
25 Thesis Statement Examples
A thesis statement is needed in an essay or dissertation . There are multiple types of thesis statements – but generally we can divide them into expository and argumentative. An expository statement is a statement of fact (common in expository essays and process essays) while an argumentative statement is a statement of opinion (common in argumentative essays and dissertations). Below are examples of each.
Strong Thesis Statement Examples

1. School Uniforms
“Mandatory school uniforms should be implemented in educational institutions as they promote a sense of equality, reduce distractions, and foster a focused and professional learning environment.”
Best For: Argumentative Essay or Debate
Read More: School Uniforms Pros and Cons

2. Nature vs Nurture
“This essay will explore how both genetic inheritance and environmental factors equally contribute to shaping human behavior and personality.”
Best For: Compare and Contrast Essay
Read More: Nature vs Nurture Debate

3. American Dream
“The American Dream, a symbol of opportunity and success, is increasingly elusive in today’s socio-economic landscape, revealing deeper inequalities in society.”
Best For: Persuasive Essay
Read More: What is the American Dream?

4. Social Media
“Social media has revolutionized communication and societal interactions, but it also presents significant challenges related to privacy, mental health, and misinformation.”
Best For: Expository Essay
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Social Media

5. Globalization
“Globalization has created a world more interconnected than ever before, yet it also amplifies economic disparities and cultural homogenization.”
Read More: Globalization Pros and Cons

6. Urbanization
“Urbanization drives economic growth and social development, but it also poses unique challenges in sustainability and quality of life.”
Read More: Learn about Urbanization

7. Immigration
“Immigration enriches receiving countries culturally and economically, outweighing any perceived social or economic burdens.”
Read More: Immigration Pros and Cons

8. Cultural Identity
“In a globalized world, maintaining distinct cultural identities is crucial for preserving cultural diversity and fostering global understanding, despite the challenges of assimilation and homogenization.”
Best For: Argumentative Essay
Read More: Learn about Cultural Identity

9. Technology
“Medical technologies in care institutions in Toronto has increased subjcetive outcomes for patients with chronic pain.”
Best For: Research Paper

10. Capitalism vs Socialism
“The debate between capitalism and socialism centers on balancing economic freedom and inequality, each presenting distinct approaches to resource distribution and social welfare.”

11. Cultural Heritage
“The preservation of cultural heritage is essential, not only for cultural identity but also for educating future generations, outweighing the arguments for modernization and commercialization.”
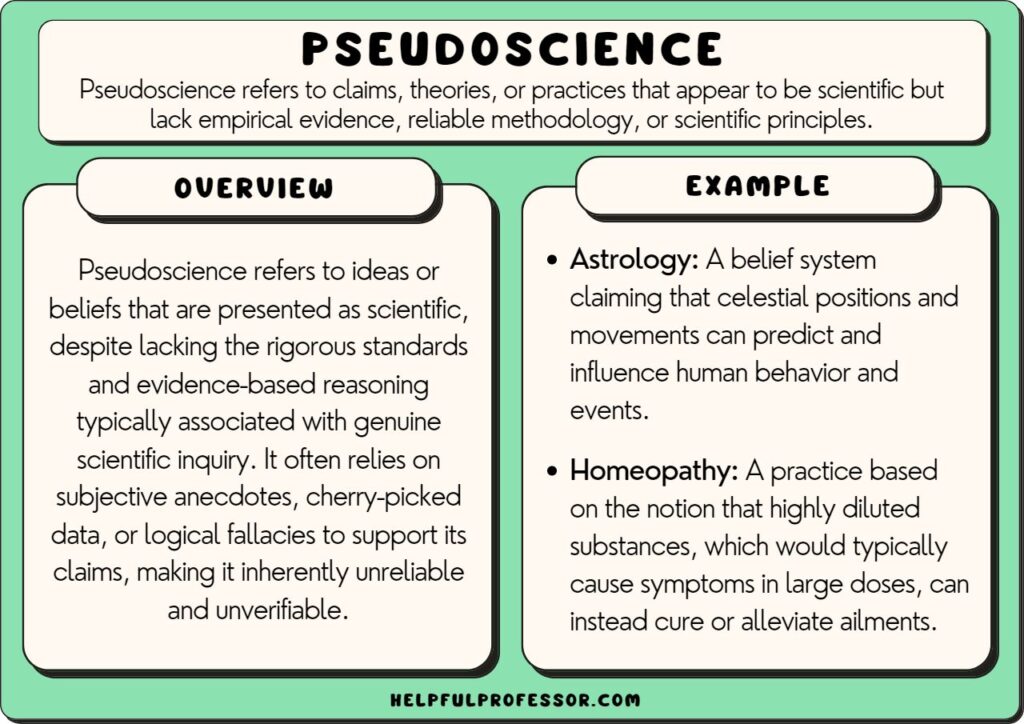
12. Pseudoscience
“Pseudoscience, characterized by a lack of empirical support, continues to influence public perception and decision-making, often at the expense of scientific credibility.”
Read More: Examples of Pseudoscience

13. Free Will
“The concept of free will is largely an illusion, with human behavior and decisions predominantly determined by biological and environmental factors.”
Read More: Do we have Free Will?

14. Gender Roles
“Traditional gender roles are outdated and harmful, restricting individual freedoms and perpetuating gender inequalities in modern society.”
Read More: What are Traditional Gender Roles?

15. Work-Life Ballance
“The trend to online and distance work in the 2020s led to improved subjective feelings of work-life balance but simultaneously increased self-reported loneliness.”
Read More: Work-Life Balance Examples
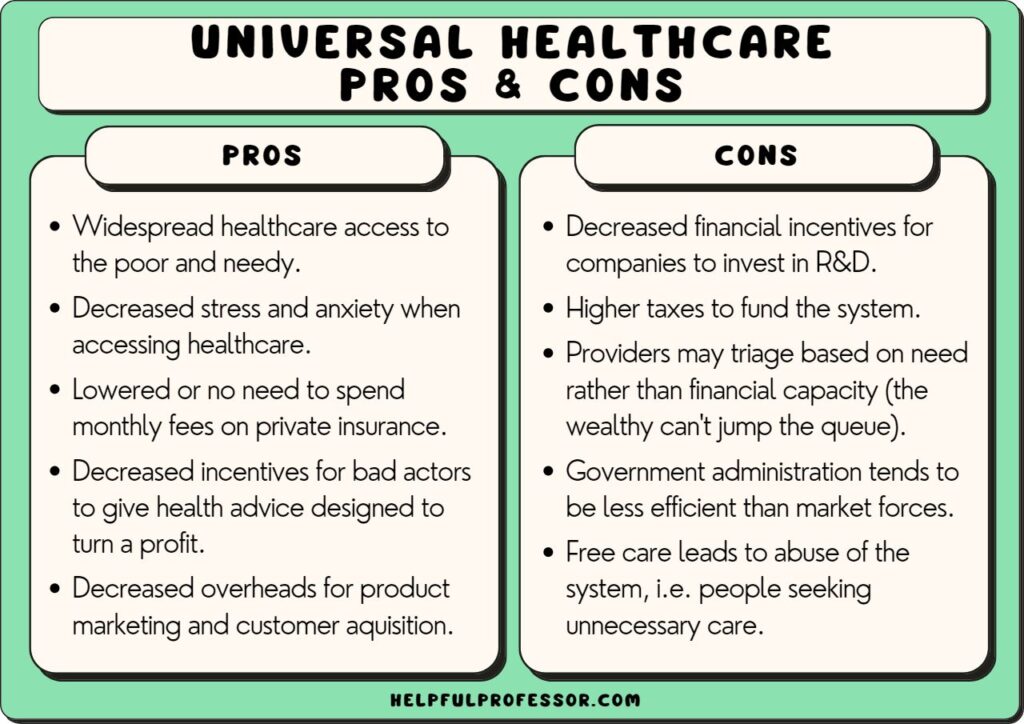
16. Universal Healthcare
“Universal healthcare is a fundamental human right and the most effective system for ensuring health equity and societal well-being, outweighing concerns about government involvement and costs.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Universal Healthcare

17. Minimum Wage
“The implementation of a fair minimum wage is vital for reducing economic inequality, yet it is often contentious due to its potential impact on businesses and employment rates.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Raising the Minimum Wage

18. Homework
“The homework provided throughout this semester has enabled me to achieve greater self-reflection, identify gaps in my knowledge, and reinforce those gaps through spaced repetition.”
Best For: Reflective Essay
Read More: Reasons Homework Should be Banned

19. Charter Schools
“Charter schools offer alternatives to traditional public education, promising innovation and choice but also raising questions about accountability and educational equity.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Charter Schools

20. Effects of the Internet
“The Internet has drastically reshaped human communication, access to information, and societal dynamics, generally with a net positive effect on society.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of the Internet

21. Affirmative Action
“Affirmative action is essential for rectifying historical injustices and achieving true meritocracy in education and employment, contrary to claims of reverse discrimination.”
Best For: Essay
Read More: Affirmative Action Pros and Cons

22. Soft Skills
“Soft skills, such as communication and empathy, are increasingly recognized as essential for success in the modern workforce, and therefore should be a strong focus at school and university level.”
Read More: Soft Skills Examples

23. Moral Panic
“Moral panic, often fueled by media and cultural anxieties, can lead to exaggerated societal responses that sometimes overlook rational analysis and evidence.”
Read More: Moral Panic Examples

24. Freedom of the Press
“Freedom of the press is critical for democracy and informed citizenship, yet it faces challenges from censorship, media bias, and the proliferation of misinformation.”
Read More: Freedom of the Press Examples

25. Mass Media
“Mass media shapes public opinion and cultural norms, but its concentration of ownership and commercial interests raise concerns about bias and the quality of information.”
Best For: Critical Analysis
Read More: Mass Media Examples
Checklist: How to use your Thesis Statement
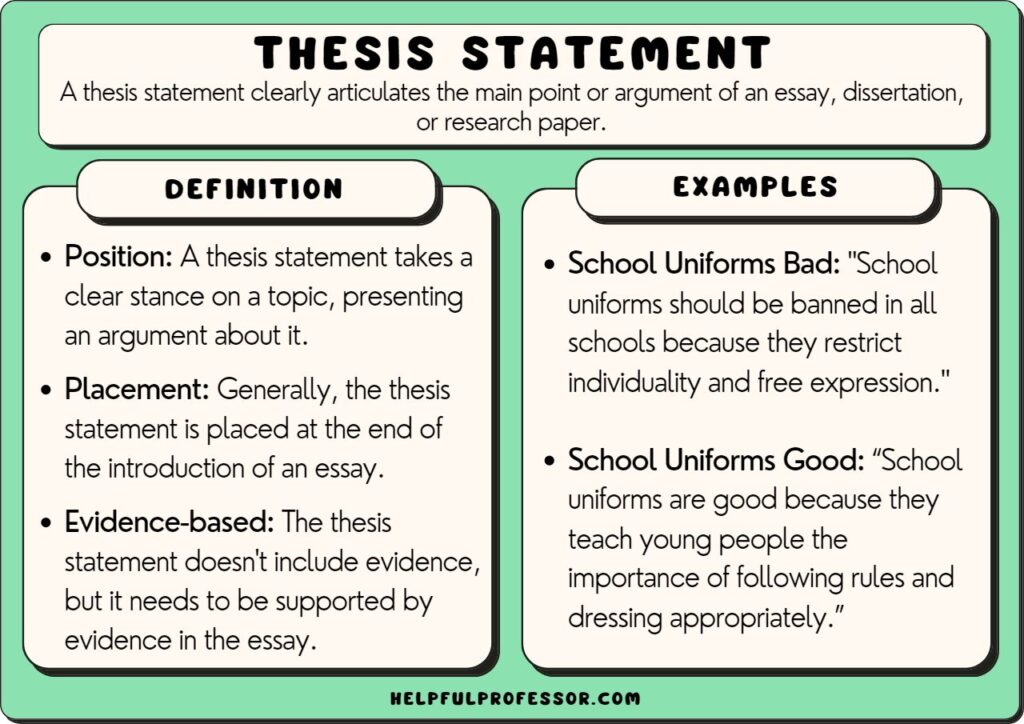
✅ Position: If your statement is for an argumentative or persuasive essay, or a dissertation, ensure it takes a clear stance on the topic. ✅ Specificity: It addresses a specific aspect of the topic, providing focus for the essay. ✅ Conciseness: Typically, a thesis statement is one to two sentences long. It should be concise, clear, and easily identifiable. ✅ Direction: The thesis statement guides the direction of the essay, providing a roadmap for the argument, narrative, or explanation. ✅ Evidence-based: While the thesis statement itself doesn’t include evidence, it sets up an argument that can be supported with evidence in the body of the essay. ✅ Placement: Generally, the thesis statement is placed at the end of the introduction of an essay.
Try These AI Prompts – Thesis Statement Generator!
One way to brainstorm thesis statements is to get AI to brainstorm some for you! Try this AI prompt:
💡 AI PROMPT FOR EXPOSITORY THESIS STATEMENT I am writing an essay on [TOPIC] and these are the instructions my teacher gave me: [INSTUCTIONS]. I want you to create an expository thesis statement that doesn’t argue a position, but demonstrates depth of knowledge about the topic.
💡 AI PROMPT FOR ARGUMENTATIVE THESIS STATEMENT I am writing an essay on [TOPIC] and these are the instructions my teacher gave me: [INSTRUCTIONS]. I want you to create an argumentative thesis statement that clearly takes a position on this issue.
💡 AI PROMPT FOR COMPARE AND CONTRAST THESIS STATEMENT I am writing a compare and contrast essay that compares [Concept 1] and [Concept2]. Give me 5 potential single-sentence thesis statements that remain objective.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Home » How to Craft a Powerful Thesis Statement for Your Essay
How to Craft a Powerful Thesis Statement for Your Essay

