paper length considerations and is also available from the authors upon request.
Aguinis, H., & Glavas, A. (2012). What we know and don’t know about corporate social responsibility: A review and research agenda. Journal of Management, 38 (4), 932–968.
Article Google Scholar
Albinger, H. S., & Freeman, S. J. (2000). Corporate social performance and attractiveness as an employer to different job seeking populations. Journal of Business Ethics, 28 (3), 243–253.
Arvidsson, S. (2010). Communication of corporate social responsibility: A study of the views of management teams in large companies. Journal of Business Ethics, 96 (3), 339–354.
Axjonow, A., Ernstberger, J., & Pott, C. (2018). The impact of corporate social responsibility disclosure on corporate reputation: A non-professional stakeholder perspective. Journal of Business Ethics, 151 (2), 429–450.
Bansal, P., Jiang, G. F., & Jung, J. C. (2015). Managing responsibly in tough economic times: Strategic and tactical CSR during the 2008–2009 global recession. Long Range Planning, 48 (2), 69–79.
Bartikowski, B., & Berens, G. (2021). Attribute framing in CSR communication: Doing good and spreading the word – But how? Journal of Business Research, 131 , 700–708.
Baumann-Pauly, D., Wickert, C., Spence, L., & Scherer, A. (2013). Organizing corporate social responsibility in small and large firms: Size matters. Journal of Business Ethics, 115 (4), 693–705.
Beji, R., Yousfi, O., Loukil, N., & Omri, A. (2021). Board diversity and corporate social responsibility: Empirical evidence from France. Journal of Business Ethics, 173 (1), 133–155.
Bolton, S., Kim, R., & O’Gorman, K. (2011). Corporate social responsibility as a dynamic internal organizational process: A case study. Journal of Business Ethics, 101 , 61–74.
Boyd, D. E., Spekman, R. E., Kamauff, J. W., & Werhane, P. (2007). Corporate social responsibility in global supply chains: A procedural justice perspective. Long Range Planning, 40 (3), 341–356.
Brunton, M., Eweje, G., & Taskin, N. (2017). Communicating corporate social responsibility to internal stakeholders: Walking the walk or just talking the talk? Business Strategy & the Environment, 26 (1), 31–48.
Bucaro, A. C., Jackson, K. E., & Lill, J. B. (2020). The influence of corporate social responsibility measures on investors’ judgments when integrated in a financial report versus presented in a separate report. Contemporary Accounting Research, 37 (2), 665–695.
Cantrell, J., Kyriazis, E., & Noble, G. (2015). Developing CSR giving as a dynamic capability for salient stakeholder management. Journal of Business Ethics, 130 (2), 403–421.
Chu, S.-C., Chen, H.-T., & Gan, C. (2020). Consumers’ engagement with corporate social responsibility (CSR) communication in social media: Evidence from China and the United States. Journal of Business Research, 110 , 260–271.
Cowper-Smith, A., & de Grosbois, D. (2011). The adoption of corporate social responsibility practices in the airline industry. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 19 (1), 59–77.
Crane, A., & Glozer, S. (2016). Researching corporate social responsibility communication: Themes, opportunities and challenges. Journal of Management Studies, 53 (7), 1223–1252.
DeTienne, K. B., & Lewis, L. W. (2005). The pragmatic and ethical barriers to corporate social responsibility disclosure: The Nike case. Journal of Business Ethics, 60 (4), 359–376.
DiMaggio, P. J., & Powell, W. W. (1983). The iron cage revisited: Institutional isomorphism and collective rationality in organizational fields. American Sociological Review, 48 (2), 147–160.
Dobele, A. R., Westberg, K., Steel, M., & Flowers, K. (2014). An examination of corporate social responsibility implementation and stakeholder engagement: A case study in the Australian mining industry. Business Strategy & the Environment, 23 (3), 145–159.
Donthu, N., & Gustafsson, A. (2020). Effects of COVID-19 on business and research. Journal of Business Research, 117 , 284–289.
Du, S., & Vieira, E. (2012). Striving for legitimacy through corporate social responsibility: Insights from oil companies. Journal of Business Ethics, 110 (4), 413–427.
Eberle, D., Berens, G., & Li, T. (2013). The impact of interactive corporate social responsibility communication on corporate reputation. Journal of Business Ethics, 118 (4), 731–746.
Elbanna, S., Andrews, R., & Pollanen, R. (2016). Strategic planning and implementation success in public service organizations: Evidence from Canada. Public Management Review , 18 (7), 1017–1042. https://doi.org/10.1080/14719037.2015.1051576
Elbanna, S., Eid, R., & Kamel, H. (2015). Measuring hotel performance using the balanced scorecard: A theoretical construct development and its empirical validation. International Journal of Hospitality Management , 51 , 105–114.
Erdiaw-Kwasie, M. O., Alam, K., & Shahiduzzaman, M. (2017). Towards understanding stakeholder salience transition and relational approach to ‘better’ corporate social responsibility: A case for a proposed model in practice. Journal of Business Ethics, 144 (1), 85–101.
Ettinger, A., Grabner-Kräuter, S., Okazaki, S., & Terlutter, R. (2021). The desirability of CSR communication versus greenhushing in the hospitality industry: The customers’ perspective. Journal of Travel Research, 60 (3), 618–638.
Ettinger, A., Grabner-Kräuter, S., & Terlutter, R. (2018). Online CSR communication in the hotel industry: Evidence from small hotels. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 68 , 94–104.
Evans, W. R., & Davis, W. (2014). Corporate citizenship and the employee: An organizational identification perspective. Human Performance, 27 (2), 129–146.
Farmaki, A. (2019). Corporate social responsibility in hotels: A stakeholder approach. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 31 (6), 2297–2320.
Fassin, Y. (2008). SMEs and the fallacy of formalising CSR. Business Ethics: A European Review, 17 (4), 364–378.
Fatima, T. (2020). Impact of employees’ perceived corporate social responsibility on organizational citizenship behavior: A proposed theoretical model. International Journal of Customer Relationship Marketing and Management , 11 (3), 25–38.
Fatima, T., & Elbanna, S. (2020). Balanced scorecard in the hospitality and tourism industry: Past, present and future. International Journal of Hospitality Management , 91 , 102656.
Frynas, J. G., & Yamahaki, C. (2016). Corporate social responsibility: Review and roadmap of theoretical perspectives. Business Ethics: A European Review, 25 (3), 258–285.
Ge, Q., & Li, T. (2021). Corporate social responsibility and shareholder wealth: New insights from information spillovers. Financial Review , p. 1.
George, B., Walker, R. M., & Monster, J. (2019). Does strategic planning improve organizational performance? A meta-analysis. Public Administration Review, 79 (6), 810–819.
Ginder, W., Kwon, W.-S., & Byun, S.-E. (2021). Effects of internal–external congruence-based CSR positioning: An attribution theory approach. Journal of Business Ethics, 169 (2), 355–369.
Gödker, K., & Mertins, L. (2018). CSR disclosure and investor behavior: A proposed framework and research agenda. Behavioral Research in Accounting, 30 (2), 37–53.
Graafland, J., & Smid, H. (2019). Decoupling among CSR policies, programs, and impacts: An empirical study. Business & Society, 58 (2), 231–267.
Graafland, J., & Zhang, L. (2014). Corporate social responsibility in China: Implementation and challenges. Business Ethics: A European Review, 23 (1), 34–49.
Green, T., & Peloza, J. (2015). How did the recession change the communication of corporate social responsibility activities? Long Range Planning, 48 (2), 108–122.
Groza, M., Pronschinske, M., & Walker, M. (2011). Perceived organizational motives and consumer responses to proactive and reactive CSR. Journal of Business Ethics, 102 (4), 639–652.
Hanke, T., & Stark, W. (2009). Strategy development: Conceptual framework on corporate social responsibility. Journal of Business Ethics, 85 (3), 507.
