- Search entire site
- Search for a course
- Browse study areas

Analytics and Data Science
- Data Science and Innovation
- Postgraduate Research Courses
- Business Research Programs
- Undergraduate Business Programs
- Entrepreneurship
- MBA Programs
- Postgraduate Business Programs
Communication
- Animation Production
- Business Consulting and Technology Implementation
- Digital and Social Media
- Media Arts and Production
- Media Business
- Media Practice and Industry
- Music and Sound Design
- Social and Political Sciences
- Strategic Communication
- Writing and Publishing
- Postgraduate Communication Research Degrees
Design, Architecture and Building
- Architecture
- Built Environment
- DAB Research
- Public Policy and Governance
- Secondary Education
- Education (Learning and Leadership)
- Learning Design
- Postgraduate Education Research Degrees
- Primary Education
Engineering
- Civil and Environmental
- Computer Systems and Software
- Engineering Management
- Mechanical and Mechatronic
- Systems and Operations
- Telecommunications
- Postgraduate Engineering courses
- Undergraduate Engineering courses
- Sport and Exercise
- Palliative Care
- Public Health
- Nursing (Undergraduate)
- Nursing (Postgraduate)
- Health (Postgraduate)
- Research and Honours
- Health Services Management
- Child and Family Health
- Women's and Children's Health
Health (GEM)
- Coursework Degrees
- Clinical Psychology
- Genetic Counselling
- Good Manufacturing Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Speech Pathology
- Research Degrees
Information Technology
- Business Analysis and Information Systems
- Computer Science, Data Analytics/Mining
- Games, Graphics and Multimedia
- IT Management and Leadership
- Networking and Security
- Software Development and Programming
- Systems Design and Analysis
- Web and Cloud Computing
- Postgraduate IT courses
- Postgraduate IT online courses
- Undergraduate Information Technology courses
- International Studies
- Criminology
- International Relations
- Postgraduate International Studies Research Degrees
- Sustainability and Environment
- Practical Legal Training
- Commercial and Business Law
- Juris Doctor
- Legal Studies
- Master of Laws
- Intellectual Property
- Migration Law and Practice
- Overseas Qualified Lawyers
- Postgraduate Law Programs
- Postgraduate Law Research
- Undergraduate Law Programs
- Life Sciences
- Mathematical and Physical Sciences
- Postgraduate Science Programs
- Science Research Programs
- Undergraduate Science Programs
Transdisciplinary Innovation
- Creative Intelligence and Innovation
- Diploma in Innovation
- Transdisciplinary Learning
- Postgraduate Research Degree
Sample written assignments
Look at sample assignments to help you develop and enhance your academic writing skills.
How to use this page
This page features authentic sample assignments that you can view or download to help you develop and enhance your academic writing skills.
PLEASE NOTE: Comments included in these sample written assignments are intended as an educational guide only. Always check with academic staff which referencing convention you should follow. All sample assignments have been submitted using Turnitin® (anti-plagiarism software). Under no circumstances should you copy from these or any other texts.
Annotated bibliography
Annotated Bibliography: Traditional Chinese Medicine (PDF, 103KB)
Essay: Business - "Culture is a Tool Used by Management" (PDF, 496KB)
Essay: Business - "Integrating Business Perspectives - Wicked Problem" (PDF, 660KB)
Essay: Business - "Overconsumption and Sustainability" (PDF, 762KB)
Essay: Business - "Post bureaucracy vs Bureaucracy" (PDF, 609KB)
Essay: Design, Architecture & Building - "Ideas in History - Postmodernism" (PDF, 545KB)
Essay: Design, Architecture & Building - "The Context of Visual Communication Design Research Project" (PDF, 798KB)
Essay: Design, Architecture & Building - "Ideas in History - The Nurses Walk and Postmodernism" (PDF, 558KB)
Essay: Health (Childhood Obesity ) (PDF, 159KB)
Essay: Health (Improving Quality and Safety in Healthcare) (PDF, 277KB)
Essay: Health (Organisational Management in Healthcare) (PDF, 229KB)
UTS HELPS annotated Law essay
(PDF, 250KB)
Essay: Science (Traditional Chinese Medicine) (PDF, 153KB)
Literature review
Literature Review: Education (Critical Pedagogy) (PDF, 165KB)
Reflective writing
Reflective Essay: Business (Simulation Project) (PDF, 119KB)
Reflective Essay: Nursing (Professionalism in Context) (PDF, 134KB)
Report: Business (Management Decisions and Control) (PDF, 244KB)
Report: Education (Digital Storytelling) (PDF, 145KB)
Report: Education (Scholarly Practice) (PDF, 261KB)
Report: Engineering Communication (Flood Mitigation & Water Storage) (PDF, 1MB)
UTS acknowledges the Gadigal people of the Eora Nation, the Boorooberongal people of the Dharug Nation, the Bidiagal people and the Gamaygal people, upon whose ancestral lands our university stands. We would also like to pay respect to the Elders both past and present, acknowledging them as the traditional custodians of knowledge for these lands.

More from Swinburne University
- Giving to Swinburne
- Student login
- Staff login
- Arts, Humanities and Social Sciences
- Built Environment and Architecture
- Engineering
- Film and Television
- Games and Animation
- Information Technology
- Media and Communication
- Trades and Apprenticeships
- Study online
- Transition to university from VCE
- Direct entry into university
- Returning to study
- Vocational Education and Training at Swinburne
- Early Entry Program
- University entry requirements
- Transferring to Swinburne
- Recognition of prior learning in the workplace
- Study Abroad in Melbourne
- Study support for indigenous students
- Guaranteed pathways from TAFE
- Short courses
- University certificates
- Pre-apprenticeships
- Apprenticeships
- Associate degrees
- Bachelor degrees
- Double degrees
- Certificates
- Traineeships
- Trade short courses
- Doctor of Philosophy
- Master degrees
- Graduate diploma courses
- Graduate certificate courses
- Studying outside of Australia
- Study on campus
- Loans and discounts for local students
- Fees for international students
- Fees for local students
- Student Services and Amenities Fee
- Scholarship conditions
- Scholarships for international students
- How to apply as a local student
- How to apply for a research degree
- How to apply as an international student
- Apply as an asylum seeker or refugee
- How to enrol
- Understanding your university offer
- Course planner
- Setting up your class timetable
- Enrol as a PhD or master degree student
- Why study in Australia?
- Plan your arrival in Melbourne
- Arriving in Melbourne
- Things to do in Melbourne
- Getting around Melbourne
- Money, living costs and banking in Australia
- International student stories
- Student email, password and Wi-Fi access
- Your student ID card and Swinburne login
- Student discounts and concessions
- Special consideration and extensions
- Accommodation
- Study and learning support
- Health and wellbeing
- Support for international students
- Independent advocacy for service
- Indigenous student services
- Financial support and advice
- AccessAbility services
- Legal advice for students
- Spiritual Wellbeing
- Assault reporting and help
- Asylum seeker and refugee support
- Care leaver support
- LGBTIQ+ community support
- Childcare for the Swinburne community
- Industry-linked projects
- Internships
- Student stories
- Professional Degrees
- Industry study tours
- Get paid to podcast
- Real industry experience stories
- Overseas exchange
- Overseas study tours
- Overseas internships
- Students currently overseas
- Improve your employability
- Career services
- Professional Purpose program
- Partner Stories
- Hosting students with disabilities
- Work with our accreditation placement students
- Benefits of working with our students
- Apprenticeships and traineeships
- Workshops, events and outreach programs
- Work experience
- Knox Innovation, Opportunity and Sustainability Centre
- Australian Synchrotron Science Education
- PrimeSCI! science education
- Student projects
- Meet our facilitators
- Meet our consultants
- Meet our leadership and management teams
- Learning design and innovation
- Hybrid working solutions
- Training needs analysis
- Why partner with Swinburne
- 4 simple steps to setting up a partnership
- Achievements and success stories
- Research engagement
- Facilities and equipment
- Achievements and recognition
- Iverson Health Innovation Research Institute
- Social Innovation Research Institute
- Space Technology and Industry Institute
- Innovative Planet Research Institute
- Research centres, groups and clinics
- Platforms and initiatives
- Indigenous research projects
- Animal research
- Biosafety and Defence
- Data management
- Funding from tobacco companies
- Human research
- Intellectual property
Assignment writing guides and samples
If you're looking for useful guides for assignment writing and language skills check out our range of study skills resources
Essay writing
- Writing essays [PDF 240KB] . Tips on writing a great essay, including developing an argument, structure and appropriate referencing.
- Sample essay [PDF 330KB] . A sample of an essay that includes an annotated structure for your reference.
Writing a critical review
- Writing a critical review [PDF 260KB] . Tips on writing a great critical review, including structure, format and key questions to address when writing a review.
- Sample critical review [PDF 260KB] . A sample of a critical review that includes an annotated structure for your reference.
Writing a business-style report
- Writing a business-style report [PDF 330KB] . A resource for business and law students Find out how to write and format business-style reports.
- Sample of a business-style report [PDF 376 KB] . A resource for business and law students. A sample of a business-style report with an annotated format.
Investigative report sample
- Sample of an investigative report [PDF 500KB] . A resource for science, engineering and technology students. How to write an investigative report, including an annotated format.
Assignment topics and editing
- Interpreting assignment topics [PDF 370 KB] . Find out how to interpret an assignment topic, including understanding key words and concepts.
- How to edit your work [PDF 189KB] . A guide for all students about how to edit and review their work.
Language skills
- Building your word power (expanding your knowledge of words) [PDF 306KB]. A guide to expanding your knowledge of words and communicating your ideas in more interesting ways.
- Handy grammar hints [PDF 217KB] . A guide to getting grammar and style right in your assignments.
Resources relevant to your study area
Science, engineering and technology.
- Writing a critical review [PDF 260KB]. Tips on writing a great critical review, including structure, format and key questions to address when writing a review.
- Sample critical review [PDF 260KB] . A sample of a critical review that includes an annotated structure for your reference.
- Sample of an investigative report [PDF 500KB] . A resource for science, engineering and technology students. How to write an investigative report, including an annotated format.
- How to edit your work [PDF 189KB] . A guide for all students about how to edit and review their work.
- Building your word power (expanding your knowledge of words) [PDF 306KB]. A guide to expanding your knowledge of words and communicating your ideas in more interesting ways.
- Handy grammar hints [PDF 217KB] . A guide to getting grammar and style right in your assignments.
Health, Arts and Design
- Sample essay [PDF 330KB] . A sample of an essay that includes an annotated structure for your reference.
- Writing a critical review [PDF 260KB]. Tips on writing a great critical review, including structure, format and key questions to address when writing a review.
- Sample critical review [PDF 260KB]. A sample of a critical review that includes an annotated structure for your reference.
- How to edit your work [PDF 189KB] . A guide for all students about how to edit and review their work.
- Handy grammar hints [PDF 217KB]. A guide to getting grammar and style right in your assignments.
Business and Law
- Sample essay [PDF 330KB]. A sample of an essay that includes an annotated structure for your reference.
- Writing a business-style report [PDF 330KB]. A resource for business and law students. Find out how to write and format business-style reports.
- Sample of a business-style report [PDF 376 KB]. A resource for business and law students. A sample of a business-style report, with an annotated format.
- Interpreting assignment topics [PDF 370 KB]. Find out how to interpret an assignment topic, including understanding key words and concepts.
- How to edit your work [PDF 189KB]. A guide for all students about how to edit and review their work.
- How it works

Academic Assignment Samples and Examples
Are you looking for someone to write your academic assignment for you? This is the right place for you. To showcase the quality of the work that can be expected from ResearchProspect, we have curated a few samples of academic assignments. These examples have been developed by professional writers here. Place your order with us now.
Assignment Sample
Discipline: Sociology
Quality: Approved / Passed
Discipline: Construction
Quality: 1st / 78%
Discipline: Accounting & Finance
Quality: 2:1 / 69%
Undergraduate
Discipline: Bio-Medical
Quality: 1st / 76%
Discipline: Statistics
Quality: 1st / 73%
Discipline: Health and Safety
Quality: 2:1 / 68%
Discipline: Business
Quality: 2:1 / 67%
Discipline: Medicine
Quality: 2:1 / 66%
Discipline: Religion Theology
Quality: 2:1 / 64%
Discipline: Project Management
Quality: 2:1 / 63%
Discipline: Website Development
Discipline: Fire and Construction
Discipline: Environmental Management
Discipline: Early Child Education
Quality: 1st / 72%
Analysis of a Business Environment: Coffee and Cake Ltd (CC Ltd)
Business Strategy
Application of Project Management Using the Agile Approach ….
Project Management
Assessment of British Airways Social Media Posts
Critical annotation, global business environment (reflective report assignment), global marketing strategies, incoterms, ex (exw), free (fob, fca), cost (cpt, cip), delivery …., it systems strategy – the case of oxford university, management and organisation in global environment, marketing plan for “b airlines”, prepare a portfolio review and remedial options and actions …., systematic identification, analysis, and assessment of risk …., the exploratory problem-solving play and growth mindset for …..
Childhood Development
The Marketing Plan- UK Sustainable Energy Limited
Law assignment.
Law Case Study
To Analyse User’s Perception towards the Services Provided by Their…
Assignment Samples
Research Methodology
Discipline: Civil Engineering
Discipline: Health & Manangement
Our Assignment Writing Service Features
Subject specialists.
We have writers specialising in their respective fields to ensure rigorous quality control.
We are reliable as we deliver all your work to you and do not use it in any future work.
We ensure that our work is 100% plagiarism free and authentic and all references are cited.
Thoroughly Researched
We perform thorough research to get accurate content for you with proper citations.
Excellent Customer Service
To resolve your issues and queries, we provide 24/7 customer service
Our prices are kept at a level that is affordable for everyone to ensure maximum help.
Loved by over 100,000 students
Thousands of students have used ResearchProspect academic support services to improve their grades. Why are you waiting?
"I am glad I gave my order to ResearchProspect after seeing their academic assignment sample. Really happy with the results. "

Law Student
"I am grateful to them for doing my academic assignment. Got high grades."