Introduction
In the realm of academic writing, a powerful thesis statement serves as the bedrock upon which your entire essay rests. It is the linchpin that holds your arguments together, the guiding star that illuminates the path of your exploration, and the foundation upon which you build a persuasive and coherent piece of work. Crafting a strong thesis statement is no mere triviality; it is a skill that can elevate your writing and captivate your readers. In this blog post, we will delve into the art of crafting a powerful thesis statement for your essay, exploring the strategies that can help you master this essential aspect of academic writing.
Picture this: you’ve been assigned an essay prompt, and you sit down to begin the writing process. As you ponder over your topic, ideas start to flood your mind, but where do you begin? How do you channel those thoughts into a concise, impactful, and memorable thesis statement? This is where our journey begins.
The thesis statement is the compass that guides your essay, providing direction and focus. It encapsulates the central argument or main idea of your piece, presenting it to your readers in a clear, assertive, and concise manner. A well-crafted thesis statement not only sets the stage for your essay but also entices your readers to delve deeper into your analysis.
Understanding the purpose of a thesis statement is paramount. It serves as a roadmap for both you and your readers, outlining the scope and purpose of your essay. A strong thesis statement establishes the tone, sets expectations, and creates a framework for your arguments, ensuring that your essay remains coherent and organized. It helps you avoid the pitfalls of wandering off-topic or losing sight of your main argument, providing a solid anchor to keep your writing on track.
To craft a compelling thesis statement, it is crucial to carefully analyze the essay prompt. Take the time to decipher its intricacies, unravel its underlying themes, and discern the key ideas it presents. By thoroughly understanding the prompt, you can identify the main focus of your essay and tailor your thesis statement accordingly. The prompt serves as your guiding light, illuminating the path you must take to develop a robust thesis statement.
When brainstorming ideas for your thesis statement, explore multiple avenues and consider different perspectives. Allow your thoughts to flow freely, employing techniques such as mind-mapping or freewriting to uncover connections and possibilities. This creative process enables you to generate unique insights and uncover potential arguments that will strengthen your thesis statement.
Once you have a pool of ideas, it is time to refine and distill them into a clear and concise thesis statement. Precision is key here. A strong thesis statement should be specific, avoiding vague or general statements. It should present a clear argument or position that you will support throughout your essay. Refining your thesis statement is an iterative process that requires revision, reflection, and a keen eye for precision.
Incorporating your thesis statement effectively within your essay is equally important. The placement of your thesis statement within the introduction sets the tone for the entire piece. It should seamlessly lead readers into your arguments, captivating their attention and motivating them to continue reading. Integrating the thesis statement throughout your essay helps maintain a sense of unity and coherence, ensuring that each paragraph aligns with and supports your central argument.
In the following sections, we will explore each step in detail, offering practical tips, techniques, and examples to guide you on your journey to crafting a powerful thesis statement for your essay. By following these strategies, you will not only enhance your writing skills but also engage your readers and leave a lasting impression. So, let us embark on this transformative adventure and unlock the true potential of your academic writing.
1: Understanding the Purpose of a Thesis Statement
A thesis statement is the heart and soul of any well-crafted essay. In this section, we will delve into the purpose of a thesis statement and its significance in guiding the direction of your writing.
At its core, a thesis statement serves as a concise summary of the main argument or central idea that you aim to convey in your essay. It is a declaration that encapsulates the essence of your work and presents it to your readers in a clear and assertive manner. Think of it as the North Star that guides both you and your audience throughout the essay, providing a sense of direction and focus.
The primary purpose of a thesis statement is to establish the purpose and scope of your essay. It acts as a roadmap, informing your readers about what they can expect from your writing. A well-crafted thesis statement sets the stage, defines the boundaries, and prepares the groundwork for the subsequent analysis and argumentation in your essay.
Clarity is of utmost importance when it comes to a thesis statement. It should convey your main point with precision and eliminate any ambiguity. By doing so, you ensure that your readers understand the central message you are trying to convey, enabling them to engage with your ideas more effectively.
Moreover, a strong thesis statement helps maintain the coherence and organization of your essay. It serves as a unifying thread that connects the different elements of your writing, ensuring that every paragraph and argument aligns with the overarching message. This cohesive structure enhances the readability and logical flow of your essay, making it easier for readers to follow and comprehend your ideas.
Crafting a powerful thesis statement involves careful consideration of the key components that make it effective. First and foremost, it should be specific and focused. Avoid vague or general statements that lack depth and fail to provide a clear direction for your essay. Instead, zero in on a particular aspect or argument that you will explore in your writing.
Additionally, a thesis statement should be assertive. It should present a strong and confident position or claim that you will support and defend throughout your essay. By taking a clear stance, you engage your readers and prompt them to consider your perspective.
It’s important to note that a thesis statement is not a mere statement of fact. It goes beyond stating the obvious and delves into the realm of analysis, interpretation, and argumentation. It should be thought-provoking and invite discussion, encouraging readers to explore the complexities of the topic at hand.
As you develop your thesis statement, keep in mind that it is not set in stone. It can evolve and adapt as you delve deeper into your research and writing process. Don’t be afraid to refine and revise your thesis statement as your understanding of the topic expands. This flexibility allows you to incorporate new insights and perspectives, enhancing the overall quality and depth of your essay.
2. Analyzing the Essay Prompt
When you receive an essay prompt, it is crucial to take the time to dissect and comprehend its nuances. The essay prompt provides valuable insights into the main ideas, themes, and objectives of your assignment. By carefully analyzing the prompt, you can identify the key elements that should be addressed in your essay.
The first step in analyzing the essay prompt is to read it thoroughly. Pay close attention to the wording and structure of the prompt. Look for keywords or phrases that provide clues about the specific focus or approach required. These keywords might include “analyze,” “compare and contrast,” “evaluate,” or “discuss.” Understanding these instructions will help you shape your thesis statement accordingly.
Next, identify the main ideas or concepts presented in the essay prompt. These are the building blocks of your essay and should be reflected in your thesis statement. Consider the central question or problem that the prompt poses and how it relates to the broader context of your subject or course.
As you analyze the essay prompt, be mindful of any subtopics or specific areas of emphasis that are mentioned. These can guide your thinking and influence the direction of your thesis statement. Take note of any limitations or constraints mentioned in the prompt, such as a specific time period, geographical context, or theoretical framework, as these factors will shape the scope of your thesis statement.
It is also essential to consider the target audience of your essay. The prompt may indicate whether the essay should be geared towards a general audience or a specific group of readers, such as experts in the field. Understanding your audience will help you tailor your thesis statement to meet their needs and expectations.
Another aspect to consider when analyzing the prompt is the desired outcome or objective of your essay. What is the purpose of your writing? Are you expected to present an argument, provide an analysis, or propose a solution? By understanding the intended outcome, you can ensure that your thesis statement aligns with the goals of the assignment.
Furthermore, take note of any additional guidelines or formatting requirements outlined in the prompt. These might include citation styles, word limits, or specific sources to be referenced. Adhering to these guidelines will ensure that your thesis statement and subsequent essay meet the specific criteria set by your instructor.
3. Brainstorming and Generating Ideas
In this section, we will explore effective techniques for brainstorming and generating ideas to support the development of a powerful thesis statement. By tapping into your creativity and employing various strategies, you can uncover compelling arguments and perspectives for your essay.
(i) Mind Mapping:
Begin by creating a mind map, a visual representation of your thoughts and ideas. Start with the main topic or concept in the center and branch out to related subtopics or supporting arguments. This technique allows you to explore different angles and connections, helping you generate a range of ideas that can contribute to your thesis statement.
(ii) Freewriting:
Set a timer for a designated period, such as 10 or 15 minutes, and write continuously without worrying about grammar, punctuation, or coherence. Let your thoughts flow freely, allowing unexpected ideas and associations to emerge. Freewriting enables you to bypass self-censorship and access your subconscious, leading to unique insights and potential thesis statement concepts.
(iii) Research and Reading:
Engage in extensive research and reading on your topic. Explore scholarly articles, books, reputable websites, and other relevant sources. As you gather information, jot down interesting ideas, arguments, or quotes that resonate with you. These can serve as inspiration for your thesis statement and provide a solid foundation for your essay.
(iv) Discussion and Collaboration:
Engage in discussions with peers, instructors, or experts in the field. Share your ideas, listen to different perspectives, and ask thought-provoking questions. Collaborative brainstorming sessions can stimulate creativity and offer valuable insights that you may not have considered on your own.
(v) Questioning Techniques:
Use questioning techniques to prompt deeper thinking and generate ideas. Ask yourself open-ended questions such as “What are the underlying causes of this issue?” or “How does this concept relate to other aspects of the topic?” These questions can help you explore different dimensions and uncover potential arguments for your thesis statement.
(vi) Reviewing Notes and Outlines:
Review any notes, outlines, or previous drafts you may have on the topic. Look for key points, supporting evidence, or connections that can contribute to your thesis statement. This review process allows you to build upon your existing knowledge and refine your understanding of the topic.
(vii) Considering Counterarguments:
Challenge your own assumptions and consider potential counterarguments. By exploring opposing viewpoints, you can strengthen your thesis statement by addressing possible objections or alternative perspectives. This approach adds depth and credibility to your argumentation.
Remember, during the brainstorming phase, quantity is more important than quality. Allow yourself to explore a wide range of ideas without judgment. Once you have generated a substantial list of potential arguments, evaluate and prioritize them based on their relevance, strength, and alignment with the essay prompt.
4. Refining Your Thesis Statement
Now that we have explored the initial steps of brainstorming and generating ideas, it’s time to shift our focus to the crucial process of refining your thesis statement. This stage involves honing in on the most compelling and precise expression of your main argument or position. By following the strategies outlined below, you can refine your thesis statement to ensure it effectively communicates the central theme of your essay.
(i) Review and Reflect:
Take a step back and carefully review your initial thesis statement. Reflect on its alignment with the essay prompt and its ability to capture the essence of your argument. Consider its clarity, relevance, and specificity. Identify any areas that may require further development or clarification.
(ii) Be Specific and Concise:
One of the key aspects of refining your thesis statement is to ensure it is specific and concise. Avoid general or vague statements that lack depth and fail to provide a clear direction for your essay. Instead, focus on a particular aspect or argument that you will explore in your writing. Use precise language and avoid broad claims that may dilute the impact of your thesis statement.
(iii) Incorporate Keywords:
Refer back to the keywords or key phrases from the essay prompt. Incorporate these words or concepts into your refined thesis statement to demonstrate a clear connection between your argument and the essay prompt. This helps to establish the relevance and coherence of your thesis statement within the context of your assignment.
(iv) Seek Precision and Clarity:
Refining your thesis statement involves striving for precision and clarity in your expression. Make sure your statement accurately reflects the main idea or argument of your essay, leaving no room for misinterpretation. Use specific language that leaves no doubt about the focus of your analysis.
(v) Evaluate and Eliminate Redundancy:
Scan your thesis statement for any redundant or unnecessary words or phrases. Streamline your statement to make it more concise and impactful. Remove any repetition or excessive wording that may detract from the clarity and strength of your thesis statement.
(vi) Test for Relevance:
As you refine your thesis statement, test it against the main body of your essay. Ensure that every argument, piece of evidence, or analysis you present directly supports and aligns with your thesis statement. This coherence ensures that your essay remains focused and cohesive throughout.
(vii) Solicit Feedback:
Don’t hesitate to seek feedback from peers, instructors, or writing tutors. Share your refined thesis statement and ask for their input and suggestions. Others may provide valuable insights or identify areas that require further refinement.
Remember, refining your thesis statement is an iterative process. Be open to revision and be willing to make adjustments as necessary. Keep in mind the overall purpose and scope of your essay, ensuring that your refined thesis statement effectively captures the essence of your argument.
By employing these strategies, you can refine your thesis statement to a clear, concise, and powerful statement that sets the stage for the rest of your essay. The refined thesis statement will act as a guiding beacon, directing your writing and captivating your readers’ attention.
5. Crafting a Clear and Concise Thesis Statement
Crafting a clear and concise thesis statement is crucial for effectively conveying the main argument or position of your essay. In this section, we will delve into the essential elements and strategies for creating a thesis statement that is both clear and concise.
(i) Identify the Main Argument:
Start by identifying the main argument or central idea that you want to convey in your essay. This should be a specific and focused statement that encapsulates the core message of your writing. Clearly articulate the position you will take or the perspective you will present.
(ii) Use Precise and Specific Language:
Choose your words carefully to ensure precision and clarity in your thesis statement. Avoid vague or general terms that lack specificity and depth. Instead, opt for specific and concrete language that clearly communicates your intentions and avoids ambiguity.
(iii) Keep it Concise:
Aim for brevity in your thesis statement. It should be concise and to the point, expressing your main argument in a succinct manner. Avoid lengthy or convoluted statements that may confuse or overwhelm your readers. By keeping it concise, you maintain focus and enhance the impact of your thesis statement.
(iv) One Main Idea:
Your thesis statement should convey one main idea or argument. Avoid introducing multiple ideas or topics within a single thesis statement, as this can lead to a lack of clarity and dilution of your main message. Stay focused on a single central point to ensure a clear and coherent thesis statement.
(v) Make it Debatable:
A strong thesis statement is one that invites discussion and presents a debatable claim. Avoid stating obvious or universally accepted facts. Instead, aim to present an argument or perspective that can be supported, challenged, or explored further within your essay. A debatable thesis statement stimulates critical thinking and engages your readers.
(vi) Consider the Scope:
Consider the scope of your essay when crafting your thesis statement. Ensure that your statement reflects the breadth and depth of your analysis, while still remaining concise. Strike a balance between providing enough information to convey your main argument and avoiding unnecessary details that can clutter your thesis statement.
(vii) Revise and Refine:
Crafting a clear and concise thesis statement often requires revision and refinement. After drafting your initial statement, review it carefully and assess its effectiveness. Consider whether it adequately captures your main argument and if there are any areas that can be further clarified or tightened. Revise as necessary to achieve the desired clarity and conciseness.
Remember, your thesis statement serves as the foundation of your essay, guiding your writing and providing a clear roadmap for your readers. By crafting a clear and concise thesis statement, you enable your audience to grasp your main argument from the outset and set the stage for a focused and coherent essay.
Take the time to carefully craft and refine your thesis statement, ensuring it captures the essence of your argument while maintaining clarity and conciseness. A well-crafted thesis statement enhances the overall quality of your essay and paves the way for a compelling and engaging piece of writing.
6. Incorporating the Thesis Statement into Your Essay
In this section, we will explore how to effectively incorporate your thesis statement into your essay. The thesis statement serves as the guiding principle of your writing, and integrating it seamlessly into your essay is essential for maintaining focus and coherence throughout your work.
(i) Introduce the Thesis Statement:
Begin your essay by introducing your thesis statement in a clear and concise manner. Provide a brief overview of the main argument or position you will be discussing in your essay. This introduction should set the tone and context for the rest of your writing, ensuring that your readers understand the purpose and direction of your essay from the very beginning.
(ii) Use Topic Sentences:
Each paragraph of your essay should align with and support your thesis statement. Begin each paragraph with a topic sentence that relates directly to your thesis. This topic sentence acts as a mini-thesis for the paragraph, outlining the main point or argument that will be discussed. By connecting each paragraph to your thesis statement, you maintain a cohesive and focused essay structure.
(iii) Provide Supporting Evidence:
As you develop your essay, provide supporting evidence, examples, or data that reinforce your thesis statement. These pieces of evidence should directly support the main argument you are making. By incorporating relevant and persuasive evidence, you strengthen the credibility and persuasiveness of your thesis statement.
(iv) Offer Analysis and Explanation:
In addition to presenting evidence, analyze and explain how each piece of evidence connects to your thesis statement. Clearly demonstrate the significance of the evidence in relation to your main argument. This analysis helps to deepen your readers’ understanding of your thesis statement and its relevance to the broader context of your essay.
(v) Address Counterarguments:
Acknowledge and address potential counterarguments to your thesis statement. Anticipate objections or alternative viewpoints and offer counterpoints or explanations to refute them. This shows that you have considered different perspectives and strengthens the overall validity of your thesis statement.
(vi) Reiterate the Thesis Statement in the Conclusion:
In your conclusion, restate your thesis statement in a slightly different way, emphasizing its importance and summarizing the main arguments you have presented in your essay. This helps to reinforce the central message of your essay and leave a lasting impression on your readers.
(vii) Revise and Edit:
As you review and edit your essay, ensure that your thesis statement remains consistent and well-integrated throughout. Check that each paragraph aligns with your thesis and contributes to the overall coherence of your essay. Make any necessary revisions to strengthen the connection between your thesis statement and the supporting content of your essay.
By effectively incorporating your thesis statement into your essay, you create a strong and cohesive piece of writing. The thesis statement acts as the backbone of your essay, guiding the content and providing a clear direction for your readers. Through thoughtful integration, you ensure that your essay remains focused, logical, and persuasive, ultimately leading to a compelling and impactful piece of work.
Crafting a powerful thesis statement is an essential skill in academic writing, as it sets the stage for a well-structured and persuasive essay. Throughout this blog, we have explored the process of understanding the purpose of a thesis statement, analyzing the essay prompt, brainstorming and generating ideas, refining the thesis statement, and incorporating it into your essay. By following these steps, you can enhance the quality of your academic writing and make a compelling impact on your readers.
As you embark on your academic journey, academiawriting.com stands as a reliable and professional resource to assist you with your writing needs. Our team of experienced writers understands the intricacies of crafting a powerful thesis statement and can help you develop an essay that meets your specific requirements. Whether you need assistance with brainstorming ideas, refining your thesis statement, or structuring your essay, academiawriting.com is here to provide expert guidance and support.
Ordering at academiawriting.com guarantees you access to a range of benefits. Our dedicated writers are well-versed in various academic disciplines and can tailor their expertise to meet your specific needs. With our commitment to delivering high-quality, original content and adhering to strict deadlines, you can trust us to provide you with a custom essay that meets the highest academic standards.
Don’t let the challenges of crafting a powerful thesis statement and writing an impactful essay hold you back. Place your order at academiawriting.com and let our experienced professionals help you succeed in your academic endeavors. We are dedicated to supporting your academic growth and ensuring your satisfaction with our services.
Take the next step towards achieving your academic goals by ordering at academiawriting.com today. Let us assist you in creating a compelling, well-structured essay that showcases your knowledge and critical thinking skills. Trust Academia Writing to be your partner in academic excellence.
By Erin Cross
You might also like:.

