

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, the complete list of high school classes.
Coursework/GPA

Are you wondering which classes to take in high school? Do you want to find out what courses may be offered for each subject?
We've compiled a complete list of high school classes for you to see all the possible course options high school students may have. We'll cover everything from science and math to electives and the humanities.
How to Use This List
This list was created by researching the classes offered at numerous high schools , both public and private, across the country. Classes are alphabetically organized by subject. While there is a separate section for AP classes at the bottom of the list, other varying levels of difficulty for the same class, such as "honors" or "introductory", were not included in order to make reading the list easier.
This list's purpose is to show you all the possible class options you may have as a high school student. You can use it as a starting point for doing a more in-depth study of your own school's course offerings.
Read through the list below, making note of any courses that you may want to take in the future, then look to see if your school offers them. To find out which classes your own high school offers, look through your school's course catalog, check the school website, or speak with your academic adviser.
What If Your School Doesn't Offer One of the Classes Listed Below?
It would be impossible for any single school to offer every course in this list ; there are simply too many. Schools decide which classes to offer based on multiple factors, including student interest, school location, and teacher expertise.
If you are interested in one of the courses listed below but don't see it offered in your school's course catalog, first talk to your guidance counselor or the department head. Your school may, in fact, offer the course, but under a different name. If there is no comparable course and you are really interested in the subject, you may be able to do an independent study or take the course at a local community college for credit. Ask your guidance counselor for more information on pursuing this option.
Complete List of High School Classes
- Business law
- Business management
- Consumer education
- Entrepreneurial skills
- Introduction to business
- Personal finance
Computer Science/ Information Technology
- App development
- Audio production
- Computer programming
- Computer repair
- Film production
- Graphic design
- Media technology
- Music production
- Video game development
- Web programming
- Word processing

- American literature
- British literature
- Contemporary literature
- Creative writing
- Communication skills
- English language and composition
- English literature and composition
- Literary analysis
- Modern literature
- Popular literature
- Technical writing
- Works of Shakespeare
- World literature
- Written and oral communication
Family and Consumer Science
- Chemistry of foods
- CPR training
- Culinary arts
- Early childhood development
- Early childhood education
- Family studies
- Fashion and retail merchandising
- Fashion construction
- Home economics
- Interior design

Foreign Language
- American Sign Language
- Ancient Greek
- Computer math
- Consumer math
- Fundamentals of math
- Integrated math
- Math applications
- Multivariable calculus
- Practical math
- Pre-algebra
- Pre-calculus
- Probability
- Quantitative literacy
- Trigonometry
Performing Arts
- Concert band
- Marching band
- Music theory
- Theater technology
- World music

Physical Education
- Lifeguard training
- Racket sports
- Specialized sports
- Weight training
- Agriculture
- Earth science
- Electronics
- Environmental science
- Environmental studies
- Forensic science
- Marine biology
- Oceanography
- Physical science

Social Studies
- Cultural anthropology
- Current events
- European history
- Global studies
- Human geography
- International relations
- Macroeconomics
- Microeconomics
- Modern world studies
- Physical anthropology
- Political studies
- Religious studies
- US government
- Women's studies
- World history
- World politics
- World religions
Visual Arts
- Art history
- Digital media
- Jewelry design
- Photography
- Printmaking
Vocational Education
- Auto body repair
- Auto mechanics
- Building construction
- Computer-aided drafting
- Cosmetology
- Criminal justice
- Driver education
- FFA (Future Farmers of America)
- Fire science
- Heating and cooling systems
- Hospitality and tourism
- JROTC (Junior Reserve Officers' Training Corps)
- Metalworking
- Production technology
- Refrigeration fundamentals
- Woodworking

Advanced Placement Classes
Ap capstones.
- AP Research
- AP Art history
- AP Music theory
- AP Studio art: 2-D design
- AP Studio art: 3-D design
- AP English Language and Composition
- AP English Literature and Composition
History & Social Science
- AP Comparative government and politics
- AP European history
- AP Human Geography
- AP Macroeconomics
- AP Microeconomics
- AP Psychology
- AP United States Government and Politics
- AP United States History
- AP World History
- Math & Computer Science
- AP Calculus AB
- AP Calculus BC
- AP Computer Science A
- AP Computer Science Principles
- AP Statistics
- AP Chemistry
- AP Environmental Science
- AP Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism
- AP Physics 1: Algebra-Based
- AP Physics 2: Algebra-Based
World Languages and Cultures
- AP Chinese Language and Culture
- AP French Language and Culture
- AP German Language and Culture
- AP Italian Language and Culture
- AP Japanese Language and Culture
- AP Spanish Language and Culture
- AP Spanish Literature and Culture
What's Next?
Now that you know all the possible high school classes out there, which ones should you take? Read our guide to get expert advice on the classes you should take in high school.
Wondering which classes you will need to take in order to graduate high school and get accepted into college? Check out our guide on the standard high school curriculum , as well as the classes college admissions officers are looking for.
Trying to decide whether to take the ACT or the SAT? Read our guide to figure out which test will get you a better score!
Christine graduated from Michigan State University with degrees in Environmental Biology and Geography and received her Master's from Duke University. In high school she scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT and was named a National Merit Finalist. She has taught English and biology in several countries.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
With 95 Kinds of High School Diplomas, What Does ‘Graduation’ Mean?

- Share article

Graduating from high school is a milestone in students’ lives. But those diplomas can mean very different things from state to state and district to district. They can indicate that students mastered challenging college-prep courses, cruised through a series of watered-down classes, or lots of things in between.
A new report tries to quantify that variation. The latest edition of “How the States Got Their Rates,” by the group Achieve, surveyed all the states and found that 95 different kinds of diplomas were conferred on graduating students in 2015. The analysis focuses on how many types of diplomas were available and the coursework and tests that students must complete to earn each type. (The study examines only math and English/language arts coursework. All the states’ coursework requirements for their various kinds of diplomas are here .)
Achieve did the same analysis for 2014 and found 93 kinds of diplomas were handed out to students. It’s part of the organization’s ongoing push to draw attention to the real variation in students’ accomplishments, even as people cheer a rising high school graduation rate .
As states report their grad rates, they rarely disclose the complexities of how many students earn each kind of diploma, Achieve has found. That makes it hard to analyze how many are getting a rigorous high school education that sets them up them well for college or work, and how many are leaving school ill-prepared for the future.
“When states offer students anything other than a college- and career-ready diploma option, we owe it to students to ensure that whichever option they choose will leave them prepared to pursue the future of their choosing after high school,” Sandy Boyd, Achieve’s chief operating officer, says in a press release accompanying the new report.

