Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- What Is a Fishbone Diagram? | Templates & Examples

What Is a Fishbone Diagram? | Templates & Examples
Published on January 2, 2023 by Tegan George . Revised on January 29, 2024.
A fishbone diagram is a problem-solving approach that uses a fish-shaped diagram to model possible root causes of problems and troubleshoot possible solutions. It is also called an Ishikawa diagram, after its creator, Kaoru Ishikawa, as well as a herringbone diagram or cause-and-effect diagram.
Fishbone diagrams are often used in root cause analysis , to troubleshoot issues in quality management or product development. They are also used in the fields of nursing and healthcare, or as a brainstorming and mind-mapping technique many students find helpful.
Table of contents
How to make a fishbone diagram, fishbone diagram templates, fishbone diagram examples, advantages and disadvantages of fishbone diagrams, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about fishbone diagrams.
A fishbone diagram is easy to draw, or you can use a template for an online version.
- Your fishbone diagram starts out with an issue or problem. This is the “head” of the fish, summarized in a few words or a small phrase.
- Next, draw a long arrow, which serves as the fish’s backbone.
- From here, you’ll draw the first “bones” directly from the backbone, in the shape of small diagonal lines going right-to-left. These represent the most likely or overarching causes of your problem.
- Branching off from each of these first bones, create smaller bones containing contributing information and necessary detail.
- When finished, your fishbone diagram should give you a wide-view idea of what the root causes of the issue you’re facing could be, allowing you to rank them or choose which could be most plausible.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
There are no built-in fishbone diagram templates in Microsoft programs, but we’ve made a few free ones for you to use that you can download below. Alternatively, you can make one yourself using the following steps:
- In a fresh document, go to Insert > Shapes
- Draw a long arrow from left to right, and add a text box on the right-hand side. These serve as the backbone and the head of the fish.
- Next, add lines jutting diagonally from the backbone. These serve as the ribs, or the contributing factors to the main problem.
- Next, add horizontal lines jutting from each central line. These serve as the potential causes of the problem.
Lastly, add text boxes to label each function.
You can try your hand at filling one in yourself using the various blank fishbone diagram templates below, in the following formats:
Fishbone diagram template Excel
Download our free Excel template below!
Fishbone diagram template Word
Download our free Word template below!
Fishbone diagram template PowerPoint
Download our free PowerPoint template below!
Fishbone diagrams are used in a variety of settings, both academic and professional. They are particularly popular in healthcare settings, particularly nursing, or in group brainstorm study sessions. In the business world, they are an often-used tool for quality assurance or human resources professionals.
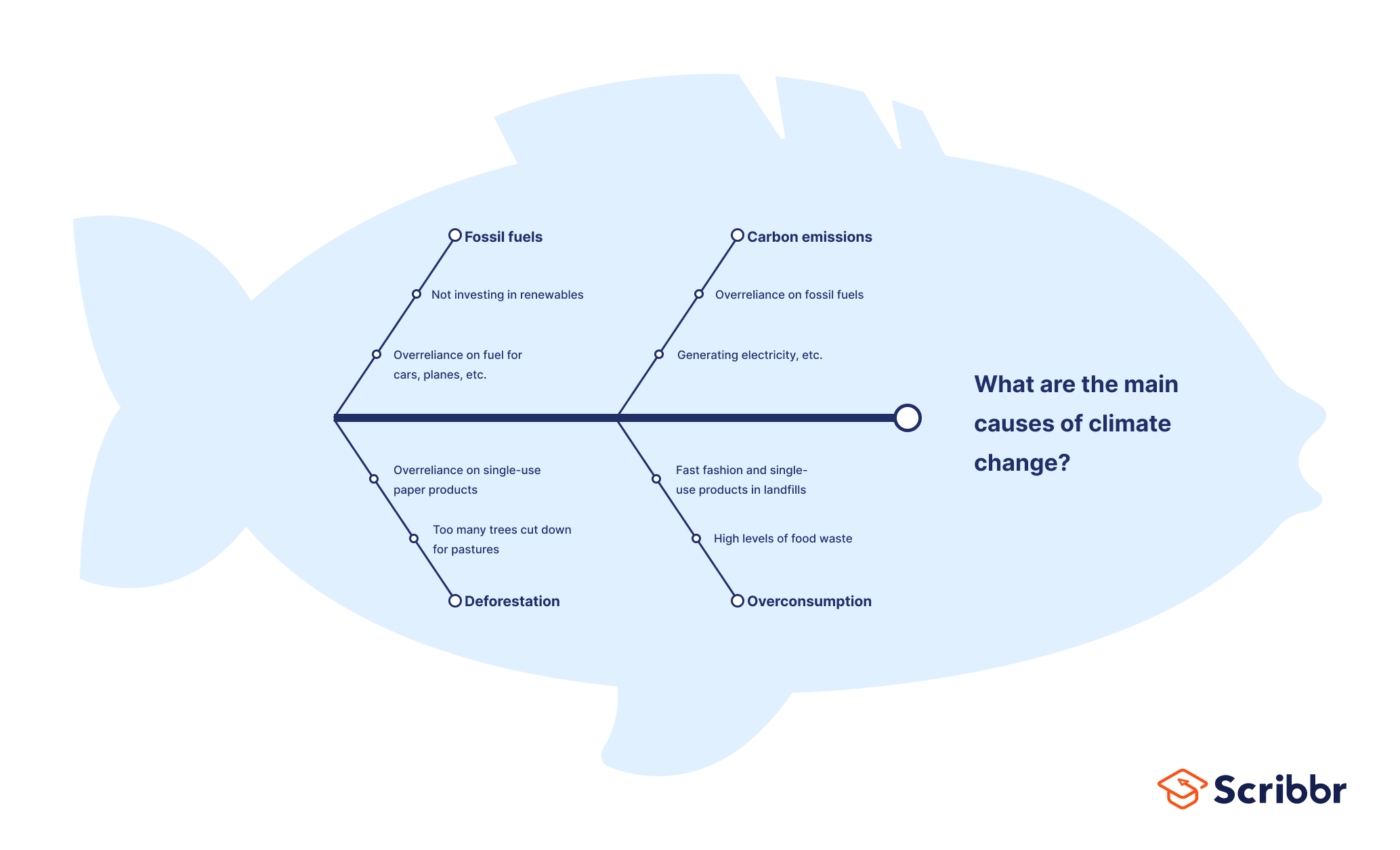
Fishbone diagram example #1: Climate change
Let’s start with an everyday example: what are the main causes of climate change?
Fishbone diagram example #2: Healthcare and nursing
Fishbone diagrams are often used in nursing and healthcare to diagnose patients with unclear symptoms, or to streamline processes or fix ongoing problems. For example: why have surveys shown a decrease in patient satisfaction?
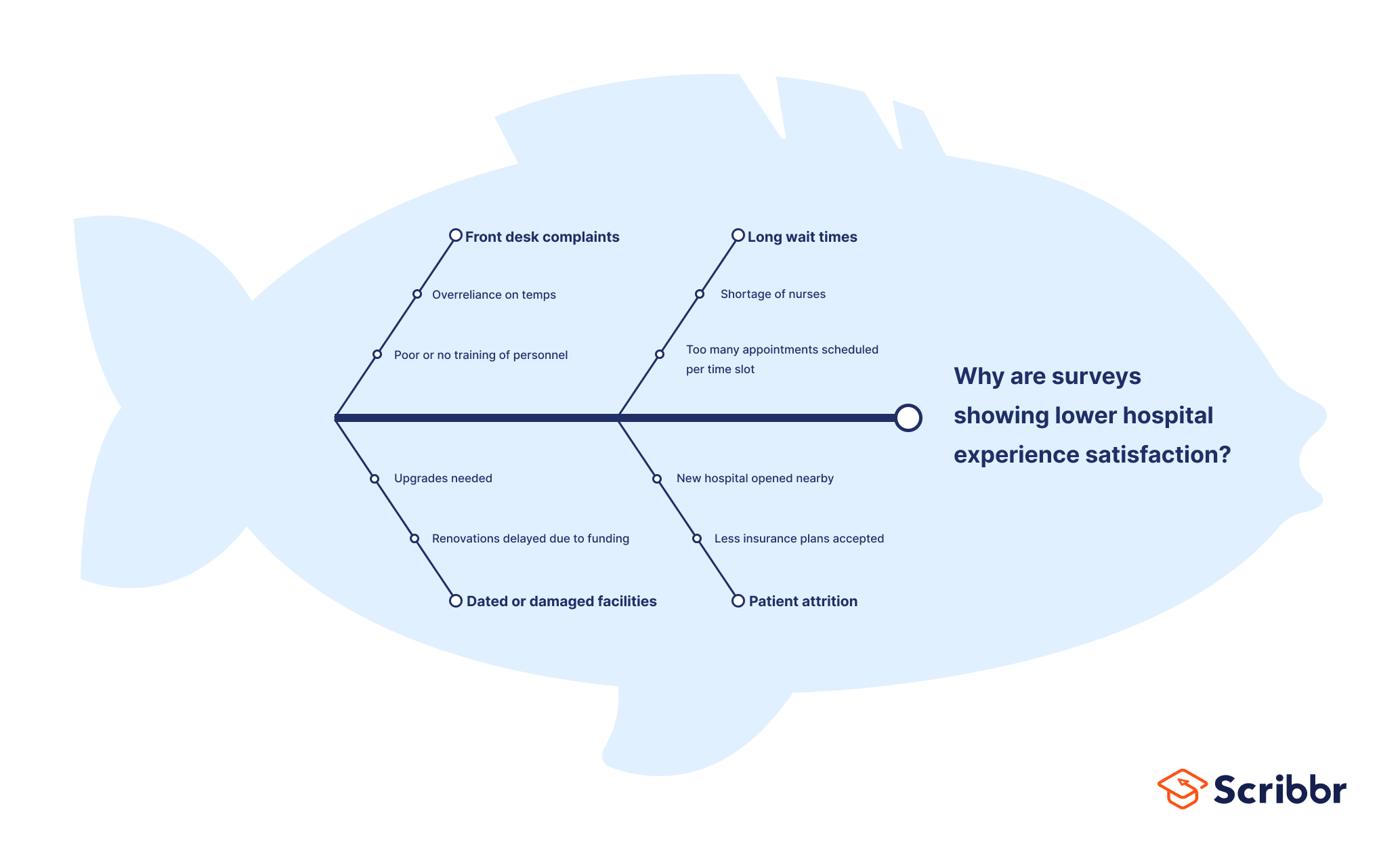
Fishbone diagram example #3: Quality assurance
QA professionals also use fishbone diagrams to troubleshoot usability issues, such as: why is the website down?
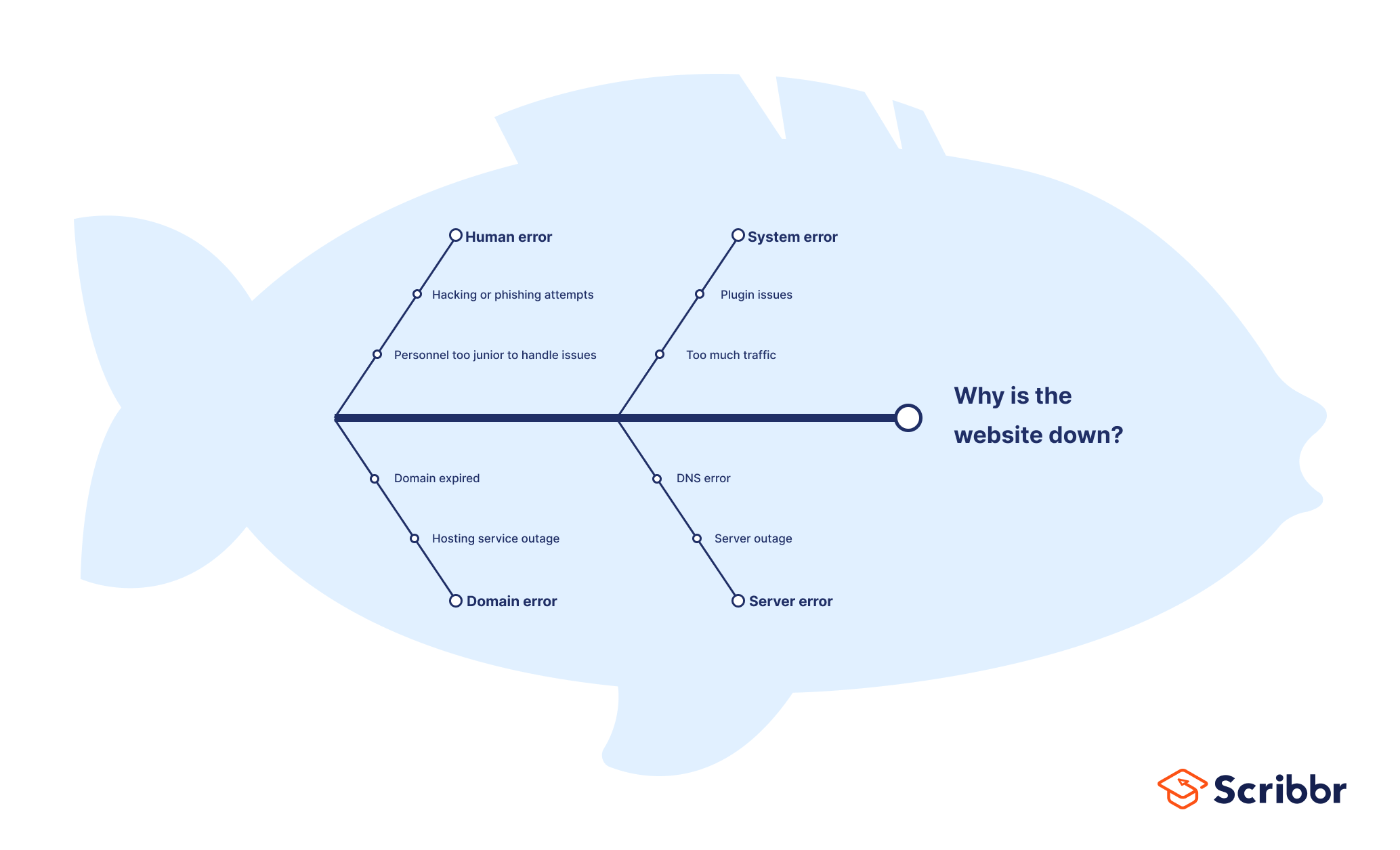
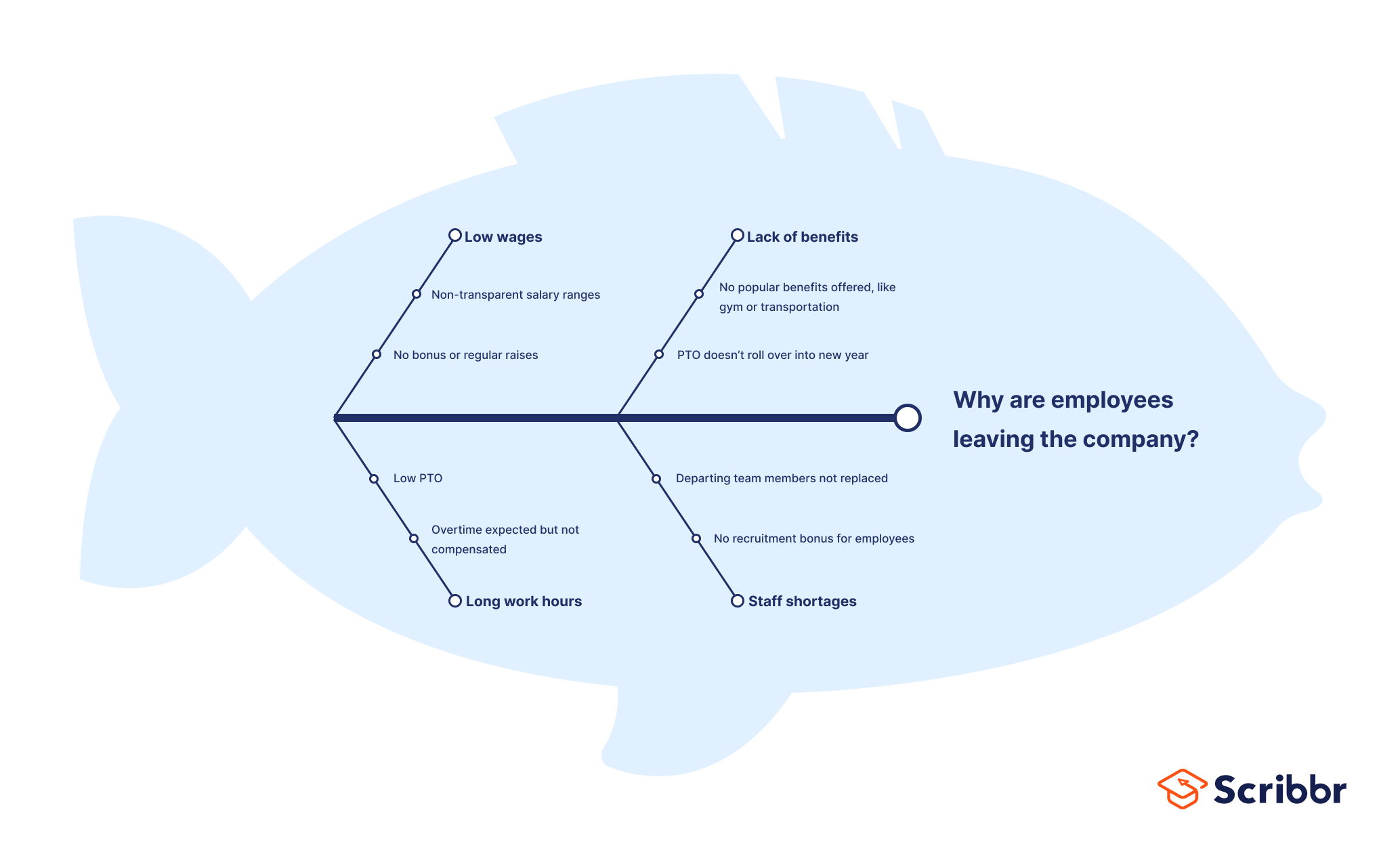
Fishbone diagram example #4: HR
Lastly, an HR example: why are employees leaving the company?
Fishbone diagrams come with advantages and disadvantages.
- Great tool for brainstorming and mind-mapping, either individually or in a group project.
- Can help identify causal relationships and clarify relationships between variables .
- Constant iteration of “why” questions really drills down to root problems and elegantly simplifies even complex issues.
Disadvantages
- Can lead to incorrect or inconsistent conclusions if the wrong assumptions are made about root causes or the wrong variables are prioritized.
- Fishbone diagrams are best suited to short phrases or simple ideas—they can get cluttered and confusing easily.
- Best used in the exploratory research phase, since they cannot provide true answers, only suggestions.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Fishbone diagrams have a few different names that are used interchangeably, including herringbone diagram, cause-and-effect diagram, and Ishikawa diagram.
These are all ways to refer to the same thing– a problem-solving approach that uses a fish-shaped diagram to model possible root causes of problems and troubleshoot solutions.
Fishbone diagrams (also called herringbone diagrams, cause-and-effect diagrams, and Ishikawa diagrams) are most popular in fields of quality management. They are also commonly used in nursing and healthcare, or as a brainstorming technique for students.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. (2024, January 29). What Is a Fishbone Diagram? | Templates & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 1, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/fishbone-diagram/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, how to define a research problem | ideas & examples, data collection | definition, methods & examples, exploratory research | definition, guide, & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Problem-Solving Flowchart: A Visual Method to Find Perfect Solutions
Lucid Content
Reading time: about 7 min
“People ask me questions Lost in confusion Well, I tell them there's no problem Only solutions” —John Lennon, “Watching the Wheels”
Despite John Lennon’s lyrics, nobody is free from problems, and that’s especially true in business. Chances are that you encounter some kind of problem at work nearly every day, and maybe you’ve had to “put out a fire” before lunchtime once or twice in your career.
But perhaps what Lennon’s saying is that, no matter what comes our way, we can find solutions. How do you approach problems? Do you have a process in place to ensure that you and your co-workers come to the right solution?
In this article, we will give you some tips on how to find solutions visually through a problem-solving flowchart and other methods.
What is visual problem-solving?
If you are a literal thinker, you may think that visual problem-solving is something that your ophthalmologist does when your vision is blurry. For the rest of us, visual problem-solving involves executing the following steps in a visual way:
- Define the problem.
- Brainstorm solutions.
- Pick a solution.
- Implement solutions.
- Review the results.
How to make your problem-solving process more visual
Words pack a lot of power and are very important to how we communicate on a daily basis. Using words alone, you can brainstorm, organize data, identify problems, and come up with possible solutions. The way you write your ideas may make sense to you, but it may not be as easy for other team members to follow.
When you use flowcharts, diagrams, mind maps, and other visuals, the information is easier to digest. Your eyes dart around the page quickly gathering information, more fully engaging your brain to find patterns and make sense of the data.
Identify the problem with mind maps
So you know there is a problem that needs to be solved. Do you know what that problem is? Is there only one problem? Is the problem sum total of a bunch of smaller problems?
You need to ask these kinds of questions to be sure that you are working on the root of the issue. You don’t want to spend too much time and energy solving the wrong problem.
To help you identify the problem, use a mind map. Mind maps can help you visually brainstorm and collect ideas without a strict organization or structure. A mind map more closely aligns with the way a lot of our brains work—participants can bounce from one thought to the next defining the relationships as they go.

Mind mapping to solve a problem includes, but is not limited to, these relatively easy steps:
- In the center of the page, add your main idea or concept (in this case, the problem).
- Branch out from the center with possible root causes of the issue. Connect each cause to the central idea.
- Branch out from each of the subtopics with examples or additional details about the possible cause. As you add more information, make sure you are keeping the most important ideas closer to the main idea in the center.
- Use different colors, diagrams, and shapes to organize the different levels of thought.
Alternatively, you could use mind maps to brainstorm solutions once you discover the root cause. Search through Lucidchart’s mind maps template library or add the mind map shape library to quickly start your own mind map.
Create a problem-solving flowchart
A mind map is generally a good tool for non-linear thinkers. However, if you are a linear thinker—a person who thinks in terms of step-by-step progression making a flowchart may work better for your problem-solving strategy. A flowchart is a graphical representation of a workflow or process with various shapes connected by arrows representing each step.
Whether you are trying to solve a simple or complex problem, the steps you take to solve that problem with a flowchart are easy and straightforward. Using boxes and other shapes to represent steps, you connect the shapes with arrows that will take you down different paths until you find the logical solution at the end.

Flowcharts or decision trees are best used to solve problems or answer questions that are likely to come up multiple times. For example, Yoder Lumber , a family-owned hardwood manufacturer, built decision trees in Lucidchart to demonstrate what employees should do in the case of an injury.
To start your problem-solving flowchart, follow these steps:
- Draw a starting shape to state your problem.
- Draw a decision shape where you can ask questions that will give you yes-or-no answers.
- Based on the yes-or-no answers, draw arrows connecting the possible paths you can take to work through the steps and individual processes.
- Continue following paths and asking questions until you reach a logical solution to the stated problem.
- Try the solution. If it works, you’re done. If it doesn’t work, review the flowchart to analyze what may have gone wrong and rework the flowchart until you find the solution that works.
If your problem involves a process or workflow , you can also use flowcharts to visualize the current state of your process to find the bottleneck or problem that’s costing your company time and money.

Lucidchart has a large library of flowchart templates to help you analyze, design, and document problem-solving processes or any other type of procedure you can think of.
Draw a cause-and-effect diagram
A cause-and-effect diagram is used to analyze the relationship between an event or problem and the reason it happened. There is not always just one underlying cause of a problem, so this visual method can help you think through different potential causes and pinpoint the actual cause of a stated problem.
Cause-and-effect diagrams, created by Kaoru Ishikawa, are also known as Ishikawa diagrams, fishbone diagrams , or herringbone diagrams (because they resemble a fishbone when completed). By organizing causes and effects into smaller categories, these diagrams can be used to examine why things went wrong or might go wrong.

To perform a cause-and-effect analysis, follow these steps.
1. Start with a problem statement.
The problem statement is usually placed in a box or another shape at the far right of your page. Draw a horizontal line, called a “spine” or “backbone,” along the center of the page pointing to your problem statement.
2. Add the categories that represent possible causes.
For example, the category “Materials” may contain causes such as “poor quality,” “too expensive,” and “low inventory.” Draw angled lines (or “bones”) that branch out from the spine to these categories.
3. Add causes to each category.
Draw as many branches as you need to brainstorm the causes that belong in each category.
Like all visuals and diagrams, a cause-and-effect diagram can be as simple or as complex as you need it to be to help you analyze operations and other factors to identify causes related to undesired effects.
Collaborate with Lucidchart
You may have superior problem-solving skills, but that does not mean that you have to solve problems alone. The visual strategies above can help you engage the rest of your team. The more involved the team is in the creation of your visual problem-solving narrative, the more willing they will be to take ownership of the process and the more invested they will be in its outcome.
In Lucidchart, you can simply share the documents with the team members you want to be involved in the problem-solving process. It doesn’t matter where these people are located because Lucidchart documents can be accessed at any time from anywhere in the world.
Whatever method you decide to use to solve problems, work with Lucidchart to create the documents you need. Sign up for a free account today and start diagramming in minutes.
Lucidchart, a cloud-based intelligent diagramming application, is a core component of Lucid Software's Visual Collaboration Suite. This intuitive, cloud-based solution empowers teams to collaborate in real-time to build flowcharts, mockups, UML diagrams, customer journey maps, and more. Lucidchart propels teams forward to build the future faster. Lucid is proud to serve top businesses around the world, including customers such as Google, GE, and NBC Universal, and 99% of the Fortune 500. Lucid partners with industry leaders, including Google, Atlassian, and Microsoft. Since its founding, Lucid has received numerous awards for its products, business, and workplace culture. For more information, visit lucidchart.com.
Related articles

Sometimes you're faced with challenges that traditional problem solving can't fix. Creative problem solving encourages you to find new, creative ways of thinking that can help you overcome the issue at hand more quickly.

