57 Product Development Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
🏆 best product development topic ideas & essay examples, 👍 good essay topics on product development.
- Nike New Product Development: Strategy and Ideas | Nike Report Marketing strategy development This stage entails formulating a marketing strategy that will be used in the process of introducing the product to the market.
- McDonald’s Company: New Product-Menu Development One of the main factors that contributed to McDonald’s introducing the balanced lifestyle menus was the changing needs of the customers. We will write a custom essay specifically for you by our professional experts 808 writers online Learn More
- Sleep and Wake Pillow Product Development & Marketing Most producers of pillows ignore the fact that people have different sleeping styles hence the need to design a variety of pillow types to suit the needs for all.
- Unilever’s Product Development: Collaborative Innovation There is the possibility of the comprehensive use of the efforts of the project partners at the preproduction, production, and marketing stages, which contribute to the achievement of positive externalities due to the synergistic effect.
- New Food Product Development In most cases the food may be free of pathogens but if the environment of preparation is full of normal flora, the possibility of gross contamination of food may take place and this is the […]
- New Product Development: Smart Shopping Cart The ability of the Smart Shopping Cart to meet the customer’s shopping demands by quickening the checkout time will help the company retailing this product to be successful in the U.S.market.
- Foldable Fabric Trolley: Product Design and Development This phase finalize the lase stage of our project, in which it demonstrates the final product design, manufacturing plan and decision analysis, refer to Figure 2.
- The Process of Product Development Thus, it is necessary to evaluate the physical qualities and functions of the developing product according to their attractiveness for the target audience and possibilities of the company to produce the product of such a […]
- New Product Development of Nokia The process of developing a new product begins when a firm identifies the need to generate a new product line to meet the needs of the customers.
- Urban Outfitters: A “Niche” Product Development In the case of Urban Outfitters, they had come up with unique business but getting Patents and trademarks was an issue.”Niche” product is a unique product or service offered in the market as a sub-segment […]
- New Product Development (NDP) The paper also conducts interviews on customers and company employees about the reception of Google China’s new products with the aim of developing an understanding on the effectiveness of NPD practices of the company.
- IDEO Product Development Strategies and Procedures David Kelly took over the leadership of IDEO since he was the owner of the largest company among the three. The increased demand for the firm’s services also led to the establishment of design centers […]
- GE: Product and Process Development Headquartered in Boston, MA, GE is a giant digital industrial conglomerate dealing in a wide a range of products and services spanning from aircraft engines and parts, medical imaging, financing and power generation to industrial […]
- Ford Motors Company’s New Product Development Ford Motors will be introducing a new product in the UAE market that the company distinguishes to be one of the most innovative products in its car-making history.
- Drink-At-Home Inc.’s New Product Development Plan In the case of the Drink-At-Home, Inc.those factors are the possibility of the final product not corresponding to the developers’ conception and the possibility that the other companies develop a similar product faster.
- General Motors Product Development The success of General Motors is credited to its effective leadership. The leadership has helped General Motors to abolish bureaucracy and encourage innovation.
- Product Development Model In order for a product to be successful in the market, several factors have to be considered to ensure that the new product is capable of overcoming the competition that is present in the market.
- The New Product Development Process Customer involvement in the product or service development process is the interaction or collaboration between the users of the product or service and the employees of a company during the period of product development to […]
- Tourism Product Development Additionally, they can be accompanied by supplementary materials, in particular, brochures that can tell buyers more about the history of a specific tourist site.
- The Article Overview – Another Look at How Toyota Integrates Product Development The authors reveal the most effective strategies that can be used to improve the process of product development. One of the major findings of the article is that many of strategies used at Toyota can […]
- New Product Development Process The first stage of a product development process is the idea generation stage where new ideas regarding new products are generated by the research and development department. The market demand is very important for a […]
- Generation of Unique Idea as a Success of the New Product Development Process The success of the new product development process hinges upon the uniqueness of the ideas generated. This method focuses on the inadequacies of the organization’s product to come up with ideas for developing improved products.
- The Acme Toy Company’s New Product Development According to its structure, the toy can be in the form of some fantastic animal. Emphasis on uncovering the innovative capabilities of a product is vital when serving it to customers.
- Smart Glasses: The Product Development The second problem is the need to change the lenses in the glasses in case of changes in vision abilities. We will draw a picture of the challenges we need to solve with our product.
- Rapid Product Development Technology In the 21st century this is not the case because today, one of the major goals of businesses is cost-efficiency and the need to reduce time-to-market.
- New Product Development and Its Evaluation This means that a group of market researchers is developing a strategy to launch a new business product to satisfy customers’ demands and to keep its position in the market.
- Product Development: Nespresso Growth Strategies The major responsibility of Nespresso marketing is to deliver and maintain the highest possible standard of living, to see that products and services offered for sale are those desired by consumers, and to distribute them […]
- Saturn Corporation’s Product Development in 2005-06 The purpose of the research is to investigate the product development strategies of Saturn corporation during 2005-2006 and evaluate their impact on the company’s performance.
- Trends in the Product Development of Private Labels of Major Retailers It is necessary to mention, that there are numerous factors, that influence the following development of the product, and it relates not only to private labels but to every if it is not only the […]
- Social Value of New Product Development Activities The marketing mix models are concerned with either: The individual effect of a marketing decision variable and The levels of the marketing mix variables as their optimal effect on the target variable or profitability New […]
- Product Development, Branding, and Pricing Strategies Definitions The assigned topic deals with the importance of interconnectivity between the development of a product, it’s branding, and price, as well as possible tactics regarding its financial value.
- The Food Company New Product Development Group Furthermore, the significance of the project to the organization could be gauged from Gerry’s move to choose the most creative person within the company to head the new project.
- Social Networking Services and Product Development As regards our particular case, where we wish to harness the power of social networking for the benefit of the university community, a number of considerations must be taken into account.
- Soren Chemicals: Product Development Jen Moritz was the Marketing Manager for The Water Treatment Group of Companies. She was responsible for the development of chemicals for treating drinking water and for maintaining pools.
- Car Seat: New Product Development Built utilizing extensive tests in ergonomic design and safety standards the Ford Prish car seat utilizes a conjunction of safety foam, impact webbing, durable materials, and safety straps to ensure the protection of an infant […]
- Product Development Strategies and Their Advantages The issue is that it may not be an easy task to justify such expenses most of the time, and many enterprises prefer approaches that are more traditional.
- New Product Development in the Highly-Competitive Bread Market Comprehensive information about market style and dynamics by determines attractive for Hovis, feasible, and profitability in line with the aims and strategic objectives.
- Fireless Cooker Product Development The production team has done a great job and is in the process of acquiring inventory that will be needed for the purpose of product manufacturing.
- Microsoft’s Challenges in Office Product Development For Office 2000, the major challenge Microsoft had to bypass was the internet [1]. The milestone concept was a good idea for Microsoft to manage the design and development of office 2000 [1].
- Squeeze Ball Product Development and Marketing Thus, the findings of the market research were to generate insight on the prevailing gaps concerning the available products in the market with the aim of fostering the intellectual, social, and physical development among children.
- Autonomous Vehicles Product Development and Launch Software experts will be expected to identify the existing opportunities, challenges, and prospects that might dictate the future of the technology.
- Pharmaceutical Product Development Inc.’s McGinty-Moss Assessment It is significant for PPD, Inc to understand its culture since organizational culture is the internal constitute of the institution. It is significant to know both the weaknesses and strengths of the organization to understand […]
- Tata Nano Company’ New Product Development In order to enhance the purchasing process, the organization will need to consider the promotion campaign, which will ensure the target Indian population in the safety of the car and the reasonability of the purchase.
- Globalization in the New Product Development Context However, the impact of the corporate entrepreneurship on the development a new products or services is still not quite obvious, and the effects of the new approach are yet to be seen.
- The Concept of Product Development The main objective will be examination of the effect of new product development processes to the Organization’s performance and general attitude towards the use of ‘Natures’ energy drink within the market environment.
- The Approaches and Methodologies of New Product Development The primary sources of data will include members of the product team, the marketing and sales managers, the manufacturing and production managers and the other employees who were involved in the new product development process.
- New Product Development: Stew Leonard’s In order to improve the ability of the new product to provide customers with the needed energy within a short duration after consumption, it is imperative for the firm to ensure that the snack product […]
- New Product Development Process at the Harmonium Media According to the trends observable in established organizations, new product development is usually the initial phase as far as generation as well as the commercialization of new products within an aggregate strategic process with regard […]
- Challenges in the New Product Development One of the ways through which the product development manager can achieve this is by ensuring participation of the various functional teams in the formulation of policies, procedures and the practices to be adopted in […]
- SmartBizSystems: New Product Development Concept In order to develop a recommendation that would help SmartBizSystems to be able to market their products, one must be able to understand the skills that are employed by the company in a bid to […]
- Textile Product Development and Engineering One of the major uses of cotton material is the production of clothing materials and one of the significant features of a good clothing material is lightness that in most cases is determined by the […]
- The Product and Service Development Process This makes it relatively easy to get increased input and active involvement of consumers in the product and service development process.
- Consumer Research in the Early Stages of New Product Development The researchers suggest that the lack of attention to this step can be due to the lack of the knowledge of effective methodology.
- Portfolio Management for New Product Development The major goals of the present study are as follows: to define the role of portfolio management, to point out the most popular techniques and define which of these dominate, to describe the portfolio methods […]
- Product Development Management For any manufacturing industry to make any meaningful success in the competitive market, proper management of the new product development process, is a must to ensure the correct products are rolled to the market at […]
- Collabo: Product Development This is meant to cover the cost of the features and the profit margins so that the firm can be efficient in its operations.
- The Process of the New Product Development Market testing and beta testing In this stage, the company will have to test the product in the market and make the necessary adjustments in relation to customer needs and expectations.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, March 2). 57 Product Development Essay Topic Ideas & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/product-development-essay-topics/
"57 Product Development Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." IvyPanda , 2 Mar. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/product-development-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '57 Product Development Essay Topic Ideas & Examples'. 2 March.
IvyPanda . 2024. "57 Product Development Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/product-development-essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "57 Product Development Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/product-development-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "57 Product Development Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/product-development-essay-topics/.
- Product Management Ideas
- Marketing Management Essay Ideas
- Software Engineering Topics
- Manufacturing Essay Topics
- Market Segmentation Titles
- Operations Management Essay Titles
- Technology Essay Ideas
- Agile Project Management Research Topics
- Operations Strategy Titles
- Consumerism Topics
- Research and Development Essay Topics
- Promotion Strategy Paper Topics
- Competitive Strategy Research Ideas
- Innovation Titles
- Private Equity Research Ideas
- Browse All Articles
- Newsletter Sign-Up

ProductDevelopment →
No results found in working knowledge.
- Were any results found in one of the other content buckets on the left?
- Try removing some search filters.
- Use different search filters.
A practical guide to product development research
Understanding your target customers' needs and behaviours is a crucial step in the new product development process. Here we explore product development research and how it can give your brand the direction is needs.
What is product development research?
Why is product development research important, stages of product development research, types of product development testing.
Product development research is the process of finding out how the product or feature you’re currently working on is progressing, whether there are any changes in your target audience’s needs and whether you need to make any adjustments to the product.
Depending on where you are in your product’s life cycle will dictate the kind of product development research you do and how it might impact your overall product development process.
In your product research process you can find out things like what features customers might be willing to pay more for, or figuring out how you can increase customer loyalty. And you might want to investigate a decline in interest or sales to make sure your product maintains success.
Whatever stage your product development is at, you’ll definitely want to keep track of its progress and stay on top of any emerging trends that might affect your product life cycle. You can do all of this with research into your product development.
It’s vital for businesses to develop products that fulfil the needs and desires of customers. This is what will keep customers happy and loyal, and it’ll ensure that the business’s products remain successful, and, better still, become even more successful.
Gauging market demand through product development research – easily done with platforms like Attest – is a surefire way to get to the root of what consumers want, allowing you to offer them truly useful and desirable products.
Surveying your target audience throughout your product development process, from its initial stages through to its final stage, launch and future iterations, is key to staying on top of trends and changes in customer needs.
Your marketing research and exploratory research should reveal the insights you need to continue reaching and satisfying your target customers. You’ll hear opinions directly from your customers, meaning that the products you go on to develop will be made for and with your customers.
Launch your product development research
Attest’s advanced market research platform and quick turnaround of survey results help you take the guesswork out of product development.

There are a few key stages of the product development research process that you should know about to make sure you create successful products that are right for your customers.
Take a look at our intro to the new product development market research (NPD) process, summarising the 9 key steps to explore throughout your project:
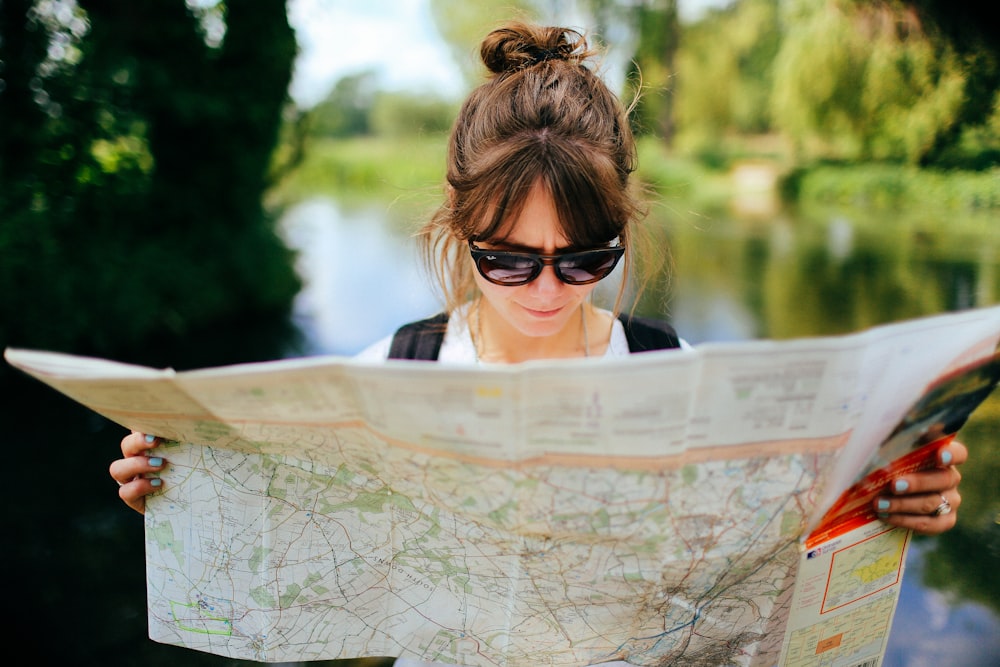
Exploratory
Exploratory research is what usually happens at the earliest stage of the new product development process.
During this stage you might not necessarily know what your outcome will be, what your product will look like, how exactly it’ll address potential customers’ needs and ensure customer satisfaction. This is when you’ll explore these areas and more to find out what direction you’ll take with your new products.
At the exploratory stage, market researchers will delve into data around consumers, their pain points and their general product usage, usually working closely with the Product team to make sure these insights are reflected in the product roadmap.
Once ideas about products and features have been developed during the exploratory stage, many companies then take an even deeper look into issues and topics that emerged in the previous stage.
Ideas you might have had earlier on in the product development process will be scrutinised here to help you understand the value of your offering to your potential customers.
Iterative development
Later in the product life cycle process is when you’ll carry out iterative development research. At this stage you’ll analyse and refine your product and its features to make sure the final product you provide to your customers is comprehensive and eliminates their pain points.
Iterative market research can be intricate and involve in-depth analysis of seemingly insignificant features. Things like A/B testing can be done at this stage – that might be testing different versions of a website button or packaging design.

There are a range of product research types that businesses typically explore when they’re defining customer preferences and prepping their potential product for the marketplace.
Each of these types of product development testing cover the spectrum of new product research, all the way from concept testing to post-launch satisfaction and ongoing success. And these testing types can be done in many different ways, ranging from small, intimate, mainly qualitative market research and focus groups to large, mainly quantitative surveys. Let’s get right into the different types of product development testing.
Concept testing
There’s absolutely no point in launching a product without being confident that the idea will resonate with consumers, and will ultimately be a success.
That’s why, right at the beginning of the new product life cycle you should carry out concept testing . This is where you’ll figure out, through extensive research, whether that product or feature you’ve been mulling over will actually give people what they’re looking for- by appealing to consumer preferences .
Concept testing can involve testing anything from brand assets like a new logo or website page to commercial features like the pricing structure, or even as a way to uncover a new customer segment.
Gain confidence in your concepts
Test your concepts with Attest’s quality audiences to help you launch successful products.
User experience research
It’s crucial for marketing, product, insights and innovation professionals to have a full understanding of how an end user interacts with the product or service on a functional level. Are customers able to navigate around the website or platform easily? Or open the physical product quickly? How do they feel as they interact with the product? How easy is it for them to complete their ultimate task?
These are the kinds of questions you should hope to answer through your user experience testing.
It’s super important at this stage to enlist real consumers who might be interested in your product. Even if the users uncover issues with your product or don’t immediately fall in love with it, that’s fine – what matters is that it’s useful insight directly from the people your product is targeted at.
Pricing research
Knowing where to price your product is a battle all companies face at some point. You need your brand to offer a quality product at a price that’s cost effective and competes with other market leaders, but you don’t want your price to be so high that people buy elsewhere, or so low that you miss out on revenue.
Through pricing research you’ll find out what your target customers are willing to pay for what you offer, allowing you to find the sweet spot – the price at which you can maximise revenue, profit and market share.
This is also the perfect time for you to find out if it’s worth your while to offer your customers any discounts, and if so, where in their journey these are most likely to be effective.

Market and competitor research
While it’s obviously super important to carry out research into your own product and offering, don’t forget to stay on top of what’s going on in your industry.
Conducting market and competitor research is vital if you want to offer your potential customers an industry-beating product.
And remember to iterate on your market and competitor research – repeat and build on your research to make sure you have a full understanding of industry trends and so you can identify new ones.
Satisfaction and loyalty research
And your product development research doesn’t end once your product’s out there in the market. Are your customers truly satisfied with your offering? Are you giving them reasons to be loyal to your brand?
It’s a mistake to assume that your customers are satisfied just because they chose to buy from your company. It’s vital that you continue assessing your customers’ happiness and desires, and to make sure you’re on top of any unmet needs.

We hope this practical guide to product development research has been useful for you, and that you can take this insight and continue developing concepts and products that wow your customers.
Always-on, iterative market research is a key way for you to discover ways you can enhance your product offering and make sure you leave customers satisfied with and loyal to your brand.
Create products that your customers really want
Gauge market demand and understand consumer preferences to create the best possible product by running NPD research with Attest.

Elliot Barnard
Customer Research Lead
Elliot joined Attest in 2019 and has dedicated his career to working with brands carrying out market research. At Attest Elliot takes a leading role in the Customer Research Team, to support customers as they uncover insights and new areas for growth.
Related articles
People want to shop green – what can brands and retailers do to help them, sustainability, why do uk consumers love neobanks, how close is the uk to becoming a cashless society, subscribe to our newsletter.
Fill in your email and we’ll drop fresh insights and events info into your inbox each week.
* I agree to receive communications from Attest. Privacy Policy .
You're now subscribed to our mailing list to receive exciting news, reports, and other updates!
Top Marketing Research Articles Related to Product Development Research
Learn all about new product development research. Quirks.com is the largest source of marketing research information.
Search Results
More Filters
Loading filters...
Article How to conduct an effective concept test: The process, methods and benefits Josh White | April 3, 2024
Article In Case You Missed It...March/April 2024 Quirk's Staff | March 1, 2024
Article Discovering the real story: How virtual IHUTs offer deeper insights Krystal Rudyk | February 7, 2024
Article UX ResearchOps: Five ways to boost research efforts Paul Hagen | February 6, 2024
Article User experience research: The top trends and best practices Alida Staff | January 19, 2024
Article In Case You Missed It...January/February 2024 Quirk's Staff | January 1, 2024
Article Product discovery: What it is and best practices UserTesting Staff | January 16, 2024
Article How to conduct a win-loss analysis Nick Kane | December 22, 2023
Article Before You Go: 10 minutes with Marat Fleytlikh, Kraft Heinz Emily C. Koenig | November 1, 2023
Article Wilton Brands strategy for great insights and analytics teamwork Maddie Swenson | October 30, 2023
Article Usage and attitude studies: What are they and how to conduct them Chloe Cook | August 14, 2023
Article Bringing Spruce Cowffee to market Elliot Savitzky, Hannah Robbins | July 1, 2023
Sponsored Article 21 Top Taste Test/Sensory Research Companies Quirk's Staff | July 1, 2023
Article Using innovation testing to create a successful product David Whitelam | June 29, 2023
Article Consumer habits are changing. Are streaming platforms ready? John Conti | April 19, 2023
Advisory boards aren’t only for executives. Join the LogRocket Content Advisory Board today →

- Product Management
- Solve User-Reported Issues
- Find Issues Faster
- Optimize Conversion and Adoption
Research and development (R&D) and the product lifecycle

Imagine a young boy searching through the December edition of Intertoys , the Dutch version of the Toys-R-Us magazine. The magazine has over 150 toys, including molding clay, step bikes, board games, M.A.S.K and G.I Joe action figures, Transformers, ThunderCats, and tons more.