Eight states have set the bar high, expecting all students to complete a “college-and career-ready” set of courses—at least three years of math, through Algebra 2, and four years of college-prep English—in order to graduate. Delaware, the District of Columbia, Georgia, Kentucky, and Tennessee fell into this category in 2014 and 2015. Minnesota, Nebraska and West Virginia joined that list in 2015.
Sixteen states don’t offer any kind of diploma that requires students to complete the college- and career-ready math and English sequence Achieve recommends. In 27 states, there are multiple diploma options, and at least one of those options in each state allows students to graduate without completing Achieve’s recommended math and English minimums.
Achieve wants to see states do a better job of explaining their various diploma options to parents and students, and to publish “accessible and clear” information about the proportions of students who earn the various kinds of diplomas. Disaggregating those numbers by student subgroup, and pairing them with information about which students are opting out of college- and career-ready diplomas in states that allow them to do so, would shed valuable light on what diplomas mean in each state, Achieve argues.
For more stories about high school graduation rates, see:
- Graduation Rate Hits Record High of 83.2 Percent. Should Obama Take Credit?
A version of this news article first appeared in the High School & Beyond blog.
Sign Up for EdWeek Update
- Trying to Conceive
- Signs & Symptoms
- Pregnancy Tests
- Fertility Testing
- Fertility Treatment
- Weeks & Trimesters
- Staying Healthy
- Preparing for Baby
- Complications & Concerns
- Pregnancy Loss
- Breastfeeding
- School-Aged Kids
- Raising Kids
- Personal Stories
- Everyday Wellness
- Safety & First Aid
- Immunizations
- Food & Nutrition
- Active Play
- Pregnancy Products
- Nursery & Sleep Products
- Nursing & Feeding Products
- Clothing & Accessories
- Toys & Gifts
- Ovulation Calculator
- Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
- How to Talk About Postpartum Depression
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
What School Subjects Do You Need in High School?
Verywell / Nusha Ashjaee
- Basic School Subjects
- College Preparation
While some high school subjects are required, others can be selected. Finally being given more of a choice in what a student studies can be freeing, but also overwhelming. What courses are best? It's most important to first consider what is needed to graduate. Then, parents and teens can work together to choose subjects that not only engage their interests but also have their future plans and goals in mind.
For example, students who plan to go to college may be required to take more years of a foreign language or other classes required by the schools they are interested in. A student who is interested in pursuing a career in construction may want to take an industrial arts class.
School Subjects
- Writing or Composition
- Trigonometry and/or Calculus
- Biology (typically has advanced class options)
- Chemistry (typically has advanced class options)
- Earth or Space sciences
- Physics (typically has advanced class options)
- U.S. Government
- U.S. History
- World History
- Foreign Language
- Physical Education/ Health
- Arts, such as music, photography, or ceramics
- Computer applications, graphic design, or web design
- Business, law
- Cooking and other life skills
- Physical education
- Trade field studies such as auto mechanics or nursing
- Personal finance
School Subjects You Need to Graduate
Ideally, teens should start high school with a basic plan of the classes they will need to take in order to graduate. Every state has different requirements for obtaining a high school diploma , and each school varies greatly in what they offer to give kids a chance to fulfill them.
The school's guidance/counseling department can help students understand the requirements for graduation and how their coursework aligns with them.
The basic requirements generally include the following:
English/Language Arts
Studying the English language and literature is an important part of high school for every student regardless of their post-school plans. In addition to studying important pieces of literature, English classes teach teens about writing and speaking.
Most states require four years of English or language arts classes. The main English classes in high school include:
Mathematics
In high school, students dig into several different types of math. Algebra and geometry are required at most high schools, and students may choose to take advanced math classes if they are offered.
Most states require three or four years of math coursework in high school. The main math classes in high school include:
Basic life sciences (e.g. biology) and physical sciences (chemistry, physics, etc.) are required at most high schools. These classes often include lab components that allow students to perform hands-on experiments.
Most states require two to three years of science coursework in high school. These may include:
Social Studies/History
Understanding how the world works is important for young adults. In high school, students will study history and government and learn about how social studies affects their lives.
Most states require three to four years of social studies coursework in high school, including:
Foreign Languages
Learning a second language is important in today's global world. While many high schools offer foreign language courses, only 11 states require students to take a foreign language course. High school students can fill these requirements by learning the basics of at least one foreign language, and they may be able to choose to take advanced classes to learn more.
Common languages offered in high school include:
- Mandarin Chinese
Other possible language offerings include Russian, Latin, American Sign Language, and German.
Physical Education and Health
Physical education and health classes can teach high schoolers how to care for their body's fitness and nutritional needs. Many states require at least one unit of P.E. to graduate. Other states have P.E. as an elective.
School Subjects for College Preparation
Students planning to go to college should consider how colleges will look at their courses during the application process. Grade point average (GPA) is important, but coursework should also demonstrate academic rigor.
When planning, it can be helpful to balance standard high school courses with some that are more challenging. Additionally, students can do this—and even get a head start on college—by taking advanced placement (AP) or college classes.
AP classes are more rigorous courses that teach subjects at an introductory college level. Some of the most common AP courses that are available include Calculus AB, U.S. History, English Literature, Biology, Statistics, Chemistry, and Psychology.
Students who take AP classes have the option to take an AP test in the spring. If they get a certain score, they can get credit for the course at many colleges.
College Credit Courses
Many high schools offer opportunities to gain college credit, and the counseling department can inform students about any such offerings as well.
These may be online or in-person classes through programs offered by colleges and universities, and they may be taught by a professor or a high school teacher. Dual-credit programs allow students to fulfill their high school requirements while obtaining some college credits free of charge.
In addition to the basic classes, there are usually plenty of opportunities to take electives in various areas of study. These can not only broaden a student's academic knowledge but also teach them valuable life skills.
In some cases, a student may be given the freedom to choose one class from a select group of options required in the school's curriculum. In others, a student may have room in their schedule to choose to study something simply based on their interests and aspirations.
Examples of elective classes may include:
Students on a vocational track may be able to gain some hands-on learning in fields such as metalworks and woodworking. Many schools even offer the opportunity to gain certificates or licenses that will help them in their future careers.
A Word From Verywell
Choosing high school classes requires planning both as a student enters school and throughout their high school experience. The right classes are challenging and engaging, but not unrealistically rigorous or overwhelming.
An ideal schedule can help a student succeed , enjoy learning, and have a good academic experience while preparing them for their future plans, whatever they may be.
It's important for teens and their parents to talk about their career aspirations. Discuss interest areas and review their schedule together to help them make the most out of their school's offerings.
Education Commission of the States. 50-state comparison .
American Councils for International Education. The National K-16 Foreign Language Enrollment Survey Report .
College Board. Program Summary Report .
By Denise Witmer Denise Witmer is a freelance writer and mother of three children, who has authored several books and countless articles on parenting teens since 1997.
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
Definition of coursework
Examples of coursework in a sentence.
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'coursework.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
1890, in the meaning defined above
Dictionary Entries Near coursework
Cite this entry.
“Coursework.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/coursework. Accessed 11 Apr. 2024.
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
Your vs. you're: how to use them correctly, every letter is silent, sometimes: a-z list of examples, more commonly mispronounced words, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), absent letters that are heard anyway, popular in wordplay, the words of the week - apr. 5, 12 bird names that sound like compliments, 10 scrabble words without any vowels, 12 more bird names that sound like insults (and sometimes are), 8 uncommon words related to love, games & quizzes.


Cal State Apply Quick Start Information and FAQs
- Last updated
- Save as PDF

What is Cal State Apply?
Cal State Apply is a Centralized Application Service (CAS) that simplifies the process of applying to California State University (CSU) programs. You start by selecting the programs you wish to apply to, then you submit one application that includes all necessary materials. Once received by Cal State Apply, your application and materials are transmitted to all of your selected programs.
Start your 2023-2024 cycle application .
Start your 2024-2025 cycle application .
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What type of student am i.
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
A Guide to the Education Section of the Common App

