

Your Contact Details
Back to blog home.

101 Must-Know Transition Phrases for Engaging Presentations Online
By Paola Pascual on Jan 17, 2024 1:43:00 PM
Giving presentations is often feared by many professionals, but if the presentation is online and you're not a native speaker, things get even trickier. One tip to make things easier? Learn useful phrases to help you navigate your presentation. In this article, you will find lots of helpful resources to give remarkable presentations . Listen to the episode above, download the checklist below, and learn some of the phrases we present. If we missed any, tell us in the comments below.
General vocabulary for presentations
Sometimes, the smallest changes in your presentations can make the biggest differences. One of them is to learn a few phrases that give you confidence during your speech. Here are some important verbs to get you started:
- To highlight
- To emphasize
- To walk you through (*very common in business presentations!)
- To send around
- To carry on (similar to continue)
- To get carried away
- To sum up (similar to summarize )
- To focus on
Vocabulary to start your presentation
Learn how to powerfully start your presentation with these 4 simple steps. Here's some vocabulary you can use:
Welcome your audience
- Good morning/afternoon/evening everyone. Thank you for joining us today, and welcome to today's webinar.
- Hello everyone, I’m very happy to be speaking with you today.
Introduce yourself
- My name is Susan, and I’m part of the design team here at Globex Corporation.
- First of all, a little bit about my background - I am the Team Lead at [Company], and I've been in charge of [your main responsibility] for [X] years.
- I'd like to tell you a bit about myself - my name is Eve I'm the Operations Manager here at [Company].
Introduce the topic and goal of the presentation
- Today, I'd like to talk about…
- This presentation will take about [X] minutes, and we will discuss...
- We've allocated [X] minutes to this presentation. and I'll talk about...
- I'd like to give you a brief breakdown of...
- I'd like to take this opportunity to talk about...
- The main goal of this presentation is…
- The purpose of this presentation is...
- My objective today is...
Read these 5 tricks the best public speakers use to captivate their audience .
Addressing questions from the audience
- If you have any questions about anything, feel free to interrupt.
- If anything isn't clear, please click on the 'raise hand' button and I'll do my best to answer your question.
- I'd be happy to answer your questions at the end of the presentation.
- If you have any questions, please kindly wait until the end to ask them. We will have [X] minutes for a Q&A session at the end.
- Since today's audience is considerably large, we will not have time for questions, but please email me at [email protected]
Learning new English words is not easy, but you can achieve effective communication through practice and repetition. If you are a Talaera student, visit the Library to practice your vocabulary for presentations. If are not part of the Talaera community yet, learn how we can help you here .
Clear out technical issues
- Can everyone hear me well? Let me know if you encounter any technical difficulties throughout the presentation.
- If you are not speaking, please put yourselves on mute.
- If you feel that the sound quality is poor throughout the presentation, please let me know.
Transition to the main topic of the presentation
- Hi everyone, I think we might still be missing a few people but I’m going to kick things off now so we have time to get through everything.
- All right, let’s dive right in!
- All right, let’s jump right in!
- Let’s get started.
- Let’s kick things off.
- I’m going to talk about
- The purpose/subject of this presentation is
- I’ve divided the presentation into 3 parts: In the first part, ... / Then in the second part, ... / Finally, I’ll go on to talk about...
- Let me begin by looking at...
- Let me start with some general information on...
Vocabulary for the main body of your presentation
Introduce a topic or section.
- Now let’s move to the first part of the presentation,
- We can see 4 advantages and two disadvantages. First,
- On the one hand… On the other hand…
- There are two steps involved. The first step is… The second step is…
- There are four stages to the project.

Transition to a new section
- All right, let’s turn to...
- Now we come to the next point, which is
- Okay so that’s [topic 1], but what about [topic 2]?
- There’s a lot more to talk about, but since we’re pushed for time , let’s move on to [topic 2].
- This leads me to my next point, which is...
Give examples and details
- For example...
- A good example of this is...
- To illustrate this point...
- This reminds me of...
- To give you an example...
- Let me elaborate further on...
Describe visual aids
- As you can see [from this infographic]
- This chart shows
- If you look at this graph, you will see
- From this chart, we can understand how
- Let me show you this [image, graph, diagram]
- On the right/left
- In the middle of
- At the top/bottom of the picture
Emphasize an idea
- This is important because
- I’d like to emphasize that
- We have to remember that
Repeat the same message with different words
- In other words
- To put it more simply
- So, what I’m saying is that
- Let me say that again.
It's easy to get stuck in the middle of a presentation, especially if English is not your mother tongue. Here are +20 Top Tips You Need To Know if you're learning business English .
Finish your presentation and summarize
The end of a presentation, together with the opening, is one of the most important parts of your speech. Read these 5 effective strategies to close your presentation and use the vocabulary below.
- That’s all I want to say for now about [topic].
- To sum up, ...
- This sums up [topic].
- So in a nutshell, ...
- So to recap, ...
- In brief, ...
- To conclude, ...
- I’d like to conclude by emphasizing the main points...
- That's it on [topic] for today. In short, we've covered...
- So, now I’d be very interested to hear your comments.
- And this brings us to the end of this presentation. I hope [topic] is a little clear after today.
- So to draw all that together, ...
Start and navigate the Q&A session
- Thank you for your attention. I hope you found this presentation useful, and I'd be happy to answer any questions.
- Thank you for listening. We now have [X] minutes left. Do you have any questions?
- Thank you for your question, [Name].
- I'm glad you asked.
- That's an interesting question.
- That's a great question, I must say. I'm not 100% sure, but off the top of my head, I can tell you that...
- Are you asking about [topic 1] or [topic 2]?
- Can you please clarify what exactly you mean by [question]? I'm not sure I fully understand.
- I'm afraid I don't have the exact figures at hand, but if you give me your email address at the end, I can follow up with you later.
- Does that answer your question?
- I hope that makes sense. Is that the kind of answer you were looking for?
Take your presentation skills to the next level.

Keep reading about presentation skills:
- 21 Helpful Tips For Remarkable and Outstanding Presentation Skills
- How To Start a Presentation: Follow These 4 Easy Steps
- How To Bring Across Your Main Idea In A Presentation Effectively
- 5 Effective Strategies To End A Presentation
- 6 Public Speaking Tricks To Captivate Your Audience
- How To Do Effective Business Storytelling According To Former Prosecutor
- 8 Little Changes That'll Make A Big Difference With Your Presentations
- 3 Quick Public Speaking Tips For Your Next Presentation
- Your Body Language May Shape Who You Are [TED Talk Lesson]
Talaera Talks - Transcript Episode 5
- Topic : Deliver impactful presentations
- Listen : Spotify , Apple Podcasts , Google Podcasts
- Duration : 22 min.
Intro Welcome to Talaera Talks , the business English communication podcast for non-native professionals. My name is Paola and I am co-hosting this show with Simon. In this podcast, we're going to be covering communication advice and tips to help express yourself with confidence in English in professional settings. So we hope you enjoy the show!
Okay, welcome back for our third episode of Talaera Talks. This is Simon, and I'm joined with Paola. Paola, how are you doing? 0:37 Hi, Simon. I'm great. Happy to do another episode. 0:41 Yeah, absolutely. And Happy Friday. 0:44 Happy Friday! 0:49 So today, our topic: Presenting in English. I'd like to start this episode with a quote I found on Harvard Business Review that I thought was really interesting. It says, "Even native English speakers often anticipate disaster when making presentations. By but for non-native speakers, the anticipatory and situational anxiety associated with their unique challenges (these challenges - being understandable, choosing the right words, speaking spontaneously), can be overwhelming. Moreover, if these concerns interfere with your willingness or ability to make business presentations, the impact can be career-limiting." So yeah, that's a pretty kind of heavy quote to start. But it is something that we see from a lot of our clients, right? 1:52 Yeah, it's super interesting. It was super interesting to read. It's something we know, but it's important to remind it that it is presentations, the topic we have today is something that is not pleasurable for anyone, not for non-native speakers, but also for native speakers. So that's something to point out. And today, we talked about that... We said that we wanted to start with those challenges or fears that we see from our clients, our learners. 2:25 Yeah, and it's usually around the same things, you know, we, at least for me, I come into contact with so many of these, so many of our students who are so competent in their, in their daily lives, what they're doing in their professional lives. And they come to me with these with these fears, like this just general lack of confidence, or imposter syndrome, right? This I don't know if I really deserve to be speaking and, you know, kind of explaining this concept to all these people. 3:05 Mm-hmm. Yes. And also the fear of not being understood, well, they know what I'm saying, well, they understand my accent. There's a lot of worries and concern around accent and our pronunciation expert, Lisa hosted a webinar, actually last week, where she explained that accent matters. But as long as people understand you, it's fine. You don't need to be perfect. Everyone has an accent. So that's also totally fine. 3:37 And this being Yeah, this being one of I think, at least for me, in my experience, one of the most frequently asked for aspects from students. So you know, and just to like, again, just say that this is a challenge for everyone, not just, you know, non-native English speakers. You know, I think all of us have a tough experience or somebody that we think of when we think about public speaking, it's, it's like this, yeah, really anxiety-riddled thing. I mean, I don't have any, you know, funny personal stories, but uh, do you, Paola? 4:20 You want me to tell my embarrassing story, don't you? 4:22 Please, you must. 4:25 So I used to teach at a university in Vietnam when I lived there, and the classes where it rains, you know, from perhaps 50 students to up to what 300 there's was a class with, you know, 2-300 students and there was a little stage it wasn't too high, but there was a little stage and I fell off. 4:46 You fell off the stage. This was during or after the presentation, or...? 4:56 It was around the beginning of the presentation. So... 5:01 During! Oh, I thought it was it was like after like you were walking off? 5:06 No, I move a lot. I use my body language quite a lot. And that was one of the moments where I overdid it, probably, and fell off. 5:17 Wow. Well, I'm glad that you're still here with us. 5:21 Yeah, you know, but that's the story that I sometimes not always tell it. But I sometimes tell it when my students say, Oh, I'm nervous, and I assume that it can happen, you know, I thought it was going to be a disaster. And then I actually ended up making friends with the students that turned out okay. 5:39 Right. Well, yeah, I mean, today, we're not necessarily going to go into the physical dimensions of how to avoid falling off the stage. But we do have some, some good tips, right? 5:54 Yes. And to provide some advice on how to deliver presentations, and lose that fear, we've divided it into three main blocks. And those are what to do before the presentation, tips for during the presentation. And then even after there's things you can do to, to get better. 6:18 Right, let's start with the first, right, what can we do before the presentation in terms of getting ready, preparing? 6:30 So preparing, it's a very general term, but one of the tips that we like to give is, think of the WHAT, WHY and NEXT. So WHAT is your presentation about? WHY should they listen to you and not look it up online (or listen to a podcast, like ours)? And in what NEXT means - what is supposed to happen next? Do they need to do anything, go on a website, send you feedback? Are you going to send them the materials? So what why our next is so straightforward and simple. But when I asked this question to our clients that are so thrown off, and they don't know what to answer sometimes, 7:10 Yeah, I think that's one of those things. And I struggle with this all the time is, when I get an idea or something like that. It's so easy to just jump over those most basic things of, you know, what, why and index, those are so, so basic, but it's such it's, they're so foundational, right? And in terms of creating something that people will understand and be able to, to really attach to. 7:41 Yep. And do you have any tips around how much you should learn? Should you write the whole thing? Or should you memorize? 7:52 Yeah, that, you know, this is a good question as well, that a lot of our learners ask in terms of, yeah, you know, I'm just going to go and write it all out. And then I'll have an idea. And I'll feel better because I can write it and change it so that it sounds more professional. It sounds like I know what I'm talking about. And I always tell people, please don't try to prepare a presentation where you're reading a script, it is just the most unnatural thing ever. And, and it, you won't end up sounding more professional, if anything, your audience is going to detach, because they're going to sense that something's not really right here, it doesn't seem genuine, right doesn't seem real, it just seems like this person is doing what he's doing, which is reading off of a script. And even still a lot of times with a lot of our learners where they know that, okay, I know this material. But I'm going to put all of my effort into making this perfect slide this perfect presentation. So I would say, focus on actually knowing the material itself really well. More than focusing on how the presentation looks, you know, these kinds of things. Because once you're in that situation where you're on the stage, and people are looking at you, at least you'll be able to Windows like kind of red Sirens of you know, panic and anxiety show up. You'll have learned the material itself so well that you can roll with that. 9:29 Yes. And you also have room for improvisation because your brain is so used to the content and you know, so well what you want to say that that's when your brain starts to come up with anecdotes and that's the fun thing that gets you hooked. And that's the main Why should people listen to you instead of reading an article online? 9:49 Exactly. Because for most of our students, you know what you're talking about. That's why you're up there. That's why you have the opportunities to speak there is because someone thinks you're qualified enough to speak to all these people. So trust in that and go with that. So yeah, so we have right not, not over learning. Don't script it right? What else can we do? 10:14 Practice, practice, practice, practice, practice in your mind, but more importantly verbalize it, say it out loud. And recording yourself is uncomfortable for everyone. But it works. I have never tried it. I always told my students should record yourself, you should record yourself and they were like, Huh. And just a few of them did it. And when we started with the webinars, I haven't done something like it before. And I said, Okay, I'll use my own tip. And it was one I'm comfortable. And two, super helpful. So if you get to go over the sound of your own voice, I would say do it. 10:54 Yeah. You know, this is one thing that I have to be totally honest here. Doing these podcasts is the first time I've actually recorded myself for a long time. And I've learned a lot about, you know, not saying the word Absolutely. 500 times, yeah, within the span of 20 minutes. So those are good learning lessons. Definitely. Okay, and then so we have that. And then the last little tip is, I would say get an English mindset before 30 minutes to an hour before the presentation. And that could be listening to a podcast, you know, like Talaera Talks, or, you know, watching a show on Netflix that's, that's in English, whatever you can do to get your kind of English mind, you know, in the zone before you go up and actually speak English. So So those are all of our kind of pre presentation tips, what you can do before, so what about during, 11:58 so for during, there's a lot of things that you can you can do to improve your presentations. But the first tip is to learn how to start to have a mind map of what am I going to do at the beginning. So you start confident already. So welcome, everyone, introduce the people introduce the topic and go to the main point, those four parts will help you have a nice start. Welcome, everyone. For example. Hi, everyone. Welcome to today's presentation. Today, we'll be talking about business events, introduce the people, you can introduce yourself , like, Hi, my name is Paula and I'm a business English instructor at Telstra, and perhaps even the audience. Today we have with us students from all different nationalities and levels, or, you know, whatever the audiences, that's also helpful for everyone to understand, introduce the topic, or give you some best practices for business emails , and a few templates, and then go to the main point. So a simple sentence like Alright, let's get down to business. So having those welcome introducing people introducing the topic and going to the main point will help you have a nice start. 13:16 Yeah, and I like that concept of that the mind map is so good. Because it's it's not the scripting, like we were talking about before, it's having a kind of a little mental checklist. So that when those first few minutes, were you're up there on the on stage, and you're like, oh god, oh, god, here we go. Here we go. You have that little checklist that I created. Okay, so I welcomed introduced the people the topic, and now to the main point, and that can get you in the zone and going I really liked that. Yeah, so so having that, that starting template. And then another thing would be, I would say slowing down, slowing it down. And this is really I think it touches on a lot of aspects. The first would be just the general anxiety, we tend to speak a lot faster when we're really anxious, you know, but by slowing down, it really helps with non native English speakers because it helps with the accent. And it helps with giving you some time to really think through your next thoughts. Now, I'm not saying that you should, while you're speaking, try to think steps three, four or five ahead of you. But giving yourself a little bit of time to Okay, I'm going through this pattern now. Now I can go to the next one, right. And doing that, you know, another with the slowing down a tip if you're really nervous to go in is prefacing your speech. So before you really get into everything, maybe after the welcome part is just to say, Hey, you know, I'm going to try to speak as clearly as possible, as English as myself. first language and really smile and maybe make a little joke about that. And I think that's a good way to open it out for the audience to show some vulnerability and and help. I mean, what do you think about that? 15:13 Yeah, I mean, we see that with, sometimes with celebrities, when they're not native speakers, and they admitted, and they, they kind of put yourself put themselves, as you said, in that vulnerable position, and that makes them even cuter. 15:28 Mm hmm. 15:29 So it's making yourself human, I think it's always a good tip. And you were saying that slowing down helps with your accent and also for yourself to gain time to really know what you're going to say. But also for the for the audience. We don't mind people making some little pulses, so that they also have time to collect their thoughts. 15:50 Right, right. Yeah. Yeah, definitely. Those are, those are two really good aspects, starting, you know, the template and then slowing down, right. Yeah, kind of diffusing the anxiety by saying, Hey, you know, this isn't my first language. And that really gets the audience on your side, right. And then another would be not reading off of your slides. I mean, this is kind of the basic, you know, what you learn in school, but it's also something that a lot of people get, yeah, get, get hooked on, just because it's like a safety net. And I would say that's where the overlearning the material that we talked about beforehand comes into play. Anything else in this? 16:42 Oh, recap for sure. After every section, do a little recap, and at the end to recap where you summarize the main points of the whole presentation? 16:54 Yeah, yeah. Good. Good. So So summarize. Yeah, yeah. And that's a that's a good, you know, I would say three aspects, four aspects that during the presentation, if you keep these in, in your mind, it's, it's, I would say, it's going to help a lot. And so now we're going to move to what can we do after the presentation? We've done it, we've walked off the stage. Whoo, I'm so glad that's over. Now, is all of our work done? No. 17:27 No, not really. That's now it's your chance to actually learn from, from everything you did. So one of the tips we suggest is try to ask for feedback. But that's not so easy, right, Simon? 17:42 Yeah, it's, I think, a big question. And that is, who do you get the feedback from? Right?

17:50 So we, we would always suggest to try and find someone you can trust someone who is honest, and who can give you objective feedback. So in some cases, that can be your manager, but sometimes it's a colleague that understands the topic, and can really provide some feedback on how you did. 18:13 Yeah. And that's, I think, in terms of learning, this is one of the most crucial thing is reflecting back on what you did, and seeing what worked, what didn't work, and how can I take that and move forward? Because especially with presenting, it's a skill, and it takes practice, practice, practice. And, and I think, for a lot of people, you should jump at the chance to do this. So that you can continue to learn and continue to grow. But be sure to reflect by Yeah, by asking for feedback and seeing what worked, 18:47 for sure. And ideally, that would be someone, perhaps from work that can see how you did and like the actual show, if not Talaera teachers also do that. So you can present your own presentation, pretending it's the actual one. And that's how we can provide feedback on the structure, the vocabulary, the language in general. 19:08 Yeah, absolutely. I do that. Oh, there you go. Absolutely. Definitely. See, I'm reflecting back and learning as we go. I'm working. I'm learning that. Yeah. But I've done that recently with a couple of students where we've gone through their deck and looked at what are their plans in terms of presenting and we've kind of gone through in detail that together. So So yeah, so that was kind of I would say the biggest thing in terms of afterward. 19:40 So we have the pre-presentation, just as a quick recap for the pre-presentation and before your presentation, always remember the what why next, what is your presentation about? Why should people listen to you and what should happen next overnight Learn the content. be super confident about what you want to talk about. But don't script it. Don't write everything down. Otherwise, it would sound like you're just reading. 20:11 Write and practice through verbalization. record yourself, even though it may be awkward, but it's a great learning technique. And then get in that English mindset beforehand by Yeah, listening to a podcast or what have you. And then during the presentation, right, starting with the template, Paolo was discussing the welcome introducing the people the topic, and then going to the main point, 20:37 slowing down a little bit. It's not necessary to go super fast. It's not only not necessary, but people will understand you better if you take your time and make some pauses. Of course, don't read off their slides. Tell them the story. 20:54 Right, right. And remember 20:56 to recap, just like we're doing now. Send them or tell them a quick summary and the main points, 21:03 right, and don't fall off the stage as well. That's ideally we forgot. Ideally, it's final for then, as the final point, right, asking for feedback, finding that person that can get you that feedback that's so important to you. Finding what worked and moving forward. 21:21 That's right. All right. Do we have it for today? 21:25 I think that is it for today. Yeah. I had a lot of Thanks. Yeah, I had a blast. And thanks for meeting up. And we have a lot of good stuff coming up with Talaera. Right. 21:38 We have webinars, our blog is busier than ever. So go on the http://blog.talaera.com/ , check out the resources. And what else? 21:51 Find us on LinkedIn. And yeah, please ask any questions, we'd be glad to get back to you. So that is it for today. And thank you to all of our listeners. So far, we're excited to keep growing this. And as always, keep learning! 22:11 And that's all we have for you today. We hope you enjoyed it, and remember to subscribe to Talaera Talks . We'll be back soon with more! And visit our website at https://talaera.com for more valuable content on business English. You can also request a free consultation on the best ways for you and your team to improve your communication skills. So have a great day and keep learning!

