The Business Process Reengineering Project: A Successful Case Study
Cite this chapter.

- Edi Snaidero &
- Andrea Tramontano
155 Accesses
It is rather difficult to relate a successful case study after months spent in the fore front, initially nurturing an idea then a project and eventually developing a new way of doing and being in business . One of the risks here is to boast or, even worse, to give a detailed account of what should have been achieved and yet remained in paper.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.

Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Copyright information
© 2004 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Snaidero, E., Tramontano, A. (2004). The Business Process Reengineering Project: A Successful Case Study. In: Process Management for the Extended Enterprise. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-17051-5_5
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-17051-5_5
Publisher Name : Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN : 978-3-642-62082-9
Online ISBN : 978-3-642-17051-5
eBook Packages : Springer Book Archive
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Business Process Management in Small Business: A Case Study

Related Papers
A business process typically crosses the borders of organizational departments and even companies. Thus, business processes are complex artifacts that challenge managers in their efforts to properly manage them. Against this background, business process models are key artifacts to represent how work is performed in organizations. There is a great deal of concern among different developing economies; including Egypt, that SMEs’ potentials are not fully utilized although they dominate these economies, and claim to contribute to their success. The question often asked is what challenges are preventing those SMEs from performing efficiently. This research focuses on examining the issues regarding SMEs in Egypt, and assessing whether Business Process Management; particularly Business Process Re-engineering, would help enhance the organization’s performance for particularly service-providing SMEs and explore the effectiveness of modelling business processes in identifying the areas needed...
Business Excellence and Management
Vlad Balanescu
Business Process Management (BPM) is considered to be the third wave in business process theory. Appearing as a response to the critique formulated regarding Business Process Reengineering, BPM tries to be a more holistic and integrated approach to management and processes. In a time where complex solutions are needed solution that incorporates elements from various concepts, Business Process Management can be, in my opinion, a link between these ideas. After a short introduction presenting general background information pertinent to the subject, the second chapter focuses on the theoretical concept of Business Process Management, its origins, definitions and key characteristics. Finally, the third chapter present a Business Process Management implementation methodology alongside with a list of key elements that should be taken into consideration when implementing BPM and a strategy oriented strategy and model in general.
Operational Research in Engineering Sciences: Theory and Applications
Andrea Dobrosavljević
Pendukeni S Haikali
Monique M J C Snoeck
Recently, Business Process Management (BPM) has gained a lot of attention both from the academic world and the industrial world. The similarities between workflow management and business process management can make one wonder whether it's all old wine in new bottles. But although there are many similarities and many results from workflow research still apply, recent technological developments have changed
Business Process Management Journal
Monika Klun
PurposeBusiness process management (BPM) has attracted much focus throughout the years, yet there have been calls questioning the future of BPM. The purpose of this paper is to explore the current state of the field through a dynamic literature review and identify the main challenges for its future development.Design/methodology/approachA dynamic co-citation network analysis identifies the “evolution” of knowledge of BPM and the most influential works. The results present the developed BPM subthemes in the form of clusters.FindingsThe focus within the field has shifted from facilitating wide-ranging business performance improvements to creating introverted optimizations within a particular BPM subgroup. The BPM field has thus experienced strong fragmentation throughout the years and has accrued into self-fueling subareas of BPM research such as business process modeling and workflow management. Those subareas often neglect related disciplines in other management, process modeling an...
Charles Møller
Business Process Management (BPM) is an emerging new field in business. However there is no academically agreed upon conceptual framework. The aim of this paper is to establish a conceptual framework grounded in the recent literature. The purpose of this work is to ensure a better foundation for future research and to discussion of the implications of BPM on Enterprise Information Systems (EIS). The starting point of this study is a focused literature review of the BPM concept. This literature review leads to the formulation of a conceptual framework for BPM which is evaluated using a quantitative lexical analysis of a broader literature sample. Finally the implication of the BPM on EIS is discussed and potential future research opportunities are outlined.
mohsen Moghaddam
Shazia Sadiq , Marta Indulska
Asian Journal of Applied Science and Technology
AJAST Journal
A business' choice for using an innovation depends on looking into the variables affecting this use and its favorable circumstances. Innovation deployment significantly influences the way business is led, the optimality of asset usage and increase in the organizations competitive advantage. This research is to identify the role Business Processing Management (BPM) play in selected SMEs in Ghana. The method utilized for this investigation was the descriptive research design. This research is exclusively embraced by the utilization of secondary data. The technique for data analysis will be by the utilization of content analysis. The study revealed that the main principles of BPM implementation in the selected SMEs are commitment from management, customer priority, teamwork, and continuous improvement. The study also showed that BPM has a direct relationship with the productivity of SMEs. The main challenges of BPM on the selected SMEs are the lack of resources, lack of experience in quality management, lack of objectives and strategies, Short term objectives concerns, lack of information technology (IT) experts. Since BPM is a broad and an intense concept that needs to be taken seriously when it comes to SMEs ensuring that the firm produces a high-quality goods and services, it was recommended that SMEs needs to have IT experts who can assist in the integration of BPM in all aspect of the business activities.
RELATED PAPERS
Gregory Plett
카지노사이트추천〃〃GCN777。COM〃〃2월바다낚시
Somtawin Jaritkhuan
Dental traumatology : official publication of International Association for Dental Traumatology
Fernanda Garcia
Rodriguésia
Silmara Nepomuceno
Brazilian Journal of Oncology
Izabella Souza , T. Silveira
Krista Duynisveld
Mariana de Jesus Pedreira Valente
Communications in Computer and Information Science
Alejandro Pérez Ordóñez
Dominik Hezel
Cabildo, n.12
José Alberto Fernández Sánchez
Sustainability
Juliana Merçon
Article, Turcomoney
Ismail OZSOY
Physics Letters B
Víctor Manuel Velazquez Aguilar
Doğu Avrupa Tarihi, Yeni Bulgular ve Yaklaşımlar
European Journal of Case Reports in Internal Medicine
Salah Qanadli
Clinical Nutrition
Francine Bossan
Indian Journal of Ophthalmology
Vikas Desai
Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena
Roberto Mulet
Mihai Mihai
OSTI OAI (U.S. Department of Energy Office of Scientific and Technical Information)
Fotouh Al-Ragom
Sociologies pratiques
Nicolas Spire
Materials Science and Engineering: C
Samuel Derrer
Journal of Clinical Medicine
Lucia Muraca
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
info Welcome to the new library homepage for students who enrolled through Northcentral University. To access the old NCU library homepage, click here . If you enrolled through National University, click here . Please be aware that the NU and NCU students have access to all of the same resources, and we will be merging library homepages by next year.
notifications Welcome to the new library homepage! If you are looking for the old homepage, click here .