Your GPA and SAT don’t tell the full admissions story
Our chancing engine factors in extracurricular activities, demographics, and other holistic details. We’ll let you know what your chances are at your dream schools — and how to improve your chances!
Our chancing engine factors in extracurricular activities, demographic, and other holistic details.
Our chancing engine factors in extracurricular activities, demographic, and other holistic details. We’ll let you know what your chances are at your dream schools — and how to improve your chances!
The Education section of the Common App is exactly what it sounds like: it’s where you tell your chosen colleges about your high school academic performance. From grades to class rank to what courses you took, colleges will want to get a detailed look at what–and how–you did in high school.
Four years of academic work creates a great deal of information to convey. As with other sections of the Common App, you’ll only have to actually enter this information once, and it will be copied to all the colleges to which you submit applications. Since basically every college requests the same or similar educational information, this can save you a lot of time and typing.
Before you begin filling out the Education section, you’ll want to gather the necessary data from your records and clarify any requirements that are unclear to you. In this post, we’ll go over the specific questions you’ll be asked and the information you’ll be expected to provide in the Education section of the Common App.
Are you unsure what a “weighted” GPA means? Wondering where and how to tell colleges that you graduated early from high school? Stressing out about listing your academic and career aspirations under the Future Plans section? Read on for more application guidance from CollegeVine on these topics and more.
Is your GPA high enough to get into your dream school? Calculate your admissions chances now.
Accessing the Education Section
First of all, to fill out the Common App’s Education section, you’ll need to get to it. In order to access the Education section of your Common App, you’ll need to log into your Common App, click on the Common App tab, and click on Education in the column on the left side.
The Education section is divided into nine subsections; click on the title of each subsection to open it up. Each part of the Education section will guide you through questions covering different aspects of your educational history, from where you’ve gone to school to how you did in school.
Below, we’ll go through each part of the Education section, from “Current or Most Recent School” to “Future Plans,” with more detailed instructions on how to complete the questions you’ll find there.
The provided screenshots are taken from a sample student Common App profile that we at CollegeVine have set up. Your own Common App profile may look slightly different, depending on what information you’ve already entered.
When you’re finished filling out a section of the Education section, hit the “Continue” button to move along to the next one. You can move directly to other parts of the Education section by clicking the appropriate header.
Current or Most Recent School Section
In this section, the Common App will collect information about the school you currently attend or have most recently attended.
Current or Recent School Lookup
Your first task is to tell the Common App what high school you attend now or most recently attended, as well as various facts about that high school. Fortunately, you don’t have to provide all this information from scratch; the Common App system includes a database of high schools that you’ll search through to find and choose yours.
When you open up the Current or Most Recent School section, you’ll see this:
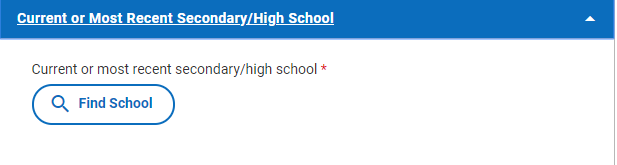
Click on the Find School link. The box below will pop up:
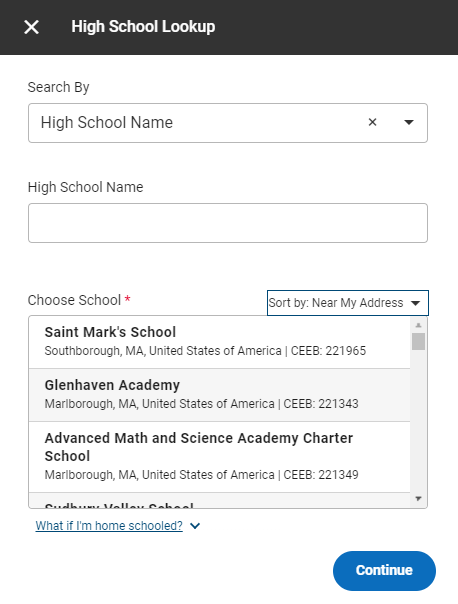
Now you can search for your high school. On the top of the box you’re given a number of search options; you can search by school name, CEEB code (a number assigned to your school by the College Board ), or location. Fill out whichever of these fields works best for you, and you’ll see your results appear below.
Scroll through the list to find your high school and click on the circle in front of its name; then click the “Continue” button to add that school as your current or most recent high school. When you return to your Current or Most Recent School section, you’ll see that your school and its contact information have been added to your Common App. Below, you can see that our sample student has designed Bronx High School of Science as their current or most recent school.
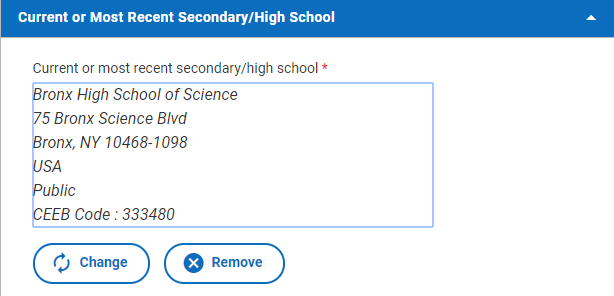
If you made a mistake or need to change what school you’ve designated, simply click “Change” or “Remove” under the school’s information and use the search function again.
If you have been homeschooled and are a member of a larger homeschooling organization, you may be able to find that organization using the search function. If not, or if you were homeschooled outside of any such organization, scroll to the bottom of your search results and choose the option that says “Home schooled.” You’ll be prompted to enter some additional information manually.
What if you can’t find your school using the search screen? First, double-check the information you’ve entered; then, triple-check it. Try typing only the first word or two of your high school’s name and going through the list, or using a different search field than you initially tried.
The search function can be a bit finicky when it comes to searching by school name, so make sure you’re using your high school’s full formal name, not a nickname. For instance, our sample student would need to search for the full name “Bronx High School of Science,” or perhaps just “Bronx” or “Bronx High School.” Even if some people refer to this school simply as “Bronx Science,” searching for that school name will not bring up the correct result.
If you absolutely can’t find your high school in the database, scroll down to the bottom of the list of school results and select “I don’t see my high school on this list.” You’ll then need to enter your school’s information manually.
Other Questions
Once you’ve designated your current or most recent school, you’ll have to answer a list of questions about that school, seen in the following screenshot. Below the screenshot, we’ll go over how to respond to each of those questions.
One more note on completing this section: if you don’t have a school counselor, fill in these answers for whoever has “overseen your academic progress,” as the Common App puts it, and will fill out the School Report section of your Common App. This might be a school principal or another school official, or a parent if you were homeschooled; it depends on your situation. Ask your counselor or school official if you have any questions about how to identify them in this section.
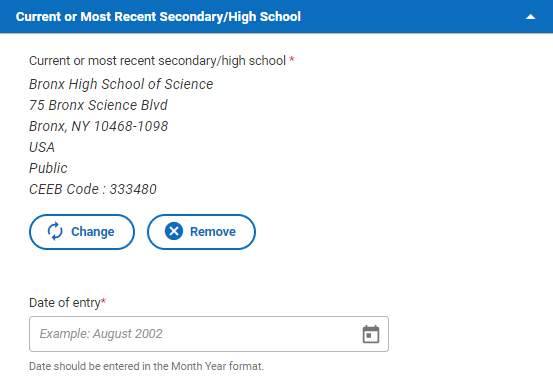
- Date of entry: Choose the month and year that you started attending this school.
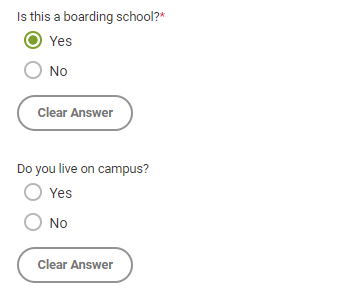
- Is this a boarding school?: Do some or all students sleep at your school? If so, answer yes; if not, answer no. If you answer yes, you’ll be asked whether you personally reside at the school; answer yes if you do, no if you don’t.
- Did you or will you graduate from this school?: Answer yes if you already graduated from this school or if you plan to graduate from this school. Answer no if you no longer attend this school but didn’t graduate from it, or if you don’t plan to graduate from this school. Once you answer this question, the Common App will ask you to specify the month and year you left or will leave this school.
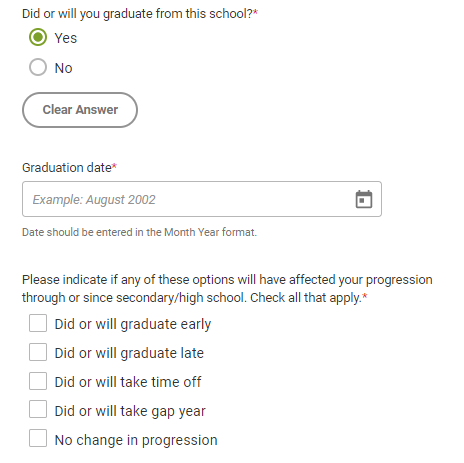
- Counselor’s prefix: Choose between Dr., Mr., or Ms. in the drop-down menu based upon which prefix your counselor uses in official correspondence.

- Counselor’s first name, counselor’s middle initial, and counselor’s last name: Fill in your counselor’s full first and last names, and check your spelling. If you don’t know your counselor’s middle initial, that’s fine; just leave that field blank.
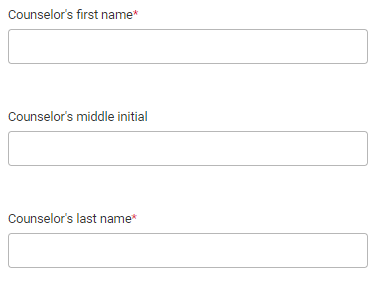
- Counselor’s job title: Fill in your counselor’s formal job title; if your school doesn’t have a counselor, fill in the job title of whichever school official you’re using for this section.

