Bioinformatics (Ph.D.)
Focus: preparing graduate students to reach the forefront of leadership in the field of bioinformatics and computational biology; and integrating research and education on the use of information technologies in biology and medicine.

Your browser is unsupported
We recommend using the latest version of IE11, Edge, Chrome, Firefox or Safari.
Richard and Loan Hill Department of Biomedical Engineering
Colleges of engineering and medicine, phd in bioinformatics.
Students must complete a minimum of 108 semester hours beyond the baccalaureate degree in order to complete the PhD program.
Coursework requirements Heading link Copy link

Students admitted with a prior master’s degree in biomedical engineering or bioinformatics or a related field must complete at least 24 hours of coursework, 12 hours of which must be bioengineering courses. In addition, at least 12 hours must be at the 500 level (excluding BME 595, 596, and 599). A maximum of 4 hours of BME 590 may be applied toward the degree, provided that credit for BME 590 or a similar course was not applied toward a prior MS degree.
Students who are directly admitted after a bachelor’s degree in biomedical engineering, bioinformatics, or a related field must complete at least 48 hours of coursework, at least 24 hours of which must be bioengineering courses. At least 20 hours must be at the 500 level (excluding BME 595, 596, and 599). A maximum of 4 hours of BME 590 may be applied toward the degree.
One semester hour of BME 595 is required for all PhD in Bioinformatics students. Each student is required to present at least one seminar in BME 595 prior to graduation.
PhD students must earn at least 60 semester hours in BME 599, in which they conduct original research and write their dissertation. You can see examples of recent dissertations by our bioinformatics students on our dissertations page .
Qualifying examination Heading link Copy link
PhD in Bioinformatics students must pass a qualifying examination before they move on to the preliminary examination phase. (Please note that this is a difference from the PhD in Biomedical Engineering.) Students must attempt the qualifying exam at the end of the first academic year, and two attempts may be made. The four-hour exam is held on the first Monday in June each year. It consists of up to nine questions that are based on the courses offered during the fall and spring terms of that academic year. Students may choose at most six questions, and the final score is calculated based on the five best-scored questions.
Preliminary examination Heading link Copy link
PhD students must pass an oral preliminary examination on their proposed dissertation topic. In this examination, students must demonstrate a capacity for independent research on an original dissertation topic within the selected field of study. Visit the Preliminary Examination page for full details.
Dissertation Heading link Copy link
Upon completion of all degree requirements and the dissertation, students must orally defend their work before the committee. Visit the Dissertation Process page for full details.
Additional resources for PhD in Bioinformatics students Heading link Copy link
- Graduate catalog page for PhD in Bioinformatics
- Graduate student resources page
- Bioinformatics PhD course checklist
- Important deadlines for graduate students
If you have any further questions about the program that aren’t answered here or on our Graduate FAQ page, please email [email protected] .
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Residents & Fellows
- Give to SMHS
Integrated Biomedical Sciences (IBS)
Genomics & bioinformatics phd program.
The PhD in Genomics and Bioinformatics is designed to develop research scientists who apply principles and methods in genomics and bioinformatics to the study of human diseases.
The PhD in Genomics and Bioinformatics provides research training areas that reflect GW faculty expertise which includes DNA/RNA sequence analysis, algorithm development, cloud computing optimization, informatics platform development, biomarker discovery, microbiome, retrovirology (HIV/AIDS), autism spectrum disorders, muscular dystrophies, cancer genomics, glycoinformatics, microRNA processing, protein trafficking, and dysregulation of mitochondrial functions. Faculty are drawn largely from the GW School of Medicine and Health Sciences and Children’s Research Institute of Children’s National Health System.
Students have access to the state of the art technologies in genomics, proteomics, microscopy, bioinformatics, pre-clinical drug trials and multi-site clinical trial networks. Resources include the GW Genomics Core , the GW Biorepository resource of biospecimens and clinical data, the McCormick Genomic and Proteomic Center, and Colonial One (the GW High Performance Computing Cluster), as well as cutting-edge core facilities for flow cytometry, imaging, and pathology.
PhD programs in the biomedical sciences are designed to meet key goals in contemporary graduate research education including 1) discipline-specific knowledge, 2) research skill development, 3) research communication skills, 4) research leadership, 5) research professionalism, and prepare graduates for a variety of science careers. To apply, please visit IBS Admissions .
The PhD in Genomics & Bioinformatics begins with interdisciplinary coursework in molecular, cellular, and systems biology in the first semester. In the second and third semester students take a comprehensive introduction to the conceptual and experimental underpinnings of computational biology, statistics, genetics, and DNA sequencing. Career development coursework in scientific writing, oral communication, and research ethics; and laboratory rotations offered through GW’s Integrated Biomedical Sciences curriculum. Following required laboratory rotations, students work with their research advisor and the Graduate Program Directors to complete remaining Genomics & Bioinformatics degree requirements, including the dissertation.
Genomics and Bioinformatics Core:
- GENO 8231: Introduction to Genomics, Proteomics, and Bioinformatics
- GENO 8232: Computational Biology and Bioinformatics - Principals and Practices
- GENO 6223: Bioinformatics
- GENO 6237: Proteomics & Biomarkers
- GENO 8998: Advanced Reading and Research Seminar Course
- GENO 8999: Dissertation Research
Some Suggested Electives:
- BIOC 6240: Next Gen Sequencing.
- PUBH 6277: Public Health Genomics
- BMSC 8219: Writing the Grant-Style Qualifier
Seminars/Journal Clubs:
CTSI-CN Informatics Seminar Series
Complete grant-style qualifier examination, advance to candidacy
Graduate Program Directors:
Ljubica Caldovic, PhD Assistant Research Professor of Genomics and Precision Medicine Children's National Health System; GWU [email protected]
Raja Mazumder, PhD Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Medicine GWU, Ross Hall 540 [email protected]
How to apply to the IBS and Genomics and Bioinformatics PhD Program For IBS Application Questions contact Colleen Kennedy, IBS Program Manager

PhD in Bioinformatics Data Science

A Ph.D. in Bioinformatics Data Science will train the next-generation of researchers and professionals who will play a key role in multi- and interdisciplinary teams, bridging life sciences and computational sciences. Students will receive training in experimental, computational and mathematical disciplines through their coursework and research. Students who complete this degree will be able to generate and analyze experimental data for biomedical research as well as develop physical or computational models of the molecular components that drive the behavior of the biological system.
Students must complete a minimum of 15 hours of coursework, plus 3 credit hours of seminar, 6 credit hours of research and 9 credit hours of doctoral dissertation. The Ph.D. requires a minimum of 33 credits. Students who are admitted directly after a B.S. degree will be required to complete up to 9 additional credits in order to fulfill the core curriculum in the following areas: Database Systems, Statistics, and Introduction to Discipline. In addition, if students entering the program with an M.S. degree are lacking equivalent prerequisites, they also will be required to complete courses in these three areas; however, these courses may fulfill the elective requirement in the Ph.D. program, if approved in the program of study.
Academic Load
PhD students holding research assistantships (or teaching) are considered full-time with 6 credit hours . Students without RA or TA are considered full-time if enrolled in at least 9 credit hours or in sustaining credit. Those enrolled for fewer than 9 credit hours are considered part-time students. Generally, a maximum load is 12 graduate credit hours; however, additional credit hours may be taken with the approval of the student’s adviser and the Graduate College. A maximum course load in either summer or winter session is 7 credit hours. Permission must be obtained from the Graduate College to carry an overload in any session.
Bioinformatics Data Science Courses
Students must take one course in each of the following areas (9 credits):
Prerequisites
Students must fulfill core curriculum in each of the following areas (3-9 credits):
Elective Courses
Students must take two courses to compliment their bioinformatics data science dissertation project (6 credits):
See Elective courses
Students must take six semesters of seminar (three 0 credit; three 1 credit) and give a presentation during three semesters.
Other Requirements:
- Formation of Graduate Dissertation Committee
- Successful completion of Graduate Preliminary Exam
- Research on a significant scientific problem
- Successful completion of Ph.D. Candidacy Exam
- Successful completion of Dissertation Defense
Formation of Graduate Committee
The student needs to establish a Dissertation Committee within the first year of study. The Committee should consist of at least four faculty members, including the primary faculty advisor (serving as the Committee Chair), a secondary faculty advisor (in a complementary field to the primary advisor), a second faculty from the home department, and one CBCB affiliate faculty outside the Departments of the primary and secondary advisors or from outside the University. Students must complete the Dissertation Committee Formation form and submit to the Associate Director.
Students should convene their dissertation committee at least once every six months.
Preliminary Examination
The preliminary examination should be taken before the end of the fourth semester and will consist of an oral exam in subjects based on the Bioinformatics Data Science core.* In recognition of the importance of the core curriculum in providing a good test of the student’s knowledge, students must achieve a minimum 3.0 GPA in the core curriculum before taking the preliminary exam. Students will not be permitted to take the preliminary examination if the core grade requirements and cumulative GPA of 3.0 has not been achieved. The exam will be administered by the Preliminary Exam Committee , which will consist of one instructor from each of the three core courses. Each member of the Committee will provide a single grade (pass, conditional pass or fail) and the final grades will be submitted via the Results of Preliminary Exam Form :
- Pass . The student may proceed to the next stage of his/her degree training.
- Conditional pass . In the event that the examination committee feels that the student did not have an adequate background or understanding in one or more specific areas, the Preliminary Exam Committee will communicate the conditional pass to the student and must provide the student with specific requirements and guidelines for completing the conditional pass. The student must inform the Preliminary Exam Committee, the Graduate Program Director and Program Committee when these conditions have been completed. The Preliminary Exam Committee will then meet with the student to ensure all recommendations have been completed and whether a re-examination is necessary. If required, the re-examination will be done using the same format and prior to the beginning of the next academic semester. If the student still does not perform satisfactorily on this re-examination, he/she will then be recommended to the Graduate Affairs Committee for dismissal from the graduate program.
- Failure . This outcome would indicate that the Examination Committee considers the student incapable of completing degree training. The student’s academic progress will be reviewed by the Graduate Affairs Committee, who will make recommendations to the Program Director regarding the student’s enrollment status. The Program Director may recommend to the Graduate College that the student be dismissed from the Program immediately.
*Students who need to complete prerequisite courses may request a deadline extension for the preliminary and subsequently the candidacy examination. Requests must be submitted to the Graduate Program Committee prior to the start of the third semester.
Candidacy Exam
The candidacy examination must be completed by the end of the sixth semester of enrollment.* It requires a formal, detailed proposal be submitted to the Dissertation Committee and an oral defense of the student’s proposed research project. Upon the recommendation of the Dissertation Committee, the student may be admitted to candidacy for the Ph.D. degree. The stipulations for admission to doctoral candidacy are that the student has (i) completed one academic years of full-time graduate study in residence at the University of Delaware, (ii) completed all required courses with the exception of BINF865 and BINF969, (iii) passed the preliminary exams, (iv) demonstrated the ability to perform research, and (v) had a research project accepted by the Dissertation Committee. Within one week of the candidacy exam, complete and submit the Recommendation for Candidacy for Doctoral Degree form for details. A copy of the completed form should be given to the Associate Director.
*Students who need to complete prerequisite courses may request a deadline extension for the preliminary and subsequently the candidacy examination. Requests must be submitted to the Graduate Program Committee prior to the start of the third semester.
Dissertation Exam
The dissertation examination of the Ph.D. program will involve the approval of the written dissertation and an oral defense of the candidate’s dissertation. The written dissertation will be submitted to the Dissertation Committee and the CBCB office at least three weeks in advance of the oral defense date. The oral defense date will be publicly announced at least two weeks prior to the scheduled date. The oral presentation will be open to the public and all members of the Bioinformatics Data Science program. The Dissertation Committee will approve the candidate’s dissertation. The student and the primary faculty advisor will be responsible for making all corrections to the dissertation document and for meeting all Graduate College deadlines. Within one week of the dissertation defense, complete and submit the Certification of Doctoral Dissertation Defense Form. A copy of the completed form should be given to the Associate Director.
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Center for Computational Biology
Computational Biology PhD
The main objective of the Computational Biology PhD is to train the next generation of scientists who are both passionate about exploring the interface of computation and biology, and committed to functioning at a high level in both computational and biological fields.
The program emphasizes multidisciplinary competency, interdisciplinary collaboration, and transdisciplinary research, and offers an integrated and customizable curriculum that consists of two semesters of didactic course work tailored to each student’s background and interests, research rotations with faculty mentors spanning computational biology’s core disciplines, and dissertation research jointly supervised by computational and biological faculty mentors.
The Computational Biology Graduate Group facilitates student immersion into UC Berkeley’s vibrant computational biology research community. Currently, the Group includes over 46 faculty from across 14 departments of the College of Letters and Science, the College of Engineering, the College of Natural Resources, and the School of Public Health. Many of these faculty are available as potential dissertation research advisors for Computational Biology PhD students, with more available for participation on doctoral committees.