Dialogue mapping is a facilitation technique used to visualize critical thinking as a group. Learn how you and your team can start dialogue mapping today to solve problems and bridge gaps in knowledge and understanding (plus get a free template!).
Bring your bright ideas to life.
or continue with
Maths with David
Problem solving. draw diagram.
In mathematics, diagrams are often a useful way of organising information and help us to see relationships. A diagram can be a rough sketch, a number line, a tree diagram or two-way table, a Venn diagram, or any other drawing which helps us to tackle a problem.
Labels (e.g. letters for vertices of a polygon) are useful in a diagram to help us be able to refer to items of interest.
A diagram can be updated as we find out new information.
Examples of using a diagram to tackle a problem
First we will read all three examples and have a quick think about them and then we will look at how a diagram can help us with each one:
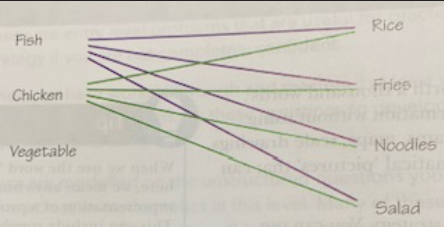
Restaurant Example
A restaurant offers a “business lunch” where people can choose either fish or chicken or vegetables for their main course, accompanied by a side portion of rice, chips, noodles or salad. How many different combined meals can they choose between?
Rectangle Area Example
To the nearest centimetre, the length and width of a rectangle is 10cm and 8cm.
- What are the limits of accuracy for the area of the rectangle?
- the lengths of the sides?
Prime Numbers Example
Masha says that if she writes out numbers in rows of six then all of the prime numbers will either be in the column that has 1 at the top, or they will be in the column that has 5 at the top. How can you find out if she is correct?
Worked Solutions to Examples
One way to tackle this would be to write out a list, being systematic to ensure that all combinations are considered.
Another is to draw out a diagram like the one below. As shown, you actually don’t need to finish the diagram in order to conclude how many combinations there are:
You could also use a 2-way table as shown below:
Drawing a rough sketch of the rectangle labelled with the boundaries of its side lengths can really help us to visualise the situation here:
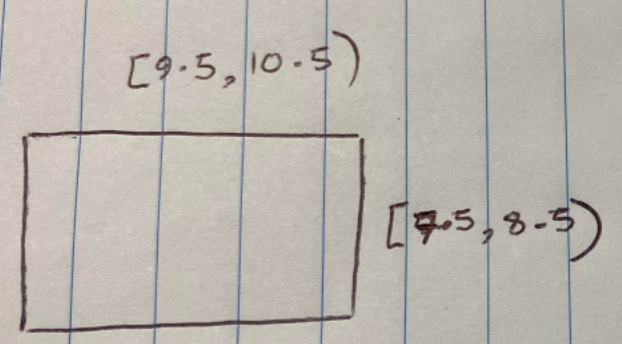
It can then be helpful to draw sketches of the smallest possible rectangle and the largest possible rectangle:
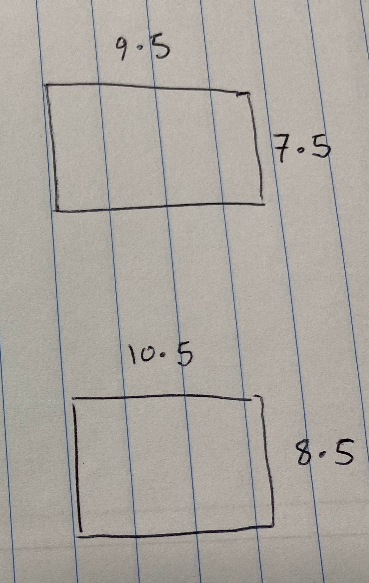
We can now answer the questions, so (a) the smallest possible area is 7.5 x 9.5 = 71.25cm 2 and the largest “possible” area is 8.5 x 10.5 = 89.25cm 2 . So the limits of accuracy are [71.25,89.25) cm 2 .
For (b), we can see from the sketches that the difference between the minimum and the maximum values is 1cm in the case of both the width and the lenght. For part (ii) we simply subtract the numbers above to give 89.25-71.25 = 18cm 2 .
Here, listing out numbers, especially for the first few is going to be helpful. We should list them as specified in the question, and we can highlight the prime numbers:
Because we know that no even numbers other than 2 are prime, we know that further prime numbers cannot be in the second, fourth or sixth column. The third column keeps adding 6s, so it is adding multiples of 3 to multiples of 3, so the numbers will always be divisible by 3, so further numbers in this column cannot be prime. So she is correct that the prime numbers must be in the first or the fifth column.
31 Questions of increasing difficulty
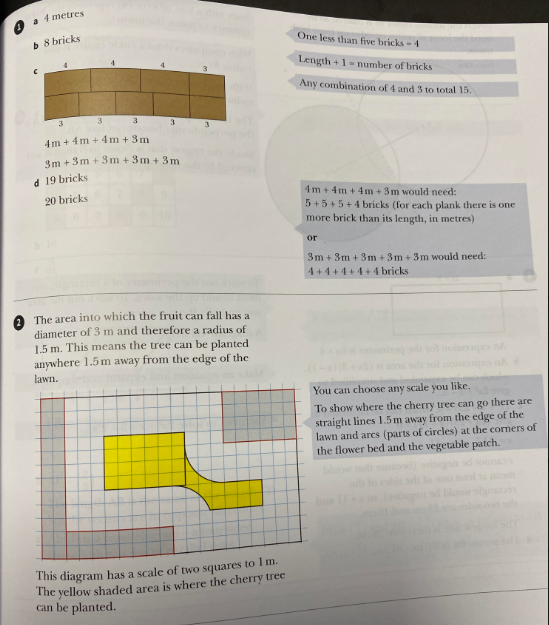
1.) In a cement factory, cement bags are placed on pallets made of planks of wood and bricks. The number of bricks needed to make a pallet is calculated as being one more than the length of the plank in metres (as shown below):
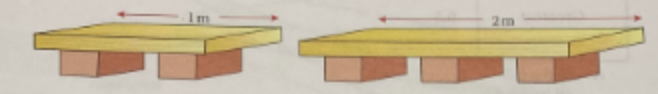
a.) What length of pallet uses five bricks?
b.) If the pallet is 7m long, how many bricks are used in it?
The factory needs pallets with a total length of 15m for the next batch of cement. It has planks of wood that are 4m long and 3m long.
c.) What combinations of planks can they have?
d.) How many bricks would be needed for each combination?
2.) Sonia wants to plant an apple tree in her garden. She needs to make sure that there is a circular area of lawn with diameter 3m around the base of the tree, so that all of the fruit will fall onto the lawn area.
Below is a (not to scale) sketch of Sonia’s garden:
Where could the tree be placed to meet her requirements?
3.) The diagram below represents towns A and B in a mountainous region:

The mountain rescue helicopters from both towns will always be sent to rescue any casualty within a 25km radius of town A or town B. The fire and rescue team from town B will travel to any accident scene closer to town B than town A.
Shade the region that the helicopters and town B’s fire an rescue team will both cover.
4.) A rectangle has length (2x+3) and width (x-1).
a.) Write an expression for the perimeter of the rectangle.
b.) Write an expression for the area of the rectangle.
The area of the rectangle is 250cm 2 .
c.) How long is the longest side?
d.) What is the perimeter of the rectangle?
5.) The probability that Hannah catches the 6.30am train to the city is 0.7.
If she misses the train, she will be late for work.
The probability that the train will be late is 0.15.
If the train is late, she will be late for work.
What is the probability that Hannah will be on time for work on a particular day?

Worked Solutions to Questions
Share this:

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Training and Development
- Beginner Guides
Blog Business
What is a Problem-Solving Flowchart & How to Make One
By Danesh Ramuthi , Aug 10, 2023
Problem-Solving Flowcharts, contrary to what many believe aren’t just aesthetic wonders — they’re almost like magical blueprints for troubleshooting those pesky problems that many of us face.
Flowcharts take business challenges and turn them into a navigable pathway. In this post, I will guide you on key aspects of problem-solving flowcharts such as what it is, the advantages of problem-solving flowcharts, how to create one and more.
Besides, you’ll also discover how to create problem-solving flowcharts with the help of Venngage’s Flowchart Maker.
And for those of you thinking, “I’m no designer, how can I create one?” worry not! I’ve got you covered. Just hop on Venggage’s Flowchart Templates and you’ll be charting your way to problem-solving glory in no time.
Click to jump ahead:
What are problem-solving flowcharts?
When to use problem-solving flowcharts, what are the advantages of flowcharts in problem-solving, what are the 7 steps of problem-solving flowcharts.
- 5 different types of problem-solving flowcharts
Best practices for designing effective problem-solving flowcharts
How to make a flowchart using venngage , problem-solving flowcharts faqs.
- Final Thoughts
Problem-Solving Flowcharts is a graphical representation used to break down problem or process into smaller, manageable parts, identify the root causes and outline a step-by-step solution.
It helps in visually organizing information and showing the relationships between various parts of the problem.
This type of flowcharts consists of different symbols and arrows, each representing different components or steps in the problem-solving process.
By following the flow of the chart, individuals or teams can methodically approach problem, analyze different aspects of it and come to a well-informed solution.
Problem-Solving Flowcharts is a versatile tool that can be used in various scenarios. Here’s when to consider utilizing one:
- Complex Problems: When faced with a multifaceted issue that involves multiple steps or variables, flowcharts can help break down the complexity into digestible parts.
- Team Collaboration: If you’re working with a team and need a common understanding of problem and its potential solutions then a flowchart provides a visual that everyone can refer to.
- Analyzing Processes: In a situation where you need to understand a particular process, whether it’s within a project or a part of regular operations then mapping it out in a flowchart can offer clarity.
- Decision Making: When various paths or decisions might be taken, a flowchart can outline the potential outcomes of each aiding in making an informed choice.
- Training and Onboarding: Flowcharts can be used in training materials to help new employees understand complex processes or procedures which makes the learning curve smoother.
- Identifying Root Causes: If you’re looking to identify the underlying causes of problem then a flowchart can facilitate a systematic approach to reaching the root of the issue.
Related: How to Use Fishbone Diagrams to Solve Complex Problems
Problem-solving flowcharts can offer several benefits to the users who are looking to solve a particular problem. Few advantages of flowcharts in problem solving are:
Visual Clarity
When you’re dealing with multifaceted problems or processes, words alone can make the situation seem even more tangled. Flowcharts distill these complexities into easily understandable visual elements.
By mapping out each phase or component of problem, flowcharts offer a bird’s eye view enabling individuals to grasp the bigger picture and the finer details simultaneously.
Sequential Representation
Flowcharts excel in laying out the sequence of events or actions. By indicating a clear starting point and illustrating each subsequent step, they guide users through a process or solution path methodically.
This linear representation ensures that no step is overlooked and each is executed in the right order.
Collaboration
Problem-solving often requires team effort and flowcharts are instrumental in fostering collaborative environments.
When a team is discussing potential solutions or trying to understand problem’s intricacies, a flowchart serves as a collective reference point.
It aids in synchronizing everyone’s understanding, minimizing miscommunications and promoting constructive discussions.
Read more about: Flowcharts Symbols and Meaning
1. Define the Problem
Before anything else, it’s essential to articulate the problem or task you want to solve clearly and accurately. By understanding exactly what needs to be addressed you can ensure that subsequent steps align with the core issue.
2. Identify the Inputs and Outputs
Determine what inputs (such as data, information or resources) will be required to solve the problem and what the desired outputs or outcomes are. Identifying these factors will guide you in structuring the steps needed to reach the end goal and ensure that all necessary resources are at hand.
3. Identify the Main Steps
Break down the problem-solving process into its main steps or subtasks. This involves pinpointing the essential actions or stages necessary to reach the solution. Create a roadmap that helps in understanding how to approach the problem methodically.
4. Use Decision Symbols
In problem-solving, decisions often lead to different paths or outcomes. Using standard symbols to represent these decision points in the flowcharts allows for a clear understanding of these critical junctures. It helps visually present various scenarios and their consequences.
5. Add Descriptions and Details
A well-designed flowcharts is concise but clear in its labeling. Using arrows and short, descriptive phrases to explain what happens at each step or decision point ensures that the flowcharts communicates the process without unnecessary complexity.
6. Revise and Refine
Creating a flowcharts is not always a one-and-done process. It may require revisions to improve its clarity, accuracy or comprehensiveness. Necessary refinement ensures that the flowcharts precisely reflects the problem-solving process and is free from errors or ambiguities.
7. Use Flowchart Tool
While it’s possible to draw a flowcharts manually, using a flowcharts tool like Venngage’s Flowchart Maker and Venngage’s Flowchart Templates can make the process more efficient and flexible. These tools come with pre-designed templates and intuitive interfaces that make it easy to create, modify and share flowcharts.
5 different types of problem-solving flowcharts
Let’s have a look at 5 most common types of flowcharts that individuals and organizations often use.
1. Process Flowchart s
A process flowcharts is a visual representation of the sequence of steps and decisions involved in executing a particular process or procedure.
It serves as a blueprint that showcases how different stages or functions are interconnected in a systematic flow and it highlights the direction of the process from its beginning to its end.
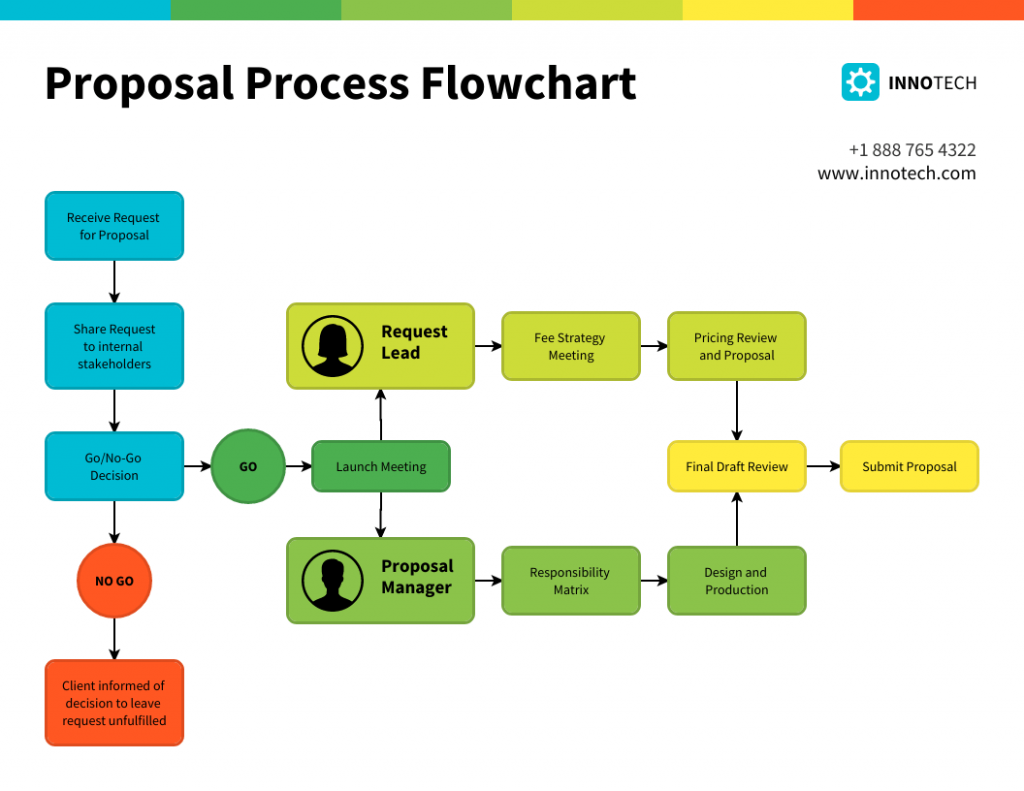
Process flowcharts are instrumental in training and onboarding, sales process , process optimization, documentation, recruitment and in any scenario where clear communication of a process is crucial.
2. Flowcharts Infographic
A flowcharts infographic is a great way to showcase the process or a series of steps using a combination of graphics, icons, symbols and concise text. It aims to communicate complex information in a clear and easy-to-understand manner, making it a popular tool for conveying information, data and instructions in a visually engaging way.

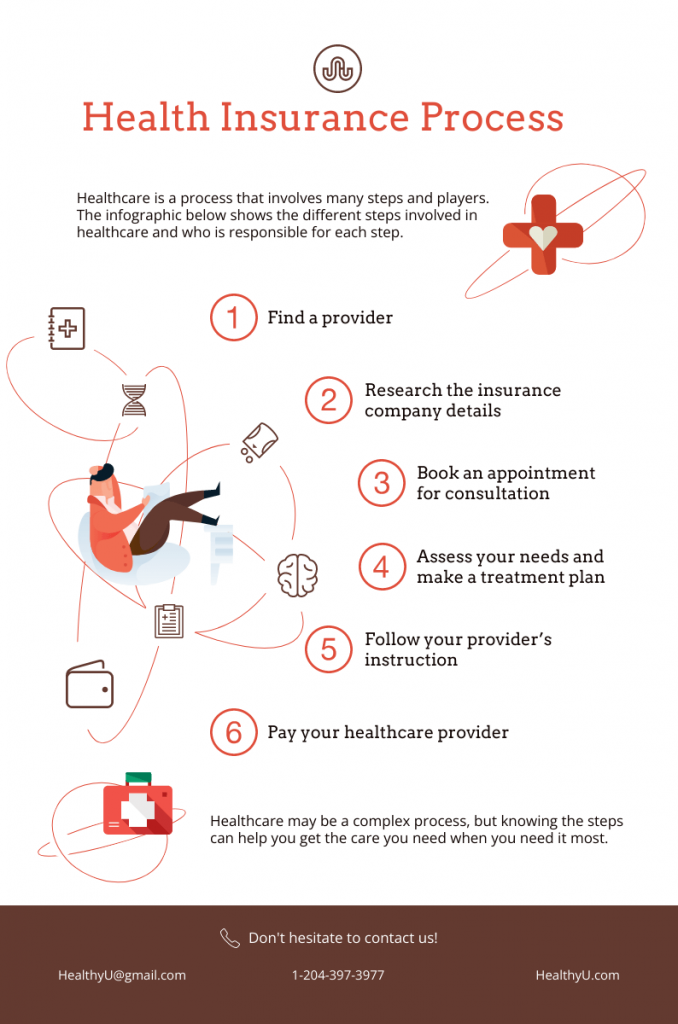
For example, you can use this flowchart to illustrate a health insurance process that visually explains the steps involved from finding a provider to paying for your healthcare provider.
3. Circular Flowcharts
A circular flowcharts is used to illustrate the flow of information, goods, services or money within a closed system or process. It gets its name from its circular shape, which emphasizes the continuous and cyclical nature of the flow.
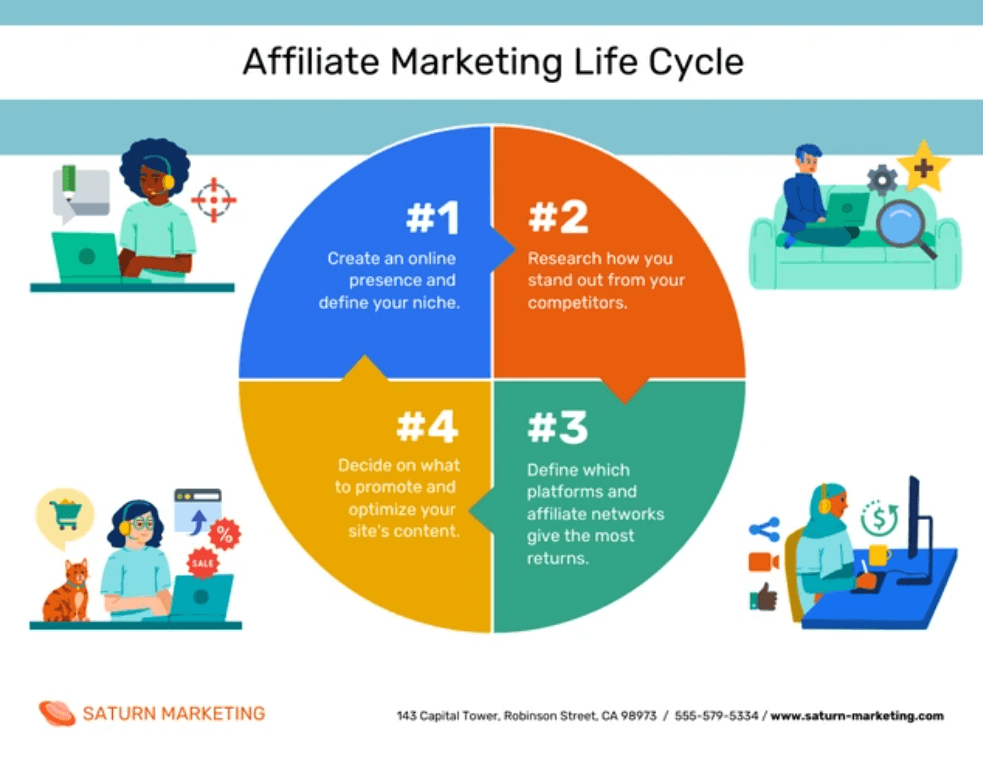
Circular flowcharts are widely used in various fields such as economics, business, engineering and process management to help visualize and understand complex systems.
In a circular flowcharts , elements are represented using various shapes and connected with arrows to indicate the direction of flow. The circular arrangement indicates that the process is ongoing and repeats itself over time.