- Counselor’s email and counselor’s phone: Fill in your counselor’s requested contact information. If your counselor is outside the United States, make sure you include the correct country code in their phone number. Also include their phone extension if they have one. Your counselor is an important element of your application, so double-check that you have transcribed this contact information correctly.
Other School Section
In this section, you’ll enter information about any other schools you’ve attended for high school, aside from the one you’re currently attending or most recently attended. For instance, if you moved to a new city during high school, this is where you’ll put information about the school you attended before you moved. If you were homeschooled for part of high school but then attended a traditional school, you’ll list your homeschooling experience as an additional school here.
When you first open up the Other School section, you’ll see the following:
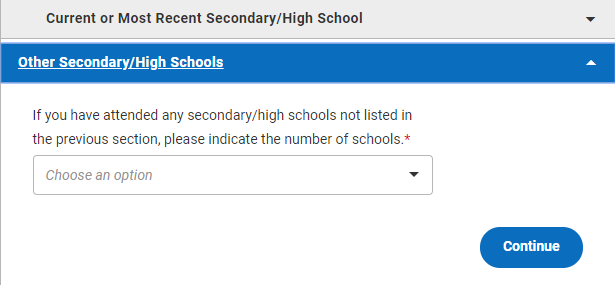
The question reads If you have attended any other schools, please indicate the number of schools . If you have not attended any other high schools, choose 0 from the dropdown menu; you won’t have to answer any other questions in this section.
If you have attended one or more other schools, choose the number of schools you’ve attended, excluding your current or most recent school—the one you talked about in the last section. For instance, if you attended a total of three different high schools including your most recent high school, you would choose 2 in this menu. You can add up to three additional high schools.
If you choose any number other than 0 for this question, you’ll need to add more information about the school(s) you attended. For each additional school, you’ll use the search function to search the Common App database, just as you did for your current or most recent school in the last section. You can refer back to that section for advice on looking up your school(s). If you were homeschooled or can’t find your school, you’ll need to enter its information manually, just as we described in the last section.
Once you’ve chosen a school, your screen should look something like the screenshot below. We’ve indicated that our sample student has attended Los Angeles School of Global Studies.
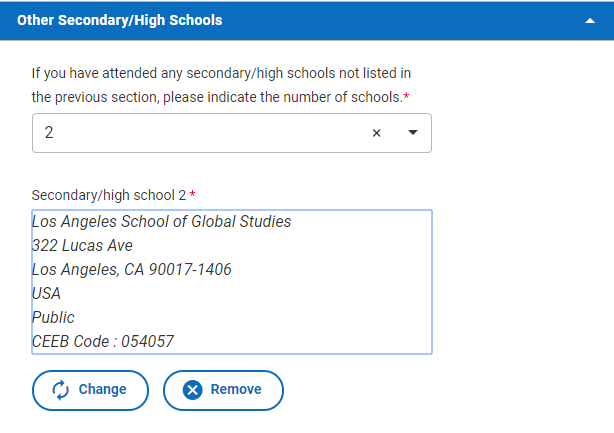
Notice that for this student, Los Angeles School of Global Studies has been labeled “School 2.” Bronx High School of Science, which our sample student designated as their current school, is School 1. Additional schools that they had attended, if there are any, would be School 3 and School 4.
Below the school information, you’ll need to enter the dates between which you attended that school. Under School 2 from date , enter the month and year you started attending that school. Under School 2 to date , enter the month and year you stopped attending that school. Repeat this process for any additional schools you might have.
College & Universities Section
In this section, you’ll provide information about any colleges or universities you have already attended. This section is relevant to you if you took any courses at a college or university while you were in high school through a “post-secondary option” or similar program. In this context, AP and IB courses do not count as college courses.
When you initially open up the Colleges & Universities section, it will look like this:
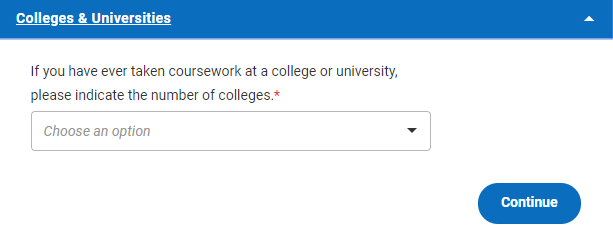
The first question reads as follows: If you have taken a college/university course, please indicate the number of colleges . If you have not taken any college courses in high school, choose “0” in the dropdown menu; there will be no further questions for you in this section.
If you have taken one or more college courses in high school, choose the number of colleges you attended using the drop-down menu, up to three colleges. (Remember, this is the number of colleges you were enrolled at, not the number of courses you took.) This will open up additional questions for you to answer.
Once you indicate that you attended one or more colleges while in high school, you should see the following list of questions for each college. Below the screenshot, we’ll go over the details of how to answer each of these questions.
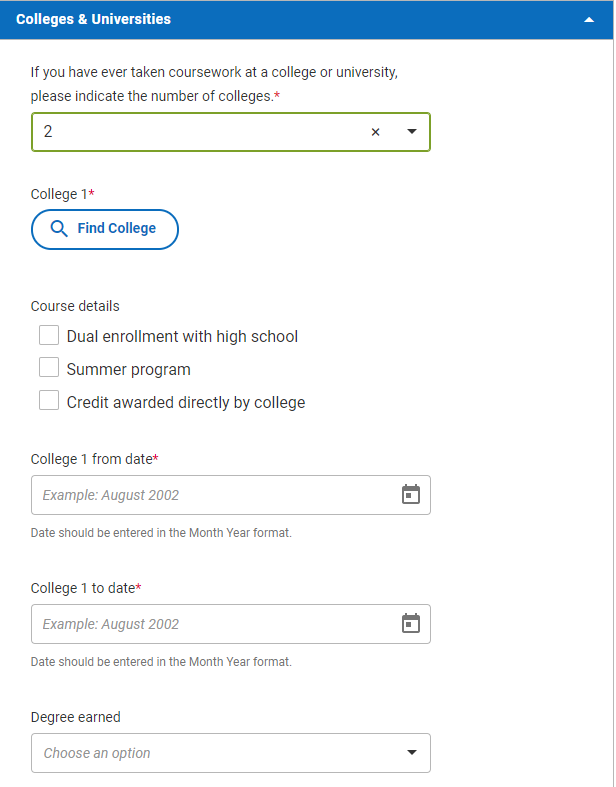
- College 1 lookup: Here, you’ll look up the college you attended in a system very similar to that which you used to look up your high school(s). Our advice above about looking up your high school(s) applies here as well. If you’ve checked and rechecked your search terms and you still can’t find your college, choose “I do not see the college I’m looking for on this list,” and manually enter the college’s information when prompted.
- College 1 from date: Choose the month and year you started attending this college.
- College 1 to date: Choose the month and year you stopped attending this college.
- Degree earned: If you earned a degree from a college while attending high school, choose the degree you earned from a drop-down list. If, like most students, you did not earn a degree from a college while attending high school, you don’t need to answer this question.
You’ll need to repeat these steps for any additional colleges you attended while you were in high school.
Grades Section
In this section, you’ll provide information about your academic performance in high school- specifically, your grades as expressed by your class rank and GPA. When you click on Grades, you’ll see a screen like the one below:
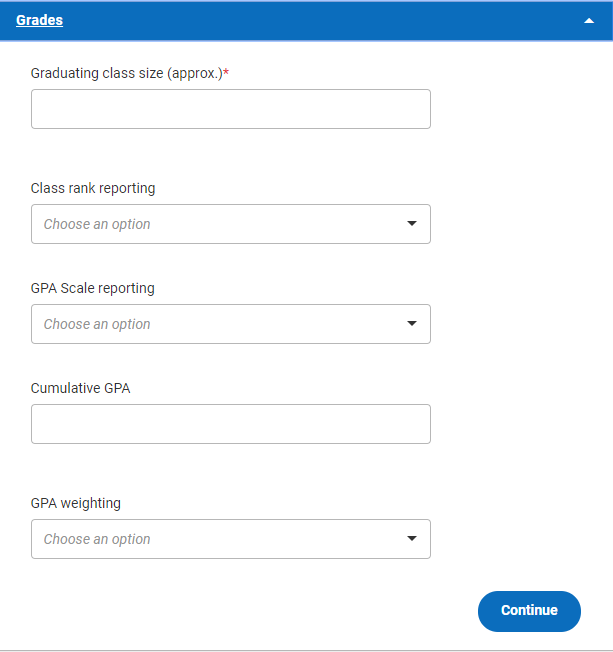
We’ll go over each of the questions you need to answer below. It’s likely that you won’t know all of these answers offhand, but your school should be able to answer them for you. In general, if you don’t know the answer to one of these questions, or if you don’t know what the question means in the context of your high school’s particular policies, you should ask your counselor or equivalent school official.
- Graduating class size: Enter the number of students in your graduating class. Be aware that this number may change from time to time as students’ plans change.
- Class rank reporting: This question covers both how your school ranks students, and what your actual rank is within your class. First, you’ll choose from the initial drop-down menu to indicate whether your high school ranks students exactly or by decile, quintile, or quartile. (Your counselor can explain what this means.) If, as with some high schools, your school has decided not to keep track of class rankings, you’ll choose None. If your school does rank students, you’ll have to answer two additional questions.
- Class rank: If your high school ranks students, you’ll either type in your numerical rank or choose your decile, quintile, or quartile rank from a drop-down menu.
- Rank weighting: If your high school ranks students, you’ll need to choose whether your rank is weighted or unweighted from the drop-down menu. Weighted rank uses weighted GPAs; unweighted rank uses unweighted GPAs. We’ll go over what that means below.
- GPA scale: Choose the number of points in your school’s GPA scale from the drop-down list. This numerical answer might be anywhere from 4 to 100, depending on your school’s grading system.
- Cumulative GPA: Enter your cumulative GPA—that is, your GPA taking into account all the high-school courses you’ve taken—just as it appears in your school’s records. (Your GPA is basically an average of the grades you’ve received on your report cards.)
- GPA weighting: Choose whether your GPA is weighted or unweighted from the drop-down menu. Essentially, a weighted GPA is one in which the number of points awarded for an A grade in the course varies, usually according to how difficult the particular course is. For instance, a high school might use a scale of zero to four for most of its courses, but a scale of zero to five for its honors, AP, or IB courses. If you don’t know your GPA on a 4.0 scale, use our GPA converter to find it .
Be aware that the colleges you’re applying to will have access to your full transcript as well as the information you enter here. They’ll see not only your GPA, but your individual grades, any outliers, and your grade trend across your high-school career. Many colleges will actually recalculate your GPA based on their own criteria, so the information you enter here may not be evaluated exactly as you might think it will be.
How does class rank and GPA affect your chances? Use our admissions calculator to see your chances of admission for free. Sign up now to see your chances.
Current or Most Recent Year Courses Section
This section is where you’ll provide detailed information about the courses you’re currently taking, or, if you are no longer in high school, the courses you took during your most recent year of high school. For most students, this will simply mean entering the classes you’re taking during your senior year. Before you start filling out this section, you’ll probably want to have a copy of your schedule on hand.
First of all, you’ll need to report how many courses you’re taking this academic year. The question reads as follows: Please list all courses you are taking this academic year. If you are not currently enrolled, please list courses from your most recent academic year. How many courses would you like to report?
Choose the number of courses you’re taking or took for the year from the drop-down menu. The number you report here will determine what questions you are prompted to answer next.
Once you’ve provided the number of courses you’re taking, you’ll enter information for each of these courses so that admissions officers can evaluate your academic course load. As an example, here’s a screenshot from our sample student’s Common App profile. Note that the sample student has responded that they are only taking one course this academic year; you’ll almost certainly be taking more than that.
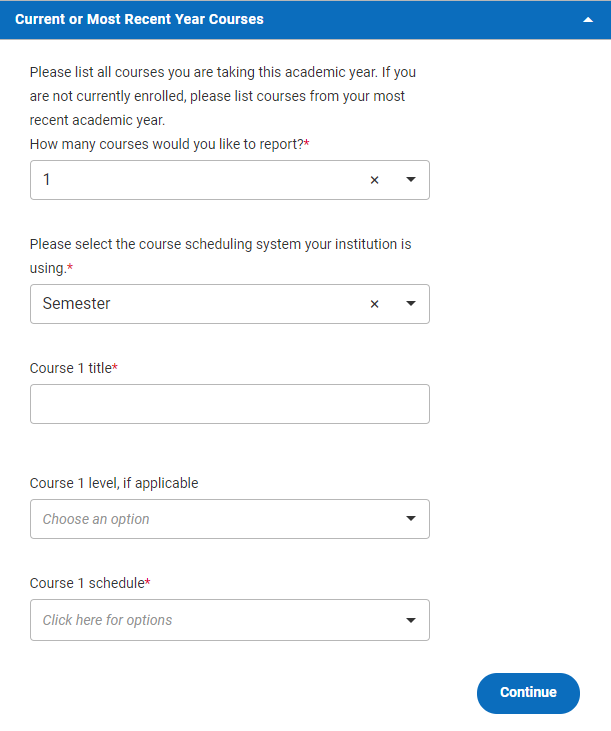
For the question Please select the course scheduling system your institution is using, you’ll be invited to choose between the options of “semester,” “trimester,” and “quarter” in the drop-down menu. This question refers to how the school year is split up at your school—into two, three, or four periods, respectively, for which a new set of grades are added to your transcript. If you’re unsure, ask your counselor which system applies to your school.
Next, you’ll be asked to enter information for each course. Under Course 1 title , type the full name of your first course. (This may be different from what you call the course on an everyday basis—you may refer to “Algebra II and Trigonometry” as simply “Trig,” but colleges will want to see the full course title.)
Under Course 1 level, if applicable , click to choose a designation that applies to your first course, if any. For instance, if your World History course is an honors course in your school’s system, you would click “Honors” here. Ask your teacher or counselor if you’re not sure about a particular course. If your course has none of these designations, don’t click anything for this question.
Under Course 1 schedule , select whichever option from the drop-down menu applies to that particular course. (The options you see here will vary depending on how you answered the question about your school’s course scheduling system.) Again, ask your teacher or counselor if you’re not sure.
You’ll repeat these steps for each of however many courses you indicated you’re taking this year or took in your most recent year. They’ll be listed as Course 2, Course 3, and so on.
Course rigor is an important factor for getting accepted to a top school. See how course rigor affects your chances of admission with CollegeVine’s chancing calculator.
Honors Section
In this section, you’ll list and describe up to five academic honors that you’ve received. Since choosing and detailing those honors can be complicated in and of itself, we at CollegeVine have chosen to write a separate post on this issue. Head over to our post on “Reporting Honors and Awards on the Common App” to learn what you should report in this section and how you should report it, from Honor Roll to summer programs to National Merit scholarships .
Community-Based Organizations Section
In this section, you’ll answer questions about any community-based organizations which may have helped you with the college application process without charging a fee. These organizations might include Questbridge, Upward Bound, the Boys and Girls Club, or others.
If you’ve been aided by a community-based organization like these, you likely know it already. If you’re not sure whether an organization that has helped you qualifies under this section, an employee or leader of that organization may be able to clarify its status for you, or your school counselor may be able to help.
When you open this section, you’ll initially see the following:
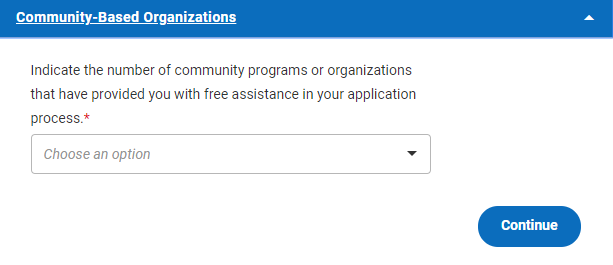
The question reads, Indicate the number of community programs or organizations that have provided you with free assistance in your application process . If no such program or organization has provided you with free assistance in the college application process, you’ll choose 0 from the drop-down menu, and you won’t need to answer any more questions in this section.
If you’ve been provided with free assistance by one or more organizations like this, choose the number of organizations that have assisted you from the drop-down menu. You can enter up to three organizations. You’ll then need to provide additional information about the organization(s) that you worked with.
If you indicate that you have been assisted by one or more community-based organizations, additional questions will appear for you to answer. That screen should look like the screenshot below. After the screenshot, we’ll provide more details on how to answer each of these questions.
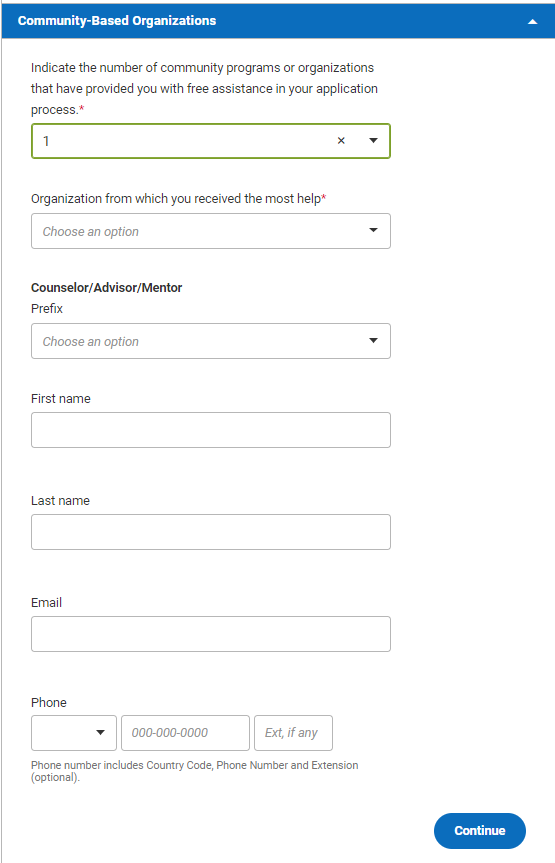
Organization 1: Choose the name of the organization that has assisted you from the drop-down list. If your organization is not listed, choose “Other.” (Hint: the list is alphabetical, and “Other” is listed under the organizations that start with O.) If you choose “Other”, an additional field will appear where you’ll type the name of your organization.
The rest of the questions in this section refer to the individual counselor, advisor, or mentor who worked directly with you in this organization. If you’re not sure whose information you should use for this section, ask whoever you have contact with in the organization, and then speak to that person directly to make sure they are comfortable having their information released.
- Counselor/Advisor/Mentor Prefix: Choose Dr., Mr., or Ms. from the drop-down menu based on what prefix your mentor uses in official correspondence.
- First name, middle initial, and last name: Enter your mentor’s full name. If you don’t know their middle initial, that’s okay—just leave that field blank.
- Email and Phone: Enter your mentor’s contact information. If you have multiple phone numbers and/or email addresses for your mentor, ask them which ones they would prefer you to use. If your mentor is outside the United States, make sure you include the correct country code for their phone number.
You’ll answer the same questions for any additional organizations that you’ve indicated have helped you in your application.
Future Plans Section
Finally, we come to the Future Plans section, where you’ll answer two simple questions about your educational and career aspirations. When you open this section, you’ll see the following:
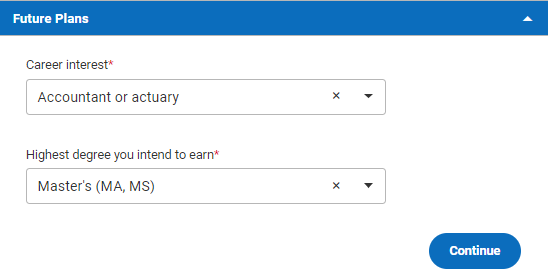
The first question reads Career interest . Here, you’ll choose from a drop-down menu of possible careers. Our sample student has indicated that they’re indicated in becoming an accountant or actuary, but you’ll have many other options. If you don’t see your intended career path in the list, you can either choose the closest available option or choose “Other.” If you haven’t yet decided on a career path, don’t worry- just choose “Undecided.”
The second question reads Highest degree you intend to earn. Here, you’ll choose from a list of possible academic degrees. Our sample student has indicated that they intend to earn a master’s degree, such as an MA or MS. Again, if your intended degree category doesn’t appear in this list, choose “Other,” and if you aren’t sure, choose “Undecided.”
Being asked to specify your future plans so early on in the application process can be a little overwhelming, but you absolutely don’t need to stress out about the questions in this section. Your answers here don’t commit you to anything. Just answer the questions as best you can, and don’t be afraid to choose “Other” or “Undecided” if those answers suit you best.
Concluding the Education Section of the Common App
When you finish the Education section of the Common App, you’re sure to breathe a sigh of relief. You’ve entered a great deal of information, and that information is extremely important to how colleges evaluate your application.
Remember, however, that your Education section doesn’t present a complete portrayal of you as a student and a person. If you’re not totally satisfied with your grades, you still have a chance to wow admissions committees with the other parts of your application, from your activities to your test scores to your essays. You can’t change your grades after the fact, but when you don’t feel like your grades represent you accurately, your full application offers many other opportunities to show yourself in the best possible light.
Be sure to check out some of CollegeVine’s blog posts on other aspects of the Common App, including:
- A User’s Guide to the Common App
- How to Receive a Common App Fee Waiver
- Reporting Honors and Awards in the Common App
- How to Fill Out the Common App Activities Section
- Why Does the Common Application Ask Where my Parents Went to College?
Curious about your chances of acceptance to your dream school? Our free chancing engine takes into account your GPA, test scores, extracurriculars, and other data to predict your odds of acceptance at over 500 colleges across the U.S. We’ll also let you know how you stack up against other applicants and how you can improve your profile. Sign up for your free CollegeVine account today to get started!
Related CollegeVine Blog Posts