The First Year
The time to degree (normative time) of the Computational Biology PhD is five years. The first year of the program emphasizes gaining competency in computational biology, the biological sciences, and the computational sciences (broadly construed). Since student backgrounds will vary widely, each student will work with faculty and student advisory committees to develop a program of study tailored to their background and interests. Specifically, all first-year students must:
- Perform three rotations with Core faculty (one rotation with a non-Core faculty is acceptable with advance approval)
- Complete course work requirements (see below)
- Complete a course in the Responsible Conduct of Research
- Attend the computational biology seminar series
- Complete experimental training (see below)
Laboratory Rotations
Entering students are required to complete three laboratory rotations during their first year in the program to seek out a Dissertation Advisor under whose supervision dissertation research will be conducted. Students should rotate with at least one computational Core faculty member and one experimental Core faculty member. Click here to view rotation policy.
Course Work & Additional Requirements
Students must complete the following coursework in the first three (up to four) semesters. Courses must be taken for a grade and a grade of B or higher is required for a course to count towards degree progress:
- Fall and Spring semester of CMPBIO 293, Doctoral Seminar in Computational Biology
- A Responsible Conduct of Research course, most likely through the Department of Molecular and Cell Biology.
- STAT 201A & STAT 201B : Intro to Probability and Statistics at an Advanced Level. Note: Students who are offered admission and are not prepared to complete STAT 201A and 201B will be required to complete STAT 134 or PH 142 first.
- CS61A : The Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs. Note: students with the equivalent background can replace this requirement with a more advanced CS course of their choosing.
- 3 elective courses relevant to the field of Computational Biology , one of which must be at the graduate level (see below for details).
- Attend the computational biology invited speaker seminar series. A schedule is circulated to all students by email and is available on the Center website. Starting with the 2023 entering class, CCB PhD students must enroll in CMPBIO 275: Computational Biology Seminar , which provides credit for this seminar series.
- 1) completion of a laboratory course at Berkeley with a minimum grade of B,
- 2) completion of a rotation in an experimental lab (w/ an experimental project), with a positive evaluation from the PI,
- a biological sciences undergraduate major with at least two upper division laboratory-based courses,
- a semester or equivalent of supervised undergraduate experimental laboratory-based research at a university,
- or previous paid or volunteer/internship work in an industry-based experimental laboratory.
Students are expected to develop a course plan for their program requirements and to consult with the Head Graduate Advisor before the Spring semester of their first year for formal approval (signature required). The course plan will take into account the student’s undergraduate training areas and goals for PhD research areas.
Satisfactory completion of first year requirements will be evaluated at the end of the spring semester of the first year. If requirements are satisfied, students will formally choose a Dissertation advisor from among the core faculty with whom they rotated and begin dissertation research.
Waivers: Students may request waivers for the specific courses STAT 201A, STAT 201B, and CS61A. In all cases of waivers, the student must take alternative courses in related areas so as to have six additional courses, as described above. For waiving out of STAT 201A/B, students can demonstrate they have completed the equivalent by passing a proctored assessment exam on Campus. For waiving out CS61A, the Head Graduate Advisor will evaluate student’s previous coursework based on the previous course’s syllabus and other course materials to determine equivalency.
Electives: Of the three electives, students are required to choose one course in each of the two following cluster areas:
- Cluster A (Biological Science) : These courses are defined as those for which the learning goals are primarily related to biology. This includes courses covering topics in molecular biology, genetics, evolution, environmental science, experimental methods, and human health. This category may also cover courses whose focus is on learning how to use bioinformatic tools to understand experimental data.
- Cluster B (Computational Sciences): These courses are defined as those for which the learning goals involve computing, inference, or mathematical modeling, broadly defined. This includes courses on algorithms, computing languages or structures, mathematical or probabilistic concepts, and statistics. This category would include courses whose focus is on biological applications of such topics.
In the below link we give some relevant such courses, but students can take courses beyond this list; for courses not on this list, the Head Graduate Advisor will determine to which cluster a course can be credited. For classes that have significant overlap between these two clusters, the department which offers the course may influence the decision of the HGA as to whether the course should be assigned to cluster A or B.
See below for some suggested courses in these categories:
Suggested Coursework Options
Second Year & Beyond
At the beginning of the fall of the second year, students begin full-time dissertation research in earnest under the supervision of their Dissertation advisor. It is anticipated that it will take students three (up to four) semesters to complete the 6 course requirement. Students are required to continue to participate annually in the computational biology seminar series.
Qualifying Examination
Students are expected to take and pass an oral Qualifying Examination (QE) by the end of the spring semester (June 15th) of their second year of graduate study. Students must present a written dissertation proposal to the QE committee no fewer than four weeks prior to the oral QE. The write-up should follow the format of an NIH-style grant proposal (i.e., it should include an abstract, background and significance, specific aims to be addressed (~3), and a research plan for addressing the aims) and must thoroughly discuss plans for research to be conducted in the dissertation lab. Click here for more details on the guidelines and format for the QE. Click here to view the rules for the composition of the committee and the form for declaring your committee.
Advancement to Candidacy
After successfully completing the QE, students will Advance to Candidacy. At this time, students select the members of their dissertation committee and submit this committee for approval to the Graduate Division. Students should endeavor to include a member whose research represents a complementary yet distinct area from that of the dissertation advisor (ie, biological vs computational, experimental vs theoretical) and that will be integrated in the student’s dissertation research. Click here to view the rules for the composition of the committee and the form for declaring your committee.
Meetings with the Dissertation Committee
After Advancing to Candidacy, students are expected to meet with their Dissertation Committee at least once each year.
Teaching Requirements
Computational Biology PhD students are required to teach at least two semesters (starting with Fall 2019 class), but may teach more. The requirement can be modified if the student has funding that does not allow teaching. Starting with the Fall 2019 class: At least one of those courses should require that you teach a section. Berkeley Connect or CMPBIO 293 can count towards one of the required semesters.
The Dissertation
Dissertation projects will represent scholarly, independent and novel research that contributes new knowledge to Computational Biology by integrating knowledge and methodologies from both the biological and computational sciences. Students must submit their dissertation by the May Graduate Division filing deadline (see Graduate Division for date) of their fifth–and final–year.
Special Requirements
Students will be required to present their research either orally or via a poster at the annual retreat beginning in their second year.
- Financial Support
The Computational Biology Graduate Group provides a competitive stipend (the stipend for 2023-24 is $43,363) as well as full payment of fees and non-resident tuition (which includes health care). Students maintaining satisfactory academic progress are provided full funding for five to five and a half years. The program supports students in the first year, while the PI/mentor provides support from the second year on. A portion of this support is in the form of salary from teaching assistance as a Graduate Student Instructor (GSI) in allied departments, such as Molecular and Cell Biology, Integrative Biology, Plant and Microbial Biology, Mathematics, Statistics or Computer Science. Teaching is part of the training of the program and most students will not teach more than two semesters, unless by choice.
Due to cost constraints, the program admits few international students; the average is two per year. Those admitted are also given full financial support (as noted above): stipend, fees and tuition.
Students are also strongly encouraged to apply for extramural fellowships for the proposal writing experience. There are a number of extramural fellowships that Berkeley students apply for that current applicants may find appealing. Please note that the NSF now only allows two submissions – once as an undergrad and once in grad school. The NSF funds students with potential, as opposed to specific research projects, so do not be concerned that you don’t know your grad school plans yet – just put together a good proposal! Although we make admissions offers before the fellowships results are released, all eligible students should take advantage of both opportunities to apply, as it’s a great opportunity and a great addition to a CV.
- National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship (app deadlines in Oct)
- Hertz Foundation Fellowship (app deadline Oct)
- National Defense Science and Engineering Graduate Fellowship (app deadline in mid-Fall)
- DOE Computational Science Graduate Fellowship (Krell Institute) (app deadline in Jan)
CCB no longer requires the GRE for admission (neither general, nor subject). The GRE will not be seen by the review committee, even if sent to Berkeley.
PLEASE NOTE: The application deadline is Wednesday, November 30 , 2023, 8:59 PST/11:59 EST
If you would like to learn more about our program, you can watch informational YouTube videos from the past two UC Berkeley Graduate Diversity Admissions Fairs: 2021 recording & 2020 recording .
We invite applications from students with distinguished academic records, strong foundations in the basic biological, physical and computational sciences, as well as significant computer programming and research experience. Admission for the Computational Biology PhD is for the fall semester only, and Computational Biology does not offer a Master’s degree.
We are happy to answer any questions you may have, but please be sure to read this entire page first, as many of your questions will be answered below or on the Tips tab.
IMPORTANT : Please note that it is not possible to select a specific PhD advisor until the end of the first year in the program, so contacting individual faculty about openings in their laboratories will not increase your chances of being accepted into the program. You will have an opportunity to discuss your interests with relevant faculty if you are invited to interview in February.
Undergraduate Preparation
Minimum requirements for admission to graduate study:
- A bachelor’s degree or recognized equivalent from an accredited institution.
- Minimum GPA of 3.0.
- Undergraduate preparation reflecting a balance of training in computational biology’s core disciplines (biology, computer science, statistics/mathematics), for example, a single interdisciplinary major, such as computational biology or bioinformatics; a major in a core discipline and a combination of interdisciplinary course work and research experiences; or a double major in core disciplines.
- Basic research experience and aptitude are key considerations for admission, so evidence of research experience and letters of recommendation from faculty mentors attesting to the applicant’s research experience are of particular interest.
- GRE – NOT required or used for review .
- TOEFL scores for international students (see below for details).
Application Requirements
ALL materials, including letters, are due November 30, 2023 (8:59 PST). More information is provided and required as part of the online application, so please create an account and review the application before emailing with questions (and please set up an account well before the deadline):
- A completed graduate application: The online application opens in early or mid-September and is located on the Graduate Division website . Paper applications are not accepted. Please create your account and review the application well ahead of the submit date , as it will take time to complete and requests information not listed here.
- A nonrefundable application fee: The fee must be paid using a major credit card and is not refundable. For US citizens and permanent residents, the fee is $135; US citizens and permanent residents may request a fee waiver as part of the online application. For all other students (international) the fee is $155 (no waivers, no exceptions). Graduate Admissions manages the fee, not the program, so please contact them with questions.
- Three letters of recommendation, minimum (up to five are accepted): Letters of recommendation must be submitted online as part of the Graduate Division’s application process. Letters are also due November 30, so please inform your recommenders of this deadline and give them sufficient advance notice. It is your responsibility to monitor the status of your letters of recommendation (sending prompts, as necessary) in the online system.
- Transcripts: Unofficial copies of all relevant transcripts, uploaded as part of the online application (see application for details). Scanned copies of official transcripts are strongly preferred, as transcripts must include applicant and institution name and degree goal and should be easy for the reviewers to read (print-outs from online personal schedules can be hard to read and transcripts without your name and the institution name cannot be used for review). Do not send via mail official transcripts to Grad Division or Computational Biology, they will be discarded.
- Essays: Follow links to view descriptions of what these essays should include ( Statement of Purpose [2-3 pages], Personal Statement [1-2 pages]). Also review Tips tab for formatting advice.
- (Highly recommended) Applicants should consider applying for extramural funding, such as NSF Fellowships. These are amazing opportunities and the application processes are great preparation for graduate studies. Please see Financial Support tab.
- Read and follow all of the “Application Tips” listed on the last tab. This ensures that everything goes smoothly and you make a good impression on the faculty reviewing your file.
The GRE general test is not required. GRE subject tests are not required. GRE scores will not be a determining factor for application review and admission, and will NOT be seen by the CCB admissions committee. While we do not encourage anyone to take the exam, in case you decide to apply to a different program at Berkeley that does require them: the UC Berkeley school code is 4833; department codes are unnecessary. As long as the scores are sent to UC Berkeley, they will be received by any program you apply to on campus.
TOEFL/IELTS
Adequate proficiency in English must be demonstrated by those applicants applying from countries where English is not the official language. There are two standardized tests you may take: the Test of English as a Foreign Language (TOEFL), and the International English Language Testing System (IELTS). TOEFL minimum passing scores are 90 for the Internet-based test (IBT) , and 570 for the paper-based format (PBT) . The TOEFL may be waived if an international student has completed at least one year of full-time academic course work with grades of B or better while in residence at a U.S. university (transcript will be required). Please click here for more information .
Application Deadlines
The Application Deadline is 8:59 pm Pacific Standard Time, November 30, 2023 . The application will lock at 9pm PST, precisely. All materials must be received by the deadline. While rec letters can continue to be submitted and received after the deadline, the committee meets in early December and will review incomplete applications. TOEFL tests should be taken by or before the deadline, but self-reported scores are acceptable for review while the official scores are being processed. All submitted applications will be reviewed, even if materials are missing, but it may impact the evaluation of the application.
It is your responsibility to ensure and verify that your application materials are submitted in a timely manner. Please be sure to hit the submit button when you have completed the application and to monitor the status of your letters of recommendation (sending prompts, as necessary). Please include the statement of purpose and personal statement in the online application. While you can upload a CV, please DO NOT upload entire publications or papers. Please DO NOT send paper résumés, separate folders of information, or articles via mail. They will be discarded unread.
The Computational Biology Interview Visit dates will be: February 25-27, 2024
Top applicants who are being considered for admission will be invited to visit campus for interviews with faculty. Invitations will be made by early January. Students are expected to stay for the entire event, arriving in Berkeley by 5:30pm on the first day and leaving the evening of the final day. In the application, you must provide the names of between 7-10 faculty from the Computational Biology website with whom you are interested in conducting research or performing rotations. This helps route your application to our reviewers and facilitates the interview scheduling process. An invitation is not a guarantee of admission.
International students may be interviewed virtually, as flights are often prohibitively expensive.
Tips for the Application Process
Uploaded Documents: Be sure to put your name and type of essay on your essays ( Statement of Purpose [2-3 pages], Personal Statement [1-2 pages]) as a header or before the text, whether you use the text box or upload a PDF or Word doc. There is no minimum length on either essay, but 3 pages maximum is suggested. The Statement of Purpose should describe your research and educational background and aspirations. The Personal Statement can include personal achievements not necessarily related to research, barriers you’ve had to overcome, mentoring and volunteering activities, things that make you unique and demonstrate the qualities you will bring to the program.
Letters of Recommendation: should be from persons who have supervised your research or academic work and who can evaluate your intellectual ability, creativity, leadership potential and promise for productive scholarship. If lab supervision was provided by a postdoc or graduate student, the letter should carry the signature or support of the faculty member in charge of the research project. Note: the application can be submitted before all of the recommenders have completed their letters. It is your responsibility to keep track of your recommender’s progress through the online system. Be sure to send reminders if your recommenders do not submit their letters.
Extramural fellowships: it is to your benefit to apply for fellowships as they may facilitate entry into the lab of your choice, are a great addition to your CV and often provide higher stipends. Do not allow concerns about coming up with a research proposal before joining a lab prevent you from applying. The fellowships are looking for research potential and proposal writing skills and will not hold you to specific research projects once you have started graduate school.
Calculating GPA: Schools can differ in how they assign grades and calculate grade point averages, so it may be difficult for this office to offer advice. The best resource for calculating the GPA for your school is to check the back of the official transcripts where a guide is often provided or use an online tool. There are free online GPA conversion tools that can be found via an internet search.
Faculty Contact/Interests: Please be sure to list faculty that interest you as part of the online application. You are not required to contact any faculty in advance, nor will it assist with admission, but are welcome to if you wish to learn more about their research.
Submitting the application: To avoid the possibility of computer problems on either side, it is NOT advisable to wait until the last day to start and/or submit your application. It is not unusual for the application system to have difficulties during times of heavy traffic. However, there is no need to submit the application too early. No application will be reviewed before the deadline.
Visits: We only arrange one campus visit for recruitment purposes. If you are interested in visiting the campus and meeting with faculty before the application deadline, you are welcome to do so on your own time (we will be unable to assist).
Name: Please double check that you have entered your first and last names in the correct fields. This is our first impression of you as a candidate, so you do want to get your name correct! Be sure to put your name on any documents that you upload (Statement of Purpose, Personal Statement).
California Residency: You are not considered a resident if you hope to enter our program in the Fall, but have never lived in California before or are here on a visa. So, please do not mark “resident” on the application in anticipation of admission. You must have lived in California previously, and be a US citizen or Permanent Resident, to be a resident.
Faculty Leadership Head Graduate Advisor and Chair for the PhD & DE John Huelsenbeck ( [email protected] )
Associate Head Graduate Advisor for PhD & DE Liana Lareau ( [email protected] )
Equity Advisor Rasmus Nielsen ( [email protected] )
Director of CCB Elizabeth Purdom ( [email protected] )
Core PhD & DE Faculty ( link )
Staff support Student Services Advisor (GSAO): Kate Chase ( [email protected] )