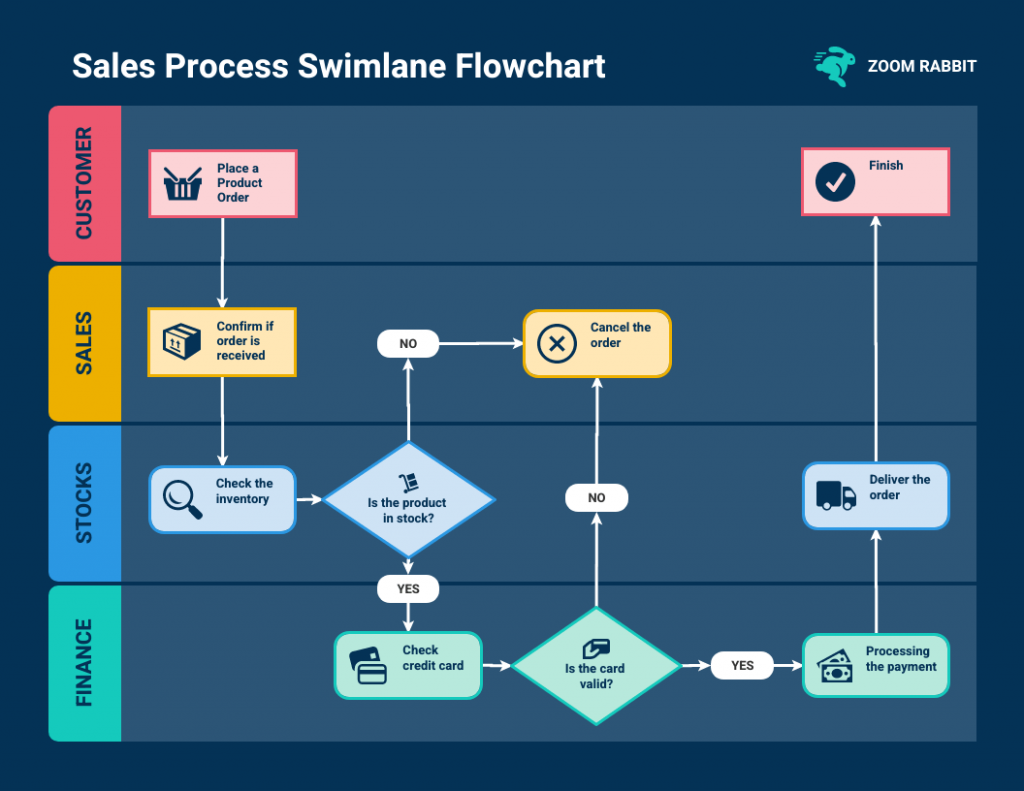
4. Swimlane flowcharts
Swimlane flowcharts , also known as cross-functional flowcharts are a specific type of flowchart that organizes the process flow into lanes or “swimlanes.”
Each lane represents a different participant or functional area involved in the process and the flowchart shows how activities or information move between these participants.
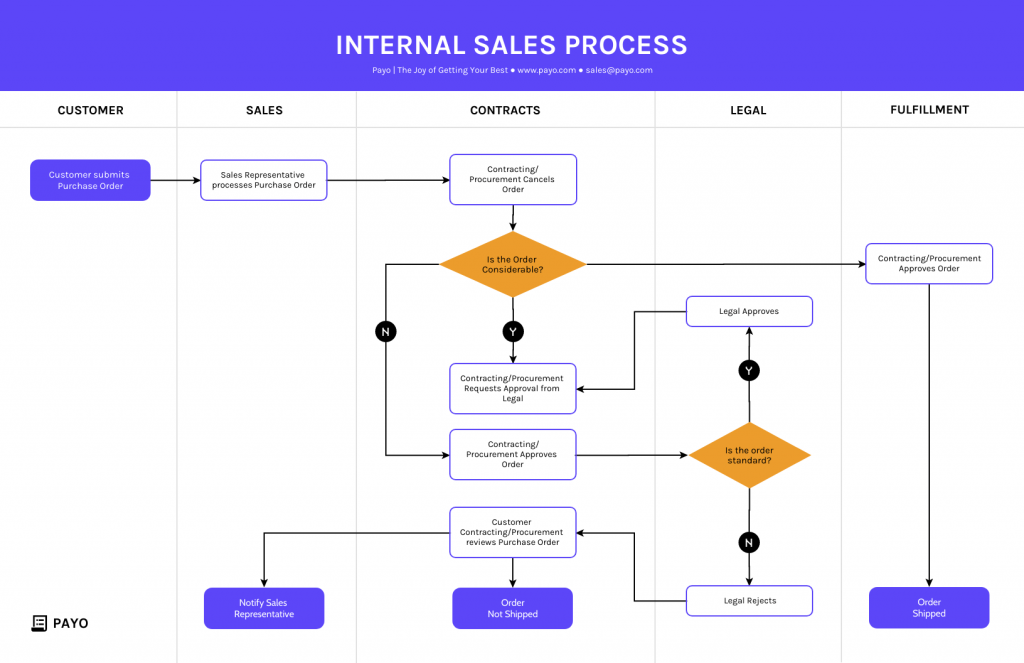
Swimlane flowcharts are particularly useful for illustrating complex processes that involve multiple stakeholders or departments.
In a swimlane flowcharts, the process is divided horizontally into lanes and each lane is labeled with the name of the department, person or role responsible for that part of the process. Vertically, the flowchart displays the sequence of steps or actions taken in the process.
5. Decision Flowchart s
Decision flowcharts, also known as decision trees or flow diagrams are graphical representations that illustrate the process of making decisions or solving problems.
They are widely used in various fields such as computer science, business mapping , engineering and problem-solving scenarios.
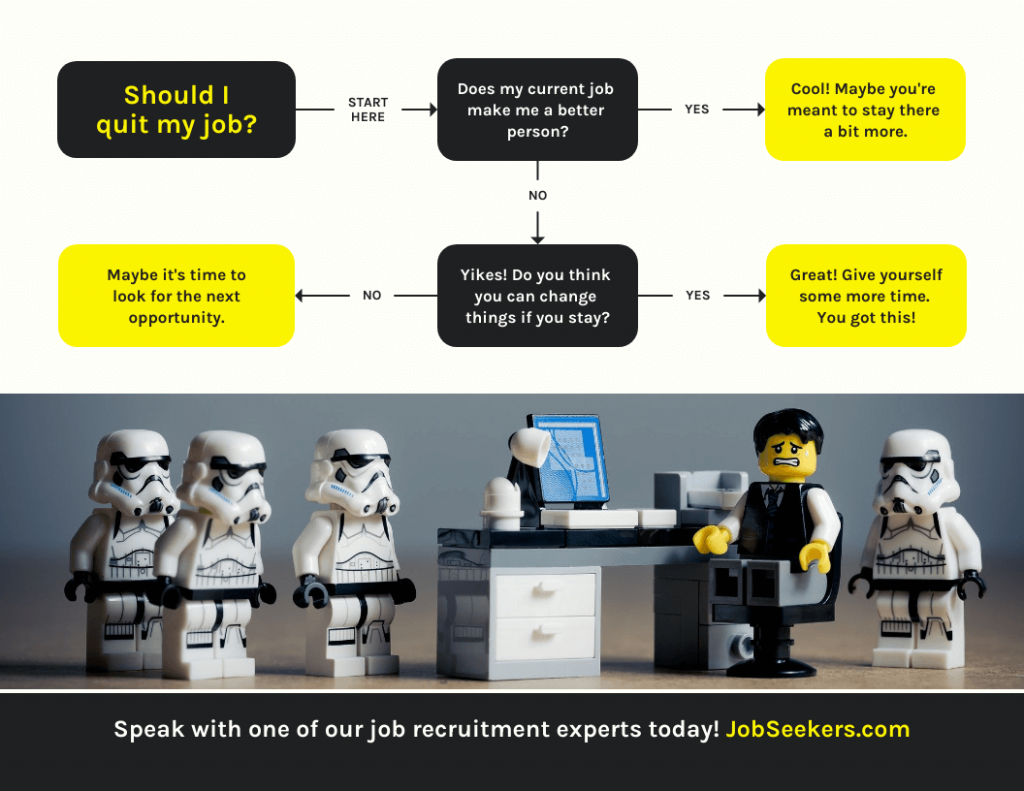
Decision flowcharts help break down complex decision-making processes into simple, sequential steps, making it easier to understand and follow.
A decision tree is a specialized flowchart used to visually represent the process of decision-making.
Businesses and other individuals can employ a decision tree analysis as a tool to aid in evaluating different options and the possible consequences associated with each choice.
Decision trees Infographics can be used to create a more nuanced type of flowchart that is more informative and visually appealing by combining a decision flowchart and the flowchart infographic.
Decision flowcharts are valuable tools for visualizing decision-making processes, analyzing complex problems and communicating them effectively to others.
Designing effective problem-solving flowcharts involves careful consideration of various factors to ensure clarity, accuracy and usability. Here are some best practices to create efficient and useful problem-solving flowcharts:
- Understand the problem first & clearly define it
- Keep it simple
- Use standard & recognizable symbols
- Ensure that the flowchart follows a logical and sequential order
- Clearly label each decision point, action and outcome
- Verify the flowchart’s accuracy by testing it
- Clearly state the decision criteria that lead to different branches
- Provide context when the flowchart is part of a larger process or system
- Review and revise the flowchart
Creating problem-solving flowchart on Venngage is incredibly simple. All you have to do is:
- Start by Signing Up and Creating an Account with Venngage
- Choose a flowchart template that best suits your needs from our library.
- Start editing your flowchart by choosing the desired shapes, labels and colors.
- You can also enhance your flowchart by incorporating icons, illustrations or backgrounds all of which are readily available in our library.
- Once done, you will have 2 options to choose from, either sharing it online for free or downloading your flowchart to your desktop by subscribing to the Premium or Business Plan.
Is flowchart the representation of problem solutions?
Flowcharts are not the representation of problem solutions per se; rather, they are a visual representation of processes, decision-making steps and actions taken to arrive at a solution to problem.
What are the 3 basic structures of flowcharts?
3 Basic Structures of Flowcharts are:
- Sequence: Simplify Complexity
- Selection (Decision): Embrace Choices
- Repetition (Loop): Emphasize Iteration
What are the elements of a good flowchart?
A good flowchart should exhibit clarity and simplicity, using consistent symbols and labels to depict a logical sequence of steps. It should be readable, with appropriate white space to avoid clutter while eliminating ambiguity through well-defined decision criteria and paths.
Can flowcharts be used for both simple and complex problem-solving?
Yes, flowcharts can be used for both simple and complex problem-solving scenarios. Flowcharts are versatile visual tools that can effectively represent various processes, decision-making steps and problem-solving approaches regardless of their complexity.
In both cases, flowcharts offer a systematic and visual means of organizing information, identifying potential problems and facilitating collaboration among team members.
Can problem-solving flowcharts be used in any industry or domain?
Problem-solving flowcharts can be used in virtually any industry or domain. The versatility and effectiveness of flowcharts make them applicable to a wide range of fields such as Business and Management, Software Development and IT, Healthcare, Education, Finance, Marketing & Sales and a lot more other industries.
Final thoughts
Problem-solving flowcharts are a valuable and versatile tool that empowers individuals and teams to tackle complex problems with clarity and efficiency.
By visually representing the step-by-step process of identifying, analyzing and resolving issues, flowcharts serve as navigational guides simplifying intricate challenges into digestible parts.
With the aid of modern tools like Venngage’s Flowchart Maker and Venngage’s Flowchart Templates , designing impactful flowcharts becomes accessible to all while revolutionizing the way problems are approached and solved.
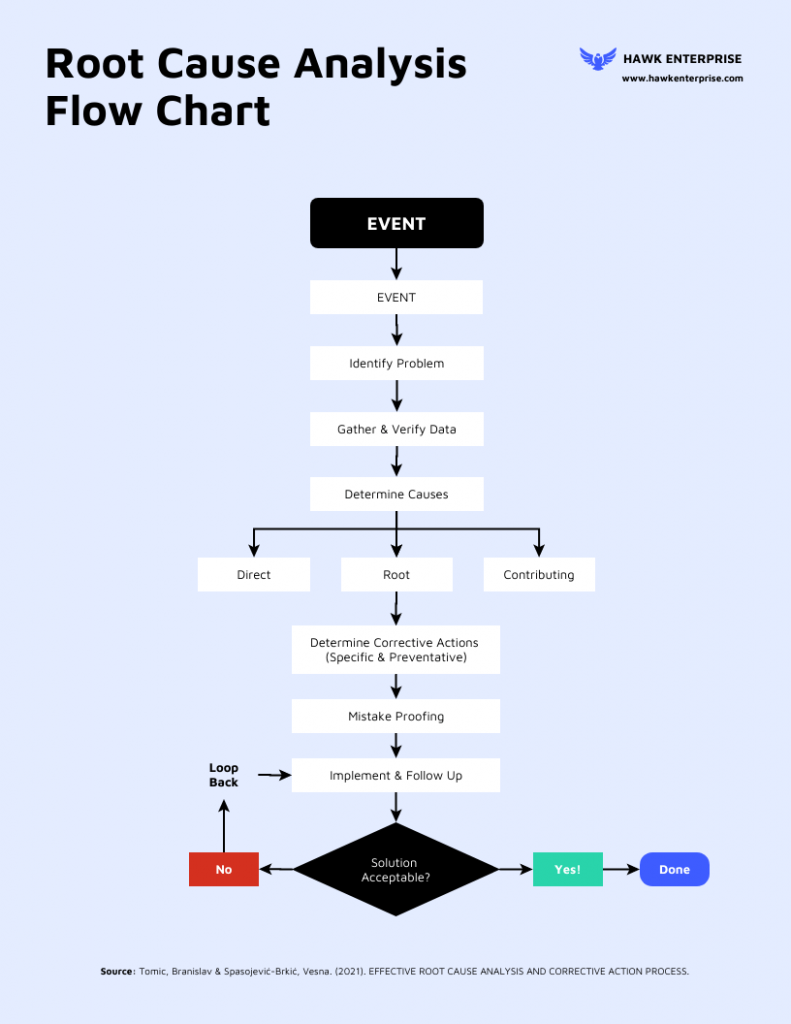
What is a Fishbone diagram?
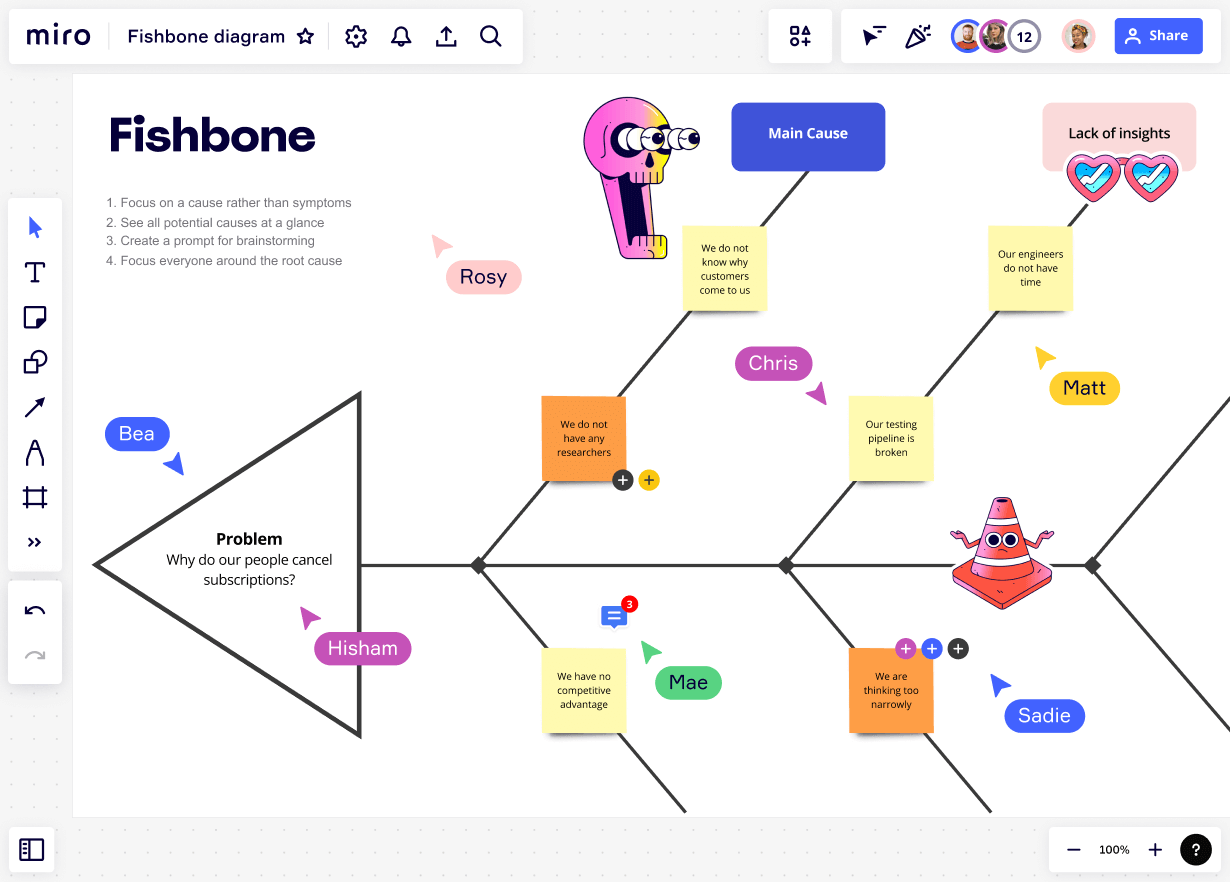
Table of Contents
Fishbone diagrams explained.
A fishbone diagram (also known as an Ishikawa fishbone diagram) is an effective problem-solving tool. Instead of focusing on a quick fix, creating a fishbone diagram helps to identify the root cause of a problem and find a long-term solution.
As a type of cause and effect diagram , the “fishbone” name comes from the diagram’s resemblance to a fish skeleton. A fishbone diagram consists of three main categories:
There’s a fish head at the head of the diagram, where you’ll outline the problem you’re trying to solve. The rest of the diagram branches out from here.
The spine stems from the head of the diagram (the problem statement), providing the outline of the fish. At the end of each spinal bone is a category that needs to be considered as part of the problem-solving process.
Branching out from each spinal bone, you’ll see a smaller rib bone. This is where the possible causes will sit to help you pinpoint the potential cause of the problem.
Benefits of fishbone diagrams
Fishbone diagrams are useful tools for improving existing processes and pinpointing causes of issues. Take a look at some benefits of performing a fishbone diagram root cause analysis:
Easily find the root cause of a problem
A fishbone diagram is a visual tool that adds structure and clarity to problem-solving. It indicates the problem and its possible causes in a single location, making it easier for teams to conduct a root cause analysis .
Prevent further problems
By finding the root cause of the problem, you fix the problem at its source and mitigate future issues. As a result, you’re far more likely to prevent the same (or similar) problems from cropping up in the future.
Collaborate with your team
A fishbone diagram is a great way to work with your team to brainstorm solutions . It’s a collaborative diagram, encouraging teams to review all the available information and discuss the best course of action.
If you’re part of a remote or hybrid team, an online platform like Miro allows you to collaborate with your team, no matter where they work. Simply share the diagram and hop on a video chat, and you can perform your root cause analysis virtually.
Example of a fishbone diagram
To see a fishbone diagram in action, look at this CEDAC Template from NEXT LEVEL Partners.
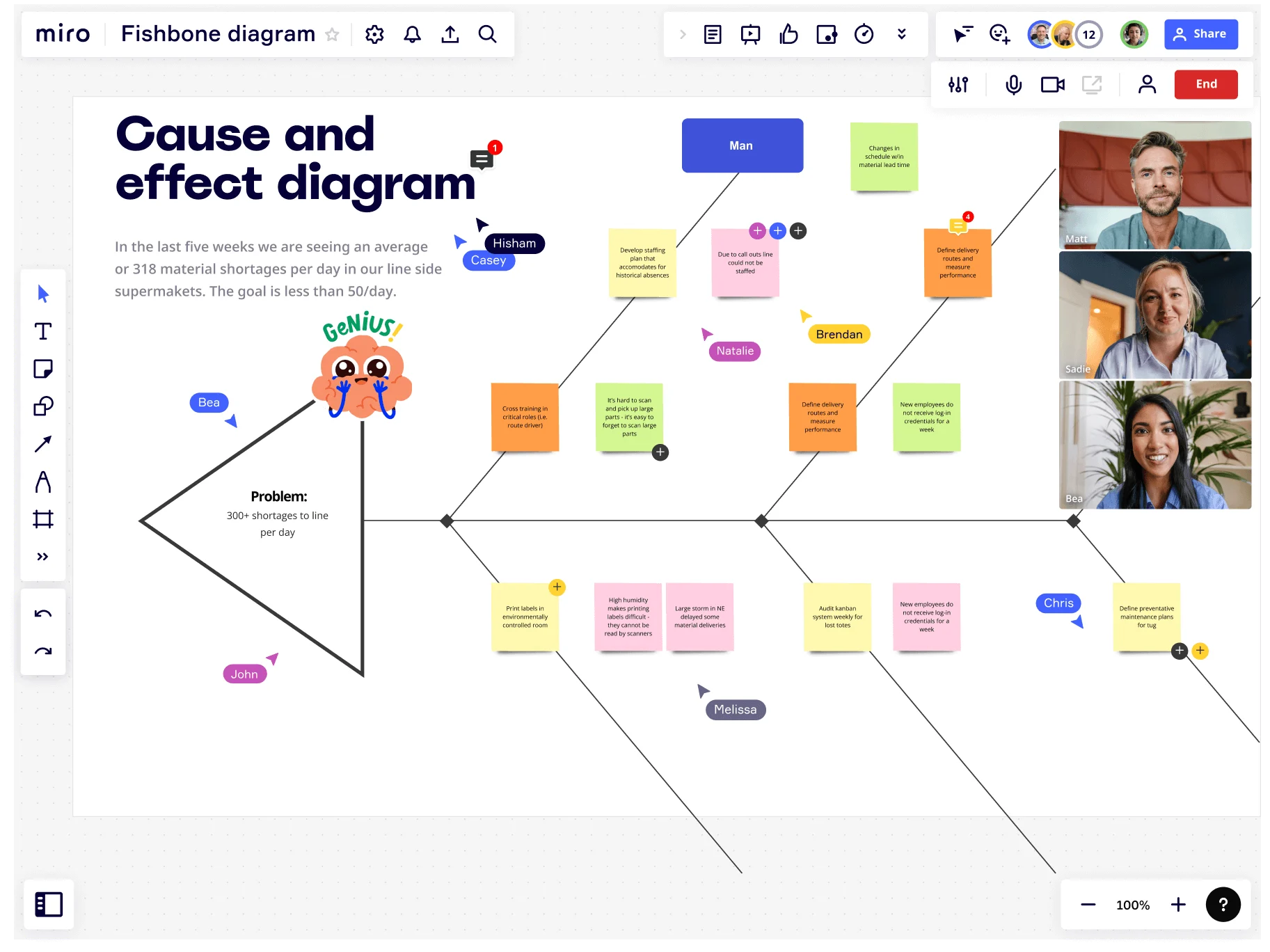
CEDAC is an acronym for Cause and Effect Diagram with the Addition of Cards. The diagram contains issues on the left-hand side of the ribs and solutions on the right-hand side.
Its inventor, Ryuji Fukuda, created CEDAC so that teams can delve deeper into their problem-solving analyses. By adding cards to the diagram, teams have a way of questioning existing information and suggesting new ideas. As a result, they’ll gain a deeper understanding of their problems and how to solve them.
Here are some of the common areas where the CEDAC model can be helpful:
Product development
Visualize issues with product development using the CEDAC diagram. Collaborate with the product team to identify the cause of the problem and use cards to identify the best possible solution.
Software features
Effectively allocate resources based on team structures and capabilities. Understand the most critical problems to solve and how they map together.
Product design
Define failures or problems with your product design, and identify effective solutions. Using the diagram’s cards, product designers can generate new and creative solutions to improve the design.
Internal processes
Pinpoint bottlenecks and figure out how to streamline and improve your business processes. Encourage team members to join in the discussion and make suggestions for improving the process going forward.
When to use a fishbone diagram
Take a look at some of the different instances when using a fishbone diagram can be useful for you and your team.
1. To analyze a problem statement
If you have a clear problem statement for your business, a fishbone diagram is a great way to analyze it in detail. You can see the problem’s culprit and decide how to fix the issue.
2. To brainstorm the causes of the problem
Also known as root cause analysis, a fishbone diagram allows you to discuss the potential causes of a problem. It’s the perfect opportunity to host a brainstorming session to identify pressing concerns and work through possible solutions.
3. To analyze a new product design
Use a fishbone diagram to map your new product design and visualize any potential hurdles before they come your way. As a result, you can put preventative measures in place before going live.
4. To improve your processes
If you’re struggling to streamline your processes and inefficiencies, a fishbone diagram can help. Use a fishbone diagram to pinpoint the troublesome areas of your process and find the cause of a problem. From there, you can determine exactly how to fix it.
5. For quality improvement
Use a fishbone diagram to visualize how and where you can improve to offer your customers a higher-quality experience. For example, you might want to improve the quality of your customer service. In this case, you can use the diagram to find areas for improvement in your existing processes.
How to make a fishbone diagram
Follow these simple steps to create an effective fishbone diagram:
1. Select the Fishbone Diagram Template
While you can always build your own diagram from scratch, you can also get a headstart by selecting this Fishbone Diagram Template . It’s free and easy to use, so you can start mapping your diagram immediately.

2. Outline your problem statement
When your diagram is ready to use, start by defining the problem. Otherwise known as a problem statement, this will sit at the head of the diagram. This must be as clear and concise as possible to find the right solution.
For example, in the diagram below, the main problem is that “40% of users cancel the subscription in the first month.” This statement clearly describes the problem and offers a solid starting point for finding a solution. Now, let’s consider how this would work if the statement were written differently — for example, “to increase customer retention.”
This statement is pretty vague, and there’s a lot of room for interpretation. Instead of focusing specifically on how to keep existing customers after the first month, teams might explore other avenues that won’t necessarily solve the actual problem.
The problem statement doesn’t have to be long and detailed. In fact, you should keep it short — ideally, no longer than a sentence. That way, it’ll be easy for your team to see the problem and won’t overcrowd the diagram. But the problem statement should always be clear and concise, leaving no room for interpretation.
If you’re new to problem statements or want a framework to guide you, look at Prime Motive’s Problem Framing Workshop Template .
3. Pinpoint your root causes
With your problem statement in place, you can now branch out and start to pinpoint the possible causes of the problem.
The specific causes will depend on what your problem statement is. For example, if your problem statement is related to product design, your root causes could include the following:
These are just a few examples. In your diagram, you might find that you have more or fewer root causes. With an intuitive platform like Miro, it’s easy to add or remove boxes based on how many you need.
When adding causes to your diagram, those with the biggest impact should be closest to the problem. The farther away a cause is from the head of the diagram, the less influence it has on the problem.
4. Identify individual causes
You can now identify the individual elements that contribute to the overall cause. These are the bones of the fish.
Let’s use an example to demonstrate how this works. Imagine that one of your root causes is “Equipment.” Here are some of the individual causes that might sit under this area:
You are using outdated and inefficient equipment
It’s expensive to replace existing equipment
There aren’t enough employees who know how to use the equipment
All of these elements could contribute to the problem you’re facing, but it’s up to you and your team to pinpoint the key elements at the root of the problem. Review all this information with your team, and you’ll be able to see which problem is most likely to have a long-term solution.
If you’re unsure how to identify the individual causes, look at the 5 Whys framework . It’s a simple brainstorming tool that helps teams explore the reasons behind a potential problem.
5. Create a plan of action
After working with your team to find the root cause of the problem, you can create an action plan for improvements. This involves mapping out the steps you need to take to solve your problem and how you’ll measure success (we suggest using the SMART Goals framework for this).
During this stage, be sure to focus on how to make lasting improvements. Don’t lose sight of the bigger picture in favor of a quick fix. The purpose of the fishbone diagram is to implement a long-lasting solution to your problem, so keep this in mind when creating your plan of action for the future.
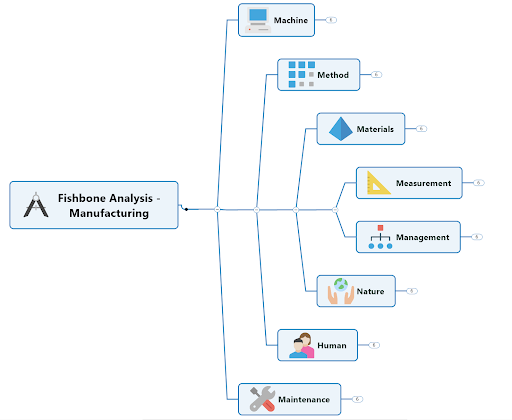
Fishbone diagram categories: the 6Ms of production
The fishbone diagram is used across various industries, but the original diagram was created to improve the manufacturing process. The six methods (6Ms) of production come from this original diagram, and engineers and designers would use this structure to cover all their bases.
The 6Ms of production are as follows:
1. Manpower
The functional activity involved in designing and delivering a product.
The production process and any other processes that contribute to the delivery of the final product.
Any systems, tools, or equipment used in manufacturing.
4. Material
The raw materials and components needed to create the end product.
5. Milieu (or Mother Nature)
Any environmental factors, such as weather, floods, or fire. Although most milieu factors can’t be controlled, there are some instances where businesses can put preventative measures in place to mitigate problems.
6. Measurement
The physical measurements (volume, distance, temperature, and so on) of a product, machine, or workspace.
The 6Ms are only relevant if you’re using the fishbone diagram to improve a manufacturing or production process. If you’re using the diagram for any other purpose, there’s no need to follow this structure.
Discover more
How to build a fishbone diagram
What is a cause and effect diagram
What is root cause analysis?
What is the 5 Whys Framework?
5 Whys: Examples, explanations, and how to find the causes of problems
Get on board in seconds
Join thousands of teams using Miro to do their best work yet.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Additional menu

Fishbone diagrams: How to use them for problem-solving
October 5, 2023 by MindManager Blog
When something goes wrong, it’s essential to understand the root cause in order to prevent it from occurring again.
However, life and business are both complex, making it difficult to identify at times the underlying causes which created the situation you’re facing now. That’s where and when a fishbone diagram can help!
In this article, we’ll dive into everything you need to know about fishbone diagrams and how to use them for problem-solving.
What is a fishbone diagram?
Fishbone diagrams (also called Ishikawa diagrams and cause-and-effect diagrams) are visualizations used to identify and illustrate the causes for a specific event. Potential causes are often brainstormed and then categorized in order to identify a problem’s root cause.
The diagram gets its name due to the branches radiating out from the main issue in a way that resembles a side view of a fish skeleton. However, the process can be applied to most mind map layouts.
Here’s a fishbone diagram example:
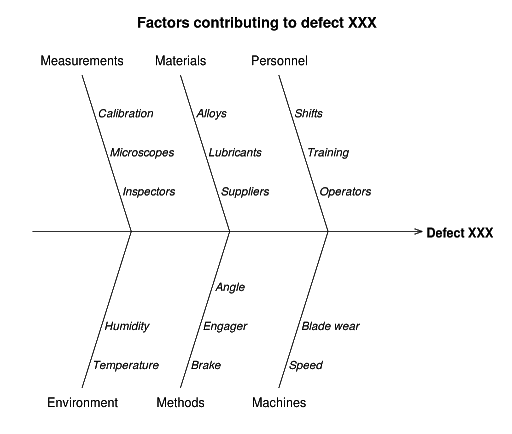
When to use fishbone diagrams
Fishbone diagrams help focus you and your team’s energy on the root cause of a problem instead of merely addressing and wasting time on the symptoms.
Here are a few common applications of Fishbone diagrams:
Manufacturing: Discover the root cause of a manufacturing issue by brainstorming and ranking the likelihood and impact of all the areas that influence the production process.
How to create a fishbone diagram in MindManager in 5 steps
Fishbone diagrams are quick to make in MindManager and the examples above are included as templates to make it even easier.
MindManager’s ease of capturing ideas during brainstorming makes it the ideal tool to capture and organize potential causes. The visual format allows you to see all the causes simultaneously, draw relationships between causes, and identify if the root cause is found multiple times within the diagram.
Here’s how to create a fishbone diagram:
- In MindManager, go to the File menu, select New and then click into the Problem-Solving folder. There you’ll find three templates for Fishbones, the manufacturing, service, and product analyses. Select a template.
- Enter the issue in the central topic.
- Next, either brainstorm potential causes and add them as floating topics initially and categorize them after the brainstorming session. Or, use each category as a guide for a mini-brainstorm session and enter the potential causes directly in the appropriate branch.
- Add more details to your causes as new subtopics or notes with the cause itself.
- Once all the potential causes have been identified, you can take the diagram a step further and rank each cause. One way to do this would be to use the Priority marker to rank the cause between 1 and 9. You can later filter the diagram and view specific priorities and hide the less important ones that will distract the focus of the team.
Key MindManager features for fishbone diagrams
There is no one single ‘right’ way to create, categorize, or rank items within a fishbone diagram.
With that said, here’s a list of ways to apply some of MindManager’s features to transform an ordinary diagram into a powerful application to visualize and empower your work.
- Use color (fonts, topic fill color) to categorize different causes.
- Change the font characteristics to emphasize different causes (e.g. bold, larger fonts, different font types, etc.).
- Use topic images to add greater context and enhance the visualizations.
- Write topic notes for more in-depth details related to each cause.
- Apply icons and tags to categorize causes.
- Hyperlink or add attachments to provide more details.
- Draw relationship lines between different connected causes throughout the diagram.
- Assign resources to any causes that you have identified. This may clarify who is responsible or accountable for that cause.
- Collapse branches for a quick overview or drill down into all the details.
- View the diagram through multiple lenses. For instance, you are not confined to the layout of the Fishbone diagram. Switch views to see the diagram as an outline, or dive in the Schedule, Icon or Tag views to see your content in groupings based on your assigned categories or due dates.
- Filter content to either show or hide topics that you have annotated with tags or icon markers. For instance, filter on all the top priority potential causes that need additional investigation.
- Share your diagram by either publishing it onto the web (and sharing a link) where anyone can open and view the Fishbone diagram interactively in their browser or export the diagram into a variety of different formats (e.g. Microsoft Word, HTML5, Microsoft Project, etc.).
Download MindManager today to get started on your fishbone diagram!
Ready to take the next step?
MindManager helps boost collaboration and productivity among remote and hybrid teams to achieve better results, faster.
Why choose MindManager?
MindManager® helps individuals, teams, and enterprises bring greater clarity and structure to plans, projects, and processes. It provides visual productivity tools and mind mapping software to help take you and your organization to where you want to be.
Explore MindManager
- How to Use Ishikawa Diagrams to Solve Business Problems
- Learn Lean Sigma
- Root Cause Analysis
Do you want to solve business problems in an efficient manner? If this is the case, you should think about using Ishikawa Diagrams. Ishikawa Diagrams, also known as fishbone diagrams or cause-and-effect diagrams, are a visual tool that can help identify the root causes of a problem. As a result, they are an ideal solution for businesses looking to improve their processes and reduce errors.
We’ll look at how Ishikawa Diagrams can be used to solve business problems in this post. We’ll look at the anatomy of an Ishikawa Diagram and show you how to make one step by step. We’ll also look at real-world examples of business problems solved with Ishikawa Diagrams and the benefits gained by doing so. Finally, we’ll go over best practises for using Ishikawa Diagrams and how to avoid common pitfalls.
Whether you’re new to Ishikawa Diagrams or want to improve your problem-solving skills, this post will walk you through how to use this powerful tool to solve business problems.
Table of Contents
What is an ishikawa diagram.
Because of its appearance, the Ishikawa Diagram is also known as the fishbone diagram after its creator, Kaoru Ishikawa. The diagram is organised with a central spine and several branches that resemble fish bones. Each branch represents a possible cause category that contributes to the problem under consideration.
Because it is a versatile and widely used tool in problem solving and process improvement, an Ishikawa diagram is known by many different names. Here are some brief explanations for the various names:
Fishbone diagram: This name comes from the visual appearance of the diagram, which looks like a fish skeleton with the problem or effect at the head and the causes branching out like the bones of the fish.
Cause-and-effect diagram: This name reflects the diagram’s purpose, which is to aid in the identification of the root causes of a problem by mapping out the various factors that contribute to it. The diagram depicts the relationships between the causes and the effects, making it easier to determine where to focus improvement efforts.
Herringbone diagram: This is another name for the diagram’s appearance. The diagram’s branches resemble the bones of a herring, a type of fish.
While the names may be used interchangeably, they all refer to the same basic problem-solving and process-improvement tool.
An Ishikawa Diagram has six main branches, which are as follows:
- Personnel – This branch includes all human-related factors that may have an impact on the problem under consideration, such as training, communication, and teamwork.
- Process – This branch includes all of the steps and procedures involved in the process or activity, as well as the equipment, materials, and workflow.
- Machines – This branch includes all the physical equipment and machinery used in the process, including tools, machines, and technology.
- Materials – The raw materials and other inputs used in the process, such as supplies, ingredients, and components, are the focus of this branch.
- Environment – This branch includes all environmental factors that may affect the process, such as temperature, humidity, lighting, and noise.
- Measurement – This branch includes all metrics and measurements used to evaluate the process, such as quality standards, performance indicators, and statistical analysis.
Each of these branches is used to identify potential causes that may be contributing to the problem under investigation. For example, if a decrease in product quality is the issue, the Ishikawa Diagram can be used to identify the various factors that could be causing this problem, such as a lack of employee training, faulty equipment, or low-quality materials. The branches are used to identify as many potential causes as possible, which can then be further evaluated to determine the underlying cause of the problem.
The Ishikawa Diagram assists teams in gaining a better understanding of the problem being analysed and developing targeted solutions to address the root cause by identifying potential causes and organising them in a clear and concise manner.
How to Create an Ishikawa Diagram
Creating an Ishikawa Diagram is a simple process that begins with identifying the problem and breaking it down into its component parts. Here’s a step-by-step tutorial for making an Ishikawa Diagram:
- Step 1: Identify the problem and write it in a box at the top of the diagram.
- Step 2: To represent the main spine of the fishbone diagram, draw a horizontal arrow pointing to the problem box.
- Step 3: Draw a diagonal arrow for each of the diagram’s six main branches (People, Process, Equipment, Materials, Environment, and Measurement). Label each arrow with the name of the corresponding branch.
- Step 4: Determine the possible causes of the problem and document them on the appropriate branch. Create as many causes as you can and add them to the diagram.
- Step 5: If necessary, divide each cause into smaller sub-causes. Include these sub-causes in your diagram as well.
- Step 6: Determine the root cause of the problem by evaluating potential causes and sub-causes. The root cause is the underlying issue that is causing the problem being investigated.
- Step 7: Create and implement solutions to the root cause.
In addition to drawing an Ishikawa Diagram by hand, several software tools are available to help you create and collaborate on these diagrams. Among the most popular software tools are:
SmartDraw : This programme provides a variety of templates and tools for creating professional-looking Ishikawa Diagrams.
Lucidchart : This cloud-based software enables teams to work together in real-time to create Ishikawa Diagrams.
Creately : For creating Ishikawa Diagrams, this tool provides a variety of templates and customization options.
Creating Ishikawa Diagrams with software tools can save time and streamline the process of collaborating with team members. These tools also make it simple to share and export the diagram in a variety of formats, making it easier to include in presentations and reports.
Using Ishikawa Diagrams in Problem-Solving
Ishikawa Diagrams are a powerful problem-solving tool that can be used in root cause analysis. Teams can analyse the causes and develop solutions to address the root cause by identifying the various factors that contribute to a problem.
The process of determining the underlying cause of a problem rather than just addressing its symptoms is known as root cause analysis. This approach assists teams in developing more effective and long-term problem solutions.
To use an Ishikawa Diagram in root cause analysis, teams must first identify the problem and draw a fishbone diagram. The diagram’s six main branches (Personnel, Process, Machine, Materials, Environment, and Measurement) are used to identify potential problem causes. Teams can analyse the root cause by brainstorming and organizing these causes on the diagram.
Teams can use the “five whys” technique in addition to an Ishikawa Diagram to identify the root cause of a problem. The five whys technique is a method of drilling down into the root cause of a problem by asking “why” five times. The goal is for the team to keep asking “why” until they find the underlying root cause of the problem.
For example, if the issue is a product delivery delay, the five whys technique could be used as follows:
- Why was the product delivery delayed? – Because the shipment was sent to the wrong address.
- Why was it sent to the wrong address? – Because the shipping label was incorrect.
- Why was the label incorrect? – Because the person who prepared it didn’t check the address.
- Why didn’t they check the address? – Because they were in a rush to finish the task.
- Why were they in a rush? – Because they were given too many tasks to complete in a short amount of time.
In this example, the root cause of the product delivery delay is that the worker was assigned too many tasks to complete in a short period of time. By identifying the root cause, the team can develop solutions to the problem, such as allocating more time for tasks or more effectively delegating responsibilities.
To Summarize here is an overview of how Ishikawa Diagrams are used in root cause analysis follows:
Step 1: Brainstorm potential causes for each branch and write them on the diagram’s appropriate branch.
Step 2: Examine each possible cause to see if it is the root cause or a symptom of the problem.
Step 3: Use 5 Whys Analysis to ask “why” five times for each potential root cause identified to determine the underlying cause of the problem. Check out our 5 Whys Analysis Template to support this
Step 4: Once the root cause has been identified, develop and implement solutions to address it.
Here is an example of how a complete Ishikawa Diagram may look with potential problems identified on it.
To summarise, Ishikawa Diagrams are an effective problem-solving tool that can be combined with the five whys technique to identify the root cause of a problem. Teams can develop more effective and long-term solutions to improve their processes and operations by analysing potential causes and asking “why” to drill down into the underlying issue.
Examples of Business Problems Solved with Ishikawa Diagrams
Ishikawa Diagrams, also known as fishbone diagrams, have been used to solve a wide range of business problems. Here are some real-world examples of business problems solved with Ishikawa Diagrams:
Quality control issues in a manufacturing plant
A manufacturing plant was experiencing quality control issues with their products. The problem was identified using an Ishikawa Diagram, which helped the team to identify the potential causes of the problem. The diagram revealed that the issues were caused by a lack of training among the employees, poor machine maintenance, and inadequate raw materials. By addressing these issues, the plant was able to improve the quality of its products and reduce waste.
A call centre has a high employee turnover rate.
A call center’s ability to provide quality customer service was being hampered by high employee turnover. An Ishikawa Diagram was used to identify the problem, which assisted the team in determining the potential causes of the high turnover rate. According to the diagram, the problems were caused by low employee morale, insufficient training, and a lack of career development opportunities. The call centre was able to improve employee satisfaction and retention rates by addressing these issues.
Inventory management in a retail store is inefficient.
A retail store’s inventory management process was inefficient, resulting in excess inventory and stockouts. An Ishikawa Diagram was used to identify the problem, which assisted the team in determining the potential causes of the inefficiencies. According to the diagram, the problems were caused by inaccurate demand forecasting, insufficient inventory tracking, and poor communication among the store’s departments. The store was able to improve its inventory management process, reduce excess inventory, and prevent stockouts by addressing these issues.
The Ishikawa Diagram was used as a problem-solving tool in each of these examples to identify potential causes of the problem. The diagram enabled the teams to brainstorm and organise the various factors that could be contributing to the problem, allowing them to drill down to the root cause. The teams were able to implement more effective and long-term solutions to improve their processes and operations by addressing the root cause.
The advantages of using Ishikawa Diagrams in these scenarios include improved quality control, reduced waste, increased employee retention and satisfaction, and increased inventory management efficiency. The diagram enabled the teams to take a structured approach to problem-solving, allowing them to identify the root cause of the problem and develop more effective solutions.
Best Practice for Ishikawa Diagrams
Ishikawa Diagrams are a powerful problem-solving tool, but they must be used correctly to produce the desired results. Some best practises for using Ishikawa Diagrams in problem-solving processes are as follows:
- Clearly define the problem: Before you create an Ishikawa Diagram, you must first define the problem you are attempting to solve. This will aid your concentration and ensure that your diagram is relevant and effective.
- Involve a diverse team: Ishikawa Diagrams work best when used in a group setting. To ensure a well-rounded perspective, try to include a diverse group of people from various departments or areas of expertise.
- Brainstorm potential causes: Encourage team members to brainstorm all potential causes of the problem when creating the diagram. This will assist you in identifying all potential root causes and ensuring that your solutions are all-inclusive.
- Use clear and concise language: When labelling the branches of the diagram, use clear and concise language to ensure that everyone understands the meaning. Avoid using jargon or abbreviations that may be confusing to some team members.
- Prioritize potential causes: After identifying all potential causes, prioritise them based on their likelihood of contributing to the problem. This will allow you to concentrate your efforts on the most pressing root causes.
- Verify the root cause: Before implementing any solutions, test your hypothesis to determine the root cause of the problem. This will help you ensure that you are treating the underlying cause of the problem rather than just the symptoms.
Avoiding Common Mistakes When Using Ishikawa Diagrams
While Ishikawa Diagrams can be a useful problem-solving tool, there are some common errors that teams can make when creating and using them. Here are some errors to avoid:
- Jumping to conclusions: It is critical to avoid jumping to conclusions before identifying and evaluating all potential causes. Rushing to solutions without fully comprehending the underlying cause of the problem can result in ineffective and costly solutions.
- Excessive diagram complexity: Keep the diagram simple and focused on the problem at hand. Overcomplicating the diagram with too many branches or irrelevant information can make determining the true root cause of the problem difficult.
- Ignoring other sources of information: While Ishikawa Diagrams are a powerful tool, they should not be used as the sole source of information in problem-solving processes. Other data sources to consider include customer feedback, process data, and employee input.
Teams can effectively use Ishikawa Diagrams to identify and address the root causes of business problems by adhering to these best practises and avoiding common pitfalls.
Finally, Ishikawa Diagrams are a useful tool for solving business problems and determining the root causes of problems. Teams can effectively use Ishikawa Diagrams to find comprehensive solutions by following best practices such as clearly defining the problem, involving a diverse team, brainstorming potential causes, and prioritising root causes.
It’s critical to remember that Ishikawa diagrams should be used in conjunction with other sources of information to ensure a well-rounded approach to problem-solving. Teams can effectively leverage the power of Ishikawa diagrams in their problem-solving processes by avoiding common mistakes such as overcomplicating the diagram and jumping to conclusions.
Finally, using Ishikawa Diagrams to solve business problems can result in better processes, higher customer satisfaction, and a more efficient organisation. Teams can achieve greater success and propel their businesses forward by mastering this powerful tool.
- Ilie, G. and Ciocoiu, C.N., 2010. Application of fishbone diagram to determine the risk of an event with multiple causes . Management research and practice , 2 (1), pp.1-20.
- Radziwill, N., 2017. Creating ishikawa (fishbone) diagrams with R. Software Quality Professional , 20 (1), pp.47-48.
Daniel Croft
Daniel Croft is a seasoned continuous improvement manager with a Black Belt in Lean Six Sigma. With over 10 years of real-world application experience across diverse sectors, Daniel has a passion for optimizing processes and fostering a culture of efficiency. He's not just a practitioner but also an avid learner, constantly seeking to expand his knowledge. Outside of his professional life, Daniel has a keen Investing, statistics and knowledge-sharing, which led him to create the website learnleansigma.com, a platform dedicated to Lean Six Sigma and process improvement insights.
Free Lean Six Sigma Templates
Improve your Lean Six Sigma projects with our free templates. They're designed to make implementation and management easier, helping you achieve better results.
5S Floor Marking Best Practices
In lean manufacturing, the 5S System is a foundational tool, involving the steps: Sort, Set…
How to Measure the ROI of Continuous Improvement Initiatives
When it comes to business, knowing the value you’re getting for your money is crucial,…
8D Problem-Solving: Common Mistakes to Avoid
In today’s competitive business landscape, effective problem-solving is the cornerstone of organizational success. The 8D…
The Evolution of 8D Problem-Solving: From Basics to Excellence
In a world where efficiency and effectiveness are more than just buzzwords, the need for…
8D: Tools and Techniques
Are you grappling with recurring problems in your organization and searching for a structured way…
How to Select the Right Lean Six Sigma Projects: A Comprehensive Guide
Going on a Lean Six Sigma journey is an invigorating experience filled with opportunities for…
Visual problem solving with flowcharts and mind maps