Our Services
College Admissions Counseling
UK University Admissions Counseling
EU University Admissions Counseling
College Athletic Recruitment
Crimson Rise: College Prep for Middle Schoolers
Indigo Research: Online Research Opportunities for High Schoolers
Delta Institute: Work Experience Programs For High Schoolers
Graduate School Admissions Counseling
Private Boarding & Day School Admissions
Online Tutoring
Essay Review
Financial Aid & Merit Scholarships
Our Leaders and Counselors
Our Student Success
Crimson Student Alumni
Our Reviews
Our Scholarships
Careers at Crimson
University Profiles
US College Admissions Calculator
GPA Calculator
Practice Standardized Tests
SAT Practice Test
ACT Practice Tests
Personal Essay Topic Generator
eBooks and Infographics
Crimson YouTube Channel
Summer Apply - Best Summer Programs
Top of the Class Podcast
ACCEPTED! Book by Jamie Beaton
Crimson Global Academy
+1 (646) 419-3178
Go back to all articles
Navigating Academic Rigor: What It Means and Why It Matters
/f/64062/800x450/48dddeec73/studying1.jpg)
In the journey through high school and into the world of college admissions, there's a term that you'll likely encounter frequently: academic rigor. But what exactly does it mean, and why does it matter?
As a high school student and aspiring college student, you’re faced with making sense of how college applicants are profiled for admissions. Well, your GPA, or grade point average, is a key indicator of your college readiness, but did you know that most colleges are going to look at your GPA in the context of academic rigor?
And, although academic rigor will be an important consideration for admissions, it’s also something you need to pursue with a balanced approach. In fact, many motivated high school students will find it difficult to strike a balance between academic achievement and other important life activities — sometimes activities as essential as resting, socializing, exercising, and relaxing…
In this blog post, we'll delve into the concept of academic rigor, its significance in both high school and college admissions, and how to navigate it successfully.
Defining Academic Rigor
Academic rigor isn't just about a class being hard or a teacher assigning lots of homework. Academic rigor is a multifaceted concept that encompasses critical thinking, combining knowledge and concepts in new ways , and complex applications of learning.
In short, academic rigor is not the same thing as academic difficulty per se .
Academic difficulty typically refers to how accessible or inaccessible the learning content is for the students being taught, or it may refer to the quantity of learning (amount of reading, homework, etc.) students are expected to do.
Academic rigor requires teaching that fosters deeper forms of questioning, understanding, and analysis — a comprehensive approach to learning that involves:
- depth of content
- conceptual complexity
- higher-level mastery of content — such as performing critical analysis, applied problem solving, or synthesizing concepts to generate new insights
- effective use of advanced study skills in tasks related to note taking, critical thinking, research, and writing…
Academic Rigor — Common Misconceptions
A common misconception about rigor is that it’s just about presenting more challenging content, more advanced concepts, and demanding greater quantities of homework!
Certainly fast-paced instruction and having to keep up with a big reading load or above average amounts of homework can all make a course “difficult.”
Most education experts agree, however, that academic rigor is really about mastering content at a deeper level and about the kinds of thinking students engage and develop.
Academic rigor is not quantified by how much gets crammed into a school day — it is measured in depth of understanding.
Interested in learning more attend one of our free events, learn how to get into ivy league universities from a former harvard admissions officer.
Wednesday, May 1, 2024 12:00 AM CUT
Join us to learn what Ivy League admissions officers look for, and how you can strategically approach each section of your Ivy League application to stand out from the fierce competition!
REGISTER NOW
In her book How to Plan Rigorous Instruction , instructional expert Robyn Jackson says that teachers can incorporate greater academic rigor by “selecting content that is ambiguous, is complex, is layered, and has implicit meaning.”
This kind of complex and ambiguous content makes fertile grounds for a key component of academic rigor: higher-order thinking.
Bloom’s Taxonomy
In 1956 educational psychologist Benjamin Bloom published the Taxonomy of Educational Objectives (aka Bloom’s Taxonomy ). Bloom put common learning processes into a hierarchical order, contrasting lower-order thinking with higher-order thinking.
Bloom’s taxonomy offers insights that can help us grasp what academic rigor really means.
Lower-Order Thinking
- memorizing and summarizing information
- understanding information on a surface level
- comparing and contrasting terms or concepts
Higher-Order Thinking
- probing and questioning ideas and concepts
- understanding and articulating nuances of meaning
- applying concepts and ideas creatively: for authentic problem solving or generating new perspectives…
By the way, this doesn’t mean lower order thinking is “inferior” in some essential way. In fact, a skilled teacher would typically understand that lower-order tasks are important foundational steps that prepare students to be successful in achieving higher levels of content mastery and understanding.
The Ingredients for Rewarding Academic Rigor
A sad reality is that too many students — and too many of their teachers perhaps — associate rigor with the quantity of work assigned — as in being asked to spend more and more time doing homework, being expected to grasp complex concepts without proper support and preparation, or having excessive amounts of reading and memorization to do every week…