- Apply Today
Current Students
- The Graduate School
My UNC Charlotte
Campus events, prospective students.
- About UNC Charlotte
- Campus Life
- Graduate Admissions
Faculty and Staff
- Human Resources
- Auxiliary Services
- Inside UNC Charlotte
- Academic Affairs
- Financial Aid
- Student Health Center
Alumni and Friends
- Alumni Association
- Advancement
- Make a Gift
Bioinformatics and Computational Biology (Ph.D.)
Program director.
- Search This Site All UCSD Sites Faculty/Staff Search Term
- Diversity, Equity and Inclusion Statement
- Academic Employment
- Newsletters
- Past Events
- California Integrated Vital Records Registration System (Cal-IVRS)
- DECENTRALIZED
- Maryland Electronic Vital Records
- Protect Privacy
- RADx-rad DCC
- Rapid Response Data Discovery for COVID-19
- Strong Heart
- UCSD SureNet
- NLM Pre & Postdoctoral Training Grant Fellowship
- NIH Predoctoral Training Program
- How to Cite a Training Grant
- Computer Science and Engineering PhD
- Bioinformatics PhD
- Internships
- Visiting Students & Scholars
- Past Research
- Publications
- Breast Cancer Biomarkers
- Decision Support Systems
- Preserving Privacy
- Medical Device Safety
Education & Training
Phd in bioinformatics and systems biology with emphasis in biomedical informatics.
The PhD curriculum for our trainees consists of formal instruction to provide the intellectual framework for conducting research.
Biomedical Informatics Core
- Informatics in Clinical Environments (MED 265): 1 Students are introduced to the basics of healthcare systems and clinical information needs through direct observation and classroom discussion. Students are introduced to medical language, disease processes, and health care practices to provide context prior to direct patient observation at primary, specialty, emergency, and inpatient sites in conjunction with clinical faculty affiliated with the training program. Students examine how clinicians use history-taking, physical examination and diagnostic testing to establish diagnoses and prognoses. Medical decision-making is introduced in the context of available informatics tools and clinical documentation and communication processes. Post-observation classroom discussions encourage students to think critically of the processes they observed and formulate hypotheses about how informatics solutions can modify the processes.
- Modeling Clinical Data and Knowledge for Computation (MED 267): This course describes existing methods for representing and communicating biomedical knowledge. The course describes existing health care standards and modeling principles required for implementing data standards, including biomedical ontologies, standardized terminologies, and knowledge resources.
1 Students with a clinical background will replace MED 265 with an additional course: Bioinformatics Applications to Human Disease (MED 263).
Bioinformatics Core
The core courses provide foundations in the biological basis of human health and disease and the statistical discovery of medical knowledge from biological experimentation. These classes are taken during the first year.
- Bioinformatics II (BENG 202) : Introduction to methods for sequence analysis, applications to genome and proteome sequences, and protein structure and sequence-structure analysis.
- Principles of Biomedical Informatics (MED 264) : students are introduced to the fundamental principles of BMI and to the problems that define modern healthcare. The extent to which BMI can address healthcare problems is explored. Topics covered include structuring of data, computing with phenotypes, integration of molecular, image and other non-traditional data types into electronic medical records, clinical decision support systems, biomedical ontologies, data and communication standards, data aggregation, and knowledge discovery.
- Bioinformatics IV (MATH 283): Analysis of modern genomic data, sequence analysis, gene expression/functional genomics analysis, and gene mapping/applied population genetics. The course focuses on statistical modeling and inference.
For the fourth core class, choose one of the following. In the event that a student completes two or more of these with suitable grades, one will count as core and the other(s) as electives.
- Algorithms in Computational Biology (CSE 280A): (Formerly CSE 206B) The course focuses on algorithmic aspects of modern bioinformatics and covers the following topics: computational gene hunting, sequencing, DNA arrays, sequence comparison, pattern discovery in DNA, genome rearrangements, molecular evolution, computational proteomics, and others. Prerequisites: CSE202 preferred or consent of instructor.
- Algorithms for Biological Data Analysis (ECE 208): This course introduces a series of general algorithmic techniques but uses computational evolutionary biology as the context. The course motivates each algorithmic concept using a specific biological application related to evolution and focuses the discussion on specific types of (big) data available in modern biological studies. Note: The instructor and the BISB program are in the process of getting approval from the Graduate Council to introduce this as a course and to allow it as a core option. While we await approval, the course is offered under a temporary course number, ECE 286, by Prof. Siavash Mirarab, with the title "Algorithms for Biological Data Analysis." The course code ECE 286 may be used by other special topics courses as well, so be sure to enroll in the correct one.
- Genomics, Proteomics, and Network Biology (Bioinformatics III, BENG 203/CSE283): This is core in the BISB track. In the BMI track, it may be taken as the 4th core class or as an elective. Anotating genomes, characterizing functional genes, profiling, reconstructioning pathways. Prerequisites: Pharm 201, BENG 202/CSE282, or consent of instructor.
All students in years 1 and 2 must take both seminars in fall, winter, and spring quarters.
- Current Trends in Biomedical Informatics (MED 262): Weekly talks by researchers introduce students to current research topics within BMI. Speakers are drawn from academia, health care organizations, industry, and government.
- Bioinformatics Student Research Talks (BNFO 283) : Weekly presentations by Bioinformatics and Systems Biology students about Research Projects that are proposed or completed. Faculty mentors are present to contribute critiques and suggestions.
All students must take one of the two ethics courses by the end of second year. However, funding sources may require that it be taken first year, so we recommend taking it the first year.
- Scientific Ethics (SOMI 226): see below description
- Ethics in Scientific Research (BIOM 219): Overview of ethical issues in scientific research, conflicts of interest; national, statewide and campus issues and requirement; ethical issues in publications; authorship; retention of research records; tracing of research records; attribution; plagiarism; copyright considerations; primary, archival and meeting summary publications; ethical procedures and policies; NIH, NSF, California and UC San Diego; case studies and precedents in ethics.
Research and Teaching
During the academic year, all students must be enrolled in the appropriate research course for their level. Students typically do three rotations in year 1 (BNFO 298) and then do research units (BNFO 299) with their thesis advisor in years 2 and later. BNFO 299 units may be varied to meet the full-time enrollment requirement of 12 units per quarter in fall, winter, and spring.
- Teaching Assistantship (TA) (BNFO 500) : Students will be a TA for two quarters during second or third year. To prepare for this teaching, students will receive training through the Center for Teaching Development at UCSD.
- Research Rotation (BNFO 298) : Taken each quarter during first year to help determine the thesis adviser.
- Graduate Research (BNFO 299): Independent work by graduate students engaged in research and writing theses. S/U grades only. May be taken for credit fifteen times.
Students must take 16 units of elective courses, including 8 units from the BMI series and 4 units from the CS series. The final 4 units can be taken from any series. The two BMI core courses MED 265 (or MED 263 for students with a clinical background) and MED 267 count as electives. Please check this BISB curriculum page for the list of all approved electives and elective series.
Formal Progress to Degree
There are three formal evaluations that students must complete prior to being awarded a PhD degree:
- Qualifying Examination: This examination must be passed prior to the end of the student’s second year of study. The written portion of the exam consists of the student preparing an NIH or NSF-style research proposal. This proposal is then defended in an oral examination. Once the student passes the oral portion of the exam, the student is deemed to be qualified for advancing into PhD thesis research.
- Advancement to PhD Candidacy: Upon completion of formal course requirements, each student is required to take a written and oral qualifying examination that admits the student to the candidacy of the PhD Program. The exam is administered by the dissertation committee, which consists of five faculty members.
- Final Examination: All students defend their thesis in a final oral examination.
How to Apply
Application for admission to graduate studies is made directly through the Bioinformatics and Systems Biology website.
To be considered for the NLM fellowship, in addition to submitting your application and documentation to the degree program of your choice, please send the following to dbmi fellowship at ucsd dot edu:
- Personal Statement- explaining why you are a good candidate for the fellowship and what you hope to accomplish as an NLM trainee, the specific kind of research and topics you are interested in studying and what your goals are after completing the fellowship.
- A current and up to date CV; and
- In the body of your email please indicate which degree program you are applying to.
- Director’s Welcome
- Participating Departments
- Frontiers in Computational Biosciences Seminar Series
- Current Ph.D. Students
- Current M.S. Students
- Bioinformatics Department Handbook
- B.I.G. Summer Institute
- The Collaboratory
- Diversity and Inclusiveness
- Helpful Information for Current Students
- Joint UCLA-USC Meeting
- Student Blog and Twitter Feed
- Social Gatherings
- Introduction to the Program
- Admissions Information
- Admissions FAQs
- Student Funding
- Curriculum and Graduate Courses
- Research Rotations
- Qualifying Exams
- Doctoral Dissertation
- Student Publications
- Capstone Project
- Undergraduate Courses
- Undergraduate and Masters Research
- Bioinformatics Minor Course Requirements
- Bioinformatics Minor FAQs
- Bioinformatics Minor End-of-Year Celebration
- For Engineering Students

