Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates

How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
Published on January 2, 2023 by Shona McCombes . Revised on September 11, 2023.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research that you can later apply to your paper, thesis, or dissertation topic .
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates, and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarize sources—it analyzes, synthesizes , and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is the purpose of a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1 – search for relevant literature, step 2 – evaluate and select sources, step 3 – identify themes, debates, and gaps, step 4 – outline your literature review’s structure, step 5 – write your literature review, free lecture slides, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a thesis , dissertation , or research paper , you will likely have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and its scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position your work in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your research addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
- Evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic.
Writing literature reviews is a particularly important skill if you want to apply for graduate school or pursue a career in research. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research problem and questions .
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research question. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list as you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some useful databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can also use boolean operators to help narrow down your search.
Make sure to read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
You likely won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on your topic, so it will be necessary to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your research question.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models, and methods?
- Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible , and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can use our template to summarize and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using. Click on either button below to download.
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It is important to keep track of your sources with citations to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography , where you compile full citation information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

To begin organizing your literature review’s argument and structure, be sure you understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat—this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organizing the body of a literature review. Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order.
Try to analyze patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text , your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, you can follow these tips:
- Summarize and synthesize: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers — add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transition words and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts
In the conclusion, you should summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance.
When you’ve finished writing and revising your literature review, don’t forget to proofread thoroughly before submitting. Not a language expert? Check out Scribbr’s professional proofreading services !
This article has been adapted into lecture slides that you can use to teach your students about writing a literature review.
Scribbr slides are free to use, customize, and distribute for educational purposes.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarize yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your thesis or dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
A literature review is a survey of credible sources on a topic, often used in dissertations , theses, and research papers . Literature reviews give an overview of knowledge on a subject, helping you identify relevant theories and methods, as well as gaps in existing research. Literature reviews are set up similarly to other academic texts , with an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion .
An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that has a short description (called an annotation ) for each of the sources. It is often assigned as part of the research process for a paper .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, September 11). How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, what is your plagiarism score.
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

5 literature review tools to ace your research (+2 bonus tools)

Table of Contents
Your literature review is the lore behind your research paper . It comes in two forms, systematic and scoping , both serving the purpose of rounding up previously published works in your research area that led you to write and finish your own.
A literature review is vital as it provides the reader with a critical overview of the existing body of knowledge, your methodology, and an opportunity for research applications.

Some steps to follow while writing your review:
- Pick an accessible topic for your paper
- Do thorough research and gather evidence surrounding your topic
- Read and take notes diligently
- Create a rough structure for your review
- Synthesis your notes and write the first draft
- Edit and proofread your literature review
To make your workload a little lighter, there are many literature review AI tools. These tools can help you find academic articles through AI and answer questions about a research paper.
Best literature review tools to improve research workflow
A literature review is one of the most critical yet tedious stages in composing a research paper. Many students find it an uphill task since it requires extensive reading and careful organization .
Using some of the best literature review tools listed here, you can make your life easier by overcoming some of the existing challenges in literature reviews. From collecting and classifying to analyzing and publishing research outputs, these tools help you with your literature review and improve your productivity without additional effort or expenses.
1. SciSpace
SciSpace is an AI for academic research that will help find research papers and answer questions about a research paper. You can discover, read, and understand research papers with SciSpace making it an excellent platform for literature review. Featuring a repository with over 270 million research papers, it comes with your AI research assistant called Copilot that offers explanations, summaries , and answers as you read.
Get started now:
Find academic articles through AI
SciSpace has a dedicated literature review tool that finds scientific articles when you search for a question. Based on semantic search, it shows all the research papers relevant for your subject. You can then gather quick insights for all the papers displayed in your search results like methodology, dataset, etc., and figure out all the papers relevant for your research.
Identify relevant articles faster
Abstracts are not always enough to determine whether a paper is relevant to your research question. For starters, you can ask questions to your AI research assistant, SciSpace Copilot to explore the content and better understand the article. Additionally, use the summarize feature to quickly review the methodology and results of a paper and decide if it is worth reading in detail.

Learn in your preferred language
A big barrier non-native English speakers face while conducting a literature review is that a significant portion of scientific literature is published in English. But with SciSpace Copilot, you can review, interact, and learn from research papers in any language you prefer — presently, it supports 75+ languages. The AI will answer questions about a research paper in your mother tongue.
Integrates with Zotero
Many researchers use Zotero to create a library and manage research papers. SciSpace lets you import your scientific articles directly from Zotero into your SciSpace library and use Copilot to comprehend your research papers. You can also highlight key sections, add notes to the PDF as you read, and even turn helpful explanations and answers from Copilot into notes for future review.
Understand math and complex concepts quickly
Come across complex mathematical equations or difficult concepts? Simply highlight the text or select the formula or table, and Copilot will provide an explanation or breakdown of the same in an easy-to-understand manner. You can ask follow-up questions if you need further clarification.

Discover new papers to read without leaving
Highlight phrases or sentences in your research paper to get suggestions for related papers in the field and save time on literature reviews. You can also use the 'Trace' feature to move across and discover connected papers, authors, topics, and more.
SciSpace Copilot is now available as a Chrome extension , allowing you to access its features directly while you browse scientific literature anywhere across the web.
Get citation-backed answers
When you're conducting a literature review, you want credible information with proper references. Copilot ensures that every piece of information provided by SciSpace Copilot is backed by a direct reference, boosting transparency, accuracy, and trustworthiness.
Ask a question related to the paper you're delving into. Every response from Copilot comes with a clickable citation. This citation leads you straight to the section of the PDF from which the answer was extracted.
By seamlessly integrating answers with citations, SciSpace Copilot assures you of the authenticity and relevance of the information you receive.
2. Mendeley
Mendeley Citation Manager is a free web and desktop application. It helps simplify your citation management workflow significantly. Here are some ways you can speed up your referencing game with Mendeley.
Generate citations and bibliographies
Easily add references from your Mendeley library to your Word document, change your citation style, and create a bibliography, all without leaving your document.
Retrieve references
It allows you to access your references quickly. Search for a term, and it will return results by referencing the year, author, or source.
Add sources to your Mendeley library by dragging PDF to Mendeley Reference Manager. Mendeley will automatically remove the PDF(s) metadata and create a library entry.
Read and annotate documents
It helps you highlight and comment across multiple PDFs while keep them all in one place using Mendeley Notebook . Notebook pages are not tied to a reference and let you quote from many PDFs.
A big part of many literature review workflows, Zotero is a free, open-source tool for managing citations that works as a plug-in on your browser. It helps you gather the information you need, cite your sources, lets you attach PDFs, notes, and images to your citations, and create bibliographies.
Import research articles to your database
Search for research articles on a keyword, and add relevant results to your database. Then, select the articles you are most interested in, and import them into Zotero.
Add bibliography in a variety of formats
With Zotero, you don’t have to scramble for different bibliography formats. Simply use the Zotero-Word plug-in to insert in-text citations and generate a bibliography.
Share your research
You can save a paper and sync it with an online library to easily share your research for group projects. Zotero can be used to create your database and decrease the time you spend formatting citations.
Sysrev is an AI too for article review that facilitates screening, collaboration, and data extraction from academic publications, abstracts, and PDF documents using machine learning. The platform is free and supports public and Open Access projects only.
Some of the features of Sysrev include:
Group labels
Group labels can be a powerful concept for creating database tables from documents. When exported and re-imported, each group label creates a new table. To make labels for a project, go into the manage -> labels section of the project.
Group labels enable project managers to pull table information from documents. It makes it easier to communicate review results for specific articles.
Track reviewer performance
Sysrev's label counting tool provides filtering and visualization options for keeping track of the distribution of labels throughout the project's progress. Project managers can check their projects at any point to track progress and the reviewer's performance.
Tool for concordance
The Sysrev tool for concordance allows project administrators and reviewers to perform analysis on their labels. Concordance is measured by calculating the number of times users agree on the labels they have extracted.
Colandr is a free, open-source, internet-based analysis and screening software used as an AI for academic research. It was designed to ease collaboration across various stages of the systematic review procedure. The tool can be a little complex to use. So, here are the steps involved in working with Colandr.
Create a review
The first step to using Colandr is setting up an organized review project. This is helpful to librarians who are assisting researchers with systematic reviews.
The planning stage is setting the review's objectives along with research queries. Any reviewer can review the details of the planning stage. However, they can only be modified by the author for the review.
Citation screening/import
In this phase, users can upload their results from database searches. Colandr also offers an automated deduplication system.
Full-text screening
The system in Colandr will discover the combination of terms and expressions that are most useful for the reader. If an article is selected, it will be moved to the final step.
Data extraction/export
Colandr data extraction is more efficient than the manual method. It creates the form fields for data extraction during the planning stage of the review procedure. Users can decide to revisit or modify the form for data extraction after completing the initial screening.
Bonus literature review tools
SRDR+ is a web-based tool for extracting and managing systematic review or meta-analysis data. It is open and has a searchable archive of systematic reviews and their data.
7. Plot Digitizer
Plot Digitizer is an efficient tool for extracting information from graphs and images, equipped with many features that facilitate data extraction. The program comes with a free online application, which is adequate to extract data quickly.
Final thoughts
Writing a literature review is not easy. It’s a time-consuming process, which can become tiring at times. The literature review tools mentioned in this blog do an excellent job of maximizing your efforts and helping you write literature reviews much more efficiently. With them, you can breathe a sigh of relief and give more time to your research.
As you dive into your literature review, don’t forget to use SciSpace ResearchGPT to streamline the process. It facilitates your research and helps you explore key findings, summary, and other components of the paper easily.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. what is rrl in research.
RRL stands for Review of Related Literature and sometimes interchanged with ‘Literature Review.’ RRL is a body of studies relevant to the topic being researched. These studies may be in the form of journal articles, books, reports, and other similar documents. Review of related literature is used to support an argument or theory being made by the researcher, as well as to provide information on how others have approached the same topic.
2. What are few softwares and tools available for literature review?
• SciSpace Discover
• Mendeley
• Zotero
• Sysrev
• Colandr
• SRDR+
3. How to generate an online literature review?
The Scispace Discover tool, which offers an excellent repository of millions of peer-reviewed articles and resources, will help you generate or create a literature review easily. You may find relevant information by utilizing the filter option, checking its credibility, tracing related topics and articles, and citing in widely accepted formats with a single click.
4. What does it mean to synthesize literature?
To synthesize literature is to take the main points and ideas from a number of sources and present them in a new way. The goal is to create a new piece of writing that pulls together the most important elements of all the sources you read. Make recommendations based on them, and connect them to the research.
5. Should we write abstract for literature review?
Abstracts, particularly for the literature review section, are not required. However, an abstract for the research paper, on the whole, is useful for summarizing the paper and letting readers know what to expect from it. It can also be used to summarize the main points of the paper so that readers have a better understanding of the paper's content before they read it.
6. How do you evaluate the quality of a literature review?
• Whether it is clear and well-written.
• Whether Information is current and up to date.
• Does it cover all of the relevant sources on the topic.
• Does it provide enough evidence to support its conclusions.
7. Is literature review mandatory?
Yes. Literature review is a mandatory part of any research project. It is a critical step in the process that allows you to establish the scope of your research and provide a background for the rest of your work.
8. What are the sources for a literature review?
• Reports
• Theses
• Conference proceedings
• Company reports
• Some government publications
• Journals
• Books
• Newspapers
• Articles by professional associations
• Indexes
• Databases
• Catalogues
• Encyclopaedias
• Dictionaries
• Bibliographies
• Citation indexes
• Statistical data from government websites
9. What is the difference between a systematic review and a literature review?
A systematic review is a form of research that uses a rigorous method to generate knowledge from both published and unpublished data. A literature review, on the other hand, is a critical summary of an area of research within the context of what has already been published.
Suggested reads!
Types of essays in academic writing Citation Machine Alternatives — A comparison of top citation tools 2023
QuillBot vs SciSpace: Choose the best AI-paraphrasing tool
ChatPDF vs. SciSpace Copilot: Unveiling the best tool for your research
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing - Quick Guide (2024)
Researching for a literature review: Websites
- What is a literature review?
- Dissertations
- Test Instruments
Appropriate websites will vary based on the topic, scope, and purpose of a project. Some recommended sites:
Scholarly Organizations - identify the premier organizations associated with the field being researched. Explore their websites for current information and learn about conferences and key scholars in the field to add to your search.
Intute - page of research websites collected and maintained by a consortium of university libraries in the U.K.
Example: Intute listing of Rhetoric websites
Although the Intute site stopped being updated in July 2011, it remains an excellent organized source to find valuable free collections and sources
Government Websites
The U.S. government may fund research in your field!
The government funds research in many areas such as education, health, and medicine. Find additional researchers or sources for information that may not be found in a traditional library catalog or database by searching for your topic and adding "site:.gov" to your search string in a search engine.

