Criteria for Good Qualitative Research: A Comprehensive Review
- Regular Article
- Open access
- Published: 18 September 2021
- Volume 31 , pages 679–689, ( 2022 )

Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article
- Drishti Yadav ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-2974-0323 1
75k Accesses
27 Citations
72 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
This review aims to synthesize a published set of evaluative criteria for good qualitative research. The aim is to shed light on existing standards for assessing the rigor of qualitative research encompassing a range of epistemological and ontological standpoints. Using a systematic search strategy, published journal articles that deliberate criteria for rigorous research were identified. Then, references of relevant articles were surveyed to find noteworthy, distinct, and well-defined pointers to good qualitative research. This review presents an investigative assessment of the pivotal features in qualitative research that can permit the readers to pass judgment on its quality and to condemn it as good research when objectively and adequately utilized. Overall, this review underlines the crux of qualitative research and accentuates the necessity to evaluate such research by the very tenets of its being. It also offers some prospects and recommendations to improve the quality of qualitative research. Based on the findings of this review, it is concluded that quality criteria are the aftereffect of socio-institutional procedures and existing paradigmatic conducts. Owing to the paradigmatic diversity of qualitative research, a single and specific set of quality criteria is neither feasible nor anticipated. Since qualitative research is not a cohesive discipline, researchers need to educate and familiarize themselves with applicable norms and decisive factors to evaluate qualitative research from within its theoretical and methodological framework of origin.
Similar content being viewed by others
Mixed methods research: what it is and what it could be
Rob Timans, Paul Wouters & Johan Heilbron

Saturation in qualitative research: exploring its conceptualization and operationalization
Benjamin Saunders, Julius Sim, … Clare Jinks

What Is Sustainability? A Review of the Concept and Its Applications
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
“… It is important to regularly dialogue about what makes for good qualitative research” (Tracy, 2010 , p. 837)
To decide what represents good qualitative research is highly debatable. There are numerous methods that are contained within qualitative research and that are established on diverse philosophical perspectives. Bryman et al., ( 2008 , p. 262) suggest that “It is widely assumed that whereas quality criteria for quantitative research are well‐known and widely agreed, this is not the case for qualitative research.” Hence, the question “how to evaluate the quality of qualitative research” has been continuously debated. There are many areas of science and technology wherein these debates on the assessment of qualitative research have taken place. Examples include various areas of psychology: general psychology (Madill et al., 2000 ); counseling psychology (Morrow, 2005 ); and clinical psychology (Barker & Pistrang, 2005 ), and other disciplines of social sciences: social policy (Bryman et al., 2008 ); health research (Sparkes, 2001 ); business and management research (Johnson et al., 2006 ); information systems (Klein & Myers, 1999 ); and environmental studies (Reid & Gough, 2000 ). In the literature, these debates are enthused by the impression that the blanket application of criteria for good qualitative research developed around the positivist paradigm is improper. Such debates are based on the wide range of philosophical backgrounds within which qualitative research is conducted (e.g., Sandberg, 2000 ; Schwandt, 1996 ). The existence of methodological diversity led to the formulation of different sets of criteria applicable to qualitative research.
Among qualitative researchers, the dilemma of governing the measures to assess the quality of research is not a new phenomenon, especially when the virtuous triad of objectivity, reliability, and validity (Spencer et al., 2004 ) are not adequate. Occasionally, the criteria of quantitative research are used to evaluate qualitative research (Cohen & Crabtree, 2008 ; Lather, 2004 ). Indeed, Howe ( 2004 ) claims that the prevailing paradigm in educational research is scientifically based experimental research. Hypotheses and conjectures about the preeminence of quantitative research can weaken the worth and usefulness of qualitative research by neglecting the prominence of harmonizing match for purpose on research paradigm, the epistemological stance of the researcher, and the choice of methodology. Researchers have been reprimanded concerning this in “paradigmatic controversies, contradictions, and emerging confluences” (Lincoln & Guba, 2000 ).
In general, qualitative research tends to come from a very different paradigmatic stance and intrinsically demands distinctive and out-of-the-ordinary criteria for evaluating good research and varieties of research contributions that can be made. This review attempts to present a series of evaluative criteria for qualitative researchers, arguing that their choice of criteria needs to be compatible with the unique nature of the research in question (its methodology, aims, and assumptions). This review aims to assist researchers in identifying some of the indispensable features or markers of high-quality qualitative research. In a nutshell, the purpose of this systematic literature review is to analyze the existing knowledge on high-quality qualitative research and to verify the existence of research studies dealing with the critical assessment of qualitative research based on the concept of diverse paradigmatic stances. Contrary to the existing reviews, this review also suggests some critical directions to follow to improve the quality of qualitative research in different epistemological and ontological perspectives. This review is also intended to provide guidelines for the acceleration of future developments and dialogues among qualitative researchers in the context of assessing the qualitative research.
The rest of this review article is structured in the following fashion: Sect. Methods describes the method followed for performing this review. Section Criteria for Evaluating Qualitative Studies provides a comprehensive description of the criteria for evaluating qualitative studies. This section is followed by a summary of the strategies to improve the quality of qualitative research in Sect. Improving Quality: Strategies . Section How to Assess the Quality of the Research Findings? provides details on how to assess the quality of the research findings. After that, some of the quality checklists (as tools to evaluate quality) are discussed in Sect. Quality Checklists: Tools for Assessing the Quality . At last, the review ends with the concluding remarks presented in Sect. Conclusions, Future Directions and Outlook . Some prospects in qualitative research for enhancing its quality and usefulness in the social and techno-scientific research community are also presented in Sect. Conclusions, Future Directions and Outlook .
For this review, a comprehensive literature search was performed from many databases using generic search terms such as Qualitative Research , Criteria , etc . The following databases were chosen for the literature search based on the high number of results: IEEE Explore, ScienceDirect, PubMed, Google Scholar, and Web of Science. The following keywords (and their combinations using Boolean connectives OR/AND) were adopted for the literature search: qualitative research, criteria, quality, assessment, and validity. The synonyms for these keywords were collected and arranged in a logical structure (see Table 1 ). All publications in journals and conference proceedings later than 1950 till 2021 were considered for the search. Other articles extracted from the references of the papers identified in the electronic search were also included. A large number of publications on qualitative research were retrieved during the initial screening. Hence, to include the searches with the main focus on criteria for good qualitative research, an inclusion criterion was utilized in the search string.
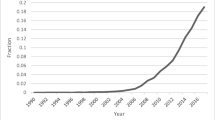
From the selected databases, the search retrieved a total of 765 publications. Then, the duplicate records were removed. After that, based on the title and abstract, the remaining 426 publications were screened for their relevance by using the following inclusion and exclusion criteria (see Table 2 ). Publications focusing on evaluation criteria for good qualitative research were included, whereas those works which delivered theoretical concepts on qualitative research were excluded. Based on the screening and eligibility, 45 research articles were identified that offered explicit criteria for evaluating the quality of qualitative research and were found to be relevant to this review.
Figure 1 illustrates the complete review process in the form of PRISMA flow diagram. PRISMA, i.e., “preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses” is employed in systematic reviews to refine the quality of reporting.
PRISMA flow diagram illustrating the search and inclusion process. N represents the number of records
Criteria for Evaluating Qualitative Studies
Fundamental criteria: general research quality.
Various researchers have put forward criteria for evaluating qualitative research, which have been summarized in Table 3 . Also, the criteria outlined in Table 4 effectively deliver the various approaches to evaluate and assess the quality of qualitative work. The entries in Table 4 are based on Tracy’s “Eight big‐tent criteria for excellent qualitative research” (Tracy, 2010 ). Tracy argues that high-quality qualitative work should formulate criteria focusing on the worthiness, relevance, timeliness, significance, morality, and practicality of the research topic, and the ethical stance of the research itself. Researchers have also suggested a series of questions as guiding principles to assess the quality of a qualitative study (Mays & Pope, 2020 ). Nassaji ( 2020 ) argues that good qualitative research should be robust, well informed, and thoroughly documented.
Qualitative Research: Interpretive Paradigms
All qualitative researchers follow highly abstract principles which bring together beliefs about ontology, epistemology, and methodology. These beliefs govern how the researcher perceives and acts. The net, which encompasses the researcher’s epistemological, ontological, and methodological premises, is referred to as a paradigm, or an interpretive structure, a “Basic set of beliefs that guides action” (Guba, 1990 ). Four major interpretive paradigms structure the qualitative research: positivist and postpositivist, constructivist interpretive, critical (Marxist, emancipatory), and feminist poststructural. The complexity of these four abstract paradigms increases at the level of concrete, specific interpretive communities. Table 5 presents these paradigms and their assumptions, including their criteria for evaluating research, and the typical form that an interpretive or theoretical statement assumes in each paradigm. Moreover, for evaluating qualitative research, quantitative conceptualizations of reliability and validity are proven to be incompatible (Horsburgh, 2003 ). In addition, a series of questions have been put forward in the literature to assist a reviewer (who is proficient in qualitative methods) for meticulous assessment and endorsement of qualitative research (Morse, 2003 ). Hammersley ( 2007 ) also suggests that guiding principles for qualitative research are advantageous, but methodological pluralism should not be simply acknowledged for all qualitative approaches. Seale ( 1999 ) also points out the significance of methodological cognizance in research studies.
Table 5 reflects that criteria for assessing the quality of qualitative research are the aftermath of socio-institutional practices and existing paradigmatic standpoints. Owing to the paradigmatic diversity of qualitative research, a single set of quality criteria is neither possible nor desirable. Hence, the researchers must be reflexive about the criteria they use in the various roles they play within their research community.
Improving Quality: Strategies
Another critical question is “How can the qualitative researchers ensure that the abovementioned quality criteria can be met?” Lincoln and Guba ( 1986 ) delineated several strategies to intensify each criteria of trustworthiness. Other researchers (Merriam & Tisdell, 2016 ; Shenton, 2004 ) also presented such strategies. A brief description of these strategies is shown in Table 6 .
It is worth mentioning that generalizability is also an integral part of qualitative research (Hays & McKibben, 2021 ). In general, the guiding principle pertaining to generalizability speaks about inducing and comprehending knowledge to synthesize interpretive components of an underlying context. Table 7 summarizes the main metasynthesis steps required to ascertain generalizability in qualitative research.
Figure 2 reflects the crucial components of a conceptual framework and their contribution to decisions regarding research design, implementation, and applications of results to future thinking, study, and practice (Johnson et al., 2020 ). The synergy and interrelationship of these components signifies their role to different stances of a qualitative research study.

Essential elements of a conceptual framework
In a nutshell, to assess the rationale of a study, its conceptual framework and research question(s), quality criteria must take account of the following: lucid context for the problem statement in the introduction; well-articulated research problems and questions; precise conceptual framework; distinct research purpose; and clear presentation and investigation of the paradigms. These criteria would expedite the quality of qualitative research.
How to Assess the Quality of the Research Findings?
The inclusion of quotes or similar research data enhances the confirmability in the write-up of the findings. The use of expressions (for instance, “80% of all respondents agreed that” or “only one of the interviewees mentioned that”) may also quantify qualitative findings (Stenfors et al., 2020 ). On the other hand, the persuasive reason for “why this may not help in intensifying the research” has also been provided (Monrouxe & Rees, 2020 ). Further, the Discussion and Conclusion sections of an article also prove robust markers of high-quality qualitative research, as elucidated in Table 8 .
Quality Checklists: Tools for Assessing the Quality
Numerous checklists are available to speed up the assessment of the quality of qualitative research. However, if used uncritically and recklessly concerning the research context, these checklists may be counterproductive. I recommend that such lists and guiding principles may assist in pinpointing the markers of high-quality qualitative research. However, considering enormous variations in the authors’ theoretical and philosophical contexts, I would emphasize that high dependability on such checklists may say little about whether the findings can be applied in your setting. A combination of such checklists might be appropriate for novice researchers. Some of these checklists are listed below:
The most commonly used framework is Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research (COREQ) (Tong et al., 2007 ). This framework is recommended by some journals to be followed by the authors during article submission.
Standards for Reporting Qualitative Research (SRQR) is another checklist that has been created particularly for medical education (O’Brien et al., 2014 ).
Also, Tracy ( 2010 ) and Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP, 2021 ) offer criteria for qualitative research relevant across methods and approaches.
Further, researchers have also outlined different criteria as hallmarks of high-quality qualitative research. For instance, the “Road Trip Checklist” (Epp & Otnes, 2021 ) provides a quick reference to specific questions to address different elements of high-quality qualitative research.
Conclusions, Future Directions, and Outlook
This work presents a broad review of the criteria for good qualitative research. In addition, this article presents an exploratory analysis of the essential elements in qualitative research that can enable the readers of qualitative work to judge it as good research when objectively and adequately utilized. In this review, some of the essential markers that indicate high-quality qualitative research have been highlighted. I scope them narrowly to achieve rigor in qualitative research and note that they do not completely cover the broader considerations necessary for high-quality research. This review points out that a universal and versatile one-size-fits-all guideline for evaluating the quality of qualitative research does not exist. In other words, this review also emphasizes the non-existence of a set of common guidelines among qualitative researchers. In unison, this review reinforces that each qualitative approach should be treated uniquely on account of its own distinctive features for different epistemological and disciplinary positions. Owing to the sensitivity of the worth of qualitative research towards the specific context and the type of paradigmatic stance, researchers should themselves analyze what approaches can be and must be tailored to ensemble the distinct characteristics of the phenomenon under investigation. Although this article does not assert to put forward a magic bullet and to provide a one-stop solution for dealing with dilemmas about how, why, or whether to evaluate the “goodness” of qualitative research, it offers a platform to assist the researchers in improving their qualitative studies. This work provides an assembly of concerns to reflect on, a series of questions to ask, and multiple sets of criteria to look at, when attempting to determine the quality of qualitative research. Overall, this review underlines the crux of qualitative research and accentuates the need to evaluate such research by the very tenets of its being. Bringing together the vital arguments and delineating the requirements that good qualitative research should satisfy, this review strives to equip the researchers as well as reviewers to make well-versed judgment about the worth and significance of the qualitative research under scrutiny. In a nutshell, a comprehensive portrayal of the research process (from the context of research to the research objectives, research questions and design, speculative foundations, and from approaches of collecting data to analyzing the results, to deriving inferences) frequently proliferates the quality of a qualitative research.
Prospects : A Road Ahead for Qualitative Research
Irrefutably, qualitative research is a vivacious and evolving discipline wherein different epistemological and disciplinary positions have their own characteristics and importance. In addition, not surprisingly, owing to the sprouting and varied features of qualitative research, no consensus has been pulled off till date. Researchers have reflected various concerns and proposed several recommendations for editors and reviewers on conducting reviews of critical qualitative research (Levitt et al., 2021 ; McGinley et al., 2021 ). Following are some prospects and a few recommendations put forward towards the maturation of qualitative research and its quality evaluation:
In general, most of the manuscript and grant reviewers are not qualitative experts. Hence, it is more likely that they would prefer to adopt a broad set of criteria. However, researchers and reviewers need to keep in mind that it is inappropriate to utilize the same approaches and conducts among all qualitative research. Therefore, future work needs to focus on educating researchers and reviewers about the criteria to evaluate qualitative research from within the suitable theoretical and methodological context.
There is an urgent need to refurbish and augment critical assessment of some well-known and widely accepted tools (including checklists such as COREQ, SRQR) to interrogate their applicability on different aspects (along with their epistemological ramifications).
Efforts should be made towards creating more space for creativity, experimentation, and a dialogue between the diverse traditions of qualitative research. This would potentially help to avoid the enforcement of one's own set of quality criteria on the work carried out by others.
Moreover, journal reviewers need to be aware of various methodological practices and philosophical debates.
It is pivotal to highlight the expressions and considerations of qualitative researchers and bring them into a more open and transparent dialogue about assessing qualitative research in techno-scientific, academic, sociocultural, and political rooms.
Frequent debates on the use of evaluative criteria are required to solve some potentially resolved issues (including the applicability of a single set of criteria in multi-disciplinary aspects). Such debates would not only benefit the group of qualitative researchers themselves, but primarily assist in augmenting the well-being and vivacity of the entire discipline.
To conclude, I speculate that the criteria, and my perspective, may transfer to other methods, approaches, and contexts. I hope that they spark dialog and debate – about criteria for excellent qualitative research and the underpinnings of the discipline more broadly – and, therefore, help improve the quality of a qualitative study. Further, I anticipate that this review will assist the researchers to contemplate on the quality of their own research, to substantiate research design and help the reviewers to review qualitative research for journals. On a final note, I pinpoint the need to formulate a framework (encompassing the prerequisites of a qualitative study) by the cohesive efforts of qualitative researchers of different disciplines with different theoretic-paradigmatic origins. I believe that tailoring such a framework (of guiding principles) paves the way for qualitative researchers to consolidate the status of qualitative research in the wide-ranging open science debate. Dialogue on this issue across different approaches is crucial for the impending prospects of socio-techno-educational research.
Amin, M. E. K., Nørgaard, L. S., Cavaco, A. M., Witry, M. J., Hillman, L., Cernasev, A., & Desselle, S. P. (2020). Establishing trustworthiness and authenticity in qualitative pharmacy research. Research in Social and Administrative Pharmacy, 16 (10), 1472–1482.
Article Google Scholar
Barker, C., & Pistrang, N. (2005). Quality criteria under methodological pluralism: Implications for conducting and evaluating research. American Journal of Community Psychology, 35 (3–4), 201–212.
Bryman, A., Becker, S., & Sempik, J. (2008). Quality criteria for quantitative, qualitative and mixed methods research: A view from social policy. International Journal of Social Research Methodology, 11 (4), 261–276.
Caelli, K., Ray, L., & Mill, J. (2003). ‘Clear as mud’: Toward greater clarity in generic qualitative research. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 2 (2), 1–13.
CASP (2021). CASP checklists. Retrieved May 2021 from https://casp-uk.net/casp-tools-checklists/
Cohen, D. J., & Crabtree, B. F. (2008). Evaluative criteria for qualitative research in health care: Controversies and recommendations. The Annals of Family Medicine, 6 (4), 331–339.
Denzin, N. K., & Lincoln, Y. S. (2005). Introduction: The discipline and practice of qualitative research. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), The sage handbook of qualitative research (pp. 1–32). Sage Publications Ltd.
Google Scholar
Elliott, R., Fischer, C. T., & Rennie, D. L. (1999). Evolving guidelines for publication of qualitative research studies in psychology and related fields. British Journal of Clinical Psychology, 38 (3), 215–229.
Epp, A. M., & Otnes, C. C. (2021). High-quality qualitative research: Getting into gear. Journal of Service Research . https://doi.org/10.1177/1094670520961445
Guba, E. G. (1990). The paradigm dialog. In Alternative paradigms conference, mar, 1989, Indiana u, school of education, San Francisco, ca, us . Sage Publications, Inc.
Hammersley, M. (2007). The issue of quality in qualitative research. International Journal of Research and Method in Education, 30 (3), 287–305.
Haven, T. L., Errington, T. M., Gleditsch, K. S., van Grootel, L., Jacobs, A. M., Kern, F. G., & Mokkink, L. B. (2020). Preregistering qualitative research: A Delphi study. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 19 , 1609406920976417.
Hays, D. G., & McKibben, W. B. (2021). Promoting rigorous research: Generalizability and qualitative research. Journal of Counseling and Development, 99 (2), 178–188.
Horsburgh, D. (2003). Evaluation of qualitative research. Journal of Clinical Nursing, 12 (2), 307–312.
Howe, K. R. (2004). A critique of experimentalism. Qualitative Inquiry, 10 (1), 42–46.
Johnson, J. L., Adkins, D., & Chauvin, S. (2020). A review of the quality indicators of rigor in qualitative research. American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education, 84 (1), 7120.
Johnson, P., Buehring, A., Cassell, C., & Symon, G. (2006). Evaluating qualitative management research: Towards a contingent criteriology. International Journal of Management Reviews, 8 (3), 131–156.
Klein, H. K., & Myers, M. D. (1999). A set of principles for conducting and evaluating interpretive field studies in information systems. MIS Quarterly, 23 (1), 67–93.
Lather, P. (2004). This is your father’s paradigm: Government intrusion and the case of qualitative research in education. Qualitative Inquiry, 10 (1), 15–34.
Levitt, H. M., Morrill, Z., Collins, K. M., & Rizo, J. L. (2021). The methodological integrity of critical qualitative research: Principles to support design and research review. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 68 (3), 357.
Lincoln, Y. S., & Guba, E. G. (1986). But is it rigorous? Trustworthiness and authenticity in naturalistic evaluation. New Directions for Program Evaluation, 1986 (30), 73–84.
Lincoln, Y. S., & Guba, E. G. (2000). Paradigmatic controversies, contradictions and emerging confluences. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), Handbook of qualitative research (2nd ed., pp. 163–188). Sage Publications.
Madill, A., Jordan, A., & Shirley, C. (2000). Objectivity and reliability in qualitative analysis: Realist, contextualist and radical constructionist epistemologies. British Journal of Psychology, 91 (1), 1–20.
Mays, N., & Pope, C. (2020). Quality in qualitative research. Qualitative Research in Health Care . https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119410867.ch15
McGinley, S., Wei, W., Zhang, L., & Zheng, Y. (2021). The state of qualitative research in hospitality: A 5-year review 2014 to 2019. Cornell Hospitality Quarterly, 62 (1), 8–20.
Merriam, S., & Tisdell, E. (2016). Qualitative research: A guide to design and implementation. San Francisco, US.
Meyer, M., & Dykes, J. (2019). Criteria for rigor in visualization design study. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 26 (1), 87–97.
Monrouxe, L. V., & Rees, C. E. (2020). When I say… quantification in qualitative research. Medical Education, 54 (3), 186–187.
Morrow, S. L. (2005). Quality and trustworthiness in qualitative research in counseling psychology. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 52 (2), 250.
Morse, J. M. (2003). A review committee’s guide for evaluating qualitative proposals. Qualitative Health Research, 13 (6), 833–851.
Nassaji, H. (2020). Good qualitative research. Language Teaching Research, 24 (4), 427–431.
O’Brien, B. C., Harris, I. B., Beckman, T. J., Reed, D. A., & Cook, D. A. (2014). Standards for reporting qualitative research: A synthesis of recommendations. Academic Medicine, 89 (9), 1245–1251.
O’Connor, C., & Joffe, H. (2020). Intercoder reliability in qualitative research: Debates and practical guidelines. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 19 , 1609406919899220.
Reid, A., & Gough, S. (2000). Guidelines for reporting and evaluating qualitative research: What are the alternatives? Environmental Education Research, 6 (1), 59–91.
Rocco, T. S. (2010). Criteria for evaluating qualitative studies. Human Resource Development International . https://doi.org/10.1080/13678868.2010.501959
Sandberg, J. (2000). Understanding human competence at work: An interpretative approach. Academy of Management Journal, 43 (1), 9–25.
Schwandt, T. A. (1996). Farewell to criteriology. Qualitative Inquiry, 2 (1), 58–72.
Seale, C. (1999). Quality in qualitative research. Qualitative Inquiry, 5 (4), 465–478.
Shenton, A. K. (2004). Strategies for ensuring trustworthiness in qualitative research projects. Education for Information, 22 (2), 63–75.
Sparkes, A. C. (2001). Myth 94: Qualitative health researchers will agree about validity. Qualitative Health Research, 11 (4), 538–552.
Spencer, L., Ritchie, J., Lewis, J., & Dillon, L. (2004). Quality in qualitative evaluation: A framework for assessing research evidence.
Stenfors, T., Kajamaa, A., & Bennett, D. (2020). How to assess the quality of qualitative research. The Clinical Teacher, 17 (6), 596–599.
Taylor, E. W., Beck, J., & Ainsworth, E. (2001). Publishing qualitative adult education research: A peer review perspective. Studies in the Education of Adults, 33 (2), 163–179.
Tong, A., Sainsbury, P., & Craig, J. (2007). Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ): A 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups. International Journal for Quality in Health Care, 19 (6), 349–357.
Tracy, S. J. (2010). Qualitative quality: Eight “big-tent” criteria for excellent qualitative research. Qualitative Inquiry, 16 (10), 837–851.
Download references
Open access funding provided by TU Wien (TUW).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Faculty of Informatics, Technische Universität Wien, 1040, Vienna, Austria
Drishti Yadav
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Drishti Yadav .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Yadav, D. Criteria for Good Qualitative Research: A Comprehensive Review. Asia-Pacific Edu Res 31 , 679–689 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40299-021-00619-0
Download citation
Accepted : 28 August 2021
Published : 18 September 2021
Issue Date : December 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s40299-021-00619-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Qualitative research
- Evaluative criteria
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- - Google Chrome
Intended for healthcare professionals
- Access provided by Google Indexer
- My email alerts
- BMA member login
- Username * Password * Forgot your log in details? Need to activate BMA Member Log In Log in via OpenAthens Log in via your institution

Search form
- Advanced search
- Search responses
- Search blogs
- Critically appraising...
Critically appraising qualitative research
- Related content
- Peer review
- Ayelet Kuper , assistant professor 1 ,
- Lorelei Lingard , associate professor 2 ,
- Wendy Levinson , Sir John and Lady Eaton professor and chair 3
- 1 Department of Medicine, Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, and Wilson Centre for Research in Education, University of Toronto, 2075 Bayview Avenue, Room HG 08, Toronto, ON, Canada M4N 3M5
- 2 Department of Paediatrics and Wilson Centre for Research in Education, University of Toronto and SickKids Learning Institute; BMO Financial Group Professor in Health Professions Education Research, University Health Network, 200 Elizabeth Street, Eaton South 1-565, Toronto
- 3 Department of Medicine, Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre
- Correspondence to: A Kuper ayelet94{at}post.harvard.edu
Six key questions will help readers to assess qualitative research
Summary points
Appraising qualitative research is different from appraising quantitative research
Qualitative research papers should show appropriate sampling, data collection, and data analysis
Transferability of qualitative research depends on context and may be enhanced by using theory
Ethics in qualitative research goes beyond review boards’ requirements to involve complex issues of confidentiality, reflexivity, and power
Over the past decade, readers of medical journals have gained skills in critically appraising studies to determine whether the results can be trusted and applied to their own practice settings. Criteria have been designed to assess studies that use quantitative methods, and these are now in common use.
In this article we offer guidance for readers on how to assess a study that uses qualitative research methods by providing six key questions to ask when reading qualitative research (box 1). However, the thorough assessment of qualitative research is an interpretive act and requires informed reflective thought rather than the simple application of a scoring system.
Box 1 Key questions to ask when reading qualitative research studies
Was the sample used in the study appropriate to its research question, were the data collected appropriately, were the data analysed appropriately, can i transfer the results of this study to my own setting, does the study adequately address potential ethical issues, including reflexivity.
Overall: is what the researchers did clear?
One of the critical decisions in a qualitative study is whom or what to include in the sample—whom to interview, whom to observe, what texts to analyse. An understanding that qualitative research is based in experience and in the construction of meaning, combined with the specific research question, should guide the sampling process. For example, a study of the experience of survivors of domestic violence that examined their reasons for not seeking help from healthcare providers might focus on interviewing a sample of such survivors (rather than, for example, healthcare providers, social services workers, or academics in the field). The sample should be broad enough to capture the many facets of a phenomenon, and limitations to the sample should be clearly justified. Since the answers to questions of experience and meaning also relate to people’s social affiliations (culture, religion, socioeconomic group, profession, etc), it is also important that the researcher acknowledges these contexts in the selection of a study sample.
In contrast with quantitative approaches, qualitative studies do not usually have predetermined sample sizes. Sampling stops when a thorough understanding of the phenomenon under study has been reached, an end point that is often called saturation. Researchers consider samples to be saturated when encounters (interviews, observations, etc) with new participants no longer elicit trends or themes not already raised by previous participants. Thus, to sample to saturation, data analysis has to happen while new data are still being collected. Multiple sampling methods may be used to broaden the understanding achieved in a study (box 2). These sampling issues should be clearly articulated in the methods section.
Box 2 Qualitative sampling methods for interviews and focus groups 9
Examples are for a hypothetical study of financial concerns among adult patients with chronic renal failure receiving ongoing haemodialysis in a single hospital outpatient unit.
Typical case sampling —sampling the most ordinary, usual cases of a phenomenon
The sample would include patients likely to have had typical experiences for that haemodialysis unit and patients who fit the profile of patients in the unit for factors found on literature review. Other typical cases could be found via snowball sampling (see below)
Deviant case sampling —sampling the most extreme cases of a phenomenon
The sample would include patients likely to have had different experiences of relevant aspects of haemodialysis. For example, if most patients in the unit are 60-70 years old and recently began haemodialysis for diabetic nephropathy, researchers might sample the unmarried university student in his 20s on haemodialysis since childhood, the 32 year old woman with lupus who is now trying to get pregnant, and the 90 year old who newly started haemodialysis due to an adverse reaction to radio-opaque contrast dye. Other deviant cases could be found via theoretical and/or snowball sampling (see below)
Critical case sampling —sampling cases that are predicted (based on theoretical models or previous research) to be especially information-rich and thus particularly illuminating
The nature of this sample depends on previous research. For example, if research showed that marital status was a major determinant of financial concerns for haemodialysis patients, then critical cases might include patients whose marital status changed while on haemodialysis
Maximum-variation sampling —sampling as wide a range of perspectives as possible to capture the broadest set of information and experiences)
The sample would include typical, deviant, and critical cases (as above), plus any other perspectives identified
Confirming-disconfirming sampling —Sampling both individuals or texts whose perspectives are likely to confirm the researcher’s developing understanding of the phenomenon under study and those whose perspectives are likely to challenge that understanding
The sample would include patients whose experiences would likely either confirm or disconfirm what the researchers had already learnt (from other patients) about financial concerns among patients in the haemodialysis unit. This could be accomplished via theoretical and/or snowball sampling (see below)
Snowball sampling —sampling participants found by asking current participants in a study to recommend others whose experiences would be relevant to the study
Current participants could be asked to provide the names of others in the unit who they thought, when asked about financial concerns, would either share their views (confirming), disagree with their views (disconfirming), have views typical of patients on their unit (typical cases), or have views different from most other patients on their unit (deviant cases)
Theoretical sampling —sampling individuals or texts whom the researchers predict (based on theoretical models or previous research) would add new perspectives to those already represented in the sample
Researchers could use their understanding of known issues for haemodialysis patients that would, in theory, relate to financial concerns to ensure that the relevant perspectives were represented in the study. For example, if, as the research progressed, it turned out that none of the patients in the sample had had to change or leave a job in order to accommodate haemodialysis scheduling, the researchers might (based on previous research) choose to intentionally sample patients who had left their jobs because of the time commitment of haemodialysis (but who could not do peritoneal dialysis) and others who had switched to jobs with more flexible scheduling because of their need for haemodialysis
It is important that a qualitative study carefully describes the methods used in collecting data. The appropriateness of the method(s) selected to use for the specific research question should be justified, ideally with reference to the research literature. It should be clear that methods were used systematically and in an organised manner. Attention should be paid to specific methodological challenges such as the Hawthorne effect, 1 whereby the presence of an observer may influence participants’ behaviours. By using a technique called thick description, qualitative studies often aim to include enough contextual information to provide readers with a sense of what it was like to have been in the research setting.
Another technique that is often used is triangulation, with which a researcher uses multiple methods or perspectives to help produce a more comprehensive set of findings. A study can triangulate data, using different sources of data to examine a phenomenon in different contexts (for example, interviewing palliative patients who are at home, those who are in acute care hospitals, and those who are in specialist palliative care units); it can also triangulate methods, collecting different types of data (for example, interviews, focus groups, observations) to increase insight into a phenomenon.
Another common technique is the use of an iterative process, whereby concurrent data analysis is used to inform data collection. For example, concurrent analysis of an interview study about lack of adherence to medications among a particular social group might show that early participants seem to be dismissive of the efforts of their local pharmacists; the interview script might then be changed to include an exploration of this phenomenon. The iterative process constitutes a distinctive qualitative tradition, in contrast to the tradition of stable processes and measures in quantitative studies. Iterations should be explicit and justified with reference to the research question and sampling techniques so that the reader understands how data collection shaped the resulting insights.
Qualitative studies should include a clear description of a systematic form of data analysis. Many legitimate analytical approaches exist; regardless of which is used, the study should report what was done, how, and by whom. If an iterative process was used, it should be clearly delineated. If more than one researcher analysed the data (which depends on the methodology used) it should be clear how differences between analyses were negotiated. Many studies make reference to a technique called member checking, wherein the researcher shows all or part of the study’s findings to participants to determine if they are in accord with their experiences. 2 Studies may also describe an audit trail, which might include researchers’ analysis notes, minutes of researchers’ meetings, and other materials that could be used to follow the research process.
The contextual nature of qualitative research means that careful thought must be given to the potential transferability of its results to other sociocultural settings. Though the study should discuss the extent of the findings’ resonance with the published literature, 3 much of the onus of assessing transferability is left to readers, who must decide if the setting of the study is sufficiently similar for its results to be transferable to their own context. In doing so, the reader looks for resonance—the extent that research findings have meaning for the reader.
Transferability may be helped by the study’s discussion of how its results advance theoretical understandings that are relevant to multiple situations. For example, a study of patients’ preferences in palliative care may contribute to theories of ethics and humanity in medicine, thus suggesting relevance to other clinical situations such as the informed consent exchange before treatment. We have explained elsewhere in this series the importance of theory in qualitative research, and there are many who believe that a key indicator of quality in qualitative research is its contribution to advancing theoretical understanding as well as useful knowledge. This debate continues in the literature, 4 but from a pragmatic perspective most qualitative studies in health professions journals emphasise results that relate to practice; theoretical discussions tend to be published elsewhere.
Reflexivity is particularly important within the qualitative paradigm. Reflexivity refers to recognition of the influence a researcher brings to the research process. It highlights potential power relationships between the researcher and research participants that might shape the data being collected, particularly when the researcher is a healthcare professional or educator and the participant is a patient, client, or student. 5 It also acknowledges how a researcher’s gender, ethnic background, profession, and social status influence the choices made within the study, such as the research question itself and the methods of data collection. 6 7
Research articles written in the qualitative paradigm should show evidence both of reflexive practice and of consideration of other relevant ethical issues. Ethics in qualitative research should extend beyond prescriptive guidelines and research ethics boards into a thorough exploration of the ethical consequences of collecting personal experiences and opening those experiences to public scrutiny (a detailed discussion of this problem within a research report may, however, be limited by the practicalities of word count limitations). 8 Issues of confidentiality and anonymity can become quite complex when data constitute personal reports of experience or perception; the need to minimise harm may involve not only protection from external scrutiny but also mechanisms to mitigate potential distress to participants from sharing their personal stories.
In conclusion: is what the researchers did clear?
The qualitative paradigm includes a wide range of theoretical and methodological options, and qualitative studies must include clear descriptions of how they were conducted, including the selection of the study sample, the data collection methods, and the analysis process. The list of key questions for beginning readers to ask when reading qualitative research articles (see box 1) is intended not as a finite checklist, but rather as a beginner’s guide to a complex topic. Critical appraisal of particular qualitative articles may differ according to the theories and methodologies used, and achieving a nuanced understanding in this area is fairly complex.
Further reading
Crabtree F, Miller WL, eds. Doing qualitative research . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 1999.
Denzin NK, Lincoln YS, eds. Handbook of qualitative research . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2000.
Finlay L, Ballinger C, eds. Qualitative research for allied health professionals: challenging choices . Chichester: Wiley, 2006.
Flick U. An introduction to qualitative research . 2nd ed. London: Sage, 2002.
Green J, Thorogood N. Qualitative methods for health research . London: Sage, 2004.
Lingard L, Kennedy TJ. Qualitative research in medical education . Edinburgh: Association for the Study of Medical Education, 2007.
Mauthner M, Birch M, Jessop J, Miller T, eds. Ethics in Qualitative Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2002.
Seale C. The quality of qualitative research . London: Sage, 1999.
Silverman D. Doing qualitative research . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2000.
Journal articles
Greenhalgh T. How to read a paper: papers that go beyond numbers. BMJ 1997;315:740-3.
Mays N, Pope C. Qualitative research: Rigour and qualitative research. BMJ 1995;311:109-12.
Mays N, Pope C. Qualitative research in health care: assessing quality in qualitative research. BMJ 2000;320:50-2.
Popay J, Rogers A, Williams G. Rationale and standards for the systematic review of qualitative literature in health services research. Qual Health Res 1998;8:341-51.
Internet resources
National Health Service Public Health Resource Unit. Critical appraisal skills programme: qualitative research appraisal tool . 2006. www.phru.nhs.uk/Doc_Links/Qualitative%20Appraisal%20Tool.pdf
Cite this as: BMJ 2008;337:a1035
- Related to doi: , 10.1136/bmj.a288
- doi: , 10.1136/bmj.39602.690162.47
- doi: , 10.1136/bmj.a1020
- doi: , 10.1136/bmj.a879
- doi: 10.1136/bmj.a949
This is the last in a series of six articles that aim to help readers to critically appraise the increasing number of qualitative research articles in clinical journals. The series editors are Ayelet Kuper and Scott Reeves.
For a definition of general terms relating to qualitative research, see the first article in this series.