Business Case Studies: Case Study Examples
- How to Write a Case Study
- How to Analyze a Case Study
- Case Study Examples
- How to Find Case Studies
- Case Study Analysis Samples
- Case Study Writing Samples

- Manufacturing Flow Analysis at COMPANY
- Case Study: Kiwi Medical Devices Ltd.
- Case Study example A paper TESLA
- Case Study Report-Peloton A paper
- << Previous: How to Analyze a Case Study
- Next: How to Find Case Studies >>
- Last Updated: Nov 14, 2023 8:20 AM
- URL: https://nu.libguides.com/buscasestudy

© Copyright 2024 National University. All Rights Reserved.
Privacy Policy | Consumer Information

Related Expertise: Culture and Change Management , Business Strategy , Corporate Strategy
Five Case Studies of Transformation Excellence
November 03, 2014 By Lars Fæste , Jim Hemerling , Perry Keenan , and Martin Reeves
In a business environment characterized by greater volatility and more frequent disruptions, companies face a clear imperative: they must transform or fall behind. Yet most transformation efforts are highly complex initiatives that take years to implement. As a result, most fall short of their intended targets—in value, timing, or both. Based on client experience, The Boston Consulting Group has developed an approach to transformation that flips the odds in a company’s favor. What does that look like in the real world? Here are five company examples that show successful transformations, across a range of industries and locations.
VF’s Growth Transformation Creates Strong Value for Investors
Value creation is a powerful lens for identifying the initiatives that will have the greatest impact on a company’s transformation agenda and for understanding the potential value of the overall program for shareholders.
VF offers a compelling example of a company using a sharp focus on value creation to chart its transformation course. In the early 2000s, VF was a good company with strong management but limited organic growth. Its “jeanswear” and intimate-apparel businesses, although responsible for 80 percent of the company’s revenues, were mature, low-gross-margin segments. And the company’s cost-cutting initiatives were delivering diminishing returns. VF’s top line was essentially flat, at about $5 billion in annual revenues, with an unclear path to future growth. VF’s value creation had been driven by cost discipline and manufacturing efficiency, yet, to the frustration of management, VF had a lower valuation multiple than most of its peers.
With BCG’s help, VF assessed its options and identified key levers to drive stronger and more-sustainable value creation. The result was a multiyear transformation comprising four components:
- A Strong Commitment to Value Creation as the Company’s Focus. Initially, VF cut back its growth guidance to signal to investors that it would not pursue growth opportunities at the expense of profitability. And as a sign of management’s commitment to balanced value creation, the company increased its dividend by 90 percent.
- Relentless Cost Management. VF built on its long-known operational excellence to develop an operating model focused on leveraging scale and synergies across its businesses through initiatives in sourcing, supply chain processes, and offshoring.
- A Major Transformation of the Portfolio. To help fund its journey, VF divested product lines worth about $1 billion in revenues, including its namesake intimate-apparel business. It used those resources to acquire nearly $2 billion worth of higher-growth, higher-margin brands, such as Vans, Nautica, and Reef. Overall, this shifted the balance of its portfolio from 70 percent low-growth heritage brands to 65 percent higher-growth lifestyle brands.
- The Creation of a High-Performance Culture. VF has created an ownership mind-set in its management ranks. More than 200 managers across all key businesses and regions received training in the underlying principles of value creation, and the performance of every brand and business is assessed in terms of its value contribution. In addition, VF strengthened its management bench through a dedicated talent-management program and selective high-profile hires. (For an illustration of VF’s transformation roadmap, see the exhibit.)
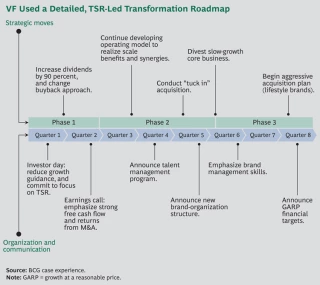
The results of VF’s TSR-led transformation are apparent. 1 1 For a detailed description of the VF journey, see the 2013 Value Creators Report, Unlocking New Sources of Value Creation , BCG report, September 2013. Notes: 1 For a detailed description of the VF journey, see the 2013 Value Creators Report, Unlocking New Sources of Value Creation , BCG report, September 2013. The company’s revenues have grown from $7 billion in 2008 to more than $11 billion in 2013 (and revenues are projected to top $17 billion by 2017). At the same time, profitability has improved substantially, highlighted by a gross margin of 48 percent as of mid-2014. The company’s stock price quadrupled from $15 per share in 2005 to more than $65 per share in September 2014, while paying about 2 percent a year in dividends. As a result, the company has ranked in the top quintile of the S&P 500 in terms of TSR over the past ten years.
A Consumer-Packaged-Goods Company Uses Several Levers to Fund Its Transformation Journey
A leading consumer-packaged-goods (CPG) player was struggling to respond to challenging market dynamics, particularly in the value-based segments and at the price points where it was strongest. The near- and medium-term forecasts looked even worse, with likely contractions in sales volume and potentially even in revenues. A comprehensive transformation effort was needed.
To fund the journey, the company looked at several cost-reduction initiatives, including logistics. Previously, the company had worked with a large number of logistics providers, causing it to miss out on scale efficiencies.
To improve, it bundled all transportation spending, across the entire network (both inbound to production facilities and out-bound to its various distribution channels), and opened it to bidding through a request-for-proposal process. As a result, the company was able to save 10 percent on logistics in the first 12 months—a very fast gain for what is essentially a commodity service.
Similarly, the company addressed its marketing-agency spending. A benchmark analysis revealed that the company had been paying rates well above the market average and getting fewer hours per full-time equivalent each year than the market standard. By getting both rates and hours in line, the company managed to save more than 10 percent on its agency spending—and those savings were immediately reinvested to enable the launch of what became a highly successful brand.
Next, the company pivoted to growth mode in order to win in the medium term. The measure with the biggest impact was pricing. The company operates in a category that is highly segmented across product lines and highly localized. Products that sell well in one region often do poorly in a neighboring state. Accordingly, it sought to de-average its pricing approach across locations, brands, and pack sizes, driving a 2 percent increase in EBIT.
Similarly, it analyzed trade promotion effectiveness by gathering and compiling data on the roughly 150,000 promotions that the company had run across channels, locations, brands, and pack sizes. The result was a 2 terabyte database tracking the historical performance of all promotions.
Using that information, the company could make smarter decisions about which promotions should be scrapped, which should be tweaked, and which should merit a greater push. The result was another 2 percent increase in EBIT. Critically, this was a clear capability that the company built up internally, with the objective of continually strengthening its trade-promotion performance over time, and that has continued to pay annual dividends.
Finally, the company launched a significant initiative in targeted distribution. Before the transformation, the company’s distributors made decisions regarding product stocking in independent retail locations that were largely intuitive. To improve its distribution, the company leveraged big data to analyze historical sales performance for segments, brands, and individual SKUs within a roughly ten-mile radius of that retail location. On the basis of that analysis, the company was able to identify the five SKUs likely to sell best that were currently not in a particular store. The company put this tool on a mobile platform and is in the process of rolling it out to the distributor base. (Currently, approximately 60 percent of distributors, representing about 80 percent of sales volume, are rolling it out.) Without any changes to the product lineup, that measure has driven a 4 percent jump in gross sales.
Throughout the process, management had a strong change-management effort in place. For example, senior leaders communicated the goals of the transformation to employees through town hall meetings. Cognizant of how stressful transformations can be for employees—particularly during the early efforts to fund the journey, which often emphasize cost reductions—the company aggressively talked about how those savings were being reinvested into the business to drive growth (for example, investments into the most effective trade promotions and the brands that showed the greatest sales-growth potential).