His eyes are focused on the pages dedicated to LEGO. The boy finds himself overcome with joy, thinking about all the possibilities to expand his LEGO city. Will he ask for the police station, the gas station, or maybe the medieval castle? He tries to imagine how each enhances his city and the additional stories they can bring.
This young boy was me back in 1986.
LEGO delivered on its mission to inspire and develop the builders of tomorrow. How do I know that to be true? Well, here I am as a product leader who is curious and enjoys experimenting and trying new ways to devise, innovate, and to meet and exceed customer needs.
LEGO is a prime example of a company that recognizes the value of being customer-obsessed, researching, observing, experimenting, and trying over and over again to build what excites and inspires generations to come. It truly harnesses the power of research and development (R&D).
In this guide, we’ll explore what R&D is, the different types of R&D, and how it can inform product development. We’ll also show you how research and development influence go-to-market and help determine whether a launch is successful.
What is research and development (R&D)?
Research and development (R&D) refers to activities and investments directed toward creating new products, improving existing products, streamlining processes, and pursuing knowledge.
The main purpose of R&D is to promote innovation and, in doing so, drive growth and increase competitiveness. Additionally, by improving processes and finding efficiency gains, R&D can lead to cost savings.
In some industries, R&D is necessary for regulatory compliance and to maintain or improve product quality.
R&D example
For an example of how R&D can impact a company’s growth, let’s look a LEGO’s research and development process.

Over 200k developers and product managers use LogRocket to create better digital experiences
LEGO works to create new building block shapes and designs and endeavors to improve their performance and safety on an ongoing basis. One of LEGO’s primary R&D efforts aims at developing sustainable production methods.
In 2015, the company invested nearly $150 million into sustainable materials R&D . It’s important to its mission to leave a positive impact on the planet for future generations to inherit.
We’ll refer to the LEGO examples throughout this guide to show what research and development efforts look like in the real world.
Research and development (R&D) vs. product development
It’s tempting to say that R&D and product development are one and the same, but while they overlap, not all product development is R&D.
To qualify as true, authentic, and real R&D, an activity must meet specific criteria that make it SUPA (yes, I just created that acronym).
SUPA stands for:
- Systematic — R&D must follow a systematic approach to solving problems or creating new products
- Advancement — R&D must involve either the creation of new knowledge, a significant improvement to existing knowledge, or a significant advancement in overall understanding
- Purpose — R&D must have the primary purpose of creating new knowledge, improving existing products radically, or creating new ones
- Uncertainty — There must be an element of uncertainty or risk involved in the work. This means you can’t always anticipate the outcome with confidence
As a product manager, most of the above should be familiar. As Marvin Gaye would have said, R&D and product management work together just like music .
R&D and the product development lifecycle
Research provides you with the necessary information and insights to inform and guide your product design. Development helps you bring ideas to life, validate them and then build and commercialize them.
The product development lifecycle is as follows:
- Ideation and concept development
- Design and prototyping
- Development
- Launch and commercialization
Let’s zoom in on each stage to see how R&D plays a role in every aspect of product development.
1. Research
The research phase involves systematically gathering market data, understanding the competitive landscape, and assessing customers in their current use of your product and their unmet needs. R&D helps you find the next big thing or game changer that gains you more market share.
2. Ideation and concept development
This step focuses on generating new ideas and concepts that push the boundaries of what you know. It requires looking at new ideas at a high-level and evaluating their potential feasibility.
3. Design and prototyping
Dip your toes further into the development waters — but make sure not to step on a LEGO while doing so.
The design and prototyping stage is where you create your hypothesis, conduct experiments, create designs, and prototype solutions to validate the assumptions made.
4. Development
During the development stage, any prototypes that fail to deliver advancements are abandoned. Those passing the validation are ready for development consideration.
5. Launch and commercialization
The activities described above will aid in making informed decisions about the product launch , pricing , and go-to-market strategy .
Example: How does R&D influence go-to-market?
Let’s refer back to our example:
LEGO was hugely successful through R&D when bringing the LEGO Mindstorms line to market.
This line empowers users to build and program robots using LEGO bricks and a microcomputer. The creation of the product line involved a multidisciplinary approach. It combined expertise in product design, software engineering, and electronics.
The R&D process started with research that identified the need for a product that allowed users to experiment with and learn about robotics.
LEGO then went through intensive ideation iterations and decided to work with experts in the field to design a system that would be easy to use and accessible to people of all ages and skill levels.
The design and prototypes were thoroughly tested and proved to validate assumptions .
The resulting product was a great success.
3 types of R&D
There are several types of research and development that you can pursue. Each type requires different approaches, resources, expertise, and generates different outcomes.
You can choose to focus on one or more R&D types, depending on your strategic objectives, resources, and capabilities.
Let’s have a look at the three major types of R&D:
Basic research
Applied research, experimental development.
Basic research aims to increase knowledge and understanding of a particular subject, with no immediate application in mind.
LEGO continuously explores new methods for connecting building blocks to each other. This research could involve looking into new materials or design principles that could improve the strength and stability of the connections between the blocks.
Applied research focuses on solving specific practical problems and developing new or improved processes, services, or products.
To reduce its carbon footprint, LEGO is researching a new plant-based plastic for its building blocks. This new material, made from sugarcane, replaces traditional petroleum-based plastic.
Experiment research involves designing, building, and testing a prototype to evaluate the feasibility and potential of new processes, services, or products.
LEGO is developing building sets that incorporate augmented reality (AR) technology. The R&D effort combines applied research with experimental development, as the company seeks to create a new product that utilizes AR to enhance the building and play experience.
How to incorporate R&D into the product development process
So you want to incorporate R&D into your product development process. Kudos to you!
Practice makes perfect. Before looking at a few ways to do this, it is important to remember that incorporating R&D into your product development process is a continuous endeavor and requires adjustments along the way.
The following strategies will help you incorporate R&D:
Prioritize R&D
Foster a culture of innovation.
- Embrace experimentation
Build user-centered
Collaborate with external partners.
The obvious one here is to ensure that R&D is a priority within your company and resources are freed up. This could include dedicating a portion of the budget, allocating capacity, or setting aside dedicated R&D time.
Encourage a culture in your company that values and supports innovation, experimentation, and risk-taking. It could include encouraging employees to pursue their own interests and providing them with the resources to do so.
Embrace experimentation, prototyping, and testing
R&D-ers love experimenting and testing their assumptions through building hypotheses, prototyping, and testing. It allows you to validate ideas, refine designs, identify and address any issues or limitations before bringing a product to market. As a product manager, you probably already have incorporated some of these practices. If not, I highly encourage you to do so.
To find an opportunity you will need to discover and unravel a need. User-centered building helps ensure that products and services are designed with the end-user in mind, leading to better, more effective problem-solving, and solutions to meet the needs of the people who will be using them.
Consider partnering with external organizations, such as universities, research institutes, or other companies, to help drive R&D. This can provide access to additional resources, expertise, and perspectives.
Example: How does R&D influence product development?
Referring back back to our example:
LEGO places a strong emphasis on user-centered design. It conducts user research to understand their needs, preferences, and behaviors and incorporate those findings into product design and development.
LEGO also collaborates with a variety of external partners, including universities, research institutions, and other companies, to drive innovation and R&D. For example, it has worked with the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) on several projects.
LEGO uses rapid prototyping and testing to iterate and improve its products and encourage employees to be creative and innovative. It does this through the LEGO IDEAS program, which provides a platform for employees to submit and vote on new product ideas.
How to analyze and interpret the results of R&D
It goes without saying that analyzing and interpreting the results of research and development is crucial. How else will you validate or disprove hypotheses, determine the success or failure, and inform future R&D decisions?
Here are some steps that will help you out:
- Define the objectives and hypothesis
- Gather and organize data
- Analyze the data
- Interpret the results
- Validate the results
- Communicate the results
- Use the results to inform future R&D decisions
1. Define the objectives and hypothesis
When you want to analyze results, it’s crucial to have a clear understanding of what you set out to achieve and what you expected to see.
2. Gather and organize data
Collect all relevant data and organize it in a way that allows for easy analysis and interpretation.
3. Analyze the data
Use appropriate statistical methods to analyze the data, such as hypothesis testing, regression analysis, or analysis of variance (ANOVA).
4. Interpret the results
Based on the analysis, interpret the results and draw meaningful conclusions. This may involve identifying patterns, correlations, or relationships between variables.
5. Validate the results
Validate the results by checking for consistency, accuracy, and reliability. It may also be necessary to perform additional tests or experiments to confirm or refute the results.
6. Communicate the results
Communicate the results of the R&D project to stakeholders, including management, investors, customers, and employees. This may involve presenting data, charts, graphs, or other visual representations of the results.
7. Use the results to inform future R&D decisions
Use the results of the R&D project to inform future R&D decisions, including what to research next, what to improve, and what to commercialize.
Proper analysis and interpretation of R&D results are crucial to make informed decisions and drive innovation and growth.
There are various strategies you can implement in your product process. It is key to define your objective and expected results and have a structured process to validate R&D success.
Featured image source: IconScout
LogRocket generates product insights that lead to meaningful action
Get your teams on the same page — try LogRocket today.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- #market analysis

Stop guessing about your digital experience with LogRocket
Recent posts:.

Leader Spotlight: The impact of macroeconomic trends on product roles, with Lori Edwards
Lori Edwards, Director of Product at Niche, discusses challenges with the transition from an individual contributor to a people manager.

Techniques for building rapport in professional settings
Effective rapport fosters trust, facilitates communication, and creates a foundation for successful collaboration and conflict resolution.

Embracing product-led growth: Principles, strategies, and metrics
The core of PLG relies on reducing time to value and relentlessly improving the user experience by creating multiple a-ha moments.

Leader Spotlight: The digital transformation of beauty school curriculum, with Corina Santoro
Corina Santoro talks about how her team made the prediction that customers in the beauty school industry are going to prefer digital learning.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
- Data, AI, & Machine Learning
- Managing Technology
- Social Responsibility
- Workplace, Teams, & Culture
- AI & Machine Learning
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Big ideas Research Projects
- Artificial Intelligence and Business Strategy
- Responsible AI
- Future of the Workforce
- Future of Leadership
- All Research Projects
- AI in Action
- Most Popular
- The Truth Behind the Nursing Crisis
- Work/23: The Big Shift
- Coaching for the Future-Forward Leader
- Measuring Culture

The spring 2024 issue’s special report looks at how to take advantage of market opportunities in the digital space, and provides advice on building culture and friendships at work; maximizing the benefits of LLMs, corporate venture capital initiatives, and innovation contests; and scaling automation and digital health platform.
- Past Issues
- Upcoming Events
- Video Archive
- Me, Myself, and AI
- Three Big Points

New Product Development
Serve more customers with inclusive product design.
Leaders can promote more inclusive product design by asking a simple set of questions about potential target markets.
Vanessa M. Patrick and Jeffrey D. Shulman
Collaboration, solving real user problems with generative ai: slack’s jackie rocca.
On the Me, Myself, and AI podcast, Jackie Rocca explains how Slack uses artificial intelligence to relieve user pain points.
Sam Ransbotham and Shervin Khodabandeh
Driving manufacturing efficiency with ai: pirelli’s daniele petecchi.
On the Me, Myself, and AI podcast, Daniele Petecchi discusses how Pirelli uses AI to develop tires more efficiently.
Making Magic With Gen AI: Capital One’s Prem Natarajan
On the Me, Myself, and AI podcast, Capital One’s Prem Natarajan explains AI’s role in enhancing the customer experience.
Digital Marketing
Micro utility with gen ai: shopify’s miqdad jaffer.
On the Me, Myself, and AI podcast, Miqdad Jaffer explains how Shopify is using generative AI to empower entrepreneurs.
Sustainability
R&d leaders must play a key role in the journey to net zero.
Executives who lead research and innovation are well placed to help their companies cut greenhouse gas emissions.
Dan Edwards and Michael Zeitlyn
Entrepreneurial ai in the enterprise: lg nova’s shilpa prasad.
On the Me, Myself, and AI podcast, LG Nova entrepreneur in residence Shilpa Prasad discusses startups innovating with AI.
Fueling Interdisciplinary Innovation With AI: Volvo’s Anders Sjögren
On the Me, Myself, and AI podcast, Volvo’s Anders Sjögren explains artificial intelligence’s use in car manufacturing.
AI & Machine Learning
Sound business: the promise of audio machine learning technologies.
Emerging machine learning technology could enhance sound creation and the detection and analysis of acoustic signals.
Innovation Strategy
Lego takes customers’ innovations further.
New research shows how companies can advance open innovation by integrating customers’ ideas into product development.
Michela Beretta, Linus Dahlander, Lars Frederiksen, and Arne Thomas
Images and inspiration with ai: pinterest’s jeremy king.
On the Me, Myself, and AI podcast, Pinterest’s Jeremy King discusses the technology behind the image-based platform.
Skills & Learning
Learning from and with ai: duolingo’s zan gilani.
On the Me, Myself, and AI podcast, Duolingo’s Zan Gilani shares how AI personalizes the language app and motivates users.
The Social Science of AI: Intel’s Elizabeth Anne Watkins
On the Me, Myself, and AI podcast, learn how social scientists help facilitate human-machine collaboration at Intel.
Technology Innovation Strategy
The incumbent’s deep tech strategy playbook.
The authors created a three-step framework aimed at helping leaders at incumbent companies identify and execute their deep-tech engagement strategies.
François Candelon, Vinit Patel, Max Männig, and John Paschkewitz
Mix creativity with the right mindset to serve up innovation.
Research finds fear of failure could keep an innovator from launching a new creative endeavor after an early success.
Dirk Deichmann and Markus Baer
The missing discipline behind failure to scale.
Many companies master new business ideation and incubation, but few follow a rigorous scaling path.
Andy Binns and Christine Griffin
Out of the lab and into a product: microsoft’s eric boyd.
On the Me, Myself, and AI podcast, Microsoft’s Eric Boyd discusses Azure and democratizing artificial intelligence.
Helping Doctors Make Better Decisions With Data: UC Berkeley’s Ziad Obermeyer
UC Berkeley’s Ziad Obermeyer discusses how machine learning and AI are being used for medical research and diagnoses.
Level Up to Strategic Data Sharing
Based on their research, the authors share four key ways companies can advance their strategic data-sharing initiatives.
Barbara H. Wixom, Ina M. Sebastian, Robert W. Gregory, and Gabriele Piccoli
Why businesses need to embrace the bioeconomy.
Developing products using materials from biological sources can yield more sustainable business models.
Donna Marshall, Aideen O’Dochartaigh, Andrea Prothero, Orlagh Reynolds, and Enrico Secchi
New Product Development Research: What It Is, Stages, and Examples

Are you thinking of bringing a new product to the market this year? Congratulations, yours will be one of more than 30,000 new entries! We’re going to help you stand out.
Yes, there are indeed that many new products being introduced to the market every year, according to Harvard Business School . However, it is estimated that an overwhelming majority of them fail.
“Many new products fail because their creators use an ineffective market segmentation mechanism. It’s time for companies to look at products the way customers do: as a way to get a job done.” – Harvard Business School.
Still want to launch? Have you rigorously tested your concept, developed a plan to turn it into a business, designed the product, and created a sound strategy for market entry?
And those are just four of the seven boxes you need to check if you really want your product to succeed. But don’t panic. If you conduct new product development research, you will gain the necessary consumer and market intelligence to make it among the few new products that survive and keep on thriving.
What Is New Product Development Research?
New product development is the process of bringing a new product to the market! And to do that, businesses conduct ongoing market research throughout the process to ensure they are creating a product based on intelligence rather than intuition. This is key.
So, market research tailored specifically to the success of a new product in the market is what is referred to as new product development research. It comprises primary and secondary, qualitative and quantitative research methods used in other forms of market research––but the difference is in the goals.
When you understand the role of new product development research, you will appreciate the process more and hopefully incorporate it in your current or future projects.
The Role of Research at Different Stages of Product Development
Net Solutions has laid out a beautiful illustration of the product development process . It is broken down into seven stages; but keep in mind that product development is an ongoing process throughout the life cycle of the product or service. Iteration happens even when the product in question isn’t broken.
While Net Solutions’ tutorial is focused on tech product development, we are going to use the steps to show you the role of new product development research in the process for any type of product.
1. Idea generation
Good business ideas come with a solution to an existing problem or a way to improve the way things are done. There are many sources for good ideas starting with personal struggles, anecdotal information, access to relevant data, and concerted efforts in research and development.
When organizations need to come up with fresh ideas, a deliberate effort must be made. Since investing in research and development is out of reach for most businesses, brainstorming and new product market research is the surest path.
An organization’s proprietary, CRM, sales, and operation data – internal secondary research – may reveal previously hidden opportunities behind customer feedback or employee experiences at work.

While this often helps with the improvement of the current product, it sometimes leads to the development of entirely new products. Productivity apps are often created this way.
Ideas may also come from qualitative and quantitative research through surveys, interviews, and direct observation. This is a good approach for people starting out in business when they don’t have access to sufficient volumes of internal data.
Thirdly, ideas may be generated by analyzing consumer conversations and news media data on social media, review sites, and discussion forums through advanced techniques such as web scraping, social listening, and sentiment analysis. This way, potential markets are identified based on themes in natural consumer conversations and trends.
2. Idea screening
The first step is essential to exploring the open avenues, but it is not enough to determine the viability of any single idea. The second stage is idea screening where the feasibility of the idea as a business opportunity is determined.
Through new product development research, the organization can pick one idea to pursue – you don’t want to implement multiple ideas at a go. The SWOT analysis is a great way to screen ideas by comparing them to the market and to each other.
The strengths of an idea are the internal attributes that make it viable. If it solves an obvious problem, then the product or service will face less difficulty during market entry. Even better is if it can be developed easily and cheaply, which makes it more affordable.
An idea may require a large initial capital investment, or the end product may depend on third parties. These internal attributes are weaknesses which make it less viable.
Opportunities around an idea may be other verticals to where it may be extended into other categories adjacent to the brand. Or there might be added benefits that weren’t previously considered. For instance, an ecommerce store may collect customer data that can be shared with the producers to improve their businesses.
Threats to the idea include competition, high market regulation, and security risks.
New product development research can help answer such questions in the SWOT analysis through consumer data as well as the study of market factors such as production costs and distribution channels.
3. Concept development
Concept development is about developing the idea to a point that it can be successfully explained to a potential customer i.e. they can buy into it. Starting at this stage, the new product development research focuses on the one idea that made it through the screening stage.
One on one interactions with target consumers can help the brand better understand the product from the user’s perspective. For instance, it can help study the balance between what the consumer gains and the tradeoff in using the product.
A modern consumer intelligence platform can help study trends and consumer expectations to create a compelling value proposition.
With an advanced market intelligence platform, the brand can understand the target market in terms of the existing competition and potential allies. The platform can also deploy its social listening antennas to find out the strengths and weaknesses of the competing products through consumer conversations and feedback.
The data gathered is analyzed and the insights used to improve the concept before proceeding to build a business on it.
4. Business analysis
After proof of concept is established, the business framework should be created before going any further with the development of the product itself. This includes how to market, price, and deliver the product.
New product development research can be used to compare the different marketing avenues available to the brand (based on budget and target audience). Social listening can help study the voice of the customer and the insights used to craft marketing messages in a way that appeals to the audience.
Other than the cost of production, other factors may influence the price of the product. Brands use secondary research to determine their pricing model through benchmarking. Modern methods such as sentiment analysis can help understand how consumers feel about the current prices, bringing in a third factor.
Delivering the product here refers to how the buyer obtains value from your product or service. Through focus groups, the brand can get a closer look at how consumers perceive the concept before it is developed into a product.