Contributors: AK wrote the first draft of the article and collated comments for subsequent iterations. LL and WL made substantial contributions to the structure and content, provided examples, and gave feedback on successive drafts. AK is the guarantor.
Funding: None.
Competing interests: None declared.
Provenance and peer review: Commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
- ↵ Holden JD. Hawthorne effects and research into professional practice. J Evaluation Clin Pract 2001 ; 7 : 65 -70. OpenUrl CrossRef PubMed Web of Science
- ↵ Hammersley M, Atkinson P. Ethnography: principles in practice . 2nd ed. London: Routledge, 1995 .
- ↵ Silverman D. Doing qualitative research . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2000 .
- ↵ Mays N, Pope C. Qualitative research in health care: assessing quality in qualitative research. BMJ 2000 ; 320 : 50 -2. OpenUrl FREE Full Text
- ↵ Lingard L, Kennedy TJ. Qualitative research in medical education . Edinburgh: Association for the Study of Medical Education, 2007 .
- ↵ Seale C. The quality of qualitative research . London: Sage, 1999 .
- ↵ Wallerstein N. Power between evaluator and community: research relationships within New Mexico’s healthier communities. Soc Sci Med 1999 ; 49 : 39 -54. OpenUrl CrossRef PubMed Web of Science
- ↵ Mauthner M, Birch M, Jessop J, Miller T, eds. Ethics in qualitative research . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2002 .
- ↵ Kuzel AJ. Sampling in qualitative inquiry. In: Crabtree F, Miller WL, eds. Doing qualitative research . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 1999 :33-45.
Qualitative Study
Affiliations.
- 1 University of Nebraska Medical Center
- 2 GDB Research and Statistical Consulting
- 3 GDB Research and Statistical Consulting/McLaren Macomb Hospital
- PMID: 29262162
- Bookshelf ID: NBK470395
Qualitative research is a type of research that explores and provides deeper insights into real-world problems. Instead of collecting numerical data points or intervene or introduce treatments just like in quantitative research, qualitative research helps generate hypotheses as well as further investigate and understand quantitative data. Qualitative research gathers participants' experiences, perceptions, and behavior. It answers the hows and whys instead of how many or how much. It could be structured as a stand-alone study, purely relying on qualitative data or it could be part of mixed-methods research that combines qualitative and quantitative data. This review introduces the readers to some basic concepts, definitions, terminology, and application of qualitative research.
Qualitative research at its core, ask open-ended questions whose answers are not easily put into numbers such as ‘how’ and ‘why’. Due to the open-ended nature of the research questions at hand, qualitative research design is often not linear in the same way quantitative design is. One of the strengths of qualitative research is its ability to explain processes and patterns of human behavior that can be difficult to quantify. Phenomena such as experiences, attitudes, and behaviors can be difficult to accurately capture quantitatively, whereas a qualitative approach allows participants themselves to explain how, why, or what they were thinking, feeling, and experiencing at a certain time or during an event of interest. Quantifying qualitative data certainly is possible, but at its core, qualitative data is looking for themes and patterns that can be difficult to quantify and it is important to ensure that the context and narrative of qualitative work are not lost by trying to quantify something that is not meant to be quantified.
However, while qualitative research is sometimes placed in opposition to quantitative research, where they are necessarily opposites and therefore ‘compete’ against each other and the philosophical paradigms associated with each, qualitative and quantitative work are not necessarily opposites nor are they incompatible. While qualitative and quantitative approaches are different, they are not necessarily opposites, and they are certainly not mutually exclusive. For instance, qualitative research can help expand and deepen understanding of data or results obtained from quantitative analysis. For example, say a quantitative analysis has determined that there is a correlation between length of stay and level of patient satisfaction, but why does this correlation exist? This dual-focus scenario shows one way in which qualitative and quantitative research could be integrated together.
Examples of Qualitative Research Approaches
Ethnography
Ethnography as a research design has its origins in social and cultural anthropology, and involves the researcher being directly immersed in the participant’s environment. Through this immersion, the ethnographer can use a variety of data collection techniques with the aim of being able to produce a comprehensive account of the social phenomena that occurred during the research period. That is to say, the researcher’s aim with ethnography is to immerse themselves into the research population and come out of it with accounts of actions, behaviors, events, etc. through the eyes of someone involved in the population. Direct involvement of the researcher with the target population is one benefit of ethnographic research because it can then be possible to find data that is otherwise very difficult to extract and record.
Grounded Theory
Grounded Theory is the “generation of a theoretical model through the experience of observing a study population and developing a comparative analysis of their speech and behavior.” As opposed to quantitative research which is deductive and tests or verifies an existing theory, grounded theory research is inductive and therefore lends itself to research that is aiming to study social interactions or experiences. In essence, Grounded Theory’s goal is to explain for example how and why an event occurs or how and why people might behave a certain way. Through observing the population, a researcher using the Grounded Theory approach can then develop a theory to explain the phenomena of interest.
Phenomenology
Phenomenology is defined as the “study of the meaning of phenomena or the study of the particular”. At first glance, it might seem that Grounded Theory and Phenomenology are quite similar, but upon careful examination, the differences can be seen. At its core, phenomenology looks to investigate experiences from the perspective of the individual. Phenomenology is essentially looking into the ‘lived experiences’ of the participants and aims to examine how and why participants behaved a certain way, from their perspective . Herein lies one of the main differences between Grounded Theory and Phenomenology. Grounded Theory aims to develop a theory for social phenomena through an examination of various data sources whereas Phenomenology focuses on describing and explaining an event or phenomena from the perspective of those who have experienced it.
Narrative Research
One of qualitative research’s strengths lies in its ability to tell a story, often from the perspective of those directly involved in it. Reporting on qualitative research involves including details and descriptions of the setting involved and quotes from participants. This detail is called ‘thick’ or ‘rich’ description and is a strength of qualitative research. Narrative research is rife with the possibilities of ‘thick’ description as this approach weaves together a sequence of events, usually from just one or two individuals, in the hopes of creating a cohesive story, or narrative. While it might seem like a waste of time to focus on such a specific, individual level, understanding one or two people’s narratives for an event or phenomenon can help to inform researchers about the influences that helped shape that narrative. The tension or conflict of differing narratives can be “opportunities for innovation”.
Research Paradigm
Research paradigms are the assumptions, norms, and standards that underpin different approaches to research. Essentially, research paradigms are the ‘worldview’ that inform research. It is valuable for researchers, both qualitative and quantitative, to understand what paradigm they are working within because understanding the theoretical basis of research paradigms allows researchers to understand the strengths and weaknesses of the approach being used and adjust accordingly. Different paradigms have different ontology and epistemologies . Ontology is defined as the "assumptions about the nature of reality” whereas epistemology is defined as the “assumptions about the nature of knowledge” that inform the work researchers do. It is important to understand the ontological and epistemological foundations of the research paradigm researchers are working within to allow for a full understanding of the approach being used and the assumptions that underpin the approach as a whole. Further, it is crucial that researchers understand their own ontological and epistemological assumptions about the world in general because their assumptions about the world will necessarily impact how they interact with research. A discussion of the research paradigm is not complete without describing positivist, postpositivist, and constructivist philosophies.
Positivist vs Postpositivist
To further understand qualitative research, we need to discuss positivist and postpositivist frameworks. Positivism is a philosophy that the scientific method can and should be applied to social as well as natural sciences. Essentially, positivist thinking insists that the social sciences should use natural science methods in its research which stems from positivist ontology that there is an objective reality that exists that is fully independent of our perception of the world as individuals. Quantitative research is rooted in positivist philosophy, which can be seen in the value it places on concepts such as causality, generalizability, and replicability.
Conversely, postpositivists argue that social reality can never be one hundred percent explained but it could be approximated. Indeed, qualitative researchers have been insisting that there are “fundamental limits to the extent to which the methods and procedures of the natural sciences could be applied to the social world” and therefore postpositivist philosophy is often associated with qualitative research. An example of positivist versus postpositivist values in research might be that positivist philosophies value hypothesis-testing, whereas postpositivist philosophies value the ability to formulate a substantive theory.
Constructivist
Constructivism is a subcategory of postpositivism. Most researchers invested in postpositivist research are constructivist as well, meaning they think there is no objective external reality that exists but rather that reality is constructed. Constructivism is a theoretical lens that emphasizes the dynamic nature of our world. “Constructivism contends that individuals’ views are directly influenced by their experiences, and it is these individual experiences and views that shape their perspective of reality”. Essentially, Constructivist thought focuses on how ‘reality’ is not a fixed certainty and experiences, interactions, and backgrounds give people a unique view of the world. Constructivism contends, unlike in positivist views, that there is not necessarily an ‘objective’ reality we all experience. This is the ‘relativist’ ontological view that reality and the world we live in are dynamic and socially constructed. Therefore, qualitative scientific knowledge can be inductive as well as deductive.”
So why is it important to understand the differences in assumptions that different philosophies and approaches to research have? Fundamentally, the assumptions underpinning the research tools a researcher selects provide an overall base for the assumptions the rest of the research will have and can even change the role of the researcher themselves. For example, is the researcher an ‘objective’ observer such as in positivist quantitative work? Or is the researcher an active participant in the research itself, as in postpositivist qualitative work? Understanding the philosophical base of the research undertaken allows researchers to fully understand the implications of their work and their role within the research, as well as reflect on their own positionality and bias as it pertains to the research they are conducting.
Data Sampling
The better the sample represents the intended study population, the more likely the researcher is to encompass the varying factors at play. The following are examples of participant sampling and selection:
Purposive sampling- selection based on the researcher’s rationale in terms of being the most informative.
Criterion sampling-selection based on pre-identified factors.
Convenience sampling- selection based on availability.
Snowball sampling- the selection is by referral from other participants or people who know potential participants.
Extreme case sampling- targeted selection of rare cases.
Typical case sampling-selection based on regular or average participants.
Data Collection and Analysis
Qualitative research uses several techniques including interviews, focus groups, and observation. [1] [2] [3] Interviews may be unstructured, with open-ended questions on a topic and the interviewer adapts to the responses. Structured interviews have a predetermined number of questions that every participant is asked. It is usually one on one and is appropriate for sensitive topics or topics needing an in-depth exploration. Focus groups are often held with 8-12 target participants and are used when group dynamics and collective views on a topic are desired. Researchers can be a participant-observer to share the experiences of the subject or a non-participant or detached observer.
While quantitative research design prescribes a controlled environment for data collection, qualitative data collection may be in a central location or in the environment of the participants, depending on the study goals and design. Qualitative research could amount to a large amount of data. Data is transcribed which may then be coded manually or with the use of Computer Assisted Qualitative Data Analysis Software or CAQDAS such as ATLAS.ti or NVivo.
After the coding process, qualitative research results could be in various formats. It could be a synthesis and interpretation presented with excerpts from the data. Results also could be in the form of themes and theory or model development.
Dissemination
To standardize and facilitate the dissemination of qualitative research outcomes, the healthcare team can use two reporting standards. The Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research or COREQ is a 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups. The Standards for Reporting Qualitative Research (SRQR) is a checklist covering a wider range of qualitative research.
Examples of Application
Many times a research question will start with qualitative research. The qualitative research will help generate the research hypothesis which can be tested with quantitative methods. After the data is collected and analyzed with quantitative methods, a set of qualitative methods can be used to dive deeper into the data for a better understanding of what the numbers truly mean and their implications. The qualitative methods can then help clarify the quantitative data and also help refine the hypothesis for future research. Furthermore, with qualitative research researchers can explore subjects that are poorly studied with quantitative methods. These include opinions, individual's actions, and social science research.
A good qualitative study design starts with a goal or objective. This should be clearly defined or stated. The target population needs to be specified. A method for obtaining information from the study population must be carefully detailed to ensure there are no omissions of part of the target population. A proper collection method should be selected which will help obtain the desired information without overly limiting the collected data because many times, the information sought is not well compartmentalized or obtained. Finally, the design should ensure adequate methods for analyzing the data. An example may help better clarify some of the various aspects of qualitative research.
A researcher wants to decrease the number of teenagers who smoke in their community. The researcher could begin by asking current teen smokers why they started smoking through structured or unstructured interviews (qualitative research). The researcher can also get together a group of current teenage smokers and conduct a focus group to help brainstorm factors that may have prevented them from starting to smoke (qualitative research).
In this example, the researcher has used qualitative research methods (interviews and focus groups) to generate a list of ideas of both why teens start to smoke as well as factors that may have prevented them from starting to smoke. Next, the researcher compiles this data. The research found that, hypothetically, peer pressure, health issues, cost, being considered “cool,” and rebellious behavior all might increase or decrease the likelihood of teens starting to smoke.
The researcher creates a survey asking teen participants to rank how important each of the above factors is in either starting smoking (for current smokers) or not smoking (for current non-smokers). This survey provides specific numbers (ranked importance of each factor) and is thus a quantitative research tool.
The researcher can use the results of the survey to focus efforts on the one or two highest-ranked factors. Let us say the researcher found that health was the major factor that keeps teens from starting to smoke, and peer pressure was the major factor that contributed to teens to start smoking. The researcher can go back to qualitative research methods to dive deeper into each of these for more information. The researcher wants to focus on how to keep teens from starting to smoke, so they focus on the peer pressure aspect.
The researcher can conduct interviews and/or focus groups (qualitative research) about what types and forms of peer pressure are commonly encountered, where the peer pressure comes from, and where smoking first starts. The researcher hypothetically finds that peer pressure often occurs after school at the local teen hangouts, mostly the local park. The researcher also hypothetically finds that peer pressure comes from older, current smokers who provide the cigarettes.
The researcher could further explore this observation made at the local teen hangouts (qualitative research) and take notes regarding who is smoking, who is not, and what observable factors are at play for peer pressure of smoking. The researcher finds a local park where many local teenagers hang out and see that a shady, overgrown area of the park is where the smokers tend to hang out. The researcher notes the smoking teenagers buy their cigarettes from a local convenience store adjacent to the park where the clerk does not check identification before selling cigarettes. These observations fall under qualitative research.
If the researcher returns to the park and counts how many individuals smoke in each region of the park, this numerical data would be quantitative research. Based on the researcher's efforts thus far, they conclude that local teen smoking and teenagers who start to smoke may decrease if there are fewer overgrown areas of the park and the local convenience store does not sell cigarettes to underage individuals.
The researcher could try to have the parks department reassess the shady areas to make them less conducive to the smokers or identify how to limit the sales of cigarettes to underage individuals by the convenience store. The researcher would then cycle back to qualitative methods of asking at-risk population their perceptions of the changes, what factors are still at play, as well as quantitative research that includes teen smoking rates in the community, the incidence of new teen smokers, among others.
Copyright © 2024, StatPearls Publishing LLC.
- Introduction
- Issues of Concern
- Clinical Significance
- Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
- Review Questions
Publication types
- Study Guide
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples
What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples
Published on June 19, 2020 by Pritha Bhandari . Revised on June 22, 2023.
Qualitative research involves collecting and analyzing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio) to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. It can be used to gather in-depth insights into a problem or generate new ideas for research.
Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research , which involves collecting and analyzing numerical data for statistical analysis.
Qualitative research is commonly used in the humanities and social sciences, in subjects such as anthropology, sociology, education, health sciences, history, etc.
- How does social media shape body image in teenagers?
- How do children and adults interpret healthy eating in the UK?
- What factors influence employee retention in a large organization?
- How is anxiety experienced around the world?
- How can teachers integrate social issues into science curriculums?
Table of contents
Approaches to qualitative research, qualitative research methods, qualitative data analysis, advantages of qualitative research, disadvantages of qualitative research, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about qualitative research.
Qualitative research is used to understand how people experience the world. While there are many approaches to qualitative research, they tend to be flexible and focus on retaining rich meaning when interpreting data.
Common approaches include grounded theory, ethnography , action research , phenomenological research, and narrative research. They share some similarities, but emphasize different aims and perspectives.
Note that qualitative research is at risk for certain research biases including the Hawthorne effect , observer bias , recall bias , and social desirability bias . While not always totally avoidable, awareness of potential biases as you collect and analyze your data can prevent them from impacting your work too much.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Each of the research approaches involve using one or more data collection methods . These are some of the most common qualitative methods:
- Observations: recording what you have seen, heard, or encountered in detailed field notes.
- Interviews: personally asking people questions in one-on-one conversations.
- Focus groups: asking questions and generating discussion among a group of people.
- Surveys : distributing questionnaires with open-ended questions.
- Secondary research: collecting existing data in the form of texts, images, audio or video recordings, etc.
- You take field notes with observations and reflect on your own experiences of the company culture.
- You distribute open-ended surveys to employees across all the company’s offices by email to find out if the culture varies across locations.
- You conduct in-depth interviews with employees in your office to learn about their experiences and perspectives in greater detail.
Qualitative researchers often consider themselves “instruments” in research because all observations, interpretations and analyses are filtered through their own personal lens.
For this reason, when writing up your methodology for qualitative research, it’s important to reflect on your approach and to thoroughly explain the choices you made in collecting and analyzing the data.
Qualitative data can take the form of texts, photos, videos and audio. For example, you might be working with interview transcripts, survey responses, fieldnotes, or recordings from natural settings.
Most types of qualitative data analysis share the same five steps:
- Prepare and organize your data. This may mean transcribing interviews or typing up fieldnotes.
- Review and explore your data. Examine the data for patterns or repeated ideas that emerge.
- Develop a data coding system. Based on your initial ideas, establish a set of codes that you can apply to categorize your data.
- Assign codes to the data. For example, in qualitative survey analysis, this may mean going through each participant’s responses and tagging them with codes in a spreadsheet. As you go through your data, you can create new codes to add to your system if necessary.
- Identify recurring themes. Link codes together into cohesive, overarching themes.
There are several specific approaches to analyzing qualitative data. Although these methods share similar processes, they emphasize different concepts.
Qualitative research often tries to preserve the voice and perspective of participants and can be adjusted as new research questions arise. Qualitative research is good for:
- Flexibility
The data collection and analysis process can be adapted as new ideas or patterns emerge. They are not rigidly decided beforehand.
- Natural settings
Data collection occurs in real-world contexts or in naturalistic ways.
- Meaningful insights
Detailed descriptions of people’s experiences, feelings and perceptions can be used in designing, testing or improving systems or products.
- Generation of new ideas
Open-ended responses mean that researchers can uncover novel problems or opportunities that they wouldn’t have thought of otherwise.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Researchers must consider practical and theoretical limitations in analyzing and interpreting their data. Qualitative research suffers from:
- Unreliability
The real-world setting often makes qualitative research unreliable because of uncontrolled factors that affect the data.
- Subjectivity
Due to the researcher’s primary role in analyzing and interpreting data, qualitative research cannot be replicated . The researcher decides what is important and what is irrelevant in data analysis, so interpretations of the same data can vary greatly.
- Limited generalizability
Small samples are often used to gather detailed data about specific contexts. Despite rigorous analysis procedures, it is difficult to draw generalizable conclusions because the data may be biased and unrepresentative of the wider population .
- Labor-intensive
Although software can be used to manage and record large amounts of text, data analysis often has to be checked or performed manually.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Chi square goodness of fit test
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to systematically measure variables and test hypotheses . Qualitative methods allow you to explore concepts and experiences in more detail.
There are five common approaches to qualitative research :
- Grounded theory involves collecting data in order to develop new theories.
- Ethnography involves immersing yourself in a group or organization to understand its culture.
- Narrative research involves interpreting stories to understand how people make sense of their experiences and perceptions.
- Phenomenological research involves investigating phenomena through people’s lived experiences.
- Action research links theory and practice in several cycles to drive innovative changes.
Data collection is the systematic process by which observations or measurements are gathered in research. It is used in many different contexts by academics, governments, businesses, and other organizations.
There are various approaches to qualitative data analysis , but they all share five steps in common:
- Prepare and organize your data.
- Review and explore your data.
- Develop a data coding system.
- Assign codes to the data.
- Identify recurring themes.
The specifics of each step depend on the focus of the analysis. Some common approaches include textual analysis , thematic analysis , and discourse analysis .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Bhandari, P. (2023, June 22). What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 15, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/qualitative-research/
Is this article helpful?

Pritha Bhandari
Other students also liked, qualitative vs. quantitative research | differences, examples & methods, how to do thematic analysis | step-by-step guide & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
About Journal
American Journal of Qualitative Research (AJQR) is a quarterly peer-reviewed academic journal that publishes qualitative research articles from a number of social science disciplines such as psychology, health science, sociology, criminology, education, political science, and administrative studies. The journal is an international and interdisciplinary focus and greatly welcomes papers from all countries. The journal offers an intellectual platform for researchers, practitioners, administrators, and policymakers to contribute and promote qualitative research and analysis.
ISSN: 2576-2141
Call for Papers- American Journal of Qualitative Research
American Journal of Qualitative Research (AJQR) welcomes original research articles and book reviews for its next issue. The AJQR is a quarterly and peer-reviewed journal published in February, May, August, and November.
We are seeking submissions for a forthcoming issue published in February 2024. The paper should be written in professional English. The length of 6000-10000 words is preferred. All manuscripts should be prepared in MS Word format and submitted online: https://www.editorialpark.com/ajqr
For any further information about the journal, please visit its website: https://www.ajqr.org
Submission Deadline: November 15, 2023
Announcement
Dear AJQR Readers,
Due to the high volume of submissions in the American Journal of Qualitative Research , the editorial board decided to publish quarterly since 2023.
Volume 8, Issue 1
Current issue.
Social distancing requirements resulted in many people working from home in the United Kingdom during the COVID-19 pandemic. The topic of working from home was often discussed in the media and online during the pandemic, but little was known about how quality of life (QOL) and remote working interfaced. The purpose of this study was to describe QOL while working from home during the COVID-19 pandemic. The novel topic, unique methodological approach of the General Online Qualitative Study ( D’Abundo & Franco, 2022a), and the strategic Social Distancing Sampling ( D’Abundo & Franco, 2022c) resulted in significant participation throughout the world (n = 709). The United Kingdom subset of participants (n = 234) is the focus of this article. This big qual, large qualitative study (n >100) included the principal investigator-developed, open-ended, online questionnaire entitled the “Quality of Life Home Workplace Questionnaire (QOLHWQ)” and demographic questions. Data were collected peak-pandemic from July to September 2020. Most participants cited increased QOL due to having more time with family/kids/partners/pets, a more comfortable work environment while being at home, and less commuting to work. The most cited issue associated with negative QOL was social isolation. As restrictions have been lifted and public health emergency declarations have been terminated during the post-peak era of the COVID-19 pandemic, the potential for future public health emergencies requiring social distancing still exists. To promote QOL and work-life balance for employees working remotely in the United Kingdom, stakeholders could develop social support networks and create effective planning initiatives to prevent social isolation and maximize the benefits of remote working experiences for both employees and organizations.
Keywords: qualitative research, quality of life, remote work, telework, United Kingdom, work from home.
(no abstract)
This essay reviews classic works on the philosophy of science and contemporary pedagogical guides to scientific inquiry in order to present a discussion of the three logics that underlie qualitative research in political science. The first logic, epistemology, relates to the essence of research as a scientific endeavor and is framed as a debate between positivist and interpretivist orientations within the discipline of political science. The second logic, ontology, relates to the approach that research takes to investigating the empirical world and is framed as a debate between positivist qualitative and quantitative orientations, which together constitute the vast majority of mainstream researchers within the discipline. The third logic, methodology, relates to the means by which research aspires to reach its scientific ends and is framed as a debate among positivist qualitative orientations. Additionally, the essay discusses the present state of qualitative research in the discipline of political science, reviews the various ways in which qualitative research is defined in the relevant literature, addresses the limitations and trade-offs that are inherently associated with the aforementioned logics of qualitative research, explores multimethod approaches to remedying these issues, and proposes avenues for acquiring further information on the topics discussed.
Keywords: qualitative research, epistemology, ontology, methodology
This paper examines the phenomenology of diagnostic crossover in eating disorders, the movement within or between feeding and eating disorder subtypes or diagnoses over time, in two young women who experienced multiple changes in eating disorder diagnosis over 5 years. Using interpretative phenomenological analysis, this study found that transitioning between different diagnostic labels, specifically between bulimia nervosa and anorexia nervosa binge/purge subtype, was experienced as disempowering, stigmatizing, and unhelpful. The findings in this study offer novel evidence that, from the perspective of individuals diagnosed with EDs, using BMI as an indicator of the presence, severity, or change of an ED may have adverse consequences for well-being and recovery and may lead to mischaracterization or misclassification of health status. The narratives discussed in this paper highlight the need for more person-centered practices in the context of diagnostic crossover. Including the perspectives of those with lived experience can help care providers working with individuals with eating disorders gain an in-depth understanding of the potential personal impact of diagnosis changing and inform discussions around developing person-focused diagnostic practices.
Keywords: feeding and eating disorders, bulimia nervosa, diagnostic labels, diagnostic crossover, illness narrative
Often among the first witnesses to child trauma, educators and therapists are on the frontline of an unfolding and multi-pronged occupational crisis. For educators, lack of support and secondary traumatic stress (STS) appear to be contributing to an epidemic in professional attrition. Similarly, therapists who do not prioritize self-care can feel depleted of energy and optimism. The purpose of this phenomenological study was to examine how bearing witness to the traumatic narratives of children impacts similar helping professionals. The study also sought to extrapolate the similarities and differences between compassion fatigue and secondary trauma across these two disciplines. Exploring the common factors and subjective individual experiences related to occupational stress across these two fields may foster a more complete picture of the delicate nature of working with traumatized children and the importance of successful self-care strategies. Utilizing Constructivist Self-Development Theory (CSDT) and focus group interviews, the study explores the significant risk of STS facing both educators and therapists.
Keywords: qualitative, secondary traumatic stress, self-care, child trauma, educators, therapists.
This study explored the lived experiences of residents of the Gulf Coast in the USA during Hurricane Katrina, which made landfall in August 2005 and caused insurmountable destruction throughout the area. A heuristic process and thematic analysis were employed to draw observations and conclusions about the lived experiences of each participant and make meaning through similar thoughts, feelings, and themes that emerged in the analysis of the data. Six themes emerged: (1) fear, (2) loss, (3) anger, (4) support, (5) spirituality, and (6) resilience. The results of this study allude to the possible psychological outcomes as a result of experiencing a traumatic event and provide an outline of what the psychological experience of trauma might entail. The current research suggests that preparedness and expectation are key to resilience and that people who feel that they have power over their situation fare better than those who do not.
Keywords: mass trauma, resilience, loss, natural disaster, mental health.
Women from rural, low-income backgrounds holding positions within the academy are the exception and not the rule. Most women faculty in the academy are from urban/suburban areas and middle- and upper-income family backgrounds. As women faculty who do not represent this norm, our primary goal with this article is to focus on the unique barriers we experienced as girls from rural, low-income areas in K-12 schools that influenced the possibilities for successfully transitioning to and engaging with higher education. We employed a qualitative duoethnographic and narrative research design to respond to the research questions, and we generated our data through semi-structured, critical, ethnographic dialogic conversations. Our duoethnographic-narrative analyses revealed six major themes: (1) independence and other benefits of having a working-class mom; (2) crashing into middle-class norms and expectations; (3) lucking and falling into college; (4) fish out of water; (5) overcompensating, playing middle class, walking on eggshells, and pushing back; and (6) transitioning from a working-class kid to a working class academic, which we discuss in relation to our own educational attainment.
Keywords: rurality, working-class, educational attainment, duoethnography, higher education, women.
This article draws on the findings of a qualitative study that focused on the perspectives of four Indian American mothers of youth with developmental disabilities on the process of transitioning from school to post-school environments. Data were collected through in-depth ethnographic interviews. The findings indicate that in their efforts to support their youth with developmental disabilities, the mothers themselves navigate multiple transitions across countries, constructs, dreams, systems of schooling, and services. The mothers’ perspectives have to be understood against the larger context of their experiences as citizens of this country as well as members of the South Asian diaspora. The mothers’ views on services, their journey, their dreams for their youth, and their interpretation of the ideas anchored in current conversations on transition are continually evolving. Their attempts to maintain their resilience and their indigenous understandings while simultaneously negotiating their experiences in the United States with supporting their youth are discussed.
Keywords: Indian-American mothers, transitioning, diaspora, disability, dreams.
This study explored the influence of yoga on practitioners’ lives ‘off the mat’ through a phenomenological lens. Central to the study was the lived experience of yoga in a purposive sample of self-identified New Zealand practitioners (n=38; 89.5% female; aged 18 to 65 years; 60.5% aged 36 to 55 years). The study’s aim was to explore whether habitual yoga practitioners experience any pro-health downstream effects of their practice ‘off the mat’ via their lived experience of yoga. A qualitative mixed methodology was applied via a phenomenological lens that explicitly acknowledged the researcher’s own experience of the research topic. Qualitative methods comprised an open-ended online survey for all participants (n=38), followed by in-depth semi-structured interviews (n=8) on a randomized subset. Quantitative methods included online outcome measures (health habits, self-efficacy, interoceptive awareness, and physical activity), practice component data (tenure, dose, yoga styles, yoga teacher status, meditation frequency), and socio-demographics. This paper highlights the qualitative findings emerging from participant narratives. Reported benefits of practice included the provision of a filter through which to engage with life and the experience of self-regulation and mindfulness ‘off the mat’. Practitioners experienced yoga as a self-sustaining positive resource via self-regulation guided by an embodied awareness. The key narrative to emerge was an attunement to embodiment through movement. Embodied movement can elicit self-regulatory pathways that support health behavior.
Keywords: embodiment, habit, interoception, mindfulness, movement practice, qualitative, self-regulation, yoga.
Historically and in the present day, Black women’s positionality in the U.S. has paradoxically situated them in a society where they are both intrinsically essential and treated as expendable. This positionality, known as gendered racism, manifests commonly in professional environments and results in myriad harms. In response, Black women have developed, honed, and practiced a range of coping styles to mitigate the insidious effects of gendered racism. While often effective in the short-term, these techniques frequently complicate Black women’s well-being. For Black female clinicians who experience gendered racism and work on the frontlines of community mental health, myriad bio-psycho-social-spiritual harms compound. This project provided an opportunity for Black female clinicians from across the U.S. to share their experiences during the dual pandemics of COVID-19 and anti-Black violence. I conducted in-depth interviews with clinicians (n=14) between the ages of 30 and 58. Using the Listening Guide voice-centered approach to data generation and analysis, I identified four voices to help answer this project’s central question: How do you experience being a Black female clinician in the U.S.? The voices of self, pride, vigilance, and mediating narrated the complex ways participants experienced their workplaces. This complexity seemed to be context-specific, depending on whether the clinicians worked in predominantly White workplaces (PWW), a mix of PWW and private practice, or private practice exclusively. Participants who worked only in PWW experienced the greatest stress, oppression, and burnout risk, while participants who worked exclusively in private practice reported more joy, more authenticity, and more job satisfaction. These findings have implications for mentoring, supporting, and retaining Black female clinicians.
Keywords: Black female clinicians, professional experiences, gendered racism, Listening Guide voice-centered approach.
The purpose of this article is to speak directly to the paucity of research regarding Dominican American women and identity narratives. To do so, this article uses the Listening Guide Method of Qualitative Inquiry (Gilligan, et al., 2006) to explore how 1.5 and second-generation Dominican American women narrated their experiences of individual identity within American cultural contexts and constructs. The results draw from the emergence of themes across six participant interviews and showed two distinct voices: The Voice of Cultural Explanation and the Tides of Dominican American Female Identity. Narrative examples from five participants are offered to illustrate where 1.5 and second-generation Dominican American women negotiate their identity narratives at the intersection of their Dominican and American selves. The article offers two conclusions. One, that participant women use the Voice of Cultural Explanation in order to discuss their identity as reflected within the broad cultural tensions of their daily lives. Two, that the Tides of Dominican American Female Identity are used to express strong emotions that manifest within their personal narratives as the unwanted distance from either the Dominican or American parts of their person.
Keywords: Dominican American, women, identity, the Listening Guide, narratives
- Open access
- Published: 11 April 2024
Pregnant and postpartum women’s experiences of the indirect impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic in high-income countries: a qualitative evidence synthesis
- Annie Tan 1 , 2 , 3 ,
- Amanda Blair 2 , 4 ,
- Caroline SE. Homer 1 , 2 ,
- Robin Digby 1 , 3 , 5 ,
- Joshua P. Vogel 1 , 2 &
- Tracey Bucknall 1 , 3 , 5
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth volume 24 , Article number: 262 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
109 Accesses
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
Pregnant and postpartum women’s experiences of the COVID-19 pandemic, as well as the emotional and psychosocial impact of COVID-19 on perinatal health, has been well-documented across high-income countries. Increased anxiety and fear, isolation, as well as a disrupted pregnancy and postnatal period are widely described in many studies. The aim of this study was to explore, describe and synthesise studies that addressed the experiences of pregnant and postpartum women in high-income countries during the first two years of the pandemic.
A qualitative evidence synthesis of studies relating to women’s experiences in high-income countries during the pandemic were included. Two reviewers extracted the data using a thematic synthesis approach and NVivo 20 software. The GRADE-CERQual (Confidence in the Evidence from Reviews of Qualitative research) was used to assess confidence in review findings.
Sixty-eight studies were eligible and subjected to a sampling framework to ensure data richness. In total, 36 sampled studies contributed to the development of themes, sub-themes and review findings. There were six over-arching themes: (1) dealing with public health restrictions; (2) navigating changing health policies; (3) adapting to alternative ways of receiving social support; (4) dealing with impacts on their own mental health; (5) managing the new and changing information; and (6) being resilient and optimistic. Seventeen review findings were developed under these themes with high to moderate confidence according to the GRADE-CERQual assessment.
Conclusions
The findings from this synthesis offer different strategies for practice and policy makers to better support women, babies and their families in future emergency responses. These strategies include optimising care delivery, enhancing communication, and supporting social and mental wellbeing.
Peer Review reports
As of February 2024 SARS-CoV-2 has infected over 774 million people, and 7 million deaths have been attributed to coronavirus 19 (COVID-19) infection [ 1 ]. Maternal and newborn health services are essential for pregnant and postpartum women, and the COVID-19 pandemic significantly altered provision and access to routine care. Reduced services, limited face-to-face care, transition to virtual and remote care, and limited access to maternity care providers were commonly cited as barriers to accessing quality care by pregnant and postpartum women [ 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 ]. Additionally, reduced lengths of stay within hospitals and restrictions on support people imposed by health facilities have impacted women receiving care and placed an additional burden on nursing and midwifery staff [ 7 , 8 , 9 ]. This had significant impacts on pregnant and postpartum women’s emotional and psychosocial wellbeing.
Pregnant women and their babies were at an increased risk of adverse effects if she contracted SARS-CoV-2 [ 10 , 11 ]. The direct impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic were largely focused on the clinical manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 such as symptoms, risk factors, management and treatment, as well as adverse maternal and newborn outcomes [ 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 ]. However, at a wider level, the impacts of policy changes, health system reforms and changes to maternity care services indirectly affected the provision of care for all women giving birth over this time period. Women’s experiences of the transition from pregnancy to motherhood were also impacted. For example, in many countries, pregnant women were encouraged to homestay at home, receive care through telehealth rather than face-to-face and reduce face-to-face education [ 16 , 17 ]. Isolation from family, friends and peers has negatively impacted women’s mental health, with increased levels of anxiety, depression and stress globally [ 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 ].
Since the beginning of the pandemic, there has been a plethora of qualitative studies on women’s experiences [ 19 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 ] – the significant volume of papers highlights the need for a clear synthesis. Reviews of qualitative evidence have reported pregnant women’s experiences of social support [ 27 ], as well as highlighting the challenges they faced as they embraced motherhood during the pandemic [ 28 ]. Collating the evidence in a systematic and transparent manner will allow policymakers to consider the indirect implications of public health restrictions on the physical, emotional, and psychosocial health and wellbeing of pregnant and postpartum women.
Qualitative evidence synthesis (QES) is an approach that can systematically collate qualitative data in a transparent manner to inform policy and practice [ 29 ]. Findings from a QES can enable a richer interpretation of a particular phenomenon and enable a greater understanding of individual experiences, views and beliefs [ 30 ]. This QES aimed to explore, describe and synthesise the experiences of pregnant and postpartum women living in high-income countries during the first two years of the COVID-19 pandemic. This research method allows a deeper understanding of their views and experiences during this time. It also facilitates identification of areas of improvement for maternity care services, to ensure high-quality care is available at all times.
A QES was undertaken to identify, evaluate and summarise findings from qualitative studies providing a cohesive and transparent documentation of the contextual variations, stakeholder preferences and experiences to ultimately influence policy and practice [ 31 , 32 ]. This type of synthesis integrates diverse perspectives, which is needed to capture the complexity of the indirect impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on pregnant and postpartum women’s experiences. This QES was structured to include findings from qualitative studies, as well as qualitative findings from mixed-methods studies. Emphasis was placed on including different types of qualitative evidence that can potentially enrich a synthesis, such as narrative data from qualitative components of mixed-methods studies or free-text from questionnaires [ 29 ].
We followed the relevant Cochrane guidelines [ 29 ] and used the “Enhancing transparency in reporting the synthesis of qualitative research” (ENTREQ) statement to guide our approach and reporting (Supplementary 1 , S1) [ 33 ]. In addition, the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines for reporting the different phases of identifying studies was used as recommended by the ENTREQ statement (S 2 ) [ 34 ]. The protocol and systematic review were not registered.