- << Previous: Dissertations
- Next: Test Instruments >>
- Last Updated: Feb 8, 2024 9:56 AM
- URL: https://libguides.bgsu.edu/litreview
How To Write An A-Grade Literature Review
3 straightforward steps (with examples) + free template.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewed By: Dr. Eunice Rautenbach | October 2019
Quality research is about building onto the existing work of others , “standing on the shoulders of giants”, as Newton put it. The literature review chapter of your dissertation, thesis or research project is where you synthesise this prior work and lay the theoretical foundation for your own research.
Long story short, this chapter is a pretty big deal, which is why you want to make sure you get it right . In this post, I’ll show you exactly how to write a literature review in three straightforward steps, so you can conquer this vital chapter (the smart way).
Overview: The Literature Review Process
- Understanding the “ why “
- Finding the relevant literature
- Cataloguing and synthesising the information
- Outlining & writing up your literature review
- Example of a literature review
But first, the “why”…
Before we unpack how to write the literature review chapter, we’ve got to look at the why . To put it bluntly, if you don’t understand the function and purpose of the literature review process, there’s no way you can pull it off well. So, what exactly is the purpose of the literature review?
Well, there are (at least) four core functions:
- For you to gain an understanding (and demonstrate this understanding) of where the research is at currently, what the key arguments and disagreements are.
- For you to identify the gap(s) in the literature and then use this as justification for your own research topic.
- To help you build a conceptual framework for empirical testing (if applicable to your research topic).
- To inform your methodological choices and help you source tried and tested questionnaires (for interviews ) and measurement instruments (for surveys ).
Most students understand the first point but don’t give any thought to the rest. To get the most from the literature review process, you must keep all four points front of mind as you review the literature (more on this shortly), or you’ll land up with a wonky foundation.
Okay – with the why out the way, let’s move on to the how . As mentioned above, writing your literature review is a process, which I’ll break down into three steps:
- Finding the most suitable literature
- Understanding , distilling and organising the literature
- Planning and writing up your literature review chapter
Importantly, you must complete steps one and two before you start writing up your chapter. I know it’s very tempting, but don’t try to kill two birds with one stone and write as you read. You’ll invariably end up wasting huge amounts of time re-writing and re-shaping, or you’ll just land up with a disjointed, hard-to-digest mess . Instead, you need to read first and distil the information, then plan and execute the writing.

Step 1: Find the relevant literature
Naturally, the first step in the literature review journey is to hunt down the existing research that’s relevant to your topic. While you probably already have a decent base of this from your research proposal , you need to expand on this substantially in the dissertation or thesis itself.
Essentially, you need to be looking for any existing literature that potentially helps you answer your research question (or develop it, if that’s not yet pinned down). There are numerous ways to find relevant literature, but I’ll cover my top four tactics here. I’d suggest combining all four methods to ensure that nothing slips past you:
Method 1 – Google Scholar Scrubbing
Google’s academic search engine, Google Scholar , is a great starting point as it provides a good high-level view of the relevant journal articles for whatever keyword you throw at it. Most valuably, it tells you how many times each article has been cited, which gives you an idea of how credible (or at least, popular) it is. Some articles will be free to access, while others will require an account, which brings us to the next method.
Method 2 – University Database Scrounging
Generally, universities provide students with access to an online library, which provides access to many (but not all) of the major journals.
So, if you find an article using Google Scholar that requires paid access (which is quite likely), search for that article in your university’s database – if it’s listed there, you’ll have access. Note that, generally, the search engine capabilities of these databases are poor, so make sure you search for the exact article name, or you might not find it.
Method 3 – Journal Article Snowballing
At the end of every academic journal article, you’ll find a list of references. As with any academic writing, these references are the building blocks of the article, so if the article is relevant to your topic, there’s a good chance a portion of the referenced works will be too. Do a quick scan of the titles and see what seems relevant, then search for the relevant ones in your university’s database.
Method 4 – Dissertation Scavenging
Similar to Method 3 above, you can leverage other students’ dissertations. All you have to do is skim through literature review chapters of existing dissertations related to your topic and you’ll find a gold mine of potential literature. Usually, your university will provide you with access to previous students’ dissertations, but you can also find a much larger selection in the following databases:
- Open Access Theses & Dissertations
- Stanford SearchWorks
Keep in mind that dissertations and theses are not as academically sound as published, peer-reviewed journal articles (because they’re written by students, not professionals), so be sure to check the credibility of any sources you find using this method. You can do this by assessing the citation count of any given article in Google Scholar. If you need help with assessing the credibility of any article, or with finding relevant research in general, you can chat with one of our Research Specialists .
Alright – with a good base of literature firmly under your belt, it’s time to move onto the next step.
Need a helping hand?
Step 2: Log, catalogue and synthesise
Once you’ve built a little treasure trove of articles, it’s time to get reading and start digesting the information – what does it all mean?
While I present steps one and two (hunting and digesting) as sequential, in reality, it’s more of a back-and-forth tango – you’ll read a little , then have an idea, spot a new citation, or a new potential variable, and then go back to searching for articles. This is perfectly natural – through the reading process, your thoughts will develop , new avenues might crop up, and directional adjustments might arise. This is, after all, one of the main purposes of the literature review process (i.e. to familiarise yourself with the current state of research in your field).
As you’re working through your treasure chest, it’s essential that you simultaneously start organising the information. There are three aspects to this:
- Logging reference information
- Building an organised catalogue
- Distilling and synthesising the information
I’ll discuss each of these below:
2.1 – Log the reference information
As you read each article, you should add it to your reference management software. I usually recommend Mendeley for this purpose (see the Mendeley 101 video below), but you can use whichever software you’re comfortable with. Most importantly, make sure you load EVERY article you read into your reference manager, even if it doesn’t seem very relevant at the time.
2.2 – Build an organised catalogue
In the beginning, you might feel confident that you can remember who said what, where, and what their main arguments were. Trust me, you won’t. If you do a thorough review of the relevant literature (as you must!), you’re going to read many, many articles, and it’s simply impossible to remember who said what, when, and in what context . Also, without the bird’s eye view that a catalogue provides, you’ll miss connections between various articles, and have no view of how the research developed over time. Simply put, it’s essential to build your own catalogue of the literature.
I would suggest using Excel to build your catalogue, as it allows you to run filters, colour code and sort – all very useful when your list grows large (which it will). How you lay your spreadsheet out is up to you, but I’d suggest you have the following columns (at minimum):
- Author, date, title – Start with three columns containing this core information. This will make it easy for you to search for titles with certain words, order research by date, or group by author.
- Categories or keywords – You can either create multiple columns, one for each category/theme and then tick the relevant categories, or you can have one column with keywords.
- Key arguments/points – Use this column to succinctly convey the essence of the article, the key arguments and implications thereof for your research.
- Context – Note the socioeconomic context in which the research was undertaken. For example, US-based, respondents aged 25-35, lower- income, etc. This will be useful for making an argument about gaps in the research.
- Methodology – Note which methodology was used and why. Also, note any issues you feel arise due to the methodology. Again, you can use this to make an argument about gaps in the research.
- Quotations – Note down any quoteworthy lines you feel might be useful later.
- Notes – Make notes about anything not already covered. For example, linkages to or disagreements with other theories, questions raised but unanswered, shortcomings or limitations, and so forth.
If you’d like, you can try out our free catalog template here (see screenshot below).

2.3 – Digest and synthesise
Most importantly, as you work through the literature and build your catalogue, you need to synthesise all the information in your own mind – how does it all fit together? Look for links between the various articles and try to develop a bigger picture view of the state of the research. Some important questions to ask yourself are:
- What answers does the existing research provide to my own research questions ?
- Which points do the researchers agree (and disagree) on?
- How has the research developed over time?
- Where do the gaps in the current research lie?
To help you develop a big-picture view and synthesise all the information, you might find mind mapping software such as Freemind useful. Alternatively, if you’re a fan of physical note-taking, investing in a large whiteboard might work for you.

Step 3: Outline and write it up!
Once you’re satisfied that you have digested and distilled all the relevant literature in your mind, it’s time to put pen to paper (or rather, fingers to keyboard). There are two steps here – outlining and writing:
3.1 – Draw up your outline
Having spent so much time reading, it might be tempting to just start writing up without a clear structure in mind. However, it’s critically important to decide on your structure and develop a detailed outline before you write anything. Your literature review chapter needs to present a clear, logical and an easy to follow narrative – and that requires some planning. Don’t try to wing it!
Naturally, you won’t always follow the plan to the letter, but without a detailed outline, you’re more than likely going to end up with a disjointed pile of waffle , and then you’re going to spend a far greater amount of time re-writing, hacking and patching. The adage, “measure twice, cut once” is very suitable here.
In terms of structure, the first decision you’ll have to make is whether you’ll lay out your review thematically (into themes) or chronologically (by date/period). The right choice depends on your topic, research objectives and research questions, which we discuss in this article .
Once that’s decided, you need to draw up an outline of your entire chapter in bullet point format. Try to get as detailed as possible, so that you know exactly what you’ll cover where, how each section will connect to the next, and how your entire argument will develop throughout the chapter. Also, at this stage, it’s a good idea to allocate rough word count limits for each section, so that you can identify word count problems before you’ve spent weeks or months writing!
PS – check out our free literature review chapter template…
3.2 – Get writing
With a detailed outline at your side, it’s time to start writing up (finally!). At this stage, it’s common to feel a bit of writer’s block and find yourself procrastinating under the pressure of finally having to put something on paper. To help with this, remember that the objective of the first draft is not perfection – it’s simply to get your thoughts out of your head and onto paper, after which you can refine them. The structure might change a little, the word count allocations might shift and shuffle, and you might add or remove a section – that’s all okay. Don’t worry about all this on your first draft – just get your thoughts down on paper.

Once you’ve got a full first draft (however rough it may be), step away from it for a day or two (longer if you can) and then come back at it with fresh eyes. Pay particular attention to the flow and narrative – does it fall fit together and flow from one section to another smoothly? Now’s the time to try to improve the linkage from each section to the next, tighten up the writing to be more concise, trim down word count and sand it down into a more digestible read.
Once you’ve done that, give your writing to a friend or colleague who is not a subject matter expert and ask them if they understand the overall discussion. The best way to assess this is to ask them to explain the chapter back to you. This technique will give you a strong indication of which points were clearly communicated and which weren’t. If you’re working with Grad Coach, this is a good time to have your Research Specialist review your chapter.
Finally, tighten it up and send it off to your supervisor for comment. Some might argue that you should be sending your work to your supervisor sooner than this (indeed your university might formally require this), but in my experience, supervisors are extremely short on time (and often patience), so, the more refined your chapter is, the less time they’ll waste on addressing basic issues (which you know about already) and the more time they’ll spend on valuable feedback that will increase your mark-earning potential.
Literature Review Example
In the video below, we unpack an actual literature review so that you can see how all the core components come together in reality.
Let’s Recap
In this post, we’ve covered how to research and write up a high-quality literature review chapter. Let’s do a quick recap of the key takeaways:
- It is essential to understand the WHY of the literature review before you read or write anything. Make sure you understand the 4 core functions of the process.
- The first step is to hunt down the relevant literature . You can do this using Google Scholar, your university database, the snowballing technique and by reviewing other dissertations and theses.
- Next, you need to log all the articles in your reference manager , build your own catalogue of literature and synthesise all the research.
- Following that, you need to develop a detailed outline of your entire chapter – the more detail the better. Don’t start writing without a clear outline (on paper, not in your head!)
- Write up your first draft in rough form – don’t aim for perfection. Remember, done beats perfect.
- Refine your second draft and get a layman’s perspective on it . Then tighten it up and submit it to your supervisor.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling Udemy Course, Literature Review Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