5. Product development
With a business plan on hand, the creator can proceed to make a prototype and a minimum viable product (MVP). These processes require both internal and external data.
A prototype is simply a visualized concept. It is important in cases where the creator needs the help of others such as VCs and talent to develop the product. For both virtual and physical products, as well as services, research may involve methods such as observation and use of existing products and interviews with experts.
An MVP is a step above prototype because it works. It does the most basic set of functions the product is designed to do. Testing data – internal secondary research – is invaluable during the improvement of the MVP into a product that’s ready to launch.
6. Product launch
The product launch is probably the most crucial stage in the new product development process. Products that don’t hit their targets at launch rarely recover. On the other hand, those that succeed at launch are likely to maintain their trajectory.
As such, new product development research is critical to understanding consumer motivations, timing the launch, and communicating effectively with the target.
Understanding consumer motivations for seeking such a solution as you have will help build anticipation for the launch. Surveys can be used to get direct feedback about individual struggles of the target consumers while social listening can be used to listen in as they share their experiences with each other.
Social listening can also reveal the trends and mood of the target consumers in order to launch the product under the most auspicious circumstances.
7. Market entry
Post launch, the new business is primarily focused on building a reputable image i.e. brand development. This means promoting the product and fostering a good relationship with the customers.
Consumer research helps understand how buyers are using the product to solve their problems. This feedback may be shared directly through email, social media DMs and comments, or business websites. It can also be expressed indirectly through social media posts, external review sites, and forums.
Capturing consumer data through CRM software is the first step to building a strong relationship with the customers. Analysis of the data over time provides useful intelligence upon which to base strategic decisions.
New Product Development Research Example
New product development research should be conducted across all industries, not just tech products. And not just for products but for services too.
For instance, a major beverage manufacturer recently used NetBase Quid ® to look into the cannabis-infused beverage trend. They think that it is an area of interest and although they are not making any decisions yet on entering the market, they still want to know what’s going on.
The idea came to them after having noticed a growth in news coverage on the subject. This was their idea generation stage.
So, they used NetBase Quid ® to look into it to see who was driving the conversation and determine whether it was a solid trend or passing fad. If it turned out to be a trend, this would be a legit signal for an emerging market opportunity for them. This is idea screening.
They went further into the analysis to see how consumers were using cannabis. For instance, were they using it with or in beverages; what kinds of beverages; and were there any preferred brands and why? Concept development has taken shape and this is where they currently are.
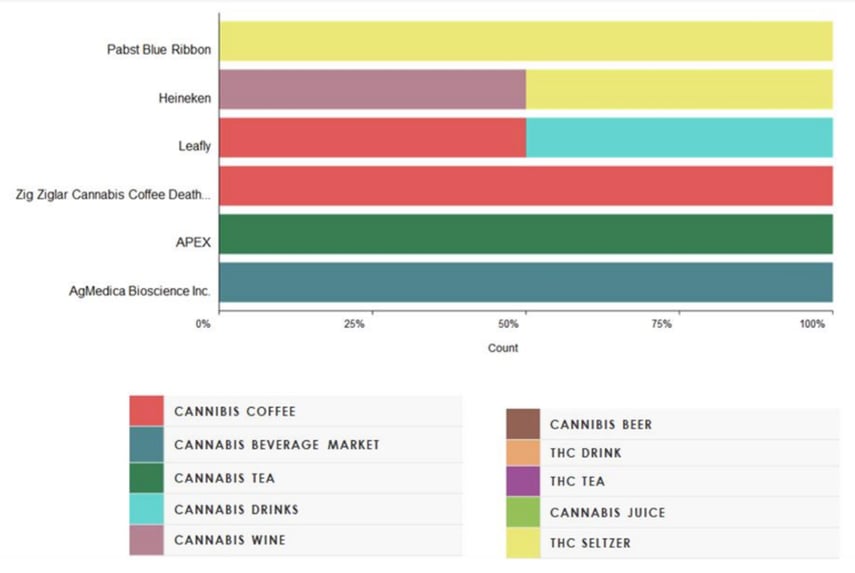
Cannabis-infused beverages.
The business analysis stage shouldn’t be too complicated for them as they are already manufacturing beverages. Through concept development, they will have determined the best way to introduce cannabis beverages to the target market.
Through product development, they would use the insights gathered from the first adopters to improve the product.
Next would be the product launch guided by comprehensive data analysis then a data-driven strategy to establish themselves as a leading brand in the category.
New product development research is an invaluable aspect of the process of turning an idea into a sustainable business.
If more than nine out of every 10 new products launched are failing, it’s because the majority of creators aren’t following the process. If they did, we’d have far fewer products being launched and a much higher success rate.
New product development research can tell you when to proceed and when to take a step back. It can help you discover the thing in your idea that makes it irrelevant to the market or poorly timed so you don’t waste your resources on a failed project.
On the flip side, it can give you the confidence you need to keep improving until you have the perfect solution for the problem you have identified.
Not only can NetBase Quid ® collect and analyze consumer and market data at large scale, the platform allows you to do it quickly, repeatedly, and inexpensively compared to traditional research. This means you have all the information you need, at all times, and more time to focus on making your product better.
Reach out for a demo today to get a special introduction to the platform by one of our in-house experts!
Have any questions? Let’s chat!

- How it Works
- Case Studies
- Research Grants
Your Guide to Product Development Research

Whether you’re wanting to create a new product or revamp an existing one, learning how to conduct product development research is crucial. Without establishing an understanding of product development research ahead of time, you could potentially waste precious time and money on unnecessary practices. In this article, we’ll take you step-by-step through the product development research process and help you find practices that suit your needs.
What is Product Development Research?
Product development refers to the complete process of brainstorming, researching, crafting, marketing, and selling products. Long story short, product development is the collective process in which a new product is created and sold. Product development also includes updating existing products; for example, when you add new features or modify an existing product, it is considered product development.
Research is an integral part of this product development process. It allows you to validate your ideas using data and ensure your product will resonate with consumers, compete within the market, hit the right price, and more. Without conducting research before launching, your product may not reach its fullest potential.
From concept testing to loyalty research, product development research consists of different processes and tests. Not all steps and tests may apply to your product development journey. This varies depending on whether you’re launching a new product, updating an existing one, what research or ideas you already have, etc.
Now, let’s dive into the product development research process.
Why Product Development Research Is Important
Product development is a major investment of funds, time, and energy for you and your entire organization. With all that at stake, you need a way to know that the product or feature you’re developing will be successful. Product development research gives you those answers at integral stages of the development process. This research can tell you if you’re on the right track or need to pivot some of your development while also giving you data that can garner the buy-in you need from leadership or potentially recruit more investors.
The Product Development Research Process
Consider this your step-by-step product development guide. If you are creating a new product from scratch, follow each step. If you are updating an existing product, use the complete guide to develop an added feature or at the appropriate step for your product.
Step 1: Exploratory Research
First things first, you’ll need to do some exploratory research . This is the preliminary research that helps you find a direction to go in. To get started, think about the pain point you will solve for your customers. Ask yourself questions like:
- What product/product feature could make customers’ lives easier?
- What problem can I alleviate for customers?
- What do customers need? What needs are not being addressed?
- Are customers satisfied with the products currently available? If not, what’s missing?
Once you identify the customer pain point you wish to solve, gather some teammates for a brainstorming session or write down a list of ideas. Get as many ideas out there as you can—they will be refined in the upcoming steps. Continue to keep the customer pain point in mind and think outside of the box. We’ll figure out the details later.
Now, you can quickly run your ideas through a SWOT analysis and start eliminating the lagging ones. SWOT analysis refers to:
- Strengths : What does your product do well? What distinguishes your product from competitors?
- Weaknesses : What does your product lack? What do competitors do better than you?
- Opportunities : How can you leverage your product’s strengths? What trends can you take advantage of?
- Threats : Who are your emerging competitors? What obstacles does the product face?
SWOT analysis will give you a better understanding of your product ideas at every angle and allows you to assess the pros and cons of each one.

Step 2: Evaluative Research
Evaluative research helps you further evaluate your concepts and identify the ones that are worth moving forward with. Also, this is a great place to start if you need to reevaluate an existing product.
Here you will open the data collection beyond you and your team by conducting research through surveys or other consumer-focused methods. Surveys allow you to tap into a larger pool of respondents and gather detailed data about your concepts. You’ll be able to get feedback, better understand your target market, and refine your ideas.
Here are some questions you can ask respondents:
- How often do you use this product/feature?
- Does this product/feature help you solve your problem?
- How satisfied are you with this product/feature?
- What would you change about this product/feature?
Similarly, concept testing is a great study to run at this stage in order to iron out the details of your concepts; We’ll talk more about concept testing later in this article.
This feedback will give you guidance on where to take your concept next and begin to set the tone for your marketing strategy. Pay attention to who your customers are and the language they speak in order to inspire your marketing messaging.
You’ll also want to do some basic competitive analysis at this stage. Get a grasp of the amount/worth of the competition in your industry. Using customer feedback and competitive analysis, you can identify what’s missing in your industry, discover your niche, and build a competitive advantage.
Step 3: Iterative Development and Finalization
At this point, you should be left with a realistic idea of what your product will look like, and you just need to sort out the details. In this stage, you will finalize your product by analyzing specific features and making sure your customers’ pain points are eliminated.
You may want to conduct another concept test using your refined ideas to test features that may not have been tested the first time around. A/B testing can also be useful to compare different versions of the product and features and make decisions based on your results.
You will also need to conduct pricing research before launching your product in order to ensure that you and your customers will get the right value.
Get everything you need for product development research, all in one place.

Types of Product Development Studies
There are various studies you can run during your product development journey, each of which covers a different area of your product and brand. These studies can be carried out in different ways such as focus groups, interviews, or surveys. We recommend running product development studies using surveys in order to get both quantitative and qualitative data from a larger audience.
Let’s look at the different product development studies.
Customer Experience
Customer experience studies are one of the best ways to get holistic feedback about your product, marketing strategy, and brand from customers.
This study would be most helpful towards the end of the product development process or once the product is launched; You’ll want to make sure that customers have the chance to experience the product before they provide feedback on it.
Understanding customer loyalty and the value they place on your product and brand is an important aspect of customer experience that shouldn’t be dismissed. Remember: Keeping existing customers is much easier than recruiting new ones.
Learn how to measure customer experience and loyalty in our guide to improving customer experience.
- Concept Testing
As we previously mentioned, concept testing is a helpful and often essential tool in product development, especially when conducting evaluative research and iterative development.
Concept testing is the process of gathering your target market’s opinions about your idea it is made available to the public or is fully developed. It allows you to adjust your vision and features prior to product production.
We’ve collected the best concept testing practices in these 4 steps to concept testing research.
Competitor Research
Of course, it’s great to focus on perfecting your product, but you cannot do this without evaluating the rest of the industry. Scope out your industry’s size, its value, and the top players. Create competitive advantages by turning your competitors’ weaknesses into your strengths. Consider why customers should buy from you over your competitors. Competitively price your product.
And don’t forget – the market is always changing. Don’t stop your research after your product launches. Continue to stay up to date with industry trends and the competition in order to get ahead.
Pricing Research
Pricing research is an essential step in product development. Finding the right price can be a challenge; You need to find a price that is high enough to bring in profit, but low enough to stay in demand.
To get this right, you’ll need to examine the competitors’ prices, find your price premium, and discover consumers’ willingness to pay.
Luckily, we’ve compiled a simple guide on how to conduct a pricing survey so you can get started.
How to Get Started with Product Development Market Research
Now that you understand the impact product development market research can have, how do you get started and put that new knowledge to use? Follow these simple steps and you’ll be reaping the rewards before you know it.
Step 1: Set Your Objectives
Start by establishing what you want to learn from your product development market research. Answer questions such as:
- What do you want to measure in your research?
- What aspects of your product do you want to research (e.g., specific features, how it suits a particular group of customers, etc.)?
- What is your primary goal – to determine if your product development is going in the right direction, to gather data to assure investors that their investment in your product is sound, or both?
Step 2: Determine the Scope of Work
Now that you have the big picture in mind, it’s time to get into more of the specifics of planning your product development market research. Make decisions in more detail about how you will carry out your research. For example:
- Who do you want to survey (age ranges, genders, locations, and so on)?
- What types of questions will you ask?
- How will you format your research (for example, will you show the respondents an image and description of the product, or will you send them a prototype to try and then survey them after they use it)?
- How many participants do you want to survey?
- How long will your research study run?
Step 3: Find Your Participants
With a solid plan in place, the next step is to gather your participants. The easiest way to do this is to choose a survey platform that can source participants for you. You already know what characteristics you want to look for in your participants, so a survey platform like GroupSolver can use survey pools and screeners to pull in your target participants.
Research and Product Development Made Simple
From product ideation and concept testing to competitive analysis and pricing research, GroupSolver® is here to help you collect data on every step of your product development journey. We’ll guide your product development decisions using your customer’s voice and agile insights – all in real-time.
View, analyze, and segment both quantitative and qualitative data with our intelligent survey platform . Our AI Open-End™ technology organizes and quantifies qualitative data, so you don’t have to. Now, you can quickly analyze qualitative data, while also collecting useful quantitative data – all in one step.
GroupSolver conducted product development research to help a snack food brand to launch a new flavor into the market , an iconic home products brand introduce a themed sandwich bag , and hundreds more launch successful products.
Learn more about our technology and research solutions or request a quick demo of our platform.
Share this article
You might enjoy these too

A Year in Review: Living through a pandemic

Lessons from the frontier

Q2&3 Product Update: making your research experience not-so-spooky
A better way to smarter insights starts now.
Request a free demo. Someone from our dedicated team will get right back to you.
- Client Sign In
Terms & Privacy
- Terms and Conditions for Services
- GDPR Privacy Notice
- Privacy Policy
- Master Subscription Agreement
- Platform Security
Sign up for our newsletter! Expert insights, industry trends, and inspiring stories delivered right to your inbox.
We’re glad you’re here! First, let’s get to know each other.
- First Name *
- Last Name *
- Work Email Address *
- Organization Name *
- How did you hear about us? * Select one Internet search (Google, Yahoo, etc.) Email from GroupSolver® LinkedIn message from GroupSolver® Social media post Conference or Event Referral by someone Other
Nice to meet you! What kind of research are you looking to do?
- Pricing Analysis
- Brand Perception
- Customer Research
Sounds good. How often do you conduct research projects?
Several times a month
About once a month
Occassionally
A few times a year
Lastly, what type of service best describes your needs?
Executive insight.
I need to quickly fact check my hypothesis to support our business decisions.
Deep Insight
I need to understand the 'why' behind the 'what' for deeper understanding.
Forward Insight
I need to understand how my customers, competitors, and markets are changing.
Subscribe to the GroupSolver® Digest
Expert insights, industry trends, and inspiring stories that are delivered right to your inbox.
- Email Address *
- I agree to receiving outreach from GroupSolver
- Name This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Apply for Impact Briefs by GroupSolver ®
Apply for an Impact Brief today and get your research up and running. We ask that you complete a short write-up describing the motivation behind your research questions and why they are impactful for society.
Number of words 500
Components Title, Research Question, Relevance to Community, How Insights & Data will be Used
- Title: 50 words or less
- Research question: 150 words and summarizes key questions to be researched
- Relevance to community: 300 words with an explanation on why proposed questions matter
- Use of data and insights: 150 words explaining who and how will use the data and insights beyond publishing
Grantees own the data and are free to use it for any publication in any other way. However, we ask that the raw data collected for Impact Briefs be available to the public.
There is no limit to the number of grants an individual or team can receive.
To apply, send application to [email protected]
Have a customer insights question? #FridayInsight has your answer.
What you get.
Free custom insights prepared by our team.
What you need to do
Submit your burning research questions to us.
What we will do
We will review questions in the order they were received and will pick one periodically to research. If your question is picked, we will design a study, collect data on our platform, and share the data with you for free the following Friday.
Submit your requests here !
BrandSpark™
Liveslides™, survey size:, research services:, access packages:, privacy overview.
Learn / Guides / Product research basics
Back to guides
Product research: the key to building a product people will love
You want to build a long-term vision for your product, and work on something that your users will buy and love—but can you really do that if you don’t understand your customers?
Probably not.
Enter product research, the key to leading your business to success through data-backed insights and smart, customer-centric product decisions.
But how can you make sure your product research is effective, and that it will benefit your customers and business? Keep reading to find out!
Last updated
Reading time.