Eligibility criteria
We defined “indirect impacts of the pandemic on women”, to mean the impact of regulations, recommendations and public health measures enforced by governments as a response to the COVID-19 pandemic had on pregnant and postpartum women and their newborns. We adopted the World Health Organization’s definition of the postpartum period beginning immediately after birth of the baby and extending to six weeks (42 days) after birth [ 35 ].
Participants within these studies were those who were pregnant or within the postpartum period, of childbearing age (15-49 years), and received any type of maternity care during the COVID-19 pandemic. Studies of women with pre-existing comorbidities were also eligible, as well as those focused on migrants, refugee populations or ethnic minority groups. To facilitate exploration of findings from women of diverse backgrounds we have used the term ‘culturally and linguistically diverse (CALD) populations’. We focussed on women living in high-income countries (HICs). Studies were included if they were conducted in countries listed in the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) [ 36 ] and Human Development Index (HDI) list of “Very high human development” list [ 37 ]. This allowed for similar contexts and countries to be compared.
Eligible study designs were those that addressed the indirect impact of COVID-19 using qualitative methodologies, including phenomenology, ethnography, grounded theory studies and case studies. We also included any study that obtained data through qualitative methods for data collection such as, interviews, focus groups, online forums and document analysis.
The decision to limit the eligibility based on year of publication, to only include studies published in the first two years of the COVID-19 pandemic (1 st Jan 2020 – 1 st Jan 2022) was to emphasise the impact of the stricter restrictions and lockdowns during this time period. Globally, public health measures to reduce spread and transmission included, mandatory quarantine, limiting movement, lockdowns, closure of schools and workplaces and shielding of vulnerable populations. These measures were significantly harsher during the first two years and subsequently relaxed as vaccine roll-outs occurred and infection rates began to decline [ 38 , 39 ]. The Oxford Coronavirus Government Response Tracker reported a stringency index which reiterates the trend of harsher restrictions implemented by governments throughout 2020-2022 time period and reflects the gradual decline after this date [ 40 ].
Search strategy
Six electronic databases (EBSCO Medline, Embase, APA PsycInfo, CINAHL and Maternity and Infant Care (MIDIRS)) were searched to identify all qualitative research articles published between 1 st January 2020 – 1 st January 2022. Search strategy included terms such as, “pregnan*”, “postpartum”, “mother”, “views”, “experiences”, “opinion*”, “indirect”, “COVID-19”, “coronavirus”. The search strategy was reviewed by a university librarian (S 3 ). Search hits from each of the databases were imported into Endnote 20 which was then used as our reference library. References were imported into Covidence for screening [ 41 ].
Study selection and sampling framework
Two review authors (AT, AB) independently screened titles, abstracts and full texts for inclusion, with any conflicts resolved by discussion or consulting a third author. Reasons for exclusion are described within PRISMA flowchart (Fig. 1 ). Sixty-eight studies were included following full-text review. The Cochrane guidelines for QES highlight that for reviews with large amounts of primary studies (50 or more) can result in a high volume of data, which can threaten quality of the synthesis. In such situations, a sampling framework can enhance the quality and diversity of the papers and ensure the number of studies and amount of data are manageable [ 42 , 43 , 44 ]. A QES worked example by Ames et al., 2019 was used as a guide to develop the sampling framework for data richness [ 45 ]. Two independent reviewers scored included studies from 1 to 5 based on the criteria outlined in Table 1 , to ensure that the sampling framework was reliable and replicable. Any conflicts were resolved by discussion, or a third review author was consulted. Studies with a score ≥4 were included for data extraction and are referred to as ‘sampled’ studies (S 4 ).
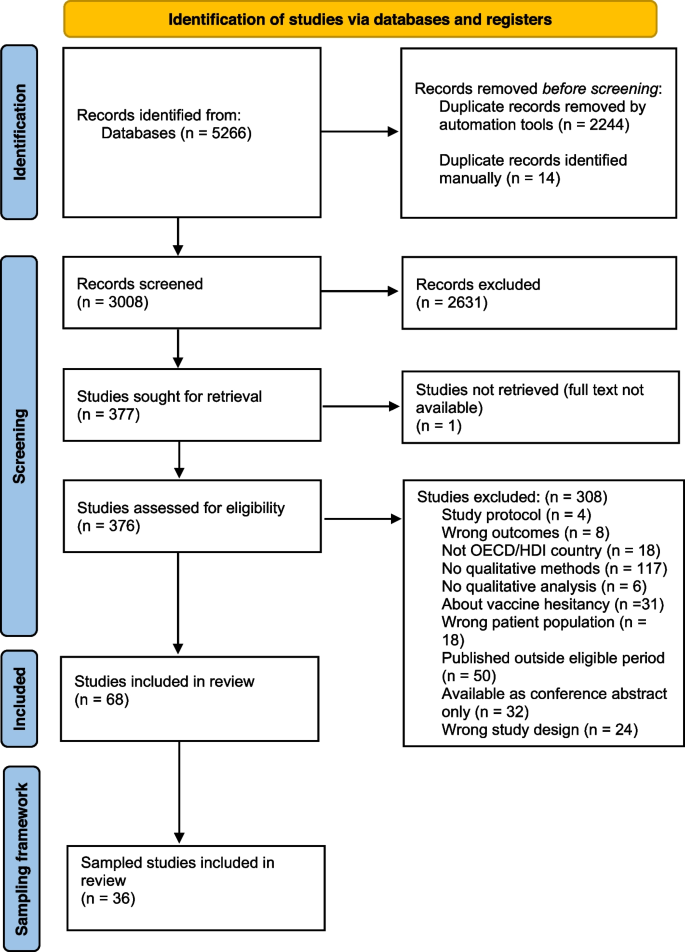
Reporting of adapted PRISMA flowchart of included and sampled studies in accordance with PRISMA and ENTREQ guidelines [ 33 ]
Quality assessment
The Critically Appraisal Skills Program (CASP) tool for qualitative research was used by two independent review authors (AT, AB) to assess methodological limitations of sampled studies (S 5 ) [ 46 ]. Any disagreements were resolved through discussion, or when required, a third review author was consulted. Sampled studies were graded as no or very minor, minor, moderate or severe concerns with methodological limitations.
Data extraction and synthesis
A “Characteristics of sampled studies” table was created in Excel and details are reported in Table 2 . Two independent reviewers familiarised themselves with the sampled studies and extracted key themes using Braun and Clarke’s reflexive approach to inductive and deductive thematic analysis [ 47 ]. Data were managed using NVivo 20 [ 48 ]. This was an iterative process as many of the themes and sub-themes overlapped and were relevant in many aspects throughout the perinatal period (Table 3 ). The findings were developed iteratively, and periodically shared with the broader team to evolve our interpretation. Any quotes taken from studies were selected as they reiterated findings, and provided additional depth and meaning to review findings.
Extracted data were populated into two tables for analysis. The first table collated quotes and author interpretations of findings (S 6 ), whilst the second table summarised these into review findings (Table 4 ).
Assessment of confidence in the review findings (GRADE-CERQual)
The GRADE-CERQual tool assesses the confidence in review findings from qualitative evidence syntheses [ 83 ]. Lewin et al., 2018 state that that “the approach has been developed to support the use of findings from qualitative evidence syntheses in decision-making, including guideline development and policy formulation” [ 83 ]. The GRADE-CERQual Interactive Summary of Qualitative Findings (iSoQ) online platform was used to manage and assess confidence in review findings [ 84 ].
Confidence in review findings was determined based on four criteria: methodological limitations, coherence, adequacy and relevance [ 83 ]. For each criterion, review authors determined if there were no or very minor, minor, moderate or serious concerns. An overall GRADE-CERQual assessment of confidence was placed on the findings, levels included: high, moderate, low and very low confidence. Review findings are considered at the highest confidence level and downgraded as there are greater concerns for each individual criterion (Table 4 ). This process was conducted by two authors, with any disagreements resolved through discussion and consulting other authors.
Managing our own reflexivity
Throughout the conceptualisation, data collection and analytical process, the authors considered their own individual views and beliefs about maternity care during the COVID-19 pandemic. As clinicians and researchers working on maternity care (including during the pandemic), we recognised that the COVID-19 period impacted indirectly on women and babies, including their experiences of care, their own anxieties and worries. We are public health professionals with diverse backgrounds including nursing and midwifery, maternal and newborn health, epidemiology and qualitative health research. We met regularly, both to explore the findings and the processes but also to ensure that we separated our individual experiences and beliefs on the interpretation of the analysis and the findings. Employing a systematic and transparent approach to the analytical process, such as including reflection notes after analysing each sampled paper, facilitated collaborative discussions, ensure objectivity and reduced the impact of personal biases.
A total of 36 studies contributed to the synthesis of qualitative evidence to understand pregnant and postpartum women’s experiences during the first two years of the pandemic. There were six over-arching themes: (1) dealing with public health restrictions; (2) navigating changing health policies; (3) adapting to alternative ways of receiving social support; (4) dealing with impacts on their own mental health; (5) managing the new and changing information; and (6) being resilient and optimistic. Seventeen sub-themes were developed within these 6 themes and illustrative quotes are presented in Table 3 to demonstrate theme development. Themes were categorised to differentiate major disruptors to the pregnancy and postpartum period and sub-themes aimed to categorise the indirect impacts that occurred within the major themes.
Characteristics of contributing studies
After applying the sampling framework (data richness score ≥4), 36 sampled studies were included for data extraction and analysis. Thirteen out of 36 studies had a score of 5 [ 49 , 52 , 57 , 58 , 61 , 62 , 63 , 66 , 68 , 69 , 71 , 77 , 82 ], with the remainder scoring 4 [ 9 , 16 , 50 , 51 , 53 , 54 , 55 , 56 , 59 , 60 , 64 , 65 , 67 , 70 , 72 , 73 , 74 , 75 , 76 , 78 , 79 , 80 , 81 , 82 ] (S 5 ). Most studies ( N =27/36, 75%) used specific qualitative methodologies, six were mixed-methods studies, two were cross-sectional studies, and one was a case series report.
Studies were conducted across nine countries, almost one-third ( N =10/36, 28%) of studies published from the UK, Canada ( N =7) and the USA ( N =7) (Table 2 ). Country-specific responses to the pandemic largely included border closures, mandatory lockdowns and restrictions on movement; it is interesting to note that Sweden did not mandate this but instead enforced social distancing practices [ 68 ]. Additionally, some studies reported on a specific sub-population of pregnant and postpartum women, for example women from ethnic minority groups, those with pre-existing comorbidities, and those who were COVID-19 positive. Some studies also included results from women with babies who were greater than 6 months of age, and any findings directly from these participants were omitted from analysis where possible.
The number of participants in studies that conducted interviews ranged from 3 to 84, and studies using qualitative data from open-ended questions or survey data included responses from 16 to 4,611 participants. Where demographic data were available, approximately 1,192 women were primiparous (having their first baby) and approximately 8,017 women were surveyed or interviewed postpartum. Sampled studies were generally of high quality and assessment of methodological limitations indicated that 29 studies were assigned “no or very minor concerns”, six studies were assigned “minor concerns”, and one study was assigned “moderate concerns”. When available, quotes obtained from studies have included additional demographic data. Factors included pregnant or postpartum status at time of data collection, parity and geographical location.
Theme 1: Dealing with public health restrictions
The rapid introduction of public health restrictions has had adverse effects on mental health, social isolation, and the pregnancy experience. Women had to navigate these restrictions and adapt accordingly, realising quickly that their pregnancy and postpartum experience was going to be very different from their expectations.
Sub-theme 1.1. Limited support networks from health care system and providers (High confidence)
Support networks were limited. Women felt that they were “on their own”, “unimportant or irrelevant” or treated as “second class citizens” after birth, because of a lack of physical supports from healthcare providers [ 51 , 60 , 61 , 62 , 70 , 72 , 74 ]. Limited or no access to physical and social support networks was commonly cited as a reason for deteriorating mental health.
Sub-theme 1.2. Balancing exposure risk and need for healthy behaviours (High confidence)
Women balanced COVID-19 exposure risks by shielding, either because of health providers recommendations [ 16 , 69 ] or because they felt it was needed to protect their baby [ 50 , 68 , 71 , 77 , 81 ]. Women delayed or postponed antenatal appointments [ 50 , 57 , 69 , 72 , 82 ], opted for induction of labour [ 74 ], or waited until labour was quite advanced before attending hospital [ 60 , 61 , 77 ]. These decisions were due to pandemic-induced fear, and the perceived risk of infection in a high-risk environment such as the hospital [ 16 , 56 , 80 ].
Sub-theme 1.3: Missing out on social opportunities (High confidence)
Women felt sad, unseen and heartbroken that they were not able to have social opportunities, especially sharing their newborns with family and friends [ 9 , 54 , 56 , 61 , 66 , 70 , 71 , 75 , 76 ]. On postnatal wards, women with older children were disappointed that their nuclear families could not visit and bond with their newborn in the early postpartum period [ 56 , 59 , 80 , 82 ]. While this was disappointing for many, one woman described still feeling well-supported, “ we were supposed to have a baby shower, the weekend after everything shut down … definitely got a lot of gifts in the mail and people who drop things off …. [we] feel like even though he’s being born in this super crazy time and he doesn’t necessarily get to meet people in person, that they are excited about him and want to support us” (USA) [ 52 ]. Primiparous women felt that they missed the opportunity to share many “firsts” with extended families - one woman said, “ this is my family’s first grandchild so it just breaks my heart they will miss her whole babyhood” (postpartum, Canada) [ 64 ].
Sub-theme 1.4 : Breastfeeding challenges and triumphs (High confidence)
Women that struggled with the lack of support around breastfeeding said, " when it came time for breastfeeding, I had no idea what to do or any challenges that could come. There were so, so, so many questions and I felt so confused during everything” (postpartum, primiparous, UK) [ 60 ]. Lactation consultations through virtual remote care was considered inadequate by most women [ 51 , 66 , 71 , 73 , 75 ], especially when practical hands-on education and assistance was needed [ 51 , 53 , 72 , 77 ]. These challenges led some women to cease breastfeeding early [ 51 , 62 , 73 ].
Conversely, public health restrictions enforcing women to stay at home allowed some women to practice responsive breastfeeding, without concern for social obligations or visitors [ 51 , 62 , 64 , 71 , 75 , 79 ]. Some women valued this flexibility - “ there’s no right or wrong way. You know, at the end of the day the ultimate goal is that my baby needs to be fed.… you know, feed him breast milk, breast milk, or formula. He’s fed. He’s happy. Sweet. That’s done. Job done! The important thing is actually [to] be kind to yourself, you know?” (postpartum, primiparous, UK) [ 62 ].
Challenges and triumphs were felt by both multiparous and primiparous women [ 51 ]. The difference between experienced and first-time mothers was stark in some studies, highlighted by multiparous women who felt ‘knowledgeable’ and ‘had the experience’, and sharing empathetic messages towards primiparous women with limited breastfeeding support [ 62 , 78 ].However, the lack of face-to-face breastfeeding support meant that first-time mothers and experienced mothers also faced hardships. As one mother recounts her sadness: “ I had virtual appointments [with lactation consultants], which I found totally useless… I was devastated that it wasn’t working with [the new baby] because it was something I was really looking forward to” (postpartum, multiparous, Canada) [ 73 ].
Theme 2: Navigating changing health policies
The ever-changing nature of the pandemic created periods of uncertainty. Women and their families were expected to accept and adapt to changing health policies which directly impacted their antenatal, labour and birth and postnatal experiences.
Sub-theme 2.1: A birthing experience filled with uncertainty and unknowns (High confidence)
Many women reported that, given the constantly changing policies, they were unsure what to expect for their labour and birth [ 9 , 49 , 60 , 75 , 77 ]. Limitations included not being able to have a water birth, use a bath or the shower, access nitrous oxide gas during labour [ 49 , 74 , 82 ] and others could not have their desired support people present [ 60 , 77 ]. In some cases, women opted for medicalised interventions to retain a sense of control - choosing a caesarean birth to ensure their partner was present at birth [ 60 , 74 ]. Women struggled with the prospect of early discharge, lacking confidence and fearing reduced support at home, with some feeling pushed out of the hospital [ 49 , 53 , 60 , 74 ]. Some women chose to leave hospital early due to the lack of support or poor experiences while in hospital [ 60 ]. Conversely, some women welcomed early discharge, wanting to be away from the hospital and to be reunited with family members [ 62 , 80 ]. Women who tested positive to COVID-19 early in the pandemic described additional challenges, such as a lack of certainty on how care was going to be managed [ 77 ]. They felt this restricted their autonomy over their labour and birth choices.
Sub-theme 2.2: Reduced support and partner presence healthcare settings (High confidence)
Due to the public health restrictions in hospitals, women often missed having their partner and family supports [ 16 , 49 , 57 , 66 , 71 ]. For example, “ one of my coping mechanisms is having my partner there to hear the same things I am hearing because I kind of shut down sometimes when I get too upset. It’s always good to have that second person listening… and walking out with strength of unity ” (pregnant, primiparous, Australia) [ 49 ]. The inability for some women to have their partners present negatively impacted women’s birthing experience [ 53 , 70 , 79 , 80 ], confidence on the postnatal ward and many expressed the sense of being “ robbed of this experience ” (pregnant, UK) [ 75 ].
Sub-theme 2.3: Transitioning to telehealth, virtual and remote care (Moderate confidence)
Public health restrictions limited face-to-face health care appointments with a maternity care provider [ 54 ]. Negative telehealth experiences were expressed predominantly by first-time mothers [ 71 ], with many saying, “ over the phone just doesn’t do it… you don’t get to look into somebody’s eyes and to trust them and for them to say, you’re okay ” (postpartum, Ireland) , adding to their anxieties. This was felt similarly by CALD women as there was a disconnect with health care providers using virtual methods and this was exacerbated for women who were not able to access interpreters [ 80 ]. Positive encounters with telehealth were associated with the increased accessibility to health services and generally preferred by multiparous women [ 54 , 65 , 68 ]. Whilst many were glad that telehealth services were available, this woman highlighted the inequities, “ I think I would question the accessibility of that. Not everyone has a smartphone and expecting people to be able to receive a video call is not necessarily the most inclusive thing ” (postpartum, primiparous, UK) [ 77 ] indicating that some women may have fallen through the gaps of maternity care.
Sub-theme 2.4: Barriers to accessing health services (High confidence)
The closure of so-called non-essential services, such as, physiotherapists, chiropractors, pools and gyms indirectly impacted women [ 66 , 74 ]. This often increased women’s anxiety, stress, feelings of helplessness and frustration [ 16 , 54 , 60 , 74 ] and incidence of postnatal depression [ 82 ]. This also limited opportunities to receive reassurance from healthcare providers, reducing women’s confidence [ 49 , 71 , 72 , 77 ]. Typically, women accessed networks for information and support, such as, family and friends with midwifery clinical expertise, or referred to recent pregnancy experience [ 52 , 68 , 75 , 79 ]. Women had to advocate strongly for physical assessments for themselves and their newborns [ 74 ].
Additionally, women from CALD populations were challenged in accessing culturally appropriate care with changes to interpretation services, “it creates like a…a gap in communication where if something you express is not clearly understood so maybe they could be left with some misinterpretation” (UK) [ 63 ]. Another example of the inequities faced by CALD women was expressed by this woman who did not receive interpretation services during appointments, “ sometimes they explained things to me by using signs and I understand a little English but it’s hard to understand medical terms and they didn’t use an interpreter for this ” (postpartum, multiparous, Canada) [ 80 ].
Theme 3: Adapting to alternative ways of receiving social support
Support networks, such as, family and friends, peer support groups (e.g. mother’s groups), and formal support from maternity care providers provide the foundation for a healthy and positive pregnancy and postpartum period. The COVID-19 pandemic forced women to adapt and seek support in different ways.
Sub-theme 3.1: Accessing support through different avenues (Moderate confidence)
Support from family and friends was accessed in different ways, for example, utilising video call technologies to be able to see faces helped with the grief of not being able to be present [ 16 ]. Women who were able to establish pregnancy and mother’s groups during the pandemic were grateful that they had these supports. Alternatively, women created or sought support through online social media platforms [ 61 , 68 , 70 , 81 ], to share a sense of camaraderie that they were not alone in their experiences [ 52 , 77 ]. In these forums, women shared information about COVID-19 developments, updates to hospital policies, and utilised others as sounding boards for advice. Some women reported greater support from partners who had transitioned to working from home [ 51 , 62 , 64 , 66 , 75 ]. Although virtual technologies allowed women to bridge the gap of social distancing, they wanted the physical connection with others.
Sub-theme 3.2: Desiring connection with family and friends (High confidence)
Women felt they needed intergenerational support to raise their newborns, and this was especially important during difficult times. Many had planned for parents to come and support them [ 81 ], as they believed that, “ the older generation have more experience on what babies need or what they feel… with my other two [children]… they knew exactly what would make them feel better ” (pregnant, multigravida, Australia) [ 49 ]. Some women struggled without the additional support, the lack of sleep impeded their physical wellbeing [ 61 , 73 , 75 ], and the isolation from family impacted their mental health [ 9 , 49 , 56 , 60 , 61 , 73 ]. In some cases, women were able to “ quarantine with family ”, providing women with a “ strong support network ” (postpartum, Canada) as they transitioned into motherhood [ 59 ]. Gradually, as public health restrictions eased, women from the UK felt government responses did not consider new mothers and babies and they called for “social bubbles” for families to receive the additional support [ 62 , 72 ]. The loss of informal support networks was apparent for some CALD women. As this woman said, “it was really hard during COVID. In Syria I had my family… but to give birth here with no one with me?! I needed someone with me, my neighbours, my friends… I felt like I was drowning” (postpartum, multiparous, Canada) [ 80 ].
Theme 4: Dealing with impacts on their own mental health
The COVID-19 pandemic placed a significant toll on pregnant and postpartum women’s mental health at all stages of the pandemic. Public health strategies failed to include protective measures for mental health, as such many women reported increased levels of fear, anxiety, stress, loneliness and depression.
Sub-theme 4.1: Managing anxiety due to virus-related fears and concerns (Moderate confidence)
Women often experienced anxiety exacerbated by the pandemic, for example, “ as a new mom you are already so nervous, so adding a pandemic to that pile of anxiety and worry ” (postpartum, Canada) [ 70 ]. This was related to possibility of infection, particularly in hospital and healthcare settings [ 9 , 56 , 57 , 69 , 82 ], and the need to protect their unborn or newborn baby [ 50 , 72 , 80 ]. Some faced additional challenges as migrants from another country, “ I found it very hard when you’re coming to the country without knowing anyone and the coronavirus, lockdown was very difficult, I was very depressed. I was very anxious… I feel worried a lot ” (UK) [ 63 ].
Sub-theme 4.2: Feeling lonely and isolated (High confidence)
Loneliness and isolation were commonly reported as women faced motherhood alone without their usual support systems. One woman said, “ it was quite sad that I couldn’t even share my pregnancy experience with anyone, and I feel like I missed out ” (postpartum, Australia) [ 54 ]. Feelings of loneliness was especially felt by mothers who were not able to have their partners present during birth or postnatally [ 61 ]. Women were not able to build supportive peer networks in their antenatal and postnatal periods [ 49 , 62 , 73 , 74 , 75 , 78 , 81 ], with one woman saying, “ there’s nothing like just meeting people or, just naturally building friendships when you go to baby groups” (postpartum, multiparous, UK) [ 62 ] emphasising the importance of developing social relationships. Cancellation of appointments and lack of face-to-face care added to feelings of “ abandonment ” and “ being forgotten ” [ 9 , 60 , 62 , 70 , 72 , 73 ].
Theme 5: Managing new and changing information
Due to the novelty of COVID-19 and lack of information about adverse effects, maternity care services had to rapidly adapt as new data came to light. Women described the need to search, access and filter useful information, a process which was challenging for many.
Sub-theme 5.1: Constantly changing advice and information (High confidence)
The constantly changing advice was distressing [ 82 ]. These changes meant a lot of uncertainty, one woman said, “ at 34 weeks I had a telephone appointment and I tried to ask what the changes in hospitals were, because of COVID and talk about the birth plan. She basically said, ‘everything is changing so quickly there is no point in us even talking about that now. Wait until your next appointment’ ” (postpartum, primiparous, UK) [ 77 ]. This limited women’s ability to adequately plan and prepare for the birth. Some women described following the updates from government officials and hospitals overwhelming [ 66 ]. As restrictions eased, women described the frustrations they had with the slow adaptations by health services, “ when I got to the hospital, they didn’t know about the restrictions having been lifted … That was really frustrating because I was like why? Why does this hospital not know?” (Australia) [ 82 ] and the differences between health services, “ restrictions have still not been lifted in ‘Hospital A’ whereas they have been eased in both ‘Hospital B’ and ‘Hospital C’ ” (pregnant, multiparous, Ireland) [ 9 ].
Sub-theme 5.2: Inadequate information from healthcare providers (Moderate confidence)
Women felt there was not enough information from healthcare providers, “ I think there was a lot of confusion; there was no good communication about what was happening to appointments. You weren’t really sure; were they happening on the phone [telehealth], when were you going to get the call? There was very little communication. So, I always felt a bit uneasy about that… ” (postpartum, primiparous, UK) [ 77 ]. Some information was contradictory [ 60 ] for example, “ I’ve found the disconnect between the information that my GP was getting and that the [hospital] was getting – they weren’t getting the same ” (Australia) [ 82 ]. Women wanted clear information that was easily accessed by the lay person [ 9 , 16 , 54 , 61 , 65 , 66 , 67 , 68 , 75 ]. They also wanted uncertainty to be acknowledged, “ it would have been useful to have some generic information that went out to women in that situation… statements from a medical professional to put people’s minds at ease ” (postpartum, Australia) [ 54 ].
Theme 6: Being resilient and optimistic
Many women were self-reliant and took it upon themselves to remain positive and proactive throughout the perinatal period.
Sub-theme 6.1: Self-help strategies to overcome challenges of the pandemic (High confidence)
Women developed their own strategies to find solace and support [ 77 ]. When asked what advice they had for other women in similar situations, advocacy for oneself was frequently reported [ 66 , 67 , 70 , 71 , 77 , 79 , 81 , 82 ]. In contrast, another woman regretted not voicing her concerns, “ I have naively trusted that the hospital gives me the information I need … Then I realized afterwards that there were many moms who were much angrier than me and said much more; insisted much more… and I simply did not; I regret it a bit ” (postpartum, Norway) [ 67 ]. Women reported coping using different strategies, such as being outdoors and active [ 16 , 52 , 54 ], limiting news and access to social media platforms [ 54 , 69 , 70 , 81 ], seeking professional help [ 58 , 73 ], informing themselves about the virus [ 58 , 71 ], drawing on their own faith and religion [ 52 , 69 ] and self-reassurance [ 50 , 52 , 62 ]. Many complied with public health restrictions, however there were some women that decided their mental health and physical wellbeing was more of a priority and broke public health restrictions to seek support from family and friends [ 62 , 66 , 73 ]. Despite the challenges faced during the pandemic, some women reported high resilience, positive childbirth and postnatal experiences, and feeling empowered by their ability to overcome challenging circumstances [ 54 , 58 , 74 ].
Sub-theme 6.2: Making the most out of the positive encounters (Moderate confidence)
The lack of visitors on the postnatal ward and in homes was described by women as “ pleasant ”, “ relaxing ” and a “ blessing in disguise ” as women were able to recover and establish undisrupted routines with their newborns [ 54 , 71 , 72 ]. A commonly reported positive outcome of limiting social obligations was the ability to establish successful breastfeeding, one woman said, “ I was inundated with visitors with my first child and often could not feed responsively… With my second child, there is none of that pressure and I can really see an enormous difference both is his feeding and in my mental health ” (postpartum, UK) [ 51 ]. Women also described health services as “ peaceful ”, as there were fewer people in waiting rooms, appointments were quick, social distancing was enforced and use of PPE limited the possibility of transmission [ 16 , 49 , 71 , 75 , 81 , 82 ].
Sub-theme 6.3: Information seeking and desire for more information (Moderate confidence)
Women obtained information from official government documents, guidelines released by professional bodies, the news, social media and platforms run by professional academics [ 53 , 66 , 68 , 72 , 81 ]. Reasons to seek information included: to clarify any uncertainties about risk and infection, keep up to date with COVID-19 guidelines and to be informed about changes to hospital policies [ 49 , 52 , 66 , 69 , 77 ]. Even once women were provided with information, poor communication and follow up left women feeling dissatisfied [ 54 ]. One woman shared advice about engaging with different information sources – “ you can’t just trust them – you’ve got to decipher through what’s true and what’s not… Is that actually having a positive influence on me, and my mental and physical health, or not? And if it’s a no, well why am I engaging in this ?” (Australia) [ 81 ].
This QES synthesised data from 36 sampled studies on pregnant and postpartum women’s experiences from high income countries during the COVID-19 pandemic. Findings were categorised under six overarching themes and 17 review findings to understand their experiences as the pandemic unfolded. Women had to navigate the transition from pregnancy to motherhood, whilst also adapting to the complexities of the COVID-19 pandemic. High to moderate confidence was placed in these review findings, indicating the strength of the evidence.
This review highlights that pregnant and postnatal women across high-income countries faced similar yet inherently unique experiences and challenges. During the pandemic, primiparous women faced moderate-to-high prenatal stress levels, as they recounted their first pregnancy experience during a time of significant uncertainty [ 85 , 86 , 87 ]. On the other hand, some evidence highlighted that multiparous women were ‘adaptive’ and felt ‘prepared’ [ 66 , 71 , 77 ]. However this was not experienced universally - many experienced mothers facing difficulties [ 9 , 73 , 80 ]. The COVID-19 pandemic and associated public health restrictions across high-income countries disrupted access and quality of care for many pregnant and postpartum women.
Reduced health service capacity and the transition to remote and virtual care due to pandemic restrictions have been heavily criticised [ 8 , 88 ]. In many contexts, women had not received high quality maternity care during the pandemic and described overtly negative experiences [ 35 , 89 , 90 ]. Women were unable to access usual supports, had limited birth choices and reduced postpartum care which resulted in stress and anxiety. These are clearly widespread experiences, regardless of context, and highlights some of the structural weaknesses and vulnerabilities of maternity care systems. This was evident in the findings for pregnant and postpartum women of culturally and linguistically diverse backgrounds. The lack of culturally appropriate care, including access to interpretation services, doulas and being unable to have their support person present are known to impair maternal health and wellbeing [ 56 , 63 , 80 ]. These factors are key elements of respectful maternity care as they help provide information, enable women’s agency and ensure emotional and social support is available [ 91 , 92 ]. Health restrictions should not limit this service for women during times of unrest, as women and babies thrive in culturally respectful maternity services [ 93 ]. We note however that CALD women continue to be an under-represented group - only three of the 36 sampled studies reported evidence specifically for CALD groups [ 56 , 63 , 80 ]. The lack of diverse perspectives included in the evidence base makes it more difficult for culturally sensitive and community-responsive policies to be developed. Further research with women from diverse backgrounds are warranted to ensure they are not unduly disadvantaged in future pandemics [ 94 ].
A key finding was the reduced presence of partner and social support throughout the pregnancy and postpartum periods. Partner support and strong connections with extended support networks reduces stress and anxiety, and can be a positive influence on the woman and her experience [ 95 , 96 , 97 ]. In the trade-off between the risk of transmission and spread of disease, expectant fathers and partners were frequently left out [ 98 , 99 ]. Similarly, studies of families and partners of intensive care unit patients during the COVID-19 pandemic reported being physically and emotionally unable to support partners and families [ 100 , 101 ]. Close family members are essential to the recovery of patients upon discharge and partners are integral to a safe and positive pregnancy, intrapartum and postpartum experience for mothers. To ensure that maternity care services can adequately respond in the future, recommendations for some degree of flexibility for women given the long-term psychosocial impact that a negative experience would have on the woman and family unit has been sought [ 8 , 87 , 88 ].
Pregnant and postpartum women’s experiences were not universally negative. Another key finding in this review highlights the resilience and optimism that some women felt. Some women perceived this time as a “blessing in disguise” – referencing the ability to stay at home, having fewer disruptions to breastfeeding, and embracing newfound time as a family unit [ 64 , 66 , 71 ]. Coping strategies reported in this study are supported by other evidence of protective factors against stressors of the COVID-19 pandemic [ 102 , 103 , 104 ].
Maternity care services need to continue delivering care during public health emergencies. There is no possibility of delaying or postponing care; and women require care over an extended period of time. Enforced lockdowns limited movement and fear of contracting the virus in hospitals lead to delays in healthcare seeking (e.g. when there is reduced fetal movements). The pandemic altered the provision of services and women’s access to care and, as a result, some countries have reported changes to the incidences of stillbirth and preterm birth [ 105 , 106 , 107 ].
Understanding women’s experiences, their preferences and satisfaction with maternity care services are essential to a safe and positive pregnancy, labour and childbirth and postpartum period. Many maternity models of care such as woman-centred and midwifery-led care places the woman at the centre of care and her experience, focusing on woman’s health needs, expectations and aspirations [ 108 , 109 ]. These models have proven to return high levels of satisfaction and are beneficial to the psychological and physiological recovery of the woman [ 110 , 111 ]. The COVID-19 pandemic has disrupted these models of care for women who were pregnant and gave birth during the pandemic. Pressures on the maternity care system and service delivery did not facilitate the midwife-woman relationship, resulting in poorer clinical outcomes [ 112 ]. Supporting women throughout their perinatal period is essential so women and their babies are able to emerge from the experience feeling prepared, safe and satisfied [ 113 , 114 ].
Moving forward, as maternity care systems adapt to a post-pandemic structure, considerations need to be made to ensure maternity services can adequately respond to future health crises. Our QES has shown that the impacts of COVID-19 went far beyond the direct impacts on women who were infected with SARS-COV2. All women giving birth over the pandemic, especially in the first two years, were indirectly impacted and as a result experienced a lack of autonomy during their pregnancy and childbirth, barriers to accessing face-to-face care and loss of social supports. This highlights the need to consider women’s views and experiences in developing policies for future responses to pandemics or public health emergencies.
We recommend that policy makers and maternity care services should: 1) optimise care delivery to maintain face-to-face care when possible and facilitate the presence of chosen support people; 2) enhance communication channels between maternity care services and women to minimise misinformation, stress and anxiety; and 3) support social and mental wellbeing to ensure women have access to adequate social support and mental health services are well resourced.
Strengths and limitations
The rigorous and systematic methodology of this QES in selecting studies for inclusion allowed us to analyse experiences of a heterogenous cohort of pregnant and postpartum women during the COVID-19 pandemic. When we started the review, the abundance of published work of women’s experiences was overwhelming, therefore strict eligibility criteria were used to ensure that findings could be obtained and compared across studies. This study was therefore limited to experiences of women in high-income countries and cannot be generalised to low- and middle-income countries.
Studies were subject to a sampling framework to ensure that a diverse, yet data rich sample of studies contributed to the development of review findings. This had its own set of limitations as the sampling framework is not a validated tool and may be biased by the user’s own interpretation. Additionally, the search strategy was limited to the first two years of the pandemic. While it is possible research was published outside of this two-year period, we felt that it was unlikely that different experiences would be reported. An updated search (December 2022) was conducted to determine if any new themes emerged, however no new themes emerged and therefore did not warrant the addition of any new studies. Almost all studies that used interviews to collect qualitative data did so via remote methods. Telephones and video conferencing tools were popular methods to conduct interviews, adhering to social distancing guidelines. Whilst this increased accessibility for participants from diverse geographical locations, there may be concerns about the depth of data obtained and exclusion of participants that are unable to access these technologies. A further consideration is the limited number of studies exploring the experiences of women from diverse backgrounds. This prevented us from more critically examining what factors and circumstances shape women’s experiences and responses.
Women’s pregnancy and postpartum experience during the COVID-19 pandemic showcased similarities despite different contexts. This QES has collated the experiences of women from high income countries sharing insight into the challenges faced and resilience of pregnant and postpartum women. The COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated many systemic shortfalls of the maternal and newborn health system – a system that is essential to the health and wellbeing of women and babies. The review findings have highlighted areas within this period where strategies to inform policy and practice could be optimised to allow for better access to care and support for women in their journey to motherhood. Future pandemic preparedness strategies need to maximise face-to-face care, optimise communication channels to combat misinformation and anxiety, include a flexible approach to public health restrictions for women and their families by allowing formal and informal support networks to be readily available and accessible, and to ensure maternal mental health is a priority.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files]. Additional information is available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
World Health Organization (WHO). WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard World Health Organization; 2021. Available from: https://covid19.who.int/.
Fisk M, Livingstone A, Pit SW. Telehealth in the Context of COVID-19: Changing Perspectives in Australia, the United Kingdom, and the United States. J Med Internet Res. 2020;22(6):e19264.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Montagnoli C, Zanconato G, Ruggeri S, Cinelli G, Tozzi AE. Restructuring maternal services during the covid-19 pandemic: Early results of a scoping review for non-infected women. Midwifery. 2021;94:102916.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Zaigham M, Linden K, Sengpiel V, Mariani I, Valente EP, Covi B, et al. Large gaps in the quality of healthcare experienced by Swedish mothers during the COVID-19 pandemic: A cross-sectional study based on WHO standards. Women and Birth. 2022;35(6):619–27.