38 Comments
Thank you very much. This page is an eye opener and easy to comprehend.
This is awesome!
I wish I come across GradCoach earlier enough.
But all the same I’ll make use of this opportunity to the fullest.
Thank you for this good job.
Keep it up!
You’re welcome, Yinka. Thank you for the kind words. All the best writing your literature review.
Thank you for a very useful literature review session. Although I am doing most of the steps…it being my first masters an Mphil is a self study and one not sure you are on the right track. I have an amazing supervisor but one also knows they are super busy. So not wanting to bother on the minutae. Thank you.
You’re most welcome, Renee. Good luck with your literature review 🙂
This has been really helpful. Will make full use of it. 🙂
Thank you Gradcoach.
Really agreed. Admirable effort
thank you for this beautiful well explained recap.
Thank you so much for your guide of video and other instructions for the dissertation writing.
It is instrumental. It encouraged me to write a dissertation now.
Thank you the video was great – from someone that knows nothing thankyou
an amazing and very constructive way of presetting a topic, very useful, thanks for the effort,
It is timely
It is very good video of guidance for writing a research proposal and a dissertation. Since I have been watching and reading instructions, I have started my research proposal to write. I appreciate to Mr Jansen hugely.
I learn a lot from your videos. Very comprehensive and detailed.
Thank you for sharing your knowledge. As a research student, you learn better with your learning tips in research
I was really stuck in reading and gathering information but after watching these things are cleared thanks, it is so helpful.
Really helpful, Thank you for the effort in showing such information
This is super helpful thank you very much.
Thank you for this whole literature writing review.You have simplified the process.
I’m so glad I found GradCoach. Excellent information, Clear explanation, and Easy to follow, Many thanks Derek!
You’re welcome, Maithe. Good luck writing your literature review 🙂
Thank you Coach, you have greatly enriched and improved my knowledge
Great piece, so enriching and it is going to help me a great lot in my project and thesis, thanks so much
This is THE BEST site for ANYONE doing a masters or doctorate! Thank you for the sound advice and templates. You rock!
Thanks, Stephanie 🙂
This is mind blowing, the detailed explanation and simplicity is perfect.
I am doing two papers on my final year thesis, and I must stay I feel very confident to face both headlong after reading this article.
thank you so much.
if anyone is to get a paper done on time and in the best way possible, GRADCOACH is certainly the go to area!
This is very good video which is well explained with detailed explanation
Thank you excellent piece of work and great mentoring
Thanks, it was useful
Thank you very much. the video and the information were very helpful.
Good morning scholar. I’m delighted coming to know you even before the commencement of my dissertation which hopefully is expected in not more than six months from now. I would love to engage my study under your guidance from the beginning to the end. I love to know how to do good job
Thank you so much Derek for such useful information on writing up a good literature review. I am at a stage where I need to start writing my one. My proposal was accepted late last year but I honestly did not know where to start
Like the name of your YouTube implies you are GRAD (great,resource person, about dissertation). In short you are smart enough in coaching research work.
This is a very well thought out webpage. Very informative and a great read.
Very timely.
I appreciate.
Very comprehensive and eye opener for me as beginner in postgraduate study. Well explained and easy to understand. Appreciate and good reference in guiding me in my research journey. Thank you
Thank you. I requested to download the free literature review template, however, your website wouldn’t allow me to complete the request or complete a download. May I request that you email me the free template? Thank you.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Literature review: your definitive guide

Joanna Wilkinson
This is our ultimate guide on how to write a narrative literature review. It forms part of our Research Smarter series .
How do you write a narrative literature review?
Researchers worldwide are increasingly reliant on literature reviews. That’s because review articles provide you with a broad picture of the field, and help to synthesize published research that’s expanding at a rapid pace .
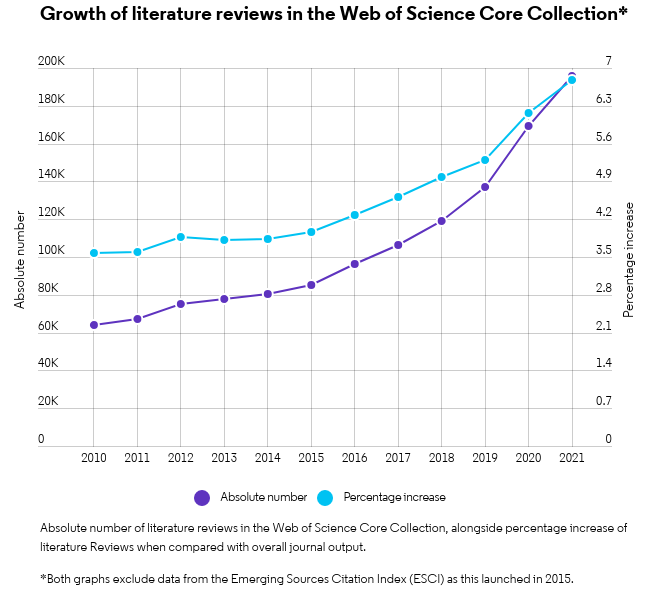
In some academic fields, researchers publish more literature reviews than original research papers. The graph below shows the substantial growth of narrative literature reviews in the Web of Science™, alongside the percentage increase of reviews when compared to all document types.
It’s critical that researchers across all career levels understand how to produce an objective, critical summary of published research. This is no easy feat, but a necessary one. Professionally constructed literature reviews – whether written by a student in class or an experienced researcher for publication – should aim to add to the literature rather than detract from it.
To help you write a narrative literature review, we’ve put together some top tips in this blog post.
Best practice tips to write a narrative literature review:
- Don’t miss a paper: tips for a thorough topic search
- Identify key papers (and know how to use them)
- Tips for working with co-authors
- Find the right journal for your literature review using actual data
- Discover literature review examples and templates
We’ll also provide an overview of all the products helpful for your next narrative review, including the Web of Science, EndNote™ and Journal Citation Reports™.
1. Don’t miss a paper: tips for a thorough topic search
Once you’ve settled on your research question, coming up with a good set of keywords to find papers on your topic can be daunting. This isn’t surprising. Put simply, if you fail to include a relevant paper when you write a narrative literature review, the omission will probably get picked up by your professor or peer reviewers. The end result will likely be a low mark or an unpublished manuscript, neither of which will do justice to your many months of hard work.
Research databases and search engines are an integral part of any literature search. It’s important you utilize as many options available through your library as possible. This will help you search an entire discipline (as well as across disciplines) for a thorough narrative review.
We provide a short summary of the various databases and search engines in an earlier Research Smarter blog . These include the Web of Science , Science.gov and the Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ).
Like what you see? Share it with others on Twitter:
[bctt tweet=”Writing a #LiteratureReview? Check out the latest @clarivateAG blog for top tips (from topic searches to working with coauthors), examples, templates and more”]
Searching the Web of Science
The Web of Science is a multidisciplinary research engine that contains over 170 million papers from more than 250 academic disciplines. All of the papers in the database are interconnected via citations. That means once you get started with your keyword search, you can follow the trail of cited and citing papers to efficiently find all the relevant literature. This is a great way to ensure you’re not missing anything important when you write a narrative literature review.
We recommend starting your search in the Web of Science Core Collection™. This database covers more than 21,000 carefully selected journals. It is a trusted source to find research papers, and discover top authors and journals (read more about its coverage here ).
Learn more about exploring the Core Collection in our blog, How to find research papers: five tips every researcher should know . Our blog covers various tips, including how to:
- Perform a topic search (and select your keywords)
- Explore the citation network
- Refine your results (refining your search results by reviews, for example, will help you avoid duplication of work, as well as identify trends and gaps in the literature)
- Save your search and set up email alerts
Try our tips on the Web of Science now.
2. Identify key papers (and know how to use them)
As you explore the Web of Science, you may notice that certain papers are marked as “Highly Cited.” These papers can play a significant role when you write a narrative literature review.
Highly Cited papers are recently published papers getting the most attention in your field right now. They form the top 1% of papers based on the number of citations received, compared to other papers published in the same field in the same year.
You will want to identify Highly Cited research as a group of papers. This group will help guide your analysis of the future of the field and opportunities for future research. This is an important component of your conclusion.
Writing reviews is hard work…[it] not only organizes published papers, but also positions t hem in the academic process and presents the future direction. Prof. Susumu Kitagawa, Highly Cited Researcher, Kyoto University
3. Tips for working with co-authors
Writing a narrative review on your own is hard, but it can be even more challenging if you’re collaborating with a team, especially if your coauthors are working across multiple locations. Luckily, reference management software can improve the coordination between you and your co-authors—both around the department and around the world.
We’ve written about how to use EndNote’s Cite While You Write feature, which will help you save hundreds of hours when writing research . Here, we discuss the features that give you greater ease and control when collaborating with your colleagues.
Use EndNote for narrative reviews
Sharing references is essential for successful collaboration. With EndNote, you can store and share as many references, documents and files as you need with up to 100 people using the software.
You can share simultaneous access to one reference library, regardless of your colleague’s location or organization. You can also choose the type of access each user has on an individual basis. For example, Read-Write access means a select colleague can add and delete references, annotate PDF articles and create custom groups. They’ll also be able to see up to 500 of the team’s most recent changes to the reference library. Read-only is also an option for individuals who don’t need that level of access.
EndNote helps you overcome research limitations by synchronizing library changes every 15 minutes. That means your team can stay up-to-date at any time of the day, supporting an easier, more successful collaboration.
Start your free EndNote trial today .

4.Finding a journal for your literature review
Finding the right journal for your literature review can be a particular pain point for those of you who want to publish. The expansion of scholarly journals has made the task extremely difficult, and can potentially delay the publication of your work by many months.
We’ve written a blog about how you can find the right journal for your manuscript using a rich array of data. You can read our blog here , or head straight to Endnote’s Manuscript Matcher or Journal Citation Report s to try out the best tools for the job.
5. Discover literature review examples and templates
There are a few tips we haven’t covered in this blog, including how to decide on an area of research, develop an interesting storyline, and highlight gaps in the literature. We’ve listed a few blogs here that might help you with this, alongside some literature review examples and outlines to get you started.
Literature Review examples:
- Aggregation-induced emission
- Development and applications of CRISPR-Cas9 for genome engineering
- Object based image analysis for remote sensing
(Make sure you download the free EndNote™ Click browser plugin to access the full-text PDFs).
Templates and outlines:
- Learn how to write a review of literature , Univ. of Wisconsin – Madison
- Structuring a literature review , Australian National University
- Matrix Method for Literature Review: The Review Matrix , Duquesne University
Additional resources:
- Ten simple rules for writing a literature review , Editor, PLoS Computational Biology
- Video: How to write a literature review , UC San Diego Psychology
Related posts
Unlocking u.k. research excellence: key insights from the research professional news live summit.

For better insights, assess research performance at the department level

Getting the Full Picture: Institutional unification in the Web of Science

Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library
- Collections
- Research Help
YSN Doctoral Programs: Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
- Biomedical Databases
- Global (Public Health) Databases
- Soc. Sci., History, and Law Databases
- Grey Literature
- Trials Registers
- Data and Statistics
- Public Policy
- Google Tips
- Recommended Books
- Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
What is a literature review?
A literature review is an integrated analysis -- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question. That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
A literature review may be a stand alone work or the introduction to a larger research paper, depending on the assignment. Rely heavily on the guidelines your instructor has given you.
Why is it important?
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Identifies critical gaps and points of disagreement.
- Discusses further research questions that logically come out of the previous studies.
APA7 Style resources
APA Style Blog - for those harder to find answers
1. Choose a topic. Define your research question.
Your literature review should be guided by your central research question. The literature represents background and research developments related to a specific research question, interpreted and analyzed by you in a synthesized way.
- Make sure your research question is not too broad or too narrow. Is it manageable?
- Begin writing down terms that are related to your question. These will be useful for searches later.
- If you have the opportunity, discuss your topic with your professor and your class mates.
2. Decide on the scope of your review
How many studies do you need to look at? How comprehensive should it be? How many years should it cover?
- This may depend on your assignment. How many sources does the assignment require?
3. Select the databases you will use to conduct your searches.
Make a list of the databases you will search.
Where to find databases:
- use the tabs on this guide
- Find other databases in the Nursing Information Resources web page
- More on the Medical Library web page
- ... and more on the Yale University Library web page
4. Conduct your searches to find the evidence. Keep track of your searches.
- Use the key words in your question, as well as synonyms for those words, as terms in your search. Use the database tutorials for help.
- Save the searches in the databases. This saves time when you want to redo, or modify, the searches. It is also helpful to use as a guide is the searches are not finding any useful results.
- Review the abstracts of research studies carefully. This will save you time.
- Use the bibliographies and references of research studies you find to locate others.
- Check with your professor, or a subject expert in the field, if you are missing any key works in the field.
- Ask your librarian for help at any time.
- Use a citation manager, such as EndNote as the repository for your citations. See the EndNote tutorials for help.
Review the literature
Some questions to help you analyze the research:
- What was the research question of the study you are reviewing? What were the authors trying to discover?
- Was the research funded by a source that could influence the findings?
- What were the research methodologies? Analyze its literature review, the samples and variables used, the results, and the conclusions.
- Does the research seem to be complete? Could it have been conducted more soundly? What further questions does it raise?
- If there are conflicting studies, why do you think that is?
- How are the authors viewed in the field? Has this study been cited? If so, how has it been analyzed?
Tips:
- Review the abstracts carefully.
- Keep careful notes so that you may track your thought processes during the research process.
- Create a matrix of the studies for easy analysis, and synthesis, across all of the studies.
- << Previous: Recommended Books
- Last Updated: Jan 4, 2024 10:52 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.yale.edu/YSNDoctoral
A Literature Review: Website Design and User Engagement
Affiliations.
- 1 ElevateU, Los Angeles, CA, USA.
- 2 University of California Institute for Prediction Technology, Department of Family Medicine, University of California, Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA, USA; UCLA Center for Digital Behavior, Department of Family Medicine, University of California, Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA, USA.
- PMID: 27499833
- PMCID: PMC4974011
Proper design has become a critical element needed to engage website and mobile application users. However, little research has been conducted to define the specific elements used in effective website and mobile application design. We attempt to review and consolidate research on effective design and to define a short list of elements frequently used in research. The design elements mentioned most frequently in the reviewed literature were navigation, graphical representation, organization, content utility, purpose, simplicity, and readability. We discuss how previous studies define and evaluate these seven elements. This review and the resulting short list of design elements may be used to help designers and researchers to operationalize best practices for facilitating and predicting user engagement.
Keywords: Website design; navigation; organization; simplicity; usability.
Grants and funding
- K01 MH090884/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH106415/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DA039458/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- PLoS Comput Biol
- v.9(7); 2013 Jul