In the aggregate, the transformation led to a much stronger EBIT performance, with increases of nearly $100 million in fiscal 2013 and far more anticipated in 2014 and 2015. The company’s premium products now make up a much bigger part of the portfolio. And the company is better positioned to compete in its market.
A Leading Bank Uses a Lean Approach to Transform Its Target Operating Model
A leading bank in Europe is in the process of a multiyear transformation of its operating model. Prior to this effort, a benchmarking analysis found that the bank was lagging behind its peers in several aspects. Branch employees handled fewer customers and sold fewer new products, and back-office processing times for new products were slow. Customer feedback was poor, and rework rates were high, especially at the interface between the front and back offices. Activities that could have been managed centrally were handled at local levels, increasing complexity and cost. Harmonization across borders—albeit a challenge given that the bank operates in many countries—was limited. However, the benchmark also highlighted many strengths that provided a basis for further improvement, such as common platforms and efficient product-administration processes.
To address the gaps, the company set the design principles for a target operating model for its operations and launched a lean program to get there. Using an end-to-end process approach, all the bank’s activities were broken down into roughly 250 processes, covering everything that a customer could potentially experience. Each process was then optimized from end to end using lean tools. This approach breaks down silos and increases collaboration and transparency across both functions and organization layers.
Employees from different functions took an active role in the process improvements, participating in employee workshops in which they analyzed processes from the perspective of the customer. For a mortgage, the process was broken down into discrete steps, from the moment the customer walks into a branch or goes to the company website, until the house has changed owners. In the front office, the system was improved to strengthen management, including clear performance targets, preparation of branch managers for coaching roles, and training in root-cause problem solving. This new way of working and approaching problems has directly boosted both productivity and morale.
The bank is making sizable gains in performance as the program rolls through the organization. For example, front-office processing time for a mortgage has decreased by 33 percent and the bank can get a final answer to customers 36 percent faster. The call centers had a significant increase in first-call resolution. Even more important, customer satisfaction scores are increasing, and rework rates have been halved. For each process the bank revamps, it achieves a consistent 15 to 25 percent increase in productivity.
And the bank isn’t done yet. It is focusing on permanently embedding a change mind-set into the organization so that continuous improvement becomes the norm. This change capability will be essential as the bank continues on its transformation journey.
A German Health Insurer Transforms Itself to Better Serve Customers
Barmer GEK, Germany’s largest public health insurer, has a successful history spanning 130 years and has been named one of the top 100 brands in Germany. When its new CEO, Dr. Christoph Straub, took office in 2011, he quickly realized the need for action despite the company’s relatively good financial health. The company was still dealing with the postmerger integration of Barmer and GEK in 2010 and needed to adapt to a fast-changing and increasingly competitive market. It was losing ground to competitors in both market share and key financial benchmarks. Barmer GEK was suffering from overhead structures that kept it from delivering market-leading customer service and being cost efficient, even as competitors were improving their service offerings in a market where prices are fixed. Facing this fundamental challenge, Barmer GEK decided to launch a major transformation effort.
The goal of the transformation was to fundamentally improve the customer experience, with customer satisfaction as a benchmark of success. At the same time, Barmer GEK needed to improve its cost position and make tough choices to align its operations to better meet customer needs. As part of the first step in the transformation, the company launched a delayering program that streamlined management layers, leading to significant savings and notable side benefits including enhanced accountability, better decision making, and an increased customer focus. Delayering laid the path to win in the medium term through fundamental changes to the company’s business and operating model in order to set up the company for long-term success.
The company launched ambitious efforts to change the way things were traditionally done:
- A Better Client-Service Model. Barmer GEK is reducing the number of its branches by 50 percent, while transitioning to larger and more attractive service centers throughout Germany. More than 90 percent of customers will still be able to reach a service center within 20 minutes. To reach rural areas, mobile branches that can visit homes were created.
- Improved Customer Access. Because Barmer GEK wanted to make it easier for customers to access the company, it invested significantly in online services and full-service call centers. This led to a direct reduction in the number of customers who need to visit branches while maintaining high levels of customer satisfaction.
- Organization Simplification. A pillar of Barmer GEK’s transformation is the centralization and specialization of claim processing. By moving from 80 regional hubs to 40 specialized processing centers, the company is now using specialized administrators—who are more effective and efficient than under the old staffing model—and increased sharing of best practices.
Although Barmer GEK has strategically reduced its workforce in some areas—through proven concepts such as specialization and centralization of core processes—it has invested heavily in areas that are aligned with delivering value to the customer, increasing the number of customer-facing employees across the board. These changes have made Barmer GEK competitive on cost, with expected annual savings exceeding €300 million, as the company continues on its journey to deliver exceptional value to customers. Beyond being described in the German press as a “bold move,” the transformation has laid the groundwork for the successful future of the company.
Nokia’s Leader-Driven Transformation Reinvents the Company (Again)
We all remember Nokia as the company that once dominated the mobile-phone industry but subsequently had to exit that business. What is easily forgotten is that Nokia has radically and successfully reinvented itself several times in its 150-year history. This makes Nokia a prime example of a “serial transformer.”
In 2014, Nokia embarked on perhaps the most radical transformation in its history. During that year, Nokia had to make a radical choice: continue massively investing in its mobile-device business (its largest) or reinvent itself. The device business had been moving toward a difficult stalemate, generating dissatisfactory results and requiring increasing amounts of capital, which Nokia no longer had. At the same time, the company was in a 50-50 joint venture with Siemens—called Nokia Siemens Networks (NSN)—that sold networking equipment. NSN had been undergoing a massive turnaround and cost-reduction program, steadily improving its results.
When Microsoft expressed interest in taking over Nokia’s device business, Nokia chairman Risto Siilasmaa took the initiative. Over the course of six months, he and the executive team evaluated several alternatives and shaped a deal that would radically change Nokia’s trajectory: selling the mobile business to Microsoft. In parallel, Nokia CFO Timo Ihamuotila orchestrated another deal to buy out Siemens from the NSN joint venture, giving Nokia 100 percent control over the unit and forming the cash-generating core of the new Nokia. These deals have proved essential for Nokia to fund the journey. They were well-timed, well-executed moves at the right terms.
Right after these radical announcements, Nokia embarked on a strategy-led design period to win in the medium term with new people and a new organization, with Risto Siilasmaa as chairman and interim CEO. Nokia set up a new portfolio strategy, corporate structure, capital structure, robust business plans, and management team with president and CEO Rajeev Suri in charge. Nokia focused on delivering excellent operational results across its portfolio of three businesses while planning its next move: a leading position in technologies for a world in which everyone and everything will be connected.
Nokia’s share price has steadily climbed. Its enterprise value has grown 12-fold since bottoming out in July 2012. The company has returned billions of dollars of cash to its shareholders and is once again the most valuable company in Finland. The next few years will demonstrate how this chapter in Nokia’s 150-year history of serial transformation will again reinvent the company.