Coxon K, Turienzo CF, Kweekel L, Goodarzi B, Brigante L, Simon A, et al. The impact of the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic on maternity care in Europe. Midwifery. 2020;88:102779.
Javaid S, Barringer S, Compton SD, Kaselitz E, Muzik M, Moyer CA. The impact of COVID-19 on prenatal care in the United States: Qualitative analysis from a survey of 2519 pregnant women. Midwifery. 2021;98:102991.
Galle A, Semaan A, Huysmans E, Audet C, Asefa A, Delvaux T, et al. A double-edged sword—telemedicine for maternal care during COVID-19: findings from a global mixed-methods study of healthcare providers. BMJ Global Health. 2021;6(2): e004575.
Kotlar B, Gerson E, Petrillo S, Langer A, Tiemeier H. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on maternal and perinatal health: a scoping review. Reproductive Health. 2021;18(1):10.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Meaney S, Leitao S, Olander EK, Pope J, Matvienko-Sikar K. The impact of COVID-19 on pregnant womens’ experiences and perceptions of antenatal maternity care, social support, and stress-reduction strategies. Women and Birth. 2021;35(3).
Allotey J, Stallings E, Bonet M, Yap M, Chatterjee S, Kew T, et al. Clinical manifestations, risk factors, and maternal and perinatal outcomes of coronavirus disease 2019 in pregnancy: living systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2020;370: m3320.
Villar J, Ariff S, Gunier RB, Thiruvengadam R, Rauch S, Kholin A, et al. Maternal and Neonatal Morbidity and Mortality Among Pregnant Women With and Without COVID-19 Infection: The INTERCOVID Multinational Cohort Study. JAMA Pediatrics. 2021;175(8). Available from: https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapediatrics/fullarticle/2779182 .
Basu A, Kim HH, Basaldua R, Choi KW, Charron L, Kelsall N, et al. A cross-national study of factors associated with women’s perinatal mental health and wellbeing during the COVID-19 pandemic. PloS one. 2021;16(4):e0249780-e.
Article Google Scholar
Yue C, Liu C, Wang J, Zhang M, Wu H, Li C, et al. Association between social support and anxiety among pregnant women in the third trimester during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) epidemic in Qingdao, China: The mediating effect of risk perception. Int J Soc psychiatry. 2020;67(2):120–7.
Vazquez-Vazquez A, Dib S, Rougeaux E, Wells JC, Fewtrell MS. The impact of the Covid-19 lockdown on the experiences and feeding practices of new mothers in the UK: Preliminary data from the COVID-19 New Mum Study. Appetite. 2021;156: 104985.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Jacob CM, Briana DD, Di Renzo GC, Modi N, Bustreo F, Conti G, et al. Building resilient societies after COVID-19: the case for investing in maternal, neonatal, and child health. The Lancet Public Health. 2020;5(11):e624–7.
Anderson E, Brigden A, Davies A, Shepherd E, Ingram J. Pregnant women’s experiences of social distancing behavioural guidelines during the Covid-19 pandemic “lockdown” in the UK, a qualitative interview study. BMC Public Health. 2021;21(1):1202.
Sanders J, Blaylock R. “Anxious and traumatised”: Users’ experiences of maternity care in the UK during the COVID-19 pandemic. Midwifery. 2021;102:103069.
Cooper M, King R. Women’s experiences of maternity care during the height of the COVID-19 pandemic in Australia. researchnowflinderseduau [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2021 Aug 30]. Available from: https://researchnow.flinders.edu.au/en/publications/womens-experiences-of-maternity-care-during-the-height-of-the-cov .
Mortazavi F, Ghardashi F. The lived experiences of pregnant women during COVID-19 pandemic: a descriptive phenomenological study. BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth. 2021;21(1):193.
Chivers BR, Garad RM, Boyle JA, Skouteris H, Teede HJ, Harrison CL. Perinatal Distress During COVID-19: Thematic Analysis of an Online Parenting Forum. J Med Internet Res. 2020;22(9): e22002.
Schaming C, Wendland J. Postnatal mental health during the COVID-19 pandemic: Impact on mothers’ postnatal sense of security and on mother-to-infant bonding. Midwifery. 2023;117: 103557.
Bradfield Z, Wynter K, Hauck Y, Vasilevski V, Kuliukas L, Wilson AN, et al. Experiences of receiving and providing maternity care during the COVID-19 pandemic in Australia: A five-cohort cross-sectional comparison. PLOS ONE. 2021;16(3): e0248488.
Vasilevski V, Sweet L, Bradfield Z, Wilson AN, Hauck Y, Kuliukas L, et al. Receiving maternity care during the COVID-19 pandemic: Experiences of women’s partners and support persons. Women and Birth. 2021;35(3).
Lalor JG, Sheaf G, Mulligan A, Ohaja M, Clive A, Murphy-Tighe S, et al. Parental experiences with changes in maternity care during the Covid-19 pandemic: A mixed-studies systematic review. Women and Birth. 2023;36(2):e203–12.
Almeida M, Shrestha AD, Stojanac D, Miller LJ. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on women’s mental health. Archives of Women’s Mental Health. 2020;23(6):741–8.
Flaherty SJ, Delaney H, Matvienko-Sikar K, Smith V. Maternity care during COVID-19: a qualitative evidence synthesis of women’s and maternity care providers’ views and experiences. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2022;22(1):438.
Al-Mutawtah M, Campbell E, Kubis H-P, Erjavec M. Women’s experiences of social support during pregnancy: a qualitative systematic review. BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth. 2023;23(1):782.
Zheng X, Zhang J, Ye X, Lin X, Liu H, Qin Z, et al. Navigating through motherhood in pregnancy and postpartum periods during the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review and qualitative meta-synthesis. J Nurs Manag. 2022;30(8):3958–71.
Noyes J BA, Cargo M, Flemming K, Harden A, Harris J, Garside R, Hannes K, Pantoja T, Thomas J,. Chapter 21: Qualitative evidence. . 2022. In: Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 63 (updated February 2022) [Internet]. Cochrane. Available from: http://www.training.cochrane.org/handbook .
Flemming K, Noyes J. Qualitative Evidence Synthesis: Where Are We at? International Journal of Qualitative Methods. 2021;20:1609406921993276.
Popay J, Rogers A, Williams G. Rationale and Standards for the Systematic Review of Qualitative Literature in Health Services Research. Qualitative Health Research. 1998;8(3):341–51.
Flemming K, Booth A, Garside R, Tunçalp Ö, Noyes J. Qualitative evidence synthesis for complex interventions and guideline development: clarification of the purpose, designs and relevant methods. BMJ Global Health. 2019;4(Suppl 1): e000882.
Tong A, Flemming K, McInnes E, Oliver S, Craig J. Enhancing transparency in reporting the synthesis of qualitative research: ENTREQ. BMC Medical Research Methodology. 2012;12(1):181.
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021;372: n71.
World Health Organization (WHO). WHO Technical Consultation on Postpartum and Postnatal Care. Geneva: WHO; 2010.
Google Scholar
Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. List of OECD Member countries - Ratification of the Convention on the OECD: OECD; 2023. Available from: https://www.oecd.org/about/document/ratification-oecd-convention.htm .
World Population Review. Human Development Index (HDI) by Country 2022-2023. Available from: https://worldpopulationreview.com/country-rankings/hdi-by-country .
Greyling T, Rossouw S, Adhikari T. The good, the bad and the ugly of lockdowns during Covid-19. PLOS ONE. 2021;16(1): e0245546.
Bu F, Steptoe A, Fancourt D. Loneliness during a strict lockdown: Trajectories and predictors during the COVID-19 pandemic in 38,217 United Kingdom adults. Social Science & Medicine. 2020;265: 113521.
Coronavirus Pandemic (COVID-19). 2020 Available from: https://ourworldindata.org/coronavirus .
Covidence. Covidence. Available from: https://www.covidence.org/ .
Bohren MA. Qualitative evidence synthesis & GRADE-CERQual. University of Melbourne. Cochrane Australia. 2021.
Downe S, Finlayson KW, Lawrie TA, Lewin SA, Glenton C, Rosenbaum S, et al. Qualitative Evidence Synthesis (QES) for Guidelines: Paper 1 – Using qualitative evidence synthesis to inform guideline scope and develop qualitative findings statements. Health Research Policy and Systems. 2019;17(1):76.
Benoot C, Hannes K, Bilsen J. The use of purposeful sampling in a qualitative evidence synthesis: A worked example on sexual adjustment to a cancer trajectory. BMC Medical Research Methodology. 2016;16(1):21.
Ames H, Glenton C, Lewin S. Purposive sampling in a qualitative evidence synthesis: a worked example from a synthesis on parental perceptions of vaccination communication. BMC Medical Research Methodology. 2019;19(1):26.
Critical Appraisal Skills Program. CASP Qualitative Studies Checklist. 2018. Available from: https://casp-uk.net/casp-tools-checklists/ .
Braun V, Clarke V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qualitative Research in Psychology. 2006;3(2):77–101.
Lumivero. NVivo (Version 13,2020), QSR International Pty Ltd; 2020. Available from: www.lumivero.com .
Atmuri K, Sarkar M, Obudu E, et al. Perspectives of pregnant women during the COVID-19 pandemic: A qualitative study. Women and Birth. 2022;35(3):280–8.
Aydin R, Aktaş S. An investigation of women’s pregnancy experiences during the COVID-19 pandemic: A qualitative study. Int J Clin Pract. 2021;75(9).
Brown A, Shenker N. Experiences of breastfeeding during COVID-19: Lessons for future practical and emotional support. Maternal & Child Nutrition. 2021;17(1): e13088.
Charvat E, Horstman HK, Jordan E, Leverenz A, Okafor B. Navigating Pregnancy during the COVID-19 Pandemic: The Role of Social Support in Communicated Narrative Sense-making. Journal of Family Communication. 2021;21(3):167–85.
Costa B, McWilliams D, Blighe S, Hudson N, Hotton M, Swan MC, et al. Isolation, Uncertainty and Treatment Delays: Parents’ Experiences of Having a Baby with Cleft Lip/Palate During the Covid-19 Pandemic. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2021;105566562110550.
Davis JA, Gibson LY, Bear NL, Finlay-Jones AL, Ohan JL, Silva DT, et al. Can Positive Mindsets Be Protective Against Stress and Isolation Experienced during the COVID-19 Pandemic? A Mixed Methods Approach to Understanding Emotional Health and Wellbeing Needs of Perinatal Women. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(13):6958.
DeJoy SB, Mandel D, McFadden N, Petrecca L. Concerns of Women Choosing Community Birth During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Qualitative Study. Journal of Midwifery & Women’s Health. 2021;66(5):624–30.
Dove-Medows E, Davis J, McCracken L, et al. A Mixed-Methods Study of Experiences During Pregnancy Among Black Women During the COVID-19 Pandemic. J Perinat Neonatal Nurs. 2022;36(2):161–72.
Farrell RM, Pierce M, Collart C, Craighead C, Coleridge M, Chien EK, et al. The impact of the emergence of COVID-19 on women's prenatal genetic testing decisions. Prenat Diagn. 2021;41(8):1009–17.
Fumagalli S, Omaghi S, Borrelli S, et al. The experiences of childbearing women who tested positive to COVID-19 during the pandemic in northern Italy. Women and Birth. 2022;35(3):242–53.
Green SM, Furtado M, Inness BE, Frey BN, McCabe RE. Characterizing Worry Content and Impact in Pregnant and Postpartum Women with Anxiety Disorders During COVID-19. Clin Psychol Psychother. 2022;29(3):1144–57.
Harrison S, Alderdice F, McLeish J, et al. You and your baby: a national survey of health and care during the 2020 Covid-19 pandemic. Oxford: National Perinatal Epidemiology Unit, University of Oxford; 2021.
Jackson L, De Pascalis L, Harrold JA, Fallon V, Silverio SA. Postpartum women's experiences of social and healthcare professional support during the COVID-19 pandemic: A recurrent cross-sectional thematic analysis. Women and Birth. 2022;35(5):511–20.
Jackson L, De Pascalis L, Harrold JA, Fallon V, Silverio SA. Postpartum women’s psychological experiences during the COVID-19 pandemic: a modified recurrent cross-sectional thematic analysis. BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth. 2021;21(1):625.
John JR, Curry G, Cunningham-Burley S. Exploring ethnic minority women’s experiences of maternity care during the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic: a qualitative study. BMJ Open. 2021;11(9): e050666.
Joy P, Aston M, Price S, Sim M, Ollivier R, Benoit B, et al. Blessings and Curses: Exploring the Experiences of New Mothers during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Nursing Reports. 2020;10(2):207–19.
Keating NE, Dempsey B, Corcoran S, McAuliffe FM, Lalor J, Higgins MF. Women’s experience of pregnancy and birth during the COVID-19 pandemic: a qualitative study. Ir J Med Sci. 2022;191(5):2177–84.
Kolker S, Biringer A, Bytautas J, Blumenfeld H, Kukan S, Carroll JC. Pregnant during the COVID-19 pandemic: an exploration of patients’ lived experiences. BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth. 2021;21(1):851.
Kynø NM, Fugelseth D, Knudsen LMM, Tandberg BS. Starting parenting in isolation a qualitative user-initiated study of parents’ experiences with hospitalization in Neonatal Intensive Care units during the COVID-19 pandemic. PloS one. 2021;16(10): e0258358.
Linden K, Domgren N, Zaigham M, Sengpiel V, Andersson ME, Wessberg A. Being in the shadow of the unknown — Swedish women's lived experiences of pregnancy during the COVID-19 pandemic, a phenomenological study. Women and Birth. 2022;35(5):440–6.
Mizrak Sahin B, Kabakci EN. The experiences of pregnant women during the COVID-19 pandemic in Turkey: A qualitative study. Women and birth. 2021;34(2):162–9.
Ollivier R, Aston DM, Price DS, Sim DM, Benoit DB, Joy DP, et al. Mental Health & Parental Concerns during COVID-19: The Experiences of New Mothers Amidst Social Isolation. Midwifery. 2021;94: 102902.
Panda S, O’Malley D, Barry P, Vallejo N, Smith V. Women’s views and experiences of maternity care during COVID-19 in Ireland: A qualitative descriptive study. Midwifery. 2021;103: 103092.
Rhodes A, Kheireddine S, Smith AD. Experiences, Attitudes, and Needs of Users of a Pregnancy and Parenting App (Baby Buddy) During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Mixed Methods Study. JMIR mHealth and uHealth. 2020;8(12): e23157.
Rice K, Williams S. Women’s postpartum experiences in Canada during the COVID-19 pandemic: a qualitative study. CMAJ Open. 2021;9(2):E556–62.
Rice K, Williams S. Making good care essential: The impact of increased obstetric interventions and decreased services during the COVID-19 pandemic. Women and Birth. 2022;35(5):484–92.
Riley V, Ellis N, Mackay L, Taylor J. The impact of COVID-19 restrictions on women’s pregnancy and postpartum experience in England: A qualitative exploration. Midwifery. 2021;101: 103061.
Saleh L, Canclini S, Greer K, Mathison C, Combs SM, Dickerson B, et al. Mothers’ Experiences of Pregnancy, Labor and Birth, and Postpartum During COVID-19 in the United States: Preliminary Results of a Mixed-Methods Study. The Journal of Perinatal & Neonatal Nursing. 2022;36(1):55–67.
Silverio SA, De Backer K, Easter A, von Dadelszen P, Magee LA, Sandall J. Women’s experiences of maternity service reconfiguration during the COVID-19 pandemic: A qualitative investigation. Midwifery. 2021;102: 103116.
Snyder K, Worlton G. Social Support During COVID-19: Perspectives of Breastfeeding Mothers. Breastfeed Med. 2021;16(1):39–45.
Spatz DL, Froh EB. Birth and Breastfeeding in the Hospital Setting during the COVID-19 Pandemic. MCN The American Journal of Maternal Child Nursing. 2021;46(1):30–5.
Stirling Cameron E, Ramos H, Aston M, Kuri M, Jackson L. “COVID affected us all:” the birth and postnatal health experiences of resettled Syrian refugee women during COVID-19 in Canada. Reproductive Health. 2021;18(1):256.
Sweet L, Bradfield Z, Vasilevski V, Wynter K, Hauck Y, Kuliukas L, et al. Becoming a mother in the ‘new’ social world in Australia during the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic. Midwifery. 2021;98: 102996.
Sweet L, Wilson AN, Bradfield Z, Hauck Y, Kuliukas L, Homer CSE, et al. Childbearing women’s experiences of the maternity care system in Australia during the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic. Women and Birth. 2022;35(3):223–31.
Lewin S, Booth A, Glenton C, Munthe-Kaas H, Rashidian A, Wainwright M, et al. Applying GRADE-CERQual to qualitative evidence synthesis findings: introduction to the series. Implementation Science. 2018;13(1):2.
iSoQ: Grade-CERqual [Internet]. 2023 [cited 2022]. Available from: https://www.cerqual.org/isoq/ .
Ataman H, Tuncer M. The effect of COVID-19 fear on prenatal distress and childbirth preference in primipara. Rev Assoc Med Bras. 2023;69(5):e20221302.
Preis H, Mahaffey B, Heiselman C, Lobel M. Vulnerability and resilience to pandemic-related stress among US women pregnant at the start of the COVID-19 pandemic. Social science & medicine. 2020;266: 113348.
Boekhorst MG, Muskens L, Hulsbosch LP, Van Deun K, Bergink V, Pop VJ, et al. The COVID-19 outbreak increases maternal stress during pregnancy, but not the risk for postpartum depression. Arch Womens Ment Health. 2021;24(6):1037–43.
Reingold RB, Barbosa I, Mishori R. Respectful maternity care in the context of COVID-19: A human rights perspective. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2020;151(3):319–21.
Tunçalp Ӧ, Pena-Rosas JP, Lawrie T, Bucagu M, Oladapo OT, Portela A, Metin Gülmezoglu A. WHO recommendations on antenatal care for a positive pregnancy experience-going beyond survival. BJOG. 2017;124(6):860–2.
World Heath Organization (WHO) Standards for improving quality of maternal and newborn care in health facilities [Internet]. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/9789241511216 .
Khaw SML, Homer CSE, Dearnley RE, O’Rourke K, Akter S, Bohren MA. A qualitative study on community-based doulas’ roles in providing culturally-responsive care to migrant women in Australia. Women and Birth. 2023;36(5):e527–35.
Essén B, Eriksson L. Paradoxes in the cultural doula concept for migrant women: Implications for gender-inclusive care versus migrant-friendly maternity care. Midwifery. 2023;126: 103805.
Asefa A. Unveiling respectful maternity care as a way to address global inequities in maternal health. BMJ Glob Health. 2021;6(1):e003559.
Murray K, Nebeker C, Carpendale E. Responsibilities for ensuring inclusion and representation in research: A systems perspective to advance ethical practices. Australian & New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry. 2019;53(9):835–8.
Rini C, Schetter CD, Hobel CJ, Glynn LM, Sandman CA. Effective social support: Antecedents and consequences of partner support during pregnancy. Personal Relationships. 2006;13(2):207–29.
Racine N, Plamondon A, Hentges R, Tough S, Madigan S. Dynamic and bidirectional associations between maternal stress, anxiety, and social support: The critical role of partner and family support. Journal of Affective Disorders. 2019;252:19–24.
Kroelinger CD, Oths KS. Partner Support and Pregnancy Wantedness. Birth. 2000;27(2):112–9.
Wells MB, Svahn J, Svedlind K, Andersson E. A qualitative study of Swedish fathers’ experiences of becoming a father during the COVID-19 pandemic. Eur J Midwifery. 2022;6:15.
Lista G, Bresesti I. Fatherhood during the COVID-19 pandemic: an unexpected turnaround. Early Hum Dev. 2020;144: 105048.
Menzel A. The coronavirus pandemic: exploring expectant fathers’ experiences. Journal for Cultural Research. 2022;26(1):83–101.
Digby R, Manias E, Haines KJ, Orosz J, Ihle J, Bucknall TK. Family experiences and perceptions of intensive care unit care and communication during the COVID-19 pandemic. Australian Critical Care. 2023;36(3):350–60.
Roberto A, Sellon A, Cherry ST, Hunter-Jones J, Winslow H. Impact of spirituality on resilience and coping during the COVID-19 crisis: A mixed-method approach investigating the impact on women. Health Care Women Int. 2020;41(11–12):1313–34.
Kinser PA, Jallo N, Amstadter AB, Thacker LR, Jones E, Moyer S, et al. Depression, Anxiety, Resilience, and Coping: The Experience of Pregnant and New Mothers During the First Few Months of the COVID-19 Pandemic. Journal of Women’s Health. 2021;30(5):654–64.
Barbosa-Leiker C, Smith CL, Crespi EJ, Brooks O, Burduli E, Ranjo S, et al. Stressors, coping, and resources needed during the COVID-19 pandemic in a sample of perinatal women. BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth. 2021;21(1):171.
Hui L, Marzan MB, Potenza S, Rolnik DL, Pritchard N, Said JM, et al. Increase in preterm stillbirths in association with reduction in iatrogenic preterm births during COVID-19 lockdown in Australia: a multicenter cohort study. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2022;227(3):491.e1–17.
De Mario C, Leonardo V, Arianna P. Increase of stillbirth and decrease of late preterm infants during the COVID-19 pandemic lockdown. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2021;106(4):456.
Calvert C, Brockway M, Zoega H, Miller JE, Been JV, Amegah AK, et al. Changes in preterm birth and stillbirth during COVID-19 lockdowns in 26 countries. Nature Human Behaviour. 2023;7(4):529–44.
Fahy K. What is woman-centred care and why does it matter? Women and Birth. 2012;25(4):149–51.
Leap N. Woman-centred or women-centred care: does it matter? British Journal of Midwifery. 2009;17(1):12–6.
Watkins V, Nagle C, Kent B, Street M, Hutchinson AM. Labouring Together: Women’s experiences of “Getting the care that I want and need” in maternity care. Midwifery. 2022;113: 103420.
Macpherson I, Roqué-Sánchez MV, Legget BNFO, Fuertes F, Segarra I. A systematic review of the relationship factor between women and health professionals within the multivariant analysis of maternal satisfaction. Midwifery. 2016;41:68–78.
Vermeulen J, Bilsen J, Buyl R, De Smedt D, Gucciardo L, Faron G, et al. Women’s experiences with being pregnant and becoming a new mother during the COVID-19 pandemic. Sex Reprod Healthc. 2022;32: 100728.
Homer CSE. Models of maternity care: evidence for midwifery continuity of care. Medical Journal of Australia. 2016;205(8):370–4.
Davison C. Woman-centred care. British Journal of Midwifery. 2021;29(5):246–8.
Download references
Acknowledgments
Not applicable.
The primary author is funded by Deakin University Postgraduate Research Scholarship as a PhD Candidate. AB is supported by the Australian Government Research Training Program, CSEH is supported by the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council Leadership Investigator Grant, and JPV is supported by the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council Emerging Leadership Investigator Grant. The funding bodies had no role in the conceptualisation of the study design and data collection, data analysis, interpretation and writing of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Nursing and Midwifery, Deakin University, Geelong, Australia
Annie Tan, Caroline SE. Homer, Robin Digby, Joshua P. Vogel & Tracey Bucknall
Maternal, Child and Adolescent Health Program, Burnet Institute, Melbourne, Australia
Annie Tan, Amanda Blair, Caroline SE. Homer & Joshua P. Vogel
Centre for Quality and Patient Safety Research, Institute of Health Transformation, Geelong, Australia
Annie Tan, Robin Digby & Tracey Bucknall
Melbourne School of Population and Global Health, The University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia
Amanda Blair
Alfred Health, Melbourne, Australia
Robin Digby & Tracey Bucknall
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
AT: Conceptualisation, Methodology, Data Collection, Formal Analysis, Writing – Original Draft. AB: Secondary Reviewer, Data Collection, Formal Analysis, Writing – Reviewing and Editing. RD: Supervision, Data Analysis, Writing – Reviewing and Editing. JPV: Supervision, Data Analysis, Writing – Reviewing and Editing. CSEH: Supervision, Data Analysis, Writing – Reviewing and Editing. TB: Primary Supervision, Methodology, Data Analysis, Writing – Reviewing and Editing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Annie Tan .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
All data included are publicly available and therefore did not require ethical approval.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary material 1., supplementary material 2., supplementary material 3., supplementary material 4., supplementary material 5., supplementary material 6., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Tan, A., Blair, A., Homer, C.S. et al. Pregnant and postpartum women’s experiences of the indirect impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic in high-income countries: a qualitative evidence synthesis. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 24 , 262 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-024-06439-6
Download citation
Received : 04 July 2023
Accepted : 24 March 2024
Published : 11 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-024-06439-6
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- COVID-19 pandemic
- Maternal and newborn health
- Qualitative synthesis
- Women’s experiences
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth
ISSN: 1471-2393
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Open access
- Published: 12 April 2024

Healthcare team resilience during COVID-19: a qualitative study
- John W. Ambrose 1 ,
- Ken Catchpole 2 ,
- Heather L. Evans 3 ,
- Lynne S. Nemeth 1 ,
- Diana M. Layne 1 &
- Michelle Nichols 1
BMC Health Services Research volume 24 , Article number: 459 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
111 Accesses
Metrics details
Resilience, in the field of Resilience Engineering, has been identified as the ability to maintain the safety and the performance of healthcare systems and is aligned with the resilience potentials of anticipation, monitoring, adaptation, and learning. In early 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic challenged the resilience of US healthcare systems due to the lack of equipment, supply interruptions, and a shortage of personnel. The purpose of this qualitative research was to describe resilience in the healthcare team during the COVID-19 pandemic with the healthcare team situated as a cognizant, singular source of knowledge and defined by its collective identity, purpose, competence, and actions, versus the resilience of an individual or an organization.
We developed a descriptive model which considered the healthcare team as a unified cognizant entity within a system designed for safe patient care. This model combined elements from the Patient Systems Engineering Initiative for Patient Safety (SEIPS) and the Advanced Team Decision Making (ADTM) models. Using a qualitative descriptive design and guided by our adapted model, we conducted individual interviews with healthcare team members across the United States. Data were analyzed using thematic analysis and extracted codes were organized within the adapted model framework.
Five themes were identified from the interviews with acute care professionals across the US ( N = 22): teamwork in a pressure cooker , consistent with working in a high stress environment; healthcare team cohesion , applying past lessons to present challenges , congruent with transferring past skills to current situations; knowledge gaps , and altruistic behaviors , aligned with sense of duty and personal responsibility to the team. Participants’ described how their ability to adapt to their environment was negatively impacted by uncertainty, inconsistent communication of information, and emotions of anxiety, fear, frustration, and stress. Cohesion with co-workers, transferability of skills, and altruistic behavior enhanced healthcare team performance.
Working within the extreme unprecedented circumstances of COVID-19 affected the ability of the healthcare team to anticipate and adapt to the rapidly changing environment. Both team cohesion and altruistic behavior promoted resilience. Our research contributes to a growing understanding of the importance of resilience in the healthcare team. And provides a bridge between individual and organizational resilience.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the complexity and dynamic nature of healthcare systems. It also created a unique opportunity to look at the concept of resilience through the lens of the healthcare team versus the more common approach of situating the concept within the individual or the organization. The early phase of the pandemic was marked by challenges, such as limited access to personal protective equipment, personnel shortages, drug shortages, and increased risks of infection [ 1 , 2 ]. Ensuring patient safety and proper functioning requires coordination and adaptation of the healthcare team and various processes across the health system infrastructure [ 3 , 4 ]. Resilience results from adaptive coordination which enables healthcare systems to maintain routine function in the face of all conditions [ 5 , 6 ].
Resilience in healthcare has been operationalized through resilience engineering, an interdisciplinary aspect of systems engineering focused on promotingpatient safety through the design, implementation, and management of healthcare systems [ 7 , 8 , 9 ] (e.g., how healthcare systems adapt and adjust to maneuver through the daily complexities and challenges to identify effective practices, prevent errors and maintain resilient performance) [ 6 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 ]. Resilient performance in healthcare is proposed to be the net result of reaching the threshold of four resilience capabilities within the system: anticipation, the ability to expect and prepare for the unexpected; monitoring, the ability to observe threats to daily system performance; responding, the ability to adapt how the performance is enacted; and learning, the ability to learn from present and past accomplishments within the system [ 12 ]. At present, there is a paucity of research on the resilience of the healthcare team as a cohesive, singular conscious source of knowledge in a highly complex healthcare system. While the resilience of both healthcare systems [ 11 , 13 ] and healthcare workers [ 14 ] has been investigated, there is a gap in knowledge specific to the resilience of the healthcare team as a unified singular consciousness. The circumstances surrounding the COVID-19 pandemic presented a unique opportunity to understand the resilience of the healthcare team in a highly complex system as a singular aware entity within the system; how it acknowledges itself, defines its purpose, and performs under extenuating circumstances. This shifts the emphasis of individual and organization resilience to the resilience in the interconnected healthcare team that extends beyond the boundary of any single person.
The adapted model situates the healthcare team as a cohesive singlular conscious source of knowledge within an intricate and highly complex system [ 15 ]. This model was designed as a bridge between resilience found in individuals within the healthcare system and the organization to emphasize the healthcare team as an aware, unified whole. Our model [ 15 ] combines the existing Systems Engineering Initiative for Patient Safety (SEIPS) model [ 16 ] (version 1), which is based on five domains (organization, person, tasks, technologies, and tools), and environment and the Advanced Team Decision Making Model [ 17 ], which includes components for team performance [ 17 , 18 , 19 ]. Team performance is comprised of team identity, team cognition, team competency, and team metacognition [ 17 , 18 , 19 ]. Team identity describes how the team identifies their purpose to help one another [ 17 ]. Team cognition describes the state of mind of the team, their focus, and common goals [ 17 ]. Team competency describes how well the team accomplishes tasks, and team metacognition describes problem solving and responsibility [ 17 , 19 ], Fig. 1 .
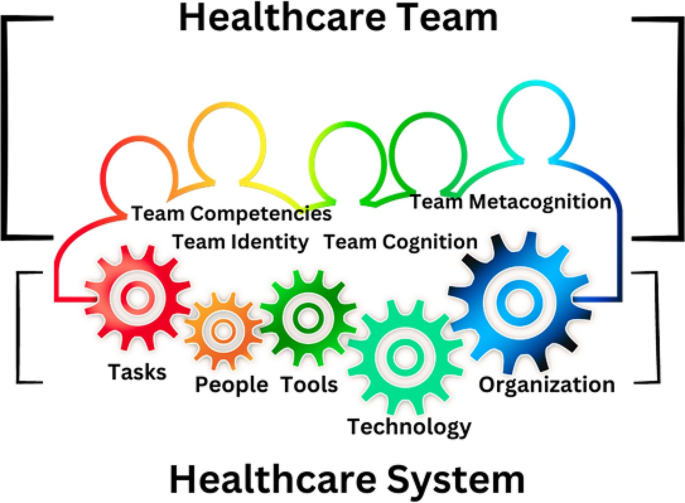
Healthcare Team as a cohesive, singular conscious source of knowledge in a highly complex system. The continuous variegated border represents the singularity and connectedness of the healthcare team within the system. The gears represent the processes, people, technology, and tasks within this highly dynamic healthcare system
The purpose of this qualitative research was to describe resilience in the healthcare team during the COVID-19 pandemic with the healthcare team situated as a singular conscious source of knowledge defined by its collective identity, purpose, competence, and actions. Additionally, we sought to identify factors that may facilitate or hinder the healthcare team from achieving the necessary capabilities to monitor, anticipate, adapt, and learn to meet the standard for resilient performance.
Methodology
A qualitative descriptive design [ 20 , 21 ] was employed. The interview guide was framed using the adapted model to explore various aspects of healthcare team performance (identity, purpose, competence, and cognition). These questions were pilot tested on the first 3 participants and no further changes were needed. Specifically, we aimed to investigate resilience capabilities, decision-making processes, and overall healthcare team performance.
Sampling strategy
A purposive snowball sample was used to identify healthcare team members who worked in U.S. acute care settings between January 2020–December 2020. This sampling method was used to ensure recruitment of participants most likely to have insight into the phenomenon of resilience in the acute care setting.
Inclusion criteria
To explore a wide range of interprofessional experience, participants were recruited across geographic regions and professional roles through personal contacts and social media [ 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 ]. Eligible participants included English-speaking individuals ages 20 and older with a valid personal email address, internet access, and the ability to participate in an online video interview. Potential participants had to be employed full or part-time for any period from January 2020–December 2020 in any of the following acute healthcare environments: emergency room (ER), intensive care unit (ICU), COVID- 19 ICU, COVID-19 floor, gastroenterology inpatient unit, endoscopy suite, operating room (OR), post anesthesia recovery room (PACU), pre-operative holding area, hospital administration, or inpatient medical and/or surgical patient care unit.
Exclusion criteria
Healthcare team members who did not complete the pre-screening survey or failed to schedule an interview were not enrolled.
National recruitment in the U.S
Upon approval by MUSC Institutional Review Board (IRB), registered under Pro00100917, fliers, social media posts on Twitter TM (version 9.34 IOS, San Francisco, California) and Facebook TM (version 390.1 IOS, Menlo Park, CA), and word of mouth were used to initiate recruitment efforts. Interested participants were sent a link to an electronic screening survey explaining the purpose of the study and verifying the respondents’ eligibility to participate. Informed consent was obtained from all subjects.
Data collection
Data were collected via an initial screening questionnaire to determine eligibility. Data were managed using REDCap™ (version 11.2.2) electronic data capture tools hosted at MUSC. Demographic data included age, sex, race, professional role, years of experience, geographic region, patient population served, practice specialty area, and deployment status during the pandemic. Deployment refers to the reassignment of personnel from their primary clinical area to another area to meet the demands of another clinical area without regard for the participant’s clinical expertise. Qualitative data were collected through semi-structured audio video recorded interviews to understand the healthcare team in their natural environment. Recorded interviews were conducted via Microsoft® Teams (version 1.5.00.17261, Microsoft Corporation) from the PIs private office to mitigate the risk of COVID-19 transmission and promote participation across the U.S.
Data monitoring and safety
The quality of the demographic data was monitored to ensure completeness. Potential participants who submitted incomplete responses on the questionnaire were excluded. Interviews were transcribed using software, transcriptions were reviewed and verified for accuracy, and then uploaded to MAXQDA Analytics Pro, Version 2022 (VERBI software) to facilitate data analysis. Transcripts were not returned to the participants. Qualitative codebooks, institutional review board (IRB) logs, and other study records were stored on a secure university server, with access limited to authorized study personnel. Adherence to Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research (COREQ) standards were maintained throughout the study and analysis [ 26 ].
Data analysis
Quantitative analysis.
Demographic data were analyzed using SPSS Statistics for MAC, version 28 (IBM). Both descriptive statistics for the continuous variables of age and years of experience (mean, standard deviation) and frequency tables (age, sex, race, role, geographic region, population served, deployment status) were analyzed.
Qualitative analysis
The Principal Investigator (PI) (JA) and senior mentor (MN) independently coded the interview transcripts. Open coding method was used to identify the categories of data [ 22 , 27 ]. Both a reflexive journal and audit trail were maintained. Codes were identified through induction from participant experiences and verified through weekly consensus meetings, while theoretical deductive analysis was guided by the adapted model and the four resilience capabilities (anticipation, monitoring, responding, learning [ 12 ]. Reflexive thematic analysis (TA) [ 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 ] was used to analyze the coded data and generate themes. Data were collected and categorized into the codebook until no further codes were identified by the PI and research mentor [ 22 , 27 ]. Participant checking was not employed.
Demographics
The eligibility pool was established based on survey completion. Eighty-nine healthcare team members opened the online screening survey; 21 were incomplete and eliminated from the dataset, which left a pool of 68 potential eligible participants. Eligible participants (100%) were contacted by email and phone to determine their interest in completing the study interview. Twenty-two participants completed screening surveys and study interviews between May–September 2021, equating to a 32.5% enrollment rate. Participant interviews lasted between 21 and 91 min with an average of 43 min. None of the interviews were repeated. Participant demographics, including descriptive statistic and role key, are noted in Tables 1 and 2 , respectively.
Five themes were identified: team work in a pressure cooker , healthcare team cohesion , applying past lessons to present challenges , knowledge gaps , and altruistic behaviors .
Teamwork in a pressure cooker
The theme teamwork in a pressure cooker describes the relentless pressures and emotional stressors (e.g., fear, anxiety, frustration, and stress) experienced by the healthcare team from the risks and potential threats associated with COVID-19 contamination and infection. Factors associated with these pressures included risk of COVID-19 exposure, lack of COVID-19 testing, rapid changes to policies and procedures from the standard, personnel shortages, limited physical space, and limited supplies. Exemplary quotes highlighting participant descriptions of these pressures or subthemes are noted in Table 3 .