Bioinformatics faculty
The Bioinformatics Interdepartmental Ph.D. Program is one of ten Home Areas within the UCLA Graduate Programs in Bioscience (GPB). Home Areas consist of faculty and students with shared interest in research areas and approaches. Each interdepartmental Home Area is aligned with a Ph.D.-granting program, provides in depth, cutting-edge training, and offers access to a wide variety of exceptional faculty mentors. Interdisciplinary Ph.D. program with integrated one-year core curriculum , over 50 elective courses, and over 20 core bioinformatics faculty spanning life & physical sciences, the Schools of Medicine and Engineering.
- Prospective graduate students are encouraged to apply for admission to the UCLA Bioinformatics Ph.D. program.
- UCLA undergraduates can get involved through the many undergraduate bioinformatics course offerings as well as an Undergraduate Minor program in Bioinformatics .
- UCLA Computer Science Masters students are encouraged to get involved through graduate courses in Bioinformatics which are applicable to their Masters program.
- There are plenty of opportunities for current UCLA students to get involved in bioinformatics research projects . Students from outside UCLA interested in research internships should contact Bioinformatics faculty directly.
What is the UCLA Bioinformatics Ph.D. Program?
We offer integrated doctoral training for students interested in working at the interface of computer science, biology, and mathematics to address the fundamental challenges of contemporary genomic-scale research. Our interdisciplinary Ph.D. program consists of an integrated one-year core curriculum, research rotations, over 50 elective courses, and faculty mentors spanning biology, mathematics, engineering, and medicine.
What is Bioinformatics?
Bioinformatics can be defined broadly as the study of the inherent structure of biological information. Some of this inherent structure is very obvious (e.g., statistical patterns that reveal crucial functional regions such as genes), while others are less obvious but still immediately fruitful (e.g., how regulatory sequences give rise to “programs” of gene expression), while others are profound long-term challenges (e.g., how the genome encodes the capabilities of the human mind). Bioinformatics is the marriage of biology and the information sciences. Long term, this is a huge intellectual project. Fortunately, it is producing immediately valuable results now, e.g.:
- Statisticians have invented analyses of DNA microchip results (expression measurements of all 30,000 human genes simultaneously) that can distinguish different types of tumors with dramatically different treatment requirements, which previously were hard to differentiate clinically.
- Evolutionary biologists have developed bioinformatics analyses of genome sequence data that reveal the precise pathways by which dangerous pathogens (like HIV) evolve drug resistance, and how to slow the evolution of multi-drug resistance.
- Computer scientists have created powerful new ways for mapping brain functions automatically from standard imaging data.
UCLA Bioinformatics History
UCLA has a strong record of bioinformatics research and graduate training. In 1999 the faculty established a graduate core curriculum in bioinformatics, which has been offered continuously since that time, and recently has been greatly expanded, demonstrating the faculty’s commitment to collaborative teaching and to long-term development of an integrated bioinformatics program. These initiatives have been recognized by a large number of awards of multi-investigator Project and Training grants in bioinformatics from NIH, NSF, DOE and other funding sources.
The Bioinformatics IDP provides an academic home for bioinformatics at UCLA that brings together the many different disciplines that this field requires. Examples of current bioinformatics research conducted by the core faculty include:
- The analysis of gene and protein sequences to reveal protein evolution and alternative splicing
- The development of computational approaches to study and predict protein structure to further our understanding of function
- The analysis of mass spectrometry data to, for example, understand the connection between phosphorylation and cancer
- The development of computational methods to utilize expression data to reverse engineer gene networks in order to more completely model cellular biology
- The study of population genetics and its connection to human disease
Research strengths
The program involves over 45 core bioinformatics faculty leading research in:
- Prediction of protein structure, function, interaction networks
- Transcriptomics via RNAseq
- Epigenomics (high-throughput methylation profiling)
- Genome-wide association for disease genes
- Stochastic network inference and modeling
- Population genomics
- Bayesian phylogenetics and comparative genomics
- Genome evolution
- Algorithmic development for high-throughput data-mining
- Expression profiling
- Genomic-scale genotyping
- Next generation sequencers (e.g. pyrosequencing)
- Chemical informatics (diversity library screening)
- Proteomics (e.g. NMR, mass spectroscopy)
- Core facilities for advanced computing: The Center for Computational Biology provides one of the largest computational Grid clusters in Southern California.
- Institute for Pure and Applied Mathematics
- Single campus that integrates schools of Medicine, Engineering, Life Sciences, Mathematical and Physical Sciences, and Public Health.
- Extensive fellowship support
Featured News
Researchers awarded $4.7 million to study genomic variation in stem cell production, dr. nandita garud recognized for her research on gut microbiome, ucla study reveals how immune cells can be trained to fight infections, ucla scientists decode the ‘language’ of immune cells, dr. eran halperin elected as fellow of international society for computational biology, recent student publications.
RECENT STUDENT PUBLICATIONS LINK-PLEASE CLICK!
Updates Coming Soon!

- Recommendations
- Notifications
- My Favorites
Favorites, recommendations, and notifications are only available for UCLA Graduate Students at this time.
Access features exclusively for UCLA students and staff.
As a student, you can:
- Add funding awards to your favorites list
- Get notified of upcoming deadlines and events
- Receive personalized recommendations for funding awards
We're Sorry
You've signed in with a UCLA undergraduate student account.
UCLA Graduate Programs

Graduate Program: Bioinformatics
UCLA's Graduate Program in Bioinformatics offers the following degree(s):
Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.)
Master of Science (M.S.)
With questions not answered here or on the program’s site (above), please contact the program directly.
Bioinformatics Graduate Program at UCLA 172 Boyer Hall 611 Charles E. Young Drive Box 951570 Los Angeles, CA 90095-1570
Visit the Bioinformatics’s faculty roster
COURSE DESCRIPTIONS
Visit the registrar's site for the Bioinformatics’s course descriptions
- Admission Requirements
- Program Statistics
(310) 825-0068
MAJOR CODE: BIOINFORMATICS
Bioinformatics PhD
Interested in a bioinformatics phd.
Our goal is to prepare highly selected students for productive research careers in genetics. Because of the central role played by genetics in all biological processes and the vastly expanding applications of genetics to virtually every aspect of modern society we believe that it is as important for our students to develop a broad perspective as it is for them to become experts in a specific area. A broad perspective is indispensable for the formulation of long-term career goals as well as for productive collaborations that have become such an integral part of modern research. While developing a broad base through appropriate courses, first-year students participate in eight-week research rotations in faculty laboratories of their choice. These rotations provide the basis for selecting the area of genetics in which the student will become an expert. Seminar courses occurring each semester focus on current topics in genetics and molecular biology and are presented by investigators within and outside of Emory. We also believe that strong presentation and communication skills are critical to becoming a top-notch scientist. As such, GMB students present periodic progress reports on their own research to the assembled Program. In summary, the GMB graduate program strives to educate and train tomorrow's top geneticists today.
The Student Experience
To provide the basis for advanced research, introductory courses covering both prokaryotic and eukaryotic systems are taken in the first year. First-year students obtain practical research training by participating in eight-week rotations in the investigators' laboratories of their choice. These rotations provide the basis for selecting dissertation topics and mentors. After completing the first year, students tailor their curriculum from a large list of specialized courses in genetics and molecular biology, as well as other areas of current biological sciences. All courses emphasize critical thinking, constructive literature evaluation, and presentation skills. Seminar courses occurring each semester focus on current topics in genetics and molecular biology and are presented by investigators within and outside of Emory. Students also present their findings in research-in-progress meetings, which are attended by their peers and the faculty. Student invited speakers, small group teaching experiences, and training in the ethical conduct of research round out the overall list of activities that occur as students conduct research and prepare their dissertation.
Research Opportunities For Bioinformatics PhD
Research interests of the faculty vary in topic, approach and model organism. This interdepartmental graduate program derives its faculty from eight different departments including those from the departments of Biology, Biochemistry, Cell Biology, Human Genetics, Microbiology & Immunology, Pathology & Laboratory Medicine, Pharmacology, and the Winship Cancer Institute. More on Research Opportunities...
Training Opportunities
The graduate program in Genetics and Molecular Biology (GMB) at Emory University offers an exciting broad based training in the fields of genetics and molecular biology and their related disciplines of biochemistry, bioinformatics, cell biology, developmental biology and statistics. Research interests of the faculty vary in topic, approach and model organism. This interdepartmental graduate program derives its faculty from ten different departments including those from the departments of Human Genetics, Biology, Biochemistry, Cell Biology, Microbiology & Immunology, Pathology & Laboratory Medicine, Pharmacology, and the Winship Cancer Institute. A wide range of research opportunities in bacterial, viral, human and eukaryotic model system genetics enable students to specialize in their area of interest while obtaining an essential foundation in genetics. Areas of emphasis listed below are supported by state-of-the-art research facilities.
Research programs of the faculty fall into six major areas:
- Regulation of Gene Expression
- Development and Differentiation
- Cancer Genetics and Biology
- Human and Medical Genetics
- Bioinformatics and Comparative Genomics
- Genome Structure, Replication, Recombination And Repair
Department News
Bojing blair jia receives siebel scholars award.
Congratulations to BISB PhD student Bojing Blair Jia on being named a 2024 Siebel Scholar!
Jeff Jaureguy receives ASHG award
Congratulations to BISB PhD student Jeff Jaureguy on being named a 2023-2025 Human Genetics Scholar by the American Society of Human Genetics!
Yue Qin - Forbes 30 Under 30 Asia 2023!
Yue Qin, a Ph.D. student in the Bioinformatics and Systems Biology graduate program, has made the Forbes 30 Under 30 Asia 2023 list in recognition of her research on using machine learning to map the structure of human cells.
Full story , Forbes' profile of Yue Qin , Press release