Hansen, D. S., Dunford, B. B., Alge, B. J., & Jackson, C. L. (2016). Corporate social responsibility, ethical leadership, and trust propensity: A multi-experience model of perceived ethical climate. Journal of Business Ethics, 137 (4), 649–662.
Hatch, M. J., & Cunliffe, A. L. (2013). Organization theory: Modern, symbolic and postmodern perspectives . OUP.
Google Scholar
He, H., & Harris, L. (2020). The impact of Covid-19 pandemic on corporate social responsibility and marketing philosophy. Journal of Business Research, 116 , 176–182.
Helmig, B., Spraul, K., & Ingenhoff, D. (2016). Under positive pressure: How stakeholder pressure affects corporate social responsibility implementation. Business & Society, 55 (2), 151–187.
Hockerts, K., & Moir, L. (2004). Communicating corporate responsibility to investors: The changing role of the investor relations function. Journal of Business Ethics, 52 (1), 85–98.
Hoque, Z. (2014). 20 years of studies on the balanced scorecard: Trends, accomplishments, gaps and opportunities for future research. The British Accounting Review, 46 (1), 33–59.
Hossain, M. (2018). Frugal innovation: A review and research agenda. Journal of Cleaner Production, 182 , 926–936.
Ingham, M., & Havard, C. (2017). CSR as strategic and organizational change at ‘Groupe La Poste.’ Journal of Business Ethics, 146 (3), 563–589.
Jamali, D. (2008). A stakeholder approach to corporate social responsibility: A fresh perspective into theory and practice. Journal of Business Ethics, 82 (1), 213–231.
Jiang, F., Zalan, T., Tse, H. H. M., & Shen, J. (2018). Mapping the relationship among political ideology, CSR mindset, and CSR strategy: A contingency perspective applied to Chinese managers. Journal of Business Ethics, 147 (2), 419–444.
Jong, M., & Meer, M. (2017). How does it fit? Exploring the congruence between organizations and their corporate social responsibility (CSR) activities. Journal of Business Ethics, 143 (1), 71–83.
Karaosmanoglu, E., Altinigne, N., & Isiksal, D. G. (2016). CSR motivation and customer extra-role behavior: Moderation of ethical corporate identity. Journal of Business Research, 69 (10), 4161–4167.
Khan, S. N. (2018). Making sense of the black box: An empirical analysis investigating strategic cognition of CSR strategists in a transitional market. Journal of Cleaner Production, 196 , 916–926.
Khan, Z., Lew, Y. K., & Park, B. I. (2015). Institutional legitimacy and norms-based CSR marketing practices. International Marketing Review, 32 (5), 463–491.
Kim, H.-R., Lee, M., Lee, H.-T., & Kim, N.-M. (2010). Corporate social responsibility and employee–company identification. Journal of Business Ethics, 95 (4), 557–569. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-010-0440-2
Kim, S. (2019). The process model of corporate social responsibility (CSR) communication: CSR communication and its relationship with consumers’ CSR knowledge, trust, and corporate reputation perception. Journal of Business Ethics, 154 (4), 1143–1159.
Kleine, A., & Hauff, M. (2009). Sustainability-driven implementation of corporate social responsibility: Application of the integrative sustainability triangle. Journal of Business Ethics, 85 , 517–533.
Klettner, A., Clarke, T., & Boersma, M. (2014). The governance of corporate sustainability: Empirical insights into the development, leadership and implementation of responsible business strategy. Journal of Business Ethics, 122 (1), 145–165.
Laguir, L., Laguir, I., & Tchemeni, E. (2019). Implementing CSR activities through management control systems: A formal and informal control perspective. Accounting, Auditing & Accountability Journal, 32 (2), 531–555.
Lattemann, C., Fetscherin, M., Alon, I., Shaomin, L., & Schneider, A.-M. (2009). CSR communication intensity in Chinese and Indian multinational companies. Corporate Governance: An International Review, 17 (4), 426–442.
Lecuyer, C., Capelli, S., & Sabadie, W. (2017). Corporate social responsibility communication effects: A comparison between investor-owned banks and member-owned banks. Journal of Advertising Research, 57 (4), 436–446.
Lee, M.-D. (2011). Configuration of external influences: The combined effects of institutions and stakeholders on corporate social responsibility strategies. Journal of Business Ethics, 102 (2), 281–298.
Lim, S.-J., & Phillips, J. (2008). Embedding CSR values: The global footwear industry’s evolving governance structure. Journal of Business Ethics, 81 (1), 143–156.
Lindgreen, A., Antioco, M., Harness, D., & Sloot, R. (2009a). Purchasing and marketing of social and environmental sustainability for high-tech medical equipment. Journal of Business Ethics, 85 , 445–462.
Lindgreen, A., & Swaen, V. (2010). Corporate social responsibility, Editorial. International Journal of Management Reviews, 112 (1), 1–7.
Lindgreen, A., Swaen, V., Harness, D., & Hoffmann, M. (2011). The role of ‘high potentials’ in integrating and implementing corporate social responsibility. Journal of Business Ethics, 99 , 73–91.
Lindgreen, A., Swaen, V., & Maon, F. (2009b). Introduction: Corporate social responsibility implementation. Journal of Business Ethics, 85 , 251–256.
Logsdon, J. M., & Wood, D. J. (2002). Business citizenship: From domestic to global level of analysis. Business Ethics Quarterly, 12 (2), 155–187.
Lu, J., & Wang, J. (2021). Corporate governance, law, culture, environmental performance and CSR disclosure: A global perspective. Journal of International Financial Markets, Institutions & Money, 70 , 101264.
Luo, J. M., Huang, G. Q., & Lam, C. F. (2019). Barriers to the implementation of corporate social responsibility in gaming industry. Journal of Quality Assurance in Hospitality & Tourism, 20 (5), 528–551.
Luo, X. R., Wang, D., & Zhang, J. (2017). Whose call to answer: Institutional complexity and firms’ CSR reporting. Academy of Management Journal, 60 (1), 321–344.
Maignan, I., & Ferrell, O. C. (2000). Measuring corporate citizenship in two countries: The case of the United States and France. Journal of Business Ethics, 23 (3), 283–297.
Maon, F., Lindgreen, A., & Swaen, V. (2009). Designing and implementing corporate social responsibility: An integrative framework grounded in theory and practice. Journal of Business Ethics, 87 , 71–89.
Marano, V., & Kostova, T. (2016). Unpacking the institutional complexity in adoption of CSR practices in multinational enterprises. Journal of Management Studies, 53 (1), 28–54.
Matten, D., & Crane, A. (2005). Corporate citizenship: Toward an extended theoretical conceptualization. Academy of Management Review, 30 (1), 166–179.
Miska, C., Witt, M. A., & Stahl, G. K. (2016). Drivers of global CSR integration and local CSR responsiveness: Evidence from Chinese MNEs. Business Ethics Quarterly, 26 (3), 317–345.
Muller, A., & Kolk, A. (2009). CSR performance in emerging markets evidence from Mexico. Journal of Business Ethics, 85 , 325–337.
Muthuri, J., Chapple, W., & Moon, J. (2009). An integrated approach to implementing community participation’ in corporate community involvement: Lessons from Magadi soda company in Kenya. Journal of Business Ethics, 85 , 431–444.
Öberseder, M., Schlegelmilch, B., Murphy, P., & Gruber, V. (2014). Consumers’ perceptions of corporate social responsibility: Scale development and validation. Journal of Business Ethics, 124 (1), 101–115.
O’Connor, A., & Shumate, M. (2010). An economic industry and institutional level of analysis of corporate social responsibility communication. Management Communication Quarterly, 24 (4), 529–551.
Osagie, E., Wesselink, R., Blok, V., Lans, T., & Mulder, M. (2016). Individual competencies for corporate social responsibility: A literature and practice perspective. Journal of Business Ethics, 135 (2), 233–252.
Park, B. I., & Ghauri, P. N. (2015). Determinants influencing CSR practices in small and medium sized MNE subsidiaries: A stakeholder perspective. Journal of World Business, 50 (1), 192–204.