Ten Simple Rules for Writing a Literature Review
Marco pautasso.
1 Centre for Functional and Evolutionary Ecology (CEFE), CNRS, Montpellier, France
2 Centre for Biodiversity Synthesis and Analysis (CESAB), FRB, Aix-en-Provence, France
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications [1] . For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively [2] . Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every single new paper relevant to their interests [3] . Thus, it is both advantageous and necessary to rely on regular summaries of the recent literature. Although recognition for scientists mainly comes from primary research, timely literature reviews can lead to new synthetic insights and are often widely read [4] . For such summaries to be useful, however, they need to be compiled in a professional way [5] .
When starting from scratch, reviewing the literature can require a titanic amount of work. That is why researchers who have spent their career working on a certain research issue are in a perfect position to review that literature. Some graduate schools are now offering courses in reviewing the literature, given that most research students start their project by producing an overview of what has already been done on their research issue [6] . However, it is likely that most scientists have not thought in detail about how to approach and carry out a literature review.
Reviewing the literature requires the ability to juggle multiple tasks, from finding and evaluating relevant material to synthesising information from various sources, from critical thinking to paraphrasing, evaluating, and citation skills [7] . In this contribution, I share ten simple rules I learned working on about 25 literature reviews as a PhD and postdoctoral student. Ideas and insights also come from discussions with coauthors and colleagues, as well as feedback from reviewers and editors.
Rule 1: Define a Topic and Audience
How to choose which topic to review? There are so many issues in contemporary science that you could spend a lifetime of attending conferences and reading the literature just pondering what to review. On the one hand, if you take several years to choose, several other people may have had the same idea in the meantime. On the other hand, only a well-considered topic is likely to lead to a brilliant literature review [8] . The topic must at least be:
- interesting to you (ideally, you should have come across a series of recent papers related to your line of work that call for a critical summary),
- an important aspect of the field (so that many readers will be interested in the review and there will be enough material to write it), and
- a well-defined issue (otherwise you could potentially include thousands of publications, which would make the review unhelpful).
Ideas for potential reviews may come from papers providing lists of key research questions to be answered [9] , but also from serendipitous moments during desultory reading and discussions. In addition to choosing your topic, you should also select a target audience. In many cases, the topic (e.g., web services in computational biology) will automatically define an audience (e.g., computational biologists), but that same topic may also be of interest to neighbouring fields (e.g., computer science, biology, etc.).
Rule 2: Search and Re-search the Literature
After having chosen your topic and audience, start by checking the literature and downloading relevant papers. Five pieces of advice here:
- keep track of the search items you use (so that your search can be replicated [10] ),
- keep a list of papers whose pdfs you cannot access immediately (so as to retrieve them later with alternative strategies),
- use a paper management system (e.g., Mendeley, Papers, Qiqqa, Sente),
- define early in the process some criteria for exclusion of irrelevant papers (these criteria can then be described in the review to help define its scope), and
- do not just look for research papers in the area you wish to review, but also seek previous reviews.
The chances are high that someone will already have published a literature review ( Figure 1 ), if not exactly on the issue you are planning to tackle, at least on a related topic. If there are already a few or several reviews of the literature on your issue, my advice is not to give up, but to carry on with your own literature review,

The bottom-right situation (many literature reviews but few research papers) is not just a theoretical situation; it applies, for example, to the study of the impacts of climate change on plant diseases, where there appear to be more literature reviews than research studies [33] .
- discussing in your review the approaches, limitations, and conclusions of past reviews,
- trying to find a new angle that has not been covered adequately in the previous reviews, and
- incorporating new material that has inevitably accumulated since their appearance.
When searching the literature for pertinent papers and reviews, the usual rules apply:
- be thorough,
- use different keywords and database sources (e.g., DBLP, Google Scholar, ISI Proceedings, JSTOR Search, Medline, Scopus, Web of Science), and
- look at who has cited past relevant papers and book chapters.
Rule 3: Take Notes While Reading
If you read the papers first, and only afterwards start writing the review, you will need a very good memory to remember who wrote what, and what your impressions and associations were while reading each single paper. My advice is, while reading, to start writing down interesting pieces of information, insights about how to organize the review, and thoughts on what to write. This way, by the time you have read the literature you selected, you will already have a rough draft of the review.
Of course, this draft will still need much rewriting, restructuring, and rethinking to obtain a text with a coherent argument [11] , but you will have avoided the danger posed by staring at a blank document. Be careful when taking notes to use quotation marks if you are provisionally copying verbatim from the literature. It is advisable then to reformulate such quotes with your own words in the final draft. It is important to be careful in noting the references already at this stage, so as to avoid misattributions. Using referencing software from the very beginning of your endeavour will save you time.
Rule 4: Choose the Type of Review You Wish to Write
After having taken notes while reading the literature, you will have a rough idea of the amount of material available for the review. This is probably a good time to decide whether to go for a mini- or a full review. Some journals are now favouring the publication of rather short reviews focusing on the last few years, with a limit on the number of words and citations. A mini-review is not necessarily a minor review: it may well attract more attention from busy readers, although it will inevitably simplify some issues and leave out some relevant material due to space limitations. A full review will have the advantage of more freedom to cover in detail the complexities of a particular scientific development, but may then be left in the pile of the very important papers “to be read” by readers with little time to spare for major monographs.
There is probably a continuum between mini- and full reviews. The same point applies to the dichotomy of descriptive vs. integrative reviews. While descriptive reviews focus on the methodology, findings, and interpretation of each reviewed study, integrative reviews attempt to find common ideas and concepts from the reviewed material [12] . A similar distinction exists between narrative and systematic reviews: while narrative reviews are qualitative, systematic reviews attempt to test a hypothesis based on the published evidence, which is gathered using a predefined protocol to reduce bias [13] , [14] . When systematic reviews analyse quantitative results in a quantitative way, they become meta-analyses. The choice between different review types will have to be made on a case-by-case basis, depending not just on the nature of the material found and the preferences of the target journal(s), but also on the time available to write the review and the number of coauthors [15] .
Rule 5: Keep the Review Focused, but Make It of Broad Interest
Whether your plan is to write a mini- or a full review, it is good advice to keep it focused 16 , 17 . Including material just for the sake of it can easily lead to reviews that are trying to do too many things at once. The need to keep a review focused can be problematic for interdisciplinary reviews, where the aim is to bridge the gap between fields [18] . If you are writing a review on, for example, how epidemiological approaches are used in modelling the spread of ideas, you may be inclined to include material from both parent fields, epidemiology and the study of cultural diffusion. This may be necessary to some extent, but in this case a focused review would only deal in detail with those studies at the interface between epidemiology and the spread of ideas.
While focus is an important feature of a successful review, this requirement has to be balanced with the need to make the review relevant to a broad audience. This square may be circled by discussing the wider implications of the reviewed topic for other disciplines.
Rule 6: Be Critical and Consistent
Reviewing the literature is not stamp collecting. A good review does not just summarize the literature, but discusses it critically, identifies methodological problems, and points out research gaps [19] . After having read a review of the literature, a reader should have a rough idea of:
- the major achievements in the reviewed field,
- the main areas of debate, and
- the outstanding research questions.
It is challenging to achieve a successful review on all these fronts. A solution can be to involve a set of complementary coauthors: some people are excellent at mapping what has been achieved, some others are very good at identifying dark clouds on the horizon, and some have instead a knack at predicting where solutions are going to come from. If your journal club has exactly this sort of team, then you should definitely write a review of the literature! In addition to critical thinking, a literature review needs consistency, for example in the choice of passive vs. active voice and present vs. past tense.
Rule 7: Find a Logical Structure
Like a well-baked cake, a good review has a number of telling features: it is worth the reader's time, timely, systematic, well written, focused, and critical. It also needs a good structure. With reviews, the usual subdivision of research papers into introduction, methods, results, and discussion does not work or is rarely used. However, a general introduction of the context and, toward the end, a recapitulation of the main points covered and take-home messages make sense also in the case of reviews. For systematic reviews, there is a trend towards including information about how the literature was searched (database, keywords, time limits) [20] .
How can you organize the flow of the main body of the review so that the reader will be drawn into and guided through it? It is generally helpful to draw a conceptual scheme of the review, e.g., with mind-mapping techniques. Such diagrams can help recognize a logical way to order and link the various sections of a review [21] . This is the case not just at the writing stage, but also for readers if the diagram is included in the review as a figure. A careful selection of diagrams and figures relevant to the reviewed topic can be very helpful to structure the text too [22] .
Rule 8: Make Use of Feedback
Reviews of the literature are normally peer-reviewed in the same way as research papers, and rightly so [23] . As a rule, incorporating feedback from reviewers greatly helps improve a review draft. Having read the review with a fresh mind, reviewers may spot inaccuracies, inconsistencies, and ambiguities that had not been noticed by the writers due to rereading the typescript too many times. It is however advisable to reread the draft one more time before submission, as a last-minute correction of typos, leaps, and muddled sentences may enable the reviewers to focus on providing advice on the content rather than the form.
Feedback is vital to writing a good review, and should be sought from a variety of colleagues, so as to obtain a diversity of views on the draft. This may lead in some cases to conflicting views on the merits of the paper, and on how to improve it, but such a situation is better than the absence of feedback. A diversity of feedback perspectives on a literature review can help identify where the consensus view stands in the landscape of the current scientific understanding of an issue [24] .
Rule 9: Include Your Own Relevant Research, but Be Objective
In many cases, reviewers of the literature will have published studies relevant to the review they are writing. This could create a conflict of interest: how can reviewers report objectively on their own work [25] ? Some scientists may be overly enthusiastic about what they have published, and thus risk giving too much importance to their own findings in the review. However, bias could also occur in the other direction: some scientists may be unduly dismissive of their own achievements, so that they will tend to downplay their contribution (if any) to a field when reviewing it.
In general, a review of the literature should neither be a public relations brochure nor an exercise in competitive self-denial. If a reviewer is up to the job of producing a well-organized and methodical review, which flows well and provides a service to the readership, then it should be possible to be objective in reviewing one's own relevant findings. In reviews written by multiple authors, this may be achieved by assigning the review of the results of a coauthor to different coauthors.
Rule 10: Be Up-to-Date, but Do Not Forget Older Studies
Given the progressive acceleration in the publication of scientific papers, today's reviews of the literature need awareness not just of the overall direction and achievements of a field of inquiry, but also of the latest studies, so as not to become out-of-date before they have been published. Ideally, a literature review should not identify as a major research gap an issue that has just been addressed in a series of papers in press (the same applies, of course, to older, overlooked studies (“sleeping beauties” [26] )). This implies that literature reviewers would do well to keep an eye on electronic lists of papers in press, given that it can take months before these appear in scientific databases. Some reviews declare that they have scanned the literature up to a certain point in time, but given that peer review can be a rather lengthy process, a full search for newly appeared literature at the revision stage may be worthwhile. Assessing the contribution of papers that have just appeared is particularly challenging, because there is little perspective with which to gauge their significance and impact on further research and society.
Inevitably, new papers on the reviewed topic (including independently written literature reviews) will appear from all quarters after the review has been published, so that there may soon be the need for an updated review. But this is the nature of science [27] – [32] . I wish everybody good luck with writing a review of the literature.
Acknowledgments
Many thanks to M. Barbosa, K. Dehnen-Schmutz, T. Döring, D. Fontaneto, M. Garbelotto, O. Holdenrieder, M. Jeger, D. Lonsdale, A. MacLeod, P. Mills, M. Moslonka-Lefebvre, G. Stancanelli, P. Weisberg, and X. Xu for insights and discussions, and to P. Bourne, T. Matoni, and D. Smith for helpful comments on a previous draft.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by the French Foundation for Research on Biodiversity (FRB) through its Centre for Synthesis and Analysis of Biodiversity data (CESAB), as part of the NETSEED research project. The funders had no role in the preparation of the manuscript.
Literature reviews
- Introduction
- Conducting your search
- Store and organise the literature
- Evaluate and critique the literature
- Different subject areas
Finding literature reviews on your topic