Understanding Plagiarism: Types, Consequences, and Prevention

The Renaissance Writer: Inspiring Brilliance in Academic Prose

How to Write a Captivating Introduction for Your Academic Paper
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Enjoy this blog? Please spread the word :)
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Developing Strong Thesis Statements

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The thesis statement or main claim must be debatable
An argumentative or persuasive piece of writing must begin with a debatable thesis or claim. In other words, the thesis must be something that people could reasonably have differing opinions on. If your thesis is something that is generally agreed upon or accepted as fact then there is no reason to try to persuade people.
Example of a non-debatable thesis statement:
This thesis statement is not debatable. First, the word pollution implies that something is bad or negative in some way. Furthermore, all studies agree that pollution is a problem; they simply disagree on the impact it will have or the scope of the problem. No one could reasonably argue that pollution is unambiguously good.
Example of a debatable thesis statement:
This is an example of a debatable thesis because reasonable people could disagree with it. Some people might think that this is how we should spend the nation's money. Others might feel that we should be spending more money on education. Still others could argue that corporations, not the government, should be paying to limit pollution.
Another example of a debatable thesis statement:
In this example there is also room for disagreement between rational individuals. Some citizens might think focusing on recycling programs rather than private automobiles is the most effective strategy.
The thesis needs to be narrow
Although the scope of your paper might seem overwhelming at the start, generally the narrower the thesis the more effective your argument will be. Your thesis or claim must be supported by evidence. The broader your claim is, the more evidence you will need to convince readers that your position is right.
Example of a thesis that is too broad:
There are several reasons this statement is too broad to argue. First, what is included in the category "drugs"? Is the author talking about illegal drug use, recreational drug use (which might include alcohol and cigarettes), or all uses of medication in general? Second, in what ways are drugs detrimental? Is drug use causing deaths (and is the author equating deaths from overdoses and deaths from drug related violence)? Is drug use changing the moral climate or causing the economy to decline? Finally, what does the author mean by "society"? Is the author referring only to America or to the global population? Does the author make any distinction between the effects on children and adults? There are just too many questions that the claim leaves open. The author could not cover all of the topics listed above, yet the generality of the claim leaves all of these possibilities open to debate.
Example of a narrow or focused thesis:
In this example the topic of drugs has been narrowed down to illegal drugs and the detriment has been narrowed down to gang violence. This is a much more manageable topic.
We could narrow each debatable thesis from the previous examples in the following way:
Narrowed debatable thesis 1:
This thesis narrows the scope of the argument by specifying not just the amount of money used but also how the money could actually help to control pollution.
Narrowed debatable thesis 2:
This thesis narrows the scope of the argument by specifying not just what the focus of a national anti-pollution campaign should be but also why this is the appropriate focus.
Qualifiers such as " typically ," " generally ," " usually ," or " on average " also help to limit the scope of your claim by allowing for the almost inevitable exception to the rule.
Types of claims
Claims typically fall into one of four categories. Thinking about how you want to approach your topic, or, in other words, what type of claim you want to make, is one way to focus your thesis on one particular aspect of your broader topic.
Claims of fact or definition: These claims argue about what the definition of something is or whether something is a settled fact. Example:
Claims of cause and effect: These claims argue that one person, thing, or event caused another thing or event to occur. Example:
Claims about value: These are claims made of what something is worth, whether we value it or not, how we would rate or categorize something. Example:
Claims about solutions or policies: These are claims that argue for or against a certain solution or policy approach to a problem. Example:
Which type of claim is right for your argument? Which type of thesis or claim you use for your argument will depend on your position and knowledge of the topic, your audience, and the context of your paper. You might want to think about where you imagine your audience to be on this topic and pinpoint where you think the biggest difference in viewpoints might be. Even if you start with one type of claim you probably will be using several within the paper. Regardless of the type of claim you choose to utilize it is key to identify the controversy or debate you are addressing and to define your position early on in the paper.
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
How to Write a Strong Thesis Statement: 4 Steps + Examples

What’s Covered:
What is the purpose of a thesis statement, writing a good thesis statement: 4 steps, common pitfalls to avoid, where to get your essay edited for free.
When you set out to write an essay, there has to be some kind of point to it, right? Otherwise, your essay would just be a big jumble of word salad that makes absolutely no sense. An essay needs a central point that ties into everything else. That main point is called a thesis statement, and it’s the core of any essay or research paper.
You may hear about Master degree candidates writing a thesis, and that is an entire paper–not to be confused with the thesis statement, which is typically one sentence that contains your paper’s focus.
Read on to learn more about thesis statements and how to write them. We’ve also included some solid examples for you to reference.
Typically the last sentence of your introductory paragraph, the thesis statement serves as the roadmap for your essay. When your reader gets to the thesis statement, they should have a clear outline of your main point, as well as the information you’ll be presenting in order to either prove or support your point.
The thesis statement should not be confused for a topic sentence , which is the first sentence of every paragraph in your essay. If you need help writing topic sentences, numerous resources are available. Topic sentences should go along with your thesis statement, though.
Since the thesis statement is the most important sentence of your entire essay or paper, it’s imperative that you get this part right. Otherwise, your paper will not have a good flow and will seem disjointed. That’s why it’s vital not to rush through developing one. It’s a methodical process with steps that you need to follow in order to create the best thesis statement possible.
Step 1: Decide what kind of paper you’re writing
When you’re assigned an essay, there are several different types you may get. Argumentative essays are designed to get the reader to agree with you on a topic. Informative or expository essays present information to the reader. Analytical essays offer up a point and then expand on it by analyzing relevant information. Thesis statements can look and sound different based on the type of paper you’re writing. For example:
- Argumentative: The United States needs a viable third political party to decrease bipartisanship, increase options, and help reduce corruption in government.
- Informative: The Libertarian party has thrown off elections before by gaining enough support in states to get on the ballot and by taking away crucial votes from candidates.
- Analytical: An analysis of past presidential elections shows that while third party votes may have been the minority, they did affect the outcome of the elections in 2020, 2016, and beyond.
Step 2: Figure out what point you want to make
Once you know what type of paper you’re writing, you then need to figure out the point you want to make with your thesis statement, and subsequently, your paper. In other words, you need to decide to answer a question about something, such as:
- What impact did reality TV have on American society?
- How has the musical Hamilton affected perception of American history?
- Why do I want to major in [chosen major here]?
If you have an argumentative essay, then you will be writing about an opinion. To make it easier, you may want to choose an opinion that you feel passionate about so that you’re writing about something that interests you. For example, if you have an interest in preserving the environment, you may want to choose a topic that relates to that.
If you’re writing your college essay and they ask why you want to attend that school, you may want to have a main point and back it up with information, something along the lines of:
“Attending Harvard University would benefit me both academically and professionally, as it would give me a strong knowledge base upon which to build my career, develop my network, and hopefully give me an advantage in my chosen field.”
Step 3: Determine what information you’ll use to back up your point
Once you have the point you want to make, you need to figure out how you plan to back it up throughout the rest of your essay. Without this information, it will be hard to either prove or argue the main point of your thesis statement. If you decide to write about the Hamilton example, you may decide to address any falsehoods that the writer put into the musical, such as:
“The musical Hamilton, while accurate in many ways, leaves out key parts of American history, presents a nationalist view of founding fathers, and downplays the racism of the times.”
Once you’ve written your initial working thesis statement, you’ll then need to get information to back that up. For example, the musical completely leaves out Benjamin Franklin, portrays the founding fathers in a nationalist way that is too complimentary, and shows Hamilton as a staunch abolitionist despite the fact that his family likely did own slaves.
Step 4: Revise and refine your thesis statement before you start writing
Read through your thesis statement several times before you begin to compose your full essay. You need to make sure the statement is ironclad, since it is the foundation of the entire paper. Edit it or have a peer review it for you to make sure everything makes sense and that you feel like you can truly write a paper on the topic. Once you’ve done that, you can then begin writing your paper.
When writing a thesis statement, there are some common pitfalls you should avoid so that your paper can be as solid as possible. Make sure you always edit the thesis statement before you do anything else. You also want to ensure that the thesis statement is clear and concise. Don’t make your reader hunt for your point. Finally, put your thesis statement at the end of the first paragraph and have your introduction flow toward that statement. Your reader will expect to find your statement in its traditional spot.
If you’re having trouble getting started, or need some guidance on your essay, there are tools available that can help you. CollegeVine offers a free peer essay review tool where one of your peers can read through your essay and provide you with valuable feedback. Getting essay feedback from a peer can help you wow your instructor or college admissions officer with an impactful essay that effectively illustrates your point.

Related CollegeVine Blog Posts

Home / Guides / Writing Guides / Parts of a Paper / How to Write a Strong Thesis Statement
How to Write a Strong Thesis Statement
A thesis can be found in many places—a debate speech, a lawyer’s closing argument, even an advertisement. But the most common place for a thesis statement (and probably why you’re reading this article) is in an essay.
Whether you’re writing an argumentative paper, an informative essay, or a compare/contrast statement, you need a thesis. Without a thesis, your argument falls flat and your information is unfocused. Since a thesis is so important, it’s probably a good idea to look at some tips on how to put together a strong one.
Guide Overview
What is a “thesis statement” anyway.
- 2 categories of thesis statements: informative and persuasive
- 2 styles of thesis statements
- Formula for a strong argumentative thesis
- The qualities of a solid thesis statement (video)
You may have heard of something called a “thesis.” It’s what seniors commonly refer to as their final paper before graduation. That’s not what we’re talking about here. That type of thesis is a long, well-written paper that takes years to piece together.
Instead, we’re talking about a single sentence that ties together the main idea of any argument . In the context of student essays, it’s a statement that summarizes your topic and declares your position on it. This sentence can tell a reader whether your essay is something they want to read.
2 Categories of Thesis Statements: Informative and Persuasive
Just as there are different types of essays, there are different types of thesis statements. The thesis should match the essay.
For example, with an informative essay, you should compose an informative thesis (rather than argumentative). You want to declare your intentions in this essay and guide the reader to the conclusion that you reach.
To make a peanut butter and jelly sandwich, you must procure the ingredients, find a knife, and spread the condiments.
This thesis showed the reader the topic (a type of sandwich) and the direction the essay will take (describing how the sandwich is made).
Most other types of essays, whether compare/contrast, argumentative, or narrative, have thesis statements that take a position and argue it. In other words, unless your purpose is simply to inform, your thesis is considered persuasive. A persuasive thesis usually contains an opinion and the reason why your opinion is true.
Peanut butter and jelly sandwiches are the best type of sandwich because they are versatile, easy to make, and taste good.
In this persuasive thesis statement, you see that I state my opinion (the best type of sandwich), which means I have chosen a stance. Next, I explain that my opinion is correct with several key reasons. This persuasive type of thesis can be used in any essay that contains the writer’s opinion, including, as I mentioned above, compare/contrast essays, narrative essays, and so on.
2 Styles of Thesis Statements
Just as there are two different types of thesis statements (informative and persuasive), there are two basic styles you can use.
The first style uses a list of two or more points . This style of thesis is perfect for a brief essay that contains only two or three body paragraphs. This basic five-paragraph essay is typical of middle and high school assignments.
C.S. Lewis’s Chronicles of Narnia series is one of the richest works of the 20th century because it offers an escape from reality, teaches readers to have faith even when they don’t understand, and contains a host of vibrant characters.
In the above persuasive thesis, you can see my opinion about Narnia followed by three clear reasons. This thesis is perfect for setting up a tidy five-paragraph essay.
In college, five paragraph essays become few and far between as essay length gets longer. Can you imagine having only five paragraphs in a six-page paper? For a longer essay, you need a thesis statement that is more versatile. Instead of listing two or three distinct points, a thesis can list one overarching point that all body paragraphs tie into.
Good vs. evil is the main theme of Lewis’s Narnia series, as is made clear through the struggles the main characters face in each book.
In this thesis, I have made a claim about the theme in Narnia followed by my reasoning. The broader scope of this thesis allows me to write about each of the series’ seven novels. I am no longer limited in how many body paragraphs I can logically use.
Formula for a Strong Argumentative Thesis
One thing I find that is helpful for students is having a clear template. While students rarely end up with a thesis that follows this exact wording, the following template creates a good starting point:
___________ is true because of ___________, ___________, and ___________.
Conversely, the formula for a thesis with only one point might follow this template:
___________________ is true because of _____________________.
Students usually end up using different terminology than simply “because,” but having a template is always helpful to get the creative juices flowing.
The Qualities of a Solid Thesis Statement
When composing a thesis, you must consider not only the format, but other qualities like length, position in the essay, and how strong the argument is.
Length: A thesis statement can be short or long, depending on how many points it mentions. Typically, however, it is only one concise sentence. It does contain at least two clauses, usually an independent clause (the opinion) and a dependent clause (the reasons). You probably should aim for a single sentence that is at least two lines, or about 30 to 40 words long.
Position: A thesis statement always belongs at the beginning of an essay. This is because it is a sentence that tells the reader what the writer is going to discuss. Teachers will have different preferences for the precise location of the thesis, but a good rule of thumb is in the introduction paragraph, within the last two or three sentences.
Strength: Finally, for a persuasive thesis to be strong, it needs to be arguable. This means that the statement is not obvious, and it is not something that everyone agrees is true.
Example of weak thesis:
Peanut butter and jelly sandwiches are easy to make because it just takes three ingredients.
Most people would agree that PB&J is one of the easiest sandwiches in the American lunch repertoire.
Example of a stronger thesis:
Peanut butter and jelly sandwiches are fun to eat because they always slide around.
This is more arguable because there are plenty of folks who might think a PB&J is messy or slimy rather than fun.
Composing a thesis statement does take a bit more thought than many other parts of an essay. However, because a thesis statement can contain an entire argument in just a few words, it is worth taking the extra time to compose this sentence. It can direct your research and your argument so that your essay is tight, focused, and makes readers think.