Courses with extra work are indeed more difficult, but that kind of difficulty doesn’t always measure up to what academic rigor is really all about.
Academic rigor means making learning challenging in a way that should foster excitement, build confidence, and help students cultivate disciplined forms of critical thinking, argumentation, and problem solving.
Rigorous learning experiences help students understand knowledge and concepts that are complex, ambiguous, or contentious, and… encourage students to think critically, creatively, and more flexibly, and to question their assumptions and think deeply, rather than simply utilize memorization and information recall.
- baylor university — “academic rigor”.
Defined this way, academic rigor shouldn’t stir up dread or angst in students. Instead, academic rigor is something that should make you feel excited and inspired, especially when your teachers add relevance and authenticity to the mix by connecting the learning to topics and real-life problems that resonate with your deeper interests and passions.
Academic Rigor in High School
Your high school years are a prime time for you to embrace academic rigor. Most high school settings offer students a variety of courses that have different levels of academic rigor.
Advanced Placement (AP), International Baccalaureate (IB), and Honors courses, for example — when taught by skilled teachers — should offer you not just accelerated pacing but also higher levels of academic rigor.
Engaging in these rigorous courses not only prepares you for the academic demands of college but also demonstrates your commitment to learning. Colleges value students who actively seek out challenges and display a willingness to explore new horizons.
Finding the Academic Rigor That’s Right for You
If you’re not finding the right opportunities for academic rigor at your school, talk to your school counselor or seek help at your school’s college and career center.
In addition to offerings at your high school, you may also find that local community colleges or other institutions of higher learning in your larger community offer college bridge programs or similar programs that allow you to enroll directly into college courses while still in high school.
Finally, another great option for finding the right opportunities to get the academic rigor you want in subjects you’re interested in is to explore online education offerings . During the pandemic online learning was sometimes seen as an unfortunate necessity, but educators, families, and students also discovered that high quality online learning options can offer both wider horizons and some surprising educational advantages.

Academic Rigor and College Admissions
Colleges are interested in applicants who have engaged with academic rigor in their high school journey. And, most likely, if you’re aspiring to attend a competitive school, you’re already well aware that taking more rigorous courses in high school can make a big difference when you apply to college.
You realize that admissions officers understand that courses with more academic rigor will help you hone your study skills and critical thinking skills — giving you an edge when it comes to applying for college and to showcasing your potential for ongoing academic success.
You’re not wrong about that...
When admissions officers evaluate your academic achievements, they’ll be considering not only your GPA (grade-point average) but also the academic rigor of the courses you completed in high school.
Except for GPA, academic rigor is perhaps more important than any other factor for college admissions at many schools: more important than class rank , than your college admissions essay , or than the letters of recommendation submitted by your teachers and counselors.
According to the National Association for College Admission Counseling (NACAC), “strength of high school curriculum” is the third most important factor for admissions out of sixteen important factors .
Moreover, the highest ranking factor — “the GPA earned in college prep courses” — also involves academic rigor. This means enrolling in at least a few Advanced Placement, Honors, IB, or similar courses can have a significant impact on college admissions.
When it comes to advanced or accelerated courses, Harvard’s admissions officers recommend that “students pursue the most demanding college-preparatory program available, consistent with each student's readiness for particular fields of study.”
Unfortunately, this pursuit of the most demanding courses can create lots of stress for high school students striving to compete to get into top colleges!
But remember that admissions officers at top schools consider the larger context of your high school environment when evaluating your academic rigor. They typically assess academic rigor not by the measure of any single course, but in the context of your cumulative high school transcript.
Does your school offer AP courses? An International Baccalaureate program? Both? Neither? We know you did not design your school’s curriculum, and we only expect you to take advantage of such courses if your high school provides them… Again, we only expect that you will excel in the opportunities to which you have access.
- yale college — “advice on selecting high school courses”.
Course selection is important, but equally important is how you perform in those courses. Admissions officers are looking for evidence of academic rigor, a superior GPA, and evidence of improving academic ability over the course of several years.
When it comes time to apply to college, submitting a transcript with a strong GPA and rigorous courses covering a range of foundational subjects should help you stand out and showcase the following qualities:
- impressive breadth and depth of background knowledge
- a motivation for lifelong learning
- superior study skills
- an ability to persevere and excel under pressure
- organizational and time management skills
What if taking classes with more rigor means it’s harder to maintain a 4.0 GPA?
In other words, you’re asking, what’s more important, the GPA or academic rigor?...
That’s a great question.
Remember that colleges and universities will in most cases be looking at your overall high school accomplishments — not looking for perfection.