Find reviews
- Run your search in the database
- Limit the results to review or literature review - often found under Document type
If there is no option to limit to reviews try adding the word "review" to your search.
- Go to the Advanced search of the database

- Type review into a search line and change the field option to Title
Note: The results may include book reviews using this method.
Useful databases to find review articles
- Annual reviews online Annual Reviews publishes analytic reviews in focused disciplines within the biomedical, physical, and social sciences. The reviews cover significant developments in the different fields.
- Web of Science Go to the Advanced Search to set the document type to "Review". Web of Science covers the sciences, social sciences, arts and humanities.
- Scopus Click on Limit to change the Document type to Review. Scopus is a multidisciplinary abstract and citation database of peer reviewed literature, book reviews and conference proceedings.
- Subject guides These guides list recommended databases useful for your particular subject area.
- << Previous: Different subject areas
- Last Updated: Dec 15, 2023 12:09 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.uq.edu.au/research-techniques/literature-reviews
- Craft and Criticism
- Fiction and Poetry
- News and Culture
- Lit Hub Radio
- Reading Lists

- Literary Criticism
- Craft and Advice
- In Conversation
- On Translation
- Short Story
- From the Novel
- Bookstores and Libraries
- Film and TV
- Art and Photography
- Freeman’s
- The Virtual Book Channel
- Behind the Mic
- Beyond the Page
- The Cosmic Library
- The Critic and Her Publics
- Emergence Magazine
- Fiction/Non/Fiction
- First Draft: A Dialogue on Writing
- Future Fables
- The History of Literature
- I’m a Writer But
- Just the Right Book
- Lit Century
- The Literary Life with Mitchell Kaplan
- New Books Network
- Tor Presents: Voyage Into Genre
- Windham-Campbell Prizes Podcast
- Write-minded
- The Best of the Decade
- Best Reviewed Books
- BookMarks Daily Giveaway
- The Daily Thrill
- CrimeReads Daily Giveaway
I Really Like Reading Bad Reviews of My Nemesis: Am I the Literary Asshole?
Kristen arnett answers your awkward questions about bad literary behavior, how do we celebrate arab american heritage month during a genocide, “palestinian lives are simply not valued, and, by inheritance, neither are palestinian americans.”, 10 great new children’s books out in april, caroline carlsonrecommends maple lam, felicita sala, laurie morrison and more, 100 tips that may (or may not) improve your next novel, ryan chapman on the craft and practice of writing fiction (and drinking gin), vampires, selkies, familiars, and more april’s best sci-fi and fantasy books, career retrospectives and historical fantasies from cixin liu, ann leckie, leigh bardugo, and others, a brief literary history of the murder ballad, in honor of beyoncé’s cowboy carter, brittany allen on the long, rich tradition of extremely violent popular song, the literary film & tv you need to stream in april, april showers bring opportunities to binge watch, march’s best reviewed nonfiction, featuring new titles by marilynne robinson, tessa hulls, kristine s. ervin, and more, for book recommendations, people are always better than algorithms, maris kreizman reveals some tricks of the trade for the semi-professional book recommender, the sickness of life: on the problems with anti-natalism, ben ware considers the emptiness of opting out, the writer next door: my life as joyce carol oates’ neighbor, “i wanted to believe that oates knew we existed. while her cat clearly knew who we were, she never did.”, rebecca solnit: how to comment on social media, “the entire measure of someone's commitment is how much they post about their commitment.”, here’s your 2024 literary film & tv preview, 53 shows and movies to stream and see this year, lit hub’s most anticipated books of 2024, 230 books we’re looking forward to reading this year, 24 sci-fi and fantasy books to look forward to in 2024, exciting new series’ and standalones from kelly link, lev grossman, sofia samatar, james s.a. corey, and more, we need your help: support lit hub, become a member, you get editors’ personalized book recs, an ad-free reading experience, and the joan didion tote bag, 40 books to understand palestine, from ghassan kanafani's "men in the sun" to adania shibli's "minor detail", unsolvable puzzles: anna shechtman on the feminist psychology behind crosswords.
Hannah Zeavin Talks to the Author of “The Riddles of the Sphinx”
How Texas Prisons Regulate Women’s Knowledge Behind Bars
Kwaneta Harris Explores Systemic Censorship Within the Criminal Justice System

10 Queer Books For People With Mommy Issues
Marissa Higgins Recommends Patricia Highsmith, Melissa Broder, Anna Dorn and More

5 Book Reviews You Need to Read This Week
"The heart is everywhere in these pages."

The Annotated Nightstand: What Julia Alvarez is Reading Now and Next
Featuring T.S. Eliot, Ellen Bass, Dorianne Laux, and Others

“California,” a Poem by David Semanki
From the Collection “Ghost Camera”

April 4, 2024

- Sheila Heti interviews Lauren Oyler
- In conversation with poet Samer Abu Hawwash
- A poetics of living rebellion
to the Lithub Daily
Support lit hub..

Lit hub Radio
News, Notes, Talk

Daily Fiction

The Obscene Bird of Night
From the obscene bird of night.

The Good Deed
From the good deed.

David Baron on What Literature Tells Us About the 2024 Eclipse

The Cosmic Library ">Welcome to Season 5 of The Cosmic Library
William egginton on the joys of jodorowsky.
From The History of Literature Podcast with Jacke Wilson

“The Small Press World is About to Fall Apart.” On the Collapse of Small Press Distribution

Advertising as Art: How Literary Magazines Pioneered a New Kind of Graphic Design

5 Reviews You Need to Read This Week

The Best Reviewed Books of the Month
Mysteries About Translators: A Reading List

Six of the Best Campus Crime Novels
- RSS - Posts
Literary Hub
Created by Grove Atlantic and Electric Literature
Sign Up For Our Newsletters
How to Pitch Lit Hub
Advertisers: Contact Us
Privacy Policy
Support Lit Hub - Become A Member
All-in-one Literature Review Software
Start your free trial.
Free MAXQDA trial for Windows and Mac
Your trial will end automatically after 14 days.
MAXQDA The All-in-one Literature Review Software
MAXQDA is the best choice for a comprehensive literature review. It works with a wide range of data types and offers powerful tools for literature review, such as reference management, qualitative, vocabulary, text analysis tools, and more.
Document viewer
Your analysis.
As your all-in-one literature review software, MAXQDA can be used to manage your entire research project. Easily import data from texts, interviews, focus groups, PDFs, web pages, spreadsheets, articles, e-books, and even social media data. Connect the reference management system of your choice with MAXQDA to easily import bibliographic data. Organize your data in groups, link relevant quotes to each other, keep track of your literature summaries, and share and compare work with your team members. Your project file stays flexible and you can expand and refine your category system as you go to suit your research.
Developed by and for researchers – since 1989

Having used several qualitative data analysis software programs, there is no doubt in my mind that MAXQDA has advantages over all the others. In addition to its remarkable analytical features for harnessing data, MAXQDA’s stellar customer service, online tutorials, and global learning community make it a user friendly and top-notch product.
Sally S. Cohen – NYU Rory Meyers College of Nursing
Literature Review is Faster and Smarter with MAXQDA

Easily import your literature review data
With a literature review software like MAXQDA, you can easily import bibliographic data from reference management programs for your literature review. MAXQDA can work with all reference management programs that can export their databases in RIS-format which is a standard format for bibliographic information. Like MAXQDA, these reference managers use project files, containing all collected bibliographic information, such as author, title, links to websites, keywords, abstracts, and other information. In addition, you can easily import the corresponding full texts. Upon import, all documents will be automatically pre-coded to facilitate your literature review at a later stage.
Capture your ideas while analyzing your literature
Great ideas will often occur to you while you’re doing your literature review. Using MAXQDA as your literature review software, you can create memos to store your ideas, such as research questions and objectives, or you can use memos for paraphrasing passages into your own words. By attaching memos like post-it notes to text passages, texts, document groups, images, audio/video clips, and of course codes, you can easily retrieve them at a later stage. Particularly useful for literature reviews are free memos written during the course of work from which passages can be copied and inserted into the final text.

Find concepts important to your generated literature review
When generating a literature review you might need to analyze a large amount of text. Luckily MAXQDA as the #1 literature review software offers Text Search tools that allow you to explore your documents without reading or coding them first. Automatically search for keywords (or dictionaries of keywords), such as important concepts for your literature review, and automatically code them with just a few clicks. Document variables that were automatically created during the import of your bibliographic information can be used for searching and retrieving certain text segments. MAXQDA’s powerful Coding Query allows you to analyze the combination of activated codes in different ways.
Aggregate your literature review
When conducting a literature review you can easily get lost. But with MAXQDA as your literature review software, you will never lose track of the bigger picture. Among other tools, MAXQDA’s overview and summary tables are especially useful for aggregating your literature review results. MAXQDA offers overview tables for almost everything, codes, memos, coded segments, links, and so on. With MAXQDA literature review tools you can create compressed summaries of sources that can be effectively compared and represented, and with just one click you can easily export your overview and summary tables and integrate them into your literature review report.

Powerful and easy-to-use literature review tools
Quantitative aspects can also be relevant when conducting a literature review analysis. Using MAXQDA as your literature review software enables you to employ a vast range of procedures for the quantitative evaluation of your material. You can sort sources according to document variables, compare amounts with frequency tables and charts, and much more. Make sure you don’t miss the word frequency tools of MAXQDA’s add-on module for quantitative content analysis. Included are tools for visual text exploration, content analysis, vocabulary analysis, dictionary-based analysis, and more that facilitate the quantitative analysis of terms and their semantic contexts.
Visualize your literature review
As an all-in-one literature review software, MAXQDA offers a variety of visual tools that are tailor-made for qualitative research and literature reviews. Create stunning visualizations to analyze your material. Of course, you can export your visualizations in various formats to enrich your literature review analysis report. Work with word clouds to explore the central themes of a text and key terms that are used, create charts to easily compare the occurrences of concepts and important keywords, or make use of the graphical representation possibilities of MAXMaps, which in particular permit the creation of concept maps. Thanks to the interactive connection between your visualizations with your MAXQDA data, you’ll never lose sight of the big picture.
AI Assist: literature review software meets AI
AI Assist – your virtual research assistant – supports your literature review with various tools. AI Assist simplifies your work by automatically analyzing and summarizing elements of your research project and by generating suggestions for subcodes. No matter which AI tool you use – you can customize your results to suit your needs.
Free tutorials and guides on literature review
MAXQDA offers a variety of free learning resources for literature review, making it easy for both beginners and advanced users to learn how to use the software. From free video tutorials and webinars to step-by-step guides and sample projects, these resources provide a wealth of information to help you understand the features and functionality of MAXQDA for literature review. For beginners, the software’s user-friendly interface and comprehensive help center make it easy to get started with your data analysis, while advanced users will appreciate the detailed guides and tutorials that cover more complex features and techniques. Whether you’re just starting out or are an experienced researcher, MAXQDA’s free learning resources will help you get the most out of your literature review.