What’s life without problems? Probably a little boring, if we’re being honest. If everything were perfect all the time, there would be no challenges, and things would get pretty monotonous. This is a rather optimistic view on what many believe to be an aggravating part of life. No matter how you feel about problems, one thing is true: problems are inevitable . You can’t always control how many problems you encounter in your life, but you can learn better ways to solve them. So, what can we do for those really complex issues that aren’t easily solved? Visual problem solving is the perfect way to see solutions and break down complex issues.
Make your own flowchart with Gleek .
What is visual problem solving?
Visual problem solving is the process of using aids like charts or diagrams to display all the aspects of a problem in order to find viable solutions. When problem solving, sometimes it’s hard to see what’s causing the problem, or other relationships and correlations that are affecting whatever it is you’re working on. Two common methods for problem solving include mind maps and flowcharts . A mind map is a non-linear diagram, used for making new ideas or breaking down complex issues. A flowchart is a linear diagram, used for making action plans and describing processes.
5 steps to solve problems
Identify the true problem
Maybe you know what the issue is in clear terms, or perhaps it’s still a little confusing. A good way to get a concrete vision of the problem you need to solve is to pose it as a question, or a short statement. You might come up with something like ‘our sales have dropped’, or, as a question ‘what can we do to increase sales?’.
Get information
Now that you have a clear objective to solve, the next step is to gather all the relevant information that pertains to the issue. This can look like statistics, comments from customers, employee feedback, and more. Once you’ve collected the data, you’ll need to analyze it from all angles to get a clear view on the topic.
Brainstorming session
Get any and all potential solution ideas out on the table. Doesn’t matter how silly an idea seems, just put anything that comes to mind on the drawing board. This is where your visual aids will really come in handy, especially mind maps. You might need more than one chart, depending on how complicated the issue is.
Choose the best idea(s)
Whether on your own or with a team, you’ll have to eliminate the potential solutions that just won’t work. To find the solution that’ll work best, it’s good to analyze it in the same way you did the problem – by looking at potential outcomes, and all facets involved.
Make an action plan
So you think you’ve found the perfect solution! Now what? If your problem is complicated, usually the solution will be too. Here is where another visual aid, like a flowchart, will be helpful. Map out the specific steps you need in order to implement your solution. Then, it’s time to put your plan into action.
These are just the basic steps you can use to start problem solving. You may find that other actions are needed during your own journey.
Common mistakes when problem solving
Mistakes? We all make them from time to time. Here are some common mistakes we are prone to when trying to fix problems.
Undefined problem – When identifying the problem, it’s possible that the problem is too big, multi-faceted, or too complex to tackle all at once. A way to avoid this is to break the problem down into chunks, following common themes.
More problems arise – This isn’t always a direct result of anything we do, but it can happen nonetheless. The best way to deal with more problems that arise when you’re trying to solve the original one is to think of the possible things that could go wrong during the solution stage. When you’re prepared for any situation, you’ll rarely have any setbacks.
No action plan – Finding a way to solve your problem doesn’t mean that the planning is over. On the contrary, you need to create a strategy to properly execute your solution so you won’t end up with a half-solved problem and even more issues than you started with.
When to use flowcharts
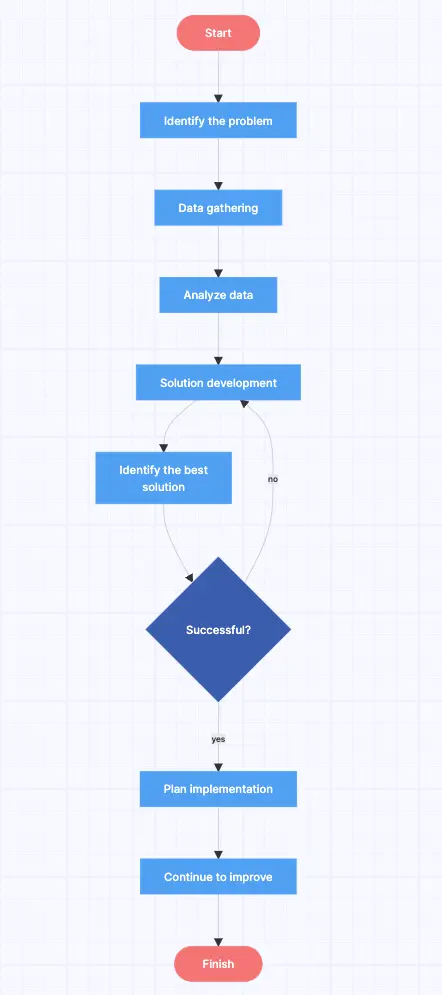
One way to chart your problems and progress is through flowcharts. For those who like to think in a step-by-step or linear fashion, flowcharts are the best way to visualize things. Let’s have a look at some situations that are best suited to flowcharts.
Big problems – Flowcharts can help break down a large problem or solution into specific steps or stages from start to finish.
Decision trees – This type of flowchart is helpful when diagramming actions that will happen as a result of other actions, whether they be in a software system or actions taken by people.
Cause and effect – Similar to a decision tree, a cause and effect flowchart is where you can analyze the potential results of various actions, past or present.
Check out our 20 flowchart templates that you can also easily edit !
When to use mind maps
Mind maps are great for brainstorming sessions, and non-linear problem solving. Here are some situations that are best visualized through a mind map.
Finding the problem – So, what is the problem exactly? Sometimes it’s hard to see. Making a mind map offers you the opportunity to see all the moving parts involved with a situation, and how they relate to one another, and can help you suss out the true problem.
Core and branching ideas – You start with a core idea, such as ‘online sales’, then add related ideas or issues branching off from that, like maybe ‘ad revenue’, or ‘social media campaigns’. Then those ideas can have their own branches. This is an easy way to analyze all aspects of a problem.
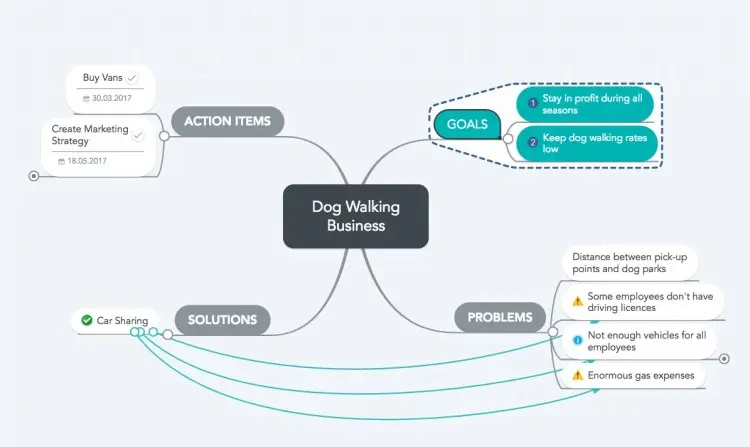
Source: Problem Solving with Mind Maps (Tutorial)
Looking to create your own flowchart? Gleek has the solution for you. With Gleek, you can create your own flowcharts using a text-based command center, without ever using your mouse. Not only can you create flowcharts, you can create many other UML-based diagrams that will wow your colleagues and bring new life to your presentations. Get started for free today .
Related posts
Uses for cross-functional flowcharts
20 editable flowchart templates & examples
What are flowchart symbols? Here’s a handy guide with examples
A step-by-step guide to creating a flowchart in Google Docs
7 stages of the product development process (flowchart example)
back to all posts
How to Use Fishbone Diagram for Problem Solving
Fishbone diagram is a problem-solving tool, used in literal terms like a fishbone. It is also known as a cause and effect diagram. The mechanism is to specifically identify the cause and effect of any business or project problem.
A fishbone diagram can help define potential reasons for an issue. This article will dive into understanding the core principles of the fishbone diagram problem solving as a tool.
In 1943 at Tokyo University, Kaoru Ishikawa created the "Fishbone Diagram." Fishbone diagrams can also be called diagrams of "cause and effect." The fishbone diagram problem solving tool is a perfect tool to dig through an issue when we try to assess the root cause and find a solution effectively.
It offers a mechanism for explicitly identifying the "effect" and then brings you to think about the potential triggers, based on typical manufacturing problems. The fishbone diagram problem solving is a basic model that makes it easy to grasp swift and efficient root causes to implement corrective behavior.
It reflects the question or impact at the fish's head or mouth. Possible contributing factors under separate causal groups are identified on the smaller "bones." A fishbone diagram can help define potential reasons for an issue that would otherwise not be discussed by encouraging the team to look through the definitions and discuss alternate reasons.
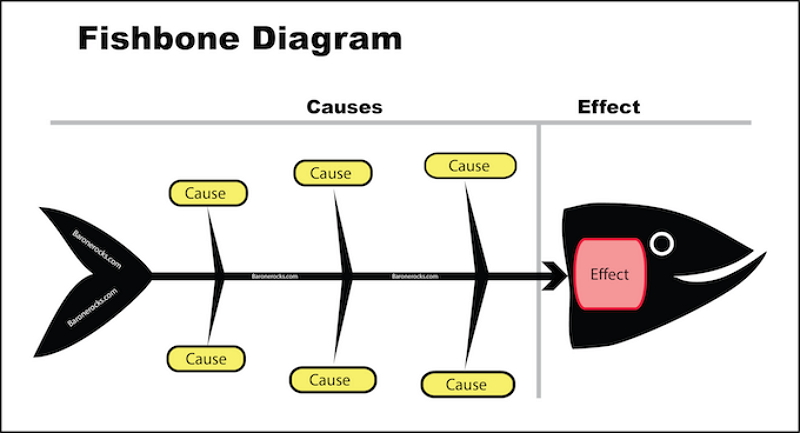
Source: EdrawMind
1.1 Why Use Fishbone Diagram for Problem Solving
The fishbone diagram makes you consider more when solving specific problems. During a brainstorming activity, various groups inspire thoughts from different areas.
The fishbone diagram brings order to the process of cause and effect . It's easy for participants to understand the main problems or issues and focus on the question across different potential triggers.
The fishbone diagram helps distinguish the causes and reasons for a problem and lets people intuitively figure out the solutions.
1.2 The Usage of Fishbone Diagram
The fishbone diagram problem solving method can be used when trying to fix problems or discover the root cause of an issue or problem, which helps you to see below the surface, and dive deeper into the real problem.
Here are several typical fishbone diagram problem solving applications:
- Manufacturing: ,nbsp;Uncover the root cause of a manufacturing problem by brainstorming and rating the likelihood and effect of all factors affecting the manufacturing cycle;
- Marketing or Product Marketing: ,nbsp;Identify the possible factors that may impede your company's popularity in the marketplace by investigating all the places that affect your product acceptance;
- Service: ,nbsp;Uncover the root cause of a business issue by brainstorming, and rate the probability and effect of all factors impacting the service delivery process.
There are 7 steps lead you to use fishbone diagram for problem solving:
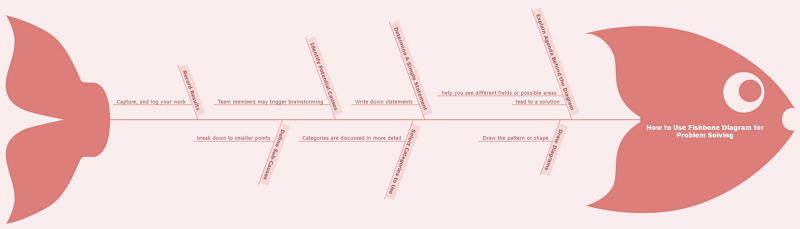
- Explain the agenda behind the diagram
Let your team members know that the diagram can help you see different fields or possible areas that might lead to a solution to your current business problem.
- Draw diagrams
Draw the pattern or shape on your whiteboard, or use a software diagramming tool to ease accessibility. If you need remote attendants to do this exercise, you can quickly build it in EdrawMind and display your computer.
- Determine a simple statement on an issue
Write down statements at the top of your page or above where you will build the diagram., which means everyone has the same idea of the issue you are concerned with.
- Select what categories to use
Categories are discussed in more detail below. For example, you can add Policies, Methods, Personnel, and Software categories.
- Identify potential causes within each category of your problem
Team members may trigger brainstorming or contribute factors that fall into this category. You can either go by category or only come up with ideas and determine which type they fit.
- Go a step deeper to define sub-causes for any cause in the category
If you decide whether something can or will break down to smaller points, build divisions from the critical point.
Team members study the diagram to determine the most relevant focus points. If you are trying to take this a step forward and fix the root cause, it helps define where you're trying to benefit your initiative. You can't solve all the root factors at once, and some can get more significant payoff than others. Check the diagram for an evaluation of where the concentration of the team is best.
- Record results
You bring the work in. Capture, and log your work. You will need to return to it later, so you don't want to miss the importance of the exercise that you got.
There are several tips that should be considered when using the fishbone diagram for solving problems:
- Using the fishbone diagram tool to keep the team focused not on signs, but the problem's causes;
- Make sure you leave ample room in the diagram between the main groups to add minor specific pointers later;
- Try making team members write every cause on sticky notes while you're brainstorming causes, moving around the community asking each person about a particular reason. Continue to go through the loops, have more pointers before all suggestions have been eliminated;
- Encourage each person to join in the brainstorming exercise and voice their own opinions;
- Remember that the strategy of "five-whys" is often used in combination with the fishbone diagram.
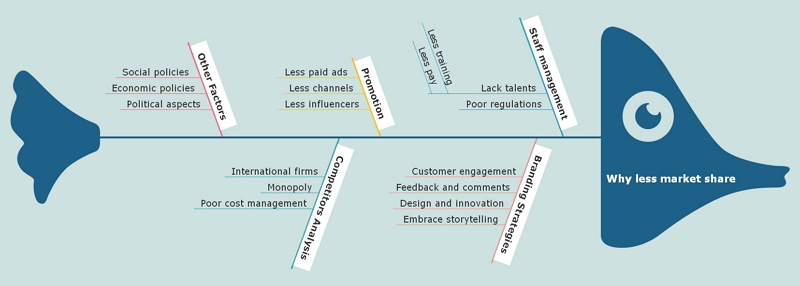
While it takes time to create a fishbone diagram , it will help you and your team define the real causes and encourage you to strengthen the process and make permanent improvements.
Regardless, whether you are using the graphical or indented fishbone hierarchy, this process optimization method will significantly help you understand the factors involved in a process. The root causes of the event are the underlying process and system issues, which allowed the contribution. Hence fishbone diagram , the problem-solving tool, is extremely crucial when discussing strategies to deal with problems.
EdrawMind is an easy-to-use, flexible mind mapping tool designed to help you generate modern, fresh visuals and mind maps. By combining the bullet points into a mind map on a project, EdrawMind lets you organize the thoughts or concepts and create essential strategies.

How to Motivate Yourself to Study

Meeting Management: How to Run a Meeting

How to Create a Fishbone Diagram on PowerPoint

How to Make Good Use of Mind Map for Students

Complete Beginner's Guide to Project Planning
How to Be Productive at Home: 7 Work-from-Home Tips

What is Problem Solving? (Steps, Techniques, Examples)
By Status.net Editorial Team on May 7, 2023 — 5 minutes to read
What Is Problem Solving?
Definition and importance.
Problem solving is the process of finding solutions to obstacles or challenges you encounter in your life or work. It is a crucial skill that allows you to tackle complex situations, adapt to changes, and overcome difficulties with ease. Mastering this ability will contribute to both your personal and professional growth, leading to more successful outcomes and better decision-making.
Problem-Solving Steps
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps:
- Identify the issue : Recognize the problem that needs to be solved.
- Analyze the situation : Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present.
- Generate potential solutions : Brainstorm a list of possible solutions to the issue, without immediately judging or evaluating them.
- Evaluate options : Weigh the pros and cons of each potential solution, considering factors such as feasibility, effectiveness, and potential risks.
- Select the best solution : Choose the option that best addresses the problem and aligns with your objectives.
- Implement the solution : Put the selected solution into action and monitor the results to ensure it resolves the issue.
- Review and learn : Reflect on the problem-solving process, identify any improvements or adjustments that can be made, and apply these learnings to future situations.
Defining the Problem
To start tackling a problem, first, identify and understand it. Analyzing the issue thoroughly helps to clarify its scope and nature. Ask questions to gather information and consider the problem from various angles. Some strategies to define the problem include:
- Brainstorming with others
- Asking the 5 Ws and 1 H (Who, What, When, Where, Why, and How)
- Analyzing cause and effect
- Creating a problem statement
Generating Solutions
Once the problem is clearly understood, brainstorm possible solutions. Think creatively and keep an open mind, as well as considering lessons from past experiences. Consider:
- Creating a list of potential ideas to solve the problem
- Grouping and categorizing similar solutions
- Prioritizing potential solutions based on feasibility, cost, and resources required
- Involving others to share diverse opinions and inputs
Evaluating and Selecting Solutions
Evaluate each potential solution, weighing its pros and cons. To facilitate decision-making, use techniques such as:
- SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats)
- Decision-making matrices
- Pros and cons lists
- Risk assessments
After evaluating, choose the most suitable solution based on effectiveness, cost, and time constraints.
Implementing and Monitoring the Solution
Implement the chosen solution and monitor its progress. Key actions include:
- Communicating the solution to relevant parties
- Setting timelines and milestones
- Assigning tasks and responsibilities
- Monitoring the solution and making adjustments as necessary
- Evaluating the effectiveness of the solution after implementation
Utilize feedback from stakeholders and consider potential improvements. Remember that problem-solving is an ongoing process that can always be refined and enhanced.
Problem-Solving Techniques
During each step, you may find it helpful to utilize various problem-solving techniques, such as:
- Brainstorming : A free-flowing, open-minded session where ideas are generated and listed without judgment, to encourage creativity and innovative thinking.
- Root cause analysis : A method that explores the underlying causes of a problem to find the most effective solution rather than addressing superficial symptoms.
- SWOT analysis : A tool used to evaluate the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to a problem or decision, providing a comprehensive view of the situation.
- Mind mapping : A visual technique that uses diagrams to organize and connect ideas, helping to identify patterns, relationships, and possible solutions.
Brainstorming
When facing a problem, start by conducting a brainstorming session. Gather your team and encourage an open discussion where everyone contributes ideas, no matter how outlandish they may seem. This helps you:
- Generate a diverse range of solutions
- Encourage all team members to participate
- Foster creative thinking
When brainstorming, remember to:
- Reserve judgment until the session is over
- Encourage wild ideas
- Combine and improve upon ideas
Root Cause Analysis
For effective problem-solving, identifying the root cause of the issue at hand is crucial. Try these methods:
- 5 Whys : Ask “why” five times to get to the underlying cause.
- Fishbone Diagram : Create a diagram representing the problem and break it down into categories of potential causes.
- Pareto Analysis : Determine the few most significant causes underlying the majority of problems.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis helps you examine the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats related to your problem. To perform a SWOT analysis:
- List your problem’s strengths, such as relevant resources or strong partnerships.
- Identify its weaknesses, such as knowledge gaps or limited resources.
- Explore opportunities, like trends or new technologies, that could help solve the problem.
- Recognize potential threats, like competition or regulatory barriers.
SWOT analysis aids in understanding the internal and external factors affecting the problem, which can help guide your solution.
Mind Mapping
A mind map is a visual representation of your problem and potential solutions. It enables you to organize information in a structured and intuitive manner. To create a mind map:
- Write the problem in the center of a blank page.
- Draw branches from the central problem to related sub-problems or contributing factors.
- Add more branches to represent potential solutions or further ideas.
Mind mapping allows you to visually see connections between ideas and promotes creativity in problem-solving.
Examples of Problem Solving in Various Contexts
In the business world, you might encounter problems related to finances, operations, or communication. Applying problem-solving skills in these situations could look like:
- Identifying areas of improvement in your company’s financial performance and implementing cost-saving measures
- Resolving internal conflicts among team members by listening and understanding different perspectives, then proposing and negotiating solutions
- Streamlining a process for better productivity by removing redundancies, automating tasks, or re-allocating resources
In educational contexts, problem-solving can be seen in various aspects, such as:
- Addressing a gap in students’ understanding by employing diverse teaching methods to cater to different learning styles
- Developing a strategy for successful time management to balance academic responsibilities and extracurricular activities
- Seeking resources and support to provide equal opportunities for learners with special needs or disabilities
Everyday life is full of challenges that require problem-solving skills. Some examples include:
- Overcoming a personal obstacle, such as improving your fitness level, by establishing achievable goals, measuring progress, and adjusting your approach accordingly
- Navigating a new environment or city by researching your surroundings, asking for directions, or using technology like GPS to guide you
- Dealing with a sudden change, like a change in your work schedule, by assessing the situation, identifying potential impacts, and adapting your plans to accommodate the change.
- How to Resolve Employee Conflict at Work [Steps, Tips, Examples]
- How to Write Inspiring Core Values? 5 Steps with Examples
- 30 Employee Feedback Examples (Positive & Negative)

Continuous Improvement Toolkit
Effective Tools for Business and Life!
How-How Diagrams: A Practical Approach to Problem Resolution

- 3 MINUTES READ
Also known as How-How Analysis and Value Driver Analysis.
Once a business problem is identified, it is important to find a solution that will permanently solve the problem. Oftentimes, you have to get to the root cause of the problem to understand why it’s happening, and this is where Six Sigma methodologies can be beneficial. Other times, you don’t even need to dig into the problem. You just need to solve it right away, and this is what is called low-hanging fruit .
These low-hanging fruit may be quick wins that require minimal resources or larger projects that may involve capital expenditure. For example, after reviewing a process , you may have identified non-value-added activities that need to be eliminated. Other examples include improving workflows and processes, changing workplace layout, enhancing customer service, mistake proofing processes, and improving management reports.
Whether tackling low-hanging fruit or fruit that is on the top of the tree (more complex challenges), it is important to come up with actionable items in order to solve the problem permanently. One effective approach for generating such actionable ideas is through the utilization of the how-how analysis .
The how-how diagram is a simple and straightforward method that is used to generate multiple ideas to solve a specific problem. It provides an effective structure for organizing possible ideas and solution options all in one place. It works by repeatedly asking “ How can this be solved? ” until you can no longer break the answers any further. Multiple answers can be given for a single question, and therefore, the result can be represented in a hierarchical tree format.

Drawing the Diagram
How-how diagrams are commonly developed during collaborative brainstorming sessions. The following steps outline a typical approach to drawing the diagram.
- With your team, clearly state the problem then write it on a post-it card. Place the problem card on the left side of a whiteboard or wall.
- Ask ‘how can this problem be solved?’. Let the team members write as many answers as possible on post-it cards, each idea separately, then stick them up to the right of your problem.
- Repeat this sequence of breaking down the problem once more. Keep asking ‘How’ until the ideas are specific enough and you are satisfied with them.
- Once you are finished, prioritize and determine the key ideas to be implemented.

Example – Energy Reduction
For example, let’s consider the goal of reducing energy consumption in a production plant. The following how-how diagram illustrates the ideas generated by a team for achieving this goal.