Economics Student
Frequently Ask Questions?
How can these samples help you.
The assignment writing samples we provide help you by showing you versions of the finished item. It’s like having a picture of the cake you’re aiming to make when following a recipe.
Assignments that you undertake are a key part of your academic life; they are the usual way of assessing your knowledge on the subject you’re studying.
There are various types of assignments: essays, annotated bibliographies, stand-alone literature reviews, reflective writing essays, etc. There will be a specific structure to follow for each of these. Before focusing on the structure, it is best to plan your assignment first. Your school will have its own guidelines and instructions, you should align with those. Start by selecting the essential aspects that need to be included in your assignment.
Based on what you understand from the assignment in question, evaluate the critical points that should be made. If the task is research-based, discuss your aims and objectives, research method, and results. For an argumentative essay, you need to construct arguments relevant to the thesis statement.
Your assignment should be constructed according to the outline’s different sections. This is where you might find our samples so helpful; inspect them to understand how to write your assignment.
Adding headings to sections can enhance the clarity of your assignment. They are like signposts telling the reader what’s coming next.
Where structure is concerned, our samples can be of benefit. The basic structure is of three parts: introduction, discussion, and conclusion. It is, however, advisable to follow the structural guidelines from your tutor.
For example, our master’s sample assignment includes lots of headings and sub-headings. Undergraduate assignments are shorter and present a statistical analysis only.
If you are still unsure about how to approach your assignment, we are here to help, and we really can help you. You can start by just asking us a question with no need to commit. Our writers are able to assist by guiding you through every step of your assignment.
Who will write my assignment?
We have a cherry-picked writing team. They’ve been thoroughly tested and checked out to verify their skills and credentials. You can be sure our writers have proved they can write for you.
What if I have an urgent assignment? Do your delivery days include the weekends?
No problem. Christmas, Boxing Day, New Year’s Eve – our only days off. We know you want weekend delivery, so this is what we do.
Explore More Samples
View our professional samples to be certain that we have the portofilio and capabilities to deliver what you need.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
Search form
How to write the best college assignments.
By Lois Weldon
When it comes to writing assignments, it is difficult to find a conceptualized guide with clear and simple tips that are easy to follow. That’s exactly what this guide will provide: few simple tips on how to write great assignments, right when you need them. Some of these points will probably be familiar to you, but there is no harm in being reminded of the most important things before you start writing the assignments, which are usually determining on your credits.
The most important aspects: Outline and Introduction
Preparation is the key to success, especially when it comes to academic assignments. It is recommended to always write an outline before you start writing the actual assignment. The outline should include the main points of discussion, which will keep you focused throughout the work and will make your key points clearly defined. Outlining the assignment will save you a lot of time because it will organize your thoughts and make your literature searches much easier. The outline will also help you to create different sections and divide up the word count between them, which will make the assignment more organized.
The introduction is the next important part you should focus on. This is the part that defines the quality of your assignment in the eyes of the reader. The introduction must include a brief background on the main points of discussion, the purpose of developing such work and clear indications on how the assignment is being organized. Keep this part brief, within one or two paragraphs.
This is an example of including the above mentioned points into the introduction of an assignment that elaborates the topic of obesity reaching proportions:
Background : The twenty first century is characterized by many public health challenges, among which obesity takes a major part. The increasing prevalence of obesity is creating an alarming situation in both developed and developing regions of the world.
Structure and aim : This assignment will elaborate and discuss the specific pattern of obesity epidemic development, as well as its epidemiology. Debt, trade and globalization will also be analyzed as factors that led to escalation of the problem. Moreover, the assignment will discuss the governmental interventions that make efforts to address this issue.
Practical tips on assignment writing
Here are some practical tips that will keep your work focused and effective:
– Critical thinking – Academic writing has to be characterized by critical thinking, not only to provide the work with the needed level, but also because it takes part in the final mark.
– Continuity of ideas – When you get to the middle of assignment, things can get confusing. You have to make sure that the ideas are flowing continuously within and between paragraphs, so the reader will be enabled to follow the argument easily. Dividing the work in different paragraphs is very important for this purpose.
– Usage of ‘you’ and ‘I’ – According to the academic writing standards, the assignments should be written in an impersonal language, which means that the usage of ‘you’ and ‘I’ should be avoided. The only acceptable way of building your arguments is by using opinions and evidence from authoritative sources.
– Referencing – this part of the assignment is extremely important and it takes a big part in the final mark. Make sure to use either Vancouver or Harvard referencing systems, and use the same system in the bibliography and while citing work of other sources within the text.
– Usage of examples – A clear understanding on your assignment’s topic should be provided by comparing different sources and identifying their strengths and weaknesses in an objective manner. This is the part where you should show how the knowledge can be applied into practice.
– Numbering and bullets – Instead of using numbering and bullets, the academic writing style prefers the usage of paragraphs.
– Including figures and tables – The figures and tables are an effective way of conveying information to the reader in a clear manner, without disturbing the word count. Each figure and table should have clear headings and you should make sure to mention their sources in the bibliography.
– Word count – the word count of your assignment mustn’t be far above or far below the required word count. The outline will provide you with help in this aspect, so make sure to plan the work in order to keep it within the boundaries.
The importance of an effective conclusion
The conclusion of your assignment is your ultimate chance to provide powerful arguments that will impress the reader. The conclusion in academic writing is usually expressed through three main parts:
– Stating the context and aim of the assignment
– Summarizing the main points briefly
– Providing final comments with consideration of the future (discussing clear examples of things that can be done in order to improve the situation concerning your topic of discussion).
Normal 0 false false false EN-US X-NONE X-NONE /* Style Definitions */ table.MsoNormalTable {mso-style-name:"Table Normal"; mso-tstyle-rowband-size:0; mso-tstyle-colband-size:0; mso-style-noshow:yes; mso-style-priority:99; mso-style-parent:""; mso-padding-alt:0in 5.4pt 0in 5.4pt; mso-para-margin:0in; mso-para-margin-bottom:.0001pt; mso-pagination:widow-orphan; font-size:11.0pt; font-family:"Calibri","sans-serif"; mso-ascii-font-family:Calibri; mso-ascii-theme-font:minor-latin; mso-hansi-font-family:Calibri; mso-hansi-theme-font:minor-latin;}
Lois Weldon is writer at Uk.bestdissertation.com . Lives happily at London with her husband and lovely daughter. Adores writing tips for students. Passionate about Star Wars and yoga.
7 comments on “How To Write The Best College Assignments”
Extremely useful tip for students wanting to score well on their assignments. I concur with the writer that writing an outline before ACTUALLY starting to write assignments is extremely important. I have observed students who start off quite well but they tend to lose focus in between which causes them to lose marks. So an outline helps them to maintain the theme focused.
Hello Great information…. write assignments
Well elabrated
Thanks for the information. This site has amazing articles. Looking forward to continuing on this site.
This article is certainly going to help student . Well written.
Really good, thanks
Practical tips on assignment writing, the’re fantastic. Thank you!
Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .
Week 3: Writing university assignments
Introduction
This week you will start to look at university writing, a very important student activity. You will first consider which aspects of your current writing will be useful when it comes to university-level writing and which might need a bit more work. Then you will move on to look at university assignments, their purposes and structure and the strategies students follow when approaching them.
Watch Anna describing what you will study this week:

Welcome to Week 3.
So far you have looked at reading: reading strategies and ways to use insights from readings in an assignment. Reading and selecting key information are two of the first steps towards writing a good assignment. It is now time to look at what university assignments ask for and how to produce a good assignment.
During Weeks 3, 4 and 5 you will concentrate on assignment writing. In particular, this week you will find out what types of assignments university students normally write, the reasons why they write them and the way they approach them. In Week 4 you will look in more detail at essay writing. In Week 5, you will learn how to clearly link ideas in your writing, so that your readers can easily understand your ideas.
By the end of this week you will be able to understand:
- the purpose and structure of your everyday writing
- the purpose and overall structure of university texts
- the main stages of the writing process
- the essay and report planning stages.
1 Everyday writing
For many of us writing is a daily activity. In a morning, for example, I might write a text message to a friend, make a ‘to do’ list and email a colleague.
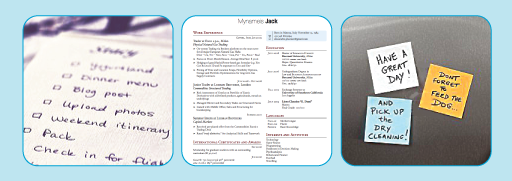
Three images: first image is of a to-do list, second image of a CV and third image of three Post-it notes on a fridge door.
Think about the types of text, that is any piece of writing, you have written in the past few days. These can be as short as a few words scribbled on a Post-it note or as long as a letter or a workplace report. Note your thoughts in the box below.
The answer is personal to you. Here are some of the texts I have written lately:
- professional emails
- a shopping list
- comments on my friends’ Facebook pages
- a birthday card
- feedback on my students’ assignments
- a page of my personal diary
- a note to my neighbour
- a workplace report
- a recipe I heard on the radio
Most people do not consider themselves to be writers, yet they write something every day. There are many types of text. Some texts may appear easy but others seem more complex to write. In the next activity you will compare some texts to understand how they differ and why some are harder to write than others.
1.1 Types and structure of everyday writing
When we write, we communicate with other people. Birthday cards, Post-it notes and text messages are all ways to send other people messages containing information. Even a personal diary and a to-do list may be read initially only by the writer, but may be shared or read in the future by other people.
Communication is therefore the main reason why people write. The particular purpose of each piece of writing depends on the situation and the people we communicate with. For example, many of us leave little notes on the fridge to remind ourselves and others to do important chores or to wish them well.
The way our texts are organised varies depending on our reason for writing and our relationship with the person or persons who will read our messages.
In this activity you will look at the purpose and structure of three texts (Figure 2).

Three images: first image is of a to-do list, second image of a thank-you letter and third image of a CV.
Look at the three texts below and match them to their typical purpose.
A to-do list
To briefly remind ourselves and others what needs to be done
A curriculum vitae (CV)
To show an employer our skills and experiences in the hope of being invited to an interview
A thank-you card
To tell somebody how much we appreciate what they have done for us
Using the following two lists, match each numbered item with the correct letter.
a. To show an employer our skills and experiences in the hope of being invited to an interview
b. To briefly remind ourselves and others what needs to be done
c. To tell somebody how much we appreciate what they have done for us
Have you ever written any of these three types of text? How easy or difficult do you or would you find writing them? Note your thoughts in the box below before comparing them with mine.
Here is my answer:
I’m one of those people who often write to-do lists. They are simple and informal, and contain just isolated words describing activities. I normally cross off each activity as soon as it is done.
I find thank-you cards and cards in general less easy to write. This is in part because in Italy, my country, people tend to phone or thank other people in person so cards are rarely written. In the UK, handwritten cards tend to follow a specific structure but I am never sure which one I should use, in which order to different people in different situations. I therefore tend to avoid cards or buy ready-made cards and just add my signature.
A curriculum vitae is generally difficult to write. My first CV was untidy, quite long and contained too much information so I had to ask a more experienced friend to help me.
All texts, even the simplest everyday ones, are written for a purpose. When we write, we have this purpose and our readers in mind and this helps us to structure our texts.
Some texts are easy to write because we understand their purpose, they are part of our culture and we are familiar with their typical structure. However, approaching unfamiliar text types may be challenging unless we know why we are writing them and how they should be organised. In many cases a model of a particular type of text or a more experienced person can help.
The next sections introduce some texts you may not be familiar with. You will look at texts written by university students, the reasons why they are written and the ways in which they are organised.
2 University assignments
At British universities, students are asked to carry out written tasks called assignments and submit them to their tutors by a set date. Assignments are part of the assessment process and, while most assignments are completed at home, some will take the form of a formal examination.
Like any other piece of writing you have written so far, assignments are written for a reason and follow a specific structure. The key is to understand these reasons and learn which structure you are expected to follow.
Students are asked to write assignments for a number of reasons:
- to demonstrate that they understand the subject matter they are being taught
- to show that they can explain key ideas and information in their own words
- to show that they can use what they have learned to solve real life problems
- to demonstrate that they can evaluate, compare and contrast different views
- to gain feedback from their tutors on their understanding and use of course content.
Depending on the specific purpose of each assignment, university students are asked to write a range of assignment types. For example, they use summaries and definitions to simply describe what they have learned from their readings. They use essays to discuss what they have learned and to show that they can use their learning to make sense of real world situations. Finally, they use reports to describe or analyse a situation and provide recommendations.
The next section looks more closely at assignment types, their purpose and structure.
2.1 Types of assignment
There is a wide range of assignment types that students may be asked to produce during their university studies. Some assignments might require them to write single-sentence responses, while others might ask them to write an extended response of 600, 800 or even 2000 words.
In this video three Open University tutors talk about the assignments students are required to complete for the courses they teach:

2.2 Distinguishing between different types of assignment
It may be more common to find one kind of assignment type in a particular subject than in others. For example, science assignments may consist of short questions that require short answers, while a social sciences assignment might consist of short answers explaining a definition or essays explaining a theory. Regardless of the subject they are studying, students will probably have to write a variety of assignment types during their studies.
You are now going to gain an overview of some of the assignment types that you are likely to encounter in your university studies. Look at the list below of descriptions of various types of assignment. Match each assignment type with its appropriate description.
An assignment that gives detailed information and analysis about a topic; it will often have different sections, with headings that have different functions; there is an introduction, different sections and a conclusion with recommendations
Short definition and explanation
A word or concept is briefly defined and explained
An assignment that focuses on one topic; it has an introduction, body paragraphs and a conclusion
Short-answer exercise
Brief answers in response to questions; the contents of one answer is not necessarily directly connected with the next
A short account of the content of something you have read, heard or viewed without details
a. An assignment that gives detailed information and analysis about a topic; it will often have different sections, with headings that have different functions; there is an introduction, different sections and a conclusion with recommendations
b. A word or concept is briefly defined and explained
c. Brief answers in response to questions; the contents of one answer is not necessarily directly connected with the next
d. A short account of the content of something you have read, heard or viewed without details
e. An assignment that focuses on one topic; it has an introduction, body paragraphs and a conclusion
During your university studies, you will be asked to complete a variety of assignment tasks to demonstrate what you have learned. Having a good understanding of what is required in the various assignments that you are asked to produce for your university modules will help you fulfil the task and get better marks.
2.3 Typical challenges
Writing a university assignment can be difficult. The following activity identifies the main challenges.
Below is a list of challenges typically experienced by students who are new to assignment writing. Think of your experience of writing longer and possibly formal texts. For example, you may have had to write a job application or a formal email. If you haven’t had such experiences, you may want to think back to your school experiences. Have you ever experienced any of the challenges listed below?
- It’s a very long time since I’ve done anything like this. I’ve forgotten how to do it.
- I’m not familiar with the British educational system. What is done in my country is quite different from what is expected here.
- I’m not clever enough to write an assignment.
- How do I organise essays and reports?
- I don’t understand the assignment title. What am I expected to do?
- I look at the blank page. I don’t know where to start or what to write.
- I can write short informal pieces but I have never written a long formal essay.
- I write too many words.
- I make too many errors and don’t know how to choose the right words.
Type your comments in the box before comparing them with mine.
The main problems students experience are caused by lack of experience and, in particular, difficulty in getting started. These difficulties arise when students have problems understanding the question and the way in which essays and reports should be organised. Some see assignment writing as daunting as it is a completely new experience.
The next section will address these challenges by focusing on the writing process.
3 The essay-writing process
Writing a successful assignment is less daunting if it is seen as a process consisting of several manageable steps. You will probably be familiar with some of these steps already: for example writing notes, putting ideas in order, selecting ideas to include, reviewing and rewriting what you have already written in order to improve it.
Another key point is that anyone writing an essay has to give themselves enough time. Generally the best assignments result from doing a little at a time over a period of days, rather than attempting to complete an assignment in one evening.
In this section you will look at this step-by-step process.
3.1 Some useful strategies
In the next activity you will look in more detail at the challenges often faced by students and the strategies they can use to complete an essay.
In the videos below, three students describe their writing process. They also mention the challenges they face and some of the strategies they use. Watch the videos and identify the challenges and strategies each student uses. Note them in the boxes below before comparing your answers with mine.

- Writing too many words
- Risk of not answering the question
- Reading the question
- Reading in order to find answers to the question
- First writing everything you know, then revising it

- Not enjoying essay writing
- Using the structure given by the assignment
- Writing thoughts about each section
- Revising the answer many times
- Circular revision process: rereading, rewriting, reviewing, rereading …
- Stopping when the answer has been answered properly and completely

- Becoming too used to his answer
- First, making a list of key points
- Then, carefully arranging these points
- Writing the first draft
- Asking someone else to read this draft
Coping with university writing is about developing strategies that help to meet a range of challenges. These students seem to have been successful in essay writing despite the various challenges they mention. They have dealt with those challenges by adopting strategies for planning what they are going to write, structuring the content of their essays and reviewing the text over and over again.
3.2 A step-by-step process
The next activity introduces you to a method that exploits all the strategies described by the three students.
In this activity you are introduced to the different stages of the essay-writing process. This process starts with activities that include reading (understanding the ideas of others), brainstorming (thinking of all you know about the topic) and note making, and proceeds through one or more cycles until you feel you have produced a full and correct answer.
The boxes show the eight stages in the process of completing an assignment. Drag each stage into the relevant blank box in the diagram.
Writing a university assignment involves going through a series of stages. It is quite normal for all writers to want to go through the cycle more than once. This may happen for many reasons. For example they may feel that they haven’t quite answered the question or they may want to go back to their readings and notes to find additional relevant material.
Many students find that the habit of breaking their writing process into manageable steps helps them not only to write university assignments but also other pieces of writing such as workplace documents.
In the next two sections you will learn how to plan an essay and a report.
4 Planning an essay: the pre-writing steps
Before writing an essay, it is important to take the time to understand its structure as this provides a useful starting point. A typical essay includes an introduction, the main body of the text, a conclusion and a list of references (Figure 3).
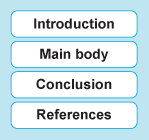
The structure of an essay consists of the introduction, the main body, the conclusion and the references.
While this is a simple structure, students often wonder what should be included in the main body of the essay. In this section you will learn how carefully reading the assignment question and carrying out some simple tasks can help you to plan the content of the main body of the essay.
4.1 Reading the essay question
Answering an essay question is only possible if a student knows and understands it. Reading the essay question is therefore a very important step that must be completed before starting the writing process.
Question 1a

Now answer the following question:
What is the first thing students should do after reading the assignment question?
Write a plan of their essay using tables or diagrams
Find the words that explain what they are required to do
Start looking for the information they can use in the essay
The correct answer is b.
It is important to carefully study the key words contained in the assignment question to find out what it is asking the student to do. These key words as known as instruction words and content words.
4.2 Identifying the instruction words
Having a good understanding of instruction words will help you to identify what type of task you are being asked to do, which, in turn, makes it more likely that an assignment answer will be relevant. These words may seem complex but they are very often used in assignment questions. Understanding instruction words makes it easier to understand the requirements of most assignments.
In the next activity you will learn some of the key words used in assignment questions.
Listed below are eight of the most common instruction words. Match each one with its definition.
Compare and contrast
Look for differences and similarities between two or more concepts or things in an organised way
Discuss/to what extent
Give reasons for and against an idea
Make an idea clear by giving an example
Give a shortened version of a written or spoken item, stating only the key points
Give a detailed account of something such as characteristics, a reading or an experience
Examine something to judge its value, importance, quality, or effectiveness
Take apart an idea and examine it in great detail in order to understand it
Give details, clarify meaning or give reasons
a. Give details, clarify meaning or give reasons
b. Take apart an idea and examine it in great detail in order to understand it
c. Give a detailed account of something such as characteristics, a reading or an experience
d. Examine something to judge its value, importance, quality, or effectiveness
e. Make an idea clear by giving an example
f. Give a shortened version of a written or spoken item, stating only the key points
g. Look for differences and similarities between two or more concepts or things in an organised way
h. Give reasons for and against an idea
4.3 Identifying key content words
Having understood what type of task is required, you need to find out what content you have to focus on. This is done by identifying the content words.
The content words are words that express key ideas that you are expected to write about. In the following example of an essay title, the content words are highlighted:
Using examples from Chapter 3, describe some biological factors that influence the health of the individual (approximately 600 words).
Once the content words and the instruction words (in this case, using examples and describe ) are clear, you should be able to rephrase the title to clarify it:
What are the biological factors that influence people’s health? I need to identify and give details about a few biological factors, and explain how each can affect health. I need to give some examples from Chapter 3 of my module materials to illustrate my explanation s .
4.4 Practice understanding the essay question
In the next activity you will practise identifying instruction and content words, and rephrasing questions into a simpler format.
Below are four essay questions. For each one complete the following tasks:
- Find the instruction words.
- Find the content words.
- Rewrite the task in your own words.
At this stage, you are not expected to know the content or the authors mentioned in these questions. Your purpose for reading them is to understand what each question asks you to do. Type your notes in the boxes before comparing your answers with mine.
- Compare and contrast our own education to date with that of one of your parents. Which points of comparison seem important to you and why?
The instruction words are:
- compare and contrast
- which important points of comparison …
The content words are:
- your own education
- one of your parents' education
- points of comparison
This question can be reworded as:
Find similarities and differences between your education and either your mother’s or your father’s education. Decide which of these similarities and differences are the most important and explain why this is the case.
Decide which primate species you would prioritise for conservation action and explain how you came to this conclusion.
- decide which ...
- primate species
- conservation action
Which primate species is it essential to protect from extinction as soon as possible? Why should each of these species be prioritised?
- Why do people codeswitch?
The instruction word is:
The content word is:.
Codeswitching describes the habit bi-lingual people have of using more than one language when they talk to each other.
Give many reasons why people codeswitch
- Describe the causes of deforestation , explain its negative effects and evaluate the solutions that have been implemented to date.
- deforestation
- negative effects
This question can be rewording as:
What are the causes of deforestation? Write about the negative effects of deforestation. Write down your ideas about how good the solutions to the problems are.
4.5 Producing a draft outline
The next stage is to write a draft outline. This can only be written on the basis of a full understanding of the question. The first draft outline helps to decide what to look for in any readings. However, after reading, it is normal to update the draft outline to reflect your improved understanding of the subject.
Look at this task:
Describe government interventions which may help people to tackle obesity . To what extent do you think these interventions can be effective ? (800 words)
As this task asks the student to describe government interventions, each section of the essay will need to provide details about one type of intervention. It is also important to consider situations and reasons why an intervention is likely to be effective as well as situations and reasons why it may fail. Each point should be illustrated with examples.
This is a possible outline:
Intervention type 1 – description – examples – why it can be effective?/not effective? + examples
Intervention type 2 – description – examples – why it can be effective?/not effective? + examples
Intervention type 3 – description – examples – why it can be effective?/not effective? + examples
Having written this plan it will be necessary to read the course materials to find:
- a definition of the term ‘government intervention’
- a definition of the term ‘obesity’ and some general information about its causes and effects
- examples of ineffective and effective government interventions
- theories about types of government intervention in the health sector.
4.6 Practice producing draft outlines
You will now look again at the essay questions you analysed in Activity 9 and evaluate different outlines that can be used to answer them.
Activity 10
Below is a list of assignment tasks. For each assignment look at the outlines provided and make notes in response to these two questions:
- Which outline best answers the question?
- What kind of information are you likely to need in order to write this essay?
- Outline 2 is the most appropriate because it provides a range of reasons why people codeswitch. It also explains the codeswitching techniques used and some examples that help to explain these reasons. Outline 1 is incorrect because it describes the techniques but doesn’t answer the question.
- definition of codeswitching
- theories about codeswitching, particularly reasons for doing so
- codeswitching techniques
Outline 2 is the most appropriate because it directly answers the question by selecting one species and using each paragraph or section to clearly give reasons for this selection. For each reason, the writer also shows that they have considered and dismissed a contrasting viewpoint (e.g. a reason for not selecting this species). This adds strength to the points they make.
The themes covered by Outline 1 provide background information but fail to directly address the question. As the requirement is to write only 800 words there is no space to provide much background information. Some of this (e.g. reasons why conservation is necessary) could be included very concisely in the introduction.
- definition of primate species
- list of species that risk extinction and their characteristics
- how important a species is to the environment: is it likely to benefit or damage it?
- theories of conservation
Outline 1 answers the question because it identifies and develops several points of comparison and clearly compares and contrasts the two experiences. It also uses the last paragraph to indicate which one is the most important and why.
Outline 2 provides information about the two educational experiences but does not compare them. Therefore, this outline does not help to answer the question.
Outline 3 is also appropriate because it compares and contrasts the two experiences. However, the points of contrast need to be clearly mentioned when looking at similarities and differences. The last paragraph clearly indicates which points of contrast are the most important and why.
- information about my own education
- education theories; in particular, factors that have an effect on people’s education as these help to explain the choice of points of contrast
Outline 1 is inappropriate because it develops two paragraphs about deforestation techniques, which are not required. It does provide examples of possible effects and solutions but does not describe them. The solutions are neither described nor evaluated.
Outline 2 is appropriate because it clearly focuses on the three key content words included in the question: causes, effects and solutions. For each of these, it provides a description and some examples. When looking at solutions, it looks at reasons in favour of and against choosing them.
- information about deforestation: causes, effects, solutions
- theories about how forest management affects people’s lives and the planet
This section has highlighted the importance of fully understanding the essay question as this helps to produce an appropriate outline. In the next section you will look at ways to represent outlines visually through a diagram.
4.7 Using diagrams to plan an assignment
Many students find that diagrams can be useful when planning their essays. This is because diagrams help them to think in a visual way about their essays and the ideas they need to include in them.
Look again at this assignment question:
Describe the causes of deforestation, explain its negative effects and evaluate the solutions that have been implemented to date.
This assignment can be outlined using a mind map as shown in Figure 4.
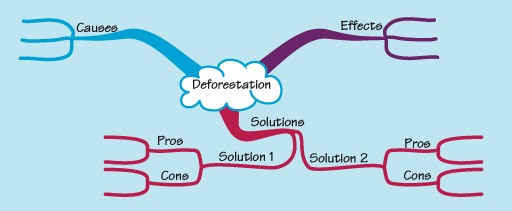
At the centre of this mind map is a cloud labelled ‘deforestation’. From this cloud stem three branches. From one branch, labelled ‘causes’, stem three branches. From another branch labelled ‘effects’ also stem three branches. From the third branch, which is labelled ‘solutions’, stem two further branches labelled ‘solutions 1’ and ‘solutions 2’. From each of these branches stem two branches labelled ‘pros’ and ‘cons’. From each of these stem two branches.
The mind map can be used while reading about deforestation to add information that could be included in the essay.
Activity 11
Draw a mind map that can be used to plan the following essay and to record the most relevant information from readings.
Before designing your mind map, look again at the suggested outline for this question. When you have finished, compare your mind map with mine and read the comments.
While reading about this topic and using this mind map (Figure 5), it is possible to enter each of the three reasons, details about explanations, evidence and alternative views and more branches.
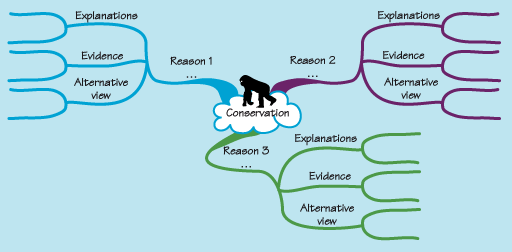
At the centre of this mind map is the word ‘conservation’. From this stem three branches labelled: Reason 1, Reason 2, Reason 3. From each of these branches stem three further branches labelled explanations, evidence and alternative view.
4.8 Using diagrams to plan a science assignment
Sometimes just reading an assignment question is not sufficient to write a draft plan. You will now look at a science assignment that requires students to describe and explain but provides no information that could help them to write a plan.
The assignment title is:
Describe and explain the greenhouse effect.
Just reading this title is insufficient to outline a text easily because the title does not contain helpful key words such as cause, effect or similarities. Before planning it is therefore necessary to read about this effect. Having done this, information needs to be arranged into steps as this will help to plan the text.
The following activity provides a useful visual technique for planning the essay.
Activity 12
Watch the following video in which Open University science tutor Phil explains to Zorica how to plan the assignment by using a diagram to visualise the information she needs to include.