The healthcare team described an unprecedented level of stress in the workplace as the healthcare team had to adjust to rapidly changing protocols. The lack of protective equipment, shortage of providers to perform patient care and a lack of a familiar clinical routine saturated them in overwhelming pressure and emotions that stuck to them as they navigated uncharted territory. Exemplary quotes highlighting the healthcare team’s descriptions of these emotions are noted in Table 4 .
“It was…uncharted territory for me.” (P1, DIR) “You were stuck in a situation you never— you didn’t know when it was going to end.” (P4, RN PACU) “They have not enough staff—they can’t do it—they—I don’t know what we’re going to do.” (P6, DIR). “When we deployed—trying to get re-accustomed to the changes—with the needs that had to be met was very difficult.” (P10, RN ENDO) “I wasn’t about to sign up for extra time working in under those stressful conditions.” (P17, RN PACU)
The fear of the unknown, combined with the constant need to adapt to rapidly changing circumstances, led to widespread stress, frustration, anxiety, and exhaustion within the healthcare team. This theme was characterized by the constant pressure both inside and outside of work experienced by the healthcare team.
“Driving to the hospital, crying, driving back from the hospital, crying, still doesn’t sum it up— surrounded by people who were just dying. And what could you do?” (P6, DIR) “It was constant. It was terrible. I couldn’t sleep at night. I’d wake up worried.” (P8, ER MD) “It was kind of like just keep sending the Calvary forward—and when one drops, you just walk over them.” (P17, RN PACU) “It was always there—COVID here, COVID there—you never could just completely get away from it. It was basically the center of everybody’s conversation everywhere you went or if you were on the phone with somebody.” (P18, RN COVID ICU) “I was having to call my parents before I’d leave my apartment to go into work— to vent to them and cry— to let out my frustration and my anxiety—and have them essentially convince me to go into work.” (P19, RN ICU). “Working so much— COVID was all that was on my brain—and it was a lot of pressure.” (P22, MGR)
Working during COVID-19 challenged the resilience of the healthcare team in the face of constant fear and uncertainty. The pressure to maintain team performance, while dealing with constant fear associated with the pandemic effected the healthcare team’s resilience.
“I have to tell you that after being in hospital—I don’t feel resilient right now— doing all the things I’ve done—I just want to be out of the hospital— [crying] I can tell you that it will stay with me the rest of my life— It will always stay with me.” (P6, DIR) “I feel like my team has used up all of their resilience. I don’t think there’s much left.” (P8, ER MD)
However, one team member stood out as an exception. They reported the pressures from the environment helped them to make decisions. This demonstrates that environmental pressures affect members of the healthcare team differently. They reported that the pressure and intensity of the situation sharpened their focus and allowed them to make choices more quickly and effectively.
“I make better decisions when I’m under pressure.” (P22, MGR)
Healthcare team cohesion
The theme healthcare team cohesion describes the unique experience of working together during the pandemic that created a means among the healthcare team to form close relationships and unite. This bond was characterized by the emergence of strong interpersonal connections among healthcare professionals during the COVID-19 pandemic. These connections shaped healthcare team relationships and were a factor in the collaborative decision-making processes within healthcare team for their day-to day functions. This cohesive bonding was fueled by the stress and uncertainty of the situation, which brought the healthcare team together illustrated by their solidarity, camaraderie, trust, and empowerment.
“All those decisions, important decisions were made together.” (P7, CRNA) “Everyone felt like they were they were, you know, in a in a battle zone and on the same side—and so that kind of brought people together.” (P8, ER MD) “I think our team worked as one.” (P11, CEO)
Solidarity described the sense of unity evident among the members of the healthcare team. This was characterized by connectedness and a sense of reliance on one another that promoted teamwork and resilience within the team from support both given and received. The sub-theme camaraderie described the close personal connection and support between the healthcare team that went beyond normal social interactions prior to the pandemic. These connections were filled with trust and respect for other healthcare team members.
“I think we were all trying to do the best we could do and help each other do the best they could do—I think early on just camaraderie helped a lot within the department and, you know, just relying on each other for support.” (P8, ER MD) “We knew that we can depend on each other and we all had different skill sets— I think that that was very important—that made us feel secure— rather than going alone.” (P10, RN ENDO) “We [The ICU Nurses] developed a sense of camaraderie that I mean, it’s nothing I’ve ever felt before, like we had to trust each other with our licenses, with our own health—my resiliency came from my coworkers.” (P14, CHG RN) “One of the things that I think the pandemic did in a positive—was—I believe that the teams that I worked for really started to solidify. We leaned on each other. I felt more of a team environment than I had had pre-pandemic—I felt that people were a bit better together. We all needed each other, and we all leaned on each other, and we gave each other support—more so than before COVID- 19.” (P15, CRNA) ”The nurses on the unit were always there for me—they became my friends— my family.” (P19, RN ICU)
The sub theme of empowerment referred to the ability of the healthcare team to confidently make decisions and assume responsibility for their actions within the healthcare setting. This process involved a sense of authority and the ability to exercise agency in decision-making together to respond and adapt to the demands the healthcare team experienced. The combination of solidarity, camaraderie, trust, and empowerment resulted in a strong sense of cohesion within the healthcare team which led to improved relationships and enhanced resilience in their performance.
“I felt that I felt that the team—we all needed each other and we all leaned on each other and we gave each other support—more so than before COVID.” (P15, CRNA) “How do you want to handle this? What’s the plan?—and we collaborated in the true sense of collaboration.” (P15, CRNA) “We just knew that we could count on each other—we knew that we could count on each other at any time if we had questions, because we all worked so closely together during this. We really became a really tight knit group, and it was great.” (P22, MGR)
The benefits of the cohesion found in the healthcare team were significant and apparent during the COVID-19 pandemic. The strengthened relationships and increased resilience allowed for improved communication and collaboration, leading to better patient care and outcomes. Despite these advantages, it was noted by one participant that the relationships developed were not sustained beyond the peak of the pandemic.
“Now that COVID is kind of at bay in our area, it’s kind of gone back to the same way it was— it has not stuck.” (P15, CRNA)
Applying past lessons to present challenges
The theme applying past lessons to present challenges describes how the knowledge and understanding gained from prior participant experiences was used to adapt to the novel clinical and infrastructural challenges faced during the pandemic. Past experiences facilitated the healthcare team to strategize ways to meet the demands of the healthcare system during this time.
Participants described two strategies the healthcare team used to improve the system’s ability to adapt and function effectively: changing roles and deploying personnel. The process of changing roles involved assigning new responsibilities to individuals based on priority-based initiatives, while deployment involved transferring clinical staff from areas with lower patient care needs to those with higher needs to optimize their utilization. Eleven participants (50%) were affected by these strategies. Of these, 73% were assigned to clinical areas for direct patient care, while the remaining 27% underwent a role change to support the operational needs of the system. The participants’ preexisting work relationships, specialized clinical expertise, and leadership abilities helped them adapt to their new clinical and non-clinical roles, which in turn enhanced the resilience of the healthcare team.
“We wanted to make sure that we were putting people into the right area where their skill set could be used the best.” (P1, DIR) “I’m known for moving people forward—I’m also well known for speaking up when I don’t think it is right and there was a lot of stuff that I didn’t think was right— and not only speaking up, I’m also going to come with the solution.” (P6, DIR)
Participants indicated the lessons learned from prior experience positively impacted team performance and improved patient care outcomes. There were two significant examples in the data: the perspective of a nurse who was redeployed to work in an obstetrics unit (P5, ENDO RN) and the perspective of a nursing director (P6, DIR) whose role was changed to develop a program to ensure adequate staffing.
“Because we [the team of interprofessionals] were all very familiar with what we had to do at the task, at handit [the experience of the provision of care] was very fluid—I think it’s because of our years of experience and working with each other for so long that it just worked out very well ”. (P5, ENDO RN) “Staff believed in me when I said I would do something— I could galvanize people because of my reputation of caring for staff, so I was chosen specifically because of my ability to move people forward in spite of things.” (P6, DIR)
Participants identified being assigned to unfamiliar clinical areas or working with unfamiliar patient populations as a barrier that hindered their ability to adapt to clinical situations. The lack of clinical competence among some personnel led to an increase in workload for other healthcare team members, who had to provide additional instruction and guidance on how to complete the task. Decision-makers who deployed nursing staff to a clinical area with higher staffing needs may have believed that the individual nurse had specific clinical skills that would be helpful in that area, and this was not the case.
“She [the patient] felt like it was that he [the new nurse]—really didn’t know what he was doing—not only were we kind of reintroduced to that role of caring for patients where we haven’t been recently, but we’re also in a teaching mode, too, for the new nurses—we had to prioritize how sick the patients were, from basic vital signs to wound dressings to respiratory, and help those new nurses know which to attend to first.” (P10, RN ENDO) “Nurses weren’t really put in a place with enough support and enough resources to be able to do a job, and to do a job that maybe they haven’t done for a few years.” (P10, RN ENDO)
The participants indicated that clinical competencies of a healthcare provider in one patient population may not necessarily be applicable to another patient group. For instance, a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) nurse who has experience in managing Extra Corporeal Membranous Oxygen (ECMO) in newborns may not have the necessary skills to care for adult ECMO patients in an adult COVID-19 intensive care unit.
“The ECMO nurse was a NICU nurse, so she really could not help me.” (P14, CHG RN)
Knowledge gaps
The theme knowledge gaps refers to the disparity between the existing knowledge of the healthcare team and the knowledge required for the team to effectively respond and adapt to the needs of the healthcare system. The lack of COVID-19 specific knowledge led to gaps in the healthcare team’s understanding, while the lack of communication made it difficult for necessary information to be effectively conveyed and received (e.g., medical logistics, human resources, and other operational policies and procedures). This knowledge gap created a barrier to healthcare team resilience as their capacities to surveil, anticipate, and respond were diminished from the lack of knowledge.
“That [information] is pretty fundamental to how you [the healthcare team] function.” (P17, RN PACU) “I don’t think any amount of preparation could have actually prepared us for how bad COVID was—but we were very, very, very unprepared.” (P18, RN COVID ICU) “It was confusing, it was disruptive to the patients that we had there. They sensed that. And that’s— OK—screw with me, screw with my colleagues, but don’t screw with the patient.” (P21, RN ENDO)
All the participants in leadership roles during the COVID-19 pandemic emphasized the importance of having a thorough understanding of the information and effectively communicating it to the frontline healthcare team members most involved in providing patient care.
“There’s nothing worse than having to learn something in the moment and not being prepared for it.” (P1, DIR) “That made us communicate in multiple ways throughout a day because we all know people learn and adapt it could be in print. It could be in person; it could be a video. We tried to have multiple ways of getting messages out and knowing we needed to repeat messages because this was so unknown, and people were so stressed.” (P11, CEO)
One team member (P13, CRNA), highlighted areas where there were gaps in knowledge in greater detail.
“It was as if the unit was being run by all these sort of substitute teachers that were called in at the last minute. Nobody knew where stuff was—nobody knew what the protocol was—the communication was terrible.” (P13, CRNA)
The cumulative effect from the knowledge gaps contributed to the lack of a practical working knowledge for the healthcare team and affected the healthcare team’s ability to anticipate what needed to be done and adapt their performance to accomplish it. Despite knowledge gaps, healthcare team members reported their capability to learn was facilitated by incremental gains in practical knowledge through their experience over time.
“—people got to be experts at protecting patients and keeping themselves safe.” (P8, ER MD) “I think it kind of was like on the job training at that point, I felt like we were all just trying to survive—learning was like—you went out —then you came back, and you would share how things went.” (P15, CRNA) “You tried to educate yourself so you could be safe.” (P17, RN PACU)
The participant responses received from the leadership (CNO, Directors, and Manager) and front-line personnel (administrative staff, nurses, and physicians) regarding the importance of communication highlighted a difference in perspective. Leadership exhibited a strong commitment toward effective communication and made efforts to ensure all healthcare team members were well informed. On the other hand, the frontline participants indicated instances where communication strategies were not perceived as effective.
“I wasn’t contacted by a manager from the unit or anything to be able to reassure, reassure me that things were being followed through and it should be okay, so that was tough.” (P10, RN ENDO) “It really seemed like there was no communication between—like staffing and the floor—we would get up to the floor and they would say, who are you? What are you doing here? What are we supposed to do with you?” (P20, RN OR)
Altruistic behaviors
The theme altruistic behaviors , encompasses the participants’ perception of their obligation and accountability to their patients and healthcare team, and their steadfastness in supporting the healthcare team even if it meant facing personal or professional repercussions. This readiness to aid the healthcare team and accept consequences showcased their altruism and commitment to the healthcare team. The team’s dedication to both their patients and each other was a primary focus driven by a strong sense of responsibility and obligation.
“I want to be able to look myself in the mirror and feel like I did the right thing—.” (P6, DIR) “My resiliency came from my coworkers. I wanted to come back to work to help them.” (P14, RN COVID ICU) “People really looked out for each other—and people were really kind and compassionate to each other—we all were in this together.” (P15, CRNA) “I’m grateful for the experience that I had and all of the different patients that I was able to help in my time there definitely solidified that being a nurse is what I needed to do—and why I chose the profession is exactly what I should have been doing.” (P19, RN ICU) “You just have to go with what seems right—.” (P22, MGR)
A defining characteristic of this theme was a willingness to endure consequences for the benefit of the healthcare team. These consequences varied from contracting the virus, facing criticism from the healthcare team, to foregoing financial incentives, and even job loss.
“I felt like I was punished for speaking up and I was punished for doing the right thing for patients.” (P6, DIR) “I mean, I literally broke the law so many times. Do you know how many times I started pressors [vasoactive drugs to increase blood pressure] on patients that I had no orders for [because a physician would not enter the ICU]?” (P14, CHG RN)
We identified five key themes based on the coded data; namely teamwork in a pressure cooker , healthcare team cohesion , applying past lessons to present challenges , knowledge gaps , and altruistic behaviors . The researchers propose that stressors arising from the COVID-19 pandemic had an impact on the healthcare team’s resilience. In addition, strong healthcare team cohesion, selfless behaviors among the healthcare team, shared knowledge, and job competence within the healthcare team, enhanced resilient performance.
The healthcare team experienced significant stress and uncertainty, due to the COVID-19 pandemic. This is consistent with previous research that has shown that the unprecedented nature of the pandemic led to challenging working conditions, limited resources, lack of information, and concerns about infecting loved ones [ 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 ]. The collective global impact of COVID-19 on healthcare systems is likely a contributing factor to these stressors [ 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 ].
Our study, along with those conducted by Anjara et al. (2021)[ 49 ] and Kaye-Kauderer et al. (2022) [ 50 ], found that solidarity and camaraderie among healthcare professionals improve resilience. Specifically, Anjara et al. observed increased collaboration among the healthcare professionals they studied in Ireland during the COVID-19 pandemic, while Kaye-Kauderer et al. identified team camaraderie among their sample of front-line healthcare workers from New York. Kinsella et al. (2023) [ 51 ] reported that COVID − 19 offered frontline workers in the UK the opportunity to work together toward a common goal. Potential explanations for these findings align with the concepts of social capital proposed by Coleman [ 52 ] and social identification with other as proposed by Drury [ 54 ]. Coleman suggests an individual’s skills and capabilities are enhanced through their interdependent relationships with others [ 52 ]. Drury found in communities affected by disasters, mutual aid and support emerged from a shared social identity, which serves to strengthen the community [ 53 ]. Brooks et al. (2021) [ 54 ] conducted a study with healthcare, police, and commercial sectors in England. They found it was important for these individuals to receive support from and provide support to their colleagues to mitigate the psychological impact of disaster exposure [ 54 ]. In addition, like our findings, Aufegger and colleague’s 2019 systematic review [ 55 ] found that social support in acute care healthcare teams creates a supportive atmosphere where team members help each other communicate problems, fulfill needs, and deal with stress.
Our results are consistent with those of Liu et al. (2020) [ 32 ] and Banerjee et al. (2021) [ 44 ] who each found that healthcare professionals frequently feel a sense of personal responsibility to overcome challenges. One potential explanation for this may be the influence of collectivism in their cultures. Similarly, our study suggests the sense of camaraderie among healthcare professionals may also contribute to a sense of responsibility and increased altruistic behavior. However, other studies have highlighted different perspectives on healthcare professionals’ sense of responsibility and duty. Godkin and Markwell’s (2003) [ 56 ] revealed that healthcare professionals’ sense of responsibility during the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) outbreak was dependent on the protective measures and support offered by the healthcare system where most SARS infected patients were hospitalized. More recently, Gray et al. (2021) reported that nurses’ sense of responsibility stems from their ethical obligations, regardless of potential personal or familial risks [ 57 ].
The altruistic behaviors described by our participants helped maintain the performance of the healthcare team. It is too soon to see the long-term impact from working in this high-pressure environment; however, past research by Liu et al. (2012) [ 58 ] and Wu (2009) [ 59 ] demonstrated that “altruistic-risk acceptance” during the SARS outbreak was shown to decrease depressive symptoms among hospital employees in China.
Our research on resilience has important implications for healthcare organizations and professionals. In order to ready themselves for forthcoming events, healthcare systems must emphasize the significance of shared knowledge and its influence on the healthcare team’s ability to foresee and monitor effectively. This knowledge can help the healthcare organization function as a unified entity, rather than as individuals in separate roles or clusters within the organization to improve healthcare team preparedness. Establishing a cohesive, clinically competent healthcare team benefits the organization and the patients served. Measures to enhance social support, improve communication and ensure clinical competence maintain healthcare team resilience.
There are several limitations to consider when interpreting the results of this study. First, the sample was obtained using purposive snowball sampling, which may have introduced sampling bias and may not accurately represent the larger population of healthcare team members who worked during the COVID-19, as 95% of the sample were white. Second, our study did not have equal representation of all interprofessional team members. It is possible that a more heterogenous sample regarding role, race and gender may have introduced additional codes. Additionally, the PI (JA) worked as a Certified Registered Nurse Anesthesiologist (CRNA) in acute care during the pandemic and personal experience may have introduced confirmation bias. Also, the focus of our research was to fill a gap in the existing knowledge of what is known about healthcare team resilience in pandemic disasters, and help to answer if and how it intersects with individual and organizational resilience. It is possible this novel conceptualization of healthcare team as a cohesive singular conscious source of knowledge did not adequately address this.
Steps to ensure rigor and mitigate any potential shortcomings of qualitative data analysis were the maintenance of a reflexive journal, a willingness of the PI to let go of unsupported ideas and constant verification of codes and themes with the research mentor (MN) for coherence and consistency within the coded data, selected methodology and research questions.
Overall, the extracted themes of teamwork in a pressure cooker; healthcare team cohesion; applying past lessons to present challenges; knowledge gaps; and altruistic behaviors illustrate comparable experiences within the healthcare team. As healthcare professionals and organizations continue to navigate the challenges of the COVID-19 pandemic and other crises, our findings provide valuable insights into how team cohesion, along with altruistic behaviors, may enhance resilience capabilities to create and maintain a unified resilient healthcare team.
Data availability
The data for this study are confidential as required by the IRB approval. To protect the anonymity of the participants, the data are not publicly available. Additional information about the research method, Interview questions, informant data, and the study in general can be requested from the corresponding author, J.A.
Berlin G, Singhal S, Lapointe M, Schulz J. Challenges emerge for the US healthcare system as COVID-19 cases rise. 2020;9.
Stevens JP, O’Donoghue A, Horng S, Tabb K. Healthcare’s earthquake: Lessons from complex adaptive systems to develop Covid-19-responsive measures and models. 2020.
Kopach-Konrad R, Lawley M, Criswell M, Hasan I, Chakraborty S, Pekny J, et al. Applying systems Engineering principles in improving Health Care Delivery. J Gen Intern Med. 2007;22(S3):431–7.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Compton WD, Fanjiang G, Grossman JH, Reid PP. Institute of Medicine (U.S.), National Academy of Engineering. Building a better delivery system: a new engineering/health care partnership [Internet]. Washington, D.C.: National Academies Press; 2005 [cited 2021 Feb 12]. http://public.ebookcentral.proquest.com/choice/publicfullrecord.aspx?p=3378176 .
Hollnagel E, Woods DD. Resilience Engineering concepts and precepts. 1st ed. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press/Routledge/Taylor & Francis Group; 2006. p. 416.
Google Scholar
Wiig S, O’Hara JK. Resilient and responsive healthcare services and systems: challenges and opportunities in a changing world. BMC Health Serv Res. 2021;21(1):1037.
Nemeth C, Wears RL, Patel S, Rosen G, Cook R. Resilience is not control: healthcare, crisis management, and ICT. Cogn Tech Work. 2011;13(3):189–202.
Article Google Scholar
Hollnagel E. Safety-II in Practice: Developing the Resilience Potentials [Internet]. 1st ed. Routledge; 2017 [cited 2022 May 7]. https://www.taylorfrancis.com/books/9781351780766 .
Braithwaite J, Wears RL, Hollnagel E. Resilient health care: turning patient safety on its head. Int J Qual Health Care. 2015;27(5):418–20.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Madni AM, Jackson S. Towards a conceptual Framework for Resilience Engineering. IEEE Syst J. 2009;3(2):181–91.
Carthey J. Institutional resilience in healthcare systems. Qual Health Care. 2001;10(1):29–32.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Hollnagel E. The Four cornerstones of Resilience Engineering. In: Dekker, editor. Resilience engineering perspcetives. E. Hollnagel&S. Ashgate: Farnham, UK; 2009. pp. 117–33.
Fridell M, Edwin S, von Schreeb J, Saulnier DD. Health System Resilience: what are we talking about? A scoping review mapping characteristics and keywords. Int J Health Policy Manag. 2019;9(1):6–16.
Article PubMed Central Google Scholar
Curtin M, Richards HL, Fortune DG. Resilience among health care workers while working during a pandemic: a systematic review and meta synthesis of qualitative studies. Clin Psychol Rev. 2022;95:102173.
Ambrose JW, Layne DM, Catchpole K, Evans H, Nemeth LS. A qualitative protocol to examine Resilience Culture in Healthcare teams during COVID-19. Healthcare. 2021;9(9):1168.
Carayon P, Hundt AS, Karsh B, Gurses AP, Alvarado CJ, Smith M, et al. Work system design for patient safety: the SEIPS model. Qual Saf Health Care. 2006;15(Suppl 1):i50–8.
Thordsen ML, Kyne MM, Klein G, A Model of Advanced Team Decision Making and Performance.: Summary Report: [Internet]. Fort Belvoir, VA: Defense Technical Information Center; 1994 Sep [cited 2021 Feb 13]. http://www.dtic.mil/docs/citations/ADA400497 .
Zsambok CE. Advanced Team Decision Making: A Model and Training Implications.
Klein GA. Sources of power: how people make decisions. MIT Press; 1988.
Doyle L, McCabe C, Keogh B, Brady A, McCann M. An overview of the qualitative descriptive design within nursing research. J Res Nurs. 2020;25(5):443–55.
Siedlecki SL. Understanding descriptive research designs and methods. Clin Nurse Spec. 2020;34(1):8–12.
Crabtree BF, Miller WL. Doing qualitative research. Second. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage; 1999. p. 406.
Bradley EH, Curry LA, Devers KJ. Qualitative Data Analysis for Health Services Research: developing taxonomy, themes, and theory. Health Serv Res. 2007;42(4):1758–72.
Gale NK, Heath G, Cameron E, Rashid S, Redwood S. Using the framework method for the analysis of qualitative data in multi-disciplinary health research. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2013;13(1):117.
Lincoln Y, Guba E. Naturalistic Inquiry. California: Sage; 1985.
Book Google Scholar
Tong A, Sainsbury P, Craig J. Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ): a 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups. Int J Qual Health Care. 2007;19(6):349–57.
Saldaña J. The coding manual for qualitative rearchers. Los Angeles, USA: Sage; 2021.
Boyatzis RE. Transforming qualitative information: thematic analysis and code development. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications Ltd; 1998.
Braun V, Clarke V. What can thematic analysis offer health and wellbeing researchers? Int J Qualitative Stud Health Well-being. 2014;9(1):26152.
Braun V, Clarke V. Thematic analysis. In: Cooper H, Camic PM, Long DL, Panter AT, Rindskopf D, Sher KJ, editors. APA handbook of research methods in psychology, Vol 2: Research designs: Quantitative, qualitative, neuropsychological, and biological [Internet]. Washington: American Psychological Association; 2012 [cited 2022 May 15]. pp. 57–71. http://content.apa.org/books/13620-004 .
Braun V, Clarke V. Conceptual and design thinking for thematic analysis. Qualitative Psychol. 2022;9(1):3–26.
Liu Y, Zhai Z, Han Y, Liu Y, Liu F, Hu D. Experiences of front-line nurses combating coronavirus disease‐2019 in China: a qualitative analysis. Public Health Nurs. 2020;37(5):757–63.
Catania G, Zanini M, Hayter M, Timmins F, Dasso N, Ottonello G, et al. Lessons from Italian front-line nurses’ experiences during the COVID‐19 pandemic: a qualitative descriptive study. J Nurs Manag. 2021;29(3):404–11.
Croghan IT, Chesak SS, Adusumalli J, Fischer KM, Beck EW, Patel SR et al. Stress, Resilience, and Coping of Healthcare Workers during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Journal of Primary Care and Community Health [Internet]. 2021;12. https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?eid=2-s2.0-85104122303&doi=10.1177%2f21501327211008448&partnerID=40&md5=96ad0164880c9725ce14d534e3c3117
Arnetz JE, Goetz CM, Arnetz BB, Arble E. Nurse reports of stressful situations during the COVID-19 pandemic: qualitative analysis of survey responses. IJERPH. 2020;17(21):8126.
Dagyaran I, Risom SS, Berg SK, Højskov IE, Heiden M, Bernild C, et al. Like soldiers on the front– a qualitative study understanding the frontline healthcare professionals’ experience of treating and caring for patients with COVID-19. BMC Health Serv Res. 2021;21(1):666.
Goh Y, Ow Yong QYJ, Chen TH, Ho SHC, Chee YIC, Chee TT. The impact of COVID-19 on nurses working in a University Health System in Singapore: a qualitative descriptive study. Int J Mental Health Nurs. 2021;30(3):643–52.
LoGiudice JA, Bartos S. Experiences of nurses during the COVID-19 pandemic: a mixed-methods study. AACN Adv Crit Care. 2021;32(1):14–26.
O’Brien JM, Bae FA, Kawchuk J, Reimche E, Abramyk CA, Kitts C et al. We were treading water. Experiences of healthcare providers in Canadian ICUs during COVID-19 visitor restrictions: a qualitative descriptive study.
Perraud F, Ecarnot F, Loiseau M, Laurent A, Fournier A, Lheureux F, et al. A qualitative study of reinforcement workers’ perceptions and experiences of working in intensive care during the COVID-19 pandemic: a PsyCOVID-ICU substudy. Sharma GA, editor. PLoS ONE. 2022;17(3):e0264287.
Shanafelt T, Ripp J, Trockel M. Understanding and addressing sources of anxiety among Health Care professionals during the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA. 2020;323(21):2133.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Speroni KG, Seibert DJ, Mallinson RK. Nurses’ perceptions on Ebola Care in the United States, Part 2: a qualitative analysis. JONA: J Nurs Adm. 2015;45(11):544–50.
Sonis J, Pathman DE, Read S, Gaynes BN, Canter C, Curran P, et al. Effects of Healthcare Organization Actions and policies related to COVID-19 on Perceived Organizational Support among U.S. internists: a National Study. J Healthc Manag. 2022;67(3):192–205.
PubMed Google Scholar
Banerjee D, Sathyanarayana Rao TS, Kallivayalil RA, Javed A. Psychosocial Framework of Resilience: navigating needs and adversities during the pandemic, a qualitative exploration in the Indian Frontline Physicians. Front Psychol. 2021;12:622132.
Freudenberg LS, Paez D, Giammarile F, Cerci J, Modiselle M, Pascual TNB, et al. Global impact of COVID-19 on Nuclear Medicine departments: an International Survey in April 2020. J Nucl Med. 2020;61(9):1278–83.
Haldane V, Morgan GT. From resilient to transilient health systems: the deep transformation of health systems in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. Health Policy Plann. 2021;36(1):134–5.
Shrestha N, Shad MY, Ulvi O, Khan MH, Karamehic-Muratovic A, Nguyen USDT, et al. The impact of COVID-19 on globalization. One Health. 2020;11:100180.
Jean WC, Ironside NT, Sack KD, Felbaum DR, Syed HR. The impact of COVID-19 on neurosurgeons and the strategy for triaging non-emergent operations: a global neurosurgery study. Acta Neurochir. 2020;162(6):1229–40.
Anjara S, Fox R, Rogers L, De Brún A, McAuliffe E. Teamworking in Healthcare during the COVID-19 pandemic: a mixed-method study. IJERPH. 2021;18(19):10371.
Kaye-Kauderer H, Loo G, Murrough JW, Feingold JH, Feder A, Peccoralo L, et al. Effects of Sleep, Exercise, and Leadership Support on Resilience in Frontline Healthcare workers during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Occup Environ Med. 2022;64(5):416–20.
Kinsella EL, Muldoon OT, Lemon S, Stonebridge N, Hughes S, Sumner RC. In it together? Exploring solidarity with frontline workers in the United Kingdom and Ireland during COVID-19. Br J Social Psychol. 2023;62(1):241–63.
Coleman JS. Social Capital in the creation of Human Capital. Am J Sociol. 1988;94:S95–120.
Drury J, Carter H, Cocking C, Ntontis E, Tekin Guven S, Amlôt R. Facilitating collective psychosocial resilience in the Public in emergencies: twelve recommendations based on the Social Identity Approach. Front Public Health. 2019;7:141.
Brooks SK, Dunn R, Amlôt R, Rubin GJ, Greenberg N. Protecting the psychological wellbeing of staff exposed to disaster or emergency at work: a qualitative study. BMC Psychol. 2019;7(1):78.
Aufegger L, Shariq O, Bicknell C, Ashrafian H, Darzi A. Can shared leadership enhance clinical team management? A systematic review. LHS. 2019;32(2):309–35.
Godkin D, Markwell H. The Duty to Care of Healthcare Professionals: Ethical Issues and Guidelines for Policy Development. Submitted to SARS Expert Panel Secretariat.:23.
Gray K, Dorney P, Hoffman L, Crawford A. Nurses’ pandemic lives: a mixed-methods study of experiences during COVID-19. Appl Nurs Res. 2021;60:151437.
Liu X, Kakade M, Fuller CJ, Fan B, Fang Y, Kong J, et al. Depression after exposure to stressful events: lessons learned from the severe acute respiratory syndrome epidemic. Compr Psychiatr. 2012;53(1):15–23.
Wu P, Fang Y, Guan Z, Fan B, Kong J, Yao Z, et al. The psychological impact of the SARS Epidemic on Hospital employees in China: exposure, risk perception, and Altruistic Acceptance of Risk. Can J Psychiatry. 2009;54(5):302–11.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors want to thank all the interviewed healthcare team participants for their time and sharing their personal stories and for their continued service during the COVID-19 pandemic. We would also like to acknowledge Ayaba Logan, the Research and Education Informationist, Mohan Madisetti, the MUSC College of Nursing Director of Research, the staff of the MUSC Center for Academic Excellence and the reviewers of this journal for their constructive criticism.
This research (software, transcription services, etc.) was solely funded by the Principal Investigator, J.A.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
College of Nursing, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, SC, USA
John W. Ambrose, Lynne S. Nemeth, Diana M. Layne & Michelle Nichols
Department of Anesthesia and Perioperative Medicine, College of Medicine, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, SC, USA
Ken Catchpole
Department of Surgery, College of Medicine, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, SC, USA
Heather L. Evans
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Conceptualization J.A., K.C., L.N., D.L., H.E., and M.N.; methodology J.A. and M.N.; J.A. led the study, recruited the interviewees, conducted interviews, led the data analysis, and drafted the manuscript. J.A., and M.N. conducted the data analyses; review and editing K.C., H.E., D.L., and M.N.; supervision M.N.; research project administration J.A. and M.N.; funding acquisition J.A. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to John W. Ambrose .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
This study presented no greater than minimal risk to participants and met exempt status per regulatory criteria established by 45 CFR 46.104 and 21 CFR 56.104. The study protocol and all materials were approved by the MUSC Institutional Review Board (IRB), [Pro00100917 ]. All study procedures were followed in accordance with these standards.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Ambrose, J.W., Catchpole, K., Evans, H.L. et al. Healthcare team resilience during COVID-19: a qualitative study. BMC Health Serv Res 24 , 459 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-10895-3
Download citation
Received : 25 February 2023
Accepted : 25 March 2024
Published : 12 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-10895-3
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Resilience Engineering
- Healthcare System
- Healthcare Administration
- Healthcare Team
- Thematic Analysis
- Qualitative Research
BMC Health Services Research
ISSN: 1472-6963
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Volume 18 Supplement 1
Integration of Refugees into National Health Systems: Enhancing Equity and Strengthening Sustainable Health Services for All
- Open access
- Published: 15 April 2024
How integration of refugees into national health systems became a global priority: a qualitative policy analysis
- Shatha Elnakib ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2316-4211 1 na1 ,
- Caitlin Jackson 1 na1 ,
- Ummekulsoom Lalani 1 ,
- Yusra Ribhi Shawar 1 , 2 &
- Sara Bennett 1
Conflict and Health volume 18 , Article number: 31 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
Despite a long history of political discourse around refugee integration, it wasn’t until 2016 that this issue emerged as a global political priority. Limited research has examined the evolution of policies of global actors around health service provision to refugees and how refugee integration into health systems came onto the global agenda. This study seeks to fill this gap.
Drawing on a document review of 20 peer-reviewed articles, 46 global policies and reports, and 18 semi-structured interviews with actors representing various bilateral, multilateral and non-governmental organizations involved with refugee health policy and funding, we analyze factors that have shaped the global policy priority of integration. We use the Shiffman and Smith Policy Framework on determinants of political priority to organize our findings.
Several important factors generated global priority for refugee integration into national health systems. Employing the above-mentioned framework, actor power increased due to network expansion through collaborations between humanitarian and development actors. Ideas took hold through the framing of integration as a human rights and responsibility sharing. While political context was influenced through several global movements, it was ultimately the influx of Syrian refugees into Europe and the increasing securitization of the refugee crisis that led to key policies, and critically, global funding to support integration within refugee hosting nations. Finally, issue characteristics, namely the magnitude of the global refugee crisis, its protractedness and the increasing urbanicity of refugee inflows, led integration to emerge as a manageable solution.
The past decade has seen a substantial reframing of refugee integration, along with increased financing sources and increased collaboration, explains this shift towards their integration into health systems. However, despite the emergence of integration as a global political priority, the extent to which efforts around integration have translated into action at the national level remains uncertain.
Introduction
The acceleration of forced displacement has emerged as one of the greatest challenges of the twenty first century. By mid-year 2022, over 100 million people were forcibly displaced, an unprecedented number since the second world war [ 1 ]. Historically, refugees resided in camps operated by UNHCR with the aspiration that one of three durable solutions – repatriation, integration into host country, or third country resettlement – would eventually become possible. The question of how to organize health service delivery to refugees in the interim was extensively debated. UNHCR’s longstanding approach to health delivery was a ‘care and maintenance’ approach, where care for refugees was provided through dedicated clinics run primarily by international non-governmental organizations (INGOs) [ 2 ]. These services, provided through hospitals and clinics, were mostly set up inside camps, often at a higher standard of care than pre-existing health systems in the host country [ 3 ]. This approach, however, had many shortcomings. It bred long-term dependence, ignored many refugees who resided outside of camp settings, and became increasingly unsustainable as contemporary crises became more protracted.
In 2016 and 2017, there was a paradigm shift away from ‘care and maintenance’ toward integration and inclusion of refugees into host country national health systems. Foreshadowing this shift, in 2016, the founder of the World Bank’s Global Program on Forced Displacement noted: “Work on forced displacement is at a crucial moment, a tipping point. It is the right time to consolidate the paradigm shift towards full global recognition that the challenge of forced displacement is an integral part of the development agenda” [ 4 ]. In the wake of the Mediterranean refugee crisis, the 2016 World Humanitarian Summit facilitated conversations around drastic reform in humanitarian response called the Grand Bargain [ 5 ]. At the summit, the World Bank committed to stepping up financing of refugees and host governments [ 6 ]. The conference also set the stage for the 2016 New York Declaration for Refugees and Migrants, which was unanimously adopted by the United Nations General Assembly [ 7 ]. The explicit position of the New York Declaration was to address the health needs of refugees by integrating them into the national health care and social protection systems of the countries that host them. At the same time, the policy calls on the international community to support host countries in this process to share the responsibility of addressing the unprecedented level of human mobility [ 7 ]. Described by UN High Commissioner for Refugees Filippo Grandi as a “political commitment of unprecedented force and resonance,” the Declaration “fills what has been a perennial gap in the international protection system – that of truly sharing responsibility for refugees” [ 8 ].
The New York Declaration for Refugees and Migrants [ 7 ] laid the foundation for the UNHCR led Comprehensive Refugee Response Framework (CRRF) [ 9 ] and Global Compact on Refugees (GCR) [ 10 ]. These global policies advocated for integration of refugees into national host systems, including national health systems. The 2018 affirmation of the GCR by States clearly demonstrated sustained support for and prioritization of refugee integration into health systems (along with broader inclusion into national systems).