Share this with a friend:
Explore our Business English Programs
Contact [email protected]
Made with ❤️ in New York City — Talaera © 2017–2024
Learn a language with our own teacher, anytime

35 Powerful Presentation Phrases in English for Engaging Your Audience
Your palms are sweating.
For a moment, your mind goes blank.
All eyes are on you.
That moment right before you start presenting – as you take in your audience – is usually the scariest. The nervousness lessens with practice, but even the most frequent public speakers still get butterflies in their stomach sometimes. Whether you’re facing an entire room of people or looking at everyone through your laptop screen, giving a presentation can still be intimidating – or exciting, once you move beyond the fear.
There’s an extra layer of challenge too if you have to speak in your non-native language. For a more professional-sounding and engaging presentation, we’ve compiled some of the most useful English presentation phrases below.
We’ll also explore what else you can do to make even more of an impact on your audience. With the right intonation, body language, and gestures, you’ll really be able to catch their attention and emphasize your points.
If this sounds interesting to you, you should check out the Creativa business meeting mastery course . There’s an entire video episode about giving a stunning presentation. You’ll learn about how to structure your ideas, deliver a report, and conclude a discussion. It covers not only fluent native phrases but also body language demonstrations that you can apply to your work right away.
On top of this, the course has plenty of other engaging, high-quality video episodes that help you present your best self in English. Curious about it? You can access a free video here .
Delivering a Powerful Presentation
To lay the groundwork for your presentation in English, here’s what you’ll have to do first:
Consider the audience
You’re probably always going to need slides, but every presentation will be different – and the audience that you’ll be presenting to won’t always find the same points interesting. Because of this, you’ll have to tailor your message to them. What style of presentation would be a good fit? For example, some audiences would want to see a lot of number-crunching, while others might be looking for more personal storytelling .
Prepare a structure
Structure is key in presentations. People have short attention spans, and they can be forgetful. At the end of the day, your goal is for them to remember at least the main points in your presentation. What message do you want to convey? Since you might be discussing a lot of information, you can make it more digestible by ensuring that there’s a logical progression and then ending with a summary.
Whatever your topic is, it’ll benefit from having a well-defined structure to guide your audience from start to finish. For a cheat sheet on this, scroll down here to download a free PDF worksheet with exercises about structuring your presentation so you can be clear and convincing. This way, you can have a presentation that’s strong in all sections – beginning, middle, and end.
Key Business Phrases
Once you’ve decided on the style and message of your presentation, you can take it up a notch by including certain English presentation phrases all throughout. Let’s break it down from start to finish:
Introduction
This is when you’ll be warming up your audience before you proceed to your main points.
Greeting the audience
If you’re presenting to people who aren’t too familiar with you, you can quickly introduce yourself and mention your role or company.
- Good morning, everyone. I’m glad to be able to present to all of you.
- Hello, everyone! It’s nice to see all of you today. I’m [name], the [position] from [company].
Describing your topic
After greeting the audience, you’ll be explaining to them what your presentation is all about. To set their expectations, you might show them an outline of the talk and mention if there’ll be any activities such as breakout discussions.
- I’ll be talking about…
- I’ll be talking about our financial metrics over the past year.
- The topic of this presentation will be…
- The topic of this presentation will be major trends in the logistics industry.
- I’ll be discussing first the [first topic], next [second topic], and finally [third topic].
- I’ll be discussing first the project’s ideation process, next our initial trial, and finally, presenting our results.
Addressing questions and technical concerns
People might be wondering if they can ask questions during your presentation, so you can clarify this at the start. If you’re providing handouts or presenting online, it’s useful to ask people to alert you about any technical concerns.
- Please feel free to ask any questions during the talk.
- For questions, there will be a Q&A section at the end.
- Can all of you see and hear me properly? Please let me know if you have any technical difficulties during the presentation.
The body will make up the bulk of your presentation. Ideally, you would go through each of your points logically while letting your audience know when you’re moving on to the next section.
The longer your presentation, the more important it is to use sequencing phrases. These act as cues that let your audience know where you are in the presentation. You can think of these as similar to detour signals that make the audience much more likely to get your meaning.
- First, let’s discuss the…
- First, let’s discuss the initial spark for this idea.
- Moving into [the next item / point] …
- Moving into item 4, we can see that this is a major pain point for our target market.
- This leads us to the next…
- This leads us to the next section, where we’ll be looking at the facts and figures.
Linking is closely related to sequencing. Similar to writing, you can have a smoother presentation by connecting your ideas rather than suddenly jumping from one point to another. You can also refer back to points that you’ve mentioned before to make your presentation more cohesive.
- In connection to what I said earlier…
- In connection to what I said earlier about growing our online presence, we can now look into potential social media campaigns.
- What this means is…
- What this means is that most of our growth is coming from a certain sector. Let’s analyze the data for this in the next section.
- This ties in with…
- This ties in with our survey findings about user reactions. I’ll go into detail about changes we’ve made to the app as a result.
Giving examples
To fully convey your point, you can bring up specific examples and case studies. These are much more memorable as well as engaging because you can tell these in the form of a story.
- For example…
- For example, costs were reduced significantly when we switched to the following materials.
- To demonstrate this point…
- To demonstrate this point, I’ll be showing you a video of a business that used this problem-solving method.
- Here’s an example of…
- Here’s an example of a seasonal product that our customers loved.
Showing visuals
Visuals naturally attract people’s attention. If you’re using slides for your presentation, take the opportunity to include images, diagrams, infographics, or even charts.
- As you can see from this…
- As you can see from this photo, we’ve redesigned our office space.
- Here’s a diagram / picture / chart that shows…
- Here’s a diagram that shows a high percentage of people are comfortable with online shopping.
- If you look at this…
- If you look at this infographic, you can see that the new color palette comes off as fun and casual.
Citing data
Citing data from research makes your presentation more persuasive. When you’re talking about results that you’ve achieved, try to bring up actual numbers – this can go a long way towards impressing your audience.
- According to this study…
- According to this study from [journal], 65% of eCommerce companies are looking for more efficient payment methods.
- Based on our research…
- Based on our research, the most enthusiastic buyers of wellness products in this city are in the 20 to 30 age range.
- Looking at the data…
- Looking at the data, you’ll notice that there’s been an 18% spike in sales since we migrated our platform.
Restating an idea
Sometimes you’ll want to restate an idea so it’s easier to understand. This also serves to emphasize it. Because of the repetition, people are more likely to remember it compared to if you’d only mentioned it once.
- In other words…
- In other words, partnering up with this client can make our operations more efficient and seamless.
- Another way of saying this is…
- Another way of saying this is that there might actually be more demand than supply by next year.
- What I mean is…
- What I mean is we’re already more than halfway to our business objective.
Handling technical issues
When you’re presenting on video call, all kinds of glitches can happen. Someone might have connection issues, you might have to figure out an app feature you’ve never used before, or background noises might keep interrupting your call. The phrases below can be very handy in these kinds of situations.
- If you can’t hear me, can you type in the chat, please?
- Could everyone mute their mic? There’s a lot of background noise.
- Sorry. The call dropped. I’m back through.
Concluding the Presentation
By this time, the hardest part is already over! Still, you’ll have to wrap up your presentation nicely by going over the key takeaways during the conclusion. Your audience might also have questions that they’ll want you to address.
Summarizing the presentation
Out of everything that you’ve discussed, what would you like people to get out of it? A short summary towards the end serves to highlight your main ideas.
- To wrap up…
- To wrap up, I’d like to point out three major takeaways.
- As a summary…
- As a summary of this report update, I would say we have seen a positive uptick in our workflow and productivity.
- All in all…
- All in all, we believe we’ve seen good results for this stage of our progress.
Thanking the audience
Similar to your greeting at the start, it’s common to address your audience again towards the end by thanking them for their time.
- Thank you for listening!
- Thank you to everyone for being here.
- I’d like to thank you all for coming here.
Addressing questions
If you’re open to questions from your audience, you can have a short question-and-answer session after your presentation.
- Do you have any questions or clarifications?
- Feel free to ask me about any of the points I made during the presentation.
- Let me know if you have any questions.
Practice is Crucial
When you’re all set with the content of your presentation, the next step is to practice your delivery. Regardless of how well you know the topic of your presentation, practicing it at least once will help you be more confident. You’ll discover potential issues that you can fix too before you go live.
Do a run-through
The most basic way to practice is to do a run-through of your entire presentation . Set a timer on your phone, open up your slides, then start talking – all while imagining that you’re already presenting to your audience. Since you’re acting as if it’s in real-time, this means avoiding any pauses where you have to look up information.
A run-through can pinpoint any weaknesses in your presentation, and you’ll notice any parts where you might be uncomfortable talking. You’ll also be able to see how much time you’ve spent so you can pace yourself accordingly.
Record yourself
A more intensive version of the run-through basic would be to record yourself presenting. You can either record your voice or take a full video of yourself. People often notice that they use filler words a lot such as “um” or “uh.” You’ll also be able to check your pronunciation and whether you sound confident and natural all throughout.
Since body language can make or break your delivery, watching a video of yourself presenting is an incredibly effective way to improve your performance. Do your facial expressions match what you’re saying? Are you maintaining good posture throughout and making efforts to connect with the audience?
When you combine a confident, approachable body language with the right business vocabulary, your ideas shine through better than ever. You can get a play-by-play of how exactly to do this with the Creativa business meeting mastery course . It features video sections that are all about making powerful transitions and expressing your points clearly during presentations. You’ll learn about specific native English phrases and gestures so you can move fluidly from one idea to the next.
Together with the other episodes, the course dives deep into how you can be a strong communicator during professional meetings. For a preview, check out this free episode .
Presenting on Video Call
Technical issues happen often enough in face-to-face presentations, but they’re even more frequent during video calls. To avoid any awkward delays when you’re presenting, get comfortable with the platform that you’ll be using.
If it’s a face-to-face presentation, double-check your slides and make sure any images or videos are showing properly. For video calls, try doing a test call on the app or even call up a friend to practice. You can also get familiar with the app’s basic features, such as screen-sharing or inviting people to breakout rooms.
But sometimes, even when you’ve practiced your presentation perfectly on video call, the unexpected can still happen. Scroll down here to download a free worksheet that we made precisely for dealing with technical issues in presentations. You’ll get an extensive list of English phrases to use for all sorts of video call glitches, along with practical tips for handling them in the moment. With enough preparation, you’ll be able to roll with surprises and conquer even video call presentations.
Let’s explore some of the most common glitches (and how you can deal with them gracefully!):
Situation 1: You’re having a hard time hearing other people because of their laggy connection.
For a presentation to work, everyone needs to have a decent internet connection. If someone’s connection drops, they won’t be able to see or hear you properly, and you won’t understand what they’re trying to say, either. In this case, let them know right away that you can’t hear them. You can also ask them to talk to you over chat instead.
Example Phrases:
- [Name], you’re cutting in and out. Would you mind reconnecting?
- Audio problems – can you type it on chat instead?
Situation 2: You get disconnected from the call.
In the case that it’s your connection that’s faulty, you might have to disconnect then reconnect your call. This can be awkward because it interrupts the flow of your presentation. Alerting your audience using certain English phrases can reassure them while getting you back on track with what you were saying.
- Sorry, guys, dropped call. But I’m back.
- Connection problems, everyone. Gonna log out and back in.
Situation 3: People are having a hard time figuring out how to turn on their audio or video.
Another reason why you’d want to be really familiar with the video platform is you might have to coach people when they experience glitches. It’s almost expected that a few people might accidentally forget to turn on their mic while speaking. Alternatively, they might have issues with turning on their camera.
- I can’t see you, [name]. [Give instructions on how to turn on their video.]
- I can’t see you, Fatima. Look for the camera icon and make sure there’s no red line through it.
- Typing in chat: “Make sure your mic’s unmuted.” [Clarify how they’ll know if they’re unmuted.]
- Typing in chat: “ Make sure your mic’s unmuted. There should be no red lines through it.
The best presentations excel in all three areas: content, structure, and delivery.
Including some of the key English phrases above will upgrade your performance. Aside from setting a professional tone, these English presentation phrases set the pace for your audience so they’re aware of where you are in the discussion. Your message will sound clearer, and your audience will be able to follow your ideas better.
The basic rules for presentations are the same, whether you’re on a video call or stepping in front of a stage. With the tips above, you’re all set to prepare an amazing presentation in English.
7 Brilliant Ways to End Any Presentation: When to Use a Presentation Thank You Address
I like building and growing simple yet powerful products for the world and the worldwide web.
Published Date : December 4, 2020
Reading Time :
As important as an introduction is to a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech presentation, the end of your presentation is what you leave your audience with. Giving a proper presentation thank you address is a helpful public speaking skill .
When is it appropriate to simply say “thank you” and close your presentation?
In what moments does a presentation require more from you?
How do you tell your audience to thank you for watching my presentation if you made a visual presentation?
What is the importance of saying thank you to your audience for listening?
We intend to answer all these questions in this article, and we hope you read the whole page to understand the complete concept of the presentation. Thank you.
How Should I End a Presentation? Different Ways of Ending a Speech Or a Presentation
As a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech expert who has attended many presentations and orations, I can tell that each presenter concludes their Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech in different ways. Most speakers will showcase presentation thank you images as a visual aid at the end of a PowerPoint, while others give a summary.
Irrespective of the speaker’s methods, here are seven ways to end a presentation or speech .
1. Closing with a Summary
Summarizing key points of your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech when concluding an oration is an age-old method of finishing your address. It is a technique speakers and writers use to close and ensure their audience remembers their main point.
Using a summary for closure is common with lectures and the traditional presentation thank-you addresses.
2. Closing with the Power of Three
The Power of Three uses a pattern of three words, phrases, or more to emphasize a point and make it more memorable. A typical phrase Julius Caesar uses is “I came, I saw, I conquered.”
3. Closing with Metaphors
Metaphors are a figure of Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech that compares two entities figuratively and makes it seem like they are the same. In basic English Language, the definition of metaphors indicates a form of comparison without using comparative words (for example, like and as).
It is ideal for Motivational speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:374">A <strong>motivational speech</strong> aims to inspire, encourage, and energize an audience. It ignites their passion, sparks action, and instills a sense of belief in themselves and their ability to achieve their goals. It is a powerful tool used in <strong>professional speaking</strong> to boost morale, drive performance, and foster a positive and collaborative environment.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:17"><strong>Key Elements:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-12:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:145"><strong>Compelling vision:</strong> Articulate a clear and inspiring vision for the future, outlining goals and aspirations that resonate with the audience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:140"><strong>Empathy and understanding:</strong> Acknowledge challenges and obstacles, demonstrating empathy and connection with the audience's experiences.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:134"><strong>Empowering message:</strong> Focus on empowering the audience, emphasizing their strengths, potential, and ability to overcome obstacles.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-10:170"><strong>Storytelling and anecdotes:</strong> Integrate relatable stories, personal experiences, or inspiring examples to illustrate points and connect with the audience emotionally.</li> <li data-sourcepos="11:1-12:0"><strong>Call to action:</strong> Provide a clear and actionable call to action, motivating the audience to take specific steps towards achieving their goals.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="13:1-13:38"><strong>Benefits of Motivational Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="15:1-20:0"> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:116"><strong>Boosts morale and motivation:</strong> Inspires individuals to strive for their full potential and overcome challenges.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:142"><strong>Promotes teamwork and collaboration:</strong> Fosters a shared purpose and encourages individuals to work together towards common goals.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:118"><strong>Enhances confidence and self-belief:</strong> Empowers individuals to believe in themselves and their ability to succeed.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-18:121"><strong>Increases creativity and innovation:</strong> Inspires individuals to think outside the box and pursue innovative solutions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="19:1-20:0"><strong>Drives positive change:</strong> Motivates individuals to take action and contribute to positive change in their personal and professional lives.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="21:1-21:46"><strong>Developing a Powerful Motivational Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="23:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:96"><strong>Define your purpose:</strong> Identify the desired outcome you want your speech to achieve.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:119"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Understand their motivations, challenges, and aspirations to tailor your message effectively.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:134"><strong>Focus on storytelling:</strong> Use compelling stories and anecdotes to illustrate your points and connect with the audience emotionally.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:170"><strong>Practice and rehearse:</strong> Hone your delivery to refine timing, vocal variety, and stage presence. Consider using <strong>public speaking tips</strong> to enhance your presentation.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Deliver with passion and authenticity:</strong> Inject your enthusiasm and genuine belief in your message to inspire the audience.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:20"><strong>Additional Tips:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:123"><strong>Use humor strategically:</strong> Use humor appropriately to lighten the mood and connect with the audience on a deeper level.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:121"><strong>Embrace your personality:</strong> Let your unique personality shine through to create a genuine and captivating connection.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:121"><strong>End with a memorable closing:</strong> Leave the audience with a powerful quote, inspiring call to action, or lasting image.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Seek </strong>feedback from trusted colleagues or advisors to refine your speech and delivery.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:371"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="36:1-36:371">A well-crafted and delivered <strong>motivational speech</strong> can be a transformative experience for both the speaker and the audience. By understanding the key elements, focusing on your audience, and honing your <strong>professional speaking</strong> skills, you can deliver speeches that ignite passion, inspire action, and empower individuals to achieve their full potential.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/motivational-speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">motivational speech presentations and graduation speeches . This type of closing works perfectly if you use an analogy, anecdote, or reference to the comparative subject during your presentation.
4. Using Facts to Recreate Engagement
Some of the most memorable Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech presentations end with things that regain the audience’s attention. If you search Google, you will find facts related to your discussion and share them to surprise your audience.
5. Using an Illustration or Image
Similar to metaphors, you can finish with stories or use an illustration to close. This method is quite common because many orators can use it to start and end their speeches.
Visual aids are essential to help drive your point across when you present, and you can also use them to close effectively.
6. Closing with a Quote or a Short Sentence
If you can condense your summary to a less wordy, short sentence, it tends to leave a longer-lasting impression on your listeners. It is essential to ensure that the short message conveys your authenticity and the importance of your message.
Using a quote is a timeless way to conclude any type of Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech or presentation. However, it is essential to have a quote relevant to your address; if not, you can make a quote out of a point you made while presenting.
7. Making a Provocative Closing
Closing provocatively uses calls to action to move your audience toward a particular goal. An example of this type of conclusion is usually observed with preachers, activists, and advertisers.
Many preachers make altar calls at the end of their sermons, and activists usually end with a wake-up call to move the audience to action.
What is the Best Way to End a PowerPoint Presentation?
PowerPoint presentations take a lot of time and can take an audience almost no time to forget. Figuring out how to make a strong closing will help give your audience something to remember.
The way you close each ppt depends on the nature of your discussion.
Closing a Persuasive PPT
Your thank you note for the presentation after a persuasive PowerPoint should win the members of your audience over. To convince them ultimately, you can include:
- A call-to-action
- Verified facts
Closing an Informative PPT
Informative PPTs share data, so the ideal closure for them is a presentation thank-you images that show:
- A summary of all the ideas you shared
- A conclusive concept map
- Bulleted key points
- A recap of the objectives of the presentation
Closing an Introductory PPT
The general concept of introductory Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech presentations is to:
If you give an initial pitch, the best presentation thank you images will give your audience a proper means to contact you or follow up on your next program.
Note: When concluding any PowerPoint, your thank you for watching my presentation slide will naturally need to follow the same pattern as the entire PPT. It is also helpful if you are creative with the presentation. Thank you.
The General Importance of Saying Thank You
Saying thank you means expressing gratitude for an action completed or a gift. In any setting, your ability to express gratitude, irrespective of whether or not you deserved the service you got, goes a long way.
Some advantages of expressing gratitude include:
What is the importance of presenting thank you images?
As a part of the audience, after listening to a speaker talk all day, especially when you can leave but stay, a minute presentation thank you would suffice.
It’s no secret that some presenters do not say thank you after their Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech , so what do you gain by thanking your audience?
- It helps you reinforce already established values.
- Strengthens speaker-audience relationships.
- Serves as a foundation for trust.
- Stimulates conversation by question and answer strategies.
- It makes you unique in numerous places.
How to Say Thank You at the End of Your Presentation: Simple Tips and Tricks
Saying thank you is not only about expressing gratitude. Often, saying thank you is a business strategy, and presenting thank you images must prove their worth for your business.
Some simple pointers to remember are:
- Remain professional
- Avoid grammatical errors as much as possible.
- Try not to seem salesy; instead, be polite.
- Employ perfect timing
Using the Right Voice Tone
Every type of presentation setting demands a specific tone type. You will need to adjust your tone to avoid being misunderstood.
Personalize It and Try to Maintain Relevance
It is rather rude to use a copy-and-paste post-presentation thank you message. Instead, it’s best to make a unique, personalized thank-you note that is audience-specific.
Additionally, it’s best to remain within the subject matter for the conclusion by sharing relevant information.
Ask Questions and Answer Previous Ones
If you have any questions before the presentation, it is best to answer them now. If you used an “any questions slide,” you can also answer questions from there.
When your time starts finishing, and you cannot answer any more questions, try to provide contact details or follow up with their concerns.
Practice the perfect end to your presentation with Orai
When to Use and When to Avoid a Thank You Presentation Slide
Using tact is a vital tool when facing Public Speaking <!-- wp:paragraph --> <p>Public speaking refers to any live presentation or speech. It can cover a variety of topics on various fields and careers (you can find out more about public speaking careers here: https://orai.com/blog/public-speaking-careers/. Public speaking can inform, entertain, or educate an audience and sometimes has visual aids.</p> <!-- /wp:paragraph --><br /><!-- wp:paragraph --> <p>Public speaking is done live, so the speakers need to consider certain factors to deliver a successful speech. No matter how good the speech is, if the audience doesn't connect with the speaker, then it may fall flat. Therefore, speakers have to use a lot more nonverbal communication techniques to deliver their message. </p> <!-- /wp:paragraph --><br /><!-- wp:heading --> <h2>Tips for public speaking</h2> <!-- /wp:heading --><br /><!-- wp:list --> <ul> <li>Have a sense of humor.</li> <li>Tell personal stories that relate to the speech you're giving.</li> <li>Dress appropriately for the event. Formal and business casual outfits work best.</li> <li>Project a confident and expressive voice.</li> <li>Always try to use simple language that everyone can understand.</li> <li>Stick to the time given to you.</li> <li>Maintain eye contact with members of your audience and try to connect with them.</li> </ul> <!-- /wp:list --> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/public-speaking/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">public speaking opportunities. Knowing when it is okay to share a thank you presentation slide and when it isn’t necessary is essential.
Some of the times when saying thank you for listening to my presentation is appropriate and essential are:
- When you have an audience that shows up voluntarily, it is essential to express gratitude.
- If you are expressing gratitude to your team for putting in hard work
- If your audience needed to travel to attend your presentation
On the other hand, there are some situations when presentation thank you images are either inappropriate or unnecessary:
- If you plan to answer questions after your presentation or host an interactive session, presentation thank you images will prompt your audience to leave the meeting.
- If your presentation has terrible news, a presentation thank you will be insensitive and inappropriate.
- When you need to assign a task or follow up on anything, it’s better to end with that than a thank you slide.
Potential Alternatives to a Presentation Thank You Image
Ending with a simple presentation, thank you, is often seen as a weak presentation. It is usually best to complete your presentation creatively or using a call-to-action.
So, in what ways can you effectively end your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech using visual aids without needing to use presentation thank you images?
Using a “One More Thing” Slide
This type of presentation thank you option introduces (for lack of a better term) the final bomb or the hidden gem. For example, if you were introducing a new product, your one more thing slide would probably show an unexpected benefit of purchasing the product to woo your audience.
This type of slide is inappropriate for every presentation, so you will have to consider the nature of your audience when inputting this idea.
A Slide that Continues the Conversation
This type of ending could feature a form of presentation thank you that continues the discussion. It may be a bunch of arguments that gear your audience’s communication with each other or with you.
Ideally, you will need to provide them with contact information so they can communicate with you after you finish. If you are searching for new prospects for partnership or employment, this is the best slide to include such details.
Closing with “Any Questions?”
This type of closing is the most common aside from the mainstream presentation thank you images. As I stated earlier, it isn’t appropriate to include a presentation thank you if you hope to continue any discussion.
Asking for questions boosts audience engagement and serves as a memory aid so they remember your presentation. However, it isn’t uncommon to have no one asking you questions while you present.
If you want to avoid the awkwardness of an unanswered no-questions slide, here are some things you can try:
- Asking the first question yourself is an icebreaker.; your inquiry has the potential to open room for more questions
- Ask a friend in the audience to break the ice with the first question.
- Asking your audience to prepare for questions in advance by providing them with the necessary materials
- Distributing pre-presenting writing material to the audience to motivate them to write down questions they might have had during your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech so that you can answer them effectively.
Practice your presentations with Orai. Get feedback on your tone, tempo, Confidence <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:305">In the context of <strong>public speaking</strong>, <strong>confidence</strong> refers to the belief in one's ability to communicate effectively and deliver one's message with clarity and impact. It encompasses various elements, including self-belief, composure, and the ability to manage one's <strong>fear of public speaking</strong>.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:16"><strong>Key Aspects:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-12:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:108"><strong>Self-belief:</strong> A strong conviction in your knowledge, skills, and ability to connect with your audience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:95"><strong>Composure:</strong> Maintaining calmness and poise under pressure, even in challenging situations.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:100"><strong>Assertiveness:</strong> Expressing your ideas clearly and concisely, avoiding hesitation or self-doubt.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-10:104"><strong>Positive self-talk:</strong> Countering negative thoughts with affirmations and focusing on your strengths.</li> <li data-sourcepos="11:1-12:0"><strong>Strong body language:</strong> Using gestures, posture, and eye contact that project confidence and professionalism.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="13:1-13:27"><strong>Benefits of Confidence:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="15:1-19:0"> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:99"><strong>Reduced anxiety:</strong> Feeling confident helps manage <strong>fear of public speaking</strong> and stage fright.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:133"><strong>Engaging delivery:</strong> Confident speakers project their voices, hold eye contact, and connect with their audience more effectively.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:137"><strong>Increased persuasiveness:</strong> A confident presentation inspires belief and motivates your audience to listen and remember your message.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-19:0"><strong>Greater impact:</strong> Confidently delivered speeches leave a lasting impression and achieve desired outcomes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="20:1-20:15"><strong>Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="22:1-26:0"> <li data-sourcepos="22:1-22:112">Overcoming <strong>fear of public speaking</strong>: Many people experience some level of anxiety when speaking publicly.</li> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:101"><strong>Imposter syndrome:</strong> Doubting your abilities and qualifications, even when objectively qualified.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:92"><strong>Negative self-talk:</strong> Internalized criticism and limiting beliefs can hamper confidence.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-26:0"><strong>Past negative experiences:</strong> Unsuccessful presentations or negative feedback can erode confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="27:1-27:24"><strong>Building Confidence:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="29:1-36:0"> <li data-sourcepos="29:1-29:102"><strong>Practice and preparation:</strong> Thoroughly rehearse your speech to feel comfortable with the material.</li> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:101"><strong>Visualization:</strong> Imagine yourself delivering a successful presentation with confidence and poise.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:100"><strong>Positive self-talk:</strong> Actively replace negative thoughts with affirmations about your abilities.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:106"><strong>Seek feedback:</strong> Ask trusted individuals for constructive criticism and use it to improve your skills.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:157">Consider a <strong>speaking coach</strong>: Working with a coach can provide personalized guidance and support to address specific challenges and confidence barriers.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-34:114"><strong>Start small:</strong> Gradually increase the size and complexity of your speaking engagements as you gain experience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="35:1-36:0"><strong>Focus on progress:</strong> Celebrate small successes and acknowledge your improvement over time.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="37:1-37:282"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="37:1-37:282"><strong>Confidence</strong> in public speaking is a journey, not a destination. By actively practicing, embracing feedback, and focusing on your strengths, you can overcome <strong>fear of public speaking</strong> and develop the <strong>confidence</strong> to deliver impactful and memorable presentations.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/confidence/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">confidence , and consciousness to help you get your presentation on point.
Thank You Letters: Taking it A Step Further
Numerous presentations, especially business idea pitching, hardly lead to immediate sales. In such a case, ending with a presentation, thank you, and contact information isn’t enough.
You will need to take it further by sending a thank you letter so they can remind you, mostly if they have already forgotten. So, how do you follow up on a potential client or previous sponsor with a presentation? Thank you.
Elements of a Good Thank You Letter
When writing an excellent thank you letter, you must consider elements to ensure that your recipient reads it and carries out the appropriate action.
You do not require a soothsayer to tell you that people do not read every letter. So, how do you beat the odds and make your message worthwhile? Here are some elements you can include to that effect.
A Strong Subject Line
If you can remember the times you intentionally opened spam mail, I am sure it had something to do with the subject. Most companies treat letters like this as spam and have no reason to read them.
However, if you can create a subject line that clearly states your intentions, you have a better chance of having your mail read.
Clearly Expressed Gratitude
Start the letter by expressing gratitude for attending your presentation and giving you time. You can also include other factors in your message that you need to express gratitude for.
A Summary of Your Presentation
They aren’t likely to have any reason to remember all the points you made during your presentation. Now is the perfect time to remind them and highlight the issues you presented they could have missed.
It’s best to use bullet points to give them room for skim reading. Additionally, if you have reached an agreement, you should include it in the letter for Clarity <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:269">In <strong>public speaking</strong>, <strong>clarity</strong> refers to the quality of your message being readily understood and interpreted by your audience. It encompasses both the content and delivery of your speech, ensuring your message resonates and leaves a lasting impact.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:16"><strong>Key Aspects:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-13:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:133"><strong>Conciseness:</strong> Avoid unnecessary details, digressions, or excessive complexity. Focus on delivering the core message efficiently.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:149"><strong>Simple language:</strong> Choose words and phrases your audience understands readily, avoiding jargon or technical terms unless you define them clearly.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:145"><strong>Logical structure:</strong> Organize your thoughts and ideas logically, using transitions and signposts to guide your audience through your message.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-10:136"><strong>Effective visuals:</strong> If using visuals, ensure they are clear, contribute to your message, and don't distract from your spoken words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="11:1-11:144"><strong>Confident delivery:</strong> Speak clearly and articulately, avoiding mumbling or rushing your words. Maintain good eye contact with your audience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="12:1-13:0"><strong>Active voice:</strong> Emphasize active voice for better flow and avoid passive constructions that can be less engaging.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="14:1-14:24"><strong>Benefits of Clarity:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="16:1-20:0"> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:123"><strong>Enhanced audience engagement:</strong> A clear message keeps your audience interested and helps them grasp your points easily.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:123"><strong>Increased credibility:</strong> Clear communication projects professionalism and expertise, building trust with your audience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-18:111"><strong>Improved persuasiveness:</strong> A well-understood message is more likely to resonate and win over your audience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="19:1-20:0"><strong>Reduced confusion:</strong> Eliminating ambiguity minimizes misinterpretations and ensures your message arrives as intended.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="21:1-21:15"><strong>Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="23:1-27:0"> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:129"><strong>Condensing complex information:</strong> Simplifying complex topics without sacrificing crucial details requires skill and practice.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:128"><strong>Understanding your audience:</strong> Tailoring your language and structure to resonate with a diverse audience can be challenging.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:85"><strong>Managing nerves:</strong> Nerves can impact your delivery, making it unclear or rushed.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-27:0"><strong>Avoiding jargon:</strong> Breaking technical habits and simplifying language requires constant awareness.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="28:1-28:22"><strong>Improving Clarity:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="30:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:117"><strong>Practice and rehearse:</strong> The more you rehearse your speech, the more natural and clear your delivery will become.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:107"><strong>Seek feedback:</strong> Share your draft speech with others and ask for feedback on clarity and comprehension.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:161"><strong>Consider a public speaking coach:</strong> A coach can provide personalized guidance on structuring your message, simplifying language, and improving your delivery.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:128"><strong>Join a public speaking group:</strong> Practicing in a supportive environment can help you gain confidence and refine your clarity.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Listen to effective speakers:</strong> Analyze how clear and impactful others achieve communication.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:250"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="36:1-36:250"><strong>Clarity</strong> is a cornerstone of impactful <strong>public speaking</strong>. By honing your message, focusing on delivery, and actively seeking feedback, you can ensure your audience receives your message clearly and leaves a lasting impression.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/clarity/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">clarity .
Answers to Prior Questions
If they had questions you could not answer while presenting, now is the perfect time to answer them. It is a gesture that shows potential clients that you care about their concerns.
Additionally, you can encourage more questions to keep the conversation going.
A Professional Closing Note
Most people have customized closing remarks that they send with each mail that usually have the following characteristics in small icons:
- Your name and position in the company
- The company’s name (and logo, if possible)
- The company’s website URL
Practice with Orai and become an expert
Final Tips For Thank You Letters and Speeches
Irrespective of how you decide to make your presentation thank you slide, these six tips will help you:
- Include a call to action for your audience.
- Try not to end with questions.
- Refer to the opening message.
- Use anecdotes to summarize.
- Incorporate the rule of three where you can.
- Avoid leaving your audience confused about whether or not your presentation is over.
Examples of Presentation Thank You Letter
Subject line: A follow-up on (topic or product)
Hi (insert name)
Express gratitude: I am grateful you took the time to attend today’s program. (Include gratitude for any other sacrifice they made.
Here is a quick recap (___)
Concerning your questions on ___, here is an attachment with detailed answers. Feel free to ask further questions.
We look forward to hearing from you.
Kind regard,
Business Signature
How should you make a clear call to action to the audience at the end of a presentation?
A powerful presentation ends with a clear, direct call to action. Don’t hope your message inspires action – explicitly tell your audience what you want them to do, why it matters, and its impact. Make it specific, compelling, and relevant, using examples or statistics to drive home the importance. Leave them knowing exactly what steps to take next and the benefits or consequences involved, maximizing your chances of a positive response.
When is it beneficial to ask a rhetorical question at the end of a talk?
Want your talk to linger? End with a powerful rhetorical question! It sparks reflection, reinforces key points, and piques curiosity, leaving your audience captivated long after the presentation ends. Use it to challenge, inspire, and make your message truly unforgettable.
How can you utilize a cartoon or animation to conclude your presentation effectively?
Utilizing a cartoon or animation to conclude your presentation effectively involves integrating visuals that complement your message. Consider incorporating a relevant cartoon that conveys a metaphor or key idea of your presentation. Using humor in the cartoon can also help engage your audience and make your message more memorable. By ending on a visual note, you can leave a lasting impression and reinforce the main points you want your audience to remember.
How should you end a presentation without a “Questions?” slide?
To wrap up a presentation without a designated “Questions?” slide, it is beneficial to encourage audience interaction throughout the presentation by allowing questions to be asked at any point. This ensures that the questions and answers are directly related to the content being discussed. However, if questions are to be fielded at the end of the presentation, a powerful technique is to conclude with a striking image that reinforces and encapsulates the central message or theme addressed during the talk. This visual aid should be a memorable takeaway for the audience, leaving a lasting impression that harmonizes with the presentation’s content. Utilizing this method, you can successfully conclude your presentation on a strong note without needing a specific “Questions?” slide.
Why is it recommended to use a summary slide instead of a “Thank You” slide at the end of a presentation?
Skip the “Questions?” slide! Encourage real-time engagement throughout, then end with a powerful image that resonates with your message. It’ll be a memorable takeaway; no dedicated question slide is needed!
How can quotes and interesting anecdotes be effectively integrated into the conclusion of a speech?
Spice up your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech conclusion: ditch the tired quotes and choose fresh voices relevant to your audience and topic. Share authentic anecdotes that resonate personally, and weave them seamlessly with your reflections for deeper impact. Memorable endings leave audiences thinking long after your final words.
When used as a closing statement, what impact can a short, memorable sentence or sound bite have on the audience?
Short and sweet: Ditch lengthy closings! Craft a concise, magnetic sentence that captures your message. In today’s attention-deficit world, it’ll linger long after your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech , leaving a powerful impression and resonating with your audience. Remember, short and impactful embodies your voice and drive home your key points. Boom!
In what situations is it appropriate to acknowledge individuals or companies at the end of a presentation?
Say thanks! Publicly acknowledging collaborators, data sources, and presentation helpers in research, information use, and preparation scenarios shows respect, professionalism, and gratitude. Use both verbal mentions and presentation software credits for maximum impact. Remember, a little appreciation goes a long way!
How can visual aids, such as a running clock or images, be employed to emphasize key points during the conclusion of a speech?
End with a bang! Use visuals like a ticking clock to build urgency or powerful images to solidify your message. Leave them on display for reflection, letting the visuals do the final talking and ensuring your key points leave a lasting impression.
How can surprising facts be used to re-engage the audience’s attention at the end of a presentation?
Surprise them! When attention fades, drop a shocking fact with stats. Use online resources to find fresh info, keeping sources handy for Q&A. It’ll re-energize them, offering new insights and solidifying your credibility. Boom!
What role can storytelling play in concluding a presentation and engaging the audience?
Storytime! Wrap up with a short, impactful story – personal or relevant to your topic. Think customer experience or a case study with heart. Make it relatable, spark empathy, and tie it back to your key points. Boom – a memorable, engaging ending that sticks!
How can I make my presentation memorable using the “power of three” communication method?
Rule of three! Organize your conclusion in trios: points, examples, and stories. Brains love patterns and threes stick! Memorable, impactful, and resonating – that’s your ending goal. Keep it simple, repeat key points, and leave them with a lasting impression.
How can I effectively end a presentation or speech to leave a lasting impression on the audience?
Nail your ending! Use the power of three: storytelling, surprising facts, or visuals to grab attention. Acknowledge others, craft a short & memorable closing, summarize key points, repeat key messages, and end with energy to inspire action. Leave a lasting impression, not a fade-out!
How can you ensure that your audience understands when your presentation has concluded?
End strong! Rule of three for impact, clear closing cue (no guessing!), confident “thank you,” and wait for applause. No fidgeting, no weak exits. Leave them wanting more, not wondering if it’s over!
Final Notes: Saying Thank You is a Vital Life Skill
As far as life goes, saying thank you properly is essential. Even if you are giving a paid lecture or presentation, thank you notes give your audience a sense of importance for participating in your work process.
An asset every public speaker has after overcoming the fear of Public Speaking <!-- wp:paragraph --> <p>Public speaking refers to any live presentation or speech. It can cover a variety of topics on various fields and careers (you can find out more about public speaking careers here: https://orai.com/blog/public-speaking-careers/. Public speaking can inform, entertain, or educate an audience and sometimes has visual aids.</p> <!-- /wp:paragraph --><br /><!-- wp:paragraph --> <p>Public speaking is done live, so the speakers need to consider certain factors to deliver a successful speech. No matter how good the speech is, if the audience doesn't connect with the speaker, then it may fall flat. Therefore, speakers have to use a lot more nonverbal communication techniques to deliver their message. </p> <!-- /wp:paragraph --><br /><!-- wp:heading --> <h2>Tips for public speaking</h2> <!-- /wp:heading --><br /><!-- wp:list --> <ul> <li>Have a sense of humor.</li> <li>Tell personal stories that relate to the speech you're giving.</li> <li>Dress appropriately for the event. Formal and business casual outfits work best.</li> <li>Project a confident and expressive voice.</li> <li>Always try to use simple language that everyone can understand.</li> <li>Stick to the time given to you.</li> <li>Maintain eye contact with members of your audience and try to connect with them.</li> </ul> <!-- /wp:list --> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/public-speaking/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">public speaking is their ability to express gratitude to their audience for the time they spent listening.
I hope you remember to say thank you creatively!
You might also like
How many words is a 5-minute speech, good attention getters for speeches with 10+ examples, quick links.
- Presentation Topics
Useful Links
- Start free trial
- The art of public speaking
- improve public speaking
- mastering public speaking
- public speaking coach
- professional speaking
- public speaking classes - Courses
- public speaking anxiety
- © Orai 2023
Automated page speed optimizations for fast site performance