Free MAXQDA Trial for Windows and Mac
Get your maxqda license, compare the features of maxqda and maxqda analytics pro, faq: literature review software.
Literature review software is a tool designed to help researchers efficiently manage and analyze the existing body of literature relevant to their research topic. MAXQDA, a versatile qualitative data analysis tool, can be instrumental in this process.
Literature review software, like MAXQDA, typically includes features such as data import and organization, coding and categorization, advanced search capabilities, data visualization tools, and collaboration features. These features facilitate the systematic review and analysis of relevant literature.
Literature review software, including MAXQDA, can assist in qualitative data interpretation by enabling researchers to organize, code, and categorize relevant literature. This organized data can then be analyzed to identify trends, patterns, and themes, helping researchers draw meaningful insights from the literature they’ve reviewed.
Yes, literature review software like MAXQDA is suitable for researchers of all levels of experience. It offers user-friendly interfaces and extensive support resources, making it accessible to beginners while providing advanced features that cater to the needs of experienced researchers.
Getting started with literature review software, such as MAXQDA, typically involves downloading and installing the software, importing your relevant literature, and exploring the available features. Many software providers offer tutorials and documentation to help users get started quickly.
For students, MAXQDA can be an excellent literature review software choice. Its user-friendly interface, comprehensive feature set, and educational discounts make it a valuable tool for students conducting literature reviews as part of their academic research.
MAXQDA is available for both Windows and Mac users, making it a suitable choice for Mac users looking for literature review software. It offers a consistent and feature-rich experience on Mac operating systems.
When it comes to literature review software, MAXQDA is widely regarded as one of the best choices. Its robust feature set, user-friendly interface, and versatility make it a top pick for researchers conducting literature reviews.
Yes, literature reviews can be conducted without software. However, using literature review software like MAXQDA can significantly streamline and enhance the process by providing tools for efficient data management, analysis, and visualization.
Ownership Structure and Firm Performance: A Comprehensive Review and Empirical Analysis
- Published: 04 April 2024
Cite this article
- Sanjana Bhakar ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-0936-9651 1 ,
- Priti Sharma 1 &
- Sanjiv Kumar 1
Ownership structure and firm performance are the two important ingredients for a firm to sustain in the market for a prolonged time. Ample research has statistically proven the significant impact of ownership structure on firm performance. Ergo, this study aims to critically review and analyse the mechanisms of ownership structure (OS) and their impact on the firm performance (FP) with the help of content analysis and systematic literature review (SLR). This study used the combined literature from Scopus and Web of Science databases from 1977 to 2022. A total of 552 relevant documents have been extracted, out of which 40 documents were found suitable based on inclusion and exclusion criteria using the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) framework of SLR has been applied using R studio software. Major findings of the study revealed that ownership concentration was found significant in affecting firm performance. However, other mechanisms such as managerial ownership, government ownership, institutional ownership, foreign ownership and family ownership showed mixed results such as positive, negative or insignificant. This study on the one side contributes to the existing literature and also helps the policymakers in maximising the performance of the firm by suggesting ways to reduce conflicts of interest between managers and shareholders and will also be significant to the practitioners, scholars and managers in comprehending dynamics of corporate governance practices. Further, it will help investors give special consideration to a particular type of ownership structure while making investment decisions.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
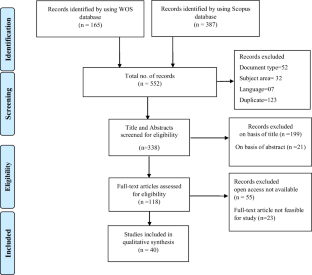
Source: Compiled by the researcher
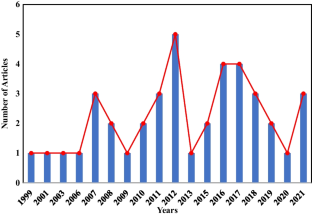
Abbreviations
Corporate governance
- Ownership structure
- Firm performance
- Ownership concentration
Concentrated ownership
Managerial ownership
Foreign ownership
Family ownership
Government ownership
State-owned
Institutional ownership
Dependent variable
Independent variable
Control variables
Abdullah, M. I., Sarfraz, M., Qun, W., & Chaudhary, M. (2019). Ownership concentration impact on firm financial performance. LogForum, 15 (1), 107–118. https://doi.org/10.17270/J.LOG.2019.317
Article Google Scholar
Abdulsamad, A. O., & Yusoff, W. F. W. (2016). Ownership structure and firm performance: A longitudinal study in Malaysia. Corporate Ownership & Control, 13 (2), 432–437. https://doi.org/10.22495/cocv13i2c2p3
Abdurrouf, M. A. (2011). The relationship between corporate governance and value of the firm in developing countries: Evidence from Bangladesh. The International Journal of Applied Economics and Finance, 5 (3), 237–244. https://doi.org/10.3923/ijaef.2011.237.244
Alabdullah, T. T. Y. (2018). The relationship between ownership structure and firm financial performance: Evidence from Jordan. Benchmarking, 25 (1), 319–333. https://doi.org/10.1108/BIJ-04-2016-0051
Alba, P., Claessens, S., & Djankov, S. (1998). Thailand's corporate financing and governance structures (No. 2003). World Bank Publications.
Alfaraih, M., Alanezi, F., & Almujamed, H. (2012). The influence of institutional and government ownership on firm performance: Evidence from Kuwait. International Business Research, 5 (10), 192–200. https://doi.org/10.5539/ibr.v5n10p192
Ali, A., Qiang, F., & Ashraf, S. (2018). Regional dynamics of ownership structure and their impact on firm performance and firm valuation: A case of Chinese listed companies. Review of International Business and Strategy, 28 (1), 128–146. https://doi.org/10.1108/RIBS-02-2017-0017
Ali Ahmed, H., & Wadud, I. K. M. (2011). Market based performance: Do ownership structures, or firm policy choice matter ? Corporate Ownership & Control, 8 (2), 89–95.
Alimehmeti, G., & Paletta, A. (2012). Ownership concentration and effects over firm performance: Evidences from Italy. European Scientific Journal, 8 (22), 39–49.
Google Scholar
Alkurdi, A., Hamad, A., Thneibat, H., & Elmarzouky, M. (2021). Ownership structure’s effect on financial performance: An empirical analysis of Jordanian listed firms. Cogent Business and Management , 8 (1). https://doi.org/10.1080/23311975.2021.1939930
Al-Matari, E. M., & Al-Arussi, A. S. (2016). The effect of the ownership structure characteristics on firm performance in oman: Empirical study. Corporate Ownership and Control, 13 (2), 93–182. https://doi.org/10.22495/cocv13i2p10
Al-Matari, E. M., Al-Swidi, A. K., Faudziah, H. B., & Al-Matari, Y. A. (2012a). The impact of board characteristics on firm performance: Evidence from nonfinancial listed companies in Kuwaiti Stock Exchange. International Journal of Accounting and Financial Reporting, 2 (2), 310-332. 6. https://doi.org/10.5296/ijafr.v2i2.2384
Al-Matari, Y. A., Al-Swidi, A. K., & Fadzil, F. H. B. (2012b). Audit committee effectiveness and performance of Saudi Arabia listed companies. Wulfenia Journal, 19 (8), 169–188.
Al-Matari, E. M., Al-Matari, Y. A., & Saif, S. A. (2017). Association between ownership structure characteristics and firm performance: Oman evidence. Academy of Accounting and Financial Studies Journal, 21 (1), 11.
Alkurdi, A., Hamad, A., Thneibat, H., & Elmarzouky, M| Collins G. Ntim (Reviewing editor) (2021). Ownership structure’s effect on financial performance: An empirical analysis of Jordanian listed firms, Cogent Business & Management , 8:1, https://doi.org/10.1080/23311975.2021.1939930 .
Amran, N. A., & Ahmad, A. C. (2013). Effects of ownership structure on Malaysian companies performance. Asian Journal of Accounting and Governance, 4 (1), 51–60.
Anderson, R. C., & Reeb, D. M. (2003). Founding-family ownership and firm performance: Evidence from the S&P 500. Journal of Finance, 58 (3), 1301–1328. https://doi.org/10.1111/1540-6261.00567
Balsmeier, B., & Czarnitzki, D. (2017). Ownership concentration, institutional development and firm performance in Central and Eastern Europe. Managerial and Decision Economics, 38 (2), 178–192. https://doi.org/10.1002/mde.2751
Basyith, A., Fauzi, F., & Idris, M. (2015). The impact of board structure and ownership structure on firm performance: An evidence from blue chip firms listed in Indonesian stock exchange. Corporate Ownership & Control , 12 (3). https://doi.org/10.22495/cocv12i4c3p2
Barontini, R., & Caprio, L. (2006). The effect of family control on firm value and performance: Evidence from continental Europe. European financial management, 12 (5), 689–723.
Beatty, A., & Harris, D. (1998). The effects of taxes, agency costs and information asymmetry on earnings man- agement: A comparison of public and private firms. The Review of Accounting Studies, 4 (3/4), 299–326. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009642403312
Ben Slimane, S., Coeurderoy, R., & Mhenni, H. (2022). Digital transformation of small and medium enterprises: A systematic literature review and an integrative framework. International Studies of Management & Organization, 52 (2), 96–120. https://doi.org/10.1080/00208825.2022.2072067
Berle, A., & Means, G. (1932). The modern corporation and private property . Macmillan.
Bhatia, S., & Srivastava, A. (2017). Do promoter holding and firm performance exhibit endogenous relationship? An analysis from emerging market of India. Management and Labour Studies, 42 (2), 107–119. https://doi.org/10.1177/0258042X17714073
Bonardo, D., Paleari, S., & Vismara, S. (2007). The non-linear relationship between managerial ownership and firm performance. Corporate Ownership & Control, 4 (4), 18–29. https://doi.org/10.22495/cocv4i4p7
Brown, L. D., & Caylor, M. L. (2004). Corporate governance and firm valuation. Journal of Accounting and Public Policy, 25 (2), 409–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaccpubpol.2006.05.005
Cai, D., Luo, J. H., & Wan, D. F. (2012). Family CEOs: Do they benefit firm performance in China? Asia Pacific Journal of Management, 29 (4), 923–947. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10490-012-9318-4
Chen, A., Kao, L., Tsao, M., & Wu, C. (2007). Building a corporate governance index from the perspectives of ownership and leadership for firms in Taiwan. Corporate Governance : An International Review, 15 (2), 251–261.
Chen, G., Firth, M., Gao, D. N., & Rui, O. M. (2006). Ownership structure, corporate governance, and fraud: Evidence from China . Journal of corporate finance, 12 (3), 424–448.
Chen, X., Kim, J. B., Wang, S. S., & Xu, X. (2007a). Firm performance and the ownership of the largest shareholder. Corporate Ownership and Control, 4 (3), 126–138. https://doi.org/10.22495/cocv4i3p11
Chen, X., Harford, J., & Li, K. (2007b). Monitoring: Which institutions matter? Journal of Financial Economics, 86 , 279–305.
Cheng, T. Y., & Lai, H. C. (2016). Ownership structure, organization stability and biotechnology company performance. Investment Management and Financial Innovations, 13 (2), 109–116. https://doi.org/10.21511/imfi.13(2).2016.12
Claessens, S., Djankov, S., Fan, J. P. H., & Lang, L. H. P. (2002). Disentangling the incentive and entrenchment effects of large shareholdings. Journal of Finance, 6 , 2741–2771.
Clarke, T. (1998). The stakeholder corporation: A business philosophy for the information age. Long Range Planning, 31 (2), 182–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0024-6301(98)00002-8
Cronqvist, H., & Fahlenbrach, R. (2009). Large shareholders and corporate policies. Rev. Financ. Stud., 22 , 3941–3976.
Demsetz, H., & Lehn, K. (1985). The structure of corporate ownership: Causes and consequences. Journal of Political Economy, 93 (6), 1155–1177.
Demsetz, H., & Villalonga, B. (2001). Ownership structure and corporate performance. Journal of Corporate Finance, 7 (3), 209–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0929-1199(01)00020-7
Escobar, D. R. O., & Escobar, E. S. O. (2022). Oil and its influence on the creation of a sustainable society: A systematic literature review. Intangible Capital, 18 (3), 402–429. https://doi.org/10.3926/ic.1833
Fama, E. F., & Jensen, M. C. (1983). Agency problems and residual claims. The Journal of Law and Economics, 26 (2), 327–349. https://doi.org/10.1086/467038
Fauzi, F., & Locke, S. (2012). Board structure, ownership structure and firm performance: A study of New Zealand listed-firms. Asian Academy of Management Journal of Accounting and Finance, 8 (2), 43–67.
Fazlzadeh, A., Hendi, A. T., & Mahboubi, K. (2011). The examination of the effect of ownership structure on firm performance in listed firms of Tehran stock exchange based on the type of the industry. Interactional Journal of Business and Management, 6 (3), 249–267.
Fooladi, M., & Nikzad Chaleshtori, G. (2011). Corporate governance and firm performance. In International Conference on Sociality and Economics Development (ICSED 2011), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, June . 17–19.
Frijns, B., Gilbert, A., & Reumers, P. (2008). Corporate ownership structure and firm performance: Evidence from the Netherlands. Corporate Ownership and Control, 6 (2), 382–392.
García-Meca, E., & Sánchez-Ballesta, J. P. (2011). Firm value and ownership structure in the Spanish capital market. Corporate Governance: The International Journal of Business in Society, 11 (1), 41–53. https://doi.org/10.1108/14720701111108835
Gaur, S. S., Bathula, H., & Singh, D. (2015). Ownership concentration, board characteristics and fIrm performance: A contingency framework. Management Decision, 53 (5), 911–931. https://doi.org/10.1108/MD-08-2014-0519
Gedajlovic, É., & Shapiro, D. (1998). Management and ownership effects: Evidence from five countries. Strategic Management Journal, 19 (6), 533–553. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1097-0266(199806)19:6
Gough, D., & Elbourne, D. (2002a). Systematic research synthesis to inform policy, practice, and democratic debate. Social Policy and Society, 1 , 225–236.
Gough, D., & Elbourne, D. (2002b). Systematic research synthesis to inform policy, practice and democratic debate. Social Policy and Society, 1 (3), 225–236. https://doi.org/10.1017/S147474640200307X
Hartzell, J. C., Sun, L., & Titman, S. (2014). Institutional investors as monitors of corporate diversification decisions: Evidence from real estate investment trusts. Journal of Corporate Finance, 25 (2), 61–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcorpfin.2013.10.006