However, the call to support refugees by integrating them into host country systems is not new. In fact, efforts and calls for the adoption of a developmental approach to forced displacement can be traced back as early as the 1960s, and in the late 1990s and early 2000s, several policies and programs were developed with a focus on promoting self-reliance, including the 1999 Self Reliance Strategy [ 11 ] introduced by UNHCR in Uganda which was one of the first in-country experiences with integration. These policies however did not translate into global policy and the ‘maintenance and care’ approach prevailed. Despite a long history of political discourse and experimentation, it wasn’t until 2016 that integration finally got on the global agenda [ 1 , 2 ]. Drawing on the Shiffman and Smith framework on determinants of political priority for global initiatives [ 12 ], we aimed to examine factors that explain the recent emergence and growth of policy attention for the integration of refugees into health systems.
Policy framework
We used Shiffman and Smith’s policy framework (Table 1 ) to analyze the factors that contributed to how refugee integration into health systems became a global political priority. The framework includes 11 factors determining political prioritization that are grouped into 4 themes: (1) actor power, (2) ideas, (3) political contexts, and (4) issue characteristics. Shiffman and Smith define global priority as “the degree to which international and national political leaders actively give attention to an issue, and back up that attention with the provision of financial, technical and human resources that are commensurate with the severity of the issue” [ 12 ]. While other frameworks for explaining political priority exist [ 13 ], the Shiffman and Smith framework is focused at global, rather than national, agenda-setting. The framework has been widely applied in global public health [ 14 , 15 , 16 ] and the factors identified in this framework closely reflected the themes that emerged from our data.
Study design
We conducted a case study of how political priority was achieved for global policies on integrating refugees into health systems. Our analysis was based on interviews with 18 key informants (Table 2 ) and a systematic search for relevant literature and documents, of which 66 documents were included in the analysis. We thematically analyzed the literature and interviews through triangulation of data.
Document review
We collected data from several data sources, including 20 peer-reviewed and 46 grey literature documents. The search included retrieving peer-reviewed articles through a comprehensive search of the following databases: Google Scholar, PubMed, and Embase. The following search terms were used: “inclusion”, “integration”, “integrated delivery of health care”, “integrated health care system*”, “integrated delivery systems” with a focus on refugees and displaced persons. The search was restricted to articles in English and those published before September 2022. The two first authors conducted title, abstract and full-text screening on the retrieved articles.
This was complemented by a grey literature search with archival research in which we collated and reviewed organizational reports, conference documents and meeting minutes and briefs, policy statements, media reports, press releases and public statements, legislations including laws, decrees, and conventions. The grey literature was collated by searching 25 organizational sites that work with refugee populations. Seminal legislation and global policies that focused on refugees and refugee service delivery, and organizational policies and decisions that described health system responses to refugee crises were included in this review. Literature that exclusively focused on migrants and did not specifically reference refugee populations was excluded. Additionally, grey literature identified through the qualitative interviews was also reviewed against the inclusion and exclusion criteria above.
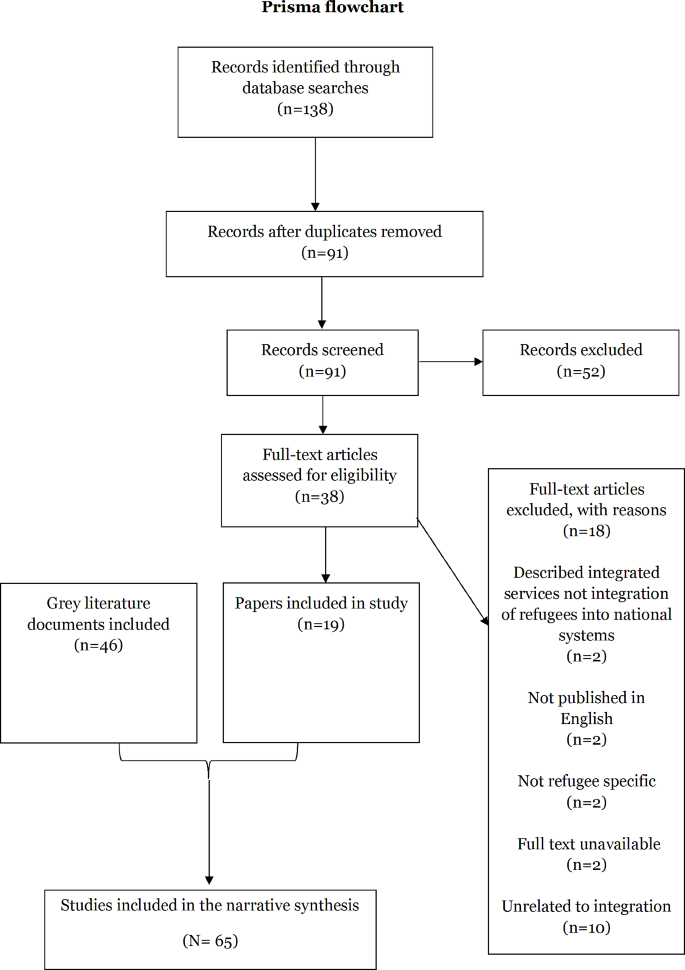
Flow diagram for peer-reviewed literature review (until September 2022)
Of the 138 peer reviewed documents identified and deduplicated, 91 were screened by title and abstract (Fig. 1 ). 52 documents were excluded. The 38 remaining articles underwent full text review and 18 were ineligible for inclusion. Ultimately, 19 peer reviewed publications were included in the study. 64 grey literature documents were identified and underwent full text review. 18 were excluded. A total of 46 grey literature documents were included in the study.
The grey and peer reviewed literature were primarily published between 2016 and 2022. Most grey literature was published by UN agencies ( n = 21), followed by the World Bank ( n = 7). The grey literature primarily comprised annual reports and policy briefs. The focus of most peer reviewed literature was on LMICs ( n = 12), followed by European countries ( n = 7). The studies were primarily qualitative, literature reviews, or normative papers focused on policy review and analysis.
Documents that were eligible for inclusion were reviewed by the first and second author, and data was extracted by the second author using a charting form sheet developed by both authors. Data entry was done in Excel and the extraction included author name, study title, year and type of publication, geographic focus, as well as information about the following themes: meaning of integration, historical evolution of discourse around integration, rationale and enablers of integration, barriers to integration, successful and unsuccessful examples, funding, and collaboration.
Key informant interviews
We conducted 18 interviews with 24 individuals centrally involved in refugee health policy and funding at the global level. While the majority of interviews were with one individual, four interviews were with 2–3 individuals who worked in the same organization. The initial group was purposively selected and was expanded upon through snowball sampling in which we asked participants to identify additional participants who can provide insight into the research question. Key informants were also identified through the research team’s knowledge of the field. We contacted 42 potential key informants and conducted 18 interviews (43% response rate). Initial interviews were conducted between September and October 2020, and after carefully reviewing these, a second round of interviews was conducted between November and December 2022 with additional respondents to try to fill in particular gaps in perspective. Table 2 lists the informants’ institutional affiliations. We stopped conducting more interviews when we reached the point of theoretical saturation [ 17 ].
Informants were contacted through a standardized email and asked to participate in a phone or online interview via Microsoft Teams (Microsoft Corporation; Redmond, WA, USA) or Zoom (Zoom Video Communications; San Jose, CA, USA). Interviews were semi-structured (See Supplementary File 1 for the interview guide). They were conducted in English and lasted for approximately an hour and were recorded, and transcribed verbatim. The first, second and third authors conducted the interviews.
Qualitative analysis
We conducted thematic analysis of the interview data and narrative synthesis of the retrieved literature. We initially used a codebook that included deductive codes based on the research questions, but then allowed new codes to emerge inductively. The first and second authors coded the data on Dedoose 9.0.62, a data management software [ 18 ]. The first author developed detailed memos and held regular debriefs with the second author to ensure consistency of coding and reflect on emerging findings.
Ethical approval
The Johns Hopkins University Institutional Review Board in Baltimore, MD, USA reviewed the protocol and determined that it did not qualify as human subjects research, thereby granting it an exemption.
Global evolution of refugee health integration policy
We summarized our findings by creating a timeline of the evolution of global policies and key events around health service delivery to refugee populations. (Fig. 2 : Abridged Timeline of Key Events Surrounding Integration; See Supplementary File 2 for the full version).
Abridged Timeline of events leading to the adoption of policies that encourage integration of refugees into health systems
At the end of WWII, displacement challenges received global attention. At this time, parallel health systems were established to temporarily support refugees while awaiting repatriation. The first key global policy of significance was the 1951 UN Convention Relating to the Status of Refugees [ 19 ]. Refugees were the responsibility of host governments. When needed and invited by hosting governments, humanitarian actors stepped in to provide aid. UNHCR oversaw refugee health with the support of implementing humanitarian organizations that provided services for refugees. There was a clear demarcation between the work of humanitarians in supporting refugees and the work of development actors, who were frequently active in refugee hosting countries. As early as 1967, Prince Sadruddin Aga Khan, then High Commissioner for Refugees, discussed the need to address refugees through a development approach, where host communities are supported as well. In an address to the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA), the High Commissioner went so far as to say that the response to the refugee situation in Africa could not be effective unless multilateral development aid was coordinated with the humanitarian refugee response. He argued that development assistance to strengthen refugee hosting regions would optimize resource use and avoid waste [ 20 ]. Another attempt to shift the paradigm toward integration took place at the 1981 International Conference on Assistance to Refugees in Africa also hosted by UNGA. Leaders called for coordinated action aimed at harmonizing humanitarian assistance with development actors to reduce the burden of refugees on national development [ 21 ]. Again, calls for integration failed to galvanize collective action.
Several major events of displacement at the end of the 20th century directed the spotlight towards the issue of refugee assistance and how best to organize services in the wake of mass population movement. By the end of 1979, 400,000 Afghans had fled to Pakistan [ 22 ]. The Berlin Wall fell in 1989, bringing the issue into public view as East German refugees freely crossed the border [ 23 ]. In the late 80s over 25,000 Sudanese youth fled to Ethiopia and Kenya [ 18 , 24 ]. There was also mass influx of refugees from the Yugoslav wars in the early 1990s [ 23 ]. Repatriation, the preferred durable solution of the era, became increasingly unfeasible due to the volume and protractedness of these displacement events.
Against a backdrop of mass displacement events and increasing funding shortfalls, new policies and programs began to develop in the late 90s and early 2000s with a focus on self-reliance for refugees. Of note is the 1999 Self Reliance Strategy introduced by UNHCR and the government of Uganda [ 25 ]. In 2001, UNHCR hosted a panel discussion on protracted refugee situations in Africa to develop better solutions for meeting the needs of refugees [ 25 ]. It was becoming clear that the traditional durable solutions for refugees, such as voluntary repatriation or third country resettlement, were not viable, and a published discussion paper suggested examining local integration [ 26 ]. It further suggested pursuing refugee self-reliance to support the needs of refugees in exile [ 26 , 19 ]. However, the move towards integration did not take off, and the Self Reliance Strategy, which was one of the first experiments with integration, failed in part due to the complexities of the host government political environment, hesitation of host governments to call attention to refugees residing outside of camps, and the lack of guidance on how to implement integration [ 25 ]. In 2005 UNHCR published the Handbook for Self-Reliance [ 27 ], further reinforcing UNHCR’s shift in focus to self-reliance by providing an operational tool for field-based staff to implement self-reliance strategies. The handbook defined self-reliance in the context of programming as “developing and strengthening livelihoods of persons of concern and reducing their vulnerability and long-term reliance on humanitarian/external assistance” [ 27 ]. UNHCR also promoted Development Assistance for Refugees (2005), which recognized the growing concerns around finding durable solutions for refugees and proposed new concepts and programs from a development approach [ 28 ].
In 2009, the UNHCR Policy on Refugee Protection and Solutions in Urban areas was adopted, bringing broader recognition to the shift in refugee concentration from camps to urban settings [ 29 ]. UNHCR also began tracking accommodation type in 2010 to substantiante the reality that refugees reside among host populations [ 30 ]. Additionally, UNHCR began to explore funding mechanisms to further operationalize integration. In an attempt to support integration of Afghan refugees into the Iranian healthsystem, UNHCR released a guidance note in 2012 to propose possible health insurance schemes to allow refugees access to essential PHC and emergency services [31]. During this period, the concept of collaboration between development and humanitarian actors to strengthen host communities was underscored in the 2014 Regional Refugee and Resilience Plan [ 32 ], which brought together 270 UN agencies, INGOS, and NGOs and was jointly implemented by UNHCR and UNDP. The Solutions Alliance was launched in 2014, bringing together a group of donor and host governments, UN agencies, multilateral financial institutions, civil society organizations, international NGOs, private sector, and academic organizations dedicated to finding innovative solutions for protracted displacement [ 33 ]. In 2015, the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) were adopted by UNGA, calling for universal health coverage for all individuals [ 34 ]. While the original iteration of the SDGs did not include any reference to refugees, reflecting the normative exclusion of refugees from discourse on sustainable development, advocacy on the part of humanitarian agencies spearheaded by UNHCR resulted in the inclusion of an indicator on refugees [ 35 ].
It was in this global environment, in 2015, that Europe experienced a significant increase in migration, known globally as the Mediterranean refugee crisis and linked to the influx of Syrian refugees, but also refugees from other countries such as Afghanistan, Eritrea, Iraq, Nigeria and Pakistan. This event served as a catalyst to change policy and mobilize stakeholders to forge new solutions for refugees. The World Bank, UN, and Islamic Development Bank met in October 2015 to discuss financing of the crisis, which in 2016 formally became the Global Concessional Financing Facility (GCFF), a financing mechanism to support countries hosting large numbers of refugees [ 36 ].
The pivotal 2016 Grand Bargain at the World Humanitarian Summit occurred in the wake of the Mediterranean refugee crisis and resulted in 65 signatories consisting of large donors and humanitarian organizations committing to improving effectiveness and efficiency in humanitarian action [ 5 ]. Of particular significance, the Summit resulted in the World Bank’s commitment to finance refugees and host governments [ 6 ] and led to the adoption of the 2016 New York Declaration for Refugees and Migrants [ 7 ]. The Humanitarian-Development Nexus and “New Way of Working” were also established in 2016, setting the stage for increased collaboration between humanitarians and development actors, particularly on refugee issues [ 37 ].
The 2016 commitments at the World Humanitarian Summit and in the New York Declaration for Refugees and Migrants produced tangible results. The CRRF [ 9 ] was a process used to develop the eventual GCR [ 10 ] that emphasized shared responsibility to support refugees and hosts. Underpinning this concept was the idea of integration. In discussing the CRRF, UNHCR notes that “allowing refugees to benefit from national services and integrating them into national development plans is essential for both refugees and the communities hosting them, and is consistent with the pledge to ‘leave no one behind’ in the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development” [ 9 ]. The World Bank’s commitments materialized with the establishment of the IDA18 Regional Sub-Window for Refugees and Host Communities, which provided an unprecedented $2 billion of dedicated funding to support low income countries that host refugees [ 38 ]. Furthermore, tworeports brought attention to integration. Yes In My Backyard? The Economics of Refugees and Their Social Dynamics in Kakuma, Kenya (2016) was jointly published by UNHCR and World Bank [ 39 ]. Forcibly Displaced: Toward a Development Approach Supporting Refugees, the Internally Displaced, and their Hosts (2017) was published by World Bank with a forward by UNHCR [ 40 ].
Finally, after 2 years of consultation and development, the Global Compact on Refugees was affirmed in 2018. The compact has four main objectives, namely to: (1) ease pressures on host countries; (2) enhance refugee self-reliance; (3) expand access to third country solutions; (4) support conditions in countries of origin for return in safety and dignity. The Compact specifically addresses health integration in Sect. 2.3 Health [ 10 ]. The 2018 affirmation of the GCR by States clearly demonstrated the support for and prioritization of refugee integration into health systems.
It was in this ideal environment for health integration that the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic tested even the most advanced health systems. While the pandemic could have soured political sentiment toward health integration, it lent support to the policy and provided clear opportunities for international support of national health systems to benefit both nationals and refugees. Many countries provided COVID-19 vaccines to refugees as part of their pandemic response, a clear shift from previous epidemic responses [ 41 , 42 ].
As illustrated by the timeline, a long history of political discourse around integration predated the 2016 events that saw the issue emerge as a political priority and prevailing paradigm. Why and how the issue acquired global priority status is investigated in the next section using the Shiffman and Smith policy framework.
Actor power: Network expansion and entrance of the World Bank onto the humanitarian scene
Network expansion through increased collaborations between humanitarian and development actors, as well as the critical engagement of World Bank, played a significant role in shifting the discourse on refugee integration into national health systems. As the custodian of the international refugee response regime, UNHCR has historically been at the helm of conversations around integration and while bridging the humanitarian development nexus was the subject of debates for decades, convergence between the humanitarian and development agendas and collaboration between actors had not materialized. Key informants credited the entrance of the World Bank onto the humanitarian scene in 2016 as a pivotal moment that translated rhetoric on a development approach to forced displacement and promoted social, economic and health integration into action. With the World Bank scaling up its involvement with refugees, including health integration, other international financial institutions (IFIs) such as the Islamic and Asian Development Bank followed suit. As one informant noted:
The big game changer is the appearance of the World Bank on the scene where, at some point, the World Bank decided that they will do what they call risky investments and healthcare services, where it’s by no means sure that it will be a success . Key Informant Interview, UN Agency .
Collaboration between the World Bank and UNCHR was evidenced by the multiple joint missions that the two actors undertook. In 2017, in preparation for the World Bank International Development Assistance (IDA) 2018–2020 refugee and host community replenishment sub-window, the World Bank and UNHCR undertook 11 joint missions. The sub-window underpins a development approach to forced displacement and promotes the integration of refugees into national host systems. It presented a paradigm shift in that it offered a large amount of concessional loans which have zero or very negligible interest rates and long repayment periods stretching over 30 to 40 years UNHCR was additionally invited to serve as an observer to the Steering Committee Meetings of the Global Concessional Financing Facility (GCFF), a newly established fund housed at the Bank that supported countries responding to refugee crises.
Speaking about the evolution of the World Bank’s role in humanitarian response in 2016 and the expansion in the network of advocates working to move this agenda forward, Niels Harild, the founder of the World Bank’s Global Program on Forced Displacement stated:
“ No one actor can do this alone. The World Bank Group needs a strong partnership approach on this agenda, working closely with bilaterals, the UN - particularly UNHCR, NGOs, research institutions, the private sector and most importantly affected Governments ” [ 4 ]. Niels Harild, World Bank Group .
Because integration in health systems was situated in broader discourse around integration of refugees into social services more generally, the network of actors that came together was not exclusive to the health sector. A diverse network of advocates from education, health and labor coalesced to advance the integration agenda. The Solutions Alliance illustrated the diversity of actors involved in this effort. The Alliance brought together actors across different sectors and specialties, drawing on the expertise of academics, civil society organizations, UN agencies, international NGOs, multilateral agencies, and host and donor governments. The Alliance closed on June 17, 2017 after it was decided that “refugee self-reliance and resilience among affected communities has now gained broad political legitimacy” [ 43 ].
Ideas: framing of integration in terms of human rights and responsibility sharing
Integration advocates were able to strategically tailor the language surrounding integration to resonate with specific audiences and linked it to the broader discourse surrounding ‘responsibility sharing’ and human rights. Despite heterogeneity in terms used by global refugee policy actors to describe the process of mainstreaming refugees into host health systems, there was consensus in understandings of the concept of integration and agreement that the preferred service delivery modality in humanitarian settings has shifted from vertical programs to integrated services delivered through existing host country health systems. There were calculated and deliberate reasons for why respondents chose different terms to describe the same phenomenon. As noted by one respondent, “ we have to be careful with that term (integration). So that’s why we will be saying integrating into service delivery ” (Key Informant Interview, UN Agency).
For many national policymakers, the term “integration’ was not associated with integration into health systems, but rather on policies focused on legal status. The term was often associated with naturalization or policy that allows refugees to become full and permanent members of society. Meanwhile, “inclusion” was typically used by policymakers to describe the inclusion of refugees in existing policies and systems. As an example, policymakers were familiar with policies advocating to include refugees in the national education system or policies to include refugees under existing national protection laws. As such, many respondents suggested national governments resisted the integration agenda because of concerns it would lead to the permanent naturalization of refugees. In place of integration, respondents used terms such as inclusion, self-reliance, and interim integration to describe the same policy concept and assuage concerns around the “permanent” presence of refugees.
Clear themes emerged in how actors framed integration to generate political priority for the issue and overcome pushback by governments. Our key informants noted that local decision-makers had strong fears that integration was a way to shift the buden of hosting onto local governments and would result in conditions that welcome refugees’ prolonged presence in their countries. Integration was deliberately and strategically framed by UNHCR in terms of ‘responsibility sharing,’ with the role of the global community in jointly addressing problems associated with displacement underscored in the discourse around integration. While usually used by the international refugee regime to discuss durable solutions for refugees, ‘responsibility sharing’ was successfully linked by actors to health integration policy, most notably expressed in the Global Compact on Refugees [ 10 ]. One informant noted:
We’ve pitched it in a more sort of hopeful manner of international responsibility sharing. And that’s been the discourse…. Used to be called burden sharing. Now it’s responsibility sharing. And so we pitched it in that sense. Key Informant Interview, UN Agency .
Moreover, the framing of integration as more than a public health issue, and instead as a human right and the invocation of rights-based language helped advance the agenda. Actors were able to align and scaffold integration within existing international norms and global calls for action that positioned refugee access to healthcare as a human right. The literature credits the 1951 Refugee Convention [ 19 ] and 1967 Protocol relating to the Status of Refugees [ 44 ] as setting the foundation for refugees’ right to health, education, and workforce participation at the same level as residents (PR01, GL32). While dating back to the 1950s, this language was revitalized by proponents of integration. In addition to bolstering their case that integration was a human right, international treaties and conventions gave actors a mechanism for holding countries accountable as signatories of the Refugee Convention.
Political context: the role of the Mediterranean refugee crisis and other concurrent global movements
Proponents of integration successfully connected integration with other global movements and leveraged an open policy window—the Mediterranean refugee crisis — to move integration policy forward. With momentum generated by the 2015 SDGs for universal health coverage, advocates pitched integration as an opportunity to upgrade national health systems and move towards universal healthcare coverage for all, including refugees and asylum seekers. At the same time, proponents were able to anchor integration policy in the broader movement within the UN system to bridge the humanitarian development nexus as the future of sustainable aid. The foundation of the 2006 Delivering as One [ 45 ] movement followed by the 2016 New Way of Working and Humanitarian Development Nexus [ 37 ] served as platform. As noted by an informant,
Interesting might be to add on, is not directly the policy frame, but I think the whole debate and discourse on the humanitarian development nexus discussion and the rationale behind that is for sure a big driver, a big push for the topic of inclusion. Key Informant Interview, European Bilateral .
Since the integration paradigm largely rested on collaboration between humanitarian and development sectors, this emerging collaborative governance structure was pivotal in creating the political context for integration and in bringing actors together for collective action.
While synergies with global movements like universal health coverage and Humanitarian Development Nexus helped advance the integration agenda, it was ultimately the Mediterranean refugee crisis and specifically inflows of Syrian refugees into Europe that galvanized action on integration. The geopolitical significance of the Syria crisis and ensuing securitization of asylum in Europe – namely the imposition of restrictions on refugee movement into European Union countries – were portrayed as opening a policy window for integration. One respondent specifically noted the role of the Syrian refugee influx in bringing the World Bank on as a key actor in refugee integration policy.
And here I’m thinking particularly of the World Bank. And we’ve talked for many, many years about the World Bank getting involved in the refugee situation so history goes back to the early 1980s. It never really happened until maybe the last four or five years it’s began to happen on a significantly greater scale. And again that’s been largely prompted by the Syrian refugee emergency . Key Informant Interview, Academia .
Many documents and policies adopted shortly after the Mediterranean refugee crisis (such as the New York Declaration (2016), the Comprehensive Refugee Response Framework (2017) and the Global Compact on Refugees (2018)) have been key in promoting integration of refugees into health systems.
Policies were ultimately strengthened by the emergence of corresponding funding instruments that helped integration become a political reality. The 2016 Global Concessional Financing Facility, established one year after the influx of refugees in Europe, established development support for countries impacted by refugees and was the precursor to the IDA Regional Sub-window for Refugees and Host Communities. Respondents described these funding mechanisms as crucial to the translation of integration policy into action.
In summary, proponents of integration successfully capitalized on global policy windows to elevate priority for integration, including the movement for universal health coverage, and the movement to bridge the humanitarian development nexus. The key catalyst however was presented as the Mediterranean refugee crisis which raised the profile of the issue, and prompted integration polices to emerge with the corresponding funding instruments needed to make integration a reality.
Issue characteristics: leveraging data and indicators to make the case for integrtaion
Several aspects of the issue generated the momentum needed for this ideological shift in thinking around refugee response. This included the unprecedented scale of mass displacement occurring in the last two decades, the protracted nature of contemporary refugee crises, and the increasingly urbanized nature of refugee concentrations. UNHCR produced data and projections on the scale of displacement, which revealed that the world was witnessing the highest rates of population movement since the Second World War [ 46 ]. Analysis done by the World Bank empirically showed that the average duration in displacement was increasing, hovering around 10 years [ 47 ]. The increasing urbanization of refugees highlighted the limits of parallel service delivery and ‘care and maintenance’ approaches that failed to meet the needs of people residing outside of the confines of refugee camps. These realities occurred against a backdrop of budgetary shortfalls and constraints. The scale of displacement was simply outstripping available funding.
Key informants credited the emergence of empirical data and economic analysis of the impact of protracted refugee crises in part to the involvement of the World Bank. Analyses published in seminal reports prepared jointly by the World Bank and UNHCR, such as the “Forcibly Displaced: Toward a Development Approach” and “In My Backyard? The Economics of Refugees and Their Social Dynamics in Kakuma, Kenya” are two prime examples. The latter made the case that refugees can have positive social and economic impacts on host countries and that integration makes economic sense; while the former, “encouraged new thinking from a socioeconomic perspective” [ 40 ]. Establishing the socioeconomic benefits of integration as a policy solution was instrumental in advancing it as the newly favored policy solution.
Our analysis reveals that while calls for integration existed as far back as 1967, the issue only rose to prominence on the global agenda, and resulted in actual policy change, in the last decade or so. We identified several factors that facilitated the political prioritization of integration. First, the existence of a technically diverse network of humanitarian actors spanning different sectors and the ascendance of the World Bank and other development actors in the network of proponents was key. A favorable political and normative environment opened a policy window that advocates strategically leveraged. In particular, the Mediterranean refugee crisis and its securitization heightened concerns around a refugee exodus into Europe and galvanized action, resulting in the emergence of new funding instruments with unprecedented financing power. The greater movement on universal health coverage instilled a sense of urgency which proponents used to advocate for the inclusion of refugees into national health systems. Moreover, framing of integration in terms of responsibility-sharing and positioning health integration as a human right helped extend the issue beyond a health frame and facilitated the mobilization of multi-donor funds. Finally, inherent characteristics of contemporary displacement, including the severity of the refugee crisis, its increasing protractedness and urbanization, and the failings of the current paradigm made integration an appealing policy solution.
Our study highlights a number of factors which may explain why national level implementation of policies integrating refugees into health systems is not as robust as one might anticipate. For example, the Solutions Alliance which brought together diverse actors and provided an ongoing forum for discussion between global agencies, country governments and NGOs perhaps closed its doors prematurely. Ongoing interaction between these stakeholders may have helped to iron out remaining challenges in implementation. The Shiffman and Smith framework also points to the importance of a shared, coherent framing of the problem and its solutions. Our findings suggest that while there is a high degree of consensus among advocates over the key policy elements of integrating refugees into health systems, the language adopted differs (e.g. integration versus inclusion versus self-reliance). It is possible that this has facilitated uptake of the policy given sensitivities in different contexts, but as other papers in this supplement have documented, there do appear to be contested elements. For example, in contexts where access to health systems is inequitable for host populations, does integration mean aligning refugees with host populations with the most privileged access, or the least access? While global policies and mechanisms are now in place to support integration of refugees into health systems, it appears that not all national governments are supportive, and further advocacy may be needed in specific contexts. Host governments still express concern that integration will exacerbate unemployment and lead to upticks in crime, despite attempts from integration advocates to present evidence against such arguments [ 39 , 40 ]. In addition, there are practical implementation challenges especially in decentralized contexts such as Uganda, where district planning and budgeting processes need to accommodate the integration of refugee populations.
Another important consideration in national level policy implementation relates to broader concerns surrounding the top-down approach to aid and international development [ 48 ]. While the integration agenda has some roots at the national level, such as the self-reliance movement in Uganda, most discourse has originated from International Organizations and high-income countries. The extent to which the top-down approach to integration might limit its implementation is yet to be fully realized but might underpin the reluctance of some national governments to adopt an integration agenda.
Perhaps one of the most significant challenges however to the full implementation of refugee integration policies is sustaining political support. It is clear that the Mediterranean refugee crisis played a major role in opening a policy window: European governments were concerned about the political cost of managing refugees who reached their own borders, and consequently were eager to support policy change in the global system and global trust funds that enhanced the prospects of refugees staying in countries of first asylum. This raises questions about the extent to which financial and technical support from the international community will materialize when crises are further from home (such as with the Rohingya refugees in Bangladesh). Further, given the protracted nature of refugee crises, host country governments are naturally concerned about the extent to which the international community will continue to support refugee integration over the longer term.
Our study should be considered in light of limitations. For one, our research question covers an extended period of time, and it may have been difficult for respondents to recall accurately events that took place more than five years ago, however a thorough document review allowed us to triangulate respondents’ recollections against documented events. Data for this study were collected in two rounds, having the benefit of allowing a more targeted second round of data collection. Finally, our study focused on chronicling events leading to the prioritization of integration as a global policy but because high level global policies seldom provide operational guidance on implementation, we were unable to speak authoritatively to implementation challenges and best practices related to integration at the national level.
Conclusions
The Shiffman and Smith framework for political priority was an appropriate tool to analyze different factors contributing to the development of global policies and mechanisms to support the integration of refugees into health systems. Overall, at the global level, stakeholder attitudes toward integration remain positive, but on-the-ground, and as described elsewhere in this supplement, there have been challenges in sustainably integrating refugees into health systems. Our analysis identifies some of the reasons why this might be the case. In moving forward, the value of sustained advocacy should not be underestimated; this is needed both to build commitment and buy in amongst host countries that are still hesitant about the integration agenda, but also to ensure support from high income countries that is both sustained over time, and across geographies that are further afield. Further, additional work is required to translate the global agreements into practical guidance for national governments and other local stakeholders. Finally, it is vital to review the health responses to recent refugee crises, such as Ukrainian refugees in Eastern Europe, Afghan refugees in Iran and Pakistan, and Venezuelan refugees throughout Latin America and the Caribbean, to evaluate the extent to which integration polices were leveraged at the onset of these crises and to develop best practices for establishing integrated health policies and systems in the emergency phase of new humanitarian crises. While work remains to be done, the processes described in this paper have fundamentally changed the way in which refugee crises and their implications for health services are framed, and has brought about a powerful alliance between development and humanitarian actors with far reaching implications that should benefit both host and refugee populations.
Data availability
Data is available upon reasonable request from the corresponding author.
Mid-Year UNHCR. Trends 2022 (Internet). cited May 6, 2023. https://www.unhcr.org/statistics/unhcrstats/635a578f4/mid-year-trends-2022.html#:~:text=UNHCR%27s%202022%20Mid%2DYear%20Trends,countries%20and%20countries%20of%20origin .
Aleinikoff TA. From Dependence to Self-Reliance: Changing the Paradigm in Protracted Refugee Situations. Washington DC: Migration Policy Institute; 2015 05/ https://www.migrationpolicy.org/sites/default/files/publications/TCM-Protection-Aleinikoff.pdf .
Spiegel P, Sheik M, Gotway-Crawford C, Salama P. Health programmes and policies associated with decreased mortality in displaced people in postemergency phase camps: a retrospective study. Lancet (Internet). 2002;360(9349):1927–34.
Article Google Scholar
Jackson S, The Evolution of World Bank Group’s Role in. Forced Displacement - Interview with Niels Harild, former manager of WBG’s Global Program on Forced Displacement (GPFD [Internet]. cited February 28, 2023. https://www.worldbank.org/en/news/feature/2016/01/06/the-evolution-of-world-bank-group-role-in-forced-displacement .
OCHA. The Grand Bargain [Internet]. cited May 6, 2023. https://interagencystandingcommittee.org/grand-bargain .
ICVA. The world bank and refugees: An ICVA Briefing Paper, Geneva ICVA. 2018 March https://www.icvanetwork.org/uploads/2021/08/World-Bank-and-Refugees-An-ICVA-Briefing-Paper.pdf .
New York Declaration for Refugees and Migrants, General Assembly UN. translator; 2016. https://www.un.org/en/development/desa/population/migration/generalassembly/docs/globalcompact/A_RES_71_1.pdf .
Grandi F. New York Declaration for Refugees and Migrants. UNHCR. https://www.unhcr.org/en-us/new-york-declaration-for-refugees-and-migrants.html .
UNHCR. Comprehensive Refugee Response Framework [Internet]. https://www.unhcr.org/en-us/comprehensive-refugee-response-framework-crrf.html .
UNHCR. Global Compact on Refugees. New York, United States: United Nations. 2018 https://www.unhcr.org/5c658aed4.pdf .
Strategy Paper. Self Reliance for Refugee Hosting Areas in Moyo, Arua and Adjumani districts 1999-2003 strategy paper. Uganda: Office of the Prime Minister; 1999.
Google Scholar
Shiffman J, Smith S. Generation of political priority for global health initiatives: A framework and case study of maternal mortality. The Lancet [Internet]. 2007;370(9595):1370-9. https://www-sciencedirect-com.proxy1.library.jhu.edu/science/article/pii/S0140673607615797 .
Jones B, Baumgartner F. The politics of attention: how Government prioritizes problems. Chicago: University of Chicago Press; 2005.
Tomlinson M, Lund C. Why does mental health not get the attention it deserves? an application of the shiffman and smith framework. PLoS Medicine [Internet]. 2012 Feb 1;9(2):e1001178. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22389632 .
Shawar YR, Shiffman J, Spiegel DA. Generation of political priority for global surgery: A qualitative policy analysis. Lancet Global Health [Internet]. 2015;3(8):e487-95. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26187491/ .
Heller O, Somerville C, Suggs LS, Lachat S, Piper J, Aya Pastrana N, Correia JC, Miranda JJ, Beran D. The process of prioritization of non-communicable diseases in the global health policy arena. Health Policy and Planning [Internet]. 2019 Jun 1;34(5):370–83. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31199439 .
Morse J. The significance of saturation. Qualitative Health Research [Internet]. 1995;5(2) https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/104973239500500201 .
SocioCultural Research Consultants L. Dedoose, web application for managing, analyzing, and presenting qualitative and mixed method research data. Los Angeles, CA; 2021.
UN General Assembly. Convention Relating to the Status of Refugees. United Nations, translator. ; 1951. https://www.unhcr.org/4ca34be29.pdf .
UNHCR. Prince Sadruddin Aga Khan, United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees, Statement to the Third Committee of the United Nations General Assembly at its 1519th meeting. ; 1967. https://www.unhcr.org/en-us/admin/hcspeeches/3ae68fb510/statement-prince-sadruddin-aga-khan-united-nations-high-commissioner-refugees.html .
International Conference on Assistance to Refugees in Africa. UN, General, Assembly. translator; 1981. https://www.unhcr.org/en-us/excom/bgares/3ae69ee31c/international-conference .
UNHCR, Afghanistan. The unending crisis. [Internet]. 1997 https://www.unhcr.org/en-us/publications/refugeemag/3b680fbfc/refugees-magazine-issue-108-afghanistan-unending-crisis-biggest-caseload.html( .
Hansen R. The comprehensive refugee response framework: A commentary. J Refug Stud [Internet]. 2018 cited 2/23/2023;31(2):131 – 51. https://doi.org/10.1093/jrs/fey020 .
Geltman PL, Grant-Knight W, Mehta SD, Lloyd-Travaglini C, Lustig S, Landgraf JM, Wise PH. The Lost boys of sudan: Functional and behavioral health of unaccompanied refugee minors resettled in the united states. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med [Internet]. 2005;159(6):585–91. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpedi.159.6.585 .
Rowley EA, Burnham GM, Drabe RM. Protracted refugee situations: Parallel health systems and planning for the integration of services. Journal of Refugee Studies [Internet]. 2006;19(2):158–86. https://api.istex.fr/ark:/67375/HXZ-SJFGS669-W/fulltext.pdf .
Jacobsen K. The forgotten solution: local integration for refugees in developing countries. UNHCR; 2001 07/ https://www.unhcr.org/3b7d24059.pdf .
UNHCR. Handbook for Self-Reliance. Geneva. 2005 08/ https://www.unhcr.org/44bf7b012.pdf .
UNHCR. Development Assistance for Refugees (DAR(Programmes. Geneva: UNHCR. 2005 01/ https://www.unhcr.org/44c487872.pdf .