NOW AVAILABLE! The Presentation Playbook Series
- Trade Show Presenter
- Testimonials
- Trade Show Staffing
- Sample Videos
- Seminar Speaker
Spark's Presentation & Public Speaking Blog
- 7 Tips to Encourage Audience Questions in Your Presentation Q&A
September 19, 2017
Ever seen a presenter ask “Any questions?” at the end of their presentation, and heard only crickets from the audience?
In my work as a professional emcee and trade show presenter , I see it often, and it always makes me cringe because it’s so awkward, and so completely avoidable.
Asking for questions and getting none kills a presentation’s momentum. It usually goes like this:
- The presenter, having run out of content, asks “Any questions?”
- The audience, having no questions, freezes in place.
- Everyone thinks they hear crickets, though there are none in the room.
- The presenter, getting no questions, says, “OK, I guess I’m done.”
OUCH. How’d that happen?
Chances are, you caught your audience by surprise. They didn’t know you’d take questions, so they didn’t think of any. When you asked, you caught them off guard.
I want your next presentation to end with a bang, not a whimper. So try these tips to encourage questions:
1. PREPPING YOUR Q&A: PRIME YOUR AUDIENCE
> TIP THEM OFF EARLY: As you start your presentation, tell your audience: “I’ll take all your questions at the end, so write down your questions as you think of them along the way.” That’ll get them active thinking of questions throughout your presentation.
> REMIND THEM: A few minutes before you take questions, say: “I’ve got one more slide to cover, then I’ll take your questions.” That’ll remind them to think of some questions if they haven’t yet.
2. STARTING YOUR Q&A: GIVE THEM A NUDGE
> LEAVE ROOM: Starting a Q&A with little or no time left discourages questions; your audience wants to leave on time too! Instead, carve out 5-10 minutes or more for questions (and cut some content to make room if needed; your audience prioritizes the information they want to get over the information you want to share).
> USE A PLANT: Have a “plant” in the audience who’ll ask the first question (one you’re comfortable answering), which encourages other audience members to ask (and saves them the awkwardness of going first) and gives them time to think of something to ask.
> CHANGE YOUR PHRASING: Your audience may interpret the phrase “Any questions?” as a sign that you don’t expect or even want questions, which discourages them from asking. Instead, encourage questions by phrasing your question with a more upbeat, expectant tone: “Who’s got a question?” or “Who’d like to go first?”
> ASK IT YOURSELF: Ask yourself a common question: “One question I get often is…” Then answer it. Again, this encourages the audience to follow suit, and gives them more time to think of a question.
3. ENDING YOUR Q&A: ADD THAT BANG!
Q&A or not, ending your presentation by saying you’re ending your presentation (“OK, I guess I’m done”) will end your presentation with a whimper. You can easily replace that whimper with a “bang” by restating your main takeaway and thanking your audience:
“Folks, I hope my presentation has shown you that when it’s raining and you want to stay dry outside, use an umbrella! You won’t regret it. Thanks so much for your time.”
And thank you so much for your time!
by Andy Saks
Posted in: Sparky Says: Presentation & Public Speaking Tips | No Comments
Add your comment
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
Search Spark’s Blog
Spark news: coming (& recent) attractions.
- Spark booth presenter shines at Las Vegas tech show
- Navy SEAL fundraiser books charity auctioneer Andy Saks
- Boston awards event books Spark master of ceremonies
- Read all Coming (& Recent) Attractions
Sparky Says: Presentation & Public Speaking Tips
- 10 Tips to Boost Donations at Your Fund the Need / Paddle Raise
- 10 PowerPoint Alternatives That Make Your Presentation Memorable
- Read all Sparky Says (Speaking Tips)
Presentation Frequently Asked Questions
- Trade show presenter 101: Your guide to booking a booth presenter (Part 1)
- Sales presentation skills: How much is your pitch actually worth?
- How do I hire the right trade show presenter?
- Read all Presentation FAQ
Spark's Client Success Stories
- Emcee tips: How Spark’s master of ceremonies made AT&T’s awards dinner fun
- Trade show booth ideas: How to get the most value from your presenter
- Trade show booth ideas: Recycle your presentation script
- Read all Spark Success Stories
Spark Presentations
Andy Saks, Owner & Lead Speaker
781-454-7600 | Email | Contact page
Don't miss exclusive Spark deals! Sign up for your Spark e-newsletter today.
- Effective Presentation Skills Tutorial
- Handling Questions and Answers

At the end of your presentation, if it is appropriate for the type of presentation, solicit questions from the audience.
Responding to Audience Questions
When someone is asking a question, make eye contact with that person, listen positively, and acknowledge by saying "thank you for that question," or say "that is an excellent question" or "that is an important question".
If the audience is in a large room and cannot hear each other's questions, repeat the question loudly for everyone to hear, before answering it.
If you know the answer to the question, respond appropriately and briefly so you can take more questions and not spend too much time on one question.
Effective Response to Question
This video clip is an example of a presenter effectively responding to an audience member's question .
Ineffective Response to Question
This video clip is an example of a presenter ineffectively responding to an audience member's question .
If the question is not relevant to the presentation, say something like, "I am really sorry that question is outside the scope of this presentation, but I will be happy to stay after the presentation and discuss it with you."
Effective Response to Off-topic Question
This video clip is an example of a presenter effectively responding to an off-topic question or one in which he or she does not know the answer .
Inappropriate Response to Off-topic Question
This video clip is an example of a presenter inappropriately responding to an off-topic question or one in which he or she does not know the answer .
If time is running out for answering all of the questions, say, "I am sorry. I am running out of time, but I will take one last question, and then I will be available at the end to answer any remaining questions."
If you do not know the answer to a question say, "That is an interesting question, and I will have to get back to you later on that" or ask the audience "Can someone help me with this?" or be gracious and acknowledge you do not know the answer at that time.
If an audience member criticizes or attacks what you had covered in your presentation, do not attack back, but separate the valid criticism from the personal attack, and respond to the criticism appropriately.
Some things not to do during the question and answer period:
- Shuffling papers or technology and not making eye contact with the questioner
- Belittling the questioner
- Calling those who want to ask questions by their physical characteristics
- Not taking questions in the sequence they are asked, but focusing on certain people or a side of the room
Asking Good Questions
If you are in the audience, know also how to ask good questions to indicate that you are following the presentation.
You can ask some general questions about any topic, and you may be genuinely curious about some things presented.
- What were the most challenging aspects, or what surprised you the most, in conducting this project?
- Why did you choose this particular methodology or argument instead of another one?
- How did you collect the data? Were there any problems in collecting data? What was the sample size?
- How did you validate your work? Did you validate with a real problem or situation?
- What are some of the limitations of your work?
- What recommendations do you have for further exploration in this project?
Learning to ask good questions at the end of a presentation demonstrates your active participation.
Previous
Take Quiz
- Preparing for the Presentation
- Organizing the Presentation
- Designing Effective Presentation Materials
- Rehearsing the Presentation
- Delivering the Presentation
- Presentation Skills Quiz
- Presentation Preparation Checklist
- Common Reasons for Ineffective Presentations


52 Phrases for Better Flowing English Presentations
/ Steven Hobson / Business English , English Presentations , Vocabulary

Do you give English presentations at work, but feel that you could communicate your message in a more objective, fluid way?
Maybe you have an English presentation coming up and want to make sure that your speech is clear and structured so that your audience doesn’t lose concentration and stays with you all the way to the end.
A technique that can help you achieve objective, clear, and structured English presentations, is to use linking phrases that join the separate parts of your presentation together.
English presentations normally consist of an introduction, the main body, individual parts of the main body, and the ending or conclusion.
To help maintain your audience’s attention, you need to signal when you are going from one part to another.
In this article, I teach you 52 phrases that do exactly this – linking the different parts together, and therefore, making your presentation flow better. You’ll find that these phrases will act as ‘signposts’ for the audience when you finish one part and start another.

52 Phrases to Improve the Flow of Your English Presentations
The introduction.
All good presentations start with a strong introduction.
There are a number of different ways you can begin your English presentation. Here’s a simple, but effective introduction structure which works for most types of business presentations:
Introduce – Introduce yourself and greet your audience. Introduce the presentation topic – Explain the reasons for listening. Outline – Describe the main parts of the presentation. Question policy – Make it clear to your audience when they can ask questions: during or at the end?
Here are some phrases which you can use to structure the introduction in this way:
1. Good morning/afternoon (everyone) (ladies and gentlemen). 2. It’s a pleasure to welcome (the President) here. 3. I’m … (the Director of …)
Introduce the presentation topic
4. By the end of the talk/presentation/session, you’ll know how to… / …you will have learned about… / 5. I plan to say a few words about… 6. I’m going to talk about… 7. The subject of my talk is…
8. My talk will be in (three parts). 9. In the first part… 10. Then in the second part… 11. Finally, I’ll go on to talk about…
Question Policy
12. Please interrupt if you have any questions. 13. After my talk, there will be time for a discussion and any questions.

Main Body
Now that you have finished the introduction, we now need to transition to the main body, and its individual parts in a smooth way.
There are three parts of the main body of a presentation where linking phrases can be used:
Beginning the Main Body Ending Parts within the Main Body Beginning a New Part
Here are some phrases which you can use for these parts:
Beginning the Main Body
14. Now let’s move to / turn to the first part of my talk which is about… 15. So, first… 16. To begin with…
Ending Parts within the Main Body
17. That completes/concludes… 18. That’s all (I want to say for now) on… 19. Ok, I’ve explained how…
Beginning a New Part
20. Let’s move to (the next part which is)… 21. So now we come to the next point, which is… 22. Now I want to describe… 23. Let’s turn to the next issue… 24. I’d now like to change direction and talk about…
Listing and Sequencing
If you need to talk about goals, challenges, and strategies in your English presentation, listing phrases can help link these together and improve the flow of your speech. If you have to explain processes, sequencing phrases are helpful:
25. There are three things to consider. First… Second… Third… 26. There are two kinds of… The first is… The second is… 27. We can see four advantages and two disadvantages. First, advantages… 28. One is… Another is… A third advantage is… Finally…
29. There are (four) different stages to the process. 30. First / then / next / after that / then (x) / after x there’s y. 31. There are two steps involved. The first step is… The second step is… 32. There are four stages to the project. 33. At the beginning, later, then, finally… 34. I’ll describe the development of the idea. First the background, then the present situation, and then the prospect for the future.
After you have presented the main body of your English presentation, you will want to end it smoothly.
Here are typical sections transitioning from the main body to the ending of the presentation, and then inviting the audience to ask questions:
Ending the Main Body Beginning the Summary and/or Conclusion Concluding An Ending Phrase Inviting Questions and/or Introducing Discussion Thanking the Audience
Ending the Main Body
35. Okay, that ends (the third part of) my talk. 36. That’s all I want to say for now on (the 2017 results).
Beginning the Summary and/or Conclusion
37. To sum up… 38. Ok, in brief, there are several advantages and disadvantages. 39. To conclude… 40. I’d like to end by emphasizing the main points. 41. I’d like to end with a summary of the main points.
42. I think we have seen that we should… 43. In my opinion, we should… 44. I recommend/suggest that we… 45. There are three reasons why I recommend this. First, … / Second, … / Finally,…
An Ending Phrase
46. Well, I’ve covered the points that I needed to present today. 47. That sums up (my description of the new model). 48. That concludes my talk for today.
Inviting Questions and/or Introducing Discussion
49. Now we have (half an hour) for questions and discussion. 50. So, now I’d be very interested to hear your comments.
Thanking the Audience
51. I’d like to thank you for listening to my presentation. 52. Thank you for listening / your attention. / Many thanks for coming.
Linking phrases are like the skeleton which holds your presentation together.
Not only do they improve the flow and help guide the audience, but by memorizing them they can also help you remember the general structure of your presentation, giving you increased confidence.
To help you memorize, I recommend saying the linking phrases on their own from the beginning to the end of your presentation while you practice.
I also suggest memorizing the introduction word for word. By doing this, you will get off to a great start, which will settle your nerves and transmit a positive first impression.