Han, K. C., & Suk, D. Y. (1998). The effect of ownership structure on firm performance: Additional evidence. Review of Financial Economics, 7 (2), 143–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1058-3300(99)80150-5
Holderness, C. G. (2009). The myth of diffuse ownership in the united states. Review of Financial Studies, 22 , 1377–1408. https://doi.org/10.1093/rfs/hhm069
Hess, K., Gunasekarage, A., & Hovey, M. (2008). State-dominant and non-state-dominant ownership concentration and firm performance: Evidence from China. International Journal of Managerial Finance, 6 (4), 264–289. https://doi.org/10.1108/17439131011074440
Irina, I., & Nadezhda, Z. (2009). The relationship between corporate governance and company performance in concentrated ownership systems : The case of Germany. Journal of Corporate Finance, 4 (12), 34–56. https://doi.org/10.17323/j.jcfr.2073-0438.3.4.2009.34-56
International Conference on Sociality and Economics Development (ICSED 2011). Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, June 17-19, 2011, International Proceedings of Economics Development and Research (IPEDR) vol.10, International Association of Computer Science and Information Technology Press (IACSIT Press), Singa
Jensen, M. C. (1986). Agency Costs of Free Cash Flow, Corporate Finance, and Takeovers. The American Economic Review, 76 (2), 323–329. http://www.jstor.org/stable/1818789
Jensen, M. C. (2000). Theory of the Firm : Governance, Residual Claims, and Organizational Forms . Cambridge: Harvard University Press
Jensen, M., & Meckling, W. H. (1976). Theory of the firm: Managerial behavior, agency costs, and ownership structure. Journal of Financial Economics, 3 , 305–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-405X(76)90026-X
Kajola, S. O. (2008). Corporate governance and firm performance : The case of Nigerian listed firms. European Journal of Economics, Finance and Administrative Sciences, 14 (14), 16–28.
Kao, M. F., Hodgkinson, L., & Jaafar, A. (2019). Ownership structure, board of directors and firm performance: Evidence from Taiwan. Corporate Governance (Bingley), 19 (1), 189–216. https://doi.org/10.1108/CG-04-2018-0144
Kapopoulos, P., & Lazaretou, S. (2007). Corporate ownership structure and firm performance: Evidence from Greek firms. Corporate Governance: An International Review, 15 (2), 144–158. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8683.2007.00551.x
Karaca, S. S., & Ekşi, İH. (2012). The relationship between ownership structure and firm performance: An empirical analysis over İstanbul Stock Exchange (ISE) listed companies. International Business Research, 5 (1), 172–181. https://doi.org/10.5539/ibr.v5n1p172
Laporšek, S., Dolenc, P., Grum, A., & Stubelj, I. (2021). Ownership structure and firm performance–The case of Slovenia. Economic Research-Ekonomska Istrazivanja . https://doi.org/10.1080/1331677X.2020.1865827
Lauterbach, B., & Vaninsky, A. (1999). Ownership structure and firm performance: Evidence from Israel. Journal of Management and Governance, 3 , 189–201.
Le, T. V., & Chizema, A. (2011). State ownership and firm performance: Evidence from the Chinese listed firms. Organizations and Markets in Emerging Economies, 2 (2), 72–90. https://doi.org/10.15388/omee.2011.2.2.14282
Lee, S. (2008). Ownership structure and financial performance: Evidence from panel data of South Korea. Corporate ownership and Control, 6 (2), 254–267.
Lepore, L., Paolone, F., Pisano, S., & Alvino, F. (2017). A cross-country comparison of the relationship between ownership concentration and firm performance: Does judicial system efficiency matter? Corporate Governance: The International Journal of Business in Society, 17 (2), 321–340. https://doi.org/10.1108/cg-03-2016-0049
Li, K., Lu, L., Mittoo, U. R., & Zhang, Z. (2015). Board independence, ownership concentration and corporate performance—Chinese evidence. International Review of Financial Analysis, 41 , 162–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.irfa.2015.05.024
Liang, C.-J., Lin, Y.-L., & Huang, T.-T. (2011). Does endogenously determined ownership matter on performance? Dynamic evidence from the emerging Taiwan market. Emerging Markets Finance and Trade, 47 (6), 120–133. https://doi.org/10.2753/REE1540-496X470607
Liberati, A., Altman, D. G., Tetzlaff, J., Mulrow, C., Gøtzsche, P. C., Ioannidis, J. P., et al. (2009). The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: Explanation and elaboration. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, 62 (10), e1–e34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2009.06.006
Lins, K. V. (2003). Equity ownership and firm value in emerging markets. The Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis, 38 (1), 159. https://doi.org/10.2307/4126768
Manawaduge, A. S., & De Zoysa, A. (2013). The structure of corporate ownership and firm performance: Sri Lankan evidence. Corporate Ownership and Control, 11 (1), 723–734. https://doi.org/10.22495/cocv11i1c8art3
Mang’unyi, E. E. (2011). Ownership structure and corporate governance and its effects on performance: A case of selected banks in Kenya. International Journal of Business Administration , 2 (3), 2. https://doi.org/10.5430/ijba.v2n3p2
Masood, F. C. (2011). Corporate governance and firm performance. International Conference on Sociality and Economic Development, 10 , 484–489.
Massaro, M., Dumay, J., & Guthrie, J. (2016). On the shoulders of giants: Undertaking a structured literature review in accounting. Accounting, Auditing & Accountability Journal, 29 (5), 767–801. https://doi.org/10.1108/AAAJ-01-2015-1939
McConnell, J. J., & Servaes, H. (1990). Additional evidence on equity ownership and corporate value. Journal of Financial Economics, 27 (2), 595–612. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-405x(90)90069-c
Millet-Reyes, B., & Zhao, R. (2010). A comparison between one-tier and two-tier board structures in France. Journal of International Financial Management and Accounting, 21 (3), 279–310. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-646x.2010.01042.x
Mitton, T. (2002). A cross-firm analysis of the impact of corporate governance on the East Asian financial crisis. Journal of financial economics, 64 (2), 215–241.
MoIlah, A. S., & Talukdar, M. B. U. (2007). Ownership structure, corporate governance, and firm’s performance in emerging markets: Evidence from Bangladesh. The International Journal of Finance, 19 (1), 4315–4333.
Morck, R., Shleifer, A., & Vishny, R. W. (1988). Management ownership and market valuation: An empirical analysis. Journal of Financial Economics, 20 , 293–315.
Mrad, M. (2015). Post-privatisation ownership structure and firm performance: What is the matter? International Journal of Monetary Economics and Finance, 8 (1), 85–108. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJMEF.2015.069171
Mugobo, V. V., Mutize, M., & Aspeling, J. (2016). The ownership structure effect on firm performance in South Africa. Corporate Ownership & Control, 13 (2), 461–464. https://doi.org/10.22495/cocv13i2c2p7
Nakano, M., & Nguyen, P. (2013). Foreign ownership and firm performance: Evidence from Japan’s electronics industry. Applied Financial Economics, 23 (1), 41–50. https://doi.org/10.1080/09603107.2012.705425
Nor, F. M., Shariff, F. M., & Ibrahim, I. (2010). The effects of concentrated ownership on the performance of the firm : Do external shareholdings and board structure matter ? Jurnal Pengurusan, 30 , 93–102.
NurulAfzan, N., & Rashidah, A. (2011). Government ownership and performance of Malaysian government-linked companies. International Research Journal of Finance and Economics, 61 , 42–56.
Nuryanah, S., & Islam, S. M. N. (2011). Corporate governance and performance: Evidence from an emerging market. Malaysian Accounting Review, 10 (1), 17–42.
Obiyo, O. C., & Lenee, L. T. (2011). Corporate governance and firm performance in Nigeria. IJEMR, 1 (4), 1–12.
Ongore, V. O. (2011). The relationship between ownership structure and firm performance : An empirical analysis of listed companies in Kenya.
Petticrew, M. (2001). Systematic reviews from astronomy to zoology: Myths and misconceptions. British Medical Journal, 322 , 98–101. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.322.7278.98
Petticrew, M., & Roberts, H. (2008). Systematic reviews in the social sciences : A practical guide. John Wiley & Sons.
Qin, Z., & Deng, X. (2009). Ownership structure and performance in family businesses at early development stage : Evidence from China. Corporate Ownership and Control, 7 (1), 135. https://doi.org/10.22495/cocv7i1p13
Queiri, A., Madbouly, A., Reyad, S., & Dwaikat, N. (2021). Corporate governance, ownership structure and firms’ financial performance: Insights from Muscat securities market (MSM30). Journal of Financial Reporting and Accounting, 19 (4), 640–665. https://doi.org/10.1108/JFRA-05-2020-0130
Rashid, M. M. (2020). Ownership structure and firm performance: The mediating role of board characteristics. Corporate Governance (Bingley), 20 (4), 719–737. https://doi.org/10.1108/CG-02-2019-0056
Rumsfeld, Donald (2011). Known and Unknown: A Memoir. New York: Penguin Group. p. xiii. http://slate.msn.com/id/2081042
Rusmin, R., Evans, J., & Hossain, M. (2012). Ownership structure, political connection and firm performance: Evidence from Indonesia. Corporate Ownership and Control, 10 (1), 434–443. https://doi.org/10.22495/cocv10i1c4art4
Saleh, A. S., Halili, E., Zeitun, R., & Salim, R. (2017a). Global financial crisis, ownership structure and firm financial performance: An examination of listed firms in Australia. Studies in Economics and Finance . https://doi.org/10.1108/SEF-09-2016-0223
Saleh, M., Zahirdin, G., & Octaviani, E. (2017b). Ownership structure and corporate performance: Evidence from property and real estate public companies in Indonesia. Investment Management and Financial Innovations, 14 (2 (contin.1)), 252–263. https://doi.org/10.21511/imfi.14(2-1).2017.10
Sanda, A., Mikailu, A. S., & Garba, T. (2005). Corporate governance mechanisms and firm financial performance in Nigeria. xxx, xxx(xxx), 1– 47.
Sanda, A. U., Mikailu, A. S., & Garba, T. (2010). Corporate governance mechanisms and firms’ financial performance in Nigeria. Afro-Asian Journal of Finance and Accounting, 2 (1), 22–39
Setia-Atmaja, L. Y. (2009). Governance mechanisms and firm value: The impact of ownership concentration and dividends. Corporate Governance: An International Review, 17 (6), 694–709. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8683.2009.00768.x
Shleifer, A., & Vishny, R. W. (1986). Large shareholders and corporate control. Journal of Political Economy, 94 (3), 461–488. https://doi.org/10.1086/261385
Shleifer, A., & Vishny, R. W. (1997). A survey of corporate governance. Journal of Finance, 52 (2), 737–783. https://doi.org/10.2307/2329497
Sun, Q., Tong, W. H., & Tong, J. (2002). How does government ownership affect firm performance? Evidence from China’s privatization experience. Journal of Business Finance & Accounting, 29 (1–2), 1–27.
Tsegba, I. N., & Achua, J. K. (2011). Does ownership structure affect firm performance? Evidence from Nigerian listed companies. Corporate Ownership and Control , 9 (1–5), 503–513. https://doi.org/10.22495/cocv9i1c5art2
Vincent, O. O. (2011). The relationship between ownership structure and firm performance: An empirical analysis of listed companies in Kenya. African Journal of Business Management, 5 (6), 2120–2128.
Wahla, K., Shah, S. Z. A., & Hussain, Z. (2010). Impact of ownership structure on firm performance evidence from non-financial listed companies at Karachi Stock Exchange. International Research Journal of Finance and Economics , 84 (3), 6–13. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJBM2014.7611
Ward, C., Yin, C., & Zeng, Y. (2018). Institutional investor monitoring motivation and the marginal value of cash. Journal of Corporate Finance, 48 , 49–75.
Vroom, G. & Mccann, B.T. (2009). Ownership structure, profit maximization and competitive behavior : Working paper series, IESE business school university of Navarra.
Warokka, A., Abdullah, H. H., & Duran, J. J. (2012). Ownership structures and firm performance : does East Asian corporate governance’s recovery work. World Review of Business Research, 2 (1), 18–35.
Weir, C., Laing, D., & McKnight, P. J. (2002). Internal and external governance mechanisms: Their impact on the performance of large UK public companies. Journal of Business Finance & Accounting, 29 (5–6), 579–611. https://doi.org/10.1111/1468-5957.00444
Weiss, C., & Hilger, S. (2012). Ownership concentration beyond good and evil: Is there an effect on corporate performance? Journal of Management & Governance, 16 (4), 727–752. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10997-011-9170-9
Welch, E. (2003). The relationship between ownership structure and performance in listed Australian companies. Australian Journal of Management, 28 (3), 287–305. https://doi.org/10.1177/031289620302800304
Yammeesri, J., Lodh, S. C., & Herath, S. K. (2006). Influence of ownership structure and corporate performance precrisis: Evidence from Thailand. International Journal of Electronic Finance, 1 (2), 181–199. https://doi.org/10.1504/ijef.2006.010315
Zeitun, R., & Al-kawari, D. (2012). Government Ownership, Business Risk, Financial Leverage and Corporate Performance: Evidence from GCC Countries. Corporate Ownership & Control, 9 (3), 123–131. https://doi.org/10.22495/cocv9i3art10
Zeitun, R., & Tian, G. G. (2007). Does ownership affect a firm’s performance and default risk in Jordan? Corporate Governance, 7 (1), 66–82. https://doi.org/10.1108/14720700710727122
Zraiq, M. A. A., & Fadzil, F. H. B. (2018). The impact of ownership structure on firm performance: Evidence from Jordan. International Journal of Accounting, Finance and Risk Management, 3 (1), 1–4. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ijafrm.20180301.12
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Commerce, Maharshi Dayanand University, Rohtak, 124001, India
Sanjana Bhakar, Priti Sharma & Sanjiv Kumar
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study from inception to the end. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were simultaneously performed equally by the authors.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Priti Sharma .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
“As we know, there are known knowns. There are things we know we know. We also know there are known unknowns. That is to say, we know there are some things we do not know. But there are also unknown unknowns, the ones we don’t know we don’t know.”- Donald Rumsfeld, 2002.
Please see Table 3 .
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Bhakar, S., Sharma, P. & Kumar, S. Ownership Structure and Firm Performance: A Comprehensive Review and Empirical Analysis. J Knowl Econ (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-024-01893-1
Download citation
Received : 31 May 2023
Accepted : 26 February 2024
Published : 04 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-024-01893-1
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Systematic literature review
- Content analysis
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