Yue Qin awarded Chancellor's Dissertation Medal
Yue Qin, a Ph.D. student in the Bioinformatics and Systems Biology graduate program, will receive the 2023 Chancellor's Dissertation Medal at commencement for her dissertation “Towards an in silico cell.” Seven graduating Ph.D. students in different disciplines were selected for this honor.
Prof. Niema Moshiri - Forbes 30 under 30 list!
Prof. Niema Moshiri has made the Forbes 30 under 30 list in recognition of tools he developed for analyzing SARS-CoV-2 sequencing data. He is both a current faculty member in BISB as well as an alumnus of the BISB PhD program.
Full story and Prof. Moshiri's entry
Jonathan Pekar, Erick Armingol, and Yue Qin awarded 2023 Siebel Scholarships
Congrats to BISB PhD students Jonathan Pekar, Erick Armingol, and Yue Qin on being named 2023 Siebel Scholars!
- Lab Members
- News and Media
- Data Download
- Publications
INFORMATION FOR
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Academic Calendar
How to Train a Biomedical Data Scientist
Learn about programs offered by the section of biomedical informatics and data science.
Introducing the new Certificate in Medical Software & Artificial Intelligence
Contributed by Xenophon (Xenios) Papademetris, PhD | Papademetris is a Professor of Biomedical Informatics & Data Science and Professor of Radiology & Biomedical Imaging. He is the Director of Image Processing and Analysis, Bioimaging Sciences, at Yale Department of Radiology and Biomedical Imaging.
On March 13, we launched our new Certificate Program in Medical Software and Medical AI. We have an initial cohort of 16 students from four continents (Asia, Africa, Europe, North America). It has taken us a little over four months to go from final approval to launch. During this time, we have recorded close to 20 hours of video lectures, plus another six to seven hours of supplementary guest expert interview videos.
Our non-degree program builds on the foundation of the recently published textbook “Introduction to Medical Software: Foundations for Digital Health, Devices, and Diagnostics” and the popular companion Yale Coursera Course “ Introduction to Medical Software ,”which has enrolled over 16,000 students from around the world.
The new certificate program will be taught by a team of experienced faculty from the Section of Biomedical Informatics and Data Science at the Yale School of Medicine with expertise in AI, data science, clinical decision support, and medical software.

The program will consist of four 4-week modules as follows:
- Introduction to Medical Software – an overview of both the regulatory and software engineering aspects of medical software
- Introduction to Artificial Intelligence – a broad overview of modern machine learning, beginning with core concepts and running all the way to modern generative AI and large language models. Frequent medical examples will ensure that students already experienced in AI will be able to enrich their knowledge base with applied examples.
- Medical Software with AI – we will focus here on how medical software design, implementation, and testing are affected when incorporating AI modules and the associated regulatory processes in this area
- Current and Emerging Applications of AI in Medicine – we will cover how AI-powered medical software is used in various settings, including radiology applications, clinical decision support in emergency medicine, clinical decision support in the context of global health, and emerging applications in genomics and other areas.
Each week of the program will consist of a pre-recorded video and a live online session where students can ask questions of both the instructors and visiting guest experts from academia and industry. Visit the Yale Biomedical Informatics & Data Science YouTube Channel to see recordings of informational webinars about this program, sample lecture videos, and freely available guest expert interviews.
If you're looking to advance your career in the medical device industry, our certificate in Medical Software and Medical Artificial Intelligence is the perfect opportunity. Enroll and take the first step toward achieving your career goals.
Applications for Spring 2024 are closed. Information for the next round of applications will follow.

Where Data Meets Biology and Medicine: PhD in CBB
Information contributed by Mark Gerstein and Steven Kleinstein | Gerstein is the Albert L Williams Professor of Biomedical Informatics and a Professor of Molecular Biophysics & Biochemistry, Computer Science, and Statistics & Data Science. Kleinstein is the Anthony N Brady Professor of Pathology and, along with Gerstein, Co-Director of Graduate Studies for Computational Biology and Bioinformatics.
The rapid acquisition of data such as electronic health record (EHR) data and other types of health data, as well as data made possible by genomics, transcriptomics, and proteomics technologies, has unveiled the gap between data availability and their biological and medical interpretation. Computational and theoretical approaches must be developed to help close this gap. Computational modeling of biomedical processes, management of biomedical data and knowledge, machine and statistical learning,algorithms, human-computer interfaces, as well as statistical and mathematical analyses, are some of the topics in the CBB (Computational Biology & Bioinformatics) curriculum.
Yale has an interdepartmental CBB PhD program, which means that students complete the CBB curriculum while being able to do their dissertation research in the laboratory of a faculty member in any relevant department at Yale.

Because of the interdisciplinary nature of the field, we anticipate that students will be extremely heterogeneous in their background and training. As a result, we are willing to meet with students to help them individually tailor the curriculum to their background and interests. The emphasis will be on gaining competency in three broad “core areas”: computational biology and bioinformatics, biological sciences (e.g. genetics), and informatics (e.g. computer science and statistics). Completion of the curriculum will typically take 4 semesters, depending in part on the prior training of the student. Since students may have very different prior training in biology and computing, the courses taken may vary considerably. In addition, students will spend a significant amount of time during this period doing intensive research rotations in faculty laboratories and attending relevant lectures and seminars.
"My experience has allowed me to see the most recent research involving AI and machine learning in healthcare," says Lucy Zheng, first-year PhD student in CBB. As part of her program, she plans to explore computational methods to enhance genetic and biomedical research. First-year PhD student Kevin Jin is interested in computational psychiatry, wearable devices, and clinical natural language processing. After his program, he hopes to apply his skills in industry.

Building the New MS in CBB with Bioinformatics Track
Information contributed by Cynthia Brandt, MD, MPH | Brandt is a Professor of Biomedical Informatics & Data Science and Professor of Biostatistics at Yale School of Medicine. She is also Vice Chair for Education in the Section of Biomedical Informatics & Data Science.
Without the workforce and the individuals who understand how data is created, how it's captured, how it's stored, and how different computational methods are necessary to analyze it, it causes a limitation that slows down what you can learn from the data that scientists are creating. Then it makes it more difficult to translate that data, which could be used for clinical trials and for medical advances.
The MS degree in CBB is a full-time 2-year program that provides students with broad training in information sciences, data science, clinical informatics, biological science, and consumer informatics. Students explore innovative ways to use data, information, and knowledge to improve the care and well-being of patients and populations, and biomedical science research. Graduates will be ready to tackle problems spanning medicine, computing, biology, data science, and more.
Applicants should typically have an undergraduate degree with a focus in health, computer science or mathematics/statistics. For the experienced clinician looking to gain a problem- solving edge or technical aficionado looking to understand clinical practice, the MS focuses on developing research skills through both coursework and structured research opportunities. Students will be expected to produce real-world solutions of publishable quality to problems in concert with faculty and practicing clinicians.
Read a feature article about this new program here.
A MS in computational biology and bioinformatics with a biomedical informatics track is expected to prepare a student for a career in biology at scientific research institutes, in clinical or health systems in data science roles, in STEM industry (beyond iust the biomedical sector), or further academic research in graduate school or beyond.

Explore the MS in Health Informatics at Yale School of Public Health
Contributed by Cynthia Brandt, MD, MPH
The Master’s in Health Informatics began in 2019 at the Yale School of Public Health within the Health Informatics Division in the Department of Biostatistics. The MS degree provides well-rounded training in Health Informatics, with a balance of core courses from such areas as information sciences, clinical informatics, clinical research informatics, consumer health and population health informatics, data science and more broadly health policy, social and behavioral science, biostatistics, and epidemiology. The program’s faculty cross-list courses and students take relevant courses in other schools and divisions at Yale. There are currently 15 ladder track faculty leading the program and the HI track in the executive MPH.
Graduates of this program will be equipped to develop, introduce, and evaluate new biomedically motivated methods in areas as diverse as data mining, natural language or text processing, cognitive science, human-computer interaction, decision support, databases, and algorithms for analyzing large amounts of data generated in public health, clinical research, and genomics/proteomics.
The length of study for the MS in HI is two academic years. First-year courses survey the field; the typical second-year courses are more technical and put greater emphasis on mastering the skills in health informatics. The degree also requires a year-long capstone project in the second year. There have been a total of 15 graduates from the program. There are currently 45 matriculated students. Applicants will typically have an undergraduate degree with a focus in health, computer science, and mathematics/statistics.

Physicians Wanted! For a Master of Health Science (MHS) with a Clinical Informatics & Data Science Focus
The Clinical Informatics and Data Science MHS is designed for graduates with clinical backgrounds who wish to gain competency in informatics and data science through core required courses and research activities. The science of informatics drives innovation that is defining future approaches to information and knowledge management in biomedical research and healthcare. Biomedical data science includes the design, implementation, and evaluation of statistical learning/machine learning models for pattern recognition, diagnosis, and prognosis, as well as other artificial intelligence (AI) models.
Required courses cover basics of clinical informatics and data science; other courses and topics cover clinical decision support, computer system architectures, networks, security, data management, human factors engineering, clinical data standards, analytical methods and data science, and medical AI.
Also, the curriculum includes other courses and electives including leadership models, processes and practices, effective interdisciplinary team management, effective communications, project management, strategic and financial planning for clinical information systems, and change management.
Executive MPH: Online and On-Campus at Yale
Directed by Hamada Hamid Altalib, DO, MPH, FAES | Associate Professor of Neurology and of Psychiatry; Track Director, Health Informatics, Executive MPH
The Executive Master of Public Health is an innovative, hybrid program that blends comprehensive online education with in-person management and leadership training on the Yale campus, creating a unique and powerful educational experience. Taught by top faculty from the Yale School of Public Health, the Yale School of Medicine, and additional experts in their fields and employing state-of-the-art tools and technology, the program aims to train professionals who seek to acquire a strong public health education, advanced training in their area of interest, and hands-on public health and leadership training.