Now put the following steps into order described by Phil and Zorica.
Infrared radiation emitted from the Sun.
Absorption of infrared by the Earth.
Re-emission of infrared to the atmosphere.
Infrared absorbed by CO 2 and H 2 O.
This activity shows the how diagrams can be used to both identify and present the steps of a process at the pre-writing stage. Depending on the number of words the student is required to write, they can then write either a paragraph or a longer text outlining each of the stages of the process.
5 Planning a report
Reports differ from essays because they normally follow a more detailed standard structure. Knowing this standard structure makes planning easier as it is only necessary to decide what specific content to place in each of its parts and for what reason.
This structure depends on the subject. The next two sections illustrate the structure of a science or technology report, and of a business report.
5.1 Planning a science or a technology report
Table 5 highlights the elements of a science or technology report, though the same general principles apply in other disciplines too.
When writing a report, it is necessary to assemble and order the material, perhaps under a set of headings (which can be added to or subdivided). The plan will help to include material that is relevant and to the point.
5.2 Planning a business report
Business studies reports follow a structure that is very similar to those normally written to help management to make decisions. The main purpose of these reports is to describe a real life business situation and to provide a list of recommendations.
While the overall structure is similar to that of a science or a technology report, the main text is usually structured using a ‘business model’, i.e. a framework that helps the writer to analyse a situation by looking at its specific features.
The following assignment task is structured using a SWOT model. SWOT stands for:
Strengths
Weaknesses
Opportunities
In other words, it is a framework that analyses a business by looking at its strengths and weaknesses as well as at any opportunities it can exploit and the threats it faces.
Below is a business studies assignment question:
Use a SWOT model to analyse the multinational company Coca-Cola.
Table 6 shows how this report should be structured.
6 This week's quiz
Well done, you’ve just completed the last of the activities for this week's study before the weekly quiz.
Remember the quizzes will let you check your understanding of what you have learned while also helping to prepare you for the badge quiz at the end of Week 4. By completing the weekly quiz you’ll also know how the quizzes work before you complete the badge quiz. So, it is a good idea to make time for them if you can.
Week 3 practice quiz .
Open the quiz in a new tab or window (by holding ctrl [or cmd on a Mac] when you click the link).
This week you looked at everyday writing, at different types of university assignments and at useful ways to break the writing process into manageable steps.
These are this week’s key learning points:
- Writing is a daily activity for most people.
- Writing is easier if you know why you are writing and how to organise ideas and information.
- Assignments are written to show a tutor that the student has understood and can use the ideas and information learned from the course materials.
- Essays and reports are two common types of assignment.
- A range of strategies can be used to deal with the challenges of assignment writing.
- A useful way to approach assignment writing is to follow a process that consists of several manageable steps.
- The first step involves understanding the instruction words and key ideas contained in the question.
- The second step consists in producing a draft plan and deciding what kind of information will be necessary to answer the question.
- Mind maps and other diagrams can help to plan essays and organise notes.
You can now go to Week 4 .
Acknowledgements
This course was written by Anna Calvi.
Except for third party materials and otherwise stated (see FAQs ), this content is made available under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 Licence .
The material acknowledged below is Proprietary and used under licence (not subject to Creative Commons Licence). Grateful acknowledgement is made to the following sources for permission to reproduce material in this unit:
Figure 1: (left) © Stacy Spensley in Flickr made available under https://creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by/ 2.0/ ; (middle) The CV Inn in Flickr made available under: https://creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by/ 2.0/ deed.en ; (right) From: http://www.stickypadblog.com/ wp-content/ uploads/ 2012/ 10/ fridgesickypad.jpg ; Figure 2: (left) © Stacy Spensley in Flickr made available under https://creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by/ 2.0/ ; (middle) © Scott Feldstein in Flickr; (right) The CV Inn in Flickr made available under: https://creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by/ 2.0/ deed.en .
Every effort has been made to contact copyright owners. If any have been inadvertently overlooked, the publishers will be pleased to make the necessary arrangements at the first opportunity.
Don't miss out:
1. Join over 200,000 students, currently studying with The Open University – http://www.open.ac.uk/ choose/ ou/ open-content
2. Enjoyed this? Find out more about this topic or browse all our free course materials on OpenLearn – http://www.open.edu/ openlearn/
3. Outside the UK? We have students in over a hundred countries studying online qualifications – http://www.openuniversity.edu/ – including an MBA at our triple accredited Business School.
Copyright © 2014 The Open University
- Utility Menu
- Writing Center
- Writing Program
- Designing Essay Assignments
by Gordon Harvey
Students often do their best and hardest thinking, and feel the greatest sense of mastery and growth, in their writing. Courses and assignments should be planned with this in mind. Three principles are paramount:
1. Name what you want and imagine students doing it
However free students are to range and explore in a paper, the general kind of paper you’re inviting has common components, operations, and criteria of success, and you should make these explicit. Having satisfied yourself, as you should, that what you’re asking is doable, with dignity, by writers just learning the material, try to anticipate in your prompt or discussions of the assignment the following queries:
- What is the purpose of this? How am I going beyond what we have done, or applying it in a new area, or practicing a key academic skill or kind of work?
- To what audience should I imagine myself writing?
- What is the main task or tasks, in a nutshell? What does that key word (e.g., analyze, significance of, critique, explore, interesting, support) really mean in this context or this field?
- What will be most challenging in this and what qualities will most distinguish a good paper? Where should I put my energy? (Lists of possible questions for students to answer in a paper are often not sufficiently prioritized to be helpful.)
- What misconceptions might I have about what I’m to do? (How is this like or unlike other papers I may have written?) Are there too-easy approaches I might take or likely pitfalls? An ambitious goal or standard that I might think I’m expected to meet but am not?
- What form will evidence take in my paper (e.g., block quotations? paraphrase? graphs or charts?) How should I cite it? Should I use/cite material from lecture or section?
- Are there some broad options for structure, emphasis, or approach that I’ll likely be choosing among?
- How should I get started on this? What would be a helpful (or unhelpful) way to take notes, gather data, discover a question or idea? Should I do research?
2. Take time in class to prepare students to succeed at the paper
Resist the impulse to think of class meetings as time for “content” and of writing as work done outside class. Your students won’t have mastered the art of paper writing (if such a mastery is possible) and won’t know the particular disciplinary expectations or moves relevant to the material at hand. Take time in class to show them:
- discuss the assignment in class when you give it, so students can see that you take it seriously, so they can ask questions about it, so they can have it in mind during subsequent class discussions;
- introduce the analytic vocabulary of your assignment into class discussions, and take opportunities to note relevant moves made in discussion or good paper topics that arise;
- have students practice key tasks in class discussions, or in informal writing they do in before or after discussions;
- show examples of writing that illustrates components and criteria of the assignment and that inspires (class readings can sometimes serve as illustrations of a writing principle; so can short excerpts of writing—e.g., a sampling of introductions; and so can bad writing—e.g., a list of problematic thesis statements);
- the topics of originality and plagiarism (what the temptations might be, how to avoid risks) should at some point be addressed directly.
3. Build in process
Ideas develop over time, in a process of posing and revising and getting feedback and revising some more. Assignments should allow for this process in the following ways:
- smaller assignments should prepare for larger ones later;
- students should do some thinking and writing before they write a draft and get a response to it (even if only a response to a proposal or thesis statement sent by email, or described in class);
- for larger papers, students should write and get response (using the skills vocabulary of the assignment) to a draft—at least an “oral draft” (condensed for delivery to the class);
- if possible, meet with students individually about their writing: nothing inspires them more than feeling that you care about their work and development;
- let students reflect on their own writing, in brief cover letters attached to drafts and revisions (these may also ask students to perform certain checks on what they have written, before submitting);
- have clear and firm policies about late work that nonetheless allow for exception if students talk to you in advance.
- Pedagogy Workshops
- Responding to Student Writing
- Commenting Efficiently
- Vocabulary for Discussing Student Writing
- Guides to Teaching Writing
- HarvardWrites Instructor Toolkit
- Additional Resources for Teaching Fellows

5 tips on writing better university assignments
Lecturer in Student Learning and Communication Development, University of Sydney
Disclosure statement
Alexandra Garcia does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
University of Sydney provides funding as a member of The Conversation AU.
View all partners
University life comes with its share of challenges. One of these is writing longer assignments that require higher information, communication and critical thinking skills than what you might have been used to in high school. Here are five tips to help you get ahead.

1. Use all available sources of information
Beyond instructions and deadlines, lecturers make available an increasing number of resources. But students often overlook these.
For example, to understand how your assignment will be graded, you can examine the rubric . This is a chart indicating what you need to do to obtain a high distinction, a credit or a pass, as well as the course objectives – also known as “learning outcomes”.
Other resources include lecture recordings, reading lists, sample assignments and discussion boards. All this information is usually put together in an online platform called a learning management system (LMS). Examples include Blackboard , Moodle , Canvas and iLearn . Research shows students who use their LMS more frequently tend to obtain higher final grades.
If after scrolling through your LMS you still have questions about your assignment, you can check your lecturer’s consultation hours.
2. Take referencing seriously
Plagiarism – using somebody else’s words or ideas without attribution – is a serious offence at university. It is a form of cheating.

In many cases, though, students are unaware they have cheated. They are simply not familiar with referencing styles – such as APA , Harvard , Vancouver , Chicago , etc – or lack the skills to put the information from their sources into their own words.
To avoid making this mistake, you may approach your university’s library, which is likely to offer face-to-face workshops or online resources on referencing. Academic support units may also help with paraphrasing.
You can also use referencing management software, such as EndNote or Mendeley . You can then store your sources, retrieve citations and create reference lists with only a few clicks. For undergraduate students, Zotero has been recommended as it seems to be more user-friendly.
Using this kind of software will certainly save you time searching for and formatting references. However, you still need to become familiar with the citation style in your discipline and revise the formatting accordingly.
3. Plan before you write
If you were to build a house, you wouldn’t start by laying bricks at random. You’d start with a blueprint. Likewise, writing an academic paper requires careful planning: you need to decide the number of sections, their organisation, and the information and sources you will include in each.
Research shows students who prepare detailed outlines produce higher-quality texts. Planning will not only help you get better grades, but will also reduce the time you spend staring blankly at the screen thinking about what to write next.