CS 224C Final Project Details
Stanford / spring 2024.
The final project is the main assignment of the course. Projects are required to be related in a reasonable way to at least one of the central topics of the course or related to other social science topics via the lens of computation. Final projects can be done in groups of 1–3 people; in our experience, groups of 3 lead to the best outcomes, so we encourage you to form a team of that size. Each project team will be assigned a mentor (a member of the teaching team), who will provide feedback on all their project-related work and generally be available.
Submission Format
The literature review, experiment protocol, and final paper must use the ACL submission format and abide by all the ACL requirements except where we have specified otherwise.
1. Literature Review: Due Apr 25th, 23:59pm PT
- General problem/task definition : What are these papers trying to solve, and why?
- Concise summaries of the articles : Do not simply copy the article text in full. We can read them ourselves. Put in your own words the major contributions of each article.
- Compare and contrast : Point out the similarities and differences of the papers. Do they agree with each other? Are results seemingly in conflict? If the papers address different subtasks, how are they related? (If they are not related, then you may have made poor choices for a lit review...). This section is probably the most valuable for the final project, as it can become the basis for a literature review section. .
- Future work : Make several suggestions for how the work can be extended. Are there open questions to answer? How do the papers relate to your final project idea?
- References section : The entries should appear alphabetically and give at least full author name(s), year of publication, title, and outlet if applicable (e.g., journal name or proceedings name). Beyond that, we are not picky about the format. Electronic references are fine but need to include the above information in addition to the link.
2. Experiment Protocol (Due May 14, 23:59pm PT)
Required sections:
- Research Questions : A statement of the project's core research questions.
- Data : A description of the dataset(s) that the project will use for either the analyses or evaluations.
- Methods or Approaches : A description of the methods or approaches that you'll be using, and a preliminary description of the approach that will be the focus of your investigation. At this early stage, some aspects of these approaches might not yet be worked out, so preliminary descriptions are fine.
- General Reasoning or Discussion : An explanation of how the data and approach come together to help answer or evaluate your core research questions.
- Summary of Progress : what you have been done, what you still need to do, and any obstacles or concerns that might prevent your project from coming to fruition.
- References : In the same format as for literature review.
3. Final Paper (Due Friday Jun 7, 23:59pm PT)
The final paper should be 8 pages long, in ACL submission format and adhering to ACL guidelines concerning references, layout, supplementary materials, and so forth. We'll provide additional guidance on writing up final papers. The course readings include many exceptionally good examples of NLP+CSS papers in this format.
There are two required paper sections that are special to our course:
Ethical Consideration : Please write an explicit discussion section of any potential ethical issues, such as around the ethical implication of the project, the use of the data, and potential applications of your work. Here are some recommendations from ACL's ethics guideline : "Ethical questions may arise when working with a variety of types of computational work with language, including (but not limited to) the collection and release of data, inference of information or judgments about individuals, real-world impact of the deployment of language technologies, and environmental consequences of large-scale computation."
- Authorship statement : At the end of your paper (after the 'Acknowledgments' section in the template), please include a brief authorship statement, explaining how the individual authors contributed to the project. You are free to include whatever information you deem important to convey. For guidance, see the second page, right column, of this guidance for PNAS authors (p. 12). We are requiring this largely because we think it is a good policy in general. This statement is required even for singly-authored papers, because we want to know whether your project is a collaboration with people outside of the class. Only in extreme cases, and after discussion with the team, would we consider giving separate grades to team members based on this statement.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The literature review uncovered 20 distinct design elements commonly discussed in research that affect user engagement. They were (1) organization - is the website logically organized, (2) content utility - is the information provided useful or interesting, (3) navigation - is the website easy to navigate, (4) graphical representation ...
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays).
3. Zotero. A big part of many literature review workflows, Zotero is a free, open-source tool for managing citations that works as a plug-in on your browser. It helps you gather the information you need, cite your sources, lets you attach PDFs, notes, and images to your citations, and create bibliographies.
Explore their websites for current information and learn about conferences and key scholars in the field to add to your search. Intute - page of research websites collected and maintained by a consortium of university libraries in the U.K. Example: Intute listing of Rhetoric websites. Although the Intute site stopped being updated in July 2011 ...
Literature Review A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources that provides an overview of a particular topic. Literature reviews are a collection of the most relevant and significant publications regarding that topic in order to provide a comprehensive look at what has been said on the topic and by whom.
As mentioned above, writing your literature review is a process, which I'll break down into three steps: Finding the most suitable literature. Understanding, distilling and organising the literature. Planning and writing up your literature review chapter. Importantly, you must complete steps one and two before you start writing up your chapter.
Find the right journal for your literature review using actual data; Discover literature review examples and templates; We'll also provide an overview of all the products helpful for your next narrative review, including the Web of Science, EndNote™ and Journal Citation Reports™. 1. Don't miss a paper: tips for a thorough topic search
A literature review is an integrated analysis-- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question.That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
A review and consolidate research on effective design and a short list of elements frequently used in research is defined to help designers and researchers to operationalize best practices for facilitating and predicting user engagement. Proper design has become a critical element needed to engage website and mobile application users. However, little research has been conducted to define the ...
The design elements mentioned most frequently in the reviewed literature were navigation, graphical representation, organization, content utility, purpose, simplicity, and readability. We discuss how previous studies define and evaluate these seven elements. This review and the resulting short list of design elements may be used to help ...
Join the 250,000+ researchers, students, and professionals using Litmaps to accelerate their literature review. Find the right papers faster. Get started for free!
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications .For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively .Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every ...
Linux distributions generally come with a free web browser, and the most popular is Firefox. Two Firefox plugins that are particularly useful for literature reviews are Unpaywall and Zotero. Keep reading to learn why. 3. Unpaywall. Often one of the hardest parts of a literature review is gaining access to the papers you want to read for your ...
Find reviews. Option 1 -. Run your search in the database. Limit the results to review or literature review - often found under Document type. Option 2 -. If there is no option to limit to reviews try adding the word "review" to your search. Go to the Advanced search of the database. Enter your search terms.
Jewish American Literature. The Language of American Jewishness: On Delmore Schwartz, Grace Paley, and the Duties of Freedom. By Lily Meyer April 2, 2024 Poetry. Sight and the Sacred: 7 New Poetry Books to Read This April. By David Woo April 2, 2024 In Conversation.
As a topic searc hed on the Web of Science, E commerce has 17.945 papers between 2010 and 2020. However, 8.482 (47,3%) of these papers are articles that constitute the sample of this study ...
Using MAXQDA as your literature review software enables you to employ a vast range of procedures for the quantitative evaluation of your material. You can sort sources according to document variables, compare amounts with frequency tables and charts, and much more. Make sure you don't miss the word frequency tools of MAXQDA's add-on module ...
A literature review is a comprehensive analysis and evaluation of scholarly articles, books and other sources concerning a particular field of study or a research question. This process involves discussing the state of the art of an area of research and identifying pivotal works and researchers in the domain. The primary purpose of a literature ...
Writing Literature Review: Useful Sites; Citation Resources; Other Academic Writings; Literature Reviews: Useful Sites. The majority of these sites focus on literature reviews in the social sciences unless otherwise noted. For systematic literature reviews, we recommend you to contact directly your subject librarian for help.
Review the most influential work around any topic by area, genre & time. Paper * Patent Grant Clinical-Trial. Web. Expert · Past Year Past 5 Years ALL · LLM Expand Tweak. Web. Try: style transfer · covid vaccine · more | ask questions · text rewriter · review by venue.
I tend to use what I call a bootstrapping method for doing literature reviews. I start with a paper that is relevant to the topic area. I then work backwards and forwards from that paper. I pull all the relevant papers that the paper cites and use a website (doesn't really matter which one) to find all the relevant papers that cite the paper.
To conduct a systematic literature review, a search strategy is created to identify the related literature (Annexure Table 3). To attain this objective, the authors have used two authentic and popular databases, i.e. Scopus and Web of Science. These two databases were searched for the extraction of documents from which 387 articles from Scopus ...
1. Literature Review: Due Apr 25th, 23:59pm PT. This is a short paper (4~5 pages, excluding references) summarizing and synthesizing several papers in the area of your final project. As noted above, 8 pages is the maximum allowed length. Groups of one should review 5 papers, groups of two should review 7 papers, and groups of three should review 9.
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in children is characterized by difficulties in social communication and restricted repetitive behavior patterns. Music therapy appears to have beneficial effects in the area of social interaction and communication. The aim of this systematic literature review is to investigate the effectiveness of music therapy programs on the development of social communication ...
The present PRISMA-guided article systematically reviews the current state of research on the autonomous sensory meridian response (ASMR). A systematic literature search was conducted in Pubmed, SCOPUS, and Web of Science (last search: March 2022) selecting all studies that conducted quantitative scientific research on the ASMR phenomenon. Fifty-four studies focusing on ASMR were retrieved ...