Designed from the ground up for working health professionals, the hybrid online program provides extensive training in leadership and management, a broad foundation in public health, specialized knowledge in areas critical to health promotion and disease prevention, and a year-long integrative experience that enables students to apply what they have learned to a real-world public health problem.
The two-year, part-time program is open to students with:
- A bachelor’s degree and at least four years of relevant work experience (need not be in the health field), OR
- A master’s degree and at least two years of relevant work experience (need not be in the health field), OR
- A doctoral (or international equivalent) degree in a field related to public health (e.g., physicians, dentists, podiatrists, pharmacists, veterinarians, attorneys, and those with a doctorate in the biological, behavioral, or social sciences)
The Health Informatics track is hosted by Yale School of Medicine's Section of Biomedical Informatics, and the track director is Professor Altalib.
Related Links
- State of Affairs: Spring Updates for Biomedical Informatics & Data Science
- Welcome to New BIDS Faculty, Fellows & Staff (BIDS Spring 2024 Newsletter)
- MD Students Explore the Big Data Issue (BIDS Spring 2024 Newsletter)
- Branching Out: Annie Hartley Envisions New D-tree Collaborations (BIDS Spring 2024 Newsletter)
- At the Intersection of AI and Medicine (BIDS Spring 2024 Newsletter)
PhD in Bioinformatics in USA: Admission, Fees, Deadlines, Eligibility, Scholarships and Jobs

Zollege Team
Content Curator | Updated On - Feb 26, 2024
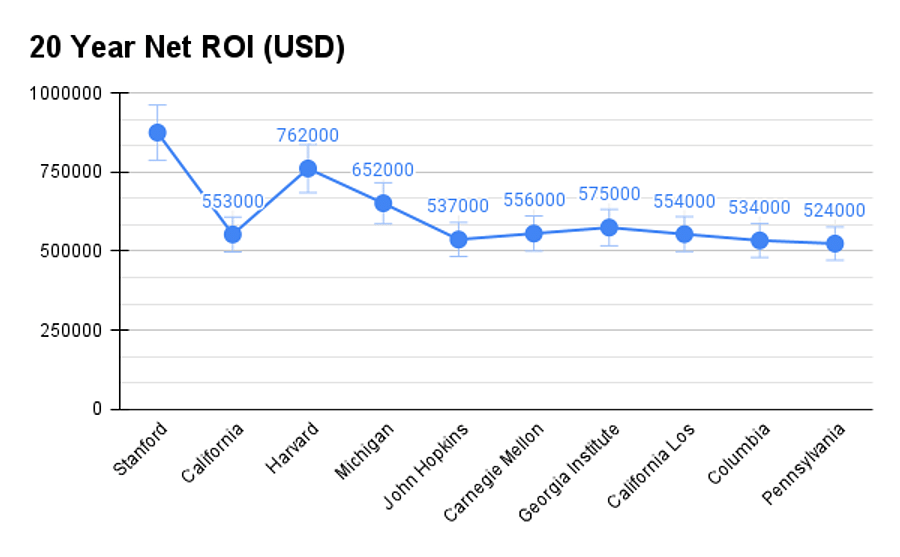
A ROI graph has been illustrated above for your reference. ROI is the monetary return value that you will receive after pursuing PhD in Bioinformtics in USA. This is calculated by summing up your tuition fees and living expenses in USA. The above picture shows the 20 year net ROI for the top universities offering PhD in Bioinformatics in USA. Harvard University and Stanford University provides the maximum return value as compared to the other universities. These universities appear in the top of US Education System . We recommend you to go through this graph to arrive at an ultimate decision in selecting your university.
A minimum GPA of 3.0 on a 4.0 scale is required. A score of at least 90 on the TOEFL iBT or 6.5 on the IELTS is usually required. The requirements of English Proficiency test scores may vary according to the university you are applying. All test score reports are required to be submitted along with the application form. Pursuing a PhD in Bioinformatics in the USA provides students with prestigious job roles such as Bioinformatics Scientist, Research Scientist, Data Scientist , etc. The average salary of a PhD in Bioinformatics graduate may range around U SD 65,000 – USD 95,000 (INR 53,89,634.25 – INR 78,77,157.75) . The salary may vary according to the company nad location of job posting.
Table of Content
Why Study PhD in Bioinformatics in the USA?
- Top Universities
- Admission Process
3.1 Admission Deadlines
3.2 Eligibility Criteria
- Admission Requirements
4.1 Admission Documents Required
- Cost of Living
- Scholarships
7.1 Top Recruiters
Work Permit
It is necessary to understand the benefits of study in USA before enrolling in any university. US universities provide ample scope and oppurtunities for career growth and stability in this job oriented market of professionals. However, the tuition fees charged is a bit expensive as compared to the other countries. Below given are some top reasons to study PhD Bioinformatics in USA:
- Pursuing a PhD in Bioinformatics in USA will open career paths for you in sectors such as academics, technology, biotech, etc in top reputed companies.
- Average salary of a PhD in Bioinformatics graduate is approximately USD 65,000 – USD 95,000 (INR 53,89,634.25 – INR 78,77,157.75) .
- According to popular opinions, the competition for PhD in Bioinformatics graduates is not so high. The job outlook is 22% more than the national average for all other occupations.
- According to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics, the employment of Bioinformatics Scientists is projected to grow by 23% within 2032
Top Universities for PhD in Bioinformatics in the USA
PhD in Bioinformatics in the USA is a highly specialized doctoral degree that focuses on the use of computer science. The annual fees however may may according to the university and mode of study you are applying for. You can pay the tuition fees in full or via installments as per your convenience in the top universities of USA . The below mentioned are the top universities in the USA offering PhD programs in Bioinformatics:
USD 1 = INR 82.92 as dated on 22nd February 2024
Admission Process for PhD in Bioinformatics in the USA
It is important to know the correct application process in order to apply for the US Universities. You must apply in the official website or portal of the university. To submit the application, you may be asked to pay an application fee. However, there are certaing Universities in USA without an application fee . The admission process for a PhD in Bioinformatics in the USA involves the following steps:
- Research properly
- Fill up the application form
- Meet Eligibility Criteria
- Prepare Application Materials
- Take Standardized Tests
- Submit Application
- Receive Decision
Admission Deadlines for PhD in Bioinformatics in the USA
The application deadlines for the top universities in USA may vary according to the year. It is suggested that you must check the admission deadlines of the program before applying. Some universities also possess an extended deadline for documents submission. Some recent admission deadlines for PhD programs in Bioinformatics at top universities in the USA:
Eligibility Criteria for PhD in Bioinformatics in the USA
In order to apply in the USA Universities you need to meet the eligibility requirements of the specific university. The eligibility requirements however may vary according toh university/college you are applying for. As an international student, the submission of English Proficiency test scores of IELTS, TOEFL or PTE is mandatory in almost all universities. General eligibility requirements that most universities may expect are mentioned below:
- A relevant bachelor's or master's degree from an accredited institution.
- Minimum GPA requirement (usually 3.0 or higher on a 4.0 scale).
- GRE scores (General Test or Subject Test) are usually required, but some universities may waive them or make them optional due to COVID-19.
- English language proficiency test scores (such as TOEFL or IELTS) for international students whose native language is not English.
- Strong research experience or potential, as demonstrated through research papers, internships, or other related experience.
- Letters of recommendation from academic or professional references.
- Statement of purpose outlining academic and research interests, career goals, and how the program aligns with them.
- Resume/CV highlighting relevant academic, research, or professional experience.
Admission Requirements for PhD in Bioinformatics in the USA
For admissions in PhD Bioinformatics, you would have to undertake ceratin exams to study in USA . The exams required for admisisons are GRE, IELTS, TOEFL, IELTS, etc. Make sure to attach the score report along with the application form. The below table shows the cutt off score for the different exams required:
Admission Documents Required for PhD in Bioinformatics in the USA
To apply in the USA Universities, you would be required to submit certain documents such as transcripts, SOP , LOR, past academic certificates, etc. These documents must be submitted along with the application form. Some universities may also have an extended deadline. To apply for a PhD program in Bioinformatics in the USA, international students must submit the following documents:
- Transcripts: Official transcripts of all undergraduate and graduate coursework.
- Standardized Test Scores: Scores from the GRE General Test, and/or GRE Subject Test in Biology or Computer Science, and/or TOEFL or IELTS.
- Letters of Recommendation: Usually, 3 letters of recommendation from academic professionals familiar with the applicant's work.
- Statement of Purpose: A written essay explaining the applicant's research interests, career goals, and why they want to pursue a PhD in Bioinformatics.
- Curriculum Vitae or Resume: A document outlining the applicant's educational and professional background.
- Application Fee: An application processing fee is required by most universities.
Cost of Living in the USA
To study in USA, you need to incur the living expenses also besides the tuition fees. These costs include accommodation, meal, utilities, etc for an international student. The cost of living in USA may vary according to the location of residence and lifestyle of a candiate. However, we have given below the cost of living in USA at an approximate basis:
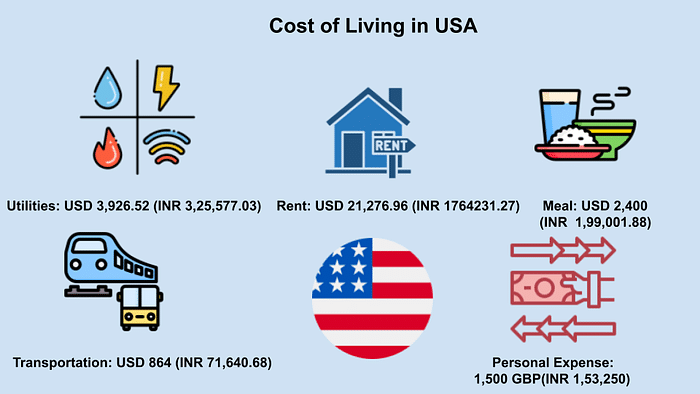
PhD in Bioinformatics Course Scholarships
To cover the tuition fees, scholarships to study in USA are also available. The scholarships cover a part of your tuition fees or awards you a stipend. US scholarships are awared on the basis of merit, financial need, etc. Some scholarships along with their eligibility and amount are given below:
Jobs after PhD in Bioinformatics in USA
Candidates are offered various prestigious jobs in USA after completing their studies. The average salary ranges around USD 65,000 – USD 95,000 (INR 53,89,634.25 – INR 78,77,157.75). However, it may vary according to the area of job location and job profile. Below given are the job profiles of freshers along with their average annual salary:
Top recruiters for PhD in Bioinformatics in the USA
The top recruiters that offer jobs to graduates after pursuing PhD in Bioinformatics in USA are Biogen, Illumina, Thermo Fisher, etc. These companies offer jobs in the popular job sectors in USA along with an attractive salary package. Some companies also offer a signing bonus to the PhD graduates. Below given are the top recruiters and the salary they offer:
STEM graduates may be eligible for an extension of an additional 24 months, making a total of 36 months of post-graduation work authorization. For this, you are required to apply to the post study work visa . It is important to note that the employment must be directly related to the student's field of study. After the OPT period, PhD graduates can apply for other work visas or can apply for permanent residency if they qualify. The post study work visas include H1-B , H2-B, P-1,P-2 , etc. Each visa has different set of criteria and limitations. These work visas alllows you to undertake many kinds of job or internships. To apply for any work visa, you would have to fill up Online Nonimmigrant Visa Application, Form DS-160. You will also have to attend an interview for the post study work visa.
Pursuing a PhD in Bioinformatics in the USA can be a great choice for students interested in the intersection of biology and computer science. Several top-ranked universities offer this program, with a range of fees and financial assistance options available for eligible students. Overall, a PhD in Bioinformatics from a top university in the USA can set you on a path to a successful and fulfilling career.
Ques. What is PhD in Bioinformatics in USA?
Ans . PhD in bioinformatics in USA is a highly specialized doctoral degree that focuses on the use of computer science. The duartion of PhD vary according to the university you are pursuing from.
Ques. What is the duration of PhD in Bioinformatics?
Ans . PhD in Bioinformatics in the USA takes 4-5 years to complete. Bioinformatics PhD programs USA duration may vary depending on the university and the specific program.
Ques. What is the average tuition fees for PhD in Bioinformatics in USA?
Ans . The tuition fees for a PhD in Bioinformatics in the USA can range from USD 20,000 to USD 60,000 per year (approximately INR 14,71,744 to INR 44,15,232). It is sugested that you must pay the tuition fees of the program as soon as the letter of acceptance arrives from the university.
Ques. What do I need for PhD in Bioinformatics in USA?
Ans . A minimum GPA of 3.0 on a 4.0 scale is required for PhD in Bioinformatics in USA. As an international student, English proficiency test scores may also be required for admisions in the top universities of USA.
Ques. Do I need to submit the scores of English Proficiency tests?
Ans . A score of at least 90 on the TOEFL iBT or 6.5 on the IELTS is usually required. The requirements of English Proficiency test scores may vary according to the university you are applying. All test score reports are required to be submitted along with the application form.
Ques. What job roles can I get after PhD in Bioinformatics?
Ans . . Pursuing a PhD in Bioinformatics in the USA provides students with prestigious job roles such as Bioinformatics Scientist, Research Scientist, Data Scientist, etc. These job roles however might vary according to the year.
Ques. What is the average salary after PhD in Bioinformatics?
Ans . The average salary of a PhD in Bioinformatics graduate may range around USD 65,000 – USD 95,000 (INR 53,89,634.25 – INR 78,77,157.75). The salary may vary according to the company nad location of job posting.
Ques. Where can I work with a degree in PhD Bioinformatics?
Ans . Pursuing a PhD in Bioinformatics in USA will open career paths for you in sectors such as academics, technology, biotech , etc . You can easily apply in these sectors with this degree.
Ques. What is the job outlook for PhD Bioinformatics?
Ans . According to popular opinions, the competition for PhD in Bioinformatics graduates is not so high. The job outlook is 22% more than the national average for all other occupations.
Ques. What is the future of a degree in PhD Bioinformatics?
Ans . According to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics, the employment of Bioinformatics Scientists is projected to grow by 23% within 2032. You can easily pursue a degree in bioinformatics as the job prospects are hige in coming years.
Ques. What are some top universities offering PhD in Bioinformatics?
Ans . The top universities offering PhD in Bioinformatics include Harvard University, Stanford University, John Hopkins University, Georgia University, etc. The annual fees however may vary according to the course structure.
Ques. Are scholarships available to study in USA?
Ans . Yes, scholarships are also available to study in USA. The scholarships cover a part of your tuition fees or awards you a stipend. US scholarships are awared on the basis of merit, financial need, etc.