Example – Spoilage Reduction
The following is another example which involves a team seeking ways to minimize spoilage in a manufacturing business.

Note in the previous example that you might use the ‘ OR ‘ symbol to indicate alternative ideas. You can also add thick borders around the ideas that has been chosen to be part of the final solution.
Wrapping Up
The how-how approach is a straightforward and systematic method for generating multiple ideas to address a specific problem. It facilitates the generation of these ideas in a structured manner by repeatedly asking “How can this be solved?” until a comprehensive solution framework is established. This approach organizes these ideas in a structured way, making it a valuable tool for solving problems.
Other Formats

Do you want to use the slides in your training courses?
How-How Diagram Training Material – $14.85
Related Articles
Why-Why Diagram

Fishbone Diagram

Related Templates

Affinity Diagram

A3 Problem Solving

Written by:
CIToolkit Content Team
35 problem-solving techniques and methods for solving complex problems

Design your next session with SessionLab
Join the 150,000+ facilitators using SessionLab.
Recommended Articles
A step-by-step guide to planning a workshop, how to create an unforgettable training session in 8 simple steps, 47 useful online tools for workshop planning and meeting facilitation.
All teams and organizations encounter challenges as they grow. There are problems that might occur for teams when it comes to miscommunication or resolving business-critical issues . You may face challenges around growth , design , user engagement, and even team culture and happiness. In short, problem-solving techniques should be part of every team’s skillset.
Problem-solving methods are primarily designed to help a group or team through a process of first identifying problems and challenges , ideating possible solutions , and then evaluating the most suitable .
Finding effective solutions to complex problems isn’t easy, but by using the right process and techniques, you can help your team be more efficient in the process.
So how do you develop strategies that are engaging, and empower your team to solve problems effectively?
In this blog post, we share a series of problem-solving tools you can use in your next workshop or team meeting. You’ll also find some tips for facilitating the process and how to enable others to solve complex problems.
Let’s get started!
How do you identify problems?
How do you identify the right solution.
- Tips for more effective problem-solving
Complete problem-solving methods
- Problem-solving techniques to identify and analyze problems
- Problem-solving techniques for developing solutions
Problem-solving warm-up activities
Closing activities for a problem-solving process.
Before you can move towards finding the right solution for a given problem, you first need to identify and define the problem you wish to solve.
Here, you want to clearly articulate what the problem is and allow your group to do the same. Remember that everyone in a group is likely to have differing perspectives and alignment is necessary in order to help the group move forward.
Identifying a problem accurately also requires that all members of a group are able to contribute their views in an open and safe manner. It can be scary for people to stand up and contribute, especially if the problems or challenges are emotive or personal in nature. Be sure to try and create a psychologically safe space for these kinds of discussions.
Remember that problem analysis and further discussion are also important. Not taking the time to fully analyze and discuss a challenge can result in the development of solutions that are not fit for purpose or do not address the underlying issue.
Successfully identifying and then analyzing a problem means facilitating a group through activities designed to help them clearly and honestly articulate their thoughts and produce usable insight.
With this data, you might then produce a problem statement that clearly describes the problem you wish to be addressed and also state the goal of any process you undertake to tackle this issue.
Finding solutions is the end goal of any process. Complex organizational challenges can only be solved with an appropriate solution but discovering them requires using the right problem-solving tool.
After you’ve explored a problem and discussed ideas, you need to help a team discuss and choose the right solution. Consensus tools and methods such as those below help a group explore possible solutions before then voting for the best. They’re a great way to tap into the collective intelligence of the group for great results!
Remember that the process is often iterative. Great problem solvers often roadtest a viable solution in a measured way to see what works too. While you might not get the right solution on your first try, the methods below help teams land on the most likely to succeed solution while also holding space for improvement.
Every effective problem solving process begins with an agenda . A well-structured workshop is one of the best methods for successfully guiding a group from exploring a problem to implementing a solution.
In SessionLab, it’s easy to go from an idea to a complete agenda . Start by dragging and dropping your core problem solving activities into place . Add timings, breaks and necessary materials before sharing your agenda with your colleagues.
The resulting agenda will be your guide to an effective and productive problem solving session that will also help you stay organized on the day!
Tips for more effective problem solving
Problem-solving activities are only one part of the puzzle. While a great method can help unlock your team’s ability to solve problems, without a thoughtful approach and strong facilitation the solutions may not be fit for purpose.
Let’s take a look at some problem-solving tips you can apply to any process to help it be a success!
Clearly define the problem
Jumping straight to solutions can be tempting, though without first clearly articulating a problem, the solution might not be the right one. Many of the problem-solving activities below include sections where the problem is explored and clearly defined before moving on.
This is a vital part of the problem-solving process and taking the time to fully define an issue can save time and effort later. A clear definition helps identify irrelevant information and it also ensures that your team sets off on the right track.
Don’t jump to conclusions
It’s easy for groups to exhibit cognitive bias or have preconceived ideas about both problems and potential solutions. Be sure to back up any problem statements or potential solutions with facts, research, and adequate forethought.
The best techniques ask participants to be methodical and challenge preconceived notions. Make sure you give the group enough time and space to collect relevant information and consider the problem in a new way. By approaching the process with a clear, rational mindset, you’ll often find that better solutions are more forthcoming.
Try different approaches
Problems come in all shapes and sizes and so too should the methods you use to solve them. If you find that one approach isn’t yielding results and your team isn’t finding different solutions, try mixing it up. You’ll be surprised at how using a new creative activity can unblock your team and generate great solutions.
Don’t take it personally
Depending on the nature of your team or organizational problems, it’s easy for conversations to get heated. While it’s good for participants to be engaged in the discussions, ensure that emotions don’t run too high and that blame isn’t thrown around while finding solutions.
You’re all in it together, and even if your team or area is seeing problems, that isn’t necessarily a disparagement of you personally. Using facilitation skills to manage group dynamics is one effective method of helping conversations be more constructive.
Get the right people in the room
Your problem-solving method is often only as effective as the group using it. Getting the right people on the job and managing the number of people present is important too!
If the group is too small, you may not get enough different perspectives to effectively solve a problem. If the group is too large, you can go round and round during the ideation stages.
Creating the right group makeup is also important in ensuring you have the necessary expertise and skillset to both identify and follow up on potential solutions. Carefully consider who to include at each stage to help ensure your problem-solving method is followed and positioned for success.
Document everything
The best solutions can take refinement, iteration, and reflection to come out. Get into a habit of documenting your process in order to keep all the learnings from the session and to allow ideas to mature and develop. Many of the methods below involve the creation of documents or shared resources. Be sure to keep and share these so everyone can benefit from the work done!
Bring a facilitator
Facilitation is all about making group processes easier. With a subject as potentially emotive and important as problem-solving, having an impartial third party in the form of a facilitator can make all the difference in finding great solutions and keeping the process moving. Consider bringing a facilitator to your problem-solving session to get better results and generate meaningful solutions!
Develop your problem-solving skills
It takes time and practice to be an effective problem solver. While some roles or participants might more naturally gravitate towards problem-solving, it can take development and planning to help everyone create better solutions.
You might develop a training program, run a problem-solving workshop or simply ask your team to practice using the techniques below. Check out our post on problem-solving skills to see how you and your group can develop the right mental process and be more resilient to issues too!
Design a great agenda
Workshops are a great format for solving problems. With the right approach, you can focus a group and help them find the solutions to their own problems. But designing a process can be time-consuming and finding the right activities can be difficult.
Check out our workshop planning guide to level-up your agenda design and start running more effective workshops. Need inspiration? Check out templates designed by expert facilitators to help you kickstart your process!
In this section, we’ll look at in-depth problem-solving methods that provide a complete end-to-end process for developing effective solutions. These will help guide your team from the discovery and definition of a problem through to delivering the right solution.
If you’re looking for an all-encompassing method or problem-solving model, these processes are a great place to start. They’ll ask your team to challenge preconceived ideas and adopt a mindset for solving problems more effectively.
- Six Thinking Hats
- Lightning Decision Jam
- Problem Definition Process
- Discovery & Action Dialogue
Design Sprint 2.0
- Open Space Technology
1. Six Thinking Hats
Individual approaches to solving a problem can be very different based on what team or role an individual holds. It can be easy for existing biases or perspectives to find their way into the mix, or for internal politics to direct a conversation.
Six Thinking Hats is a classic method for identifying the problems that need to be solved and enables your team to consider them from different angles, whether that is by focusing on facts and data, creative solutions, or by considering why a particular solution might not work.
Like all problem-solving frameworks, Six Thinking Hats is effective at helping teams remove roadblocks from a conversation or discussion and come to terms with all the aspects necessary to solve complex problems.
2. Lightning Decision Jam
Featured courtesy of Jonathan Courtney of AJ&Smart Berlin, Lightning Decision Jam is one of those strategies that should be in every facilitation toolbox. Exploring problems and finding solutions is often creative in nature, though as with any creative process, there is the potential to lose focus and get lost.
Unstructured discussions might get you there in the end, but it’s much more effective to use a method that creates a clear process and team focus.
In Lightning Decision Jam, participants are invited to begin by writing challenges, concerns, or mistakes on post-its without discussing them before then being invited by the moderator to present them to the group.
From there, the team vote on which problems to solve and are guided through steps that will allow them to reframe those problems, create solutions and then decide what to execute on.
By deciding the problems that need to be solved as a team before moving on, this group process is great for ensuring the whole team is aligned and can take ownership over the next stages.
Lightning Decision Jam (LDJ) #action #decision making #problem solving #issue analysis #innovation #design #remote-friendly The problem with anything that requires creative thinking is that it’s easy to get lost—lose focus and fall into the trap of having useless, open-ended, unstructured discussions. Here’s the most effective solution I’ve found: Replace all open, unstructured discussion with a clear process. What to use this exercise for: Anything which requires a group of people to make decisions, solve problems or discuss challenges. It’s always good to frame an LDJ session with a broad topic, here are some examples: The conversion flow of our checkout Our internal design process How we organise events Keeping up with our competition Improving sales flow
3. Problem Definition Process
While problems can be complex, the problem-solving methods you use to identify and solve those problems can often be simple in design.
By taking the time to truly identify and define a problem before asking the group to reframe the challenge as an opportunity, this method is a great way to enable change.
Begin by identifying a focus question and exploring the ways in which it manifests before splitting into five teams who will each consider the problem using a different method: escape, reversal, exaggeration, distortion or wishful. Teams develop a problem objective and create ideas in line with their method before then feeding them back to the group.
This method is great for enabling in-depth discussions while also creating space for finding creative solutions too!
Problem Definition #problem solving #idea generation #creativity #online #remote-friendly A problem solving technique to define a problem, challenge or opportunity and to generate ideas.
4. The 5 Whys
Sometimes, a group needs to go further with their strategies and analyze the root cause at the heart of organizational issues. An RCA or root cause analysis is the process of identifying what is at the heart of business problems or recurring challenges.
The 5 Whys is a simple and effective method of helping a group go find the root cause of any problem or challenge and conduct analysis that will deliver results.
By beginning with the creation of a problem statement and going through five stages to refine it, The 5 Whys provides everything you need to truly discover the cause of an issue.
The 5 Whys #hyperisland #innovation This simple and powerful method is useful for getting to the core of a problem or challenge. As the title suggests, the group defines a problems, then asks the question “why” five times, often using the resulting explanation as a starting point for creative problem solving.
5. World Cafe
World Cafe is a simple but powerful facilitation technique to help bigger groups to focus their energy and attention on solving complex problems.
World Cafe enables this approach by creating a relaxed atmosphere where participants are able to self-organize and explore topics relevant and important to them which are themed around a central problem-solving purpose. Create the right atmosphere by modeling your space after a cafe and after guiding the group through the method, let them take the lead!
Making problem-solving a part of your organization’s culture in the long term can be a difficult undertaking. More approachable formats like World Cafe can be especially effective in bringing people unfamiliar with workshops into the fold.
World Cafe #hyperisland #innovation #issue analysis World Café is a simple yet powerful method, originated by Juanita Brown, for enabling meaningful conversations driven completely by participants and the topics that are relevant and important to them. Facilitators create a cafe-style space and provide simple guidelines. Participants then self-organize and explore a set of relevant topics or questions for conversation.

6. Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD)
One of the best approaches is to create a safe space for a group to share and discover practices and behaviors that can help them find their own solutions.
With DAD, you can help a group choose which problems they wish to solve and which approaches they will take to do so. It’s great at helping remove resistance to change and can help get buy-in at every level too!
This process of enabling frontline ownership is great in ensuring follow-through and is one of the methods you will want in your toolbox as a facilitator.
Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD) #idea generation #liberating structures #action #issue analysis #remote-friendly DADs make it easy for a group or community to discover practices and behaviors that enable some individuals (without access to special resources and facing the same constraints) to find better solutions than their peers to common problems. These are called positive deviant (PD) behaviors and practices. DADs make it possible for people in the group, unit, or community to discover by themselves these PD practices. DADs also create favorable conditions for stimulating participants’ creativity in spaces where they can feel safe to invent new and more effective practices. Resistance to change evaporates as participants are unleashed to choose freely which practices they will adopt or try and which problems they will tackle. DADs make it possible to achieve frontline ownership of solutions.
7. Design Sprint 2.0
Want to see how a team can solve big problems and move forward with prototyping and testing solutions in a few days? The Design Sprint 2.0 template from Jake Knapp, author of Sprint, is a complete agenda for a with proven results.
Developing the right agenda can involve difficult but necessary planning. Ensuring all the correct steps are followed can also be stressful or time-consuming depending on your level of experience.
Use this complete 4-day workshop template if you are finding there is no obvious solution to your challenge and want to focus your team around a specific problem that might require a shortcut to launching a minimum viable product or waiting for the organization-wide implementation of a solution.
8. Open space technology
Open space technology- developed by Harrison Owen – creates a space where large groups are invited to take ownership of their problem solving and lead individual sessions. Open space technology is a great format when you have a great deal of expertise and insight in the room and want to allow for different takes and approaches on a particular theme or problem you need to be solved.
Start by bringing your participants together to align around a central theme and focus their efforts. Explain the ground rules to help guide the problem-solving process and then invite members to identify any issue connecting to the central theme that they are interested in and are prepared to take responsibility for.
Once participants have decided on their approach to the core theme, they write their issue on a piece of paper, announce it to the group, pick a session time and place, and post the paper on the wall. As the wall fills up with sessions, the group is then invited to join the sessions that interest them the most and which they can contribute to, then you’re ready to begin!
Everyone joins the problem-solving group they’ve signed up to, record the discussion and if appropriate, findings can then be shared with the rest of the group afterward.
Open Space Technology #action plan #idea generation #problem solving #issue analysis #large group #online #remote-friendly Open Space is a methodology for large groups to create their agenda discerning important topics for discussion, suitable for conferences, community gatherings and whole system facilitation
Techniques to identify and analyze problems
Using a problem-solving method to help a team identify and analyze a problem can be a quick and effective addition to any workshop or meeting.
While further actions are always necessary, you can generate momentum and alignment easily, and these activities are a great place to get started.
We’ve put together this list of techniques to help you and your team with problem identification, analysis, and discussion that sets the foundation for developing effective solutions.
Let’s take a look!
- The Creativity Dice
- Fishbone Analysis
- Problem Tree
- SWOT Analysis
- Agreement-Certainty Matrix
- The Journalistic Six
- LEGO Challenge
- What, So What, Now What?
- Journalists
Individual and group perspectives are incredibly important, but what happens if people are set in their minds and need a change of perspective in order to approach a problem more effectively?
Flip It is a method we love because it is both simple to understand and run, and allows groups to understand how their perspectives and biases are formed.
Participants in Flip It are first invited to consider concerns, issues, or problems from a perspective of fear and write them on a flip chart. Then, the group is asked to consider those same issues from a perspective of hope and flip their understanding.
No problem and solution is free from existing bias and by changing perspectives with Flip It, you can then develop a problem solving model quickly and effectively.
Flip It! #gamestorming #problem solving #action Often, a change in a problem or situation comes simply from a change in our perspectives. Flip It! is a quick game designed to show players that perspectives are made, not born.
10. The Creativity Dice
One of the most useful problem solving skills you can teach your team is of approaching challenges with creativity, flexibility, and openness. Games like The Creativity Dice allow teams to overcome the potential hurdle of too much linear thinking and approach the process with a sense of fun and speed.
In The Creativity Dice, participants are organized around a topic and roll a dice to determine what they will work on for a period of 3 minutes at a time. They might roll a 3 and work on investigating factual information on the chosen topic. They might roll a 1 and work on identifying the specific goals, standards, or criteria for the session.
Encouraging rapid work and iteration while asking participants to be flexible are great skills to cultivate. Having a stage for idea incubation in this game is also important. Moments of pause can help ensure the ideas that are put forward are the most suitable.
The Creativity Dice #creativity #problem solving #thiagi #issue analysis Too much linear thinking is hazardous to creative problem solving. To be creative, you should approach the problem (or the opportunity) from different points of view. You should leave a thought hanging in mid-air and move to another. This skipping around prevents premature closure and lets your brain incubate one line of thought while you consciously pursue another.
11. Fishbone Analysis
Organizational or team challenges are rarely simple, and it’s important to remember that one problem can be an indication of something that goes deeper and may require further consideration to be solved.
Fishbone Analysis helps groups to dig deeper and understand the origins of a problem. It’s a great example of a root cause analysis method that is simple for everyone on a team to get their head around.
Participants in this activity are asked to annotate a diagram of a fish, first adding the problem or issue to be worked on at the head of a fish before then brainstorming the root causes of the problem and adding them as bones on the fish.
Using abstractions such as a diagram of a fish can really help a team break out of their regular thinking and develop a creative approach.
Fishbone Analysis #problem solving ##root cause analysis #decision making #online facilitation A process to help identify and understand the origins of problems, issues or observations.
12. Problem Tree
Encouraging visual thinking can be an essential part of many strategies. By simply reframing and clarifying problems, a group can move towards developing a problem solving model that works for them.
In Problem Tree, groups are asked to first brainstorm a list of problems – these can be design problems, team problems or larger business problems – and then organize them into a hierarchy. The hierarchy could be from most important to least important or abstract to practical, though the key thing with problem solving games that involve this aspect is that your group has some way of managing and sorting all the issues that are raised.
Once you have a list of problems that need to be solved and have organized them accordingly, you’re then well-positioned for the next problem solving steps.
Problem tree #define intentions #create #design #issue analysis A problem tree is a tool to clarify the hierarchy of problems addressed by the team within a design project; it represents high level problems or related sublevel problems.
13. SWOT Analysis
Chances are you’ve heard of the SWOT Analysis before. This problem-solving method focuses on identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats is a tried and tested method for both individuals and teams.
Start by creating a desired end state or outcome and bare this in mind – any process solving model is made more effective by knowing what you are moving towards. Create a quadrant made up of the four categories of a SWOT analysis and ask participants to generate ideas based on each of those quadrants.
Once you have those ideas assembled in their quadrants, cluster them together based on their affinity with other ideas. These clusters are then used to facilitate group conversations and move things forward.
SWOT analysis #gamestorming #problem solving #action #meeting facilitation The SWOT Analysis is a long-standing technique of looking at what we have, with respect to the desired end state, as well as what we could improve on. It gives us an opportunity to gauge approaching opportunities and dangers, and assess the seriousness of the conditions that affect our future. When we understand those conditions, we can influence what comes next.
14. Agreement-Certainty Matrix
Not every problem-solving approach is right for every challenge, and deciding on the right method for the challenge at hand is a key part of being an effective team.
The Agreement Certainty matrix helps teams align on the nature of the challenges facing them. By sorting problems from simple to chaotic, your team can understand what methods are suitable for each problem and what they can do to ensure effective results.
If you are already using Liberating Structures techniques as part of your problem-solving strategy, the Agreement-Certainty Matrix can be an invaluable addition to your process. We’ve found it particularly if you are having issues with recurring problems in your organization and want to go deeper in understanding the root cause.
Agreement-Certainty Matrix #issue analysis #liberating structures #problem solving You can help individuals or groups avoid the frequent mistake of trying to solve a problem with methods that are not adapted to the nature of their challenge. The combination of two questions makes it possible to easily sort challenges into four categories: simple, complicated, complex , and chaotic . A problem is simple when it can be solved reliably with practices that are easy to duplicate. It is complicated when experts are required to devise a sophisticated solution that will yield the desired results predictably. A problem is complex when there are several valid ways to proceed but outcomes are not predictable in detail. Chaotic is when the context is too turbulent to identify a path forward. A loose analogy may be used to describe these differences: simple is like following a recipe, complicated like sending a rocket to the moon, complex like raising a child, and chaotic is like the game “Pin the Tail on the Donkey.” The Liberating Structures Matching Matrix in Chapter 5 can be used as the first step to clarify the nature of a challenge and avoid the mismatches between problems and solutions that are frequently at the root of chronic, recurring problems.
Organizing and charting a team’s progress can be important in ensuring its success. SQUID (Sequential Question and Insight Diagram) is a great model that allows a team to effectively switch between giving questions and answers and develop the skills they need to stay on track throughout the process.
Begin with two different colored sticky notes – one for questions and one for answers – and with your central topic (the head of the squid) on the board. Ask the group to first come up with a series of questions connected to their best guess of how to approach the topic. Ask the group to come up with answers to those questions, fix them to the board and connect them with a line. After some discussion, go back to question mode by responding to the generated answers or other points on the board.
It’s rewarding to see a diagram grow throughout the exercise, and a completed SQUID can provide a visual resource for future effort and as an example for other teams.
SQUID #gamestorming #project planning #issue analysis #problem solving When exploring an information space, it’s important for a group to know where they are at any given time. By using SQUID, a group charts out the territory as they go and can navigate accordingly. SQUID stands for Sequential Question and Insight Diagram.
16. Speed Boat
To continue with our nautical theme, Speed Boat is a short and sweet activity that can help a team quickly identify what employees, clients or service users might have a problem with and analyze what might be standing in the way of achieving a solution.
Methods that allow for a group to make observations, have insights and obtain those eureka moments quickly are invaluable when trying to solve complex problems.
In Speed Boat, the approach is to first consider what anchors and challenges might be holding an organization (or boat) back. Bonus points if you are able to identify any sharks in the water and develop ideas that can also deal with competitors!
Speed Boat #gamestorming #problem solving #action Speedboat is a short and sweet way to identify what your employees or clients don’t like about your product/service or what’s standing in the way of a desired goal.
17. The Journalistic Six
Some of the most effective ways of solving problems is by encouraging teams to be more inclusive and diverse in their thinking.
Based on the six key questions journalism students are taught to answer in articles and news stories, The Journalistic Six helps create teams to see the whole picture. By using who, what, when, where, why, and how to facilitate the conversation and encourage creative thinking, your team can make sure that the problem identification and problem analysis stages of the are covered exhaustively and thoughtfully. Reporter’s notebook and dictaphone optional.
The Journalistic Six – Who What When Where Why How #idea generation #issue analysis #problem solving #online #creative thinking #remote-friendly A questioning method for generating, explaining, investigating ideas.
18. LEGO Challenge
Now for an activity that is a little out of the (toy) box. LEGO Serious Play is a facilitation methodology that can be used to improve creative thinking and problem-solving skills.
The LEGO Challenge includes giving each member of the team an assignment that is hidden from the rest of the group while they create a structure without speaking.
What the LEGO challenge brings to the table is a fun working example of working with stakeholders who might not be on the same page to solve problems. Also, it’s LEGO! Who doesn’t love LEGO!
LEGO Challenge #hyperisland #team A team-building activity in which groups must work together to build a structure out of LEGO, but each individual has a secret “assignment” which makes the collaborative process more challenging. It emphasizes group communication, leadership dynamics, conflict, cooperation, patience and problem solving strategy.
19. What, So What, Now What?
If not carefully managed, the problem identification and problem analysis stages of the problem-solving process can actually create more problems and misunderstandings.
The What, So What, Now What? problem-solving activity is designed to help collect insights and move forward while also eliminating the possibility of disagreement when it comes to identifying, clarifying, and analyzing organizational or work problems.
Facilitation is all about bringing groups together so that might work on a shared goal and the best problem-solving strategies ensure that teams are aligned in purpose, if not initially in opinion or insight.
Throughout the three steps of this game, you give everyone on a team to reflect on a problem by asking what happened, why it is important, and what actions should then be taken.
This can be a great activity for bringing our individual perceptions about a problem or challenge and contextualizing it in a larger group setting. This is one of the most important problem-solving skills you can bring to your organization.
W³ – What, So What, Now What? #issue analysis #innovation #liberating structures You can help groups reflect on a shared experience in a way that builds understanding and spurs coordinated action while avoiding unproductive conflict. It is possible for every voice to be heard while simultaneously sifting for insights and shaping new direction. Progressing in stages makes this practical—from collecting facts about What Happened to making sense of these facts with So What and finally to what actions logically follow with Now What . The shared progression eliminates most of the misunderstandings that otherwise fuel disagreements about what to do. Voila!
20. Journalists
Problem analysis can be one of the most important and decisive stages of all problem-solving tools. Sometimes, a team can become bogged down in the details and are unable to move forward.
Journalists is an activity that can avoid a group from getting stuck in the problem identification or problem analysis stages of the process.
In Journalists, the group is invited to draft the front page of a fictional newspaper and figure out what stories deserve to be on the cover and what headlines those stories will have. By reframing how your problems and challenges are approached, you can help a team move productively through the process and be better prepared for the steps to follow.
Journalists #vision #big picture #issue analysis #remote-friendly This is an exercise to use when the group gets stuck in details and struggles to see the big picture. Also good for defining a vision.
Problem-solving techniques for developing solutions
The success of any problem-solving process can be measured by the solutions it produces. After you’ve defined the issue, explored existing ideas, and ideated, it’s time to narrow down to the correct solution.
Use these problem-solving techniques when you want to help your team find consensus, compare possible solutions, and move towards taking action on a particular problem.
- Improved Solutions
- Four-Step Sketch
- 15% Solutions
- How-Now-Wow matrix
- Impact Effort Matrix
21. Mindspin
Brainstorming is part of the bread and butter of the problem-solving process and all problem-solving strategies benefit from getting ideas out and challenging a team to generate solutions quickly.
With Mindspin, participants are encouraged not only to generate ideas but to do so under time constraints and by slamming down cards and passing them on. By doing multiple rounds, your team can begin with a free generation of possible solutions before moving on to developing those solutions and encouraging further ideation.
This is one of our favorite problem-solving activities and can be great for keeping the energy up throughout the workshop. Remember the importance of helping people become engaged in the process – energizing problem-solving techniques like Mindspin can help ensure your team stays engaged and happy, even when the problems they’re coming together to solve are complex.
MindSpin #teampedia #idea generation #problem solving #action A fast and loud method to enhance brainstorming within a team. Since this activity has more than round ideas that are repetitive can be ruled out leaving more creative and innovative answers to the challenge.
22. Improved Solutions
After a team has successfully identified a problem and come up with a few solutions, it can be tempting to call the work of the problem-solving process complete. That said, the first solution is not necessarily the best, and by including a further review and reflection activity into your problem-solving model, you can ensure your group reaches the best possible result.
One of a number of problem-solving games from Thiagi Group, Improved Solutions helps you go the extra mile and develop suggested solutions with close consideration and peer review. By supporting the discussion of several problems at once and by shifting team roles throughout, this problem-solving technique is a dynamic way of finding the best solution.
Improved Solutions #creativity #thiagi #problem solving #action #team You can improve any solution by objectively reviewing its strengths and weaknesses and making suitable adjustments. In this creativity framegame, you improve the solutions to several problems. To maintain objective detachment, you deal with a different problem during each of six rounds and assume different roles (problem owner, consultant, basher, booster, enhancer, and evaluator) during each round. At the conclusion of the activity, each player ends up with two solutions to her problem.
23. Four Step Sketch
Creative thinking and visual ideation does not need to be confined to the opening stages of your problem-solving strategies. Exercises that include sketching and prototyping on paper can be effective at the solution finding and development stage of the process, and can be great for keeping a team engaged.
By going from simple notes to a crazy 8s round that involves rapidly sketching 8 variations on their ideas before then producing a final solution sketch, the group is able to iterate quickly and visually. Problem-solving techniques like Four-Step Sketch are great if you have a group of different thinkers and want to change things up from a more textual or discussion-based approach.
Four-Step Sketch #design sprint #innovation #idea generation #remote-friendly The four-step sketch is an exercise that helps people to create well-formed concepts through a structured process that includes: Review key information Start design work on paper, Consider multiple variations , Create a detailed solution . This exercise is preceded by a set of other activities allowing the group to clarify the challenge they want to solve. See how the Four Step Sketch exercise fits into a Design Sprint
24. 15% Solutions
Some problems are simpler than others and with the right problem-solving activities, you can empower people to take immediate actions that can help create organizational change.
Part of the liberating structures toolkit, 15% solutions is a problem-solving technique that focuses on finding and implementing solutions quickly. A process of iterating and making small changes quickly can help generate momentum and an appetite for solving complex problems.
Problem-solving strategies can live and die on whether people are onboard. Getting some quick wins is a great way of getting people behind the process.
It can be extremely empowering for a team to realize that problem-solving techniques can be deployed quickly and easily and delineate between things they can positively impact and those things they cannot change.
15% Solutions #action #liberating structures #remote-friendly You can reveal the actions, however small, that everyone can do immediately. At a minimum, these will create momentum, and that may make a BIG difference. 15% Solutions show that there is no reason to wait around, feel powerless, or fearful. They help people pick it up a level. They get individuals and the group to focus on what is within their discretion instead of what they cannot change. With a very simple question, you can flip the conversation to what can be done and find solutions to big problems that are often distributed widely in places not known in advance. Shifting a few grains of sand may trigger a landslide and change the whole landscape.
25. How-Now-Wow Matrix
The problem-solving process is often creative, as complex problems usually require a change of thinking and creative response in order to find the best solutions. While it’s common for the first stages to encourage creative thinking, groups can often gravitate to familiar solutions when it comes to the end of the process.
When selecting solutions, you don’t want to lose your creative energy! The How-Now-Wow Matrix from Gamestorming is a great problem-solving activity that enables a group to stay creative and think out of the box when it comes to selecting the right solution for a given problem.
Problem-solving techniques that encourage creative thinking and the ideation and selection of new solutions can be the most effective in organisational change. Give the How-Now-Wow Matrix a go, and not just for how pleasant it is to say out loud.
How-Now-Wow Matrix #gamestorming #idea generation #remote-friendly When people want to develop new ideas, they most often think out of the box in the brainstorming or divergent phase. However, when it comes to convergence, people often end up picking ideas that are most familiar to them. This is called a ‘creative paradox’ or a ‘creadox’. The How-Now-Wow matrix is an idea selection tool that breaks the creadox by forcing people to weigh each idea on 2 parameters.
26. Impact and Effort Matrix
All problem-solving techniques hope to not only find solutions to a given problem or challenge but to find the best solution. When it comes to finding a solution, groups are invited to put on their decision-making hats and really think about how a proposed idea would work in practice.
The Impact and Effort Matrix is one of the problem-solving techniques that fall into this camp, empowering participants to first generate ideas and then categorize them into a 2×2 matrix based on impact and effort.
Activities that invite critical thinking while remaining simple are invaluable. Use the Impact and Effort Matrix to move from ideation and towards evaluating potential solutions before then committing to them.
Impact and Effort Matrix #gamestorming #decision making #action #remote-friendly In this decision-making exercise, possible actions are mapped based on two factors: effort required to implement and potential impact. Categorizing ideas along these lines is a useful technique in decision making, as it obliges contributors to balance and evaluate suggested actions before committing to them.
27. Dotmocracy
If you’ve followed each of the problem-solving steps with your group successfully, you should move towards the end of your process with heaps of possible solutions developed with a specific problem in mind. But how do you help a group go from ideation to putting a solution into action?
Dotmocracy – or Dot Voting -is a tried and tested method of helping a team in the problem-solving process make decisions and put actions in place with a degree of oversight and consensus.
One of the problem-solving techniques that should be in every facilitator’s toolbox, Dot Voting is fast and effective and can help identify the most popular and best solutions and help bring a group to a decision effectively.
Dotmocracy #action #decision making #group prioritization #hyperisland #remote-friendly Dotmocracy is a simple method for group prioritization or decision-making. It is not an activity on its own, but a method to use in processes where prioritization or decision-making is the aim. The method supports a group to quickly see which options are most popular or relevant. The options or ideas are written on post-its and stuck up on a wall for the whole group to see. Each person votes for the options they think are the strongest, and that information is used to inform a decision.
All facilitators know that warm-ups and icebreakers are useful for any workshop or group process. Problem-solving workshops are no different.
Use these problem-solving techniques to warm up a group and prepare them for the rest of the process. Activating your group by tapping into some of the top problem-solving skills can be one of the best ways to see great outcomes from your session.
- Check-in/Check-out
- Doodling Together
- Show and Tell
- Constellations
- Draw a Tree
28. Check-in / Check-out
Solid processes are planned from beginning to end, and the best facilitators know that setting the tone and establishing a safe, open environment can be integral to a successful problem-solving process.
Check-in / Check-out is a great way to begin and/or bookend a problem-solving workshop. Checking in to a session emphasizes that everyone will be seen, heard, and expected to contribute.
If you are running a series of meetings, setting a consistent pattern of checking in and checking out can really help your team get into a groove. We recommend this opening-closing activity for small to medium-sized groups though it can work with large groups if they’re disciplined!
Check-in / Check-out #team #opening #closing #hyperisland #remote-friendly Either checking-in or checking-out is a simple way for a team to open or close a process, symbolically and in a collaborative way. Checking-in/out invites each member in a group to be present, seen and heard, and to express a reflection or a feeling. Checking-in emphasizes presence, focus and group commitment; checking-out emphasizes reflection and symbolic closure.
29. Doodling Together
Thinking creatively and not being afraid to make suggestions are important problem-solving skills for any group or team, and warming up by encouraging these behaviors is a great way to start.
Doodling Together is one of our favorite creative ice breaker games – it’s quick, effective, and fun and can make all following problem-solving steps easier by encouraging a group to collaborate visually. By passing cards and adding additional items as they go, the workshop group gets into a groove of co-creation and idea development that is crucial to finding solutions to problems.
Doodling Together #collaboration #creativity #teamwork #fun #team #visual methods #energiser #icebreaker #remote-friendly Create wild, weird and often funny postcards together & establish a group’s creative confidence.
30. Show and Tell
You might remember some version of Show and Tell from being a kid in school and it’s a great problem-solving activity to kick off a session.
Asking participants to prepare a little something before a workshop by bringing an object for show and tell can help them warm up before the session has even begun! Games that include a physical object can also help encourage early engagement before moving onto more big-picture thinking.
By asking your participants to tell stories about why they chose to bring a particular item to the group, you can help teams see things from new perspectives and see both differences and similarities in the way they approach a topic. Great groundwork for approaching a problem-solving process as a team!
Show and Tell #gamestorming #action #opening #meeting facilitation Show and Tell taps into the power of metaphors to reveal players’ underlying assumptions and associations around a topic The aim of the game is to get a deeper understanding of stakeholders’ perspectives on anything—a new project, an organizational restructuring, a shift in the company’s vision or team dynamic.
31. Constellations
Who doesn’t love stars? Constellations is a great warm-up activity for any workshop as it gets people up off their feet, energized, and ready to engage in new ways with established topics. It’s also great for showing existing beliefs, biases, and patterns that can come into play as part of your session.
Using warm-up games that help build trust and connection while also allowing for non-verbal responses can be great for easing people into the problem-solving process and encouraging engagement from everyone in the group. Constellations is great in large spaces that allow for movement and is definitely a practical exercise to allow the group to see patterns that are otherwise invisible.
Constellations #trust #connection #opening #coaching #patterns #system Individuals express their response to a statement or idea by standing closer or further from a central object. Used with teams to reveal system, hidden patterns, perspectives.
32. Draw a Tree
Problem-solving games that help raise group awareness through a central, unifying metaphor can be effective ways to warm-up a group in any problem-solving model.
Draw a Tree is a simple warm-up activity you can use in any group and which can provide a quick jolt of energy. Start by asking your participants to draw a tree in just 45 seconds – they can choose whether it will be abstract or realistic.
Once the timer is up, ask the group how many people included the roots of the tree and use this as a means to discuss how we can ignore important parts of any system simply because they are not visible.
All problem-solving strategies are made more effective by thinking of problems critically and by exposing things that may not normally come to light. Warm-up games like Draw a Tree are great in that they quickly demonstrate some key problem-solving skills in an accessible and effective way.
Draw a Tree #thiagi #opening #perspectives #remote-friendly With this game you can raise awarness about being more mindful, and aware of the environment we live in.
Each step of the problem-solving workshop benefits from an intelligent deployment of activities, games, and techniques. Bringing your session to an effective close helps ensure that solutions are followed through on and that you also celebrate what has been achieved.
Here are some problem-solving activities you can use to effectively close a workshop or meeting and ensure the great work you’ve done can continue afterward.
- One Breath Feedback
- Who What When Matrix
- Response Cards
How do I conclude a problem-solving process?
All good things must come to an end. With the bulk of the work done, it can be tempting to conclude your workshop swiftly and without a moment to debrief and align. This can be problematic in that it doesn’t allow your team to fully process the results or reflect on the process.
At the end of an effective session, your team will have gone through a process that, while productive, can be exhausting. It’s important to give your group a moment to take a breath, ensure that they are clear on future actions, and provide short feedback before leaving the space.
The primary purpose of any problem-solving method is to generate solutions and then implement them. Be sure to take the opportunity to ensure everyone is aligned and ready to effectively implement the solutions you produced in the workshop.
Remember that every process can be improved and by giving a short moment to collect feedback in the session, you can further refine your problem-solving methods and see further success in the future too.
33. One Breath Feedback
Maintaining attention and focus during the closing stages of a problem-solving workshop can be tricky and so being concise when giving feedback can be important. It’s easy to incur “death by feedback” should some team members go on for too long sharing their perspectives in a quick feedback round.
One Breath Feedback is a great closing activity for workshops. You give everyone an opportunity to provide feedback on what they’ve done but only in the space of a single breath. This keeps feedback short and to the point and means that everyone is encouraged to provide the most important piece of feedback to them.
One breath feedback #closing #feedback #action This is a feedback round in just one breath that excels in maintaining attention: each participants is able to speak during just one breath … for most people that’s around 20 to 25 seconds … unless of course you’ve been a deep sea diver in which case you’ll be able to do it for longer.
34. Who What When Matrix
Matrices feature as part of many effective problem-solving strategies and with good reason. They are easily recognizable, simple to use, and generate results.
The Who What When Matrix is a great tool to use when closing your problem-solving session by attributing a who, what and when to the actions and solutions you have decided upon. The resulting matrix is a simple, easy-to-follow way of ensuring your team can move forward.
Great solutions can’t be enacted without action and ownership. Your problem-solving process should include a stage for allocating tasks to individuals or teams and creating a realistic timeframe for those solutions to be implemented or checked out. Use this method to keep the solution implementation process clear and simple for all involved.
Who/What/When Matrix #gamestorming #action #project planning With Who/What/When matrix, you can connect people with clear actions they have defined and have committed to.
35. Response cards
Group discussion can comprise the bulk of most problem-solving activities and by the end of the process, you might find that your team is talked out!
Providing a means for your team to give feedback with short written notes can ensure everyone is head and can contribute without the need to stand up and talk. Depending on the needs of the group, giving an alternative can help ensure everyone can contribute to your problem-solving model in the way that makes the most sense for them.
Response Cards is a great way to close a workshop if you are looking for a gentle warm-down and want to get some swift discussion around some of the feedback that is raised.
Response Cards #debriefing #closing #structured sharing #questions and answers #thiagi #action It can be hard to involve everyone during a closing of a session. Some might stay in the background or get unheard because of louder participants. However, with the use of Response Cards, everyone will be involved in providing feedback or clarify questions at the end of a session.
Save time and effort discovering the right solutions
A structured problem solving process is a surefire way of solving tough problems, discovering creative solutions and driving organizational change. But how can you design for successful outcomes?
With SessionLab, it’s easy to design engaging workshops that deliver results. Drag, drop and reorder blocks to build your agenda. When you make changes or update your agenda, your session timing adjusts automatically , saving you time on manual adjustments.
Collaborating with stakeholders or clients? Share your agenda with a single click and collaborate in real-time. No more sending documents back and forth over email.
Explore how to use SessionLab to design effective problem solving workshops or watch this five minute video to see the planner in action!