Need to understand your users?
Hotjar gives you the tools you need to lead user-driven product research and development processes.
Product research: what it is and why it matters
Product research is a vital first step before introducing new features, a new product, or entering a different stage of the product lifecycle. It enhances your understanding of what the customer wants so you can make user-led product decisions and address customer needs.
What is product research?
Product research is the process of gathering information about your product's purpose, development direction, and which solutions you should offer to create customer delight. Product research is conducted through surveying and studying users to identify their needs and understand what they demand from your product, and usually happens at these stages in the product lifecycle:
Before launch : to understand which initiatives you should include and prioritize based on customer needs, and to develop a product-market fit.
Testing and feedback: to understand how the customer perceives new iterations, learn what they like or don’t like, and how you can improve the product to delight them.
Soft launch: to analyze how effective and useful your Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is among a segment of customers, and identify changes to make before releasing the full product to market.
Post-launch: to study customers' reactions and behavior after launch for continuous discovery , analyze customer satisfaction, and identify potential bugs or improvement areas.
Why product research matters for product teams
If you don't know what your customers want from your product, even your most brilliant idea risks failure. Here's how product research helps you align your product ideas with customer needs:
Understand user needs and pain points: your product needs to solve the customer's most pressing issues, but how can it do that if you don't know what issues they’re having? Product research helps you gather data and behavioral insights to understand your users’ problems and build the solutions they need.
Align user needs with business goals: understanding customers' needs and how they align with your product and business goals helps you plan a product roadmap that'll serve both the users and your company.
Higher scope for innovation and accuracy: when you have clarity about what your customers need, you can find innovative ways to solve their problems and build a product they'll love.
Gain a competitive edge: researching your competitors will help you understand how to differentiate your product and uncover gaps in the market, which can help you decide what features to build.
Simpler and more impactful prioritization: with product research, your entire team is clear on how to prioritize initiatives to achieve customer delight , making it easier for you to manage your product backlog .
Why and how product research can vary across product teams
Product research validates your ideas and gives you a better understanding of your user throughout the product development process. But the responsibility to conduct product research doesn’t fall solely on the product manager— people across departments should also be conducting product research.
Since product research isn't a single, standard process, the purpose and level of contribution can vary at different stages of the product lifecycle and across roles and departments:
1. Product managers
A product manager's primary goals are to understand user needs, learn business goals, and determine market requirements to create a product vision and roadmap.
They also use product analytics to validate ideas around iterations and product features—all of which require extensive product research.
A product manager’s main research aims are to ensure that product development decisions are data-informed and customer-centric, and address users' needs to build a great product.
Common research methods include interviews, surveys, competitor studies, and analyzing user behavior and product experience insights.
2. Product designers
Product designers need to empathize with users to create an intuitive product experience that users will enjoy.
During product research, designers might observe customers in real-time to note their reactions, responses, and behaviors around different elements of the product's design. For example, they might observe how users interact with the UI to identify product elements or features that seem to slow down or confuse individual users.
Product designers use these insights to improve the user experience ( UX ) and create a seamless product experience ( PX ) for easy navigation and usage.
Their research methods include customer feedback forms and behavior tools (like heatmaps and session recordings) to understand where users are facing issues and how design changes can fix them.
3. Researchers
Researchers study user behavior, needs, and motivations to translate insights into new and better product opportunities and better-informed product decisions.
Researchers constantly conduct product research to monitor trends over time and see how user behavior patterns are changing in response to product iterations—and how to improve them.
But, here’s the catch: this data is not readily available. So, researchers use a combination of quantitative and qualitative research methods like surveys, feedback forms, and customer interviews to get recurring data.
4. Product research by lifecycle stage
Product research processes, methods, and findings will change as your product reaches new stages of development:
If you're developing new features for an existing product , you want to understand the customer's current needs, how they've changed over time, and their reaction to recent iterations. This helps you understand which initiatives and ideas you should prioritize and introduce next.
When you're developing a completely new product, product research will be different. Here you don't have historical information about user response and behavior patterns from your previous developments, so you need to perform in-depth product research to understand your target customer's needs and pain points.
4 elements of successful product research
Product research is necessary to avoid misguided product development decisions, identify potential issues with your product, and get an in-depth insight into your customer's mind. This research helps you create a well-thought-out strategy for building a product customers love.
But you need to take some proactive steps to make your research successful:
1. Use accurate and unbiased data collection methods
The primary goal of your research is to collect accurate data that tells you about how your customers experience your product—what they like or don't like, what they want or need, and what issues they encounter.
But your research won't be useful or actionable if you use unreliable data collection methods .
The best way to ensure the data you collect is accurate and unbiased is to use reliable methods like surveys, customer interviews , and tools that provide consistent real-time product experience insights (like Hotjar!).
Only with accurate data can you be confident in making truly customer-centric decisions to build the best product.
Pro tip: use Hotjar Heatmaps and Session Recordings to study customers' behavior patterns on your site. These tools give you an unbiased look at how your customers scroll, click, move, and navigate your website, which can help you identify potential issues and improvement areas.
For example, if you use heatmaps and notice that users aren’t scrolling down your home screen to where you’ve included testimonials and product use-cases, you can use this information in your research to place them further up the page.
2. Conduct thorough competitive and comparative analysis
Product research isn't just relevant for studying customers and their needs—it's also key to understanding your competitors and where you stand in the market.
Conduct a thorough analysis of your competitors' products, audience, and processes. This will help you analyze what's working for your audience, what gaps you can fill, and how to create a better, more efficient product for your customers.
You can complement your research efforts by carrying comparative analysis of what you're missing out on. Study your competitors and identify which features they’re providing that you’re not and what makes them unique. This will tell you where you’re lacking and help you create an optimization plan for better results and customer satisfaction.
For example, if you understand how your competitors are launching features—and how their customers are responding to them—you can use those insights to develop and introduce your next feature, and build a better product that delights your customers and stands apart from the crowd.
3. Leverage existing research material
Marketplace and trade reports—analysis reports by institutions and organizations in your industry—give you valuable insight into product processes used by companies over the years and indicate how consumer trends have changed.
This goes beyond your first-hand information and adds a historical touch to your research, so you can discover new product opportunities by taking inspiration from what’s worked before (or learn from what hasn't).
For example, you may come across an innovative way to collect customer feedback or an efficient way to test product features that might not have crossed your mind. You can explore this idea with the help of historical data.
4. Segment results based on business goals
Your product research is irrelevant if you can’t use it to make more effective decisions and product improvements.
Enter segmentation, which is when you categorize your research findings based on business goals, so information doesn't get mixed up or lost in translation. You can also document your findings so product team members can refer to them from time to time for guided decisions.
Segmentation can also help you align your short-term and long-term goals to make the research more valuable for use in the future.
For example, you may want to study your customers' major pain points around a specific feature, at first—but later, when you're introducing a suite of new products, you might want to look at the issues your previous product didn’t solve, potential initiatives that can complement your new products, or gaps in your past marketing strategy. This will help you better address these areas for your new product.
How to measure the success of your product research
Measuring the success of your product research isn't exactly straightforward: tangible product results come much later when you receive feedback for the product, so it’s challenging to gauge the effectiveness of your research process in the beginning.
You can get some clarity around how research is translating into benefits for your users and business by attaching Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to your product during the initial stages.
It's important to know what success means to you before starting product research. Be clear on the question you are trying to answer first.
Much like a scientific experiment, you should identify the aims and objectives and develop a hypothesis to test. Design your research methodology around the hypothesis.
You might choose a survey, a literature review, or something else. The results, once analyzed, should illustrate a statistical significance in your findings to prove or disprove your hypothesis—a true measure of research success.
Here's a list of questions you should answer to determine the success of your product research:
Do you understand the major triggers and pain points of your customer?
Have you analyzed your products in comparison to competitors and identified gaps?
Have you converted your research into data points and findings?
Have you used the research report to introduce modifications in your product roadmap or created a new one from scratch?
Did this research give you a good idea of what the customer wants from your product?
Do you understand which initiatives you need to prioritize?
How you answer these questions will tell you whether you have sufficient information or need to change your product research strategy and collect additional data.
Ultimately though, the best measure of product research success is the knowledge you gain about your customers—and how you use that knowledge to build a product they'll love.
3 ways Hotjar can assist your product research for better results and efficiency
1. use recordings and heatmaps after releasing features to get user behavior insights.
One of the most direct ways to get feedback and insights about your customers' needs, pain points, and responses to product features is to understand their behavior in context as they experience your product.
Heatmaps give you insight into the elements of your page that drive the most clicks and conversions while highlighting things you can optimize for better results. These findings can be used in your research to identify potential areas for improvement.
Session Recordings give you a play-by-play of individual user activity in your product to show you their navigation path, mouse scrolls, and clicks. Real-time behavior patterns tell you what the customer is struggling with presently , so you can improve product design, navigation, and experience.
2. Leverage surveys to get validation and feedback
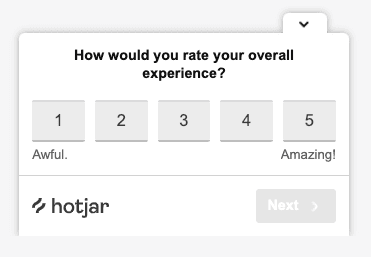
If you want to know exactly what your customers are thinking and let voice of the customer (VoC) data guide your product strategy, use qualitative tools like Hotjar's Incoming Feedback widget and Surveys.
Try placing surveys and feedback widgets on high-traffic visitor points of your product to get direct, unbiased, and genuine feedback from the customer at the best time: when they’re experiencing your site. This helps you understand user needs more intuitively so you can validate ideas and features.
3. Use Hotjar integrations to prioritize features and get buy-in for ideas
Product research is a comprehensive process, and it’s challenging to do it regularly. However, the process becomes more efficient when stakeholders and team members have access to customer feedback as soon as it’s available.
Hotjar integrates with tools like Slack and Zapier to help you seamlessly communicate with stakeholders and get buy-in for your ideas then and there, so you can move forward with your product improvements.
Final thoughts
Product research lies at the very core of product management. If research isn't conducted throughout the entire development process, you risk misalignment and a resulting product that doesn't meet users' needs.
You need to understand what users need right now to build a truly user-centric product—and product research can help you achieve just that.
Use Hotjar's qualitative and quantitative product insights tools to organize your product research efforts and really understand how your customers experience your product.
FAQs about product research
What’s the difference between product research and market research.
The primary difference is that product research involves studying the product (customer needs, feedback, pain points, issues) while market research involves analyzing the market (competitors, consumers, demand).
How do you conduct product research?
Define your product and its vision
Identify your target customer
Understand your customer's needs and pain points
Conduct research using qualitative and quantitative methods
Convert the research into data findings and insights
Use the analysis to guide your product strategy
How can using product research tools help?
Product research tools help you identify consumer trends, study user patterns, and analyze user behavior for data collection. Some useful product research tools are Hotjar, Zendesk, Product Plan, Jira, and ProductBoard.
What is Product Development Research and how to do it?

Product Marketer at Zeda.io
Jacob Koshy
May 2, 2023

Transform Insights into Impact
Build Products That Drive Revenue and Delight Customers!
66% of customers expect companies to understand their needs. But how do you understand the needs and demands of your customers?
This is where product development research comes in. It not only helps the product managers to understand customer needs but also enables them to address these requirements in perfect ways. In return, product managers can drive higher customer satisfaction, loyalty, and high revenue.
Let us discuss everything you need to know about product development research.
What is Product Development Research?
Product development research is the process of crafting, developing, and selling a product. It includes the crucial steps of market research, user research, and also coming up with a marketing plan to market the product to prospects. It also refers to tracking the progress of a product you are currently working on, its appeal to the target audience, and identifying potential changes you need to make to make the product more attractive.
Development cannot take place in isolation from research. It is a crucial process that directs the development of a product. It helps you to identify, understand and analyze consumer needs so that you can cater to them accordingly and increase your desirability in the market. It includes the processes of concept testing, loyalty testing, and many other tests that validate the product.
Why is Product Development Research important?

Product development research lays the groundwork for all the important functions of product development, marketing, and sales. It makes sure all your activities are data-driven and not just based on assumptions, minimizing the chances of errors.
Let us try to understand why product development research is important with the following points.
- It ensures you are giving your customers what they really want. Sometimes you may have a different idea of the benefits and features that you want to offer your customers, which they might not even need. Research saves you from committing errors like this and ensures you don’t waste resources.
- It helps you identify customers and market trends so that you can devise your strategies accordingly.
- It helps you to identify gaps and drawbacks in the current development plan and helps you brainstorm and analyze ways to improve.
- It enables you to forecast the demand for the product and develop unique ways to promote, market, and sell.
- It allows you to identify specific features that customers might be willing to pay more for and help you figure out ways for increasing customer loyalty.
How does the product development research process looks like?

There are primarily 3 broad stages of product development research. Let's discuss.
1. Exploratory research
This occurs in the earliest stage of product development research. During this time, you have no idea of what your product is going to look like, what features it will have, or what will be the pricing structure. In this stage, you explore ideas and dig into data around customers to understand their pain points and needs.
Idea generation
When you are at the first stage of product development, you generally have no direction. The research will help you to lay the foundation of an idea and how to work around it. This process should focus on answering these vital questions.
- What type of product do you want to build?
- Who is the target audience?
- What do they really need?
- How can you address their need with your product?
- What segment of the market would you like to target?
Idea screening
This will help you evaluate potential ideas based on the criteria gained by market research. For example, if you have a new idea, the screening will help you test the feasibility by evaluating the budget requirements, relevance, constraints, risks, and challenges.
It starts with the generation of an ‘idea’ or ‘ideas’. It can come from you or your team members or anyone who is involved in the development process. Once you have the idea, you have to evaluate it against special criteria like benefits/value, target audience, complexity, profitability, and market situation. If the idea shows potential even after weighing against each criterion, you need to gather evidence-based resources to support that idea. You can start doing qualitative and quantitative research to understand prospects' points of view. After compiling all the important research data, you can now start refining your ideas into actual product concepts.
Evaluative research
Ideas that emerged during the previous stage will be scrutinized in this stage. This will help you identify the ones that are worth moving forward and discard the ones that aren’t promising enough. Data collection through surveys can be one of the methods used in this stage to gather details about your product concept.
Concept development and testing
It is the process of gathering information and insight about your product concept from the target audience. It helps you adjust your vision and ideas based on the results of the research.
Market research
This process is essential to examine the different forces of the market that not only pertain to the customers but also competitors, economic stability, government policies, and all other factors that can influence the lifeline of the product.
2. Iterative research
This stage is to analyze and refine your product to ensure it appeals to the customers. Iterative research is detailed and in-depth and focuses on developing the critical features of the product. It can start from testing the different versions of the product to finalizing the packaging.
Development
The development of the product initiates in this stage. From the technology stack to the product labels, everything is analyzed and planned in this step. All the team members pool in their ideas and start working on developing the product after it has been approved.
Before the product is launched in the market, tests are conducted to test its performance of the product. This may include evaluating the product’s performance, safety, quality, and compliance with standards.
Commercialization
This is the final step when the product is introduced in the market. Before launching the product into the market, all the important factors like pricing, packing labels, marketing, and sales channel are decided.
How to perform Product Development Research effectively?
As a product manager, you cannot afford to mess up product development research. All the steps should be carefully planned and executed to ensure success. Make sure to read the steps attentively to know all about conducting effective research.

Step 1: Ideation
Ideation is the process of identifying the type of product you want to build. Suppose you have recognized an opportunity for introducing a new product in the market, but are unsure about what type of product you want to create. This is when you can hold internal sessions with your team to discuss the idea and concept of the product. The processes of combining, adapting, substituting, eliminating, and rearranging will play a crucial role in creating the perfect product idea.
Step 2: Market research
Market research means collecting information and analyzing the crucial players in the market. From competitors, target audience, geographical location, and economic stability to government policies, you have to have a thorough understanding of the market landscape to develop a strong product strategy .
Step 3: Demand analysis
The demand for a product drives the financial decisions of a company. Knowing the demand for a particular product is essential to know the feasibility of a particular product. If a product has low demand, there is no use in investing in the product. Conducting demand analysis will give you information about how many units you need to produce, which are the geographical area you need to target, and forecast your revenue from the product.
Step 4: Concept testing and validation
After you have gathered all the best ideas for product development, it is time to test and validate it. This focuses on clarifying the idea of the product by focusing on questions such as-
- Is the concept understood by the team?
- What pain points can be addressed by the product?
- Who will the product users be and how will they use them?
- What are the possible strengths and weaknesses of the product?
You can validate these questions by conducting qualitative research to test the viability of the product in front of your prospective customers in the form of surveys or interviews.
Step 5: User experience research
User research or UX research is the process of discovering user behavior, motivation, and need of your customers through analysis, observation, and other types of feedback . It will help you dismiss assumptions and find common information about target customers, and recognize their needs and requirements.
Step 6: MVP research or prototype research
A minimum viable product or MVP is a model of the product with enough features to allow customers to use it to validate the product ideas. Creating an MVP and letting early adopting customers use it will help you get an insight into the product experience from their feedback.
Step 7: Pricing research
Pricing research will help you determine an appropriate price for your product. A suitable price should neither be too low as it will impact your profit margin nor too high to make it unaffordable for the consumers. Research will help you come up with a suitable price that appeals to your consumers while ensuring profit.
Step 8: Competitor research
Competitor research is one of the important steps you cannot miss at any cost. Researching your competitors thoroughly will give you a base for comparison so that you can develop your own unique strategy for product creation and promotion. You can research your competitors from various sources like social media, google search, software listing sites, etc.
Step 9: Satisfaction and loyalty research
Satisfaction and loyalty research is vital to understanding the user experience of your product. Once you have launched your product, feedbacks are most likely to come in. You have to carefully analyze and address those feedback in a way that leaves the consumers content.
Best Practices while doing Product Development Research
Here are some of the best practices you should follow to get the most effective results from your product development research.
1. Dig deeper into consumer needs
Just identifying the needs of your consumers based on a survey is not enough. You have to dig deeper into their needs to have a comprehensive understanding.
What kind of challenges do they face? What are they looking for in a product? How much are they willing to pay? What section of consumers will use your product? All these questions will help you create a viable product.
2. Involve customers in your development process
There is no one better than the customer to show you what and how they want in a product. They are the ultimate users of your product so involving them in the development process will only increase the chances of success. You can generate polls, surveys, and feedback sessions to ask prospective customers about their ideas and opinions.

3. Expand your research horizon
Generally, you research only the targeted market and location while developing a product. It helps you get specific insights into the market you want to operate in. Broadening your research horizon is necessary to help you get a thorough understanding of the perceptions related to your product. Don’t limit your research to the target market, try to understand the national and international scenarios related to your product.
Product development research is not as complex as it sounds if you know how to do it correctly. If you know how to address their pain points in the most appropriate and innovative way, you already know you are way ahead of the competition.
Zeda.io is there to support you in your product development research process. It is the ultimate product management tool to help you build the right product for your consumers. Check it out now!
Join Product Café Newsletter!
Sip on the freshest insights in Product Management, UX, and AI — straight to your inbox.
By subscribing, I agree to receive communications by Zeda.
IN THIS ARTICLE:
Latest articles
What is it like to be a product manager in india.
Zeda.io is a product management suite that brings all the things needed to define, manage, and collaborate on your product at one place.
What is Backlog Grooming? - Definition, Overview & Tips
A product backlog is a list of tasks that the product development team creates from the product roadmap. Here is how you should groom it for efficiency.
Top 10 Product Influencers You Should Follow on Twitter
The best place to learn from industry-leading PMs is on Twitter. We have got a perfect list of our favorite 10 product influencers for you.
Decide what to build next with AI-powered Insights
- What are product discovery techniques?
- 8 key product discovery techniques link
Elevating Product Discovery With the Power of AI
Explore how to leverage the potential of AI in the process of product discovery. Discover how Zeda.io's AI insights can be game-changer in the product management realm
How to Collect Customer Feedback: 13 Effective Methods to Try
Here are 13 effective ways to collect customer feedback to make customer-centric decisions and build innovative products.
Driving Product Success with Customer Insights
Discover what is customer insights and how to gather them and more. Learn the crucial role customer insights or consumer insights play in your product success
Download a resourse
Non tincidunt amet justo ante imperdiet massa adipiscing.
App Sign Up
Subscribe to newsletter, book a demo, ai-powered product discovery for customer-focused teams.
- Solutions Corporate Market Analysis Customer Experience Product Lifecycle Brand Strategy Research & Insights Higher Education Enrollment Management Academic Program Development Student Success Operations & Finance Advancement Marketing Grants Research & Insights K-12 Education Curriculum and Instruction Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion Academic Program Planning and Impact Strategic Planning Teacher Recruitment and Retention Operational Planning School Climate Research & Insights
- Data Analysis
- Qualitative Research
- Strategic Advising
- Benchmarking & Best Practices
- Market Modeling
- Research & Insights By Industry Corporate Higher Education K–12 Education By Type Insights Blog Reports & Briefs Case Studies Webinars All Research & Insights
- Client Testimonials
- Current Openings
- Recruitment Process
- Social Impact
- Careers in Research
- Careers in Sales and Account Management
- Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
- Client Login
Four Stages of Product Development Where Qualitative Research Counts
- March 13, 2024
- Topic: Corporate , Product Lifecycle
- Resource type: Insights Blog
Customer expectations for their products are higher than ever, and companies are struggling to keep up.
In a recent survey, we found that one in three consumers is struggling to find products that meet their needs. Companies that do not gather customer insights and incorporate them into product development will lose customers to their competitors. In fact, that same survey showed that 72% of customers are willing to try new products to find one that meets their needs.
Companies have several options for collecting customer feedback on products, the most common of which are customer surveys. However, there are a few stages of the product development process where companies can benefit from going beyond a survey by gathering qualitative data. This data allows companies to discover rich and valuable insights that can direct areas for future research or development.
What is Qualitative Product Feedback?
Qualitative product feedback involves asking customers questions directly. The two most common formats are customer interviews and focus groups. This approach allows companies to gather in-depth feedback and ask follow-up questions to delve deeper into the reasoning behind responses. The open-ended questions center on a product’s value, features, and product experience allowing companies to build products and features customers want.
Though asking interview questions may seem straightforward and relatively easy, it is critical to enlist an experienced facilitator. A skilled moderator ensures that questions are asked in a way that gets the desired insights without influencing customers’ responses. They also need to correctly code and accurately interpret the responses without bias or assumptions.
By gathering and incorporating qualitative product feedback companies can:
- Understand customer’s perceptions and preferences on various aspects of your company and products
- Gather unanticipated feedback that would not be collected from a formatted survey
- Clarify customer’s opinions by asking for follow-up questions that provide more context
When to Collect Product Feedback
There are four key stages of product development where qualitative feedback is critical.
1. Initial Product Development
Qualitative research can help narrow and refine potential product concepts during the initial idea-generation phase of product development. Its approaches can produce a detailed picture of customers’ experiences with a product and reveal unmet needs and untapped opportunities.
For example, a company looking to update a product can interview current customers about the existing product and gather opinions on potential features. Gathering direct feedback at this stage allows companies to identify the products and features customers are most interested in and why.
2. Product Refinement
Customer feedback is also critical in the product refinement stage. Even if you confirmed a product is in demand in earlier development stages, your produced product may not align with what customers are willing to buy.
Gathering feedback on proposed elements (features, pricing, etc.,) and allowing customers to beta test and evaluate products helps companies determine if the proposed product is viable and identify what additional refinement is necessary.
In this phase, engaging an audience that spans different age groups, ethnicities, income levels, and genders is critical to take cultural differences and considerations into account that may not be top of mind for design or marketing teams.
3. Pre-launch
Companies need to fine-tune how they will market the new product before releasing it. Qualitative feedback at this stage can help companies identify what themes and elements of the product resonate most with customers.
A common example is focus groups that are shown new messaging or ads before launch. This allows researchers to collect a group’s reaction to new concepts and spark conversation on what resonates and what’s falling off the mark. Not only does collecting direct customer feedback help companies optimize their messaging, but it can also produce customer quotes that can showcase the product’s value, enhancing marketing and sales strategies .
4. Post-launch
Most rigorous post-launch reviews include some type of customer experience survey to evaluate the product’s performance. By conducting follow-up qualitative research, companies can collect additional data and context to clarify the results of the post-launch surveys.
For example, if a typically loyal and engaged customer segment expresses dissatisfaction with functionality or a lack of desire to buy a new product, qualitative research can uncover the reasons why and allow a company to direct future product improvements.
While it is hard to foresee every potential product pitfall, a well-designed research plan that includes qualitative feedback can identify potential concerns with product features at different stages in product development and bring to light new perceptions and interpretations that companies can leverage to further enhance their products.
18 Questions to Ask During New Product Development

Related Content
- Reports & Briefs
Product Concept Testing: The Secret to Meeting Customer Needs
- Corporate , Customer Experience , Product Lifecycle
Critical Questions for New Product Development
- Corporate , Product Lifecycle
Related Tags
- Corporate , New Product Development , Product Development , Qualitative Research
Related Research & Insights

Product Development Strategy Guide
Research & Insights
Receive industry-leading insights directly in your inbox.
If you have difficulty accessing any part of this website or the products or services offered by Hanover Research, please contact us at [email protected] for support.
Become a client
Access the best custom research to help hit your organization’s goals . Request your custom consult below and a member of our team will be in touch.
Have questions? Please visit our contact page .
Let us come to you!
Receive industry insights directly in your inbox.
Our newsletters are packed with helpful tips, industry guides, best practices, case studies, and more. Enter your email address below to opt in:
Integrations
What's new?
Prototype Testing
Live Website Testing
Feedback Surveys
Interview Studies
Card Sorting
Tree Testing
In-Product Prompts
Participant Management
Automated Reports
Templates Gallery
Choose from our library of pre-built mazes to copy, customize, and share with your own users
Browse all templates
Financial Services
Tech & Software
Product Designers
Product Managers
User Researchers
By use case
Concept & Idea Validation
Wireframe & Usability Test
Content & Copy Testing
Feedback & Satisfaction
Content Hub
Educational resources for product, research and design teams
Explore all resources
Question Bank
Research Maturity Model
Guides & Reports
Help Center
Future of User Research Report
The Optimal Path Podcast
Sep 6, 2021
Product development strategy: How to define the direction of your new product
Let's explore what a product development strategy is, why it matters, types of strategies and examples, and how you can create one for your product.