Author: Steven Hobson
Steven is a business English coach, a certified life coach, writer, and entrepreneur. He helps international professionals build confidence and improve fluency speaking English in a business environment.
Related posts

2 Success Principles for Achieving Your English Goals

How to Improve Your Understanding of Native Speakers

How to Speak English with Confidence
The Art of Question & Answer: Handling Audience Questions Like a Pro
Hrideep barot.
- Presentation , Public Speaking

If you have ever given a presentation , you might know how witty and challenging a question-and-answer session can get. Not knowing the answer to a question can be quite unnerving and leave a bad impression even after a fabulous presentation. This blog will help you bridge that gap before your next presentation. We will talk about how to maintain your composure as you deal with questions and also the different types of difficult questions one can face.
Why should I have a Question-and-answer session?
Having a Question and Answer (Q&A) session serves multiple valuable purposes. It transforms one-sided communication into a two-way exchange, turning lectures or speeches into engaging discussions. This interaction not only enhances audience engagement but also promotes collaboration and the collective building of knowledge. Historically, great questions have driven innovation and change, such as Isaac Newton’s curiosity about gravity. During a Q&A , encouraging audience participation by inviting questions and making eye contact with various attendees creates a sense of connection and keeps the session lively, much like a talk show host engaging their audience.
Including a question and answer (Q&A) session after your presentation holds numerous advantages and is a pivotal aspect of engaging with your audience effectively.
Let’s delve into these reasons:
1. audience engagement and participation: .
Inviting questions at the end of your presentation allows your audience to actively participate, transforming your session into an interactive experience. As Albert Einstein aptly put it, “The important thing is not to stop questioning.”
2. Addressing Confusion and Skepticism:
Your presentation might leave some audience members perplexed or unconvinced. Before you begin, it’s vital to gauge your audience’s understanding. As Aristotle noted, “Rhetoric may be defined as the faculty of observing in any given case the available means of persuasion.” Q&A provides an excellent opportunity to clarify doubts and bolster your argument.
3. Expanding on Your Message:
Often, time constraints force you to condense crucial information during your presentation. Q&A, however, empowers you to elaborate on your points, share practical examples, and address any opposition, creating a more comprehensive understanding. This aligns with Robert Frost’s sentiment: “Education is the ability to listen to almost anything without losing your temper or your self-confidence.”
4. Fostering Natural Interaction:
Effective public speaking thrives on interaction. Audiences seek speakers who communicate openly and naturally. Q&A brings a conversational and relatable dimension to your presentation. As Maya Angelou wisely said, “I’ve learned that people will forget what you said, people will forget what you did, but people will never forget how you made them feel.”
5. Challenging Your Expertise:
The unpredictability of Q&A keeps you on your toes. You must be well-prepared and nimble to handle a variety of questions and objections. Eleanor Roosevelt’s words resonate: “You gain strength, courage, and confidence by every experience in which you stop to look fear in the face.”
How do you answer Questions effectively?
Handling a question-and-answer session effectively requires preparation, communication skills, and adaptability. Whether you’re conducting a Q&A session as a speaker, presenter, or moderator, here are some tips to help you manage it effectively:
1. Preparation is Key:
Know your audience: Research your audience’s demographics, interests, and knowledge level. Tailor your responses to their needs and expectations. Imagine you’re hosting a Q&A session about pets. Knowing your audience means finding out if they’re mostly cat lovers, dog enthusiasts, or perhaps reptile fans. This helps you tailor your answers to their specific interests, like offering dog training tips for dog lovers and habitat ideas for reptile enthusiasts.
Anticipate questions: Develop a list of potential questions that might arise during the session. This can help you prepare concise and informative answers. If you’re giving a presentation about a superhero movie, anticipate questions like “Who’s the main villain?” or “What are the special powers of the hero?” Prepare concise answers to these common questions to keep the audience engaged.
Review your material: Revisit your presentation or discussion content before the Q&A session. This will help you recall key points and examples that may be relevant to questions. For Ex: You’re a teacher conducting a Q&A after a science class. Before the session, review your notes on the periodic table. This ensures that when a student asks, “What are the noble gases?” you can confidently explain their properties.
2. Set Expectations:
Clearly explain how the Q&A session will be structured. For example, inform the audience whether questions will be taken throughout the session or only at the end. Mention any time constraints.
Let the audience know if you have topics you’d like to cover or all questions are welcome.
For example: Think of a cooking class where you’re the instructor. Before starting, inform your students that they can ask questions anytime during the class. This sets the expectation that it’s an interactive learning experience.
3. Active Listening:
Give the questioner your full attention. Make eye contact, nod to acknowledge understanding, and avoid interrupting.
Repeat or rephrase the question if needed to ensure clarity and show that you are actively engaged with the questioner.
Imagine you’re a detective in a mystery novel. When a witness asks, “Did you see the suspect?”, listen attentively, nod to acknowledge, and ask follow-up questions to gather all the details. This demonstrates active listening.
4. Take a pause
Before answering any question there is a key aspect that makes you look smart and composed- “The Pause.” The Pause is where you gather your thoughts and prepare your answer in a gist. You decide how to answer the question and tackle it swiftly. If you perhaps don’t know the answer, what is the best way to say you will get back with an answer, and so on? You can get a firm grip on your audience as they wait for you to speak and then speak with utmost clarity, that is the power of Pauses.
5. Be Concise and Clear:
Answer each question briefly and directly. Avoid going off on tangents or providing excessive background information.
Use plain language and avoid jargon that might confuse the audience. Suppose you’re explaining how to play a video game. Instead of going into a lengthy backstory, say, “To win, you must collect all the magical crystals and defeat the dragon boss.” This clear and concise explanation keeps players engaged.
6. Stay Calm and Confident:
If you don’t know the answer to a question, admit it gracefully. Offer to research or follow up later, and don’t try to bluff your way through.
Maintain a calm and composed demeanor even in the face of challenging or critical questions. Focus on addressing the question, not the tone.
This is also where your preparation becomes your backbone and provides you the confidence to deal with your audience.
Also, I want you to remember that knowledge is very vast- The more you gain knowledge the more you realize how little you know! Do not worry about admitting that you don’t know an answer, you can provide whatever information you have and later get back to them when you do find one.
7. Manage Time:
Allocate a specific amount of time for the Q&A session and communicate this at the outset. Stick to the schedule to ensure you cover all planned topics. If necessary, prioritize questions based on relevance or importance.
Think of a soccer coach during a practice session. Allocate specific time for different drills and stick to the schedule. This ensures that all aspects of the game are covered within the session.
8. Field Diverse Questions:
Encourage a wide range of questions, including those that challenge your viewpoint or prompt discussion. This diversity can lead to more engaging and informative sessions.
For Example: In a book club discussion, encourage members to ask questions about various aspects of the book, from plot details to character motivations. This diversity of questions leads to a more engaging conversation.
9. Moderate Effectively:
As someone who has to give direction to the discussion, try to maintain control of the session and ensure questions are relevant to the topic and audience. Politely redirect or filter out off-topic or inappropriate questions.
Give everyone a chance to ask questions, and manage time to allow for a variety of voices to be heard.
Pretend you’re a radio DJ taking calls from listeners. If someone goes off-topic, gently steer the conversation back to the music or topic of the show to maintain a cohesive experience.
10. Encourage Feedback:
After the Q&A, ask the audience for feedback on the session’s effectiveness. This can help you improve future sessions and tailor them to the audience’s needs.
Example: After a group art project, ask each participant what they liked and what could be improved. This feedback helps everyone learn from the experience and create better art in the future.
11. Follow-Up:
If you promised to provide additional information or research an answer, do so promptly after the session. This demonstrates your commitment to addressing the audience’s needs.
12. Reflect and Improve:
After each session, take time to analyze what went well and what could be improved. Consider seeking feedback from colleagues or mentors to refine your Q&A skills for future engagements.
Can I answer a Question with a Question?
Many a time we think is it disrespectful to answer a question with a question, or perhaps even condescending? However, answering a question with a question can be an effective communication technique when used thoughtfully, but it’s essential to be mindful of the context and tone to avoid coming across as disrespectful or condescending.
Consider, for instance, a scenario where someone asks, “Do you know where my keys are?” Responding with, “Have you checked your coat pocket?” instead of a direct “yes” or “no” can be helpful. However, if someone in a team meeting asks, “How do we solve this problem?” replying with, “Well, what solutions have you considered?” can encourage collaborative problem-solving. So, while answering a question with a question can be a valuable tool for prompting critical thinking or guiding discussions, it’s crucial to gauge the situation and intent to ensure it’s used appropriately.
Types of Difficult Questions:
Often times in presentations we don’t get softball questions that are easy to handle but rather some sort of pushback. The audience tries to gauge your authenticity or simply disagrees with you. These are what we call Difficult questions. They are inquiries that pose challenges beyond their surface. They require careful consideration, provoke thought, or test one’s knowledge, often demanding more than a simple yes or no answer. Handling difficult questions effectively is a skill that involves not only providing accurate responses but also managing the dynamics of the discussion and the emotions of those asking. In this exploration, we’ll delve deeper into these challenging types of questions, dissect their nuances, and offer strategies for responding adeptly and constructively.
1. When You Don’t Know the Answer:
- Challenge: It’s common to face questions to which you don’t have an immediate answer, especially in complex or unfamiliar topics.
- Example: In a technical presentation, someone asks a highly technical question beyond your expertise.
- Admit it gracefully: Acknowledge that you don’t have the answer, but express your willingness to find it.
- Offer a partial answer: Share what you do know or suggest possible resources or experts to consult.
- Follow up: Make a commitment to research and provide a comprehensive response after the session.
2. Too Many Questions at the Same Time (Machine Gun Questioning):
- Challenge: Some audience members may bombard you with multiple questions all at once, making it difficult to respond coherently.
- Example: An audience member asks, “How does this technology work, and what are its applications? Can you explain its impact on the industry?”
- Politely request clarification: Ask the person to specify which question they’d like you to address first.
- Address one question at a time: Break down the multiple questions into individual responses to maintain clarity.
- Control the pace: Politely request that questions be asked one at a time to facilitate a more organized discussion.
3. Audience Member Makes a Statement and Tries to Take Over:
- Challenge: Some individuals may attempt to dominate the Q&A session by making lengthy statements or challenging your expertise.
- Example: An audience member insists on sharing their own knowledge and experience, seemingly to undermine your credibility.
- Acknowledge their input: Politely thank them for their perspective and acknowledge their knowledge.
- Redirect the focus: Gently guide the conversation back to the topic or the question at hand.
- Set boundaries: Establish ground rules for the Q&A session at the beginning, emphasizing that questions should be concise and relevant.
4. Emotional Questions Driven by Anger:
- Challenge: Emotionally charged questions, often stemming from anger or frustration, can be challenging to handle without escalating tension.
- Example: An audience member confronts you with anger about a controversial topic you’re discussing.
- Stay calm and empathetic: Maintain composure, listen attentively, and acknowledge the person’s emotions.
- Avoid confrontation: Refrain from responding with defensiveness or aggression, as it can escalate the situation.
- Reframe the question: Politely ask the person to rephrase their question in a more constructive and specific manner.
5. Off-Topic Questions:
- Challenge: Sometimes, audience members ask questions that are unrelated to the topic of your presentation or discussion.
- Example: In a business presentation on marketing strategies, someone asks about your personal hobbies.
- Politely redirect: Acknowledge the question but gently steer the conversation back to the main topic.
- Offer to discuss later: Suggest discussing off-topic questions after the session to avoid derailing the current discussion.
6. Provocative Questions:
- Challenge: These questions are designed to provoke a reaction or create controversy.
- Example: During a political debate, someone asks a loaded question aimed at stirring up emotions rather than seeking a constructive answer.
- Stay composed: Maintain a calm and respectful demeanor when responding, regardless of the provocation.
- Address the core issue: Focus on the underlying topic or concern within the provocative question rather than getting drawn into the emotional aspect.
7. Incomprehensible Questions:
- Challenge: Some questions are poorly phrased or unclear, making it challenging to discern the intent behind them.
- Example: An audience member asks a question with convoluted language and vague references.
- Seek clarification: Politely ask the person to rephrase or clarify their question to ensure you understand it correctly.
- Paraphrase and respond: Restate what you believe the question is about, and answer based on your interpretation. The person can then confirm or correct your understanding.
8. Condescending Questions:
- Challenge: These questions are posed in a belittling or patronizing manner, often implying that the person asking believes they know better.
- Example: An audience member asks, “Do you even understand the basics of this topic?”
- Maintain professionalism: Respond with professionalism and confidence, avoiding any temptation to match the condescension.
- Address the question’s substance: Focus on providing a well-informed and concise response to demonstrate your expertise.
9. Overly Technical Questions:
- Challenge: In technical or specialized discussions, questions may become overly complex, making it challenging for a broader audience to follow.
- Example: A highly technical question filled with industry-specific jargon is asked in a general audience setting.
- Simplify the response: Offer a simplified explanation or analogy to make the answer accessible to a broader audience.
- Offer follow-up resources: Suggest additional reading or resources for those interested in delving deeper into the technical details.
Handling these challenging question scenarios effectively requires a combination of good communication skills, patience, and tact. Remember that the goal is to maintain a productive and respectful dialogue with your audience while addressing their concerns and inquiries.
People Also Ask:
Why is it important to know how to take the audience’s questions when you are presenting.
It is crucial to know how to handle audience questions when presenting for several reasons. Firstly, audience questions signify engagement and interest in your topic, making it an opportunity to further connect with your audience and demonstrate your expertise. Secondly, addressing questions allows you to clarify any misunderstandings or provide additional context, ensuring that your message is well-received and understood. Moreover, handling questions effectively helps you maintain control over the presentation’s flow, ensuring that it stays on track and doesn’t deviate too far from your intended message. Lastly, audience questions can provide valuable feedback, enabling you to gauge the audience’s comprehension and adapt your presentation in real time if necessary, leading to a more successful and impactful presentation overall.
Who is responsible for answering questions from the audience at the time of the presentation?
The responsibility for answering questions from the audience during a presentation primarily falls on the presenter (most likely You). You’re the one who’s been preparing and practicing your presentation for weeks, months, or maybe even years. You’re the guru on the stage, the oracle of information. When those curious souls in the audience raise their hands or type away with their burning questions, it’s your time to shine. You get to flex your brain muscles and give them answers that will make their heads spin (in a good way, of course). It’s your duty to facilitate a productive Q&A session by actively listening to each question, providing thoughtful and accurate responses, and ensuring that the discussion remains relevant to the topic at hand. However, in some cases, especially during larger presentations or panel discussions, a moderator or facilitator may assist in managing the question-and-answer
In conclusion, mastering the art of Q&A, and handling audience questions like a pro, is a skill that can transform any presentation, discussion, or public speaking engagement. By understanding the diverse types of questions that may arise and adopting effective strategies to address them, you can create an interactive and engaging dialogue with your audience. From riddles that stimulate creativity to emotionally charged inquiries that demand empathy, each question offers a unique opportunity to connect, educate, and inspire.
Remember, the key to success lies in active listening, clear communication, and maintaining composure, even in the face of challenging questions. Whether you’re a speaker, presenter, moderator, or simply someone engaged in a meaningful conversation, the ability to navigate difficult questions with finesse not only enhances your credibility but also fosters a more enriching and enlightening exchange of ideas. So, embrace the art of Q&A, and with practice and patience, you’ll continue to refine this valuable skill, ensuring that your interactions with your audience are both memorable and impactful.
To learn more about how to conduct presentations and improve your communication skills in the workplace you can try our coaching program here .
Enroll in our transformative 1:1 Coaching Program
Schedule a call with our expert communication coach to know if this program would be the right fit for you

7 Keys to Emcee Like a Pro: Unlock Your Hosting Potential

8 Ways to Rise Above the Noise to Communicate Better

How to Negotiate: The Art of Getting What You Want

- [email protected]
- +91 98203 57888
Get our latest tips and tricks in your inbox always
Copyright © 2023 Frantically Speaking All rights reserved
Kindly drop your contact details so that we can arrange call back
Select Country Afghanistan Albania Algeria AmericanSamoa Andorra Angola Anguilla Antigua and Barbuda Argentina Armenia Aruba Australia Austria Azerbaijan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesh Barbados Belarus Belgium Belize Benin Bermuda Bhutan Bosnia and Herzegovina Botswana Brazil British Indian Ocean Territory Bulgaria Burkina Faso Burundi Cambodia Cameroon Canada Cape Verde Cayman Islands Central African Republic Chad Chile China Christmas Island Colombia Comoros Congo Cook Islands Costa Rica Croatia Cuba Cyprus Czech Republic Denmark Djibouti Dominica Dominican Republic Ecuador Egypt El Salvador Equatorial Guinea Eritrea Estonia Ethiopia Faroe Islands Fiji Finland France French Guiana French Polynesia Gabon Gambia Georgia Germany Ghana Gibraltar Greece Greenland Grenada Guadeloupe Guam Guatemala Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Honduras Hungary Iceland India Indonesia Iraq Ireland Israel Italy Jamaica Japan Jordan Kazakhstan Kenya Kiribati Kuwait Kyrgyzstan Latvia Lebanon Lesotho Liberia Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Madagascar Malawi Malaysia Maldives Mali Malta Marshall Islands Martinique Mauritania Mauritius Mayotte Mexico Monaco Mongolia Montenegro Montserrat Morocco Myanmar Namibia Nauru Nepal Netherlands Netherlands Antilles New Caledonia New Zealand Nicaragua Niger Nigeria Niue Norfolk Island Northern Mariana Islands Norway Oman Pakistan Palau Panama Papua New Guinea Paraguay Peru Philippines Poland Portugal Puerto Rico Qatar Romania Rwanda Samoa San Marino Saudi Arabia Senegal Serbia Seychelles Sierra Leone Singapore Slovakia Slovenia Solomon Islands South Africa South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands Spain Sri Lanka Sudan Suriname Swaziland Sweden Switzerland Tajikistan Thailand Togo Tokelau Tonga Trinidad and Tobago Tunisia Turkey Turkmenistan Turks and Caicos Islands Tuvalu Uganda Ukraine United Arab Emirates United Kingdom United States Uruguay Uzbekistan Vanuatu Wallis and Futuna Yemen Zambia Zimbabwe land Islands Antarctica Bolivia, Plurinational State of Brunei Darussalam Cocos (Keeling) Islands Congo, The Democratic Republic of the Cote d'Ivoire Falkland Islands (Malvinas) Guernsey Holy See (Vatican City State) Hong Kong Iran, Islamic Republic of Isle of Man Jersey Korea, Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Republic of Lao People's Democratic Republic Libyan Arab Jamahiriya Macao Macedonia, The Former Yugoslav Republic of Micronesia, Federated States of Moldova, Republic of Mozambique Palestinian Territory, Occupied Pitcairn Réunion Russia Saint Barthélemy Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan Da Cunha Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia Saint Martin Saint Pierre and Miquelon Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Sao Tome and Principe Somalia Svalbard and Jan Mayen Syrian Arab Republic Taiwan, Province of China Tanzania, United Republic of Timor-Leste Venezuela, Bolivarian Republic of Viet Nam Virgin Islands, British Virgin Islands, U.S.


Improve your practice.
Enhance your soft skills with a range of award-winning courses.
Guide for Handling Questions after a Presentation
October 19, 2017 - Dom Barnard
The questions at the end of a presentation can be terrifying for many speakers as they can’t be controlled and are hard to prepare for. However, questions form an important part of the presentation for the whole audience as they allow for clarification and consolidation of learning.
The presenter can enhance the usefulness of the question and answer session by treating it as a formal part of the presentation that requires as much careful planning and control as the delivery of the core material.
Identify possible questions and scope in your preparation
The background work that you undertook whilst planning your presentation is the key to handling questions effectively and understanding what type of audience you’ll be faced with. If you have defined a focus for your presentation and have explored this thoroughly in your research and planning, you are more likely to be able to confidently respond to questions.
When planning your presentation, you will need to prepare prompts for questions that are open and straightforward, for example saying “That’s the end of my presentation. I’ll be taking questions for the next 10 minutes”.
You might also want to define topics for discussion before taking questions, by stating the areas you’re willing to field questions in. Your preparation will help you identify topics you are not confident with and want to avoid in the questioning.

Set some rules for asking questions
At the start of your presentation, make it clear when you would prefer to deal with questions – as you go along or at the end of the presentation.
Some speakers prefer questions to be raised as they arise during the presentation. The advantage of this approach is that any misunderstandings can be dealt with immediately. However, there is also a danger that the question will disrupt or distract the speaker, or that questions are raised that would have been covered later in the presentation.
If you leave questions until the end, plan to leave plenty of time for questions so that the audience doesn’t feel rushed.
Framework for responding to questions
Answering questions under pressure can make you say things you shouldn’t have – the nerves can force you to give an inappropriate response. In your panic you might have misinterpreted the question or given away company information that was sensitive. Use the following framework to help you respond effectively to your audience.
Practice answering AI-generated questions on your speech or presentation with VirtualSpeech .
1. Listen to the whole question
You don’t have to answer a question immediately. Pause for a few seconds, actively listen to all parts of the question and think about the best way to answer.
Frequently questions can change direction at the last moment, particularly if the questioner is thinking on their feet. This can throw you if you have already started to prepare an answer. Remember that questioners will frequently try to make a point whilst asking their question – it’s therefore important to both hear the content of the question and try to decipher the questioner’s intention.
2. Understand the context
If you are worried that you haven’t understood a question, ask them to clarify what they mean. Check for confirmation by paraphrasing the question back to the questioner – “You want me to list the improvements of X?”.

3. Involve the whole audience
It is important to remember that even though you are taking a question from one member of the audience, you are still responsible for the interest of the other audience members. This is particularly important in large groups as the audience will become bored if the presentation descends into a series of one-to-one discussions.
To involve the rest of the audience, make sure the whole audience has heard and understood the question by repeating it or paraphrasing it to the audience.
4. Respond concisely
When you reply to a question, direct your answer to both the questioner and other members of the audience. Try to keep your responses as focused as possible, leaving space for other questions. To avoid going into too much detail, check back with the questioner to see if you have answered their query – “Does that answer your question in enough detail?”.
We’ll cover different ways to respond in a later section.
5. Allow follow-up questions via email
You can also encourage your audience to ask questions after the event has finished by providing your email address. This shows a high level of respect for your audience and implies that the topic still has much further scope for enquiry.
Two good resources for handling questions
- What’s the art of answering a tricky question?
- Dodging the Question
Practice Answering Questions
Practice answering questions after your presentation using a 4 step process. Learn More
Options for answering the question
There are five possible choices depending on how well you understand and can answer the question. It’s okay to say that you don’t know the answer to something. This can add to your credibility instead of trying to waffle through an answer you don’t really know.
If you have a good answer for the question from the audience, go ahead and answer it in a short and clear message.
Ask a question back the audience member, such as “Can you clarify what you mean by that”. You can also attack the question if it is not related to the issue, factually inaccurate, personal or based on false assumptions. Be careful with this method.
Ask the question back to the audience or pass it to another panel member if possible. If suitable, another technique is to imply the question has been asked already, with you stating you don’t want to cover old ground.
Tell the audience member you will talk to them after the event. This gives you more time to think of a good answer and there is less pressure to give a perfect answer.
Or mention that that point is coming up in a slide.
This involves answering the question but changing the subject. You can also give a partial answer or give a negative answer, saying that something else will happen instead.
Avoid answering questions that fall outside of the remit of your talk: “I’m afraid that really falls outside of my objectives for today’s presentation. Perhaps we can resume discussion of that particular point later?”

Diagram Explained : Once you receive a question, you’ll have a few moments to think about it and reframe it in a way that makes sense to you. This will give you five choices on how to react – you can answer, reflect, deflect, defer or change the scope of the question. Once you’ve answered concisely, you can then follow up to check if the person asking the question is satisfied and then continue with the presentation.
Strategies to use when struggling to answer
Here are some strategies to use when you are struggling to answer the question posed to you. For more information, read this article on Dodging the Question .
- Acknowledge the question without answering it – “That’s a good question, let’s consider the impact by looking at…”
- The question fails to tackle the important issue.
- The question is based on a false assumption.
- The question is factually inaccurate.
- The question is too personal or objectionable.
- Decline to answer. Refuse to answer on the basis that it is not your area of responsibility or it is sensitive company information – “You will have to ask [name] because I wasn’t involved in that particular project.”
- Partial answer
- Start to answer but change the subject
- Negative answer. You state what won’t happen instead of what will happen
- Answer a similar question
- State or imply the question has already been answered – “We’ve already covered that topic”
Things to avoid
When handling questions and answers, you will still need to be as professional as you have been for the main delivery of your presentation. There are some common dangers to avoid.
Answering the question you wished you’d been asked
A common trick played by politicians, this strategy ignores the precise nature of the question and uses a predetermined answer to the broad topic area. If handled poorly, this technique is very obvious to the audience and frustrating to the questioner.
Giving a lengthy response
This is the process whereby you make a lengthy response, including all the information you’d left out in planning the main presentation. Your unplanned response will be unstructured and rambling, so keep things focused and brief. If you find yourself rambling, ask them to talk to you after.