In general, a wise goal would be to know your limits, but within those limits, pursue the most challenging and relevant courses possible.
That said, here are some tips to help you avoid self-sabotaging your GPA!
- Start early in terms of enrolling in rigorous courses and
- Avoid cramming too many college prep courses into your schedule in a single school year
- When the time approaches to select your courses for the next term or school year, get advice from counselors and teachers about how high to aim
- Research the content and course requirements before deciding if an advanced or accelerated course is a good fit
- Think about your overall time commitments for the school year
- Be strategic and practical when it comes to maintaining good grades
- Seek out an experienced tutor as soon as possible if there’s any doubt about your ability to succeed on your own
- Test the waters early in harder classes — there’s often a brief window of time when you can drop one course and add an alternative course if you discover you’re really not prepared to succeed in the more advanced course
All of this brings us to our next topic — the temptation to take on too much academic rigor…
The Risks of Overloading on Rigor
Remember, your wellbeing is just as important as your academic pursuits!
While academic rigor is undeniably valuable, overloading on rigor without careful planning can lead to burnout, stress, and negative impacts on your mental health.
Most students will find that taking on more academic rigor is challenging. But, excelling academically should be just that — challenging — and not debilitating!
Unfortunately one common mistake is taking on too many AP courses or other college prep courses in the same year, or taking accelerated classes in subjects that don’t match your aptitudes or that you’re not properly prepared for academically.
When your efforts to pursue academic rigor start triggering excessive stress, frustration, or self doubt, you may be taking on too much, or you may not be getting the learning support you need to persevere and to succeed.
It’s commendable to aim high, and it’s understandable that students aspiring to college feel pressure to take on more… But honoring your passions and meaningful personal interests, balancing your commitments to extracurriculars , part-time jobs, or family responsibilities, and recognizing and accepting your limits — as well as pushing your limits — are all important to success.
Some stress is normal and healthy. Too much stress can be overwhelming and lead to more serious health issues — anxiety, depression, eating disorders, sleep disorders, and so on…
Warning Signs of Taking on Too Much
- tense muscles, headaches, a tight jaw, teeth-grinding, a racing heart and sweaty palms
- trouble sleeping
- low energy, tiredness or exhaustion
- the feeling of being on edge and irritable
- difficulty concentrating
- loss of motivation
- the feeling of being overwhelmed.
Source: “Stress and Stress Management” Raising Children.net
The odds are tremendous that you’ll succeed and thrive over the long run by aiming high if you also take ownership of your own prior commitments, limitations, and self-care needs:
- Striking a balance between challenge and achievement
- Seeking support or resources for more effective — and less stressful — academic planning
- Practicing self-care strategies to prevent burnout while still embracing academic challenges
Your aspirations for college and your college journey should fit into, not trample, your larger life journey !

Being Intentional & Making Informed Decisions
As you navigate the path of academic rigor, it's crucial to make informed decisions that align with your personal interests and future goals.
- Consider factors such as your passions, career aspirations, current workload, and available support.
- Engage in conversations with your teachers, guidance counselors, and parents or guardians to gather insights and advice.
Academic rigor should be pursued with intention. It's not about ticking off boxes but about enriching your learning experience.
The College Board has some great recommendations for guiding decisions when choosing your high school classes:
- Pursue your passions and interests
- Pursue a well-rounded education
- Build a strong holistic college profile by maintaining a balance when it comes to academic rigor, breadth of learning, GPA, and extracurriculars
- Be willing to try new things
- Take courses that colleges recommend, including a reasonable number of accelerated and advanced courses available to you
In essence, your pursuit of academic rigor is valuable as a means to an end, not an end in itself!
Being intentional is about seeing your educational journey as one with lots of opportunities for new challenges and growth, not as one with an endless number conquests and prescribed requirements to live up to.
The journey of education is about personal development, evolving self-awareness, aligning your decision making with your values, and cultivating intellectual curiosity.
Final Thoughts
As you navigate the labyrinth of high school scheduling and college admissions, academic rigor should be more than a buzzword and more than another requirement on an endless checklist…
First, keep in mind what academic rigor really means when looking at the educational opportunities available at your school.
Try to identify and enroll in courses that will foster deeper learning and higher order thinking.
The teachers and courses that truly offer you academic rigor will provide learning experiences that are supportive, intentional, and appreciative of different learning styles and interests.
This means you’ll be academically challenged and intellectually stimulated with engaging inquiry, analysis, and critical thinking. And, your teachers will typically be helping you discover the real-world relevance of your learning — providing opportunities for authentic research or problem solving.
This kind of academic rigor will help you develop the kinds of higher order thinking you’ll need not only to boost your college applications but to nurture your curiosity and confidence and prepare you for greater success in college and professionally…
Second, remember that academic rigor is only one piece of the puzzle... Your pursuit of academic rigor should not overshadow your self-care needs, negatively impact your GPA, isolate you from peers, or keep you from growing and thriving through participation in meaningful extracurricular experiences .
Finally, don’t pretend there is not a lot at stake when it comes to the impact your college journey has on your future opportunities, friendships, and careers. But also don’t think you need to do it all without the rights resources and community…
The trick is to turn this high stakes journey into one that excites you and propels you forward, and not one that leaves you feeling exhausted, anxious, isolated, or burned out.
The good news is you really don’t have to go it alone…

In fact, the students at Crimson enjoy the journey and succeed beyond their expectations by benefiting from personalized advising, tutoring, and counseling and the support of a whole community of like-minded peers from around the world …
Did you know that students who sign on to Crimson Education’s College App, access the Crimson student community, and take advantage of Crimson advising and counseling support are 7x more likely to get into their top-choice schools?
In your pursuit of academic rigor, remember that it's not just about the destination but the transformative journey that molds you into a well-rounded and intellectually curious individual. Embrace the challenges, find your balance, and thrive in your academic endeavors.
And, get help when you need it… You don’t need to go it alone and you don’t need to learn how to get into college the hard way, or after it’s too late. With the right guidance from knowledgeable Crimson Advisors, with help from supportive tutors and counselors, and like-minded students, as well as tools and resources to manage all your next steps, your college journey becomes an exhilarating, friend-filled and more fun-filled adventure.

We encourage you to explore Crimson Education's wealth of resources and counseling services. We’ll help you discover your own amazing potential as you chart a college journey that nurtures your passions and lives up to your dreams.
Learn more about our College Admissions Counseling Services , or go ahead and book a free consultation with a Crimson counselor today. Together, we’ll make sure you’re on the best path to the college of your dreams…
Find out about our Crimson App and how to access your own personalized application roadmap.
More Articles
What do top colleges look for exclusive insights from a former admissions officer.
/f/64062/800x450/0a349379ad/how-to-stand-out-to-colleges.jpg)
Class of 2028 Regular Decision Notification Dates
/f/64062/800x450/b07c2f9591/early-action-decision-international-students.jpg)
How to Get Into University of Chicago: Essential Criteria & Guidance for Applicants
/f/64062/1920x800/6230b7bd62/uchicago-background.png)
Home » Resources » How Much Does Course Rigor Matter for College Admissions?
How Much Does Course Rigor Matter for College Admissions?
- By Sheila A.
- March 1, 2021