Giada Gastaldello
Content Marketing Manager at Maze
Scroll Down
To stay competitive, companies need to find new ways to innovate and deliver continuous value to their customers. Yet creating winning products requires more than an innovative idea. Careful planning and strategy are a must for success. You'll need a clear direction to follow to optimize resources, identify priorities, and ensure a smooth product development process.
In this article, we’ll look at what a product development strategy is and how you can develop a great one for your product. For expert insights and best practices, we spoke to Vicky Volvovski , Senior Director & Head of Product Management at Postlight and former Head of Product at Zapier; Enzo Avigo , Co-founder & CEO at June and former Product Manager at Intercom, Zalando, and N26; and Ian Booth , Senior Product Manager at EduMe.
What is a product development strategy?
A product development strategy is a fundamental part of the new product development process (NPD) . It’s a high-level plan that describes the actions needed to develop new products or upgrade existing ones and introduce them to current or new markets.
New product development strategies link together the product vision and the strategic steps to realize that vision. In other words, a product development strategy guides a company's product development efforts—from concept to testing to launch—and aligns the new product's features and functionalities with the business strategy and target market needs.
The benefits of defining an effective product development strategy
Defining a product development strategy before you begin development is crucial. It will set the direction of your product and help you set clear goals. Let’s dive into the top three benefits of developing a strategy for your new product.
1. It gives you clarity
There are a million things that could get prioritized and a million directions that the product could go in. A product strategy allows you to say “yes” to the things that are aligned with your direction and say “no” to the rest.
Vicky Volvovski , Senior Director and Head of Product Management at Postlight
When you’re building a new product, deciding what to do, and most importantly, what not to do, is challenging. A product development strategy gives you a clear direction to follow. It helps you set priorities and make decisions that align with the company's overall strategy. "Sometimes the things you say 'no' to might be good ideas, but they don't align," explains Vicky. "That’s where product strategy gives you clarity."
2. It improves decision-making
The more your team can understand the strategy, the more they can make decisions in their day-to-day that help you reach that goal rather than having people pulling in different directions because they don’t understand what you're working towards.
When goals and priorities are well understood, product teams can make better decisions throughout the development process. They will know what ideas are worth pursuing, what features they should prioritize, or how to adjust the plan if challenges arise. This brings us to the third benefit.
3. It maximizes product development efficiency
I think a clear strategy is really what differentiates the companies that move fast from the others. If you know what you want to achieve and communicate it clearly to your teams, they will be able to find the best way to reach the goal. It maximizes the time and energy of all the people who work in your company.

Enzo Avigo , Co-founder and CEO at June
When product teams have a well-defined strategy to follow, they can better manage resources, estimate timeframes and costs, and make quick, confident decisions. Enzo points out that a product development strategy not only is a way to optimize resources but it also keeps your teams motivated and your organization healthy.
Product development strategies and examples
Now that you know how a product development strategy can benefit your organization, let's look at three different types of strategies you can adopt and some real-life examples of product development strategies.
Data-driven product strategies
Being data-driven means making decisions based on data and key metrics. Data-driven companies break down the product development strategy into quantitative objectives to measure progress and success. What to measure and why usually depends on the company's high-level strategy. Product teams translate the high-level strategy into key metrics and generate initiatives to achieve the desired goals.
N26 is a company that adopts a data-driven approach to product development strategy. The company was founded with this vision: A global digital bank to transform the way we manage money .
“One of the ways to achieve our vision was to reach as many people as possible and increase our user base,” says Enzo Avigo, Co-founder of June and former Product Manager at N26. He and his team identified the metrics they wanted to move, such as the conversion rate and the number of active users, and worked on the main product initiatives to unlock those metrics.
While data-driven companies use data to lead the decision-making process, data-informed companies acknowledge the limitations of data and use them to inform their decisions. Learn more about the difference between data-informed and data-driven .
Vision-driven product strategies
A vision-driven strategy starts with a view of the future—a clear picture of what the company wants to build. Innovation is driven by intuitive vision and personal goals rather than market research data. Founders of such companies rely on this type of strategy when they want to create truly innovative products and explore a market where users don’t know much about the new product and what features they’d like.
Yet “vision-driven” doesn’t mean that product teams won't use data. Insights and data are still needed to understand user behavior, test assumptions, or understand how to upgrade the product in the future.
Apple is one of the best examples of a company executing a vision-driven product strategy. Historically, Apple was known to build the products first and then find the market for them. In an interview , Steve Jobs explained: "We do no market research. We just want to make great products. When we created the iTunes Music Store, we did that because we thought it would be great to be able to buy music electronically, not because we had plans to redefine the music industry."
Research-driven product strategy
This third type of product strategy is based on market and user research . Product teams start the new product development process with product discovery and use research to inform their decision-making at all stages of the process. They reach out to users to understand their needs and expectations and based on data and user feedback, they determine how to build a product that satisfies those needs and delivers value to customers.
One example of a research-driven product strategy is Intercom. During his time as Product Manager at Intercom, Enzo Avigo worked in the platform group. The team was developing the Intercom App Store , where users can browse and install third-party apps and integrations. User research was crucial to figure out what to build. “We knew that the more integrations our users had, the better retention they had,” says Enzo. “We created the platform group to make sure that all the users could find the right app, for the right use case, at the right moment.”
While this is a "formal" distinction between different types of strategies, the most successful products employ a mix of these strategies: they are driven by data, do research, and have a clear vision of where they want to get to.
Bring your customers' voice to product decisions
Create and share dynamic surveys with your customers, and track results in real-time to validate ideas and fuel product decisions.
How to create a winning product development strategy
As we saw, there are different approaches to product development . But whatever strategy you choose, here are some simple steps to develop and execute a successful new product development strategy.
1. Define your vision
Your product development strategy is the bridge between your product vision and the actions needed to realize that vision. So, as a first step, you’ll need to clearly define where you want your product to go and what you want to achieve. In simple words, your vision communicates the intent behind your product and the high-level goal driving your product development.
Sometimes, companies use mission and vision statements interchangeably, but they have different purposes. A mission statement focuses on the here and now and what the company is doing to achieve its goals. A vision statement focuses on the future and where the company wants to be in the long run.
One example of a successful vision statement would be Google's: To provide access to the world’s information in one click .
2. Do your research
A successful product development strategy has to be rooted in real user problems and goals and a real market opportunity.
The second step is to conduct in-depth research of your target audience, existing market, and competitors . In this way, you and your team can mitigate risks, use accurate data to inform your decision-making and increase your chances of building a successful product.
First, define and understand your ideal audience. Who are your target customers, and what problems are they facing? How will your product solve their problems? Interviews, surveys , or product analytics are just a few methods to get to know your users and identify their wants and needs.
Ian Booth, Senior Product Manager at EduMe, explains: "We have fantastic customer support and user research teams who constantly communicate with the customers and understand what they’re looking for from a strategy perspective. They’re so focused on being the champion for the user within the conversations that we’re having."
As a product manager, you're trying to balance the commercial side and the user side. You want to make sure that you’re not missing any information. Leaning on internal teams such as Customer Support and Research to champion the user's voice for me is the best route to go.

Ian Booth , Senior Product Manager at EduMe
Second, conduct market research and competitor analysis to learn what other products are available in the market, understand how users perceive your product compared to your competitors' offers, and identify what makes you unique. This is a fundamental step to decide how you will position and differentiate yourself in the market.
Learn more about how market validation justifies product investment by assessing how viable your product idea would be in the market.
3. Set product goals
When you have a deep understanding of your target market, you should use the data gathered to establish a series of goals you want your product to achieve to deliver value to customers and gain a competitive advantage. Set SMART goals that are specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, and timely. They will help you decide what to build next and give you a tool to measure the success of your product.
We always have a really good objective to focus on and good key results to track success. If you’re able to set them early, track, and understand them, you can determine if your product launch is successful because you can see the actual progression.
As part of our product development process at Maze, we always include a summary of our goals in the product development strategy document and regularly track our progress on every goal. This allows our product team to make decisions and align on the next steps.
4. Plan the product roadmap
It’s now time to define the initiatives, features, and releases that will help transform your goals into action. A product roadmap is a high-level visual that allows you and your team to execute the strategy. Product managers use roadmaps to plan tasks, communicate priorities, allocate resources, and see the evolution of a product over time.
A product development strategy ensures that all the initiatives in the roadmap are linked to the product’s vision and goals so that you can start development with a detailed and solid plan.
Product discovery plays a crucial role in helping product teams understand their customers and decide which products or features to prioritize and build.
Looking for a comprehensive list of product management tools? Check out our list of the best 13 product management tools to streamline your workflow.
Final thoughts
We’d like to conclude with a piece of advice from Enzo Avigo, Co-founder and CEO at June:
Strategy is like chess. You can think for hours before you start the game, but nothing ever happens until you play. The same occurs with product strategy. The best thing to do is not to think about the perfect strategy but move a piece, build something, and see what it yields. So usually, building the easiest prototype or finding a way to validate your assumptions.
Rapid prototyping can help you explore and validate ideas early in the product development process. With tools like Maze, you can test prototypes with users and get actionable results that help you make informed product decisions.
We hope this article has provided an insight into what a product development strategy should include. Now it's your turn. Start testing things out and get ready to launch a successful product.
Frequently asked questions
A product development strategy is a strategic plan that guides the new product development process. It aligns product teams around the product vision and outlines the actions needed to bring new products to market or upgrade the performance of existing products.
What are the main product development strategies?
Companies can consider three main types of product development strategies: data-driven strategies rely on data and analytics, vision-driven strategies are based on intuition and personal experience, and research-driven strategies depend on market and user research.

- Client Testimonials
- Our Affiliations
- Career Opportunities
- Brand Research
- Customer Experience Research
- Marketing Effectiveness Research
- Product Development Research
- Clear Seas Research Dashboard
- Data Analytics
- Panel Access / Sample / List Rental
- Programming
- Video Surveys / Voice of the Customer
- Site Preparation
- Tile and Stone
- Food & Beverage
- Manufacturing
- myCLEARopinion
- My Dashboards
- My Downloads
Product Development
See How Innovation And Product Development Research Can Drive Your Decisions During Product Life Cycle.

Gaining valuable feedback from potential and current customers on your current offerings, and creating a better understanding of what unmet needs exist enables you to develop customized solutions that will be valued. In today’s marketplace the ability to provide a high quality product/service that meets customer needs at a fair price is a minimum requirement. You need to understand if your target customer is as excited by your offering as you are. Specifically, you may seek to answer:
- What are the wants/needs of my target customers? What do they expect?
- Do the products/services I offer fulfill customer needs? How so? Are they relevant?
- Are there critical unmet needs in the marketplace?
- What are the key drivers of purchase decisions in my category?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of my product/concept?
- How do target customers view and connect to competitive products/services?
- How are my competitors positioned in the market?
- How can I best position my product/services for success?
- What is the potential for a new product?
- Which of my concepts offers the greatest potential (appeal, purchase consideration, etc.)?
Contact Clear Seas Research to get started developing a custom research solution to help guide you in your product development efforts to ensure you provide the most appropriate product/service for your target audience.
- We are so excited! You’ve done the hardest part, you’ve now found a team that will work hard to help you achieve your research goals. Please share a little bit more with us so we can match your research needs with the most qualified team member. Are you looking for...
- A general capabilities presentation
- A custom research solution designed with the specific goals of your organization
- An off the shelf industry report because time is of the essence
- Access to industry professionals for research recruiting
- I need something else completely
- I'm new to research and don't know what I need
- Hidden Checkbox Count
- * First Last
- [email protected] *
- (###) ###-####
By clicking “Get Started Now”, you acknowledge that you have read BNP Media’s Privacy Policy, agree to its terms, and consent to allow BNP Media to use your information consistent with the Privacy Policy. To read our Privacy Policy, please click here .
- Email This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
200+ Research Title Ideas To Explore In 2024