Passing the blame
Passing the blame to others comes across as weak and evasive. If an idea from the audience is a good one, acknowledge its value. If it isn’t, make a polite rebuttal and move on.
Defensive answers
Occasionally, questions can really put you on the spot, but it is important to remain calm and in control. An aggressive or defensive reply will be seen as weakness on your part and will spoil the effect of an otherwise successful presentation.
Handling difficult questions
It is important not to start responding to a difficult question before you have thought about the answer. Repeating the question and asking for clarification will help create some space for your thoughts.
Sometimes you will need to think about a question for a moment before responding. You may be able to buy a little bit of thinking time to help focus your response. Useful strategies include searching for an appropriate visual aid to help focus your response or simply pausing for a moment or two to think. For even more time, suggest that you’ll come back to the topic later (but don’t forget to do this).
7 myths when answering tough questions during presentations
Sometimes questions are too difficult to answer. Don’t worry about admitting that you don’t know something or haven’t considered an alternative approach. An enthusiastic “That’s an interesting idea, I’d not thought of that” is much more positive than a mumbled “I don’t know ”. Remember that a presentation is a two-way process and it is important to show that you are learning from your audience as well.
Finally, you can come across a questioner who disagrees strongly with your argument. Although this can feel very awkward, remember that you are still responsible for the whole audience and that you cannot allocate all of your question time to one individual.
If you feel that you have answered the initial question, announce that you will move on and suggest that you might continue discussion after the presentation. If the questioner persists, assert your position calmly by saying “I’m afraid I need to move on”.
You can read more on this topic here: Responding to questions effectively (PDF)
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Beginner Guides How To Make a Good Presentation [A Complete Guide]
How To Make a Good Presentation [A Complete Guide]
Written by: Krystle Wong Jul 20, 2023

A top-notch presentation possesses the power to drive action. From winning stakeholders over and conveying a powerful message to securing funding — your secret weapon lies within the realm of creating an effective presentation .
Being an excellent presenter isn’t confined to the boardroom. Whether you’re delivering a presentation at work, pursuing an academic career, involved in a non-profit organization or even a student, nailing the presentation game is a game-changer.
In this article, I’ll cover the top qualities of compelling presentations and walk you through a step-by-step guide on how to give a good presentation. Here’s a little tip to kick things off: for a headstart, check out Venngage’s collection of free presentation templates . They are fully customizable, and the best part is you don’t need professional design skills to make them shine!
These valuable presentation tips cater to individuals from diverse professional backgrounds, encompassing business professionals, sales and marketing teams, educators, trainers, students, researchers, non-profit organizations, public speakers and presenters.
No matter your field or role, these tips for presenting will equip you with the skills to deliver effective presentations that leave a lasting impression on any audience.
Click to jump ahead:
What are the 10 qualities of a good presentation?
Step-by-step guide on how to prepare an effective presentation, 9 effective techniques to deliver a memorable presentation, faqs on making a good presentation, how to create a presentation with venngage in 5 steps.
When it comes to giving an engaging presentation that leaves a lasting impression, it’s not just about the content — it’s also about how you deliver it. Wondering what makes a good presentation? Well, the best presentations I’ve seen consistently exhibit these 10 qualities:
1. Clear structure
No one likes to get lost in a maze of information. Organize your thoughts into a logical flow, complete with an introduction, main points and a solid conclusion. A structured presentation helps your audience follow along effortlessly, leaving them with a sense of satisfaction at the end.
Regardless of your presentation style , a quality presentation starts with a clear roadmap. Browse through Venngage’s template library and select a presentation template that aligns with your content and presentation goals. Here’s a good presentation example template with a logical layout that includes sections for the introduction, main points, supporting information and a conclusion:

2. Engaging opening
Hook your audience right from the start with an attention-grabbing statement, a fascinating question or maybe even a captivating anecdote. Set the stage for a killer presentation!
The opening moments of your presentation hold immense power – check out these 15 ways to start a presentation to set the stage and captivate your audience.
3. Relevant content
Make sure your content aligns with their interests and needs. Your audience is there for a reason, and that’s to get valuable insights. Avoid fluff and get straight to the point, your audience will be genuinely excited.
4. Effective visual aids
Picture this: a slide with walls of text and tiny charts, yawn! Visual aids should be just that—aiding your presentation. Opt for clear and visually appealing slides, engaging images and informative charts that add value and help reinforce your message.
With Venngage, visualizing data takes no effort at all. You can import data from CSV or Google Sheets seamlessly and create stunning charts, graphs and icon stories effortlessly to showcase your data in a captivating and impactful way.

5. Clear and concise communication
Keep your language simple, and avoid jargon or complicated terms. Communicate your ideas clearly, so your audience can easily grasp and retain the information being conveyed. This can prevent confusion and enhance the overall effectiveness of the message.
6. Engaging delivery
Spice up your presentation with a sprinkle of enthusiasm! Maintain eye contact, use expressive gestures and vary your tone of voice to keep your audience glued to the edge of their seats. A touch of charisma goes a long way!
7. Interaction and audience engagement
Turn your presentation into an interactive experience — encourage questions, foster discussions and maybe even throw in a fun activity. Engaged audiences are more likely to remember and embrace your message.
Transform your slides into an interactive presentation with Venngage’s dynamic features like pop-ups, clickable icons and animated elements. Engage your audience with interactive content that lets them explore and interact with your presentation for a truly immersive experience.

8. Effective storytelling
Who doesn’t love a good story? Weaving relevant anecdotes, case studies or even a personal story into your presentation can captivate your audience and create a lasting impact. Stories build connections and make your message memorable.
A great presentation background is also essential as it sets the tone, creates visual interest and reinforces your message. Enhance the overall aesthetics of your presentation with these 15 presentation background examples and captivate your audience’s attention.
9. Well-timed pacing
Pace your presentation thoughtfully with well-designed presentation slides, neither rushing through nor dragging it out. Respect your audience’s time and ensure you cover all the essential points without losing their interest.
10. Strong conclusion
Last impressions linger! Summarize your main points and leave your audience with a clear takeaway. End your presentation with a bang , a call to action or an inspiring thought that resonates long after the conclusion.
In-person presentations aside, acing a virtual presentation is of paramount importance in today’s digital world. Check out this guide to learn how you can adapt your in-person presentations into virtual presentations .
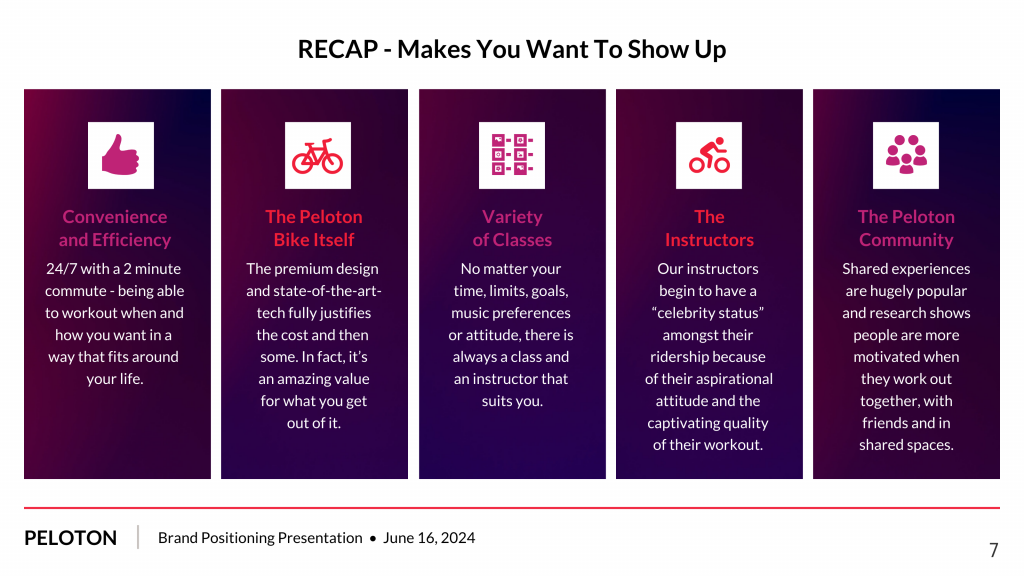
Preparing an effective presentation starts with laying a strong foundation that goes beyond just creating slides and notes. One of the quickest and best ways to make a presentation would be with the help of a good presentation software .
Otherwise, let me walk you to how to prepare for a presentation step by step and unlock the secrets of crafting a professional presentation that sets you apart.
1. Understand the audience and their needs
Before you dive into preparing your masterpiece, take a moment to get to know your target audience. Tailor your presentation to meet their needs and expectations , and you’ll have them hooked from the start!
2. Conduct thorough research on the topic
Time to hit the books (or the internet)! Don’t skimp on the research with your presentation materials — dive deep into the subject matter and gather valuable insights . The more you know, the more confident you’ll feel in delivering your presentation.
3. Organize the content with a clear structure
No one wants to stumble through a chaotic mess of information. Outline your presentation with a clear and logical flow. Start with a captivating introduction, follow up with main points that build on each other and wrap it up with a powerful conclusion that leaves a lasting impression.
Delivering an effective business presentation hinges on captivating your audience, and Venngage’s professionally designed business presentation templates are tailor-made for this purpose. With thoughtfully structured layouts, these templates enhance your message’s clarity and coherence, ensuring a memorable and engaging experience for your audience members.
Don’t want to build your presentation layout from scratch? pick from these 5 foolproof presentation layout ideas that won’t go wrong.

4. Develop visually appealing and supportive visual aids
Spice up your presentation with eye-catching visuals! Create slides that complement your message, not overshadow it. Remember, a picture is worth a thousand words, but that doesn’t mean you need to overload your slides with text.
Well-chosen designs create a cohesive and professional look, capturing your audience’s attention and enhancing the overall effectiveness of your message. Here’s a list of carefully curated PowerPoint presentation templates and great background graphics that will significantly influence the visual appeal and engagement of your presentation.
5. Practice, practice and practice
Practice makes perfect — rehearse your presentation and arrive early to your presentation to help overcome stage fright. Familiarity with your material will boost your presentation skills and help you handle curveballs with ease.
6. Seek feedback and make necessary adjustments
Don’t be afraid to ask for help and seek feedback from friends and colleagues. Constructive criticism can help you identify blind spots and fine-tune your presentation to perfection.
With Venngage’s real-time collaboration feature , receiving feedback and editing your presentation is a seamless process. Group members can access and work on the presentation simultaneously and edit content side by side in real-time. Changes will be reflected immediately to the entire team, promoting seamless teamwork.
7. Prepare for potential technical or logistical issues
Prepare for the unexpected by checking your equipment, internet connection and any other potential hiccups. If you’re worried that you’ll miss out on any important points, you could always have note cards prepared. Remember to remain focused and rehearse potential answers to anticipated questions.
8. Fine-tune and polish your presentation
As the big day approaches, give your presentation one last shine. Review your talking points, practice how to present a presentation and make any final tweaks. Deep breaths — you’re on the brink of delivering a successful presentation!
In competitive environments, persuasive presentations set individuals and organizations apart. To brush up on your presentation skills, read these guides on how to make a persuasive presentation and tips to presenting effectively .

Whether you’re an experienced presenter or a novice, the right techniques will let your presentation skills soar to new heights!
From public speaking hacks to interactive elements and storytelling prowess, these 9 effective presentation techniques will empower you to leave a lasting impression on your audience and make your presentations unforgettable.
1. Confidence and positive body language
Positive body language instantly captivates your audience, making them believe in your message as much as you do. Strengthen your stage presence and own that stage like it’s your second home! Stand tall, shoulders back and exude confidence.
2. Eye contact with the audience
Break down that invisible barrier and connect with your audience through their eyes. Maintaining eye contact when giving a presentation builds trust and shows that you’re present and engaged with them.
3. Effective use of hand gestures and movement
A little movement goes a long way! Emphasize key points with purposeful gestures and don’t be afraid to walk around the stage. Your energy will be contagious!
4. Utilize storytelling techniques
Weave the magic of storytelling into your presentation. Share relatable anecdotes, inspiring success stories or even personal experiences that tug at the heartstrings of your audience. Adjust your pitch, pace and volume to match the emotions and intensity of the story. Varying your speaking voice adds depth and enhances your stage presence.

5. Incorporate multimedia elements
Spice up your presentation with a dash of visual pizzazz! Use slides, images and video clips to add depth and clarity to your message. Just remember, less is more—don’t overwhelm them with information overload.
Turn your presentations into an interactive party! Involve your audience with questions, polls or group activities. When they actively participate, they become invested in your presentation’s success. Bring your design to life with animated elements. Venngage allows you to apply animations to icons, images and text to create dynamic and engaging visual content.
6. Utilize humor strategically
Laughter is the best medicine—and a fantastic presentation enhancer! A well-placed joke or lighthearted moment can break the ice and create a warm atmosphere , making your audience more receptive to your message.
7. Practice active listening and respond to feedback
Be attentive to your audience’s reactions and feedback. If they have questions or concerns, address them with genuine interest and respect. Your responsiveness builds rapport and shows that you genuinely care about their experience.

8. Apply the 10-20-30 rule
Apply the 10-20-30 presentation rule and keep it short, sweet and impactful! Stick to ten slides, deliver your presentation within 20 minutes and use a 30-point font to ensure clarity and focus. Less is more, and your audience will thank you for it!
9. Implement the 5-5-5 rule
Simplicity is key. Limit each slide to five bullet points, with only five words per bullet point and allow each slide to remain visible for about five seconds. This rule keeps your presentation concise and prevents information overload.
Simple presentations are more engaging because they are easier to follow. Summarize your presentations and keep them simple with Venngage’s gallery of simple presentation templates and ensure that your message is delivered effectively across your audience.

1. How to start a presentation?
To kick off your presentation effectively, begin with an attention-grabbing statement or a powerful quote. Introduce yourself, establish credibility and clearly state the purpose and relevance of your presentation.
2. How to end a presentation?
For a strong conclusion, summarize your talking points and key takeaways. End with a compelling call to action or a thought-provoking question and remember to thank your audience and invite any final questions or interactions.
3. How to make a presentation interactive?
To make your presentation interactive, encourage questions and discussion throughout your talk. Utilize multimedia elements like videos or images and consider including polls, quizzes or group activities to actively involve your audience.
In need of inspiration for your next presentation? I’ve got your back! Pick from these 120+ presentation ideas, topics and examples to get started.
Creating a stunning presentation with Venngage is a breeze with our user-friendly drag-and-drop editor and professionally designed templates for all your communication needs.
Here’s how to make a presentation in just 5 simple steps with the help of Venngage:
Step 1: Sign up for Venngage for free using your email, Gmail or Facebook account or simply log in to access your account.
Step 2: Pick a design from our selection of free presentation templates (they’re all created by our expert in-house designers).
Step 3: Make the template your own by customizing it to fit your content and branding. With Venngage’s intuitive drag-and-drop editor, you can easily modify text, change colors and adjust the layout to create a unique and eye-catching design.
Step 4: Elevate your presentation by incorporating captivating visuals. You can upload your images or choose from Venngage’s vast library of high-quality photos, icons and illustrations.
Step 5: Upgrade to a premium or business account to export your presentation in PDF and print it for in-person presentations or share it digitally for free!
By following these five simple steps, you’ll have a professionally designed and visually engaging presentation ready in no time. With Venngage’s user-friendly platform, your presentation is sure to make a lasting impression. So, let your creativity flow and get ready to shine in your next presentation!
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
The Throughline Blog
Practical Media Training and Public Speaking Tips
A Better Solution To "Do You Have Any Questions?"
If you’re like most speakers, you probably get to the end of your presentation and open up the floor by asking “Do you have any questions?”
Unfortunately, many people in an audience are uncomfortable being the first one to speak. Sometimes, no one says anything at all. You may pause for a few seconds in the hopes that someone will eventually break the silence—but sometimes they don’t.
Speakers can do several things in that situation, including these three techniques:
- Say something like, “You know, one of the questions I’m asked a lot is…” and answer it yourself.
- Ask an audience member a specific question, such as, “I spoke about Subject X earlier. What did you think about that?”
- Use an icebreaker. I once read about a speaker who used this joke: “Since no one wants to ask the first question, does anyone want to ask the second one?”

“Does anyone have any thoughts ?”
That’s a subtle distinction, but possibly an important one. By asking for thoughts, he was allowing a much broader scope of interaction than he would have allowed by merely soliciting questions. He wanted to know if anything he had said had triggered an idea, surprised someone, or reminded someone of something related. And it seemed to work in that small group; almost every time he asked for thoughts, someone spoke up.
I’ve started experimenting with this slight linguistic twist. I don’t have enough data yet to know whether or not it makes a big difference. My early experiences suggest it may help—if not substantially, enough to warrant its usage.
- presentation training
- public speaking
Share this article
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share on Email
STAY UP TO DATE WITH THE THROUGHLINE NEWSLETTER
Join the thousands of professionals who receive our email newsletter. Improve your public speaking and media interviewing skills—and enhance your career— by signing up.
Public Speaking Skills Training
Since 2004, we have helped speakers prepare for the world’s biggest stages, including TED, the World Economic Forum, and a presidential announcement speech. We’re committed to your long-term growth, and we’ll be with you every step of the way.
Comments (3)
Brad, one small psychological trick that can help in this situation is to change from the plural to the singular in your prompt. “Does anyone have any questions” is an abstract. Each audience member wonders right along with you.. “Yeah, I wonder if anyone does?” They have no personal responsibility to take action. Change to “Do you have a question?” or “What are your thoughts?” and it puts the onus back on the individual to do something. An even stronger cue is to give them a direct command to take action in a specific way. “Now it’s your turn to guide the discussion. Raise your hand and ask me what I should clarify or go into more detail on.” You are shifting the entire psychological dynamic from “Sit quietly and listen while I talk at you” to the reverse. That is hard inertia to overcome, and you need to be very specific about how they are to make the change.
Ken, Thank you so much for your comment – that’s terrific advice. I will begin experimenting with all of your suggested phrases during my media training workshop next Monday, and will report back about my experience. One of the best part of this blog is learning from readers who have more expertise on a given subject than I do. Thanks for taking the time to leave your comment and provide me with a quality education. Best wishes, Brad
Great suggestions for getting an audience to participate. I think the subtle psychological difference in asking for “thoughts” instead of questions is that many people wonder how their question makes them look. Is my question a dumb question or of interest to others? Is it too confrontational? Will I look smart or uninformed? Once the stage is set by a few questions or comments, people become a bit more brave.
More from the throughline blog

In Presentation Training How to Hide a Lavalier Mic Wire

In Presentation Training Are Your Stories Making You Appear Inauthentic?

In Presentation Training Why You Should Have Three Speech Opens
This website or its third party tools use cookies, which are necessary to its functioning and required to achieve the purposes illustrated in the privacy policy . If you want to know more or withdraw your consent to all or some of the cookies, please refer to the privacy policy. By closing this banner or continuing to browse otherwise, you agree to the use of cookies.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
What It Takes to Give a Great Presentation
- Carmine Gallo

Five tips to set yourself apart.
Never underestimate the power of great communication. It can help you land the job of your dreams, attract investors to back your idea, or elevate your stature within your organization. But while there are plenty of good speakers in the world, you can set yourself apart out by being the person who can deliver something great over and over. Here are a few tips for business professionals who want to move from being good speakers to great ones: be concise (the fewer words, the better); never use bullet points (photos and images paired together are more memorable); don’t underestimate the power of your voice (raise and lower it for emphasis); give your audience something extra (unexpected moments will grab their attention); rehearse (the best speakers are the best because they practice — a lot).
I was sitting across the table from a Silicon Valley CEO who had pioneered a technology that touches many of our lives — the flash memory that stores data on smartphones, digital cameras, and computers. He was a frequent guest on CNBC and had been delivering business presentations for at least 20 years before we met. And yet, the CEO wanted to sharpen his public speaking skills.
- Carmine Gallo is a Harvard University instructor, keynote speaker, and author of 10 books translated into 40 languages. Gallo is the author of The Bezos Blueprint: Communication Secrets of the World’s Greatest Salesman (St. Martin’s Press).
Partner Center
Presentation Skills: How to answer those killer questions
Feb 19, 2017 by maurice decastro in communication skills , presentation skills , presentation tips.