Must See Articles

Masters in Management in USA: Universities, Application Proc...
Masters in Management in USA teaches leadership, marketing and management skills to the candidates. Over 300 top reputed colleges and universities pro...

MS in Biotechnology in USA: Top Universities, Fees, Scholars...
MS in Biotechnology in USA is a two-year advanced degree course available in various universities in the USA. Candidates can pursue MS in Biotechnolog...

MS in Industrial Engineering in USA: Top Universities, Admis...
MS in Industrial Engineering in USA is one of the fastest growing courses that offers a lot of possibilities and exposure for the candidate. MS in Ind...

BBA in USA: Top Universities, Cost, Eligibility, Scholarship...
BBA in USA is a three to four-year undergraduate program available in a range of departments like Management, Accounting, International Business, and ...

MS in Mechanical Engineering in USA: Top Universities, Fees,...
MS in mechanical engineering in USA is offered by a number of colleges and universities. Masters in mechanical engineering in USA is a two year progra...

MS in Mathematics in USA: Top Colleges, Fees, Scholarships a...
MS in mathematics in USA is the top choice for international students. MS in Mathematics programs in the United States take 1.5- 2 years and include 3...

PhD in USA: Top Universities, Fees, Admission, Scholarships ...
PhD in USA offers aspirants with a structured degree program that allows comprehensive training alongside independent research approaches. PhD in USA ...

MS in Robotics in USA: Top Universities, Course Fees, Schola...
MS in Robotics in USA is an advanced program of 1-2 years course. The course is studied in 40 universities across the country. Candidates having a bac...

College of Science
Bioinformatics.
Northeastern University’s Master of Science program in Bioinformatics provides cross-disciplinary training in biology, computer science, and informational technology for today’s cutting-edge jobs in the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries.
Northeastern University is committed to delivering cutting-edge programs that foster interdisciplinary thinking, research, and the pursuit of innovation-driven discoveries that have an impact on lives. That commitment and vision are at the very core of the MS in Bioinformatics. The program’s cross-disciplinary training prepares graduates to succeed in multiple roles in this new and growing field.
Combining challenging academics in biology, computer science, and information technology with real-world experience, the program helps students integrate the knowledge, skills, experience, and confidence they need to achieve their goals and make a difference in our world. The Master of Science in Bioinformatics is structured to provide students with the skills and knowledge to develop, evaluate, and deploy bioinformatics and computational biology applications. The program is designed to prepare students for employment in the biotechnology sector, where the need for knowledgeable life scientists with quantitative and computational skills has exploded in the past decade.
Concentrations:
- Bioinformatics Enterprise: The Bioinformatics Enterprise concentration integrates business and management skills with the science of bioinformatics. Students learn the fundamental concepts of leadership, entrepreneurship and innovation, financial decision making, and marketing. They gain teamwork, management, and business development skills in the process and graduate prepared to become scientist-managers.
- Biotechnology: The Biotechnology concentration provides students without a biotechnology background to obtain a strong foundation in basic biotechnology concepts and skills. Individuals, particularly those who are working in fields other than biotechnology, will acquire competency and learn new practical skills enabling them to increase productivity and allow for transitions into more biotechnology-related fields.
- Data Analytics: The Data Analytics concentration is designed to provide students with foundational knowledge in data science—including data management, machine learning, data mining, statistics, and visualizing and communicating data—that can be applied to data-driven decision making in any discipline.
- Health Informatics: The Health Informatics concentration will help prepare students to successfully address the combined clinical, technical, and business needs of health-related professionals.
- Medical Health Informatics: The Medical Health Informatics concentration will help prepare students to successfully address the combined medical needs from a patient's health perspective, technical, and business needs.
- Omics: The omics concentration will prepare students to analyze large data sets related to genomics, proteomics, transcriptomics and new-omics fields as they evolve.
- Coursework Option: Students are not required to declare a concentration. With the elective option, students select 12 credits of electives in place of concentration-specific courses.
More Details
Unique features.
- Our online format allows students to participate in the program anywhere in the world
- Students gain up to six months of work experience through co-op position
- With only one additional class, a student can also earn a graduate certificate in data science
- 94% employment after graduation in industry or research in last three years
Program Objectives
- Attain core knowledge in bioinformatics programming
- Integrate knowledge from biological, computational, and mathematical disciplines
- Gain professional work experience via co-op
Looking for something different?
A graduate degree or certificate from Northeastern—a top-ranked university—can accelerate your career through rigorous academic coursework and hands-on professional experience in the area of your interest. Apply now—and take your career to the next level.
Program Costs
Finance Your Education We offer a variety of resources, including scholarships and assistantships.
How to Apply Learn more about the application process and requirements.
Requirements
- Online application
- Application fee
- Transcripts from all institutions attended
- Personal statement
- 2 letters of recommendation
- GRE not required
- Degree earned or in progress at a U.S / Canadian institution
- Degree earned or in progress at an institution where English is the only medium of instruction
- Official exam scores from either the TOEFL iBT (institution code is 3682), IELTS, PTE exam, or Duolingo English Test. Scores are valid for 2 years from the test date.
Learn more about applying to the College of Science.
Are You an International Student? Find out what additional documents are required to apply.
Admissions Details Learn more about the College of Science admissions process, policies, and required materials.
Admissions Dates
Learn more about applying to the College of Science and our admissions deadlines.
Industry-aligned courses for in-demand careers.
For 100+ years, we’ve designed our programs with one thing in mind—your success. Explore the current program requirements and course descriptions, all designed to meet today’s industry needs and must-have skills.
View curriculum
Students in the MS in Bioinformatics program gain real-world knowledge, awareness, perspective, and confidence during a three- or six-month graduate co-op in industry or academia. As a recognized leader in experiential learning and a trusted source of high-caliber students, Northeastern enjoys relationships with more than 3,000 public- and private-sector employers on seven continents. Recent bioinformatics co-op partners have included:
- Broad Institute
- Harvard Medical School
- Brigham and Women’s Hospital
- Dana-Farber Cancer Institute
- Seattle Children’s Research Institute
Our Faculty
Northeastern University faculty represents a broad cross-section of professional practices and fields, including finance, education, biomedical science, management, and the U.S. military. They serve as mentors and advisors and collaborate alongside you to solve the most pressing global challenges facing established and emerging markets.

By enrolling in Northeastern, you’ll gain access to students at 13 campus locations, 300,000+ alumni, and 3,000 employer partners worldwide. Our global university system provides students unique opportunities to think locally and act globally while serving as a platform for scaling ideas, talent, and solutions.
Below is a look at where our Science & Mathematics alumni work, the positions they hold, and the skills they bring to their organization.
Where They Work
- State Street
- Liberty Mutual Insurance
What They Do
- Engineering
- Business Development
- Information Technology
What They're Skilled At
- Project Management
- Data Analysis
Learn more about Northeastern Alumni on Linkedin.
Related Articles

Computational Biology vs. Bioinformatics: What’s the Difference?

Earning a Bioinformatics Degree: Career Outlook and Job Prospects

7 Popular Bioinformatics Careers
Opening Doors: Rhonda Harrison (ENG’98,’04, GRS’04)
Bu alum, the first black woman in the united states to earn a phd in bioinformatics, is a ceo, a dei speaker, and a role model.

Rhonda Harrison (ENG’98,’04, GRS’04), CEO of Biopharmix Consulting
Rhonda Harrison (ENG’98,’04, GRS’04), the CEO of Biopharmix Consulting, says she is working to foster diversity in STEM workplaces and to inspire students. “I hope to do for young people what I had done for me some 40 years ago, when someone came to me and said, ‘Hey, this is what a scientist looks like, and you can be one, too.’” Photo courtesy of Rhonda Harrison
Alene Bouranova
They are determined to use their experience, influence, and positions to help make their business, organization, and world more inclusive. They are breaking barriers—and then reaching back to help those behind them overcome the same hurdles. They are BU alumni, faculty, and staff—of every race, ethnicity, age, and gender—and they are “Opening Doors” for the next generation.
Rhonda Harrison’s graduation from Boston University in 2004 marked two major milestones: Harrison (ENG’98,’04, GRS’04) was the first woman and first Black person to earn a PhD in bioinformatics in the United States.
Two decades later, Harrison, founder and CEO of Biopharmix Consulting, works as an independent diversity, equity, and inclusion speaker . And she’s a role model for others working to foster diversity in STEM workplaces and inspire students.
Bioinformatics is an interdisciplinary field that combines computer science with biology to analyze and interpret biological data. It was in its early stages when Harrison was working on her doctorate. She would go on to work on some of the field’s groundbreaking projects, including the world’s first fruit fly genetics database and the early stages of the ENCODE project , which mapped the human genome.
But long before she was a pioneer in both science and computing, Harrison, the daughter of a software engineer, was a kid from New Jersey who went to computer camp in the summer. Despite her interest in technology, she never considered pursuing a career in computer science—until a high school counselor sent her to a women in tech event.
That event was the start of her science “herstory,” as Harrison puts it. She studied computer graphics at UMass Amherst, and after graduating, took a job as a bioinformatics programmer at a Rutgers University research institute to avoid being recruited by defense companies during the Cold War era. That job spurred a lifelong love for the intersection of technology and medicine as well as an interest in the world of academia.
She was later recruited to BU by Temple Smith , a College of Engineering professor emeritus of biomedical engineering, to pursue a master’s in biomedical engineering and then a PhD in bioinformatics.
“I love that bioinformatics is a profession that benefits humankind and the human experience,” Harrison says.
Bostonia recently spoke with Harrison about her accomplishments and why having diverse role models matters.
With Rhonda Harrison
Bostonia: how did you first develop an interest in stem.
Harrison: I was a “computing kid” more than a general technology or biology kid. My dad was a software engineer; we had personal computers at home before that was widespread. Sometimes my dad would say, “Come help me with something,” and I would read off strings of hexadecimal code for him to type in and process. I would actually fall asleep to the sound of 132-column papers coming through on the computers with text on them. I went to computer camp as a kid and eventually became a camp counselor. But it wasn’t until I attended an event in high school that I saw myself being a scientist. I was pulled out for a presentation with some other kids who were promising in STEM. The presentation was just for girls, and it was about careers in science and tech and featured these women who were engineers and scientists talking about their jobs and doing cool things. That was a pivotal event for me in my science herstory. I had never really pictured what a career in science could look like until that day. So, I continued in computing in college and then discovered biology and computing.
Bostonia: You’ve had a hand in some really exciting projects, particularly in the early days of bioinformatics. Can you talk about some of those career highlights and the things you got to work on?
Harrison: My time at the Waksman Institute at Rutgers was really inspiring and amazing. I had the opportunity to create the first fruit fly database: in the sciences, there are about 8 to 10 model organisms that scientists in any field study more than others, [such as fruit flies]. I was part of the fruit fly community and developed the first Drosophila melanogaste r gene database. My experience at Rutgers made me realize that I wanted to do more in academia. That’s when Temple Smith easily lured me to BU for what was meant to be a PhD program [in bioinformatics], but didn’t have a permanent home by the time I was finishing my coursework. So, I left with my master’s [in biomedical engineering] and crossed over to MIT to work at the Whitehead Institute as a staff programmer. That was amazing. That’s where I got to work with Todd Phillip, one of the early pioneers of “ multi-omics ” research. We were doing precision medicine, where we were using AI to look at cancer cells to be able to tell whether they were acute myeloid or acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells in order to help doctors prescribe the appropriate medications. I helped develop a database for that. Then I got the call from BU. They said, “The bioinformatics program has a home, and we’d love to have you back as a student.” So, I returned to BU as a PhD candidate. As a postdoc, I worked with George Church at Harvard Medical School on the ENCODE project . It was the first ENCODE pilot project to try to determine what biomarkers in the human genome can be used to cure diseases. I developed gene panel design and data management protocols and workflows for that. Then I left academia and started to build my business skills.
Bostonia: You recently launched a diversity and inclusion outreach company. What’s your hope for that initiative?
Harrison: I had a sort of epiphany a while back. I realized I wasn’t role modeling for the people who would benefit from seeing my face and seeing my gender and skin color. I thought, well, how do I help humanity by being a role model and fostering diversity? I decided that I was going to hit the road and present to schools and such about my scientific history—or even the history of the genome project [ Human Genome Project ] and the women who worked on that. In the science community, we do all of this work and put our names in an author list [when we publish], but you can’t necessarily tell someone’s race or gender or anything else from just a name. So, there isn’t always role modeling happening in that regard either. My brand, RhondaHarrison.com , is my attempt to foster diversity in STEM workplaces and inspire students with my and others’ journeys. I hope to do for young people what I had done for me some 40 years ago, when someone came to me and said, “Hey, this is what a scientist looks like, and you can be one, too.”
I hope to do for young people what I had done for me some 40 years ago, when someone came to me and said, ‘Hey, this is what a scientist looks like, and you can be one, too.’ Rhonda Harrison
Bostonia: Why is it so important to have diverse role models?
There’s a lot of passive learning that happens when you’re young, when your synapses are still forming and you’re taking in information. As you’re going through your day, your career, your life, that learning can be hindered by not seeing diversity, and instead being indoctrinated by what you see around you or the media you consume. [Having diverse role models] broadens people’s perspectives and helps youth imagine themselves having vibrant and productive professional lives. That’s not just exclusive to kids. I think it’s really important for adults, too, to see diversity and imagine things they couldn’t before, or just to see people who don’t look like them having similar journeys. That’s uplifting for humanity.
This Series