During the planning stage, using programs like OneNote from Microsoft Office or Outline for Mac can make the task easier as they allow you to organise information in tabs. These bits of information can be easily rearranged for later drafting. Navigating through the tabs is also easier than scrolling through a long Word file.
4. Choose the right words
Which of these sentences is more appropriate for an assignment?
a. “This paper talks about why the planet is getting hotter”, or b. “This paper examines the causes of climate change”.
The written language used at university is more formal and technical than the language you normally use in social media or while chatting with your friends. Academic words tend to be longer and their meaning is also more precise. “Climate change” implies more than just the planet “getting hotter”.
To find the right words, you can use SkELL , which shows you the words that appear more frequently, with your search entry categorised grammatically. For example, if you enter “paper”, it will tell you it is often the subject of verbs such as “present”, “describe”, “examine” and “discuss”.
Another option is the Writefull app, which does a similar job without having to use an online browser.
5. Edit and proofread
If you’re typing the last paragraph of the assignment ten minutes before the deadline, you will be missing a very important step in the writing process: editing and proofreading your text. A 2018 study found a group of university students did significantly better in a test after incorporating the process of planning, drafting and editing in their writing.
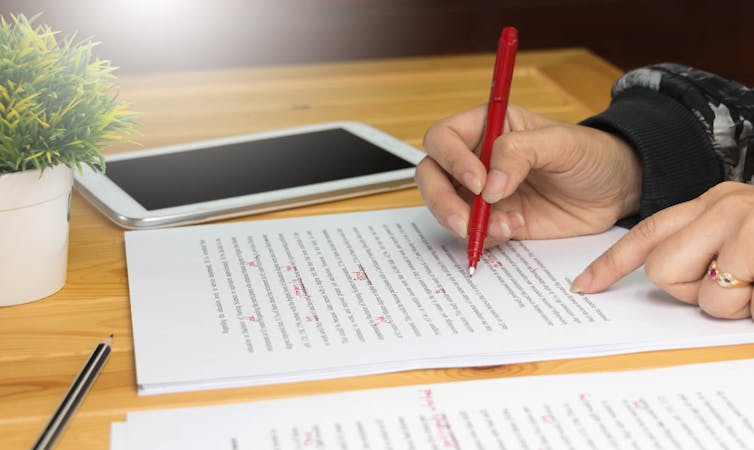

You probably already know to check the spelling of a word if it appears underlined in red. You may even use a grammar checker such as Grammarly . However, no software to date can detect every error and it is not uncommon to be given inaccurate suggestions.
So, in addition to your choice of proofreader, you need to improve and expand your grammar knowledge. Check with the academic support services at your university if they offer any relevant courses.
Written communication is a skill that requires effort and dedication. That’s why universities are investing in support services – face-to-face workshops, individual consultations, and online courses – to help students in this process. You can also take advantage of a wide range of web-based resources such as spell checkers, vocabulary tools and referencing software – many of them free.
Improving your written communication will help you succeed at university and beyond.
- College assignments
- University study
- Writing tips
- Essay writing
- Student assessment

Sydney Horizon Educators (Identified)

Scholarships Manager

Audience Development Coordinator (fixed-term maternity cover)

Lecturer (Hindi-Urdu)

Director, Defence and Security

Understanding Assignments
What this handout is about.
The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This handout will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms and practices into meaningful clues to the type of writing your instructor expects. See our short video for more tips.
Basic beginnings
Regardless of the assignment, department, or instructor, adopting these two habits will serve you well :
- Read the assignment carefully as soon as you receive it. Do not put this task off—reading the assignment at the beginning will save you time, stress, and problems later. An assignment can look pretty straightforward at first, particularly if the instructor has provided lots of information. That does not mean it will not take time and effort to complete; you may even have to learn a new skill to complete the assignment.
- Ask the instructor about anything you do not understand. Do not hesitate to approach your instructor. Instructors would prefer to set you straight before you hand the paper in. That’s also when you will find their feedback most useful.
Assignment formats
Many assignments follow a basic format. Assignments often begin with an overview of the topic, include a central verb or verbs that describe the task, and offer some additional suggestions, questions, or prompts to get you started.
An Overview of Some Kind
The instructor might set the stage with some general discussion of the subject of the assignment, introduce the topic, or remind you of something pertinent that you have discussed in class. For example:
“Throughout history, gerbils have played a key role in politics,” or “In the last few weeks of class, we have focused on the evening wear of the housefly …”
The Task of the Assignment
Pay attention; this part tells you what to do when you write the paper. Look for the key verb or verbs in the sentence. Words like analyze, summarize, or compare direct you to think about your topic in a certain way. Also pay attention to words such as how, what, when, where, and why; these words guide your attention toward specific information. (See the section in this handout titled “Key Terms” for more information.)
“Analyze the effect that gerbils had on the Russian Revolution”, or “Suggest an interpretation of housefly undergarments that differs from Darwin’s.”
Additional Material to Think about
Here you will find some questions to use as springboards as you begin to think about the topic. Instructors usually include these questions as suggestions rather than requirements. Do not feel compelled to answer every question unless the instructor asks you to do so. Pay attention to the order of the questions. Sometimes they suggest the thinking process your instructor imagines you will need to follow to begin thinking about the topic.
“You may wish to consider the differing views held by Communist gerbils vs. Monarchist gerbils, or Can there be such a thing as ‘the housefly garment industry’ or is it just a home-based craft?”
These are the instructor’s comments about writing expectations:
“Be concise”, “Write effectively”, or “Argue furiously.”
Technical Details
These instructions usually indicate format rules or guidelines.
“Your paper must be typed in Palatino font on gray paper and must not exceed 600 pages. It is due on the anniversary of Mao Tse-tung’s death.”
The assignment’s parts may not appear in exactly this order, and each part may be very long or really short. Nonetheless, being aware of this standard pattern can help you understand what your instructor wants you to do.
Interpreting the assignment
Ask yourself a few basic questions as you read and jot down the answers on the assignment sheet:
Why did your instructor ask you to do this particular task?
Who is your audience.
- What kind of evidence do you need to support your ideas?
What kind of writing style is acceptable?
- What are the absolute rules of the paper?
Try to look at the question from the point of view of the instructor. Recognize that your instructor has a reason for giving you this assignment and for giving it to you at a particular point in the semester. In every assignment, the instructor has a challenge for you. This challenge could be anything from demonstrating an ability to think clearly to demonstrating an ability to use the library. See the assignment not as a vague suggestion of what to do but as an opportunity to show that you can handle the course material as directed. Paper assignments give you more than a topic to discuss—they ask you to do something with the topic. Keep reminding yourself of that. Be careful to avoid the other extreme as well: do not read more into the assignment than what is there.
Of course, your instructor has given you an assignment so that he or she will be able to assess your understanding of the course material and give you an appropriate grade. But there is more to it than that. Your instructor has tried to design a learning experience of some kind. Your instructor wants you to think about something in a particular way for a particular reason. If you read the course description at the beginning of your syllabus, review the assigned readings, and consider the assignment itself, you may begin to see the plan, purpose, or approach to the subject matter that your instructor has created for you. If you still aren’t sure of the assignment’s goals, try asking the instructor. For help with this, see our handout on getting feedback .
Given your instructor’s efforts, it helps to answer the question: What is my purpose in completing this assignment? Is it to gather research from a variety of outside sources and present a coherent picture? Is it to take material I have been learning in class and apply it to a new situation? Is it to prove a point one way or another? Key words from the assignment can help you figure this out. Look for key terms in the form of active verbs that tell you what to do.
Key Terms: Finding Those Active Verbs
Here are some common key words and definitions to help you think about assignment terms:
Information words Ask you to demonstrate what you know about the subject, such as who, what, when, where, how, and why.
- define —give the subject’s meaning (according to someone or something). Sometimes you have to give more than one view on the subject’s meaning
- describe —provide details about the subject by answering question words (such as who, what, when, where, how, and why); you might also give details related to the five senses (what you see, hear, feel, taste, and smell)
- explain —give reasons why or examples of how something happened
- illustrate —give descriptive examples of the subject and show how each is connected with the subject
- summarize —briefly list the important ideas you learned about the subject
- trace —outline how something has changed or developed from an earlier time to its current form
- research —gather material from outside sources about the subject, often with the implication or requirement that you will analyze what you have found
Relation words Ask you to demonstrate how things are connected.
- compare —show how two or more things are similar (and, sometimes, different)
- contrast —show how two or more things are dissimilar
- apply—use details that you’ve been given to demonstrate how an idea, theory, or concept works in a particular situation
- cause —show how one event or series of events made something else happen
- relate —show or describe the connections between things
Interpretation words Ask you to defend ideas of your own about the subject. Do not see these words as requesting opinion alone (unless the assignment specifically says so), but as requiring opinion that is supported by concrete evidence. Remember examples, principles, definitions, or concepts from class or research and use them in your interpretation.
- assess —summarize your opinion of the subject and measure it against something
- prove, justify —give reasons or examples to demonstrate how or why something is the truth
- evaluate, respond —state your opinion of the subject as good, bad, or some combination of the two, with examples and reasons
- support —give reasons or evidence for something you believe (be sure to state clearly what it is that you believe)
- synthesize —put two or more things together that have not been put together in class or in your readings before; do not just summarize one and then the other and say that they are similar or different—you must provide a reason for putting them together that runs all the way through the paper
- analyze —determine how individual parts create or relate to the whole, figure out how something works, what it might mean, or why it is important
- argue —take a side and defend it with evidence against the other side
More Clues to Your Purpose As you read the assignment, think about what the teacher does in class:
- What kinds of textbooks or coursepack did your instructor choose for the course—ones that provide background information, explain theories or perspectives, or argue a point of view?
- In lecture, does your instructor ask your opinion, try to prove her point of view, or use keywords that show up again in the assignment?
- What kinds of assignments are typical in this discipline? Social science classes often expect more research. Humanities classes thrive on interpretation and analysis.
- How do the assignments, readings, and lectures work together in the course? Instructors spend time designing courses, sometimes even arguing with their peers about the most effective course materials. Figuring out the overall design to the course will help you understand what each assignment is meant to achieve.
Now, what about your reader? Most undergraduates think of their audience as the instructor. True, your instructor is a good person to keep in mind as you write. But for the purposes of a good paper, think of your audience as someone like your roommate: smart enough to understand a clear, logical argument, but not someone who already knows exactly what is going on in your particular paper. Remember, even if the instructor knows everything there is to know about your paper topic, he or she still has to read your paper and assess your understanding. In other words, teach the material to your reader.
Aiming a paper at your audience happens in two ways: you make decisions about the tone and the level of information you want to convey.
- Tone means the “voice” of your paper. Should you be chatty, formal, or objective? Usually you will find some happy medium—you do not want to alienate your reader by sounding condescending or superior, but you do not want to, um, like, totally wig on the man, you know? Eschew ostentatious erudition: some students think the way to sound academic is to use big words. Be careful—you can sound ridiculous, especially if you use the wrong big words.
- The level of information you use depends on who you think your audience is. If you imagine your audience as your instructor and she already knows everything you have to say, you may find yourself leaving out key information that can cause your argument to be unconvincing and illogical. But you do not have to explain every single word or issue. If you are telling your roommate what happened on your favorite science fiction TV show last night, you do not say, “First a dark-haired white man of average height, wearing a suit and carrying a flashlight, walked into the room. Then a purple alien with fifteen arms and at least three eyes turned around. Then the man smiled slightly. In the background, you could hear a clock ticking. The room was fairly dark and had at least two windows that I saw.” You also do not say, “This guy found some aliens. The end.” Find some balance of useful details that support your main point.
You’ll find a much more detailed discussion of these concepts in our handout on audience .
The Grim Truth
With a few exceptions (including some lab and ethnography reports), you are probably being asked to make an argument. You must convince your audience. It is easy to forget this aim when you are researching and writing; as you become involved in your subject matter, you may become enmeshed in the details and focus on learning or simply telling the information you have found. You need to do more than just repeat what you have read. Your writing should have a point, and you should be able to say it in a sentence. Sometimes instructors call this sentence a “thesis” or a “claim.”
So, if your instructor tells you to write about some aspect of oral hygiene, you do not want to just list: “First, you brush your teeth with a soft brush and some peanut butter. Then, you floss with unwaxed, bologna-flavored string. Finally, gargle with bourbon.” Instead, you could say, “Of all the oral cleaning methods, sandblasting removes the most plaque. Therefore it should be recommended by the American Dental Association.” Or, “From an aesthetic perspective, moldy teeth can be quite charming. However, their joys are short-lived.”
Convincing the reader of your argument is the goal of academic writing. It doesn’t have to say “argument” anywhere in the assignment for you to need one. Look at the assignment and think about what kind of argument you could make about it instead of just seeing it as a checklist of information you have to present. For help with understanding the role of argument in academic writing, see our handout on argument .
What kind of evidence do you need?
There are many kinds of evidence, and what type of evidence will work for your assignment can depend on several factors–the discipline, the parameters of the assignment, and your instructor’s preference. Should you use statistics? Historical examples? Do you need to conduct your own experiment? Can you rely on personal experience? See our handout on evidence for suggestions on how to use evidence appropriately.
Make sure you are clear about this part of the assignment, because your use of evidence will be crucial in writing a successful paper. You are not just learning how to argue; you are learning how to argue with specific types of materials and ideas. Ask your instructor what counts as acceptable evidence. You can also ask a librarian for help. No matter what kind of evidence you use, be sure to cite it correctly—see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial .
You cannot always tell from the assignment just what sort of writing style your instructor expects. The instructor may be really laid back in class but still expect you to sound formal in writing. Or the instructor may be fairly formal in class and ask you to write a reflection paper where you need to use “I” and speak from your own experience.
Try to avoid false associations of a particular field with a style (“art historians like wacky creativity,” or “political scientists are boring and just give facts”) and look instead to the types of readings you have been given in class. No one expects you to write like Plato—just use the readings as a guide for what is standard or preferable to your instructor. When in doubt, ask your instructor about the level of formality she or he expects.
No matter what field you are writing for or what facts you are including, if you do not write so that your reader can understand your main idea, you have wasted your time. So make clarity your main goal. For specific help with style, see our handout on style .
Technical details about the assignment
The technical information you are given in an assignment always seems like the easy part. This section can actually give you lots of little hints about approaching the task. Find out if elements such as page length and citation format (see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial ) are negotiable. Some professors do not have strong preferences as long as you are consistent and fully answer the assignment. Some professors are very specific and will deduct big points for deviations.
Usually, the page length tells you something important: The instructor thinks the size of the paper is appropriate to the assignment’s parameters. In plain English, your instructor is telling you how many pages it should take for you to answer the question as fully as you are expected to. So if an assignment is two pages long, you cannot pad your paper with examples or reword your main idea several times. Hit your one point early, defend it with the clearest example, and finish quickly. If an assignment is ten pages long, you can be more complex in your main points and examples—and if you can only produce five pages for that assignment, you need to see someone for help—as soon as possible.
Tricks that don’t work
Your instructors are not fooled when you:
- spend more time on the cover page than the essay —graphics, cool binders, and cute titles are no replacement for a well-written paper.
- use huge fonts, wide margins, or extra spacing to pad the page length —these tricks are immediately obvious to the eye. Most instructors use the same word processor you do. They know what’s possible. Such tactics are especially damning when the instructor has a stack of 60 papers to grade and yours is the only one that low-flying airplane pilots could read.
- use a paper from another class that covered “sort of similar” material . Again, the instructor has a particular task for you to fulfill in the assignment that usually relates to course material and lectures. Your other paper may not cover this material, and turning in the same paper for more than one course may constitute an Honor Code violation . Ask the instructor—it can’t hurt.
- get all wacky and “creative” before you answer the question . Showing that you are able to think beyond the boundaries of a simple assignment can be good, but you must do what the assignment calls for first. Again, check with your instructor. A humorous tone can be refreshing for someone grading a stack of papers, but it will not get you a good grade if you have not fulfilled the task.
Critical reading of assignments leads to skills in other types of reading and writing. If you get good at figuring out what the real goals of assignments are, you are going to be better at understanding the goals of all of your classes and fields of study.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift

Basic essay structure

Improve your writing
Organise your essays to demonstrate your knowledge, show your research and support your arguments
Essays are usually written in continuous, flowing, paragraphed text and don’t use section headings. This may seem unstructured at first, but good essays are carefully structured.
How your assignment content is structured is your choice. Use the basic pattern below to get started.
Essay structure
An essay consists of three basic parts:, introduction.
The essay itself usually has no section headings. Only the title page, author declaration and reference list are written as headings, along with, for example, appendices. Check any task instructions, and your course or unit handbook, for further details.
Content in assignment introductions can vary widely. In some disciplines you may need to provide a full background and context, whereas other essays may need only a little context, and others may need none.
An introduction to an essay usually has three primary purposes:
- To set the scene
- To tell readers what is important, and why
- To tell the reader what the essay is going to do (signposting)
A standard introduction includes the following five elements:
- A statement that sets out the topic and engages the reader.
- The background and context of the topic.
- Any important definitions, integrated into your text as appropriate.
- An outline of the key points, topic, issues, evidence, ideas, arguments, models, theories, or other information, as appropriate. This may include distinctions or contrasts between different ideas or evidence.
- A final sentence or two which tells the reader your focal points and aims.
You should aim to restrict your introduction to information needed for the topic and only include background and contextual information which helps the reader understand it, or sets the scene for your chosen focal points.
In most essays you will have a considerable range of options for your focus. You will be expected to demonstrate your ability to select the most relevant content to address your focal points.
There are some exceptions. For example, if an assignment brief specifically directs the essay focus or requires you to write broadly about a topic. These are relatively rare or are discipline-specific so you should check your task instructions and discipline and subject area conventions.
Below are examples of an opening statement, a summary of the selected content, and a statement at the end of the introduction which tells the reader what the essay will focus on and how it will be addressed. We've use a fictional essay.
The title of our essay is: 'Cats are better than dogs. Discuss.'
To submit this essay you also would need to add citations as appropriate.
Example of opening statements:
People have shared their lives with cats and dogs for millenia. Which is better depends partly on each animal’s characteristics and partly on the owner’s preferences.
Here is a summary of five specific topics selected for the essay, which would be covered in a little more detail in the introduction:
- In ancient Egypt, cats were treated as sacred and were pampered companions.
- Dogs have for centuries been used for hunting and to guard property. There are many types of working dog, and both dogs and cats are now kept purely as pets.
- They are very different animals, with different care needs, traits and abilities.
- It is a common perception that people are either “cat-lovers” or “dog-lovers”.
- It is a common perception that people tend to have preferences for one, and negative beliefs about and attitudes towards, the other.
Example of closing statements at the end of the introduction:
This essay will examine both cats’ and dogs’ behaviour and abilities, the benefits of keeping them as pets, and whether people’s perceptions of their nature matches current knowledge and understanding.
Main body: paragraphs
The body of the essay should be organised into paragraphs. Each paragraph should deal with a different aspect of the issue, but they should also link in some way to those that precede and follow it. This is not an easy thing to get right, even for experienced writers, partly because there are many ways to successfully structure and use paragraphs. There is no perfect paragraph template.
The theme or topic statement
The first sentence, or sometimes two, tells the reader what the paragraph is going to cover. It may either:
- Begin a new point or topic, or
- Follow on from the previous paragraph, but with a different focus or go into more-specific detail. If this is the case, it should clearly link to the previous paragraph.
The last sentence
It should be clear if the point has come to an end, or if it continues in the next paragraph.
Here is a brief example of flow between two summarised paragraphs which cover the historical perspective:
It is known from hieroglyphs that the Ancient Egyptians believed that cats were sacred. They were also held in high regard, as suggested by their being found mummified and entombed with their owners (Smith, 1969). In addition, cats are portrayed aiding hunters. Therefore, they were both treated as sacred, and were used as intelligent working companions. However, today they are almost entirely owned as pets.
In contrast, dogs have not been regarded as sacred, but they have for centuries been widely used for hunting in Europe. This developed over time and eventually they became domesticated and accepted as pets. Today, they are seen as loyal, loving and protective members of the family, and are widely used as working dogs.
There is never any new information in a conclusion.
The conclusion usually does three things:
- Reminds your readers of what the essay was meant to do.
- Provides an answer, where possible, to the title.
- Reminds your reader how you reached that answer.
The conclusion should usually occupy just one paragraph. It draws together all the key elements of your essay, so you do not need to repeat the fine detail unless you are highlighting something.
A conclusion to our essay about cats and dogs is given below:
Both cats and dogs have been highly-valued for millenia, are affectionate and beneficial to their owners’ wellbeing. However, they are very different animals and each is 'better' than the other regarding care needs and natural traits. Dogs need regular training and exercise but many owners do not train or exercise them enough, resulting in bad behaviour. They also need to be 'boarded' if the owner is away and to have frequent baths to prevent bad odours. In contrast, cats do not need this level of effort and care. Dogs are seen as more intelligent, loyal and attuned to human beings, whereas cats are perceived as aloof and solitary, and as only seeking affection when they want to be fed. However, recent studies have shown that cats are affectionate and loyal and more intelligent than dogs, but it is less obvious and useful. There are, for example, no 'police' or 'assistance' cats, in part because they do not have the kinds of natural instincts which make dogs easy to train. Therefore, which animal is better depends upon personal preference and whether they are required to work. Therefore, although dogs are better as working animals, cats are easier, better pets.
Download our basic essay structure revision sheet
Download this page as a PDF for your essay structure revision notes
Better Essays: Signposting