Questions can be a major source of anxiety for many presenters.
In our presentation skills courses we are often asked to help people to answer questions more professionally.
It’s a much bigger issue than many people think.
When we probe a little deeper to understand the issue, our delegates often ask 3 questions:
1. ‘How do I respond confidently to a question I simply don’t know the answer to?’
2. ‘What if I don’t understand the question?
3. ‘How do I deal with hostile questions?’
Our first task is to re-frame the way we think about being asked questions. For many people that presents a significant challenge.
It is often perceived as the moment of truth
We’ve spent hours crafting our presentation to ensure its content rich and helpful. We know our content well and have practiced exhaustively.
We’ve left nothing to chance; so what’s the problem?
It’s as simple as it is frightening. We convince ourselves that our entire reputation depends on how we answer questions.
Unfortunately, there can be a touch of truth behind that limiting belief. That’s why it’s the cause of so much anxiety amongst presenters.
There’s plenty you can do to answer those challenging questions with confidence and credibility. Before we explore them, try to avoid this mistake.
Don’t answer a question saying:
“That is a really good question and I am glad you asked it.”
Quite often, it’s not a good question? If it’s not a good question the response sounds glib. If it is a good question, does that mean the others aren’t?
How you would feel if you asked the next question and the presenter didn’t acknowledge it as a ‘really good question’.
Just answer the question.
The scary six
Our job as presenters extends beyond crafting a content rich, compelling, presentation. We also have to deliver it in a way that is congruent with our message. We have to anticipate difficult questions too.
Surround yourself with a small group of people you trust and respect. Share your presentation with them giving each person a specific role.
Devil’s advocate
Ask them to be contentious, oppose your view and challenge the strength of your presentation.
Their role is to criticise you and to create an atmosphere of hostility and distrust.
The energy thief
Get them to look for a negative aspect of everything you say.
The know all
Encourage them to actively demonstrate that they know more than you on the topic.
Let them tell you in the most respectful way that they don’t agree with you.
The wanderer
They demonstrate that they haven’t listened to a word you said.
It’s not an excercise for the faint hearted because it takes courage.
It is, however an investment worth making.
Once the scary six have taken you and your presentation apart, take another look at your presentation.
As painful and as strange as it may sound, remember it’s not real and it won’t happen. You, however, will be prepared for anything.
What exactly should you do with those awkward questions?
Killer question 1 – You don’t know the answer
The old saying ‘honesty is the best policy’, has stood the test of time because it’s true. The moment you try to bluff your way through a question you don’t know the answer to, you lose your credibility.
Try this instead.
Step into the question. In other words, take a step forward towards your audience. If you are seated then lean forward into the table or desk.
Have you noticed how common it is for people to be on the ‘back foot’ when they don’t know the answer to a question?
Your challenge is to be on the front foot and to step into or lean into the question.
Acknowledge the person who asked the question with eye contact. After that, bring the rest of the room into your response with eye contact too. Once you’ve moved forward and made eye contact, confidently say, ‘I don’t know, but I’ll find out and let you know’.
You have a few choices at this point. You can:
Ask the audience
“I don’t know the answer to that but I wonder whether anyone else in the audience does.”
“Can anyone help answer that question?”
Share a thought
You may not have the answer but you may have a view. Share a thought or perspective on the question if you have one.
‘I don’t know, but I’ll find out and let you know. In the meantime I have a thought on the issue. Please keep in mind that it’s not the answer to your question as I’ve already stated I don’t know the answer but here is a thought…
What’s your view on that?’
Ask for a moment
If you need a little time to think about the question, ask for it.
‘I need a few moments to think about that.’
This also take a little courage but remember, you don’t need to rush in to giving an answer.
Give yourself a little time to think. Your audience will respect you for it.
Postpone the answer
It may well be that you know the answer but under pressure the answer has slipped your mind. This is another opportunity to be honest.
‘ Given the importance of the question, I’d like to give you the most complete answer I can. I will need to get back to you in…’
Killer question 2 – You don’t understand the question
I’ve long held the view that most people don’t really listen. I believe that many do something else – they wait to speak.
“Most people don’t listen with the intent to understand; they listen with the intent to reply.” Stephen R. Covey
That is often the reason why we don’t understand the question. The solution is relatively simple; we need to really listen. That means:
– Listen – to the entire question
– Breathe – don’t leap straight into a response
– Check – ‘Let me just check that I understand you correctly, you are asking me if…’
‘To make sure that I’ve understood you correctly are you asking…’
If you still don’t understand the question, don’t panic. Take a deep breath and ask them to clarify what they mean. Explain politely that you are still not clear you understand the question.
Killer question 3 – It’s a hostile question
Most audiences are on your side. They are friendly, open and are keen to learn from you. That said, every now and then you may get what we call hostile questions.
They feel hostile because of the emotional charge. The questioner may wave their pen at you challenging or criticizing your perspective.
If this happens, your job is to remain calm. Depersonalize the attack and avoid being over defensive; easier said than done I know.
Your first priority is to diffuse the emotional charge and to take care of the rest of the audience whilst respecting the questioner.
Treat them the same as any other member of the audience. Answer their question as honestly and as professionally as you can.
Avoid matching your tone of voice to theirs. Stay calm, professional and polite. Remember that your audience will align with whoever is more courteous and respectful.
Very occasionaly it appears as though the questioner is looking for more of an argument rather than an answer. This is rare but if it happens, you owe it to the rest of your audience to close it down.
You do have some options:
– You can acknowledge their concern and suggest that the two of you meet separately after the presentation to discuss the matter in greater detail.
– If the questioner persists you can calmly assert:
‘I’m afraid I need to move on now.’
It’s possible that you may need to repeat this two or three times.
– A simple but powerful technique you can use to respectfully regain control of your presentation is to:
That means listening very closely and carefully to the perspective of the questioner.
You have listened closely enough to find something you can sincerely agree with. That does not mean you agree with a point they make even if you don’t. It means you listen intently for something that does make sense to you that you can agree with. When there is such a high emotional charge in a question it’s often fueled by passion and a need to be heard.
The questioner isn’t a bad person. They are simply someone who feels very strongly about what you are saying and may not share your perspective. Once you have listened closely enough to find something you can genuinely agree with, no matter how small, there is only one thing left to do.
You acknowledge that you agree with that element of their argument. Tell them that you understand their perspective or that the specific point they just made makes sense to you. Then you pause and you stay silent.
It’s more than a pause of course, as you are signalling to the questioner that you have nothing else to say on the matter.
You don’t say a word and watch what happens next.
Try to understand the motivation behind the question and tone. Share what you are picking up from them: “It sounds like your main concern is with the process. Is that correct?” This will encourage them to focus on the point they are trying to make. It will also give you a little time to consider a response.
One of the many key distinctions between a Mindful Presenter and a mediocre presenter is the ability to handle challenging questions professionally and effectively.
That distinction is achieved through the conscious focus and effort to:
– See questions as an opportunity to learn and engage, rather than be judged
– Listen very carefully to the question
– Lose the ‘headstuff’; in other words not making it all about you
– Pause and breathe
– Repeat the question if necessary and appropriate
– Understand the motivation behind the question
– Respect the questioner and the audience
– Anticipate difficult questions whilst crafting the presentation
– Stay calm, focused and on message
– Close the questions down politely and move on
If you need help answering those killer questions:
– Book yourself onto a powerful public speaking course .
– Invest in some really good one to one public speaking coaching .
– Get yourself some excellent presentation training
Image courtesy of: iStock.com
- Connect Now
Share this article
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share on LinkedIn
To join one of our workshops or lean more, complete our enquiry form or call us on +44 (0)20 7666 3453 and we can get connected.
- Our Approach
- The Benefits
- Public Speaking Courses
- Presentation Training
- The Complete Mindful Presenter
- One-to-One Public Speaking Coaching
- Coaching Development Package
- What Our Clients Say
- The Truth Series
- Our Podcast
- Style Review
- Mindful Selling 4D
- Mindful Leadership
Blog Sign Up
Recent posts.
- Public speaking masterclass
- 10 Reasons to Join Our Next Public Speaking Masterclass
- 4 types of presentation energy: Survival, Safety, Shallow & Smart
- 12 Public Speaking & Presentation Tips For Q&A Success
- 10 Novel public speaking ideas from unexpected sources
- Bullet Point
- Communication Skills
- Mindful Selling
- Mindfulness
- Presentating training
- Presentation Skills
- Presentation Tips
- Public Speaking
- Sales Skills
- Storytelling
- virtual presentation
- Virtual Presentations
- Who are you?
- Learning Centre
- Presentation Skills Review
- Our Clients
- Testimonials
- Presentation Skills Training
- Public Speaking Coaching London
- Public Speaking Anxiety Course
- Phone: +44 (0)20 7666 3453
- Email: [email protected]
- Address: Mindful Presenter Ltd 86-90 Paul Street, London, EC2A 4NE
Sign up for our newsletter and download your free guide to authentic public speaking.

Presentation Guru
The most successful ways to answer questions from your audience.

Every presenter will eventually have to deal with questions from an audience, but what are the best ways to prepare for the questions they may ask? In this article Simon gives a few tips to make sure you’re always ready to answer your audience’s questions effectively, and with confidence .
Let’s face it, presentations are scary. And that’s quite right – they should be. Nerves show you care. If you’re not nervous, why are you bothering? I’ve met good presenters and I’ve met presenters who aren’t nervous: I can count the number of presenters who are in both camps on the thumbs of one foot.
So far, so obvious. But when I ask clients what the most scary bit of presentations is, they most common answer I get is, the questions section.
If I probe deeper, the reasons it’s the most nerve-wracking include things like:
- I can control the rest of the presentation but not this bit
- I can’t rehearse the questions – or the answers!
- I have to think too fast
- I might not know the answers
- I might find out people didn’t like it
- I might have made a mistake
The scary bit, then. The bit of the presentation which brings even experienced presenters out in a cold sweat. Before we get into the tools and techniques for handling questions, let’s look at some of these, very quickly. We can shoot a few of these issues down without breaking sweat – particularly the last few…
Get your ego out of the way
Let’s face it, if you’ve made mistakes, wouldn’t you like to know? If you’d rather people didn’t tell you that you’ve screwed up, you’re not ever going to get a job on my team. The same is true if you’d rather not know that people didn’t like it. Grow up.
And while we’re at it, if you don’t know the answers, that’s fine. Not ideal, but it’s not the end of the world. So long as you know enough, it’s okay. Not knowing the answers is only a problem if you don’t know too many of the answers.
So let’s move on and look at bit more at the ‘real’ issues.
The first thing to say is that more or less any and all of the tricks you learn as a presenter for handling nerves can be used at the start of questions. At the moment when you invite the questions, do your nerves-control-techniques , just like you did at the start of the presentation. (If you don’t have any, pay me to learn some 😉 )
The second key point is very simple. People only ask questions for one of two reasons. Firstly, to show off and secondly because they’re interested. The first group will be transparent to the audience, so don’t lose any sleep over anyone whose ego is bigger than their common sense. The second group, those who ask questions because they want to know more, are to be celebrated. They’re a good thing. Honestly.
Remember, people only ask questions if they care. The very fact that they’re asking questions is a great thing because it shows you did the key thing a presentation is supposed to do – you got them interested. When the questions happen, allow yourself a little smile inside. Result!
Predicting the future – and guessing the questions
But what about this idea that you don’t know what the questions are going to be?
Sorry, but that’s tosh. You might not be able to predict exactly what question, but you can certainly predict the sort of question. A structured, sensible process for designing your presentation – whatever process you use – will certainly throw up more content than you can fit into your presentation. The process of designing your presentation should start off by deciding what to remove.
Chances are, the questions you get will lie in that area you’ve cut out. And if that’s the case, you know what the content is, so you can design your answers just like you’d design the rest of your presentation . Simple.
Well yes… but just because it’s simple doesn’t mean it’s easy. Just ask anyone who’s ever tried to lose weight. The rules of “Eat less: move more” are simple – but not easy!
So let’s break it down a bit to make it more practical. I’m going to start by looking at how to handle the worst case scenario… the blank head where you just don’t know the answer. (Note, I’m dealing with it first because it’s easy to get out of the way, not because it happens often!)
I have no idea
The worst case scenario is simply not to know the answer, so let’s deal with that first. The best way I’ve ever found to handle this issue is to be honest about it, but to respond in a very structured way, so that my credibility stays intact. The formula is this:
- I don’t know, but it’s a good point
- so I’ll find out
- and if you give me your email address I’ll get back to you about it
- by lunchtime on Thursday
Obviously you change the time in the last part to be something you can handle. The first line is a simple admission that you’ve not got the answer to hand. The second part is where you start to recover. The last line is the critical one though. This is how you sound credible to the audience.
Try it for yourself: just say the first line and see how ‘shallow’ it sounds. Then start from the beginning and go through the first two lines. It’s better, but it’s not trustworthy. Finally, run through the whole set of lines and see how much more ‘weight’ the whole thing has when you make a specific promise.
It goes without saying that you need to deliver on that promise!
I still have no idea
A couple of alternative techniques are useful here, too… you can use these in a mix-and-match way.
- Open up to the audience. Try something like “That’ a very good question – what does everyone else in the room think?”. If you do it with enough style and you’ve used an approach up until that point which has been sufficiently collaborative and informal, it can work seamlessly.
- Use a broader-brush answer . Sometimes the question isn’t one that requires a very specific response. You’d be surprised how often one broad-brush answer can be applied to different questions. Take a few moments to consider if this is one of those times. If you’ve got (say) five or six such ‘generic’ answers sorted out in your head before you start your presentation you can often apply one of them instead of trying to improvise an answer.
Save yourself some thinking and PREP
Answering questions means you have to think hard and fast – about both the content of what you say and the way that you say it. One very handy trick is to use structured formulae to give your response a shape. That way you only need to think about the actual content – halving the work on your brain. Once you’ve learned these tools, not only will you love ‘em, you’ll spot them almost every time you listen to a political interview.
This formula is particularly handy for dealing with challenging questions: it stands for Past, Present and Future.
You use it like this:
- “You’re absolutely right to point out that in the past our response times have been too slow. It often took us up to a week to get back to users who emailed in with questions – although the average response time was only 36 hours.”
- “What we’re doing right now is investing in training 14 new members of the online help team. They’re all experts in the software already, so we’re just bringing them up to speed about how the helpdesk works.”
- “What this means that starting next Monday we’ll have a bigger response team standing by, as these new people come on-stream: they should all be up-and-running within only ten days.”
(Numbers 1, 2 and 3 representing Past, Present and Future, in this example.)
This is the most subtle of the formulae, and it stands for Point, Reason, Example, Point. The last point is a restatement of the first one to really hammer it home, not a new point.
The Reason section of your response deals with big picture, data and statistical responses. It puts a logical set of facts to your audience. To make it more impactful with your audience you need to back it up with an Example . Finally you recap your Point .
This example shows you how I used it to respond to a challenging question about women’s rights from someone who was genuinely surprised that women and (more or less) equal rights to men in the UK, including being able to vote…
- “Do I believe women should have the right to vote? Yes, absolutely!”
- “Let’s face it, women make up a bit over half the population of the country and they bring in about forty-eight percent of our GDP – nearly half the money they country gets in.”
- “In fact, in my own household, my wife has a great job and bring in nearly twice the amount I do. It makes her the economic head of the household, although we don’t think of it in those terms. It would seem daft to have the economic head of the household able to vote!”
- “So yeah, absolutely, I think women should vote!”
I’ve labeled the PREP parts as numbers 1 to 4 so you can see what’s what, but the words should flow naturally.
That’s it. Actually it’s not – there’s always more to be said… but it’s a great start.
Predict your questions, prepare your answers. Celebrate them when you get them, and use formulae to help you structure your answers. You’ll be great!
Don’t finish with questions
It all too easily means your presentation gradually runs out of energy and finishes with a whimper. Better to end with a bang. What I do is to take the questions and then when there are (almost) no questions left, go back into ‘ delivery ’ mode to give a very (very!) brief summary before wrapping up with my trademark close. It means the presentation finishes with high energy, on my terms…
- Latest Posts

Simon Raybould
+simon raybould, latest posts by simon raybould ( see all ).
- Motivational Speakers – Are They All They’re Cracked Up To Be? - 4th April 2017
- Do I Really Need Slides in Every Presentation? - 18th October 2016
- The Most Successful Ways to Answer Questions From Your Audience - 8th September 2016

Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Follow The Guru

Join our Mailing List
Join our mailing list to get monthly updates and your FREE copy of A Guide for Everyday Business Presentations

The Only PowerPoint Templates You’ll Ever Need
Anyone who has a story to tell follows the same three-act story structure to...

How to get over ‘Impostor Syndrome’ when you’re presenting
Everybody with a soul feels like an impostor sometimes. Even really confident and experienced...

8 tips for encouraging questions in your presentation
by Olivia Mitchell | 8 comments

Most of us would like people in the audience to ask questions. A lively Q&A session is stimulating and engaging for the audience. But sometimes you ask for questions, and you’re just met with blank gazes back from your audience. It’s a let-down and your presentation ends on a sour note.
Questions from the audience are like young fragile seedlings – they need nurturing. Consider when you’re in the audience – what stages do you have to mentally go through in order to ask a question? It might go something like this:

So as the presenter, you need to nurture your audience’s questions through these four stages. Here are 8 tips to help make them through:
1. Pitch your presentation at the right level for your audience
The first stage of questions is birth – they have to be born in your audience’s mind. If your presentation is too simple for the level of knowledge in your audience – it’s all material they’ve covered before – they won’t have any questions. Conversly, if it’s too complicated for them, they’ll turn off rather than risk asking a question which might make them look stupid.
2. Don’t cover every aspect of your topic in the presentation
If you cover everything there is to know on the topic – you won’t leave room for questions. So don’t be exhaustive in your coverage.
3. Let your audience know you would like questions and when to ask them
Near the beginning of your presentation let your audience know that you welcome questions. Then let them know when to ask them. There are a number of options:
Take questions throughout your presentation
Tell people they can interrupt you throughout the presentation to ask questions as they come to mind. This has several benefits:
- people won’t have to remember their question till later
- if they’re uncertain about something they can get that clarified at the time
- questions on a particular issue are dealt with at the same time that you’re discussing that issue.
The downside to this strategy is that it can take you off track if people ask irrelevant questions or questions that you’re going to cover later in the presentation. If you find it tricky to get back into the flow of your presentation after an interruption it may not be the best strategy for you. Finally, it can throw the timing of your presentation if people ask a lot of questions on a particular issue. This strategy is best used in longer presentations and training courses where timing is less critical.
Take questions at defined points of your presentation
Tell people you will have an opportunity for questions after you’ve finished each part of your presentation. This option is a useful halfway point between having questions throughout and leaving them till the end of the presentation. You can also decide how long to take questions for during each break in your presentation, and so control the timing better.
4. Let them ask a question as soon as they have one
If you’re serious about ensuring that people get their questions answered, invite people to interrupt you and ask their question. It’s the only way to ensure this. That’s when the question is burning for them. The longer you make people wait, the less likely they are to remember it. Once you’ve moved onto a new topic, their question will seem less relevant. Joey Asher from Talking Points blog says:
Questions aren’t to be feared. They’re to be embraced. There’s no better way to connect with an audience than to allow them free rein to ask as many questions as they want.
5. Invite people to write down their questions as they think of them
If you don’t want to take questions throughout, you can help people remember their questions by suggesting that they write them down.
6. Validate every question
It takes courage to ask a question. It’s public speaking – just not from the front of the room. People are held back by wondering if their question is stupid or did they miss something and you already answered it. So you need to do your bit to make it a safe environment for people to ask questions. Do that by responding warmly to all questions that are asked – even if the question is stupid or you had already covered it. I don’t recommend saying “Good question”. It’s become a cliche which is often used when the presenter can’t immediately think of the answer.
7. Have people discuss in pairs any questions they may have
If your audience seems a little shy, give them an opportunity to discuss their questions with one other person before they ask them in front of the whole of the audience. Here’s how do do this:
“I’m going to ask for questions in a moment. Please turn to the person next to you and discuss together any questions you have. Then I’ll answer those questions.”
This has several benefits:
- It gives people the opportunity to try out their question in front of one person before risking humiliation in front of the whole audience.
- Any questions that are answered by material you’ve already covered can be answered by their partner.
- It gives people the opportunity to rehearse and fine-tune their question so that it will be shorter and clearer when they ask you.
8. Answer questions clearly and succinctly
If you answer every question with a long-winded and incoherent ramble, people are going to be reluctant to ask you another one. They’ll conclude they’re unlikely to get a useful answer from you. Nor do they want to subject the rest of the audience to another ramble.
More resources on other blogs
Five ways to make presentations Q&A friendly from Joey Asher at Talking Points. He also recommends validating every question:
Smiling at the questioner is like rewarding a dog for sitting on command. Once rewarded, the chances are the audience will ask more.
John Windsor has a useful post Making the most of a Q&A session . He stresses anticipating the questions that might be asked. And also advises that you recap and conclude your presentation after the Q&A session. That provides a stronger ending to your presentation than just lettting questions peter out.
Andrew Dlugan discusses Leading the perfect Q&A . This covers all elements of the Q&A session from both the audience’s point of view and the presenters.
Free Course
How to tame your fear of public speaking.
In this video-training series (plus workbook with transcripts) you’ll learn:
- The three things you must know BEFORE you begin to tackle your fear of public speaking
- Why the positive-negative thought classification doesn’t work for fear of public speaking
- The two powerful self-talk tweaks that can make an immediate difference.
You have Successfully Subscribed!
I ask for your email address to deliver the course to you and so that I can keep on supporting and encouraging you with tips, ideas and inspiration. I will also let you know when my group program is open for enrolment. I will keep your email safe and you can unsubscribe at any time.
Hi again Olivia – just seen this following someone else’s link. It’s something I blogged about myself a while ago – and in retrospect I probably over-stated my case: http://www.curved-vision.co.uk/presentation-skills-blog/2008/03/29/questions-or-not/
To me, it’s important to differentiate between two types of question. Firstly, you’ve got questions of fact (“Did you say 200%?”) which seem to me to be necessary at any point because otherwise people won’t be able to make much of anything you say after that.
Secondly though, there are questions of “application” for lack of a better term. Things like “So in my position, would it make sense to….?”. I love these questions as it shows the audience has bitten what I’ve said and is running with it. My instinct is that these questions should only surface at the end (in fact if the presentation is well structured this is probably the only place it CAN surface!).
And, for the “during the presentation so askers don’t forget”, I’ve also seen Twitter used effectively – either as a displayed backchannel – so that the whole audience can see, or just visible to those who have the necessary hardware. Quite often, small questions can be answered by someone else in the audience (like whispering to the person next to you – only there are lots of people next to you!), or the presenter/room host can skim them at the end & answer the key ones.
Hi Emma Yes, that’s a great use of the backchannel. Thank you for adding it to this post. Olivia
You actually make it seem really easy with your presentation however I to find this topic to be actually one thing which I believe I might never understand. It seems too complex and very wide for me. I am taking a look forward to your next publish, I will attempt to get the dangle of it!
Nice response in return of this query with real arguments and explaining the whole thing concerning that.
Các c? ?ã có câu Nh?t dáng nhì da th? ba là váy c??i”.
Right here is the right website for anybody who wishes to find out about this topic. You understand a whole lot its almost hard to argue with you (not that I actually would want to…HaHa). You definitely put a new spin on a topic that has been written about for years. Wonderful stuff, just wonderful!
Look no more, as I will give you the 918Kiss Free Obtain along with the 918Kiss Free Credit score. Let’s check out every thing that 918Kiss does proper. The opposite thing which makes Lucky Palace so special is its versatile. Lucky Palace has easily grow to be probably the most most popular online casino played all over Malaysia. In addition, there are several online on line casino platforms however the most effective and safest is SCR888 / 918KISS. SCR888 / 918KISS is certainly one of the top-notch on-line casinos in Malaysia and emerges as a reliable platform with none fear of inhibition. Should you try one webpage, you might imagine you’ve tried all web sites.For example XE88 platform Nevertheless, whatever the similarities between one site and one other, many web on line casino websites typically fluctuate significantly. Regardless of whether its recollections of outdated companions, associates, and family, individuals we could see every day or might have put some distance between, each previous sport we burden up is a window to the previous and that’s extraordinary. Games today spotlight fully organized scores or soundtracks including properly-recognized music which are just as nice as what we would see in different mediums, however it looks like we have misplaced one thing en route, as effectively. I messed round per week ago and I couldn’t let you recognize whether they’d music by any means. Don’t let this opportunity slip previous you. Wistfulness may appear to be a cop-out the reply; all things considered, considering again on the previous with rose-tinted displays are frequently what fanatics of anything retro is reprimanded with.
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- 15 ways to improve your presentations in 2009 : Speaking about Presenting - [...] When you’re just starting out presenting, it makes sense to take questions near the end of your presentation. It’s…
- IPDI » Blog Archive » Innovation Brainstorm: Public Speaking and Twitter - [...] with asking the audience for “out-loud” questions as well. It’s good practice to stop for questions throughout your presentation…
- Best Presentation Tips | Speaking about Presenting: Presentation Tips from Olivia Mitchell - [...] 8 tips for encouraging questions in your presentation [...]
- How to Present While People are Twittering — Pistachio - [...] with asking the audience for “out-loud” questions as well. It’s good practice to stop for questions throughout your presentation…
- The first five stages of speaker development - [...] to look for in a presentation skills trainer 8 tips for encouraging questions in your presentation How to survive…
- Sparring Sessions With Questions | The Public Speak King - [...] http://www.speakingaboutpresenting.com/audience/presentation-question-time/ Share this:TwitterFacebookLike this:LikeBe the first to like [...]
- How to Handle Questions during your Presentation | Moving People to Action - [...] Olivia Mitchell on 8 steps to encourage questions from the audience [...]
Got an important presentation coming up?
Got an important presentation coming up and: You have so much content that you can't figure out what to leave out? Don't know where to begin your design process? Worried that your material won't be of value? Feeling overwhelmed and can't get started? Can't figure out your theme? Concerned you won't be engaging? Time is running out?