Pedersen, E. R. G., Gwozdz, W., & Hvass, K. K. (2018). Exploring the relationship between business model innovation, corporate sustainability, and organisational values within the fashion industry. Journal of Business Ethics, 149 (2), 267–284.
Peloza, J., Hudson, S., & Hassay, D. (2009). The marketing of employee volunteerism. Journal of Business Ethics, 85 , 371–386.
Pham, H. S. T., & Tran, H. T. (2020). CSR disclosure and firm performance: The mediating role of corporate reputation and moderating role of CEO integrity. Journal of Business Research, 120 , 127–136.
Pisani, N., Kourula, A., Kolk, A., & Meijer, R. (2017). How global is international CSR research? Insights and recommendations from a systematic review. Journal of World Business, 52 (5), 591–614.
Platonova, E., Asutay, M., Dixon, R., & Mohammad, S. (2018). The impact of corporate social responsibility disclosure on financial performance: Evidence from the GCC Islamic banking sector. Journal of Business Ethics, 151 (2), 451–471.
Polonsky, M., & Jevons, C. (2009). Global branding and strategic CSR: An overview of three types of complexity. International Marketing Review, 26 (3), 327–347.
Pomering, A., & Dolnicar, S. (2009). Assessing the prerequisite of successful CSR implementation: Are consumers aware of CSR initiatives? Journal of Business Ethics, 85 , 285–301.
Popay, J., Roberts, H. M., Sowden, A. J., Petticrew, M., Arai, L., Rodgers, M., & Britten, N. (2006). Guidance on the conduct of narrative synthesis in systematic reviews. A product from the ESRC methods programme . Version 1.
Pope, S., & Wæraas, A. (2016). CSR-washing is rare: A conceptual framework, literature review, and critique. Journal of Business Ethics, 137 (1), 173–193.
Porter, M. E., & Kramer, M. R. (2006). Strategy & society: The link between competitive advantage and corporate social responsibility. Harvard Business Review, 84 (12), 78–92.
Quintana-García, C., Marchante-Lara, M., & Benavides-Chicón, C. G. (2018). Social responsibility and total quality in the hospitality industry: Does gender matter? Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 26 (5), 722–739.
Rama, D., Milano, B., Salas, S., & Liu, C.-H. (2009). CSR implementation: Developing the capacity for collective action. Journal of Business Ethics, 85 , 463–477.
Reimer, M., Van Doorn, S., & Heyden, M. L. M. (2018). Unpacking functional experience complementarities in senior leaders’ influences on CSR strategy: A CEO-Top Management Team Approach. Journal of Business Ethics, 151 (4), 977–995.
Rhou, Y., Singal, M., & Koh, Y. (2016). CSR and financial performance: The role of CSR awareness in the restaurant industry. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 57 , 30–39.
Risi, D., & Wickert, C. (2017). Reconsidering the ‘symmetry’ between institutionalization and professionalization: The case of corporate social responsibility managers. Journal of Management Studies, 54 (5), 613–646.
Rodríguez Bolívar, M. P., Garde Sánchez, R., & López Hernández, A. M. (2015). Managers as drivers of CSR in state-owned enterprises. Journal of Environmental Planning & Management, 58 (5), 777–801.
Russo, A., & Tencati, A. (2009). Formal vs. informal CSR strategies: Evidence from Italian micro, small, medium-sized, and large firms. Journal of Business Ethics, 85 , 339–353.
Saxton, G. D., Ren, C., & Guo, C. (2021). Responding to diffused stakeholders on social media: Connective power and firm reactions to CSR-related Twitter messages. Journal of Business Ethics, 172 (2), 229–252.
Schaefer, S. D., Terlutter, R., & Diehl, S. (2019). Is my company really doing good? Factors influencing employees’ evaluation of the authenticity of their company’s corporate social responsibility engagement. Journal of Business Research, 101 , 128–143.
Schoeneborn, D., Morsing, M., & Crane, A. (2020). Formative perspectives on the relation between CSR communication and CSR practices: Pathways for walking, talking, and t(w)alking. Business & Society, 59 (1), 5–33.
Seitanidi, M., & Crane, A. (2009). Implementing CSR through partnerships: Understanding the selection, design and institutionalisation of nonprofit-business partnerships. Journal of Business Ethics, 85 , 413–429.
Sendlhofer, T. (2020). Decoupling from moral responsibility for CSR: Employees’ visionary procrastination at a SME. Journal of Business Ethics, 167 (2), 361–378.
Serra-Cantallops, A., Peña-Miranda, D. D., Ramón-Cardona, J., & Martorell-Cunill, O. (2018). Progress in research on CSR and the hotel industry (2006–2015). Cornell Hospitality Quarterly, 59 (1), 15–38.
Shahzad, A. M., & Sharfman, M. P. (2017). Corporate social performance and financial performance: Sample-selection issues. Business & Society, 56 (6), 889–918.
Shaukat, A., Qiu, Y., & Trojanowski, G. (2016). Board attributes, corporate social responsibility strategy, and corporate environmental and social performance. Journal of Business Ethics, 135 (3), 569–585.
Shen, J., & Benson, J. (2016). When CSR is a social norm: How socially responsible human resource management affects employee work Behavior. Journal of Management, 42 (6), 1723–1746.
Skard, S., & Thorbjørnsen, H. (2014). Is publicity always better than advertising? The role of brand reputation in communicating corporate social responsibility. Journal of Business Ethics, 124 (1), 149–160.
Skouloudis, A., & Evangelinos, K. (2014). Exogenously driven CSR: Insights from the consultants’ perspective. Business Ethics: A European Review, 23 (3), 258–271.
Spalding, T. L., & Murphy, G. L. (1996). Effects of background knowledge on category construction. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 22 (2), 525–538.
Stekelorum, R., Laguir, I., & Elbaz, J. (2019). Transmission of CSR requirements in supply chains: Investigating the multiple mediating effects of CSR activities in SMEs. Applied Economics, 51 (42), 4642–4657.
Story, J., & Neves, P. (2015). When corporate social responsibility (CSR) increases performance: Exploring the role of intrinsic and extrinsic CSR attribution. Business Ethics: A European Review, 24 (2), 111–124.
Subramaniam, N., Kansal, M., & Babu, S. (2017). Governance of mandated corporate social responsibility: Evidence from Indian government-owned firms. Journal of Business Ethics, 143 (3), 543–563.
Tan, W., Tsang, A., Wang, W., & Zhang, W. (2020). Corporate social responsibility (CSR) disclosure and the choice between bank debt and public debt. Accounting Horizons, 34 (1), 151–173.
Thorne, L., Mahoney, L., Gregory, K., & Convery, S. (2017). A comparison of Canadian and U.S. CSR strategic alliances, CSR reporting, and CSR performance: Insights into implicit-explicit CSR. Journal of Business Ethics, 143 (1), 85–98.
Tourky, M., Kitchen, P., & Shaalan, A. (2020). The role of corporate identity in CSR implementation: An integrative framework. Journal of Business Research, 117 , 694–706.
Tranfield, D., Denyer, D., & Smart, P. (2003). Towards a methodology for developing evidence-informed management knowledge by means of systematic review. British Journal of Management, 14 (3), 207–222.
Trapp, N. L. (2014). Stakeholder involvement in CSR strategy-making? Clues from sixteen Danish companies. Public Relations Review, 40 (1), 42–49.
Turker, D. (2009). Measuring corporate social responsibility: A scale development study. Journal of Business Ethics, 85 (4), 411–427.
United Nations. (2020). The sustainable development goals report 2020 . United Nations.
van Marrewijk, M. (2003). Concepts and definitions of CSR and corporate sustainability: Between agency and communion. Journal of Business Ethics, 44 (2), 95–105.
van Tulder, R., van Wijk, J., & Kolk, A. (2009). From chain liability to chain responsibility. Journal of Business Ethics, 85 (2), 399–412.