Paragraphs main body of an assessment

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples
How to Write an Essay Introduction | 4 Steps & Examples
Published on February 4, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on July 23, 2023.
A good introduction paragraph is an essential part of any academic essay . It sets up your argument and tells the reader what to expect.
The main goals of an introduction are to:
- Catch your reader’s attention.
- Give background on your topic.
- Present your thesis statement —the central point of your essay.
This introduction example is taken from our interactive essay example on the history of Braille.
The invention of Braille was a major turning point in the history of disability. The writing system of raised dots used by visually impaired people was developed by Louis Braille in nineteenth-century France. In a society that did not value disabled people in general, blindness was particularly stigmatized, and lack of access to reading and writing was a significant barrier to social participation. The idea of tactile reading was not entirely new, but existing methods based on sighted systems were difficult to learn and use. As the first writing system designed for blind people’s needs, Braille was a groundbreaking new accessibility tool. It not only provided practical benefits, but also helped change the cultural status of blindness. This essay begins by discussing the situation of blind people in nineteenth-century Europe. It then describes the invention of Braille and the gradual process of its acceptance within blind education. Subsequently, it explores the wide-ranging effects of this invention on blind people’s social and cultural lives.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Step 1: hook your reader, step 2: give background information, step 3: present your thesis statement, step 4: map your essay’s structure, step 5: check and revise, more examples of essay introductions, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
Your first sentence sets the tone for the whole essay, so spend some time on writing an effective hook.
Avoid long, dense sentences—start with something clear, concise and catchy that will spark your reader’s curiosity.
The hook should lead the reader into your essay, giving a sense of the topic you’re writing about and why it’s interesting. Avoid overly broad claims or plain statements of fact.
Examples: Writing a good hook
Take a look at these examples of weak hooks and learn how to improve them.
- Braille was an extremely important invention.
- The invention of Braille was a major turning point in the history of disability.
The first sentence is a dry fact; the second sentence is more interesting, making a bold claim about exactly why the topic is important.
- The internet is defined as “a global computer network providing a variety of information and communication facilities.”
- The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education.
Avoid using a dictionary definition as your hook, especially if it’s an obvious term that everyone knows. The improved example here is still broad, but it gives us a much clearer sense of what the essay will be about.
- Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is a famous book from the nineteenth century.
- Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is often read as a crude cautionary tale about the dangers of scientific advancement.
Instead of just stating a fact that the reader already knows, the improved hook here tells us about the mainstream interpretation of the book, implying that this essay will offer a different interpretation.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Next, give your reader the context they need to understand your topic and argument. Depending on the subject of your essay, this might include:
- Historical, geographical, or social context
- An outline of the debate you’re addressing
- A summary of relevant theories or research about the topic
- Definitions of key terms
The information here should be broad but clearly focused and relevant to your argument. Don’t give too much detail—you can mention points that you will return to later, but save your evidence and interpretation for the main body of the essay.
How much space you need for background depends on your topic and the scope of your essay. In our Braille example, we take a few sentences to introduce the topic and sketch the social context that the essay will address:
Now it’s time to narrow your focus and show exactly what you want to say about the topic. This is your thesis statement —a sentence or two that sums up your overall argument.
This is the most important part of your introduction. A good thesis isn’t just a statement of fact, but a claim that requires evidence and explanation.
The goal is to clearly convey your own position in a debate or your central point about a topic.
Particularly in longer essays, it’s helpful to end the introduction by signposting what will be covered in each part. Keep it concise and give your reader a clear sense of the direction your argument will take.
As you research and write, your argument might change focus or direction as you learn more.
For this reason, it’s often a good idea to wait until later in the writing process before you write the introduction paragraph—it can even be the very last thing you write.
When you’ve finished writing the essay body and conclusion , you should return to the introduction and check that it matches the content of the essay.
It’s especially important to make sure your thesis statement accurately represents what you do in the essay. If your argument has gone in a different direction than planned, tweak your thesis statement to match what you actually say.
To polish your writing, you can use something like a paraphrasing tool .
You can use the checklist below to make sure your introduction does everything it’s supposed to.
Checklist: Essay introduction
My first sentence is engaging and relevant.
I have introduced the topic with necessary background information.
I have defined any important terms.
My thesis statement clearly presents my main point or argument.
Everything in the introduction is relevant to the main body of the essay.
You have a strong introduction - now make sure the rest of your essay is just as good.
- Argumentative
- Literary analysis
This introduction to an argumentative essay sets up the debate about the internet and education, and then clearly states the position the essay will argue for.
The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education. The use of the internet in academic contexts is on the rise, and its role in learning is hotly debated. For many teachers who did not grow up with this technology, its effects seem alarming and potentially harmful. This concern, while understandable, is misguided. The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its critical benefits for students and educators—as a uniquely comprehensive and accessible information source; a means of exposure to and engagement with different perspectives; and a highly flexible learning environment.
This introduction to a short expository essay leads into the topic (the invention of the printing press) and states the main point the essay will explain (the effect of this invention on European society).
In many ways, the invention of the printing press marked the end of the Middle Ages. The medieval period in Europe is often remembered as a time of intellectual and political stagnation. Prior to the Renaissance, the average person had very limited access to books and was unlikely to be literate. The invention of the printing press in the 15th century allowed for much less restricted circulation of information in Europe, paving the way for the Reformation.
This introduction to a literary analysis essay , about Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein , starts by describing a simplistic popular view of the story, and then states how the author will give a more complex analysis of the text’s literary devices.
Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is often read as a crude cautionary tale. Arguably the first science fiction novel, its plot can be read as a warning about the dangers of scientific advancement unrestrained by ethical considerations. In this reading, and in popular culture representations of the character as a “mad scientist”, Victor Frankenstein represents the callous, arrogant ambition of modern science. However, far from providing a stable image of the character, Shelley uses shifting narrative perspectives to gradually transform our impression of Frankenstein, portraying him in an increasingly negative light as the novel goes on. While he initially appears to be a naive but sympathetic idealist, after the creature’s narrative Frankenstein begins to resemble—even in his own telling—the thoughtlessly cruel figure the creature represents him as.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
Your essay introduction should include three main things, in this order:
- An opening hook to catch the reader’s attention.
- Relevant background information that the reader needs to know.
- A thesis statement that presents your main point or argument.
The length of each part depends on the length and complexity of your essay .
The “hook” is the first sentence of your essay introduction . It should lead the reader into your essay, giving a sense of why it’s interesting.
To write a good hook, avoid overly broad statements or long, dense sentences. Try to start with something clear, concise and catchy that will spark your reader’s curiosity.
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons:
- It gives your writing direction and focus.
- It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point.
Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
The structure of an essay is divided into an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement , a body containing your in-depth analysis and arguments, and a conclusion wrapping up your ideas.
The structure of the body is flexible, but you should always spend some time thinking about how you can organize your essay to best serve your ideas.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, July 23). How to Write an Essay Introduction | 4 Steps & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/introduction/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a thesis statement | 4 steps & examples, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, how to conclude an essay | interactive example, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Education Studies
Exemplar assignments.
These are representative examples of good work, not demonstration models of perfection. They are intended to reassure you that good work can be presented in many different ways. We are grateful to your predecessors who wrote them and gave permission for us to show them to you. Please do not circulate them to anyone else. Work should not be copied from these extracts either - this can be identified by plagiarism checking.
The University provides additional help with academic writing which we would encourage you to pursue. Further examples of Masters-level writing can be found at: http://www2.warwick.ac.uk/fac/soc/ces/students/studentsupport/academicwritingpg/ .This page also gives access to the Postgraduate Taught marking criteria which may help you when reading these extracts, and further links to guidance on academic writing.
IE9D3 - Improving Schools in Areas of Socio-Economic Disadvantage
IE9D3 - Anonymised Mixed Ability Setting in English.pdf
IE9D3 - Anonymized Moodle.pdf
IE9D3 - Anonymized Primary Transition.pdf
IE9D5 - Independent Study (Teach First)
Ie9d4 - making a difference: sustained school improvement project (dissertation).
Dissertation 1
Dissertation 2
- Jump to menu
- Student Home
- Accept your offer
- How to enrol
- Student ID card
- Set up your IT
- Orientation Week
- Fees & payment
- Academic calendar
- Special consideration
- Transcripts
- The Nucleus: Student Hub
- Referencing
- Essay writing
- Learning abroad & exchange
- Professional development & UNSW Advantage
- Employability
- Financial assistance
- International students
- Equitable learning
- Postgraduate research
- Health Service
- Events & activities
- Emergencies
- Volunteering
- Clubs and societies
- Accommodation
- Health services
- Sport and gym
- Arc student organisation
- Security on campus
- Maps of campus
- Careers portal
- Change password
Examples of Reflective Writing
Types of reflective writing assignments.
A journal requires you to write weekly entries throughout a semester. May require you to base your reflection on course content.
A learning diary is similar to a journal, but may require group participation. The diary then becomes a place for you to communicate in writing with other group members.
A logbook is often used in disciplines based on experimental work, such as science. You note down or 'log' what you have done. A log gives you an accurate record of a process and helps you reflect on past actions and make better decisions for future actions.
A reflective note is often used in law. A reflective note encourages you to think about your personal reaction to a legal issue raised in a course.
An essay diary can take the form of an annotated bibliography (where you examine sources of evidence you might include in your essay) and a critique (where you reflect on your own writing and research processes).
a peer review usually involves students showing their work to their peers for feedback.
A self-assessment task requires you to comment on your own work.
Some examples of reflective writing
Social science fieldwork report (methods section), engineering design report, learning journal (weekly reflection).
Brookfield, S 1987, Developing critical thinkers: challenging adults to explore alternative ways of thinking and acting , Open University Press, Milton Keynes.
Mezirow, J 1990, Fostering critical reflection in adulthood: a guide to transformative and emancipatory learning , Jossey-Bass, San Francisco.
Schön, DA 1987, Educating the reflective practitioner , Jossey-Bass. San Francisco.
We thank the students who permitted us to feature examples of their writing.
Prepared by Academic Skills, UNSW. This guide may be distributed or adapted for educational purposes. Full and proper acknowledgement is required.
Essay and assignment writing guide
- Essay writing basics
- Essay and assignment planning
- Answering assignment questions
- Editing checklist
- Writing a critical review
- Annotated bibliography
- How do I write reflectively?
- Examples of reflective writing
- ^ More support
Study Hacks Workshops | All the hacks you need! 7 Feb – 10 Apr 2024
Discover your Library: Main Library 21 May 2024
Templates for college and university assignments
Include customizable templates in your college toolbox. stay focused on your studies and leave the assignment structuring to tried and true layout templates for all kinds of papers, reports, and more..

Keep your college toolbox stocked with easy-to-use templates
Work smarter with higher-ed helpers from our college tools collection. Presentations are on point from start to finish when you start your project using a designer-created template; you'll be sure to catch and keep your professor's attention. Staying on track semester after semester takes work, but that work gets a little easier when you take control of your scheduling, list making, and planning by using trackers and planners that bring you joy. Learning good habits in college will serve you well into your professional life after graduation, so don't reinvent the wheel—use what is known to work!

- Why Choose Us
- Vision and Mission
- Hire Writers
- How it Works

Free Sample of Assignments
List of free assignment samples for academic writing help. Our goal is to help students with assignment writing, and you may use our vast library of examples of assignments for free. Look at our sample assignments to know the quality of our work.
- 4500+ Experts Online to Assist You 24*7
- A A+ Grade Guaranteed Top Quality
- AI Free Content
- Accounting 440
- Architecture 2
- Business 2760
- Business Environment 560
- Childcare 9
- Communications 18
- Computer Science 4
- Corporate Strategy 12
- Criminology 5
- Cultural Studies 4
- Consumer Behaviour 1
- Dissertation 5
- Economics 17
- Education 120
- Employbility Skills 6
- Engineering 2
- English Literature 7
- Entrepreneurship 18
- Entrepreneurship And Small Business Management 590
- Environmental Studies 2
- Event Management 4
- Finance 550
- Finance Management 7
- General Studies 13
- Geography 1
- Health Social Care 640
- Hospitality 19
- Human Resource 910
- Information Systems 2
- Information Technology 13
- International Relations 4
- International Studies 5
- Languages 1
- Leadership 440
- Management 2235
- Managing Customer Experience 17
- Managing Innovation 17
- Marketing 930
- Marketing Essentials 440
- Music Assignment Samples 1
- Organisation Behaviour 144
- Philosophy 1
- Planning For Growth 124
- Project Management 148
- Psychology 16
- Research Technology 92
- Social Policy 5
- Social Work 8
- Sociology 5
- Statistics 5
- Tourism 520
Free Assignment Sample that Can Propel Students to Success
We are an assignment help services provider with extensive expertise in academic writing. We understand that custom-written papers assist students in performing better in their academics. We strongly oppose plagiarism and cheating. But we ensure that an adequate sample of assignments can help students become better writers.
Our experts have prepared university sample assignment to show the quality of our work. With the help of samples, we reflect our experts' in-depth knowledge and expertise in academic writing. We share the sample of assignments of different subjects as per the student's requirements.
How Can Students Use Examples of Assignments to Improve Writing Skills?
Assignment Desk provides examples of assignments that help students write their assignments. We offer assignment examples and the best academic suggestions, with the help of our expert researchers. Students have the opportunity to look at university assignment examples on our website. And after that they will know precisely what to expect from us:
- Our experts provide high-quality, well-researched, and structured academic work.
- Assignment Desk's experts are specialists in providing a wide range of subjects.
- We cover all academic writing requirements like essays, assignments, dissertations, reports, case studies, coursework, etc.
Students can utilise the assignment sample they receive from us in various ways. Including as a source of inspiration, information, and argumentation. They may also choose the topic for their write-up and utilise the example assignment body as a solid structure to analyse. Using our assignments examples, students might also get help in: syntax, vocabulary, technical terminology, referencing, bibliography, academic style, and organisation.
Once students have mastered how to handle a specific university academic task, they will have an extra opportunity to improve their writing. The next step in your academic career is to choose the best college assignments examples or university assignment examples to meet all assignment requirements.
10,700+ Happy Customers
Here is what our customers have to say about our services!
It is not very simple to get a degree in the finance field. You always need expert help in this field. I am so lucky because I got the financial assignment help from your platform.
Daniel Davison , Poole , UK
Matching the balances in the balance sheet is the highest achievement I will ever get, but experts at Assignment Desk made it possible with the accounting assignment help that I took.
Joel O'Donnell , Plymouth, UK
I am never comfortable with handling numbers since the start of my education. So, I struggled with finances as well. So, I decided to seek finance assignment help from the experts at the Assignment Desk.
Tyler Stephenson , Suffolk , UK
When I have to complete many tasks in a short time limit, the best way to finish them is with the help with finance assignment experts. They do all work with quality while following rules and time limits. I do not have to take stress because of their quick service and response time. I just wanted to say thanks.
Demi Bradshaw , York , UK
I needed help with accounting assignments and was on the constant lookout for different ways to improve in this area. While searching, I came across assignment helper and thought to give it a try. Honestly, this was the best decision of my life. Thank you. Thanks to the superb team for delivering high-quality projects. I admire your work ethic.
Brooke Tucker , Slough , UK

Please rotate your device
We don't support landscape mode yet. Please go back to portrait mode for the best experience
We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. If you continue to use this site we will assume that you are happy with it. Know more
Calculate the Price
Professional Academic Help at Pocket-Friendly Prices!
Estimated Price
Limited Time Offer
Exclusive Library Membership + FREE Wallet Balance
1 Month Access !
5000 Student Samples
10,000 Answers by Experts
Get $300 Now
- Google Meet
- Mobile Dialer