Choosing a compelling research title is a critical step in the research process, as it serves as the gateway to capturing the attention of readers and potential collaborators. A well-crafted research title not only encapsulates the essence of your study but also entices readers to delve deeper into your work.
In this blog post, we will explore the significance of research title ideas, the characteristics of an effective title, strategies for generating compelling titles, examples of successful titles, common pitfalls to avoid, the importance of iterative refinement, and ethical considerations in title creation.
Characteristics of a Good Research Title
Table of Contents
Clarity and Precision
A good research title should communicate the core idea of your study clearly and precisely. Avoid vague or overly complex language that might confuse readers.
Relevance to the Research Topic
Ensure that your title accurately reflects the content and focus of your research. It should provide a clear indication of what readers can expect from your study.
Conciseness and Avoidance of Ambiguity
Keep your title concise and to the point. Avoid unnecessary words or phrases that may add ambiguity. Aim for clarity and directness to make your title more impactful.
Use of Keywords
Incorporating relevant keywords in your title can enhance its visibility and accessibility. Consider the terms that researchers in your field are likely to search for and integrate them into your title.
Reflecting the Research Methodology or Approach
If your research employs a specific methodology or approach, consider incorporating that information into your title. This helps set expectations for readers and indicates the uniqueness of your study.
What are the Strategies for Generating Research Title Ideas?
- Brainstorming
- Individual Brainstorming: Set aside time to generate title ideas on your own. Consider different angles, perspectives, and aspects of your research.
- Group Brainstorming: Collaborate with peers or mentors to gather diverse perspectives and insights. Group brainstorming can lead to innovative and multidimensional title ideas.
- Keyword Analysis
- Identifying Key Terms and Concepts: Break down your research into key terms and concepts. These will form the foundation of your title.
- Exploring Synonyms and Related Terms: Expand your search by exploring synonyms and related terms. This can help you discover alternative ways to express your research focus.
- Literature Review
- Examining Existing Titles in the Field: Review titles of relevant studies in your field to identify common patterns and effective strategies.
- Analyzing Successful Titles for Inspiration: Analyze successful research titles to understand what makes them stand out. Look for elements that resonate with your own research.
- Consultation with Peers and Mentors
- Seek feedback from peers and mentors during the title creation process. External perspectives can offer valuable insights and help refine your ideas.
- Use of Online Tools and Title Generators
- Explore online tools and title generators designed to aid in the generation of creative and relevant research titles. While these tools can be helpful, exercise discretion and ensure the generated titles align with the essence of your research.
200+ Research Title Ideas: Category-Wise
Technology and computer science.
- “Cybersecurity Measures in the Age of Quantum Computing”
- “Machine Learning Applications for Predictive Maintenance”
- “The Impact of Augmented Reality on Learning Outcomes”
- “Blockchain Technology: Enhancing Supply Chain Transparency”
- “Human-Computer Interaction in Virtual Reality Environments”
Environmental Science and Sustainability
- “Evaluating the Efficacy of Green Infrastructure in Urban Areas”
- “Climate Change Resilience Strategies for Coastal Communities”
- “Biodiversity Conservation in Tropical Rainforests”
- “Renewable Energy Adoption in Developing Economies”
- “Assessing the Environmental Impact of Plastic Alternatives”
Health and Medicine
- “Precision Medicine Approaches in Cancer Treatment”
- “Mental Health Interventions for Youth in Urban Settings”
- “Telemedicine: Bridging Gaps in Rural Healthcare Access”
- “The Role of Gut Microbiota in Metabolic Disorders”
- “Ethical Considerations in Genetic Editing Technologies”
Social Sciences and Psychology
- “Social Media Influence on Body Image Perception”
- “Impact of Cultural Diversity on Team Performance”
- “Psychological Resilience in the Face of Global Crises”
- “Parental Involvement and Academic Achievement in Adolescents”
- “Exploring the Dynamics of Online Communities and Identity”
Business and Economics
- “Sustainable Business Practices and Consumer Behavior”
- “The Role of Big Data in Financial Decision-Making”
- “Entrepreneurship and Innovation in Emerging Markets”
- “Corporate Social Responsibility and Brand Loyalty”
- “Economic Implications of Remote Work Adoption”
Education and Pedagogy
- “Inclusive Education Models for Diverse Learning Needs”
- “Gamification in STEM Education: A Comparative Analysis”
- “Online Learning Effectiveness in Higher Education”
- “Teacher Training for Integrating Technology in Classrooms”
- “Assessment Strategies for Measuring Critical Thinking Skills”
Psychology and Behavior
- “The Influence of Social Media on Adolescent Well-being”
- “Cognitive Biases in Decision-Making: A Cross-Cultural Study”
- “The Role of Empathy in Conflict Resolution”
- “Positive Psychology Interventions for Workplace Satisfaction”
- “Exploring the Relationship Between Sleep Patterns and Mental Health”
Biology and Genetics
- “Genetic Markers for Predisposition to Neurodegenerative Diseases”
- “CRISPR-Cas9 Technology: Ethical Implications and Future Prospects”
- “Evolutionary Adaptations in Response to Environmental Changes”
- “Understanding the Microbiome’s Impact on Immune System Function”
- “Epigenetic Modifications and Their Role in Disease Development”
Urban Planning and Architecture
- “Smart Cities: Balancing Technological Innovation and Privacy”
- “Revitalizing Urban Spaces: Community Engagement in Design”
- “Sustainable Architecture: Integrating Nature into Urban Designs”
- “Transit-Oriented Development and Its Impact on City Dynamics”
- “Assessing the Cultural Significance of Urban Landscapes”
Linguistics and Communication
- “The Influence of Language on Cross-Cultural Communication”
- “Language Development in Multilingual Environments”
- “The Impact of Nonverbal Communication on Interpersonal Relationships”
- “Digital Communication and the Evolution of Language”
- “Language Processing in Bilingual Individuals: A Neuroscientific Approach”
Political Science and International Relations
- “The Role of Social Media in Political Mobilization”
- “Global Governance in the Era of Transnational Challenges”
- “Human Rights and the Ethics of Intervention in International Affairs”
- “Political Polarization: Causes and Consequences”
- “Climate Change Diplomacy: Assessing International Agreements”
Physics and Astronomy
- “Dark Matter: Unraveling the Mysteries of the Universe”
- “Quantum Entanglement and Its Potential Applications”
- “The Search for Exoplanets in Habitable Zones”
- “Astrophysical Phenomena: Exploring Black Holes and Neutron Stars”
- “Advancements in Quantum Computing Algorithms”
Education Technology (EdTech)
- “Adaptive Learning Platforms: Personalizing Education for Every Student”
- “The Impact of Virtual Reality Simulations on STEM Education”
- “E-Learning Accessibility for Students with Disabilities”
- “Gamified Learning: Enhancing Student Engagement and Retention”
- “Digital Literacy Education: Navigating the Information Age”
Sociology and Anthropology
- “Cultural Shifts in Modern Society: An Anthropological Exploration”
- “Social Movements in the Digital Age: Activism and Connectivity”
- “Gender Roles and Equality: A Cross-Cultural Perspective”
- “Urbanization and Its Effects on Traditional Societal Structures”
- “Cultural Appropriation: Understanding Boundaries and Respect”
Materials Science and Engineering
- “Nanostructured Materials: Innovations in Manufacturing and Applications”
- “Biodegradable Polymers: Towards Sustainable Packaging Solutions”
- “Materials for Energy Storage: Advancements and Challenges”
- “Smart Materials in Healthcare: From Diagnosis to Treatment”
- “Robust Coatings for Extreme Environments: Applications in Aerospace”
History and Archaeology
- “Digital Reconstruction of Historical Sites: Preserving the Past”
- “Trade Routes in Ancient Civilizations: A Comparative Study”
- “Archaeogenetics: Unraveling Human Migrations Through DNA Analysis”
- “Historical Linguistics: Tracing Language Evolution Over Millennia”
- “The Archaeology of Conflict: Studying War through Artifacts”
Marketing and Consumer Behavior
- “Influencer Marketing: Impact on Consumer Trust and Purchasing Decisions”
- “The Role of Brand Storytelling in Consumer Engagement”
- “E-commerce Personalization Strategies: Balancing Customization and Privacy”
- “Cross-Cultural Marketing: Adapting Campaigns for Global Audiences”
- “Consumer Perceptions of Sustainable Products: A Market Analysis”
Neuroscience and Cognitive Science
- “Neuroplasticity and Cognitive Rehabilitation: Implications for Therapy”
- “The Neuroscience of Decision-Making: Insights from Brain Imaging”
- “Cognitive Aging: Understanding Memory Decline and Cognitive Resilience”
- “The Role of Neurotransmitters in Emotional Regulation”
- “Neuroethical Considerations in Brain-Computer Interface Technologies”
Public Health and Epidemiology
- “Epidemiological Trends in Infectious Diseases: Lessons from Global Outbreaks”
- “Public Health Interventions for Reducing Non-Communicable Diseases”
- “Health Disparities Among Marginalized Communities: Addressing the Gaps”
- “The Impact of Climate Change on Vector-Borne Diseases”
- “Community-Based Approaches to Promoting Health Equity”
Robotics and Automation
- “Human-Robot Collaboration in Manufacturing: Enhancing Productivity and Safety”
- “Autonomous Vehicles: Navigating the Path to Mainstream Adoption”
- “Soft Robotics: Engineering Flexibility for Real-World Applications”
- “Ethical Considerations in the Development of AI-powered Robotics”
- “Bio-Inspired Robotics: Learning from Nature to Enhance Machine Intelligence”
Literature and Literary Criticism
- “Postcolonial Narratives: Deconstructing Power Structures in Literature”
- “Digital Storytelling Platforms: Changing the Landscape of Narrative Arts”
- “Literature and Cultural Identity: Exploring Representations in Global Contexts”
- “Eco-Critical Perspectives in Contemporary Literature”
- “Feminist Literary Criticism: Reinterpreting Classic Texts Through a New Lens”
Chemistry and Chemical Engineering
- “Green Chemistry: Sustainable Approaches to Chemical Synthesis”
- “Nanomaterials for Drug Delivery: Innovations in Biomedical Applications”
- “Chemical Process Optimization: Towards Energy-Efficient Production”
- “The Chemistry of Taste: Molecular Insights into Food Flavors”
- “Catalytic Converters: Advancements in Pollution Control Technologies”
Cultural Studies and Media
- “Media Representations of Social Movements: Framing and Impact”
- “Pop Culture and Identity: Exploring Trends in a Globalized World”
- “The Influence of Social Media on Political Discourse”
- “Reality Television and Perceptions of Reality: A Cultural Analysis”
- “Media Literacy Education: Navigating the Digital Information Age”
Astronomy and Astrophysics
- “Gravitational Waves: Probing the Cosmos for New Discoveries”
- “The Life Cycle of Stars: From Birth to Supernova”
- “Astrobiology: Searching for Extraterrestrial Life in the Universe”
- “Dark Energy and the Accelerating Expansion of the Universe”
- “Cosmic Microwave Background: Insights into the Early Universe”
Social Work and Community Development
- “Community-Based Mental Health Interventions: A Social Work Perspective”
- “Youth Empowerment Programs: Fostering Resilience in Vulnerable Communities”
- “Social Justice Advocacy in Contemporary Social Work Practice”
- “Intersectionality in Social Work: Addressing the Complex Needs of Individuals”
- “The Role of Technology in Enhancing Social Services Delivery”
Artificial Intelligence and Ethics
- “Ethical Considerations in AI Decision-Making: Balancing Autonomy and Accountability”
- “Bias and Fairness in Machine Learning Algorithms: A Critical Examination”
- “Explainable AI: Bridging the Gap Between Complexity and Transparency”
- “The Social Implications of AI-Generated Content: Challenges and Opportunities”
- “AI and Personal Privacy: Navigating the Ethical Dimensions of Data Usage”
Linguistics and Computational Linguistics
- “Natural Language Processing: Advancements in Understanding Human Communication”
- “Multilingualism in the Digital Age: Challenges and Opportunities”
- “Cognitive Linguistics: Exploring the Relationship Between Language and Thought”
- “Speech Recognition Technologies: Applications in Everyday Life”
- “Syntax and Semantics: Unraveling the Structure of Language”
Geology and Earth Sciences
- “Geological Hazards Assessment in Urban Planning: A Case Study”
- “Paleoclimatology: Reconstructing Past Climate Patterns for Future Predictions”
- “Geomorphological Processes in Coastal Landscapes: Implications for Conservation”
- “Volcanic Activity Monitoring: Early Warning Systems and Mitigation Strategies”
- “The Impact of Human Activities on Soil Erosion: An Ecological Perspective”
Political Economy and Global Governance
- “Global Trade Agreements: Assessing Economic Impacts and Equity”
- “Political Economy of Energy Transition: Policies and Socioeconomic Effects”
- “The Role of International Organizations in Global Governance”
- “Financial Inclusion and Economic Development: A Comparative Analysis”
- “The Political Economy of Pandemics: Governance and Crisis Response”
Food Science and Nutrition
- “Nutrigenomics: Personalized Nutrition for Optimal Health”
- “Functional Foods: Exploring Health Benefits Beyond Basic Nutrition”
- “Sustainable Food Production: Innovations in Agriculture and Aquaculture”
- “Dietary Patterns and Mental Health: A Comprehensive Review”
- “Food Allergies and Sensitivities: Mechanisms and Management Strategies”
Sociology and Technology
- “Digital Inequalities: Examining Access and Usage Patterns Across Demographics”
- “The Impact of Social Media on Social Capital and Community Building”
- “Technological Surveillance and Privacy Concerns: A Sociological Analysis”
- “Virtual Communities: An Exploration of Identity Formation in Online Spaces”
- “The Social Dynamics of Online Activism: Mobilization and Participation”
Materials Science and Nanotechnology
- “Nanomaterials for Biomedical Imaging: Enhancing Diagnostic Precision”
- “Self-Healing Materials: Advances in Sustainable and Resilient Infrastructure”
- “Smart Textiles: Integrating Nanotechnology for Enhanced Functionality”
- “Multifunctional Nanoparticles in Drug Delivery: Targeted Therapies and Beyond”
- “Nanocomposites for Energy Storage: Engineering Efficient Capacitors”
Communication and Media Studies
- “Media Convergence: The Evolution of Content Delivery in the Digital Age”
- “The Impact of Social Media Influencers on Consumer Behavior”
- “Crisis Communication in a Hyperconnected World: Lessons from Global Events”
- “Media Framing of Environmental Issues: A Comparative Analysis”
- “Digital Detox: Understanding Media Consumption Patterns and Well-being”
Developmental Psychology
- “Early Childhood Attachment and Its Long-Term Impact on Adult Relationships”
- “Cognitive Development in Adolescence: Challenges and Opportunities”
- “Parenting Styles and Academic Achievement: A Cross-Cultural Perspective”
- “Identity Formation in Emerging Adulthood: The Role of Social Influences”
- “Interventions for Promoting Resilience in At-Risk Youth Populations”
Aerospace Engineering
- “Advancements in Aerodynamics: Redefining Flight Efficiency”
- “Space Debris Management: Mitigating Risks in Earth’s Orbit”
- “Aerodynamic Design Optimization for Supersonic Flight”
- “Hypersonic Propulsion Technologies: Pushing the Boundaries of Speed”
- “Materials for Space Exploration: Engineering Solutions for Harsh Environments”
Political Psychology
- “Political Polarization and Public Opinion: Exploring Cognitive Biases”
- “Leadership Styles and Public Perception: A Psychological Analysis”
- “Nationalism and Identity: Psychological Factors Shaping Political Beliefs”
- “The Influence of Emotional Appeals in Political Communication”
- “Crisis Leadership: The Psychological Dynamics of Decision-Making in Times of Uncertainty”
Marine Biology and Conservation
- “Coral Reef Restoration: Strategies for Biodiversity Conservation”
- “Ocean Plastic Pollution: Assessing Impacts on Marine Ecosystems”
- “Marine Mammal Communication: Insights from Bioacoustics”
- “Sustainable Fisheries Management: Balancing Ecological and Economic Concerns”
- “The Role of Mangrove Ecosystems in Coastal Resilience”
Artificial Intelligence and Creativity
- “Generative AI in Creative Industries: Challenges and Innovations”
- “AI-Enhanced Creativity Tools: Empowering Artists and Designers”
- “Machine Learning for Music Composition: Bridging Art and Technology”
- “Creative AI in Film and Entertainment: Transforming Storytelling”
- “Ethical Considerations in AI-Generated Art and Content”
Cultural Anthropology
- “Cultural Relativism in Anthropological Research: Opportunities and Challenges”
- “Rituals and Symbolism: Unraveling Cultural Practices Across Societies”
- “Migration and Cultural Identity: An Ethnographic Exploration”
- “Material Culture Studies: Understanding Societies through Objects”
- “Indigenous Knowledge Systems: Preserving and Promoting Cultural Heritage”
Quantum Computing and Information Science
- “Quantum Information Processing: Algorithms and Applications”
- “Quantum Cryptography: Securing Communication in the Quantum Era”
- “Quantum Machine Learning: Enhancing AI through Quantum Computing”
- “Quantum Computing in Finance: Opportunities and Challenges”
- “Quantum Internet: Building the Next Generation of Information Networks”
Public Policy and Urban Planning
- “Smart Cities and Inclusive Urban Development: A Policy Perspective”
- “Public-Private Partnerships in Infrastructure Development: Lessons Learned”
- “The Impact of Transportation Policies on Urban Mobility Patterns”
- “Housing Affordability: Policy Approaches to Addressing Urban Challenges”
- “Data-Driven Decision-Making in Urban Governance: Opportunities and Risks”
Gerontology and Aging Studies
- “Healthy Aging Interventions: Promoting Quality of Life in Older Adults”
- “Social Isolation and Mental Health in Aging Populations: Interventions and Support”
- “Technology Adoption Among Older Adults: Bridging the Digital Divide”
- “End-of-Life Decision-Making: Ethical Considerations and Legal Frameworks”
- “Cognitive Resilience in Aging: Strategies for Maintaining Mental Sharpness”
Examples of Effective Research Titles
Illustrative Examples from Various Disciplines
Here are examples of effective research titles from different disciplines:
- “Unlocking the Mysteries of Neural Plasticity: A Multidisciplinary Approach”
- “Sustainable Urban Development: Integrating Environmental and Social Perspectives”
- “Quantum Computing: Navigating the Path to Practical Applications”
Analysis of What Makes Each Title Effective
- Clear indication of the research focus.
- Inclusion of key terms relevant to the field.
- Incorporation of a multidisciplinary or integrated approach where applicable.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid in Research Title Creation
A. Vagueness and Ambiguity
Vague or ambiguous titles can deter readers from engaging with your research. Ensure your title is straightforward and leaves no room for misinterpretation.
B. Overuse of Jargon
While technical terms are essential, excessive jargon can alienate readers who may not be familiar with the specific terminology. Strike a balance between precision and accessibility.
C. Lack of Alignment with Research Objectives
Your title should align seamlessly with the objectives and findings of your research. Avoid creating titles that misrepresent the core contributions of your study.
D. Lengthy and Complicated Titles
Lengthy titles can be overwhelming and may not effectively convey the essence of your research. Aim for brevity while maintaining clarity and informativeness.
E. Lack of Creativity and Engagement
A bland title may not capture the interest of potential readers. Inject creativity where appropriate and strive to create a title that sparks curiosity.
Ethical Considerations in Research Title Creation
- Avoiding Sensationalism and Misleading Titles
Ensure that your title accurately represents the content of your research. Avoid sensationalism or misleading language that may compromise the integrity of your work.
- Ensuring Accuracy and Integrity in Representing Research Content
Your title should uphold the principles of accuracy and integrity. Any claims or implications in the title should be supported by the actual findings of your research.
Crafting a captivating research title is a nuanced process that requires careful consideration of various factors. From clarity and relevance to creativity and ethical considerations, each element plays a crucial role in the success of your title.
By following the outlined strategies and avoiding common pitfalls for research title ideas, researchers can enhance the visibility and impact of their work, contributing to the broader scholarly conversation. Remember, your research title is the first impression readers have of your work, so make it count.
Related Posts

Step by Step Guide on The Best Way to Finance Car

The Best Way on How to Get Fund For Business to Grow it Efficiently

Researched by Consultants from Top-Tier Management Companies

Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories
Top 10 Product Market Research Templates with Samples and Examples

Deepika Dhaka
Product Market Research is important for businesses to plan and make good choices. It's like a strong base that helps them make smart decisions and grow steadily. Companies can learn important things by looking closely at how the market works, what customers do, and what's popular in the industry. This helps them improve their products, determine who their customers are, and make better marketing plans.
A compelling illustration of the indispensable role of Product Market Research in achieving business success is evident in the case of Netflix.
As the streaming industry evolved, Netflix consistently conducted thorough research to comprehend shifting viewer preferences, content consumption habits, and emerging technological trends. This proactive approach allowed the company to shift from its initial DVD rental model to a streaming service, reshaping the entertainment landscape. By analyzing data on user behavior, content engagement, and regional variations, Netflix effectively curated a diverse array of original programming that resonated with global audiences, propelling it to become a household name in the streaming sphere. This example shows how important Product Market Research is for helping companies to be flexible, creative, and stand out in tough and competitive markets.
If you're someone who is in charge of finding out what people want for a new product, you might find it hard. The biggest problem is figuring out how to do this research in a way that helps your new product succeed. Well, that's where we can help!
Here comes Product Market Research Templates!
Best Product Market Research Templates for New Product Development
This blog will walk you through the most popular templates to prepare for effective research that ensures that none of your resources are wasted. Also, the 100% customizable nature of the templates provides you with the desired flexibility to edit your presentations. The content-ready slides give you the much-needed structure.
Let’s begin exploring these pre-designed templates!
Template 1: New Product Market Research PowerPoint Presentation
This Complete Deck is your one-stop solution for conducting thorough research for new products. It equips you with well-structured slides on the customer preferences survey form and overview slides for survey outcomes. It contains easy-to-understand graphics, pie charts, and well-formatted tables to assist you best. It will help you save time you would have otherwise wasted drafting the forms and creating the resulting structure. Download this presentation now to have a handy resource.

Download this template
Template 2: Market Research for New Product PPT Slide
This PowerPoint Slide will help you understand and communicate the two aspects. These are the market research process and the new product development process. The market research process includes steps like primary & secondary research, concept volumetric and packaging testing, consumer usage research, advertising research pre-testing, and marketing monitoring. On the other hand, the new product development process includes identifying consumer views, product concept and packaging development, testing the product, brand positioning and advertising development, and product launch and post-launch. Download this template now for a consolidated view of these crucial processes.

(Leverage our Qualitative and Quantitative Data Analysis Templates to uncover meaningful patterns, translating data into actionable strategies. Download today for a transformative analysis experience!)
Template 3: Product Market Research Outcome Analysis
This PPT Template is ideal if you want to plan and present the product market research outcome analysis. It includes factors like growth drivers, restraints, challenges, and opportunities, which are also abbreviated as DRCO for easy recall. If you're working on a new product or business, you can use this slide to organize your thoughts and plan what you need to focus on. Download this helpful resource now!
Template 4: Budgeting for Product Launch Market Research
If you are struggling to draft a budget for your research, here’s an effective tool to the rescue. This Budgeting framework includes five columns entailing business objective, research objective, priority, methodologies, and the annual budget. This content-ready slide is your one-stop solution to all your budgeting challenges. It will help you give a crystal clear- justification for the money involved. Download it today to create an effective and efficient budget.
Template 5: Quarterly Market Research Roadmap for Product Launch
Use this PPT Template to create an achievable and practical roadmap for your research. It encompasses a yearly roadmap divided into four quarters and covers activities such as market and community research, identifying target customers, devising a unique value proposition (USP), and determining market strategy. It also includes other tasks such as testing product and overall approach, rolling out marketing campaigns, and monitoring product life cycle. If you want to add or remove the activities as per your requirement, you can easily do it here. Download this PPT Slide now to ensure easy communication of tasks and timeline to the members helping you with the research.
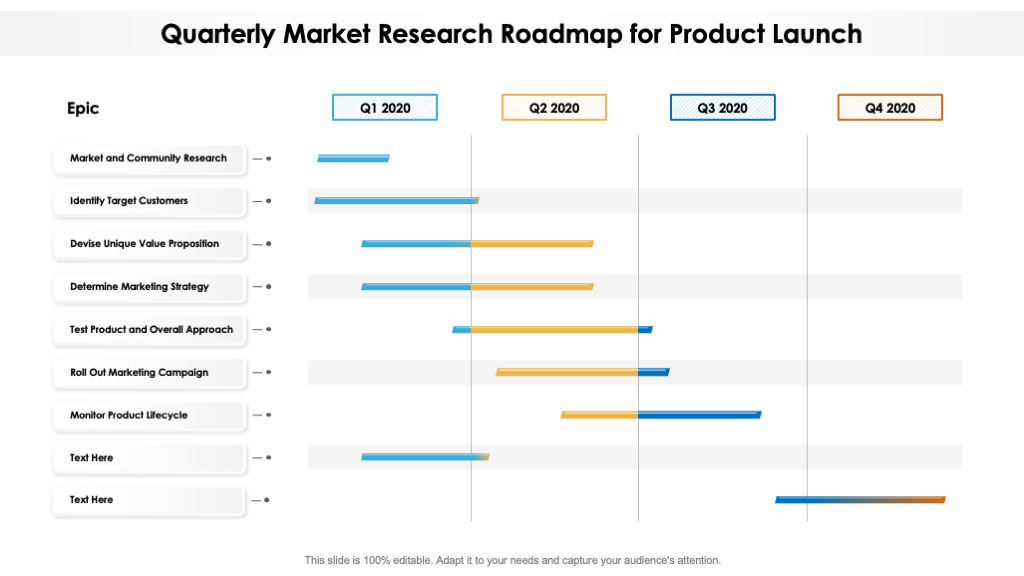
Template 6: New Product Market Research Survey Form Template
Streamline your product development process with this user-friendly template, designed to gather valuable insights on customer preferences and expectations. Easily customizable, this template offers a structured approach to crafting surveys that unveil critical market trends. From identifying target audiences to refining product features, this template empowers you to make informed decisions backed by thorough research. Download this template now!