Verk, N., Golob, U., & Podnar, K. (2021). A dynamic review of the emergence of corporate social responsibility communication. Journal of Business Ethics, 168 (3), 491–515.
Vlachos, P. A., Tsamakos, A., Vrechopoulos, A. P., & Avramidis, P. K. (2009). Corporate social responsibility: Attributions, loyalty, and the mediating role of trust. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 37 (2), 170–180.
Walters, G., & Anagnostopoulos, C. (2012). Implementing corporate social responsibility through social partnerships. Business Ethics: A European Review, 21 (4), 417–433.
Wickert, C., Scherer, A. G., & Spence, L. J. (2016). Walking and talking corporate social responsibility: Implications of firm size and organizational cost. Journal of Management Studies, 53 (7), 1169–1196.
Wood, D. J. (1991). Corporate social performance revisited. Academy of Management Review, 16 (4), 691–718.
Yin, J., & Jamali, D. (2016). Strategic corporate social responsibility of multinational companies subsidiaries in emerging markets: Evidence from China. Long Range Planning, 49 (5), 541–558.
Zamir, F., & Saeed, A. (2020). Location matters: Impact of geographical proximity to financial centers on corporate social responsibility (CSR) disclosure in emerging economies. Asia Pacific Journal of Management, 37 (1), 263–295.
Zerbini, F. (2017). CSR initiatives as market signals: A review and research agenda. Journal of Business Ethics, 146 (1), 1–23.
Zhang, L., Shan, Y. G., & Chang, M. (2021). Can CSR disclosure protect firm reputation during financial restatements? Journal of Business Ethics, 173 (1), 157–184.
Zheng, Q., Luo, Y., & Maksimov, V. (2015). Achieving legitimacy through corporate social responsibility: The case of emerging economy firms. Journal of World Business, 50 (3), 389–403.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
College of Business and Economics, Qatar University, P.O. Box 2713, Doha, Qatar
Tahniyath Fatima & Said Elbanna
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Said Elbanna .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (DOCX 140 kb)
Rights and permissions.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Fatima, T., Elbanna, S. Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Implementation: A Review and a Research Agenda Towards an Integrative Framework. J Bus Ethics 183 , 105–121 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-022-05047-8
Download citation
Received : 25 May 2021
Accepted : 20 January 2022
Published : 02 February 2022
Issue Date : February 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-022-05047-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Corporate social responsibility implementation
- CSR strategy
- CSR complexity
- CSR formulation
- CSR implementation framework
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Three Essays on Corporate Social Responsibility
- Burbano, Vanessa Cuerel
- Advisor(s): Snyder, Jason ;
- Lieberman, Marvin
This dissertation explores the effect of corporate social responsibility (CSR) practices on the firm and contributes to an understanding of how CSR practices can contribute to companies’ competitive advantage. In Chapter 1, I use three randomized field experiments implemented in online labor marketplaces to provide causal evidence of the effect of CSR on employee outcomes that have been shown to be critical to firm performance: salary requirements and employee performance. Workers were recruited for short-term jobs and I manipulated whether or not they received information about the employer’s CSR program. I then observed the payment workers were willing to accept for the job and their performance on the job. Surveys administered at the end of the experiments gauging workers’ perceptions about the received CSR information also provide insight into the distinct mechanisms through which CSR affects the different employee outcomes. This paper contributes to an understanding of how CSR adds value to the firm and highlights the role of the employee in explaining this relationship. It also demonstrates how online labor markets can be used as settings for field experimental research in strategic management more broadly.
In Chapter 2, we examine pro bono work in the legal services industry. Using a screening model we show that law firms use pro bono engagements to gain information about associates’ expected productivity as an equity partner. Using a dataset of the top 200 US law firms in 2010 we demonstrate empirical support for our model’s predictions. Our findings thus suggest that the conventional wisdom that CSR practices are used to provide information about the quality of the firm to the employee is backwards; rather, we find that pro bono engagements are used to provide information about the quality of the employee to the firm.
In Chapter 3, we explore what drives firms to combine poor environmental performance with communication about positive environmental performance, resulting in “greenwashing”. Although some explanation of firm greenwashing has been put forth, a comprehensive analysis of the determinants of firm greenwashing is lacking. Drawing from existing work in management, strategy, sociology and psychology, we propose a comprehensive framework that examines the external (both institutional and market), organizational and individual drivers of greenwashing and then use this framework to develop recommendations for managers, policymakers, and NGOs to decrease greenwashing.
Enter the password to open this PDF file:

- Search by keyword
- Search by citation
Page 1 of 2
Board gender diversity and corporate social responsibility
Based on a total of 1,590 listed non-financial firms on the Taiwan Stock Exchange and the Taipei Exchange (formerly the Over The Counter securities market) covering the period of 2007~2020, this study examines...
- View Full Text
The role of internal CSR in guiding the digitalisation of work
In the context of the increased use of digital technologies at work and the various reported positive and negative outcomes for workers, this paper deals with the effects of internal corporate social responsib...
Assessing the impact of corporate social responsibility communication on nonprofit organisations in South Africa
The aim of the study was to investigate whether the content of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) messages predicts communication outcomes in South African nonprofit organisations (NPOs). The study found a ...
Corporate social responsibility, sustainable environmental practices and green innovation; perspectives from the Ghanaian manufacturing industry
As the discourse around business ethics and sustainable development intensifies, many organizations are adopting initiatives in corporate social responsibility (CSR) as a strategic tool to satisfy regulatory r...
Assessment of corporate social responsibility practices in selected public libraries in South-West and North-Central, Nigeria
This study explored corporate social responsibility practices in selected public libraries in south-west and north-central Nigeria. The study adopts multiple case-study design, and qualitative research approac...
Navigating the myriad of corporate quality standards: a CSR and stakeholder perspective
Quality standards (QS) (e.g., ISO 9001) play an important role in assuring the quality of goods and services for organizational stakeholders on a global scale. Recent work has highlighted the role of QS in com...
Translating brand reputation into equity from the stakeholder’s theory: an approach to value creation based on consumer’s perception & interactions
This study is to examine the translation of a reputable brand into equity and how consumers’ perceptions can trigger value creation from commitment and pursuit of CSR by an organization and adopting the same a...

Synthesising synergies between CSR and BHR for corporate accountability: an integrated approach
While an emerging literature considers Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) as obligatory, voluntarism has dominated the scholarship and policymaking related to CSR. Almost parallel to this literature, the fi...
Corporate social responsibility communication in the ICT sector: digital issues, greenwashing, and materiality
Digitalization brings with it new social and governance issues and heightened responsibility, particularly for corporations. In recent years, society has demanded more transparency from companies about digital...

Responsible government and responsible business: the challenge of harnessing CSR in a new epoch
Much has been written of the implications for government policy on ‘responsible business’ but a comprehensive review of the subject is needed. This literature review will offer an assessment of varied insights...
Is capital structure associated with corporate social responsibility?
Based on a total of 1,590 listed non-financial firms on the Taiwan Stock Exchange and the Taipei Exchanges covering the period of 2007 ~ 2020, this study examines whether a firm's capital structure is affected...
Towards a definition of sustainable banking - a consolidated approach in the context of guidelines and strategies
Sustainable development efforts, initiated by the SDGs and the Paris Agreement on climate change, are bringing banking to the center of the debate, which calls for, among other things, sustainable banking. In ...
Correction: When and where does it pay to be green? – A look into socially responsible investing and the cost of equity capital
The original article was published in International Journal of Corporate Social Responsibility 2023 8 :1
How Corporate Sociopolitical Activism (CSA) impacts portfolio allocations: an experiment
If a firm signals that they identify on one end of the conservative-liberal spectrum, will political affiliation help predict how an investor will allocate their investment dollars to that firm? Using an exper...
Challenges of CSR in Sub-Saharan Africa: clarifying the gaps between the regulations and human rights issues
This paper discusses the practice of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) and its challenges in Sub-Saharan Africa. The main purpose is to highlight and clarify the gaps between CSR regulations and human righ...