Resent Search

Management Assignment Writing

Technical Assignment Writing

Finance Assignment Writing

Medical Nursing Writing

Resume Writing

Civil engineering writing

Mathematics and Statistics Projects

CV Writing Service

Essay Writing Service

Online Dissertation Help

Thesis Writing Help

RESEARCH PAPER WRITING SERVICE

Case Study Writing Service

Electrical Engineering Assignment Help

IT Assignment Help

Mechanical Engineering Assignment Help

Homework Writing Help

Science Assignment Writing

Arts Architecture Assignment Help

Chemical Engineering Assignment Help

Computer Network Assignment Help

Arts Assignment Help

Coursework Writing Help

Custom Paper Writing Services

Personal Statement Writing

Biotechnology Assignment Help
C Programming Assignment Help

MBA Assignment Help

English Essay Writing

MATLAB Assignment Help

Narrative Writing Help

Report Writing Help

Get Top Quality Assignment Assistance

Online Exam Help

Macroeconomics Homework Help

Change Management Assignment Help

Operation management Assignment Help

Strategy Assignment Help

Human Resource Management Assignment Help

Psychology Assignment Writing Help
Algebra Homework Help

Best Assignment Writing Tips

Statistics Homework Help

CDR Writing Services

TAFE Assignment Help

Auditing Assignment Help

Literature Essay Help

Online University Assignment Writing

Economics Assignment Help

Programming Language Assignment Help

Political Science Assignment Help

Marketing Assignment Help

Project Management Assignment Help

Geography Assignment Help

Do My Assignment For Me

Business Ethics Assignment Help

Pricing Strategy Assignment Help

The Best Taxation Assignment Help

Finance Planning Assignment Help

Solve My Accounting Paper Online

Market Analysis Assignment

4p Marketing Assignment Help

Corporate Strategy Assignment Help

Project Risk Management Assignment Help

Environmental Law Assignment Help

History Assignment Help

Geometry Assignment Help

Physics Assignment Help

Clinical Reasoning Cycle

Forex Assignment Help

Python Assignment Help

Behavioural Finance Assignment Help

PHP Assignment Help

Social Science Assignment Help

Capital Budgeting Assignment Help

Trigonometry Assignment Help

Java Programming Assignment Help

Corporate Finance Planning Help

Sports Science Assignment Help

Accounting For Financial Statements Assignment Help

Robotics Assignment Help

Cost Accounting Assignment Help

Business Accounting Assignment Help

Activity Based Accounting Assignment Help

Econometrics Assignment Help

Managerial Accounting Assignment Help

R Studio Assignment Help

Cookery Assignment Help

Solidworks assignment Help

UML Diagram Assignment Help

Data Flow Diagram Assignment Help

Employment Law Assignment Help

Calculus Assignment Help

Arithmetic Assignment Help

Write My Assignment

Business Intelligence Assignment Help

Database Assignment Help

Fluid Mechanics Assignment Help

Web Design Assignment Help

Student Assignment Help

Online CPM Homework Help

Chemistry Assignment Help

Biology Assignment Help

Corporate Governance Law Assignment Help

Auto CAD Assignment Help

Public Relations Assignment Help

Bioinformatics Assignment Help

Engineering Assignment Help

Computer Science Assignment Help

C++ Programming Assignment Help

Aerospace Engineering Assignment Help

Agroecology Assignment Help

Finance Assignment Help

Conflict Management Assignment Help

Paleontology Assignment Help

Commercial Law Assignment Help

Criminal Law Assignment Help

Anthropology Assignment Help

Biochemistry Assignment Help

Get the best cheap assignment Help

Online Pharmacology Course Help

Urgent Assignment Help

Paying For Assignment Help

HND Assignment Help

Legitimate Essay Writing Help

Best Online Proofreading Services

Need Help With Your Academic Assignment

Assignment Writing Help In Canada

Assignment Writing Help In UAE

Online Assignment Writing Help in the USA

Assignment Writing Help In Australia

Assignment Writing Help In the UK

Scholarship Essay Writing Help

University of Huddersfield Assignment Help

Ph.D. Assignment Writing Help

Law Assignment Writing Help

Website Design and Development Assignment Help
How to Make a Cover Page for a University Assignment
Your cover sheet for your assignment is the first thing your teacher will see in college. It's not anything less than an immediate result. It could be the turning point of your marks. The task of writing is a necessary part of academic life. Students are often faced with a variety of schoolwork, expositions, assignments, and ventures. Each one leaves many traces of the overall class performance. Apart from that, they can be a good way to demonstrate some useful and critical thinking and research, logic and writing skills to students. Students must think about the task writing and composition and determine whether they require passes. The first thing your teachers look over during your assignments is the cover page. This week we will look at how to write your cover page correctly using examples.
Cover pages of an assignment play the largest part in academic writing assignments. It is thought to be the case that the page could aid you in grabbing the attention of your teachers and professors quickly. If you can create an attractive, impressive and suitable cover page for a university assignment , it could also enable your instructors to read through the entire task. If the assignment you submit is worthy of your reader's attention, it is not impossible to receive praise from your readers. Therefore, it can be beneficial to you when it comes to getting high academic grades.
What is an assignment cover sheet?
A cover sheet within an assignment is a piece of paper that students use to complete their tasks. It provides a short description of the is included in the assignment. It allows the student to read through the project brief in a limited amount of time. Additionally, some universities offer templates for cover sheets in a standard format, and they just require printing and filing just like another type of form.
It is, therefore, an integral part of every assignment. It can get you noticed and make you stand out. It's not difficult. It is possible to have your cover page created by our assignment help specialists in India Assignment Help. No matter if you are unsure of how to create the cover page to complete your assignment, Our experts will help you in creating. There are free cover page test tests on our website.
But why are The Pages Cover Page Important?
Cover pages of assignments are the very first item that teachers will see. If the cover page isn't properly arranged or not prepared and contains insufficient information, and is not properly formatted, it can give an impression to your teachers that you're not committed enough to the task at hand. Therefore, it could have a negative impact on your academic marks.
However, it is a good idea to write an organized and well-designed cover page for your university assignment, including all the details, such as the student's name, the assignment title, the details of the subject, the deadline and the teacher's name, you will leave an impression that is positive to the teacher. It will be a guarantee of receiving excellent academic grades.
Some examples of Cover Pages for University Assignments
Study Cover Page: Case Study Cover Page:
In general, study assignments are typically given by professors at universities to postgraduate and graduate students. In case-study assignments, students need to conduct a thorough and comprehensive study of a specific phenomenon. Here is a sample or example of the cover page for assignment on case studies:
Research Paper Cover Page:
It's another crucial assignment that teachers at universities assign their students. The purpose of an assignment for research papers is to share your research conclusions as well as analysis, arguments and solutions for a particular social issue, situation or trend. We have provided an example or the page that covers this assignment:
What's the format for The Cover Page of The University assignment?
Most university students adhere to the MLA format for writing their university assignments. In this style, the title and the specifics of the task will be included on the first page of the assignment. The cover page is the name given to this page.. Though sometimes, professors require students to write an individual covering page for themselves, they will use this to illustrate the assignment by adding the cover page on top of the very first webpage of their assignment.
The most effective strategies and tricks for how to write a college assignment are cover pages.
The name of The University & The Title of the Cover Page:
The first step is to need to begin making your cover page by using the name of the university you attend. The title of the assignment is typically added to the front of your cover page, following the name of the institution. The title's name plays the biggest role on the cover page because it occupies more space across the entire page. It is recommended to write the title in the middle of the page's cover.
Name of student:
Generally speaking, in all forms of writing and articles, the author's name should be listed on the first page. On the page that you cover for your college assignment, it is important to provide your name. In this case, it's useful to mention your complete name. Aside from that, your school name, enrollment number and academic year are also tacked into the assignment described below.
Course Name:
If you are a student at the university, it is important to give some specifics about the program or degree you're pursuing.
Subject Details-:
The cover page of your assignment at university It is also important to include certain details about the topic to be covered, like the subject's name, some short definitions of it, and a brief description of the subject.
Deadline for Submission or Data:
Also, you must mention the deadline date or submission date for the assignment, according to the instructions of your instructor. It will be beneficial to you to submit your assignment by the deadline, as the instructor will be aware of it right away.
Name of the teacher or Professor
When you've finished describing all of the information about yourself, then you need to be sure to mention the name of the professor to whom you were assigned that specific assignment. If the teacher sees your personal name in the assignments, they'll realize the level of attention you paid to your task and make an impression that is positive on the instructor.

Top 10 Best Universities Ranking list in India 2022

Generic Conventions: Assignment Help Services

Research Paper Topics For Medical

Top 5 Resources for Writing Excellent Academic Assignments

How to Write a Literature Review for Academic Purposes

Tips for Writing a killer introduction to your assignment

How To Write A Compelling Conclusion For Your University Assignment

Research Papers Topics For Social Science

Best 150 New Research Paper Ideas For Students

7 Best Plagiarism Checkers for Students And Teachers in 2024
Enquiry form.

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Common Assignments: Example
The example annotation below includes the citation, a summary in the first paragraph, the critique/analysis in the second paragraph, and the application in the third paragraph.
Gathman, A. C., & Nessan, C. L. (1997). Fowler's stages of faith development in an honors science-and-religion seminar. Zygon , 32 (3), 407–414. https://doi.org/10.1111/0591-2385.00099
The authors described the construction and rationale of an honors course in science and religion that was pedagogically based on Lawson's learning cycle model. In Lawson's model, the student writes a short paper on a subject before a presentation of the material and then writes a longer paper reevaluating and supporting his or her views. Using content analysis, the authors compared the students' answers in the first and second essays, evaluating them based on Fowler's stages of development. The authors presented examples of student writing with their analysis of the students' faith stages. The results demonstrated development in stages 2 through 5.
The authors made no mention of how to support spiritual development in the course. There was no correlation between grades and level of faith development. Instead, they were interested in the interface between religion and science, teaching material on ways of knowing, creation myths, evolutionary theory, and ethics. They exposed students to Fowler's ideas but did not relate the faith development theory to student work in the classroom. There appears to have been no effort to modify the course content based on the predominant stage of development, and it is probably a credit to their teaching that they were able to conduct the course with such diversity in student faith development. However, since Fowler's work is based largely within a Western Christian setting, some attention to differences in faith among class members would have been a useful addition to the study.
Fowler's work would seem to lend itself to research of this sort, but this model is the only example found in recent literature. This study demonstrates the best use of the model, which is assessment. While the theory claimed high predictive ability, the change process that the authors chronicled is so slow and idiosyncratic that it would be difficult to design and implement research that had as its goal measurement of movement in a faith development continuum.
Related Resources
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Application
- Next Page: Literature Reviews
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This page features authentic sample assignments that you can view or download to help you develop and enhance your academic writing skills. PLEASE NOTE: Comments included in these sample written assignments are intended as an educational guide only. Always check with academic staff which referencing convention you should follow. All sample ...
Sample of an investigative report [PDF 500KB]. A resource for science, engineering and technology students. How to write an investigative report, including an annotated format. Assignment topics and editing. Interpreting assignment topics [PDF 370 KB]. Find out how to interpret an assignment topic, including understanding key words and concepts.
The basic structure is of three parts: introduction, discussion, and conclusion. It is, however, advisable to follow the structural guidelines from your tutor. For example, our master's sample assignment includes lots of headings and sub-headings. Undergraduate assignments are shorter and present a statistical analysis only.
Example. This is an example of including the above mentioned points into the introduction of an assignment that elaborates the topic of obesity reaching proportions: Background: The twenty first century is characterized by many public health challenges, among which obesity takes a major part. The increasing prevalence of obesity is creating an ...
During Weeks 3, 4 and 5 you will concentrate on assignment writing. In particular, this week you will find out what types of assignments university students normally write, the reasons why they write them and the way they approach them. In Week 4 you will look in more detail at essay writing. In Week 5, you will learn how to clearly link ideas ...
This guide includes tips on writing common course assignments. Both in traditional and online classrooms, journal entries are used as tools for student reflection. By consciously thinking about and comparing issues, life experiences, and course readings, students are better able to understand links between theory and practice and to generate ...
is right or wrong, so write the assignment in whichever order feels best for you. The introduction might be up to around 10% of the word count (e.g. up to 200 words for a 2000 word assignment). Don't forget your conclusion At the end of the assignment, you need to summarise the key points you've made. You won't be introducing
Courses and assignments should be planned with this in mind. Three principles are paramount: 1. Name what you want and imagine students doing it. However free students are to range and explore in a paper, the general kind of paper you're inviting has common components, operations, and criteria of success, and you should make these explicit ...
Essay writing process. The writing process of preparation, writing, and revisions applies to every essay or paper, but the time and effort spent on each stage depends on the type of essay.. For example, if you've been assigned a five-paragraph expository essay for a high school class, you'll probably spend the most time on the writing stage; for a college-level argumentative essay, on the ...
Here are five tips to help you get ahead. 1. Use available sources of information. Beyond instructions and deadlines, lecturers make available an increasing number of resources. But students often ...
What this handout is about. The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This handout will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms ...
This example guides you through the structure of an essay. It shows how to build an effective introduction , focused paragraphs , clear transitions between ideas, and a strong conclusion . Each paragraph addresses a single central point, introduced by a topic sentence , and each point is directly related to the thesis statement .
Identify content words, limit words and action or direction words in your assignment task. Content words - usually nouns - tell you what to consider. Action or direction words - verbs - tell you what to do. Limit words - tell when/during what period, or how much/how many, or which ones to include, which to exclude. Research and reading.
An essay consists of three basic parts: Introduction. Body. Conclusion. The essay itself usually has no section headings. Only the title page, author declaration and reference list are written as headings, along with, for example, appendices. Check any task instructions, and your course or unit handbook, for further details.
Table of contents. Step 1: Hook your reader. Step 2: Give background information. Step 3: Present your thesis statement. Step 4: Map your essay's structure. Step 5: Check and revise. More examples of essay introductions. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
Executive summaries are common in the Walden MBA program, but they are also found as part of some government and business documents. As a student, you should complete an executive summary when specifically requested to do so. An executive summary is a comprehensive review of a larger document. For example, a 35-page report may begin with a ...
Exemplar Assignments. These are representative examples of good work, not demonstration models of perfection. They are intended to reassure you that good work can be presented in many different ways. We are grateful to your predecessors who wrote them and gave permission for us to show them to you. Please do not circulate them to anyone else.
Types of reflective writing assignments. A journal requires you to write weekly entries throughout a semester.May require you to base your reflection on course content. A learning diary is similar to a journal, but may require group participation. The diary then becomes a place for you to communicate in writing with other group members.
Templates for college and university assignments. Include customizable templates in your college toolbox. Stay focused on your studies and leave the assignment structuring to tried and true layout templates for all kinds of papers, reports, and more. Category. Color. Create from scratch. Show all.
An abstract appears after a paper's cover page but before the body of the paper. Per APA 7, Section 2.9, to format an abstract, center the title "Abstract" at the top of a new page in bold text. Note that the bolding is a change from APA 6 guidelines, which recommended plain text. The body of the abstract for course papers should be.
List of free assignment samples for academic writing help. Our goal is to help students with assignment writing, and you may use our vast library of examples of assignments for free. Look at our sample assignments to know the quality of our work. Get Assignment Help. 4500+ Experts Online to Assist You 24*7. A.
In general, study assignments are typically given by professors at universities to postgraduate and graduate students. In case-study assignments, students need to conduct a thorough and comprehensive study of a specific phenomenon. Here is a sample or example of the cover page for assignment on case studies: Research Paper Cover Page:
Grammar and Puncuation Terms. Paper Layout and Word Processing Terms. Scholarly Writing. Common Course Assignments. Precision, Clarity, and Academic Expression. Point of View. Objectivity. Avoiding Bias. Active and Passive Voice.