EasyBib Writing Resources
Writing a paper.
- Academic Essay
- Argumentative Essay
- College Admissions Essay
- Expository Essay
- Persuasive Essay
- Research Paper
- Thesis Statement
- Writing a Conclusion
- Writing an Introduction
- Writing an Outline
- Writing a Summary
EasyBib Plus Features
- Citation Generator
- Essay Checker
- Expert Check Proofreader
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tools
Plagiarism Checker
- Spell Checker
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Grammar and Plagiarism Checkers
Grammar Basics
Plagiarism Basics
Writing Basics
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
- How to Cite
- Language & Lit
- Rhyme & Rhythm
- The Rewrite
- Search Glass
How to Create a Thesis Statement for a Persuasive Essay
A strong thesis statement is key to writing a persuasive essay. The thesis statement presents your topic to the reader, provides your opinion on that topic and summarizes the argument you’ll make in the paper by offering evidence for your opinion. A good thesis statement should capture all of these essential details in just one or two sentences. The thesis statement generally appears after a brief introduction of your topic, often as the last sentence of your first paragraph. The following information will help you write a thesis statement for a persuasive essay.
Express an Opinion
When you sit down to write a thesis statement, make sure that you have a clear opinion about your topic. That’s because a thesis statement must include a claim that others might dispute. Your thesis summarizes the argument you’ll be making in your paper, so you want to make sure that your point of view is clear and debatable. An easy way to test your thesis is to ask yourself whether your reader could challenge or oppose your thesis statement. If your thesis simply states facts that someone couldn’t disagree with, you may simply be summarizing an issue rather than presenting a clear point of view.
Be Specific
A strong thesis statement is focused and specific. The reader should know exactly what you’re going to argue and why. “Online education is a great choice for students” is a weak thesis because it’s not specific or focused enough. A stronger thesis would be, “Online classes are a better choice than traditional classroom learning because they’re more flexible for students and teachers, they're less expensive and they let students works at their own pace.”
Include Evidence
It’s important to include evidence in your thesis statement to help support your opinion. Doing so tells readers that you understand the topic and have performed some research, which gives you more credibility as a persuasive writer. It also creates a road map for readers, so they know what evidence you’ll discuss with more detail in the paper. For example, if your thesis is, “Companies should not test their products on animals because it’s inhumane and unethical, and it doesn’t always lead to accurate results,” the reader knows right away what your opinion is and what evidence you'll provide to support that opinion in your paper.
Pass the "How and Why" Test
Your thesis statement should answer one or both of two key questions: “how” and “why.” For example, if you think that online learning is more effective for students than traditional instruction, then your thesis should tell readers how or why it’s more effective. If a reader can't determine the "how" or "why" from your thesis statement, your thesis might be too open-ended, and you may need to revise it to be more specific or to clarify your point of view.
- The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill: Thesis Statements
- Purdue Online Writing Lab: Tips and Examples for Writing Thesis Statements
- Odyssey: From Paragraph to Essay; William J. Kelly and Deborah L. Lawton.
Amy Mahoney has been a writer for more than 15 years. Her articles have appeared in newspapers and magazines including “The Boston Globe,” “Reader’s Digest” and the “Miami Herald.” She holds a Master of Fine Arts in fiction.
How to Write a Persuasive Essay (This Convinced My Professor!)
.png)
Table of contents

Meredith Sell
You can make your essay more persuasive by getting straight to the point.
In fact, that's exactly what we did here, and that's just the first tip of this guide. Throughout this guide, we share the steps needed to prove an argument and create a persuasive essay.
This AI tool helps you improve your essay > This AI tool helps you improve your essay >

Key takeaways: - Proven process to make any argument persuasive - 5-step process to structure arguments - How to use AI to formulate and optimize your essay
Why is being persuasive so difficult?
"Write an essay that persuades the reader of your opinion on a topic of your choice."
You might be staring at an assignment description just like this 👆from your professor. Your computer is open to a blank document, the cursor blinking impatiently. Do I even have opinions?
The persuasive essay can be one of the most intimidating academic papers to write: not only do you need to identify a narrow topic and research it, but you also have to come up with a position on that topic that you can back up with research while simultaneously addressing different viewpoints.
That’s a big ask. And let’s be real: most opinion pieces in major news publications don’t fulfill these requirements.
The upside? By researching and writing your own opinion, you can learn how to better formulate not only an argument but the actual positions you decide to hold.
Here, we break down exactly how to write a persuasive essay. We’ll start by taking a step that’s key for every piece of writing—defining the terms.
What Is a Persuasive Essay?
A persuasive essay is exactly what it sounds like: an essay that persuades . Over the course of several paragraphs or pages, you’ll use researched facts and logic to convince the reader of your opinion on a particular topic and discredit opposing opinions.
While you’ll spend some time explaining the topic or issue in question, most of your essay will flesh out your viewpoint and the evidence that supports it.
The 5 Must-Have Steps of a Persuasive Essay
If you’re intimidated by the idea of writing an argument, use this list to break your process into manageable chunks. Tackle researching and writing one element at a time, and then revise your essay so that it flows smoothly and coherently with every component in the optimal place.
1. A topic or issue to argue
This is probably the hardest step. You need to identify a topic or issue that is narrow enough to cover in the length of your piece—and is also arguable from more than one position. Your topic must call for an opinion , and not be a simple fact .
It might be helpful to walk through this process:
- Identify a random topic
- Ask a question about the topic that involves a value claim or analysis to answer
- Answer the question
That answer is your opinion.
Let’s consider some examples, from silly to serious:
Topic: Dolphins and mermaids
Question: In a mythical match, who would win: a dolphin or a mermaid?
Answer/Opinion: The mermaid would win in a match against a dolphin.
Topic: Autumn
Question: Which has a better fall: New England or Colorado?
Answer/Opinion: Fall is better in New England than Colorado.
Topic: Electric transportation options
Question: Would it be better for an urban dweller to buy an electric bike or an electric car?
Answer/Opinion: An electric bike is a better investment than an electric car.
Your turn: Walk through the three-step process described above to identify your topic and your tentative opinion. You may want to start by brainstorming a list of topics you find interesting and then going use the three-step process to find the opinion that would make the best essay topic.
2. An unequivocal thesis statement
If you walked through our three-step process above, you already have some semblance of a thesis—but don’t get attached too soon!
A solid essay thesis is best developed through the research process. You shouldn’t land on an opinion before you know the facts. So press pause. Take a step back. And dive into your research.
You’ll want to learn:
- The basic facts of your topic. How long does fall last in New England vs. Colorado? What trees do they have? What colors do those trees turn?
- The facts specifically relevant to your question. Is there any science on how the varying colors of fall influence human brains and moods?
- What experts or other noteworthy and valid sources say about the question you’re considering. Has a well-known arborist waxed eloquent on the beauty of New England falls?
As you learn the different viewpoints people have on your topic, pay attention to the strengths and weaknesses of existing arguments. Is anyone arguing the perspective you’re leaning toward? Do you find their arguments convincing? What do you find unsatisfying about the various arguments?
Allow the research process to change your mind and/or refine your thinking on the topic. Your opinion may change entirely or become more specific based on what you learn.
Once you’ve done enough research to feel confident in your understanding of the topic and your opinion on it, craft your thesis.
Your thesis statement should be clear and concise. It should directly state your viewpoint on the topic, as well as the basic case for your thesis.
Thesis 1: In a mythical match, the mermaid would overcome the dolphin due to one distinct advantage: her ability to breathe underwater.
Thesis 2: The full spectrum of color displayed on New England hillsides is just one reason why fall in the northeast is better than in Colorado.
Thesis 3: In addition to not adding to vehicle traffic, electric bikes are a better investment than electric cars because they’re cheaper and require less energy to accomplish the same function of getting the rider from point A to point B.
Your turn: Dive into the research process with a radar up for the arguments your sources are making about your topic. What are the most convincing cases? Should you stick with your initial opinion or change it up? Write your fleshed-out thesis statement.
3. Evidence to back up your thesis
This is a typical place for everyone from undergrads to politicians to get stuck, but the good news is, if you developed your thesis from research, you already have a good bit of evidence to make your case.
Go back through your research notes and compile a list of every …
… or other piece of information that supports your thesis.
This info can come from research studies you found in scholarly journals, government publications, news sources, encyclopedias, or other credible sources (as long as they fit your professor’s standards).
As you put this list together, watch for any gaps or weak points. Are you missing information on how electric cars versus electric bicycles charge or how long their batteries last? Did you verify that dolphins are, in fact, mammals and can’t breathe underwater like totally-real-and-not-at-all-fake 😉mermaids can? Track down that information.
Next, organize your list. Group the entries so that similar or closely related information is together, and as you do that, start thinking through how to articulate the individual arguments to support your case.
Depending on the length of your essay, each argument may get only a paragraph or two of space. As you think through those specific arguments, consider what order to put them in. You’ll probably want to start with the simplest argument and work up to more complicated ones so that the arguments can build on each other.
Your turn: Organize your evidence and write a rough draft of your arguments. Play around with the order to find the most compelling way to argue your case.
4. Rebuttals to disprove opposing theses
You can’t just present the evidence to support your case and totally ignore other viewpoints. To persuade your readers, you’ll need to address any opposing ideas they may hold about your topic.
You probably found some holes in the opposing views during your research process. Now’s your chance to expose those holes.
Take some time (and space) to: describe the opposing views and show why those views don’t hold up. You can accomplish this using both logic and facts.
Is a perspective based on a faulty assumption or misconception of the truth? Shoot it down by providing the facts that disprove the opinion.
Is another opinion drawn from bad or unsound reasoning? Show how that argument falls apart.
Some cases may truly be only a matter of opinion, but you still need to articulate why you don’t find the opposing perspective convincing.
Yes, a dolphin might be stronger than a mermaid, but as a mammal, the dolphin must continually return to the surface for air. A mermaid can breathe both underwater and above water, which gives her a distinct advantage in this mythical battle.
While the Rocky Mountain views are stunning, their limited colors—yellow from aspen trees and green from various evergreens—leaves the autumn-lover less than thrilled. The rich reds and oranges and yellows of the New England fall are more satisfying and awe-inspiring.
But what about longer trips that go beyond the city center into the suburbs and beyond? An electric bike wouldn’t be great for those excursions. Wouldn’t an electric car be the better choice then?
Certainly, an electric car would be better in these cases than a gas-powered car, but if most of a person’s trips are in their hyper-local area, the electric bicycle is a more environmentally friendly option for those day-to-day outings. That person could then participate in a carshare or use public transit, a ride-sharing app, or even a gas-powered car for longer trips—and still use less energy overall than if they drove an electric car for hyper-local and longer area trips.
Your turn: Organize your rebuttal research and write a draft of each one.
5. A convincing conclusion
You have your arguments and rebuttals. You’ve proven your thesis is rock-solid. Now all you have to do is sum up your overall case and give your final word on the subject.
Don’t repeat everything you’ve already said. Instead, your conclusion should logically draw from the arguments you’ve made to show how they coherently prove your thesis. You’re pulling everything together and zooming back out with a better understanding of the what and why of your thesis.
A dolphin may never encounter a mermaid in the wild, but if it were to happen, we know how we’d place our bets. Long hair and fish tail, for the win.
For those of us who relish 50-degree days, sharp air, and the vibrant colors of fall, New England offers a season that’s cozier, longer-lasting, and more aesthetically pleasing than “colorful” Colorado. A leaf-peeper’s paradise.
When most of your trips from day to day are within five miles, the more energy-efficient—and yes, cost-efficient—choice is undoubtedly the electric bike. So strap on your helmet, fire up your pedals, and two-wheel away to your next destination with full confidence that you made the right decision for your wallet and the environment.
3 Quick Tips for Writing a Strong Argument
Once you have a draft to work with, use these tips to refine your argument and make sure you’re not losing readers for avoidable reasons.
1. Choose your words thoughtfully.
If you want to win people over to your side, don’t write in a way that shuts your opponents down. Avoid making abrasive or offensive statements. Instead, use a measured, reasonable tone. Appeal to shared values, and let your facts and logic do the hard work of changing people’s minds.
Choose words with AI

You can use AI to turn your general point into a readable argument. Then, you can paraphrase each sentence and choose between competing arguments generated by the AI, until your argument is well-articulated and concise.
2. Prioritize accuracy (and avoid fallacies).
Make sure the facts you use are actually factual. You don’t want to build your argument on false or disproven information. Use the most recent, respected research. Make sure you don’t misconstrue study findings. And when you’re building your case, avoid logical fallacies that undercut your argument.
A few common fallacies to watch out for:
- Strawman: Misrepresenting or oversimplifying an opposing argument to make it easier to refute.
- Appeal to ignorance: Arguing that a certain claim must be true because it hasn’t been proven false.
- Bandwagon: Assumes that if a group of people, experts, etc., agree with a claim, it must be true.
- Hasty generalization: Using a few examples, rather than substantial evidence, to make a sweeping claim.
- Appeal to authority: Overly relying on opinions of people who have authority of some kind.
The strongest arguments rely on trustworthy information and sound logic.
Research and add citations with AI

We recently wrote a three part piece on researching using AI, so be sure to check it out . Going through an organized process of researching and noting your sources correctly will make sure your written text is more accurate.
3. Persuasive essay structure

If you’re building a house, you start with the foundation and go from there. It’s the same with an argument. You want to build from the ground up: provide necessary background information, then your thesis. Then, start with the simplest part of your argument and build up in terms of complexity and the aspect of your thesis that the argument is tackling.
A consistent, internal logic will make it easier for the reader to follow your argument. Plus, you’ll avoid confusing your reader and you won’t be unnecessarily redundant.
The essay structure usually includes the following parts:
- Intro - Hook, Background information, Thesis statement
- Topic sentence #1 , with supporting facts or stats
- Concluding sentence
- Topic sentence #2 , with supporting facts or stats
- Concluding sentence Topic sentence #3 , with supporting facts or stats
- Conclusion - Thesis and main points restated, call to action, thought provoking ending
Are You Ready to Write?
Persuasive essays are a great way to hone your research, writing, and critical thinking skills. Approach this assignment well, and you’ll learn how to form opinions based on information (not just ideas) and make arguments that—if they don’t change minds—at least win readers’ respect.
Share This Article:

10 Longest Words in English Defined and Explained
.webp)
Finding the OG Writing Assistant – Wordtune vs. QuillBot

What’s a Split Infinitive? Definition + When to Avoid It
Looking for fresh content, thank you your submission has been received.