When and where does it pay to be green? – A look into socially responsible investing and the cost of equity capital
We investigate the circumstances under which socially responsible investing (SRI) enhances firm long-term financial performance, and therefore provides incentives for firms to self-regulate their environmental...
The Correction to this article has been published in International Journal of Corporate Social Responsibility 2023 8 :4
Corporate social responsibility. A strategy for social and territorial sustainability
Globalization and financial processes have progressively generated an intense and problematic phenomenon of disconnection between companies and their territories. Breaking of the spatial link has often led to ...
“Issues emanating from business impact on climate, environmental sustainability and CSR (Corporate Social Responsibility): steps towards pragmatism in extant realities”: “Brand translation to equity from ‘CSR as a potential tool in climate change mitigation and enhancing financial performances in organizations”
The relationship between ‘CSR and Brands to the sustainable business environment coupled with climatic changes and environmental issues; ‘while emphasizing the potentials of ‘CSR from brand reputation translat...
Wheat and chaff: the degree to which strategic management principles are integrated within corporate social responsibility reporting among large Canadian firms
This empirical study examines the degree to which strategic principles are reflected in the corporate social responsibility (CSR) reporting practices among Canada’s largest corporations. In a two-phased approa...
ESG in the boardroom: evidence from the Malaysian market
This study examines the influence of boards’ characteristics with respect to independence, diversity, and diligence on the environment, social, governance (ESG) disclosure among Bursa Malaysia companies. The b...
New corporate social responsibility brand evaluation in a developing country: Uzbekistan
Organizations strive to satisfy salient and unmet consumer needs by providing value through their products and services. If environmentally sustainable “green” brands successfully exist by addressing environme...
Sustainability performance indicator trends: a Canadian industry-based analysis
This study aims to examine the trends in the sustainability performance indicators disclosed in sustainability reports by Canadian companies. Our sample is comprised of eight companies in four sectors and our ...
How does CSR of food company affect customer loyalty in the context of COVID-19: a moderated mediation model
Because of COVID-19 in the world, enterprises and consumers pay more and more attention to environmental protection, food safety and health issues. The purpose of this paper is to take China's food company as ...
Management control systems in response to social and environmental risk in large Nordic companies
This empirical study investigates the relationships between management control systems and social and environmental risks. Building on Simons’ Levers of Control conceptual framework, this study proposes that c...
Corporate social responsibility in international business literature: results from text data mining of the Journal of International Business Studies
Corporate social responsibility has been an important theme in management at least since the 1960s. International business became a recognized subfield in management around the same time. Logically, there migh...
The long-term transformation of the concept of CSR: towards a more comprehensive emphasis on sustainability
This article adds to the discussion of the long-term transformation of CSR, presenting a perspective on the interplay between CSR debate and public discourse on business responsibility. 50 years after Milton F...
Novel CSR & novel coronavirus: corporate social responsibility inside the frame of coronavirus pandemic in Greece
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) becomes popular as big international firms gain more power than states and global issues engender concerns to people from all over the world. The pandemic of novel coronav...
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): motivations and challenges of a Multinational Enterprise (MNE) subsidiary’s engagement with host communities in Ghana
This paper aims to explore the motivations and challenges of engaging host communities in CSR practices within the context of Newmont Ahafo Mines (NAM), a subsidiary of a Multinational Mining Enterprise (MNE) ...
Examining the role of environmental corporate social responsibility in building green corporate image and green competitive advantage
Green concern is making a profound impact on building green competitive advantage (GCA) across the globe. Apparel sector of Bangladesh is at crossroads regarding sustainability of firms. Green initiatives are ...
Cultural influence on innovativeness - links between “The Culture Map” and the “Global Innovation Index”
In the ongoing debate on the relation of cultural differences and national innovativeness this research aims to find out which of the seven cultural dimensions of The Culture Map (communicating, evaluating, leadi...
CSR reporting by Chinese and Western MNEs: patterns combining formal homogenization and substantive differences
In light of the growing economic might and intensification of global activities of Chinese multinational enterprises (MNE), this paper looks into the nature of their corporate social responsibility (CSR) repor...
Microfinance institutions’ operational self-sufficiency in sub-Saharan Africa: empirical evidence
The topic of financial sustainability in microfinance institutions has become more important as an increasing number of Microfinance Institutions (MFIs) seek operational self-sufficiency, which translates into...
Do Millennials pay attention to Corporate Social Responsibility in comparison to previous generations? Are they motivated to lead in times of transformation? A qualitative review of generations, CSR and work motivation
The purpose of this qualitative review is to analyze empirical studies on whether the existing generations differ in their work beliefs, i.e. in their internal CSR perceptions and their leadership motivation, ...
Impact of strategic management, corporate social responsibility on firm performance in the post mandate period: evidence from India
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is like a chameleon, that changes its colour according to the context it is in. In the developed economy, it takes the form of sustainability and/ or philanthropy, whereas...
Green bonds issuance: insights in low- and middle-income countries
Former reports of Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) tended to focus on the equity side of investing, and today green bonds also offer and introduce sustainability factors. This paper is about the rele...
Corporate social responsibility and stakeholder engagement in Ghana’s mining sector: a case study of Newmont Ahafo mines
Even though the concept of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) has been applauded for several decades, the concept of stakeholder engagement is relatively new to the Ghanaian mining sector. This study invest...
Sustainability in the automotive industry, importance of and impact on automobile interior – insights from an empirical survey
Sustainability is currently one of the main issues in all media and in society as a whole and is increasingly discussed in science from different sides and areas. Especially for the automotive industry, sustai...
Implementing part-time leadership as instrument for sustainable HR management
This paper discusses the suitability of part-time leadership as instrument for a sustainable Human Resources Management (HRM) policy. The concept of part-time leadership is introduced and discussed based on a ...
Looking through the African lenses: a critical exploration of the CSR activities of Chinese International Construction Companies (CICCs) in Africa
The importance of Chinese International Construction Companies (CICCs) within the construction sector in Africa can no longer be ignored, as these firms hold a considerable amount of market share within the Af...
Mechanisms for development in corporate citizenship: a multi-level review
Social Responsibility, referred to in this study as Corporate Citizenship (CC) has experienced continued growth in significance among academics and corporate leaders. The absence of a multi-level approach to w...
Competition and microfinance institutions’ performance: evidence from India
This paper empirically examines whether competition (measured by using the new measure of competition, the Boone Indicator) moderates the relationship between Microfinance Institutions’ (MFIs) social and finan...
Optimal growth under socially responsible investment: a dynamic theoretical model of the trade-off between financial gains and emotional rewards
Socially responsible investment (SRI) evolved, along the last two decades, from an almost unexplored topic in science to a recurrent theme of research and debate in Economics and Finance. The growing interest ...
Understanding the purpose of benefit corporations: an empirical study on the Italian case
Rethinking the traditional understanding of organizational purpose appears to be necessary. A teleological paradigm shift seems to be on its way, changing the focus of attention from considering business organ...
Climate change adaptation, coffee, and corporate social responsibility: challenges and opportunities
Climate change is making a profound impact on agricultural production across the globe. Coffee (especially the Arabica variety) is one of the most severely affected crops. Adaptive measures are therefore neede...
Corporate social responsibility and accountability: a new theoretical foundation for regulating CSR
The absence of consensus on what should constitute Corporate Social Responsibility has inhibited consistent CSR legislation around the world. This paper poses a fundamental question on what should constitute C...
CSR commitments, perceptions of hypocrisy, and recovery
This paper examines perceived hypocrisy when a failure is aligned with prior social performance. It is hypothesized that commitment to a CSR domain creates greater performance expectations thus exacerbating th...
Grey zone in – greenwash out. A review of greenwashing research and implications for the voluntary-mandatory transition of CSR
As public concern over greenwashing has grown in the last two decades, academic research has increased correspondingly, and there is now a substantial body of research addressing issues related to greenwashing...