Managing Director & Senior Partner
San Francisco - Bay Area

Managing Director & Senior Partner, Chairman of the BCG Henderson Institute
ABOUT BOSTON CONSULTING GROUP
Boston Consulting Group partners with leaders in business and society to tackle their most important challenges and capture their greatest opportunities. BCG was the pioneer in business strategy when it was founded in 1963. Today, we work closely with clients to embrace a transformational approach aimed at benefiting all stakeholders—empowering organizations to grow, build sustainable competitive advantage, and drive positive societal impact.
Our diverse, global teams bring deep industry and functional expertise and a range of perspectives that question the status quo and spark change. BCG delivers solutions through leading-edge management consulting, technology and design, and corporate and digital ventures. We work in a uniquely collaborative model across the firm and throughout all levels of the client organization, fueled by the goal of helping our clients thrive and enabling them to make the world a better place.
© Boston Consulting Group 2024. All rights reserved.
For information or permission to reprint, please contact BCG at [email protected] . To find the latest BCG content and register to receive e-alerts on this topic or others, please visit bcg.com . Follow Boston Consulting Group on Facebook and X (formerly Twitter) .
Subscribe to our Business Transformation E-Alert.
Brought to you by:

Overview of the Business Case Writing Process
By: Gerry Yemen
Why would busy executives participate in business case studies? The relationship that develops between executives and faculty through the case writing process is a powerful example of sharing and…
- Length: 2 page(s)
- Publication Date: Apr 12, 2012
- Discipline: Entrepreneurship
- Product #: UV6103-PDF-ENG
What's included:
- Educator Copy
$4.95 per student
degree granting course
$8.95 per student
non-degree granting course
Get access to this material, plus much more with a free Educator Account:
- Access to world-famous HBS cases
- Up to 60% off materials for your students
- Resources for teaching online
- Tips and reviews from other Educators
Already registered? Sign in
- Student Registration
- Non-Academic Registration
- Included Materials
Why would busy executives participate in business case studies? The relationship that develops between executives and faculty through the case writing process is a powerful example of sharing and trust. And because a number of executives are unaware of what exactly the process entails, they ask for a description of it. This note describing the process may be customized to suit the needs of all case writers.
Apr 12, 2012
Discipline:
Entrepreneurship
Darden School of Business
UV6103-PDF-ENG
We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience, including personalizing content. Learn More . By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .

Business Case Study

Although personal experiences are the first things one would look into, understanding, and analyzing what others went through is also an excellent method for learning. Not everyone goes through the same things in life; there will always be differences in our experiences. By studying and making some case analysis on the experiences of others can give you the insight you didn’t think you needed. In the corporate world, this is called a business case study.
What Is a Business Case Study?
Studying the deals and transactions of a business can benefit business owners, students, clients, and the company being investigated. The report you present is called a business case study. On technical terms, a business case study is a real-life or imaginary business situation documented and used as instructional material. Business students and trainees examine these documents to formulate solutions and action plans to hypothetical problems. Some companies publish their case studies so that prospective clients can understand what they do and how they can assist them. This can also serve as a marketing strategy to advertise their successes.
Showering in Benefits
Business schools use business management report case study examples to prepare students for the many situations that can happen in the real world. Case analysis helps them exercise their critical thinking skills and problem-solving skills. In law schools, business law case studies are even present. But schools, business books, and academic settings are not the only ones that use business case studies. The corporate world is full of companies that report their undertakings as case studies. There are many benefits that a company can gain from business case study presentations. Here are four benefits companies should consider when deciding to publish their business cases:
Storytelling
When writing a case study that centers on a service or product, the company gets the chance to market and discuss their products comprehensively. Case studies, like stories, have a beginning, middle, and end. Utilizing these parts can help advertise the product.
Peer to Peer Influence
Just because the company publishes the case study, the basis of its content is the client’s point of view. By using direct quotes, statistics, and other elements, the reader can make a business case study analysis with a bias of the previous client’s influence.
Real-Life Examples
Business case studies give the company a platform to showcase the product or service as applied in real-life.
Word of Mouth
When a customer is satisfied and intrigued by the case study he has read, there is a high chance that he could become a vessel for word of mouth marketing when he talks about the company and its case to his peers.
14+ Business Case Study Examples
Business case studies take a lot of time to formulate. They may be a documentation plan of something that already happened; they still take a lot of time to format. To help you in making a case study, here are 10+ business case study examples you can look into.
1. SaaS Business Case Study Template Example