Thesis Statement for Persuasive Essay
Crafting a compelling thesis for a persuasive essay is fundamental in anchoring your argument and driving your message home. A persuasive thesis not only states your position but also presents the argument you’ll use to sway your reader. This guide unveils the art of formulating influential persuasive essay thesis statements , offering examples and expert tips to ensure your essay resonates with conviction and persuasive power. Dive in to fortify your argumentative prowess.
What is a Persuasive Essay Thesis Statement? – Definition
A persuasive essay thesis statement is a concise summary of the main point or claim of the essay. It serves as a roadmap for readers, indicating the stance the writer is taking on a particular issue or topic and the key arguments they will use to convince readers of their perspective. Essentially, it’s the heart of your argument, capturing the essence of what you’re trying to persuade your audience to believe or do.
What is the Best Thesis Statement Example for Persuasive Essay?
While the “best” thesis statement is subjective and depends on the topic and target audience, a strong example might be:
“Given the environmental, economic, and health benefits, cities should invest more in cycling infrastructure to promote bicycle commuting, reduce traffic congestion, and decrease air pollution.”
This good thesis statement not only clearly states the writer’s perspective but also outlines the main arguments they’ll use to persuade readers.
100 Thesis Statement Examples for Persuasive Essay

Size: 206 KB
A persuasive essay thesis is a declarative sentence that condenses the central argument you intend to make. It’s more than just a statement of intent: it’s a bold proclamation of your viewpoint on an issue. A compelling thesis can differentiate a strong essay from a weak one. Dive into these examples to understand the diversity and depth a persuasive essay thesis can achieve.
- “School uniforms should be mandatory as they foster equality, reduce distractions, and improve student focus.”
- “Solar energy is not only environmentally friendly but also economically viable, and governments should provide more incentives for its adoption.”
- “Animal testing for cosmetics is both unethical and unnecessary and should be banned globally.”
- “Fast food chains should be required to display calorie counts on their menus to promote healthier eating habits.”
- “Online education provides flexibility, accessibility, and personalized learning experiences, making it superior to traditional classroom settings.”
- “The death penalty is an outdated form of punishment and should be abolished due to its potential for wrongful executions.”
- “Parents should monitor their children’s internet use to protect them from the dangers of cyberbullying and exposure to inappropriate content.”
- “Companies should prioritize corporate social responsibility over profits to ensure sustainable and ethical operations.”
- “Vaccinations should be mandatory for public school entry to protect the greater community from preventable diseases.”
- “Single-use plastics are a major environmental concern, and there should be a global ban on their production and sale.”
- “Public transport should be made free to decrease traffic congestion and reduce air pollution.”
- “Professional athletes should be held to higher standards of behavior due to their influence on younger fans.”
- “Parents should have an active role in their children’s education, including the right to choose schools and curricula.”
- “Governments should regulate and limit the exposure of children to advertising to protect them from consumerist indoctrination.”
- “The age for legal alcohol consumption should be raised to 21 to combat the rise in youth alcohol-related incidents.”
- “The government should fund and promote STEM education to ensure a competitive workforce in the global market.”
- “Smoking in public places should be banned due to its detrimental health effects on non-smokers.”
- “Teens under 18 should not be allowed to access social media platforms to protect their mental health.”
- “The global community should take more aggressive actions to combat climate change and protect future generations.”
- “Freedom of the press is essential for a functioning democracy, and any attempts to limit it are detrimental to society.”
- “The gig economy exploits workers and lacks job security; therefore, stricter regulations should be enforced.”
- “GMO foods, when properly regulated, can solve global hunger issues and should be embraced.”
- “Gender pay gaps exist and are a result of systemic sexism; companies should be mandated to ensure equal pay.”
- “Limiting screen time for children promotes healthier physical and mental development.”
- “Mandatory voting ensures everyone’s voice is heard and should be implemented to strengthen democratic processes.”
- “Public figures should have a limited right to privacy due to their influence and role in society.”
- “Advertisements targeting children should be banned to prevent early consumerism.”
- “Body cameras for law enforcement officers are essential to promote transparency and accountability.”
- “Whistleblowers play a crucial role in democratic societies and should be protected by law from retaliation.”
- “Cultural appropriation in fashion and art belittles original traditions and should be discouraged.”
- “Educational institutions should focus more on practical skills rather than theoretical knowledge to prepare students for real-world challenges.”
- “Restricting the sale of sugary beverages can lead to a significant reduction in obesity rates.”
- “Children’s exposure to violent video games directly correlates with aggressive behavior, and such games should have age restrictions.”
- “The censorship of art is a violation of freedom of expression and stifles the creative spirit.”
- “Mental health education should be a mandatory part of school curricula to address and destigmatize mental health issues.”
- “Homeschooling, when done effectively, can offer a more personalized and efficient education than traditional schools.”
- “Organic farming practices should be promoted and subsidized by governments due to their environmental and health benefits.”
- “The excessive use of antibiotics in agriculture poses long-term health risks, necessitating stricter regulations.”
- “Workplace wellness programs not only benefit employees but also lead to increased productivity and should be adopted by all companies.”
- “Governments should impose heavier taxes on junk food to curb the increasing rates of health issues related to poor diet.”
- “Higher education should be made affordable for all, as it’s a fundamental right and not a luxury.”
- “Celebrities endorsing political candidates can unduly influence the public, and such endorsements should be approached with skepticism.”
- “Urban planning must prioritize green spaces due to their psychological and environmental benefits.”
- “Euthanasia, when done under strict regulations, is an act of mercy and should be legally allowed.”
- “The global community must cooperate to tackle the refugee crisis and ensure safe resettlement and support.”
- “Artificial intelligence, without proper ethical guidelines, poses a threat to job markets and privacy.”
- “Zero-waste lifestyles are crucial for sustainability, and consumer practices should align with this goal.”
- “Fast fashion contributes to environmental degradation, and consumers should support sustainable clothing brands.”
- “Limitations on free speech in the name of national security can lead to authoritarianism and should be scrutinized.”
- “Digital literacy is as fundamental as reading and writing in the 21st century, and schools should integrate it into their curricula.”
- “The increasing privatization of natural resources threatens public access and should be regulated.”
- “Adopting a plant-based diet can dramatically reduce one’s carbon footprint and combat climate change.”
- “In an era of misinformation, critical thinking skills are paramount and should be emphasized in education.”
- “Universal healthcare is a fundamental human right and should not be tied to employment or economic status.”
- “Cybersecurity measures are not just an IT concern but are crucial for national security.”
- “Regulating tech giants is essential to prevent monopolies and protect user data.”
- “Banning beauty contests can help alleviate societal pressures and stereotypes regarding physical appearance.”
- “Space exploration, beyond its scientific benefits, can unify humanity and should be pursued more aggressively.”
- “Sports organizations should take a stricter stance against doping to maintain the integrity of competitions.”
- “Mandatory parental leave can ensure better family bonding and equalize career opportunities between genders.”
- “Animal testing for cosmetics is not only cruel but also ineffective and outdated, necessitating its global ban.”
- “Educational reforms should emphasize financial literacy to equip students with the skills to navigate the modern economic landscape.”
- “Promotion of renewable energy sources over fossil fuels is not just environmentally beneficial but also economically viable in the long run.”
- “Public transport should be heavily subsidized to encourage use and combat urban air pollution.”
- “Parents should limit screen time for children due to its detrimental effects on physical health and cognitive development.”
- “In light of the opioid crisis, holistic and non-addictive pain management methods should be promoted and made more accessible.”
- “Cultural appropriation in the fashion and entertainment industries perpetuates stereotypes and should be addressed through increased awareness and regulations.”
- “Privacy rights are increasingly jeopardized in the digital age, necessitating stronger data protection laws.”
- “The gender wage gap is not only a matter of fairness but also an economic inefficiency that should be addressed through legislative reforms.”
- “The rise of isolationism in global politics undermines international collaboration and poses threats to global security and prosperity.”
- “Teachers should be remunerated based on skill and effectiveness rather than years of service, promoting a merit-based system.”
- “The legal drinking age should be reconsidered in light of scientific evidence on brain development and societal impacts.”
- “The portrayal of mental health in media, if inaccurate, can perpetuate stigma, emphasizing the need for informed and sensitive representation.”
- “Trade wars harm global economies more than they protect local industries and should be approached with caution.”
- “Gerrymandering undermines the principles of democracy, and independent bodies should be responsible for electoral redistricting.”
- “Public libraries play a crucial role in community development and should receive adequate funding and support.”
- “The proliferation of fake news can be curbed through media literacy education and stricter platform regulations.”
- “The decriminalization of certain drugs can lead to reduced criminal activity and better health outcomes.”
- “Historical monuments associated with divisive figures should be placed in context rather than removed, promoting education over erasure.”
- “The adoption of electric vehicles should be incentivized to rapidly reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change.”
- “Childhood vaccinations should be mandatory, given their role in preventing outbreaks of life-threatening diseases.”
- “Modern education should evolve to incorporate emotional intelligence training to foster empathy and interpersonal skills.”
- “Prohibitive costs of tertiary education perpetuate socio-economic disparities; governments should implement tuition-free university policies.”
- “Whistleblowers play a crucial role in maintaining institutional integrity and should be protected from retaliation.”
- “Plastic waste is one of the prime environmental threats; introducing biodegradable alternatives should be a priority for industries.”
- “Diverse representation in film and television is not just about fairness but also about accurately reflecting the world we live in.”
- “Urban agriculture can address food security issues in growing cities and should be promoted through policies and community initiatives.”
- “Excessive consumerism contributes to environmental degradation; embracing minimalism can lead to a more sustainable future.”
- “Telecommuting, propelled by technological advancements, can lead to better work-life balance and reduced city congestion.”
- “Unregulated cryptocurrency can pose financial risks; there is a pressing need for standardized global regulations.”
- “Limiting advertisement in children’s TV programming can lead to healthier eating habits and reduce materialistic tendencies.”
- “Promoting bilingual education from an early age can lead to cognitive benefits and cultural appreciation.”
- “Offshore drilling poses significant environmental risks, and its expansion should be curbed in favor of sustainable energy sources.”
- “Body cameras for law enforcement officers can ensure transparency and accountability in policing.”
- “The modern gig economy, while offering flexibility, often circumvents labor rights and needs comprehensive regulation.”
- “Online data breaches are becoming common, and companies should face stricter penalties for compromising user data.”
- “Promotion of community gardens can foster social ties and address urban food deserts.”
- “Implementing a universal basic income can address wealth disparities and provide a safety net in rapidly changing job markets.”
- “Arts education, often undervalued, plays a crucial role in fostering creativity and should receive equal emphasis as STEM subjects.”
- “Sustainable tourism ensures local community benefits and environmental protection, and should be the industry standard.”
Persuasive Essay Thesis Statement Examples for High School
High school students often grapple with formulating compelling arguments in their essays. These thesis statement for high school examples are tailored to the perspectives and concerns of high schoolers, offering a starting point to craft persuasive essays on various contemporary issues.
- Uniforms in School: “Mandatory school uniforms stifle individual expression and fail to address the underlying issues of bullying and peer pressure in schools.”
- Homework Volume: “The excessive amount of homework assigned to high school students is counterproductive to learning, leading to burnout and diminishing returns on student effort.”
- School Start Times: “High schools should start later in the morning to align with adolescent sleep patterns, thereby improving academic performance and mental health.”
- Standardized Testing: “Reliance on standardized testing for college admissions is an outdated approach that doesn’t truly reflect a student’s capabilities or potential.”
- Extra-Curricular Importance: “Extra-curricular activities are as vital as academic subjects in developing a well-rounded education and should be given equal importance in school evaluations.”
- Cellphones in Class: “Banning cellphones in classrooms ignores their potential as valuable learning tools and overlooks the importance of teaching digital responsibility.”
- Sports in School: “High school sports programs, while beneficial, receive disproportionate funding at the expense of other crucial educational programs.”
- Summer Vacations: “Extended summer vacations are an outdated model; year-round schooling with more frequent short breaks would better support learning retention.”
- Student Council Power: “Student councils should have a tangible say in school operations, encouraging youth civic engagement and responsibility.”
- Health Education: “Comprehensive sex education in high schools is crucial for informed decision-making and reducing teen pregnancies and STIs.”
Persuasive Essay Thesis Statement Examples for College
College-level persuasive essays demand a higher degree of critical thinking and specificity. These thesis statement examples delve into deeper societal and academic issues, providing college students with a foundation to develop nuanced arguments and insights in their writings.
- Tuition Fees: “The skyrocketing cost of college tuition limits access to higher education and exacerbates socio-economic disparities.”
- Curriculum Flexibility: “Colleges should offer more interdisciplinary courses, allowing students to tailor their education to align with their career and personal interests.”
- Campus Safety: “Increased measures for campus safety are imperative to foster a conducive learning environment and protect students.”
- Online Learning: “Online courses should be given the same credence as in-person classes, offering flexibility and catering to the modern learner’s needs.”
- Fraternity and Sorority Culture: “Greek life in colleges, while rich in tradition, needs comprehensive reforms to address issues of hazing and exclusionary practices.”
- Mental Health Services: “With rising cases of mental health issues among college students, universities must prioritize and expand on-campus mental health services.”
- Internship Opportunities: “Colleges should actively integrate more internship opportunities into curricula, bridging the gap between academic learning and real-world application.”
- Diversity and Inclusion: “Higher education institutions must actively promote diversity and inclusion, not just in enrollment, but also in curriculum and campus culture.”
- Foreign Language Requirements: “Mandating foreign language courses for all majors is unnecessary and restricts students from exploring more relevant subjects.”
- Textbook Costs: “The exorbitant cost of college textbooks is unjustified, urging the need for universities to promote open-source or affordable alternatives.”
These thesis statements resonate with the concerns and challenges faced by students at high school and college levels, making them ideal starting points for persuasive essays. Y ou may also be interested to browse through our other Analytical Essay thesis statement .
What is a thesis statement used for in persuasive writing?
A thesis statement in persuasive writing serves as the anchor of the entire essay. It states the primary argument or claim that the writer seeks to prove. Acting as a roadmap, it informs the reader about the main topic and the stance of the writer on that topic. The efficacy of a persuasive essay largely hinges on how compelling and clear its strong thesis statement is. Without it, readers might be left unsure about the writer’s intent or the purpose of the essay.
Is a claim a thesis statement for a persuasive essay?
Yes, in persuasive writing, the thesis statement is often referred to as a claim. While all thesis statements express the main idea of a piece, in persuasive essays, this statement specifically claims a position that the writer will argue for. This claim seeks to persuade the reader of its validity, backed by evidence in the body of the essay. It’s essential that the claim is debatable, meaning there must be opposing viewpoints on the topic, so the writer has something to persuade the reader about.
How do you write a thesis statement for a persuasive essay? – Step by Step Guide
- Choose a Debatable Topic: Ensure the topic has multiple viewpoints, giving you something to persuade your reader about.
- Take a Stance: Decide your position on the topic. This becomes the foundation of your claim.
- Research Supporting Evidence: Before finalizing your thesis, research to ensure there’s ample evidence to support your claim.
- Be Specific: Your thesis statement should be clear and specific. Avoid vague or general statements.
- Keep it Concise: Ideally, a thesis statement should be one or two sentences long. It needs to be straightforward and to the point.
- Positioning: Place your thesis statement at the end of your introductory paragraph to provide readers with a clear guide to your essay’s direction.
- Revisit and Revise: As you write, you might find your direction slightly shifting. Always revisit your thesis statement to ensure it aligns with the content of your essay.
Tips for Writing a Descriptive Essay Thesis Statement
- Be Clear and Vivid: Since descriptive essays aim to paint a picture, ensure your thesis provides a snapshot of what you’ll describe.
- Engage the Senses: Allude to the sensory details you’ll include in your essay. This sets the tone for the vivid descriptions to follow.
- Avoid Subjectivity: While your experience is personal, avoid overtly subjective statements. Let the descriptions evoke feelings in the reader.
- Stay Focused: A descriptive thesis should focus on a single object, event, person, or place, ensuring the essay remains cohesive.
- Use Strong Language: Use powerful adjectives and verbs to convey emotion and create a strong mental image for the reader.
Remember, while the specific thesis statement provides direction, it’s the body of the essay that elaborates and brings the description to life. Ensure coherence between the thesis and the detailed descriptions that follow.
Thesis Statement Generator for Persuasive Essay
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Write a Thesis Statement for Persuasive Essay advocating for climate change action.
Create a Thesis Statement for Persuasive Essay on the necessity of education reform.
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
How to Write a Persuasive Essay: Tips and Tricks

Allison Bressmer

Most composition classes you’ll take will teach the art of persuasive writing. That’s a good thing.
Knowing where you stand on issues and knowing how to argue for or against something is a skill that will serve you well both inside and outside of the classroom.
Persuasion is the art of using logic to prompt audiences to change their mind or take action , and is generally seen as accomplishing that goal by appealing to emotions and feelings.
A persuasive essay is one that attempts to get a reader to agree with your perspective.