UNHCR. UNHCR policy on refugee protection and solutions in urban areas. UNCHR. 2009 09/ https://www.unhcr.org/en-us/protection/hcdialogue%20/4ab356ab6/unhcr-policy-refugee-protection-solutions-urban-areas.html .
Refugee Data Finder [Internet]. cited May 6, 2023 https://www.unhcr.org/refugee-statistics/methodology/data-content/ .
UNHCR. A Guidance Note on Health Insurance Schemes for Refugees and other Persons of Concern to UNHCR. Geneva, Switzerland: UNHCR; 2012 March https://www.unhcr.org/media/guidance-note-health-insurance-schemes-refugees-and-other-persons-concern-unhcr .
2014 Syria Regional Response Plan Strategic Overview. United Nations. 2014. https://www.unhcr.org/52b170e49.pdf .
UNDP. The Solutions Alliance [Internet]. https://www.undp.org/geneva/solutions-alliance .
Transforming our world : the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. UN General Assembly, translator. ; 2015. https://daccess-ods.un.org/tmp/46974.8862087727.html .
Petra Nahmias (UNHCR, Natalia Krynsky Baal JIPS). Including forced displacement in the SDGs: a new refugee indicator. ; 2019. https://www.unhcr.org/blogs/including-forced-displacement-in-the-sdgs-a-new-refugee-indicator/ .
Global Concessional Financing Facility [Internet]. cited May 6, 2023. Available from: global concessional financing facility (GCFF for Jord and Leb by WB).
OCHA. The Humanitarian- Development Nexus: A New Way of Working. OCHA. 2017 https://agendaforhumanity.org/sites/default/files/20170228%20NWoW%2013%20high%20res.pdf .
World Bank. IDA18 Regional Sub-Window for Refugees and Host Communities [Internet]. https://ida.worldbank.org/en/replenishments/ida18-replenishment/ida18-regional-sub-window-for-refugees-host-communities .
Sanghi, Apurva Onder, Harun Vemuru, Varalakshmi. Yes in my backyard? The economics of refugees and their social dynamics in Kakuma, Kenya. Washington DC: 2016 /12/01 http://documents.worldbank.org/curated/en/308011482417763778/Yes-in-my-backyard-The-economics-of-refugees-and-their-social-dynamics-in-Kakuma-Kenya .
World Bank. Forcibly Displaced : Toward a Development Approach Supporting Refugees, the Internally Displaced, and Their Hosts. Washington, DC, World Bank Group. : 2017 https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/25016 License: CC BY 3.0 IGO.
Bowser DM, Agarwal-Harding P, Sombrio AG, Shepard DS, Harker Roa A. Integrating venezuelan migrants into the colombian health system during COVID-19. Health systems and reform [Internet]. 2022 Jan 1;8(1):2079448. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/ https://doi.org/10.1080/23288604.2022.2079448 .
UNHCR. UNHCR COVID-19 VACCINE ACCESS REPORT. 2021. UNHCR; 2022. https://www.unhcr.org/media/40058 .
Closure of the Solutions Alliance [Internet]. https://solutionsalliance.org/closure-solutions-alliance/ .
Protocol relating to the Status of Refugees. United Nations General Assembly, translator. ; 1966. https://www.ohchr.org/sites/default/files/protocolrefugees.pdf .
Follow-up to the outcome of the Millennium Summit. United Nations General Assembly, translator. ; 2006. https://documents-dds-ny.un.org/doc/UNDOC/GEN/N06/621/41/PDF/N0662141.pdf?OpenElement .
UNHCR. Figures at a Glance [Internet]. June 16, cited February 28, 2022. https://www.unhcr.org/figures-at-a-glance.html .
Devictor X. How many years have refugees been in exile? Washington, D.C: World Bank Group; 2016 http://hdl.handle.net/10986/25056 .
Crescenzi R, RodrÃguez-Pose A, Internet (Reconciling top-down and bottom-up development policies. Environment and Planning A (2011 Apr 1;43(4):773–80. http://econpapers.repec.org/article/pioenvira/v_3a43_3ay_3a2011_3ai_3a4_3ap_3a773-780.htm .
Download references
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank Dr. Paul Spigel for his review and thoughtful comments on a draft of this manuscript.
This study was jointly funded by the the Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office (FCDO, the Medical Research Council MRC, and Wellcome and Economic and Social Research Council ESRC).
Author information
Shatha Elnakib and Caitlin Jackson joint first authorship.
Authors and Affiliations
Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, MD, USA
Shatha Elnakib, Caitlin Jackson, Ummekulsoom Lalani, Yusra Ribhi Shawar & Sara Bennett
Paul H. Nitze School of Advanced International Studies, Washington, DC, USA
Yusra Ribhi Shawar
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
SB and UL conceived the study. UL, SB and YS contributed to study design, tool development, and interpretation of results. SE, UL, and CJ contributed to data collection. SE and CJ conducted data analysis and interpretation with inputs from SB and drafted the manuscript. All authors contributed to manuscript revision and have approved the final version.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Shatha Elnakib .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors declare they have no competing interests. The opinions expressed are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the funding agencies.
About this supplement
This article has been published as part of Conflict and Health Volume 18 Supplement 1, 2024: Integration of Refugees into National Health Systems: Enhancing Equity and Strengthening Sustainable Health Services for All. The full contents of the supplement are available online at https://conflictandhealth.biomedcentral.com/articles/supplements/volume-18-supplement-1 .
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Supplementary material 2, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Elnakib, S., Jackson, C., Lalani, U. et al. How integration of refugees into national health systems became a global priority: a qualitative policy analysis. Confl Health 18 (Suppl 1), 31 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13031-024-00587-4
Download citation
Received : 10 July 2023
Accepted : 25 March 2024
Published : 15 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13031-024-00587-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Refugee Integration
- Health systems
- Policy analysis
- Shiffman and Smith Policy Framework
Conflict and Health
ISSN: 1752-1505
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- Open access
- Published: 28 February 2023
Complex and alternate consent pathways in clinical trials: methodological and ethical challenges encountered by underserved groups and a call to action
- Amy M. Russell 1 na1 ,
- Victoria Shepherd ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-7687-0817 2 na1 ,
- Kerry Woolfall 3 ,
- Bridget Young 3 ,
- Katie Gillies 4 ,
- Anna Volkmer 5 ,
- Mark Jayes 6 ,
- Richard Huxtable 7 ,
- Alexander Perkins 8 ,
- Nurulamin M. Noor 9 ,
- Beverley Nickolls 10 &
- Julia Wade 11
Trials volume 24 , Article number: 151 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
2828 Accesses
4 Citations
38 Altmetric
Metrics details
Informed consent is considered a fundamental requirement for participation in trials, yet obtaining consent is challenging in a number of populations and settings. This may be due to participants having communication or other disabilities, their capacity to consent fluctuates or they lack capacity, or in emergency situations where their medical condition or the urgent nature of the treatment precludes seeking consent from either the participant or a representative. These challenges, and the subsequent complexity of designing and conducting trials where alternative consent pathways are required, contribute to these populations being underserved in research. Recognising and addressing these challenges is essential to support trials involving these populations and ensure that they have an equitable opportunity to participate in, and benefit from, research. Given the complex nature of these challenges, which are encountered by both adults and children, a cross-disciplinary approach is required.
A UK-wide collaboration, a sub-group of the Trial Conduct Working Group in the MRC-NIHR Trial Methodology Research Partnership, was formed to collectively address these challenges. Members are drawn from disciplines including bioethics, qualitative research, trials methodology, healthcare professions, and social sciences. This commentary draws on our collective expertise to identify key populations where particular methodological and ethical challenges around consent are encountered, articulate the specific issues arising in each population, summarise ongoing and completed research, and identify targets for future research. Key populations include people with communication or other disabilities, people whose capacity to consent fluctuates, adults who lack the capacity to consent, and adults and children in emergency and urgent care settings. Work is ongoing by the sub-group to create a database of resources, to update NIHR guidance, and to develop proposals to address identified research gaps.
Collaboration across disciplines, sectors, organisations, and countries is essential if the ethical and methodological challenges surrounding trials involving complex and alternate consent pathways are to be addressed. Explicating these challenges, sharing resources, and identifying gaps for future research is an essential first step. We hope that doing so will serve as a call to action for others seeking ways to address the current consent-based exclusion of underserved populations from trials.
Peer Review reports
Informed consent is seen as a cornerstone in the ethical conduct of clinical trials. However, in populations or settings where there are challenges to seeking or providing consent, alternative consent arrangements may be required. These challenges may arise due to communication barriers, where a participant’s capacity to provide consent fluctuates over time, where capacity is lost during a trial, or they are deemed to lack the capacity to consent at the outset. These challenges may be particularly pronounced in emergency settings where the urgent nature of the condition and the need for immediate action preclude the ability to seek prior consent for either adults or children. Populations where consent may pose a challenge have historically been excluded from trials and are recognised as being underserved by research as a result [ 1 ]. For example, one in three patients with hip fractures have a concomitant cognitive impairment, yet eight out of ten hip fracture trials exclude this population despite evidence that those with cognitive impairment are likely to experience different outcomes [ 2 ]. Even trials in conditions associated with cognitive impairment frequently exclude people with impaired capacity to consent [ 3 ]. This exclusion of relevant subgroups of patients risks presenting biased estimates of treatment effects [ 4 , 5 ] and limits the ability to provide evidence-based care for these groups.
For many of these populations, research inequity contributes to the health disparities that they already encounter [ 6 ]. For example, adults with intellectual disabilities die on average 10–15 years earlier than those without intellectual disabilities in the UK and the USA [ 7 , 8 ], yet 90% of clinical trials are designed in a way that automatically excludes them from participating [ 9 ]. The importance of widening opportunities for the participation of underserved populations in research has received recognition both in the UK and beyond, resulting in national and international initiatives to improve inclusivity and diversity in the design, conduct, and reporting of clinical trials [ 1 , 10 , 11 , 12 ]. Research funders increasingly require researchers to address issues around inclusivity and representativeness in their funding applications [ 13 ]. However, the challenges of conducting trials where consent is complex, and where consent-based exclusion denies populations the opportunity to participate in and benefit from research, have received less attention [ 14 ].
The ethical and methodological issues surrounding trials involving complex and alternative consent pathways have led to the formation of a new UK multi-institutional collaboration to collectively address some of these challenges. This collaboration forms a sub-group of the Trial Conduct Working Group in the MRC-NIHR Trial Methodology Research Partnership, consisting of members from disciplines including trials methodology, qualitative research, healthcare, bioethics, and social sciences. This paper summarises and discusses contexts where researchers may encounter particular methodological and ethical challenges around consent. The focus is on trials where the process of consent is challenging and alternative consent pathways are required, rather than where the informational content required for consent to be valid is complex [ 15 ], or where the trial design is complex such as a multistage randomised controlled trial [ 16 ].
Drawing on our experiences as an interdisciplinary group of researchers with an interest in complex and alternate consent pathways in trials, we will focus on key populations where consent-based challenges contribute to their exclusion: adults with communication or other disabilities [ 17 ], adults who lack the capacity to consent [ 18 ], adults whose capacity to consent fluctuates or is lost during a trial [ 19 ], and adults and children requiring emergency and urgent care [ 20 ]. The question of alternative consent pathways for children in non-emergency research will not be addressed in this article as it requires specific attention [ 21 ]. For each population, we articulate the challenges around inclusion in trials, summarise current evidence and ongoing work, and identify areas for future research. We hope that this will serve as a cri de cœur for others seeking ways to address the consent-based exclusion of underserved populations from trials.
Trials involving adults with communication, hearing, and sight disabilities
Despite the fact that the majority of legislation delineating consent processes urges professionals to make adjustments for people with communication, hearing, and visual impairments, they may be excluded from research simply due to the fact that obtaining informed consent is more challenging [ 22 ]. Communication disabilities can comprise a range of difficulties that impact a person’s ability to understand spoken or written information (sounds, words, or sentences) and express themselves verbally or non-verbally (articulate sounds/letters, select words, or use relevant grammar and sentence forms) in spoken, written, or picture form. Difficulties in accessing and comprehension of information are one of the most common barriers in consent scenarios across several diagnoses including dementia [ 23 ], stroke [ 24 ], and brain injury [ 25 ], as well as developmental disorders such as autism and learning/intellectual disabilities [ 26 ]. Other difficulties that can impede a person’s ability to access spoken or written information include hearing or visual impairments, which may or may not be associated with an underlying condition. The use of British Sign Language interpreters or translation of written materials to other languages including Braille is extremely important for those with hearing or visual impairment [ 27 ]. Beyond this, the heterogeneity amongst people with communication disabilities requires adaptations to be tailored to individual needs based on knowledge of the person’s communication strengths and difficulties. People with stroke-related language impairments (aphasia), for example, may benefit from the information being presented using active language, shorter sentences, or written keywords [ 28 ].
The challenges
Making changes to support communication needs is complex. Some researchers find current guidance such as the Mental Capacity Act Code of Practice [ 27 ] and Health Research Authority guidance [ 29 ] difficult to interpret and implement [ 30 , 31 ]. Researchers acknowledge a lack of skills, knowledge, and confidence in being able to adapt their language and communication to meet the needs of people with communication disabilities [ 31 ]. Other barriers identified include the lack of specific training, tools, time and access to ethically approved materials [ 31 , 32 , 33 ].
There is limited evidence relating to the inclusion of people with communication disabilities in the informed consent process. This is in part because people with communication disabilities often have been excluded from study recruitment processes [ 17 , 30 , 31 , 33 , 34 , 35 ], and because studies that have included them have tended not to report the recruitment and consent methods used [ 32 ].
Current research and guidance
People with communication disabilities may not be included in the informed consent process for different reasons: this group is frequently defined as ineligible for inclusion in studies per se, solely due to their communication disabilities [ 31 ]; even where included, researchers may consult proxies (e.g. family members) because they assume that people with communication disabilities lack the mental capacity to provide informed consent [ 17 , 31 , 33 ]; researchers may find the consent process for this group too challenging and time-consuming [ 31 ]. Reluctance to include people with communication disabilities in the consent process may follow challenges involving people with significant communication disabilities in patient and public involvement and engagement activity, and current involvement guidance does not provide specific information about how to include this group [ 36 ]. Recent UK studies have helped to contextualise these findings, by examining the legal, policy, and governance frameworks that apply to the recruitment of people with communication disabilities [ 30 , 37 , 38 ]. Whilst not specific to trials, these frameworks provide guidance for facilitating the inclusion of this group in the informed consent process. This includes recommendations to co-produce information materials with people with communication disabilities and to adapt communication environments and processes to improve their accessibility. These recommendations are supported by research that has developed and tested communication methods to support decision-making during the informed consent process for people with post-stroke aphasia [ 22 , 32 , 39 ] and intellectual disability [ 33 , 40 ].
In recent examples, researchers have been able to create and use accessible consent materials and implement these within stroke trials [ 41 , 42 , 43 ] using practical, evidence-based resources [ 22 , 44 , 45 ]. These have been co-produced to ensure the language is accessible, readable, and accompanied by transparent visual representations and alternative mediums (video for example). Furthermore, the recent ASSENT [ 46 ] and CONSULT [ 47 ] projects have developed inclusive consent guidance and resources to aid researchers.
Future research
More research is required to explore the inclusion of people with communication disabilities in the informed consent process in trials, in terms of current practice and professional and participant experience. Most existing research appears to have focused on two main groups: people with post-stroke aphasia and people with intellectual disabilities. Future research should explore the experiences and needs of people with different types of communication disabilities, for example, people living with dementia or with other progressive neurological conditions.
Further research is required to develop and evaluate additional tools, resources, and training interventions to support researchers to work with people with communication disabilities more easily and effectively during the informed consent process [ 37 ]. Evaluation should include the exploration of usability, acceptability to professionals and participants, and cost-effectiveness. In addition, studies should explore how researchers can form successful and equitable collaborations with people with communication disabilities as part of trial public involvement and engagement activity in order to co-produce inclusive consent processes and materials [ 48 ].
Trials involving adults whose capacity fluctuates or is lost during a trial
Informed consent can only be obtained from individuals who have the capacity to give consent. Fluctuating capacity can refer to situations where a person’s condition is cyclical (moving from an acute phase to a recovery phase) [ 49 ] or where their capacity is influenced by other factors including but not limited to health or environment [ 50 , 51 ]. It can also relate to capacity that is task-specific, where an individual may have the capacity to consent to certain aspects of a trial but may struggle to give informed consent to all aspects or understand long-term follow-up processes.
Fluctuating capacity raises three main challenges: (1) the potential exclusion of those believed to have fluctuating capacity where no clear assessment process is in place, (2) the need for a process of consent-taking at each data collection time point, and (3) the need to incorporate planning for a loss of capacity, temporary or otherwise, when creating trial processes, patient information and consent materials. Without forward planning, unanticipated lost capacity during data collection may lead to withdrawal and/or missing data and the unnecessary exclusion of participants [ 52 ].
Capacity is often framed (and commonly understood and implemented by recruiting staff) in binary terms as something a person has or does not have [ 53 , 54 ], which has been critiqued in certain populations and cultural contexts [ 55 ]. In England and Wales, the Mental Capacity Act 2005 makes it clear that capacity is task-specific. Once assessed, capacity is not an end point but an ongoing process of engagement with a participant.
An intention to carry out capacity assessments is often alluded to in trial protocols without further detail being given on why certain individuals will be assessed, who will conduct assessments, and what criteria they will use [ 9 ]. The Mental Capacity Act 2005 and the Code of Practice (2007) exist to protect individuals, but not to impede their right to participate in research, something researchers should acknowledge. However, there is a lack of practical guidance in these documents which results in uncertainty about how researchers should best assess capacity. This can lead to inconsistent approaches to assessment. Capacity should be assumed in individuals, and capacity assessments should also only take place after the individual has been given clear information, appropriate to their needs, and there is a question raised about their ability to provide informed consent. This again raises challenges for trials where standard information is required that can be complex, lengthy, and difficult to adapt to the needs of different groups (for example, people with communication disabilities) [ 56 , 57 ].
Suggestions for alternative forms of consent that may support those whose capacity fluctuates have been developed by researchers working with specific populations [ 58 ], including process consent in dementia research [ 59 ]. These distinguish between time and task-specific capacity and the capacity to take a longitudinal view, implying an understanding of future risks and benefits [ 49 ]. However, research to date often focuses on distinct populations, e.g. people receiving palliative care [ 60 ], people living with dementia, and stroke survivors. Attention to managing fluctuations in capacity is less often seen in population-wide trials. To reduce blanket exclusions for certain populations, and misuse of lack of capacity being used as an exclusion criterion, further research resulting in clear guidance is required.
Standardised tools for capacity assessment have been developed, but there is no gold standard for the assessment of capacity in clinic or in research, nor is there an agreement that any one tool can sufficiently capture the complexity of capacity assessment [ 61 ]. Current Mental Capacity Act-compliant tools remain difficult to adapt to the heterogeneity of the populations for whom capacity fluctuates [ 62 , 63 , 64 ]. Capacity assessment processes are also often only employed in certain trials which anticipate that their target population will require them.
Consent needs to be understood as task- and time-specific and requiring accessible information. Research is needed to generate guidance on what to do if capacity is lost during follow up and it must be based on a defined process of establishing the wishes of participants at the initial consent stages. More evidence is required on the best methods for capacity assessment and how to support researchers to assess capacity. Trials need to build protocols for how to prevent exclusion of those who may fluctuate in capacity to consent and on how to manage data collection from those whose capacity does fluctuate.
Trials involving adults who lack the capacity to consent
Even with support, some people will be unable to provide their own consent to take part in a trial. The exclusion of adults who lack the capacity to consent has been widely documented [ 18 , 65 , 66 ] and is due to a range of intersecting methodological and systemic barriers to their inclusion [ 34 ]. Specific consent-based challenges include the complexity of the patchwork of legal frameworks that govern trials involving adults lacking capacity both within the UK [ 67 ] and internationally [ 68 ], and the uncertainties of applying them in practice [ 69 ]. In the UK, clinical trials of an investigational medicinal product involving adults lacking capacity are governed by the Medicines for Human Use (Clinical Trials) Regulations [ 70 ], with other types of trials covered by mental capacity legislation such as the Mental Capacity Act in England and Wales [ 71 ]. In both cases, there are provisions for an alternative decision-maker to be involved in enrolment decisions, usually a family member or close friend, or someone acting in a professional capacity who is not involved in the research if no one is able or willing to act in a personal capacity [ 70 , 71 ]. For clinical trials, the alternative decision-maker is termed a legal representative and provides consent based on the person’s presumed will [ 70 ], and for other types of research, they act as a consultee and are asked to provide advice about participation based on the person’s wishes and preferences [ 29 ]. However, little guidance is available to families and health and social care professionals about their role in making decisions about trial participation, nor the legal basis for their decision [ 72 ].
Due in part to this legal complexity, a lack of knowledge about research involving adults who lack capacity, and paternalistic attitudes generally, may result in gatekeeping practices by researchers and health and social care professionals towards this population [ 73 , 74 ]. Involving health and social care professionals as a consultee or legal representative relies on them having the time and willingness to be involved. Some may be concerned about being unable to determine or represent the wishes and preferences that a person may hold and so may decline to become involved [ 38 ]. Other challenges arise due to the difficulties in identifying and contacting consultees and legal representatives [ 75 ]. Even when they have been identified, family members are less likely to agree to research participation on the person’s behalf than patients themselves [ 76 ]. This may be due to families’ difficulties in knowing what that person’s wishes and preferences would be about participation [ 77 ]. People rarely discuss their research preferences in the event that they might lose capacity, and there is no current mechanism in the UK for prospectively appointing a consultee or legal representative to make decisions about research [ 78 ].
Procedures for identifying and approaching consultees and legal representatives are one of the issues that research ethics committees (RECs) consider when reviewing applications for trials involving adults who lack capacity, alongside arrangements for assessing capacity to consent where required [ 29 ]. However, RECs’ resistance to the inclusion of adults who lack capacity in a trial, and whether there is sufficient justification to do so, is cited as one of the greatest barriers to their inclusion [ 79 , 80 ]. RECs do not interpret the legal frameworks consistently or, at times, correctly, with inaccurate terminology and requirements being cited [ 37 , 72 , 81 ]. There have been calls for greater explicitness and accuracy when applications for ethical review of these studies are both submitted and reviewed [ 72 , 81 ] and for incorporating more adaptations and accommodations into the recruitment process such as ensuring information is cognitively accessible [ 37 ].
Recent research has identified a number of barriers and facilitators to involving adults lacking consent in trials [ 19 , 34 ] leading to the creation of guidance, for example, for recruiting adults with impaired mental capacity at the end of life in research [ 19 ]. Recent initiatives to address the inclusion of underserved groups in research more broadly, such as the NIHR INCLUDE project [ 1 ], have led to the development of the INCLUDE Impaired Capacity to Consent Framework which is a tool to help researchers to design and conduct trials that are more inclusive of people with impaired capacity to consent [ 82 ].
Other studies have focused on the role of personal consultees and legal representatives. This includes a study that found that making ethically complex decisions about research on behalf of someone else can be challenging for many family members, with some experiencing a decisional and emotional burden as a result [ 83 ]. Current work includes the development of the first decision aid for families making decisions about research on behalf of someone who lacks the capacity to consent [ 84 ] which is currently being evaluated as a ‘Study Within a Trial’ (or ‘SWAT’) (CONSULT) [ 85 ] and the development of resources to help researchers [ 47 ].
Despite the ongoing work, there is a need for a more sustained effort to ensure that these groups have an equitable opportunity to participate in trials. More research is needed into how researchers can design more inclusive trials, and the involvement of health and social care professionals as nominated consultees, and the use of professional legal representatives when necessary. Unlike questions about why other underserved groups have been excluded from research, the legal position regarding people who lack capacity is that their inclusion requires justification [ 29 ]. Clearer guidance is required on how this justification is understood and interpreted.
A number of recommendations for further research at a policy and legislation level have been previously made, including proposals by the Nuffield Council on Bioethics [ 86 ] that consideration be given to extend the role of the welfare attorney in England and Wales to include decisions about research, both within the Mental Capacity Act [ 71 ] and the Clinical Trials Regulations [ 70 ]. There is also uncertainty about the role of Lasting Power of Attorney in decisions about research participation [ 78 ], with families wanting greater support and guidance when making decisions [ 83 ].
Adult and paediatric emergency and urgent care trials
Trials involving adults in emergency situations may encounter additional complexities. The challenges of obtaining consent from patients who are suddenly unable to communicate or convey their own wishes are encountered in trial contexts ranging from intrapartum [ 87 ] and acute coronary syndrome [ 88 ] to acute stroke where it has been described as the rate-limiting step in treatment RCTs [ 89 ]. Emergency and urgent care trials are conducted in a range of settings including prehospital [ 90 ] and critical care [ 91 ].
Historically, children have not received evidence-based healthcare in emergency and critical care settings due to their exclusion from trials arising from similar practical and ethical issues to those encountered in adult trials in these time-critical settings [ 92 ]. In order to increase the chances of saving a child’s life, treatments need to be given without delay, so there is no time to seek informed consent from parents or legal representatives. Even if there is a brief window of opportunity for recruitment discussions, parents may not be present or may be highly distressed and lack the capacity to make an informed decision about the use of their child’s information and potential ongoing involvement [ 93 ].
Emergency research is when treatment needs to be given urgently [ 94 ] and recruitment cannot be delayed until the patient either regains capacity or a consultee or legal representative can be found [ 95 ]. In such circumstances, research without prior consent (RWPC, also referred to as ‘deferred consent’) is permissible in many jurisdictions including the USA, Canada, parts of Australasia, and the UK through both the Mental Capacity Act [ 71 ] and the 2006 Amendment to the 2004 EU Clinical Trials Regulations [ 96 ]. However, there are variations in the provisions for RWPC in emergency research, both between and within countries [ 97 ]. Within the UK, for example, the law in Scotland does not provide any ‘exemptions’ or alternatives for the involvement of adults not able to consent for themselves in clinical trials in emergency situations [ 94 ]. This meant that trials such as RECOVERY-RS [ 98 ], which compared respiratory strategies for patients with COVID-19 respiratory failure, could not recruit Scottish patients. Similarly, the UK-REBOA trial in life-threatening torso haemorrhage was unable to recruit in Scotland despite being coordinated from there [ 99 ].
In recognition of the need to conduct these vital trials with children, various legal frameworks for paediatric trials have also been amended nationally and internationally, enabling research to be conducted without prior consent. In 2008, UK legislation was amended to allow research without prior consent in such circumstances [ 100 ], yet there was a lack of knowledge about how and when research teams should broach these research discussions with parents in a way that avoided further burdening families. There was also a need for guidance to inform what should happen when a child dies after trial enrolment without parents’ prior knowledge or consent. Despite the 2008 legislation that enabled much-needed research on emergency treatments for children, there was hesitancy amongst clinical and research communities about conducting trials involving critically ill children [ 101 ].
The use of RWPC in both adult and child populations is ethically complex, with diverse views about the acceptability of enrolling acutely ill patients without consent [ 102 ]. There are particular challenges around gaining ethical approval for the use of RWPC in borderline or ‘middle ground’ cases where a patient may be conscious or coherent, yet their condition or the lack of time limits the possibility of informed consent [ 103 ]. These, and other challenges [ 34 ], can lead to consent-based recruitment bias which means that patients enrolled in RCTs may not necessarily be representative of critically ill patients in clinical practice [ 20 , 104 ]. This has the potential to cause harm by obscuring any treatment effect [ 105 ].
A recent study in the UK (Perspectives Study) explored consent and recruitment in adult critical care research [ 106 ] and identified strategies to enhance consent and recruitment processes. This led to the development of good practice guidance and other resources including an accessible animation for members of the public [ 107 ]. An animation aimed at adults enrolled in emergency care research which describes RWPC was developed by another research team (CoMMiTED Study) [ 108 ]. Systematic reviews have explored stakeholders’ views about the acceptability of RWPC [ 109 ], including ethnic minority populations’ views [ 110 ]. Such studies have found that RWPC is generally acceptable to patients, families, and practitioners but highlighted the importance of contextual factors.
The CATheter infections in Children Trial (CATCH) was the first UK trial to include research without prior consent when comparing the effectiveness of different types of central venous catheters to prevent bloodstream infections in children. An embedded study (called CONNECT [ 111 ]) explored parent and practitioner views and experiences of recruitment and consent and found that parents were momentarily shocked or surprised when they were informed that their child had already been entered into CATCH without their consent [ 101 ]. However, initial concerns were often quickly addressed by practitioner explanations about why it had not been possible to seek consent before enrolment and how the trial interventions were already used in clinical care. To prevent burden and assist decision-making, parents stated it was important for the research staff to assess the appropriate timing of research discussions after a child’s enrolment in a trial. They suggested that the researcher should consult with the bedside nurse about appropriate timing and only approach parents after the initial emergency situation has passed, when a child’s condition has stabilised [ 101 ]. The CONNECT study used these findings alongside wider research, involving practitioners, families [ 112 ], and children [ 113 ] with experience in emergency care, to develop guidance for future paediatric and neonatal trials [ 114 ]. Since its publication in 2015, CONNECT guidance has informed the successful conduct of five studies. This includes the first clinical trial of a drug for long-lasting seizures (EcLiPSE trial), which successfully recruited to time and target with a 93% consent rate and led to changes in clinical guidelines for children in status epilepticus [ 115 ].
Research into consent in emergency settings is high on the trials methodological research agenda and was identified as a research priority by Clinical Trials Units in a UK survey [ 116 ]. Areas for future research involving adults identified by the Perspectives Study included the need for evidence-based guidance on the procedures for professionals acting as a consultee or legal representative and identifying strategies to communicate with relatives of critically ill patients about research, including where a participant enrolled without prior consent subsequently dies [ 106 ]. The NIHR RfPB-funded study ‘ENHANCE’ will begin in 2023 and aims to address this gap in knowledge through the involvement of bereaved families and other key stakeholders.
Ongoing work in paediatric populations aims to assess and refine CONNECT guidance in low- and middle-income countries. Further work is needed to explore views on research without prior consent in underserved populations, such as parents who do not speak English and who are often excluded from qualitative studies and guidance development.
The need for more guidance for RECs who are reviewing emergency and urgent care trials and support for consent processes for patients and members of the public who join research teams and advise on studies, has also been highlighted [ 106 , 109 , 117 ].
Conclusions
The need for alternative consent processes that address the inadvertent exclusion of certain populations has been detailed in this article. Drives for trial efficiency, lack of funding, or time for adaptation often result in the exclusion of certain populations. However, inequities in health outcomes will continue to be exacerbated by health research until trials become more inclusive of underserved populations. Alongside methodological innovation, further research is required to establish good practice, develop evidence-based guidance, and support skill acquisition in the global research workforce. Our key recommendations for future research are summarised in Table 1 . Importantly, this should be done in collaboration with people with lived experience and those who care for them.
The populations detailed above are not the only areas where consent is complex or alternative pathways are required. Some trials have complex consent processes, not because of their recruited population, but due to an innovative treatment or trial design, such as cluster RCTs and Trials within Cohorts (TwiCs) [ 118 ]. As we progress with the innovation of trial design, we must progress methodological innovation in consent at the same pace or risk leaving certain populations behind. Many of the methodological lessons learnt and proposed adjustments, such as the routine provision of accessible information, could also benefit other underserved groups including those with lower literacy levels and English language proficiency, as well as the wider population of potential research participants.
The TMRP Complex and Alternate Consent Pathways group is driving forward this research agenda in the UK and is open to new members to share methodological learning. We have updated the NIHR Clinical Trials Toolkit [ 119 ] to reflect the most up-to-date research in this area. However, as this commentary has shown, current guidance remains limited in its utility and requires greater clarity and practical applicability for researchers, participants, family members, and ethical review committees. We are keen to use the momentum of the group to identify others with an interest in this area in order to collaboratively develop the research agenda and address the consent-based ethical and methodological challenges in trials. Many of these issues are not restricted to the UK but are encountered internationally, which raises additional challenges when conducting multi-national trials [ 58 , 97 , 120 ]. We encourage researchers from other regions and jurisdictions to share their experiences and ongoing research programmes and to contribute to developing an international research agenda to address these global challenges.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable as no dataset was generated.
Witham MD, Anderson E, Carroll C, Dark PM, Down K, Hall AS, et al. Developing a roadmap to improve trial delivery for under-served groups: results from a UK multi-stakeholder process. Trials. 2020;21:694.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Mundi S, Chaudhry H, Bhandari M. Systematic review on the inclusion of patients with cognitive impairment in hip fracture trials: a missed opportunity? Can J Surg. 2014;57:E141–5.
Taylor JS, DeMers SM, Vig EK, Borson S. The disappearing subject: exclusion of people with cognitive impairment and dementia from geriatrics research. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2012;60:413–9.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Jensen JS, Reiter-Theil S, Celio DA, Jakob M, Vach W, Saxer FJ. Handling of informed consent and patient inclusion in research with geriatric trauma patients – a matter of protection or disrespect? Clin Interv Aging. 2019;14:321–34.
Thomalla G, Boutitie F, Fiebach JB, Simonsen CZ, Nighoghossian N, Pedraza S, et al. Effect of informed consent on patient characteristics in a stroke thrombolysis trial. Neurology. 2017;89:1400–7.
Vassallo M. Research and reducing inequity in healthcare. Age Ageing. 2019;48:474–5.
Landes SD, Stevens JD, Turk MA. Cause of death in adults with intellectual disability in the United States. J Intellect Disabil Res. 2021;65 Part 1:47–59.
Article Google Scholar
Learning Disabilities Mortality review (LeDeR) report 2020: University of Bristol Norah Fry Centre for Disability Studies; 2020. https://www.bristol.ac.uk/media%02library/sites/sps/leder/LeDeR%20programme%20annual%20report%2013.05.2021%20FINAL.pdf .
Feldman MA, Bosett J, Collet C, Burnham-Riosa P. Where are persons with intellectual disabilities in medical research? A survey of published clinical trials. J Intellect Disabil Res. 2014;58:800–9.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Striving for diversity in research studies. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:1429–30.
Spong CY, Bianchi DW. Improving public health requires inclusion of underrepresented populations in research. JAMA. 2018;319:337.
Centre for Drug Evaluation and Research. Enhancing the diversity of clinical trial populations — eligibility criteria, enrollment practices, and trial designs guidance for industry: FDA; 2020. https://www.fda.gov/regulatory%02information/search-fda-guidance-documents/enhancing-diversity-clinical-trial-populations-eligibility-criteria%02enrollment-practices-and-trial .
National Institute for Health Research. Best research for best health: the next chapter. 2021.
Google Scholar
Treweek S, Pitkethly M, Cook J, Fraser C, Mitchell E, Sullivan F, et al. Strategies to improve recruitment to randomised trials. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.MR000013.pub6 .
Pietrzykowski T, Smilowska K. The reality of informed consent: empirical studies on patient comprehension—systematic review. Trials. 2021;22:57.
Nathe JM, Krakow EF. The challenges of informed consent in high-stakes, randomized oncology trials: a systematic review. MDM Policy Pract. 2019;4:2381468319840322.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Brady MC, Fredrick A, Williams B. People with aphasia: capacity to consent, research participation and intervention inequalities. Int J Stroke. 2013;8:193–6.
Shepherd V, Wood F, Griffith R, Sheehan M, Hood K. Protection by exclusion? The (lack of) inclusion of adults who lack capacity to consent to research in clinical trials in the UK. Trials. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-019-3603-1 .
Evans CJ, Yorganci E, Lewis P, Koffman J, Stone K, Tunnard I, et al. Processes of consent in research for adults with impaired mental capacity nearing the end of life: systematic review and transparent expert consultation (MORECare_Capacity statement). BMC Med. 2020;18:221.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Holcomb JB, Weiskopf R, Champion H, Gould SA, Sauer RM, Brasel K, et al. Challenges to effective research in acute trauma resuscitation: consent and endpoints. Shock. 2011;35:107–13.
Ward RM, Benjamin DK, Davis JM, Gorman RL, Kauffman R, Kearns GL, et al. The need for pediatric drug development. J Pediatr. 2018;192:13–21.
Jayes M, Palmer R. Initial evaluation of the Consent Support Tool: a structured procedure to facilitate the inclusion and engagement of people with aphasia in the informed consent process. Int J Speech Lang Pathol. 2014;16:159–68.
Moye J, Marson DC. Assessment of decision-making capacity in older adults: an emerging area of practice and research. J Gerontol Series B. 2007;62:P3–11.
Kagan A, Kimelman MDZ. Informed consent in aphasia research: myth or reality. Clin Aphasiol. 1995;23:65–75.
Triebel KL, Martin RC, Novack TA, Dreer L, Turner C, Pritchard PR, et al. Treatment consent capacity in patients with traumatic brain injury across a range of injury severity. Neurology. 2012;78:1472–8.
Hamilton J, Ingham B, McKinnon I, Parr JR, Tam LY-C, Couteur AL. Mental capacity to consent to research? Experiences of consenting adults with intellectual disabilities and/or autism to research. Br J Learn Disabil. 2017;45:230–7.
Department of Constitutional Affairs. Mental Capacity Act 2005: code of practice. The Stationary Office. 2007. https://doi.org/10.1108/eb003163 .