- Google Docs
Size: 100 KB

2. Business Case Study Template Example

Size: 76 KB
3. Free Business Case Study Template

Size: 170 KB
4. Free Saas Business Case Study Template

Size: 119 KB
5. Sample Business Case Studies Example

Size: 455 KB
6. Small business Case Studies Example

7. Basic Business Case Studies Example

Size: 113 KB
8. Industry Business Case Study Example

Size: 773 KB
9. Formal Business Case Studies Example

10. Printable Business Case Studies Example

Size: 944 KB
11. Green Business Case Study Example

12. Business Risk Case Studies Example

Size: 17 MB
13. Business Case Studies Template

Size: 134 KB
14. Business Mutual Case Study Example

Size: 943 KB
15. Business Case Studies in DOC

Size: 23 KB
How to Conduct a Standard Business Case Study
The process of writing a case study takes a lot of effort. You need to make sure to write every part comprehensively. From the executive summary to the conclusion, every little detail must stay consistent. Here are just a few ways to accomplish the technical writing and publishing of a case study.
Step 1: Provide Data
When writing a case summary , you need to be sure to have all the right data. There will be a lot of cases you might want to look into, to pick the right one, make sure they contain a significant challenge, a satisfying solution to any business risk , and a good amount of benefits. Having the correct information before you even start can ensure a successful case study.
Step 2: Write it Down
You need to make sure you get to write the case study correctly. Many technical writing elements should come into play. The writer’s voice should be relatable to the reader. Your titles and subheads should be eye-catching. Simple language can go a long way. Adding statistics and other numerical facts can boost your reliability. And remember to write from the very beginning to the very end.
Step 4: Provide Your Contacts
Publishing a case study comes with a distribution agreement. With that in mind, you need to put your contact information on your case study. This helps other companies, clients, and students reach you easily. You need to make sure your phone number, website, and email signature are present. The more people contact you, the more you boost your ROI.
Step 5: Design
One way to add more appeal to your case study is by giving it a stunning design. Why not hire a graphic designer for that? Having a professional add well-crafted designs to your case studies can help you get the reader’s attention. You can also let him add infographics to make it visually informative.
Step 6: Get Ready to Publish
The last step is to, of course, to publish it. You can’t really call it a real case study if it isn’t published. Publish it, distribute it, and you are good to go.
They say history repeats itself. To prevent the mishaps of the past from happening again, you need to study the tales and stories of those who have experience. Only then can you prepare yourself for what’s to come.
AI Generator
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Artificial intelligence in strategy
Can machines automate strategy development? The short answer is no. However, there are numerous aspects of strategists’ work where AI and advanced analytics tools can already bring enormous value. Yuval Atsmon is a senior partner who leads the new McKinsey Center for Strategy Innovation, which studies ways new technologies can augment the timeless principles of strategy. In this episode of the Inside the Strategy Room podcast, he explains how artificial intelligence is already transforming strategy and what’s on the horizon. This is an edited transcript of the discussion. For more conversations on the strategy issues that matter, follow the series on your preferred podcast platform .
Joanna Pachner: What does artificial intelligence mean in the context of strategy?
Yuval Atsmon: When people talk about artificial intelligence, they include everything to do with analytics, automation, and data analysis. Marvin Minsky, the pioneer of artificial intelligence research in the 1960s, talked about AI as a “suitcase word”—a term into which you can stuff whatever you want—and that still seems to be the case. We are comfortable with that because we think companies should use all the capabilities of more traditional analysis while increasing automation in strategy that can free up management or analyst time and, gradually, introducing tools that can augment human thinking.
Joanna Pachner: AI has been embraced by many business functions, but strategy seems to be largely immune to its charms. Why do you think that is?
Subscribe to the Inside the Strategy Room podcast
Yuval Atsmon: You’re right about the limited adoption. Only 7 percent of respondents to our survey about the use of AI say they use it in strategy or even financial planning, whereas in areas like marketing, supply chain, and service operations, it’s 25 or 30 percent. One reason adoption is lagging is that strategy is one of the most integrative conceptual practices. When executives think about strategy automation, many are looking too far ahead—at AI capabilities that would decide, in place of the business leader, what the right strategy is. They are missing opportunities to use AI in the building blocks of strategy that could significantly improve outcomes.
I like to use the analogy to virtual assistants. Many of us use Alexa or Siri but very few people use these tools to do more than dictate a text message or shut off the lights. We don’t feel comfortable with the technology’s ability to understand the context in more sophisticated applications. AI in strategy is similar: it’s hard for AI to know everything an executive knows, but it can help executives with certain tasks.
When executives think about strategy automation, many are looking too far ahead—at AI deciding the right strategy. They are missing opportunities to use AI in the building blocks of strategy.
Joanna Pachner: What kind of tasks can AI help strategists execute today?
Yuval Atsmon: We talk about six stages of AI development. The earliest is simple analytics, which we refer to as descriptive intelligence. Companies use dashboards for competitive analysis or to study performance in different parts of the business that are automatically updated. Some have interactive capabilities for refinement and testing.
The second level is diagnostic intelligence, which is the ability to look backward at the business and understand root causes and drivers of performance. The level after that is predictive intelligence: being able to anticipate certain scenarios or options and the value of things in the future based on momentum from the past as well as signals picked in the market. Both diagnostics and prediction are areas that AI can greatly improve today. The tools can augment executives’ analysis and become areas where you develop capabilities. For example, on diagnostic intelligence, you can organize your portfolio into segments to understand granularly where performance is coming from and do it in a much more continuous way than analysts could. You can try 20 different ways in an hour versus deploying one hundred analysts to tackle the problem.
Predictive AI is both more difficult and more risky. Executives shouldn’t fully rely on predictive AI, but it provides another systematic viewpoint in the room. Because strategic decisions have significant consequences, a key consideration is to use AI transparently in the sense of understanding why it is making a certain prediction and what extrapolations it is making from which information. You can then assess if you trust the prediction or not. You can even use AI to track the evolution of the assumptions for that prediction.
Those are the levels available today. The next three levels will take time to develop. There are some early examples of AI advising actions for executives’ consideration that would be value-creating based on the analysis. From there, you go to delegating certain decision authority to AI, with constraints and supervision. Eventually, there is the point where fully autonomous AI analyzes and decides with no human interaction.
Because strategic decisions have significant consequences, you need to understand why AI is making a certain prediction and what extrapolations it’s making from which information.
Joanna Pachner: What kind of businesses or industries could gain the greatest benefits from embracing AI at its current level of sophistication?
Yuval Atsmon: Every business probably has some opportunity to use AI more than it does today. The first thing to look at is the availability of data. Do you have performance data that can be organized in a systematic way? Companies that have deep data on their portfolios down to business line, SKU, inventory, and raw ingredients have the biggest opportunities to use machines to gain granular insights that humans could not.
Companies whose strategies rely on a few big decisions with limited data would get less from AI. Likewise, those facing a lot of volatility and vulnerability to external events would benefit less than companies with controlled and systematic portfolios, although they could deploy AI to better predict those external events and identify what they can and cannot control.
Third, the velocity of decisions matters. Most companies develop strategies every three to five years, which then become annual budgets. If you think about strategy in that way, the role of AI is relatively limited other than potentially accelerating analyses that are inputs into the strategy. However, some companies regularly revisit big decisions they made based on assumptions about the world that may have since changed, affecting the projected ROI of initiatives. Such shifts would affect how you deploy talent and executive time, how you spend money and focus sales efforts, and AI can be valuable in guiding that. The value of AI is even bigger when you can make decisions close to the time of deploying resources, because AI can signal that your previous assumptions have changed from when you made your plan.