Assessing and managing sustainability in international perspective: corporate sustainability across cultures – towards a strategic framework implementation approach
Sustainability constitutes an essential element in corporate contexts by now. Corporate sustainability may be addressed differently, either selectively or integrated. The holistic approach opted for primarily ...
Acting as a benefit corporation and a B Corp to responsibly pursue private and public benefits. The case of Paradisi Srl (Italy)
Benefit Corporations and B Corps represent alternative models of enterprise that bridge the for-profit and not-for-profit model (hybrid organizations). Italy is the first country outside the US to pass Benefit...
Purpose-driven leadership for sustainable business: From the Perspective of Taoism
In recent years, the topic of “purpose” has been actively studied and discussed by the academic scholars and business practitioners. The purpose revolution has significantly changed the way companies are doing...
- Editorial Board
- Sign up for article alerts and news from this journal
Annual Journal Metrics
2023 Speed 11 days submission to first editorial decision for all manuscripts (Median) 226 days submission to accept (Median)
2023 Usage 601,176 downloads 17 Altmetric mentions
- More about our metrics
- ISSN: 2366-0074 (electronic)
- ISSN: 2366-0066 (print)

6 inspiring CSR report examples for CSRD compliance
.jpg)
CSR reporting, which is also known as sustainability reporting, has been a common practice for some time now. However, with the implementation of the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) , it has become a mandatory task for many companies based in the European Union. Considering the number of reporting businesses out there, a good CSR report design isn’t a luxury - it is a necessity. Just because you have to structure your report according to certain standards, it doesn't mean your report should be boring. This article provides some excellent examples of CSR reports to inspire you for the year 2025.
What is CSR reporting?
Before jumping in, let's take a step back to understand what CSR reporting is. CSR stands for Corporate Social Responsibility , and it refers to a company's willingness to take responsibility for the social and environmental impacts of its operations. The ultimate goal is to promote sustainable and ethical business practices that prioritise the well-being of stakeholders, including employees, customers, communities, and the environment. These reports are usually published on an annual basis and aim to foster transparency and accountability.
What is the difference between ESG and CSR reports?
You may have also heard of an ESG report. Although the terms CSR and ESG are often used interchangeably, there is a difference between them . Both are forms of sustainability reporting, but the main difference is in metrics. An ESG report aims to measure the efforts stated in CSR reports and show where the company is in its sustainable journey. ESG is an extension of CSR.
Why is CSRD important for CSR reporting?
The Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) is a framework that was recently established by the European Union (EU) to standardise and enhance the disclosure of sustainability information by companies. The CSRD aims to expand the scope of previous directives and improve the overall quality of sustainability reporting.
It is important to note that there is a difference between CSR and CSRD. A CSR report refers to the documents or output that outline a company’s activities and performance, while the CSRD is a framework that provides guidelines for what to include within these CSR reports. While CSR initiatives are usually voluntary, compliance with CSRD is mandatory. Companies are required to disclose sustainability-related information following European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS) to promote comparability.
Does CSRD apply to your company? Start planning your CSR report now!
According to a study by KPMG , 96% of the top 250 companies in the world follow some form of sustainability reporting. This indicates that, as your business grows, you have to become more accountable for your company's sustainable efforts. The implementation of the CSRD in the European Union (EU) has pushed many companies into the direction of reporting on sustainability much sooner than expected. From this year onwards, these companies are expected to fully comply with the CSRD, and as a result, they should currently be preparing their report for the upcoming year. Your company may also need to do the same. Therefore, you should not underestimate the value of a well-designed CSR report and take action now. We will inspire you with several examples of good CSR report design and what makes them great.
Examples of great CSR reports (and what makes them good)
When searching for CSR reports in Google, you will find plenty. What you will find, however, is that most of these reports are still in PDF and actual engaging CSR reports are hard to come by. We believe that interactivity is the key to reader engagement. To demonstrate, we provide you with several examples of great recent CSR reports and will explain what makes them pleasurable to read.
BMW Group - Sustainability strategy up to 2030
The BMW Group has decided to present its sustainability strategy for the coming years in a digital slide publication. Sliding from left to right is intuitive for any reader - online or offline. This type of navigation guides the viewer through the content in a linear way, ensuring that the story is told in the right order. In addition, the report is easy on the eyes thanks to the incorporation of high-quality photography that matches the message. Alongside the images, the descriptions are short and to the point, making it more inviting to read.
View the report
Meta - Sustainability Report 2023
Meta's sustainability report for 2023 has a very clean and sleek design. While not the most innovative form of CSR report design, its clean design is very effective and easy on the eyes. As one of the top-performing companies in the world, extensive reporting is a given. Meta has made a smart choice to separate its content, effectively creating a digital "cover" for the actual report, which is (yet again) in PDF format. The reason why this is effective is that readers will quickly scan topics and conclude whether this report contains information that is relevant to them. Those who want more in-depth information can refer to the full report with the click of a button. This is a great example if you want to go for a clean and minimal design, while also providing the full scope of your CSR report.
ROC Amsterdam - CSR strategy up to 2026
This interactive CSR report by ROC Amsterdam takes the reader on a journey through their strategy up to 2026. When we say 'journey', we mean it literally. This publication is an excellent example of why interactive content works so well in capturing the reader's attention. With a plethora of visuals, interactive elements and animations, the reader is invited to engage with the content. With linear navigation from destination A to B, the user is guided through the story in a logical order. Who said CSR reports needed to be boring?
Tony Chocolonely - Annual FAIR Report 2021/2022
For fair trade companies such as Tony's Chocolonely, CSR reporting is a given. Their report for 2021 - 2022 showcases efforts in sustainable operations and social responsibilities in style. The report is unmistakably Tony Chocolonely's thanks to the use of their iconic fonts and brand colours. Graphs, charts and other statistics are visualised in colourful infographics accompanied by dynamic elements to draw attention. Although a serious topic, Tony Chocolonely perfectly demonstrates that CSR reporting can be playful.
Albert Heijn - Sustainability Report 2023
Albert Heijn is a well-known supermarket chain that is also known for its innovative work in the food tech industry. The recently released 2023 sustainability report, highlights last year's sustainable efforts. The report features the brand's recognisable style and easy-to-use navigation. By separating the main content of the report into a separate document, the consumer can access concise information and also refer to more in-depth information as needed. Although containing lots of data up to several layers deep, the design feels lightweight and user-friendly.
Girls Who Code - Annual Report 2022
Girls Who Code published an interactive annual report in 2022 that combines cleanliness with playful elements. Presenting the report as a web page that is part of the main website, makes it easy for readers to find. Important information is emphasised by revealing it through scroll animations. Lastly, data is visualised in colourful rand colours without excessive motion. Overall the report reads comfortably and manages to find a balance between professionalism and playfulness.
What will your CSR report for 2024 look like?
Now that you are inspired, how will you structure your 2024 CSR report? There’s no need to figure it out alone - Maglr can help. Whether you prefer to use templates, design freely or require help from our in-house design team , we can offer you the needed support to make your CSR report a success. Request a demonstration or free trial today.

Stay in the loop
Subscribe to our newsletter to receive free updates of our latest blogs, inspirational examples and new platform releases.
More articles

Why and how to get started with accessible web design (+ free resources)

4 Ways to use interactive embeds within your website

Reach your audience with online magazines
Start your interactive story.
Improve the reading experience of the content you share with clients. Request a trial or contact sales for a live demonstration.
Opinions on Corporate Social Responsibility Essay
Introduction, reference list.
Corporate social responsibility is an essential aspect in the business world. It is an obligation for a business organization to pursue long term goals that are good for the society. It can also be termed as the continuing commitment by business firms to behave in an ethical manner and contribute to economic development while at the same time enhancing the quality of life of the employees and their families.
The business firm should also enhance the lives of the local community and the entire society around which it operates (Kotler, 2005). This piece of work looks at an individual, Karl Mark, evaluating him with respect to corporate social responsibility and its effects on his career.