Zuscak SJ, Peisah C, Ferguson A. A collaborative approach to supporting communication in the assessment of decision-making capacity. Disabil Rehabil. 2016;38:1107–14.
Health Research Authority. Health Research Authority: Mental Capacity Act. Health Research Authority. https://www.hra.nhs.uk/planning-and-improving-research/policies-standards-legislation/mental-capacity-act/ . Accessed 16 Jul 2021.
Ryan H, Heywood R, Jimoh O, Killett A, Langdon PE, Shiggins C, et al. Inclusion under the Mental Capacity Act (2005): a review of research policy guidance and governance structures in England and Wales. Health Expect. 2021;24:152–64.
Jayes MJ, Palmer RL. Stroke research staff’s experiences of seeking consent from people with communication difficulties: results of a national online survey. Top Stroke Rehabil. 2014;21:443–51.
Penn C, Frankel T, Watermeyer J, Müller M. Informed consent and aphasia: evidence of pitfalls in the process. Aphasiology. 2009;23:3–32.
Taua C, Neville C, Hepworth J. Research participation by people with intellectual disability and mental health issues: an examination of the processes of consent. Int J Ment Health Nurs. 2014;23:513–24.
Shepherd V. An under-represented and underserved population in trials: methodological, structural, and systemic barriers to the inclusion of adults lacking capacity to consent. Trials. 2020;21:445.
Townend E, Brady M, McLaughlan K. A systematic evaluation of the adaptation of depression diagnostic methods for stroke survivors who have aphasia. Stroke. 2007;38:3076–83.
Jayes M, Moulam L, Meredith S, Whittle H, Lynch Y, Goldbart J, et al. Making public involvement in research more inclusive of people with complex speech and motor disorders: the I-ASC Project. Qual Health Res. 2021;31:1260–74.
Jimoh OF, Ryan H, Killett A, Shiggins C, Langdon PE, Heywood R, et al. A systematic review and narrative synthesis of the research provisions under the Mental Capacity Act (2005) in England and Wales: recruitment of adults with capacity and communication difficulties. PLoS One. 2021;16:e0256697.
Heywood R, Ryan H, Killett A, Langdon P, Plenderleith Y, Shiggins C, et al. Lost voices in research: exposing the gaps in the Mental Capacity Act 2005. Med Law Int. 2019;19:81–112.
Stein J, Brady Wagner LC. Is informed consent a “yes or no” response? Enhancing the shared decision-making process for persons with aphasia. Top Stroke Rehabil. 2006;13:42–6.
Cameron L, Murphy J. Obtaining consent to participate in research: the issues involved in including people with a range of learning and communication disabilities. Br J Learn Disabil. 2007;35:113–20.
Thomas SA, Drummond AE, Lincoln NB, Palmer RL, das Nair R, Latimer NR, et al. Behavioural activation therapy for post-stroke depression: the BEADS feasibility RCT. Health Technol Assess. 2019;23:1–176.
Hilari K, Behn N, Marshall J, Simpson A, Thomas S, Northcott S, et al. Adjustment with aphasia after stroke: study protocol for a pilot feasibility randomised controlled trial for SUpporting wellbeing through PEeR Befriending (SUPERB). Pilot Feasibility Stud. 2019;5:14.
Palmer R, Dimairo M, Cooper C, Enderby P, Brady M, Bowen A, et al. Self-managed, computerised speech and language therapy for patients with chronic aphasia post-stroke compared with usual care or attention control (Big CACTUS): a multicentre, single-blinded, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18:821–33.
Consent Support Tool, J&R Press. https://www.jr-press.co.uk/consent-support-tool.html . Accessed 13 May 2022.
Pearl G, Cruice M. Facilitating the involvement of people with aphasia in stroke research by developing communicatively accessible research resources. Top Lang Disord. 2017;37:67–84.
ASSENT project. https://www.uea.ac.uk/groups-and-centres/assent . Accessed 13 May 2022.
Capacity and consent to research. CONSULT. https://www.capacityconsentresearch.com/ . Accessed 27 Sep 2021.
Volkmer A, Broomfield K. Seldom heard voices in service user involvement: J&R Press; 2022.
Griffith R. Assessing capacity in cases of fluctuating decision-making ability. Br J Nurs. 2020;29. https://doi.org/10.12968/bjon.2020.29.15.908 .
Stroup S, Appelbaum P. The subject advocate: protecting the interests of participants with fluctuating decisionmaking capacity. IRB. 2003;25:9–11.
Bracken-Roche D, Bell E, Racine E. The “vulnerability” of psychiatric research participants: why this research ethics concept needs to be revisited. Can J Psychiatr. 2016;61:335–9.
Crow G, Wiles R, Heath S, Charles V. Research ethics and data quality: the implications of informed consent. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2006;9:83–95.
Clough B. What about us? A case for legal recognition of interdependence in informal care relationships. J Soc Welf Fam Law. 2014;36:129–48.
Clough B. Disability and vulnerability: challenging the capacity/incapacity binary. Soc Policy Soc. 2017;16:469–81.
Akpa-Inyang F, Chima SC. South African traditional values and beliefs regarding informed consent and limitations of the principle of respect for autonomy in African communities: a cross-cultural qualitative study. BMC Med Ethics. 2021;22:111.
Isaacs T, Murdoch J, Demjén Z, Stevenson F. Examining the language demands of informed consent documents in patient recruitment to cancer trials using tools from corpus and computational linguistics. Health (London). 2020. https://doi.org/10.1177/1363459320963431 .
Duong Q, Mandrekar SJ, Winham SJ, Cook K, Jatoi A, Le-Rademacher JG. Understanding verbosity: funding source and the length of consent forms for cancer clinical trials. J Cancer Educ. 2021;36:1248–52.
Lindley RI, Kane I, Cohen G, Sandercock PA. Factors influencing the use of different methods of consent in a randomized acute stroke trial: the Third International Stroke Trial (IST-3). Int J Stroke. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1177/17474930211037123 .
Dewing J. Participatory research: a method for process consent with persons who have dementia. Dementia. 2007;6:11–25.
Casarett DJ, Karlawish JH. Are special ethical guidelines needed for palliative care research? J Pain Symptom Manag. 2000;20:130–9.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Pennington C, Davey K, ter Meulen R, Coulthard E, Kehoe PG. Tools for testing decision-making capacity in dementia. Age Ageing. 2018;47:778–84.
Kim SYH, Caine ED, Currier GW, Leibovici A, Ryan JM. Assessing the competence of persons with Alzheimer’s disease in providing informed consent for participation in research. AJP. 2001;158:712–7.
Casarett DJ. Assessing decision-making capacity in the setting of palliative care research. J Pain Symptom Manag. 2003;25:S6–13.
Dunn LB, Nowrangi MA, Be M, Palmer BW, Jeste DV, Saks ER. Assessing decisional capacity for clinical research or treatment: a review of instruments. Am J Psychiatry. 2006;163(8):1323–34. https://doi.org/10.1176/ajp.2006.163.8.1323 .
Trivedi RB, Humphreys K. Participant exclusion criteria in treatment research on neurological disorders: are unrepresentative study samples problematic? Contemp Clin Trials. 2015;44:20–5.
Sheehan KJ, Fitzgerald L, Hatherley S, Potter C, Ayis S, Martin FC, et al. Inequity in rehabilitation interventions after hip fracture: a systematic review. Age Ageing. 2019;48:489–97.
Shepherd V. Research involving adults lacking capacity to consent: the impact of research regulation on “evidence biased” medicine. BMC Med Ethics. 2016;17:8.
Tridente A, Holloway PAH, Hutton P, Gordon AC, Mills GH, et al. Methodological challenges in European ethics approvals for a genetic epidemiology study in critically ill patients: the GenOSept experience. BMC Med Ethics. 2019;20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12910-019-0370-1 .
Fletcher JR, Lee K, Snowden S. Uncertainties when applying the Mental Capacity Act in dementia research: a call for researcher experiences. Ethics Soc Welfare. 2019;13:183–97.
The Medicines for Human Use (Clinical Trials) Regulations. 2004. SI No.1031. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-023-07159-6 . https://www.legislation.gov.uk/uksi/2004/1031/contents/ .
HMSO, London. Mental Capacity Act 2005. https://www.legislation.gov.uk/ukpga/2005/9/contents .
Shepherd V, Wood F, Griffith R, Sheehan M, Hood K. Research involving adults lacking capacity to consent: a content analysis of participant information sheets for consultees and legal representatives in England and Wales. Trials. 2019;20:233.
Bravo G, Wildeman S, Dubois M-FF, Kim SY, Cohen C, Graham J, et al. Substitute consent practices in the face of uncertainty: a survey of Canadian researchers in aging. Int Psychogeriatr. 2013;25:1821–30.
Shepherd V, Griffith R, Sheehan M, Wood F, Hood K. Healthcare professionals’ understanding of the legislation governing research involving adults lacking mental capacity in England and Wales: a national survey. J Med Ethics. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1136/medethics-2017-104722 .
Shepherd V, Davies J. Conducting a randomized controlled trial in care homes: the challenges of recruiting residents who lack capacity to consent. SAGE Research Methods Cases: Medicine and Health. 2020. https://doi.org/10.4135/9781529726626 .
Mason S, Barrow H, Phillips A, Eddison G, Nelson A, Cullum N, et al. Brief report on the experience of using proxy consent for incapacitated adults. J Med Ethics. 2006;32:61–2.
Shepherd V, Sheehan M, Hood K, Griffith R, Wood F. Constructing authentic decisions: proxy decision-making for research involving adults who lack capacity to consent. J Med Ethics. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1136/medethics-2019-106042 .
Shepherd V, Griffith R, Hood K, Sheehan M, Wood F. “There’s more to life than money and health”: family caregivers’ views on the role of Power of Attorney in proxy decisions about research participation for people living with dementia. Dementia (London). 2019. https://doi.org/10.1177/1471301219884426 .
Head MG, Walker SL, Nalabanda A, Bostock J, Cassell JA. Researching scabies outbreaks among people in residential care and lacking capacity to consent: a case study. Public Health Ethics. 2015;10:90–5.
Griffiths S, Manger L, Chapman R, Weston L, Sherriff I, Quinn C, et al. Letter on “Protection by exclusion? The (lack of) inclusion of adults who lack capacity to consent to research in clinical trials in the UK”. Trials. 2020;21:104. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-020-4054-4 .
Dixon-Woods M, Angell EL. Research involving adults who lack capacity: how have research ethics committees interpreted the requirements? J Med Ethics. 2009;35:377–81.
Implementation of the ‘INCLUDE Impaired Capacity to Consent Framework’ for researchers. Cardiff University. https://www.cardiff.ac.uk/centre-for-trials-research/research/studies-and-trials/view/implementation-of-the-include-impaired-capacity-to-consent-framework-for-researchers . Accessed 9 Aug 2022.
Shepherd V, Hood K, Sheehan M, Griffith R, Wood F. ‘It’s a tough decision’: a qualitative study of proxy decision-making for research involving adults who lack capacity to consent in UK. Age and Ageing. 2019;48(6):903–9. https://doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afz115 .
Shepherd V, Wood F, Griffith R, Sheehan M, Hood K. Development of a decision support intervention for family members of adults who lack capacity to consent to trials. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2021;21:30.
Shepherd V, Wood F, Gillies K, Martin A, O’Connell A, Hood K. Feasibility, effectiveness and costs of a decision support intervention for consultees and legal representatives of adults lacking capacity to consent (CONSULT): protocol for a randomised study within a trial. 2022;23:957. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-022-06887-5 .
Nuffield Council on Bioethics. Dementia: ethical issues. 2009:172. https://www.nuffieldbioethics.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/07/Dementia-short-guide.pdf .
Vernon G, Alfirevic Z, Weeks A. Issues of informed consent for intrapartum trials: a suggested consent pathway from the experience of the Release trial [ISRCTN13204258]. Trials. 2006;7:13.
Iwanowski P, Budaj A, Członkowska A, Wąsek W, Kozłowska-Boszko B, Olędzka U, et al. Informed consent for clinical trials in acute coronary syndromes and stroke following the European Clinical Trials Directive: investigators’ experiences and attitudes. Trials. 2008;9:45.
Rose D, Kasner S. Informed consent: the rate-limiting step in acute stroke trials. Front Neurol. 2011;2. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2011.00065 .
Armstrong S, Langlois A, Siriwardena N, Quinn T. Ethical considerations in prehospital ambulance based research: qualitative interview study of expert informants. BMC Med Ethics. 2019;20:88.
Ecarnot F, Quenot J-P, Besch G, Piton G. Ethical challenges involved in obtaining consent for research from patients hospitalized in the intensive care unit. Ann Transl Med. 2017;5(Suppl 4):S41.
Kanthimathinathan HK, Scholefield BR. Dilemmas in undertaking research in paediatric intensive care. Arch Dis Child. 2014;99:1043–9.
Maitland K, Molyneux S, Boga M, Kiguli S, Lang T. Use of deferred consent for severely ill children in a multi-centre phase III trial. Trials. 2011;12:90.
Research in emergency settings. Health Research Authority. https://www.hra.nhs.uk/planning-and-improving-research/policies-standards-legislation/research-emergency-settings/ . Accessed 17 May 2022.
Medical Research Council. MRC Ethics Guide 2007: Medical research involving adults who cannot consent. MRC; 2007. https://www.ukri.org/wp%20content/uploads/2021/08/MRC%020208212-Medical-research-involving-adults-who-cannot-consent.pdf .
The Medicines for Human Use (Clinical Trials) Amendment (No.2) Regulations 2006. https://www.legislation.gov.uk/uksi/2006/1928/contents/made .
Kompanje EJO, Maas AIR, Menon DK, Kesecioglu J. Medical research in emergency research in the European Union member states: tensions between theory and practice. Intensive Care Med. 2014;40:496–503.
Perkins GD, Ji C, Connolly BA, Couper K, Lall R, Baillie JK, et al. Effect of noninvasive respiratory strategies on intubation or mortality among patients with acute hypoxemic respiratory failure and COVID-19: the RECOVERY-RS randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2022;327:546–58.
Jansen JO, Cochran C, Boyers D, Gillies K, Lendrum R, Sadek S, et al. The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of resuscitative endovascular balloon occlusion of the aorta (REBOA) for trauma patients with uncontrolled torso haemorrhage: study protocol for a randomised clinical trial (the UK-REBOA trial). Trials. 2022;23:384.
The Medicines for Human Use (Clinical Trials) and Blood Safety and Quality (Amendment) Regulations 2008. https://www.legislation.gov.uk/uksi/2008/941/contents/made . Accessed 13 May 2022.
Woolfall K, Frith L, Gamble C, Gilbert R, Mok Q, Young B, et al. How parents and practitioners experience research without prior consent (deferred consent) for emergency research involving children with life threatening conditions: a mixed method study. BMJ Open. 2015;5:e008522.
van der Graaf R, Hoogerwerf M-A, de Vries MC. The ethics of deferred consent in times of pandemics. Nat Med. 2020;26:1328–30.
Berger BJ. Minimum risk and HEAT-PPCI: innovative ideas for informed consent in emergency medical research. Ann Emerg Med. 2014;64:A17–9.
Zimmermann JB, Horscht JJ, Weigand MA, Bruckner T, Martin EO, Hoppe-Tichy T, et al. Patients enrolled in randomised clinical trials are not representative of critically ill patients in clinical practice: observational study focus on tigecycline. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2013;42:436–42.
Roberts I, Prieto-Merino D, Shakur H, Chalmers I, Nicholl J. Effect of consent rituals on mortality in emergency care research. Lancet. 2011;377:1071–2.
Paddock K, Woolfall K, Frith L, Watkins M, Gamble C, Welters I, et al. Strategies to enhance recruitment and consent to intensive care studies: a qualitative study with researchers and patient–public involvement contributors. BMJ Open. 2021;11:e048193.
Perspectives Study - Institute of Population Health - University of Liverpool. https://www.liverpool.ac.uk/population-health/research/groups/perspectives/ . Accessed 19 May 2022.
Deferred consent in Emergency Research-a patient video. 2022. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=P--SEfQOd3w .
Fitzpatrick A, Wood F, Shepherd V. Trials using deferred consent in the emergency setting: a systematic review and narrative synthesis of stakeholders’ attitudes. Trials. 2022;23:411.
Raven-Gregg T, Shepherd V. Exploring the inclusion of under-served groups in trials methodology research: an example from ethnic minority populations’ views on deferred consent. Trials. 2021;22:589.
University of Liverpool. CONNECT - consent methods in paediatric emergency and urgent care trials. https://www.liverpool.ac.uk/population-health-sciences/research/connect/ . Accessed 20 Mar 2020.
Woolfall K, Young B, Frith L, Appleton R, Iyer A, Messahel S, et al. Doing challenging research studies in a patient-centred way: a qualitative study to inform a randomised controlled trial in the paediatric emergency care setting. BMJ Open. 2014;4:e005045.
Roper L, Sherratt FC, Young B, McNamara P, Dawson A, Appleton R, et al. Children’s views on research without prior consent in emergency situations: a UK qualitative study. BMJ Open. 2018;8:e022894.
Woolfall K, Frith L, Dawson A, Gamble C, Lyttle MD, Group the C advisory, et al. Fifteen-minute consultation: an evidence-based approach to research without prior consent (deferred consent) in neonatal and paediatric critical care trials. Arch Dis Childhood Educ Pract. 2016;101:49–53.
Lyttle MD, Rainford NEA, Gamble C, Messahel S, Humphreys A, Hickey H, et al. Levetiracetam versus phenytoin for second-line treatment of paediatric convulsive status epilepticus (EcLiPSE): a multicentre, open-label, randomised trial. Lancet. 2019;393:2125–34.
Tudur Smith C, Hickey H, Clarke M, Blazeby J, Williamson P. The trials methodological research agenda: results from a priority setting exercise. Trials. 2014;15:32.
Shepherd V, Hood K, Wood F. Unpacking the ‘Black Box of Horrendousness’: a qualitative exploration of the barriers and facilitators to conducting trials involving adults lacking capacity to consent. Trials. 2022;23(471). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-022-06422-6 .
Young-Afat DA, Verkooijen HAM, van Gils CH, van der Velden JM, Burbach JP, Elias SG, et al. Brief report: staged-informed consent in the cohort multiple randomized controlled trial design. Epidemiology. 2016;27:389–92.
NIHR. NIHR Clinical Trials Toolkit. https://www.ct-toolkit.ac.uk/ . Accessed 12 Sep 2022.
Shepherd V. Advances and challenges in conducting ethical trials involving populations lacking capacity to consent: a decade in review. Contemp Clin Trials. 2020;95:106054.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the wider contributors to the Complex and Alternate Consent Pathways group and the MRC-NIHR Trials Methodology Research Partnership who have participated in the discussions at various stages of this work. JW would like to acknowledge the support of the QuinteT research group, University of Bristol.
No funding was received for this work. VS is supported by a National Institute of Health Research Advanced Fellowship (CONSULT) funded by the Welsh government through Health and Care Research Wales (NIHR-FS(A)-2021). AMR is supported by a Wellcome Trust Fellowship (Capacity, Consent and Autonomy https://capacityconsent.leeds.ac.uk/ ) (219754/Z/19/Z). AV is supported by a National Institute for Health Research Advanced Fellowship (NIHR302240). KG is supported by funding from the Chief Scientist Office of the Scottish Government’s Health and Social Care Directorate (CZU/3/3). This work was supported by the MRC-NIHR Trials Methodology Research Partnership (MR/S014357/1). RH is supported in part by the Wellcome Trust (209841/Z/17/Z and 223290/Z/21/Z), EPSRC (EP/T020792/1), and the NIHR Biomedical Research Centre at University Hospitals Bristol and Weston NHS Foundation Trust and the University of Bristol. RH also serves on various local, regional, and national ethics committees and related groups. None of the organisations played a role in the drafting of this article, and the opinions stated are those of the authors.
Author information
Amy M. Russell and Victoria Shepherd are joint first authors.
Authors and Affiliations
Leeds Institute of Health Sciences, University of Leeds, Leeds, UK
Amy M. Russell
Centre for Trials Research, Cardiff University, 4th floor Neuadd Meirionnydd, Heath Park, Cardiff, CF14 4YS, UK
Victoria Shepherd
Department of Public Health, Policy and Systems, Institute of Population Health, University of Liverpool, Liverpool, UK
Kerry Woolfall & Bridget Young
Health Services Research Unit, University of Aberdeen, Aberdeen, UK
Katie Gillies
Department of Psychology and Language Sciences, University College London, London, UK
Anna Volkmer
Department of Health Professions, Manchester Metropolitan University, Manchester, UK
Centre for Ethics in Medicine, Population Health Science, Bristol Medical School, University of Bristol, Bristol, UK
Richard Huxtable
Department of Non-communicable Disease Epidemiology, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, London, UK
Alexander Perkins
Medical Research Council Clinical Trials Unit at University College London (MRC CTU at UCL), Institute of Clinical Trials and Methodology, University College London, London, UK
Nurulamin M. Noor
Centre for Evaluation and Methods, Wolfson Institute of Population Health, Queen Mary University London, London, UK
Beverley Nickolls
Population Health Science, Bristol Medical School, University of Bristol, Bristol, UK
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
The original idea for this Complex and Alternate Consent Pathways group (C&ACP) arose from the discussions in the Trial Methodology Research Partnership (TMRP) Qualitative Research group and the Inclusivity subgroup of the Trial Conduct Working Group and was led by JW. All authors are members of the C&ACP group and contributed to the iterative discussion of the content and structure of the manuscript. AR and VS wrote the first draft of the paper, and all authors contributed to the revision of it. The authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Victoria Shepherd .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Russell, A.M., Shepherd, V., Woolfall, K. et al. Complex and alternate consent pathways in clinical trials: methodological and ethical challenges encountered by underserved groups and a call to action. Trials 24 , 151 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-023-07159-6
Download citation
Received : 01 October 2022
Accepted : 09 February 2023
Published : 28 February 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-023-07159-6
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Informed consent
- Clinical trials
- Underserved populations
ISSN: 1745-6215
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]

Barriers to HIV Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis Use Among Women in the US: A Systematic Literature Review
Article sidebar, main article content.
Introduction: The high acquisition rate of HIV infection among women in the United States is concerning. Despite the FDA approving the first pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) drug in 2012, PrEP utilization remains significantly lower among women. This literature review aims to analyze the current body of research concerning HIV PrEP usage among women in the US.
Methods: A search of three medical databases was conducted. After the screening, 19 studies were selected for analysis. A risk of bias assessment was performed.
Results: A final set of records meeting the inclusion criteria (n=19) was included in the review for data collection and analysis. The study methodology for these research articles included interview-based designs (semi-structured and brief formats) in 1-on-1 meetings, focus groups, surveys, and retrospective data analysis. Participants' HIV risk characteristics were reported by way of sexual behavior, drug use, combined sexual behavior and drug use, and living in a high HIV rate neighborhood. Nineteen themes were identified and organized into three categories: (1) Common medication administration barriers, (2) PrEP-specific barriers, and (3) Situational barriers. The three most common themes reported by participants included a concern about side effects, low perceived risks of HIV, and lack of PrEP information. The CASP Qualitative Checklist and risk assessment summary showed acceptable validity among studies.
Discussion: This review identifies significant barriers hindering women's PrEP utilization, which would benefit from more prevalent stakeholder communication and education directed to at-risk populations. Inconsistently reported descriptive data on participants and the low patient populations make it difficult to generalize outcomes.
Article Details
How to cite.
- Endnote/Zotero/Mendeley (RIS)
Most read articles by the same author(s)
- Peter Trinh, Barbara Tafuto, Yasheca Ebanks, Zahra Zunaed, Doreen Lechner, Competency-Based Self-Assessment Tools: A Mixed-Methods Retrospective Analysis of Need , Principles and Practice of Clinical Research: Vol. 7 No. 4 (2021): Principles and Practice of Clinical Research
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Patient Cent Res Rev
- v.11(1); Spring 2024
- PMC11000705

Research Frameworks: Critical Components for Reporting Qualitative Health Care Research
Qualitative health care research can provide insights into health care practices that quantitative studies cannot. However, the potential of qualitative research to improve health care is undermined by reporting that does not explain or justify the research questions and design. The vital role of research frameworks for designing and conducting quality research is widely accepted, but despite many articles and books on the topic, confusion persists about what constitutes an adequate underpinning framework, what to call it, and how to use one. This editorial clarifies some of the terminology and reinforces why research frameworks are essential for good-quality reporting of all research, especially qualitative research.
Qualitative research provides valuable insights into health care interactions and decision-making processes – for example, why and how a clinician may ignore prevailing evidence and continue making clinical decisions the way they always have. 1 The perception of qualitative health care research has improved since a 2016 article by Greenhalgh et al. highlighted the higher contributions and citation rates of qualitative research than those of contemporaneous quantitative research. 2 The Greenhalgh et al. article was subsequently supported by an open letter from 76 senior academics spanning 11 countries to the editors of the British Medical Journal . 3 Despite greater recognition and acceptance, qualitative research continues to have an “uneasy relationship with theory,” 4 which contributes to poor reporting.
As an editor for the Journal of Patient-Centered Research and Reviews , as well as Human Resources for Health , I have seen several exemplary qualitative articles with clear and coherent reporting. On the other hand, I have often been concerned by a lack of rigorous reporting, which may reflect and reinforce the outdated perception of qualitative research as the “soft option.” 5 Qualitative research is more than conducting a few semi-structured interviews, transcribing the audio recordings verbatim, coding the transcripts, and developing and reporting themes, including a few quotes. Qualitative research that benefits health care is time-consuming and labor-intensive, requires robust design, and is rooted in theory, along with comprehensive reporting. 6
What Is “Theory”?
So fundamental is theory to qualitative research that I initially toyed with titling this editorial, “ Theory: the missing link in qualitative health care research articles ,” before deeming that focus too broad. As far back as 1967, Merton 6 warned that “the word theory threatens to become meaningless.” While it cannot be overstated that “atheoretical” studies lack the underlying logic that justifies researchers’ design choices, the word theory is so overused that it is difficult to understand what constitutes an adequate theoretical foundation and what to call it.
Theory, as used in the term theoretical foundation , refers to the existing body of knowledge. 7 , 8 The existing body of knowledge consists of more than formal theories , with their explanatory and predictive characteristics, so theory implies more than just theories . Box 1 9 – 12 defines the “building blocks of formal theories.” 9 Theorizing or theory-building starts with concepts at the most concrete, experiential level, becoming progressively more abstract until a higher-level theory is developed that explains the relationships between the building blocks. 9 Grand theories are broad, representing the most abstract level of theorizing. Middle-range and explanatory theories are progressively less abstract, more specific to particular phenomena or cases (middle-range) or variables (explanatory), and testable.
The Building Blocks of Formal Theories 9
The importance of research frameworks.
Researchers may draw on several elements to frame their research. Generally, a framework is regarded as “a set of ideas that you use when you are forming your decisions and judgements” 13 or “a system of rules, ideas, or beliefs that is used to plan or decide something.” 14 Research frameworks may consist of a single formal theory or part thereof, any combination of several theories or relevant constructs from different theories, models (as simplified representations of formal theories), concepts from the literature and researchers’ experiences.
Although Merriam 15 was of the view that every study has a framework, whether explicit or not, there are advantages to using an explicit framework. Research frameworks map “the territory being investigated,” 8 thus helping researchers to be explicit about what informed their research design, from developing research questions and choosing appropriate methods to data analysis and interpretation. Using a framework makes research findings more meaningful 12 and promotes generalizability by situating the study and interpreting data in more general terms than the study itself. 16
Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks
The variation in how the terms theoretical and conceptual frameworks are used may be confusing. Some researchers refer to only theoretical frameworks 17 , 18 or conceptual frameworks, 19 – 21 while others use the terms interchangeably. 7 Other researchers distinguish between the two. For example, Miles, Huberman & Saldana 8 see theoretical frameworks as based on formal theories and conceptual frameworks derived inductively from locally relevant concepts and variables, although they may include theoretical aspects. Conversely, some researchers believe that theoretical frameworks include formal theories and concepts. 18 Others argue that any differences between the two types of frameworks are semantic and, instead, emphasize using a research framework to provide coherence across the research questions, methods and interpretation of the results, irrespective of what that framework is called.
Like Ravitch and Riggan, 22 I regard conceptual frameworks (CFs) as the broader term. Including researchers’ perspectives and experiences in CFs provides valuable sources of originality. Novel perspectives guard against research repeating what has already been stated. 23 The term theoretical framework (TF) may be appropriate where formal published and identifiable theories or parts of such theories are used. 24 However, existing formal theories alone may not provide the current state of relevant concepts essential to understanding the motivation for and logic underlying a study. Some researchers may argue that relevant concepts may be covered in the literature review, but what is the point of literature reviews and prior findings unless authors connect them to the research questions and design? Indeed, Sutton & Straw 25 exclude literature reviews and lists of prior findings as an adequate foundation for a study, along with individual lists of variables or constructs (even when the constructs are defined), predictions or hypotheses, and diagrams that do not propose relationships. One or more of these aspects could be used in a research framework (eg, in a TF), and the literature review could (and should) focus on the theories or parts of theories (constructs), offer some critique of the theory and point out how they intend to use the theory. This would be more meaningful than merely describing the theory as the “background” to the study, without explicitly stating why and how it is being used. Similarly, a CF may include a discussion of the theories being used (basically, a TF) and a literature review of the current understanding of any relevant concepts that are not regarded as formal theory.
It may be helpful for authors to specify whether they are using a theoretical or a conceptual framework, but more importantly, authors should make explicit how they constructed and used their research framework. Some studies start with research frameworks of one type and end up with another type, 8 , 22 underscoring the need for authors to clarify the type of framework used and how it informed their research. Accepting the sheer complexity surrounding research frameworks and lamenting the difficulty of reducing the confusion around these terms, Box 2 26 – 31 and Box 3 offer examples highlighting the fundamental elements of theoretical and conceptual frameworks while acknowledging that they share a common purpose.
Examples of How Theoretical Frameworks May Be Used
Examples of how conceptual frameworks may be used, misconceptions about qualitative research.
Qualitative research’s “uneasy relationship with theory” 4 may be due to several misconceptions. One possible misconception is that qualitative research aims to build theory and thus does not need theoretical grounding. The reality is that all qualitative research methods, not just Grounded Theory studies focused on theory building, may lead to theory construction. 16 Similarly, all types of qualitative research, including Grounded Theory studies, should be guided by research frameworks. 16
Not using a research framework may also be due to misconceptions that qualitative research aims to understand people’s perspectives and experiences without examining them from a particular theoretical perspective or that theoretical foundations may influence researchers’ interpretations of participants’ meanings. In fact, in the same way that participants’ meanings vary, qualitative researchers’ interpretations (as opposed to descriptions) of participants’ meaning-making will differ. 32 , 33 Research frameworks thus provide a frame of reference for “making sense of the data.” 34
Studies informed by well-defined research frameworks can make a world of difference in alleviating misconceptions. Good qualitative reporting requires research frameworks that make explicit the combination of relevant theories, theoretical constructs and concepts that will permeate every aspect of the research. Irrespective of the term used, research frameworks are critical components of reporting not only qualitative but also all types of research.
Acknowledgments
In memory of Martie Sanders: supervisor, mentor, and colleague. My deepest gratitude for your unfailing support and guidance. I feel your loss.
Conflicts of Interest: None.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This review aims to synthesize a published set of evaluative criteria for good qualitative research. The aim is to shed light on existing standards for assessing the rigor of qualitative research encompassing a range of epistemological and ontological standpoints. Using a systematic search strategy, published journal articles that deliberate criteria for rigorous research were identified. Then ...
While many books and articles guide various qualitative research methods and analyses, there is currently no concise resource that explains and differentiates among the most common qualitative approaches. We believe novice qualitative researchers, students planning the design of a qualitative study or taking an introductory qualitative research course, and faculty teaching such courses can ...
Abstract. This paper aims to provide an overview of the use and assessment of qualitative research methods in the health sciences. Qualitative research can be defined as the study of the nature of phenomena and is especially appropriate for answering questions of why something is (not) observed, assessing complex multi-component interventions ...
The purpose of this article is to outline what a qualitative systematic review is and explore what it can contribute to our understanding of pain. A qualitative systematic review brings together research on a topic, systematically searching for research evidence from primary qualitative studies and drawing the findings together.
Current methodological issues in qualitative case study research. The future of qualitative research will be influenced and constructed by the way research is conducted, and by what is reviewed and published in academic journals (Morse, Citation 2011).If case study research is to further develop as a principal qualitative methodological approach, and make a valued contribution to the field of ...
Ethics in qualitative research goes beyond review boards' requirements to involve complex issues of confidentiality, reflexivity, and power. Over the past decade, readers of medical journals have gained skills in critically appraising studies to determine whether the results can be trusted and applied to their own practice settings.
Qualitative research involves the studied use and collection of a variety of empirical materials - case study, personal experience, introspective, life story, interview, observational, historical, interactional, and visual texts - that describe routine and problematic moments and meanings in individuals' lives.
Qualitative research is a type of research that explores and provides deeper insights into real-world problems. Instead of collecting numerical data points or intervene or introduce treatments just like in quantitative research, qualitative research helps generate hypotheses as well as further investigate and understand quantitative data.
The first review (Culver et al., Citation 2003) examined the publication of qualitative research across three sport psychology journals from 1990 to 1999 and found that 17.3% of all published articles were qualitative studies.
Qualitative research relies on nuanced judgements that require researcher reflexivity, yet reflexivity is often addressed superficially or overlooked completely during the research process. In this AMEE Guide, we define reflexivity as a set of continuous, collaborative, and multifaceted practices through which researchers self-consciously ...
Review. is multidisciplinary, we encourage authors to consult the debates and articles on qualitative research standards and transparency discussed in their own disciplinary associations and journals. Ethics . Papers should report if they received ethical approval from an Institutional Review Board (or similar body). We note that transparency ...
Qualitative research involves collecting and analyzing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio) to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. It can be used to gather in-depth insights into a problem or generate new ideas for research. Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research, which involves collecting and ...
Qualitative research is a type of research that explores and provides deeper insights into real-world problems.[1] Instead of collecting numerical data points or intervene or introduce treatments just like in quantitative research, qualitative research helps generate hypotheses as well as further investigate and understand quantitative data. Qualitative research gathers participants ...
American Journal of Qualitative Research (AJQR) is a quarterly peer-reviewed academic journal that publishes qualitative research articles from a number of social science disciplines such as psychology, health science, sociology, criminology, education, political science, and administrative studies.The journal is an international and interdisciplinary focus and greatly welcomes papers from all ...
The GRADE-CERQual (Confidence in the Evidence from Reviews of Qualitative research) was used to assess confidence in review findings. Sixty-eight studies were eligible and subjected to a sampling framework to ensure data richness. In total, 36 sampled studies contributed to the development of themes, sub-themes and review findings.
Qualitative codebooks, institutional review board (IRB) logs, and other study records were stored on a secure university server, with access limited to authorized study personnel. Adherence to Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research (COREQ) standards were maintained throughout the study and analysis . Data analysis
Qualitative research has ample possibilities within the arena of healthcare research. This article aims to inform healthcare professionals regarding qualitative research, its significance, and applicability in the field of healthcare. ... Review of the Literature. In quantitative research, the researchers do an extensive review of scientific ...
For qualitative analysis of the interviews, the research team first created a deductive codebook using the determinants of implementation behavior (DIB) framework (Huijg et al., Citation 2014), which queries 18 behavior-change factors thought to influence implementation behavior, based on the Theoretical Domains Framework (Atkins et al ...
Background Despite a long history of political discourse around refugee integration, it wasn't until 2016 that this issue emerged as a global political priority. Limited research has examined the evolution of policies of global actors around health service provision to refugees and how refugee integration into health systems came onto the global agenda. This study seeks to fill this gap ...
Thus, to capture a snapshot of the current state of qualitative research and qualitative data analysis practices in HRD, we conducted a review of Human Resource Development Quarterly (HRDQ) between 1990 and the current issue (Volume 33, Issue 3) in 2019 and identified 59 qualitative articles. The types of qualitative research included: 24 case ...
A UK-wide collaboration, a sub-group of the Trial Conduct Working Group in the MRC-NIHR Trial Methodology Research Partnership, was formed to collectively address these challenges. Members are drawn from disciplines including bioethics, qualitative research, trials methodology, healthcare professions, and social sciences.
In this article, we review some principles of the collection, analysis, and management of qualitative data to help pharmacists interested in doing research in their practice to continue their learning in this area. Qualitative research can help researchers to access the thoughts and feelings of research participants, which can enable ...
Introduction: The high acquisition rate of HIV infection among women in the United States is concerning. Despite the FDA approving the first pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) drug in 2012, PrEP utilization remains significantly lower among women. This literature review aims to analyze the current body of research concerning HIV PrEP usage among women in the US.
INTRODUCTION. Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses.1,2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results.3,4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the ...
Qualitative research provides valuable insights into health care interactions and decision-making processes - for example, why and how a clinician may ignore prevailing evidence and continue making clinical decisions the way they always have.1 The perception of qualitative health care research has improved since a 2016 article by Greenhalgh et al. highlighted the higher contributions and ...