Opening Doors: Alejandro Garcia-Amaya (CGS’05, Questrom’07)
Opening doors.
October 23, 2023
Opening Doors: Fundación ConEducación
July 31, 2023
Opening Doors: Arianne Kidder and Jason Robart
April 21, 2023
Opening Doors: Esther Kisaghu (SPH’06)
Series home
Explore Related Topics:
- Share this story
- 0 Comments Add
Writer/Editor Twitter Profile

Alene Bouranova is a Pacific Northwest native and a BU alum (COM’16). After earning a BS in journalism, she spent four years at Boston magazine writing, copyediting, and managing production for all publications. These days, she covers campus happenings, current events, and more for BU Today . Fun fact: she’s still using her Terrier card from 2013. When she’s not writing about campus, she’s trying to lose her Terrier card so BU will give her a new one. She lives in Cambridge with her plants. Profile
Alene Bouranova can be reached at [email protected]
Comments & Discussion
Boston University moderates comments to facilitate an informed, substantive, civil conversation. Abusive, profane, self-promotional, misleading, incoherent or off-topic comments will be rejected. Moderators are staffed during regular business hours (EST) and can only accept comments written in English. Statistics or facts must include a citation or a link to the citation.
Post a comment. Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Latest from Bostonia
Campus reacts and responds to israel-hamas war, reading list: what the pandemic revealed, remembering com’s david anable, cas’ john stone, “intellectual brilliance and brilliant kindness”, one good deed: christine kannler (cas’96, sph’00, camed’00), william fairfield warren society inducts new members, spreading art appreciation, restoring the “black angels” to medical history, in the kitchen with jacques pépin, feedback: readers weigh in on bu’s new president, com’s new expert on misinformation, and what’s really dividing the nation, the gifts of great teaching, sth’s walter fluker honored by roosevelt institute, alum’s debut book is a ramadan story for children, my big idea: covering construction sites with art, former terriers power new professional women’s hockey league, five trailblazing alums to celebrate during women’s history month, alum beata coloyan is boston mayor michelle wu’s “eyes and ears” in boston neighborhoods, bu alum nina yoshida nelsen (cfa’01,’03) named artistic director of boston lyric opera, my big idea: blending wildlife conservation and human welfare.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Department of Biomedical Informatics offers a PhD in Biomedical Informatics in the areas of Artificial Intelligence in Medicine (AIM) and Bioinformatics and Integrative Genomics (BIG). The AIM PhD track prepares the next generation of leaders at the intersection of artificial intelligence and medicine. The program's mission is to train exceptional computational students, harnessing large ...
73 degrees at universities and colleges in United States - Find 73 PhD Programmes in Bioinformatics & Biostatistics to study abroad. ... Bioinformatics degrees combine advanced knowledge of Biology with software programming, machine learning, data mining and interpretation. Bioinformatics scientists gather biological data and turn it into ...
The Bioinformatics PhD curriculum focuses heavily on computational genomics, computational chemistry and the data sciences. Your first two years in the program include core coursework, giving you two to three years to focus solely on your research. In your first year, you'll choose a specialty track in which to hone your expertise.
The PhD in Bioinformatics program offers unique interdisciplinary training for graduate students in the science, engineering, medicine, and ethics of twenty-first-century cell biology jointly through the College of Engineering and the Graduate School of Arts & Sciences. The program aims to prepare top researchers for careers in both academia ...
Bioinformatics (Ph.D.) Focus: preparing graduate students to reach the forefront of leadership in the field of bioinformatics and computational biology; and integrating research and education on the use of information technologies in biology and medicine. Bioinformatics (Ph.D.) Course Description and Catalog.
Students admitted with a prior master's degree in biomedical engineering or bioinformatics or a related field must complete at least 24 hours of coursework, 12 hours of which must be bioengineering courses. In addition, at least 12 hours must be at the 500 level (excluding BME 595, 596, and 599). A maximum of 4 hours of BME 590 may be applied toward the degree, provided that credit for BME ...
The PhD in Genomics & Bioinformatics begins with interdisciplinary coursework in molecular, cellular, and systems biology in the first semester. In the second and third semester students take a comprehensive introduction to the conceptual and experimental underpinnings of computational biology, statistics, genetics, and DNA sequencing.
PhD in Bioinformatics Data Science. A Ph.D. in Bioinformatics Data Science will train the next-generation of researchers and professionals who will play a key role in multi- and interdisciplinary teams, bridging life sciences and computational sciences. Students will receive training in experimental, computational and mathematical disciplines ...
The main objective of the Computational Biology PhD is to train the next generation of scientists who are both passionate about exploring the interface of computation and biology, and committed to functioning at a high level in both computational and biological fields. The program emphasizes multidisciplinary competency, interdisciplinary ...
The Ph.D. in Bioinformatics and Computational Biology is an interdisciplinary program that provides students with the skills and knowledge to analyze large scale biological data and develop new computational strategies. BCB PhD graduates are employed worldwide in academia and industry. Key program application deadlines: Jan. 1 for Fall ...
Genomics, Proteomics, and Network Biology (Bioinformatics III, BENG 203/CSE283): This is core in the BISB track. In the BMI track, it may be taken as the 4th core class or as an elective. Anotating genomes, characterizing functional genes, profiling, reconstructioning pathways. Prerequisites: Pharm 201, BENG 202/CSE282, or consent of instructor.
The HMS Department of Biomedical Informatics offers a PhD in Biomedical Informatics in the areas of Bioinformatics and Integrative Genomics (BIG) and Artificial Intelligence in Medicine (AIM). The Bioinformatics and Integrative Genomics (BIG) track led by Program Director Dr. Peter Park and Associate Director Dr. Maha Farhat, provides students with the tools to conduct original research and ...
Researchers in the field of bioinformatics and computational biology collect, store, analyze, and present complex biological data using high-performance computing. Through this work, critical contributions are made to disease detection, drug design, forensics, agriculture, and environmental sciences. This research-oriented program trains a new ...
Program Manager, PhD in Biomedical Informatics. Email Cathy Haskell. 617-432-7856. BIG PhD Program. Overview The Bioinformatics and Integrative Genomics (BIG) PhD track is an interdisciplinary program that trains future leaders in the field of bioinformatics and genomics. Our mission is to provide our graduate students with the tools to conduct ...
PhD Program. Prospective students who have completed a bachelor's degree may apply for admission to the PhD program. The PhD requires a total of 64 credits, consisting of lecture, laboratory and seminar courses and research credits. While there is a set of required core courses, the precise course of study will be determined in consultation ...
The Biological and Medical Informatics (BMI) Graduate Program at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) prepares scientists to use tools from mathematics to physics and from chemistry to biology to gather, store, analyze, predict, and disseminate information about biology. The field is essential, for without quantitative analysis of ...
Prospective Students. BU Bioinformatics offers the Doctor of Philosophy [PhD] and the Master of Science [MS] degrees. PhD Students attain a common core of knowledge, with emphasis on their ability to integrate biological and mathematical disciplines. The MS program prepares students for the most cutting-edge industrial positions in Bioinformatics.
The Bioinformatics Interdepartmental Ph.D. Program is one of ten Home Areas within the UCLA Graduate Programs in Bioscience (GPB). Home Areas consist of faculty and students with shared interest in research areas and approaches. Each interdepartmental Home Area is aligned with a Ph.D.-granting program, provides in depth, cutting-edge training ...
0 PhD programmes from all around the world - PhDportal. Agriculture & Forestry. Applied Sciences & Professions. Arts, Design & Architecture. Environmental Studies & Earth Sciences. Hospitality, Leisure & Sports. Humanities. Journalism & Media. Law.
Bioinformatics Graduate Program at UCLA 172 Boyer Hall 611 Charles E. Young Drive Box 951570 Los Angeles, CA 90095-1570 FACULTY Visit the Bioinformatics's faculty roster
The graduate program in Genetics and Molecular Biology (GMB) at Emory University offers an exciting broad based training in the fields of genetics and molecular biology and their related disciplines of biochemistry, bioinformatics, cell biology, developmental biology and statistics. Research interests of the faculty vary in topic, approach and ...
Yue Qin - Forbes 30 Under 30 Asia 2023! June 8, 2023. Yue Qin, a Ph.D. student in the Bioinformatics and Systems Biology graduate program, has made the Forbes 30 Under 30 Asia 2023 list in recognition of her research on using machine learning to map the structure of human cells.
A MS in computational biology and bioinformatics with a biomedical informatics track is expected to prepare a student for a career in biology at scientific research institutes, in clinical or health systems in data science roles, in STEM industry (beyond iust the biomedical sector), or further academic research in graduate school or beyond.
PhD in Bioinformatics in the USA takes 4-5 years to complete. Bioinformatics PhD programs USA duration may vary depending on the university and the specific program. The tuition fees for a PhD in Bioinformatics in the USA can range from USD 20,000 to USD 60,000 per year (approximately INR 14,71,744 to INR 44,15,232). It is sugested that you ...
Students in the MS in Bioinformatics program gain real-world knowledge, awareness, perspective, and confidence during a three- or six-month graduate co-op in industry or academia. As a recognized leader in experiential learning and a trusted source of high-caliber students, Northeastern enjoys relationships with more than 3,000 public- and ...
BU alum, the first Black woman in the United States to earn a PhD in bioinformatics, is a CEO, a DEI speaker, and a role model. Rhonda Harrison (ENG'98,'04, GRS'04), CEO of Biopharmix Consulting
Despite the number of conferred graduate degrees in computer and information sciences nearly tripling between the 2010-11 and 2020-21 academic years, tech fields are facing a widening skills gap.