Ready for some tips on how to produce a well-written, well-rounded, well-structured persuasive essay? Just say yes. I don’t want to have to write another essay to convince you!
How Do I Write a Persuasive Essay?
What are some good topics for a persuasive essay, how do i identify an audience for my persuasive essay, how do you create an effective persuasive essay, how should i edit my persuasive essay.
Your persuasive essay needs to have the three components required of any essay: the introduction , body , and conclusion .
That is essay structure. However, there is flexibility in that structure.
There is no rule (unless the assignment has specific rules) for how many paragraphs any of those sections need.
Although the components should be proportional; the body paragraphs will comprise most of your persuasive essay.

How Do I Start a Persuasive Essay?
As with any essay introduction, this paragraph is where you grab your audience’s attention, provide context for the topic of discussion, and present your thesis statement.
TIP 1: Some writers find it easier to write their introductions last. As long as you have your working thesis, this is a perfectly acceptable approach. From that thesis, you can plan your body paragraphs and then go back and write your introduction.
TIP 2: Avoid “announcing” your thesis. Don’t include statements like this:
- “In my essay I will show why extinct animals should (not) be regenerated.”
- “The purpose of my essay is to argue that extinct animals should (not) be regenerated.”
Announcements take away from the originality, authority, and sophistication of your writing.
Instead, write a convincing thesis statement that answers the question "so what?" Why is the topic important, what do you think about it, and why do you think that? Be specific.
How Many Paragraphs Should a Persuasive Essay Have?
This body of your persuasive essay is the section in which you develop the arguments that support your thesis. Consider these questions as you plan this section of your essay:
- What arguments support your thesis?
- What is the best order for your arguments?
- What evidence do you have?
- Will you address the opposing argument to your own?
- How can you conclude convincingly?

TIP: Brainstorm and do your research before you decide which arguments you’ll focus on in your discussion. Make a list of possibilities and go with the ones that are strongest, that you can discuss with the most confidence, and that help you balance your rhetorical triangle .
What Should I Put in the Conclusion of a Persuasive Essay?
The conclusion is your “mic-drop” moment. Think about how you can leave your audience with a strong final comment.
And while a conclusion often re-emphasizes the main points of a discussion, it shouldn’t simply repeat them.
TIP 1: Be careful not to introduce a new argument in the conclusion—there’s no time to develop it now that you’ve reached the end of your discussion!
TIP 2 : As with your thesis, avoid announcing your conclusion. Don’t start your conclusion with “in conclusion” or “to conclude” or “to end my essay” type statements. Your audience should be able to see that you are bringing the discussion to a close without those overused, less sophisticated signals.

If your instructor has assigned you a topic, then you’ve already got your issue; you’ll just have to determine where you stand on the issue. Where you stand on your topic is your position on that topic.
Your position will ultimately become the thesis of your persuasive essay: the statement the rest of the essay argues for and supports, intending to convince your audience to consider your point of view.
If you have to choose your own topic, use these guidelines to help you make your selection:
- Choose an issue you truly care about
- Choose an issue that is actually debatable
Simple “tastes” (likes and dislikes) can’t really be argued. No matter how many ways someone tries to convince me that milk chocolate rules, I just won’t agree.
It’s dark chocolate or nothing as far as my tastes are concerned.
Similarly, you can’t convince a person to “like” one film more than another in an essay.
You could argue that one movie has superior qualities than another: cinematography, acting, directing, etc. but you can’t convince a person that the film really appeals to them.

Once you’ve selected your issue, determine your position just as you would for an assigned topic. That position will ultimately become your thesis.
Until you’ve finalized your work, consider your thesis a “working thesis.”
This means that your statement represents your position, but you might change its phrasing or structure for that final version.
When you’re writing an essay for a class, it can seem strange to identify an audience—isn’t the audience the instructor?
Your instructor will read and evaluate your essay, and may be part of your greater audience, but you shouldn’t just write for your teacher.
Think about who your intended audience is.
For an argument essay, think of your audience as the people who disagree with you—the people who need convincing.
That population could be quite broad, for example, if you’re arguing a political issue, or narrow, if you’re trying to convince your parents to extend your curfew.
Once you’ve got a sense of your audience, it’s time to consult with Aristotle. Aristotle’s teaching on persuasion has shaped communication since about 330 BC. Apparently, it works.

Aristotle taught that in order to convince an audience of something, the communicator needs to balance the three elements of the rhetorical triangle to achieve the best results.
Those three elements are ethos , logos , and pathos .
Ethos relates to credibility and trustworthiness. How can you, as the writer, demonstrate your credibility as a source of information to your audience?
How will you show them you are worthy of their trust?

- You show you’ve done your research: you understand the issue, both sides
- You show respect for the opposing side: if you disrespect your audience, they won’t respect you or your ideas
Logos relates to logic. How will you convince your audience that your arguments and ideas are reasonable?

You provide facts or other supporting evidence to support your claims.
That evidence may take the form of studies or expert input or reasonable examples or a combination of all of those things, depending on the specific requirements of your assignment.
Remember: if you use someone else’s ideas or words in your essay, you need to give them credit.
ProWritingAid's Plagiarism Checker checks your work against over a billion web-pages, published works, and academic papers so you can be sure of its originality.
Find out more about ProWritingAid’s Plagiarism checks.
Pathos relates to emotion. Audiences are people and people are emotional beings. We respond to emotional prompts. How will you engage your audience with your arguments on an emotional level?

- You make strategic word choices : words have denotations (dictionary meanings) and also connotations, or emotional values. Use words whose connotations will help prompt the feelings you want your audience to experience.
- You use emotionally engaging examples to support your claims or make a point, prompting your audience to be moved by your discussion.
Be mindful as you lean into elements of the triangle. Too much pathos and your audience might end up feeling manipulated, roll their eyes and move on.
An “all logos” approach will leave your essay dry and without a sense of voice; it will probably bore your audience rather than make them care.
Once you’ve got your essay planned, start writing! Don’t worry about perfection, just get your ideas out of your head and off your list and into a rough essay format.
After you’ve written your draft, evaluate your work. What works and what doesn’t? For help with evaluating and revising your work, check out this ProWritingAid post on manuscript revision .
After you’ve evaluated your draft, revise it. Repeat that process as many times as you need to make your work the best it can be.
When you’re satisfied with the content and structure of the essay, take it through the editing process .
Grammatical or sentence-level errors can distract your audience or even detract from the ethos—the authority—of your work.
You don’t have to edit alone! ProWritingAid’s Realtime Report will find errors and make suggestions for improvements.
You can even use it on emails to your professors:
Try ProWritingAid with a free account.
How Can I Improve My Persuasion Skills?
You can develop your powers of persuasion every day just by observing what’s around you.
- How is that advertisement working to convince you to buy a product?
- How is a political candidate arguing for you to vote for them?
- How do you “argue” with friends about what to do over the weekend, or convince your boss to give you a raise?
- How are your parents working to convince you to follow a certain academic or career path?
As you observe these arguments in action, evaluate them. Why are they effective or why do they fail?
How could an argument be strengthened with more (or less) emphasis on ethos, logos, and pathos?
Every argument is an opportunity to learn! Observe them, evaluate them, and use them to perfect your own powers of persuasion.
Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
Allison Bressmer is a professor of freshman composition and critical reading at a community college and a freelance writer. If she isn’t writing or teaching, you’ll likely find her reading a book or listening to a podcast while happily sipping a semi-sweet iced tea or happy-houring with friends. She lives in New York with her family. Connect at linkedin.com/in/allisonbressmer.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, 113 perfect persuasive essay topics for any assignment.
General Education

Do you need to write a persuasive essay but aren’t sure what topic to focus on? Were you thrilled when your teacher said you could write about whatever you wanted but are now overwhelmed by the possibilities? We’re here to help!
Read on for a list of 113 top-notch persuasive essay topics, organized into ten categories. To help get you started, we also discuss what a persuasive essay is, how to choose a great topic, and what tips to keep in mind as you write your persuasive essay.
What Is a Persuasive Essay?
In a persuasive essay, you attempt to convince readers to agree with your point of view on an argument. For example, an essay analyzing changes in Italian art during the Renaissance wouldn’t be a persuasive essay, because there’s no argument, but an essay where you argue that Italian art reached its peak during the Renaissance would be a persuasive essay because you’re trying to get your audience to agree with your viewpoint.
Persuasive and argumentative essays both try to convince readers to agree with the author, but the two essay types have key differences. Argumentative essays show a more balanced view of the issue and discuss both sides. Persuasive essays focus more heavily on the side the author agrees with. They also often include more of the author’s opinion than argumentative essays, which tend to use only facts and data to support their argument.
All persuasive essays have the following:
- Introduction: Introduces the topic, explains why it’s important, and ends with the thesis.
- Thesis: A sentence that sums up what the essay be discussing and what your stance on the issue is.
- Reasons you believe your side of the argument: Why do you support the side you do? Typically each main point will have its own body paragraph.
- Evidence supporting your argument: Facts or examples to back up your main points. Even though your opinion is allowed in persuasive essays more than most other essays, having concrete examples will make a stronger argument than relying on your opinion alone.
- Conclusion: Restatement of thesis, summary of main points, and a recap of why the issue is important.
What Makes a Good Persuasive Essay Topic?
Theoretically, you could write a persuasive essay about any subject under the sun, but that doesn’t necessarily mean you should. Certain topics are easier to write a strong persuasive essay on, and below are tips to follow when deciding what you should write about.
It’s a Topic You Care About
Obviously, it’s possible to write an essay about a topic you find completely boring. You’ve probably done it! However, if possible, it’s always better to choose a topic that you care about and are interested in. When this is the case, you’ll find doing the research more enjoyable, writing the essay easier, and your writing will likely be better because you’ll be more passionate about and informed on the topic.
You Have Enough Evidence to Support Your Argument
Just being passionate about a subject isn’t enough to make it a good persuasive essay topic, though. You need to make sure your argument is complex enough to have at least two potential sides to root for, and you need to be able to back up your side with evidence and examples. Even though persuasive essays allow your opinion to feature more than many other essays, you still need concrete evidence to back up your claims, or you’ll end up with a weak essay.
For example, you may passionately believe that mint chocolate chip ice cream is the best ice cream flavor (I agree!), but could you really write an entire essay on this? What would be your reasons for believing mint chocolate chip is the best (besides the fact that it’s delicious)? How would you support your belief? Have enough studies been done on preferred ice cream flavors to support an entire essay? When choosing a persuasive essay idea, you want to find the right balance between something you care about (so you can write well on it) and something the rest of the world cares about (so you can reference evidence to strengthen your position).
It’s a Manageable Topic
Bigger isn’t always better, especially with essay topics. While it may seem like a great idea to choose a huge, complex topic to write about, you’ll likely struggle to sift through all the information and different sides of the issue and winnow them down to one streamlined essay. For example, choosing to write an essay about how WWII impacted American life more than WWI wouldn’t be a great idea because you’d need to analyze all the impacts of both the wars in numerous areas of American life. It’d be a huge undertaking. A better idea would be to choose one impact on American life the wars had (such as changes in female employment) and focus on that. Doing so will make researching and writing your persuasive essay much more feasible.

List of 113 Good Persuasive Essay Topics
Below are over 100 persuasive essay ideas, organized into ten categories. When you find an idea that piques your interest, you’ll choose one side of it to argue for in your essay. For example, if you choose the topic, “should fracking be legal?” you’d decide whether you believe fracking should be legal or illegal, then you’d write an essay arguing all the reasons why your audience should agree with you.
Arts/Culture
- Should students be required to learn an instrument in school?
- Did the end of Game of Thrones fit with the rest of the series?
- Can music be an effective way to treat mental illness?
- With e-readers so popular, have libraries become obsolete?
- Are the Harry Potter books more popular than they deserve to be?
- Should music with offensive language come with a warning label?
- What’s the best way for museums to get more people to visit?
- Should students be able to substitute an art or music class for a PE class in school?
- Are the Kardashians good or bad role models for young people?
- Should people in higher income brackets pay more taxes?
- Should all high school students be required to take a class on financial literacy?
- Is it possible to achieve the American dream, or is it only a myth?
- Is it better to spend a summer as an unpaid intern at a prestigious company or as a paid worker at a local store/restaurant?
- Should the United States impose more or fewer tariffs?
- Should college graduates have their student loans forgiven?
- Should restaurants eliminate tipping and raise staff wages instead?
- Should students learn cursive writing in school?
- Which is more important: PE class or music class?
- Is it better to have year-round school with shorter breaks throughout the year?
- Should class rank be abolished in schools?
- Should students be taught sex education in school?
- Should students be able to attend public universities for free?
- What’s the most effective way to change the behavior of school bullies?
- Are the SAT and ACT accurate ways to measure intelligence?
- Should students be able to learn sign language instead of a foreign language?
- Do the benefits of Greek life at colleges outweigh the negatives?
- Does doing homework actually help students learn more?
- Why do students in many other countries score higher than American students on math exams?
- Should parents/teachers be able to ban certain books from schools?
- What’s the best way to reduce cheating in school?
- Should colleges take a student’s race into account when making admissions decisions?
- Should there be limits to free speech?
- Should students be required to perform community service to graduate high school?
- Should convicted felons who have completed their sentence be allowed to vote?
- Should gun ownership be more tightly regulated?
- Should recycling be made mandatory?
- Should employers be required to offer paid leave to new parents?
- Are there any circumstances where torture should be allowed?
- Should children under the age of 18 be able to get plastic surgery for cosmetic reasons?
- Should white supremacy groups be allowed to hold rallies in public places?
- Does making abortion illegal make women more or less safe?
- Does foreign aid actually help developing countries?
- Are there times a person’s freedom of speech should be curtailed?
- Should people over a certain age not be allowed to adopt children?
Government/Politics
- Should the minimum voting age be raised/lowered/kept the same?
- Should Puerto Rico be granted statehood?
- Should the United States build a border wall with Mexico?
- Who should be the next person printed on American banknotes?
- Should the United States’ military budget be reduced?
- Did China’s one child policy have overall positive or negative impacts on the country?
- Should DREAMers be granted US citizenship?
- Is national security more important than individual privacy?
- What responsibility does the government have to help homeless people?
- Should the electoral college be abolished?
- Should the US increase or decrease the number of refugees it allows in each year?
- Should privately-run prisons be abolished?
- Who was the most/least effective US president?
- Will Brexit end up helping or harming the UK?