Abiding by corporate social responsibility practices is not only beneficial to a business organization but also to individuals who participate in it. An individual’s perception and view about the idea of corporate social responsibility influences ones life greatly in terms of career progression and the behavior of the general public towards the individual.
This therefore dictates that it is advisable to support the idea of corporate social responsibility for the sake of one’s prosperity as well as that of the society at large despite the cost that could be involved.
Karl Marx was an active economic activist and socialist who was involved with many activities during his lifetime. It is evident that Karl Marx would totally support the idea of corporate social responsibility.
This is because of his nature and how he perceived life in general. He cared more about the communities and would therefore support any effort aimed at supporting the society in any way. He was against capitalism and supported collective gain among the society members (Marx, not dated).
In his career, Karl Mark was able to succeed due to the support he gave to the society in regard to advocating for developmental projects aimed at helping members of the society in an effort to uplift their living standards. Karl Mark’s economic and socialist work gained considerable support from people due to the fact that the benefits associated with the activities were clear (Marx, Easton and Guddat, 1997).
Business organizations should operate bearing in mind that the society is a crucial element that contributes towards their success. Without the support of the people who surround a business organization, it is difficult for it to succeed in its undertakings. This is because it requires a symbiotic relationship to be established between a business enterprise and the society around it.
This is so as both need each other for success. A business organization may need the society as buyers as well suppliers. They could also be a source of workforce in various positions for example marketers bearing in mind that they are in a better position to reach as many clients as possible.
The business should therefore go an extra mile in providing services to the society as a way of fulfilling corporate social responsibility. This could be through undertaking of some developmental projects that aim at enhancing the lives of the people.
Throughout his entire life, Karl Marx attempted to gain a deeper understanding of the society and its nature in an effort to ensure that their rights are fulfilled. He for example supported aspects like education and enlightenment of the people so that they would be in a position to fight for their rights and social justice.
Provision of educative programs by business enterprises to the community is a form of corporate social responsibility and plays a great role in ensuring that members of the society are well equipped with some knowledge and skills which in turn allows them to live a better and sustainable life for instance through securing employment opportunities (Eastman, 1959).
There are various benefits associated with corporate social responsibility. For example, it avoids excessive regulation, it is ethical and improves an individual’s and firm’s public image, enhances the social environment and more so, some socially responsible actions are profitable. It is also a good way of correcting social problems that might have been caused by various activities.
In cases of a business, it provides a competitive advantage, attracts and retains employees through motivation and attracts investors. It therefore follows that business enterprises should always foster corporate social responsibility.
Although Karl Mark received a lot of objections from the authorities such as the governments, he tried his best to enhance the lives of the society and for this reason his name and work will live to be remembered over the years. This is more so because of his contribution towards the understanding of society (Foot, 2004).
From the above discussion, it is evident that corporate social responsibility is critical to economic development due to the fact that it empowers societies.
Abiding by corporate social responsibility practices is not only beneficial to a business organization but also to individuals who participate in it. An individual’s perception and view about the idea of corporate social responsibility influences his or her career and how the general public reacts towards him or her.
Eastman, M. (1959). Capital, the Communist Manifesto and Other Writings . New York: Modern Library.
Foot, P. (2004). Karl Marx: the Best Hated Man, Socialist review . Web.
Kotler, P. (2005). Corporate Social Responsibility: Doing the Most Good for Your Company and Your Cause . New Jersey: John Wiley and Sons.
Marx, K. (n d). Economic and Philosophical Manuscripts of 1844 . Web.
Marx K, Easton, D.L and Guddat H.K. (1997). Writings of the Young Marx on Philosophy and Society . New York: Hackett Publishing.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 4). Opinions on Corporate Social Responsibility. https://ivypanda.com/essays/opinions-on-corporate-social-responsibility-essay/
"Opinions on Corporate Social Responsibility." IvyPanda , 4 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/opinions-on-corporate-social-responsibility-essay/.
IvyPanda . (2024) 'Opinions on Corporate Social Responsibility'. 4 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "Opinions on Corporate Social Responsibility." February 4, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/opinions-on-corporate-social-responsibility-essay/.
1. IvyPanda . "Opinions on Corporate Social Responsibility." February 4, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/opinions-on-corporate-social-responsibility-essay/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Opinions on Corporate Social Responsibility." February 4, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/opinions-on-corporate-social-responsibility-essay/.
- Karl Marx and the "Communist Manifesto"
- The Communist Manifesto by Karl Marx
- Karl Marx: Philosophical Views
- Karl Marx: A Hero or a Villain?
- Karl Marx’s Life and Philosophical Ideas
- Karl Marx’s Theory of Alienation
- Karl Marx's Take on Work Process
- Karl Marx’s and Max Weber's Ideas
- The Theory of Production Relations by Karl Marx
- Karl Marx's Ideology and Education
- Sports and Business: The Complicacies and the Benefits
- Desk Research on the Low Cost Airline Sector in Europe
- Characteristics of Japanese Employment Relations
- Municipal government strategies for controlling personnel costs during the fiscal storm
- Tourism Destination in the United Arab Emirates
My Job as a Csr at Family Dollar
This essay about my role as a Customer Service Representative (CSR) at Family Dollar outlines the multifaceted aspects of the job, focusing on customer interaction, inventory management, and the execution of promotional campaigns. It discusses the daily responsibilities, such as ensuring customer satisfaction, handling stock, and setting up sales displays, which require strong communication, organizational skills, and problem-solving abilities. The essay highlights the challenges faced in a retail environment and the skills developed, notably in understanding consumer behavior and managing complex situations. It emphasizes that working as a CSR at Family Dollar is not just a job, but a comprehensive learning experience that offers growth in various professional competencies, preparing one for future career advancements in retail or any customer-focused industry.
How it works
Working as a Customer Service Representative (CSR) at Family Dollar offers a unique vantage point into the retail industry, particularly within a discount store chain that serves millions of customers. My job encompasses a range of responsibilities that require both interpersonal skills and operational knowledge, reflecting the dynamic nature of retail work. This essay outlines my daily functions, the challenges I face, and the valuable skills I’ve developed during my tenure at Family Dollar.
As a CSR at Family Dollar, my primary responsibility is to ensure that customers have a positive shopping experience from the moment they enter the store until they complete their purchases.
This involves greeting customers, answering their questions, guiding them to products, and handling checkout processes. Additionally, I am tasked with handling returns and exchanges, addressing customer complaints, and sometimes resolving conflicts. These tasks demand strong communication skills and a patient demeanor, as delivering satisfactory solutions to various customer issues is crucial to maintaining the store’s reputation and customer loyalty.
One of the most challenging aspects of my job is inventory management. Family Dollar stores typically operate with a wide range of products, from groceries to household items. It is crucial to keep track of inventory levels, manage stock rooms, and ensure that the shelves are neatly organized and well-stocked. This part of the job requires attention to detail and effective time management, especially during deliveries when new stock arrives and needs to be sorted and shelved efficiently.
Another significant challenge is the implementation of promotional campaigns. Family Dollar often runs sales and promotions, and as a CSR, it is my duty to update pricing, set up displays according to the promotional standards, and ensure that promotional materials are visible and attractive. This involves coordinating with management and other team members, which enhances my skills in teamwork and organization.
Beyond the operational tasks, working at Family Dollar has honed my problem-solving skills. Retail environments are fast-paced and unpredictable, requiring CSRs to think on their feet. Whether it’s handling a sudden rush of customers, dealing with a product shortage, or resolving a payment issue, I’ve learned to quickly analyze situations and devise effective solutions. This skill is not only valuable in my current role but is transferable to many other sectors and career paths.
Moreover, the job has deepened my understanding of consumer behavior. Interacting with a diverse clientele helps me grasp what drives customer satisfaction and loyalty. This insight is particularly valuable in a discount retail setting where customers are not just looking for low prices but also value good service and a pleasant shopping environment.