Over to you
The problem-solving process can often be as complicated and multifaceted as the problems they are set-up to solve. With the right problem-solving techniques and a mix of creative exercises designed to guide discussion and generate purposeful ideas, we hope we’ve given you the tools to find the best solutions as simply and easily as possible.
Is there a problem-solving technique that you are missing here? Do you have a favorite activity or method you use when facilitating? Let us know in the comments below, we’d love to hear from you!
thank you very much for these excellent techniques
Certainly wonderful article, very detailed. Shared!
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Going from a mere idea to a workshop that delivers results for your clients can feel like a daunting task. In this piece, we will shine a light on all the work behind the scenes and help you learn how to plan a workshop from start to finish. On a good day, facilitation can feel like effortless magic, but that is mostly the result of backstage work, foresight, and a lot of careful planning. Read on to learn a step-by-step approach to breaking the process of planning a workshop into small, manageable chunks. The flow starts with the first meeting with a client to define the purposes of a workshop.…

How does learning work? A clever 9-year-old once told me: “I know I am learning something new when I am surprised.” The science of adult learning tells us that, in order to learn new skills (which, unsurprisingly, is harder for adults to do than kids) grown-ups need to first get into a specific headspace. In a business, this approach is often employed in a training session where employees learn new skills or work on professional development. But how do you ensure your training is effective? In this guide, we'll explore how to create an effective training session plan and run engaging training sessions. As team leader, project manager, or consultant,…

Effective online tools are a necessity for smooth and engaging virtual workshops and meetings. But how do you choose the right ones? Do you sometimes feel that the good old pen and paper or MS Office toolkit and email leaves you struggling to stay on top of managing and delivering your workshop? Fortunately, there are plenty of online tools to make your life easier when you need to facilitate a meeting and lead workshops. In this post, we’ll share our favorite online tools you can use to make your job as a facilitator easier. In fact, there are plenty of free online workshop tools and meeting facilitation software you can…
Design your next workshop with SessionLab
Join the 150,000 facilitators using SessionLab
Sign up for free
MindManager
Guide to understanding Ishikawa diagrams
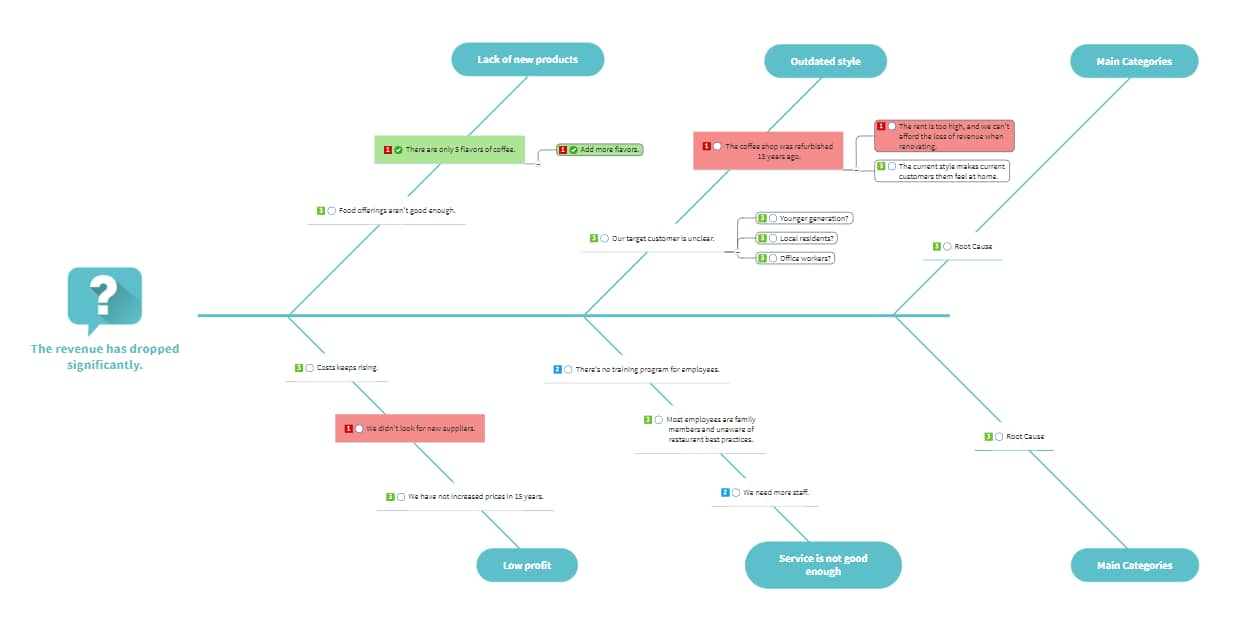
What is an Ishikawa diagram?
An Ishikawa diagram is designed to show the potential causes of a specific event or process. It is commonly used in product development to brainstorm and outline the different steps within a given process, allocate resources, and determine whether quality control issues are likely to arise.
The diagram is named after its creator, Kaoru Ishikawa. Visually, the diagram's structure resembles the skeleton of a fish. The ribs represent the causes of an event, and the skeleton's head indicates the outcome. Because of this structure, Ishikawa diagrams are sometimes referred to as fishbone diagrams . They are also referred to as Fishikawa, herringbone diagrams, or cause and effect diagrams .
An Ishikawa diagram places the central problem, known as the 'effect,' on the far right of the diagram. A line, known as the 'spine,' is drawn to the left, and other branches, which are types of causes known as 'affinities,' shoot off above and below it. Smaller branches can then be added to these affinities to add specific causes during brainstorming sessions.
Types of Ishikawa diagrams
The different types of Ishikawa diagrams include:
The 6Ms Ishikawa diagram
The 6M diagram organizes information into six categories: man, machine, material, method, mother nature, and measurement. It is most commonly used in the manufacturing industry. For instance, it could be used to identify bottlenecks slowing down the manufacturing process in a candle business.
The 8Ps Ishikawa diagram
The 8P diagram organizes information into eight categories: procedures, policies, place, product, people, processes, price, and promotion. It is most commonly used in the service industry. For instance, it could be used to improve the efficiency of a housekeeping business.
The 4S's Ishikawa diagram
The 4S diagram organizes information into four categories: suppliers, systems, surroundings, and skills. It is most commonly used in the service industry. For instance, a restaurant could use it to determine why the number of customers has declined over the past year.
Simple fishbone
A simple fishbone diagram has no predetermined causes or categories of causes. This is useful for organizations that want to create and set their own unique affinities. For instance, a software company will have very different affinities to a pet food manufacturer.
3Ms/Man machine material fishbone
The 3M diagram, also known as the 'man, machine, material' fishbone, organizes information into three categories: manpower, machinery, and materials. It is most commonly used in the manufacturing industry. For instance, it could be used in a food processing plant to determine why product quality has declined.
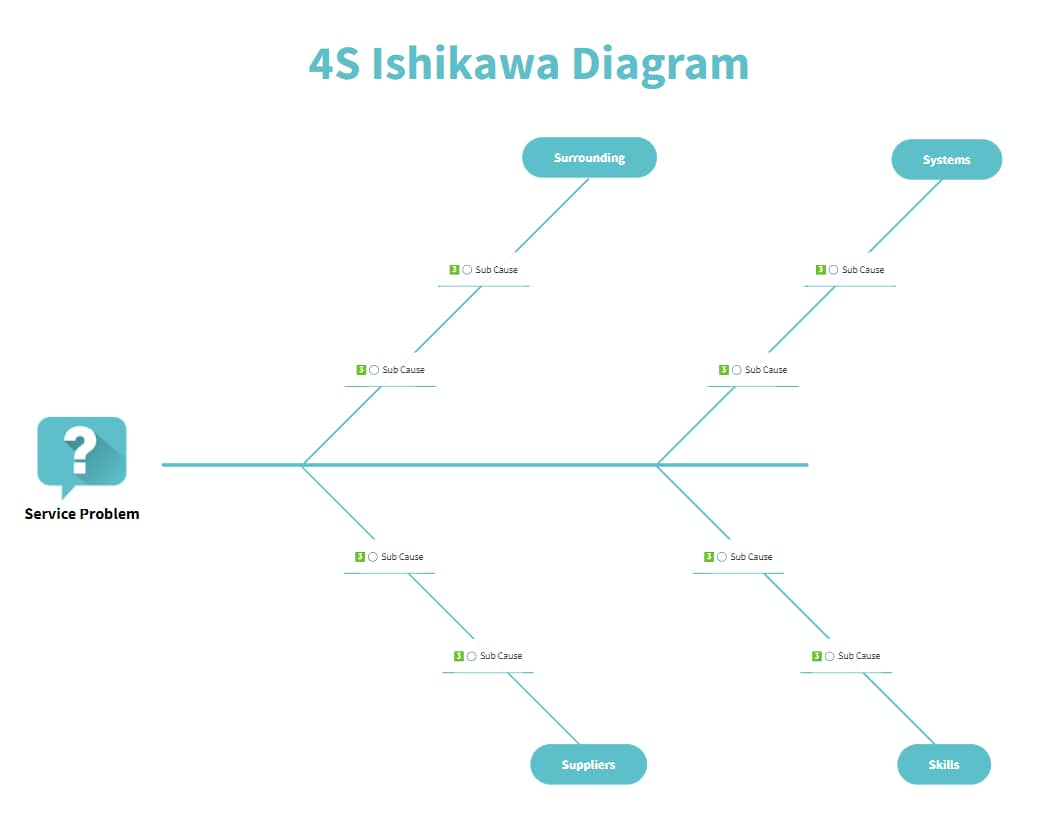
When to use an Ishikawa diagram
Ishikawa diagrams are a useful way to clearly visualize the potential causes of a specific event or problem. For instance, a team can use an Ishikawa diagram to identify bottlenecks or weaknesses within a business proposal and make the required adjustments.
Some popular use cases for Ishikawa diagrams include:
Product development
Ishikawa diagrams are often used in product development to outline the steps involved in the process clearly. This helps teams to determine which resources will be required at specific times and can also help to identify potential quality control issues.
Troubleshooting processes
Organizations often use Ishikawa diagrams to troubleshoot processes and resolve problems within a system. This is because the diagram makes it easy to consider all the possible causes of an issue within each category.
For instance, the 4S's diagram suggests that the possible causes could be related to suppliers, systems, surroundings, or skills.
Root cause analysis
Ishikawa diagrams are often used to identify the underlying cause of a failure in a product or process.
Problem-solving teams should first create a problem statement that includes information such as: what product failed, failure observations, the number of failed units, and the customer's description of the failure.
They should then create an Ishikawa diagram, which visually depicts the hypotheses that could explain this failure. The diagram elements should help explain what was responsible for the failure.
Benefits of Ishikawa diagrams
Some of the key benefits of Ishikawa diagrams include:
Helps identify potential causes of a problem
Showing all of the causes in the chain illustrates every possible reason that could lead to a problem simultaneously.
Even if the solution isn't immediately obvious, having a clear visualization makes it possible to eliminate some false positives quickly. This can stimulate team members to work out the potential causes of a problem more quickly.
Reveals areas of weakness or bottlenecks in current processes
Ishikawa diagrams make it easy to understand the correlation between relationships. This makes it obvious when certain stages of the process restrict the system's flow. As a result, any weakness or potential bottlenecks can quickly be identified and monitored before they cause issues.
Accelerates problem-solving
Given that Ishikawa diagrams provide an overview of all the potential causes of a certain result, it facilitates brainstorming, which can accelerate problem-solving. It also helps teams maintain their focus because it provides a clear pathway to analyze every involved pathway.
How to make an Ishikawa diagram
Here is how you can create an Ishikawa fishbone diagram in four easy steps.
- Identify and agree on the exact problem. The first step of creating an Ishikawa diagram involves identifying, agreeing, and writing down a problem statement. Determine the exact issue, who is involved, and when and where the problem occurs.
- Document the problem. Write the problem statement in a box on the right-hand side, and then draw a horizontal line from your problem statement. The fish's head represents the problem statement, and the horizontal line resembles the fish's spine.
- Brainstorm the major categories of causes. Brainstorm with your team to decide how to categorize the significant factors causing the problem. For instance, these could be systems, materials, equipment, people, or external forces. Draw a line off the spine of the fish diagram for each cause. Then, label each line at the top.
- Identify potential causes of the problem. Identify the potential causes of the problem that may be behind each factor. Draw shorter lines off the bones of the fish diagram to help you visualize these potential causes. You may need to draw smaller sub-branch lines off a cause line if that particular cause is a bit more complex.
- Analyze the diagram. At this stage, you should have a fully fleshed fishbone diagram that indicates all the possible causes of the problem statement. You can now research the issue further using investigations and surveys. Once you have narrowed down the possible causes, you should be able to find the culprit.
Why use MindManager to make Ishikawa diagrams
You can make Ishikawa diagrams by hand or in any graphic design program or use a program specifically designed for Ishikawa diagram making. MindManager , an industry-leading Ishikawa diagram software, allows you to create complex, detailed Ishikawa diagrams with ease.
MindManager's key benefits include:
- User-friendly, intuitive interface
- Extensive image library—over 700 topic images, icons, and symbols to add to your Ishikawa diagrams
- Premade Ishikawa diagram templates
- Convenient file storage, retrieval, and sharing
- Powerful integrations with file storage apps like Box and OneDrive
- Google Docs integration via Zapier
- Various tools and features to facilitate brainstorming and strategic planning
- Google Chrome extension—MindManager Snap—to easily collect and import text, links, and images from the web
MindManager helps you synthesize ideas and information by providing a simple, intuitive framework for organizing your thoughts. With MindManager, you and your team can clarify complexity and collaborate in new and unexpected ways.
Ishikawa diagram templates
MindManager comes pre-installed with many Ishikawa diagram templates. To use these templates:
- Open MindManager
- Click NEW in the navigation menu
- Select the template you want to use
- A preview screen will appear - check to see if you'd like to use your selected template
- Select 'Create Map'
- Customize the template for your specific project

Ishikawa diagram FAQs
What does an ishikawa diagram show.
An Ishikawa diagram shows the potential causes of a specific event or process.
What is an Ishikawa diagram used for?
An Ishikawa diagram is typically used in manufacturing and product development to outline the sequence of steps in a process. This can help teams identify a problem's potential causes, reveal areas of weakness or bottlenecks in current processes, and accelerate problem-solving.
Using Ishikawa diagrams to identify the causes of a problem
Ishikawa diagrams are designed to show the potential causes of a specific event or process. They are typically used during product development, root cause analysis, and troubleshooting processes.
They can help your organization to identify the potential causes of a problem, reveal areas of weakness or bottlenecks in current processes, and ultimately accelerate problem-solving within teams.
Visualize more with MindManager
Want to visualize your processes and remove the bottlenecks within your organization? Give MindManager a try today and start building Ishikawa diagrams with our easy-to-use templates.
Related Articles
by MindManager Blog
9 essential problem solving tools: the ultimate guide
July 7, 2020

Using fishbone diagrams for problem solving
December 30, 2019
Other types of maps and charts
Task and project management, problem solving/ decision making, brainstorming, organizing data, process mapping, try the full version of mindmanager free for 30 days.