Template 7: New Product Market Research Survey Outcome Template
Get a comprehensive view of your survey results with this feature-packed slide entailing fool-proof graphics and visuals. If you use this slide, it will just need a glance to understand your customer preferences. It covers crucial questions that you need to know before developing a new product. Download this template now for informed and data-driven decision-making!
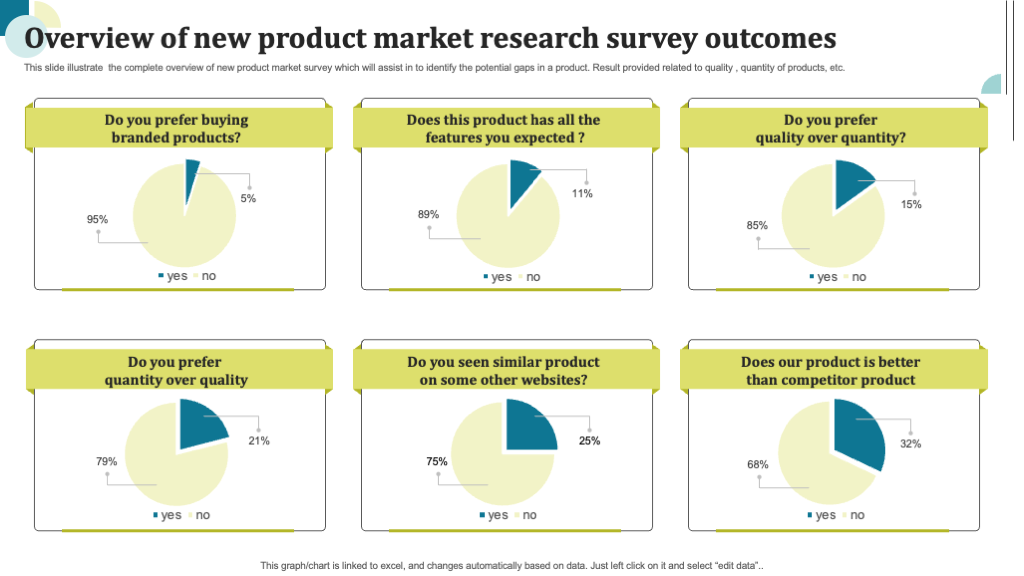
Template 8: Product Market Research Survey Result Page
This template presents your survey findings in an elaborated manner, using clear visuals to reveal customer preferences. Streamline decision-making by identifying key trends for well-informed product strategies. It encompasses essential customer details like their professions and highlights customer responses, categorizing them by country. With user-friendly graphics, this PPT template simplifies complex information, making it easily understandable. Get it today!
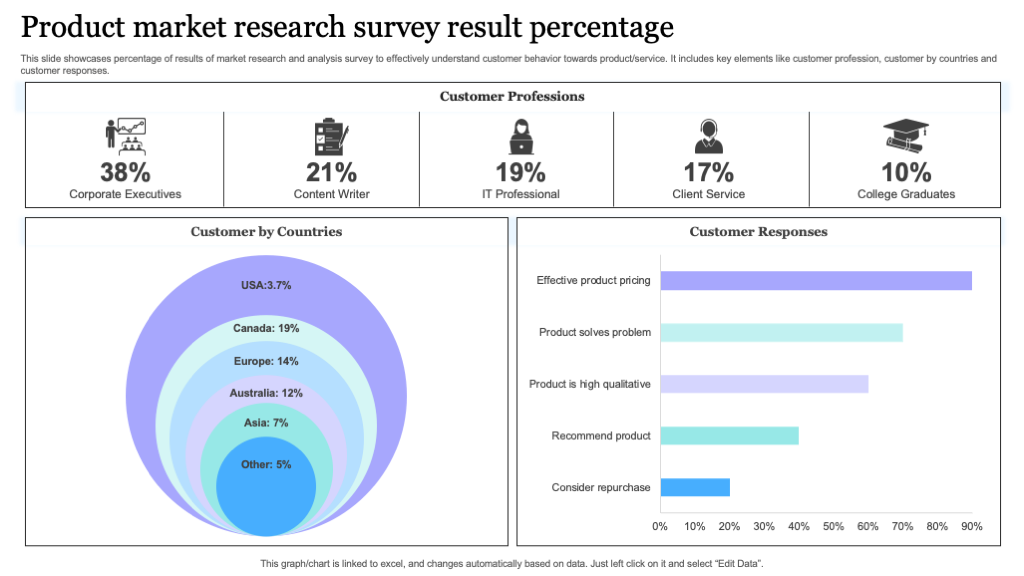
Download the template
Template 9: Survey Result Reporting Dashboard Template
Presenting a comprehensive report derived from a product market research survey, this slide highlights customer feedback. It encompasses vital components, including desired ingredients, new product concept assessment, and demographic insights grouped by gender, marital status, age, and education. It delves into key evaluation factors such as uniqueness, problem-solving ability, effectiveness, trend appeal, and safety. Instantly grasp the survey outcomes with this template. Download now for a concise overview of the report!
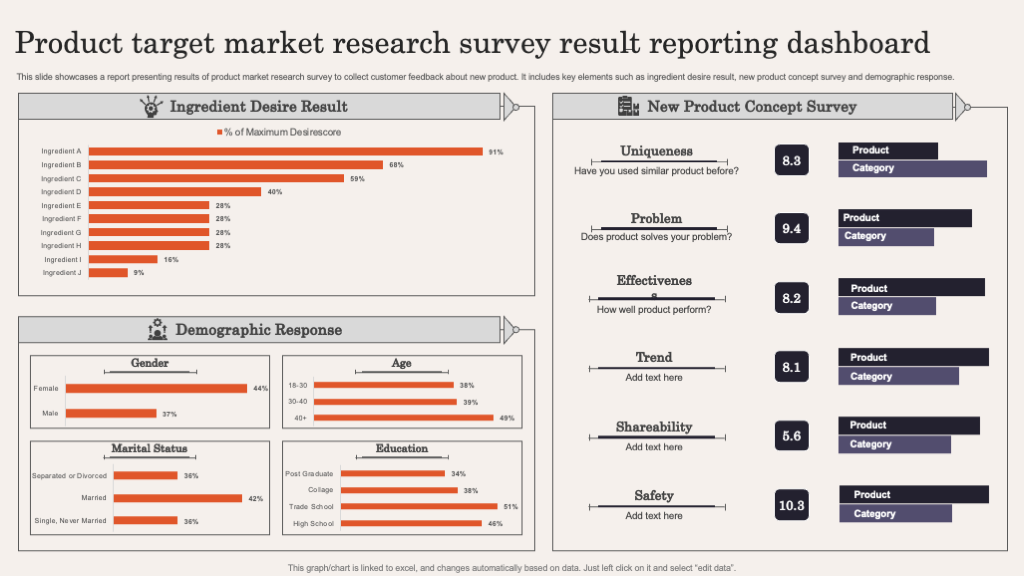
Template 10: Market Research Survey Questionnaire Template
If you are struggling to create a survey questionnaire with a well-structured format, this PPT Slide is the best choice. It contains important questions you must ask for a new product development market research, such as “What is your first impression of the product?”, “What is your household income group” and how valuable the product is for the consumer. Each of these questions is an objective type providing easy-to-choose answers for the consumer. Get it now to obtain the real response.
Conduct Your Best Research Ever
By understanding the ever-evolving needs and preferences of our customers, we fortify our foundations, innovate relentlessly, and position ourselves for success. The strategic insights gained from thorough research become the building blocks of our growth, enabling us to craft products that truly resonate with our audience.
Whether you're a seasoned industry professional or an aspiring entrepreneur, harness the power of informed decisions by leveraging SlideTeam's meticulously crafted templates. Take the first step towards success. Download these templates now!
PS: If you are looking for Product Proposal Templates, here’s a handy guide with the most popular samples and examples.
Explore our Monthly, Semi-annual, and Annual plans here to download the premium templates on any topic.
FAQs on Product Market Research
What is product market research.
Product market research involves studying the market to understand what customers want and need, as well as how they behave. It helps businesses make informed decisions about their products and marketing strategies by collecting and analyzing data about customer preferences, trends, and competition.
How to do market research for new products?
To conduct market research for new products, you can follow these steps:
- Define Your Goals: Understand what you want to learn and achieve.
- Identify Your Target Audience: Determine who your potential customers are.
- Collect Data: Use surveys, interviews, online research, and more to gather information.
- Analyze Data: Look for patterns, preferences, and trends in the collected information.
- Evaluate Competition: Study similar products and their success in the market.
- Make Decisions: Based on your findings, make informed decisions about your new product.
What is the objective of product research?
The objective of product research is to gather insights and information that help in developing, launching, and promoting products successfully. It aims to understand customer needs, preferences, and behaviors, evaluate market demand, identify competitive advantages, and guide strategic decisions throughout the product's lifecycle.
What are the five product levels?
The five product levels represent different layers of a product's offering:
- Core Product: The basic benefit or problem-solving function that the product provides.
- Generic Product: The basic features and attributes of the product.
- Expected Product: The set of attributes that customers expect to receive when they purchase the product.
- Augmented Product: Additional features, benefits, or services that exceed customer expectations.
- Potential Product: The future possibilities and innovations that the product could offer.
Why is product research important in marketing?
Product research is vital in marketing for several reasons:
- Customer Understanding: It helps in comprehending customer needs, preferences, and behaviors.
- Innovation: Research guides the development of new and improved products.
- Market Positioning: It assists in identifying unique selling points and differentiating from competitors.
- Reduced Risk: Research minimizes the risk of product failure by aligning products with customer demands.
- Effective Marketing Strategies: Insights from research inform targeted marketing campaigns and communication.
Related posts:
- Must-have Marketing Research Proposal Example Templates with Samples
- Top 10 Product Launching and Marketing Playbook Templates with Samples and Examples
- Top 10 Modern Marketers Playbook Templates with Examples and Samples
- The Ultimate PowerPoint Template Toolkit For Effective Strategic Management in 2021
Liked this blog? Please recommend us

Top 7 Research Budget Templates with Samples and Examples

Research Project Proposal Templates That Ace Your Funding Quest!

Top 11 Product Proposal Templates to Highlight Your Key Strategies

Top 10 Templates to Present Qualitative and Quantitative Data Analysis in Research Proposal
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA - the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

Digital revolution powerpoint presentation slides

Sales funnel results presentation layouts
3d men joinning circular jigsaw puzzles ppt graphics icons

Business Strategic Planning Template For Organizations Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Future plan powerpoint template slide

Project Management Team Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Brand marketing powerpoint presentation slides

Launching a new service powerpoint presentation with slides go to market

Agenda powerpoint slide show

Four key metrics donut chart with percentage

Engineering and technology ppt inspiration example introduction continuous process improvement

Meet our team representing in circular format

6 Product Development Resume Examples to Land You a Role in 2023
Product developers excel at creating innovative solutions that cater to the needs and desires of their target market. In the same vein, your resume should be like a well-designed product, showcasing your unique features and value proposition to potential employers. In this guide, we'll explore X outstanding product development resume examples that will help you engineer your own success story in 2023.