Joanna Pachner: Can you provide any examples of companies employing AI to address specific strategic challenges?
Yuval Atsmon: Some of the most innovative users of AI, not coincidentally, are AI- and digital-native companies. Some of these companies have seen massive benefits from AI and have increased its usage in other areas of the business. One mobility player adjusts its financial planning based on pricing patterns it observes in the market. Its business has relatively high flexibility to demand but less so to supply, so the company uses AI to continuously signal back when pricing dynamics are trending in a way that would affect profitability or where demand is rising. This allows the company to quickly react to create more capacity because its profitability is highly sensitive to keeping demand and supply in equilibrium.
Joanna Pachner: Given how quickly things change today, doesn’t AI seem to be more a tactical than a strategic tool, providing time-sensitive input on isolated elements of strategy?
Yuval Atsmon: It’s interesting that you make the distinction between strategic and tactical. Of course, every decision can be broken down into smaller ones, and where AI can be affordably used in strategy today is for building blocks of the strategy. It might feel tactical, but it can make a massive difference. One of the world’s leading investment firms, for example, has started to use AI to scan for certain patterns rather than scanning individual companies directly. AI looks for consumer mobile usage that suggests a company’s technology is catching on quickly, giving the firm an opportunity to invest in that company before others do. That created a significant strategic edge for them, even though the tool itself may be relatively tactical.
Joanna Pachner: McKinsey has written a lot about cognitive biases and social dynamics that can skew decision making. Can AI help with these challenges?
Yuval Atsmon: When we talk to executives about using AI in strategy development, the first reaction we get is, “Those are really big decisions; what if AI gets them wrong?” The first answer is that humans also get them wrong—a lot. [Amos] Tversky, [Daniel] Kahneman, and others have proven that some of those errors are systemic, observable, and predictable. The first thing AI can do is spot situations likely to give rise to biases. For example, imagine that AI is listening in on a strategy session where the CEO proposes something and everyone says “Aye” without debate and discussion. AI could inform the room, “We might have a sunflower bias here,” which could trigger more conversation and remind the CEO that it’s in their own interest to encourage some devil’s advocacy.
We also often see confirmation bias, where people focus their analysis on proving the wisdom of what they already want to do, as opposed to looking for a fact-based reality. Just having AI perform a default analysis that doesn’t aim to satisfy the boss is useful, and the team can then try to understand why that is different than the management hypothesis, triggering a much richer debate.
In terms of social dynamics, agency problems can create conflicts of interest. Every business unit [BU] leader thinks that their BU should get the most resources and will deliver the most value, or at least they feel they should advocate for their business. AI provides a neutral way based on systematic data to manage those debates. It’s also useful for executives with decision authority, since we all know that short-term pressures and the need to make the quarterly and annual numbers lead people to make different decisions on the 31st of December than they do on January 1st or October 1st. Like the story of Ulysses and the sirens, you can use AI to remind you that you wanted something different three months earlier. The CEO still decides; AI can just provide that extra nudge.
Joanna Pachner: It’s like you have Spock next to you, who is dispassionate and purely analytical.
Yuval Atsmon: That is not a bad analogy—for Star Trek fans anyway.
Joanna Pachner: Do you have a favorite application of AI in strategy?
Yuval Atsmon: I have worked a lot on resource allocation, and one of the challenges, which we call the hockey stick phenomenon, is that executives are always overly optimistic about what will happen. They know that resource allocation will inevitably be defined by what you believe about the future, not necessarily by past performance. AI can provide an objective prediction of performance starting from a default momentum case: based on everything that happened in the past and some indicators about the future, what is the forecast of performance if we do nothing? This is before we say, “But I will hire these people and develop this new product and improve my marketing”— things that every executive thinks will help them overdeliver relative to the past. The neutral momentum case, which AI can calculate in a cold, Spock-like manner, can change the dynamics of the resource allocation discussion. It’s a form of predictive intelligence accessible today and while it’s not meant to be definitive, it provides a basis for better decisions.
Joanna Pachner: Do you see access to technology talent as one of the obstacles to the adoption of AI in strategy, especially at large companies?
Yuval Atsmon: I would make a distinction. If you mean machine-learning and data science talent or software engineers who build the digital tools, they are definitely not easy to get. However, companies can increasingly use platforms that provide access to AI tools and require less from individual companies. Also, this domain of strategy is exciting—it’s cutting-edge, so it’s probably easier to get technology talent for that than it might be for manufacturing work.
The bigger challenge, ironically, is finding strategists or people with business expertise to contribute to the effort. You will not solve strategy problems with AI without the involvement of people who understand the customer experience and what you are trying to achieve. Those who know best, like senior executives, don’t have time to be product managers for the AI team. An even bigger constraint is that, in some cases, you are asking people to get involved in an initiative that may make their jobs less important. There could be plenty of opportunities for incorporating AI into existing jobs, but it’s something companies need to reflect on. The best approach may be to create a digital factory where a different team tests and builds AI applications, with oversight from senior stakeholders.
The big challenge is finding strategists to contribute to the AI effort. You are asking people to get involved in an initiative that may make their jobs less important.
Joanna Pachner: Do you think this worry about job security and the potential that AI will automate strategy is realistic?
Yuval Atsmon: The question of whether AI will replace human judgment and put humanity out of its job is a big one that I would leave for other experts.
The pertinent question is shorter-term automation. Because of its complexity, strategy would be one of the later domains to be affected by automation, but we are seeing it in many other domains. However, the trend for more than two hundred years has been that automation creates new jobs, although ones requiring different skills. That doesn’t take away the fear some people have of a machine exposing their mistakes or doing their job better than they do it.
Joanna Pachner: We recently published an article about strategic courage in an age of volatility that talked about three types of edge business leaders need to develop. One of them is an edge in insights. Do you think AI has a role to play in furnishing a proprietary insight edge?
Yuval Atsmon: One of the challenges most strategists face is the overwhelming complexity of the world we operate in—the number of unknowns, the information overload. At one level, it may seem that AI will provide another layer of complexity. In reality, it can be a sharp knife that cuts through some of the clutter. The question to ask is, Can AI simplify my life by giving me sharper, more timely insights more easily?
Joanna Pachner: You have been working in strategy for a long time. What sparked your interest in exploring this intersection of strategy and new technology?
Yuval Atsmon: I have always been intrigued by things at the boundaries of what seems possible. Science fiction writer Arthur C. Clarke’s second law is that to discover the limits of the possible, you have to venture a little past them into the impossible, and I find that particularly alluring in this arena.
AI in strategy is in very nascent stages but could be very consequential for companies and for the profession. For a top executive, strategic decisions are the biggest way to influence the business, other than maybe building the top team, and it is amazing how little technology is leveraged in that process today. It’s conceivable that competitive advantage will increasingly rest in having executives who know how to apply AI well. In some domains, like investment, that is already happening, and the difference in returns can be staggering. I find helping companies be part of that evolution very exciting.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Strategic courage in an age of volatility