Parents are often surprised to learn that GPA isn’t the only factor college admissions officers weigh when they look at a student’s classes. Course rigor is another important consideration that is often overlooked—and it is one of the most provocative topics Signet’s tutors discuss with parents.
When parents go into the college application process focused solely on their student’s GPA, that myopic viewpoint can lead to outsized expectations of where their student should apply and anticipate acceptance.
Course rigor is a critical component of college preparedness because, beyond grades, it demonstrates a student’s ability to navigate challenging material successfully. Not every A is created equal, and in a scenario where two students have identical grades, the student with the more arduous courses will typically come out ahead.
A student’s GPA certainly matters, but the difficulty or strength of their curriculum matters just as much. And it’s this academic rigor—the rigor of a student’s combined course load—that proves their preparedness, determination, and mental toughness to college admissions officers.
Course Rigor vs GPA: Which Matters More for College Admissions?
When it comes to college applications, the most important elements have remained the same for the last 10+ years. Research by the National Association for College Admissions Counseling (NACAC) shows that colleges weight the following factors most heavily:
- overall GPA
- grades in college preparatory coursework (e.g., AP and Honors courses)
- strength of curriculum (i.e., course rigor)
- standardized test scores (ACT and SAT test scores)
A student’s grade point average (GPA) is fairly self-explanatory: the higher the GPA, the better.
As for test scores, the COVID-19 pandemic has resulted in some shifting of the importance of SAT or ACT test score submission. As we’ve written about, many colleges have gone test-optional in the last 12 months , meaning that they do not require students to submit a standardized test score to be considered for admission. However, many students will still benefit from studying for and submitting a standardized test score, as test-optional colleges will review submitted scores . The conversation around standardized testing is a nuanced one right now; contact us if you’d like to discuss your student’s individual situation to determine whether testing is right for them.
What Does Course Rigor Mean for High School Students?
Course rigor, or “strength of curriculum,” helps complete a student’s academic narrative. The more challenging the student’s chosen courses, the greater their course rigor. (Note that course rigor is not an indicator of how challenging a course will be to a particular student. It simply recognizes the course as generally challenging.)
Classes with designations such as AP, Honors, Regents, Accelerated, IB, and others, are generally considered to be rigorous courses with higher strength of curriculum.
Why does curriculum strength matter? It indicates two important qualities to college admissions officers:
- the student actively seeks out academic challenges
- the student succeeds in these rigorous courses by getting good grades
How Do Admissions Officers Evaluate Academic Rigor of Your Student’s Curriculum?
Let’s look at how course rigor appears in the eyes of a college admissions office. Suppose an admissions officer is reviewing two students, both of whom attended the same high school and both of whom have a 4.0 GPA. If one student has taken several Honors or AP courses every year, while the other has only one or two classes with demonstrated academic rigor, the 4.0 GPA starts to have a different value for each student.
Though both students got the same grades, the first student has a better case for admission.
Ultimately, admissions officers view curriculum strength as an indicator that students are prepared for challenging college courses and also able to succeed in them. Since college courses can move swiftly and require significant independent study and time management , it’s important that students be able to keep up.
Colleges also take into consideration the kinds of courses that are available at your student’s high school. For example, if your student doesn’t have access to Honors or AP courses, they won’t be expected to have taken them or ranked against other students who have had those opportunities. Each student is evaluated according to the resources available to them.
How to Help Students Decide What Classes to Take Next Year
Because academic rigor plays such an important role in college admissions , even the classes your student enrolls in during middle school can affect their curriculum trajectory. If your student is capable of doing the work in Honors or AP-level courses, they should be enrolling in them as early as freshman year of high school. If your student tries to jump into an Honors track in subsequent years, they may be held back by certain prerequisites or introductory classes that have to be taken first.
At the same time, pushing your student into classes that are too demanding or that move too quickly can leave them feeling demoralized and overwhelmed. Academic rigor is important, but your student has other needs that must also be met for them to thrive. Colleges look for applicants who seek challenges outside the classroom , which requires students to have the time and bandwidth to get involved in extracurriculars.
When choosing courses, consider the homework load and how that may impact extracurricular commitments and overall stress levels as well. Choosing the appropriate level of rigor and encouraging your student to stretch a bit (but not too much) outside their comfort zone is probably the right fit.

More Resources

Parent Coaching Cards
Podcast: shereem herndon-brown: the black family’s guide to college admissions.

Podcast: Van Tran: Embracing the Pivot
- 160 Alewife Brook Pkwy #1247 Cambridge, MA 02138
- [email protected]
- 617.714.5262
Signet Education is a member of the National Association for College Admission Counseling and subscribes to the Statement of Principles of Good Practice.
What does “challenging” or “advanced” mean in high school?
Advanced or challenging high school courses typically cover more material and require more independent work than standard courses. Students in advanced classes are expected to read, write, and think at a higher level. These courses may also have higher expectations for participation and require engagement in classroom discussions and group projects.
Also Found On

As we have previously mentioned, we value our writers' time and hard work and therefore require our clients to put some funds on their account balance. The money will be there until you confirm that you are fully satisfied with our work and are ready to pay your paper writer. If you aren't satisfied, we'll make revisions or give you a full refund.
Finished Papers
- Plagiarism report. .99
- High priority status .90
- Full text of sources +15%
- 1-Page summary .99
- Initial draft +20%
- Premium writer +.91

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Take math at the highest level offered by your school, such as at an honors or AP level. There are three AP Math classes: Calculus AB, Calculus BC, and Statistics. There are four IB Math classes that cover roughly the same material but vary in difficulty and speed. Take pre-calculus and calculus, if possible.
The shift in coursework from high school to college is a transformative journey that challenges students to embrace independence, deepen their academic engagement, and refine their critical thinking skills. Understanding the differences in academic rigor, class structure, independence, and assessment methods can empower students to navigate the ...
We've compiled a complete list of high school classes for you to see all the possible course options high school students may have. We'll cover everything from science and math to electives and the humanities. How to Use This List. This list was created by researching the classes offered at numerous high schools, both public and private, across ...
1. Timing of the course-taking matters. Students who fall behind in taking courses in a timely manner have a reduced chance of enrolling in postsecondary education. Exhibits 1 through 3 display students' math, science, and English language arts (ELA) course-taking by grade in relation to postsecondary enrollment.
This section only applies to undergraduate applicants. Use this section to add your high school coursework as it appears on your transcript. College or university courses taken concurrently while in high school must be reported in College Coursework for each college or university attended. Remember to visit A-G Matching after completing the ...
A new report finds that there are 95 different kinds of high school diplomas nationwide, and that many fall short of requiring students to complete courses that prepare them for college or good jobs.
Science. Basic life sciences (e.g. biology) and physical sciences (chemistry, physics, etc.) are required at most high schools. These classes often include lab components that allow students to perform hands-on experiments. Most states require two to three years of science coursework in high school. These may include:
The meaning of COURSEWORK is work that is assigned or performed as part of a course of study. How to use coursework in a sentence. ... When Brandenn was four, his parents started him on the Perkins County elementary-school coursework, and within two years he'd finished the fourth-grade curriculum.
Taking advanced classes in high school can provide numerous benefits for students. Advanced classes, such as honors classes, college-level classes like AP or IB, or classes taken at a college, prepare students for college coursework, may earn you college credit, and demonstrate academic ability. Some high schools might also provide additional ...
Yes. No. Top. A high school elective is a course that's not part of your core curriculum. Electives are usually required for high school graduation, but you can take whatever classes interest you. Electives give you a chance to learn new skills and explore career paths.
Cal State Apply is a Centralized Application Service (CAS) that simplifies the process of applying to California State University (CSU) programs. You start by selecting the programs you wish to apply to, then you submit one application that includes all necessary materials. Once received by Cal State Apply, your application and materials are ...
A relevant coursework resume section—if you're curious whether to use one, how to list classes, and where to include it, this guide on adding coursework to resumes is for you. Christian Eilers, CPRW. Career Expert. "Lady Gaga and the Sociology of Fame". "The Physics of Star Trek". "South Park and Contemporary Social Issues".
If you have not taken any college courses in high school, choose "0" in the dropdown menu; there will be no further questions for you in this section. If you have taken one or more college courses in high school, choose the number of colleges you attended using the drop-down menu, up to three colleges. (Remember, this is the number of ...
High School Student Resume; College Graduate Resume; Undergraduate Resume; Best Examples of Resumes for Any Job; 1. What Does Relevant Coursework Mean and How to Include It on Your Resume. Relevant coursework is a list of subjects and courses you took at school that are pertinent to the position you're applying for. You can include relevant ...
Try reviewing notes from courses in your high school level on Studocu and then quiz yourself on what you've learned. Take time for yourself. As your grades become more important and you begin to plan for a life beyond compulsory education, high school can be an incredibly stressful time in any young person's life.
Academic rigor is a multifaceted concept that encompasses critical thinking, combining knowledge and concepts in new ways , and complex applications of learning. In short, academic rigor is not the same thing as academic difficulty per se. Academic difficulty typically refers to how accessible or inaccessible the learning content is for the ...
What Does Course Rigor Mean for High School Students? Course rigor, or "strength of curriculum," helps complete a student's academic narrative. The more challenging the student's chosen courses, the greater their course rigor. (Note that course rigor is not an indicator of how challenging a course will be to a particular student. It ...
An articulated adult school, high school course is one in which a determination has been made that a course offered at the secondary level is comparable to a specific community college course. Articulated courses can be applied to Las Positas Requirements, but cannot (per Title 5 Code) be granted college credit, unless the student or course has ...
What Does High School Coursework Mean - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. Scribd is the world's largest social reading and publishing site.
A bachelor's degree is a postsecondary educational opportunity that some students decide to pursue after high school. In this post, you'll learn the answers to common questions around bachelor's degrees. ... The type of job you can get with a bachelor's degree is usually based on the major and other coursework a student took while in ...
Advanced or challenging high school courses typically cover more material and require more independent work than standard courses. Students in advanced classes are expected to read, write, and think at a higher level. These courses may also have higher expectations for participation and require engagement in classroom discussions and group projects.
"T o me, an A grade means that a student has consistently exceeded the expected effort in a course. This could mean putting in clear above-and-beyond work on most weekly assignments, performing ...
We offer a free originality report, title, and reference page, along with the previously mentioned limitless revisions. 535. Finished Papers. Jam Operasional (09.00-17.00) +62 813-1717-0136 (Corporate) +62 812-4458-4482 (Recruitment) 1811Orders prepared. 100% Success rate.