In conclusion, my role as a CSR at Family Dollar is more than just a job; it is a multifaceted learning experience that teaches me about retail management, customer service, and effective communication. Each day presents new challenges and opportunities to grow professionally and personally. The skills I’ve developed here are foundational for any career in retail or customer service, providing me with a strong platform to advance my professional life. Through this role, I’ve not only contributed to the success of my store but also prepared myself for future challenges in the fast-evolving retail industry.
Remember, this essay is a starting point for inspiration and further research. For more personalized assistance and to ensure your essay meets all academic standards, consider reaching out to professionals at [EduBirdie](https://edubirdie.com/?utm_source=chatgpt&utm_medium=answer&utm_campaign=essayhelper).
Cite this page
My Job As A Csr At Family Dollar. (2024, Apr 29). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/my-job-as-a-csr-at-family-dollar/
"My Job As A Csr At Family Dollar." PapersOwl.com , 29 Apr 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/my-job-as-a-csr-at-family-dollar/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). My Job As A Csr At Family Dollar . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/my-job-as-a-csr-at-family-dollar/ [Accessed: 2 May. 2024]
"My Job As A Csr At Family Dollar." PapersOwl.com, Apr 29, 2024. Accessed May 2, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/my-job-as-a-csr-at-family-dollar/
"My Job As A Csr At Family Dollar," PapersOwl.com , 29-Apr-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/my-job-as-a-csr-at-family-dollar/. [Accessed: 2-May-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). My Job As A Csr At Family Dollar . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/my-job-as-a-csr-at-family-dollar/ [Accessed: 2-May-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Truth About CSR. Most of these programs aren't strategic—and that's OK. Summary. Despite the widely accepted ideal of "shared value," research led by Harvard Business School's ...
5 Corporate Social Responsibility Examples. 1. Lego's Commitment to Sustainability. As one of the most reputable companies in the world, Lego aims to not only help children develop through creative play, but foster a healthy planet. Lego is the first, and only, toy company to be named a World Wildlife Fund Climate Savers Partner, marking its ...
Chapter 1 Introduction. Corporate Social Responsibility is a rapidly developing, key business issue. It is a concept that has attracted worldwide attention. Due to the demands for enhanced transparency and corporate citizenship, CSR started to embrace social, ethical as well as environmental challenges. Today, companies are aware of the social ...
There is a long and varied history associated with the evolution of the concept of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR). However, a historical review is missing in the academic literature that portrays the evolution of the academic understanding of the concept alongside with the public and international events that influenced the social expectations with regards to corporate behavior. The aim ...
Introduction. Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is defined as the voluntary activities undertaken by a company to operate in an economic, social and environmentally sustainable manner. The Government of Canada understands that responsible corporate behavior by Canadian companies operating internationally not only enhances their chances for ...
There has, in recent times, been an increasing interest in understanding corporate social (and environmental) responsibility (CSR) and, in particular, CSR reporting in developing countries. However, many of these studies fail to investigate fully the contextual factors that influence CSR and reporting in those countries, preferring to rely on theories and hypotheses developed from studies ...
How Corporate Social Responsibility Works . Corporate social responsibility is a way of doing business that aims to increase a company's social impact while meeting business objectives such as growth and revenue goals. It can also refer to any effort to improve a company's eco-friendliness or carbon footprint.
Corporate Social Responsibility touches numerous aspects of life, all of which are meant to conserve resources and ensure the good of the public. As the needs of the consumers/public are catered for, the socially responsible company also benefits in numerous ways. This paper looks into the importance of ethical behaviour and Corporate Social ...
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) was usually referred to as a concept where companies initiate voluntary action towards social and environmental concerns in the context of business operations related to the stakeholders of the company prior to the CSR Act 2013 in India. Post-2013, the voluntary initiative was replaced by regulatory guidelines to address social and environmental concerns.
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) is a form of corporate self-regulation incorporated into the business, which functions as an instrument by which a corporation examines and ensures its active conformity with the provisions of the law, ethical norms, and global practices. We will write a custom essay on your topic. 809 writers online.
This introduction to the Thematic Collection on Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) tracks the evolution of CSR research published in the Journal of Management Studies from 2006 until 2021. Alongside the mainstreaming of CSR within management studies, CSR research in JMS has progressed from a business-centric to a society-centric focus. The business-centric focus centres on the financial ...
Corporate Social Responsibility. Introduction. Corporate social responsibility (CSR) is a self-controlling model of business that helps business organizations to be socially accountable to the public, stakeholders, and self. Through CSR, companies have conscious of how that affects society environmentally, socially, and economically as they do ...
In spite of accruing concerted scholarly and managerial interest since the 1950s in corporate social responsibility (CSR), its implementation is still a growing topic as most of it remains academically unexplored. As CSR continues to establish a stronger foothold in organizational strategies, understanding its implementation is needed for both academia and industry. In an attempt to respond to ...
2.2. Corporate social responsibility. The proposed a fairly well-known definition of CSR as an aggregation of corporate obligations expected by the whole community (Carroll, Citation 1979; L. Zhao et al., Citation 2022).Elkington (Citation 1998) saw that the concept of modern CSR is based on so-called the triple bottom line principle, namely the balanced relationship between profit, people and ...
Adidas Group's Corporate Social Responsibility. To increase the effectiveness of production procedures and to meet the new difficulties facing the fashion industry, it is crucial to be able to ensure the safety and wellbeing of the personnel in working conditions. Corporate Social Responsibility: Shell and BP.
This dissertation explores the effect of corporate social responsibility (CSR) practices on the firm and contributes to an understanding of how CSR practices can contribute to companies' competitive advantage. In Chapter 1, I use three randomized field experiments implemented in online labor marketplaces to provide causal evidence of the ...
Board gender diversity and corporate social responsibility. Based on a total of 1,590 listed non-financial firms on the Taiwan Stock Exchange and the Taipei Exchange (formerly the Over The Counter securities market) covering the period of 2007~2020, this study examines...
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is the concept according to which companies integrate social and environmental concerns in their business operations and in their interaction with their ...
This paper investigates how the market value of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) disclosure within the framework of family-owned enterprise. It also explores the mediator of investor attention between CSR disclosures and market value, alongside the moderator of marketization on the relationship between CSR disclosures and investor attention.
the prices of Dollar was witnessed. Corporate Social Responsibility became a matter of utmost importance for diverse groups demanding change in the business. During the 1980's to 2000, corporations recognized and started accepting a responsibility towards society. Corporate social responsibility (CSR) focuses on the wealth
Adoption of CSR initiatives have a significant impact on sustainable business strategies. Patil et al., (2017) explored the effect of corporate social responsibility on socioeconomic development. According to their study's findings, the CSR contribute to societal improvement and economic growth to some extent only.
Banerjee, S2007, Corporate social responsibility: The good, the bad and the ugly, Edward Elgar, Cheltenham, UK. Beurden, P. & Go¨ssling, T 2008, 'The Worth of Values - A Literature Review on the Relation between Corporate Social and Financial Performance', Journal of Business Ethics, vol. 82, is. 1, pp. 407-424.
At first, CSR emerged as an idea developed by American business ethicists and corporate executives who argued that companies can and should not focus single-mindedly on profit maximization. Companies were rather supposed to follow business practices that combine profit-making with moral standards and what was referred to as 'service to the ...
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR), defined in terms of the. responsiveness of businesses t o stakeholders' legal, ethical, social and environmenta l. expectations, is one outcome of these ...
CSR reporting, which is also known as sustainability reporting, has been a common practice for some time now. However, with the implementation of the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD), it has become a mandatory task for many companies based in the European Union.Considering the number of reporting businesses out there, a good CSR report design isn't a luxury - it is a ...
There are various benefits associated with corporate social responsibility. For example, it avoids excessive regulation, it is ethical and improves an individual's and firm's public image, enhances the social environment and more so, some socially responsible actions are profitable.
Reflective essay on CSR - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. REflective essay on CSR
Essay Example: Working as a Customer Service Representative (CSR) at Family Dollar offers a unique vantage point into the retail industry, particularly within a discount store chain that serves millions of customers. My job encompasses a range of responsibilities that require both interpersonal