Bias Busters Collection

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
CASE STUDY. This case study evaluates the process and methodologies used in certifying the win/loss review process as a Six Sigma Black Belt project at Microsoft Corporation. It shares the insights gained from a process improvement perspective but does not cover broader benefits and results, such as improvements in win rates or revenue performance.
Business Process Management Cases -. Learning from Real-World Experience. While the body of knowledge on busi ness process management has matured duri ng. the past decades (Dum as et al. 2013 ...
Download book PDF. Download book EPUB. Business Process Management Cases ... "The book is a useful and comprehensive summary of several real-life case studies for organizations and researchers. ... (WU Vienna), Austria. His research areas include Business Process Management, Conceptual Modelling and Enterprise Systems. He has published more ...
PDF | The pandemic of COVID-19 has compelled companies and people worldwide to reassess their work practices fundamentally. ... BUSINESS PROCESS CASE STUDY IN MAYBANK. October 2021; DOI:10.13140 ...
1. Abstract. Qualitative case study methodology enables researchers to conduct an in-depth exploration of intricate phenomena within some. specific context. By keeping in mind research students ...
The writer can also include alternatives available to the protagonist. Conclusion(2-3 paragraphs) In the conclusion, the writer should draw the reader's attention back to the protagonist of the case and briefly revisit the case study's central problem. Footnotes. All jargon should be defined for students in footnotes.
A Successful Case Study Edi Snaidero1 and Andrea Tramontano 4.1 A Product-Oriented Company Opts to Become Customer-Oriented It is rather difficult to relate a successful case study after months spent in the fore front, initially nurturing an idea then a project and eventually de-veloping a new way of doing and being in business. One of the ...
(Business Process Methodology*) [6] to an Emer-gency Department (ED) of a public hospital1. A fea-ture of BP-M* concerns the use of simulation during the analysis and the restructuring of processes. While several studies have shown the usefulness of computer simulations, real case applications are still lacking, es-
Rather than discussing case study in general, a targeted step-by-step plan with real-time research examples to conduct a case study is given. Introduction In recent years, a great increase in the number of students working on their final dissertation across business and management disciplines has been noticed ( Lee & Saunders, 2017 ).
A business process typically crosses the borders of organizational departments and even companies. Thus, business processes are complex artifacts that challenge managers in their efforts to properly manage them. Against this background, business process models are key artifacts to represent how work is performed in organizations.
successful deployment of its business strategy of organic expansion into international markets, horizontal integration through smart acquisitions and alliances that maintains their long-term strategic objective being the most recognized and respected brands in the world. 3.2) Starbucks SWOT Analysis: Strengths:
Business Process Reengineering xvii standard. The book should therefore, be of interest to the following readers: • Undergraduate or Masters level students of process management or management change; who wish to gain a fuller understanding of the academic writings, research and concepts which underline the methodology.
ON THE CASE STUDY METHOD The case study method embraces the full set of procedures needed to do case study research. These tasks include designing a case study, collecting the study's data, ana- ... 1986, p. 23)—for example, responses to a researcher's instruments in an experiment or responses to questionnaires in a survey. For instance ...
Business Case Studies: Case Study Examples. Welcome! Click on the images or links below to view the case study examples written by National University Faculty and Students. Use these examples for guidance in your writing or analyzing process.
Learning Busines s Process Models: A Case Study 387. The respective five model components are hereby described: Component 1: An acting sub-process - the process that acts in order to accomplish ...
Five Case Studies of Transformation Excellence. November 03, 2014 By Lars Fæste , Jim Hemerling , Perry Keenan, and Martin Reeves. In a business environment characterized by greater volatility and more frequent disruptions, companies face a clear imperative: they must transform or fall behind. Yet most transformation efforts are highly complex ...
15 Real-Life Case Study Examples. Now that you understand what a case study is, let's look at real-life case study examples. In this section, we'll explore SaaS, marketing, sales, product and business case study examples with solutions. Take note of how these companies structured their case studies and included the key elements.
The relationship that develops between executives and faculty through the case writing process is a powerful example of sharing and…. Length: 2 page (s) Publication Date: Apr 12, 2012. Discipline: Entrepreneurship. Product #: UV6103-PDF-ENG.
In addition, three case studies are explained and discussed. Applying the Augmented Stage-Gate framework results in successful commercialization process in all three cases where the teams transferred the technology via a spin-o startup with a patent, non-prot use with trade secret, and licensing. e benets of this study can be used as a
Step 1: Provide Data. When writing a case summary, you need to be sure to have all the right data. There will be a lot of cases you might want to look into, to pick the right one, make sure they contain a significant challenge, a satisfying solution to any business risk, and a good amount of benefits.
Abstract and Figures. This thesis is a case study for a Roofing company based in Phoenix Arizona. The topic of the thesis is Business Process Improvement and overviews the popular methods such as ...
1.1 The purpose and nature of business activity 4 - The concept of adding value and how added value can be increased. Case Study: Adding Value in the Technology Industry - Apple Inc. Background: Apple Inc. is a global technology company renowned for its innovative products and strong brand loyalty. The company has successfully utilized the concept of adding value to differentiate itself in the ...
The short answer is no. However, there are numerous aspects of strategists' work where AI and advanced analytics tools can already bring enormous value. Yuval Atsmon is a senior partner who leads the new McKinsey Center for Strategy Innovation, which studies ways new technologies can augment the timeless principles of strategy.
In a case study it was fount that 6% e mployees are on regular pay roll. and 94% em ployees are on contractual employees. The t urnover is increased. from 35% to 65% due to BPO. Production has ...