Ishikawa Diagram Example | A Step-by-Step Guide for Effective Problem Solving | 2024 Reveal
Jane Ng • 13 Nov 2023 • 5 min read
When it comes to tackling organizational issues, a picture is worth a thousand words. Enter the Ishikawa diagram, a visual masterpiece that simplifies the art of problem-solving.
In this post, we’ll explore Ishikawa diagram example, and explore how to use this type of diagram. Say goodbye to confusion and hello to a streamlined approach for addressing the root causes that might be hindering your organization’s success.
Table Of Contents
What is a ishikawa diagram, how to make a ishikawa diagram, fishbone diagram example cause and effect, fishbone diagram example manufacturing, ishikawa diagram 5 whys.
- Fishbone Diagram Example Healthcare
- Fishbone Diagram Example for Business
Fishbone Diagram Environment Example
Fishbone diagram example for food industry, key takeaways .
An Ishikawa diagram, also known as a fishbone diagram or cause-and-effect diagram, is a visual representation used to analyze and display the potential causes of a specific problem or effect. This diagram is named after Professor Kaoru Ishikawa , a Japanese quality control statistician, who popularized its use in the 1960s.
The structure of an Ishikawa diagram resembles the skeleton of a fish, with the “head” representing the problem or effect and the “bones” branching off to depict different categories of potential causes. These categories typically include:
- Methods: Processes or procedures that may contribute to the problem.
- Machines: Equipment and technology involved in the process.
- Materials: Raw materials, substances, or components involved.
- Manpower: Human factors such as skills, training, and workload.
- Measurement: The methods used to evaluate and assess the process.
- Environment: The external factors or conditions that may influence the problem.
To create an Ishikawa diagram, a team or individual gathers relevant information and brainstorms potential causes within each category. This method helps identify the root causes of a problem, fostering a deeper understanding of the issues at hand.
The visual nature of the diagram makes it an effective communication tool within teams and organizations, promoting collaborative problem-solving efforts.
Ishikawa diagrams are widely used in quality management, process improvement, and problem-solving initiatives across various industries.
Creating an Ishikawa diagram involves a simple process of identifying and categorizing potential causes for a specific problem or effect. Here’s a concise step-by-step guide:
- Define the Problem: Clearly articulate the problem you aim to analyze – this becomes the “head” of your fishbone diagram.
- Draw the Fishbone: Create a horizontal line across the center of the page, extending diagonal lines for main categories (Methods, Machines, Materials, Manpower, Measurement, Environment).
- Brainstorm Causes: Identify processes or procedures (Methods), equipment (Machines), raw materials (Materials), human factors (Manpower), evaluation methods (Measurement), and external factors (Environment).
- Identify Sub-Causes: Extend lines under each main category to outline specific causes within each.
- Analyze and Prioritize Causes: Discuss and prioritize identified causes based on their significance and relevance to the problem.
- Document Causes: Write down identified causes on the appropriate branches to maintain clarity.
- Review and Refine: Collaboratively review the diagram, making adjustments for accuracy and relevance.
- Use Software Tools (Optional): Consider digital tools for a more polished Ishikawa diagram.
- Communicate and Implement Solutions: Share the diagram for discussion and decision-making, using insights gained to develop targeted solutions.
Following these steps enables the creation of a valuable Ishikawa diagram for effective problem analysis and resolution in your team or organization.
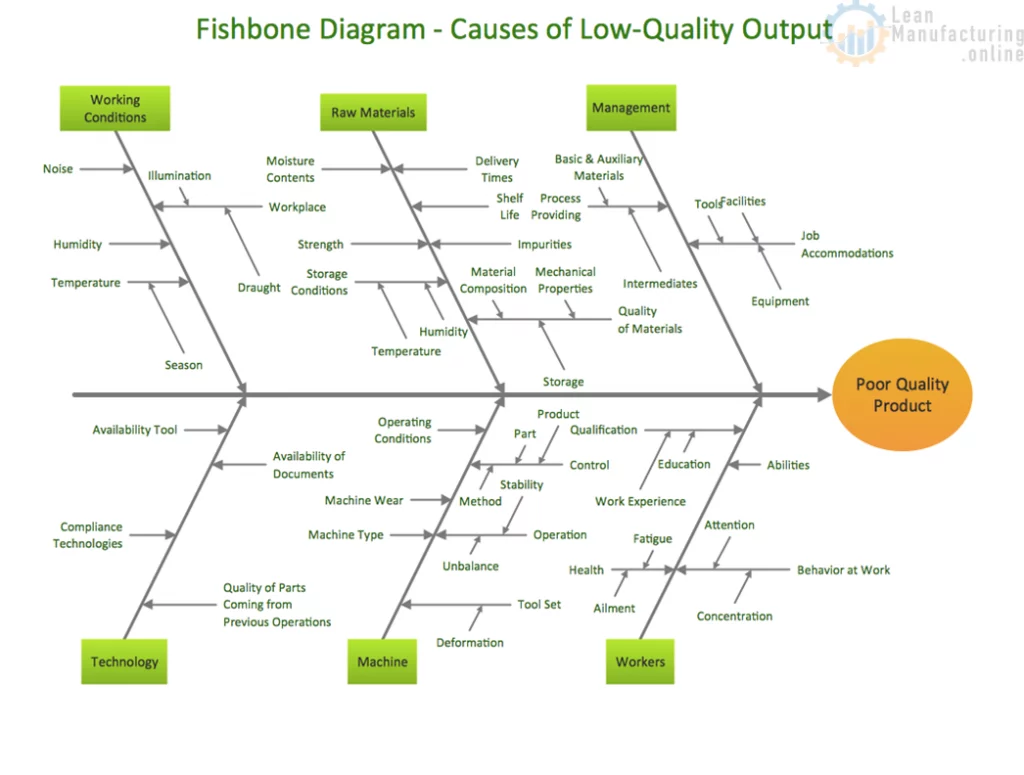
Ishikawa Diagram Example
Looking for a Ishikawa diagram example? Here are examples of how an Ishikawa or fishbone diagram is made in various industries.
Here is a Ishikawa diagram example – Cause and Effect
Problem/Effect: High website bounce rate
- Methods: Unintuitive navigation, confusing checkout process, poorly structured content
- Materials: Low-quality images and videos, outdated brand messaging, lack of visual appeal
- Manpower: Insufficient UX testing, lack of content optimization, inadequate web analytics skills
- Measurement: No defined website KPIs, lack of A/B testing, minimal customer feedback
- Environment: Overly promotional messaging, too many popups, irrelevant recommendations
- Machines: Web hosting downtime, broken links, lack of mobile optimization
Here is a Ishikawa diagram example for manufacturing
Problem/Effect: High rate of product defects
- Methods: Outdated manufacturing processes, insufficient training on new equipment, inefficient layout of workstations
- Machines: Equipment failure, lack of preventive maintenance, improper machine settings
- Materials: Defective raw materials, variability in material properties, improper material storage
- Manpower: Insufficient operator skills, high turnover, inadequate supervision
- Measurement: Inaccurate measurements, unclear specifications
- Environment: Excessive vibration, temperature extremes, poor lighting
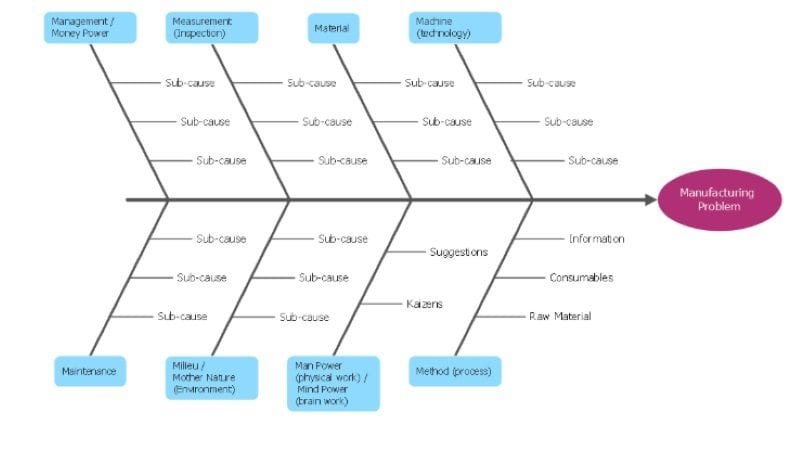
Problem/Effect: Low patient satisfaction scores
- Methods: Long wait times for appointments, inadequate time spent with patients, poor bedside manner
- Materials: Uncomfortable waiting room chairs, outdated patient education pamphlets
- Manpower: High clinician turnover, inadequate training on new system
- Measurement: Inaccurate patient pain assessments, lack of feedback surveys, minimal data collection
- Environment: Cluttered and dull facility, uncomfortable clinic rooms, lack of privacy
- Machines: Outdated clinic equipment
Fishbone Diagram Example Healthcare
Here is a Ishikawa diagram example for healthcare
Problem/Effect: Increase in hospital-acquired infections
- Methods: Inadequate hand-washing protocols, poorly defined procedures
- Materials: Expired medications, defective medical devices, contaminated supplies
- Manpower: Insufficient staff training, high workload, poor communication
- Measurement: Inaccurate diagnostic tests, improper use of equipment, unclear health records
- Environment: Uncleaned surfaces, presence of pathogens, poor air quality
- Machines: Medical equipment failure, lack of preventive maintenance, outdated technology
Fishbone Diagram Example for Business
Here is a Ishikawa diagram example for business
Problem/Effect: Declining customer satisfaction
- Methods: Poorly defined processes, inadequate training, inefficient workflows
- Materials: Low-quality inputs, variability in supplies, improper storage
- Manpower: Insufficient staff skills, inadequate supervision, high turnover
- Measurement: Unclear objectives, inaccurate data, poorly tracked metrics
- Environment: Excessive office noise, poor ergonomics, outdated tools
- Machines: IT system downtime, software bugs, lack of support
Here is a Ishikawa diagram example for the environment
Problem/Effect: Increase in industrial waste contamination
- Methods: Inefficient waste disposal process, improper recycling protocols
- Materials: Toxic raw materials, non-degradable plastics, hazardous chemicals
- Manpower: Lack of sustainability training, resistance to change, insufficient oversight
- Measurement: Inaccurate emissions data, unmonitored waste streams, unclear benchmarks
- Environment: Extreme weather events, poor air/water quality, habitat destruction
- Machines: Equipment leaks, outdated technology with high emissions
Here is a Ishikawa diagram example for the food industry
Problem/Effect: Increase in foodborne illnesses
- Materials: Contaminated raw ingredients, improper ingredient storage, expired ingredients
- Methods: Unsafe food prep protocols, inadequate employee training, poorly designed workflows
- Manpower: Insufficient food safety knowledge, lack of accountability, high turnover
- Measurement: Inaccurate expiration dates, improper calibration of food safety equipment
- Environment: Unsanitary facilities, presence of pests, poor temperature control
The Ishikawa diagram is a potent tool for unraveling the complexities of issues by categorizing potential factors.
To enrich the collaborative experience of creating Ishikawa diagrams, platforms like AhaSlides prove invaluable. AhaSlides supports real-time teamwork, enabling seamless idea contribution. Its interactive features, including live polling and Q&A sessions, inject dynamism and engagement into the brainstorming process.
What is the application of Ishikawa diagram with example?
Application of Ishikawa Diagram with Example:
Application: Problem analysis and root cause identification.
Example: Analyzing production delays in a manufacturing plant.
How do you write an Ishikawa diagram?
- Define the Problem: Clearly articulate the issue.
- Draw the “Fishbone:” Create main categories (Methods, Machines, Materials, Manpower, Measurement, Environment).
- Brainstorm Causes: Identify specific causes within each category.
- Identify Sub-Causes: Extend lines for detailed causes under each main category.
- Analyze and Prioritize: Discuss and prioritize identified causes.
What are the 6 elements of fishbone diagram?
6 Elements of Fishbone Diagram: Methods, Machines, Materials, Manpower, Measurement, Environment.
Ref: Tech Target | Scribbr

A writer who wants to create practical and valuable content for the audience
More from AhaSlides
Venn Diagram Examples for Problem Solving
Updated on: 13 September 2022
What is a Venn Diagram?
Venn diagrams define all the possible relationships between collections of sets. The most basic Venn diagrams simply consist of multiple circular boundaries describing the range of sets.

The overlapping areas between the two boundaries describe the elements which are common between the two, while the areas that aren’t overlapping house the elements that are different. Venn diagrams are used often in math that people tend to assume they are used only to solve math problems. But as the 3 circle Venn diagram below shows it can be used to solve many other problems.
Though the above diagram may look complicated, it is actually very easy to understand. Although Venn diagrams can look complex when solving business processes understanding of the meaning of the boundaries and what they stand for can simplify the process to a great extent. Let us have a look at a few examples which demonstrate how Venn diagrams can make problem solving much easier.
Example 1: Company’s Hiring Process
The first Venn diagram example demonstrates a company’s employee shortlisting process. The Human Resources department looks for several factors when short-listing candidates for a position, such as experience, professional skills and leadership competence. Now, all of these qualities are different from each other, and may or may not be present in some candidates. However, the best candidates would be those that would have all of these qualities combined.

The candidate who has all three qualities is the perfect match for your organization. So by using simple Venn Diagrams like the one above, a company can easily demonstrate its hiring processes and make the selection process much easier.
A colorful and precise Venn diagram like the above can be easily created using our Venn diagram software and we have professionally designed Venn diagram templates for you to get started fast too.
Example 2: Investing in a Location
The second Venn diagram example takes things a step further and takes a look at how a company can use a Venn diagram to decide a suitable office location. The decision will be based on economic, social and environmental factors.

In a perfect scenario you’ll find a location that has all the above factors in equal measure. But if you fail to find such a location then you can decide which factor is most important to you. Whatever the priority because you already have listed down the locations making the decision becomes easier.
Example 3: Choosing a Dream Job
The last example will reflect on how one of the life’s most complicated questions can be easily answered using a Venn diagram. Choosing a dream job is something that has stumped most college graduates, but with a single Venn diagram, this thought process can be simplified to a great extent.
First, single out the factors which matter in choosing a dream job, such as things that you love to do, things you’re good at, and finally, earning potential. Though most of us dream of being a celebrity and coming on TV, not everyone is gifted with acting skills, and that career path may not be the most viable. Instead, choosing something that you are good at, that you love to do along with something that has a good earning potential would be the most practical choice.

A job which includes all of these three criteria would, therefore, be the dream job for someone. The three criteria need not necessarily be the same, and can be changed according to the individual’s requirements.
So you see, even the most complicated processes can be simplified by using these simple Venn diagrams.
Join over thousands of organizations that use Creately to brainstorm, plan, analyze, and execute their projects successfully.

More Related Articles
Great article, and all true, but.. I hate venn diagrams! I don’t know why, they’ve just never seemed to work for me. Frustrating!
Hey thanks for writing. It helped me in many ways Thanks again 🙂
Hi Nishadha,
Nice article! I love Venn Diagrams because nothing comes to close to expressing the logical relationships between different sets of elements that well. With Microsoft Word 2003 you can create fantastic looking and colorful Venn Diagrams on the fly, with as many elements and colors as you need.
Hi Worli, Yes, Venn diagrams are a good way to solve problems, it’s a shame that it’s sort of restricted to the mathematics subject. MS Word do provides some nice options to create Venn diagrams, although it’s not the cheapest thing around.
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Please enter an answer in digits: fourteen − 8 =
Download our all-new eBook for tips on 50 powerful Business Diagrams for Strategic Planning.
The Mathematics Master
How to Use Tape Diagram for Problem Solving
September 19, 2023
Imagine having a simple yet powerful tool at your fingertips to unravel math mysteries! That's where tape diagrams step into the spotlight.
Think of them as your math buddy – a visual representation resembling a snippet of tape that opens up a world of number connections. Whether you’ve heard them referred to as strip diagrams, bar models, fraction strips, or length models, they all point to the same idea. With tape diagrams, you’re not just solving math problems; you’re crafting a visual journey that untangles the knots of mathematical concepts . These diagrams are like keys to unlock the doors of word problems, helping you quickly organize information and share your brilliant mathematical insights.
What are Tape Diagrams?
Imagine a visual aid that effortlessly guides you through mathematical puzzles – that’s the magic of tape diagrams. These rectangular wonders, resembling strips of tape, are here to simplify your computations. Tape diagrams are your trusty sidekick if you grapple with word problems built on ratios.
Every student’s toolkit should include the skill of creating and using tape diagrams. Why? Because these diagrams hold the key to understanding mathematical concepts and depicting relationships within problems. With tape diagrams, you’re solving problems and bringing mathematical ideas to life. They become your artistic canvas, allowing you to showcase your problem-solving strategies and share your mathematical thoughts.
- Mastering Tape Diagrams
Tape diagrams might sound complex, but fear not! Let’s walk through the steps to craft these problem-solving marvels. Think of tape diagrams as your creative toolkit – they slice daunting tasks into bite-sized graphical goodness. Whether wrestling with tricky word problems or tackling equations head-on, tape diagrams are your reliable companion, making math a visual adventure. So, let’s dive into the artistic journey of creating tape diagrams, one step at a time.
Step 1: Analyze the Problem
Take a moment to read and dissect the problem statement or equation. This initial step is like getting to know the characters before writing a story – it’s essential! By absorbing the problem’s essence, you’ll grasp the scenario and envision pathways to crack it wide open.
Step 2: Gather Your Tools
Now that you’re on a first-name basis with the problem, it’s time to dissect it further. Think of it as breaking down a complex puzzle into its elemental pieces. What parts of the problem are like the corner pieces of a jigsaw puzzle, crucial for completing the whole picture? Identify these components, the building blocks that will populate your tape diagram.
Step 3: It’s Time to Draw the Tape Diagram
With your mental toolkit assembled, it’s time to create your masterpiece – the tape diagram. Envision a long, rectangular canvas resembling a piece of tape. Divide this canvas into smaller sections using neat little boxes. These sections will represent the components you identified in Step 2. Depending on the complexity of the problem, your diagram might have just a couple of sections or a handful. There’s no hard and fast rule, but aim for at least two sections to give your diagram a solid foundation.
Step 4: Solution
Your tape diagram is like a map guiding you to the treasure of the solution. It’s time to put your diagram to work. Solve the problem using the insights your diagram provides. Label the sections, incorporate your gathered information, and let the magic happen.
Putting It into Practice
Now, let’s bring all this theory to life with an example. Imagine a problem where you need to divide your allowance among different expenses. This is where your tape diagram steps in, carving out sections for each expense and revealing the mathematical treasure of how much to allocate where.
Tape diagrams might be simple in concept, but they’re versatile and mighty in practice. They’re not just sketches on paper but your companions on your mathematical journey, making complex problems a visual delight. So, the next time math gives you a puzzling stare, remember that tape diagrams are your secret weapon – transforming numbers into captivating stories of logic and creativity.
Example: Create a tape diagram that represents these equations.
( i ) \(4 + 8 = 12\)
( ii ) \(9 + 6 = 15\)
( i ) Crafting a tape diagram for \(4 + 8 = 12\) involves making four equal cells and adding eight more.
Another option for visual representation could be a complete rectangle divided into two segments, depicted below. It’s worth noting that the rectangle representing \(8\) is longer than the one corresponding to \(4\).
( ii ) Constructing a tape diagram to visualize \(9 + 6 = 15\) involves crafting nine identical cells and adding six more.
Another way to depict this would be a complete rectangle divided into two sections, as presented below. It’s important to observe that the rectangle representing \(9\) is longer than the one representing \(6\).
Tape Diagram for Multiplication and Division
Tape diagrams can also serve as a visual aid for word problems involving multiplication and division.
Examples: Draw a tape diagram that represents these equations.
( i ) \(3 × 9 = 27\)
( ii ) \(2 × 4 = 8\)
( i ) In the case of \(3 × 9 = 27\), \(3\) and \(9\) are called factors. To illustrate this with a tape diagram, let’s create nine equal cells, with three inscribed within each cell as a demonstration.
( ii ) To represent \(2 × 4 = 8\), sketch four identical cells and jot down the number \(2\) within each cell. This serves as an illustrative tape diagram for multiplication.
In essence, the tape diagram stands as an efficient tool for cracking mathematical puzzles. Compared to rote memorization, which can fall flat if grounded in understanding, the beauty of the tape diagram lies in its adaptability. It empowers students not only to master the “how” but also the “why” – fostering a genuine grasp of concepts. By embracing these visual aids, students embark on improved comprehension. As they unravel problems with the guidance of tape diagrams, they enhance their problem-solving prowess and nurture a deeper connection with the world of mathematics.
What are alternate terms for tape diagrams?
Tape diagrams often go by other names, such as strip diagrams, bar models, length models, or fraction strips. These terms are commonly used interchangeably to refer to this visual representation tool.
Why is it called a tape diagram?
A tape diagram earns its name from its resemblance to a strip of tape. This visual tool aids in tackling a variety of calculations, including ratios, addition , subtraction, and, most notably, multiplication . Its simplicity and effectiveness make it a versatile asset in mathematics.
What advantages do tape diagrams offer?
Tape diagrams shine by preventing students from memorizing concepts they may need help understanding. They encouraged a deeper understanding of mathematical ideas and proved to be particularly effective in successfully solving word problems in mathematics.
- Math Calculator
- math education
- Math Playground
- math stations
- mathematical puzzles
- multiplication and division
- strip diagrams
- Tape Diagrams
- tips and tricks
Can't find your query?
Fill out the form below with your query and we will get back to you in 24 hours.
Browse other categories
- Mathematics
- Online Calculator
Most commonly used free online Calculators
Quadratic calculator.
A quadratic Calculator is used to find t...
Sig Fig Calculator
An online sig fig calculator can convert...
Discriminant Calculator
A discriminant calculator can be used fo...
Dot Product Calculator
Introducing the Dot Product Calculator! ...
Endpoint Calculator
An online endpoint calculator can accura...
Completing the Square Calculator
The Completing the Square Calculator is ...
Square Root Calculator
You must be familiar with square roots i...
Pythagorean Theorem Calculator
The Pythagorean Theorem Calculator uses ...
The most Popular Blogs among people
Cartesian coordinates system – dimensions, formula....
Cartesian coordinates, sometimes called rectangular coordinates, are t...
Math Playground: A Hands-On Approach to Learning M...
Step into the math playground, where the wonders of numbers come to li...
How to Graph a Parabola – Formula, Properties, and...
When you discharge an arrow or throw a stone, it arcs into the air and...
Subscribe for the latest updates
Say goodbye to manual calculations and do math within a fraction of seconds with our easy to use and accurate free online calculators.
For enquiries call:
+1-469-442-0620

What is Problem Solving? Process, Techniques, Examples
Home Blog others What is Problem Solving? Process, Techniques, Examples
Whether tackling a technical issue at work or finding our way around a roadblock unnoticed by Google Maps, problem-solving is a daily occurrence for most people. But how prepared are you to overcome life's challenges? Do you rely on a structured process to ensure successful outcomes, or do you navigate through problems impulsively?
Here's the crux: the strength of your problem-solving skills significantly impacts the ease and success of your life, both professionally and personally. Practical problem-solving is a valuable career and life skill. You're in the right place if you're eager to enhance your problem-solving abilities efficiently.
In this blog post, I will delve into what is problem solving the steps, techniques, and exercises of the problem-solving process. Whether seeking to troubleshoot technical issues or navigate life's complexities, mastering organized problem-solving can elevate your capabilities and lead to more favorable outcomes.
What is Problem Solving? And Its Importance
First, let me help you understand what is problem solving. Problem-solving is a comprehensive process involving identifying issues, prioritizing based on urgency and severity, analyzing root causes, gathering pertinent Information, devising and assessing solutions, making informed decisions, and planning and executing implementation strategies.
This skill set also encompasses critical thinking, effective communication, active listening, creativity, research, data analysis, risk assessment, continuous learning, and decision-making abilities. Effective problem-solving strategies mitigate potential losses or damages and enhance self-confidence and reputation. Problem-solving is essential in personal and professional contexts as it allows individuals and teams to navigate obstacles, make informed decisions, and drive progress.
Importance:
- Enhances Decision-Making: Effective problem solving leads to better decision-making by evaluating various options and selecting the most suitable solution.
- Promotes Innovation: Problem solving encourages innovation and creativity as individuals seek new approaches to tackle challenges.
- Improves Efficiency: By resolving issues efficiently, problem solving helps streamline processes and optimize resource allocation.
- Builds Resilience: Successfully overcoming obstacles builds confidence and resilience, enabling
- individuals and teams to tackle future challenges with greater confidence.
Problem-solving Process
Now that we have a clear understanding of the problem solving definition as to what is problem solving let us now navigate the problem solving process. Effective problem-solving is a valuable skill sought after by employers in various fields. Here's a breakdown of a common problem-solving process, presented in a pointwise manner:
1. Identifying the Problem
The first step in the problem-solving process is clearly defining the issue. This involves gathering relevant Information, observing patterns or trends, and understanding the impact of the problem on stakeholders.
2. Analyzing the Situation
Once the problem is identified, it's essential to analyze its root causes and contributing factors. This may involve conducting research, gathering data, and exploring different perspectives to comprehensively understand the situation.
3. Generating Solutions
With a clear understanding of the problem solving methods, brainstorming potential solutions is the next step. Encouraging creativity and considering various alternatives can lead to innovative ideas. Evaluating each solution based on feasibility, effectiveness, and alignment with goals and values is crucial.
4. Evaluating Options
After generating a list of potential solutions, it's essential to carefully evaluate each option. This involves weighing the pros and cons, considering potential risks and benefits, and assessing the likelihood of success. Consulting with relevant stakeholders or experts can provide valuable insights during this stage.
5. Selecting the Best Solution
Based on the evaluation, one or more solutions are the most viable options. It's essential to prioritize solutions that address the root cause of the problem and have the most significant potential for long-term success. Communicating the chosen solution effectively to stakeholders is crucial for garnering support and buy-in.
6. Implementing the Solution
Once a solution is selected, it's time to put it into action. This involves developing a detailed action plan, allocating resources, and assigning responsibilities. Effective communication, coordination, and monitoring are essential during the implementation phase to ensure smooth execution and timely resolution of the problem.
7. Monitoring and Reviewing
After implementing the solution, it's essential to monitor its progress and evaluate its effectiveness over time. This may involve collecting feedback, analyzing performance metrics, and making adjustments as needed. Continuous monitoring and review allow for ongoing improvement and refinement of the problem-solving process.
How to Solve Problems in 5 Simple Steps?
Here's a breakdown of the 5 problem-solving steps for your understanding:
1. Define the Problem (Understand & Gather Information)
- Identify the Issue: Clearly understand what the problem is. What isn't working, or what needs improvement?
- Gather Information: Talk to people involved, collect data, and research relevant details to get a well-rounded picture of the situation.
- Ask Why? Don't just focus on symptoms. Ask "why" several times to identify the root cause of the problem.
Example: Let's say customer complaints about slow website loading times have increased.
2. Brainstorm Solutions (Think Creatively & Be Open-Minded)
- Think Outside the Box: Don't settle for the first solution that comes to mind. Brainstorm a variety of options, even seemingly unconventional ones.
- Consider All Angles: Evaluate the problem from different perspectives. What are potential solutions from a technical standpoint? From a user experience point of view?
- Build on Ideas: Don't shut down ideas prematurely. Encourage others to build upon and refine suggestions collaboratively.
Example: Potential solutions for slow website loading times could include optimizing images, upgrading server capacity, or implementing a content delivery network (CDN).
3. Evaluate & Choose a Solution (Consider Feasibility & Impact)
- Weigh the Pros & Cons: Analyze the feasibility, resource requirements, and potential risks and benefits of each solution.
- Align with Goals: Ensure the chosen solution directly addresses the root cause of the problem and aligns with your overall objectives.
- Prioritize Impact: Choose the solution with the most significant potential to achieve a positive outcome and lasting improvement.
Example: Upgrading server capacity might be a very effective solution, but it could be expensive. Optimizing images is a more feasible solution that could yield significant improvement.
4. Implement the Solution (Take Action & Communicate Clearly)
- Develop a Plan: Create a clear action plan outlining the steps involved in implementing the chosen solution. Assign tasks and set deadlines.
- Communication is Key: Clearly communicate the plan to everyone involved, including stakeholders and team members.
- Monitor Progress: Track the implementation process and make adjustments as needed based on the results.
Example: The website optimization plan might involve tasks like image resizing, code minification, and implementing caching mechanisms.
5. Evaluate the Outcome (Learn & Adapt)
- Measure Success: Assess whether the implemented solution effectively resolved the problem. Did it meet your goals?
- Lessons Learned: Reflect on what worked well and what could be improved during the problem-solving process.
- Continuous Improvement: Use this experience to refine your problem-solving approach and enhance your skills for future challenges. Enroll in free online certification courses for professional development and skill enhancement.
Example: After website optimization, monitor website loading times and customer feedback to see if the issue has been resolved. If not, repeat the process, considering new solutions based on the learnings from this attempt.
Remember, problem-solving is an iterative process. Be prepared to adapt your approach as you gather more Information and evaluate the effectiveness of your solutions.
Essential Things to Consider in Each of the Problem-solving Steps
Creative problem solving requires careful consideration at each stage. Here are vital things to focus on:
1. Identifying & Defining the Problem
- Gather Information: Consult stakeholders, review data, and gain insights from various perspectives.
- Identify Root Cause: Address the underlying reason, not just symptoms.
- Define Scope: Clearly outline the problem's boundaries to maintain focus.
2. Analyzing the Problem
- Consider Multiple Perspectives: Explore diverse angles to uncover potential factors.
- Brainstorm Freely: Foster creativity without judgment to generate innovative ideas.
- Analyze Impact: Evaluate the severity and consequences of the problem if left unresolved.
- Think Creatively: Explore unconventional solutions beyond initial ideas.
- Consider Feasibility: Assess the practicality and resource requirements of each option.
- Identify Potential Risks & Benefits: Weigh the pros and cons to select the most balanced approach.
4. Evaluating and Selecting a Solution
- Align with Goals: Ensure the chosen solution addresses the core issue and aligns with objectives.
- Consider Long-Term Impact: Choose solutions with lasting benefits beyond immediate results.
- Team Input: Involve team members to gain diverse perspectives during evaluation.
5. Implementing the Solution
- Develop a Clear Plan: Outline implementation steps with clear timelines and responsibilities.
- Communication is Key: Ensure all stakeholders understand the plan to facilitate smooth execution.
- Monitor Progress: Track implementation and adjust as needed based on results.
6. Evaluating the Outcome
- Measure Effectiveness: Assess if the solution effectively resolves the problem or needs refinement.
- Lessons Learned: Identify successes and areas for improvement to enhance future problem-solving efforts.
Problem Solving Examples
Let us look at problem solving example scenarios in a typical workplace: , example 1: project deadline challenge .
- Situation: You're a project manager leading a team that is developing a new marketing campaign website. The launch date is approaching, but a critical developer is unexpectedly out sick for a week.
- Action: You immediately assess the workload and delegate tasks among the remaining team members. You identify an opportunity to streamline a design element, reducing development time. You also reach out to a freelancer with a proven track record to fill in for the missing developer on specific tasks.
- Result: The team successfully launches the website on time and within budget. The streamlined design element is praised by stakeholders for its user-friendliness.
- Highlight: This example showcases your problem-solving skills, leadership, adaptability, and ability to manage resources effectively under pressure.
Example 2: Client Communication Breakdown
- Situation: You're a Customer Service Representative for an e-commerce company. A regular customer expresses extreme dissatisfaction with a recent purchase due to a malfunctioning product and a negative experience with a previous representative.
- Action: You actively listen to the customer's concerns, apologizing for the inconvenience. You then troubleshoot the product issue and offer a solution (replacement or refund). Additionally, you acknowledge the previous negative experience and offer to ensure better communication going forward.
- Result: The customer is satisfied with the resolution and expresses appreciation for your attentiveness and problem-solving approach. They remain a loyal customer of the company.
- Highlight: This example demonstrates your active listening skills, empathy, ability to de-escalate situations, and commitment to customer satisfaction.
By following these examples of problem-solving skills, you can effectively tackle challenges and achieve successful outcomes. Also, explore KnowledgeHut’ s best online courses for further skill enhancement.
Problem Solving Techniques
Effective problem-solving techniques are essential for tackling challenges and achieving desired outcomes. Here are some problem solving tools and techniques commonly used in problem-solving:
- Brainstorming : Encourages the generation of a wide range of ideas and solutions in a non-judgmental environment. This technique promotes creativity and can uncover innovative approaches to problems.
- Root Cause Analysis : Focuses on identifying the underlying causes of a problem rather than just addressing its symptoms. By pinpointing root causes, solutions can be targeted more effectively to prevent recurrence.
- Fishbone Diagram (Ishikawa Diagram): Provides a visual representation of the various factors contributing to a problem, categorized into branches such as people, process, equipment, environment, and management. This technique helps analyze complex issues and identify potential causes.
- SWOT Analysis : Evaluates the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats associated with a problem or situation. This technique helps assess the internal and external factors influencing the problem and guides decision-making.
- Pareto Analysis: Focuses on identifying and prioritizing the most significant causes contributing to a problem. By allocating resources to address the vital few rather than the trivial many, this technique maximizes impact and efficiency.
- 5 Whys : Involves asking "why" repeatedly to trace the root cause of a problem. This iterative questioning technique helps uncover more profound layers of causation beyond surface-level symptoms.
- Decision Matrix Analysis: Helps evaluate multiple options by systematically comparing their pros and cons against predetermined criteria. This technique facilitates objective decision-making by considering various factors and their relative importance.
By incorporating these problem-solving techniques in the workplace, you can approach problems systematically, generate creative solutions, and develop a well-rounded plan for achieving success.
Conquering challenges is a key to professional success, and practical problem-solving equips you to do just that. By following a structured approach, you can transform from a bystander to a solution-oriented individual. This involves gathering Information to clearly define the problem and identify its root cause. Analyzing the situation from various angles and brainstorming freely unlock creative solutions. Evaluating potential solutions ensures you choose the one that aligns with your goals and is feasible to implement. Clear communication and a well-defined plan are crucial for successful execution. Finally, reflecting on the outcome allows you to learn and continuously improve your problem-solving skills, making you an invaluable asset in any environment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The best method involves identifying the problem, brainstorming solutions, evaluating options, implementing the chosen solution, and assessing outcomes for improvement.
The principles include defining the problem, generating alternatives, evaluating options, implementing solutions, and reviewing outcomes for continuous improvement.
Different types include analytical problem-solving, creative problem-solving, critical thinking, decision-making, and systematic problem-solving.
The significant elements include understanding the problem, devising a plan, executing the plan, and evaluating the results.
The skills encompass critical thinking, decision-making, and analytical reasoning. These abilities aid in identifying, analyzing, and resolving problems effectively.