Recent posts
- Why striving to be authentic can be a trap
- The first time is never the best
- The Need to be Knowledgeable
- Would you wear clothes that clash?
- An unconventional approach to overcoming the fear of public speaking
Connect With Me

Recommended Books
Click here to see my favorite presentation books.
I earn a small commission when you buy a book from this page. Thank you!
- Audience (22)
- Content (62)
- Delivery (31)
- Nervousness (30)
- Powerpoint (37)
- Presentation blogs (2)
- Presentation books (4)
- Presentation critiques (9)
- Presentation myths (6)
- Presentation philosophy (5)
- Presentation research (11)
- Presentation skills (23)
- Presenting with Twitter (10)
- Visual thinking (3)
How to Tame your Fear of Public Speaking
- Do you have to perform perfectly?
- Do you beat yourself up if you don't?
- Would you talk to a friend the way you talk to yourself?
- Does it make sense that if you changed the way you talked to yourself, you could reduce your fear of public speaking?
I will show you exactly how in this free video training series and workbook.
Discover more from Speaking about Presenting
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
Presentation Skills

- Introduction
- Storytelling
- Presentation Outlines
- Tools for Creating Presentations
- Designing Presentation Slides
- Finding & Citing Media
- Preparing & Testing Technology
Handling Audience Questions
- Presentation Anxiety
- Online Presentations
- Feedback Form
- Co-Curricular Recognition Form
- Faculty Resources
The Question & Answer (or Q&A) session happens at the end of your presentation—audience members are free to ask you questions about your content and your ideas, and you have the chance to show how well you know your research.
But what happens if someone asks a tough question?
In this section, we'll look at how to handle audience questions so you can feel more in control of the situation.
Tips for Answering Questions in a Presentation
Make sure you understand the question and that you've heard everything the person wants to learn.
Re-state the question in your own words and have the person confirm that you've heard and understood their question. For example, you could say, "Are you asking…?" or "Did you mean…?" before rephrasing the person's question.
Be direct and honest. If you don't know the answer, that's okay too, but you should try your best to respond in a way that will satisfy the person who asked you the question.
Use a story that is relatable to the audience to build a better connection with your audience.
If someone asks you a difficult question, don't get rattled! Make sure you're polite, professional, and courteous. Be prepared for your presentation—think about what people might ask you during your presentation and either include the content in your session or leave it for the Q&A.
How to Handle Different Types of Questions
Handling questions from audience members can be one of the most difficult aspects of presenting your work. So, what kinds of questions might come up during your Q&A session?
Check the boxes below to learn more about a few different types of questions and how to handle them.
Direct Questions
Direct questions are the typical questions we use when we want information. Direct questions require direct answers. You want to be clear and concise with your response, and you'll likely only need one sentence to answer the question.
There are three types of direct questions:
- True/False (Yes/No) : You either confirm or deny what the questioner has asked you.
- Multiple Choice : You state which option is true based on two or more choices included in the question.
- Fill in the Blank : Your answer will provide missing information for the questioner.
Hostile Questions
Hostile questions are often designed to challenge the narrative, structure, and conclusions of your presentation. These types of questions can range from annoying comments or rude interruptions to mild differences of opinion to highly charged challenges.
It's important to handle these kinds of disagreeable questions without getting hostile back. Remember: You have the power to control and optimize these difficult situations.
Types of Hostile Questions
Four common types of hostile questions include:
Example: "Your conclusion here is unrealistic, don't you think so?"
With these types of questions, you can respond with a simple “No,” immediately followed by a recap of the issue under consideration.
For example: "No, my conclusion is based on… and…"
In this case, long answers can be effective for diffusing the hostility. Maintain a neutral expression, and maintain eye contact with the questioner. Focus on the issue at hand and use this time to reinforce your ideas. Don’t let your emotions dictate your response.
Example: "How can you suggest such a flawed idea to solve this issue?"
What's essential about your response here is that you do not repeat the inflammatory word (in this case, it would be "flawed"). Keep a cool head, and summarize the issue without repeating the word that the questioner used.
For example: You might start your response saying, “The issue at hand is what impact this solution will have on our user group going forward… ”
You can then use this time to provide more information about how you came to this solution for this particular user group. Respond on your terms, not the terms of the questioner.
Example: "What kinds of sources did you look at to come to your conclusion?"
This type of hostile question is difficult to convey in a written form because they will sound similar to a direct question. The question is not using any inflammatory words or asking you to agree with a negative, but the question may still be hostile depending on the tone
In these situations, ignore the tone and respond as if the question was asked in a completely straightforward way–as difficult as that may be. Stay calm and give the questioner the information in a simple, direct way.
Example: "Given your background and limited knowledge on this subject, why did you even choose this topic for your presentation?"
Negative preconditions refer to the inclusion of negative assumptions or statements about the presenter or their work before the question is even asked. By framing the question in a negative way first, the presenter is then put into a defensive position, which makes it harder to provide a confident or satisfactory answer.
Similar to inflammatory trigger words, try to ignore the negative preconditions and focus exclusively on the issue at hand.
For example: "During this project I learned… which has a major impact on… As I stated earlier in the presentation, I was drawn to this topic because of… and… which has helped me…"
It's important to note that these kinds of negative preconditions are not constructive or helpful in the classroom—ideally, your professor will confront the person who asked a question like this!
Multi-Part Questions
Multi-part questions are questions that have multiple distinct parts or sub-questions. Instead of asking a single, straightforward question, the questioner will weave together different inquires in the same question.
For example: "I appreciated that your project focused on renewable energy sources—I was curious about a few things: What are the advantages of those sources in Ontario? Are they more expensive than our current energy solutions? What's their potential for widespread adoption here?"
As a presenter, it can be difficult to keep track of all these different questions—in most cases, the questioner genuinely wants more information, but they know you'll only have time to call on them once during the Q&A session.
You can approach this situation by answering each part separately. It can help to pretend a different questioner asked each question. Make sure that you're concise with your answers so that other audience members can ask their questions as well.
If you're having trouble remembering each part of the multi-part question, you can ask: "Could you remind me of your next question?" There's nothing wrong with briefly asking the questioner to repeat a part of their question—it shows that you care about providing a complete answer for your audience.
Long-winded 'Questions'
Long-winded 'questions' are more of an experience than a question.
In this situation, an audience member will flood you with their opinions or personal stories and there may or may not be a question tacked on to the end of their speech—but you're still expected to respond to them.
For example: "This is more of a comment, but your presentation reminded me of a project I worked on where I had to… It's refreshing to see someone else explore this topic, I only just learned about it last term when we… I was hoping to learn more about… I added something similar in my presentation for… … …"
A simple way to handle this situation is to acknowledge the higher-level, big picture ideas in what the person has said, and to then talk to the central idea of their 'question'. You don't need to address all the smaller opinions or ideas the person has shared—just stay focused on the key ideas or arguments from your presentation.
You could start by saying, "Clearly, there are a lot of issues going on here. Overall, I would say…" and then either answer the question or summarize your key ideas in about 2-3 sentences. Then you can move on to the next questioner.
Watch the video below to learn about the tone you should use during your Q&A session. You'll also learn specific phrases you can use to clarify questions or communicate when you're not sure about an answer.
Tips to Run a Successful Q&A Session
Successful presenters prepare for the Q&A session with the same focus and detail as their presentations—this is a chance for you share extra details, clarify any confusion, and make a great last impression on your audience.
Check the boxes below to learn what you should do before and during your presentation to create a smooth, successful Q&A!
Before Your Presentation
You might not know exactly which questions you'll be asked during your Q&A session, but there are still ways you can prepare yourself.
Try the following three techniques before your next presentation:
Work out the answers to these questions as you're working on your presentation—these questions can help you figure out where you might need to do more research. Decide which questions you'll incorporate into your presentation, and which ones you'll leave to the Q&A session.
Test out your presentation with a friend, a family member, or a tutor at Sheridan's Tutoring Centre . Ideally, you want to test your presentation on someone with little to no knowledge about your topic—they can help point out areas that aren't clear so you can add more detail. You can book a free tutoring appointment on TutorOcean .
Spend time practicing your answers by speaking them out loud. The more you prepare, the more natural you will sound during your Q&A session!
During Your Q&A Session
Use an open-ended question (e.g., "Who has the first question?" "What topic should we start discussing?") rather than a 'yes/no' question (e.g., "Are there any questions?" to get the conversation started.
If you've waited about 30 seconds and no one is asking a question, you could start the Q&A by talking about something that interested you in you research. For example, "When I started my research, I had a lot of questions about 'X'. A key part of 'X' is…"
Repeating questions serves two main functions: First, it allows you to clarify what the questioner has asked; second, it helps to make sure your audience has heard the question.
You don't need a quick answer for everything—give yourself the chance to think about what the questioner has asked, what you know about the topic, and what information might help the questioner.
Aim for 2-3 sentences in your answer. If you feel like your answer needs to be longer, offer a summary of your ideas in 2-3 sentences and then offer to either talk to the questioner after your presentation or to e-mail the questioner (or the class) with a longer response.
It's better to say, "I don't know, but let me look that up and I'll send a note to the class" than it is to make up an inaccurate or misleading answer.
If someone asks you a difficult question, respond calmly and politely. Help the questioner feel heard by briefly acknowledging their concern or point or question, and then offer to follow up with them after the Q&A session is over.
End your Q&A session by thanking everyone for their thought-provoking questions. Make sure that you return the favour by engaging with your classmates during the Q&A session of their presentations too!
- Last Updated: Jan 12, 2024 2:29 PM
- URL: https://sheridancollege.libguides.com/presentationskills
Connect with us

- PRESENTATION SKILLS
Dealing With Presentation Questions
Search SkillsYouNeed:
Presentation Skills:
- A - Z List of Presentation Skills
- Top Tips for Effective Presentations
- General Presentation Skills
- What is a Presentation?
- Preparing for a Presentation
- Organising the Material
- Writing Your Presentation
- Deciding the Presentation Method
- Managing your Presentation Notes
- Working with Visual Aids
- Presenting Data
- Managing the Event
- Coping with Presentation Nerves
- Dealing with Questions
- How to Build Presentations Like a Consultant
- 7 Qualities of Good Speakers That Can Help You Be More Successful
- Self-Presentation in Presentations
- Specific Presentation Events
- Remote Meetings and Presentations
- Giving a Speech
- Presentations in Interviews
- Presenting to Large Groups and Conferences
- Giving Lectures and Seminars
- Managing a Press Conference
- Attending Public Consultation Meetings
- Managing a Public Consultation Meeting
- Crisis Communications
- Elsewhere on Skills You Need:
- Communication Skills
- Facilitation Skills
- Teams, Groups and Meetings
- Effective Speaking
- Question Types
Subscribe to our FREE newsletter and start improving your life in just 5 minutes a day.
You'll get our 5 free 'One Minute Life Skills' and our weekly newsletter.
We'll never share your email address and you can unsubscribe at any time.
Many otherwise extremely competent and confident presenters will tell you that they really dread the question and answer session of a presentation.
They seek ways to ‘avoid’ difficult questions. But it doesn’t have to be like that.
Dealing with questions in a presentation is a skill which anyone can master.
Perhaps the most important thing to understand is that, as a general rule, if people ask you questions, even hostile ones, it’s not to trip you up but because they genuinely want the answer.
Staying in Control of the Questions
Most people dread the question session because they fear losing control.
A little thought and some early planning can avoid this risk. But you can also avoid it by remembering that any presentation is an information exchange. It is as much for you to hear what people want to know as for them to hear from you.
However, if your presentation starts to get diverted by an interesting question, try saying something like:
“I think we’re getting a bit off topic here. Let’s put that to one side and you and I can chat about it later. Come and find me at the end and we’ll exchange contact details.”
“I’d really like to get on with the presentation, otherwise I may not have time to finish, but let’s talk about this later.”
Setting out some Ground Rules
At the start of your presentation, you should make it clear whether and when you would prefer to deal with questions - as you go along or at the end of the presentation.
Some speakers prefer questions to be raised as they arise during the presentation. The advantage of this approach is that any misunderstandings can be dealt with immediately. However, there is also a danger that the question will disrupt or distract the speaker, or that questions are raised that would have been covered later in the presentation.
Top tip! Categorising Questions
If you like to deal with questions as they arise, but you are concerned about the pitfalls, there is an easy way to handle this. In your introduction, explain that there are three types of questions:
- The sort that seeks clarification of something that has just been said – you will answer those immediately;
- The sort that asks a related question about something that you plan to cover later – you will answer those later in the presentation; and
- The sort that is best dealt with offline because most of the audience probably won’t be interested, or it’s outside the topic of the presentation – you will make a note of the question and come back to the questioner afterwards.
When a Type 2 or 3 question is asked, you can then say something like:
“ That’s a Type 2 question, so I’ll park that for now, and cover it later. If you don’t think I’ve covered it by the end, remind me, and I’ll go over it.”
Other speakers prefer to deal with questions at the end of the presentation.
If you prefer this approach, ensure that you set aside sufficient time for questions but also limit the amount of time available. The amount of time will depend on the type of presentation you are giving but usually 10 minutes of question time should be sufficient.
The big advantage of this approach is that if you talk too quickly, you will simply have a longer question session: a big incentive to talk slowly and carefully, and make sure that your audience understands everything as you go.
You should not close the presentation with the question and answer session.
When you have finished answering questions, make sure that you have the last word with a strong assertion of your main message(s).
In other words, you can thank the audience for their questions and then summarise once again the main point or points that your presentation was designed to communicate.
An Introduction to Question Sessions
The main rule of question sessions is to treat your audience with the respect you would like to have shown to you, and answer their questions directly and honestly.
If they have asked a question, it is because they want to know the answer.
It is very unlikely that anyone will ask a question solely to trip you up, although this does happen.
If a question is provocative, answer it directly. Never be rude to the questioner or show you are upset. Do not compromise yourself but maintain your point of view and never lose your temper.
This tactic can be difficult to maintain but the key is being assertive.
Visit our section on assertiveness to learn some more tips, start with: Assertiveness - An Introduction .
Managing Questions
Listen carefully to the question and, if the audience is large, repeat it to ensure everyone in the audience has heard.
If you’re not sure you understood correctly, paraphrase it back to the questioner and check that you have it right. Answer briefly and to the point.
If you do not know the answer, then say so and offer to find out. Then ensure that you follow up . To be able to respond, you will need the questioner’s name and email address, so make sure that you speak to them before they or you leave.
“ I don’t know ” is a very acceptable answer to some difficult questions and it is much more acceptable than stumbling through an answer or making something up. “ I don’t know, but I’ll find out and let you know ” is even more acceptable.
Relax and do not feel as if you have to know everything. If you don’t know it is better to be honest than to try to pretend.
Trust takes a long time to build up, but it can be lost in moments, and audiences will almost always know when you are not being genuine.
An Alternative Tactic: Involving your Audience
If you are speaking to a well-informed audience, a professional group for example , and the question is a fairly general one to which you do not know the answer, consider asking the room if anyone else would like to respond. You may have the world expert on that subject sitting there who would be delighted to share their expertise with you all. If you have noticed someone in particular, you can even say:
“ I noticed that Professor X is in the room, so I wonder if he would like to comment on that to save me displaying my ignorance ”
“ My colleague over there is more familiar with that area than I am so, while I don’t want to put him on the spot, maybe he would be prepared to shed some light on this? ”
Most people will be fine with that approach, especially if they really do know more about it than you, and it will mean that the room gets a much better response. Yes, you’re the one standing at the front, but you don’t know everything.
You may also find our general pages on questioning useful see Questioning and Question Types .
Continue to: Coping with Presentation Nerves Managing the Presentation Event
See Also: Preparing for a Presentation | Organising the Material Deciding the Presentation Method Working with Visual Aids
Blog > The Right Way to do a Question Slide in your PowerPoint Presentation
The Right Way to do a Question Slide in your PowerPoint Presentation
01.20.20 • #powerpointtips #presentation #engagement.
You just finished your presentation. You’re asking your audience if there are any questions. Nobody, or one or two people at best raise their hands, but you’re quite sure that your audience actually has a lot more to ask. Does that sound familiar?
If it does (which is likely, as many presenters experience that phenomenon), you’re in the right place. Some may take the silence after asking the audience if there are any questions personal, as if they are not a good enough speaker or as if they just held a terrible presentation. Others may be happy and think that they explained everything so well that there are no more questions to ask. In reality, probably none of those is the case. It all comes down to the way you ask questions – and here’s how to ask them (well – first here’s how not to ask them!)

How not to ask Questions
The absolute worst, but sadly often used method to ask your audience about any questions they have is the “Any Questions?” – Slide, which is, like you may guess from the name, a simple slide at the end of the presentation with the words “Questions?” or “Any Questions?” on it. Why is it so bad? Well, first of all, it’s extremely unspecific. It’s likely to overwhelm your attendees. They will try to force their brains to think of something to ask, but due to the amount of information you just gave them in your presentation often can’t think of anything. Another factor is the fear of public speaking many have. There may be someone in the audience who wants to ask a question, but is too shy to raise their hand and actually ask it – often out of fear of asking a “stupid” question.

How to ask Questions (in order to get Questions)
So here is what you came for: Better ways to get your audience to talk to you and actually ask about what they would like to know.
1. Use a Q&A Tool
Let your audience ask questions via their smartphones or notebooks – even anonymously – and be sure no one ever holds back any questions. Q&A tools such as SlideLizard are integrated seamlessly to PowerPoint. Your attendees connect their devices with your presentation and are then able to send in as many questions as they want by simply typing them into their phones. The question will arrive directly at your presenter’s view. You’ll see it immediately after it has been asked. The huge advantage is that you can answer the questions even during the presentation, or wait until after you’ve finished. Also, be sure to invite your audience at the beginning to ask any questions they have via the Q&A tool, and inform them about when you will answer them.
2. Ask specific questions
We recommend leaving out the “Any Questions?” slide at the end, but if you still insist on using something similar, this is the way to go. It is an insanely easy tip, but it has great impact. Instead of just asking if there are any questions, you just assume there are some and ask your own questions accordingly. Here are some good examples:
- What was unclear?
- What else would you like to know?
- What would you like to know more about?
- What was missing in my presentation?
- What was surprising for you?
- What was new to you?
- What did you find most interesting?
Notice how none of these questions can be answered with “Yes” or “No”. That is key to getting your audience to actually reflect on the input and talk. Also, don’t fill your slides with all of these reflective questions, as that may again overwhelm the audience. Decide what you would like to know and use 1 – 3 of the prompts.

3. Do a Poll/Quiz at the end
Even though this is not a conventional way of a Q&A session, it will still show you and your audience whether they have understood what you just talked about or not. Create a little trivia quiz and test your audience. By looking at the result of each individual question, you’ll see if you have to explain something again or if the majority already got it. For this method, you can again use tools like SlideLizard , that have an integrated poll function where you can analyze the results even after the presentation is done. Of course, you can also combine this third method with one of the previous ones.
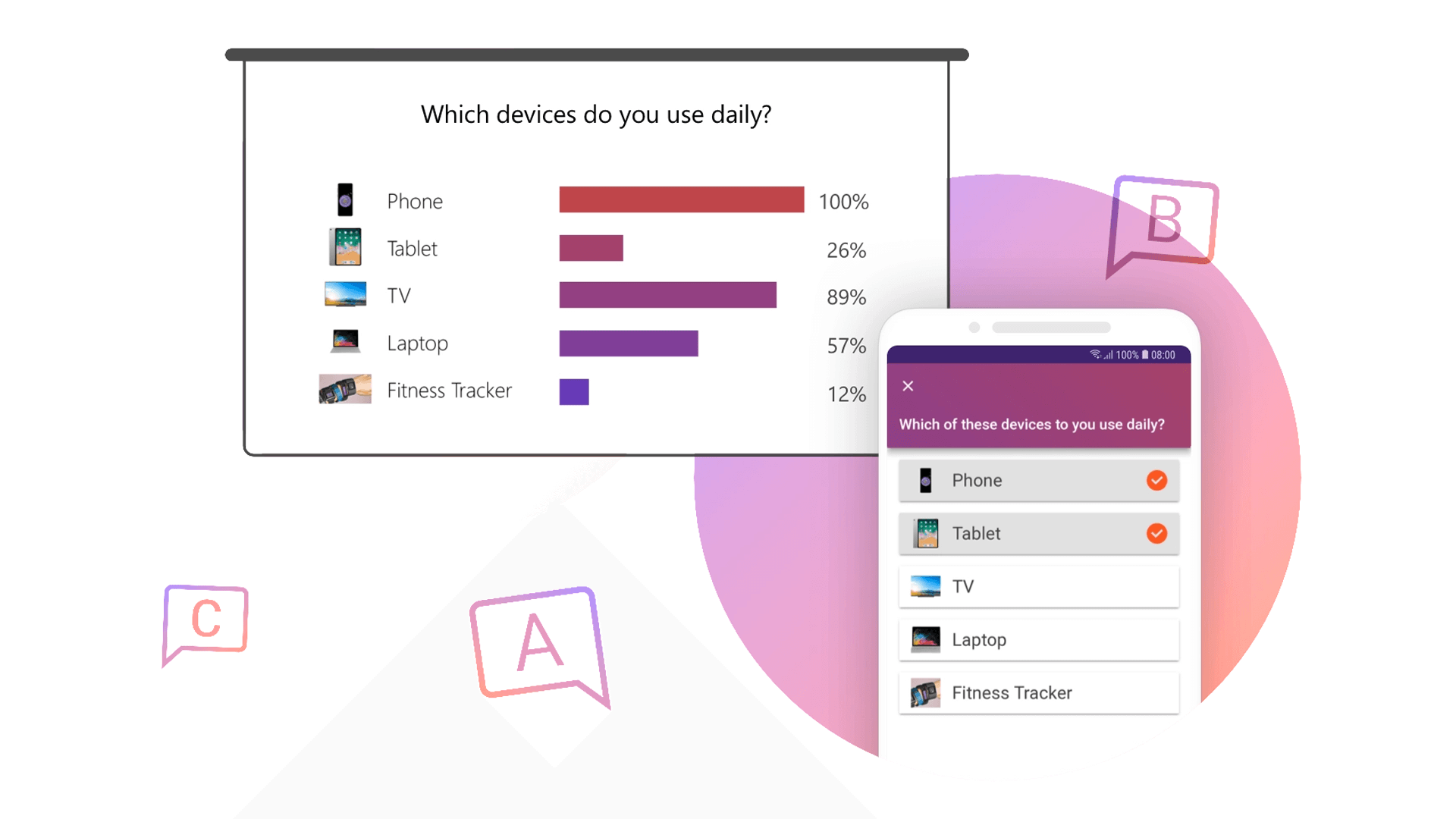
Get Inspired
A good beginning and ending are essential for giving an awesome presentation – similar to a book. The beginning makes you want to keep on reading, and the ending makes it memorable. If you want to get some inspiration and learn innovative new ways for creating title and final slides, check out this guide: 10 creative ideas for title and end slides .
Related articles
About the author.

Pia Lehner-Mittermaier
Pia works in Marketing as a graphic designer and writer at SlideLizard. She uses her vivid imagination and creativity to produce good content.
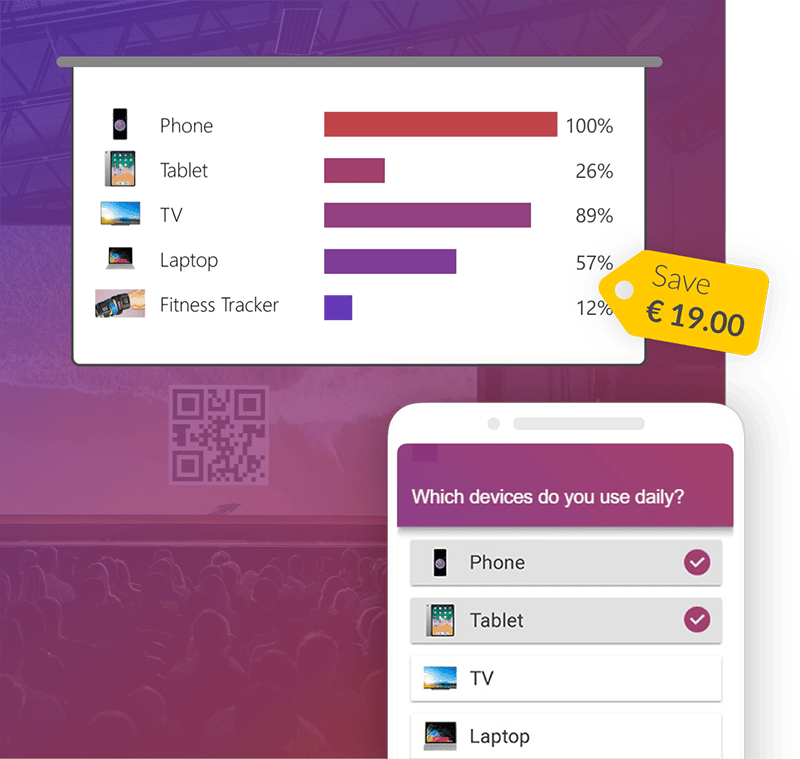
Get 1 Month for free!
Do you want to make your presentations more interactive.
With SlideLizard you can engage your audience with live polls, questions and feedback . Directly within your PowerPoint Presentation. Learn more

Top blog articles More posts

6 Tips to turn your boring slides into stunning presentations

Free Christmas PowerPoint Template
Get started with Live Polls, Q&A and slides
for your PowerPoint Presentations
The big SlideLizard presentation glossary
Student response system (srs).
With Student Response Systems (SRS) it is possible to get live student feedback in the classroom. Questions and answers can usually be asked and given anonymously, which increases participation and engagement. An SRS may be used for any grade, including university.
Glossophobia
Glossophobia means the strong fear of public speaking.
Multimedia Presentation
A multmedia presentation is a speech in which several types of visual and audio aids are combined in the same speech with the help of computer software. .
Concept Presentation
In a concept presentation, you have to give general information as well as try to convince the audience with good arguments and deliver a solution concept.
Be the first to know!
The latest SlideLizard news, articles, and resources, sent straight to your inbox.
- or follow us on -
We use cookies to personalise content and analyse traffic to our website. You can choose to accept only cookies that are necessary for the website to function or to also allow tracking cookies. For more information, please see our privacy policy .
Cookie Settings
Necessary cookies are required for the proper functioning of the website. These cookies ensure basic functionalities and security features of the website.
Analytical cookies are used to understand how visitors interact with the website. These cookies help provide information about the number of visitors, etc.

How to handle questions during a presentation
Posted by Belinda Huckle | On January 29, 2022 | In Presentation Training, Tips & Advice
In this Article...quick links
1. Tell the audience in advance when you will be taking questions
2. anticipate questions in advance, 3. realise that questions are a good thing, 4. make eye contact with the questioner, 5. always take a brief pause before launching into your answer, 6. be sure that you understand the question they are asking or point that they’re making, 7. acknowledge how valuable the question they’re asking is, 8. always keep your cool, 9. be honest if you don’t know the answer, 10. answer in sections if the question is a long one, 11. check-in with the questioner after you have given your response, follow us on social media for more great presentation tips:.
You’ve prepared your presentation, practised it a dozen times and you’re ready to go. But what’s the one thing that might throw you off course, undermine your confidence and your credibility? An awkward question. One that comes at an inopportune time, or one that’s difficult, or one with a complicated answer, or one you can’t answer! So it will come as no surprise that a question we get asked frequently centres around how to handle questions during a presentation!
Think about your work or everyday life, when someone asks you a question, how do you usually respond? Do you take a minute to think about your answer before launching into an explanation?
Do you interpret their question as a challenge of your authority/knowledge/intelligence and become defensive? Do you answer a question with another question? Did you notice that we’re asking a lot of questions right now…?
There are seemingly a thousand ways to answer a question and the kind of answer you give and how you deliver it can go a long way in helping to build positive relationships with other people, as well as facilitating constructive and helpful debates and conversations about certain issues and topics.