Resume Examples
Resume guidance.
- High Level Resume Tips
- Must-Have Information
- Why Resume Headlines & Titles are Important
- Writing an Exceptional Resume Summary
- How to Impress with Your Work Experience
- Top Skills & Keywords
- Go Above & Beyond with a Cover Letter
- Resume FAQs
- Related Resumes
Common Responsibilities Listed on Product Development Resumes:
- Conduct market research to identify customer needs and preferences
- Develop product concepts and prototypes based on research findings
- Collaborate with cross-functional teams (engineering, design, marketing, etc.) to refine product concepts and ensure feasibility
- Create product specifications and requirements documents
- Manage the product development process from ideation to launch
- Conduct user testing and gather feedback to inform product improvements
- Develop pricing and positioning strategies for new products
- Monitor and analyze product performance metrics to identify areas for improvement
- Stay up-to-date on industry trends and emerging technologies to inform product development decisions
- Manage relationships with external vendors and partners involved in product development
- Ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards
- Develop and execute go-to-market plans for new products.
You can use the examples above as a starting point to help you brainstorm tasks, accomplishments for your work experience section.
Product Development Resume Example:
- Developed and launched a new product line, resulting in a 25% increase in revenue and a 15% increase in market share within the first year.
- Collaborated with the marketing team to develop a successful go-to-market strategy, resulting in a 30% increase in product awareness and adoption.
- Conducted user testing and gathered feedback to inform product improvements, resulting in a 20% increase in customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Managed the product development process from ideation to launch for a complex software solution, resulting in a successful launch and a 40% increase in sales within the first six months.
- Conducted market research and developed pricing and positioning strategies for new products, resulting in a 25% increase in profit margins and a 10% increase in market share.
- Managed relationships with external vendors and partners involved in product development, resulting in a 20% reduction in development costs and a 15% increase in product quality.
- Developed and executed a successful product roadmap, resulting in a 30% increase in revenue and a 20% increase in customer retention.
- Conducted market research and identified emerging technologies to inform product development decisions, resulting in a 25% increase in product innovation and a 15% increase in market share.
- Monitored and analyzed product performance metrics to identify areas for improvement, resulting in a 20% increase in product efficiency and a 10% increase in customer satisfaction.
- Product development strategy
- Market research and analysis
- Product roadmap creation
- Go-to-market strategy development
- User testing and feedback analysis
- Pricing and positioning strategy
- Vendor and partner management
- Emerging technology identification
- Product performance metrics analysis
- Cross-functional collaboration
- Customer satisfaction and retention
- Product innovation
- Product efficiency improvement
- Software development process management
- Agile project management
Product Development Manager Resume Example:
- Led the development and launch of a new product line, resulting in a 25% increase in revenue and a 15% increase in market share within the first year.
- Implemented a customer feedback program, resulting in a 20% increase in customer satisfaction scores and a 10% reduction in product returns.
- Managed a team of 15 product developers and engineers, resulting in a 30% increase in team productivity and a 15% reduction in development costs.
- Developed and executed a product roadmap, resulting in a 50% increase in product adoption and a 20% increase in revenue within the first year.
- Collaborated with cross-functional teams to launch a new product feature, resulting in a 10% increase in customer engagement and a 5% increase in customer retention.
- Managed a product development budget of $5M, resulting in a 10% reduction in development costs and a 5% increase in profit margins.
- Led the development and launch of a new product category, resulting in a 40% increase in revenue and a 20% increase in market share within the first year.
- Developed and implemented a product marketing strategy, resulting in a 30% increase in product awareness and a 15% increase in customer acquisition.
- Managed a team of 20 product developers and engineers, resulting in a 25% increase in team productivity and a 10% reduction in development costs.
- Cross-functional team collaboration
- Product marketing strategy
- Budget management
- Team leadership and management
- Customer feedback analysis
- Product launch execution
- Product lifecycle management
- Data-driven decision making
- Competitive analysis
- Risk management
- Stakeholder communication
Product Development Engineer Resume Example:
- Implemented a new testing process, reducing product defects by 30% and improving customer satisfaction scores by 20%.
- Collaborated with cross-functional teams to develop and execute a cost reduction strategy, resulting in a 10% decrease in product manufacturing costs.
- Managed the development and launch of a new product, resulting in a 20% increase in sales and a 15% increase in customer retention.
- Developed and executed a product testing plan, reducing product defects by 25% and improving product quality scores by 20%.
- Collaborated with the marketing team to develop and execute a successful product launch campaign, resulting in a 30% increase in website traffic and a 25% increase in social media engagement.
- Developed and launched a new product line, resulting in a 30% increase in revenue and a 20% increase in market share within the first year.
- Implemented a new product development process, reducing time-to-market by 25% and improving team productivity by 30%.
- Collaborated with cross-functional teams to develop and execute a product improvement plan, resulting in a 15% increase in customer satisfaction scores and a 10% increase in product ratings.
- Product development and launch
- Product testing and quality improvement
- Cost reduction strategies
- Project management
- Product improvement planning
- Time-to-market optimization
- Marketing and product launch campaigns
- Data analysis and performance metrics
- Technical problem-solving
- CAD and 3D modeling
- Rapid prototyping
- Design for manufacturability
- Material selection and testing
- Intellectual property and patent management
- Risk assessment and mitigation
- Lean manufacturing principles
- Continuous improvement methodologies
- Strong communication and presentation skills
Director of Product Development Resume Example:
- Developed and executed a product strategy that resulted in a 25% increase in revenue and a 15% increase in customer satisfaction within the first year.
- Lead the development of a new product line that generated $5M in revenue within the first six months of launch.
- Managed a team of 15 product developers, resulting in a 20% increase in team productivity and a 10% reduction in time-to-market.
- Collaborated with cross-functional teams to launch a new product that exceeded sales targets by 30% and increased market share by 15%.
- Developed and implemented a pricing strategy that resulted in a 10% increase in profit margins and a 5% increase in customer retention.
- Managed a product development budget of $10M, resulting in a 5% reduction in costs and a 10% increase in ROI.
- Lead the development and launch of a new product that generated $20M in revenue within the first year and increased market share by 10%.
- Analyzed customer feedback and market trends to identify opportunities for product improvement, resulting in a 15% increase in customer satisfaction and a 10% increase in sales.
- Managed a team of 20 product developers, resulting in a 25% increase in team productivity and a 20% reduction in time-to-market.
- Product strategy development
- Market analysis and trend identification
- Pricing strategy development
- Budget management and cost reduction
- Team leadership and productivity improvement
- New product development and launch
- Customer satisfaction and retention improvement
- Sales target achievement and market share growth
- ROI maximization
VP of Product Development Resume Example:
- Developed and launched a new product line that generated $10M in revenue within the first year, exceeding the company's sales goals by 20%.
- Lead a team of 15 product managers and designers to create a product roadmap that resulted in a 30% increase in customer satisfaction and a 25% increase in retention rates.
- Implemented a data-driven approach to product development, resulting in a 40% reduction in time to market and a 15% increase in product quality.
- Managed the successful launch of a new product that generated $5M in revenue within the first six months, exceeding sales goals by 10%.
- Collaborated with cross-functional teams to develop and implement a product strategy that resulted in a 25% increase in market share and a 20% increase in customer engagement.
- Developed and maintained relationships with key stakeholders, resulting in a 15% increase in customer satisfaction and a 10% increase in customer retention rates.
- Lead the development and launch of a new product that generated $15M in revenue within the first year, exceeding sales goals by 30%.
- Implemented a customer feedback program that resulted in a 20% increase in customer satisfaction and a 15% increase in retention rates.
- Developed and managed a product budget of $5M, resulting in a 10% reduction in costs and a 5% increase in profitability.
- Product launch management
- Stakeholder relationship management
- Team leadership and development
- Product quality improvement
- Competitive analysis and positioning
New Product Development Manager Resume Example:
- Developed and launched a new product line that generated $5M in revenue within the first year, exceeding sales targets by 20%.
- Lead a cross-functional team of 15 professionals to develop and launch 10 new products, resulting in a 30% increase in market share within the first 6 months.
- Implemented a new product development process that reduced time-to-market by 25% and increased product success rate by 15%.
- Identified and evaluated potential new product opportunities, resulting in the launch of a new product line that generated $2M in revenue within the first year.
- Collaborated with engineering and design teams to develop and launch a new product that exceeded sales targets by 25% and increased market share by 10%.
- Managed a product development budget of $3M, delivering all projects on time and within budget, resulting in a 95% project success rate.
- Developed and executed a product development strategy that resulted in a 50% increase in revenue and a 20% increase in market share within the first year.
- Lead a cross-functional team of 20 professionals to develop and launch 15 new products, resulting in a 40% increase in customer base and a 25% increase in customer satisfaction.
- Implemented a product lifecycle management process that reduced product development costs by 30% and increased product quality by 20%.
- Cross-functional team leadership
- Customer satisfaction enhancement
- Collaboration and communication
- Innovation and creativity
- Technical knowledge and expertise
- Vendor and supplier management
- Agile and lean methodologies
High Level Resume Tips for Product Developments:
Must-have information for a product development resume:.
Here are the essential sections that should exist in an Product Development resume:
- Contact Information
- Resume Headline
- Resume Summary or Objective
- Work Experience & Achievements
- Skills & Competencies
Additionally, if you're eager to make an impression and gain an edge over other Product Development candidates, you may want to consider adding in these sections:
- Certifications/Training
Let's start with resume headlines.
Why Resume Headlines & Titles are Important for Product Developments:
Product development resume headline examples:, strong headlines.
- Product Development Manager with a proven track record of launching successful consumer products in the tech industry
- Agile Product Development Specialist with expertise in leading cross-functional teams and implementing lean methodologies to drive product innovation
- Strategic Product Development Leader with a focus on market research and customer insights to develop and launch high-demand products
Why these are strong: These resume headlines are strong for Product Development professionals as they highlight key skills and experiences that are highly valued in the industry. The first headline emphasizes the candidate's ability to launch successful products in a competitive tech industry, which is a crucial factor for hiring managers. The second headline showcases the candidate's expertise in agile methodologies and cross-functional team leadership, which are essential for driving product innovation. Finally, the third headline highlights the candidate's strategic mindset and focus on market research and customer insights, which are critical for developing and launching high-demand products.
Weak Headlines
- Product Development Manager with Experience in Innovation and Design Thinking
- Skilled Product Developer with Knowledge in Agile Methodologies and Prototyping
- Product Development Professional with a Focus on Market Research and Customer Insights
Why these are weak:
- These resume headlines need improvement for Product Developments as they lack specificity and don't emphasize the unique value or accomplishments that the candidates bring to the table. The first headline mentions experience in innovation and design thinking, but doesn't provide any context or results, such as successful product launches or patents. The second headline highlights skills but doesn't mention any specific products or projects the candidate has worked on, or any measurable achievements such as increased revenue or decreased time to market. The third headline mentions a focus on market research and customer insights, but fails to showcase any specific research methods or insights that could strengthen the candidate's profile.
Writing an Exceptional Product Development Resume Summary:
Resume summaries are crucial for Product Developments professionals as they provide a concise yet impactful way to showcase their skills, experience, and unique value proposition. A well-crafted summary can immediately capture the attention of hiring managers, setting the tone for the rest of the resume and positioning the candidate as an ideal fit for the role.
For Product Developments specifically, an effective resume summary should highlight the candidate's ability to drive product development and deliver customer value through innovation and creativity.
Key points that Product Developments professionals should convey in a resume summary include:
Relevant Experience: Clearly mention the number of years of experience you have in product development, highlighting any notable achievements or career highlights. If you have experience with different types of products or industries that are particularly relevant to the job, mention that too.
Technical and Domain Expertise: Showcase your knowledge of product development methodologies (Agile, Scrum, etc.), as well as any industry-specific knowledge that would be beneficial to the role (e.g., software development, hardware development, consumer electronics).
Innovation and Creativity: Highlight your ability to think outside the box, generate new ideas, and develop innovative solutions to complex problems.
Collaboration and Teamwork: In any product development role, collaboration and teamwork are essential components. Emphasize your ability to work with cross-functional teams, collaborate with stakeholders, and create a shared vision for the product.
Customer-Centric Mindset: Demonstrate your ability to identify customer needs, empathize with users, and incorporate their feedback into the product development process.
Analytical and Problem-Solving Skills: Show that you can analyze data, identify trends, and make informed decisions to optimize product performance and drive growth.
To create a compelling resume summary for Product Developments, use your best judgment to choose the right combination of these key points that align closest with the individual role you’re applying for. Remember, your resume summary will be one of the first things that a potential employer will see about you and your product development career.
Product Development Resume Summary Examples:
Strong summaries.
- Strategic Product Development Manager with 10 years of experience leading cross-functional teams to deliver innovative products that meet customer needs. Skilled in market research, product design, and project management, resulting in a 30% increase in revenue for the company.
- Agile Product Development Manager with a background in software engineering and 7 years of experience in the tech industry. Proficient in Scrum methodologies, adept at managing multiple projects simultaneously, and delivering high-quality products on time and within budget. Successfully launched a new product that generated $1M in revenue within the first year.
- User-focused Product Development Manager with 5 years of experience in the healthcare industry. Combining user research, design thinking, and data analysis to create products that improve patient outcomes and user satisfaction. Led the development of a new medical device that received FDA approval and increased patient compliance by 40%.
Why these are strong:
- These resume summaries are strong for Product Development Managers as they highlight the candidates' key skills, accomplishments, and industry-specific experience. The first summary emphasizes the candidate's strategic approach to product development and their ability to drive revenue growth. The second summary showcases the candidate's proficiency in Agile methodologies and their success in delivering high-quality products on time and within budget. Lastly, the third summary demonstrates the candidate's user-focused approach and their success in developing a new medical device that received FDA approval and improved patient outcomes.
Weak Summaries
- Product Development professional with experience in creating innovative products and collaborating with cross-functional teams to drive growth and profitability. Seeking a challenging role in a dynamic organization to leverage my skills and expertise in product development.
- Experienced Product Development Manager with a track record of successfully launching products in various industries. Skilled in project management, market research, and product design. Seeking a new opportunity to contribute to product success in a forward-thinking company.
- Product Development Specialist with expertise in product ideation, prototyping, and testing. Passionate about creating products that solve customer pain points and drive business growth. Seeking a challenging role in a fast-paced environment to utilize my skills and experience.
- These resume summaries need improvement as they lack specific achievements, quantifiable results, and unique value propositions. The first summary provides only a general overview of the candidate's experience without mentioning any specific accomplishments or industries. The second summary mentions a track record of success but doesn't provide any concrete examples of product performance or company growth that resulted from the candidate's expertise. The third summary mentions expertise in product ideation, prototyping, and testing, but doesn't provide any quantifiable results or details on the candidate's successes in implementing these approaches, which would make their profile more compelling to potential employers.
Resume Objective Examples for Product Developments:
Strong objectives.
- Results-driven and detail-oriented Product Development professional seeking an entry-level position to apply my strong problem-solving skills and passion for innovation to drive product success and contribute to the growth of a dynamic organization.
- Recent graduate with a degree in Product Development and a background in engineering, eager to utilize my knowledge of product design, prototyping, and testing to create impactful products in a fast-paced and collaborative environment.
- Creative and analytical Product Development specialist with experience in project management and cross-functional team collaboration, seeking a challenging role to leverage my skills in product ideation, development, and launch to drive business growth and customer satisfaction.
- These resume objectives are strong for up and coming Product Developments because they showcase the candidates' relevant skills, education, and eagerness to learn and contribute to the success of the organization. The first objective emphasizes the candidate's results-driven mindset and problem-solving skills, which are important attributes for a Product Development professional. The second objective showcases the candidate's educational background and technical knowledge, demonstrating a strong foundation for success in the role. Lastly, the third objective highlights the candidate's experience in project management and cross-functional collaboration, making them a promising fit for a Product Development position where they can further develop their skills and contribute to the company's growth.
Weak Objectives
- Seeking a Product Development role where I can utilize my skills and knowledge to contribute to the success of the company.
- Recent graduate with a degree in engineering, seeking a Product Development position to gain experience in the field.
- Aspiring Product Development professional with a passion for innovation and technology, looking for an opportunity to learn and grow in a dynamic environment.
- These resume objectives need improvement for up and coming Product Developments because they lack specificity and don't effectively showcase the unique value or skills the candidates possess. The first objective is generic and doesn't provide any information about the candidate's background, passion, or relevant experience. The second objective only mentions the candidate's degree and doesn't highlight any specific skills or interests related to Product Development. The third objective mentions a passion for innovation and technology, but it doesn't elaborate on the candidate's expertise, skills, or any particular area of Product Development they are interested in, which would make their profile more appealing to potential employers.
Generate Your Resume Summary with AI
Speed up your resume creation process with the ai resume builder . generate tailored resume summaries in seconds., how to impress with your product development work experience:, best practices for your work experience section:.
- Emphasize your experience in the entire product development lifecycle, from ideation to launch and post-launch support.
- Showcase your ability to identify and solve problems, and how you have implemented solutions to improve products or processes.
- Highlight your experience working with cross-functional teams, including engineering, design, marketing, and sales.
- Demonstrate your understanding of market trends and customer needs, and how you have used this knowledge to inform product decisions.
- Quantify your impact on product success, such as revenue growth, user acquisition, or customer satisfaction.
- Mention any experience with agile methodologies, product roadmapping, or project management tools.
- Show your ability to adapt to changing priorities and pivot strategies when necessary.
- Use specific examples to illustrate your contributions to successful product launches or updates.
- Highlight any experience with A/B testing, user research, or data analysis to inform product decisions.
- Finally, make sure to tailor your language and terminology to the specific company and industry you are applying to.
Example Work Experiences for Product Developments:
Strong experiences.
Successfully launched a new product line, conducting market research, developing product specifications, and collaborating with cross-functional teams to ensure timely delivery and customer satisfaction.
Led the development of a new feature for an existing product, utilizing agile methodologies and user feedback to prioritize and implement key functionalities, resulting in a 25% increase in user engagement.
Managed a team of product managers, providing mentorship and guidance to drive product innovation and growth, resulting in a 15% increase in revenue and a 20% improvement in team satisfaction scores.
Conducted competitive analysis and market research to identify new product opportunities, resulting in the successful launch of a new product line and a 30% increase in revenue within the first year.
Collaborated with engineering and design teams to develop and launch a new product feature, utilizing user feedback and data analysis to optimize user experience and increase customer retention by 20%.
Implemented a product roadmap and prioritization process, resulting in a 40% increase in team efficiency and a 50% improvement in project success rate.
- These work experiences are strong because they demonstrate the candidate's ability to drive product innovation and growth through effective leadership, collaboration, and data-driven decision-making. The use of specific metrics and action-oriented language highlights the candidate's impact and success in launching new products, optimizing user experience, and improving team efficiency and satisfaction. Hiring managers can quickly understand the candidate's value and potential as a skilled and strategic Product Development professional.
Weak Experiences
Assisted in the development of a new product, providing input on design and functionality.
Conducted market research to identify potential competitors and market trends.
Attended team meetings and provided updates on progress.
Collaborated with cross-functional teams to develop and launch a new product.
Conducted user testing and gathered feedback to inform product improvements.
Assisted in creating product documentation and training materials.
- Worked on multiple projects simultaneously, managing timelines and deliverables.
- Conducted user research to inform product design decisions.
- Provided support to the product team as needed.
- These work experiences are weak because they lack specificity, quantifiable results, and strong action verbs. They provide generic descriptions of tasks performed without showcasing the impact of the individual's work or the benefits brought to the company. To improve these bullet points, the candidate should focus on incorporating metrics to highlight their achievements, using more powerful action verbs, and providing clear context that demonstrates their leadership qualities and direct contributions to successful outcomes.
Top Skills & Keywords for Product Development Resumes:
Top hard & soft skills for product developments, hard skills.
- New Product Development
- Product Design and Engineering
- Product Testing and Quality Assurance
- Manufacturing and Production Processes
- Supply Chain Management
- Cost Analysis and Budgeting
- Intellectual Property Management
- Regulatory Compliance
- Project Management
- Cross-functional Team Collaboration
- Vendor and Supplier Management
- Technical Writing and Documentation
Soft Skills
- Leadership and Team Management
- Communication and Presentation Skills
- Collaboration and Cross-Functional Coordination
- Problem Solving and Critical Thinking
- Adaptability and Flexibility
- Time Management and Prioritization
- Empathy and Customer-Centric Mindset
- Decision Making and Strategic Planning
- Conflict Resolution and Negotiation
- Creativity and Innovation
- Active Listening and Feedback Incorporation
- Emotional Intelligence and Relationship Building
Go Above & Beyond with a Product Development Cover Letter
Product development cover letter example: (based on resume).
As a company that prides itself on innovation and creativity, Product Developments understands the importance of standing out from the crowd. Pairing your resume with a well-crafted cover letter can help you do just that. A cover letter is an extension of your resume, an opportunity to showcase your passion for the industry and your understanding of the company's needs. It can be the key to landing an interview and ultimately securing your dream job.
Here are some compelling reasons for submitting a cover letter:
- Personalize your application and showcase your genuine interest in Product Developments and the role you are applying for
- Illustrate your unique value proposition and how your skills align with the specific job requirements at Product Developments
- Communicate your understanding of the company's mission and how you plan to contribute to its success
- Share success stories and achievements that couldn't be accommodated in your resume, highlighting your ability to innovate and problem-solve
- Demonstrate your writing and communication skills, which are essential for any role at Product Developments
- Differentiate yourself from other applicants who might have opted not to submit a cover letter, showing your commitment to going above and beyond in your job search.
In short, a cover letter is an opportunity to showcase your personality, skills, and passion for the industry. It can help you stand out from the competition and demonstrate your commitment to securing a role at Product Developments.
Resume FAQs for Product Developments:
How long should i make my product development resume.
Based on industry standards and best practices, a Product Development resume should ideally be one to two pages long. It should be concise and highlight the most relevant skills, experiences, and achievements that are directly related to the job requirements. It is important to focus on the impact of your work and quantify your achievements wherever possible. Additionally, including a summary or objective statement at the beginning of the resume can help to quickly convey your career goals and qualifications to potential employers. Overall, the goal is to create a clear and compelling resume that showcases your strengths and demonstrates your potential value to the Product Development team.
What is the best way to format a Product Development resume?
Here are some guidelines for formatting a resume, specifically for the Product Development field. Firstly, it is important to highlight your experience and skills related to product development. This can include experience in product design, research and development, prototyping, testing, and project management. Use bullet points to list your accomplishments and responsibilities in each of these areas. Secondly, make sure to include any relevant education or certifications, such as a degree in engineering or a certification in project management. Thirdly, use a clean and professional format that is easy to read. Avoid using fancy fonts or colors that may distract from the content of your resume. Lastly, tailor your resume to the specific job you are applying for. Highlight the skills and experiences that are most relevant to the position and use keywords from the job description to make
Which Product Development skills are most important to highlight in a resume?
Some important Product Development skills to highlight in a resume are: 1. Product Design: This skill involves creating and developing new products or improving existing ones. It includes understanding customer needs, market trends, and technical specifications. 2. Project Management: Product Development involves managing projects from conception to launch. Highlighting your project management skills, including budgeting, scheduling, and team management, can demonstrate your ability to deliver products on time and within budget. 3. Technical Skills: Product Development requires technical knowledge of the product and the manufacturing process. Highlighting your technical skills, such as CAD design, prototyping, and testing, can demonstrate your ability to develop high-quality products. 4. Communication Skills: Product Development involves working with cross-functional teams, including engineers, designers, and marketing professionals. Highlighting your communication skills, including the ability to collaborate, present ideas, and negotiate, can demonstrate your ability to work effectively with others. 5. Innovation: Product Development requires creativity and innovation to develop new products that meet customer needs. Highlighting your ability to think outside the box and develop unique solutions can demonstrate your potential to drive innovation within the company. Overall, highlighting these skills in your resume can demonstrate your ability to
How should you write a resume if you have no experience as a Product Development?
If you have no experience as a Product Development, you can still write a strong resume by highlighting your relevant skills and experiences. Here are some tips: 1. Focus on transferable skills: Think about the skills you have developed in other roles that could be applied to Product Development. For example, if you have experience in project management, problem-solving, or communication, highlight these skills on your resume. 2. Emphasize relevant coursework: If you have taken courses in Product Development or related fields, include them on your resume. This shows that you have some knowledge of the field and are actively working to develop your skills. 3. Highlight relevant internships or volunteer work: If you have completed internships or volunteer work that is relevant to Product Development, include them on your resume. This shows that you have some practical experience in the field, even if it is not paid work. 4. Use a functional resume format: A functional resume format focuses on your skills and experiences rather than your work history
Compare Your Product Development Resume to a Job Description:
- Identify opportunities to further tailor your resume to the Product Development job
- Improve your keyword usage to align your experience and skills with the position
- Uncover and address potential gaps in your resume that may be important to the hiring manager
Related Resumes for Product Developments:
Product development resume example, product development manager resume example, product development engineer resume example, director of product development resume example, vp of product development resume example, new product development manager resume example, more resume guidance:.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Product Development, Branding, and Pricing Strategies Definitions. The assigned topic deals with the importance of interconnectivity between the development of a product, it's branding, and price, as well as possible tactics regarding its financial value. The Food Company New Product Development Group.
New research on product development from Harvard Business School faculty on issues including what marketers can learn from consumers whose preferences lie outside of the mainstream, and how to best incorporate customer opinion when creating a new product. Page 1 of 12 Results
Product research is a foundational step in building user-centric products. It allows you to understand customer needs, preferences, and market trends, informing the development of successful solutions to user problems. Read on for the ultimate guide to product research, including methods, processes, and best practices—plus our favorite tips ...
Product development research is the process of finding out how the product or feature you're currently working on is progressing, whether there are any changes in your target audience's needs and whether you need to make any adjustments to the product. Depending on where you are in your product's life cycle will dictate the kind of ...
Article Elliot Savitzky, Hannah Robbins July 1, 2023. Sponsored Article Quirk's Staff July 1, 2023. Article David Whitelam June 29, 2023. Article John Conti April 19, 2023. Learn all about new product development research new product research. Quirks.com is the largest source of marketing research information.
Research provides you with the necessary information and insights to inform and guide your product design. Development helps you bring ideas to life, validate them and then build and commercialize them. The product development lifecycle is as follows: Research. Ideation and concept development. Design and prototyping.
Lego Takes Customers' Innovations Further. New research shows how companies can advance open innovation by integrating customers' ideas into product development. Michela Beretta, Linus Dahlander, Lars Frederiksen, and Arne Thomas. September 12, 2023. New Product Development.
It does the most basic set of functions the product is designed to do. Testing data - internal secondary research - is invaluable during the improvement of the MVP into a product that's ready to launch. 6. Product launch. The product launch is probably the most crucial stage in the new product development process.
Step 2: Evaluative Research. Evaluative research helps you further evaluate your concepts and identify the ones that are worth moving forward with. Also, this is a great place to start if you need to reevaluate an existing product. Here you will open the data collection beyond you and your team by conducting research through surveys or other consumer-focused methods.
A product manager's main research aims are to ensure that product development decisions are data-informed and customer-centric, and address users' needs to build a great product. Common research methods include interviews, surveys, competitor studies, and analyzing user behavior and product experience insights. 2. Product designers.
Product Development Research with SightX. The SightX platform is the only tool you'll ever need for market research: a single, unified solution for consumer engagement, data collection, advanced analysis, and reporting. While powerful enough for insights teams at Fortune 500 companies, the user-friendly interface makes it simple for anyone to ...
Learn how they deliver superior value to customers, innovate, and boost growth while keeping the customer at the center of their new product development process. 1. Google. Our first product development example is a big one. Founded in 1998 by Sergey Brin and Larry Page, Google began as an online search company, but it now offers hundreds of ...
Product development research is the process of crafting, developing, and selling a product. It includes the crucial steps of market research, user research, and also coming up with a marketing plan to market the product to prospects. It also refers to tracking the progress of a product you are currently working on, its appeal to the target ...
There are four key stages of product development where qualitative feedback is critical. 1. Initial Product Development. Qualitative research can help narrow and refine potential product concepts during the initial idea-generation phase of product development. Its approaches can produce a detailed picture of customers' experiences with a ...
As the research situation becomes unique for each product development process, trust in the research findings is strongly related to the presence of the researcher in the development process.
One example of a successful vision statement would be Google's: To provide access to the world's information in one click. 2. Do your research. A successful product development strategy has to be rooted in real user problems and goals and a real market opportunity.
Step 3: Find a full-service market research partner. The most challenging and time-consuming piece of new product development research (both qualitative and quantitative) is recruiting. This is recruiting in terms of finding participants for testing or finding survey respondents for a larger study.
e-mail: [email protected], phone: +371 29429895. Abstract. New product development is the main factor of economic progress in building. the economic competitive advantage. The life cycle of ...
See How Innovation And Product Development Research Can Drive Your Decisions During Product Life Cycle. Product Development Research Product development research helps you determine not only where your current product/service is in the product life cycle but what features are most valued and what elements customers are willing to pay a premium for.
Textile product development: basic concepts and critical factors. Y.E. El Mogahzy, in Engineering Textiles, 2009 Abstract: Product development is the primary recipe for success in today's competitive market. In order to remain competitive, an organization must sell more products, create new products and find new market opportunities for existing intellectual properties.
Group Brainstorming: Collaborate with peers or mentors to gather diverse perspectives and insights. Group brainstorming can lead to innovative and multidimensional title ideas. Identifying Key Terms and Concepts: Break down your research into key terms and concepts. These will form the foundation of your title.
Template 1: New Product Market Research PowerPoint Presentation. This Complete Deck is your one-stop solution for conducting thorough research for new products. It equips you with well-structured slides on the customer preferences survey form and overview slides for survey outcomes. It contains easy-to-understand graphics, pie charts, and well ...
Lead the development of a new product line that generated $5M in revenue within the first six months of launch. Managed a team of 15 product developers, resulting in a 20% increase in team productivity and a 10% reduction in time-to-market. Product Manager. 09/2022 - 12/2022.