KnowledgeHut .
KnowledgeHut is an outcome-focused global ed-tech company. We help organizations and professionals unlock excellence through skills development. We offer training solutions under the people and process, data science, full-stack development, cybersecurity, future technologies and digital transformation verticals.
Avail your free 1:1 mentorship session.
Something went wrong
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Is Your AI-First Strategy Causing More Problems Than It’s Solving?
- Oguz A. Acar

Consider a more balanced and thoughtful approach to AI transformation.
The problem with an AI-first strategy lies not within the “AI” but with the notion that it should come “first” aspect. An AI-first approach can be myopic, potentially leading us to overlook the true purpose of technology: to serve and enhance human endeavors. Instead, the author recommends following 3Ps during an AI transformation: problem-centric, people-first, and principle-driven.
From technology giants like Google to major management consultants like McKinsey , a rapidly growing number of companies preach an “AI-first” strategy. In essence, this means considering AI as the ultimate strategic priority , one that precedes other alternative directions. At first glance, this strategy seems logical, perhaps even inevitable. The figures speak for themselves: the sheer volume of investment flowing into AI technologies shows the confidence levels in an increasingly AI-driven future.
- Oguz A. Acar is a Chair in Marketing at King’s Business School, King’s College London.
Partner Center
Netflix's hit sci-fi series '3 Body Problem' is based on a real math problem that is so complex it's impossible to solve
- The three-body problem is a centuries-old physics question that puzzled Isaac Newton .
- It describes the orbits of three bodies, like planets or stars, trapped in each other's gravity.
- The problem is unsolvable and led to the development of chaos theory.

While Netflix's "3 Body Problem" is a science-fiction show, its name comes from a real math problem that's puzzled scientists since the late 1600s.
In physics, the three-body problem refers to the motion of three bodies trapped in each other's gravitational grip — like a three-star system.
It might sound simple enough, but once you dig into the mathematics, the orbital paths of each object get complicated very quickly.
Two-body vs. three- and multi-body systems
A simpler version is a two-body system like binary stars. Two-body systems have periodic orbits, meaning they are mathematically predictable because they follow the same trajectory over and over. So, if you have the stars' initial positions and velocities, you can calculate where they've been or will be in space far into the past and future.
However, "throwing in a third body that's close enough to interact leads to chaos," Shane Ross, an aerospace and ocean engineering professor at Virginia Tech, told Business Insider. In fact, it's nearly impossible to precisely predict the orbital paths of any system with three bodies or more.
While two orbiting planets might look like a ven diagram with ovular paths overlapping, the paths of three bodies interacting often resemble tangled spaghetti. Their trajectories usually aren't as stable as systems with only two bodies.
All that uncertainty makes what's known as the three-body problem largely unsolvable, Ross said. But there are certain exceptions.
The three-body problem is over 300 years old
The three-body problem dates back to Isaac Newton , who published his "Principia" in 1687.
In the book, the mathematician noted that the planets move in elliptical orbits around the sun. Yet the gravitational pull from Jupiter seemed to affect Saturn's orbital path.
Related stories
The three-body problem didn't just affect distant planets. Trying to understand the variations in the moon's movements caused Newton literal headaches, he complained.
But Newton never fully figured out the three-body problem. And it remained a mathematical mystery for nearly 200 years.
In 1889, a Swedish journal awarded mathematician Henri Poincaré a gold medal and 2,500 Swedish crowns, roughly half a year's salary for a professor at the time, for his essay about the three-body problem that outlined the basis for an entirely new mathematical theory called chaos theory .
According to chaos theory, when there is uncertainty about a system's initial conditions, like an object's mass or velocity, that uncertainty ripples out, making the future more and more unpredictable.
Think of it like taking a wrong turn on a trip. If you make a left instead of a right at the end of your journey, you're probably closer to your destination than if you made the mistake at the very beginning.
Can you solve the three-body problem?
Cracking the three-body problem would help scientists chart the movements of meteors and planets, including Earth, into the extremely far future. Even comparatively small movements of our planet could have large impacts on our climate, Ross said.
Though the three-body problem is considered mathematically unsolvable, there are solutions to specific scenarios. In fact, there are a few that mathematicians have found.
For example, three bodies could stably orbit in a figure eight or equally spaced around a ring. Both are possible depending on the initial positions and velocities of the bodies.
One way researchers look for solutions is with " restricted " three-body problems, where two main bodies (like the sun and Earth) interact and a third object with much smaller mass (like the moon) offers less gravitational interference. In this case, the three-body problem looks a lot like a two-body problem since the sun and Earth comprise the majority of mass in the system.
However, if you're looking at a three-star system, like the one in Netflix's show "3 Body Problem," that's a lot more complicated.
Computers can also run simulations far more efficiently than humans, though due to the inherent uncertainties, the results are typically approximate orbits instead of exact.
Finding solutions to three-body problems is also essential to space travel, Ross said. For his work, he inputs data about the Earth, moon, and spacecraft into a computer. "We can build up a whole library of possible trajectories," he said, "and that gives us an idea of the types of motion that are possible."
- Main content
Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Artificial Intelligence
Title: on size and hardness generalization in unsupervised learning for the travelling salesman problem.
Abstract: We study the generalization capability of Unsupervised Learning in solving the Travelling Salesman Problem (TSP). We use a Graph Neural Network (GNN) trained with a surrogate loss function to generate an embedding for each node. We use these embeddings to construct a heat map that indicates the likelihood of each edge being part of the optimal route. We then apply local search to generate our final predictions. Our investigation explores how different training instance sizes, embedding dimensions, and distributions influence the outcomes of Unsupervised Learning methods. Our results show that training with larger instance sizes and increasing embedding dimensions can build a more effective representation, enhancing the model's ability to solve TSP. Furthermore, in evaluating generalization across different distributions, we first determine the hardness of various distributions and explore how different hardnesses affect the final results. Our findings suggest that models trained on harder instances exhibit better generalization capabilities, highlighting the importance of selecting appropriate training instances in solving TSP using Unsupervised Learning.
Submission history
Access paper:.
- HTML (experimental)
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .
Follow Polygon online:
- Follow Polygon on Facebook
- Follow Polygon on Youtube
- Follow Polygon on Instagram
Site search
- What to Watch
- What to Play
- PlayStation
- All Entertainment
- Dragon’s Dogma 2
- FF7 Rebirth
- Zelda: Tears of the Kingdom
- Baldur’s Gate 3
- Buyer’s Guides
- Galaxy Brains
- All Podcasts
Filed under:
- Entertainment
The 3-body problem is real, and it’s really unsolvable
Oh god don’t make me explain math
Share this story
- Share this on Facebook
- Share this on Reddit
- Share All sharing options
Share All sharing options for: The 3-body problem is real, and it’s really unsolvable
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/73224177/3_Body_Problem_n_S1_E4_00_26_53_00RC.jpg_3_Body_Problem_n_S1_E4_00_26_53_00RC.0.jpg)
Everybody seems to be talking about 3 Body Problem , the new Netflix series based on Cixin Liu’s Remembrance of Earth’s Past book trilogy . Fewer people are talking about the two series’ namesake: The unsolvable physics problem of the same name.
This makes sense, because it’s confusing . In physics, the three-body problem attempts to find a way to predict the movements of three objects whose gravity interacts with each of the others — like three stars that are close together in space. Sounds simple enough, right? Yet I myself recently pulled up the Wikipedia article on the three-body problem and closed the tab in the same manner that a person might stagger away from a bright light. Apparently the Earth, sun, and moon are a three-body system? Are you telling me we don’t know how the moon moves ? Scientists have published multiple solutions for the three-body problem? Are you telling me Cixin Liu’s books are out of date?
All I’d wanted to know was why the problem was considered unsolvable, and now memories of my one semester of high school physics were swimming before my eyes like so many glowing doom numbers. However, despite my pains, I have readied several ways that we non-physicists can be confident that the three-body problem is, in fact, unsolvable.
Reason 1: This is a special definition of ‘unsolvable’
:no_upscale()/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25343152/3BP_103_Unit_03306RC.jpg_3BP_103_Unit_03306RC.jpg)
The three-body problem is extra confusing, because scientists are seemingly constantly finding new solutions to the three-body problem! They just don’t mean a one-solution-for-all solution. Such a formula does exist for a two-body system, and apparently Isaac Newton figured it out in 1687 . But systems with more than two bodies are, according to physicists, too chaotic (i.e., not in the sense of a child’s messy bedroom, but in the sense of “chaos theory”) to be corralled by a single solution.
When physicists say they have a new solution to the three-body problem, they mean that they’ve found a specific solution for three-body systems that have certain theoretical parameters. Don’t ask me to explain those parameters, because they’re all things like “the three masses are collinear at each instant” or “a zero angular momentum solution with three equal masses moving around a figure-eight shape.” But basically: By narrowing the focus of the problem to certain arrangements of three-body systems, physicists have been able to derive formulas that predict the movements of some of them, like in our solar system. The mass of the Earth and the sun create a “ restricted three-body problem ,” where a less-big body (in this case, the moon) moves under the influence of two massive ones (the Earth and the sun).
What physicists mean when they say the three-body problem has no solution is simply that there isn’t a one-formula-fits-all solution to every way that the gravity of three objects might cause those objects to move — which is exactly what Three-Body Problem bases its whole premise on.
Reason 2: 3 Body Problem picked an unsolved three-body system on purpose
:no_upscale()/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25325944/3_Body_Problem_n_S1_E3_00_34_33_04RC.jpg_3_Body_Problem_n_S1_E3_00_34_33_04RC.jpg)
Henri Poincaré’s research into a general solution to the three-body problem formed the basis of what would become known as chaos theory (you might know it from its co-starring role in Jurassic Park ). And 3 Body Problem itself isn’t about any old three-body system. It’s specifically about an extremely chaotic three-body system, the exact kind of arrangement of bodies that Poincaré was focused on when he showed that the problem is “unsolvable.”
[ Ed. note: The rest of this section includes some spoilers for 3 Body Problem .]
In both Liu’s books and Netflix’s 3 Body Problem , humanity faces an invasion by aliens (called Trisolarans in the English translation of the books, and San-Ti in the TV series) whose home solar system features three suns in a chaotic three-body relationship. It is a world where, unlike ours, the heavens are fundamentally unpredictable. Periods of icy cold give way to searing heat that give way to swings in gravity that turn into temporary reprieves that can never be trusted. The unpredictable nature of the San-Ti environment is the source of every detail of their physicality, their philosophy, and their desire to claim Earth for their own.
In other words, 3 Body Problem ’s three-body problem is unsolvable because Liu wanted to write a story with an unsolvable three-body system, so he chose one of the three-body systems for which we have not discovered a solution, and might never.
Reason 3: Scientists are still working on the three-body problem
Perhaps the best reason I can give you to believe that the three-body problem is real, and is really unsolvable, is that some scientists published a whole set of new solutions for specific three-body systems very recently .
If physicists are still working on the three-body problem, we can safely assume that it has not been solved. Scientists, after all, are the real experts. And I am definitely not.
The next level of puzzles.
Take a break from your day by playing a puzzle or two! We’ve got SpellTower, Typeshift, crosswords, and more.
Sign up for the newsletter Patch Notes
A weekly roundup of the best things from Polygon
Just one more thing!
Please check your email to find a confirmation email, and follow the steps to confirm your humanity.
Oops. Something went wrong. Please enter a valid email and try again.
Loading comments...

Best Buy is offering free trials for Apple TV Plus, Apple Arcade, and more

Pokémon Go Spotlight Hour schedule for April 2024

Invincible season 2 finale, Netflix’s Ripley, and more new TV this week

All the House of the Dragon season 2 news we’ve heard so far

All the Gen V season 2 news we’ve heard so far

I didn’t like Sex and the City, and then I watched it
- Share full article
For more audio journalism and storytelling, download New York Times Audio , a new iOS app available for news subscribers.

- March 30, 2024 • 9:00 Solving the ‘3 Body Problem’
- March 29, 2024 • 5:26 The Latest on Sean Combs’s Legal Woes
- March 28, 2024 • 9:10 Before Beyoncé: Black Artists Who Crossed Over to Country
- March 27, 2024 • 3:50 A Boxing Novel That Brings the Heat
- March 22, 2024 • 7:47 New Music for Your Weekend
- March 21, 2024 • 6:57 A Surreal New TV Series About Life, Love and Fruit
- March 20, 2024 • 9:37 Curl Up With a Delicious Recipe
- March 15, 2024 • 7:20 Kacey Musgraves Finds Inner Peace on Her New Album
- March 14, 2024 • 5:47 5 Minutes to Love Jazz Flute
- March 12, 2024 • 3:45 Tuxedos Stole the Show at This Year’s Oscars
- March 11, 2024 • 9:13 Oscar Highlights: The Good, the Ken and the Naked
- March 8, 2024 • 6:09 The Alt-Rock Legend Kim Gordon Has a New Album
Solving the ‘3 Body Problem’
Unpacking netflix’s new hit with the times’s cosmic affairs correspondent..
Produced by Alex Barron
Edited by Lynn Levy
Engineered by Efim Shapiro
Featuring Dennis Overbye
The show “3 Body Problem” premiered on March 21 and quickly became one of Netflix’s most-watched titles. It is an adventure story about a group of scientists contending with an extraterrestrial threat. But despite its science fiction trappings, the show is often based in real — and complex — scientific concepts, whether string theory or nanomaterials. In this episode, Dennis Overbye, The Times’s cosmic affairs correspondent, breaks down some of the more brain-bending science behind “3 Body Problem.”
On today’s episode

Dennis Overbye is the cosmic affairs correspondent for The Times, covering physics and astronomy.

The New York Times Audio app is home to journalism and storytelling, and provides news, depth and serendipity. If you haven’t already, download it here — available to Times news subscribers on iOS — and sign up for our weekly newsletter.
Dennis Overbye is the cosmic affairs correspondent for The Times, covering physics and astronomy. More about Dennis Overbye
Advertisement
- Link copied

Supporting next-generation educational programs that combine the metaverse experience with a problem-solving mindset
Multidisciplinary professional services organization
Show resources
カーボンニュートラル社会の実現 エネルギービジネスの変革に向けたカウントダウン(pdf), creating social value - ey is fulfilling its corporate responsibilities through ey ripples, in which it leverages the professional knowledge of its people across various fields to carry out pro bono activities that benefit society., ey japan is playing its part by operating a next-generation educational program utilizing the latest technologies..
- Controlling a self-made avatar within the metaverse provides children with an opportunity to think about how to communicate with others.
- Using design thinking to find the best solutions to a problem.
- Showing how a pro bono project for EY Ripples leverages how EY does business to create a positive impact in society.

Experiencing the metaverse and creating avatars using VR headsets and tablets
The workshop enabled children to create and control their own avatars and to think about different ways to communicate with others.
This next-generation educational program is being carried out in conjunction with Education A³ of Fukuoka City (Representative Director: Yuichi Kusaba ) which is a Certified NPO Corporation. Education A³ is working to eliminate disparities within children’s education, particularly in the Fukuoka area, by operating alternative schools for children who are unable to attend mainstream education. The program aims to help these children nurture problem-solving abilities and ways of thinking that differ from what they would learn in mainstream classes.
It has four sessions and caters to students across a variety of age ranges, from the third grade of elementary school to high school. The first session was held at EY Digital Hub Fukuoka, facility established by EY to lead Japan’s digital transformation. Members of EY Strategy and Consulting’s Technology Consulting team provided a communication experience using the metaverse and virtual reality (VR).
The children were each provided with tablets to enter a virtual recreation of Fukuoka City’s Torikai Hachimangu shrine. They explored the shrine and its grounds using an avatar (a virtual character of themselves) which they created and took part in an information-gathering activity. They also used VR headsets to be more immersed in the virtual world, where they worked on clearing missions.
EY Japan also supported the building of the metaverse version of Torikai Hachimangu shrine that was used in the program. For c.1800 years, the shrine has been a center of faith and communication within the region so we gave thought to how to optimize the shrine in a way that would be relevant to the modern world.
EY Japan is also proposing and developing projects which unite cutting-edge technologies, including the metaverse, with our support for companies and organizations that are exploring new initiatives or are interested in merging real and digital environments. Building a metaverse version of Torikai Hachimangu shrine is just one example of our work.
The team from EY Japan used the same approach to create the metaverse experience for children as they do when giving a client demonstration in their everyday roles. Firstly, it was important that the children had a visceral experience of the metaverse by using a VR headset. Today, children are often referred to as digital natives and can quickly familiarize themselves with how to operate technology, with younger children tending to master it the fastest. One of the children at the session commented: “When I entered the metaverse, it was surprising at the start. But then it was fun, and I thought that modern technology is amazing.”

A particular highlight for the children was the time spent creating their own avatars. They were completely free to choose items such as their avatar’s face, hairstyle and clothing, making the avatar an aspirational model, rather than an accurate likeness of each child. Operating an avatar within the metaverse provided children who are unable to attend school with an opportunity to think about how to communicate with others.
Experiencing the opportunities for work and play in the metaverse helps to give children hope for the future. I also think that in an era of rapid change children can learn an important skill through early exposure to design thinking: they learn how to develop their own solution to a given problem. Yuichi Kusaba, Representative Director, Education A³

Working toward design thinking that gets to the heart of problem solving
The design thinking workshop was a valuable learning opportunity, not only for the children but also for the EY team. We were able to adjust the workshop content based on the children’s level of engagement, and establish our fundamental approach to design thinking.
The second and subsequent sessions were held as online workshops about design thinking. Team members from EY wavespace™, an innovation support hub that facilitates collaboration between various stakeholders, provided opportunities to learn how to think in a way that gets to the heart of a problem and, in turn, to its solution.
Design thinking is a method of applying the thought patterns used by designers in business situations: finding the fundamental solution to an issue can be a source of innovation. Design includes elements of planning and conceptualization and design thinking is included in programs at major US universities as a method for innovative thinking.
The EY team acted as facilitators and led discussions on issues familiar to children. They helped organize the many ideas suggested by the children to solve the problem and encouraged them to continue their discussions. The children in each group then presented their proposed solution.
This was the children’s first experience of design thinking. The second and subsequent sessions focused on junior high school students, who exchanged opinions using an online conferencing system and an online whiteboard tool to post and develop ideas. Many of the children appeared to initially find this difficult so the team responded by adjusting the difficulty of the program. When the children gained a better understanding of the scenario, they were able to contribute and get more involved.
One of the participants commented, “This was the first time do this. I don’t usually get opportunities to think so deeply about a topic, so it was really fun.” Building a basic approach to design thinking with content easily understood by junior high school students also proved a learning experience for the EY Japan team.
As adults tend to view things through existing frameworks, it was striking how the children could come up with novel ideas that were free of bias.

The children discussed creating new snacks suitable for field trips, generating far more innovative ideas than adults would.
A success that aligns with EY’s Purpose and how we do business
We want to combine new technologies like the metaverse with design thinking to enable children to find their own solutions to a problem.” This was the thinking behind the program and it was a project that also resonates with EY’s global shared purpose of Building a better working world. Innovation is generated through the intersection of many different approaches so, as well as being a pro bono project for the EY Ripples program, this was also an initiative that leveraged how EY does business to impact society. In this way, the program was a great success.

Yosuke Amano , EY wavespace™ Tokyo Leader
EY wavespace™
EY wavespace™ brings together business, design and technology, enabling companies to accelerate transformation, drive innovation and create measurable outcomes. With human-centered design and collaboration at our core methodologies, we support our clients reimagine what’s possible and reframe their thinking to solve problems together.
EY is fulfilling its corporate responsibilities through EY Ripples, and EY Japan is playing its part by operating a next-generation educational program utilizing the latest technologies.
About this article
Connect with us
Our locations
EY Client Portal
Legal and privacy
EY refers to the global organization, and may refer to one or more, of the member firms of Ernst & Young Global Limited, each of which is a separate legal entity. Ernst & Young Global Limited, a UK company limited by guarantee, does not provide services to clients.
EY | Assurance | Consulting | Strategy and Transactions | Tax
EY is a global leader in assurance, consulting, strategy and transactions, and tax services. The insights and quality services we deliver help build trust and confidence in the capital markets and in economies the world over. We develop outstanding leaders who team to deliver on our promises to all of our stakeholders. In so doing, we play a critical role in building a better working world for our people, for our clients and for our communities.
EY refers to the global organization, and may refer to one or more, of the member firms of Ernst & Young Global Limited, each of which is a separate legal entity. Ernst & Young Global Limited, a UK company limited by guarantee, does not provide services to clients. For more information about our organization, please visit ey.com.
© 2020 EYGM Limited. All Rights Reserved.
EYG/OC/FEA no.
This material has been prepared for general informational purposes only and is not intended to be relied upon as accounting, tax, or other professional advice. Please refer to your advisors for specific advice.

Welcome to EY.com
In addition to cookies that are strictly necessary to operate this website, we use the following types of cookies to improve your experience and our services: Functional cookies to enhance your experience (e.g. remember settings), and Performance cookies to measure the website's performance and improve your experience . , and Marketing/Targeting cookies , which are set by third parties, allow us to execute marketing campaigns, manage our relationship with you, build a profile of your interests and provide you with content or service offerings in accordance with your preferences.
We have detected that Do Not Track/Global Privacy Control is enabled in your browser; as a result, Marketing/Targeting cookies , which are set by third parties that allow us to execute marketing campaigns, manage our relationship with you, build a profile of your interests and provide you with content or service offerings in accordance with your preferences are automatically disabled.
You may withdraw your consent to cookies at any time once you have entered the website through a link in the privacy policy, which you can find at the bottom of each page on the website.
Review our cookie policy for more information.
Customize cookies
I decline optional cookies

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A fishbone diagram is a problem-solving approach that uses a fish-shaped diagram to model possible root causes of problems and troubleshoot possible solutions. It is also called an Ishikawa diagram, after its creator, Kaoru Ishikawa, as well as a herringbone diagram or cause-and-effect diagram. Fishbone diagrams are often used in root cause ...
1. Define the problem. Diagnose the situation so that your focus is on the problem, not just its symptoms. Helpful problem-solving techniques include using flowcharts to identify the expected steps of a process and cause-and-effect diagrams to define and analyze root causes.. The sections below help explain key problem-solving steps.
To perform a cause-and-effect analysis, follow these steps. 1. Start with a problem statement. The problem statement is usually placed in a box or another shape at the far right of your page. Draw a horizontal line, called a "spine" or "backbone," along the center of the page pointing to your problem statement. 2.
A diagram can be a rough sketch, a number line, a tree diagram or two-way table, a Venn diagram, or any other drawing which helps us to tackle a problem. Labels (e.g. letters for vertices of a polygon) are useful in a diagram to help us be able to refer to items of interest. A diagram can be updated as we find out new information.
Also called: cause-and-effect diagram, Ishikawa diagram. This cause analysis tool is considered one of the seven basic quality tools. The fishbone diagram identifies many possible causes for an effect or problem. It can be used to structure a brainstorming session. It immediately sorts ideas into useful categories.
The Fishbone Diagram, also known by various other names such as Ishikawa Diagram, Cause and Effect Diagram or 6Ms, is a visual tool used in problem-solving and root cause analysis.Originating from the quality management sector, it is used as a systematic approach to identify, explore, and display possible causes of a specific problem.
Problem-Solving Flowcharts is a graphical representation used to break down problem or process into smaller, manageable parts, identify the root causes and outline a step-by-step solution. It helps in visually organizing information and showing the relationships between various parts of the problem. This type of flowcharts consists of different ...
A fishbone diagram (also known as an Ishikawa fishbone diagram) is an effective problem-solving tool. Instead of focusing on a quick fix, creating a fishbone diagram helps to identify the root cause of a problem and find a long-term solution. As a type of cause and effect diagram, the "fishbone" name comes from the diagram's resemblance ...
Problem solving diagrams. Mapping your way out of a problem is the simplest way to see where you are, and where you need to end up. Not only do visual problem maps let you plot the most efficient route from Point A (dysfunctional situation) to Point B (flawless process), problem mapping diagrams make it easier to see: ...
Here's how to create a fishbone diagram: In MindManager, go to the File menu, select New and then click into the Problem-Solving folder. There you'll find three templates for Fishbones, the manufacturing, service, and product analyses. Select a template. Enter the issue in the central topic. Next, either brainstorm potential causes and add ...
Tools to Aid Visual Problem Solving. While there is a myriad of tools to help you draw things, Creately is definitely one of the easiest ways to visualize your problem. We support mind maps, flowcharts, concept maps and 50+ other diagram types which you can use for visual problem-solving. Our professionally designed templates and productivity ...
Here's a step-by-step tutorial for making an Ishikawa Diagram: Step 1: Identify the problem and write it in a box at the top of the diagram. Step 2: To represent the main spine of the fishbone diagram, draw a horizontal arrow pointing to the problem box.
When problem solving, sometimes it's hard to see what's causing the problem, or other relationships and correlations that are affecting whatever it is you're working on. Two common methods for problem solving include mind maps and flowcharts. A mind map is a non-linear diagram, used for making new ideas or breaking down complex issues.
The fishbone diagram problem solving tool is a perfect tool to dig through an issue when we try to assess the root cause and find a solution effectively. It offers a mechanism for explicitly identifying the "effect" and then brings you to think about the potential triggers, based on typical manufacturing problems. ...
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps: Identify the issue: Recognize the problem that needs to be solved. Analyze the situation: Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present. Generate potential solutions: Brainstorm a list of possible ...
Problem solving is the process of identifying a problem, developing possible solution paths, and taking the appropriate course of action. ... RCA uses a specific set of steps, with associated tools like the "5 Why Analysis" or the "Cause and Effect Diagram," to identify the origin of the problem, so that you can:
The how-how diagram is a simple and straightforward method that is used to generate multiple ideas to solve a specific problem. It provides an effective structure for organizing possible ideas and solution options all in one place. It works by repeatedly asking " How can this be solved? " until you can no longer break the answers any further.
Create innovative solutions and solve tough problems fast with these problem-solving techniques! Features . ... Participants in this activity are asked to annotate a diagram of a fish, first adding the problem or issue to be worked on at the head of a fish before then brainstorming the root causes of the problem and adding them as bones on the ...
Ishikawa diagrams are often used to identify the underlying cause of a failure in a product or process. Problem-solving teams should first create a problem statement that includes information such as: what product failed, failure observations, the number of failed units, and the customer's description of the failure.
An Ishikawa diagram, also known as a fishbone diagram or cause-and-effect diagram, is a visual representation used to analyze and display the potential causes of a specific problem or effect. This diagram is named after Professor Kaoru Ishikawa, a Japanese quality control statistician, who popularized its use in the 1960s.
A simple Venn diagram example. The overlapping areas between the two boundaries describe the elements which are common between the two, while the areas that aren't overlapping house the elements that are different. Venn diagrams are used often in math that people tend to assume they are used only to solve math problems.
Your tape diagram is like a map guiding you to the treasure of the solution. It's time to put your diagram to work. Solve the problem using the insights your diagram provides. Label the sections, incorporate your gathered information, and let the magic happen. Putting It into Practice. Now, let's bring all this theory to life with an example.
Here's a breakdown of a common problem-solving process, presented in a pointwise manner: 1. Identifying the Problem. The first step in the problem-solving process is clearly defining the issue. This involves gathering relevant Information, observing patterns or trends, and understanding the impact of the problem on stakeholders.
Summary. The problem with an AI-first strategy lies not within the "AI" but with the notion that it should come "first" aspect. An AI-first approach can be myopic, potentially leading us ...
Netflix. The three-body problem is a centuries-old physics question that puzzled Isaac Newton. It describes the orbits of three bodies, like planets or stars, trapped in each other's gravity. The ...
By doing visual brainteasers like the ones in this list, you're sharpening those skills. Think of it as a workout for your brain. 1. Math puzzles. Brainsnack. Don't read the word "math ...
View PDF HTML (experimental) Abstract: We study the generalization capability of Unsupervised Learning in solving the Travelling Salesman Problem (TSP). We use a Graph Neural Network (GNN) trained with a surrogate loss function to generate an embedding for each node. We use these embeddings to construct a heat map that indicates the likelihood of each edge being part of the optimal route.
In other words, 3 Body Problem 's three-body problem is unsolvable because Liu wanted to write a story with an unsolvable three-body system, so he chose one of the three-body systems for which ...
Edited by Lynn Levy. Engineered by Efim Shapiro. Featuring Dennis Overbye. The show "3 Body Problem" premiered on March 21 and quickly became one of Netflix's most-watched titles. It is an ...
Working toward design thinking that gets to the heart of problem solving. The design thinking workshop was a valuable learning opportunity, not only for the children but also for the EY team. We were able to adjust the workshop content based on the children's level of engagement, and establish our fundamental approach to design thinking.