- What’s the best way to reduce the spread of Ebola?
- Is the Keto diet a safe and effective way to lose weight?
- Should the FDA regulate vitamins and supplements more strictly?
- Should public schools require all students who attend to be vaccinated?
- Is eating genetically modified food safe?
- What’s the best way to make health insurance more affordable?
- What’s the best way to lower the teen pregnancy rate?
- Should recreational marijuana be legalized nationwide?
- Should birth control pills be available without a prescription?
- Should pregnant women be forbidden from buying cigarettes and alcohol?
- Why has anxiety increased in adolescents?
- Are low-carb or low-fat diets more effective for weight loss?
- What caused the destruction of the USS Maine?
- Was King Arthur a mythical legend or actual Dark Ages king?
- Was the US justified in dropping atomic bombs during WWII?
- What was the primary cause of the Rwandan genocide?
- What happened to the settlers of the Roanoke colony?
- Was disagreement over slavery the primary cause of the US Civil War?
- What has caused the numerous disappearances in the Bermuda triangle?
- Should nuclear power be banned?
- Is scientific testing on animals necessary?
- Do zoos help or harm animals?
- Should scientists be allowed to clone humans?
- Should animals in circuses be banned?
- Should fracking be legal?
- Should people be allowed to keep exotic animals as pets?
- What’s the best way to reduce illegal poaching in Africa?
- What is the best way to reduce the impact of global warming?
- Should euthanasia be legalized?
- Is there legitimate evidence of extraterrestrial life?
- Should people be banned from owning aggressive dog breeds?
- Should the United States devote more money towards space exploration?
- Should the government subsidize renewable forms of energy?
- Is solar energy worth the cost?
- Should stem cells be used in medicine?
- Is it right for the US to leave the Paris Climate Agreement?
- Should athletes who fail a drug test receive a lifetime ban from the sport?
- Should college athletes receive a salary?
- Should the NFL do more to prevent concussions in players?
- Do PE classes help students stay in shape?
- Should horse racing be banned?
- Should cheerleading be considered a sport?
- Should children younger than 18 be allowed to play tackle football?
- Are the costs of hosting an Olympic Games worth it?
- Can online schools be as effective as traditional schools?
- Do violent video games encourage players to be violent in real life?
- Should facial recognition technology be banned?
- Does excessive social media use lead to depression/anxiety?
- Has the rise of translation technology made knowing multiple languages obsolete?
- Was Steve Jobs a visionary or just a great marketer?
- Should social media be banned for children younger than a certain age?
- Which 21st-century invention has had the largest impact on society?
- Are ride-sharing companies like Uber and Lyft good or bad for society?
- Should Facebook have done more to protect the privacy of its users?
- Will technology end up increasing or decreasing inequality worldwide?

Tips for Writing a Strong Persuasive Essay
After you’ve chosen the perfect topic for your persuasive essay, your work isn’t over. Follow the three tips below to create a top-notch essay.
Do Your Research
Your argument will fall apart if you don’t fully understand the issue you’re discussing or you overlook an important piece of it. Readers won’t be convinced by someone who doesn’t know the subject, and you likely won’t persuade any of them to begin supporting your viewpoint. Before you begin writing a single word of your essay, research your topic thoroughly. Study different sources, learn about the different sides of the argument, ask anyone who’s an expert on the topic what their opinion is, etc. You might be tempted to start writing right away, but by doing your research, you’ll make the writing process much easier when the time comes.
Make Your Thesis Perfect
Your thesis is the most important sentence in your persuasive essay. Just by reading that single sentence, your audience should know exactly what topic you’ll be discussing and where you stand on the issue. You want your thesis to be crystal clear and to accurately set up the rest of your essay. Asking classmates or your teacher to look it over before you begin writing the rest of your essay can be a big help if you’re not entirely confident in your thesis.
Consider the Other Side
You’ll spend most of your essay focusing on your side of the argument since that’s what you want readers to come away believing. However, don’t think that means you can ignore other sides of the issue. In your essay, be sure to discuss the other side’s argument, as well as why you believe this view is weak or untrue. Researching all the different viewpoints and including them in your essay will increase the quality of your writing by making your essay more complete and nuanced.
Summary: Persuasive Essay Ideas
Good persuasive essay topics can be difficult to come up with, but in this guide we’ve created a list of 113 excellent essay topics for you to browse. The best persuasive essay ideas will be those that you are interested in, have enough evidence to support your argument, and aren’t too complicated to be summarized in an essay.
After you’ve chosen your essay topic, keep these three tips in mind when you begin writing:
- Do your research
- Make your thesis perfect
- Consider the other side
What's Next?
Need ideas for a research paper topic as well? Our guide to research paper topics has over 100 topics in ten categories so you can be sure to find the perfect topic for you.
Thinking about taking an AP English class? Read our guide on AP English classes to learn whether you should take AP English Language or AP English Literature (or both!)
Deciding between the SAT or ACT? Find out for sure which you will do the best on . Also read a detailed comparison between the two tests .

Christine graduated from Michigan State University with degrees in Environmental Biology and Geography and received her Master's from Duke University. In high school she scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT and was named a National Merit Finalist. She has taught English and biology in several countries.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
- Translators
- Graphic Designers
Please enter the email address you used for your account. Your sign in information will be sent to your email address after it has been verified.
25 Thesis Statement Examples That Will Make Writing a Breeze

Understanding what makes a good thesis statement is one of the major keys to writing a great research paper or argumentative essay. The thesis statement is where you make a claim that will guide you through your entire paper. If you find yourself struggling to make sense of your paper or your topic, then it's likely due to a weak thesis statement.
Let's take a minute to first understand what makes a solid thesis statement, and what key components you need to write one of your own.

A thesis statement always goes at the beginning of the paper. It will typically be in the first couple of paragraphs of the paper so that it can introduce the body paragraphs, which are the supporting evidence for your thesis statement.
Your thesis statement should clearly identify an argument. You need to have a statement that is not only easy to understand, but one that is debatable. What that means is that you can't just put any statement of fact and have it be your thesis. For example, everyone knows that puppies are cute . An ineffective thesis statement would be, "Puppies are adorable and everyone knows it." This isn't really something that's a debatable topic.
Something that would be more debatable would be, "A puppy's cuteness is derived from its floppy ears, small body, and playfulness." These are three things that can be debated on. Some people might think that the cutest thing about puppies is the fact that they follow you around or that they're really soft and fuzzy.
All cuteness aside, you want to make sure that your thesis statement is not only debatable, but that it also actually thoroughly answers the research question that was posed. You always want to make sure that your evidence is supporting a claim that you made (and not the other way around). This is why it's crucial to read and research about a topic first and come to a conclusion later. If you try to get your research to fit your thesis statement, then it may not work out as neatly as you think. As you learn more, you discover more (and the outcome may not be what you originally thought).
Additionally, your thesis statement shouldn't be too big or too grand. It'll be hard to cover everything in a thesis statement like, "The federal government should act now on climate change." The topic is just too large to actually say something new and meaningful. Instead, a more effective thesis statement might be, "Local governments can combat climate change by providing citizens with larger recycling bins and offering local classes about composting and conservation." This is easier to work with because it's a smaller idea, but you can also discuss the overall topic that you might be interested in, which is climate change.
So, now that we know what makes a good, solid thesis statement, you can start to write your own. If you find that you're getting stuck or you are the type of person who needs to look at examples before you start something, then check out our list of thesis statement examples below.
Thesis statement examples
A quick note that these thesis statements have not been fully researched. These are merely examples to show you what a thesis statement might look like and how you can implement your own ideas into one that you think of independently. As such, you should not use these thesis statements for your own research paper purposes. They are meant to be used as examples only.
- Vaccinations Because many children are unable to vaccinate due to illness, we must require that all healthy and able children be vaccinated in order to have herd immunity.
- Educational Resources for Low-Income Students Schools should provide educational resources for low-income students during the summers so that they don't forget what they've learned throughout the school year.
- School Uniforms School uniforms may be an upfront cost for families, but they eradicate the visual differences in income between students and provide a more egalitarian atmosphere at school.
- Populism The rise in populism on the 2016 political stage was in reaction to increasing globalization, the decline of manufacturing jobs, and the Syrian refugee crisis.
- Public Libraries Libraries are essential resources for communities and should be funded more heavily by local municipalities.
- Cyber Bullying With more and more teens using smartphones and social media, cyber bullying is on the rise. Cyber bullying puts a lot of stress on many teens, and can cause depression, anxiety, and even suicidal thoughts. Parents should limit the usage of smart phones, monitor their children's online activity, and report any cyber bullying to school officials in order to combat this problem.
- Medical Marijuana for Veterans Studies have shown that the use of medicinal marijuana has been helpful to veterans who suffer from Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). Medicinal marijuana prescriptions should be legal in all states and provided to these veterans. Additional medical or therapy services should also be researched and implemented in order to help them re-integrate back into civilian life.
- Work-Life Balance Corporations should provide more work from home opportunities and six-hour workdays so that office workers have a better work-life balance and are more likely to be productive when they are in the office.
- Teaching Youths about Consensual Sex Although sex education that includes a discussion of consensual sex would likely lead to less sexual assault, parents need to teach their children the meaning of consent from a young age with age appropriate lessons.
- Whether or Not to Attend University A degree from a university provides invaluable lessons on life and a future career, but not every high school student should be encouraged to attend a university directly after graduation. Some students may benefit from a trade school or a "gap year" where they can think more intensely about what it is they want to do for a career and how they can accomplish this.
- Studying Abroad Studying abroad is one of the most culturally valuable experiences you can have in college. It is the only way to get completely immersed in another language and learn how other cultures and countries are different from your own.
- Women's Body Image Magazines have done a lot in the last five years to include a more diverse group of models, but there is still a long way to go to promote a healthy woman's body image collectively as a culture.
- Cigarette Tax Heavily taxing and increasing the price of cigarettes is essentially a tax on the poorest Americans, and it doesn't deter them from purchasing. Instead, the state and federal governments should target those economically disenfranchised with early education about the dangers of smoking.
- Veganism A vegan diet, while a healthy and ethical way to consume food, indicates a position of privilege. It also limits you to other cultural food experiences if you travel around the world.
- University Athletes Should be Compensated University athletes should be compensated for their service to the university, as it is difficult for these students to procure and hold a job with busy academic and athletic schedules. Many student athletes on scholarship also come from low-income neighborhoods and it is a struggle to make ends meet when they are participating in athletics.
- Women in the Workforce Sheryl Sandberg makes a lot of interesting points in her best-selling book, Lean In , but she only addressed the very privileged working woman and failed to speak to those in lower-skilled, lower-wage jobs.
- Assisted Suicide Assisted suicide should be legal and doctors should have the ability to make sure their patients have the end-of-life care that they want to receive.
- Celebrity and Political Activism Although Taylor Swift's lyrics are indicative of a feminist perspective, she should be more politically active and vocal to use her position of power for the betterment of society.
- The Civil War The insistence from many Southerners that the South seceded from the Union for states' rights versus the fact that they seceded for the purposes of continuing slavery is a harmful myth that still affects race relations today.
- Blue Collar Workers Coal miners and other blue-collar workers whose jobs are slowly disappearing from the workforce should be re-trained in jobs in the technology sector or in renewable energy. A program to re-train these workers would not only improve local economies where jobs have been displaced, but would also lead to lower unemployment nationally.
- Diversity in the Workforce Having a diverse group of people in an office setting leads to richer ideas, more cooperation, and more empathy between people with different skin colors or backgrounds.
- Re-Imagining the Nuclear Family The nuclear family was traditionally defined as one mother, one father, and 2.5 children. This outdated depiction of family life doesn't quite fit with modern society. The definition of normal family life shouldn't be limited to two-parent households.
- Digital Literacy Skills With more information readily available than ever before, it's crucial that students are prepared to examine the material they're reading and determine whether or not it's a good source or if it has misleading information. Teaching students digital literacy and helping them to understand the difference between opinion or propaganda from legitimate, real information is integral.
- Beauty Pageants Beauty pageants are presented with the angle that they empower women. However, putting women in a swimsuit on a stage while simultaneously judging them on how well they answer an impossible question in a short period of time is cruel and purely for the amusement of men. Therefore, we should stop televising beauty pageants.
- Supporting More Women to Run for a Political Position In order to get more women into political positions, more women must run for office. There must be a grassroots effort to educate women on how to run for office, who among them should run, and support for a future candidate for getting started on a political career.
Still stuck? Need some help with your thesis statement?
If you are still uncertain about how to write a thesis statement or what a good thesis statement is, be sure to consult with your teacher or professor to make sure you're on the right track. It's always a good idea to check in and make sure that your thesis statement is making a solid argument and that it can be supported by your research.
After you're done writing, it's important to have someone take a second look at your paper so that you can ensure there are no mistakes or errors. It's difficult to spot your own mistakes, which is why it's always recommended to have someone help you with the revision process, whether that's a teacher, the writing center at school, or a professional editor such as one from ServiceScape .
Related Posts

The Concluding Paragraph: How to End Your Essay

Writing a Strong Statement of the Problem in Research
- Academic Writing Advice
- All Blog Posts
- Writing Advice
- Admissions Writing Advice
- Book Writing Advice
- Short Story Advice
- Employment Writing Advice
- Business Writing Advice
- Web Content Advice
- Article Writing Advice
- Magazine Writing Advice
- Grammar Advice
- Dialect Advice
- Editing Advice
- Freelance Advice
- Legal Writing Advice
- Poetry Advice
- Graphic Design Advice
- Logo Design Advice
- Translation Advice
- Blog Reviews
- Short Story Award Winners
- Scholarship Winners

Need an academic editor before submitting your work?