This is especially true in workplace environments, where you may be giving a presentation to your client, or delivering the quarterly business results to your team.
Questions may arise from the audience , which do have the potential to throw your presentation off course or set a bad tone in the room if not handled well. Some people can even inadvertently come across as rude, curt or dismissive when answering questions, simply because they feel attacked or they’re rushing to get back to their presentation before they lose their train of thought.
So in today’s blog post you’ll learn how to handle questions during a presentation. We’ve given you some specific advice to follow when answering questions and how to always remain courteous, on-track and respectful of the question-asker – so that in turn, you look professional and knowledgeable.
One of things that can sometimes throw you off course is being asked a question when you are mid-flow through a presentation or least expect it. It can interrupt your train of thought and momentarily put you off balance.
One way to avoid this is to agree in advance when you will be taking questions; anytime, at the end of each section, or at the end of the presentation. This way you won’t be surprised when they come up.
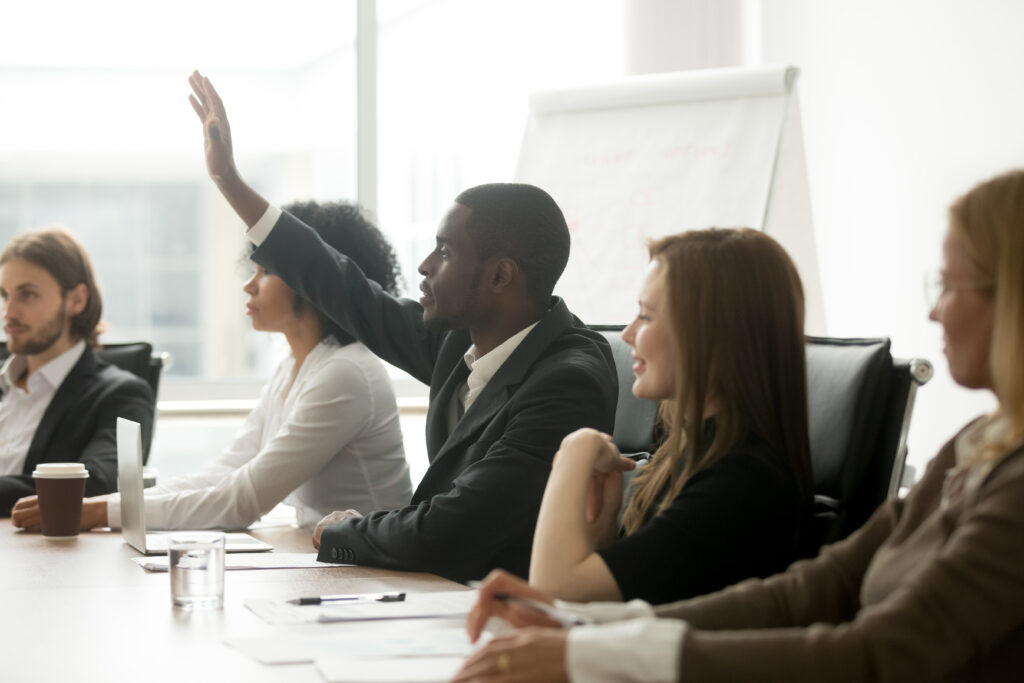

Whilst you are preparing your slides or deck, think about the questions you might be asked around the content and formulate your answers ahead of time.
Look at the content through the eyes of the audience and try to anticipate where their views might differ or where they might need clarification. If you are presenting to your executive board , you might be questioned on how your ideas affect or support the bottom line. Whereas a presentation to middle management on streamlining processes might raise problems about additional resources for support.
Therefore, is there any additional data or information that you could take along to the presentation that might help you to answer some of these questions?
You won’t be able to predict every question in advance, but by giving it some thought it will give you a foundation on which to base your answers and hopefully make it clearer to you how to handle questions during a presentation that you might be expecting!
It’s important to remember first and foremost that the fact that people are asking you a question in the first place means that they’re interested and engaged in what you have to say.
Either they want more information, they need clarification, they’re curious to know more, or they want to test your thinking, logic, and recommendations.
So, a question should always be taken as a good sign, and met with an extra boost of enthusiasm and confidence on your side .
Unfortunately, we’ve seen all too many presenters use the fact that someone has asked a question as an opportunity to adjust their microphone, check their slides, straighten their clothes, drink some water, wander around the room or stage… And we can’t say how much of a big no-no this is! It is definitely not how to handle questions during a presentation!
Becoming immediately and significantly distracted when someone is asking you a question can make you look as though you don’t really care about the question being asked, and can be quite disrespectful.
So be sure to maintain eye contact, nod regularly , and give the questioner your full attention.
Remember that it’s not just about your verbal response, your body language can be a powerful tool or a dead give away if you are feeling anxious or unconfident.
So be sure to show your interest in the question and questioner.

No matter whether someone is asking for some data or facts from you, questioning your way of doing things, or simply asking for more information, the first thing to do is to pause briefly after they’re finished asking their question, even if you know what your answer will be straight away.
There are 3 main reasons for this:
- It gives the person time to finish their question, and add any clarifying points.
- It shows that you are taking the time to consider the question, which shows respect.
- It gives you time to think of the best answer, and deliver it eloquently, rather than launching in, rushing through, and coming across as confused or uncertain.

One of the best communication techniques in life and business is to clarify and even repeat or paraphrase a question or point someone is making to you, as it helps avoid misunderstandings.
This is no less true while giving presentations as well, so when needed be sure to ask the questioner to expand or fine tune their point.
Remember, if you don’t understand the question, chances are you’ll give the wrong answer.
Repeating or paraphrasing a question also has the added bonus of ensuring that everyone else in the room has heard the question as well. Plus it gives you some extra thinking time too!
Don’t forget, if there is someone in the room who can add additional weight to your answer or expand in another area which is relevant, don’t be afraid to invite them to contribute also.
The old saying, “There are no silly questions” definitely rings true here, so you need to communicate this by making the questioner feel that their question was valid and constructive.
This needs to be done genuinely, and there are plenty of good ways to express an acknowledgement before giving your response:
- “That’s a question I asked myself”
- “That’s a question a lot of people have asked us recently”
- “I’m not surprised you’re asking that given …”
- “I think the point you’re making is a good one”
- “That’s a question we have discussed at length within our team”
- “Many thanks for your question. You’ve reminded me to touch on …”
- “In most situations, you’d be right, and I would agree with you”
- “That’s a really interesting point and not one we had considered”
It’s a good idea to practise these regularly, but always make sure the way you acknowledge the question is genuine or you’ll sound rehearsed and not authentic or credible as a presenter.
If a question is off-topic and not relevant to the presentation you might want to ask where the question is coming from, answer briefly and offer to give a more detailed response at a later date.
When it comes time to actually give your answer don’t get angry or defensive, no matter what the question is. This is not how to handle questions during a presentation in a professional, credible way!
We’ve all seen those video clips of celebs or politicians losing their temper after an interviewer asks them a less-than-favourable-question, and the only one who almost always comes off looking silly is the interviewee themselves.
So if you find yourself in a similar situation, even if the question was intended to be intentionally provocative, losing it or getting visibly emotional will make you come across as immature and unprofessional. If you feel yourself getting emotional, simply ask if you can get back to them at a later time.
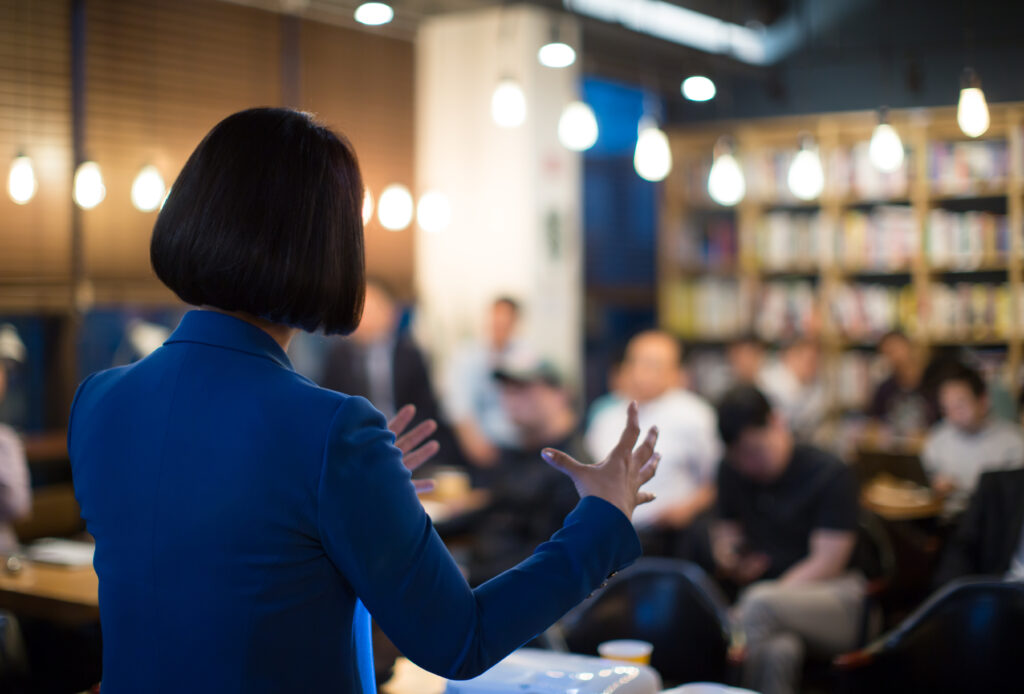

We all have to admit to bluffing our way through an answer to a question we’re just not 100% sure of every now and then… But a presentation is not the time to do it.
Making up an answer or trying to dance around the question completely is a surefire way to come across like you don’t know what you’re talking about, which can really undermine your confidence for the rest of the presentation. Instead, here are some options for managing questions when you don’t know the (entire) answer.
- Tell them what you do know. E.g. if someone asks “What is the current rate of inflation?” you may not know the exact answer so you could reply by saying “I’m not sure of the precise rate of inflation right now, though I can look that up for you if you like. What I can tell you is that it is rising faster now than it has done for many years.”
- Tell them why you don’t know. E.g. if someone were to ask the above inflation question, you could reply by saying “The rate of inflation is extremely volatile at the moment. Let me look up the most recent data and get that figure to you straight after the presentation.”
- Tell them someone else knows. Again, using the inflation question, you might reply “That’s a hot topic at the moment and our CFO has just published a report looking at the current rate of inflation and the drivers behind it. I’ll email that report to you later this week.”
- Tell them you don’t know. It’s not ideal to admit that you don’t have the answer to hand but it’s better than making up the answer. In this scenario it’s imperative that you acknowledge the question so that you still come across as confident and in control rather than nervous and on the back foot. E.g you could say “That’s a very valid question you raise. I don’t have that data with me but I will send that information to straight after this presentation.”
Curly questions can really rock our confidence so stay calm, take your time and remember that no one expects you to know everything. You’re only human after all!
If the question is a particularly long one, ‘chunk’ up your answer into sections so your answer stays clear and concise.
For example, if someone asks you when a project is going to be completed, you might say:
“That’s actually a critical question as timings on this project are particularly tight (acknowledging worth). Based on our last status update, stage 1 will be completed by xxx, stage 2 by xxx and stage 3 by xxx.”
Or, if their question is multi-part, answer each part separately before moving onto the next.
You could say something like “And to address the second part of your question…”

After you finish your answer it’s important to check-in with the questioner to make sure that you’ve answered the question to their satisfaction. You can do this by simply asking:
- “Does that answer your question?”
- “Can I provide you with any more detail?”
Or, you can also check in non-verbally, such as by making eye contact with them and smiling. If you get a smile back, you can assume you’ve answered the question to their satisfaction. If you get a puzzled look or a frown, we recommend you follow up with a verbal check-in.
So, by learning how to handle questions during a presentation, following all these important points, and being thoroughly prepared before your presentation, it will help to calm your nerves and leave you feeling ready to engage with your audience, stimulate constructive conversations, all while looking confident, professional and in control.
And if you’re going back into the meeting room after a long period of remote working you can brush up on your in-person presentation skills by reading this blog .
Tailored and personalised presentation skills training
If you’re specifically looking to learn how to handle questions during a presentation, or more generally to build the presentation skills of your team (or yourself) through personalised training or coaching that is tailored to your business, we can help.
For nearly 20 years we have been the Business Presentation Skills Experts , training & coaching thousands of people in an A-Z of global blue-chip organisations – check out what they say about our programs .
To find out more, click on one of the buttons below:
Header image credit.

Written By Belinda Huckle
Co-Founder & Managing Director
Belinda is the Co-Founder and Managing Director of SecondNature International. With a determination to drive a paradigm shift in the delivery of presentation skills training both In-Person and Online, she is a strong advocate of a more personal and sustainable presentation skills training methodology.
Belinda believes that people don’t have to change who they are to be the presenter they want to be. So she developed a coaching approach that harnesses people’s unique personality to build their own authentic presentation style and personal brand.
She has helped to transform the presentation skills of people around the world in an A-Z of organisations including Amazon, BBC, Brother, BT, CocaCola, DHL, EE, ESRI, IpsosMORI, Heineken, MARS Inc., Moody’s, Moonpig, Nationwide, Pfizer, Publicis Groupe, Roche, Savills, Triumph and Walmart – to name just a few.
A total commitment to quality, service, your people and you.

Honesty is the only policy when presenting. Blatantly admitting, “I don’t know”, in front of an audience can be a credibility disaster. What to do?
No one can know the answer to every question. It’s how the inevitable is handled that separates the amateurs from the Pros.
Use the following Seven Strategies to field even the toughest questions with tact and poise.
1. Reflection
Repeat the question and reflect it back to your audience, “Does anyone here have any experience with that?”
When you allow the audience to help you, they will save you without ever realizing it. In fact, the audience will revere you because adults love to be involved and share their knowledge. After you have fielded all contributions, summarize, and add your own ideas, if any have been sparked.
Summarizing at the end helps you to maintain control and authority. Always repeat questions before answering for the same reason.
2. I’ll Get Back to You
This trusted standard works well if you do Three Things…
- Write the question down. Be conspicuous. Make sure everyone knows you are writing the question down. I go so far as telling the audience, “I am writing this question down.”
- Tell the questioner exactly when you will get back to them. Be honest. Then do it. Can you get back to them by the end of the day? If it is an allday program, can you get back to them after lunch?
- Be sure to get the questioner’s contact information if you don’t have it.
These Three Things give this Strategy power. This is not smoke and mirrors. It is real-time Customer Service- go the extra mile, expand your knowledge, impress your audience.
3. Defer to the Expert
This is a more sophisticated version of the Reflection technique.
Sometimes a question is legitimately outside your area of expertise. You may be a marketing expert, and someone asks a question about engineering. The question requires an engineer.
If there is an engineer in the room you could say, “Sally, you’re an engineer. Do you have any insights into that?” If there are no engineers in the room, state that you will confer with an engineer and get back to them .
Notice I have just combined two techniques.
4. Compliment the Questioner
Two Things make this Strategy effective…
- Rarity Some presenters respond to EVERY question with, “Great question.” If you do this, break the habit immediately. Otherwise, you will lose one of the most effective techniques in your toolbox when you don’t know the answer.
This Strategy works, when sincere, because audience’s love to be complimented. They like to “stump” the teacher. The audience becomes focused on how smart they are instead of judging the presenter.
You can also combine this technique with I’ll Get Back to You .
5. Answer a Question with a Question
Sometimes questions are too narrow or too general to answer. Reserve the right, as the expert, to open a question up or close it down by asking a question in response.
Once upon a time I was a software trainer. One day a woman asked me a very specific question, “What does that button do?” I had no idea, but I didn’t confess, “I don’t know.”
Instead, I asked her a question, “What is your goal in pushing that button?” She elaborated and explained what she wanted to accomplish. I knew a way to help, and it didn’t involve pushing that button!
She was happy. I was honest, credible, helpful, and very happy.
6. Parallel Answer
If you don’t know the bull’s eye answer to a question, offer what you do know quickly to demonstrate some credibility and then combine with a previous technique.
Many moons ago, when I was a software trainer, I used to be an expert in Lotus, a now extinct spreadsheet package. As Microsoft Excel eclipsed Lotus, I had to learn Excel so I could teach it. I was on a learning curve. Sometimes I would be asked a question about Excel that I didn’t know the answer to, but I did know the answer in Lotus.
Quickly I would say, “I know that is possible in Lotus. I can find out if that is possible in Excel. I’m writing this question down. I’ll research it at the break and get back to you .” Refrain from droning on and on about your parallel knowledge.
Brevity is the key to this technique. Be sure to combine with Reflection or I’ll Get Back to You to hit the bull’s eye answer for your audience.
7. Set Rules
Prevention is the best medicine. You can avoid many Difficult Questions by Setting Rules in the beginning. Whenever you present, you are the Leader. So, take the Lead and Set Rules up front.
If you Set Rules and follow them, the audience respects you. If you make rules up as you go, you lose credibility. This has been my experience.
The number of Rules you set will vary depending on the topic and your audience. When I taught Programming Languages and Software, I set lots of Rules because I knew the questions would be many and varied.
Example… I would start a Software Seminar by saying, “I welcome general questions at any time about anything on the Agenda. If you have questions about a specific project or a subject outside the Agenda, please see me at a break for private consultation. Because we have limited time, I may stop taking questions and comments sometimes to make certain we cover every Agenda topic today.”
Setting Rules is critical. Lead and Set Rules conversationally at the beginning of your presentation to Prevent most Difficult Questions.
No one can know the answer to every question. It is possible to handle the inevitable situation with honesty and credibility like a Pro. Use these Seven Strategies to enjoy Difficult Questions, learn from them, and impress your audience.
About the Author
Mary Sandro helps professionals deliver brief, logically sound, emotionally engaging presentations that get an audience to take action. Learn to excel at presenting and love the process in just 60 Minutes with the Get Them MarchingFramework. Includes instant online access and optional live coaching. Visit www.ProEdgeSkills.com or call 800-731-0601.
About Mary Sandro
Mary Sandro helps organizations deliver exceptional customer service and standout presentations. In 1994 she founded ProEdge Skills, Inc. to deliver engaging training programs, videos, coaching, and train-the-trainer licenses that empower employees to achieve goals. Learn more at www.ProEdgeSkills.com or call 800-731-0601.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
1. Recap your main points. After you've covered your content, sum it up for the audience so that they remember what you've just told them. (Remember the old saying, "Tell them what you're going to ...
Seed someone in the audience like a friend or colleague to ask the first question. Sometimes, having someone break through the silence and ask the first question will help others speak up or ask follow-up questions. Answer your own question at the end of the presentation. Use phrasing like, "When I first started this project, my main question ...
General vocabulary for presentations. Sometimes, the smallest changes in your presentations can make the biggest differences. One of them is to learn a few phrases that give you confidence during your speech. Here are some important verbs to get you started: To outline. To clarify. To highlight. To emphasize.
Addressing questions and technical concerns. People might be wondering if they can ask questions during your presentation, so you can clarify this at the start. If you're providing handouts or presenting online, it's useful to ask people to alert you about any technical concerns. Examples: Please feel free to ask any questions during the talk.
6. Closing with a Quote or a Short Sentence. If you can condense your summary to a less wordy, short sentence, it tends to leave a longer-lasting impression on your listeners. It is essential to ensure that the short message conveys your authenticity and the importance of your message.
So try these tips to encourage questions: 1. PREPPING YOUR Q&A: > TIP THEM OFF EARLY: As you start your presentation, tell your audience: "I'll take all your questions at the end, so write down your questions as you think of them along the way.". That'll get them active thinking of questions throughout your presentation.
Beforehand, think through the types of questions audience members might ask. Put yourself in your shoes and ask yourself what concerns they might have about how your message impacts their job ...
At the end of your presentation, if it is appropriate for the type of presentation, solicit questions from the audience. Responding to Audience Questions. When someone is asking a question, make eye contact with that person, listen positively, and acknowledge by saying "thank you for that question," or say "that is an excellent question" or ...
Here are some phrases which you can use to structure the introduction in this way: Introduce. 1. Good morning/afternoon (everyone) (ladies and gentlemen). 2. It's a pleasure to welcome (the President) here. 3. I'm … (the Director of …) Introduce the presentation topic.
Audience Engagement and Participation: Inviting questions at the end of your presentation allows your audience to actively participate, transforming your session into an interactive experience. As Albert Einstein aptly put it, "The important thing is not to stop questioning.". 2. Addressing Confusion and Skepticism:
1. Listen to the whole question. You don't have to answer a question immediately. Pause for a few seconds, actively listen to all parts of the question and think about the best way to answer. Frequently questions can change direction at the last moment, particularly if the questioner is thinking on their feet.
Apply the 10-20-30 rule. Apply the 10-20-30 presentation rule and keep it short, sweet and impactful! Stick to ten slides, deliver your presentation within 20 minutes and use a 30-point font to ensure clarity and focus. Less is more, and your audience will thank you for it! 9. Implement the 5-5-5 rule. Simplicity is key.
Speakers can do several things in that situation, including these three techniques: Say something like, "You know, one of the questions I'm asked a lot is…" and answer it yourself. Ask an audience member a specific question, such as, "I spoke about Subject X earlier. What did you think about that?".
Here are a few tips for business professionals who want to move from being good speakers to great ones: be concise (the fewer words, the better); never use bullet points (photos and images paired ...
Killer question 1 - You don't know the answer. The old saying 'honesty is the best policy', has stood the test of time because it's true. The moment you try to bluff your way through a question you don't know the answer to, you lose your credibility. Try this instead. Step into the question.
Answering questions means you have to think hard and fast - about both the content of what you say and the way that you say it. One very handy trick is to use structured formulae to give your response a shape. That way you only need to think about the actual content - halving the work on your brain.
Here are 8 tips to help make them through: 1. Pitch your presentation at the right level for your audience. The first stage of questions is birth - they have to be born in your audience's mind. If your presentation is too simple for the level of knowledge in your audience - it's all material they've covered before - they won't ...
Overall, I would say…" and then either answer the question or summarize your key ideas in about 2-3 sentences. Then you can move on to the next questioner. ... Work out the answers to these questions as you're working on your presentation—these questions can help you figure out where you might need to do more research. Decide which ...
Other speakers prefer to deal with questions at the end of the presentation. If you prefer this approach, ensure that you set aside sufficient time for questions but also limit the amount of time available. The amount of time will depend on the type of presentation you are giving but usually 10 minutes of question time should be sufficient.
So here is what you came for: Better ways to get your audience to talk to you and actually ask about what they would like to know. 1. Use a Q&A Tool. Let your audience ask questions via their smartphones or notebooks - even anonymously - and be sure no one ever holds back any questions. Q&A tools such as SlideLizard are integrated ...
1. Tell the audience in advance when you will be taking questions. One of things that can sometimes throw you off course is being asked a question when you are mid-flow through a presentation or least expect it. It can interrupt your train of thought and momentarily put you off balance. One way to avoid this is to agree in advance when you will ...
Use the following Seven Strategies to field even the toughest questions with tact and poise. 1. Reflection. Repeat the question and reflect it back to your audience, "Does anyone here have any experience with that?" When you allow the audience to help you, they will save you without ever realizing it.
Asking questions after a presentation is not just about seeking clarity on what was discussed. It's a golden opportunity to delve deeper, engage with the speaker, and enhance your understanding of the subject matter. But knowing which questions to ask isn't always straightforward. ... You might say, ...
In short, step 3 will enable you to respond to a question with a well-developed answer. For example, if your boss asks you why you feel ready for a next-level job, give the reasons you believe ...
One of the most influential data visualization booksupdated with new techniques, technologies, and examples Visualize This demonstrates how to explain data visually, so that you can present and communicate information in a way that is appealing and easy to understand. Today, there is a continuous flow of data available to answer almost any question. Thoughtful charts, maps, and analysis can ...