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

4.6.1: Persuasion/Argument
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 165710

- https://www.lanecc.edu/ via OpenOregon
Learning Objectives
- Determine the purpose and structure of persuasion in writing.
- Identify bias in writing.
- Assess various rhetorical devices.
- Distinguish between fact and opinion.
- Understand the importance of visuals to strengthen arguments.
- Write a persuasive essay.
THE PURPOSE OF PERSUASIVE WRITING
The purpose of persuasion in writing is to convince, motivate, or move readers toward a certain point of view, or opinion. The act of trying to persuade automatically implies more than one opinion on the subject can be argued.
The idea of an argument often conjures up images of two people yelling and screaming in anger. In writing, however, an argument is very different. An argument is a reasoned opinion supported and explained by evidence. To argue in writing is to advance knowledge and ideas in a positive way. Written arguments often fail when they employ ranting rather than reasoning.
Most of us feel inclined to try to win the arguments we engage in. On some level, we all want to be right, and we want others to see the error of their ways. More times than not, however, arguments in which both sides try to win end up producing losers all around. The more productive approach is to persuade your audience to consider your opinion as a valid one, not simply the right one.
THE STRUCTURE OF A PERSUASIVE ESSAY
The following five features make up the structure of a persuasive essay:
- Introduction and thesis
- Opposing and qualifying ideas
- Strong evidence in support of claim
- Style and tone of language
- A compelling conclusion
CREATING AN INTRODUCTION AND THESIS
The persuasive essay begins with an engaging introduction that presents the general topic. The thesis typically appears somewhere in the introduction and states the writer’s point of view.
Avoid forming a thesis based on a negative claim. For example, “The hourly minimum wage is not high enough for the average worker to live on.” This is probably a true statement, but persuasive arguments should make a positive case. That is, the thesis statement should focus on how the hourly minimum wage is low or insufficient.
ACKNOWLEDGING OPPOSING IDEAS AND LIMITS TO YOUR ARGUMENT
Because an argument implies differing points of view on the subject, you must be sure to acknowledge those opposing ideas. Avoiding ideas that conflict with your own gives the reader the impression that you may be uncertain, fearful, or unaware of opposing ideas. Thus it is essential that you not only address counterarguments but also do so respectfully.
Try to address opposing arguments earlier rather than later in your essay. Rhetorically speaking, ordering your positive arguments last allows you to better address ideas that conflict with your own, so you can spend the rest of the essay countering those arguments. This way, you leave your reader thinking about your argument rather than someone else’s. You have the last word.
Acknowledging points of view different from your own also has the effect of fostering more credibility between you and the audience. They know from the outset that you are aware of opposing ideas and that you are not afraid to give them space.
It is also helpful to establish the limits of your argument and what you are trying to accomplish. In effect, you are conceding early on that your argument is not the ultimate authority on a given topic. Such humility can go a long way toward earning credibility and trust with an audience. Audience members will know from the beginning that you are a reasonable writer, and audience members will trust your argument as a result. For example, in the following concessionary statement, the writer advocates for stricter gun control laws, but she admits it will not solve all of our problems with crime:
Although tougher gun control laws are a powerful first step in decreasing violence in our streets, such legislation alone cannot end these problems since guns are not the only problem we face.
Such a concession will be welcome by those who might disagree with this writer’s argument in the first place. To effectively persuade their readers, writers need to be modest in their goals and humble in their approach to get readers to listen to the ideas. See Table 10.5 “Phrases of Concession” for some useful phrases of concession.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{1}\)
Try to form a thesis for each of the following topics. Remember the more specific your thesis, the better.
- Foreign policy
- Television and advertising
- Stereotypes and prejudice
- Gender roles and the workplace
- Driving and cell phones
Collaboration
Please share with a classmate and compare your answers. Choose the thesis statement that most interests you and discuss why.
BIAS IN WRITING
Everyone has various biases on any number of topics. For example, you might have a bias toward wearing black instead of brightly colored clothes or wearing jeans rather than formal wear. You might have a bias toward working at night rather than in the morning, or working by deadlines rather than getting tasks done in advance. These examples identify minor biases, of course, but they still indicate preferences and opinions.
Handling bias in writing and in daily life can be a useful skill. It will allow you to articulate your own points of view while also defending yourself against unreasonable points of view. The ideal in persuasive writing is to let your reader know your bias, but do not let that bias blind you to the primary components of good argumentation: sound, thoughtful evidence and a respectful and reasonable address of opposing sides.
The strength of a personal bias is that it can motivate you to construct a strong argument. If you are invested in the topic, you are more likely to care about the piece of writing. Similarly, the more you care, the more time and effort you are apt to put forth and the better the final product will be.
The weakness of bias is when the bias begins to take over the essay—when, for example, you neglect opposing ideas, exaggerate your points, or repeatedly insert yourself ahead of the subject by using I too often. Being aware of all three of these pitfalls will help you avoid them.
THE USE OF I IN WRITING
The use of I in writing is often a topic of debate, and the acceptance of its usage varies from instructor to instructor. It is difficult to predict the preferences for all your present and future instructors, but consider the effects it can potentially have on your writing.
Be mindful of the use of I in your writing because it can make your argument sound overly biased. There are two primary reasons:
- Excessive repetition of any word will eventually catch the reader’s attention—and usually not in a good way. The use of I is no different.
- The insertion of I into a sentence alters not only the way a sentence might sound but also the composition of the sentence itself. I is often the subject of a sentence. If the subject of the essay is supposed to be, say, smoking, then by inserting yourself into the sentence, you are effectively displacing the subject of the essay into a secondary position. In the following example, the subject of the sentence is underlined:
Smoking is bad. I think smoking is bad.
In the first sentence, the rightful subject, smoking, is in the subject position in the sentence. In the second sentence, the insertion of I and think replaces smoking as the subject, which draws attention to I and away from the topic that is supposed to be discussed. Remember to keep the message (the subject) and the messenger (the writer) separate.
Developing Sound Arguments
Does my essay contain the following elements?
- An engaging introduction
- A reasonable, specific thesis that is able to be supported by evidence
- A varied range of evidence from credible sources
- Respectful acknowledgement and explanation of opposing ideas
- A style and tone of language that is appropriate for the subject and audience
- Acknowledgement of the argument’s limits
- A conclusion that will adequately summarize the essay and reinforce the thesis
FACT AND OPINION
Facts are statements that can be definitely proven using objective data. The statement that is a fact is absolutely valid. In other words, the statement can be pronounced as true or false. For example, 2 + 2 = 4. This expression identifies a true statement, or a fact, because it can be proved with objective data.
Opinions are personal views, or judgments. An opinion is what an individual believes about a particular subject. However, an opinion in argumentation must have legitimate backing; adequate evidence and credibility should support the opinion. Consider the credibility of expert opinions. Experts in a given field have the knowledge and credentials to make their opinion meaningful to a larger audience.
For example, you seek the opinion of your dentist when it comes to the health of your gums, and you seek the opinion of your mechanic when it comes to the maintenance of your car. Both have knowledge and credentials in those respective fields, which is why their opinions matter to you. But the authority of your dentist may be greatly diminished should he or she offer an opinion about your car, and vice versa.
In writing, you want to strike a balance between credible facts and authoritative opinions. Relying on one or the other will likely lose more of your audience than it gains.
The word prove is frequently used in the discussion of persuasive writing. Writers may claim that one piece of evidence or another proves the argument, but proving an argument is often not possible. No evidence proves a debatable topic one way or the other; that is why the topic is debatable. Facts can be proved, but opinions can only be supported, explained, and persuaded.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{2}\)
On a separate sheet of paper, take three of the theses you formed in Exercise 1, and list the types of evidence you might use in support of that thesis.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{3}\)
Using the evidence you provided in support of the three theses in Exercise 2, come up with at least one counterargument to each. Then write a concession statement, expressing the limits to each of your three arguments.
USING VISUAL ELEMENTS TO STRENGTHEN ARGUMENTS
Adding visual elements to a persuasive argument can often strengthen its persuasive effect. There are two main types of visual elements: quantitative visuals and qualitative visuals.
Quantitative visuals present data graphically. They allow the audience to see statistics spatially. The purpose of using quantitative visuals is to make logical appeals to the audience. For example, sometimes it is easier to understand the disparity in certain statistics if you can see how the disparity looks graphically. Bar graphs, pie charts, Venn diagrams, histograms, and line graphs are all ways of presenting quantitative data in spatial dimensions.
Qualitative visuals present images that appeal to the audience’s emotions. Photographs and pictorial images are examples of qualitative visuals. Such images often try to convey a story, and seeing an actual example can carry more power than hearing or reading about the example. For example, one image of a child suffering from malnutrition will likely have more of an emotional impact than pages dedicated to describing that same condition in writing.
WRITING AT WORK
When making a business presentation, you typically have limited time to get across your idea. Providing visual elements for your audience can be an effective timesaving tool. Quantitative visuals in business presentations serve the same purpose as they do in persuasive writing. They should make logical appeals by showing numerical data in a spatial design. Quantitative visuals should be pictures that might appeal to your audience’s emotions. You will find that many of the rhetorical devices used in writing are the same ones used in the workplace.
WRITING A PERSUASIVE ESSAY
Choose a topic that you feel passionate about. If your instructor requires you to write about a specific topic, approach the subject from an angle that interests you. Begin your essay with an engaging introduction. Your thesis should typically appear somewhere in your introduction.
Start by acknowledging and explaining points of view that may conflict with your own to build credibility and trust with your audience. Also state the limits of your argument. This too helps you sound more reasonable and honest to those who may naturally be inclined to disagree with your view. By respectfully acknowledging opposing arguments and conceding limitations to your own view, you set a measured and responsible tone for the essay.
Make your appeals in support of your thesis by using sound, credible evidence. Use a balance of facts and opinions from a wide range of sources, such as scientific studies, expert testimony, statistics, and personal anecdotes. Each piece of evidence should be fully explained and clearly stated.
Make sure that your style and tone are appropriate for your subject and audience. Tailor your language and word choice to these two factors, while still being true to your own voice.
Finally, write a conclusion that effectively summarizes the main argument and reinforces your thesis.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{4}\)
Choose one of the topics you have been working on throughout this section. Use the thesis, evidence, opposing argument, and concessionary statement as the basis for writing a full persuasive essay. Be sure to include an engaging introduction, clear explanations of all the evidence you present, and a strong conclusion.
key takeaways
- The purpose of persuasion in writing is to convince or move readers toward a certain point of view, or opinion.
- An argument is a reasoned opinion supported and explained by evidence. To argue, in writing, is to advance knowledge and ideas in a positive way.
- A thesis that expresses the opinion of the writer in more specific terms is better than one that is vague.
- It is essential that you not only address counterarguments but also do so respectfully.
- It is also helpful to establish the limits of your argument and what you are trying to accomplish through a concession statement.
- To persuade a skeptical audience, you will need to use a wide range of evidence. Scientific studies, opinions from experts, historical precedent, statistics, personal anecdotes, and current events are all types of evidence that you might use in explaining your point.
- Make sure that your word choice and writing style is appropriate for both your subject and your audience.
- You should let your reader know your bias, but do not let that bias blind you to the primary components of good argumentation: sound, thoughtful evidence and respectfully and reasonably addressing opposing ideas.
- You should be mindful of the use of I in your writing because it can make your argument sound more biased than it needs to.
- Facts are statements that can be proven using objective data.
- Opinions are personal views, or judgments, that cannot be proven.
- In writing, you want to strike a balance between credible facts and authoritative opinions.
- Quantitative visuals present data graphically. The purpose of using quantitative visuals is to make logical appeals to the audience.
- Qualitative visuals present images that appeal to the audience’s emotions.
- This section was originally from Writing for Success, found at the University of Minnesota open textbook project. Full license information: This is a derivative of Writing for Success by a publisher who has requested that they and the original author not receive attribution, originally released and is used under CC BY-NC-SA. This work, unless otherwise expressly stated, is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Strong Thesis Statement Examples. 1. School Uniforms. "Mandatory school uniforms should be implemented in educational institutions as they promote a sense of equality, reduce distractions, and foster a focused and professional learning environment.". Best For: Argumentative Essay or Debate. Read More: School Uniforms Pros and Cons.
Placement of the thesis statement. Step 1: Start with a question. Step 2: Write your initial answer. Step 3: Develop your answer. Step 4: Refine your thesis statement. Types of thesis statements. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about thesis statements.
Crafting a powerful thesis statement is an essential skill in academic writing, as it sets the stage for a well-structured and persuasive essay. Throughout this blog, we have explored the process of understanding the purpose of a thesis statement, analyzing the essay prompt, brainstorming and generating ideas, refining the thesis statement, and ...
The thesis statement or main claim must be debatable. An argumentative or persuasive piece of writing must begin with a debatable thesis or claim. ... rewritten, or redistributed without permission. This website collects and publishes the ideas of individuals who have contributed those ideas in their capacities as faculty-mentored student ...
Step 4: Revise and refine your thesis statement before you start writing. Read through your thesis statement several times before you begin to compose your full essay. You need to make sure the statement is ironclad, since it is the foundation of the entire paper. Edit it or have a peer review it for you to make sure everything makes sense and ...
In your introduction, you want to introduce the topic. Then, you want to preview the arguments you will use to support your position. You want to conclude by writing your thesis statement. Your thesis statement is brief, usually one or two sentences. In a persuasive essay, it does more than just tell the reader your position on the issue.
This persuasive type of thesis can be used in any essay that contains the writer's opinion, including, as I mentioned above, compare/contrast essays, narrative essays, and so on. 2 Styles of Thesis Statements. Just as there are two different types of thesis statements (informative and persuasive), there are two basic styles you can use. The ...
How to Write a Persuasive Essay: The Main Components. 1. Introduction: Capturing Attention and Stating the Thesis. The introduction serves as the gateway to your persuasive essay. Begin by grabbing the reader's attention with a compelling hook—an anecdote, a surprising fact, or a thought-provoking question.
Pass the "How and Why" Test. Your thesis statement should answer one or both of two key questions: "how" and "why.". For example, if you think that online learning is more effective for students than traditional instruction, then your thesis should tell readers how or why it's more effective. If a reader can't determine the "how" or ...
2. An unequivocal thesis statement. If you walked through our three-step process above, you already have some semblance of a thesis—but don't get attached too soon! A solid essay thesis is best developed through the research process. You shouldn't land on an opinion before you know the facts. So press pause. Take a step back.
A persuasive essay thesis statement is a concise summary of the main point or claim of the essay. It serves as a roadmap for readers, indicating the stance the writer is taking on a particular issue or topic and the key arguments they will use to convince readers of their perspective. Essentially, it's the heart of your argument, capturing ...
A thesis statement like this one is particularly good for an essay in which you are trying to persuade your readers of the merits of one thing, whether it is a sport, a food, a movie, an animal ...
The Structure of a Persuasive Essay. The following features make up a persuasive essay: ... Try to form a thesis for each of the following topics. Remember the more specific your thesis, the better. ... take three of the thesis statements you formed in Exercise 1 and list the types of evidence you might use in support of that thesis. Using the ...
Make a claim. Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim. Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim) Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives. The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays.
TIP 1: Be careful not to introduce a new argument in the conclusion—there's no time to develop it now that you've reached the end of your discussion! TIP 2: As with your thesis, avoid announcing your conclusion. Don't start your conclusion with "in conclusion" or "to conclude" or "to end my essay" type statements.
List of 113 Good Persuasive Essay Topics. Below are over 100 persuasive essay ideas, organized into ten categories. When you find an idea that piques your interest, you'll choose one side of it to argue for in your essay. For example, if you choose the topic, "should fracking be legal?" you'd decide whether you believe fracking should ...
What that means is that you can't just put any statement of fact and have it be your thesis. For example, everyone knows that puppies are cute. An ineffective thesis statement would be, "Puppies are adorable and everyone knows it." This isn't really something that's a debatable topic. Something that would be more debatable would be, "A puppy's ...
Remember that the thesis statement is a kind of "mapping tool" that helps you organize your ideas, and it helps your reader follow your argument. After the topic sentence, include any evidence in this body paragraph, such as a quotation, statistic, or data point, that supports this first point. Explain what the evidence means. Show the reader ...
Avoid forming a thesis based on a negative claim. For example, "The hourly minimum wage is not high enough for the average worker to live on." This is probably a true statement, but persuasive arguments should make a positive case. That is, the thesis statement should focus on how the hourly minimum wage is low or insufficient.